Patents
Literature
81 results about "Microdialysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
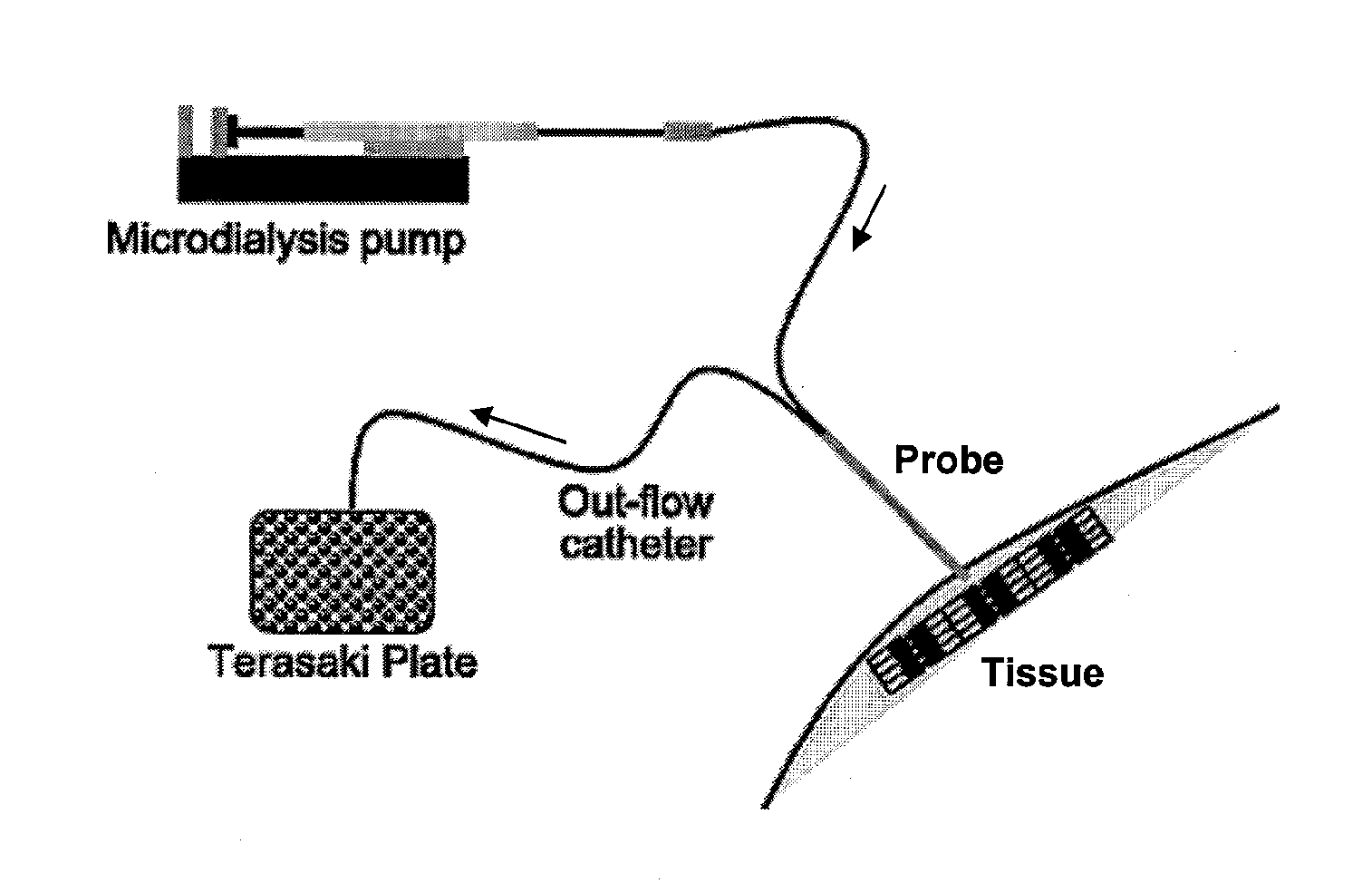
Microdialysis is a minimally-invasive sampling technique that is used for continuous measurement of free, unbound analyte concentrations in the extracellular fluid of virtually any tissue. Analytes may include endogenous molecules (e.g. neurotransmitter, hormones, glucose, etc.) to assess their biochemical functions in the body, or exogenous compounds (e.g. pharmaceuticals) to determine their distribution within the body. The microdialysis technique requires the insertion of a small microdialysis catheter (also referred to as microdialysis probe) into the tissue of interest. The microdialysis probe is designed to mimic a blood capillary and consists of a shaft with a semipermeable hollow fiber membrane at its tip, which is connected to inlet and outlet tubing. The probe is continuously perfused with an aqueous solution (perfusate) that closely resembles the (ionic) composition of the surrounding tissue fluid at a low flow rate of approximately 0.1-5μL/min. Once inserted into the tissue or (body)fluid of interest, small solutes can cross the semipermeable membrane by passive diffusion. The direction of the analyte flow is determined by the respective concentration gradient and allows the usage of microdialysis probes as sampling as well as delivery tools. The solution leaving the probe (dialysate) is collected at certain time intervals for analysis.
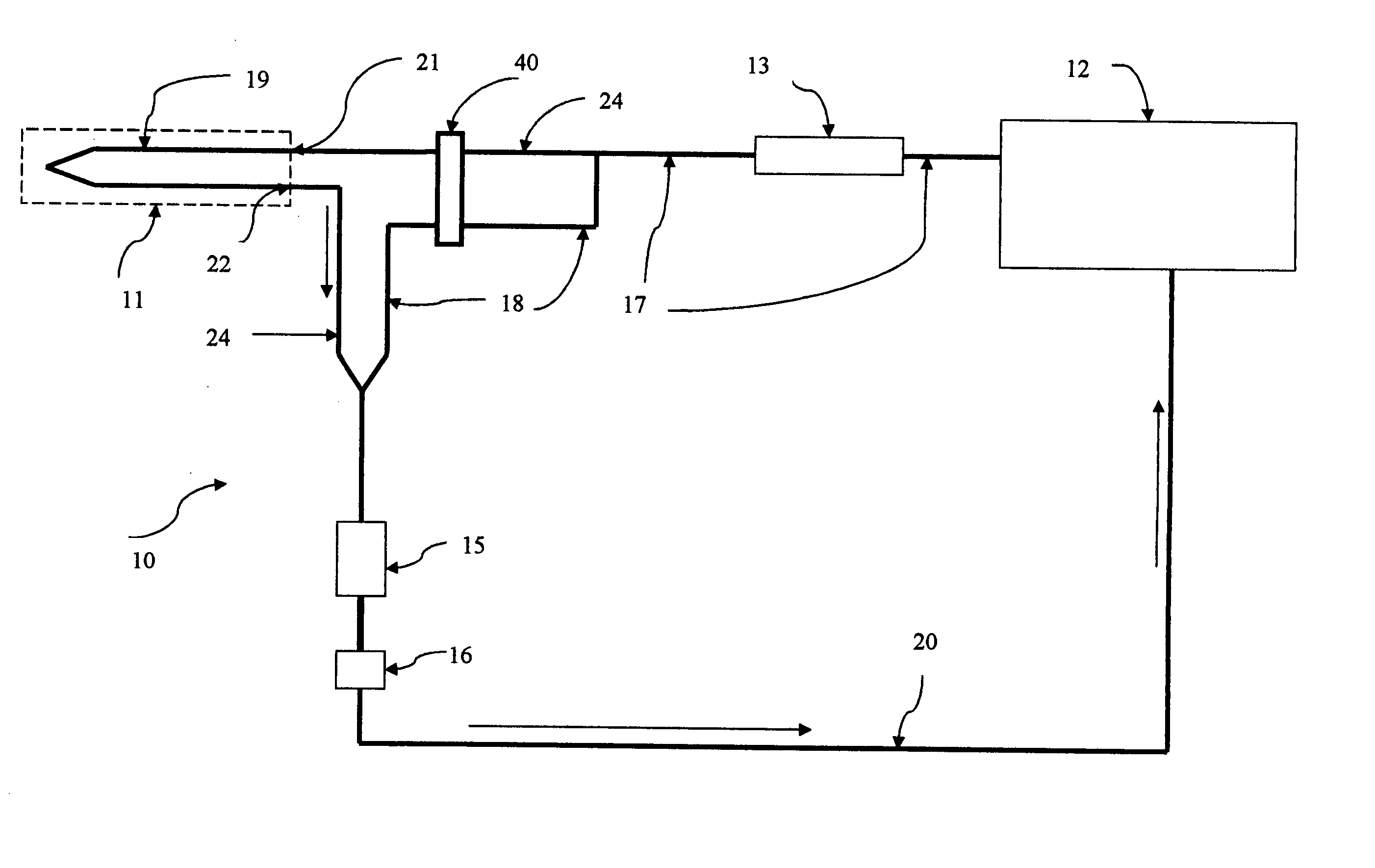
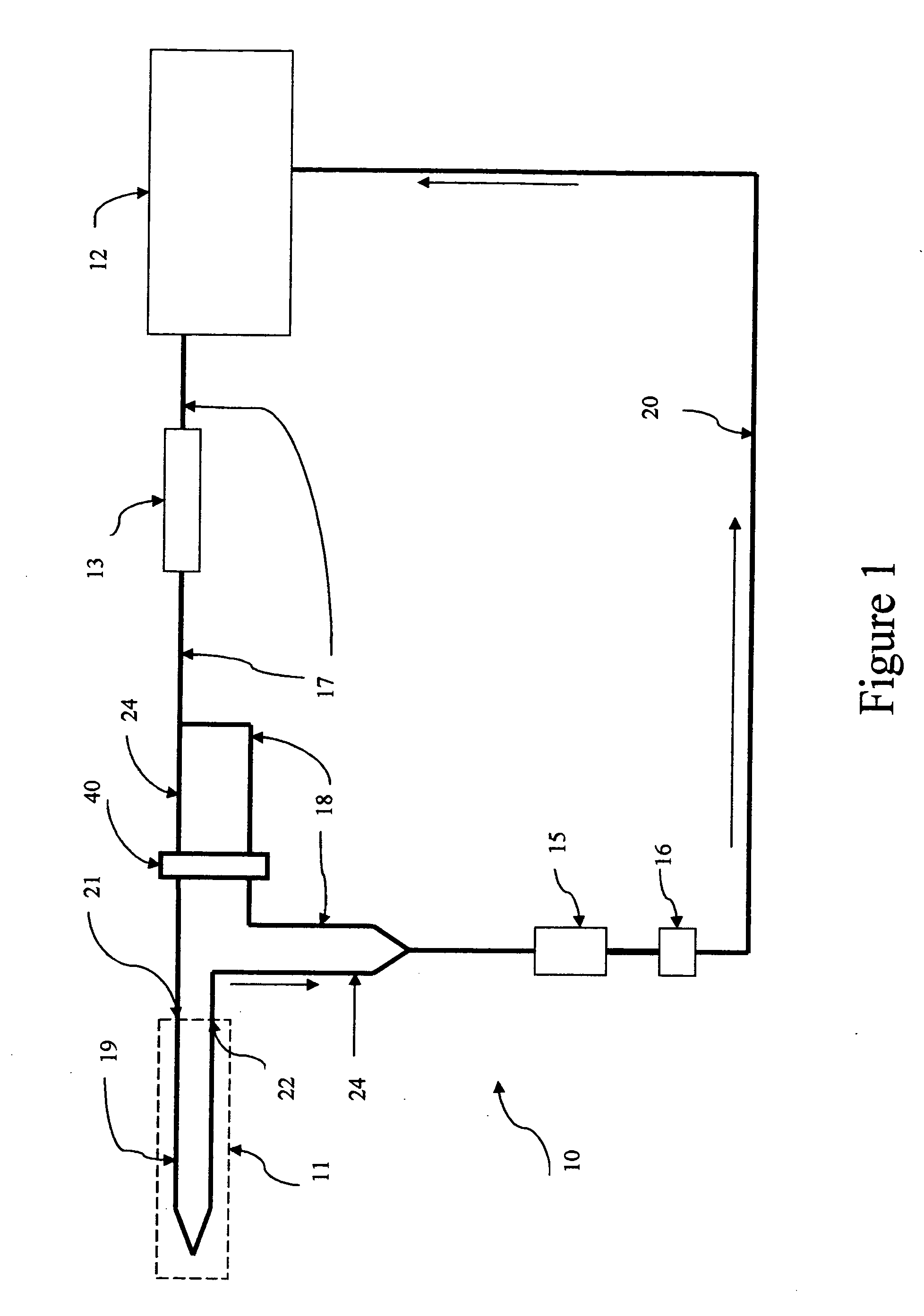
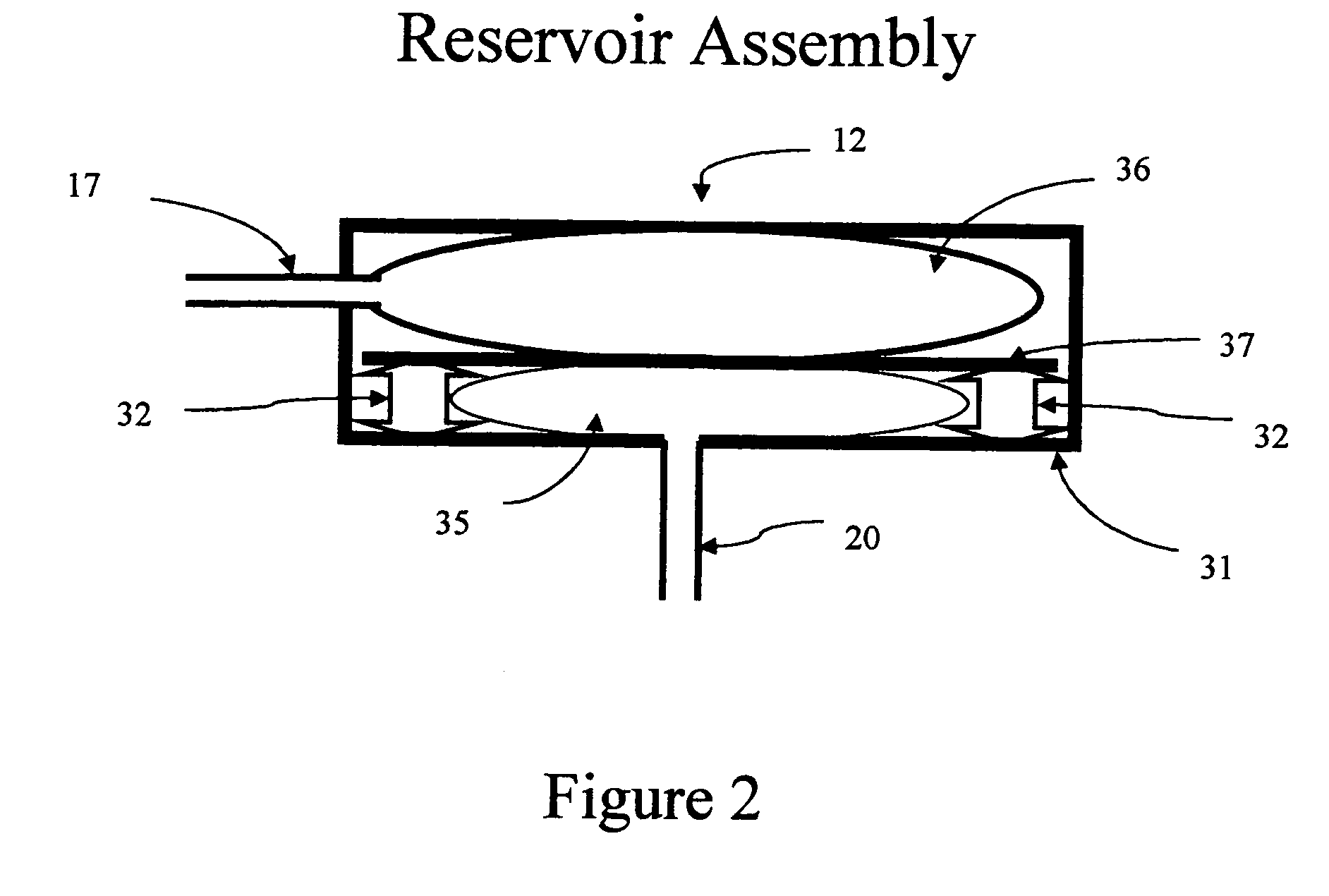
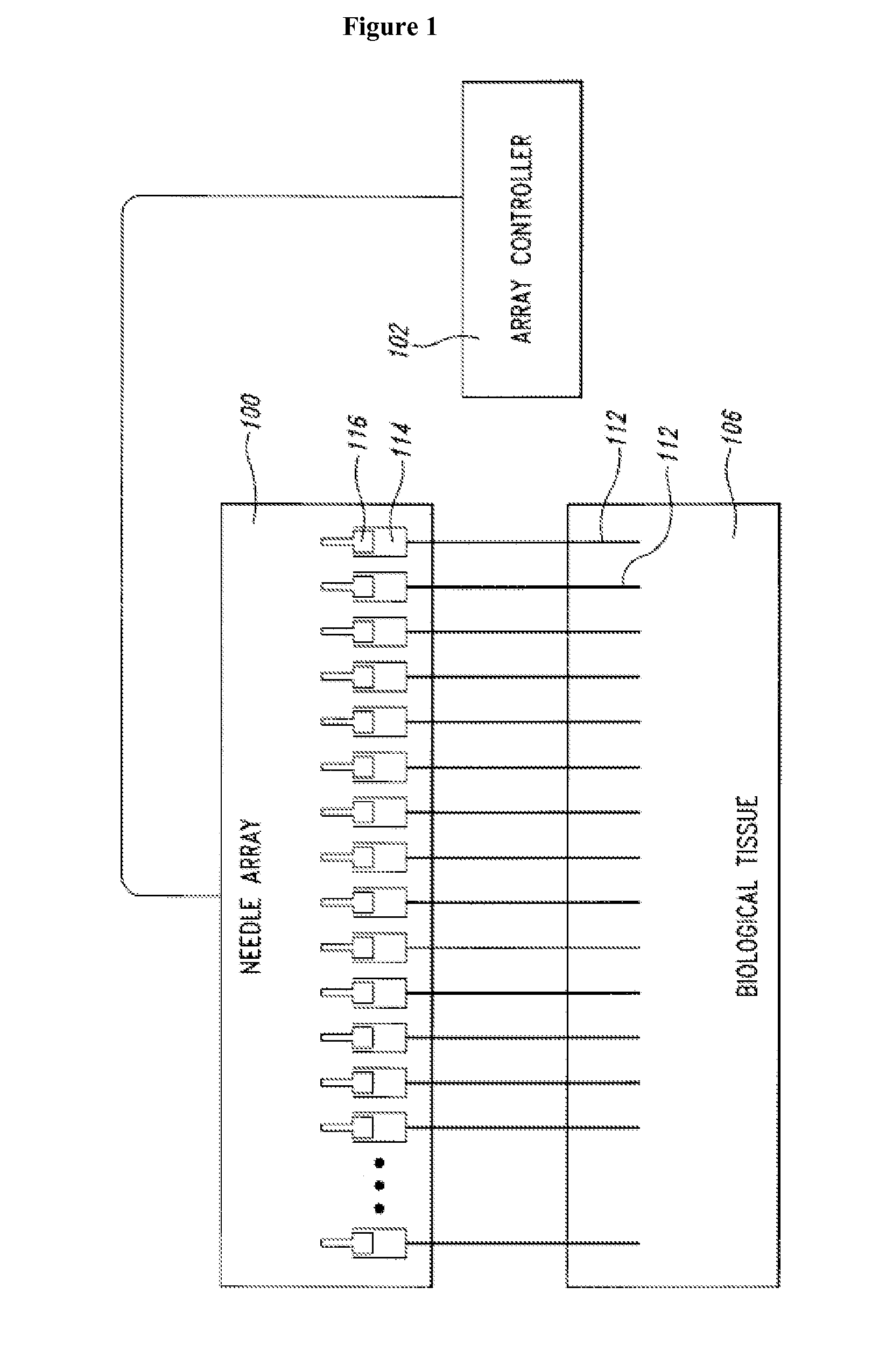
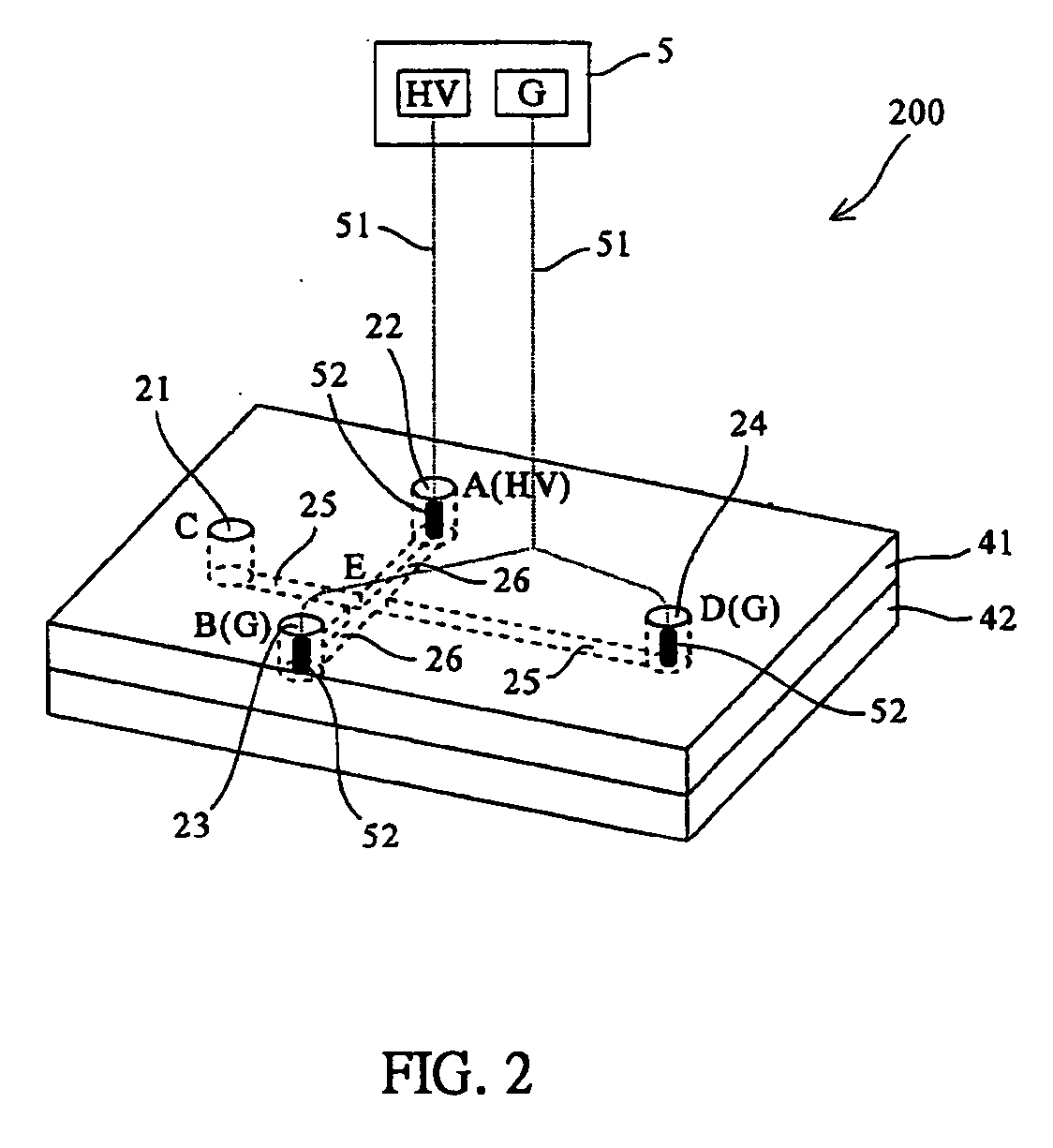
Self-calibrating body analyte monitoring system
InactiveUS20050209518A1Accurate measurementMinimize timeMedical devicesPressure infusionAnalyteMonitoring system
A self-calibrating monitoring system based on microdialysis for measurement of a body analyte is disclosed. In one embodiment, perfusate containing a known concentration of body analyte is mixed with an enzyme solution after passing through a microdialysis needle and instead of passing through the microdialysis needle to measure the body analyte and to calibrate the analysis chamber that measures the body analyte.
