Protein containing material biomass and methods of production
A protein, biomass technology, applied in the protein composition of plant materials, microbial/unicellular algae protein processing, and unicellular algae protein composition, etc., can solve balanced amino acid nutritional deficiencies, sensory taste and odor characteristics unpleasant, not Optimal balance and other issues to achieve the effect of nutritionally balanced nutrition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0126] Embodiment 2-processing after fermentation
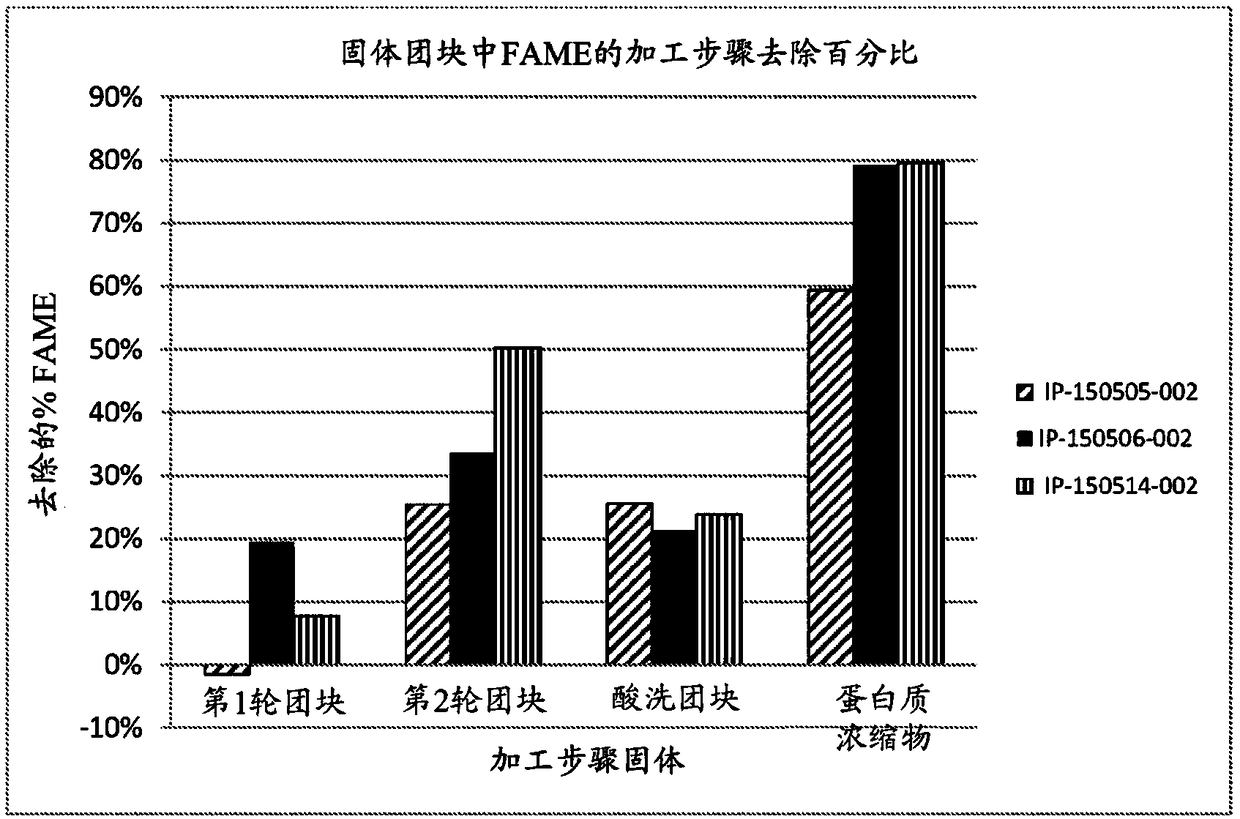
[0127] After fermentation and growth according to Example 1, 100 kg of chytrid (Acitridiochytrium) broth (40 kg solids at 50% protein) were harvested. After centrifugation, the biomass was washed with an aqueous solution, followed by another centrifugation and the washed biomass was pasteurized at 65°C for 15 seconds in a single-pass HTST pasteurizer. The pasteurized biomass was then lysed and homogenized in a recirculating bead mill using 200-proof ethanol at a 1:1 (v / v) ratio of ethanol to solvent to remove lipids and carbohydrates. Cells were lysed using 1.0 mm beads in a bead mill for 15 min at 35 °C, centrifuged to remove mixed oils and re-passed under the same conditions for another 15 min. The defatted biomass was then centrifuged and the pellet resuspended in water with antioxidants to undergo a pickling step by washing with H 2 SO 4 This was done by lowering the pH to 3.5 for 30 minutes and then raising the pH to ...
