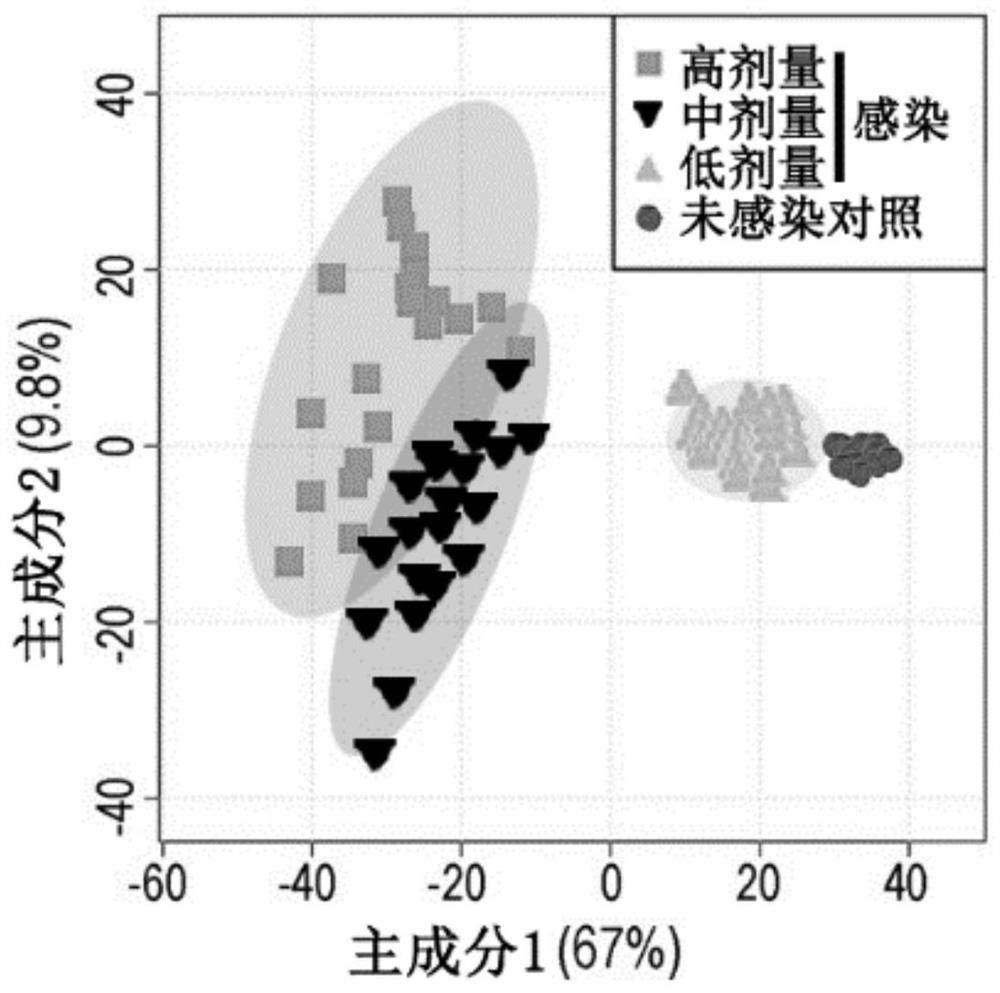
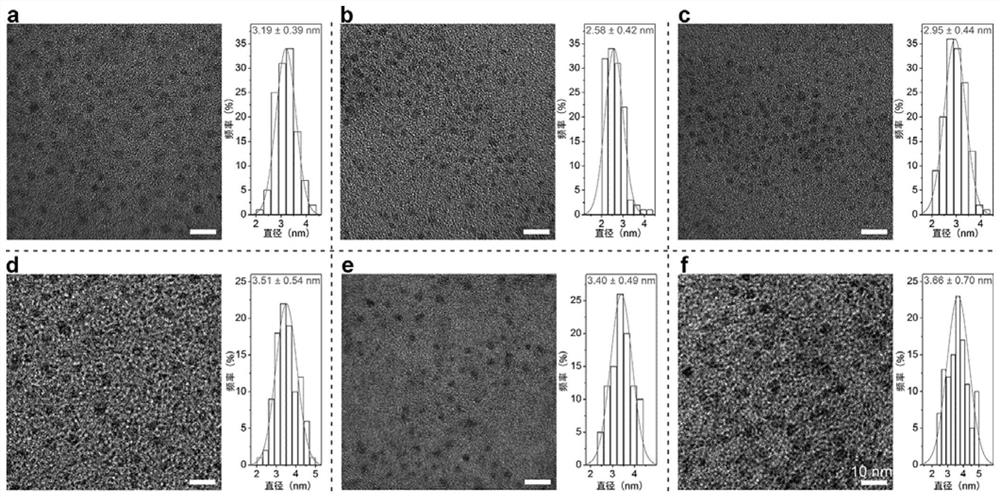
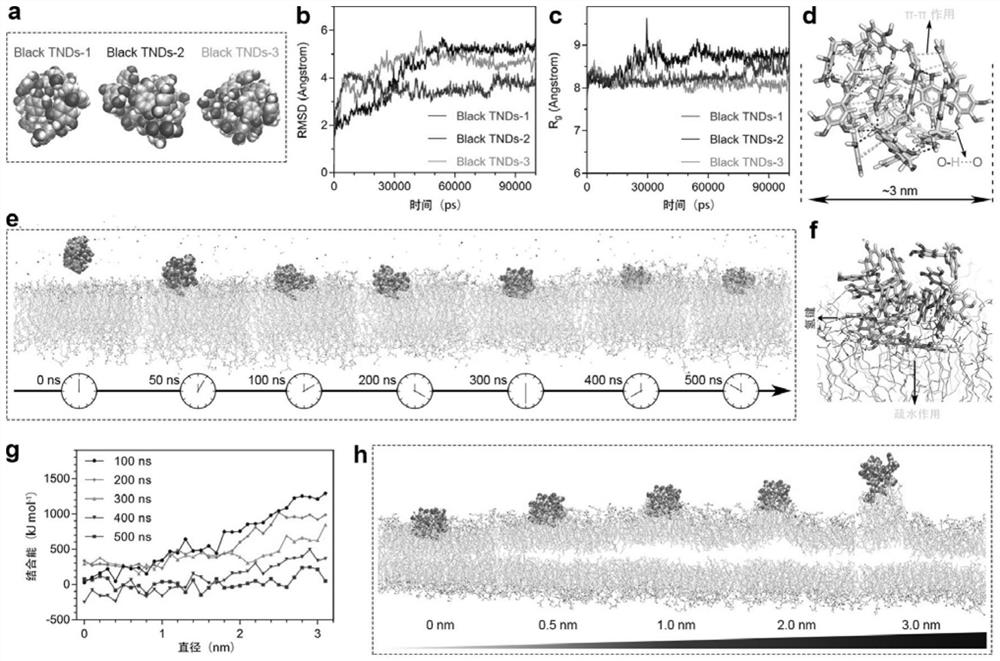
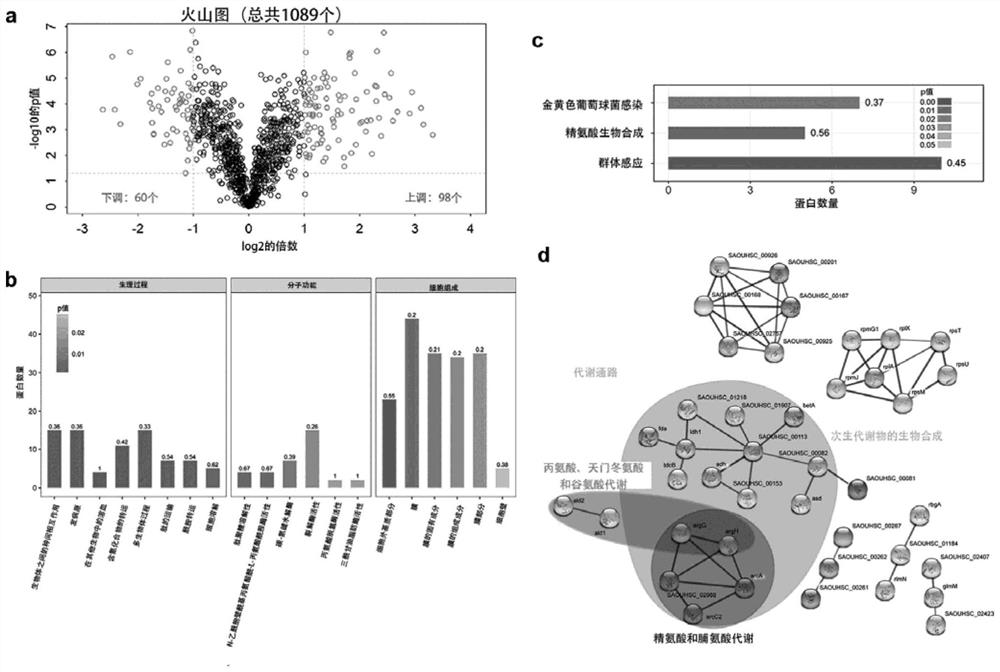
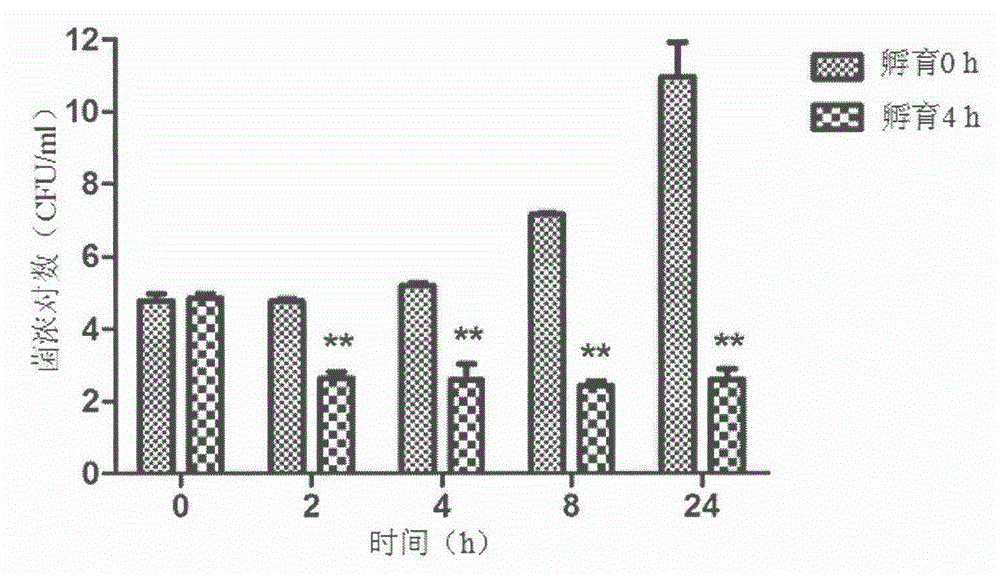
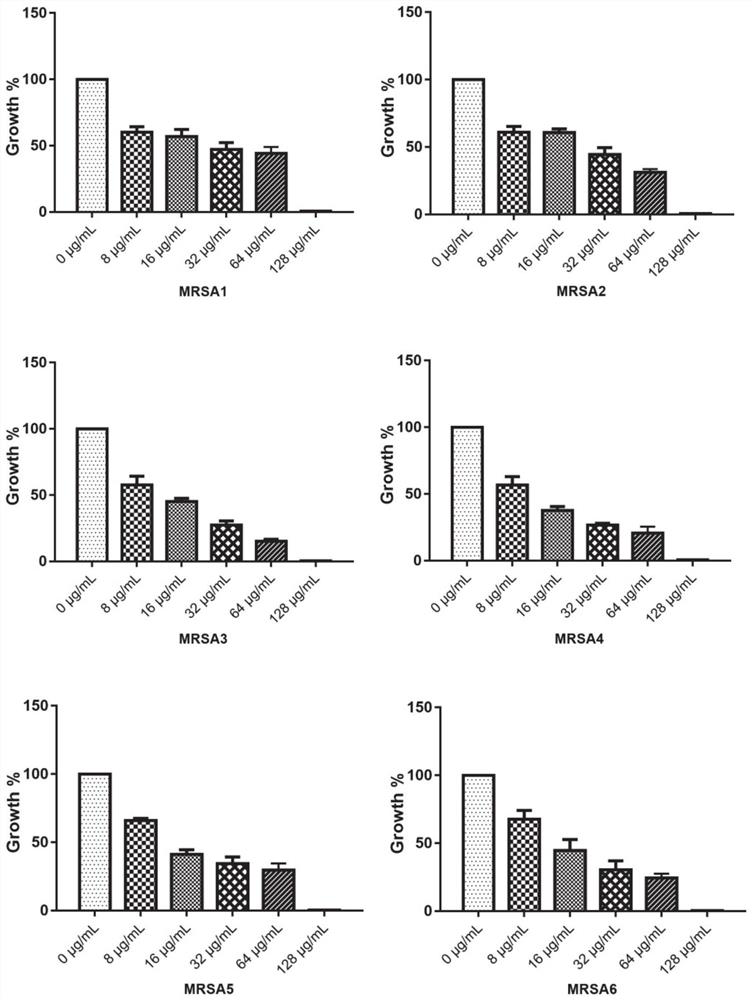
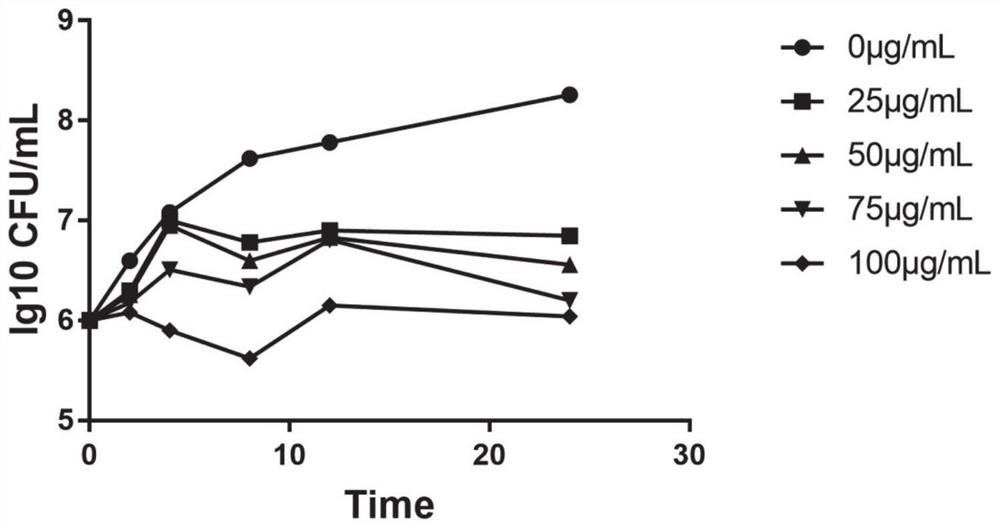
Patents
Literature
44 results about "MRSA infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Overview. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection is caused by a type of staph bacteria that's become resistant to many of the antibiotics used to treat ordinary staph infections.