Owner:THERAFUSE
System and method for site specific therapy
InactiveUS7717871B2Optimize allocationLower the volumeDialysis systemsMedical devicesEngineeringPhysical therapy
A system, including catheter apparatus, and related method for performing site specific therapy. The catheter apparatus can include one or more semipermeable microcatheters for use in performing site specific microdialysis. The system and method are particularly suited for use in addressing cerebral edema by affecting the osmolar relationship between fluids making up the brain tissue. Also disclosed is an apparatus having a delivery / recovery mechanism in the form of a pump reservoir and one or more catheters in the form of semipermeable microcatheters, for use in delivering and / or recovering fluid to and / or from a tissue site or for performing tissue engineering outside of the body. The apparatus can be used in a method to perform site specific microtherapy, including for the treatment of avascular necrosis, compartment syndrome, cerebral edema, and to improve skin flap survival in the course of reconstructive surgery.
Owner:TWIN STAR MEDICAL
System and Method for Pseudo-Continuous Measurement of Metabolite Concentrations in a Mammalian Body
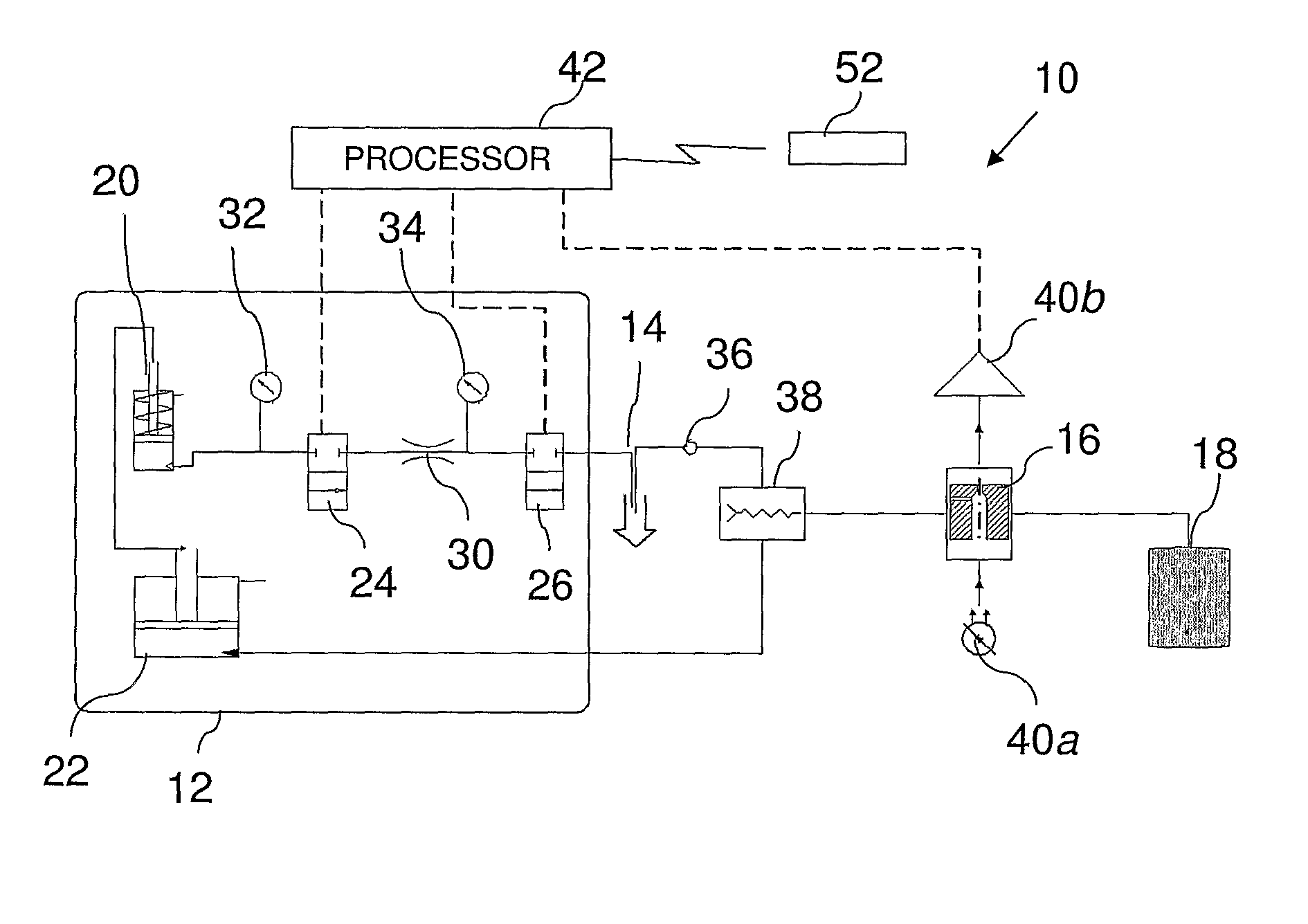
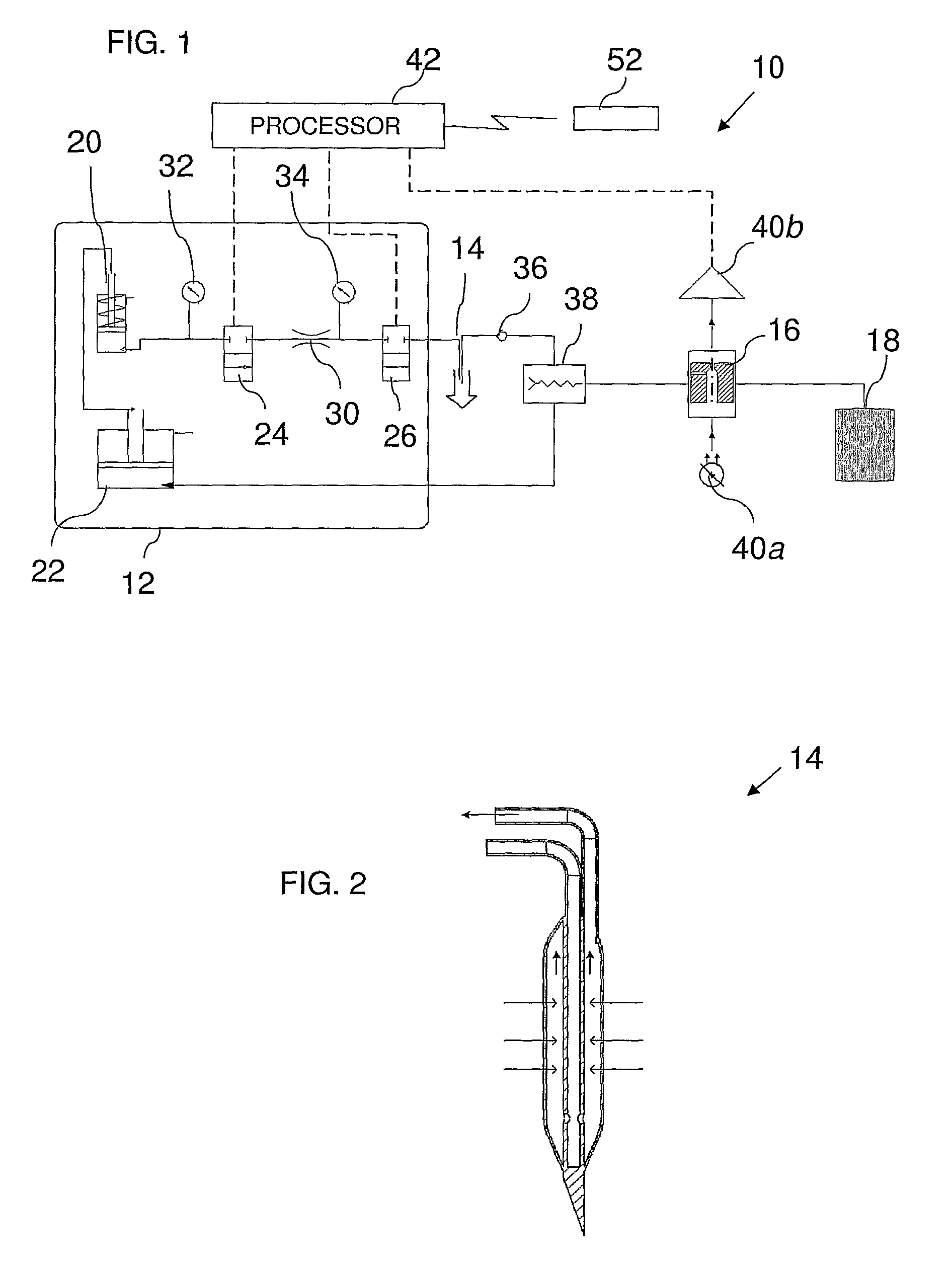
A metabolite monitoring system comprising a microdialysis probe including a semi-permeable membrane and a probe flow path passing from an inlet through a sensing volume adjacent to said semi-permeable membrane to an outlet, a fluid delivery device for delivering dialysate to said inlet; and a metabolite monitoring system associated with said outlet for monitoring a concentration of at least one metabolite in said dialysate from said microdialysis probe, wherein said fluid delivery device is configured to deliver a pulsed flow of said dialysate to said inlet.
Owner:G SENSE LTD
Droplet-based digital microdialysis
The invention relates to a droplet-based digital microdialysis method that utilizes discrete perfusate droplets marched through a microchannel in an intermittent manner. The droplets sequentially reside on a microdialysis membrane that is in contact with the test fluid, e.g., fluid in an extracellular space. The droplets remain stationary at the membrane site for a period of time for rapid equilibration with the test fluid, and is then marched to an outlet port for processing. The invention further relates to microdialysis probes and methods based on the droplet-based digital microdialysis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS
Microdialysis needle assembly
InactiveUS20050208648A1Easy and comfortable to wearEasy to wear and comfortableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBody fluid
A device for the measurement of analytes in a body fluid including a support with an upper surface, a layer adhered to the upper surface, the layer being of a hardenable material wherein at least one microfluidic channel has been etched after the layer is at least partially hardened, and a semipermeable membrane at least partially covering the layer.
Owner:THERAFUSE
Pump for low flow rates
InactiveUS6860993B2Simple and cost-effective to manufactureEasy to manufactureFlexible member pumpsUltrafiltrationUltrafiltrationEvaporation
The present invention concerns a pump for flow rates from about 1 to 1000 nl / min in which liquid transport takes place by evaporation of a transport liquid through a wettable membrane. The pumps according to the invention are particularly suitable for applications in the field of medical diagnostics such as microdialysis or ultrafiltration.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
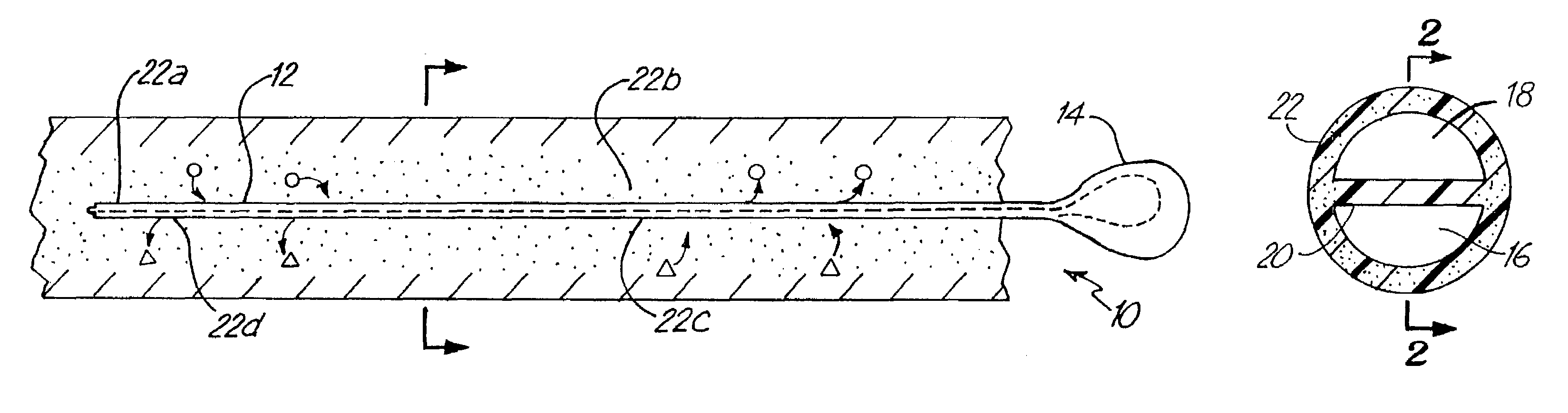
Microdialysis probe with inserting means and assembly
InactiveUS20050119588A1Easy to produceDialysis systemsAnimal teeth treatmentDialysis membranesCatheter
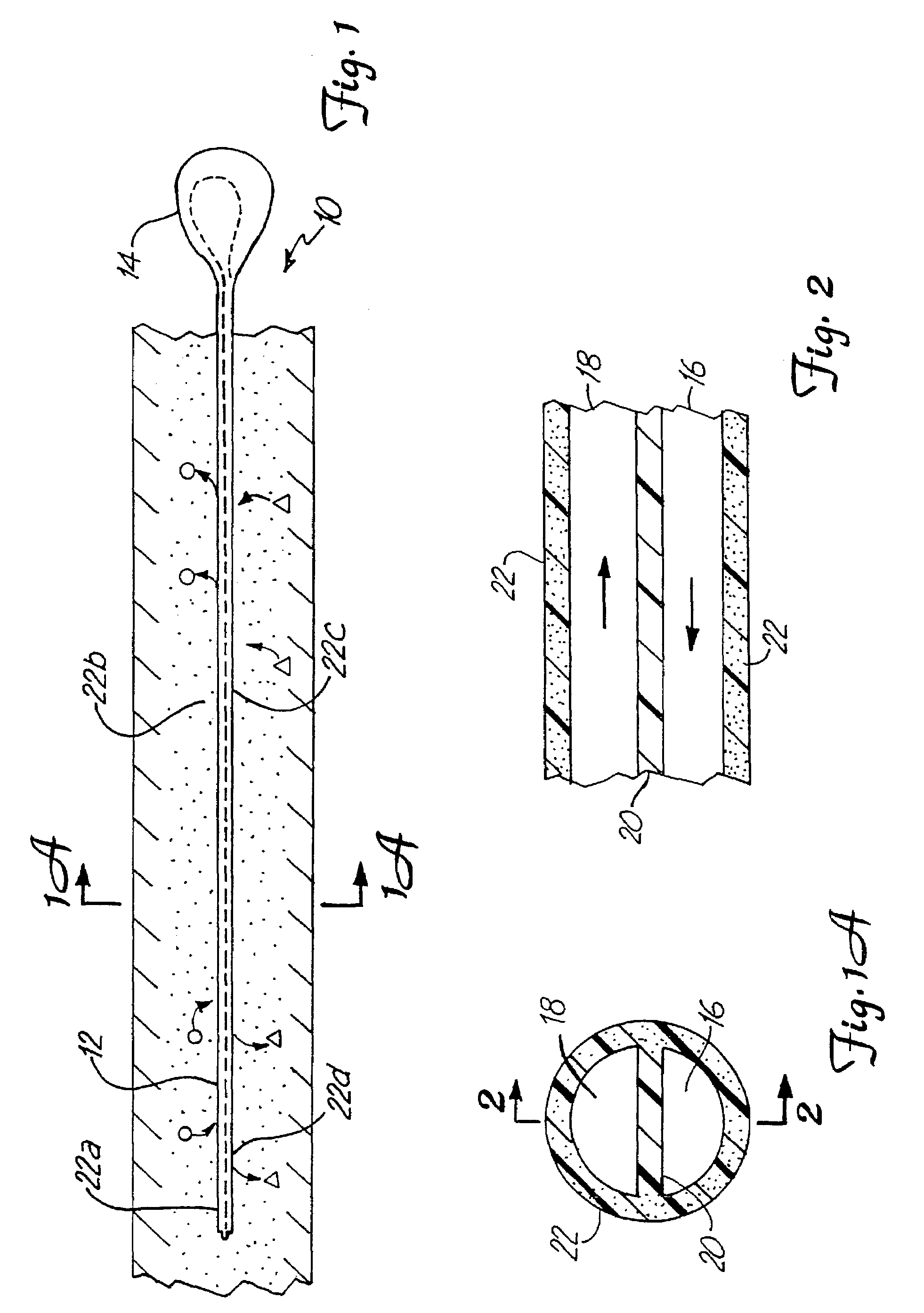
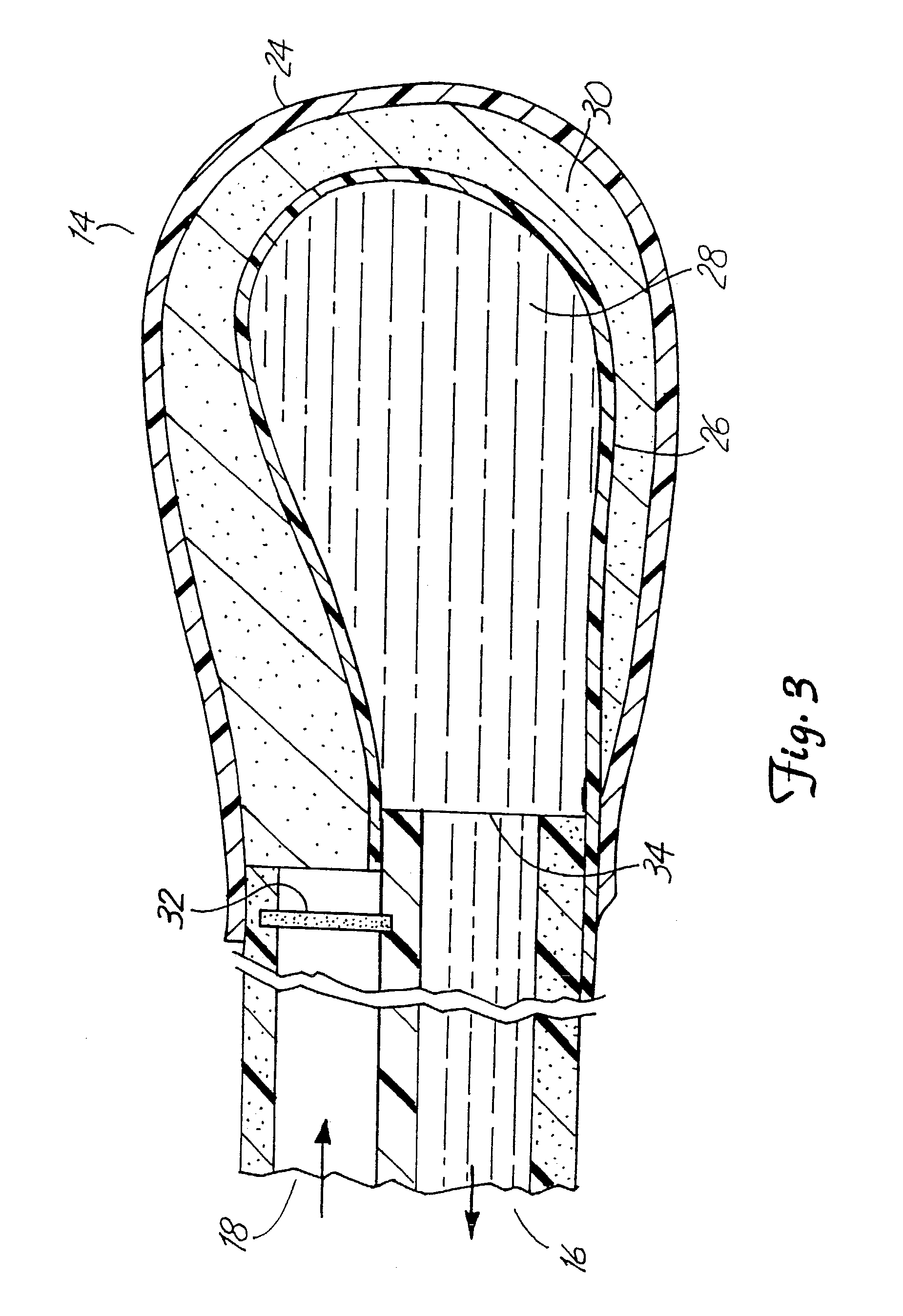
A microdialysis probe comprises a tubiform probe body, a tubiform dialysis membrane disposed distally of the probe body, and flexible conduits for adducing and abducing dialysis fluid, distal end portions of which are disposed in the probe body. Apart from the conduit portions disposed externally of the probe body the probe is substantially rotationally symmetrical. One of the conduits, preferably the abducing conduit, comprises an S-shaped portion inside of the probe, adjacent to the distal end of the other conduit. Also disclosed is an assembly of the probe and a cannula for inserting it into tissue; after insertion the cannula can be withdrawn in a proximal direction.
