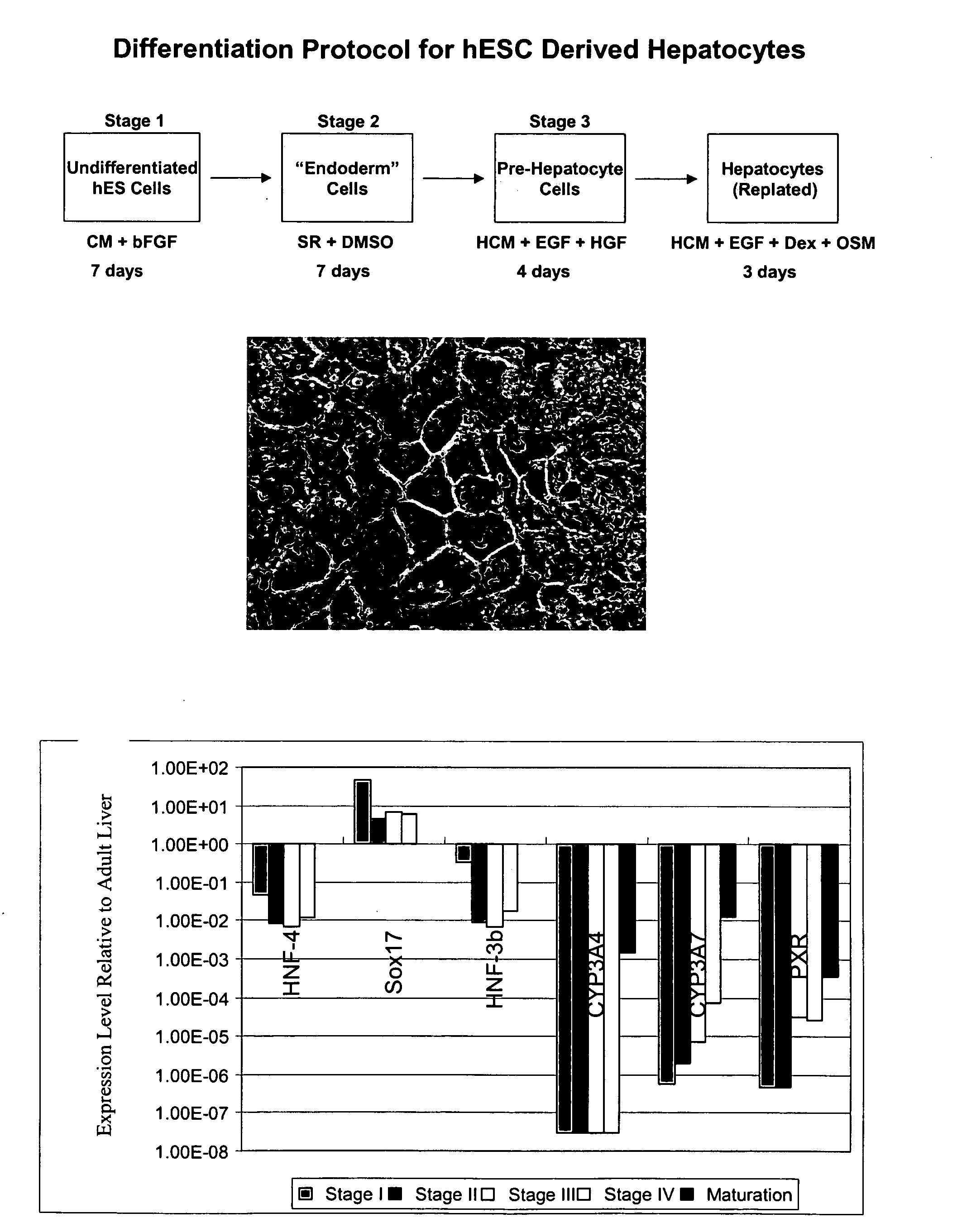
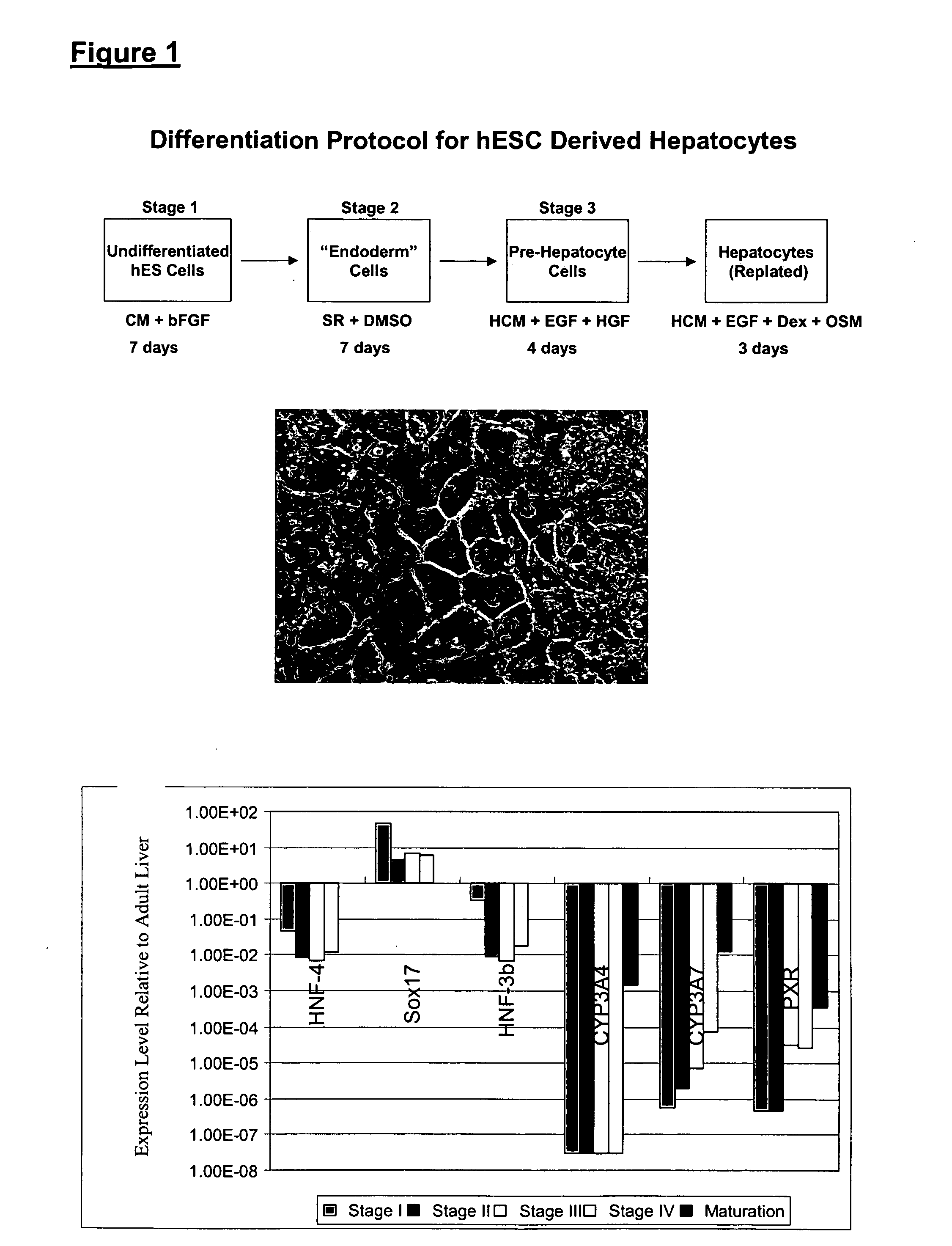
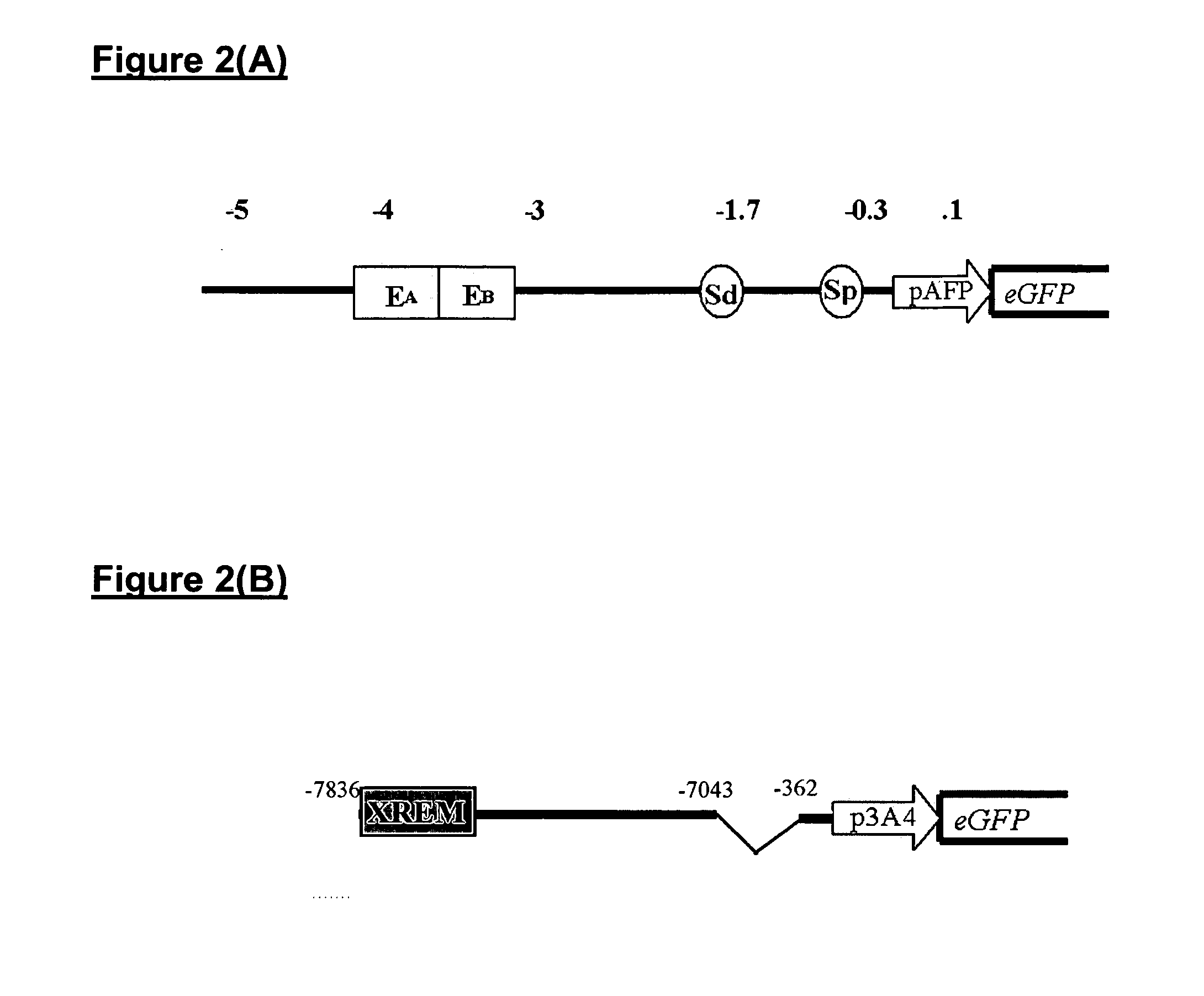
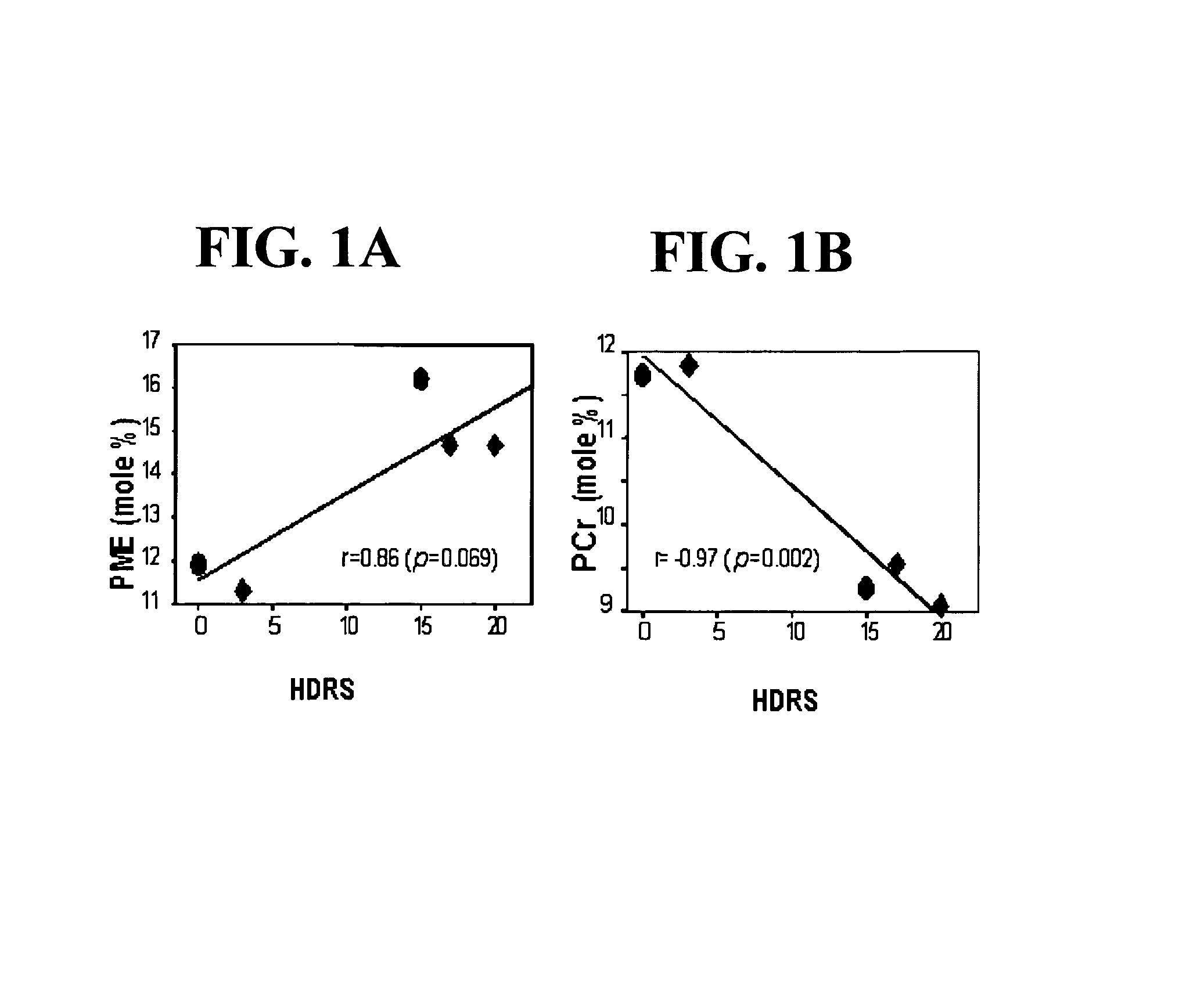
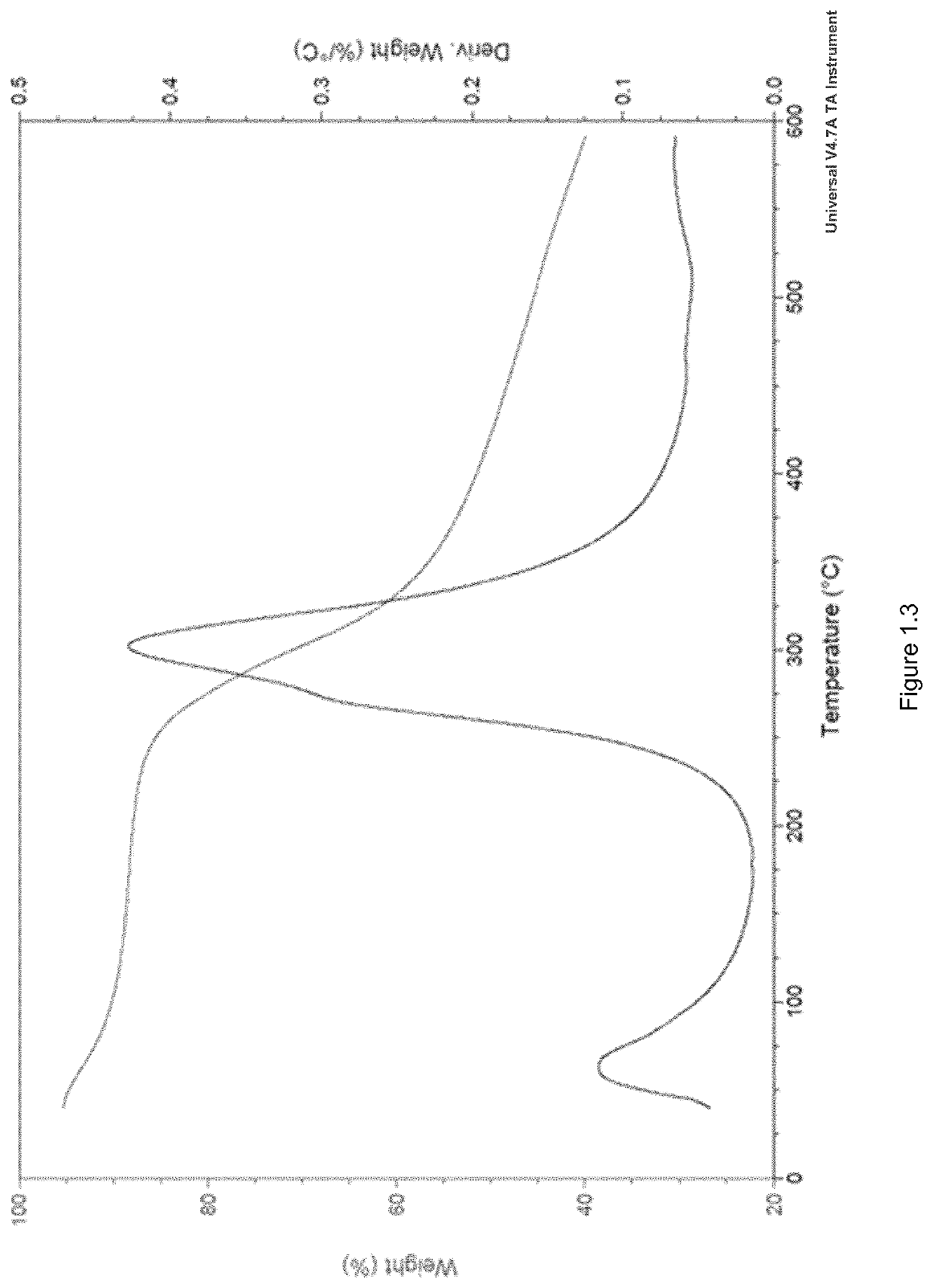
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Metabolic change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metabolic changes are the most common sign of aging within cells. This increases the risk of diseases such as type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertension. Insulin resistance is a major metabolic syndrome observed in older adults. This can lead to hepatic gluconeogenesis, adipose lipogenesis, defective glycogen synthesis, and glucose uptake.