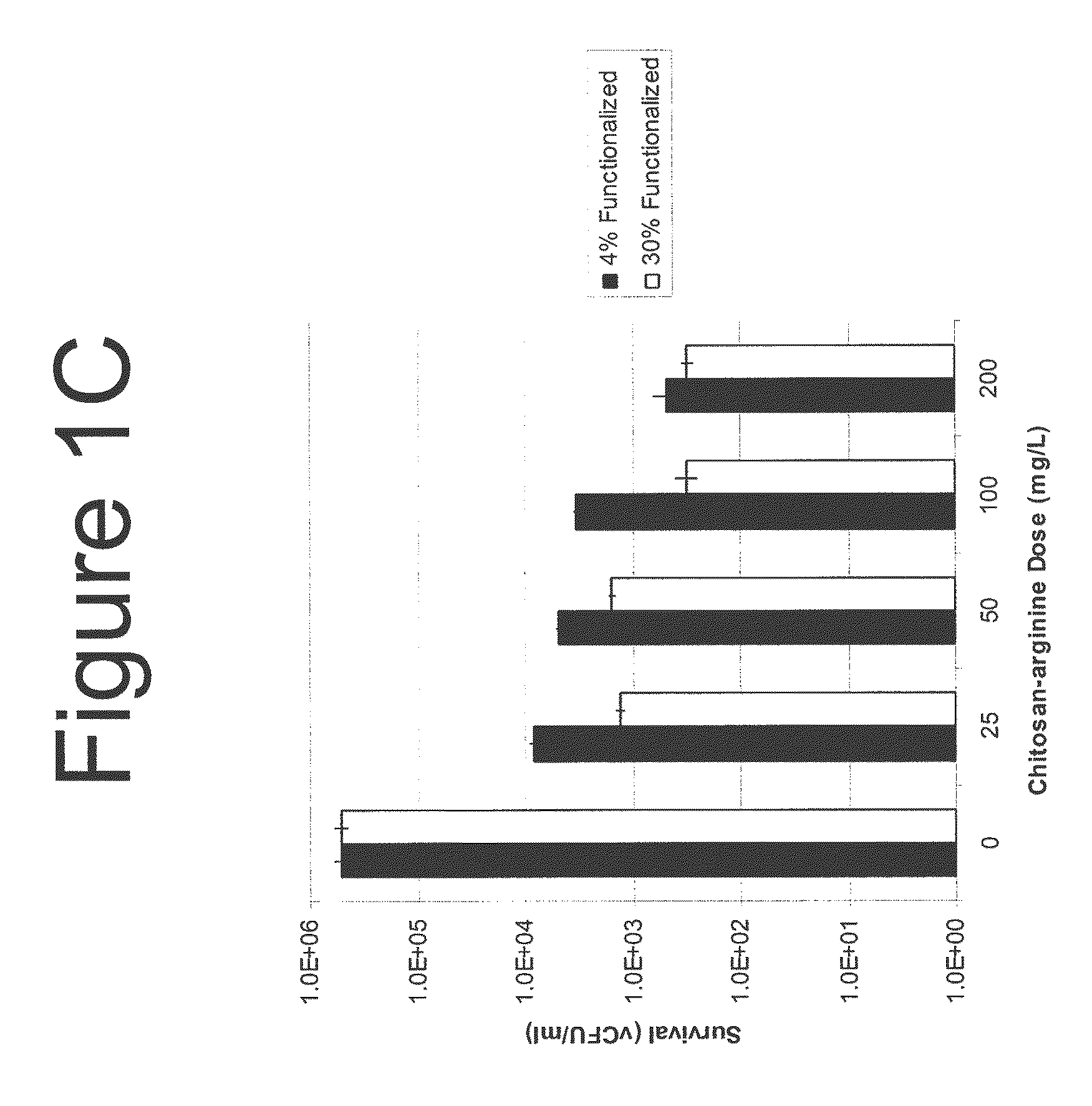
Methods and Compositions for the Prevention of and Treatment of Infections Utilizing Chitosan-Derivative Compounds
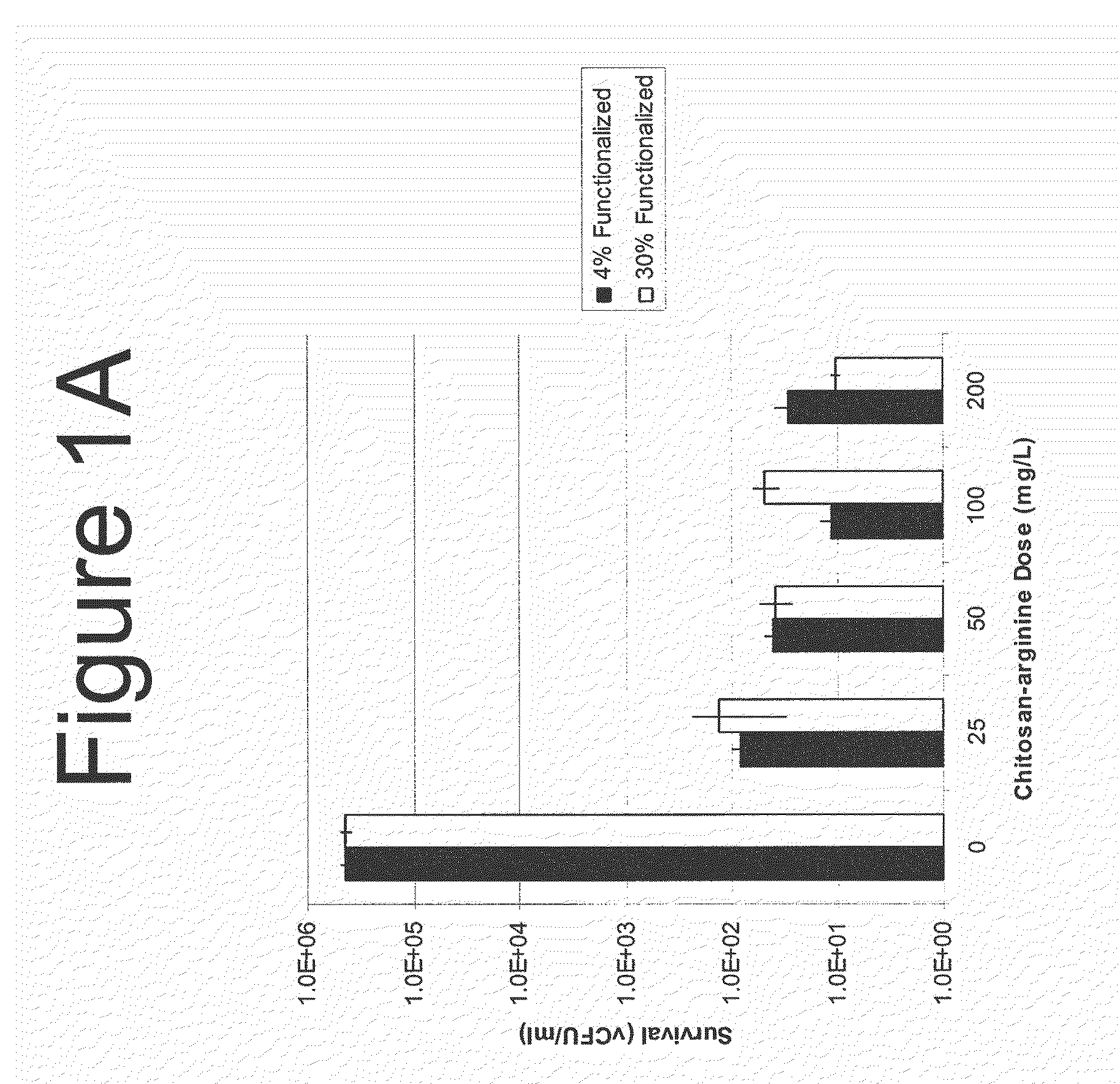
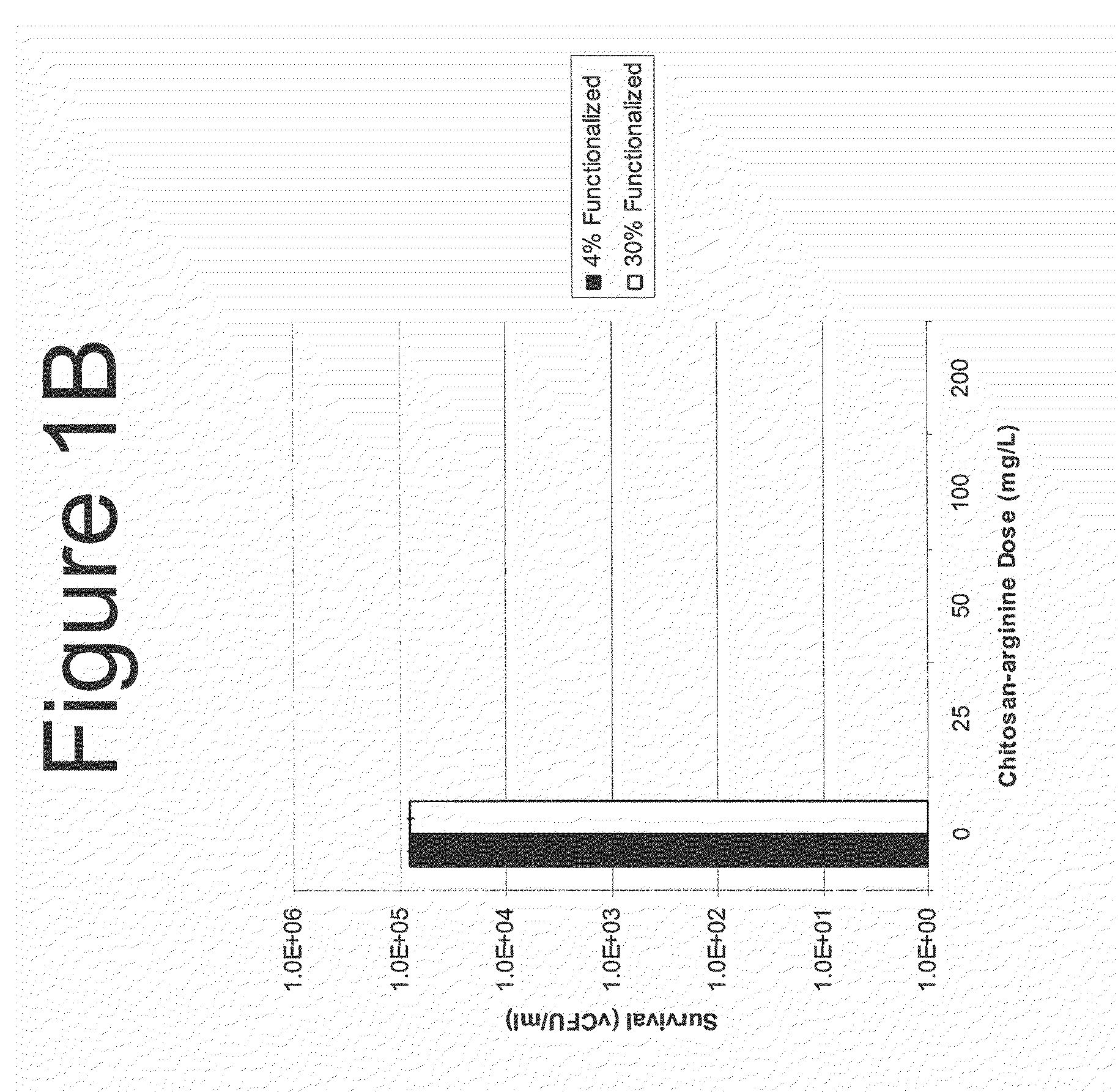
The present invention is directed to the treatment and prevention of nosocomial infections or MRSA infections utilizing soluble chitosan or chitosan derivative compounds. These chitosan-derivative compounds, e.g., chitosan-arginine and chitosan-acid amines, exhibit bactericidal activity against bacterial pathogens, e.g., drug resistant bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Owner:SYNEDGEN
Methods and compositions for the prevention of and treatment of infections utilizing chitosan-derivative compounds
ActiveUS9012429B2Reduced growth rateAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesResistant bacteria
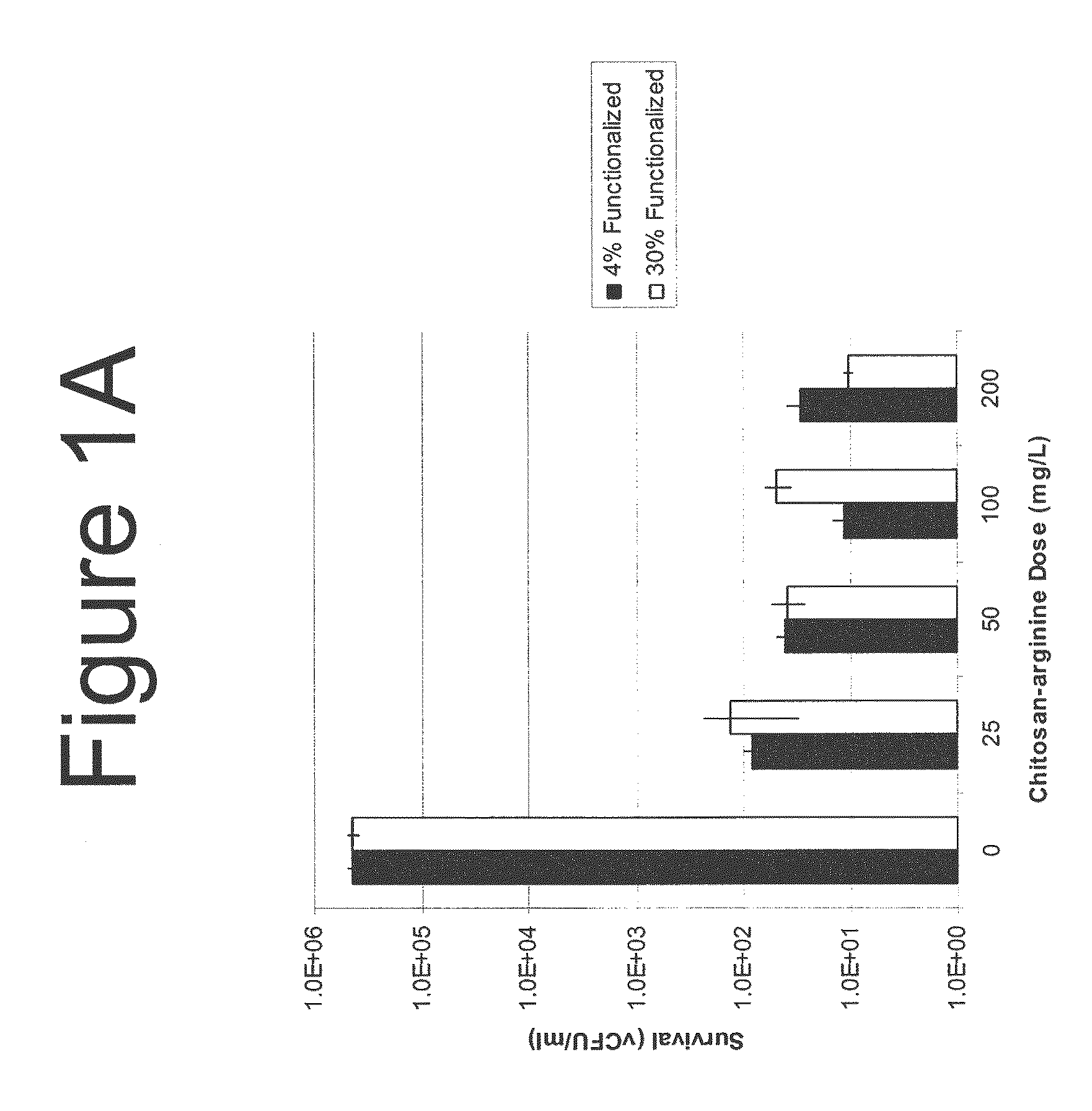
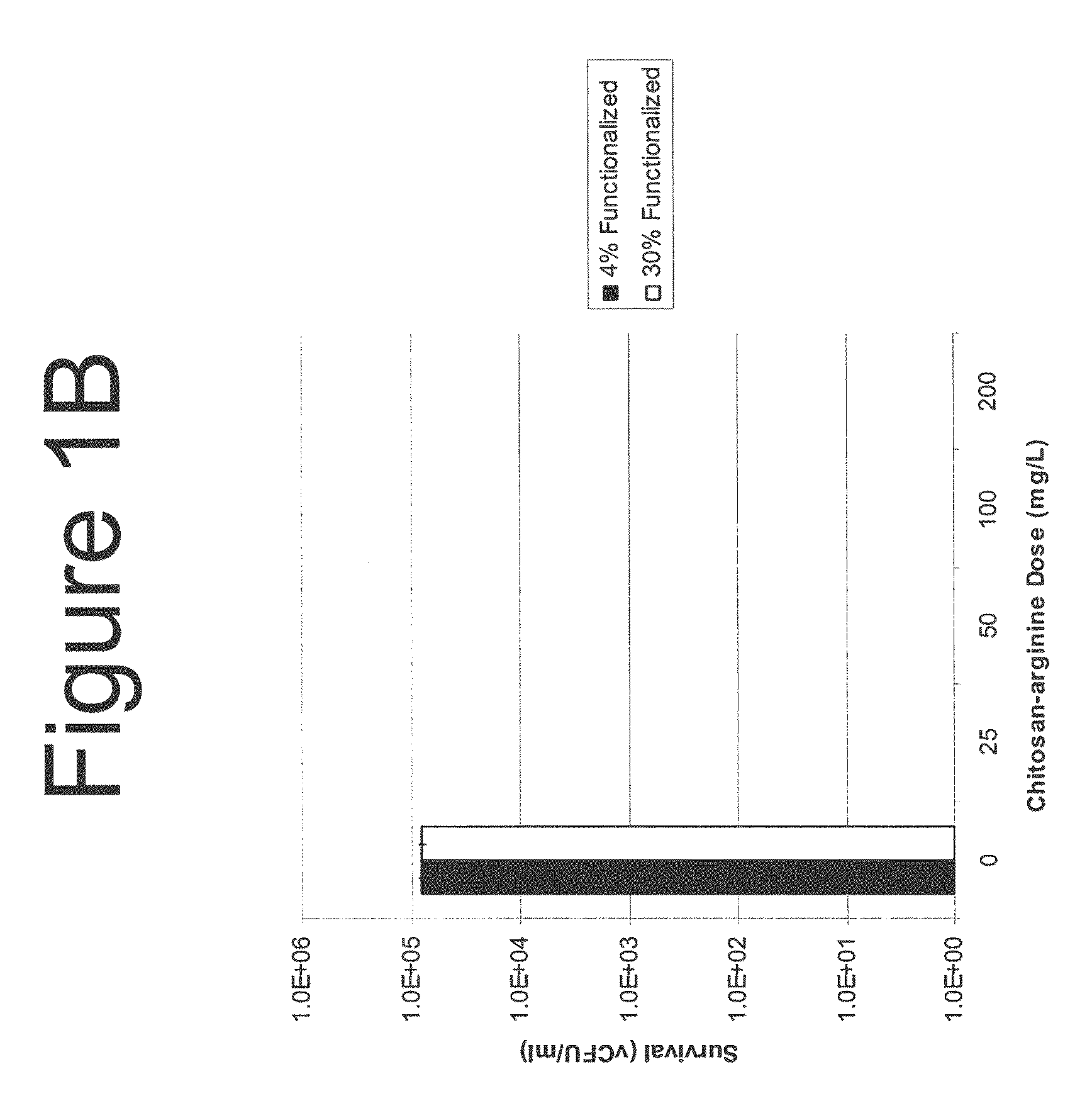
The present invention is directed to the treatment and prevention of nosocomial infections or MRSA infections utilizing soluble chitosan or chitosan derivative compounds. These chitosan-derivative compounds, e.g., chitosan-arginine and chitosan-acid amines, exhibit bactericidal activity against bacterial pathogens, e.g., drug resistant bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Owner:SYNEDGEN
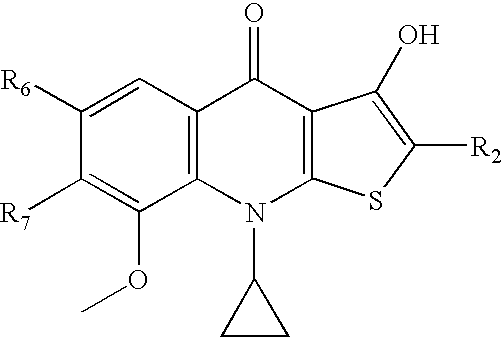
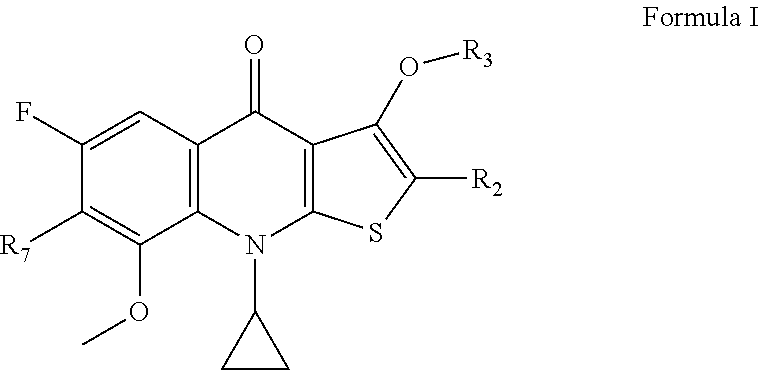
Hydroxylthienoquinolones and related compounds as anti-infective agents
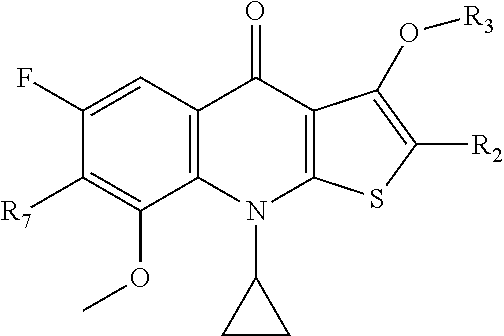
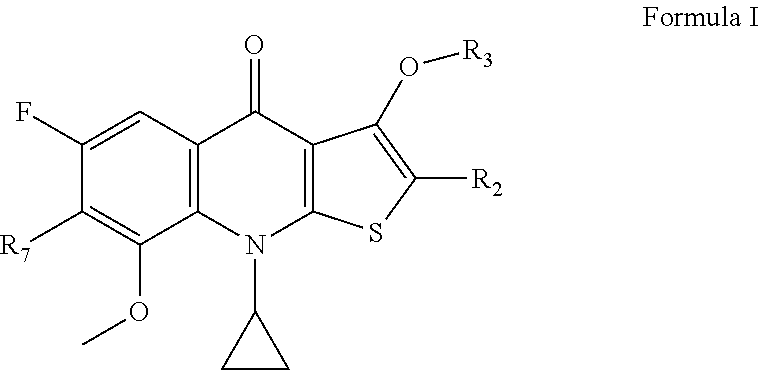
Disclosed herein are hydroxylthienoquinolones and related compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts useful as antiviral agents and having the general formulain which the variables R2, R6, and R7 are defined herein. Certain compounds provided herein possess potent antibacterial, antiprotozoal, or antifungal activity and are particularly efficacious for the treatment of MRSA infections. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions, pharmaceutical compositions containing a hydroxylthienoquinolone in combination with one or more other active agent, and methods of treating microbial infections in animals by administering an effective amount of a hydroxylthienoquinolone or related compound to an animal suffering from a microbial infection.