Owner:MICROBIOTECHSE
Screening method for Chinese-medicine effective ingredient
InactiveCN1939348AAffect accuracyQuick searchBiological testingPlant ingredientsSerum protein albuminAdditive ingredient
A method for screening the active components of Chinese-medicinal material includes such steps as mixing the liquid extract of the Chinese-medicinal material to be screened with serum albumin solution, sampling by equilibrium dialysis or microdialysis to obtain reactive dialytic liquid, mixing the liquid extract of the Chinese-medicinal material to be screened with the blank solution not containing serum albumin, sampling by equilibrium dialysis or microdialysis to obtain blank dialytic liquid, respective efficient liquid-phase chromatography analysis for said reactive dialytic liquid and blank dialytic liquid, and calculating the albumin combining percentage of each component.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for testing plant endogenous hormones
InactiveCN101738441APrevent extractionReal-time measurementComponent separationAcetic acidAbscisic acid
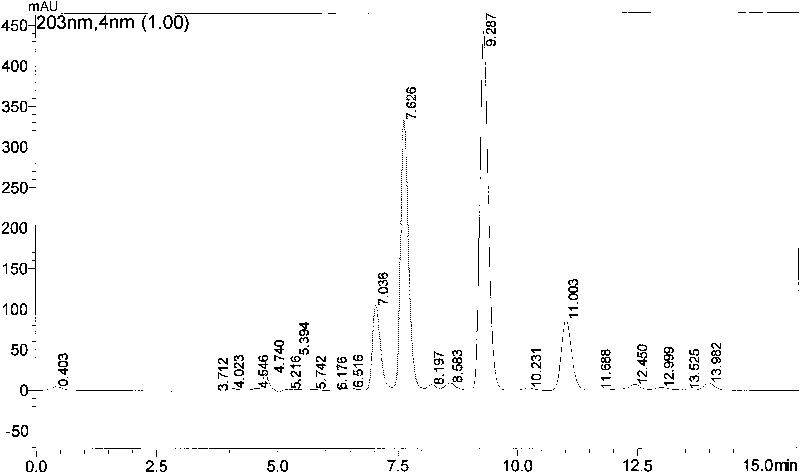
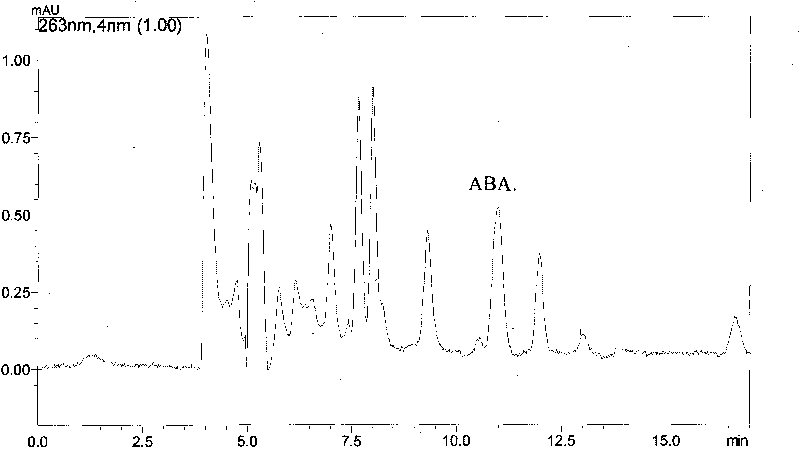
The invention provides a method for testing plant endogenous hormones, comprises the following steps of: carrying out microdialysis sampling on a plant body; carrying out sample injection on the acquired dialyzate on a high-performance liquid chromatograph; and simultaneously separating and determining four main plant endogenous hormones: gibberellic acid (GA), cytokinin (6-BA), indolylacetic acid (IAA) and abscisic acid (ABA). Compared with the traditional method for testing the plant endogenous hormones, the invention realizes the intravital test on the plant endogenous hormones and can reduce the damage to the plant body to maximum extent; in addition, the invention can simply and conveniently extract samples, has simple operation, can really reflect the change of the content of the endogenous hormones in the plant body in the vital movement progress and realize the real-time, intravital and on-line test on the plant endogenous hormones.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
System and method for site specific therapy
InactiveUS20100286586A1Optimize allocationLower the volumeWound drainsDialysis systemsFlap survivalReconstructive surgery
A system, including catheter apparatus, and related method for performing site specific therapy. The catheter apparatus can include one or more semipermeable microcatheters for use in performing site specific microdialysis. The system and method are particularly suited for use in addressing cerebral edema by affecting the osmolar relationship between fluids making up the brain tissue.Also disclosed is an apparatus having a delivery / recovery mechanism in the form of a pump reservoir and one or more catheters in the form of semipermeable microcatheters, for use in delivering and / or recovering fluid to and / or from a tissue site or for performing tissue engineering outside of the body. The apparatus can be used in a method to perform site specific microtherapy, including for the treatment of avascular necrosis, compartment syndrome, cerebral edema, and to improve skin flap survival in the course of reconstructive surgery.
Owner:TWIN STAR MEDICAL
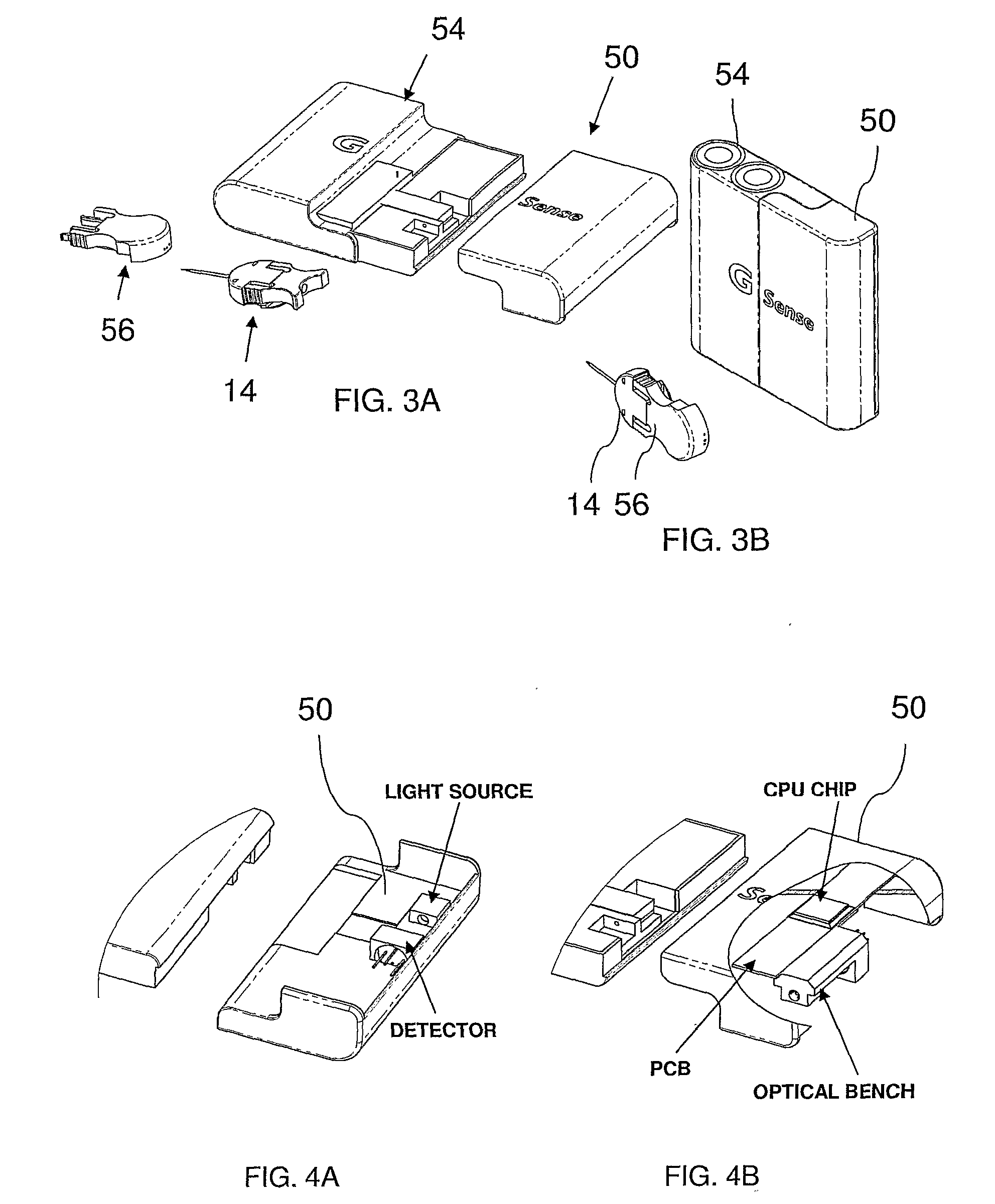
Microdialysis probe
InactiveUS6929618B1Easy to installSemi-permeable membranesMulti-lumen catheterDialysis membranesNon invasive
A microdialysis probe includes a dialysis membrane located and supported between a closed distal end of the probe and a proximal end of the same, the membrane essentially surrounding a space for passage of perfusion liquid. The probe has an inlet and outlet for perfusion liquid, where a position indicating object at the distal part of the probe allows non-invasive examination of the location of the distal part of the microdialysis probe.
Owner:CMAMICRODIALYSIS HLDG
Methods for drug delivery
InactiveUS20140323907A1Eliminating many of the microfluidic engineering hurdlesAvoiding central regionOrganic active ingredientsSurgical needlesSolid tissueBiomedical engineering
Methods and devices for delivering an agent to a solid tissue in vivo for assessment of efficacy are described. One method involves withdrawing of a needle from and injecting of the agent into the solid tissue; another method involves delivering the agent using a plurality of microdialysis probes to a solid tissue.