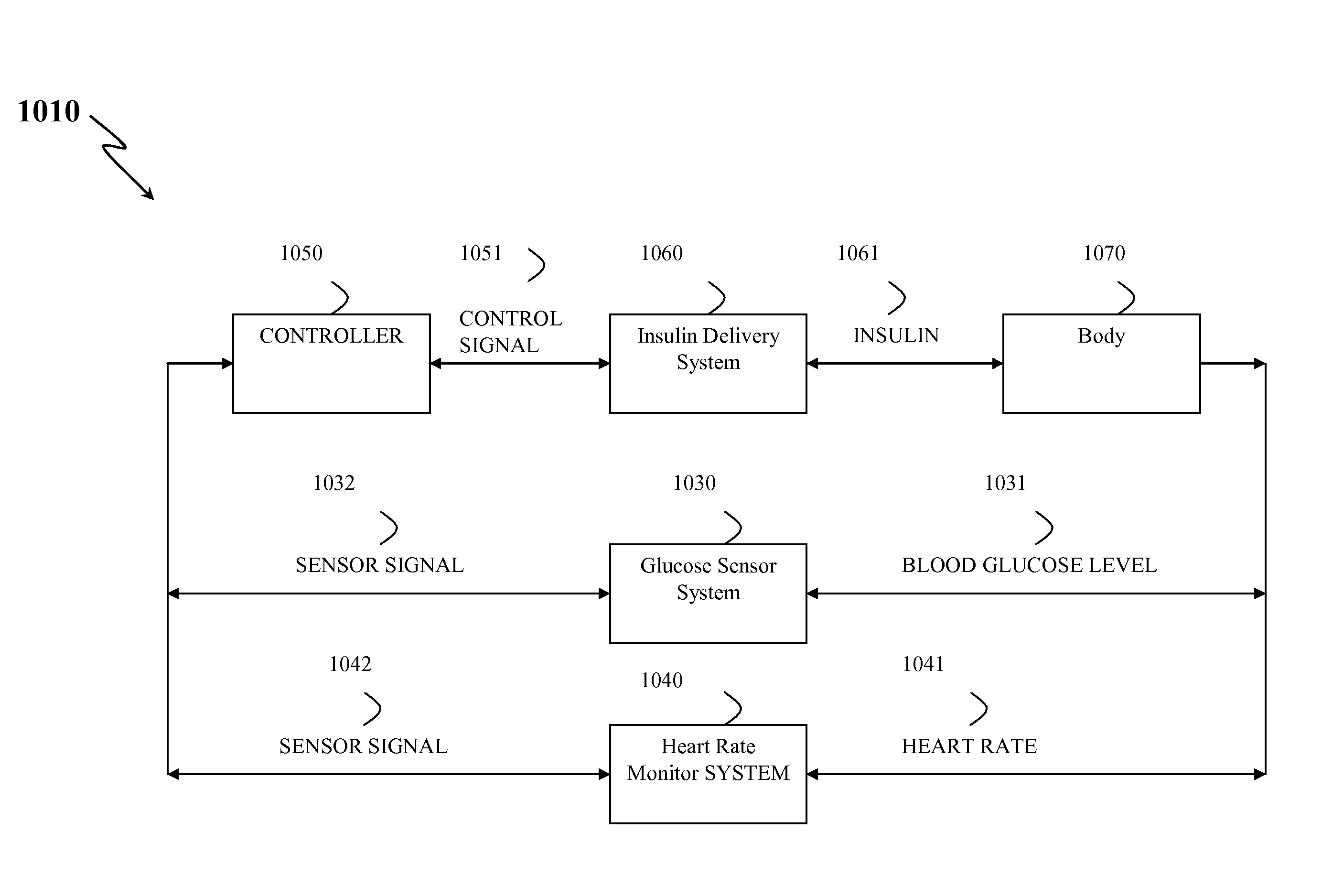
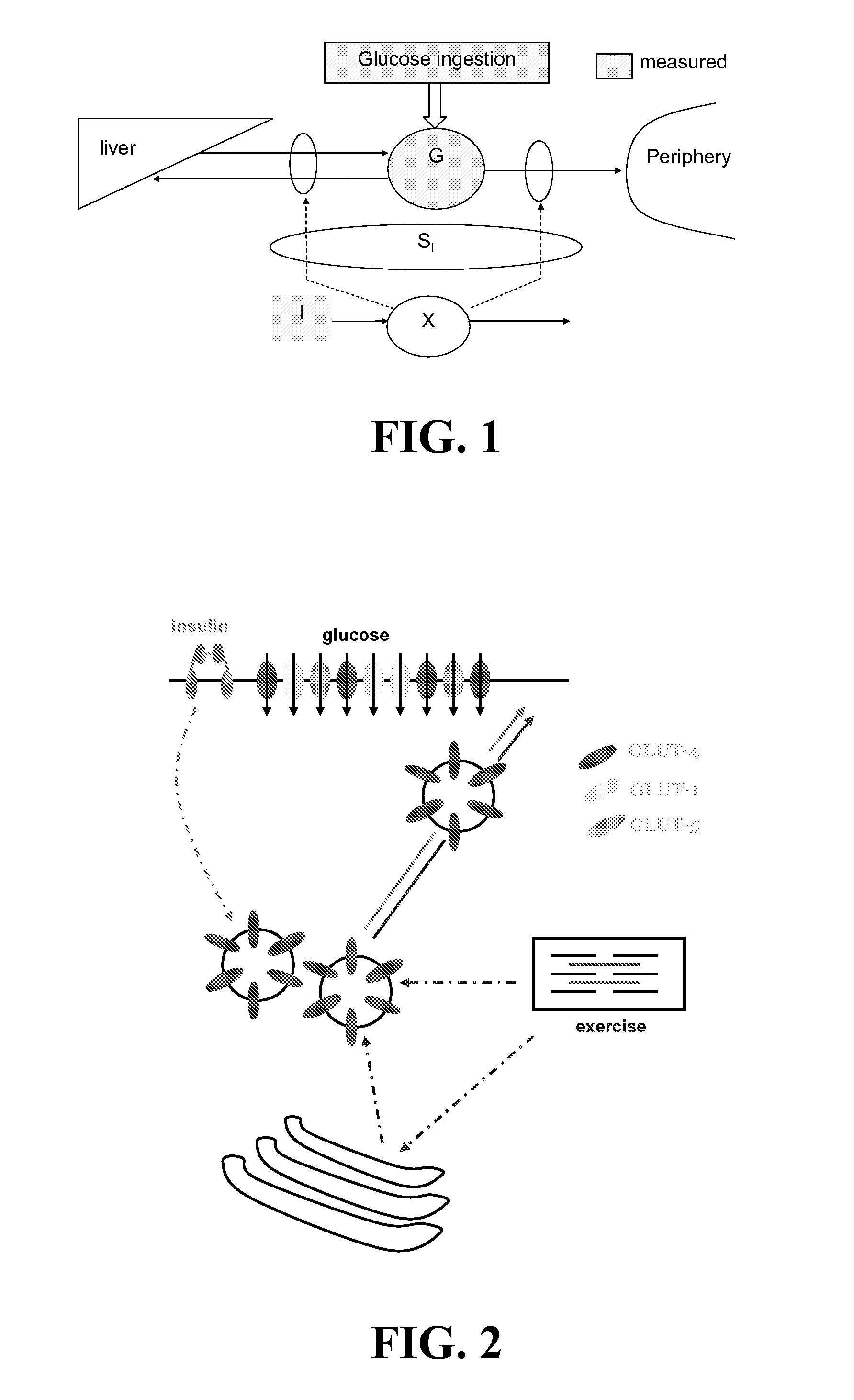
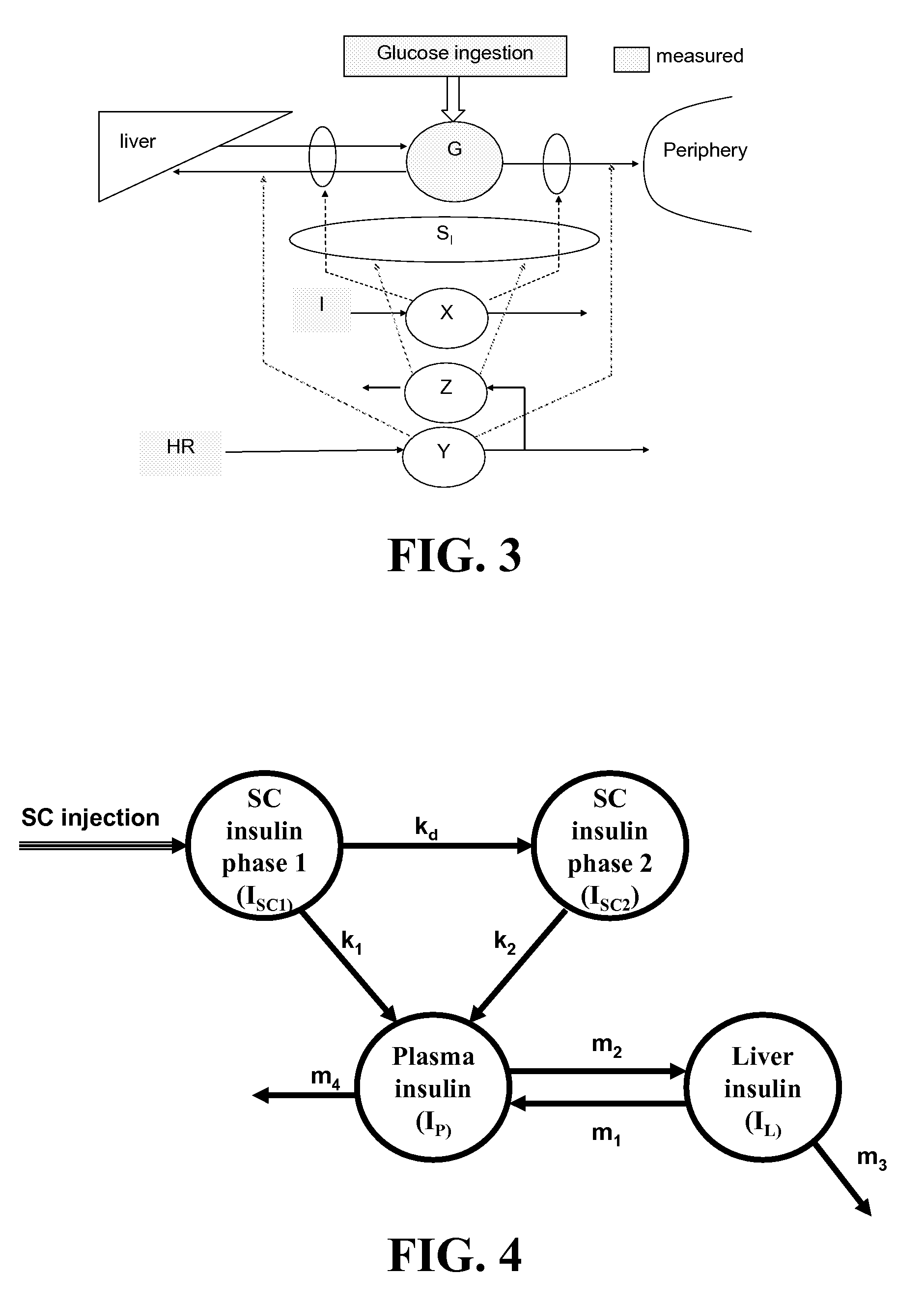
Method, System, and Computer Program Product for the Detection of Physical Activity by Changes in Heart Rate, Assessment of Fast Changing Metabolic States, and Applications of Closed and Open Control Loop in Diabetes
ActiveUS20100057043A1Minimize frequencyAvoid the needMedical simulationDrug and medicationsClosed loopHypoglycemia
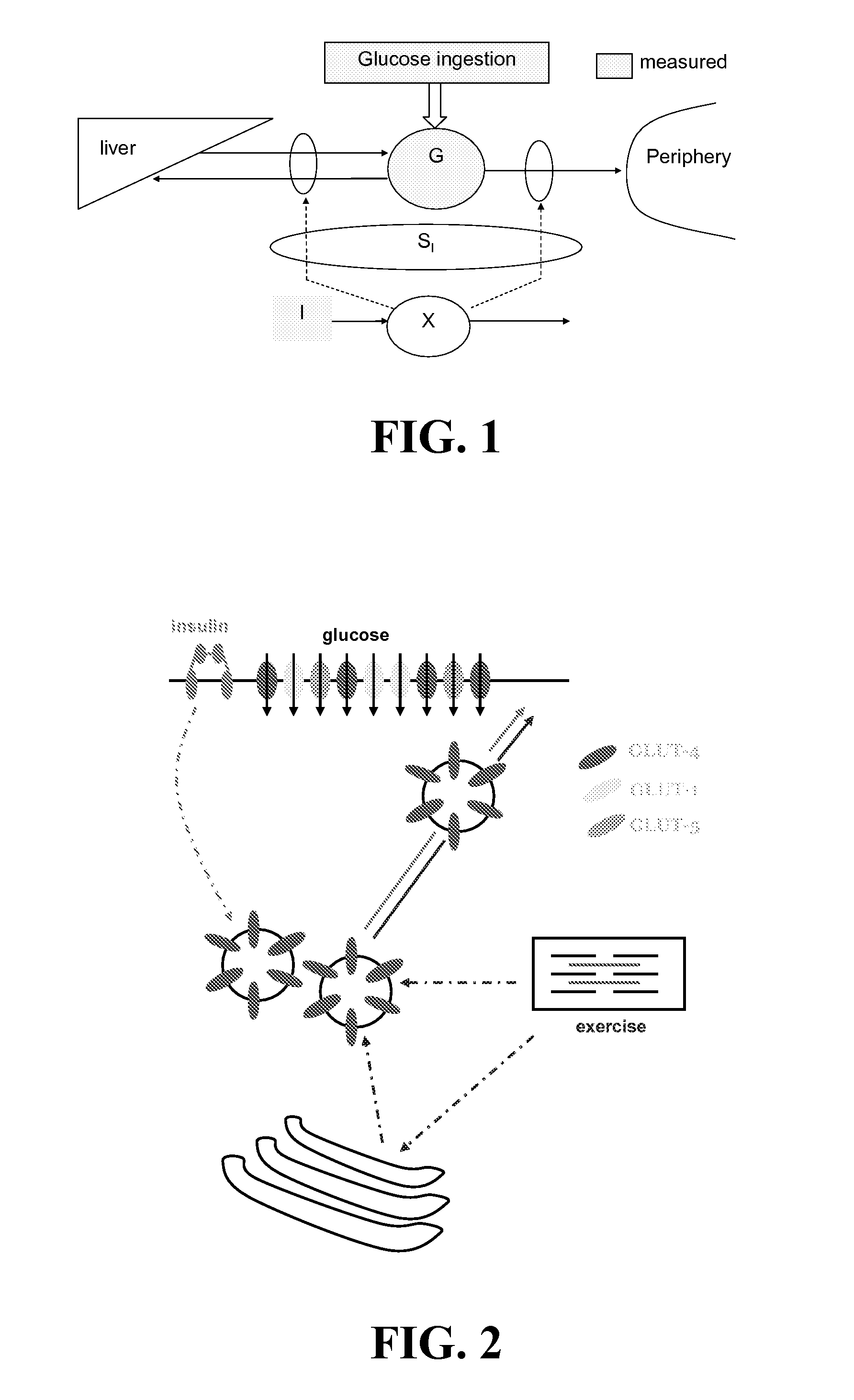
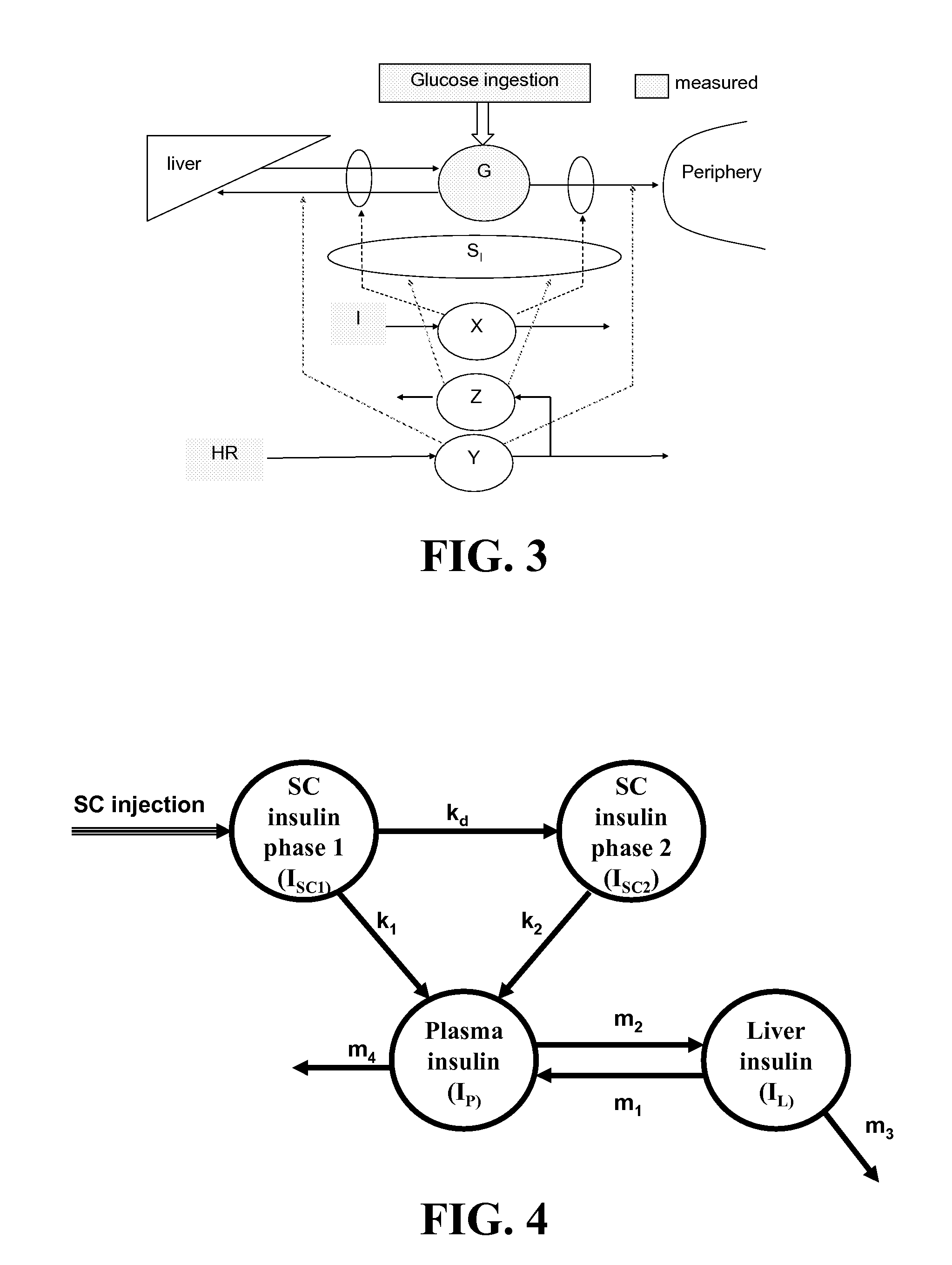
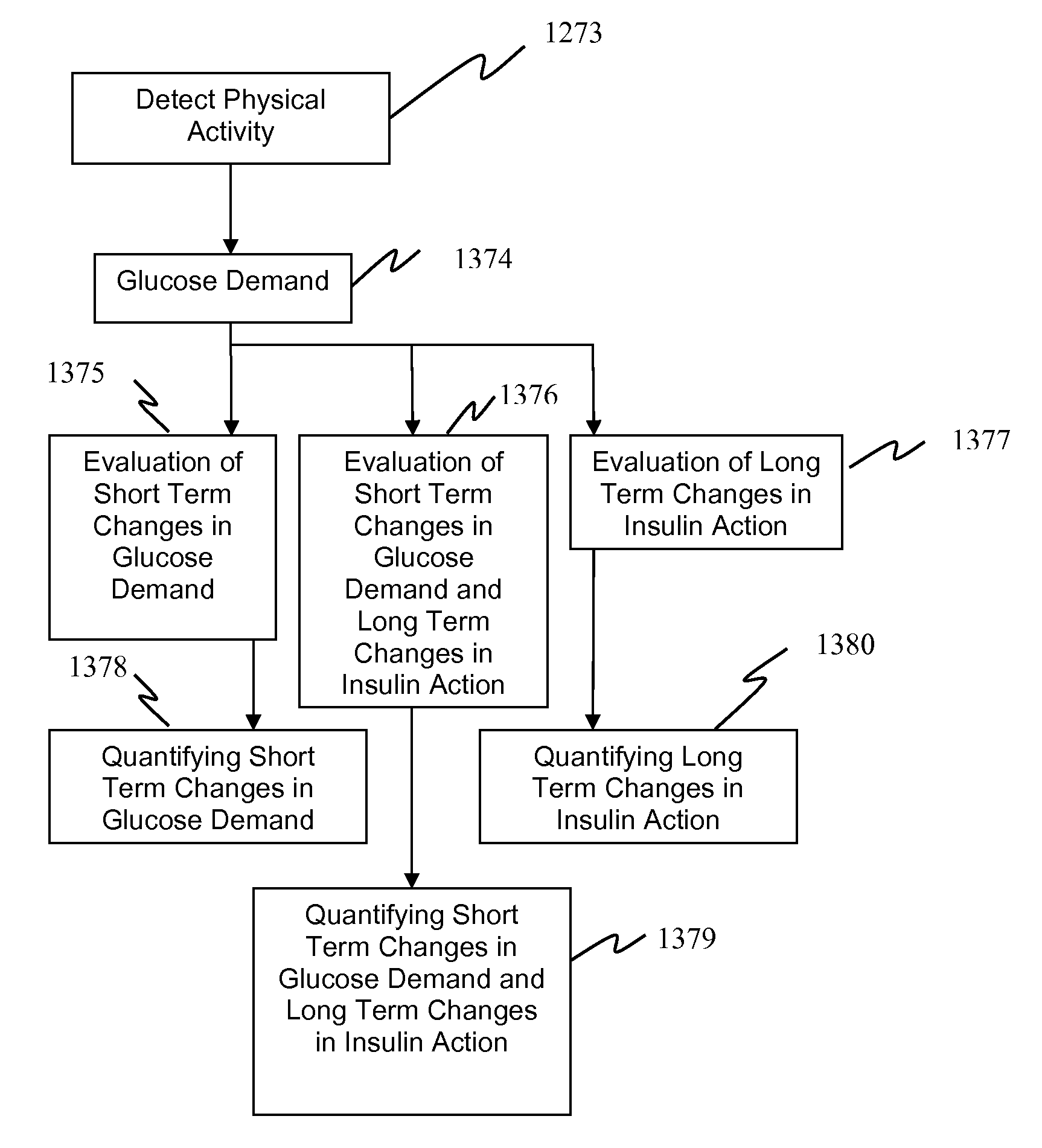
A method, system, and computer program product related to the detection of physical activity using changes in heart rate. The method, system, and computer program product evaluates short term glucose demand and long term insulin action due to physical activity. The method, system, and computer program product is further related to the improvement of open and closed loop control of diabetes by accounting for the metabolic changes due to physical activity. The method, system, and computer program product is directed to detecting in real time the short and long term effects of physical activity on insulin action via heart rate analysis, and recommending changes in insulin dosing to compensate for the effects of physical activity. With these recommendations, the open and closed loop control of diabetes can be improved and steps can be taken to prevent hypoglycemia that may result from increased insulin sensitivity due to physical activity.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method, system, and computer program product for the detection of physical activity by changes in heart rate, assessment of fast changing metabolic states, and applications of closed and open control loop in diabetes
ActiveUS8585593B2Minimize frequencyAvoid the needMedical simulationDrug and medicationsClosed loopHypoglycemia
A method, system, and computer program product related to the detection of physical activity using changes in heart rate. The method, system, and computer program product evaluates short term glucose demand and long term insulin action due to physical activity. The method, system, and computer program product is further related to the improvement of open and closed loop control of diabetes by accounting for the metabolic changes due to physical activity. The method, system, and computer program product is directed to detecting in real time the short and long term effects of physical activity on insulin action via heart rate analysis, and recommending changes in insulin dosing to compensate for the effects of physical activity. With these recommendations, the open and closed loop control of diabetes can be improved and steps can be taken to prevent hypoglycemia that may result from increased insulin sensitivity due to physical activity.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Detection of reactions and metabolic changes with fluorscent materials
InactiveUS20030012692A1High throughput screeningImprove throughputCompound screeningAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSurface reactionHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A system, method and device for the detection of reactions between analytes, (e.g., DNA, biomolecules, or cells) and a second compound are disclosed. The present invention includes a coating of a fluorescent material having a fluorescence that changes with temperature. The fluorescent material is associated with a substrate, and can be used for any type of surface reaction that requires determination of temperature conditions at an interface between the surface and the reaction analyte subject to assay. The substrate may be, for example, a microarray chip or microplate, preferably suitable for use in high-throughput screening of biomolecules or cells. Substrates containing the fluorescent material also can be used to compensate for temperature variations in refractive index in optical sensors.
Owner:CORNING INC
Compounds, compositions and methods for treating neuropsychiatric disorders
InactiveUS20060088614A1Neurological deficit scoreNavigation performance in was impairedBiocideAnimal repellantsHigh energyMental health
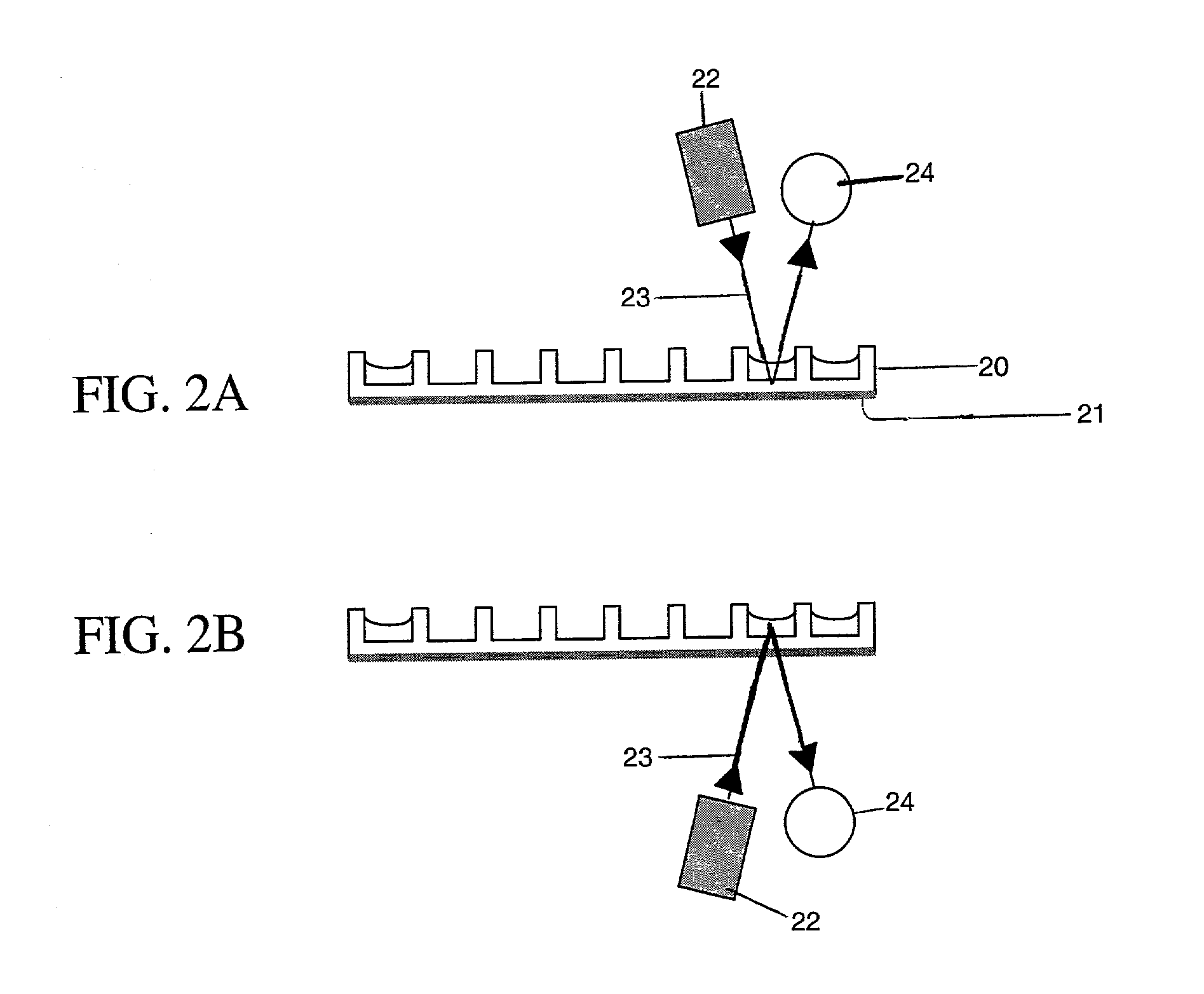
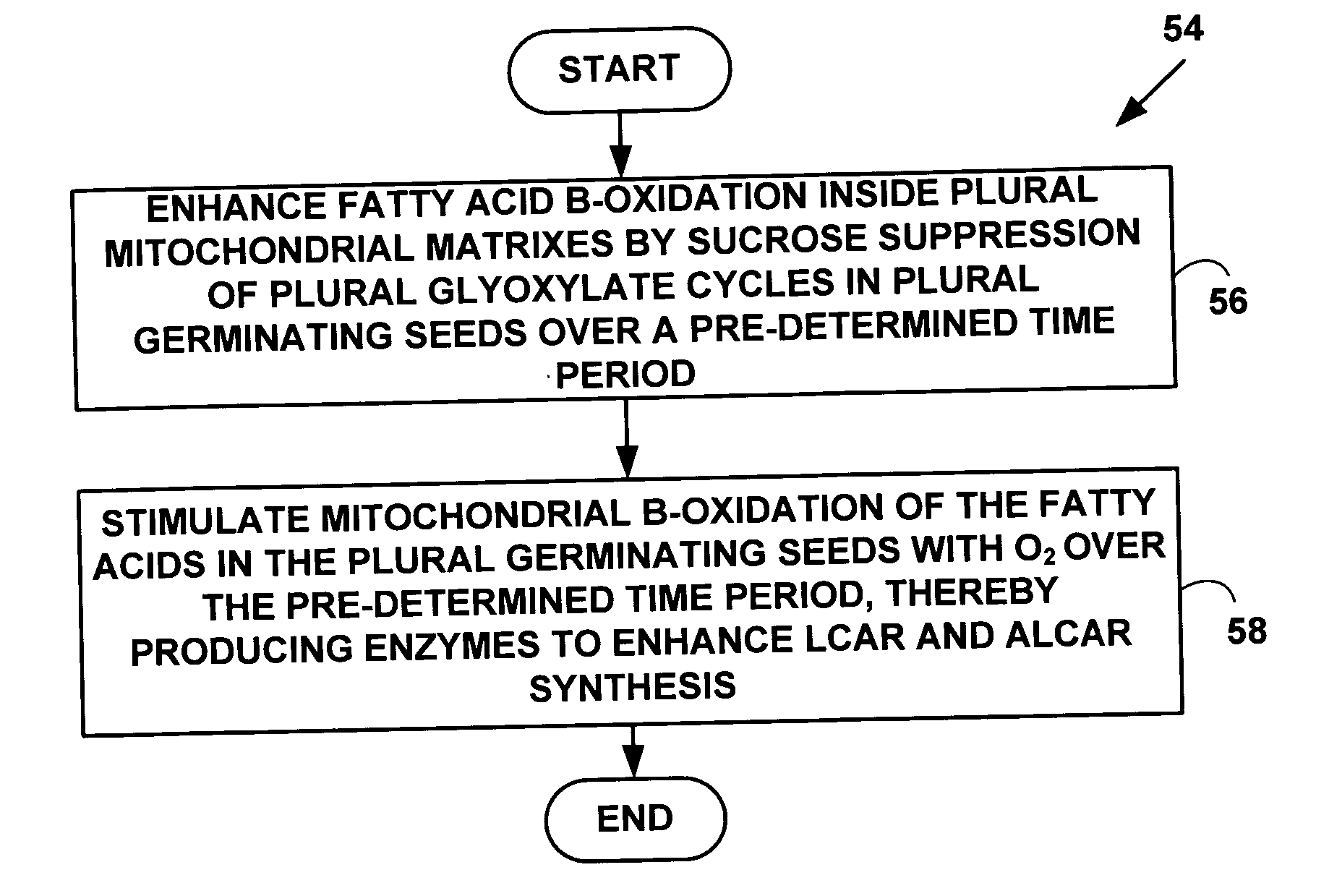
Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) and L-carntine (LCAR) are nutraceuticals with indications in treating a variety of mental health disorders. A metabolomics-guided bioprocess method is presented to enhance ALCAR and LCAR formation in germinating plant seeds. Metabolic fluxes are manipulated by germination in bioreactors to increase oxygen availability as well as provide an aseptic environment to alter carbohydrate consumption and feedback repress gluconeogenesis. Large shifts in sunflower seed fatty acid, phospholipid and high-energy metabolism change the germination environment and these metabolic changes lead to an approximate 1000-fold increase in natural LCAR and ALCAR production by the seeds. The resulting LCAR and ALCAR products from the seeds are used for treating mental health disorders including Alzheimer's disease, geriatric depression, non-geriatric depression and schizophrenia.