Owner:ACHILLION PHARMA INC
System and method for hemostatic wound dressing
InactiveUS20140213548A1Cost effectiveInherent propertyBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismWound dressingCost effectiveness
The present invention relates a novel hemostatic wound dressing, preferably comprising chitosan and an oxygen carrier such as a perfluorocarbon, and methods to treat hemorrhaging wounds and MRSA infections. The present invention helps with coagulation / clot formation as well as providing oxygen to the wound, all while being cost effective and competitive with current hemostatic dressings.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for sieving active component or matter and active component therefrom
InactiveCN101070556AStrong specificityHigh false negativeAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementActive matterAnti mrsa
One kind of union biosensor technology and isolation technique, From natural medicine, selection and separation have the combination PBP2a active method of organizing minute or active material, the method will PBP2a coating on the sample pool biosensor match as a solid base to extract natural medicines the mobile phase of the selected combination with PBP2a in the role of natural medicine, will be an integrated component of the higher value after isolation and purification, has been a collaborative antagonistic MRSA activity combined with PBP2a occurred role of the active component, the Preparation synergistic components can be used to beta - lactam antibiotics treatment of MRSA infection drugs or lead compounds. This method has time-saving, the high flux, to reduce effort, the specificity to be strong, the result accurate, can real-time monitoring many kinds of merits.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Compositions and Methods for Diagnosing and Treating Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
ActiveUS20100197649A1Suitable for topical applicationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCefoxitinMRSA infection
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application
ActiveCN109082414AEffectively eliminateGood bodyAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
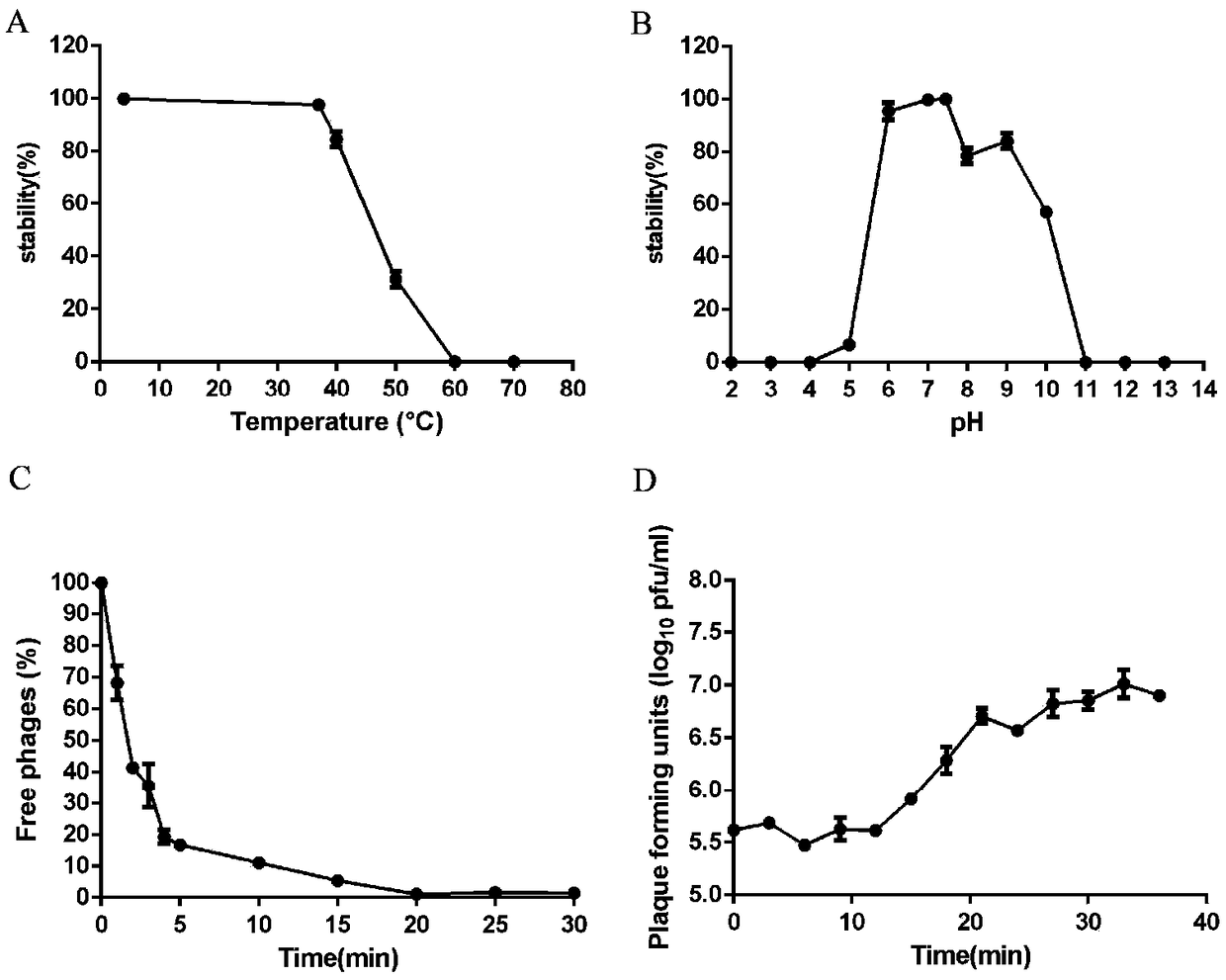
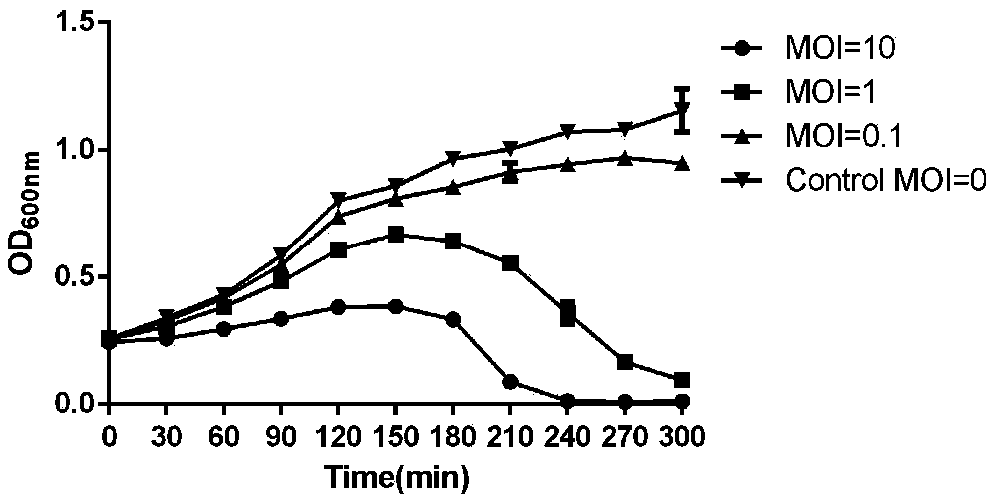
The invention discloses staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application. The staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and the application have the advantages that staphylococcus aureus can be specifically effectively eliminated by the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage, excellent in-vivo and in-vitro antibacterial effects can be realized by the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage for medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus, experimental foundations can be provided to clinically developing preparations for preventing and treating medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection, and the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage has great clinical application potential; the skin abscess average areas of nude mice of bacteriophage treatment groups are 47.32 mm<2> in skin abscess models when MOI(multiplicity of infection) is equal to 10, and the average bacterium load is 3.553*10<7> CFU / g; the skin abscess average areas of nude mice of MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus) infection groups are 150.4 mm<2>, and the average bacterium load is 2.284*10<8> CFU / g; the skin abscess areas of the mice of the bacteriophage treatment groups are smaller than the skin abscess areas of the mice of the MRSA infection groups, the colony count of the mice of the bacteriophage treatment groups is lower than the colony count of the mice of the MRSA infection groups, and the difference of the skin abscess areas and the colony count has statistical significance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
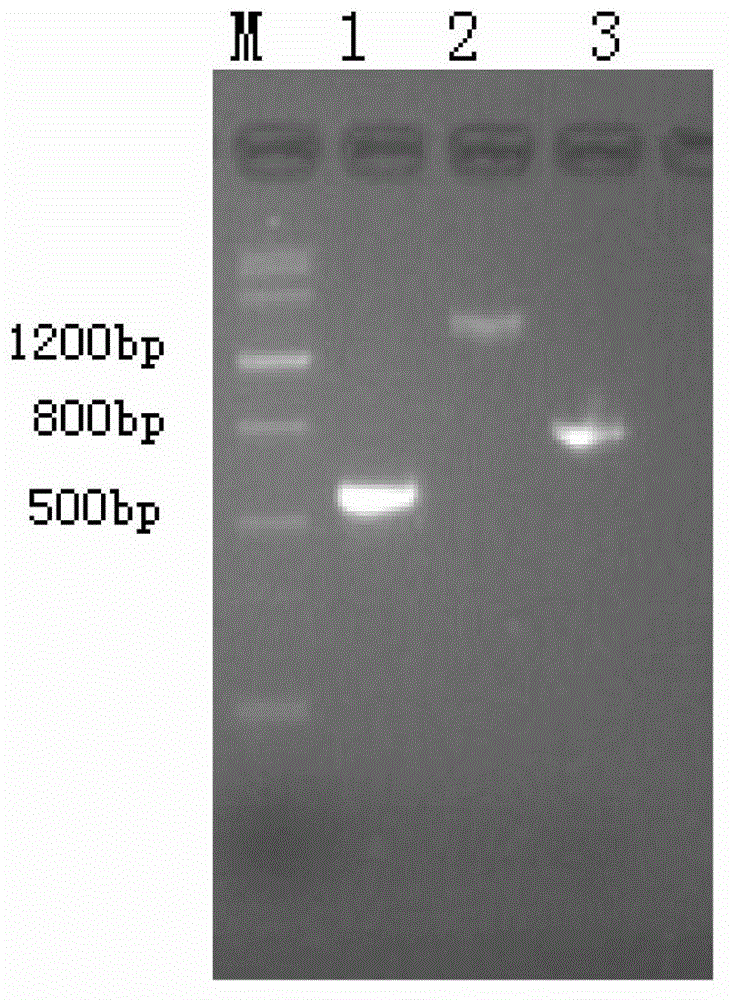
qPCR method and reagent for quickly detecting MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus)
PendingCN108624658AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesEasy patentMicrobiological testing/measurementMethicillin resistant StaphylococcusMicrobiology
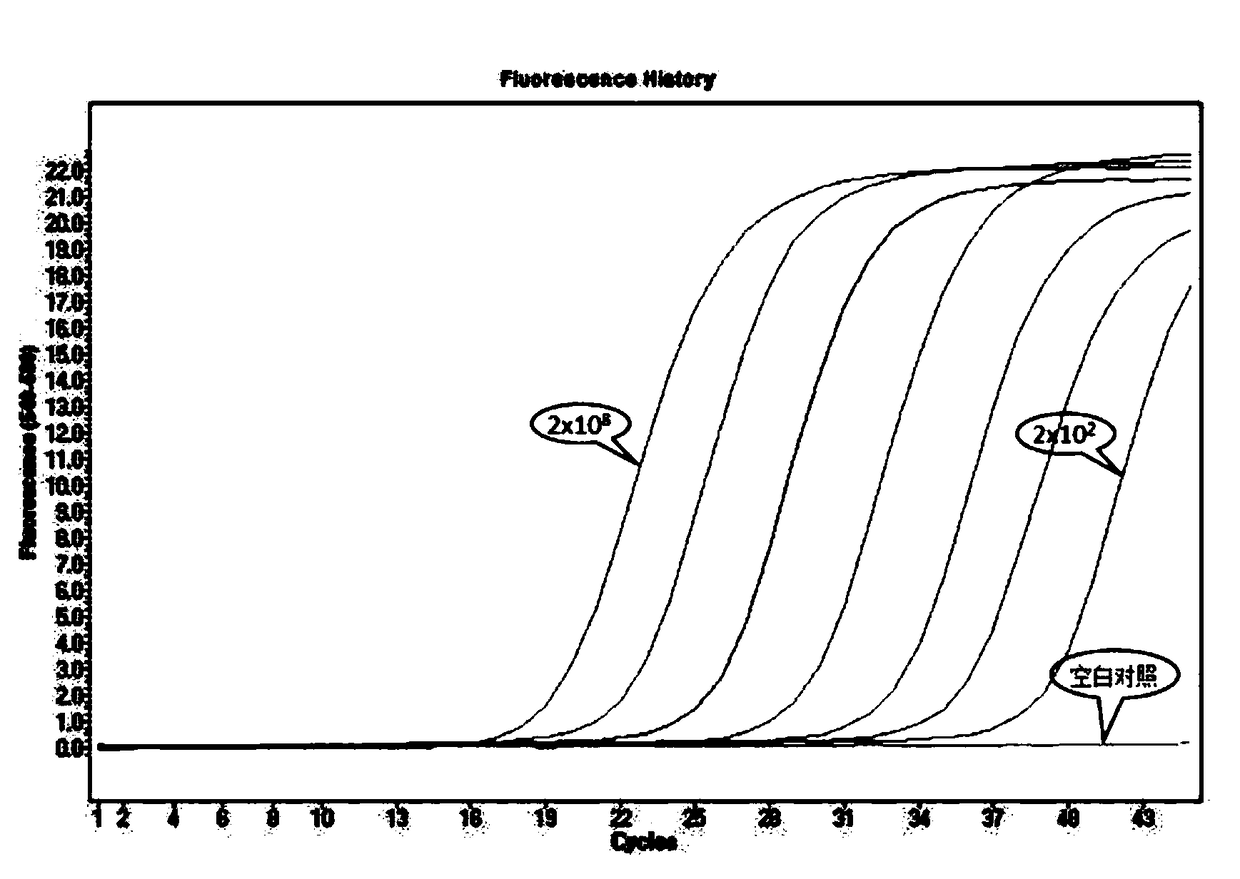
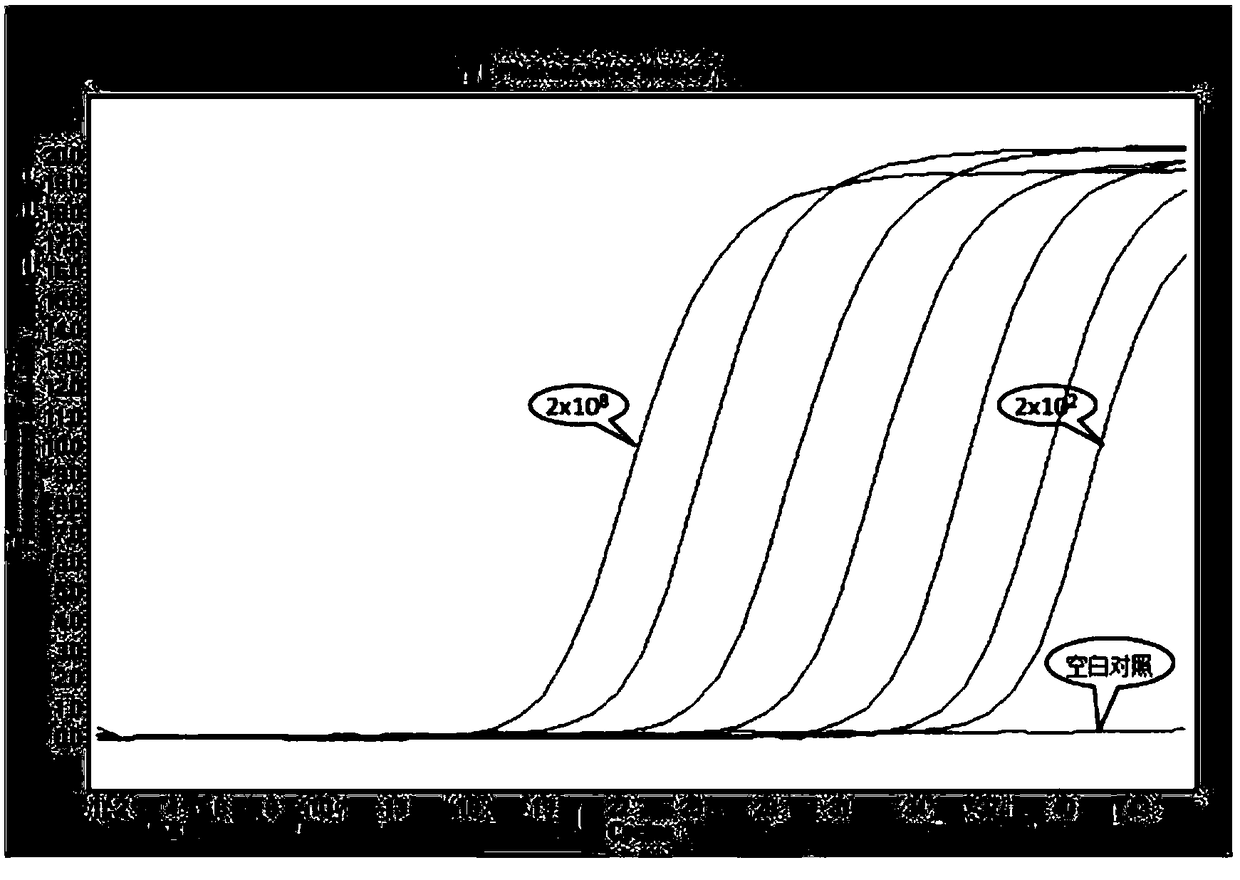
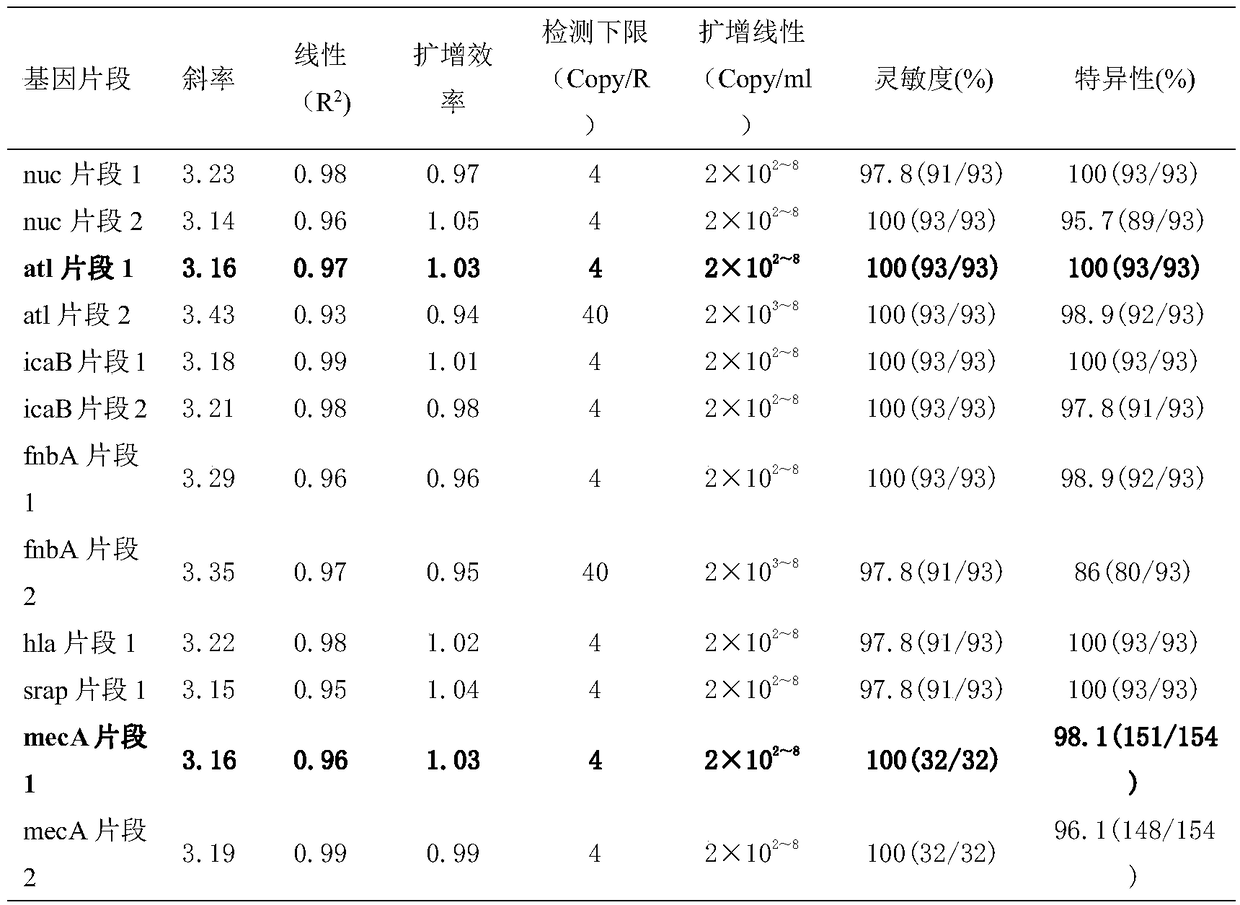
The invention provides a qPCR method and a reagent for quickly detecting MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus). The qPCR method comprises the following steps: (1) preliminary preparationprocedure; (2) nucleic acid extraction and purification; (3) primer / probe design, synthesis and labeling; (4) qPCR amplification and result judgment; (5) detection lower limit and amplification linearrange test; (6) gene fragment sensitivity and specificity calculation; (7) diagnostic sensitivity and specificity calculation; (8) a statistical method. The qPCR method and the reagent provided by the invention have the benefits that the detection lower limit is as low as 4cfu / reaction, and the amplification linear range reaches 2.0*10<2-8> Copies / ml; the sensitivity and the specificity of MRSA identification are 100 percent (352 / 352) and are 100 percent (77 / 77) respectively, and the sensitivity and the specificity of MRSA detection are 100 percent (94 / 94) and 95.4 percent (94 / 98) respectively; the qPCR method is simple and convenient, quick, high in sensitivity and good in specificity and not only can improve the diagnostic ability of MRSA infection, but also can realize the quick detection, thereby gaining time for early and accurate treatment.