Embodiment 3-
[0128] Example 3 - Analysis
[0129] The dry protein concentrate (DPC) obtained from the batch processed as described in Examples 1-2 was analyzed and found to have the amino acid composition as shown in Table 3 below.
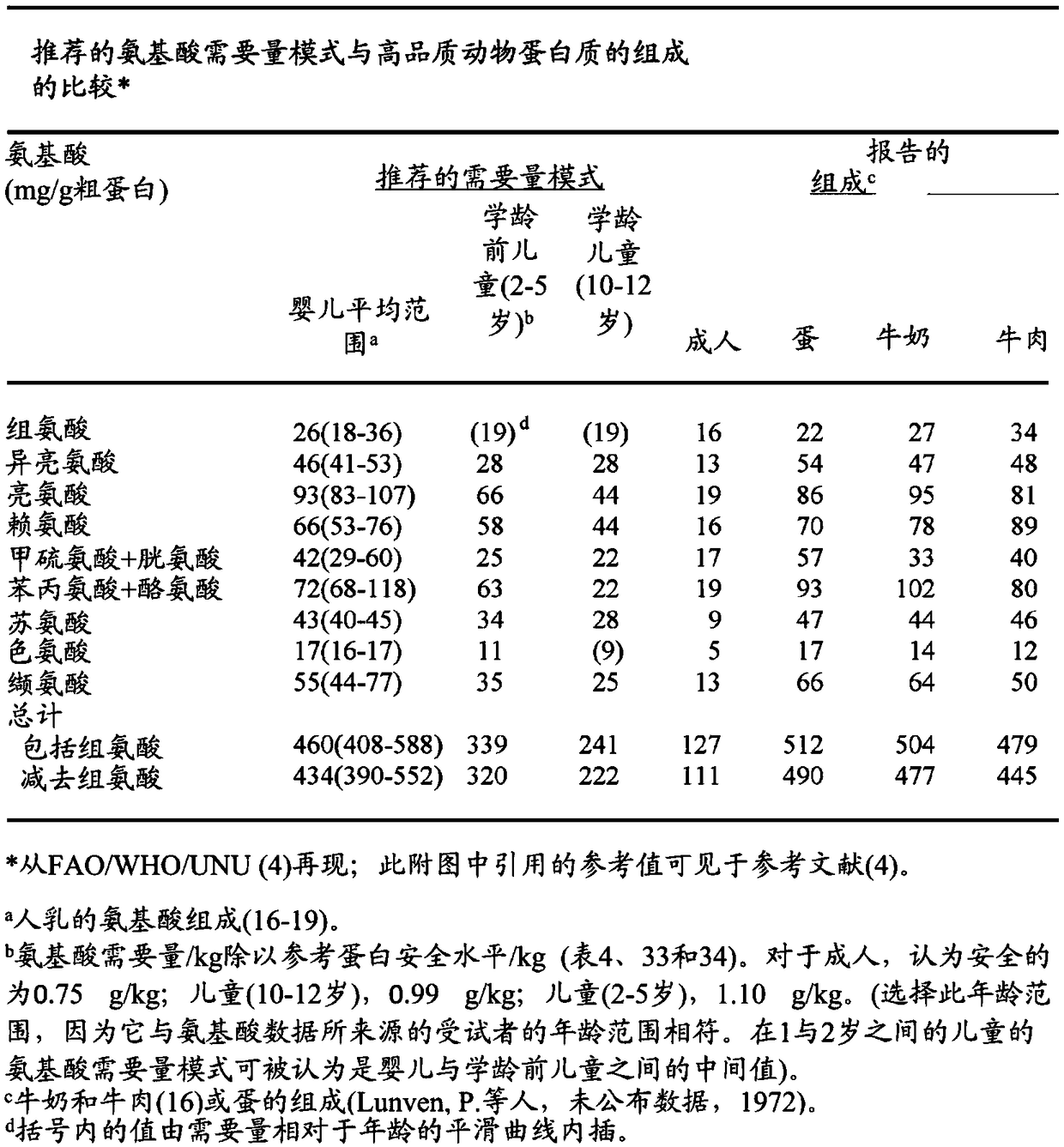
[0130] Table 3 below shows the UCLAA score for the dry protein concentrate (DPC) of the present invention. The UCLAA is calculated as explained herein and shown to be greater than or equal to 1.0 for each of the nine essential amino acids in humans, and thus the protein composition has a UCLAA score greater than 1.0. Table 3 also compares the dry protein concentrate of the present invention with other commercially available protein compositions such as whey, soy and pea protein, showing that whey protein has a UCLAA score of 0.88, soy protein 0.93, and pea protein 0.73.