Owner:PETTEGREW JAY W +2
Method of increasing yield of spinosad by improving fermentation condition of saccharopolyspora spinosa based on metabonomics
InactiveCN104450834AImprove fermentation yieldComponent separationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method of increasing the yield of spinosad by improving the fermentation condition of saccharopolyspora spinosa based on metabonomics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining intracellular metabolite of the saccharopolyspora spinosa; (2) analyzing the capability of the saccharopolyspora spinosa of producing the spinosad; (3) carrying out PLS analysis; and (4) carrying out process analysis. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the metabolite change law in the process of producing the spinosad by virtue of fermentation of the saccharopolyspora spinosa is revealed by utilizing the metabonomics means and combining multivariate statistics, and a metabolic change mechanism related to production of the spinosad is further explained; by analyzing the spinosad production capability and the metabolic level of the saccharopolyspora spinosa in different growth environments, the metabolin related to the production of the spinosad is found, thus providing a direction for optimizing the culture process of the saccharopolyspora spinosa and increasing the fermentation yield of the spinosad. The invention also provides new thinking and method for study in other culture technological processes of producing macrolides microorganisms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for constructing physiological toxicokinetic model of nonylphenol in rat
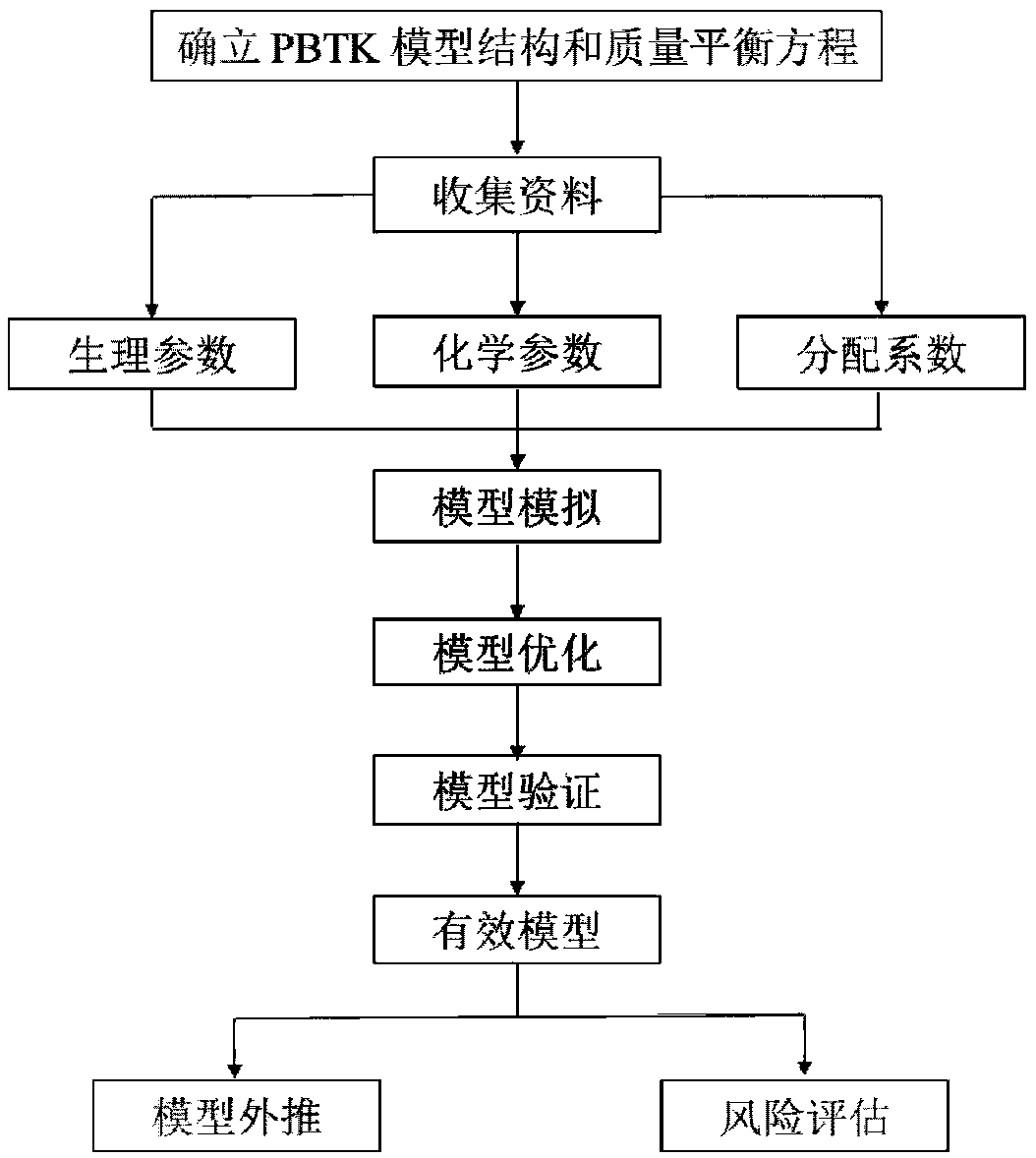
ActiveCN109285588AImproved risk assessment methodChemical processes analysis/designComputational theoretical chemistryToxicantModel parameters
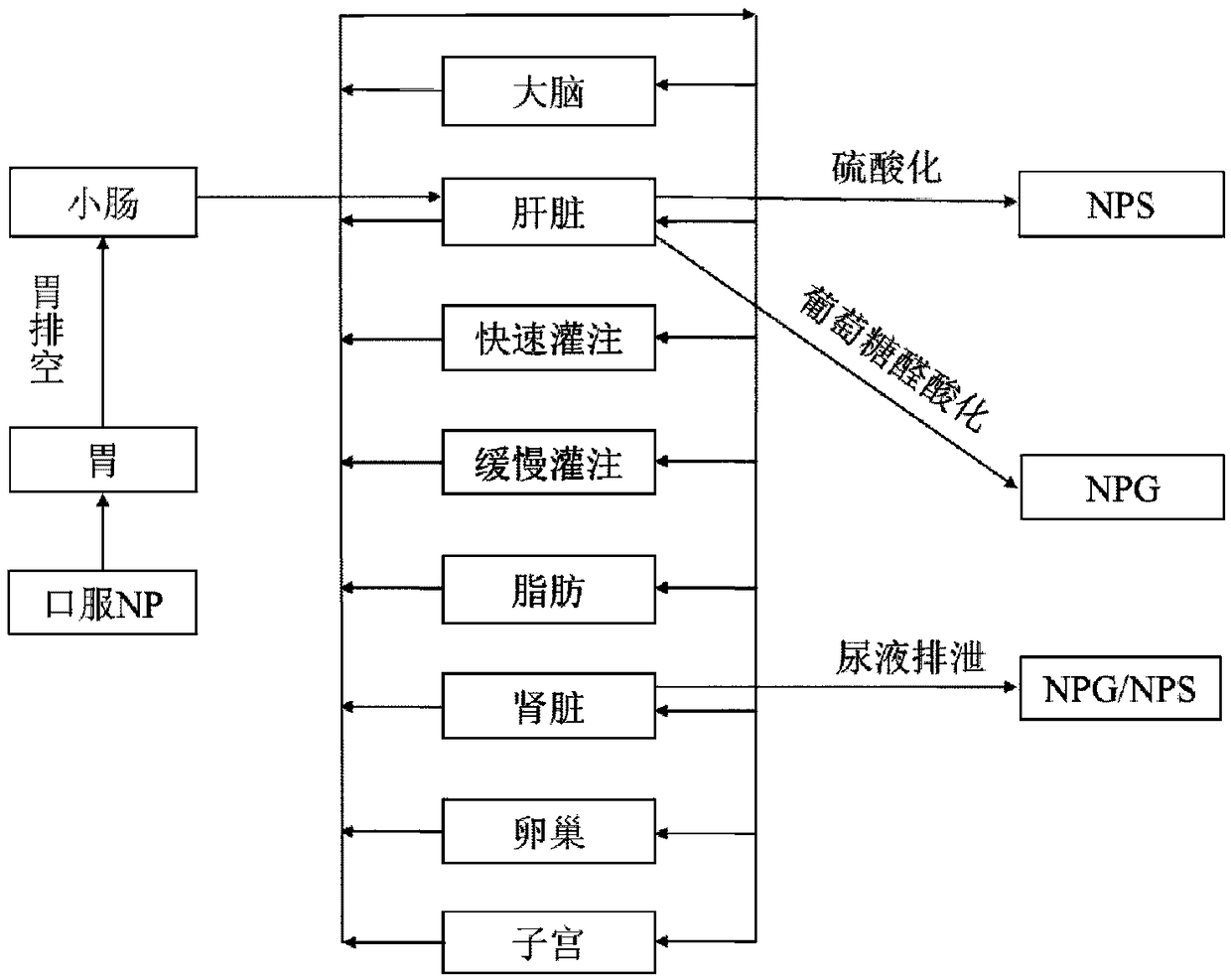
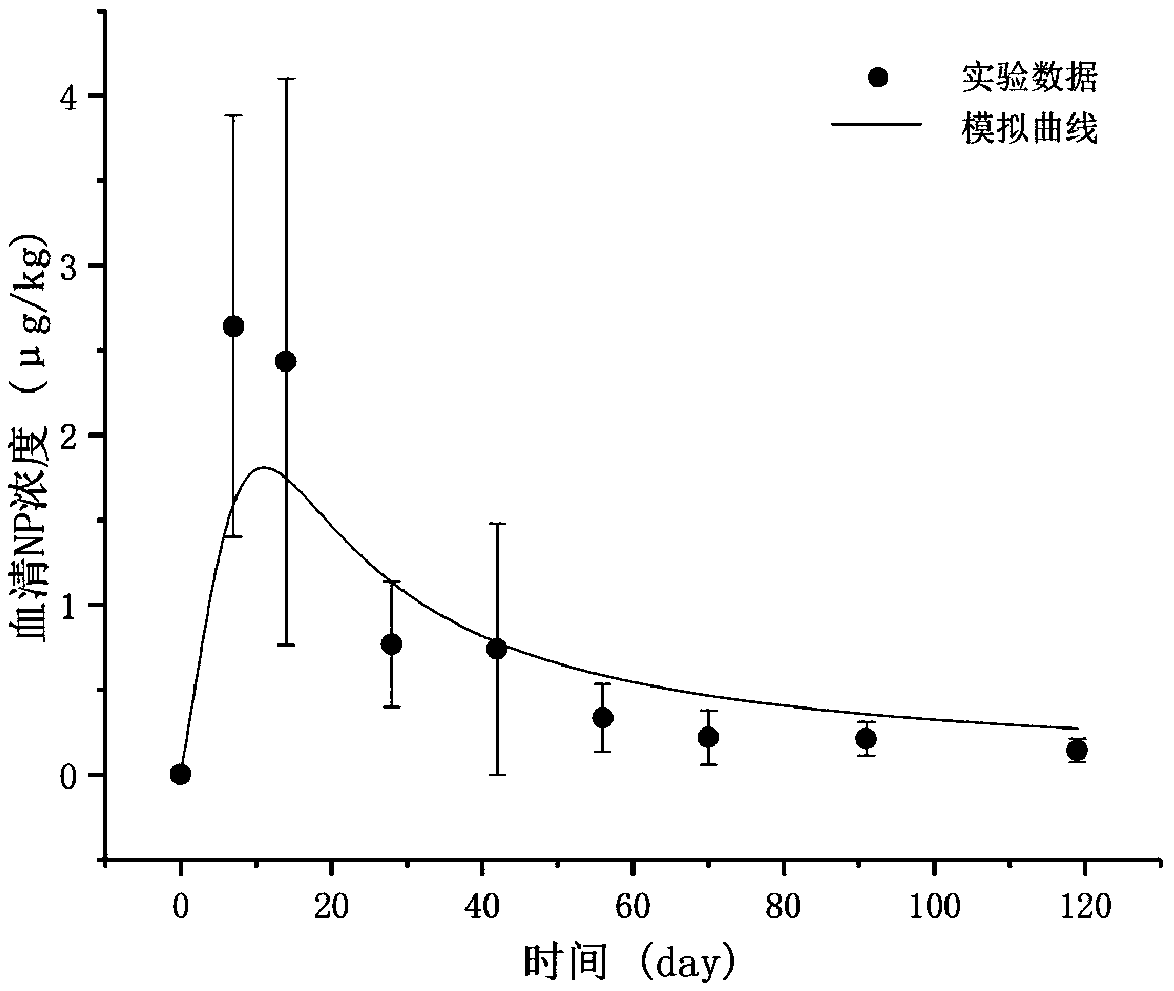
The invention provides a method for constructing a physiological toxicokinetic model of nonylphenol in a rat, the method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a model structure; (2) establishing a model differential equation; (3) establishing and collecting model parameters; (4) performing model optimization; (5) performing model verification; and (6) performing model effect evaluation. The physiological toxicokinetic model of the nonylphenol established by the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristic of species extrapolation, so that the method has a special value in toxicant toxicity and risk evaluation. Compared with a classical compartmental model, the compartments and most parameters of the model have the physiological significance, the exposure leveland the metabolic change condition of toxicants in blood and other tissue organs can be predicted, and the model can assist in the research of the substance toxicology mechanism and improve the risk degree evaluation process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Hyperpolarized micro-nmr system and methods
InactiveCN109477872AAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMetaboliteLiving sample
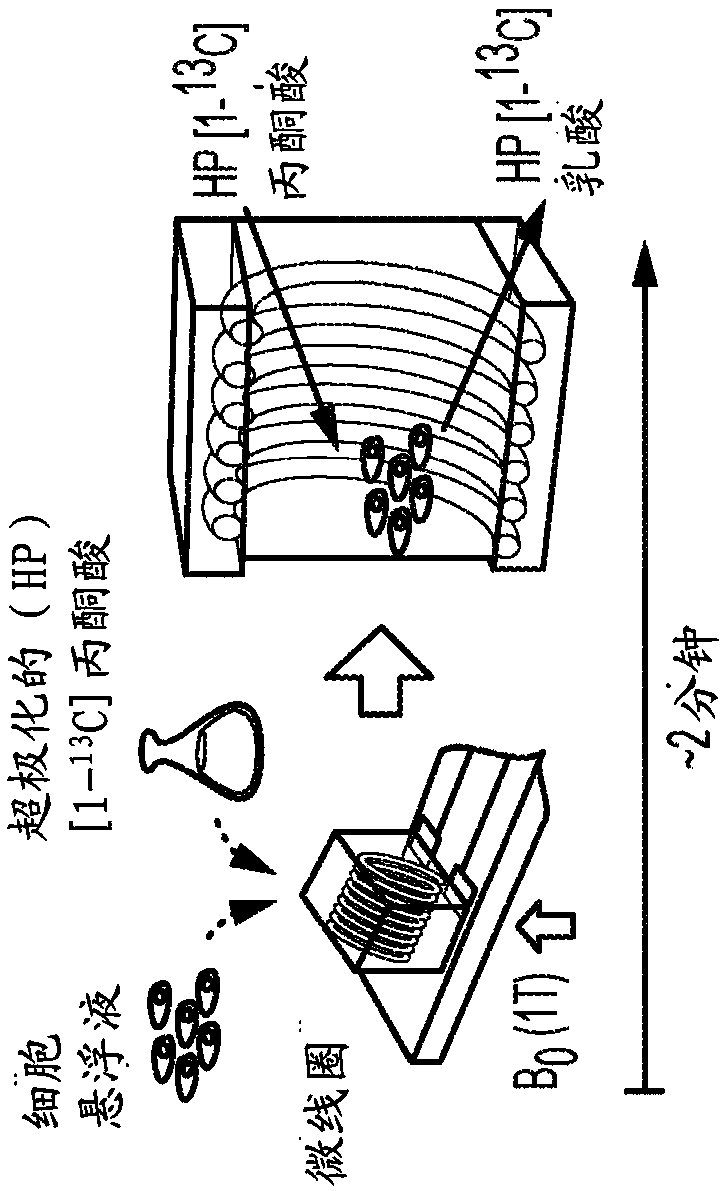
Described herein are micro-coil hyperpolarized NMR systems and methods for measuring metabolic flux in living and non-living samples. Such systems can perform high throughput measurements (with multiple coils) of metabolic flux without destroying the material, making it useful to analyze tumor biopsies, cancer stem cells, and the like. In certain embodiments, a hyperpolarized micromagnetic resonance spectrometer (HMRS), described herein, is used to achieve real-time, significantly more sensitive (e.g., 103-fold more sensitive) metabolic analyses of live cells or non-living samples. In this platform, a suspension mixed with hyperpolarized metabolites is loaded into a miniaturized detection coil (e.g., about 2 [mu]L), where the flux analysis can be completed within a minute without significant changes in viability. The sensitive and rapid analytical capability of the provided systems enables rapid assessment of metabolic changes by a given drug, which may direct therapeutic choices in patients.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Somatic data collecting and analyzing method and system
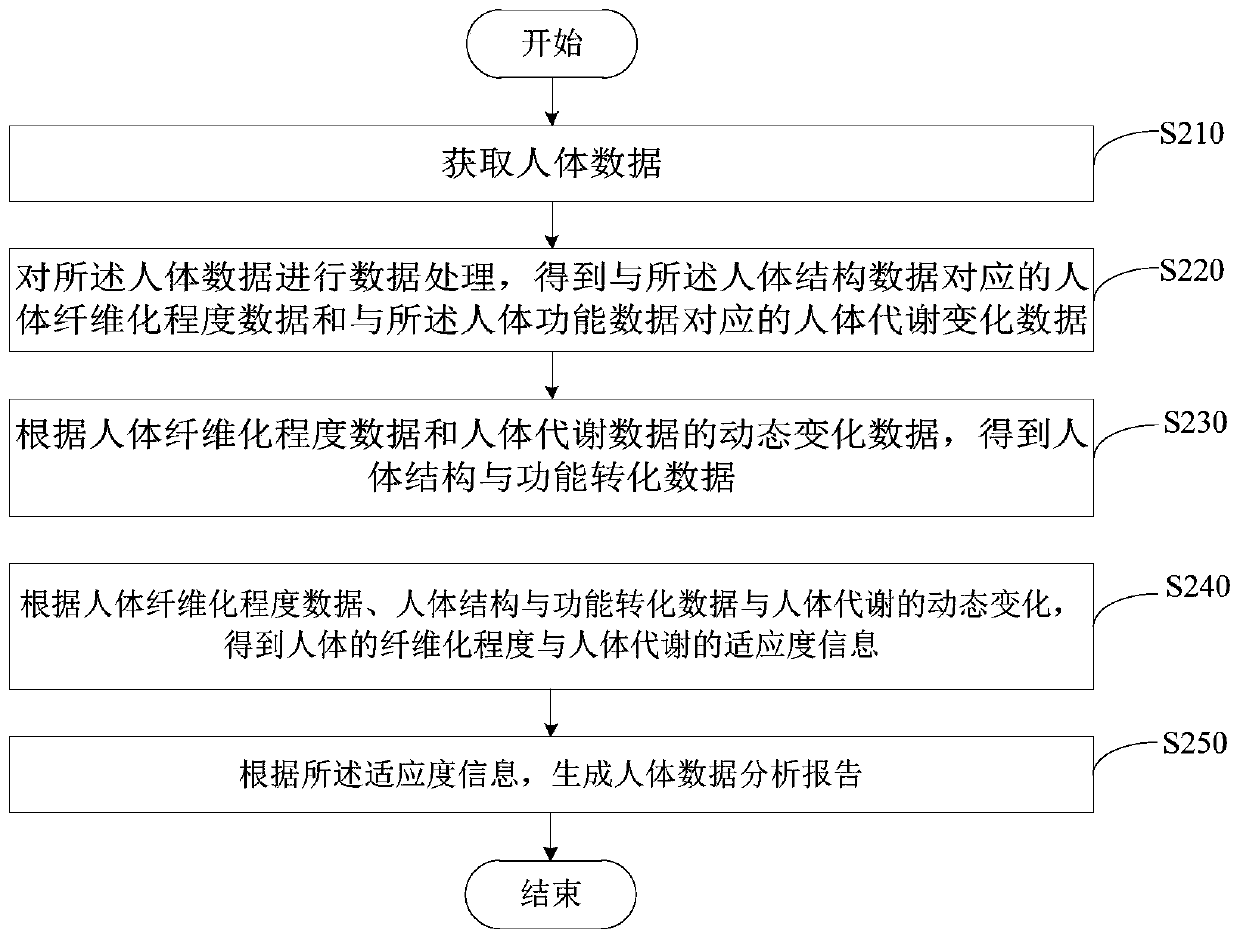
ActiveCN107368689ARealize four-dimensional evaluationSpecial data processing applicationsStructure and functionFibrosis
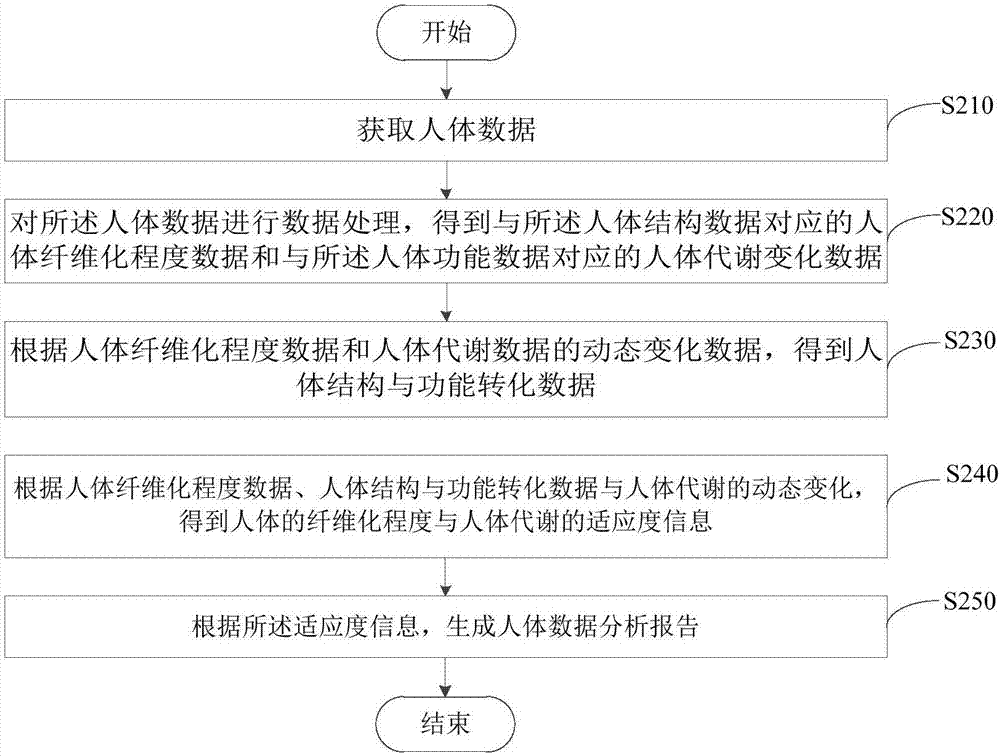
The embodiment of the invention provides a somatic data collecting and analyzing method and system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining somatic data; performing data processing on the somatic data, and obtaining somatic fibrosis degree data corresponding to somatic structure data and somatic metabolic change data corresponding to somatic function data; by means of the principle of relative balance of damage and repair in a stable whole, on the basis of the somatic fibrosis degree data and the somatic metabolic change data, obtaining somatic structure and function conversion data; according to the somatic fibrosis degree, somatic structure and function conversion data and the somatic metabolic change data, obtaining somatic fibrosis degree and somatic metabolic adaptability information; according to the adaptability information, generating a somatic data analysis report. The somatic structure data, the somatic structure and function conversion data and the somatic function data are combined for performing data analysis, the condition of somatic structure and function adaptability is obtained, and therefore somatic timer shaft and spatiality four-dimensional assessment is achieved.