Owner:深圳市宝安区沙井人民医院 +1
Compound and medicament for treating MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) infection
InactiveCN103360385AStrong specificityLittle side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsInfected patientPhotosens
The invention provides a compound and a preparation method thereof. The compound has a structure shown in a structural formula (I), wherein MRAS-expressed beta-lactamase can activate photosensitive groups in the compound provided by the invention, so as to generate active oxygen for exterminating MRAS without influencing a microbe and normal tissue which have unexpressed beta-lactamase, and therefore, the compound provided by the invention can achieve the beneficial effects of high efficiency, high specificity and less side effect, can be used as a photosensitizer for PACT treatment of MRSA infection and can provide a powerful tool for treating clinical patients with MRSA injection.
Owner:上海交通大学医学院附属第三人民医院
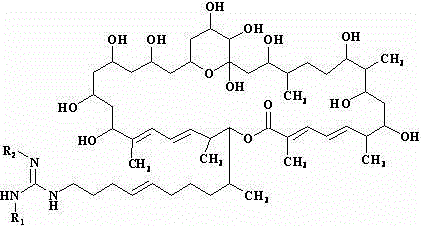
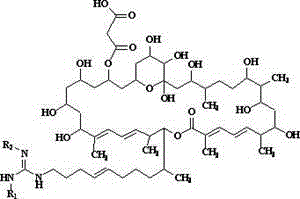
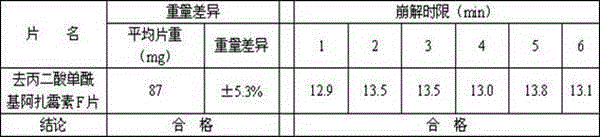
De-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F, preparation method thereof and application thereof to preparation of MRSA infection therapeutic drug
ActiveCN103044439AAvoid the disadvantage of easy alkylation of 29-position hydroxylImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin resistant StaphylococcusMalonic acid
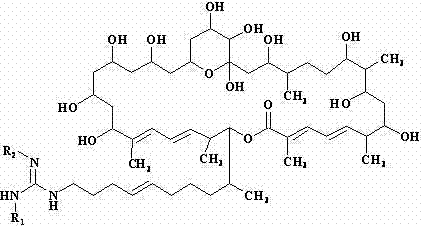
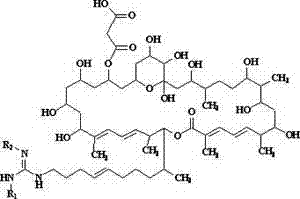
The invention discloses a de-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F, a preparation method thereof and the application thereof to preparation of an MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) infection therapeutic drug. Azalomycin F reacts in an alkaline methanol solution to produce de-malonate azalomycin F, the de-malonate azalomycin F is separated to obtain the de-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F. The MRSA activity test shows that the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) of the obtained de-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F to MRSA tester strain is 0.25-0.50 Mug / mL, which is 8-16 times of that of azalomycin F, and the de-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F has enhanced stability and water solubility. The de-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F has remarkable MRSA activity and a favorable development prospect and can be used for preparing an MRSA infection therapeutic drug.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of clemastine fumarate in preparation for resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
ActiveCN111920805AEnhanced inhibitory effectAchieve inhibitionAntibacterial agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsClemastine FumarateStaphylococcus aureus
The invention particularly relates to an application of clemastine fumarate in an anti-MRSA preparation. The MRSA has high toxicity, shows drug resistance to most clinically common antibiotic drugs, is widely distributed in a daily environment, and is a troublesome pathogenic strain. In order to develop an active substance with an inhibition effect on the drug-resistant bacteria, the invention screens and verifies that the clemastine fumarate has a good inhibition effect on MRSA from clinical drugs, and is expected to be applied to the development of anti-MRSA infection related drugs.
Owner:MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG PROVINCE SHANDONG UNIV
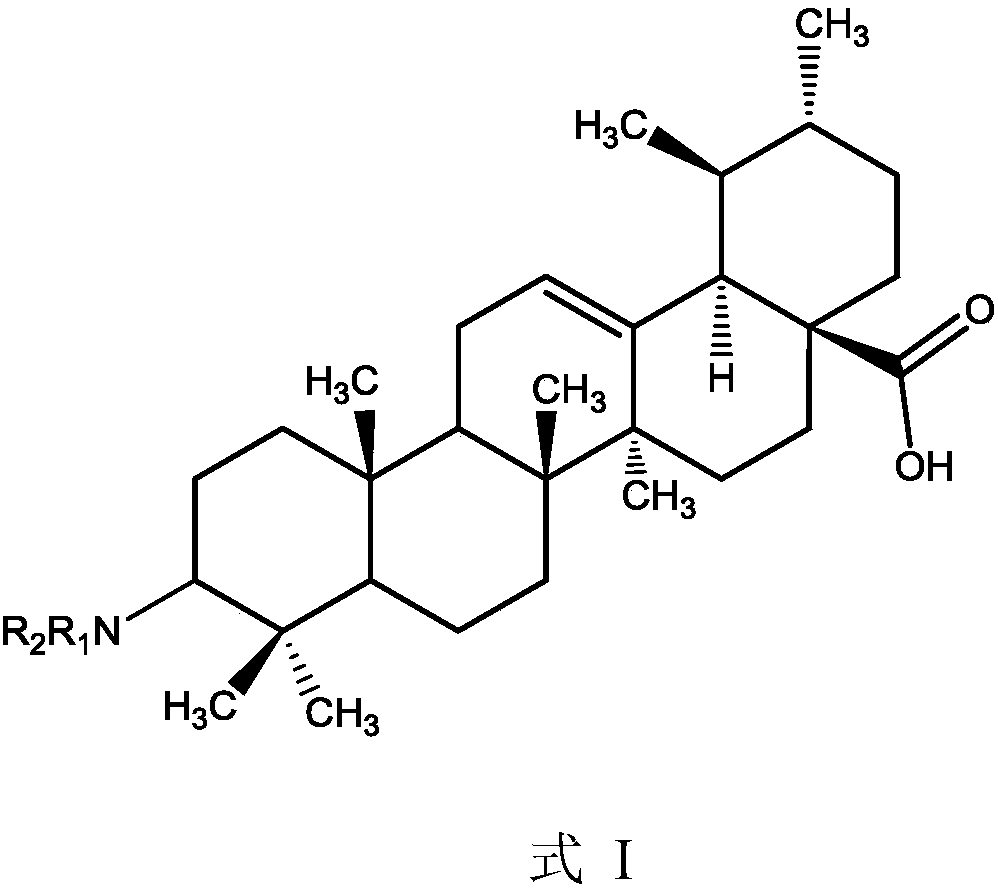
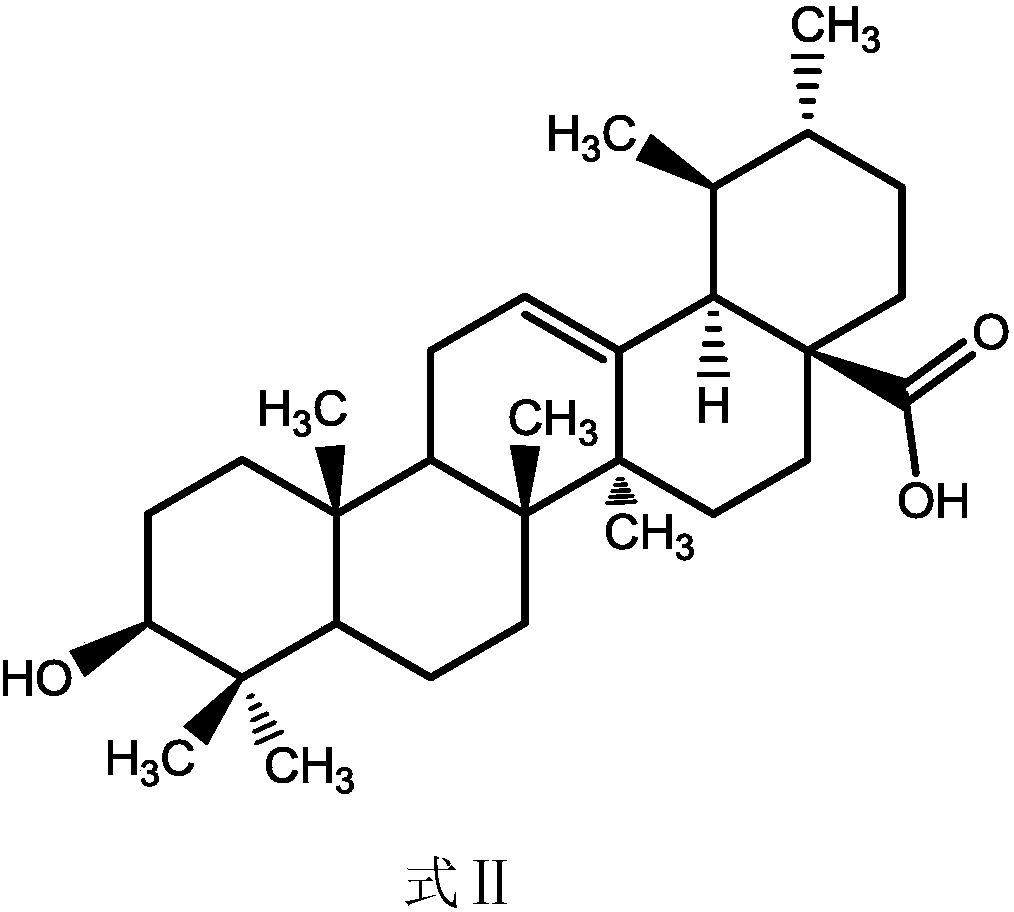
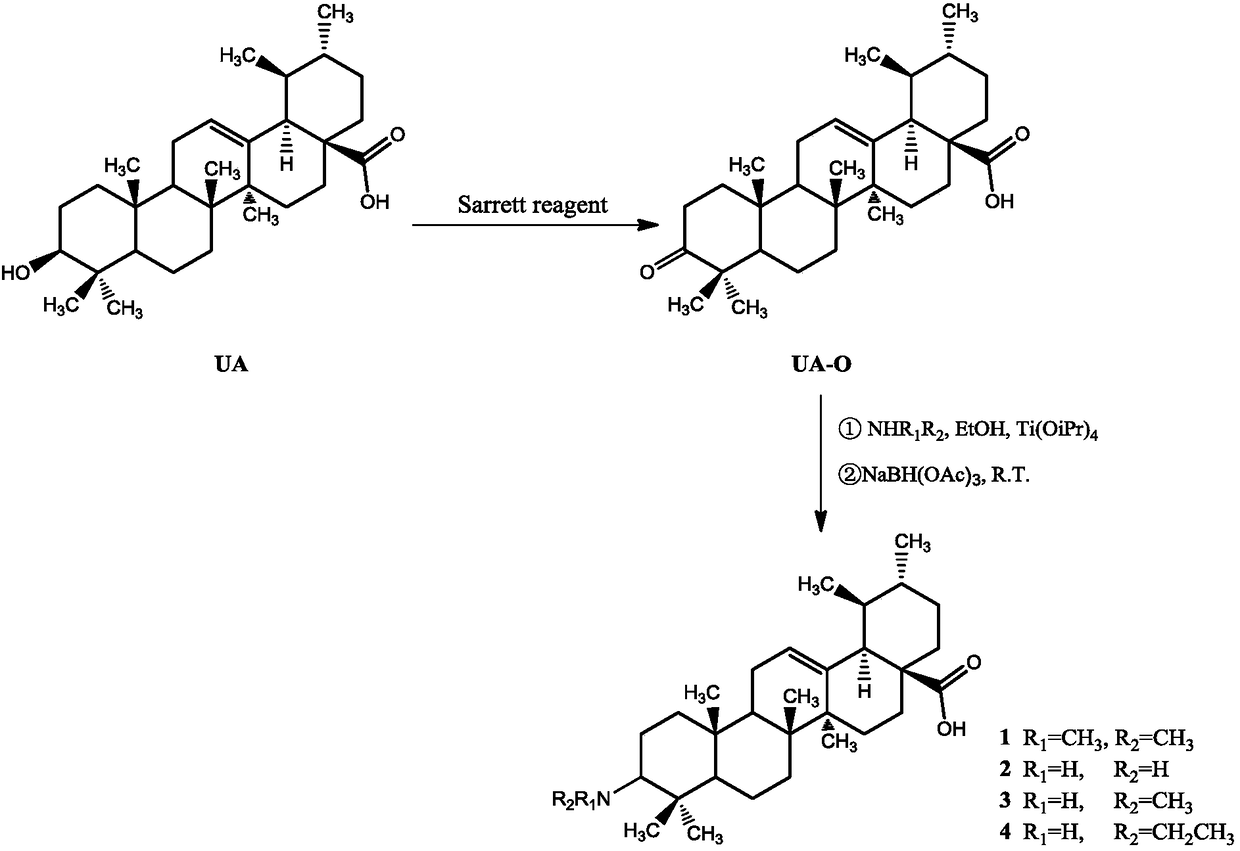
Ursolic acid derivative, preparation method thereof, and application thereof in preparation of drug for treating MRSA infection
ActiveCN108822179AGuaranteed not to be oxidizedOxidation mildAntibacterial agentsSteroidsSolubilitySodium triacetoxyborohydride
The invention discloses an ursolic acid derivative, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof in the preparation of a drug for treating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. The preparation method comprises the following steps: oxidizing ursolic acid by a Sarrett reagent to obtain a 3-hydroxy oxidation product of ursolic acid, and carrying out reductive amination on the 3-hydroxy oxidation product of ursolic acid by isopropyl titanate and sodium triacetoxyborohydride in order to prepare the ursolic acid derivative. Anti-MRSA activity test proves that theMIC of the obtained ursolic acid derivative on MRSA test strains is 16-32 [mu]g / mL, the anti-MRSA activity of the ursolic acid derivative is 4-8 times higher than that of the ursolic acid, and the derivative can form a salt together with equimolar hydrochloric acid in order to significantly improve the water solubility. The ursolic acid derivative has a significant anti-MRSA activity and a good development prospect, and can be used to prepare the drug for treating the MRSA infection.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