Owner:PRESAGE BIOSCI
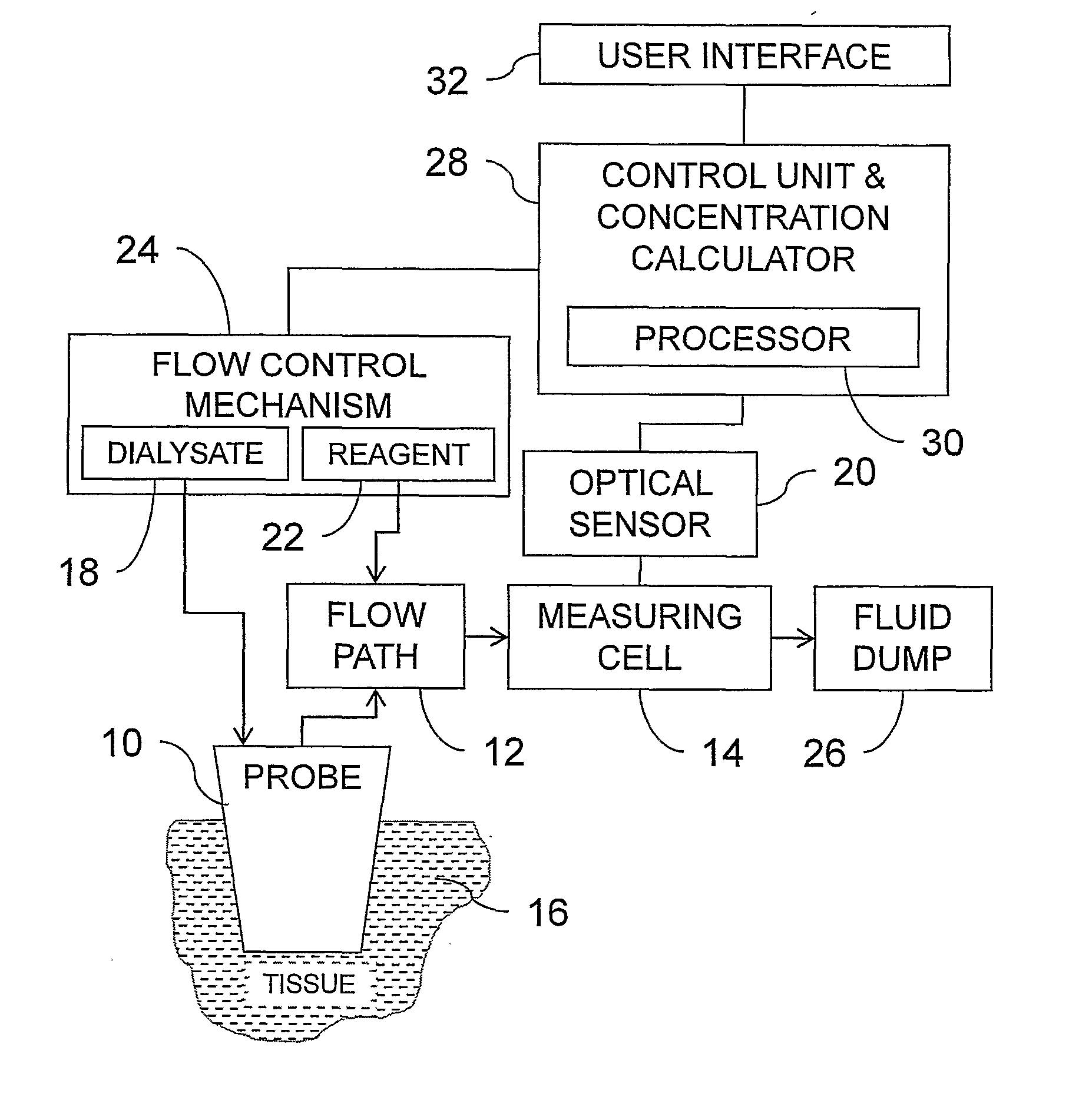
Systems and methods for implementing rapid response monitoring of blood concentration of a metabolite
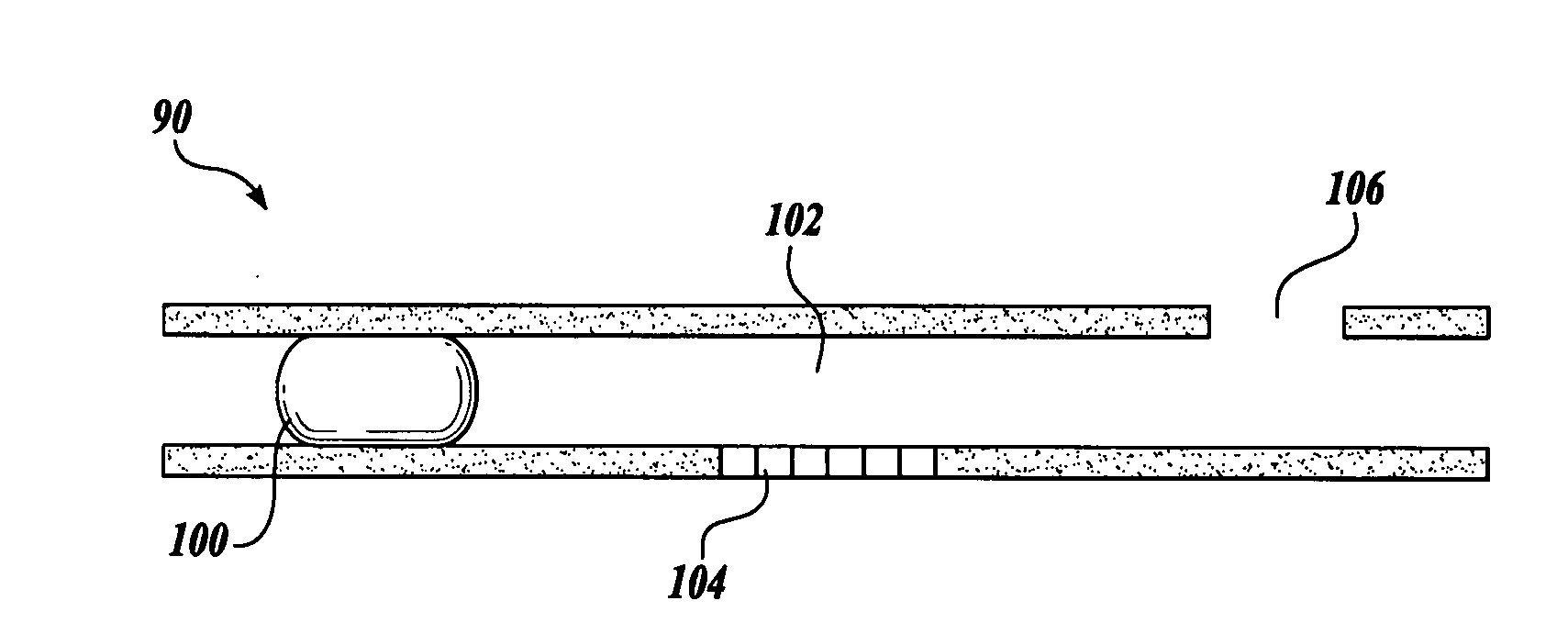
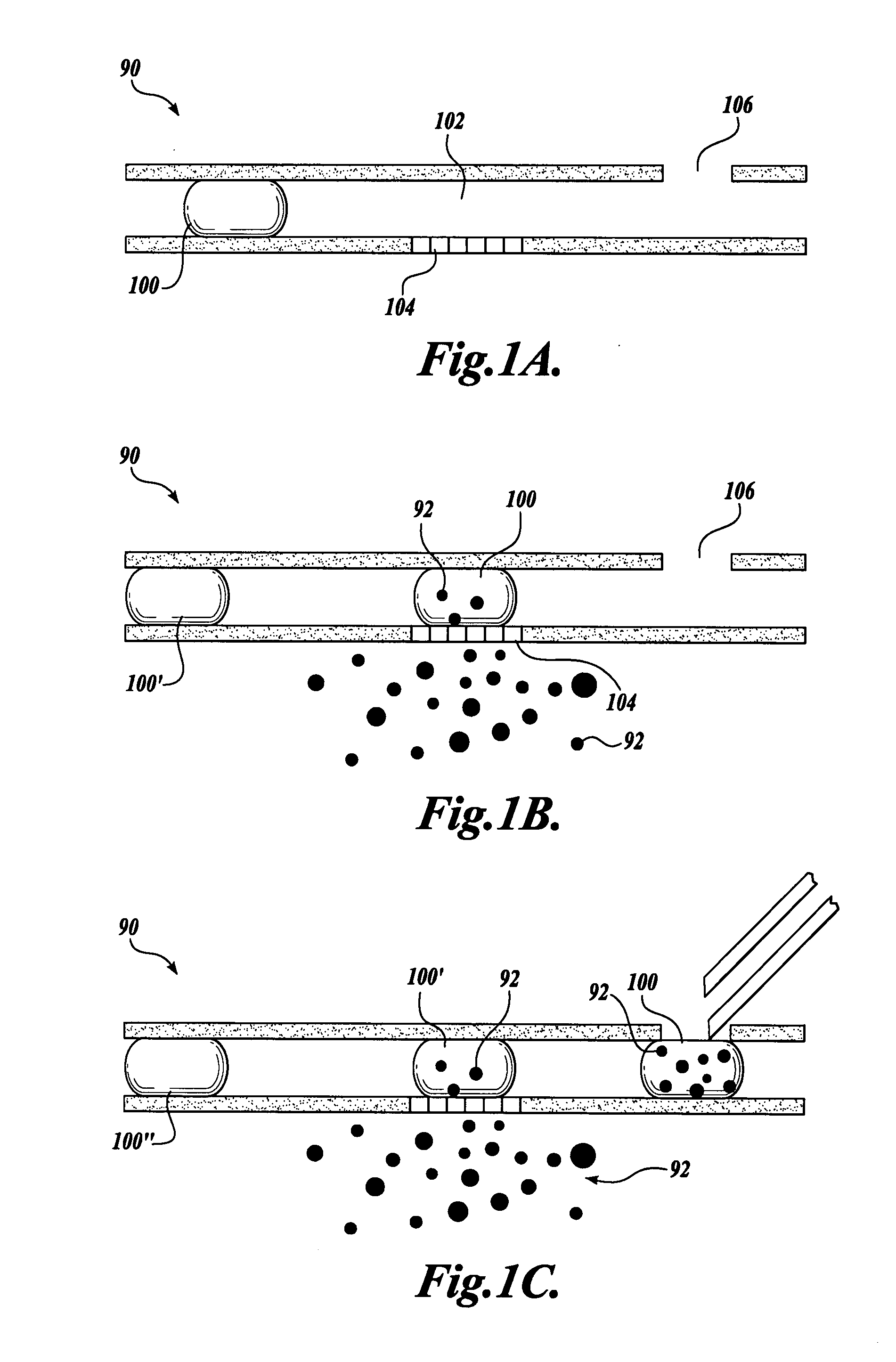
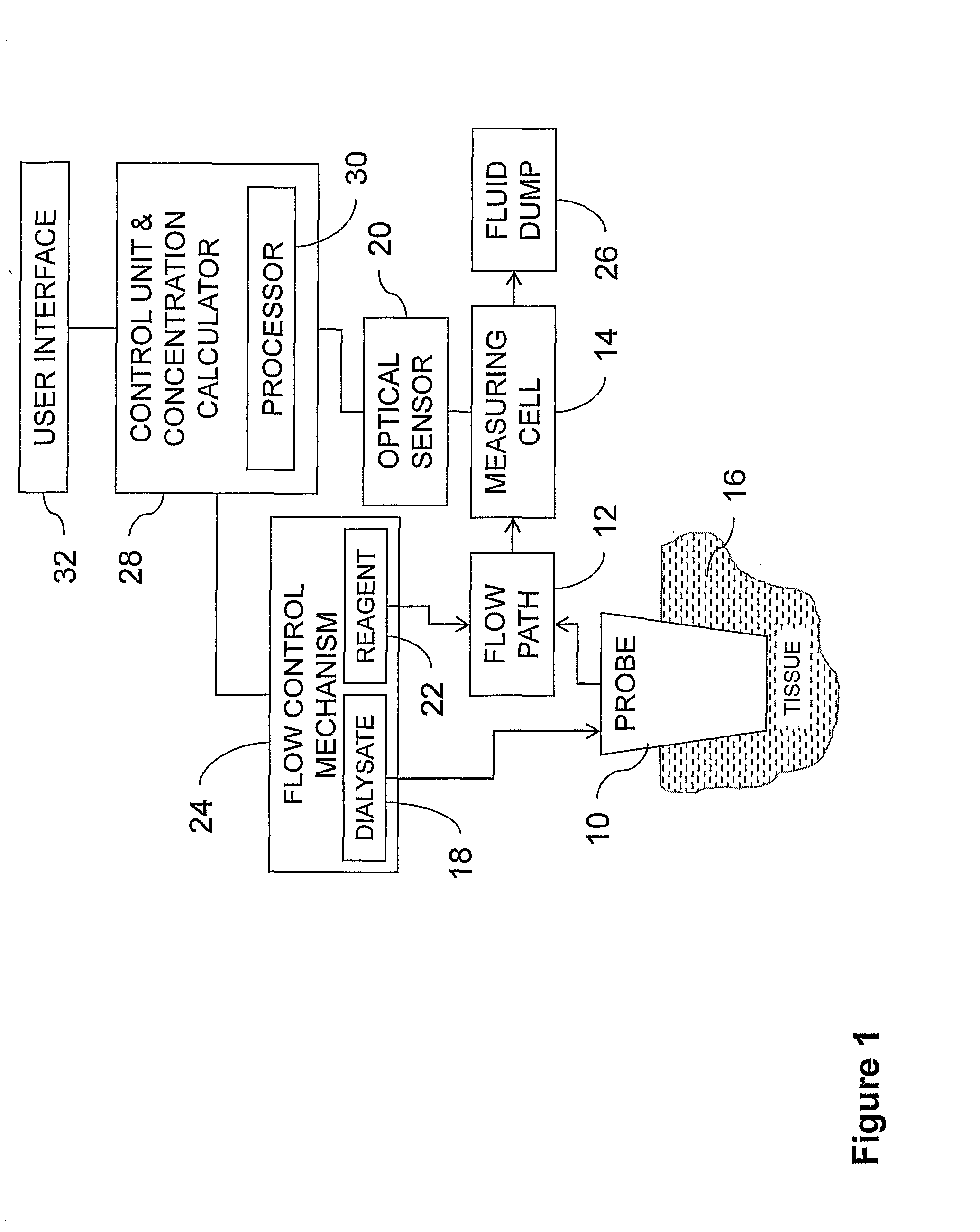
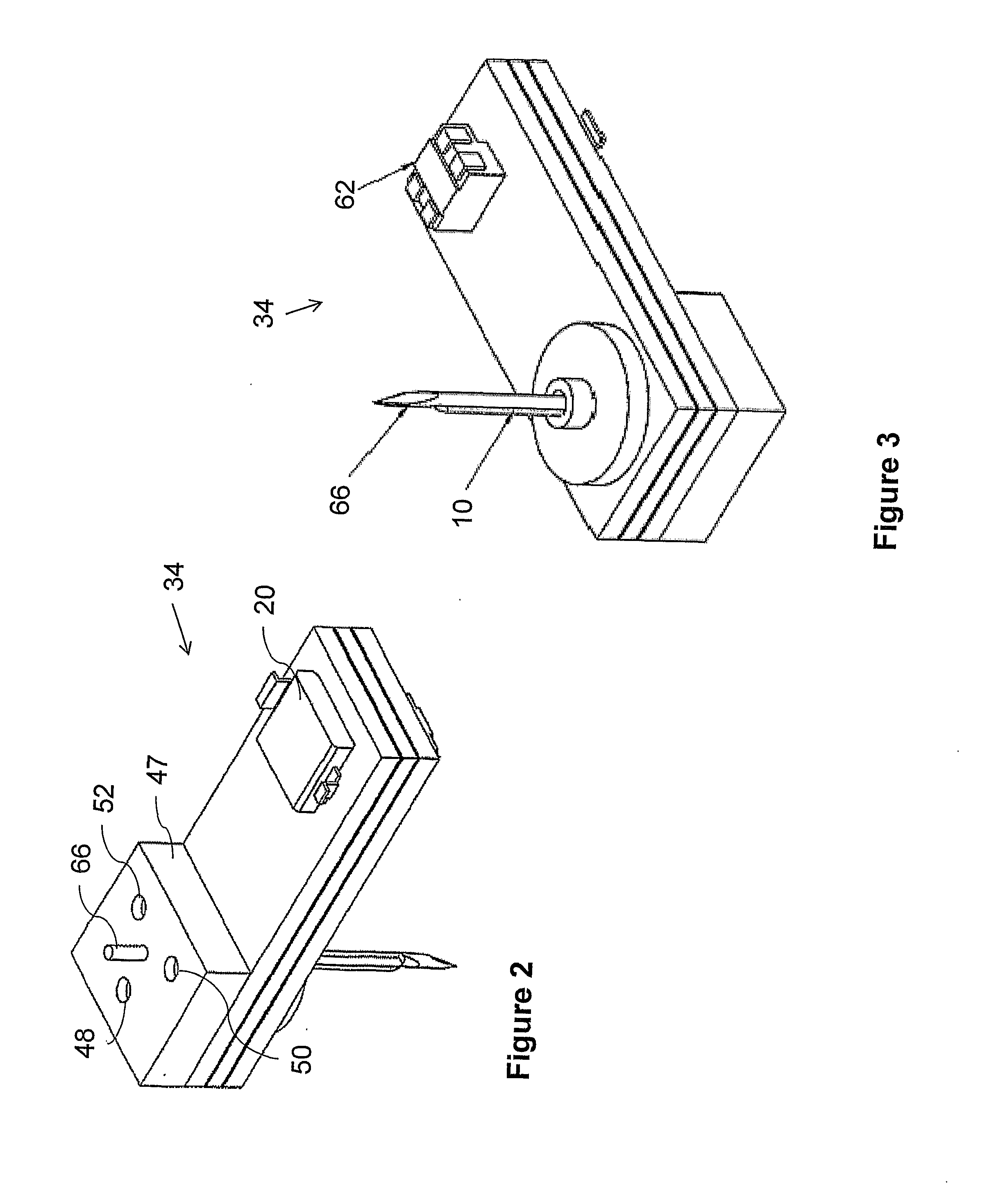
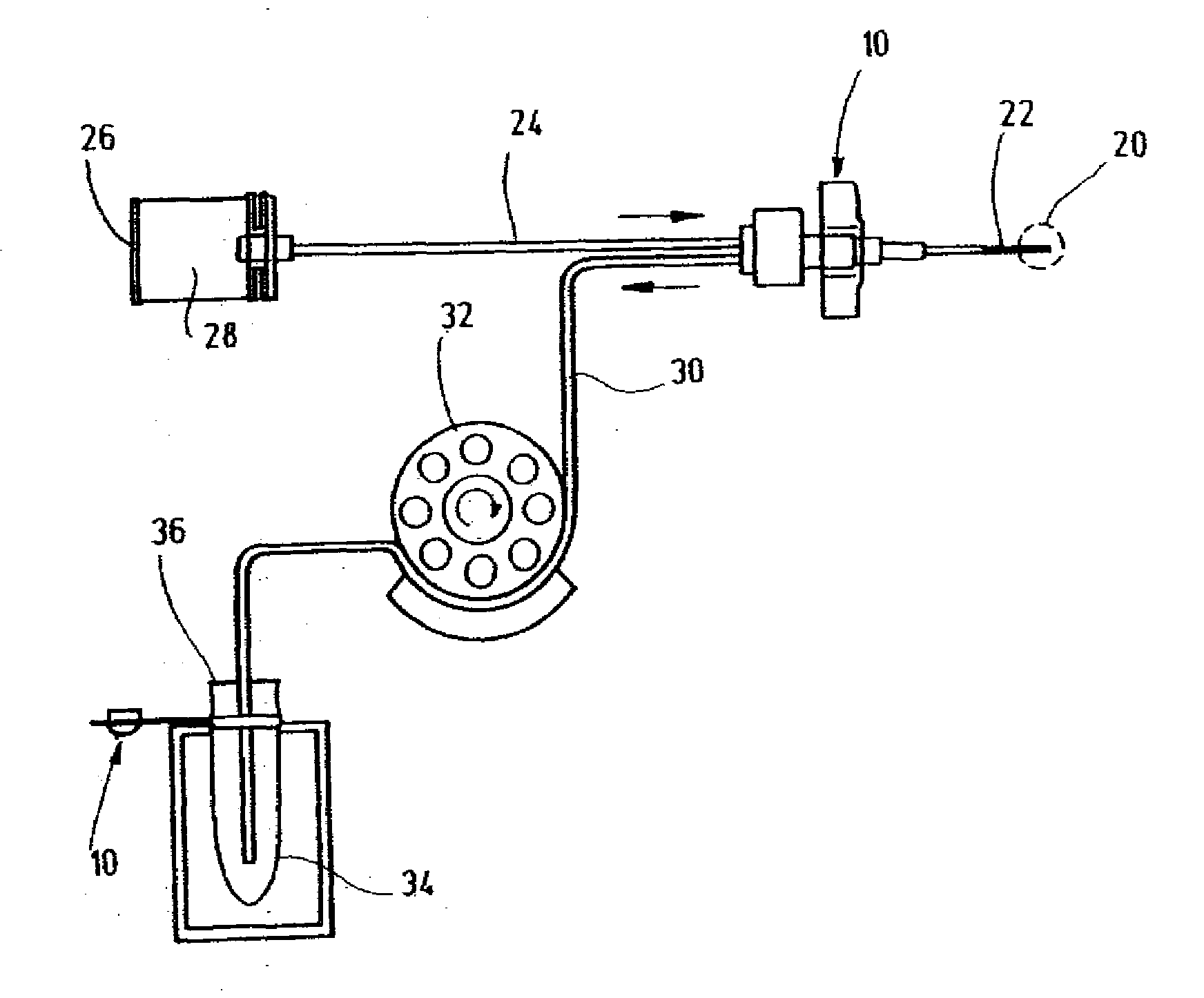
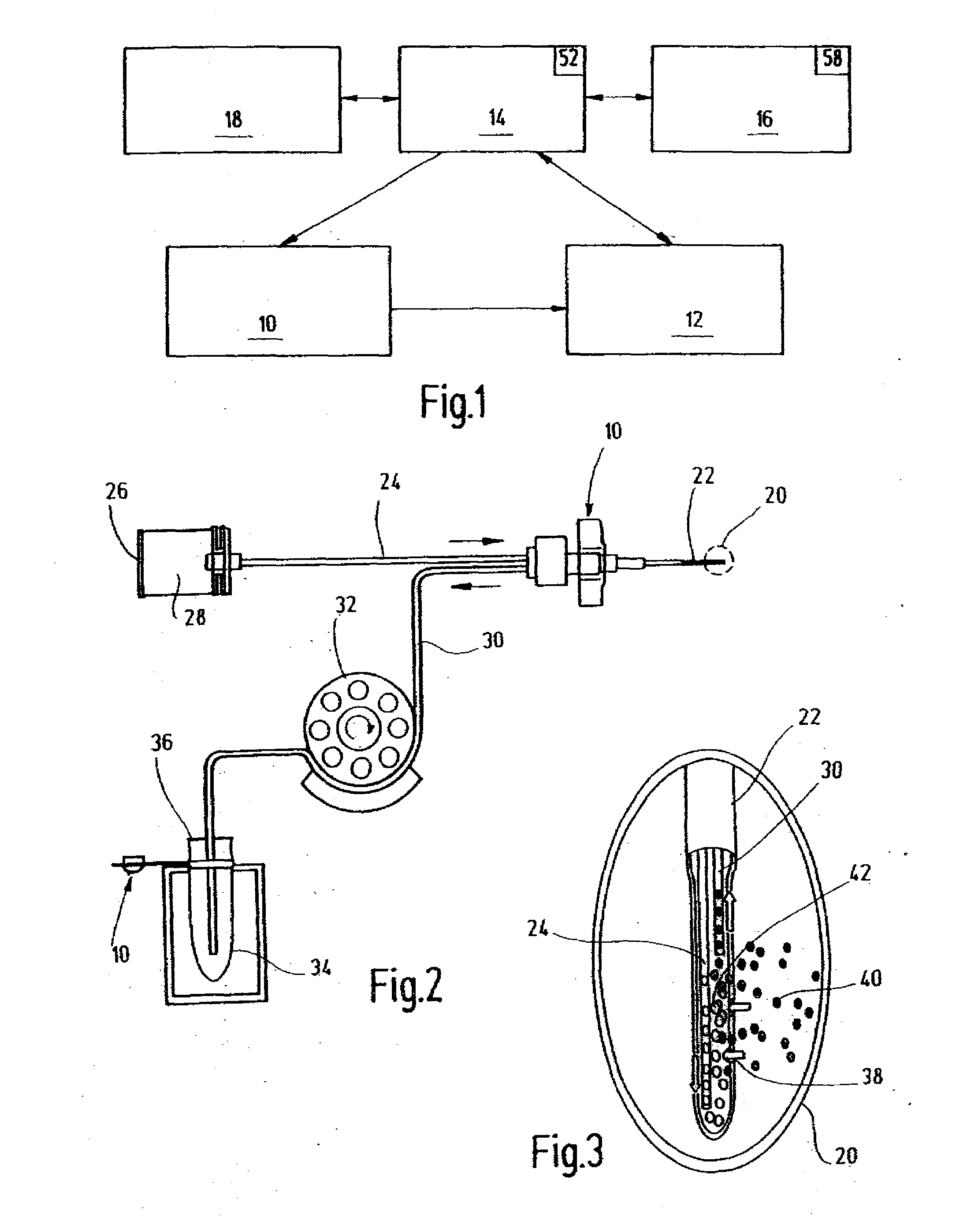
Systems and methods for monitoring the concentration of glucose or other metabolites by way of a low-volume microdialysis-probe (10) operative in accordance with a pulsed mode of flow through a flow path (12) defined by a layered structure. Also described are a system and a method for deployment of the microdialysis probe (10) within the body and a technique for deriving a metabolite concentration of the basis of a rate of change of an optical parameter.