Owner:董云鹏
Slow magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance device and process for metabolomics profiling of tissues and biofluids
ActiveUS20130257432A1Enhances sample filling factorEliminate the effects ofManufacture of electrical instrumentsElectric/magnetic detectionMagic angle spinningTissue biopsy
A slow Magic-Angle Spinning NMR device and method are detailed that provide high resolution and high sensitivity metabolic profiling of biological samples. A new 1H-PASS sequence suppresses line broadening in the various biological samples. The device and method allow metabolic changes in small animals to be tracked through continuous investigations of minimally-invasive blood and tissue biopsy samples over a sustained period and allow intact biological objects with sizes up to a few centimeters to be studied.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Nutritional agent for enhancing endurance and promoting anti-hypoxic tolerance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107006856AGood curative effectQuick resultsOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderNutritional statusSide effect
Altitude stress is an acute altitude sickness and is a high altitude sickness with a series of symptoms and function metabolic change caused by the changes in air pressure difference, less oxygen content, dry air, cold and ultraviolet ray intensity resulted from incapability of body to adapt to the altitude after people reaches a certain altitude (generally at the altitude of 2700m or above). The nutritional agent for enhancing endurance and promoting anti-hypoxic tolerance is characterized in that the nutritional agent is prepared from the following raw materials: pseudo-ginseng, rhodiola rosea, acanthopanax, lycium barbarum polysaccharide and acceptable ingredients. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to overcome the defects of the prior art and provide the nutritional agent for enhancing endurance and promoting anti-hypoxic tolerance and a preparation method thereof. The nutritional agent can reduce the verifiable side effect and has an excellent effect.
Owner:陈霞
Detection method for hydroxysafflor yellow A metabolic product
ActiveCN106370743AData processing is simpleThe positive effect is clearComponent separationChemical structureMetabolite
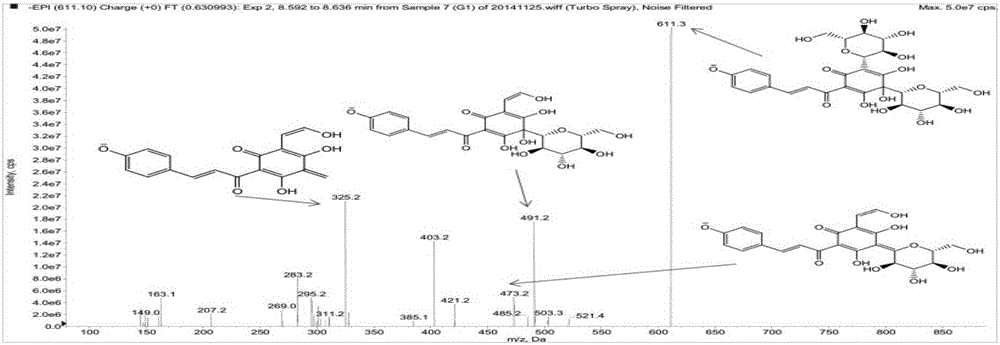
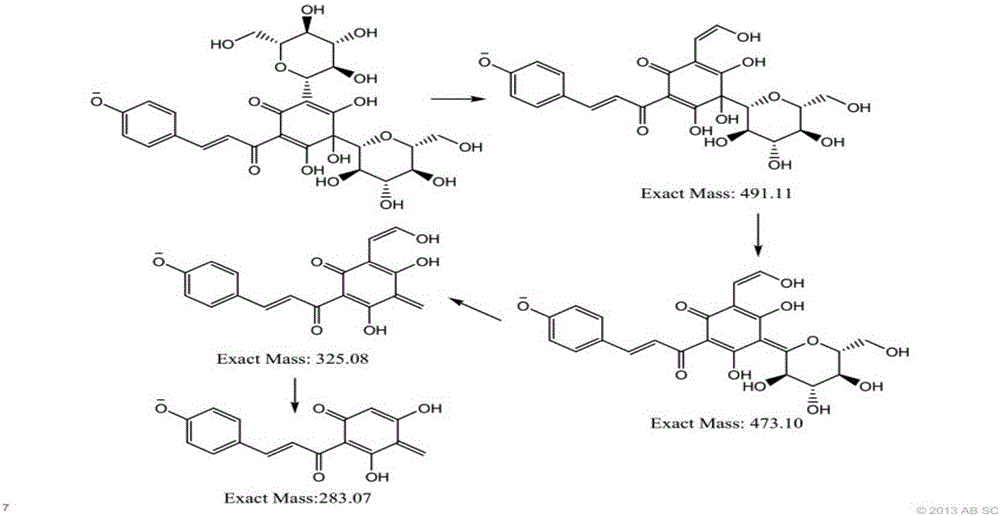
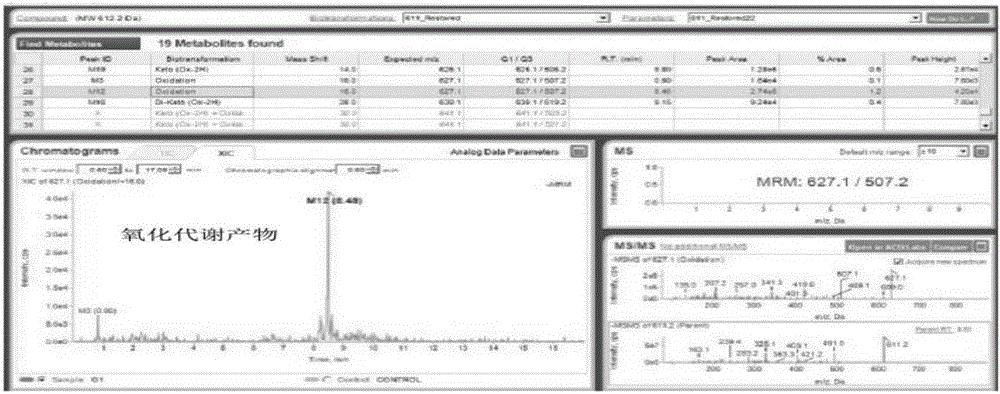
The invention discloses a detection method for hydroxysafflor yellow A metabolic products. The method includes the steps of: 1) performing intravenous injection to an SD rat with a safflower extract and aceglutamide injection, performing orbid blood sampling, and centrifugally separating the blood sample to obtain plasma; 2) sucking the plasma with a micro sample injector, adding acetonitrile with volume ratio of plasma to acetonitrile being 1:3-3.5, uniformly mixing the substances with vortex and centrifuging the mixture to obtain a supernatant, blow-drying the supernatant with nitrogen gas, dissolving the dried substance in acetonitrile, and centrifuging the solution to obtain a supernatant as a detection sample; and 3) detecting and analyzing the sample through high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupoles linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry, and analyzing the metabolic products in a p-MRM-IDA-EPI mode. In the invention, a p-MRM method is employed in the mass spectrum with combination of Light Sight software to quickly identify and analyze the sample for tracing metabolic change of component change and structure change in the plasma; 11 hydroxysafflor yellow A metabolic products are found in the result. The method can be used for obtaining a time change curve of the hydroxysafflor yellow A and the metabolic product thereof in plasma, and successfully deduces and identifies the molecular structures of seven metabolic products and isomers of the hydroxysafflor yellow A. The method, compared with a chemical structure analytic method, is more quick and sensitive.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for real-time detection of monoamine neurotransmitter change in brains of animals under smoke exposure condition
ActiveCN106645492ARealize online detectionHigh sensitivityComponent separationDialysate sampleElectrochemical detector
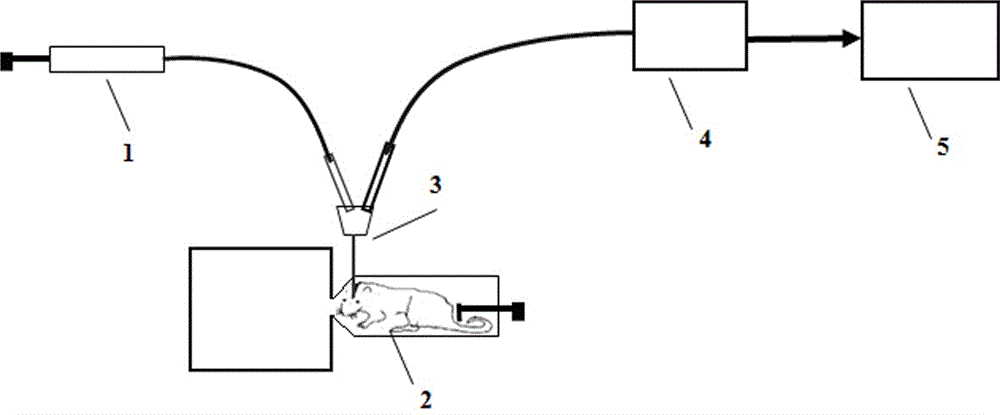
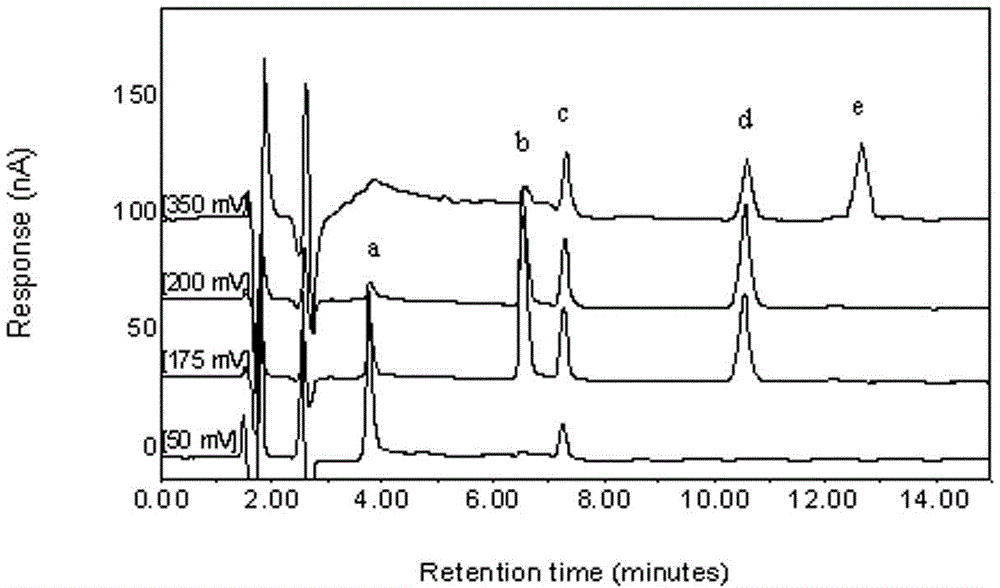
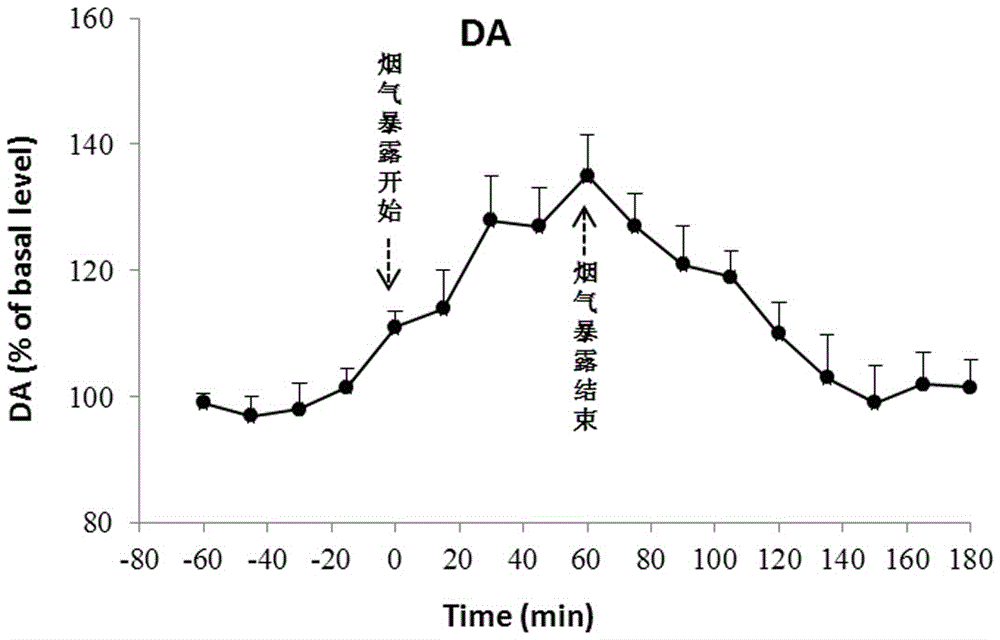
A method for real-time detection of monoamine neurotransmitter change in brains of animals under a smoke exposure condition is characterized by exposing the animals to smoke in real time by adopting an animal oro-nasal inhalation smoke exposure system, collecting an animal brain tissue sample through an on-line microdialysis technique, and quickly analyzing monoamine neurotransmitters and metabolite thereof in a brain dialysate sample by using a high performance liquid chromatography / coularray detector, so as to detect monoamine neurotransmitter change characteristics in the brains of the animals before and after smoke exposure in real time. According to the method provided by the invention, exposure to the smoke of the animals is more similar to the manner of human beings smoking tobacco products, the technical difficulty of incapability of real-time simulating and evaluating of monoamine neurotransmitter change caused by smoke inhaling (nicotine intaking) is overcome, the method has the advantages of simple operation, accurate and reliable result and the like, and compared with the prior art, a new method for monitoring monoamine neurotransmitter metabolic change in the brains of the animals after smoke exposure is created.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