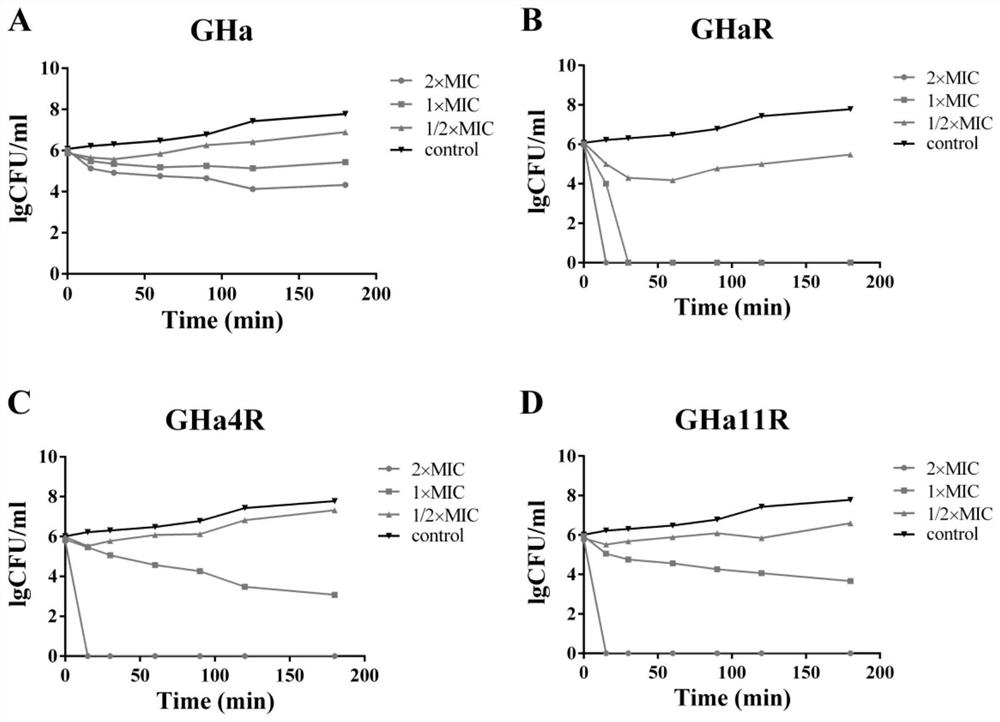
Antibacterial peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN112341522AStrong anti-MRSA activityFast anti-MRSA activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiofilmMRSA infection
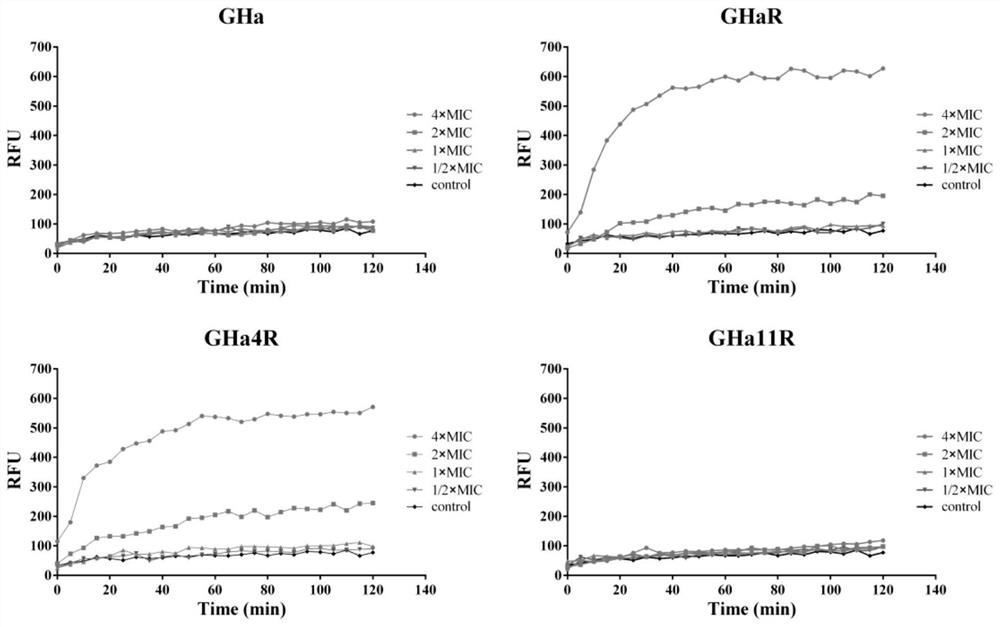
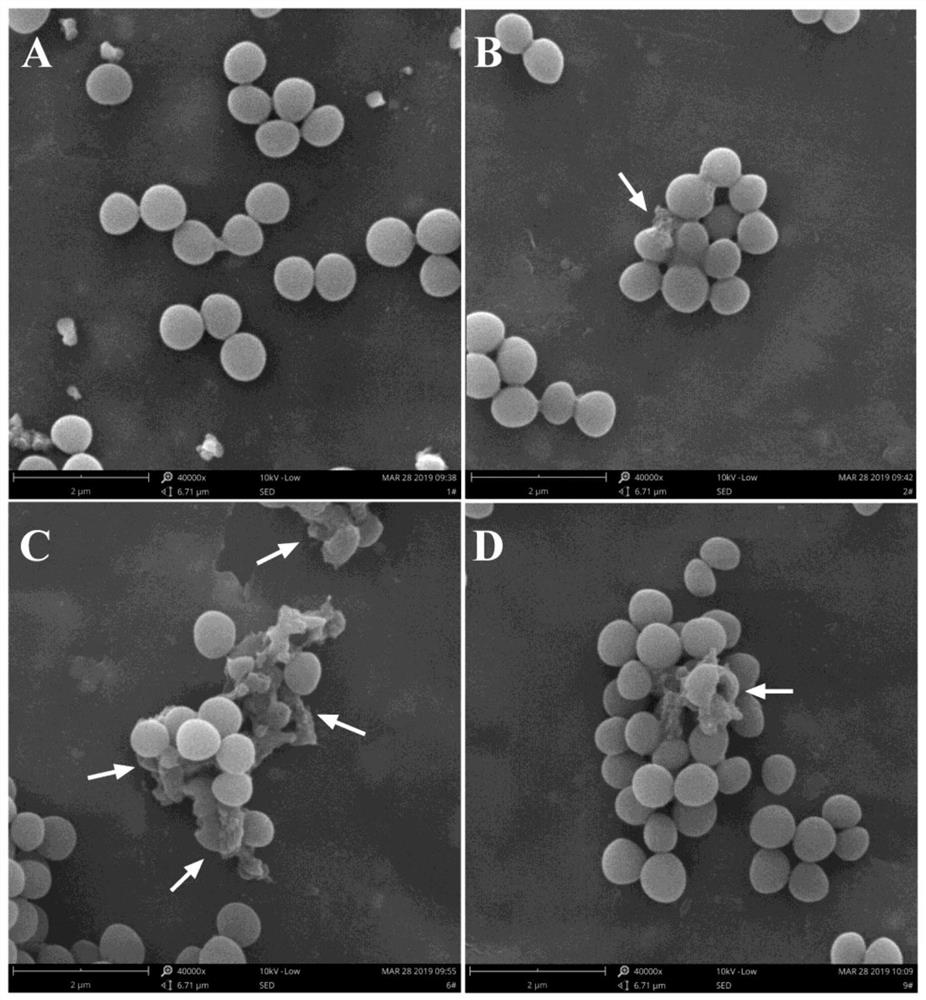
The invention provides an antibacterial peptide and an application thereof. The antibacterial peptide is derivative peptides GHaR, GHa4R and GHa11R of a Temporin-GHa (GHa), and Belongs to the field ofapplication of peptide antibiotics. Antibacterial peptide GHa is directionally modified to obtain the derivative peptides GHaR, GHa4R and GHa11R. The GHaR, the GHa4R and the GHa11R provided have stronger and faster anti-MRSA activity, and the GHa11R is likely to become a new penetrating peptide. GHaR and GHa11R have high-efficiency anti-MRSA biofilm activity, do not easily generate drug resistance, and have low cytotoxicity and high cell selectivity, so that the GHaR and the GHa11R become novel antibacterial drug candidates with great prospects in treating MRSA infection.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Nano drug delivery system of equisetin and derivative thereof as well as preparation and application of nano drug delivery system in skin soft-tissue infection
InactiveCN107802598ALarge specific surface areaHigh porosityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPorosityDual release
The invention relates to a novel multifunctional nano drug delivery system of MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus) equisetin and a derivative thereof as well as a preparation and application of the nano drug delivery system in skin soft-tissue infection MRSA, with the combination of nano techniques and electrostatic spinning techniques, nano electrostatic spinning yarns which are applied to skin soft-tissue infection and have the advantages of being large in specific surface area, high in porosity, good in air and moisture permeability and the like are prepared from the nano drugdelivery system, and a novel clinical treatment scheme is provided for skin soft-tissue infection MRSA. By adopting the nano drug delivery system, not only are problems of drug delivery systems for treating skin soft-tissue infection MRSA of MRSA equisetin and the derivative thereof solved, but also the bioavailability of medicines is improved, dual slow release is achieved, and the nano drug delivery system can be applied to treatment on skin soft-tissue infection.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL INST OF FIELD SURGERY OF PLA ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
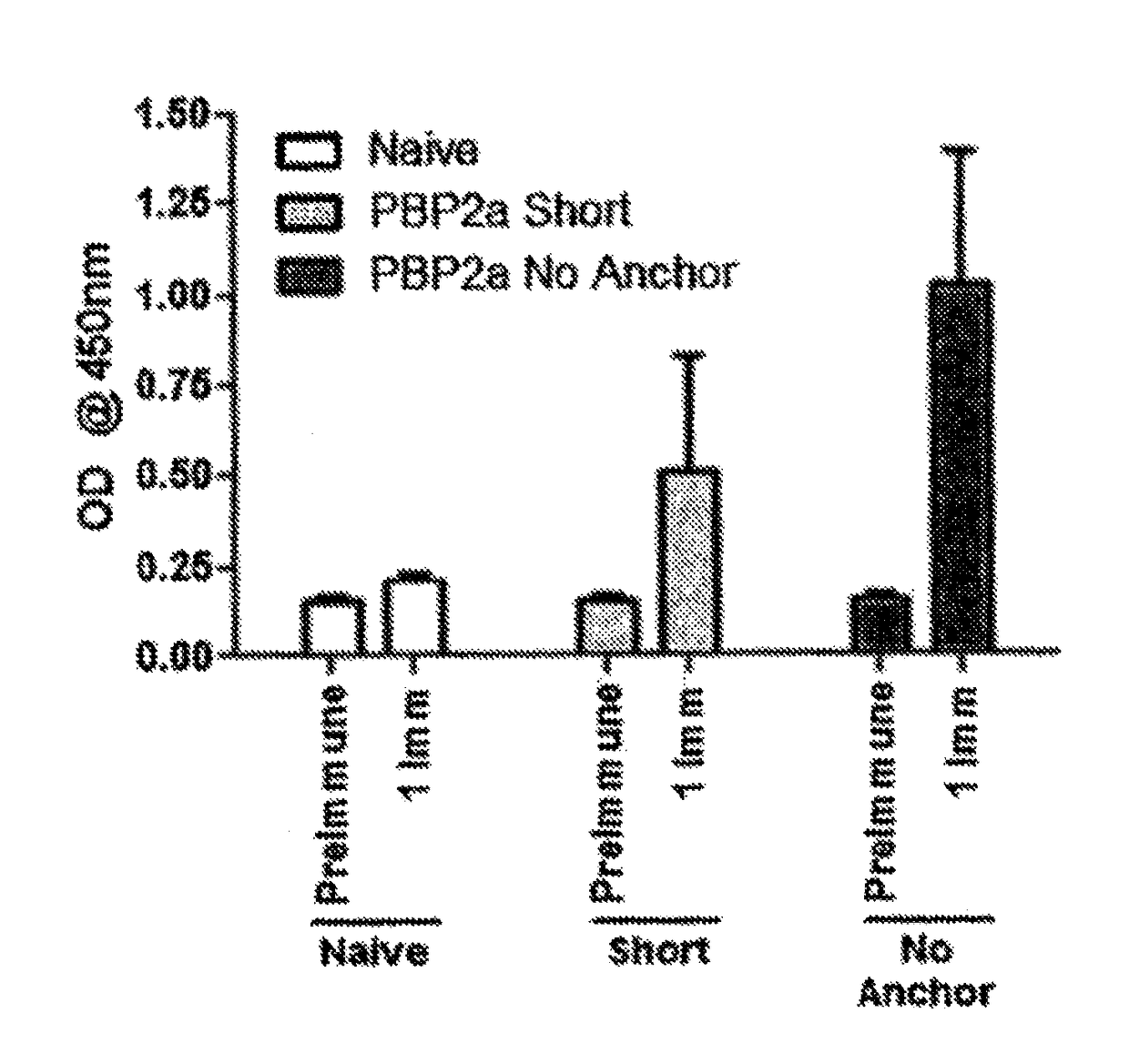
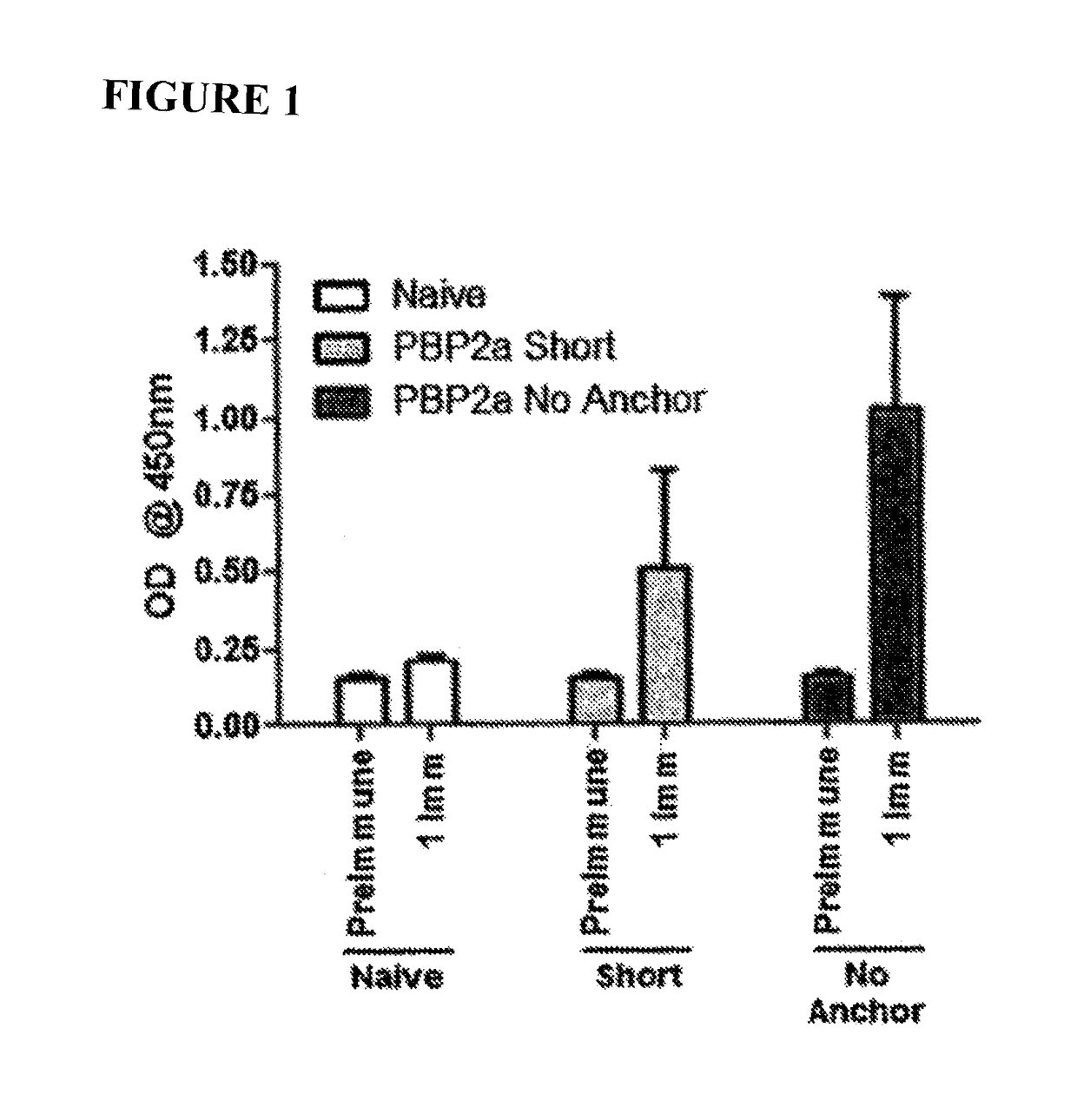
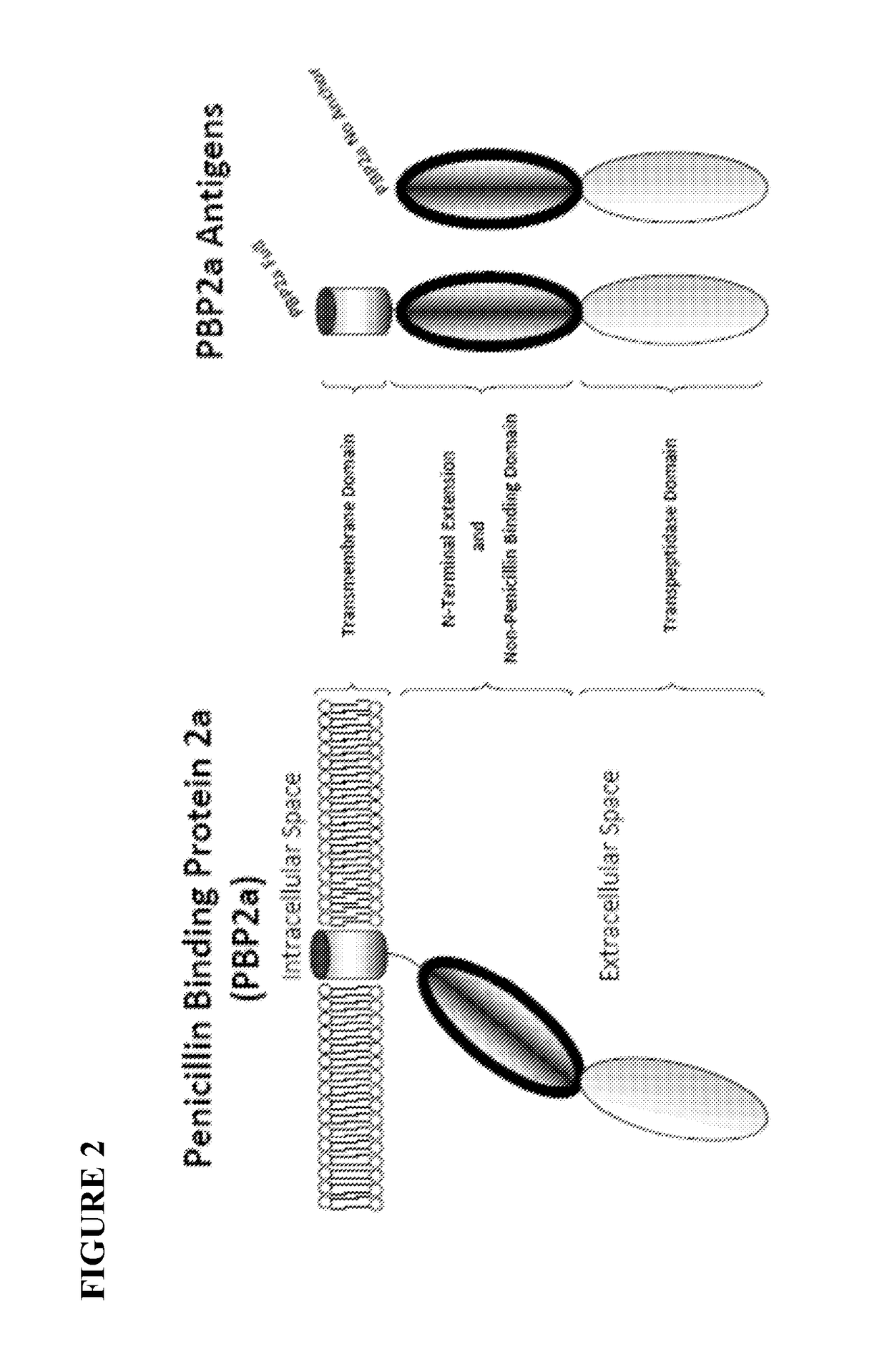
Proteins comprising MRSA PBP2a and fragments thereof, nucleic acids encoding the same, and compositions and their use to prevent and treat MRSA infections
Nucleic acid molecules which encode an MRSA PBP2a protein or a fragment thereof which comprises at least 245 amino acid are disclosed. Compositions comprising the nucleic acid molecules are disclosed. Novel proteins which comprise a MRSA PBP2a protein or a fragment thereof which comprises at least 245 amino acid are disclosed are disclosed. Methods of inducing an immune response against MRSA PBP2a are disclosed, as are methods of treating an individual who has been diagnosed with MRSA and methods of preventing MRSA infection in an individual.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) vaccine recombinant proteantigen I12C, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103059139AHigh expressionEasy to separate and purifyAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenAdjuvant
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) vaccine recombinant protein I12C. The fusion protein is composed of two active segments of MRSA iron ion surface determination protein IsdB and an active segment of ClfA antigen molecule, and the segments are used by connecting peptides. The fusion protein has the advantages of high purity, high expression quantity, high efficiency and high safety, and is convenient for separation and purification. The preparation method is simple and easy to amplify, and has favorable repetitiveness. After using the aluminum adjuvant, the fusion protein can be used for preparing an anti-MRSA subunit vaccine and preparing a detection kit for MRSA. The animal experiment proves that the fusion protein can effectively stimulate the mechanisms to generate high humoral immune response and favorable immunoprotection function of resisting MRSA infection.