[0131] Table 3 - Comparison of UCLAA scores for various proteins
[0132]
[0133]
[0134] As shown in Table 3, histidine has the lowest UCLAA score of 1.01, and thus the protein compo...
Embodiment 4
[0136] Table 4 below shows the relationship between dry protein concentrate (DPC) prepared according to the present invention using a defined fermentation medium according to Examples 1-2 or Table 1 relative to various reference proteins such as egg, spirulina or chlorella protein. Comparison. DPC values are shown as % of amino acid sum and total protein based on Dumas total N x 6.25.
[0137] Table 4
[0138]
[0139] Table 4 shows that each of the compared proteins lacks some important pathways. Eggs and spirulina lack lysine, spirulina also lacks tryptophan, and chlorella lacks methionine. The algae protein concentrate of the present invention provides a more nutritionally balanced protein composition and thus better quality food products as evidenced by UCLAA scores and other nutritional parameters.
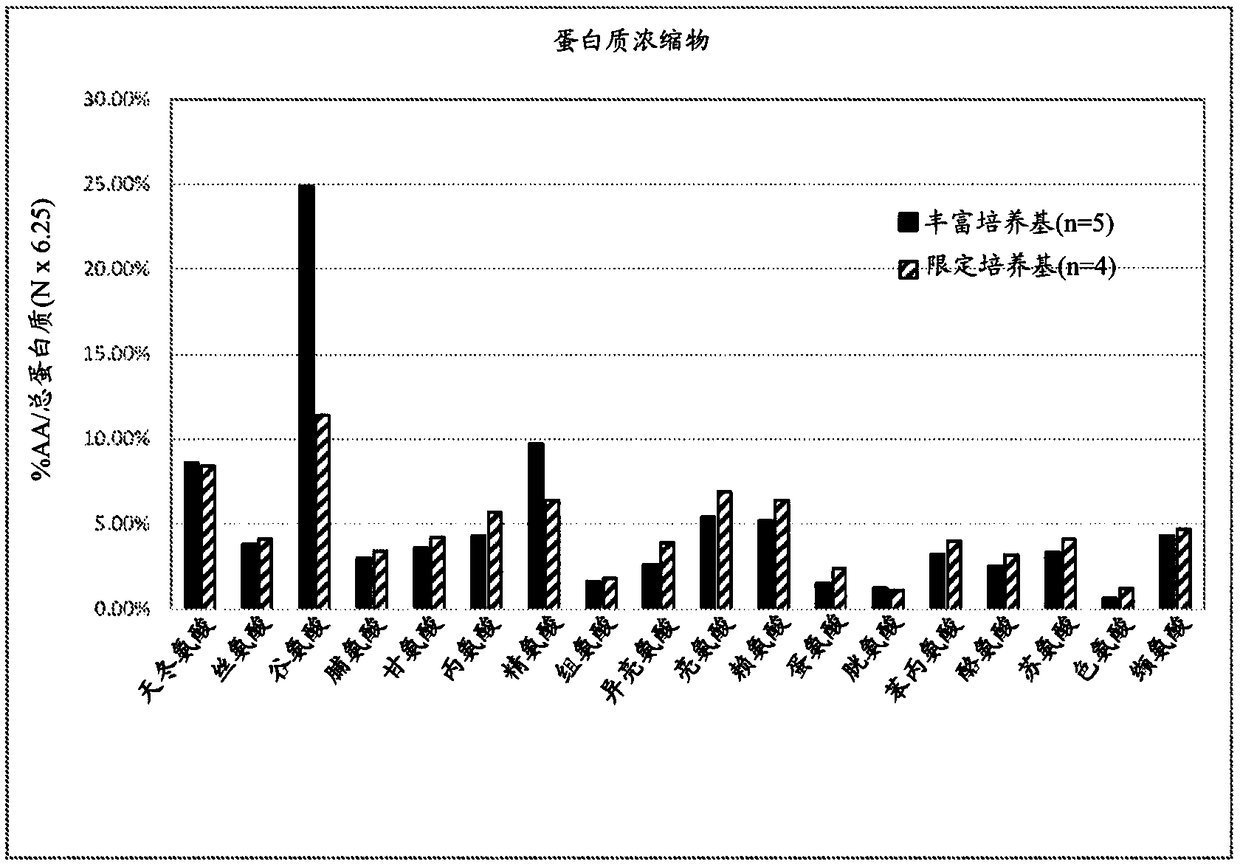
[0140] Table 5 below shows how the total amino acid composition in the final protein composition changes during fermentation with the use of rich medium (containing o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com