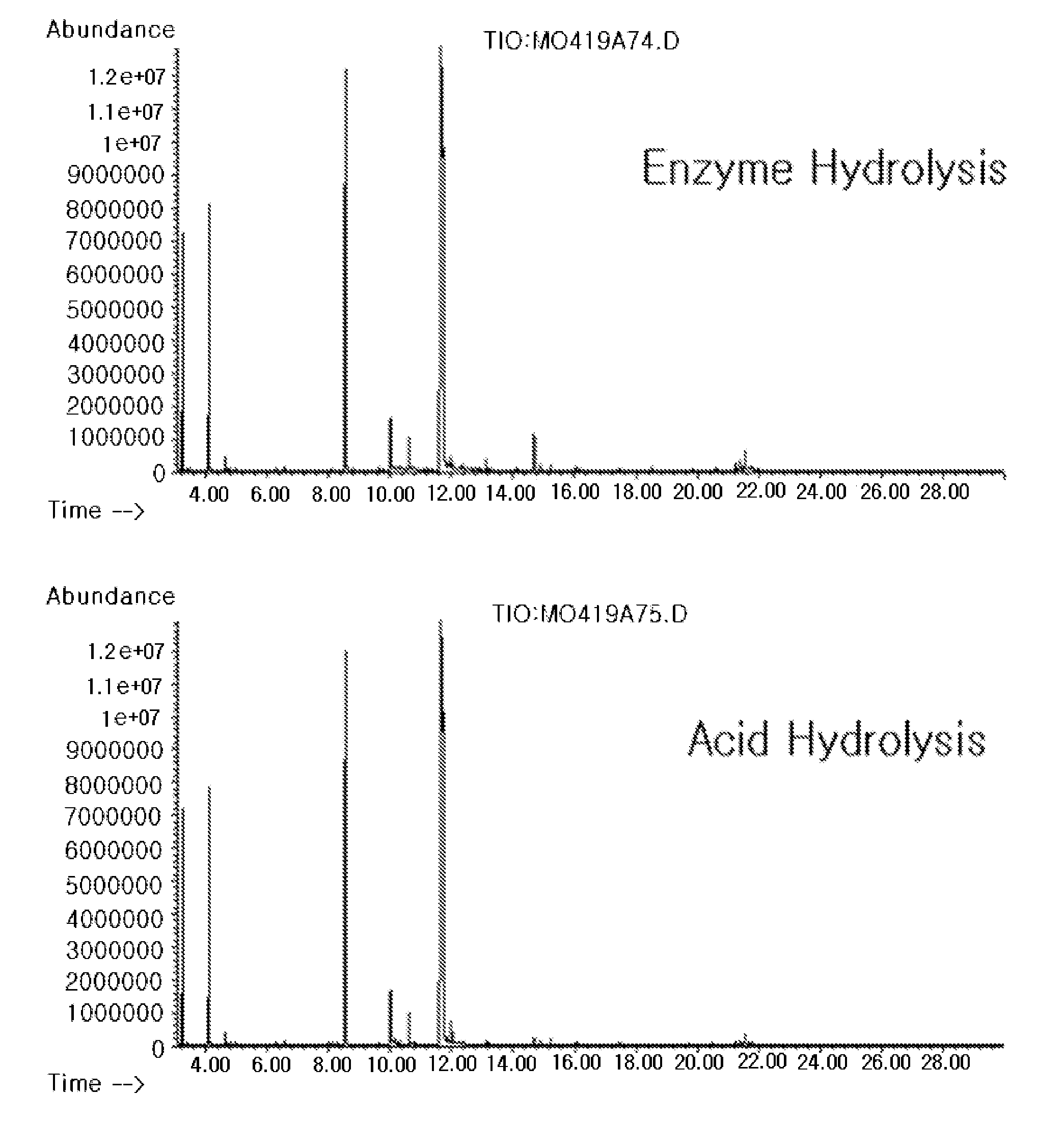
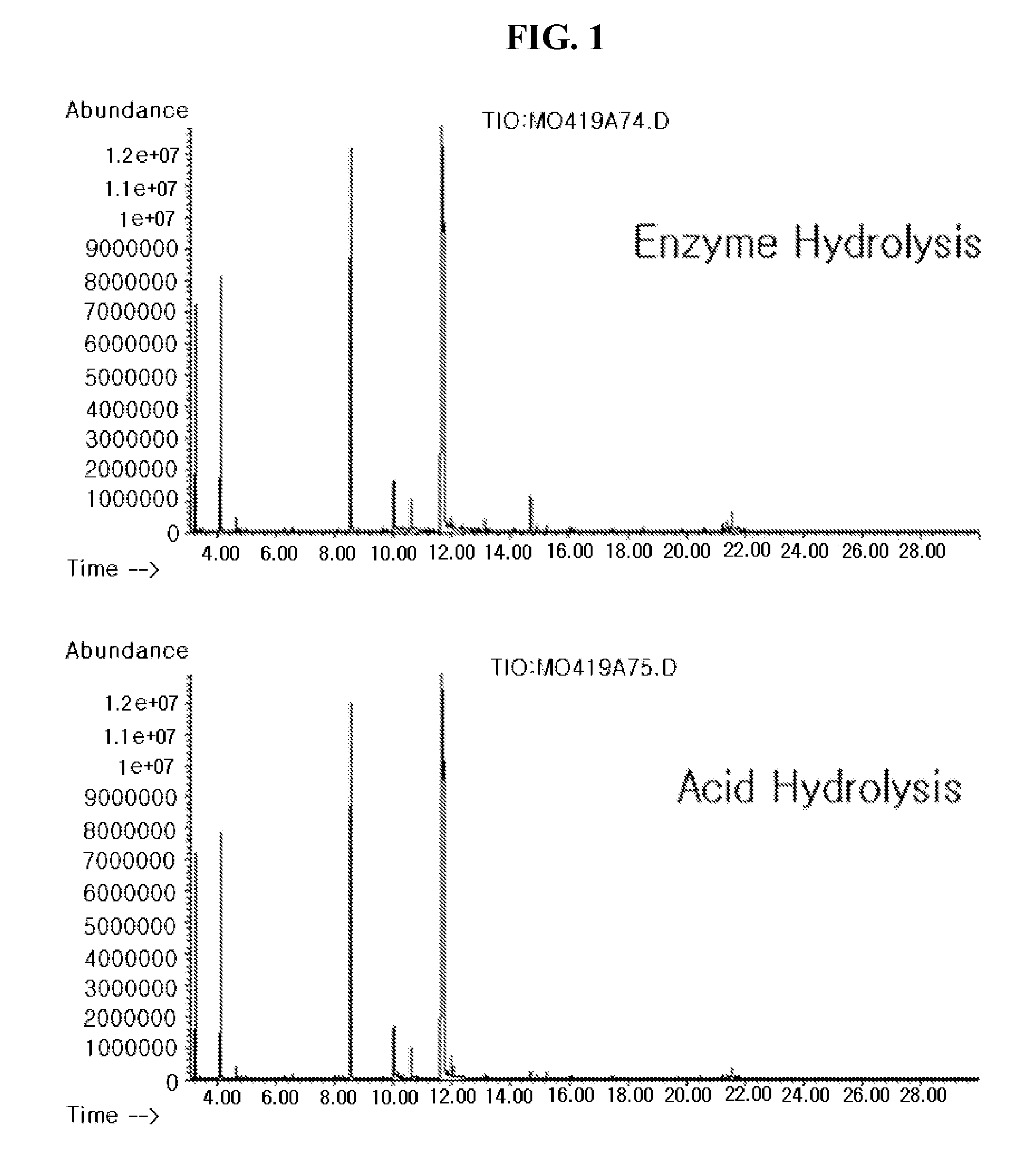
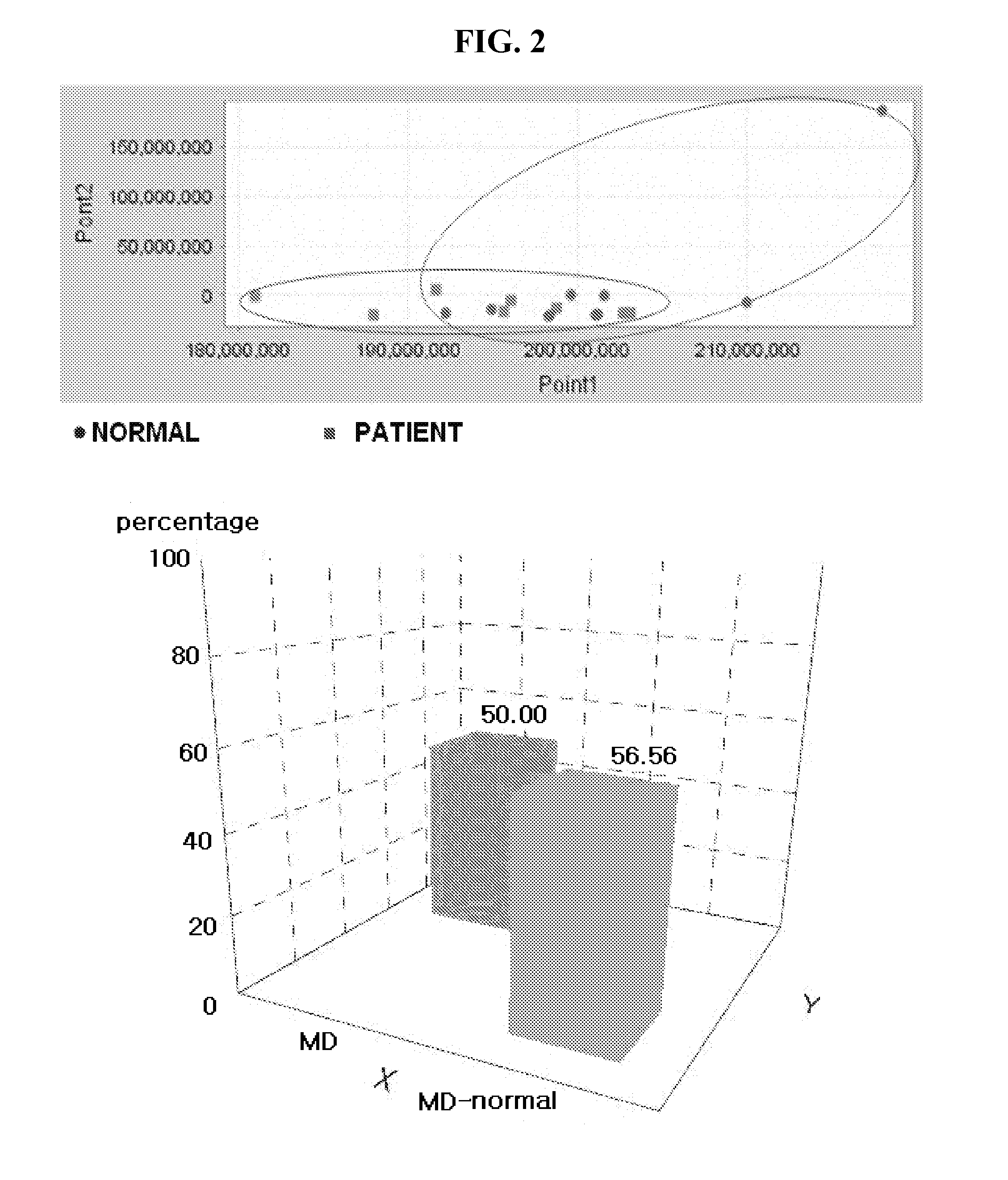
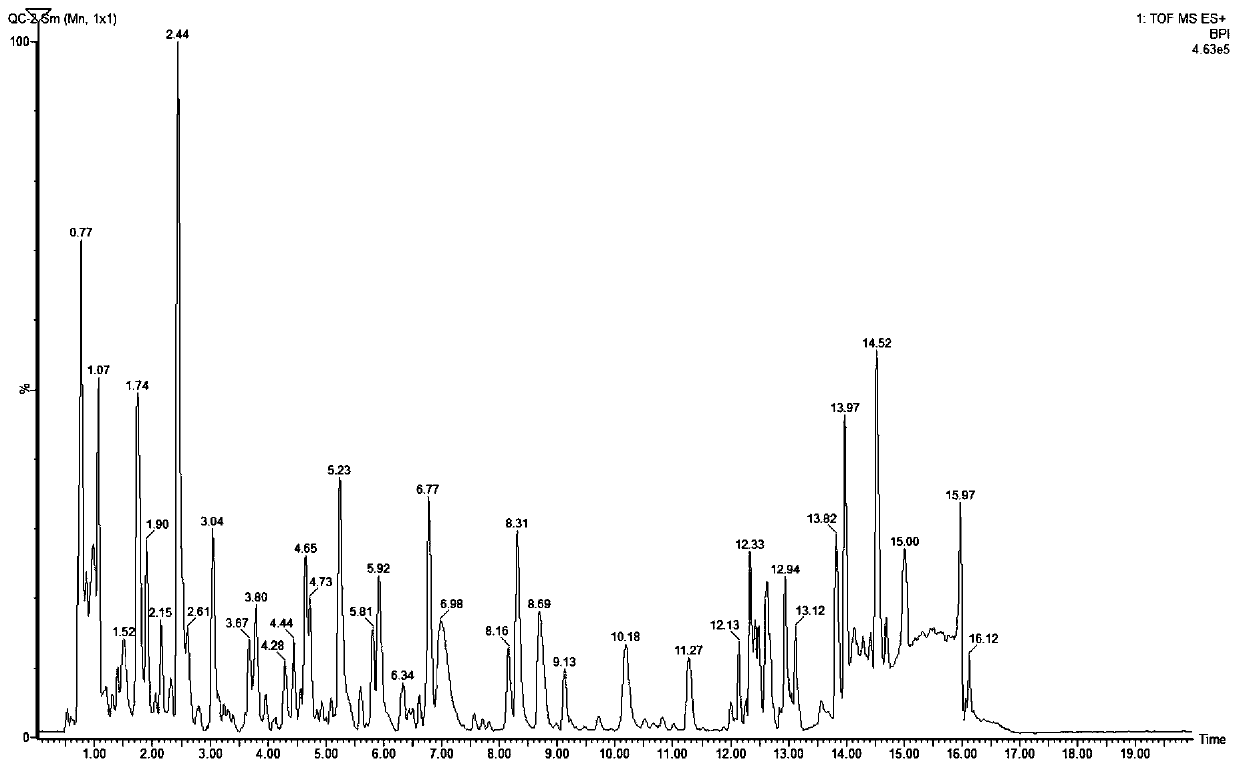
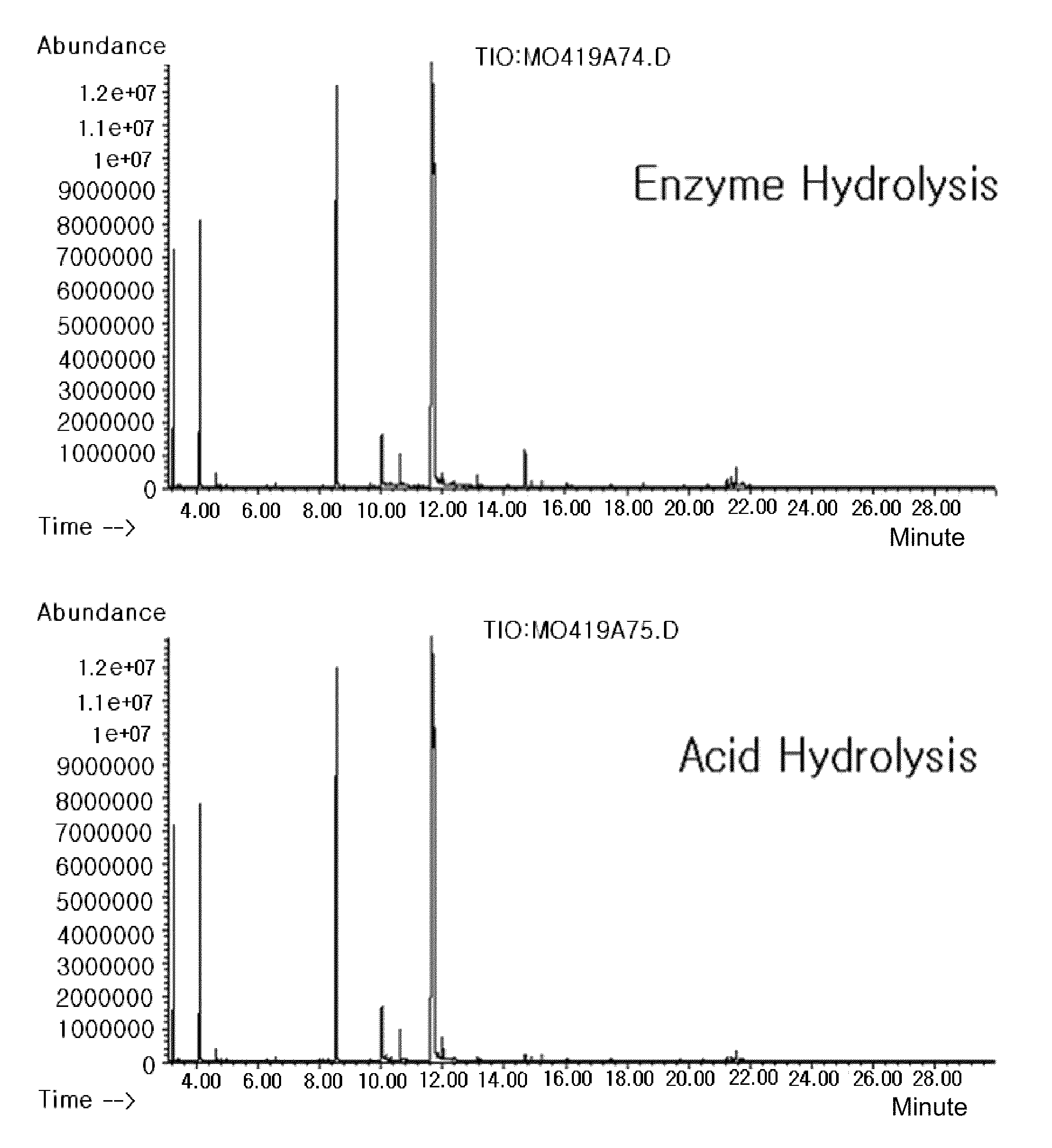
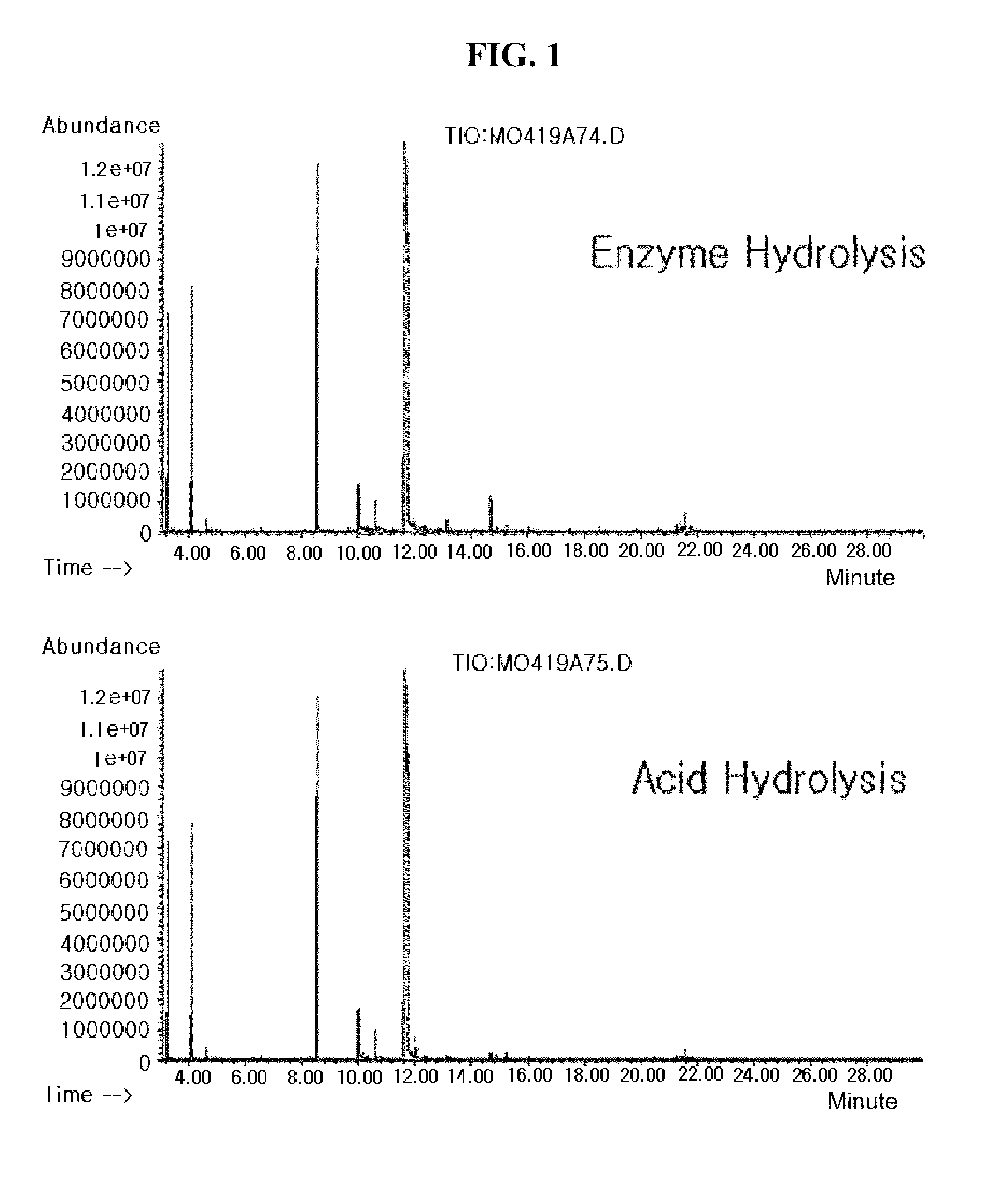
Method for analysis of metabolite difference between two biological samples using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080076181A1Component separationWithdrawing sample devicesMetabolitePrincipal component analysis
Disclosed is a method of extracting all metabolites existing in a biological sample to detect a comprehensive difference between metabolites of a control group and a test group, thereby verifying significance thereof. More particularly, the invention comprises a first step of analyzing a fraction extracted with a solid phase extraction method, a fraction obtained by extracting the remnant fraction with a liquid-liquid extraction method and fractions extracted with the liquid-liquid extraction method at two pH different from each other after the hydrolysis, with a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; a second step of converting the chromatogram result into numerical values capable of being statistically processed; and a third step of analyzing the numerical values with a principal component analysis (PCA) and a discriminant analysis (DA) to detect a difference between the control group and the test group. According to the invention, the difference between the two groups can be comprehensively detected with the areas of the peaks on the chromatogram, without a standard material or verified quantitative method. Therefore, it is possible to detect the metabolic change in the organism due to the disease or gene mutation, without an accurate quantitative analysis of the metabolites.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Cold-coagulation-blood-stasis-syndrome-resistant differential metabolite metabolic pathway and study method of Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction
InactiveCN110794074AHigh diagnostic valueEfficient revealComponent separationEndogenous metabolismDisease
The invention discloses a cold-coagulation-blood-stasis-syndrome-resistant differential metabolite metabolic pathway and study method of a Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction. The method comprises: detecting and analyzing endogenous metabolites changed at different time points after cold-coagulation blood-stasis symptoms forming of a female rat under an ice-water bath and epinephrine induction and Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction intervention by using an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry so as to obtain a fingerprint spectrum; with a multivariate variable statistical analysis method, carrying out screening from a plurality of variables and identifying 21 significantly changed metabolites; and enriching eight metabolic pathways related to different development stages of the cold-coagulation blood-stasis symptom by using ametaboanalyst open-source online metabonomics analysiswebsite. According to the invention, the related metabolic changes in the occurrence and development process of the old-coagulation blood-stasis symptoms and the treatment process of the Chinese angelica-based cold-coagulation blood-stasis treatment decoction are studied by using a dynamic analysis method; the disease occurrence and development mechanisms at different time points can be revealed;and the abnormal metabolic network regulated and controlled by medicines in the treatment process can be clarified.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
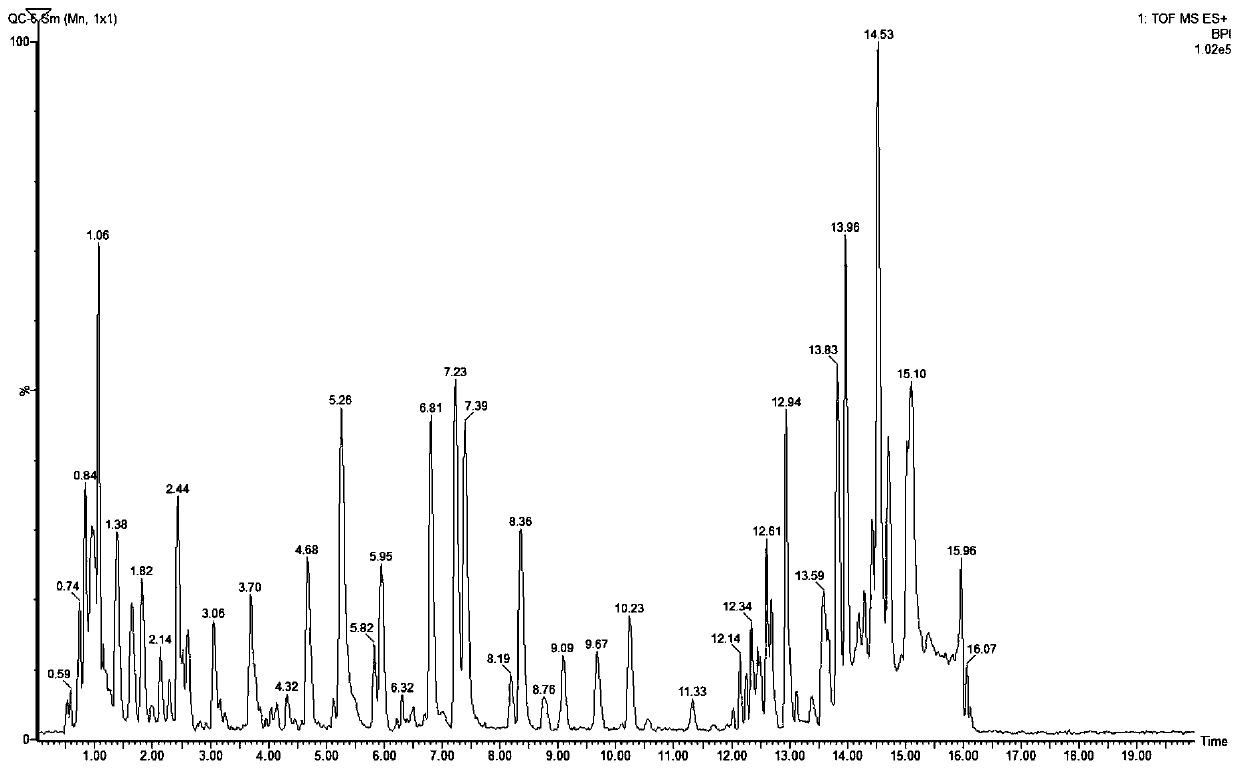
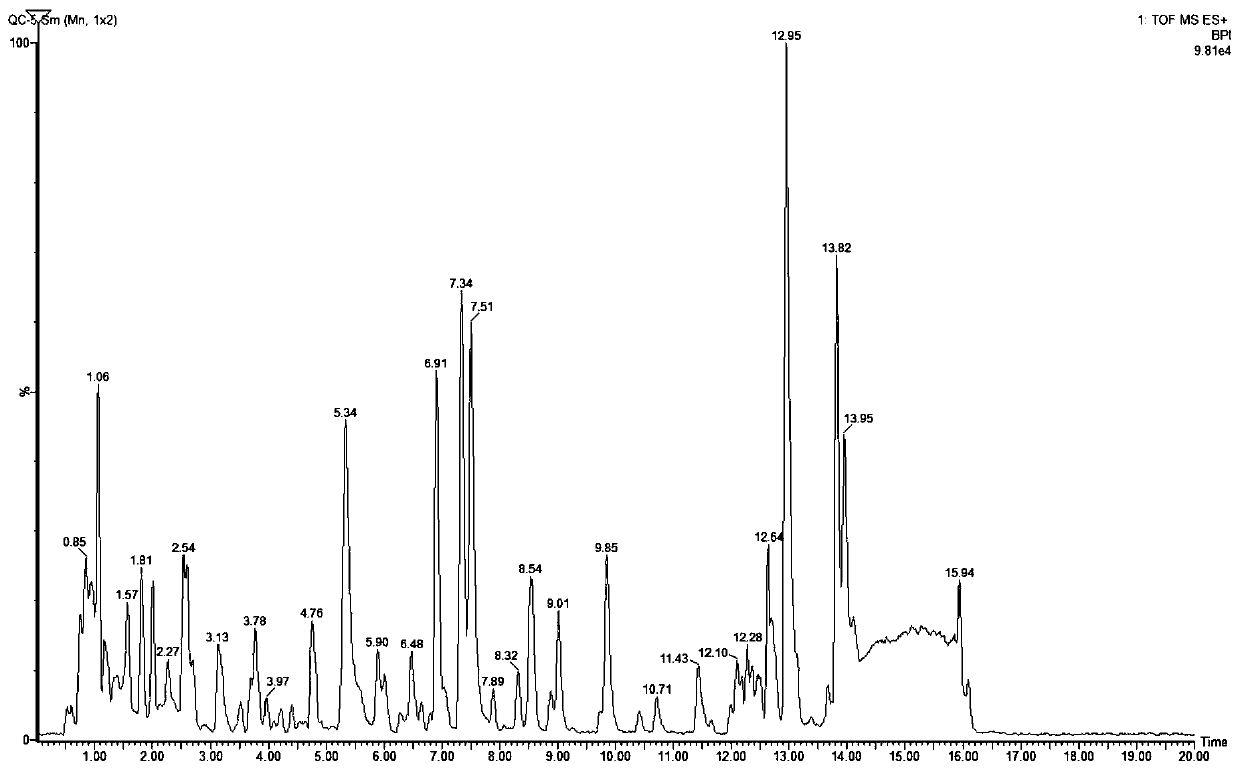
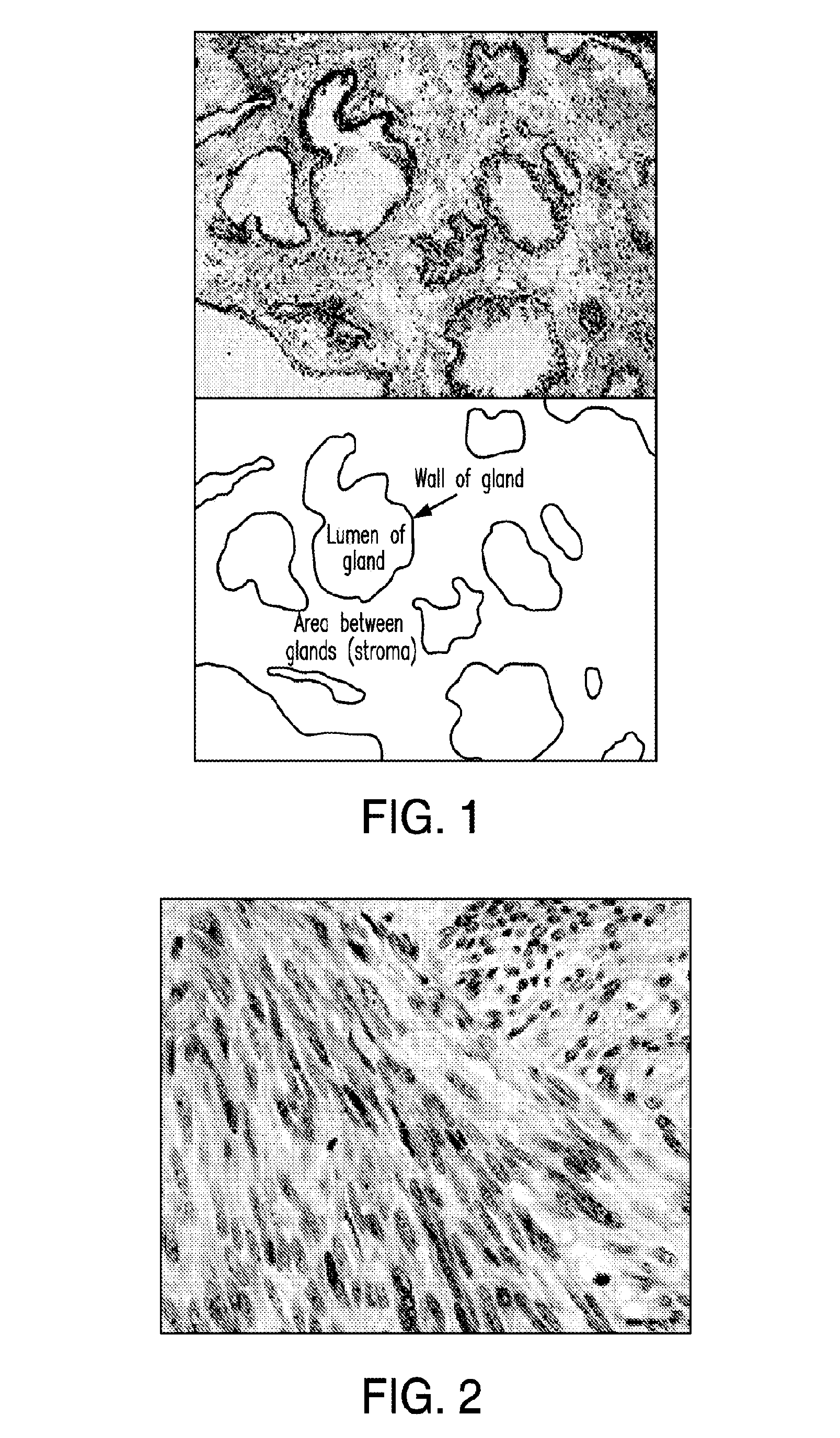
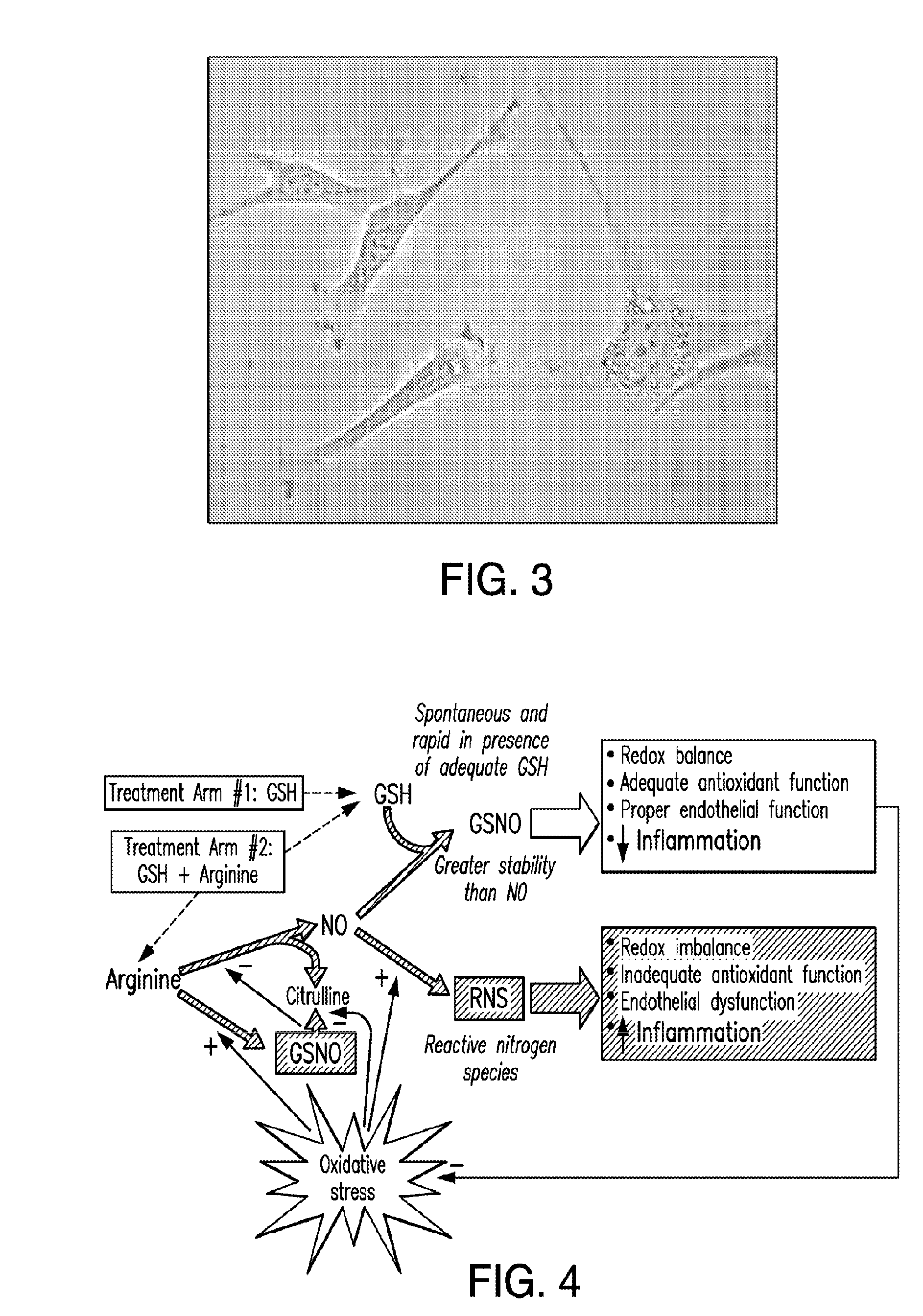
Liposomally encapsulated reduced glutathione for management of cancer and disruption of cancer energy cycles
InactiveUS20130202681A1CripplingDisabling its growth processMetabolism disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
A method of treatment of cancer with a formulation of liposomally encapsulated glutathione, that is preferably used orally, increases the level of glutathione in tissues in order to prevent and reverse the metabolic changes in cells that results in the formation of the metabolic “fuel supply” that supports cancer cells, and without which the cells can die out. The method prevents the oxidative stress that damages normal support cells such as stromal fibroblast cells. By blocking the “fuel supply,” the invention can protect, prevent and reverse these cells from the steps of autophagy and mitophagy, that results in the cells decreasing the normal production of ATP for energy and using aerobic glycolysis for energy production. The use of oral liposomally encapsulated glutathione will maintain the presence and normal function of caveolin in fibroblast and other cells, thus preventing their conversion to autophagic tumor stromal cells.