Owner:G SENSE LTD
Integrative microdialysis and chip-based electrophoresis system with online labeling function and analytical method using same
InactiveUS20050284763A1Easy to separateShorten the timeSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisAnalysis method
An integrative microdialysis and chip-based electrophoresis system and analytical method using the same are disclosed. The system combines the microdialysis probe sampling technique and continuous pressure flow feeding coupled with chip-based electrophoresis analysis. It is capable of performing online sampling as well as rapid and continuous monitoring and analysis of biological samples. The system offers the advantages of real-time on-chip dye labeling, simple apparatus setup and easy operation.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
System and method for pseudo-continuous measurement of metabolite concentrations in a mammalian body
A metabolite monitoring system comprising a microdialysis probe including a semi-permeable membrane and a probe flow path passing from an inlet through a sensing volume adjacent to said semi-permeable membrane to an outlet, a fluid delivery device for delivering dialysate to said inlet; and a metabolite monitoring system associated with said outlet for monitoring a concentration of at least one metabolite in said dialysate from said microdialysis probe, wherein said fluid delivery device is configured to deliver a pulsed flow of said dialysate to said inlet.
Owner:G SENSE LTD
Microdialysis probe
Provided are novel devices, systems, and methods for performing microanalysis of a localized biochemical milieu, and / or for highly localized drug delivery and treatment evaluation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Microfluidic Liposome Synthesis, Purification and Active Drug Loading
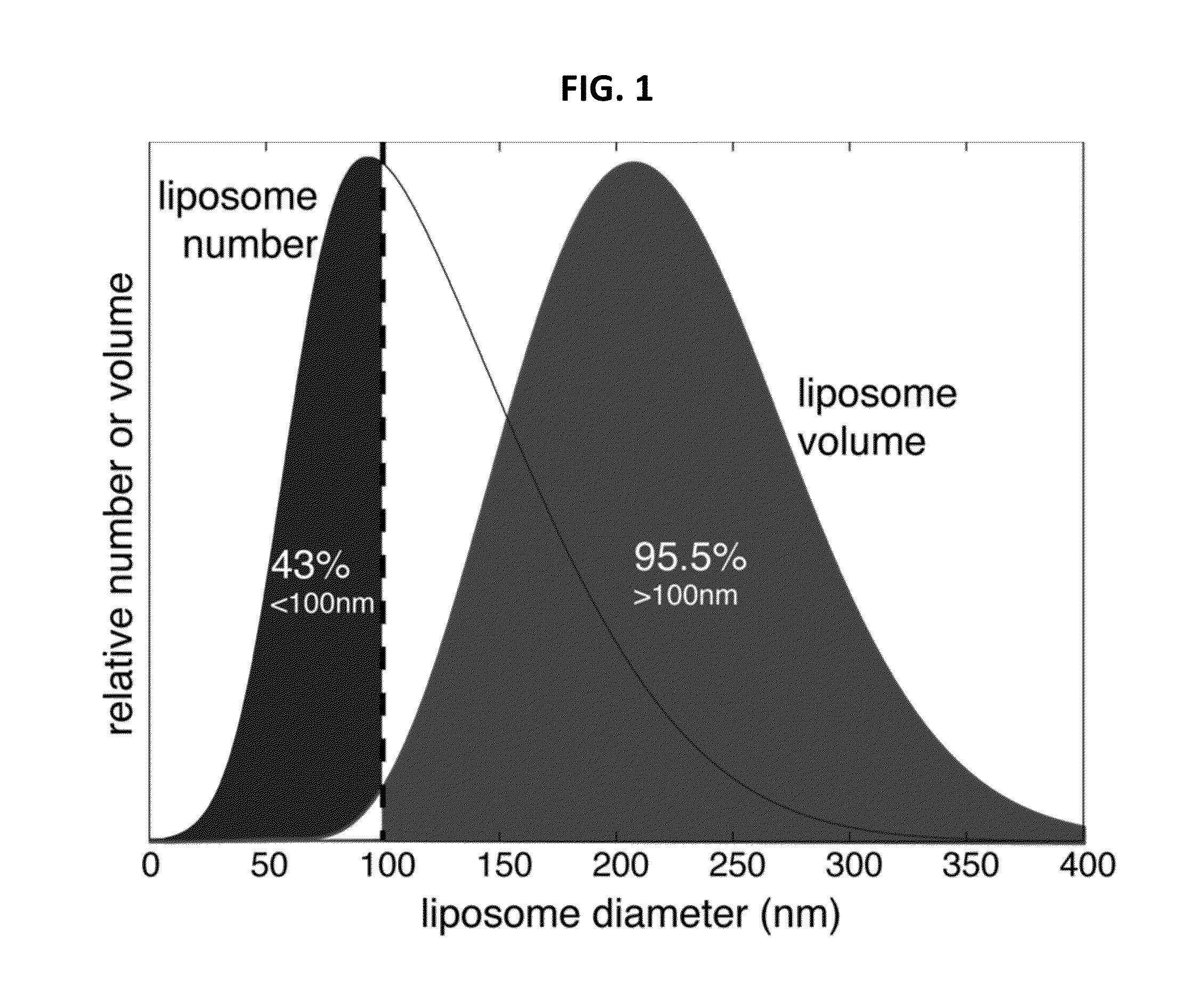
ActiveUS20150115488A1Improve throughputLow levelOrganic active ingredientsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsContinuous flowLiposome
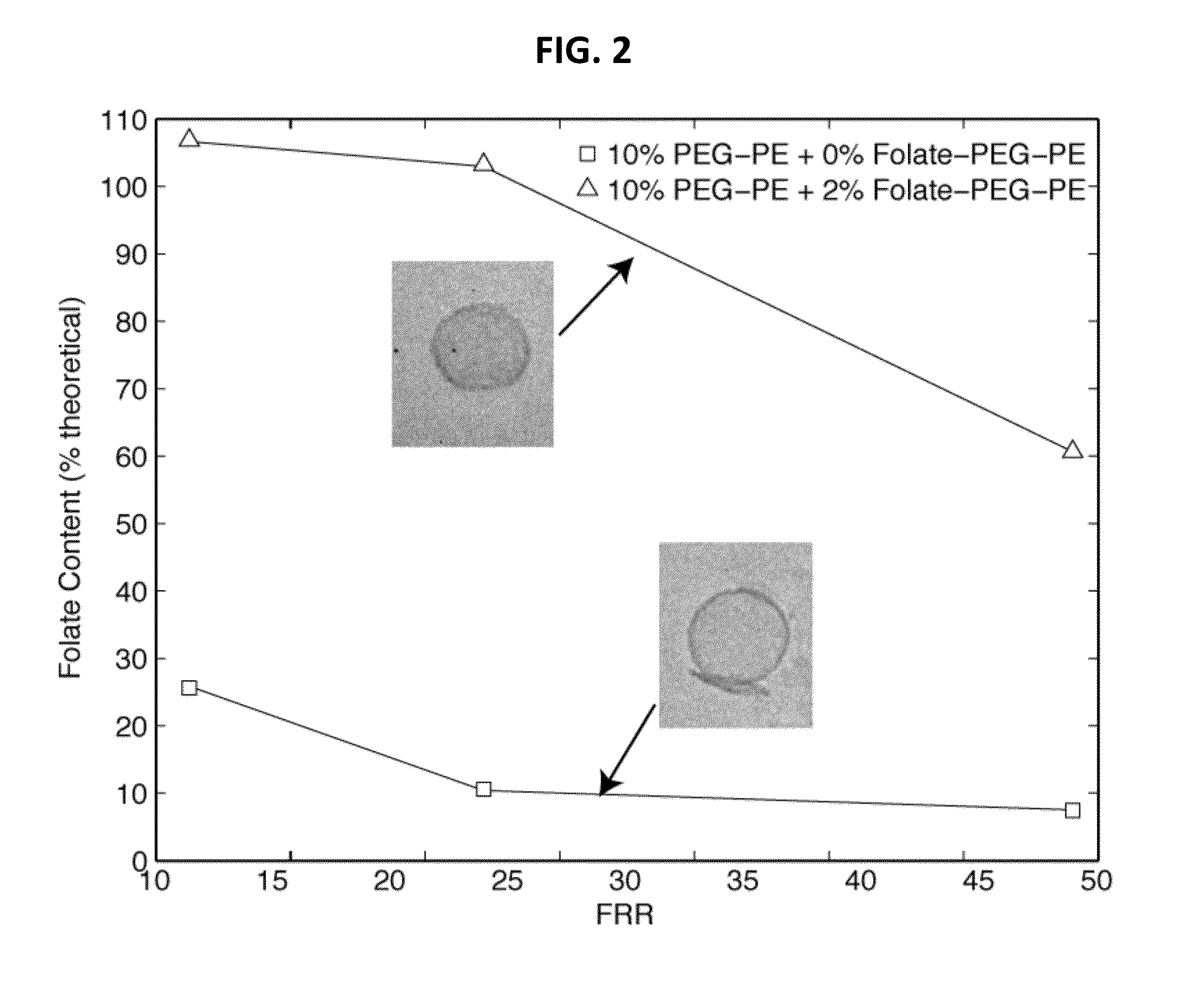
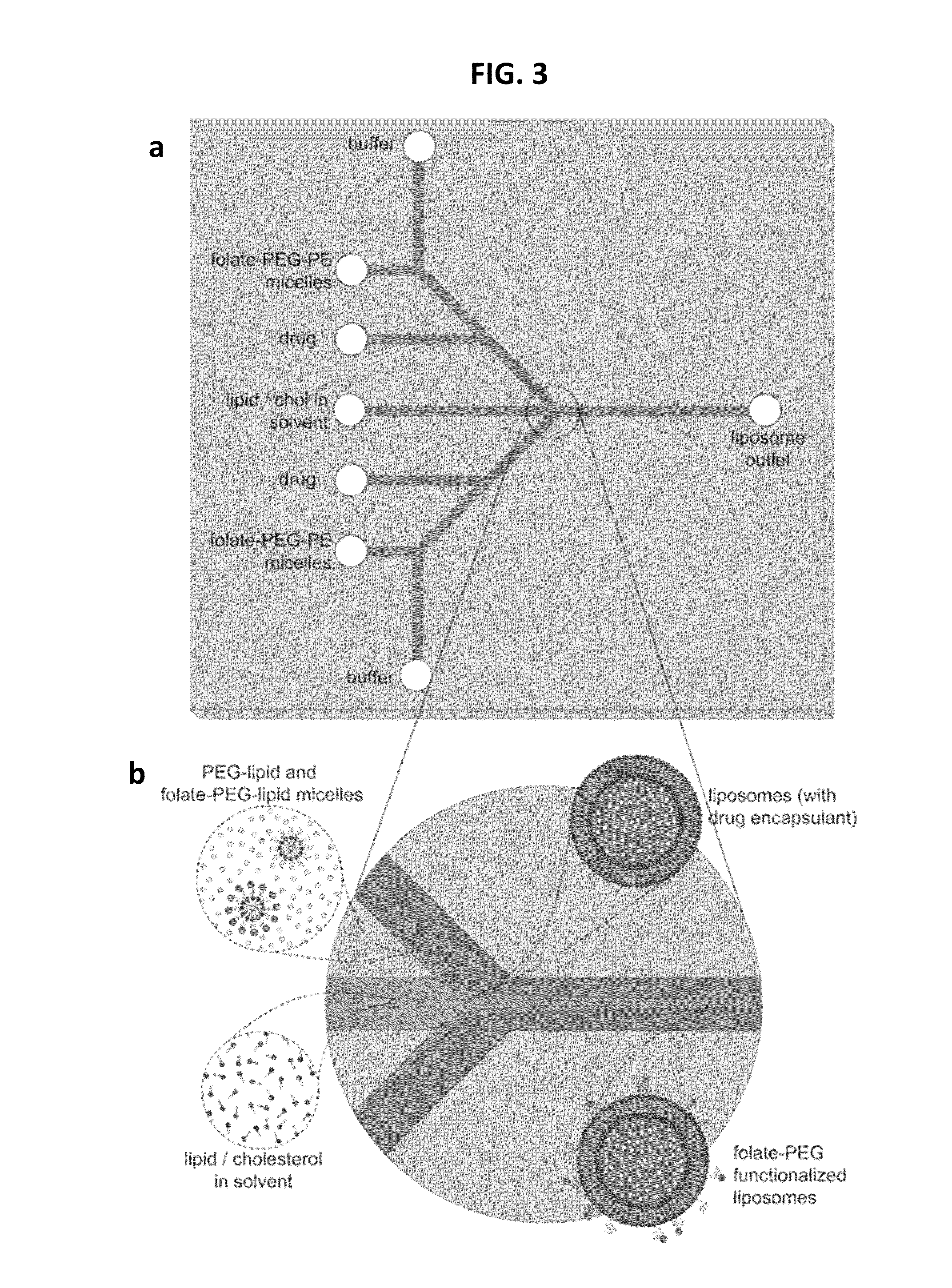
Microfluidic methods and systems are provided for continuous flow synthesis and active loading of liposomes, which include a liposome formation region configured to form a population of liposomes and a microdialysis region downstream from the liposome formation region and configured to form a transmembrane gradient for active drug loading of the liposomes. Microfluidic methods and systems for high throughput production of liposomes are also provided featuring high aspect ratio microchannels.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Catalyst for Producing Polyester and Method for Producing Polyester