Owner:CHENGDU OLYMVAX BIOPHARM +1
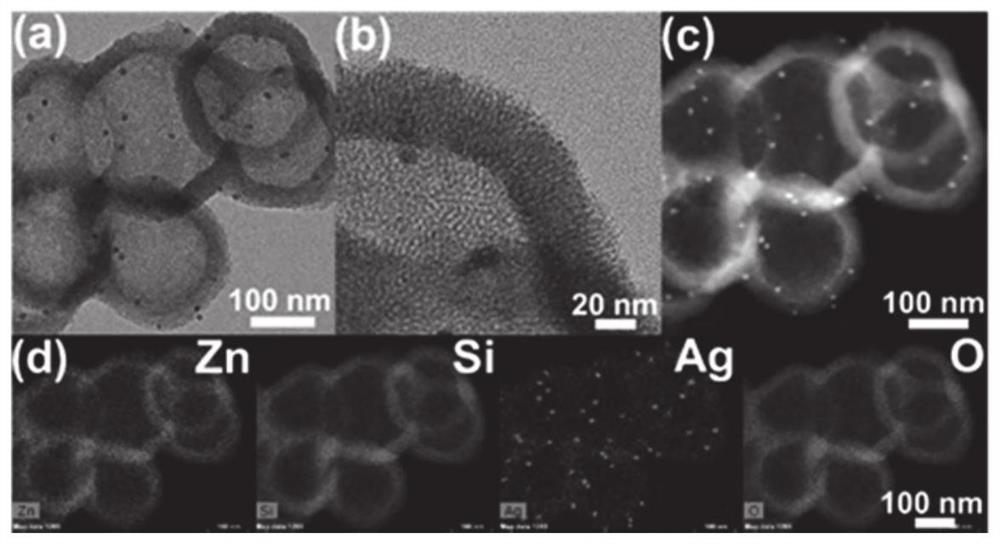
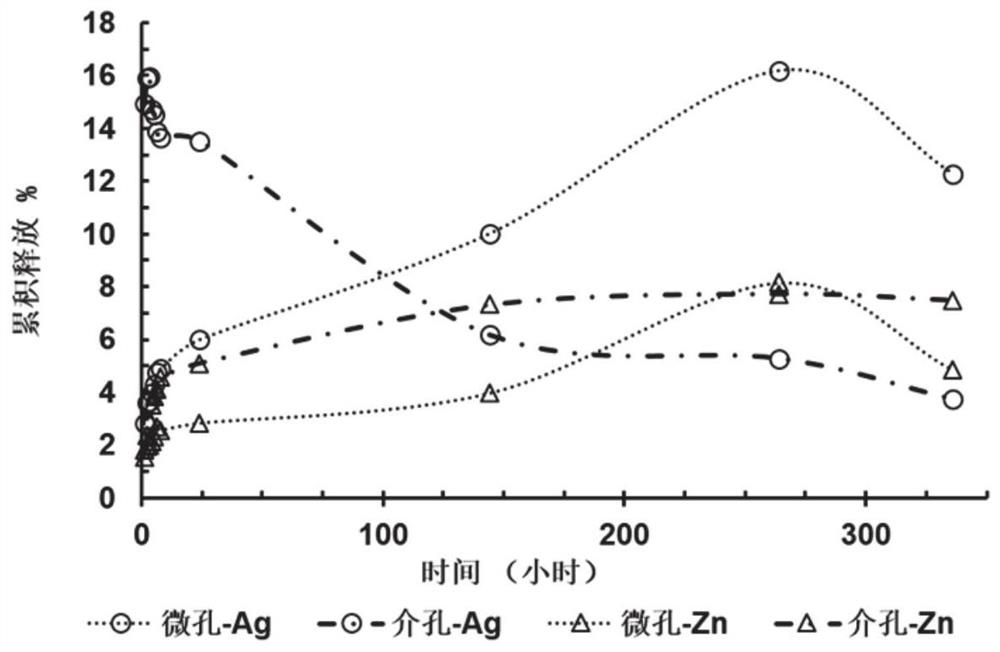
Nanoreactor, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112826832ASimple preparation techniquePlay a double roleAntibacterial agentsInorganic active ingredientsSilica nanoparticlesNanoreactor
The invention discloses a nanoreactor, a preparation method and an application thereof. The nanoreactor is metal-loaded hollow silicon dioxide nanoparticles; the metal comprises metal I and metal II; the metal I comprises any one of a silver element, a copper element, a cobalt element, a nickel element and a magnesium element; and the metal II is a zinc element. The nanoparticles obtained by adopting the preparation method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of uniform size, high surface area, ordered mesopores and large pore volume. In addition, the nanoreactor can also be used as an ideal antibacterial agent for treating MRSA infection.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Synthesis and application of antibacterial medicine ASC for targeted treatment of MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus), SAU (staphylococcus aureus) and super bacterium infection
ActiveCN109535180AEffective treatmentReduced colonizationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsProtein targetAntibiotic Y
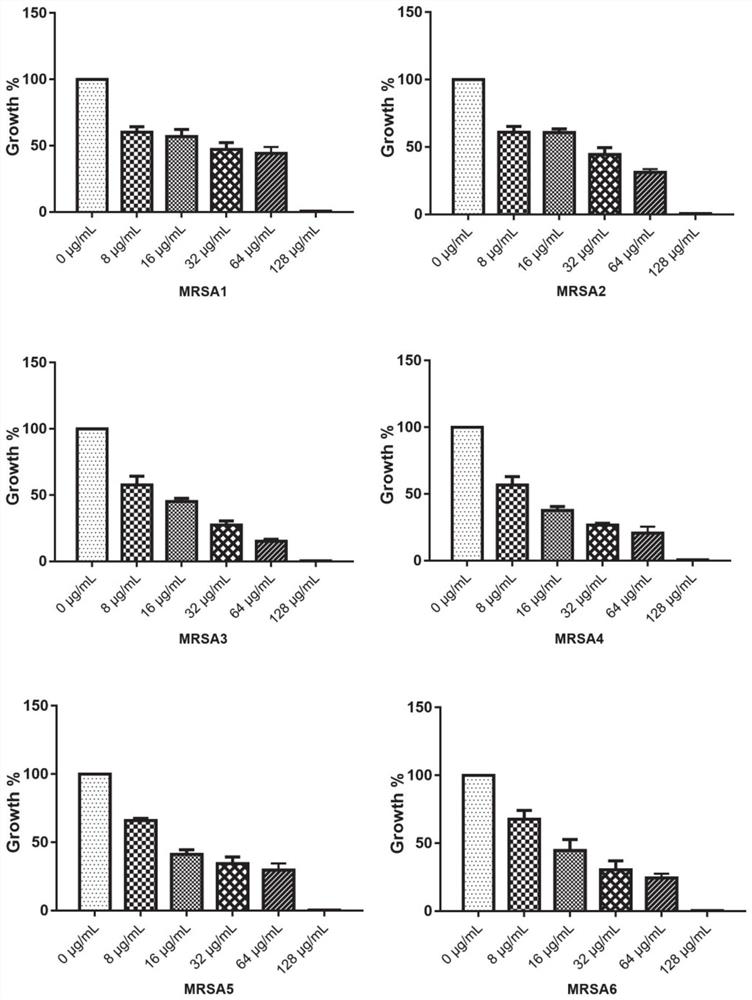
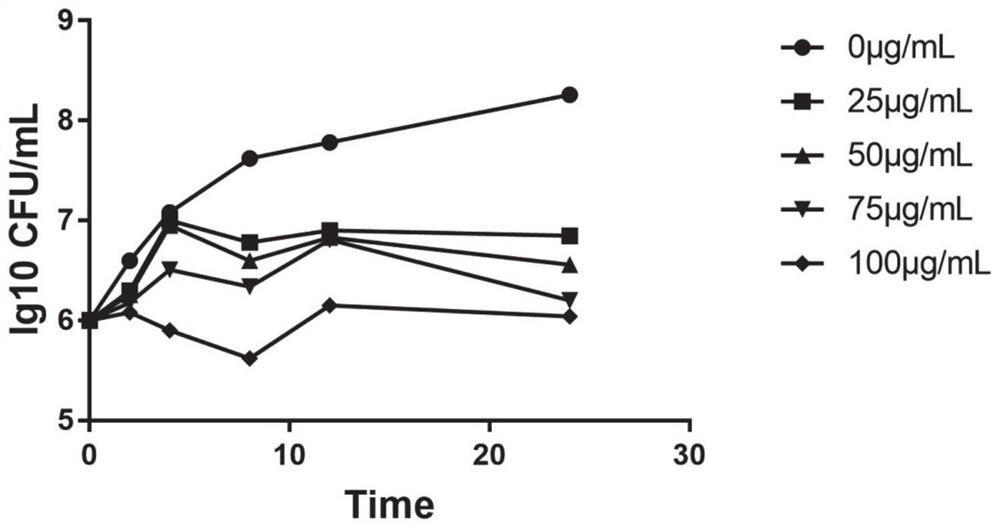
The invention relates to synthesis and application of an antibacterial medicine ASC for targeted treatment of MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus) and SAU (staphylococcus aureus) infection and for treatment of super bacterium infection by being cooperated with antibiotics. The effective concentration of the ASC for treating the MRSA infection is 2 mug / mL; the efficacy is 4 times higher than the efficacy of standard medicine oxacillin; the dosage of 35 mg / kg can realize the specific effect treatment on mouse heart and lung MRSA infection, and the MRSA colonization quantity in liver, spleen and kidney tissues of the mouse can be obviously reduced. The ASC is also a broad spectrum inhibitor of antibiotic drug resistant target protein metal beta-lactamase, and can be cooperated with beta-lactamase, aminoglycoside and tetracycline type medicine to realize the targeted treatment of SAU infection; through the dose of 1 mug / mL, the curative effects of antibiotics can be improvedto 4 to 128 times; through the dose of 64 or 8 mug / mL, the curative effect of Xianfeng V on NDM-1 or CcrA producing medicine-resistance bacteria E.coli is improved by 32 times.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
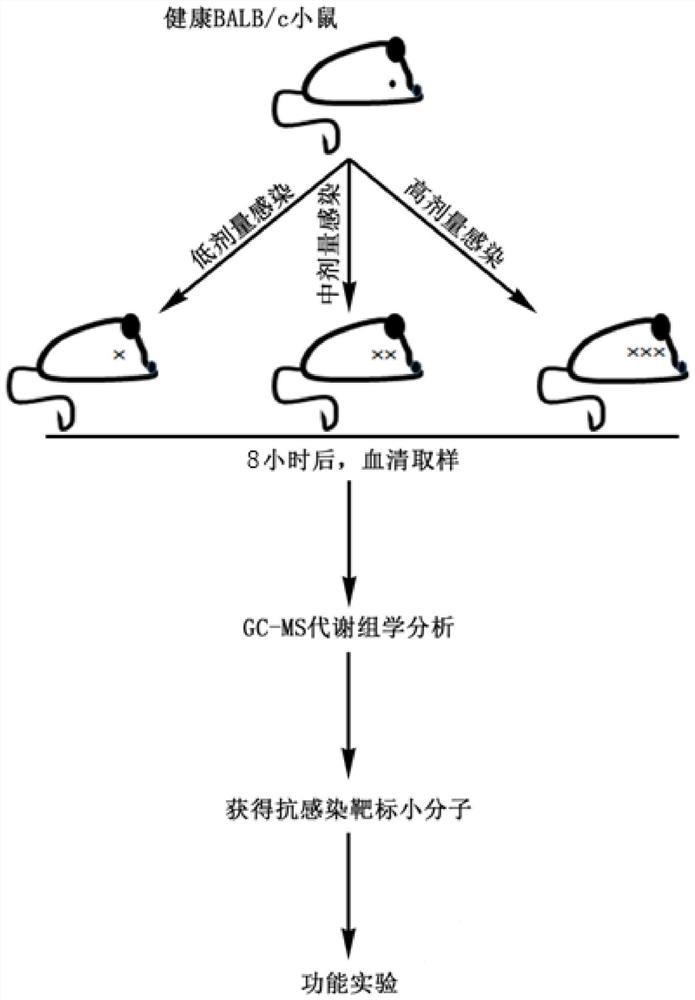
Use of small molecule compound in improving ability of host to remove pathogenic bacteria and preparing drugs resistant to pathogenic bacteria infection
PendingCN111714482AImprove cleanlinessImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStaphylococcus aureusSynergy
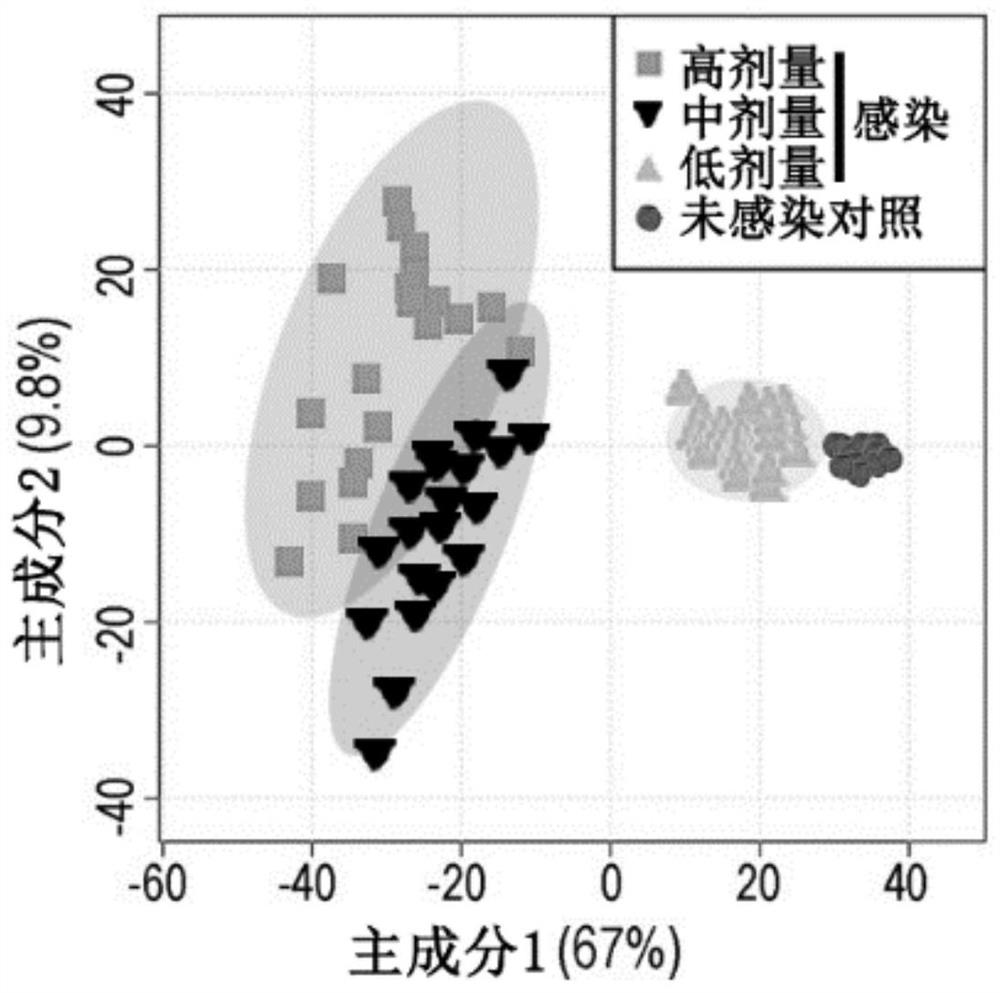
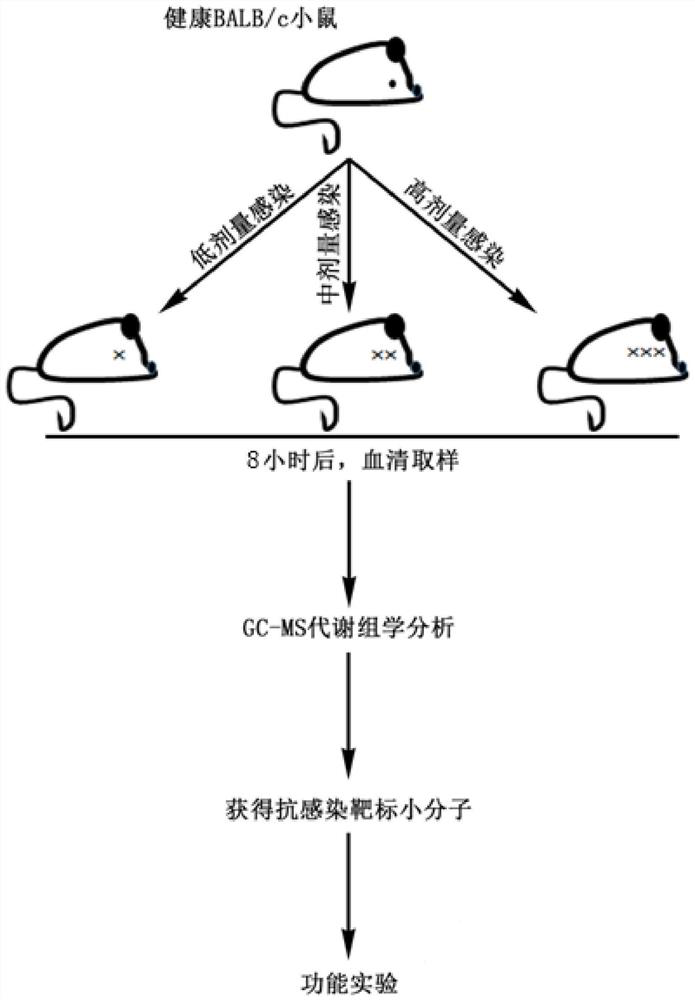
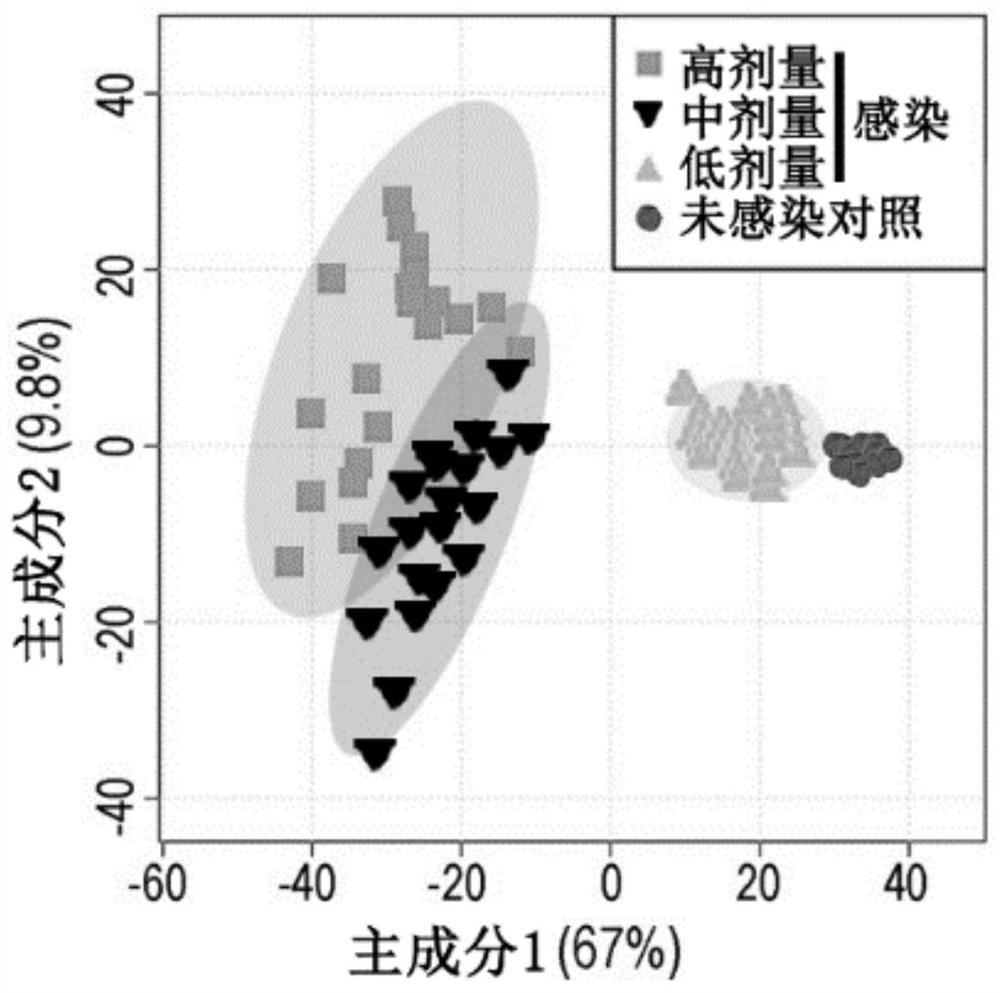
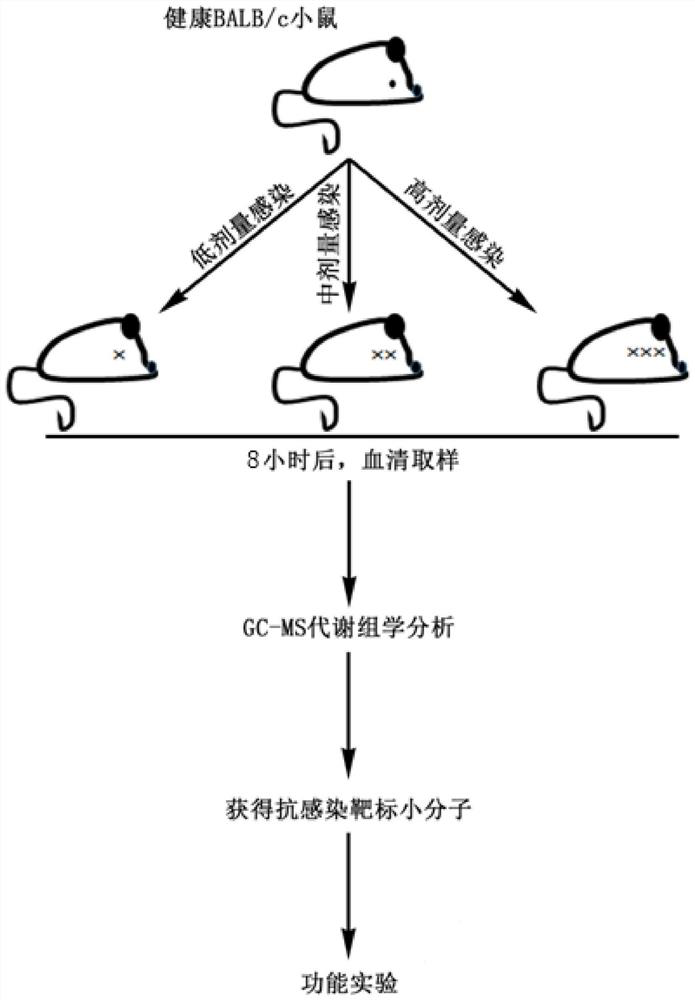
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a use of a small molecule compound in improving the ability of a host to remove pathogenic bacteria and preparing drugs resistant to pathogenic bacteria infection. The metabonomics technology is utilized, the metabolic change in the serum of mice infected with the pathogenic bacteria is analyzed, and thereby the small molecule compound that can improve the ability of the host to remove and resist the pathogenic bacteria, reduce the content of the pathogenic bacteria in the host and improve a survival rate, and especiallycan improve the ability of the host to resist Staphylococcus aureus / MRSA infections is screened out. Aiming at the application of the small molecule compound, the effect of the small molecule compound is realized by taking the metabolic regulation of the immunity of the host as a cut-in point and regulating the own immunity of the host to resist pathogenic bacteria infections, so that the methodcan eliminate the risk of producing drug-resistant bacteria. In addition, the small molecule compound can better protect the host in synergy with an antibiotic, the shortening of a use period of the antibiotic is facilitated, and the production of drug-resistant bacteria is minimized.