Owner:GUILFORD FREDERICK TIMOTHY
Promoter-reporter cells for determining drug metabolism, drug interactions, and the effects of allotype variation
InactiveUS20080152632A1Minimizing immune responsePromote excretionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDrug interactionPromoter activity
This invention provides a system for rapid determination of pharmacologic effects on target tissue types in cell populations cultured in vitro. The cells contain a promoter-reporter construct that reflects a toxicologic or metabolic change caused by the agent being screened. The promoter is taken from a gene known to be up- or down-regulated according to the metabolic state of the cell, and linked to a reporter gene that provides an external signal for monitoring promoter activity. The promoter-reporter cells may be produced by placing these genetic alterations into a line of human embryonic stem cells, bulking up the cells to any extent desired, and then differentiating the cells into the desired tissue type. This disclosure explains some of the powerful features of the promoter-reporter cells of this invention, and shows various ways the skilled reader can use the invention for pharmaceutical development and testing, or to monitor graft survival.
Owner:CXR BIOSCI
Compounds, compositions and methods for treating neuropsychiatric disorders
Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) and L-carntine (LCAR) are nutraceuticals with indications in treating a variety of mental health disorders. A metabolomics-guided bioprocess method is presented to enhance ALCAR and LCAR formation in germinating plant seeds. Metabolic fluxes are manipulated by germination in bioreactors to increase oxygen availability as well as provide an aseptic environment to alter carbohydrate consumption and feedback repress gluconeogenesis. Large shifts in sunflower seed fatty acid, phospholipid and high-energy metabolism change the germination environment and these metabolic changes lead to an approximate 1000-fold increase in natural LCAR and ALCAR production by the seeds. The resulting LCAR and ALCAR products from the seeds are used for treating mental health disorders including Alzheimer's disease, geriatric depression, non-geriatric depression and schizophrenia.
Owner:PETTEGREW JAY W +2
Screening method
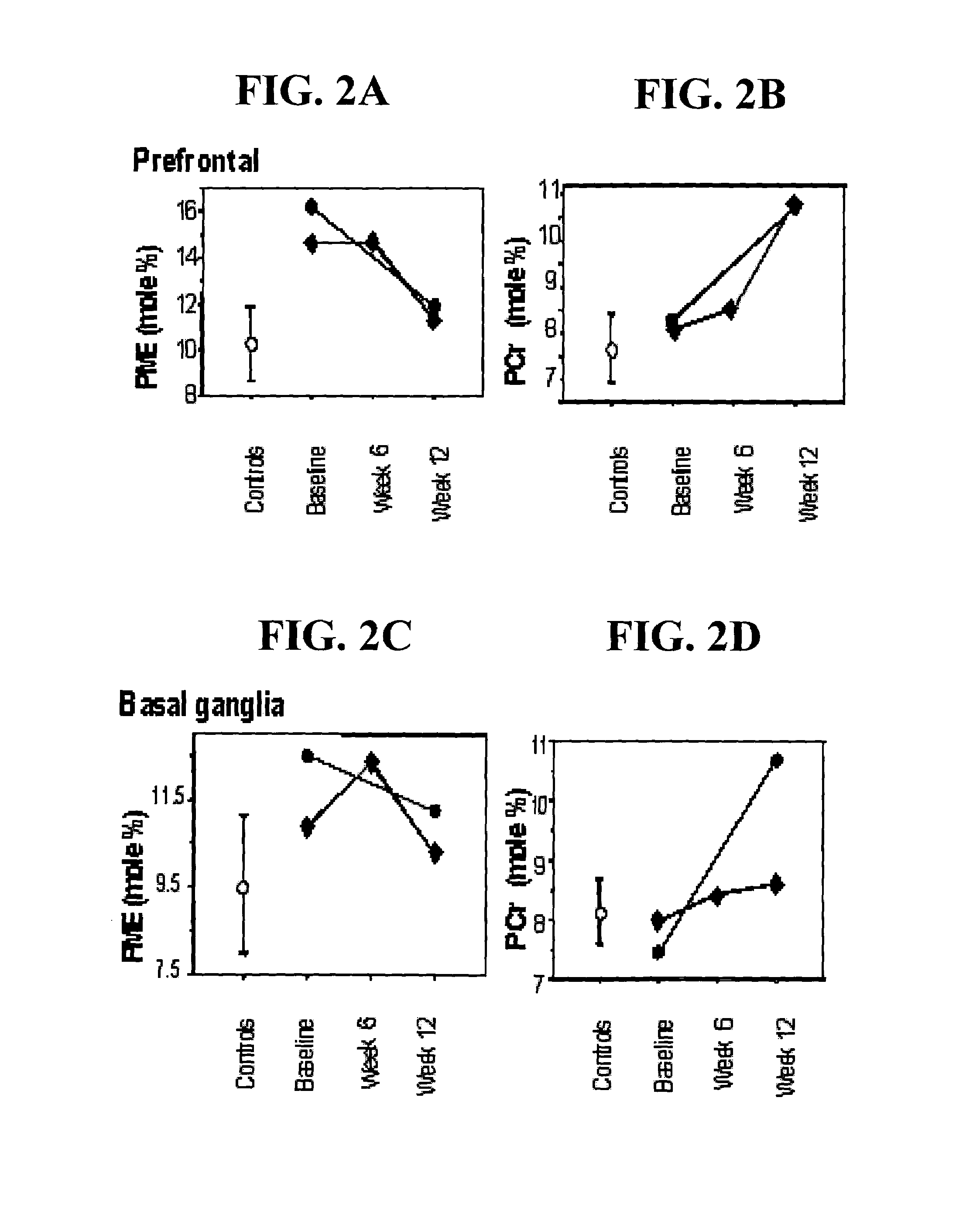
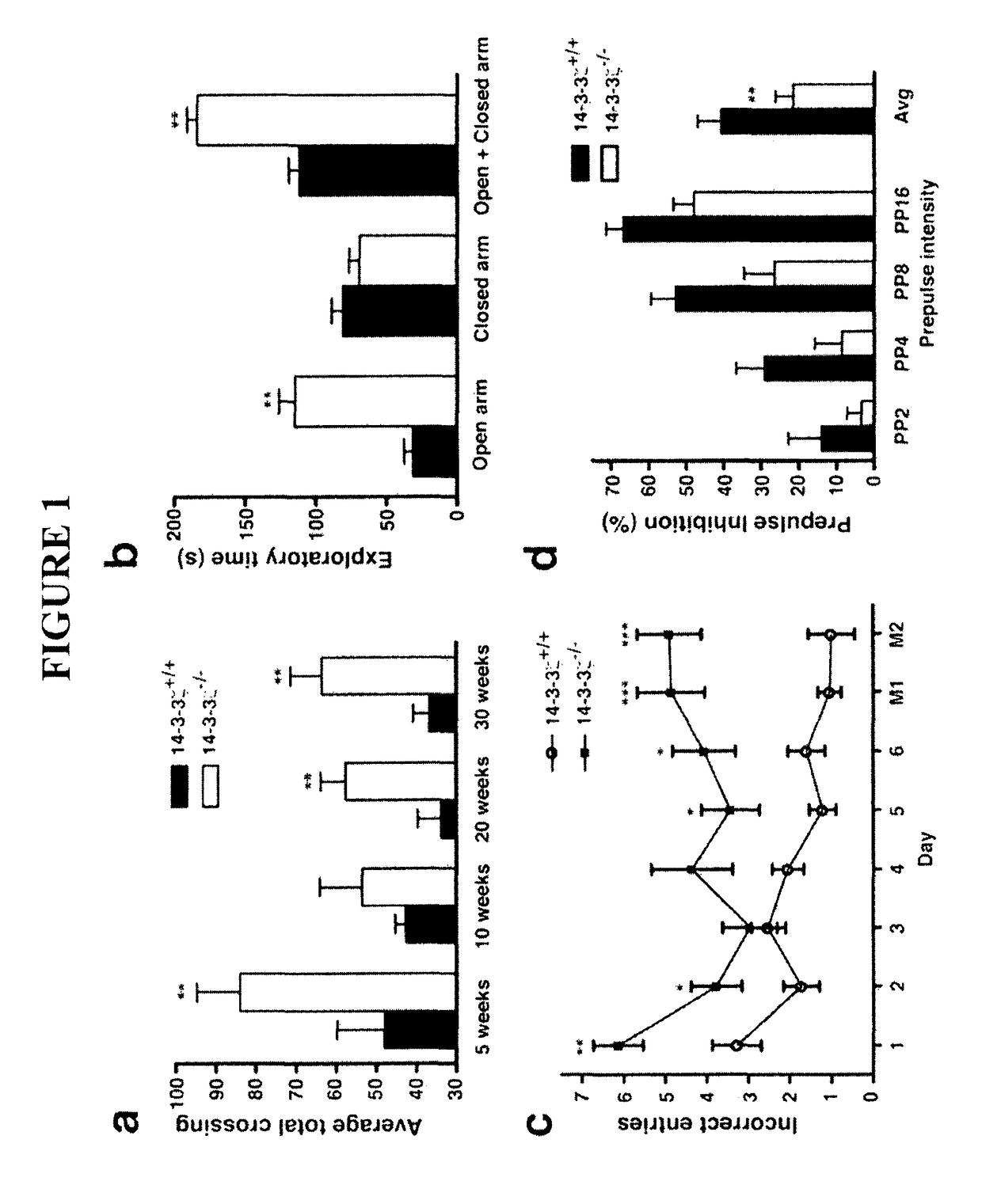
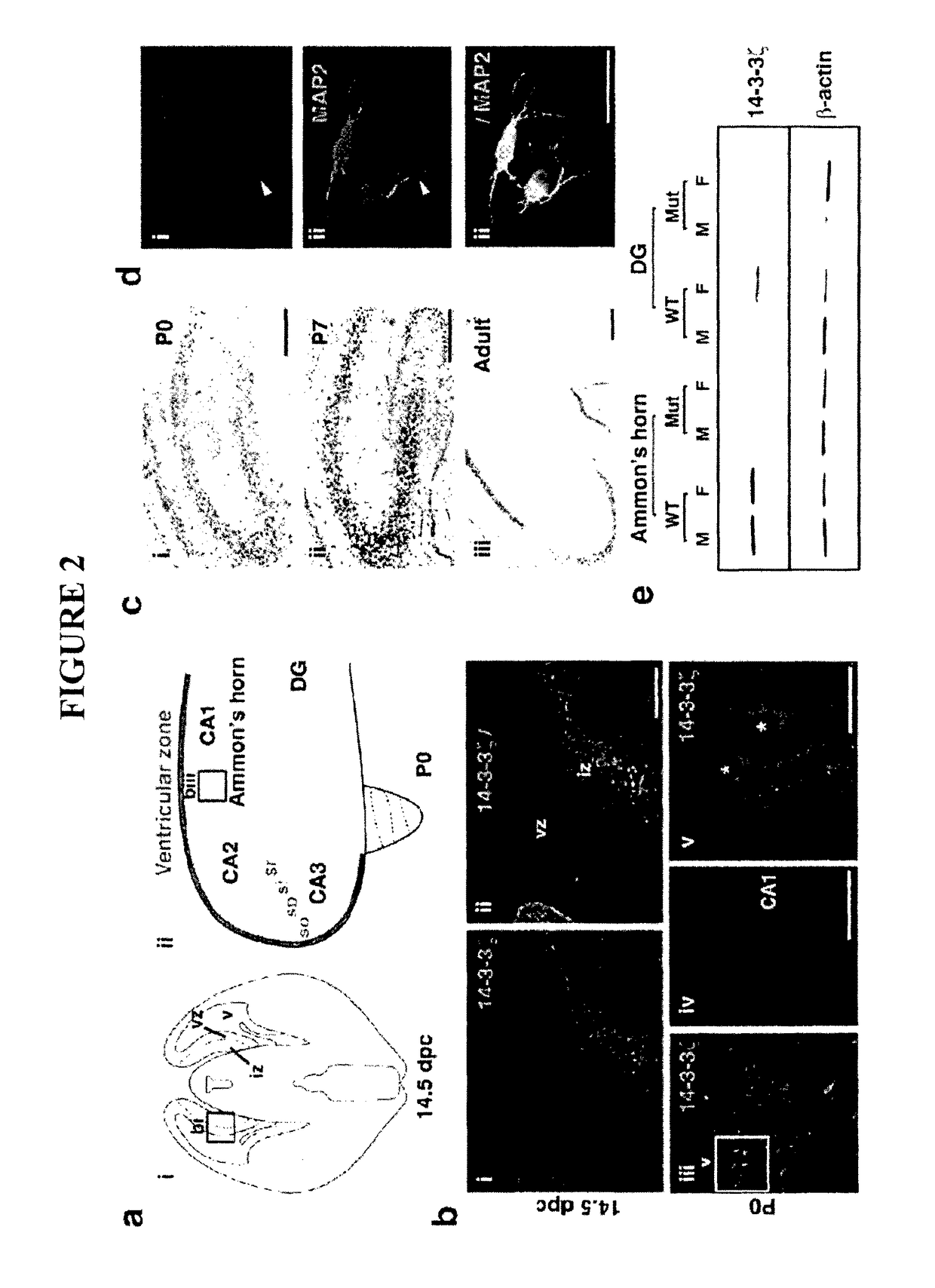
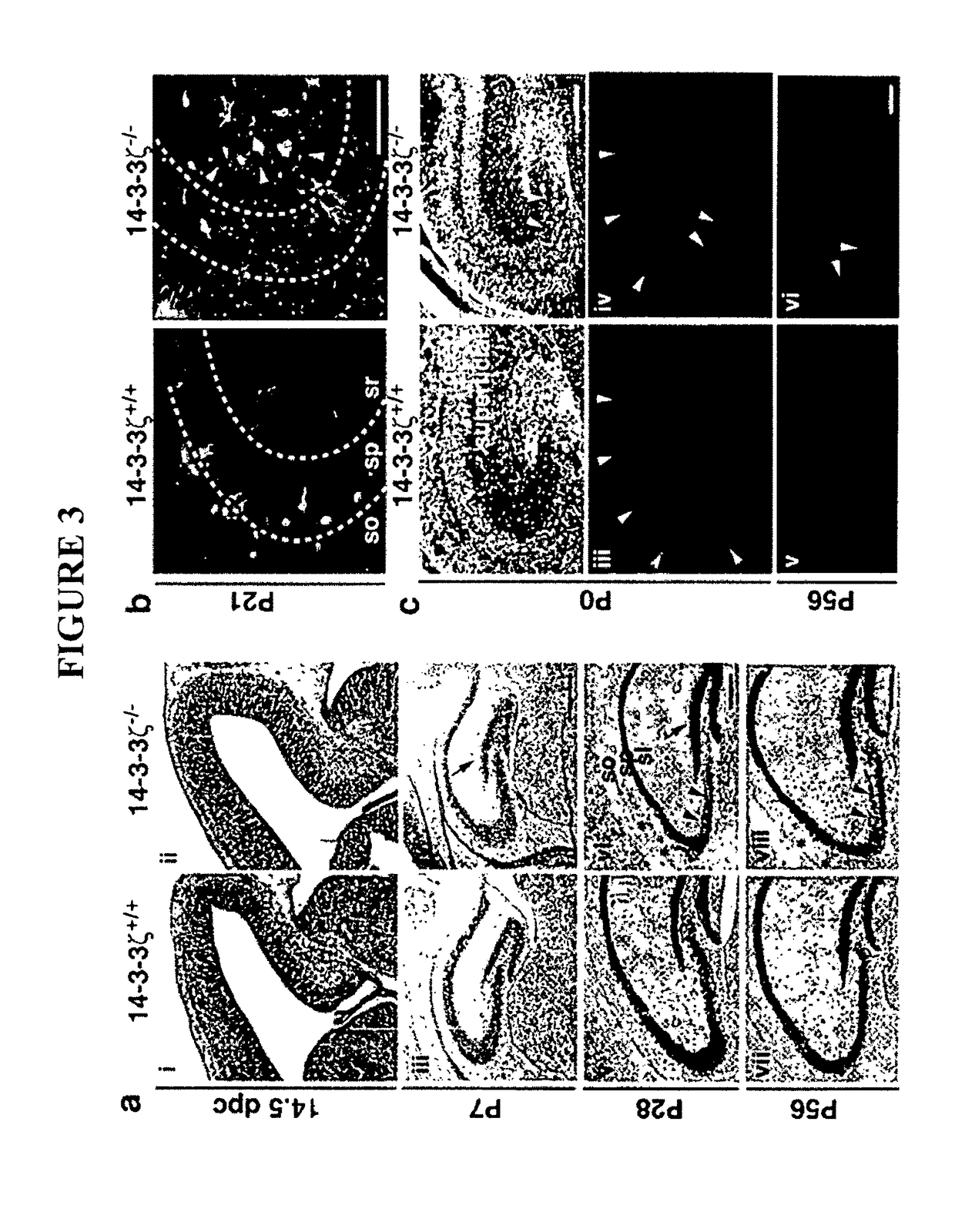
The present invention provides a method of screening a mammal for the onset or predisposition to the onset of a neuropsychiatric disorder. More particularly, the present invention provides a method of screening a mammal for the onset or predisposition to the onset of schizophrenia by screening for a decrease in the functional level of protein 14-3-3ζ. In a related aspect, the present invention also provides a means of monitoring a patient diagnosed with a neuropsychiatric disorder, such as schizophrenia, by screening for changes to functional levels of protein 14-3-3ζ. This may be useful, for example, in the context of evaluating the effectiveness of a prophylactic or therapeutic treatment regime or otherwise monitoring the impact of physiological or metabolic changes which may occur in a patient. The method of the present invention is useful in a wide range of applications including, inter alia, providing a means of identifying mammals susceptible to the onset of a neuropsychiatric condition, such as a condition characterized by one or more symptoms of schizophrenia, thereby enabling the implementation of prophylactic or early therapeutic intervention in an effort to either minimize or prevent the onset of the condition. It also provides a means of confirming diagnoses which would otherwise be based solely on an assessment of positive and negative symptoms.