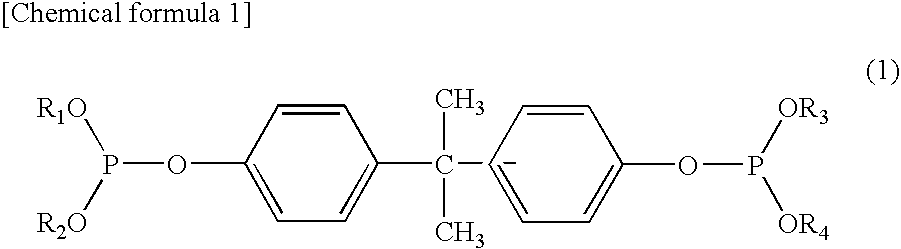
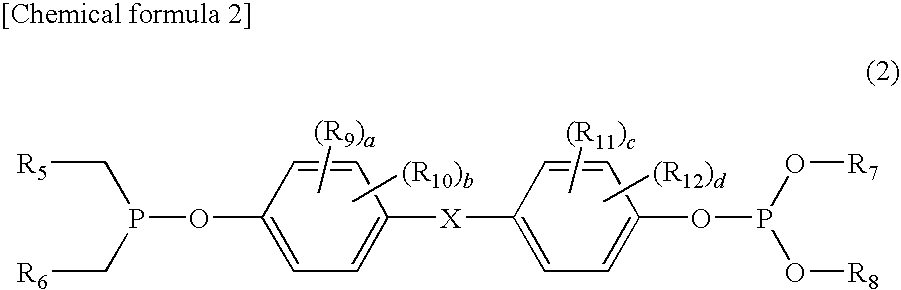
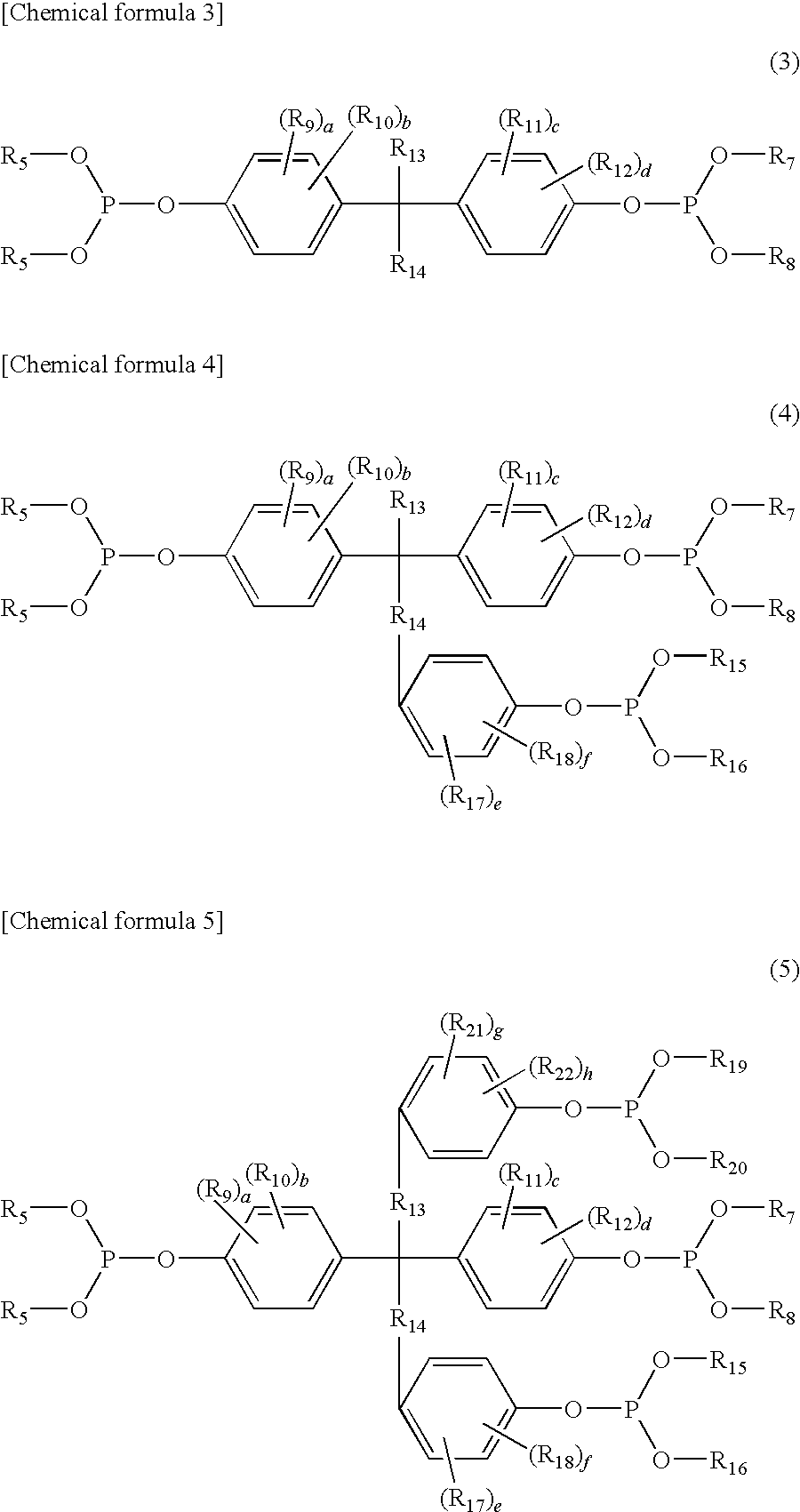
InactiveUS20100305296A1Improved color toneImprove heat resistanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhosphorus organic compoundsPolyesterSemipermeable membrane
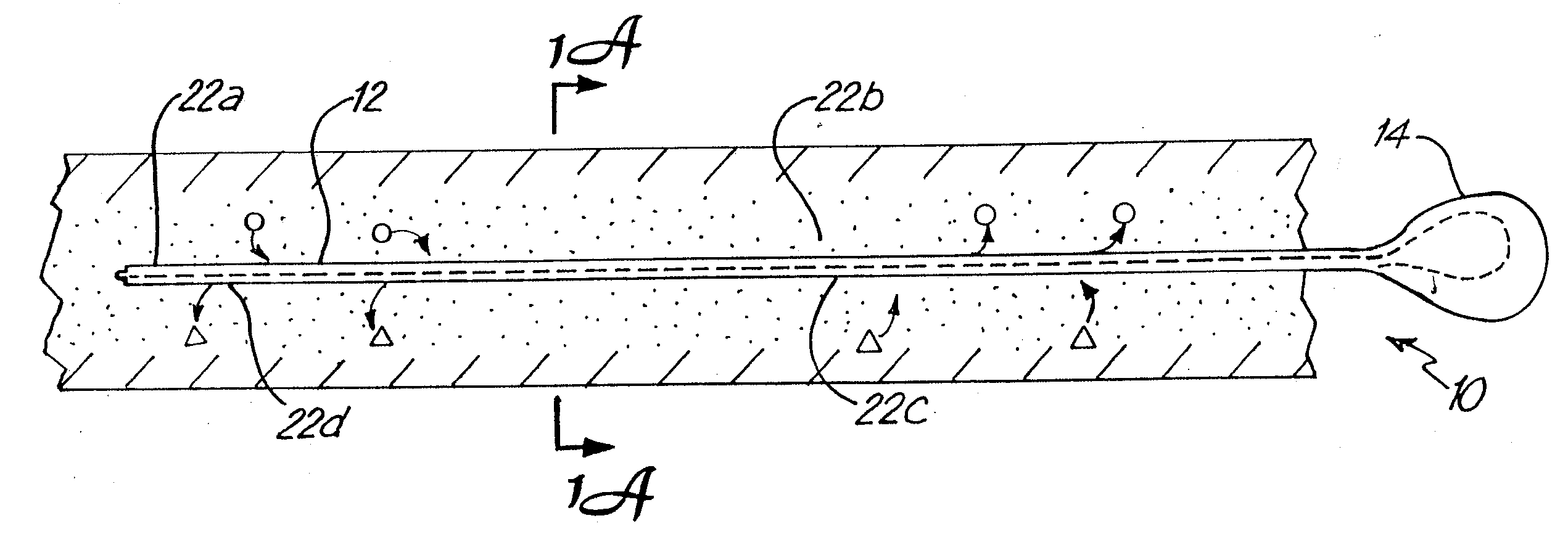
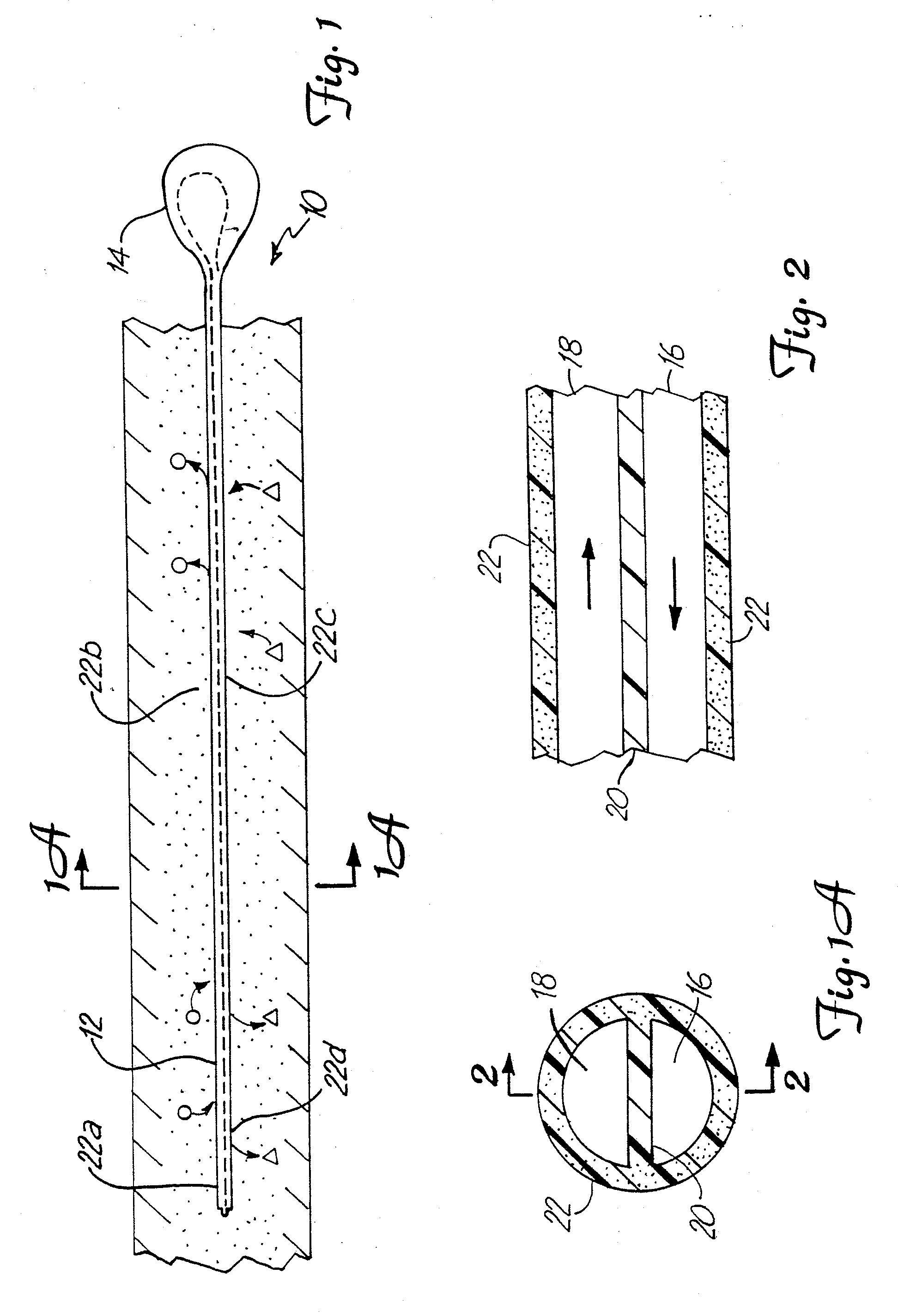
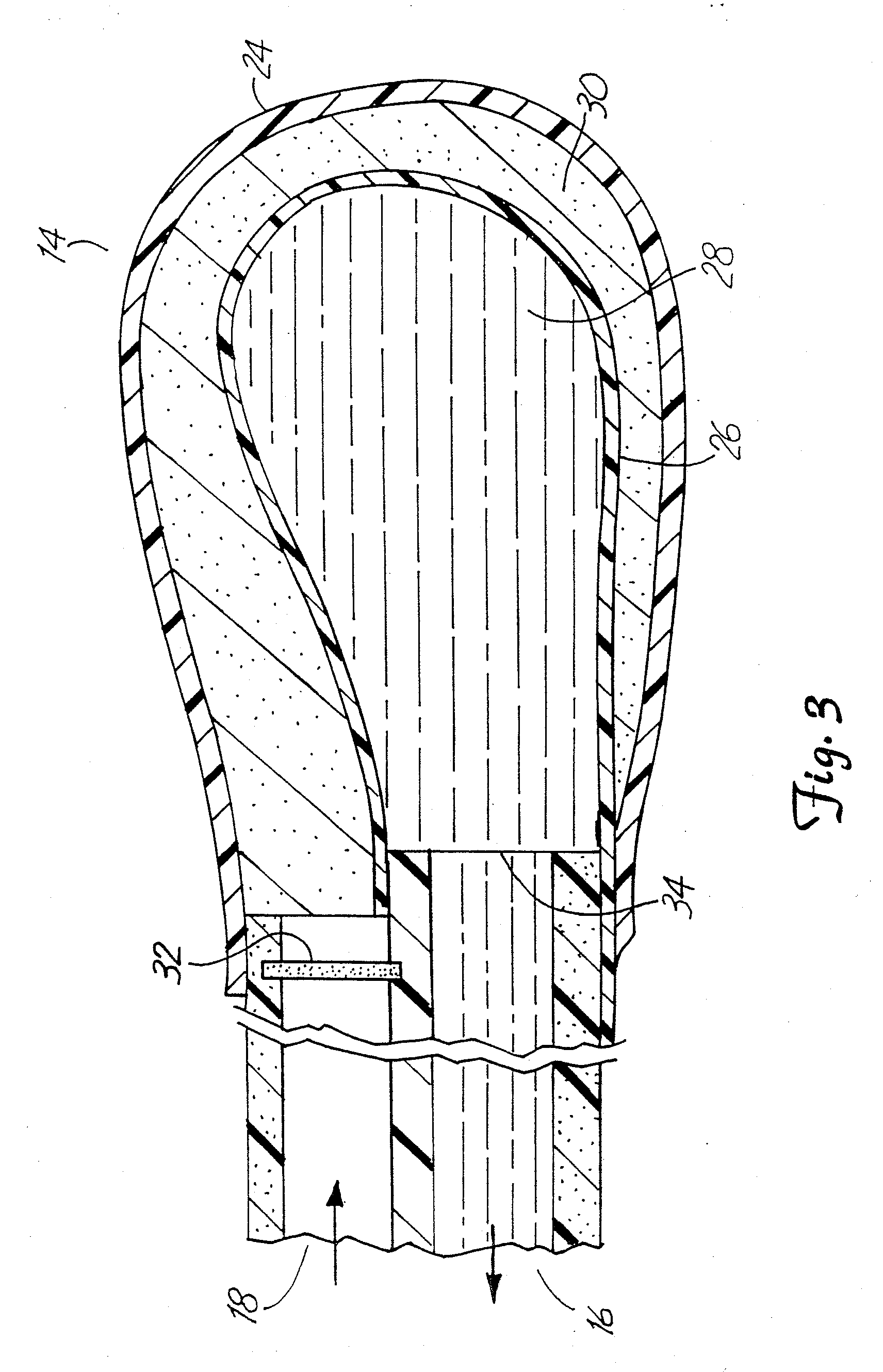
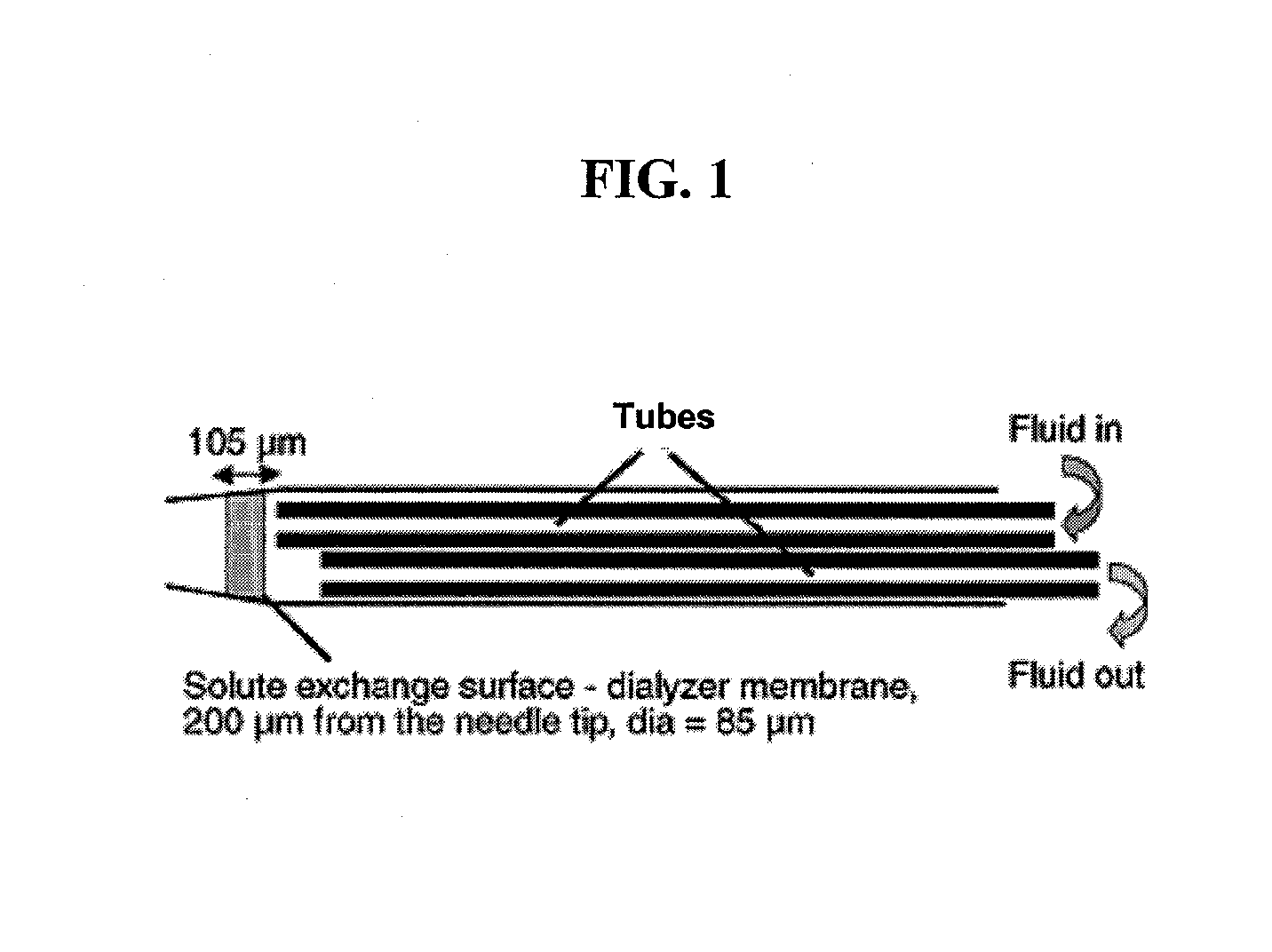
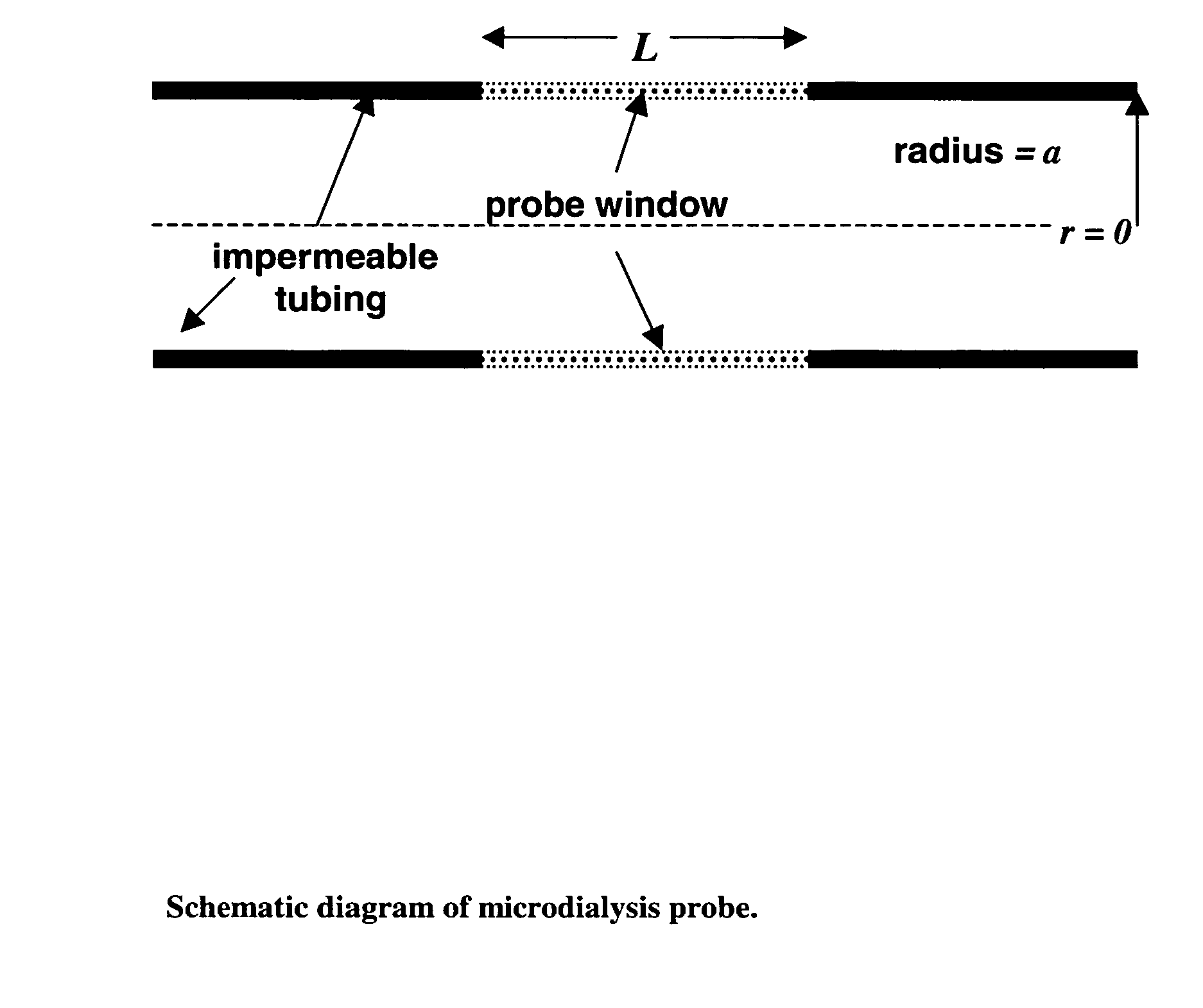
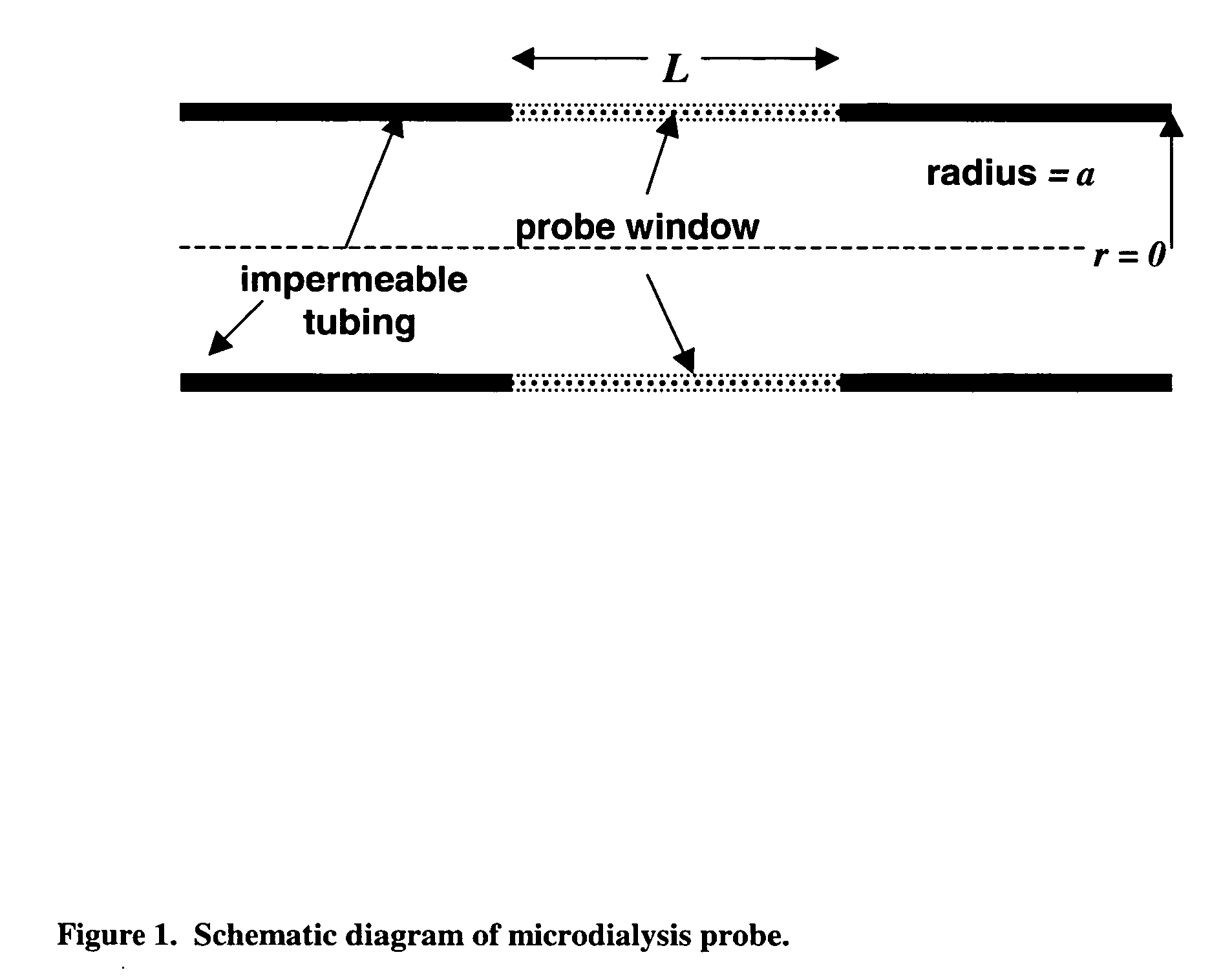
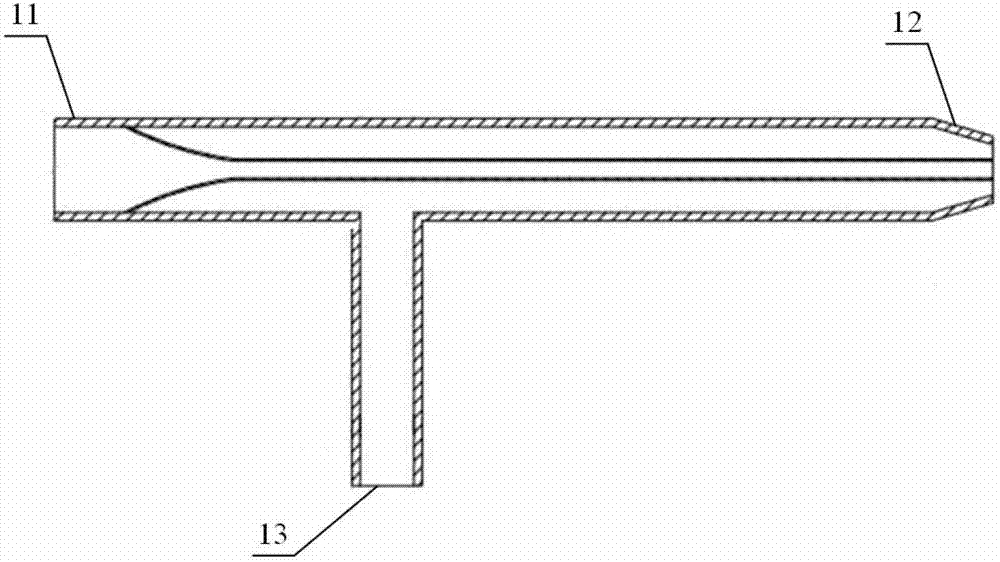
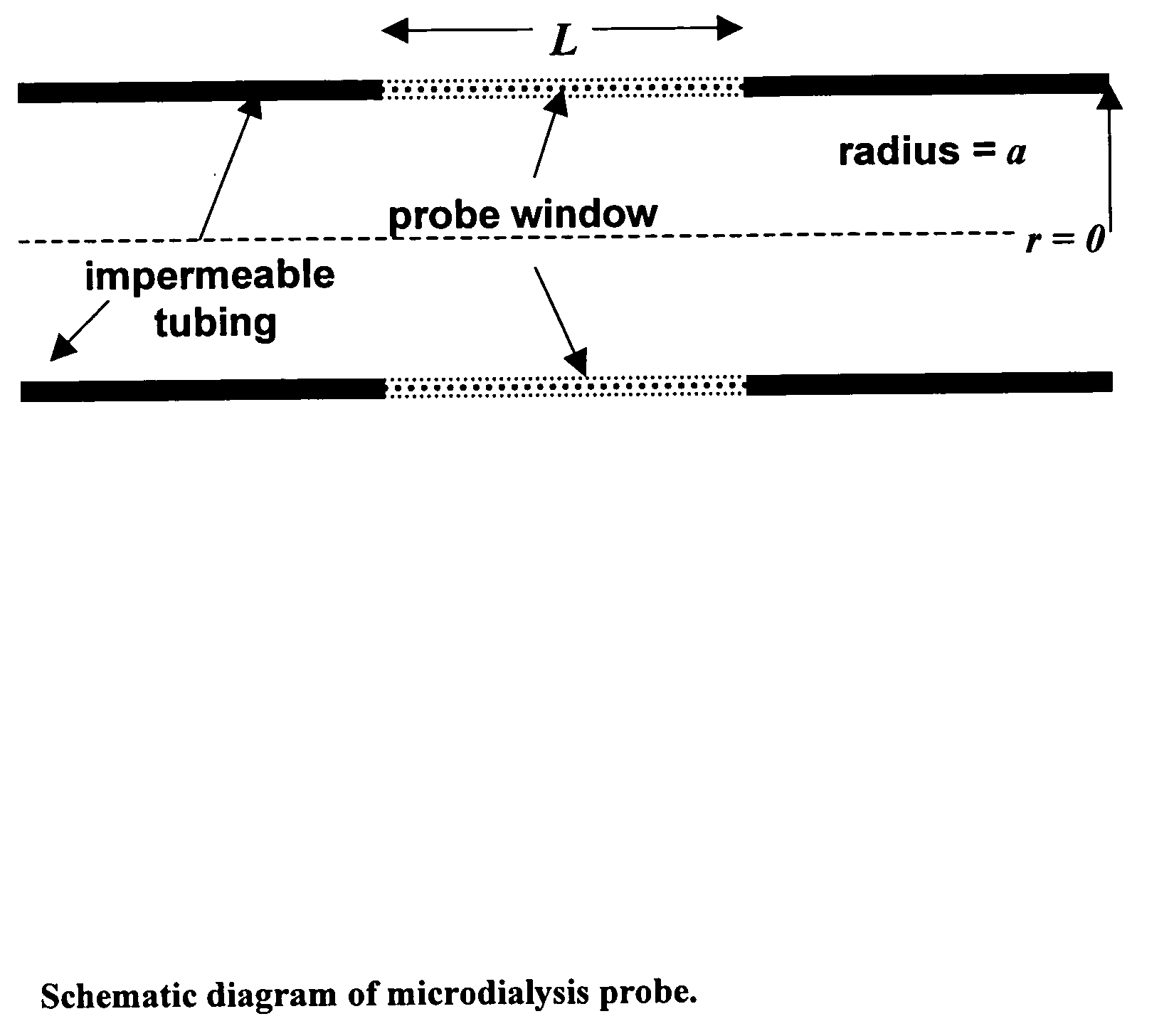
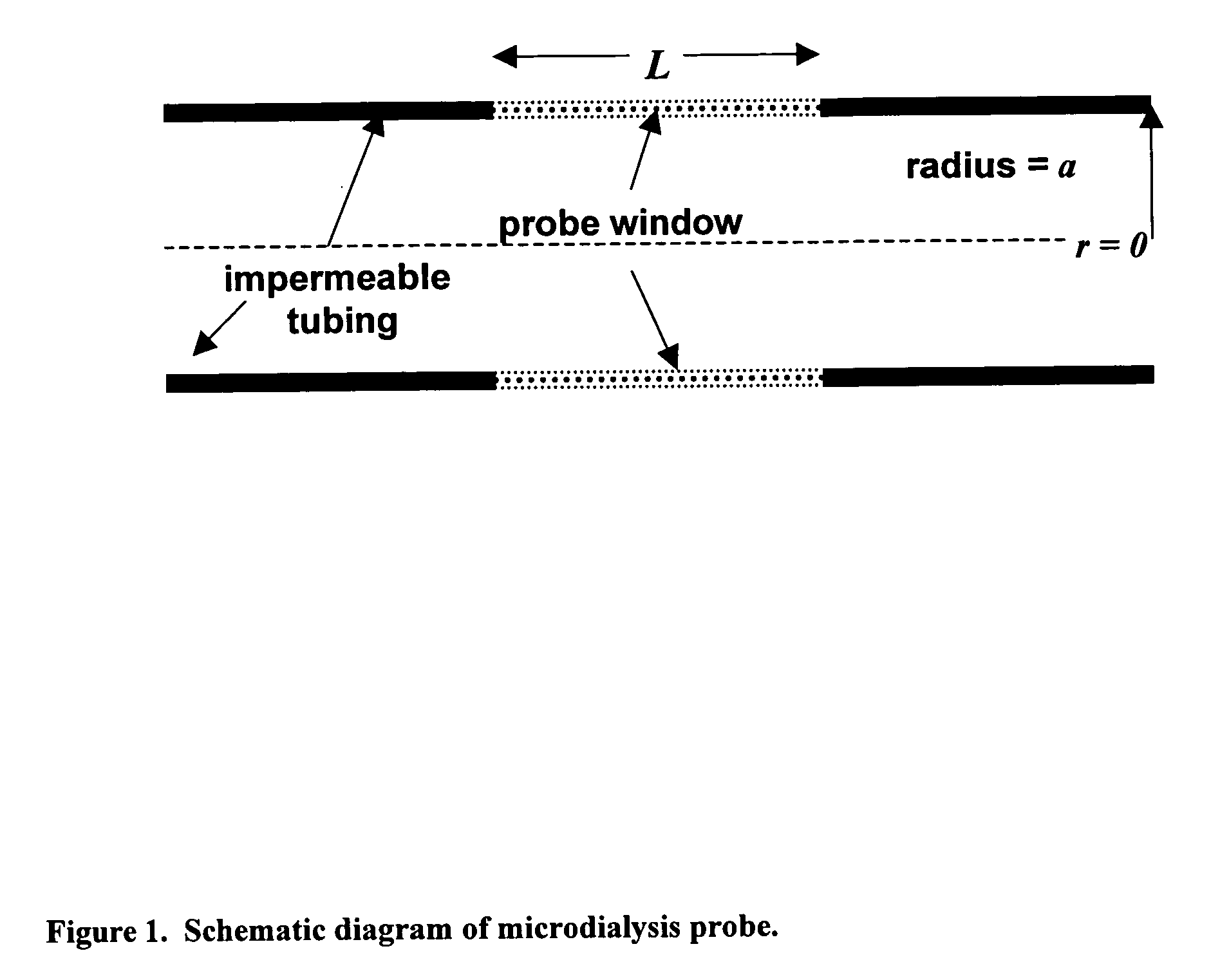
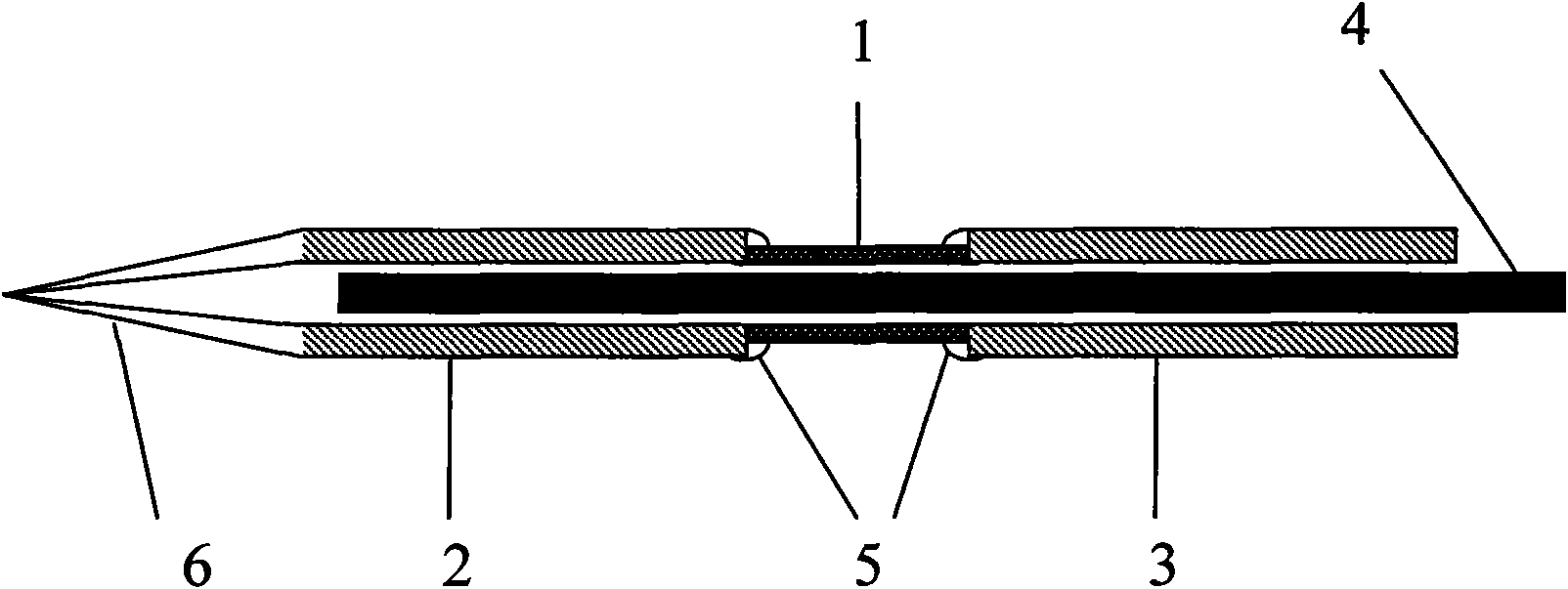
The invention relates to an improved linear microdialysis probe comprising a continuous length of flexible tubing (1) having at least one window (4) formed therein, said window covering at least one pan of the circumference of the tubing, while the remaining part forms at least one unbroken connection between a first end of said tubing and a second end of said tubing, said ends adapted to be attached to an inlet for perfusion liquid and the other end forming an outlet for the dialysate, said at least one window (4) exposing a tubular semipermeable membrane (2).
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method for use of microdialysis
InactiveUS20070106140A1Fast resultsAccurately permeabilitySensorsBlood characterising devicesResting timeHigh rate
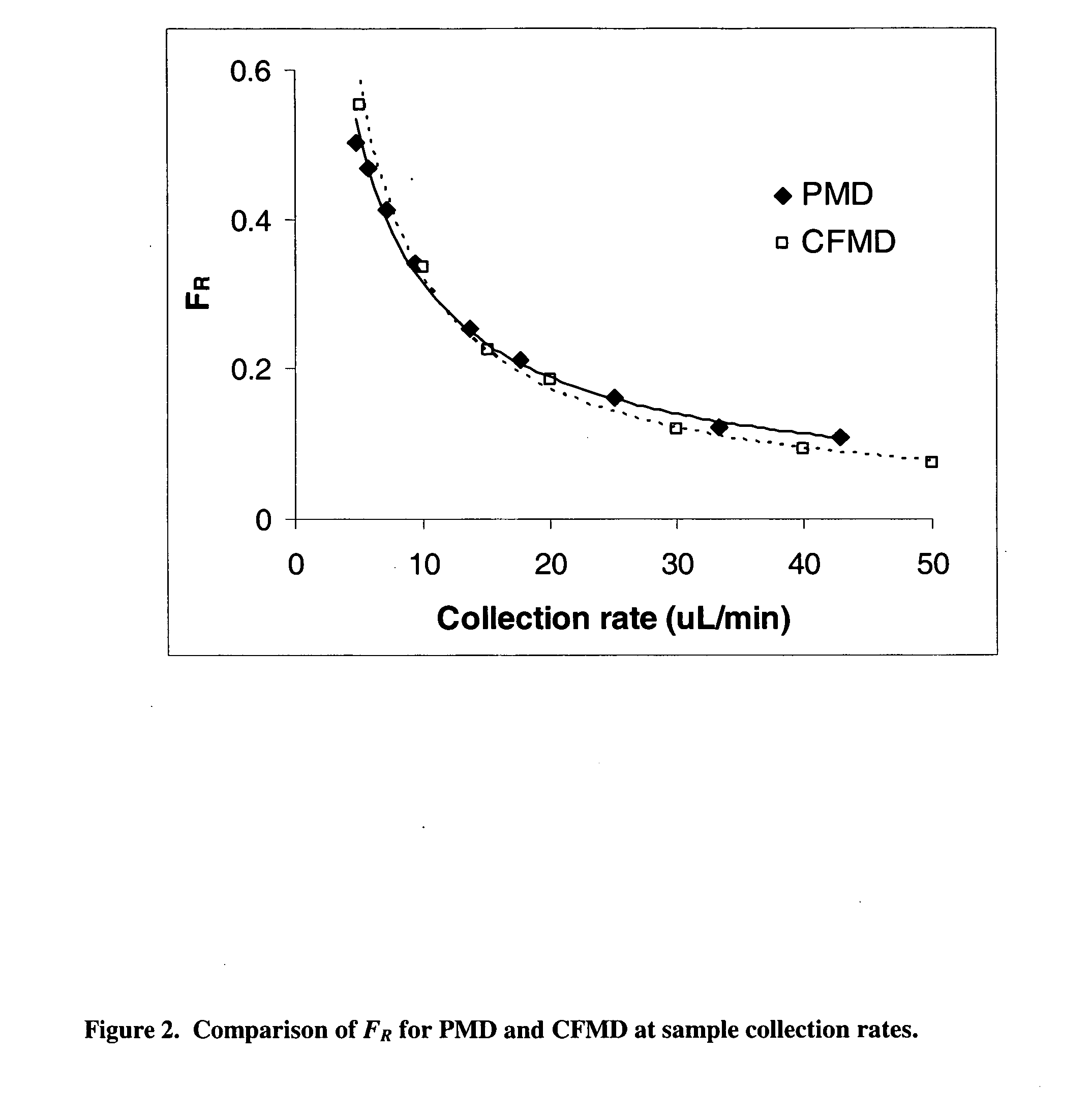
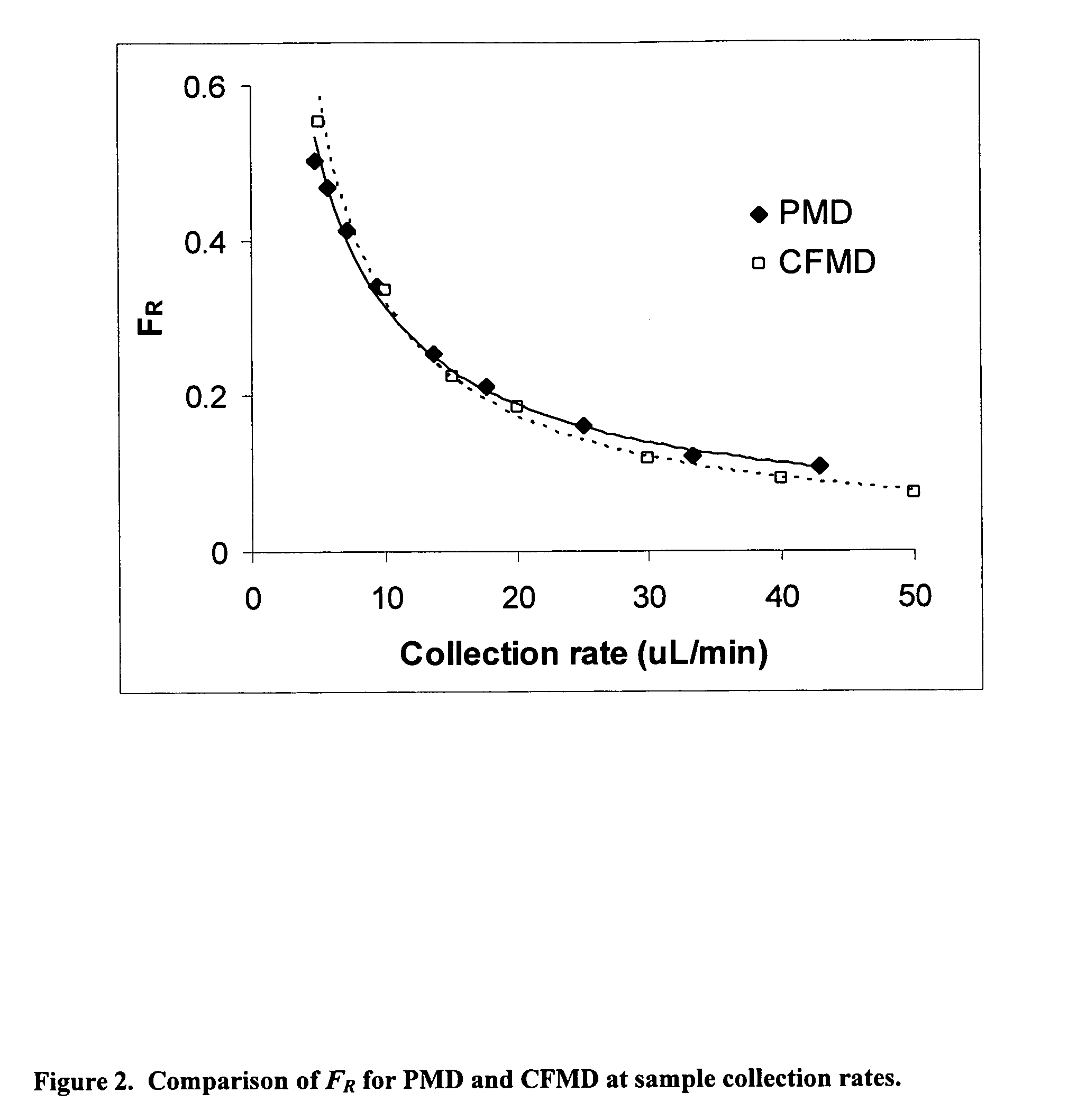
It has been surprisingly found that very accurate measurements of mass transfer can be made rapidly by permitting diffusion of an agent desired to be measured into a small, known volume of receiver or out of a known volume of donor, then rapidly pumping or flushing (“pulsing”) the receiver with a known volume of fluid. More specifically, a novel method of transferring small quantities of a contained material (either dissolved or suspended) between two media, based on such pulsing, hereinafter called pulsatile microdialysis (PMD), is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, one medium (the dialysate) is inside a