Owner:SHENZHEN INT INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Application of small molecular compound to improvement of pathogenic bacteria clearing capacity of host and application to preparation of pathogenic bacteria infection resistant drugs
PendingCN111714496AImprove cleanlinessImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to application of a small molecular compound to improvement of the pathogenic bacteria clearing capacity of a host and application of the small molecular compound to preparation of pathogenic bacteria infection resistant drugs. According to the invention, a metabonomics technology is utilized, and metabolic changes of the serumof mice infected with pathogenic bacteria are analyzed, so that a small molecular compound capable of improving the pathogenic bacteria clearing capability and resistance capability of a host, reducing the content of pathogenic bacteria in the host, improving the survival rate and particularly improving the staphylococcus aureus / MRSA infection resistance capability of the host can be screened out. Directed at the application of the small molecule compound, and the effect of the small molecule compound is realized by taking metabolism to adjust the immunity of the host as an entry point for adjusting the immunity of a host to resist pathogenic bacteria infection, so that the risk of generating drug-resistant bacteria can be eliminated by the method. Besides, the small molecular compound can play a better role in protecting the host in the synergistic effect of antibiotics, is beneficial to shortening the service cycle of the antibiotics, and reduces the generation of drug-resistant bacteria as much as possible.
Owner:深圳市益米诺医药科技有限公司
Application of small molecule compound to improvement of capacity of host for clearing pathogenic bacteria and to preparation of drug for resisting pathogenic bacterium infection
PendingCN111714495AImprove cleanlinessImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStaphylococcus aureusSynergy
The present invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to application of a small molecule compound to improvement of capacity of a host for clearing pathogenic bacteria and topreparation of a drug for resisting pathogenic bacterium infection. The present invention utilizes a metabonomics technology to analyze the metabolic changes in the serum of mice infected with pathogenic bacteria, thereby screening the small molecule compound which can improve the capacity of the host for clearing and resisting pathogenic bacteria, reduce the content of pathogenic bacteria in thehost, improve the survival rate, and especially improve the capacity of the host for resisting staphylococcus aureus / MRSA infection. The invention aims at the application of the small molecule compound, and the effect is achieved by taking metabolic regulation of the immunity of the host as the entry point and regulating the immunity of the host to resist pathogenic infections. Therefore, the method can eliminate the risk of drug-resistant bacteria. In addition, the small molecule compound can better protect the host in synergy with antibiotics, can shorten the use period of antibiotics and minimize the production of drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:SHENZHEN INT INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Preparation method and application of tea nanodots
ActiveCN113440565ASolve residual problemsSolve pollutionAntibacterial agentsNanomedicineBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a preparation method and antibacterial application of tea nanodots; and the method comprises the following steps of: crushing, extracting, separating, purifying, concentrating, drying and the like to obtain the tea nanodots (TNDs) with the particle size of 3 nm, which are assembled by at least six or more catechins through hydrogen bonds and pi-pi conjugates. The antibacterial activity and stability of the TNDs are superior to those of corresponding monomer small molecules and a mixture of the monomer small molecules; and researches on a mouse skin MRSA wound infection model and an MRSA infection pneumonia model find that: compared with clinical antibiotic vancomycin, the TNDs have a better curative effect. Due to the dual antibacterial mechanisms of physical transmembrane and targeted bacterial amino acid metabolism of the tea nanodots, the drug resistance of bacteria to the tea nanodots is not easy to generate; and meanwhile, the TNDs have good biocompatibility and in-vivo safety and have a certain clinical application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Antibody against staphylococcus aureus manganese ion binding protein c and its application
ActiveCN110845611BAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaManganese ion bindingInfection induced
The invention discloses an antibody against Staphylococcus aureus manganese ion-binding protein C and application thereof, wherein the epitope peptide recognized by the antibody against Staphylococcus aureus manganese ion-binding protein C includes at least MntC 126‑128aa , the amino acid sequence is LDN; the antibody is produced by culturing host cells expressing the vector to produce monoclonal antibodies, and the produced monoclonal antibodies are secreted into the supernatant, and purified by chromatography. The antibody of the invention can treat sepsis caused by MRSA infection, and has important significance in preventing and treating Staphylococcus aureus infection.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
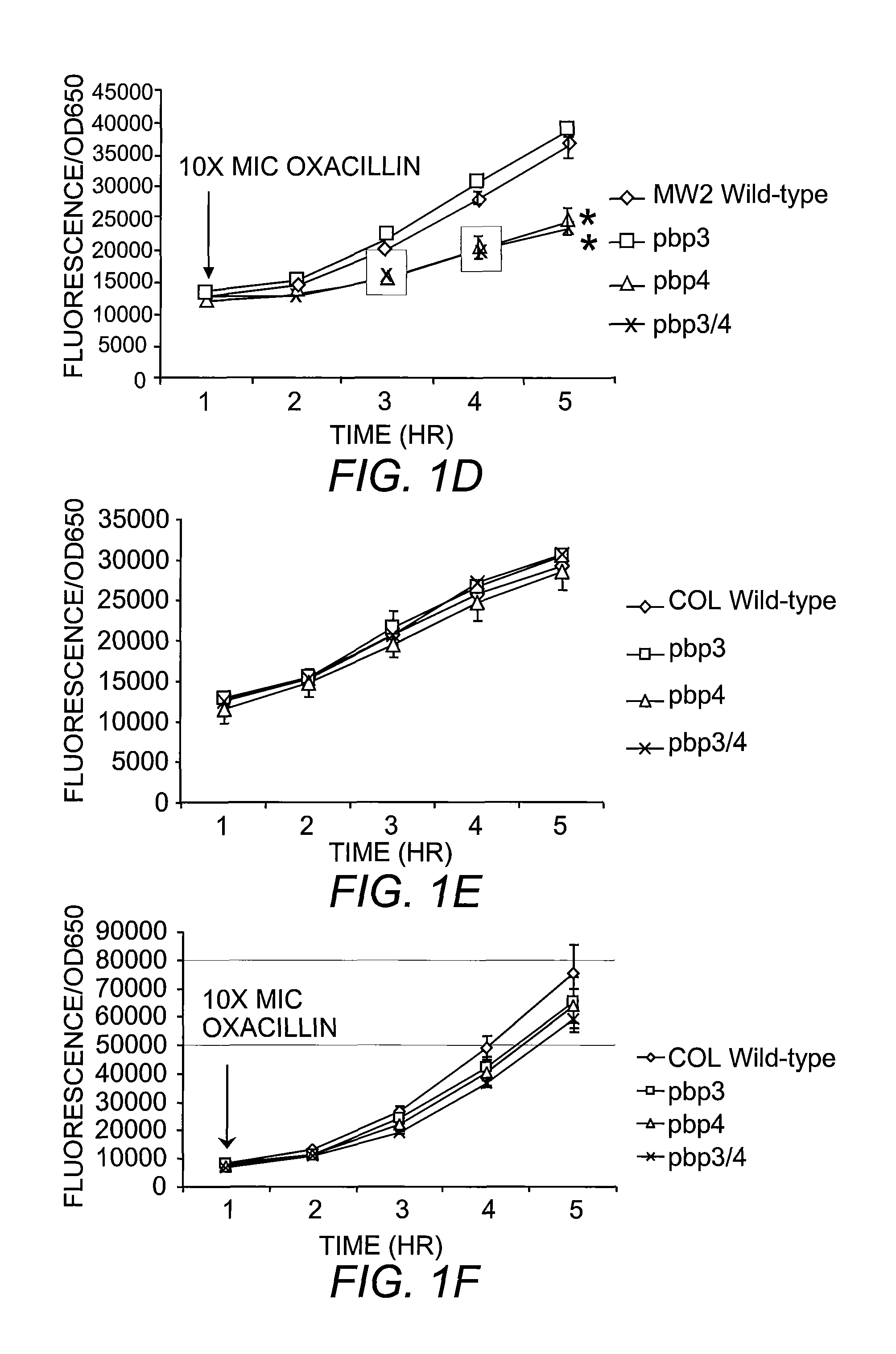
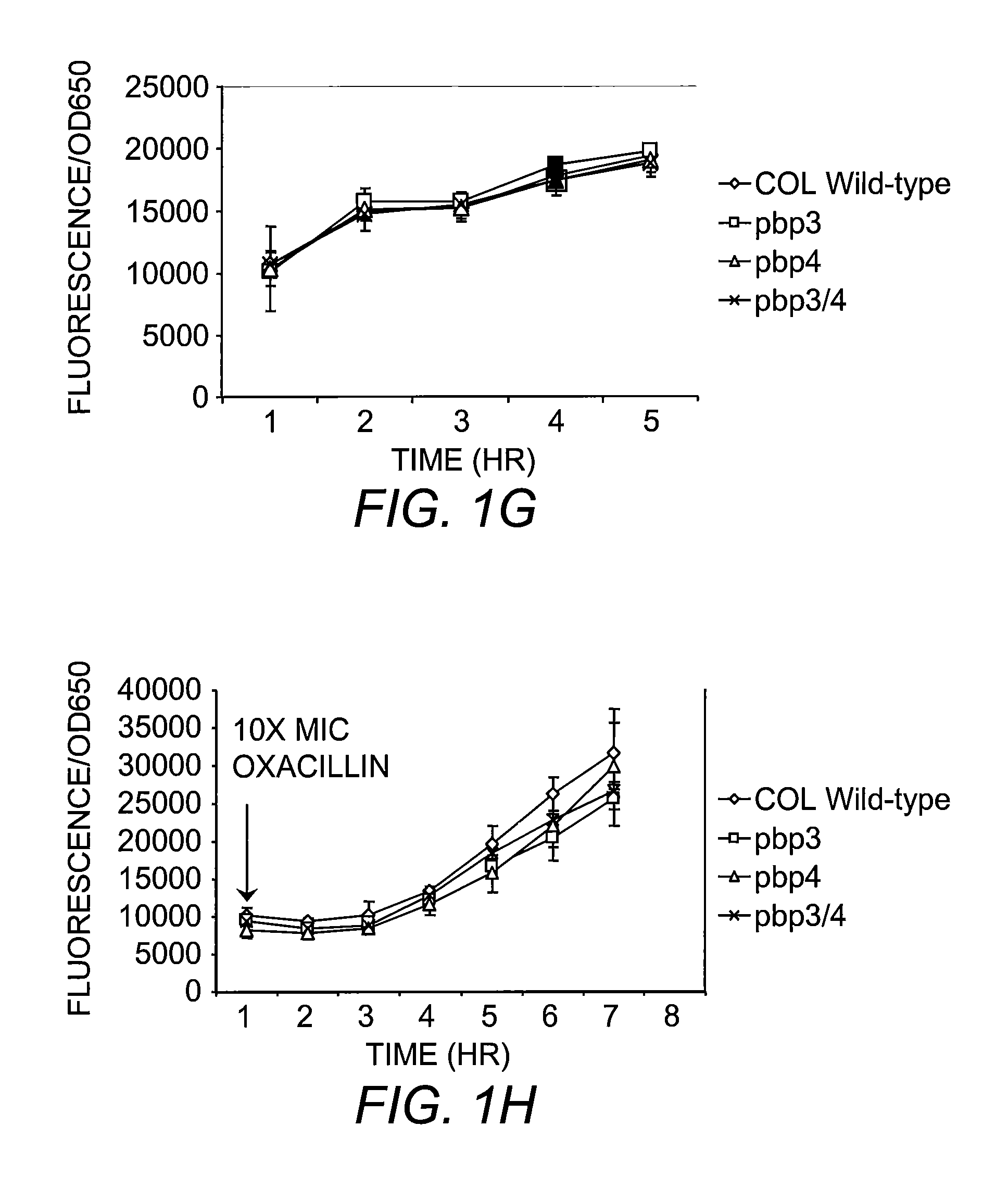
Compositions and methods for diagnosing and treating community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
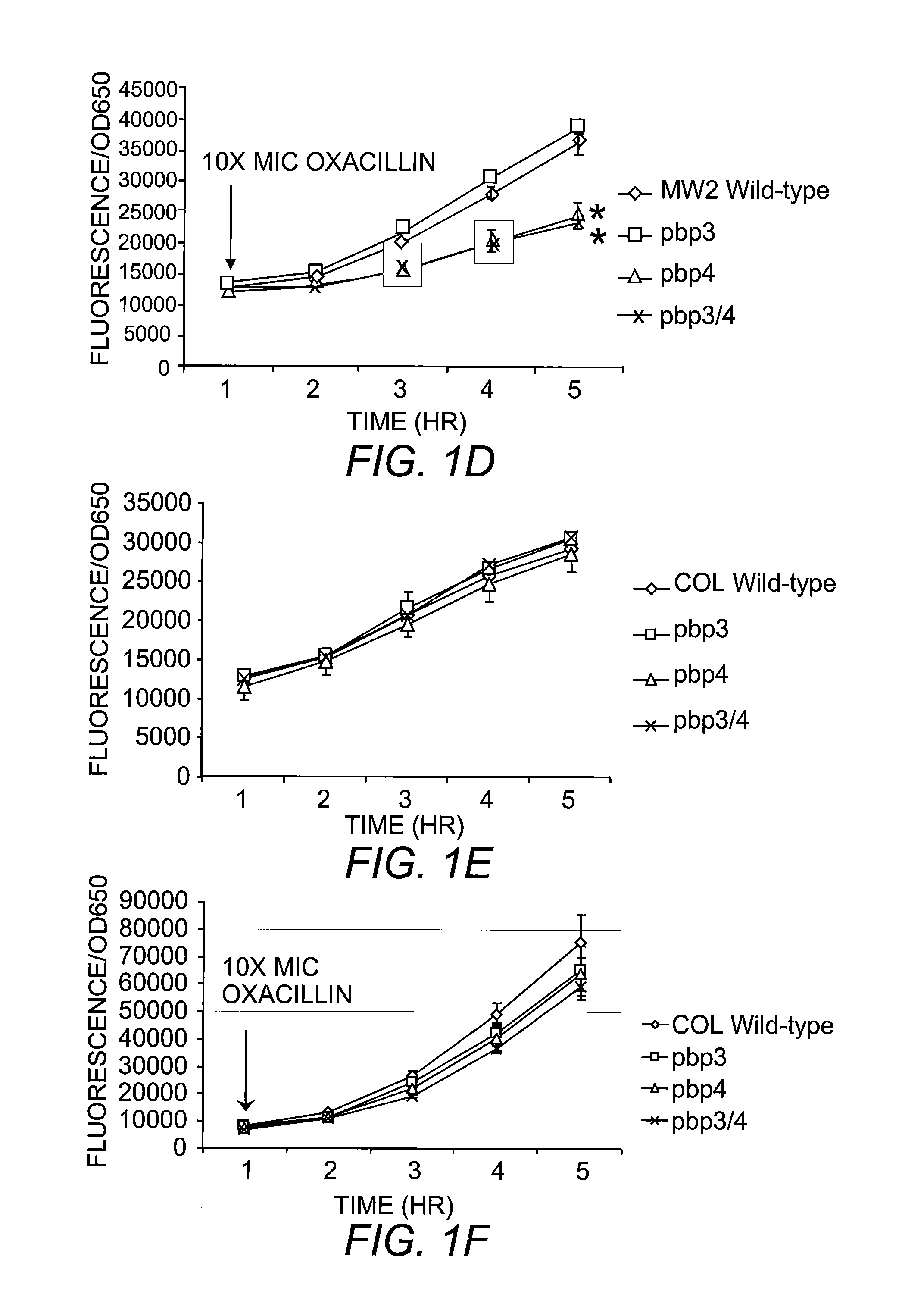
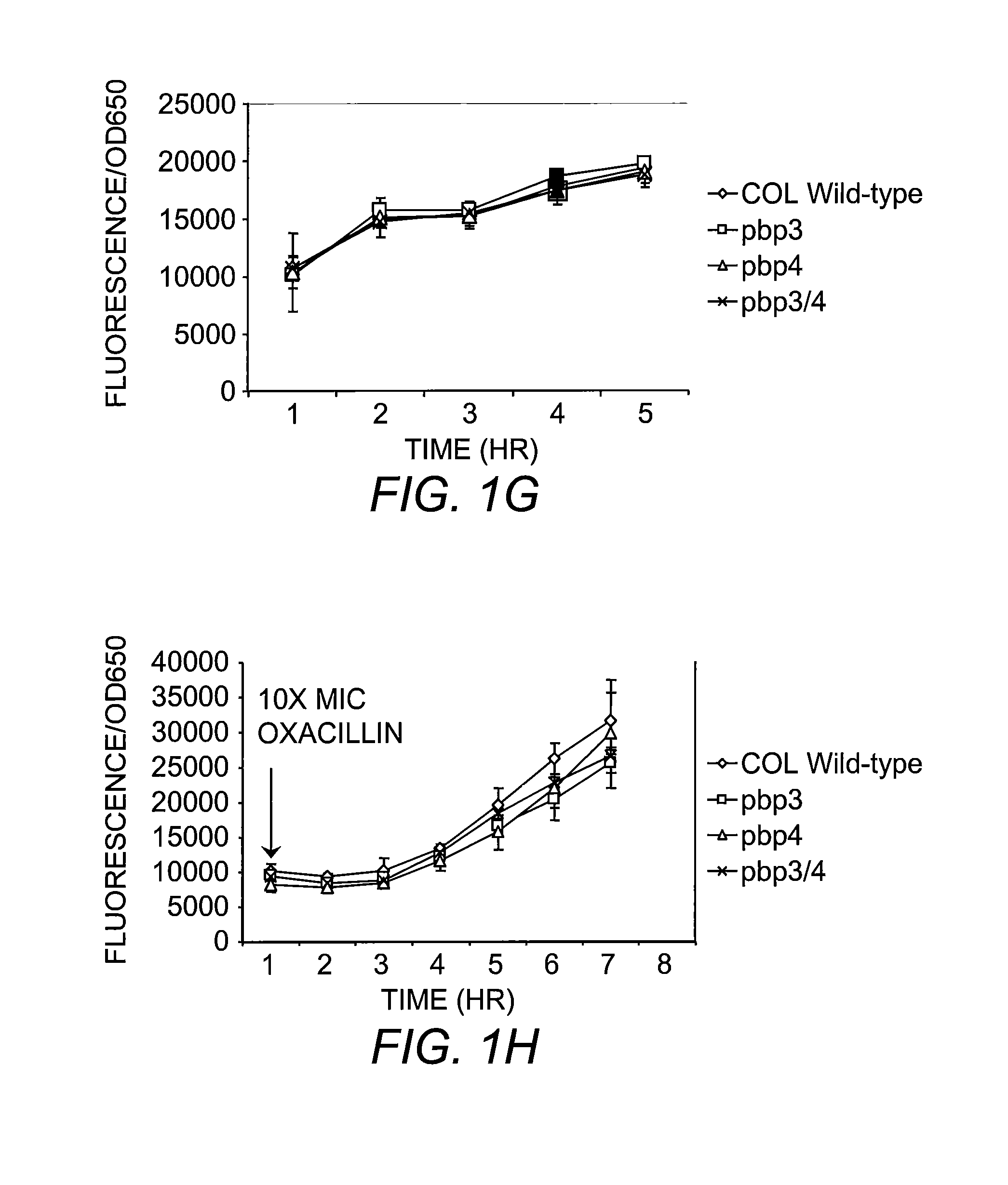
The present invention includes compositions and methods for diagnosing and treating CA-MRSA infections in patients. The methods are based on the finding that combining cefoxitin and a synthetic penicillin in a treatment regimen results in a synergistic effect of the two drugs, an effect that is related to PBP4 activity in CA-MRSA isolates. Also provided is a CA-MRSA-specific biomarker which can be used to detect the presence of a CA-MRSA infection in a patient.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
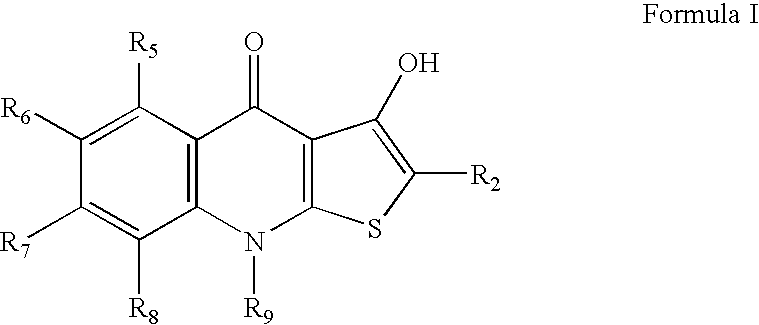
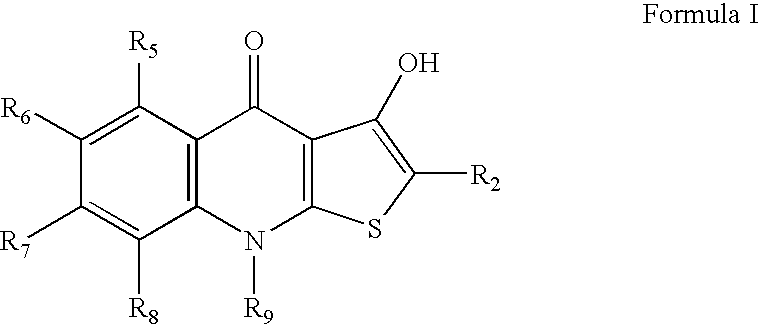
2-substituted-thienoquinolones and related compounds as Anti-infective agents
Disclosed herein are 2-substituted-thienoquinolones and related compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts useful as antiviral agents and having the general formulain which the variables R2, R3, and R7 are defined herein. Certain compounds provided herein possess potent antibacterial, antiprotozoal, or antifungal activity and are particularly efficacious for the treatment of MRSA infections. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions, pharmaceutical compositions containing a 2-substituted-thienoquinolone in combination with one or more other active agent, and methods of treating microbial infections in animals by administering an effective amount of a 2-substituted-thienoquinolone to an animal suffering from a microbial infection.