Owner:PRECISION MEDICINE HLDG PTY LTD
Method for analysis metabolite difference between biological samples
Disclosed is a method of extracting all metabolites existing in a biological sample to detect a comprehensive difference between metabolites of a control group and a test group, thereby verifying significance thereof. More particularly, the invention comprises a first step of analyzing a fraction extracted with a solid phase extraction method, a fraction obtained by extracting the remnant fraction with a liquid-liquid extraction method and fractions extracted with the liquid-liquid extraction method at two pH different from each other after the hydrolysis, with a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; a second step of converting the chromatogram result into numerical values capable of being statistically processed; and a third step of analyzing the numerical values with a principal component analysis (PCA) and a discriminant analysis (DA) to detect a difference between the control group and the test group. According to the invention, the difference between the two groups can be comprehensively detected with the areas of the peaks on the chromatogram, without a standard material or verified quantitative method. Therefore, it is possible to detect the metabolic change in the organism due to the disease or gene mutation, without an accurate quantitative analysis of the metabolites.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Bio-electronic system
InactiveUS20110184256A1Safe humiditySafe vibrationAnimal reproductionDiagnostic recording/measuringNotification ReceiverElectronic systems
The bio-informatics system of the present invention serves to identify by electronic means, in body fluids of domestic and / or wild mammals, the metabolic changes that occur in each of the physiological moments of economic, scientific, and technological importance, associated with the female reproduction and with the health of animals in general. The system encrypts the information, analyzes it, memorizes when each one of the metabolic variables reach a predetermined level, and informs a receiver of the event.
Owner:BARCELO ROJAS CARLOS ALBERTO
Activators of Plant Metabolic Changes
InactiveUS20190350208A1Promote absorptionImprove solubilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSulfateBlue green algae
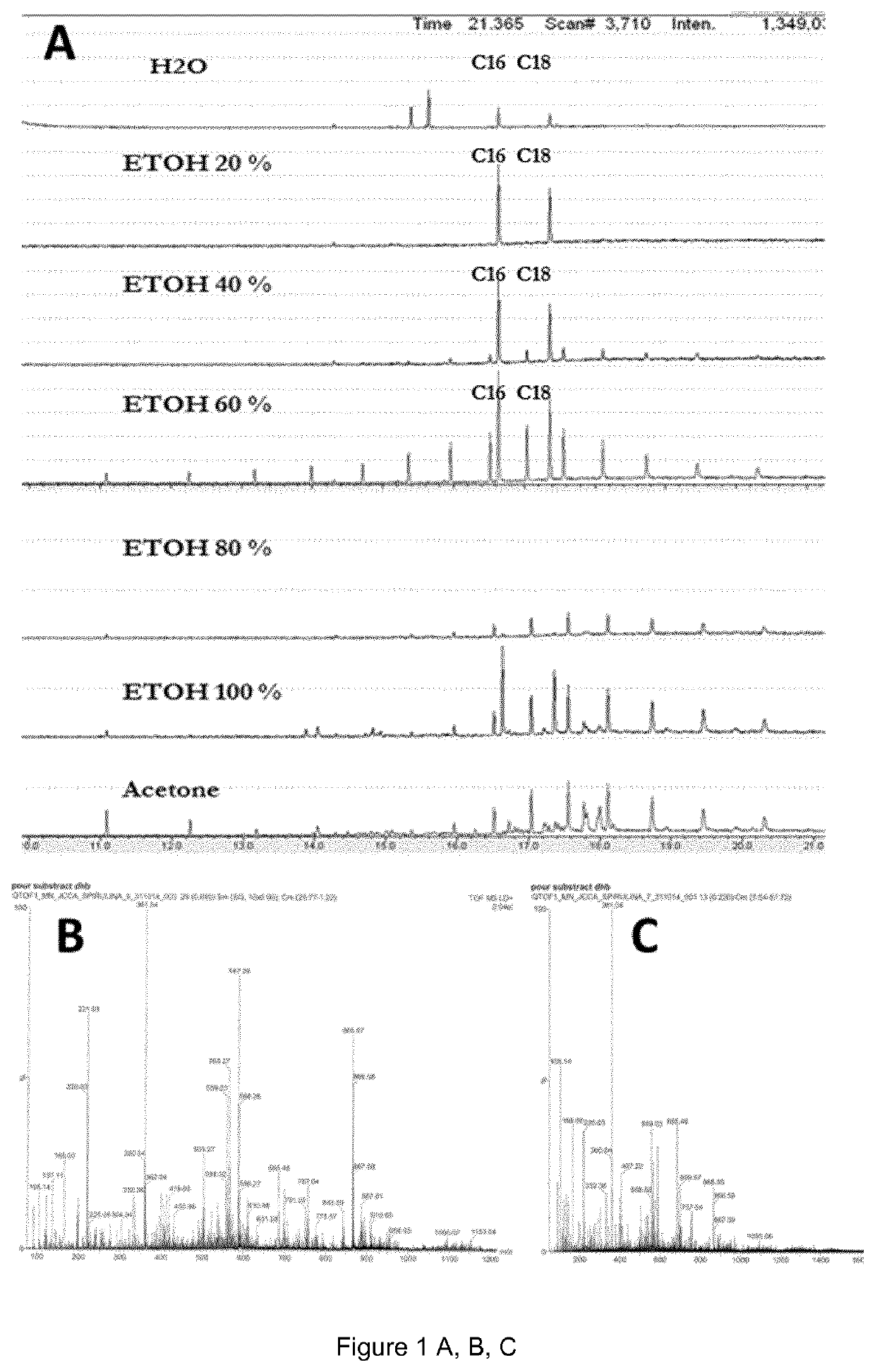
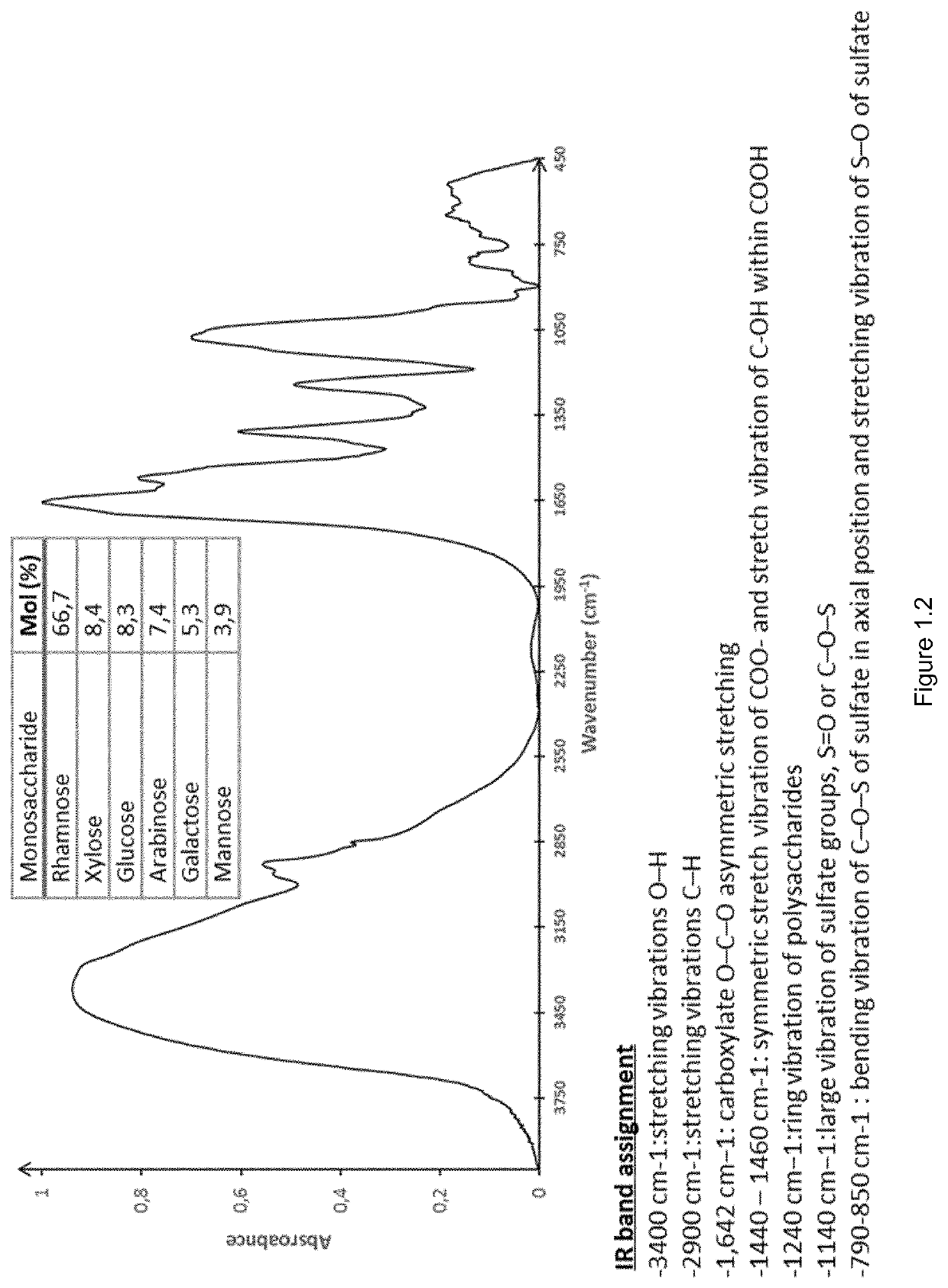
The present invention relates to a composition comprising saccharides extracted from blue-green algae biomass, the said saccharides comprising—from 55% to 60% of rhamnose by weight, —from 6.5% to 10% of uronic acid by weight, —from 5% to 15% of sulfate groups by weight, and—less than 10% of xylose, glucose and galactose or a mixture thereof calculated by weight upon the total of the composition being 100%.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MONS +1
Human body data acquisition and analysis system
ActiveCN107368689BRealize four-dimensional evaluationInstrumentsMedical reportsHuman bodyStructure and function
The embodiment of the invention provides a somatic data collecting and analyzing method and system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining somatic data; performing data processing on the somatic data, and obtaining somatic fibrosis degree data corresponding to somatic structure data and somatic metabolic change data corresponding to somatic function data; by means of the principle of relative balance of damage and repair in a stable whole, on the basis of the somatic fibrosis degree data and the somatic metabolic change data, obtaining somatic structure and function conversion data; according to the somatic fibrosis degree, somatic structure and function conversion data and the somatic metabolic change data, obtaining somatic fibrosis degree and somatic metabolic adaptability information; according to the adaptability information, generating a somatic data analysis report. The somatic structure data, the somatic structure and function conversion data and the somatic function data are combined for performing data analysis, the condition of somatic structure and function adaptability is obtained, and therefore somatic timer shaft and spatiality four-dimensional assessment is achieved.
Owner:董云鹏
Apparatus for Circumferential Suction Step Multibiopsy of the Esophagus or Other Luminal Structure with Serial Collection, Storage and Processing of Biopsy Specimens within a Removable Distal Cassette for In Situ Analysis
InactiveUS20090124928A1Easy to useAccurate identificationSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsOesophageal tubeStaining
A circumferential suction step multibiopsy apparatus for performing a medical procedure has an elongated flexible member with an aperture extending longitudinally therethrough and an actuator positioned within the aperture. The open tube shaft is connected to a side arm for suction or irrigation including radiopaque contrast and dye staining. There is a cassette removably connected to the actuator for cutting and serially collecting biopsy specimens, for in situ chemical, biological or genetic testing by immediate reaction with the biopsy specimens before metabolic changes, degradation or contamination can occur or for fixation, staining and other processing and analysis.
Owner:ZKZ SCI CORP
Universal, non-invasive, early detection system for cancers
InactiveUS20180209978A1Lower maximum velocityReduce penetrationUnknown materialsDsRNA virusesDevelopmental stageSurvivability
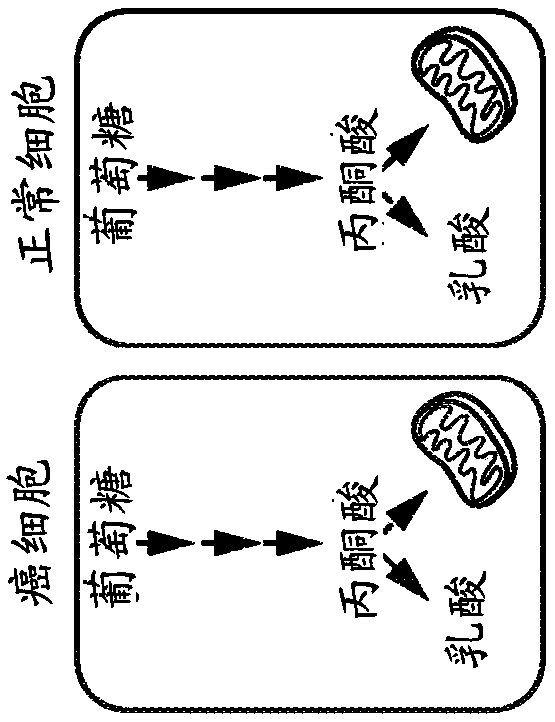
The present invention provides a universal system that detects cancer cells at all stages including early developmental stages as well as matured cancerous tumors. The system relates to monitoring the environment surrounding abnormally metabolizing cells, e.g., predominantly glycolytic cells, cancerous cells, precancerous cells, and / or cells with reduced mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain activity. Nanosensors detect chemical signatures of the organic compounds released by cancer cells into bodily fluids or to the air to detect cancerous or precancerous metabolisms in samples such as urine, saliva, sweat, blood or breath. Treatments provided in recognition of the signature metabolic changes occurring in cancer cells target the abnormal metabolism generally with special emphasis relating to changed mitochondrial metabolism and cell survivability. The treatments include, but are not limited to: therapeutic compositions and methods for treating, delaying, slowing or preventing one or more cancers.
Owner:POSTREL RICHARD
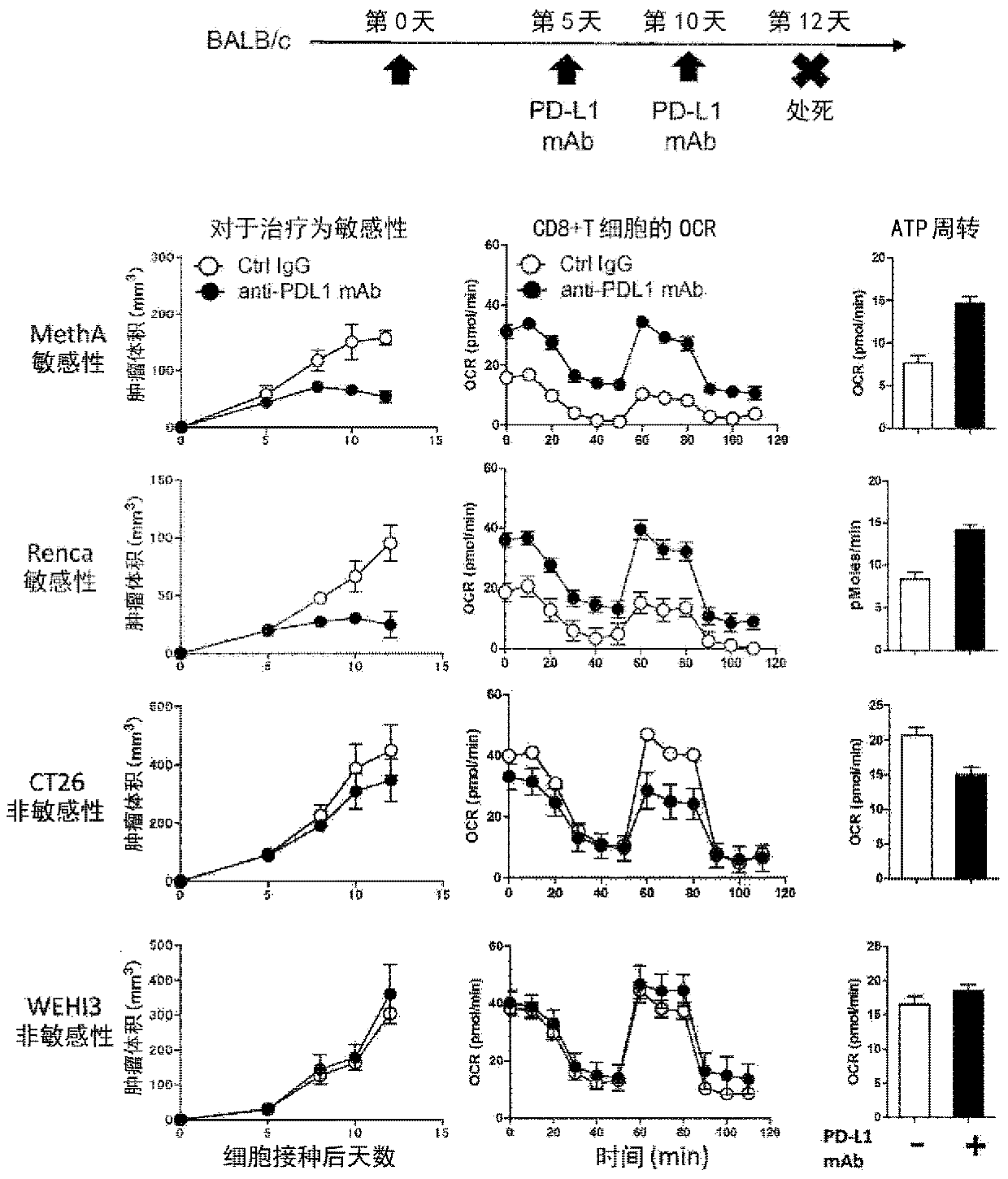
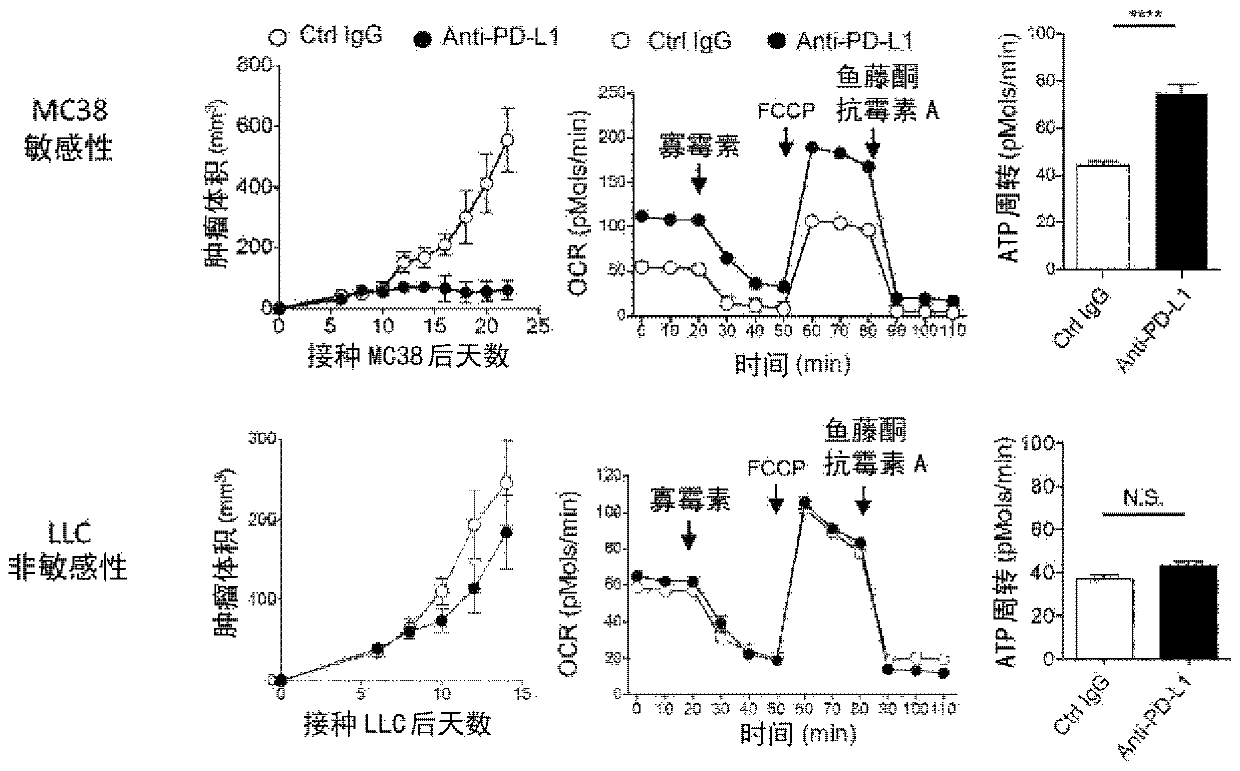
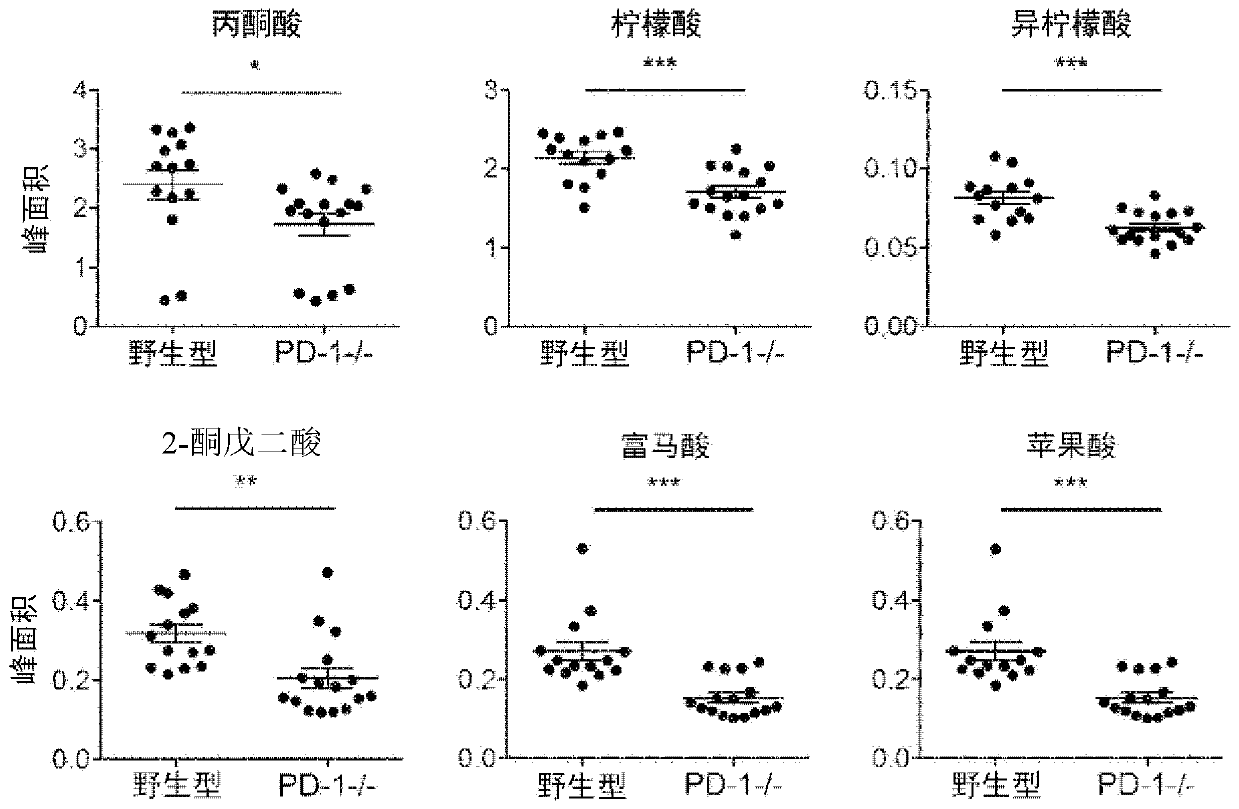
Effectiveness determination marker in disease treatment by pd-1 signal inhibitor