small, permeable tube (microdialysis probe window) and the other (external medium) is outside. The transfer of material between the two media can be utilized, for example, to sample drug concentrations in the external medium, or the release of drugs from systems within the dialysate, or for other measurements as disclosed herein. In PMD, a dialysate fluid is pumped into a microdialysis probe window, allowed to occupy the probe window while at rest for some resting time, and then flushed at a high rate out as a single pulse. A model that is based on a Fick's Laws was solved, and equations were derived to calculate the effects of various experimental parameters. The models were verified against experimental data using methazolamide, warfarin and benzocaine as test drugs. The data followed the mathematical models. For cases in which the concentration of free drug in the medium outside the probe was constant or changed very slowly, the concentration calibration plots were linear. In simulated first order uptake studies, the PMD and direct donor sampling data were in nearly exact agreement with the theoretical values of k=0.09 min−1. In another experiment, the free concentration of warfarin sodium in the medium outside the probe was made to decline rapidly in a known first order manner, with rate constants as high as 0.077 sec−1. The concentration in the external medium calculated from the PMD data was in nearly exact agreement with the known concentration at various times, and the experimental rate constants were in nearly exact agreement with the theoretical rate constants. For binding of methazolamide to activated charcoal, and for the binding of sodium warfarin to bovine serum albumin, PMD was able to generate sufficient data points to accurately characterize the rapid initial binding. This invention demonstrates that PMD is an accurate method of sampling drug concentrations and measuring rates and extents of a number of processes, including protein binding, adsorption to binding agents such as activated charcoal, release from microemulsion drug delivery systems, and the determination of drug diffusion coefficients, and for various other purposes which will occur to those skilled in the art. Compared to known methods such as traditional (continuous) microdialysis, the present invention offers the ability to sample more frequently, and over much shorter time intervals, thereby accurately obtaining data not heretofore available.