Owner:ACHILLION PHARMA INC
De-malonate monoacyl azalomycin F, preparation method thereof and application thereof to preparation of MRSA infection therapeutic drug
ActiveCN103044439BAvoid the disadvantage of easy alkylation of 29-position hydroxylImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin resistant StaphylococcusMalonic acid
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Synthesis and application of a class of antibacterial drug asc for targeted treatment of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus aureus and superbug infection
ActiveCN109535180BEffective treatmentReduced colonizationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimicrobial drugSugar amine
The invention relates to the synthesis and application of a class of antibacterial drugs ASC for targeted therapy of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Staphylococcus aureus (SAU) infections and synergistic antibiotic therapy for superbug infections. The effective concentration of ASC in the treatment of MRSA infection is 2 μg / mL, which is 4 times stronger than that of the standard drug oxacillin; the dose of 35 mg / kg specifically treats MRSA infection in the heart and lung of mice, and makes the liver, spleen, The colonization of MRSA in kidney tissue was significantly reduced. ASC is also a broad-spectrum inhibitor of metallo-β-lactamase, a class of antibiotic-resistant target proteins, and can synergize with β-lactam, aminoglycoside and tetracycline drugs to target the treatment of SAU infection: the dose of 1 μg / mL makes these antibiotics effective A 4-128-fold increase, the dose of 64 or 8 μg / mL makes Pioneer V resistant to NDM-1 or CcrA-producing bacteria E.coli The curative effect is increased by 32 times.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Non-beta lactam antibiotics
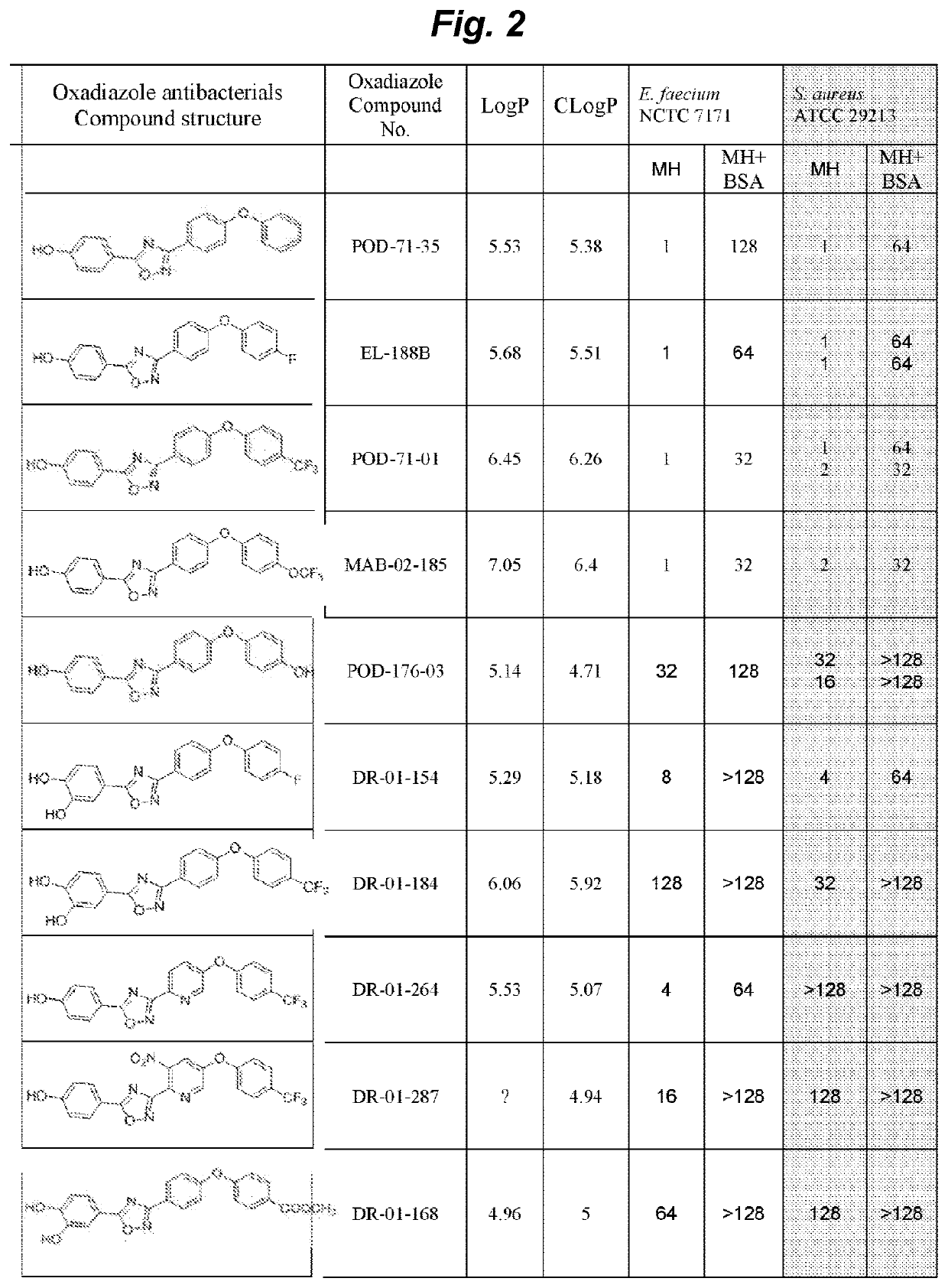
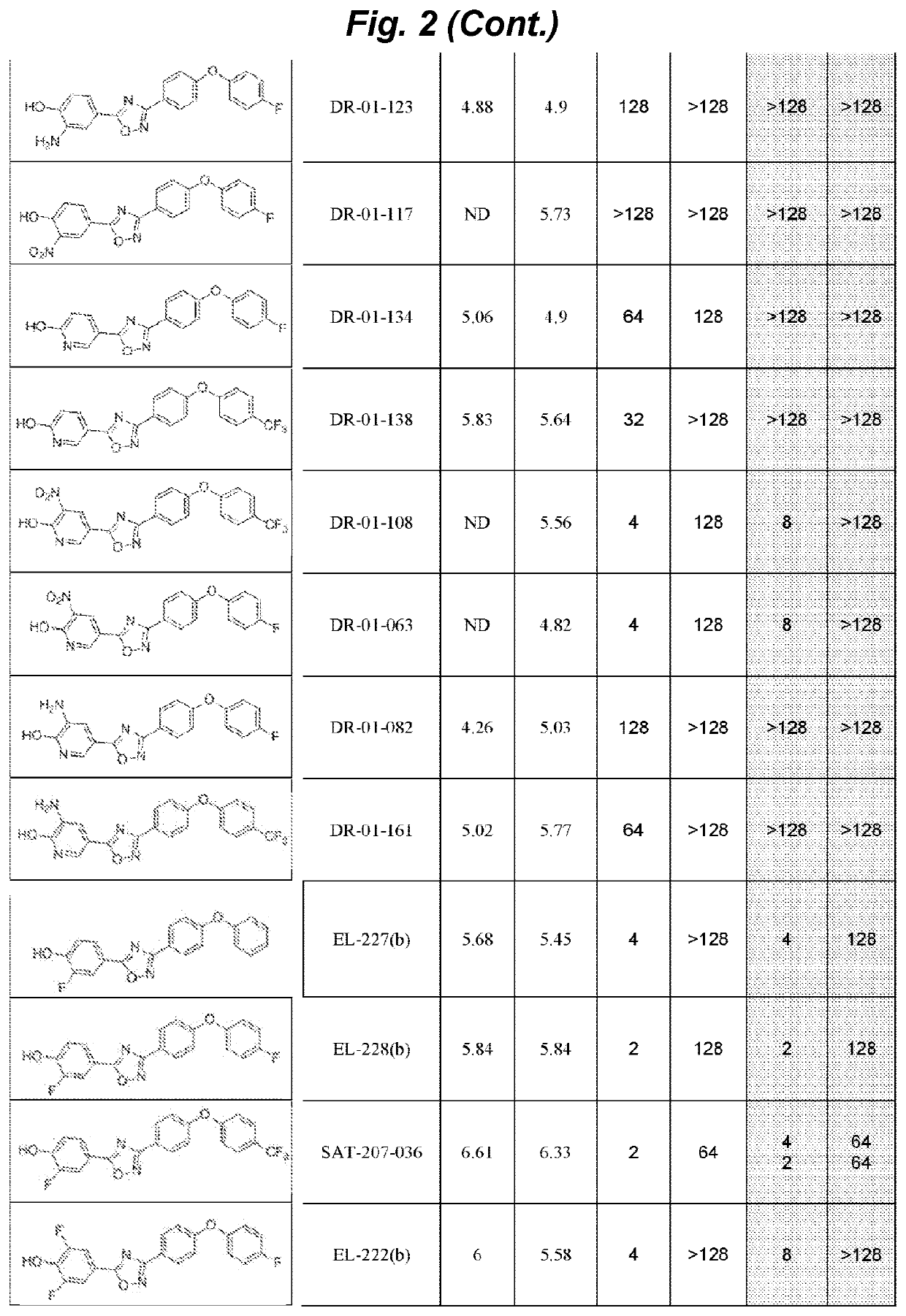
The invention provides a newly discovered oxadiazole class of antibiotics. The oxadiazoles impair cell-wall biosynthesis and exhibit activities against the Gram-positive bacteria such as the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant and linezolid-resistant S. aureus. For example, 5-(1H-indol-5-yl)-3-(4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)phenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole (antibiotic 75b) was efficacious in a mouse model of MRSA infection, exhibiting a long half-life, a high volume of distribution, and low clearance. Antibiotic 75b antibiotic is bactericidal and is orally bioavailable. This class of antibiotics can be used as a therapeutic agent against infections by Gram-positive bacteria such as MRSA.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Pharmaceutical composition for resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa)
InactiveCN104971342AAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseStaphylococcus cohnii
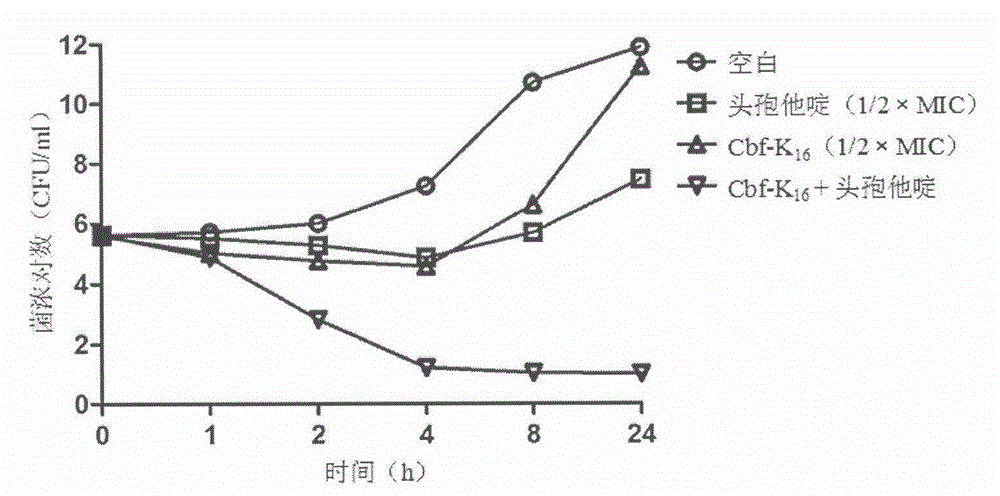
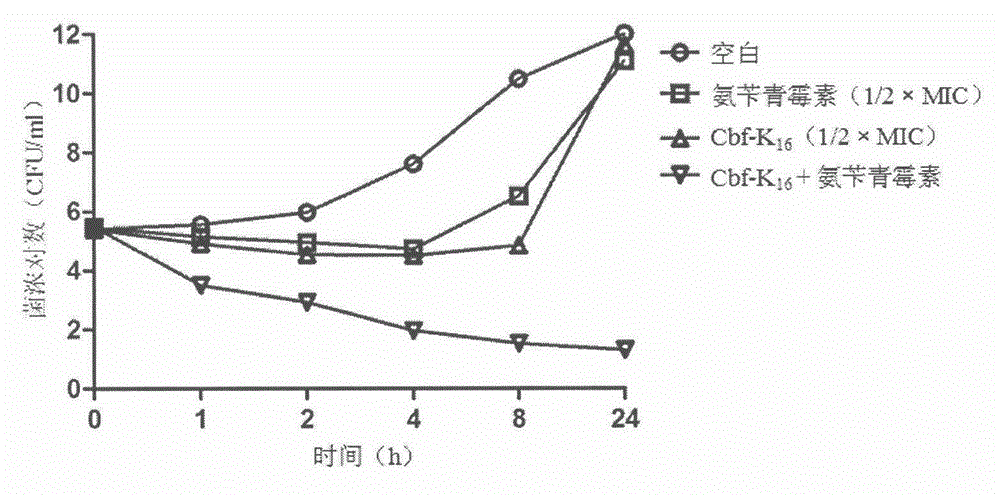
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa). The pharmaceutical composition has an mrsa infection-resistant effect. Ceftazidime and ampicillin have the effect of inhibiting the synthesis of a bacterial cell wall, while cbf-k16 is a cationic antimicrobial peptide and has a cell membrane penetrating effect. The in-vitro antibacterial activity of the peptide cbf-k16 and ceftazidim or ampicillin which are combined to be used is researched by using a chessboard method and a bactericidal curve method, and the result shows that the pharmaceutical composition has remarkable in-vitro synergic mrsa-resistant activity. Meanwhile, in-vivo researches show that the pharmaceutical composition composed of the peptide cbf-k16 and ceftazidim or ampicillin has a remarkable effect on treating animal generalized infection caused by mrsa, and therefore the pharmaceutical composition is proved to have remarkable in-vivo and in-vitro synergic antibacterial activity for mrsa and have a relatively good application prospect on the aspect of clinically treating diseases infected by mrsa.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Application of clemastine fumarate in preparation against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveCN111920805BEnhanced inhibitory effectAchieve inhibitionAntibacterial agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsClemastine FumaratePharmaceutical Substances
The present invention specifically relates to the application of clemastine fumarate in anti-MRSA preparations. MRSA has high toxicity and is resistant to most common clinical antibiotics, and the strain is widely distributed in the daily environment, so it is a difficult pathogenic strain. In order to develop an active substance that has an inhibitory effect on the above-mentioned drug-resistant bacteria, the present invention screened and verified that clemastine fumarate has a good inhibitory effect on MRSA from clinical drugs, and is expected to be applied to the development of drugs related to anti-MRSA infection.
Owner:MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG PROVINCE SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com