Provided is a marker that determines effectiveness prior to or in an early stage of disease treatment with a PD-1 signal inhibitor. A biomarker that can serve as an indicator of metabolic change related to T-cell mitochondrial activity and / or T-cell activation in a subject is used as a biomarker for predicting or determining the effectiveness of treatment with a PD-1 signal inhibitor. The following can be used as the indicator: intestinal flora-related metabolites in serum or plasma; energy metabolism-related metabolites in serum or plasma; amino acid metabolism-related metabolites and / or derivatives thereof in serum or plasma; oxygen consumption level and / or ATP turnover rate in peripheral CD8+ cells; amino acids in T-cells; and T-bet in peripheral CD8+ cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 and application of rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 in resisting cell damage
ActiveCN110511933AOrganic active ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionCell damageApoptosis
The invention discloses a rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 and an application of the rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 in resisting cell damage. The sequence of the rat long-chain non-coding lncRNA-lncMSTRG10078 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or has homology with more than 190% of SEQ ID NO.1; according to the invention, objective existence of the sequence is proved through PCR; a full-length transcript of the sequence can be cloned; a pcDNA 3.0-lncMSTRG10078 overexpression vector is constructed, GH3 cells are transfected, and results show that overexpression of lncMSTRG10078 can significantly regulate mitochondrial respiratory chain subunits, inflammation, apoptosis and metabolic changes so as to resist cell damage; flow results can show that overexpression of lncMSTRG10078 can significantly inhibit the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis, and further prove that the sequence can enhance the effect of cells on resisting cell damage.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for modulating autophagy
PendingUS20200268837A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPharmacometricsFatty acid
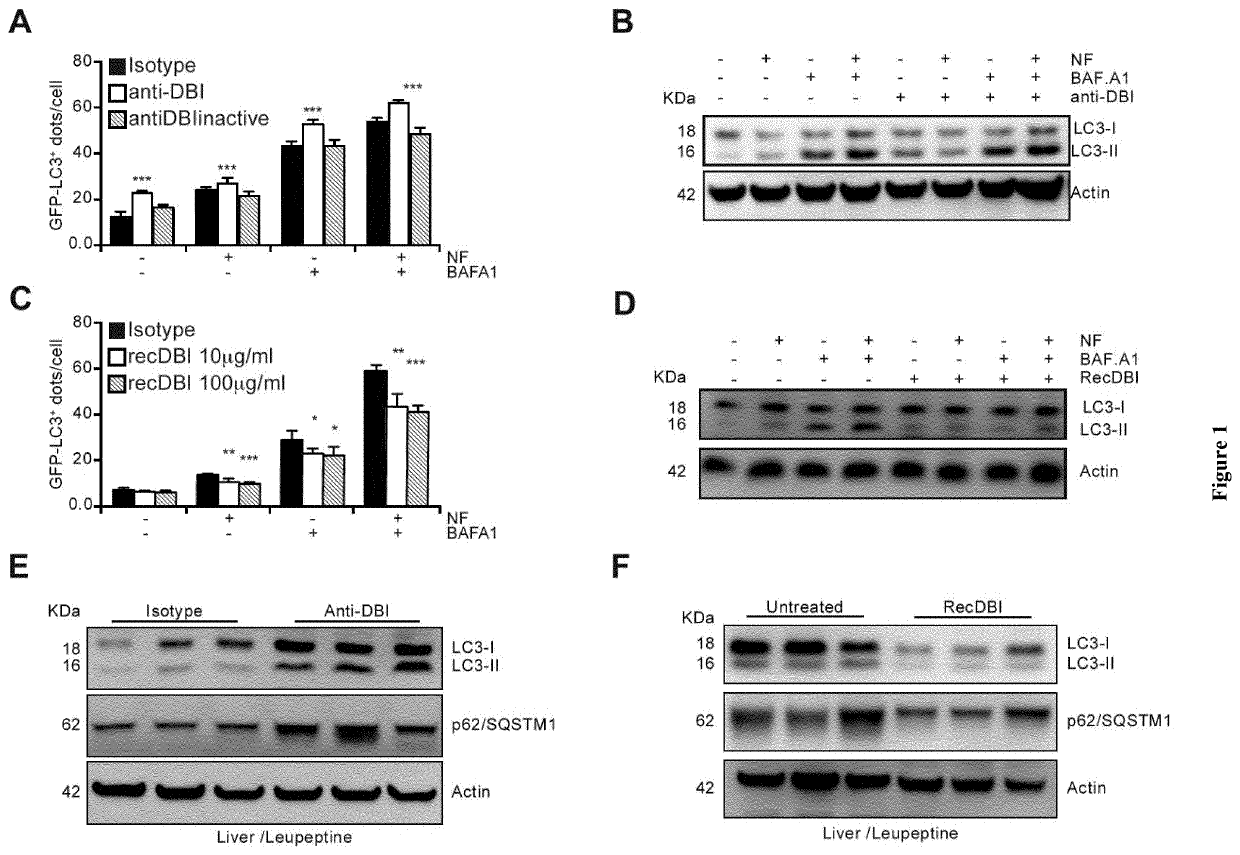
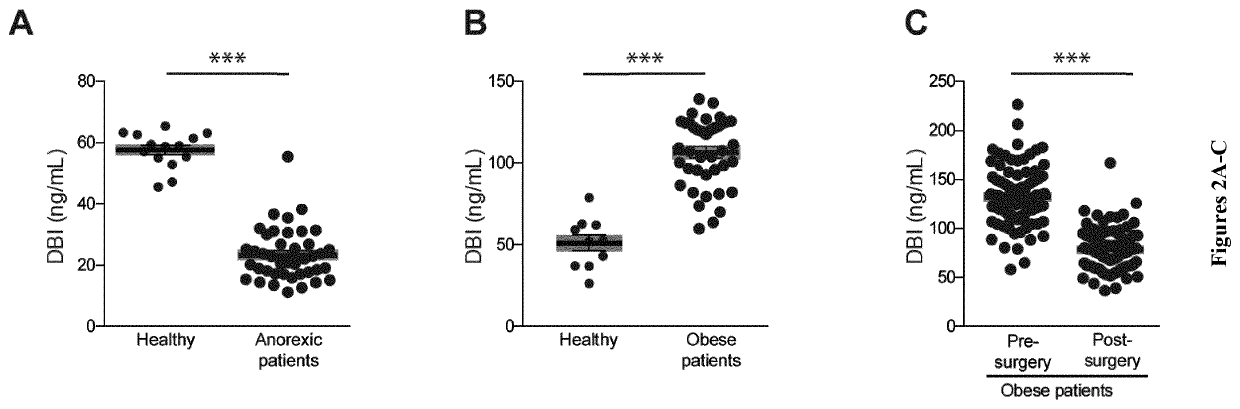
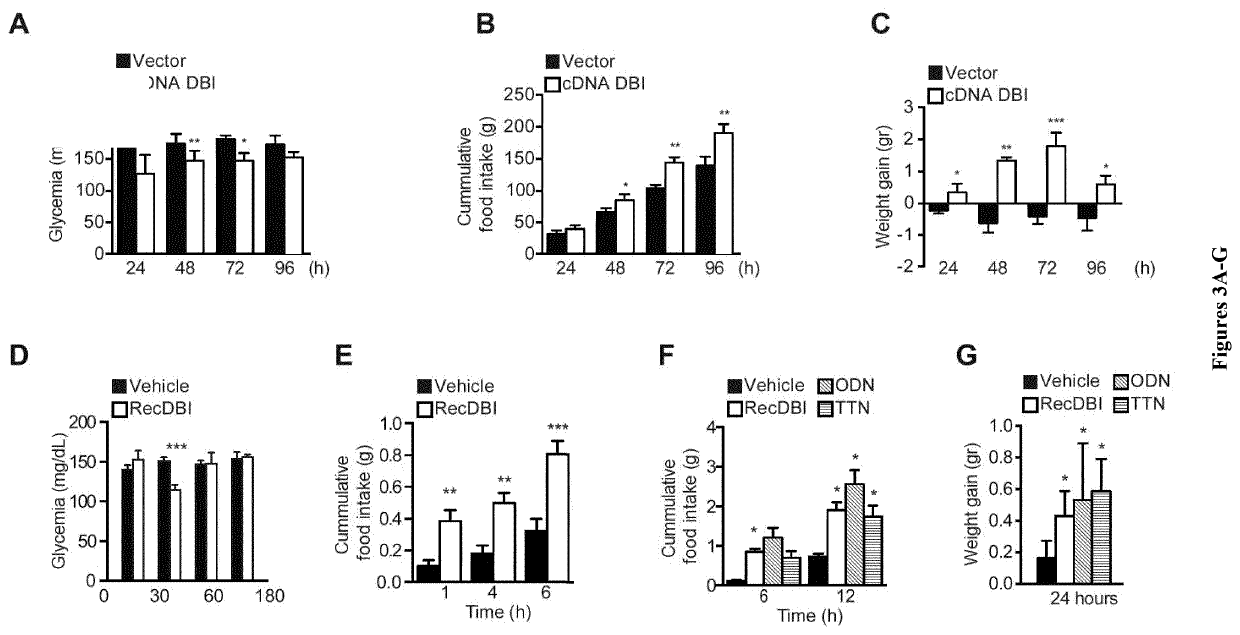
Autophagy is typically activated by starvation, allowing cells and organisms to mobilize their energy reserves. It is known that pharmacological modulation of autophagy represents a therapeutic potential. Here the inventors report that a protein that is released from cells in an unconventional, autophagy-dependent manner, namely, diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI), regulates autophagy. In particular, the inventors demonstrate that DBI inhibits autophagy and that the supply of recombinant DBI to mice enhanced glycolysis, enhanced lipogenesis, and inhibited fatty acid oxidation. The inventors show that neutralisation of DBI by a monoclonal antibody and an active immunization by means of an immunogenic DBI derivative eliciting autoantibodies induce autophagy and lead to metabolic changes that increase starvation-induced weight loss, reduce food intake upon refeeding, and reduce weight gain in response to hypercaloric diets. Accordingly, the present invention relates to methods and pharmaceutical compositions for modulating autophagy based on the modulation of the activity or expression of DBI.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
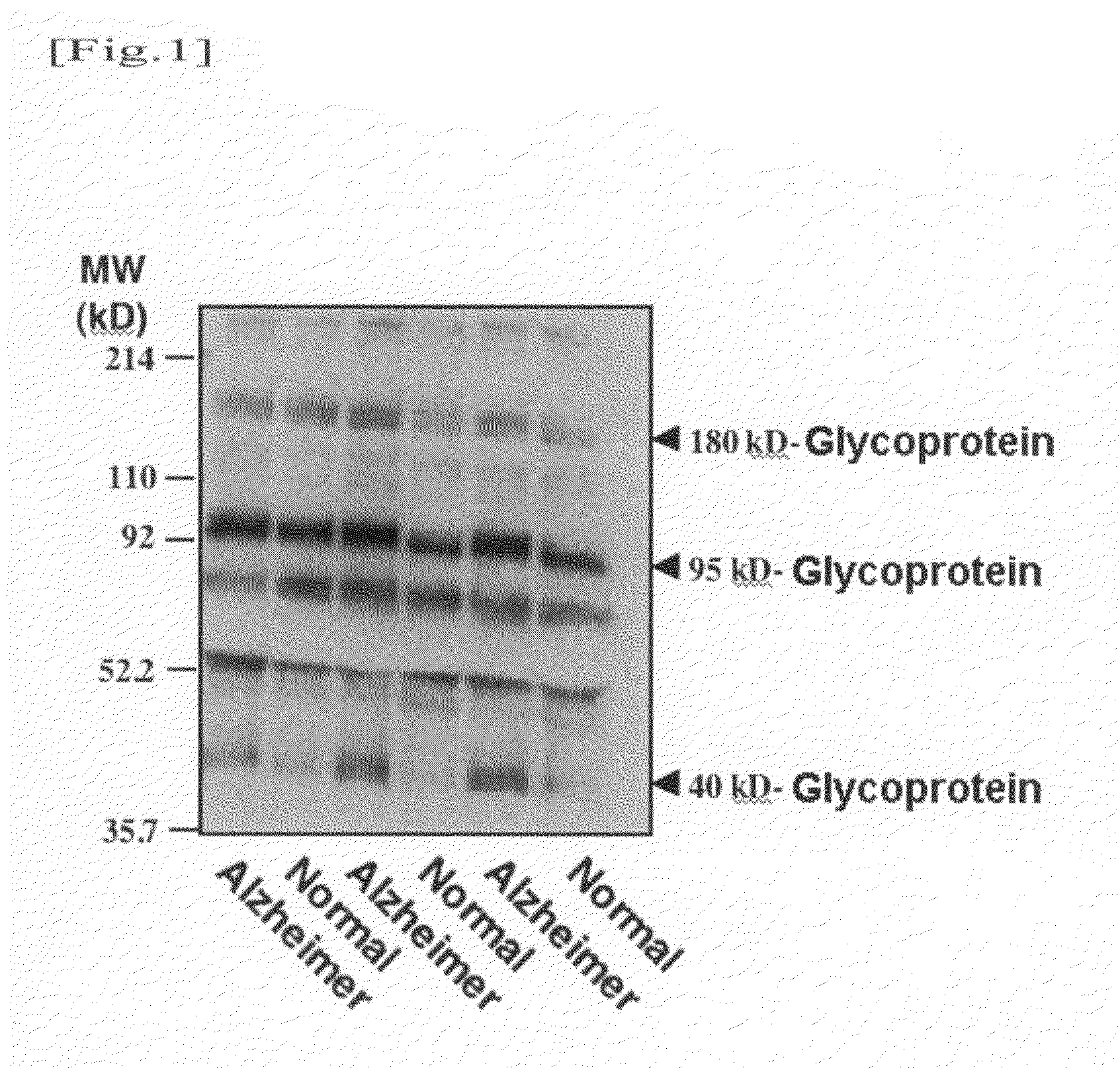
Method for diagnosing alzheimer's disease using serum glycoprotein as biomarker
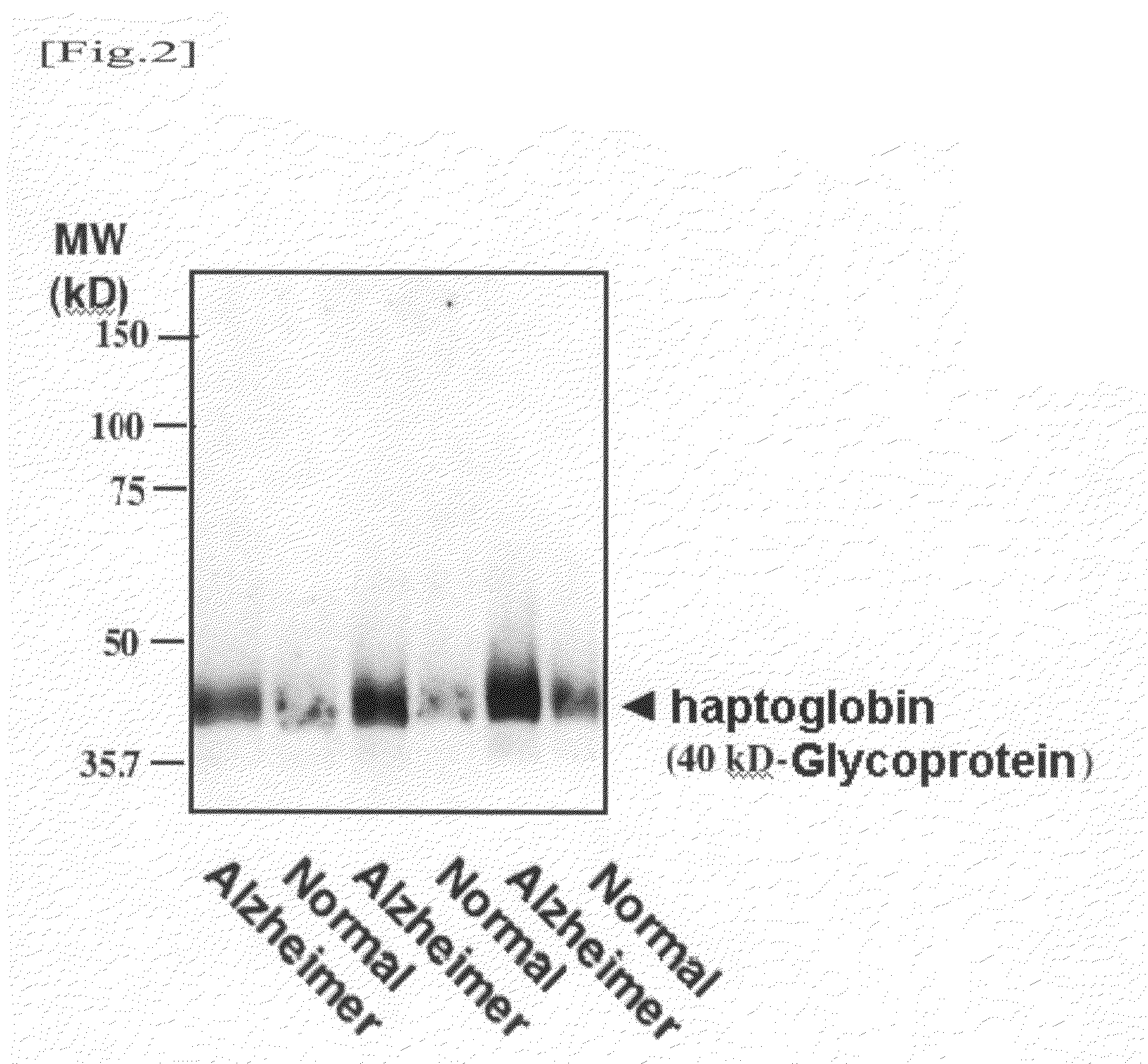
InactiveUS20110076704A1Cleavage of an amyloid precursor proteinHigh activityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeptide preparation methodsSerum igeDisease
It is an object of the present invention to detect a change in the metabolism of a glycoprotein having an α2,6-sialyl residue, which is contained in blood, so as to provide an agent and a method for diagnosing sporadic Alzheimer's disease. The present invention provides an agent for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease, which comprises lectin used for detecting an α2,6-sialyl residue-containing glycoprotein.
Owner:RIKEN
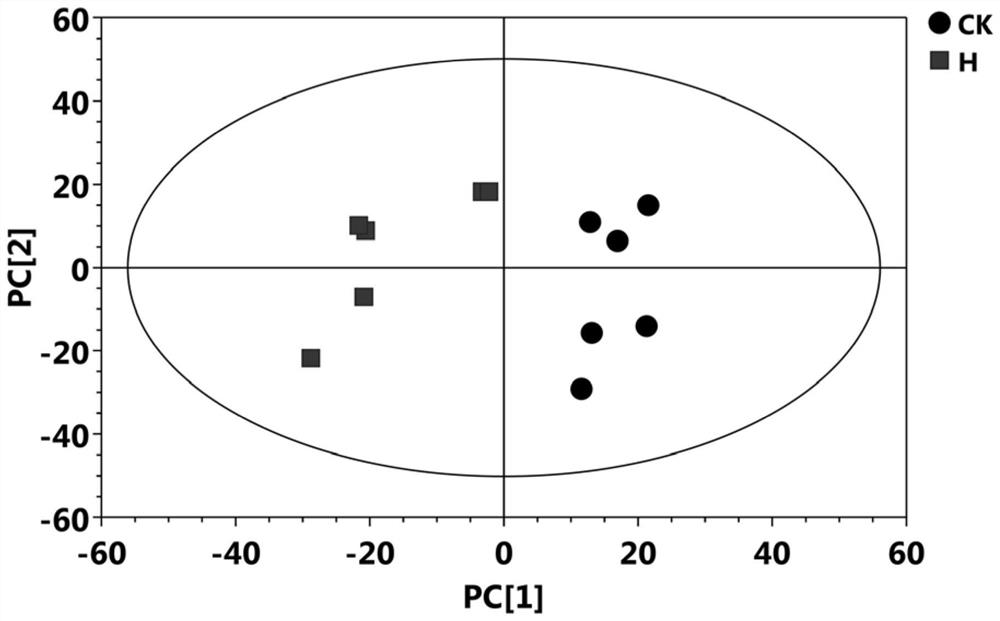
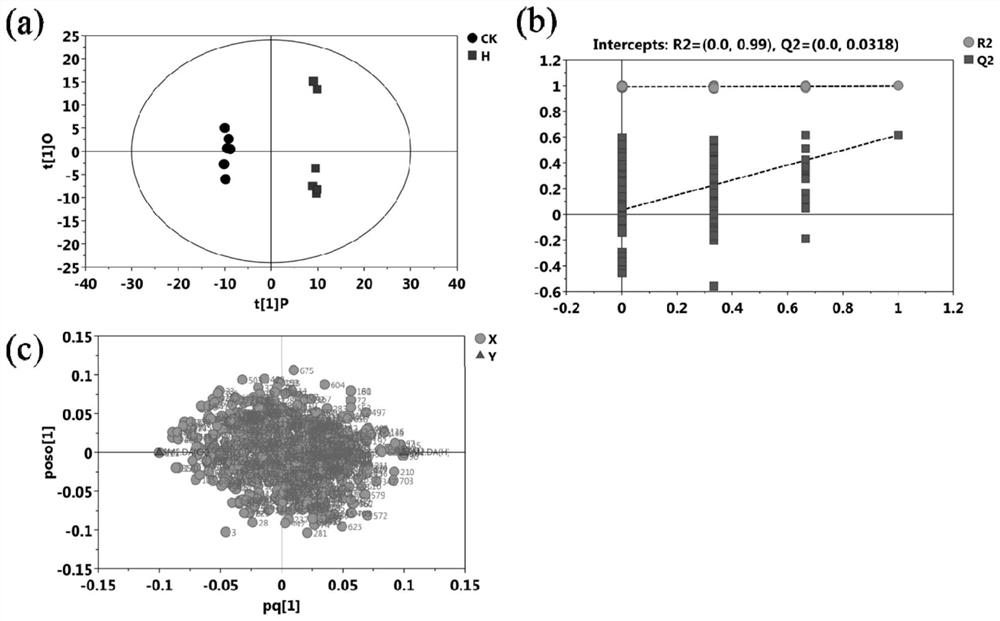
Method for screening key metabolites responding to high-temperature stress of poplar
The invention discloses a method for screening key metabolites responding to high-temperature stress of a poplar. The method comprises the following steps: detecting metabolic change rules of poplar leaves under high-temperature stress through a GC / TOF-MS technology, and screening micromolecular metabolites and metabolic pathways of the poplar responding to high temperature, thereby explaining a regulation and control mechanism of the poplar on high-temperature stress response metabonomics level. 67 differential metabolites are screened out, and differential genes are mainly enriched in valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis under high-temperature stress, galactose metabolism, and a metabolic pathway of glycine, serine and threonine. The invention also provides an important referencebasis for tree high-temperature stress research, and provides a valuable reference for woody ornamental plant high-temperature resistance research.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Liposomally encapsulated reduced glutathione for management of cancer, including with other pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS20150030668A1Promote recoveryIncreased myocardial tissue levelBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
This invention proposes an agent to block the “fuel supply” that energizes cancer cell growth by protecting surrounding cells to the cancer, particularly stromal fibroblast cells. The invention disables the products of surrounding cells useable for energy conversion by the cancer cell thereby crippling the cell and disabling its growth process. This application describes the use of a formulation of liposomally encapsulated glutathione that is preferably used orally to increase the level of glutathione in tissues in order to prevent and reverse the metabolic changes in cells that results in the formation of the metabolic fuel that supports cancer cells and to prevent the oxidative stress that damages normal support cells such as fibroblasts and can prevent and reverse these cells from the steps of autophagy and mitophagy that results in the cells decreasing the normal mitochondrial production of ATP for energy and resorting to the use of aerobic glycolysis for energy production. The use of oral liposomally encapsulated glutathione will maintain the presence and normal function of caveolin in fibroblast and other cells, thus preventing their conversion to autophagic tumor stromal cells. By stopping the formation of autophagic cells, the production of the metabolic fuel needed by cancer cells is stopped, which results in the death of the cancer cells. Compositions using liposomally encapsulated glutathione and other compounds that enhance the favorable effects of liposomal glutathione on cancer disease are referenced.
Owner:GUILFORD FREDERICK TIMOTHY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com