Owner:BELLANTONE ROBERT ARTHUR
Jugular vein microdialysis probe and probe guiding device
InactiveCN101703817AEasy to implantEfficient use ofGuide wiresVeterinary instrumentsDialysis membranesVein
The invention discloses a jugular vein microdialysis probe and a probe guiding device. The probe part comprises a dialysis membrane, a connecting pipe, a liquid inlet pipe, a liquid outlet pipe, an inner sleeve and an outer sleeve; and the probe guiding device part comprises a guiding pipe, a fixed base, a fixed spiral plate and a guiding pipe cap. The jugular vein microdialysis probe and probe guiding device of the invention can be used to reduce the soaking time of the microdialysis probe and increase the operational performance of the probe.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Stable generating device of trace organic matters
ActiveCN102728499AQuality is easy to controlStable concentrationPreparing sample for investigationLiquid spraying apparatusEngineeringProduct gas
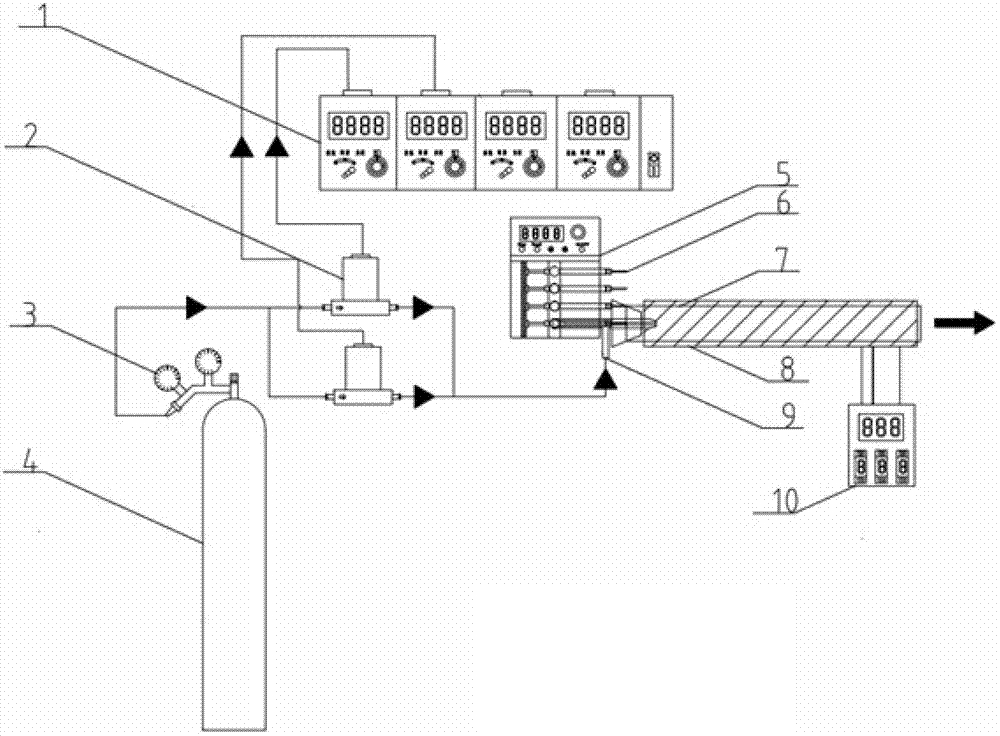
The invention relates to a stable generating device of trace organic matters, and is aimed to provide a stable generating device of trace organic matters. The device comprises a microinjector, and an mistorizer with a three-way structure, in which three channels are respectively as follows: an inserting hole of the microinjector, a gas inlet and a tubular outlet end of the mistorizer; a quartz tube with a heating sleeve arranged outside, one end of the quartz tube is an outlet of the trace organic matters and the other end is provided with a plug with a through hole, wherein the tubular outlet end of the mistorizer stretches into the inner cavity of the quartz tube after penetrating through the plug; and a gas source for providing gas for atomizing the organic matters, wherein the gas source is connected with a gas pressure reducing valve and a gas flow meter in turn by a pipe, and the gas flow meter is connected to the gas outlet of the mistorizer; the tail part of the microinjector is connected with a microdialysis pump, and the needle tip part of the microinjectoor is located inside the inserting hole on the mistorizer. The device has good stability and repeatability. The quality of the produced trace organic matters is controllable and the organic matters with stable trace concentration 10<-9>-10<-12>g / Nm<3> can be produced finally.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and Device for Determining the Glucose Concentration in Tissue Liquid
InactiveUS20080153118A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConcentrations glucoseTissue fluid
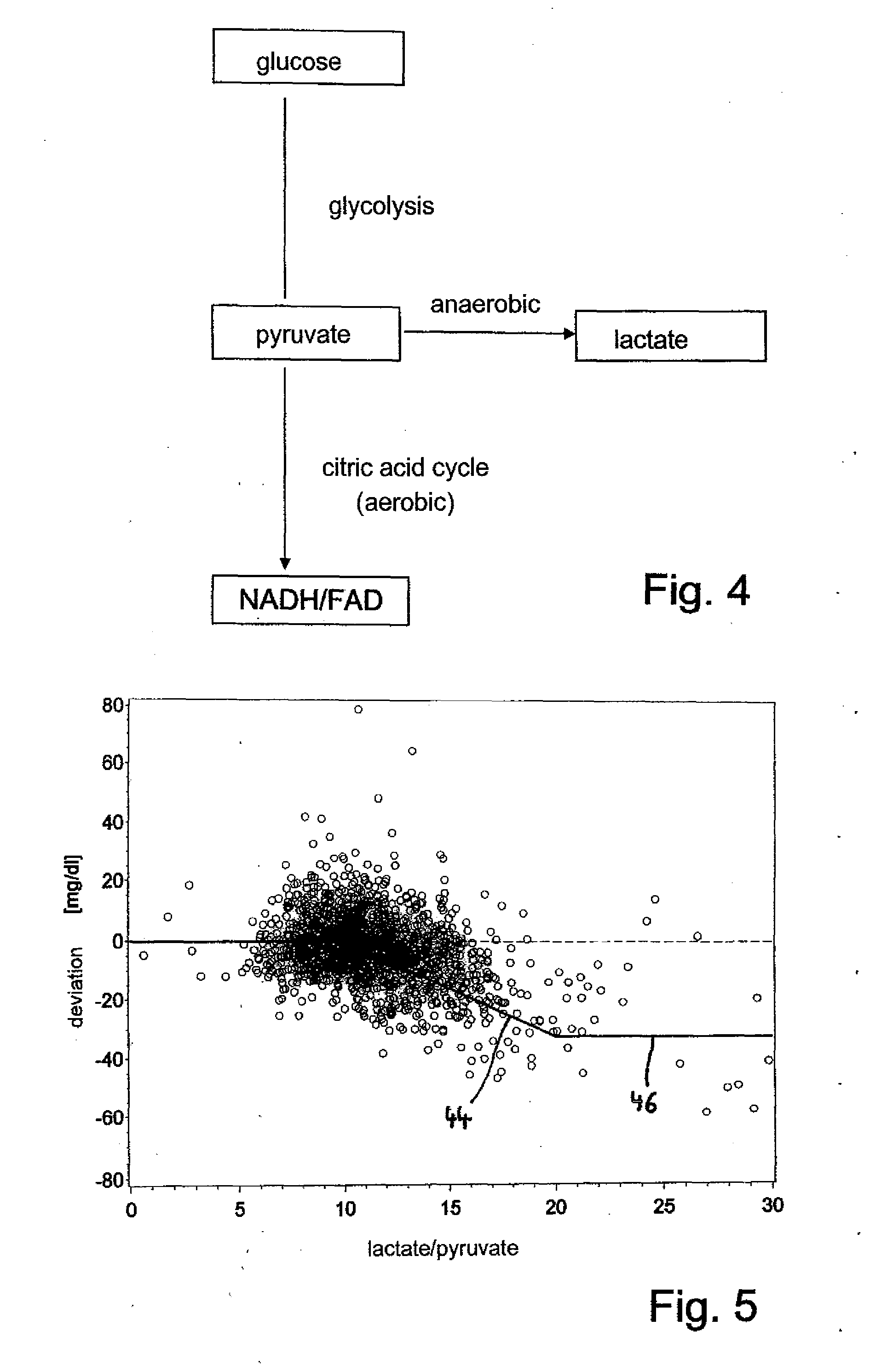
The invention relates to a method and a device for determining the glucose concentration in tissue fluid whereby test values for glucose and for an endogenous reference substance are detected in a sample liquid obtained by microdialysis, microperfusion or ultrafiltration, and the glucose value is corrected in accordance with the test value for the reference substance. The recovery rate for glucose is determined from a non-linear relationship with the recovery rate for the ionic reference substance, and the test value for glucose is corrected therewith. In addition, the concentration of lactate and / or pyruvate is used as a further reference substance in the sample liquid to make further corrections.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Implantable biosensor with automatic calibration
Implantable self-calibrating biosensor Subcutaneously or intracorporeally implantable biosensor, characterized by a closed microfluidic circuit with calibrating fluids, which communicates by a backward micro-dialysis logic with the exterior of said circuit, an open and in contact with the tissues and the interstitial fluid working electrode, for its self-calibration. One or more working electrodes may be positioned inside openable boxes from EAP, and be opened for the duration of the measurement and closed immediately after, succeeding one another in the measurement, as their sensitivity is diminished.
Owner:TSOUKALIS ACHILLEAS
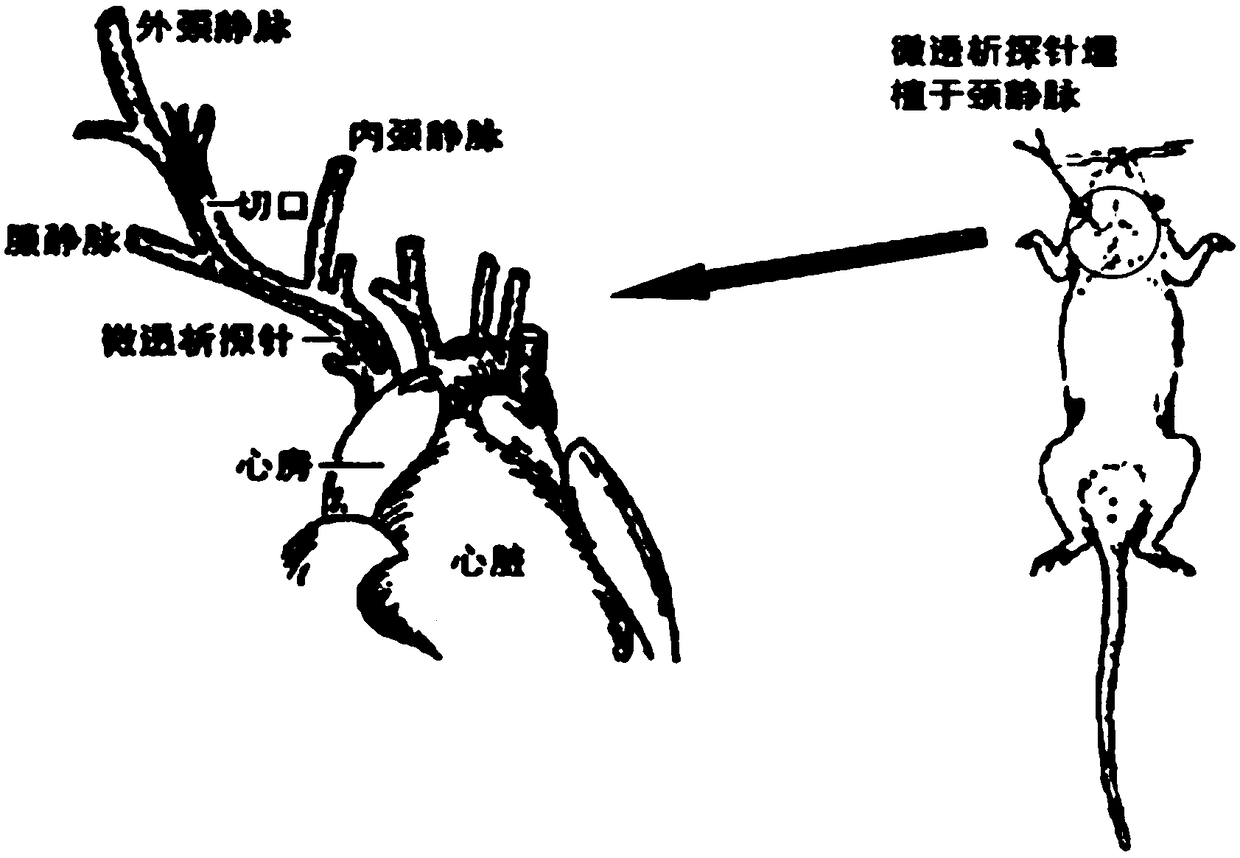
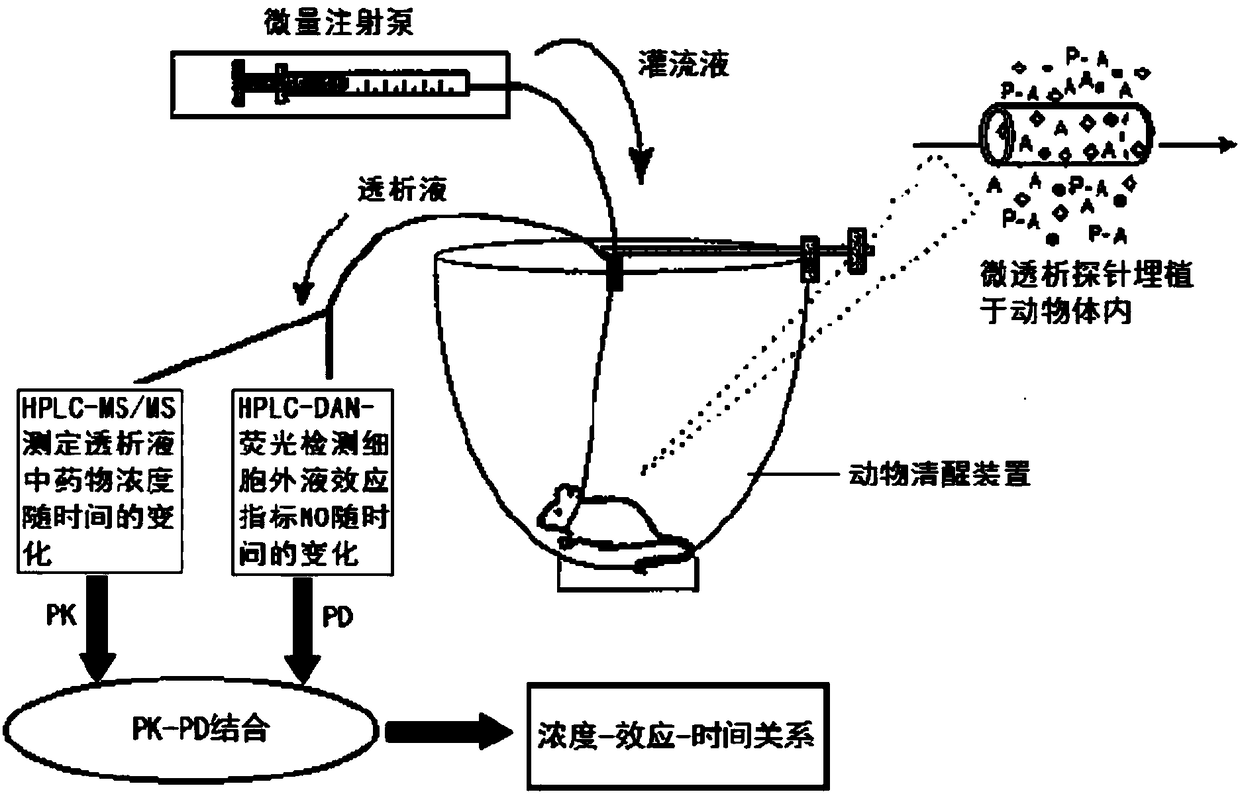
Blood dialysate detection method, and application thereof in pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of pulse activating injection
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and concretely relates to a blood dialysate detection method, and an application thereof in the pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of a pulseactivating injection. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a conscious rat in-vivo microdialysis sampling device collected blood dialysate, analyzing the drug concentration of active ingredients in the blood dialysate by high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrography, and detecting the drug effect index NO in the blood dialysate by high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection technique. A conscious rat in vivo microdialysis technique adopted in the invention overcomes the influences of animal anesthesia and blood loss on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic behaviors, is successfully used in the studying of the plasma concentration-time and drug effect-time relationships of the pulse activating injection against rat myocardialischemia, and can be used to establish a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic combination model. A study result shows that when an appropriate blood endogenous biomarker is selected as a drug effect index, the conscious animal in vivo microdialysis sampling technique becomes an ideal tool for pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic combination studying.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
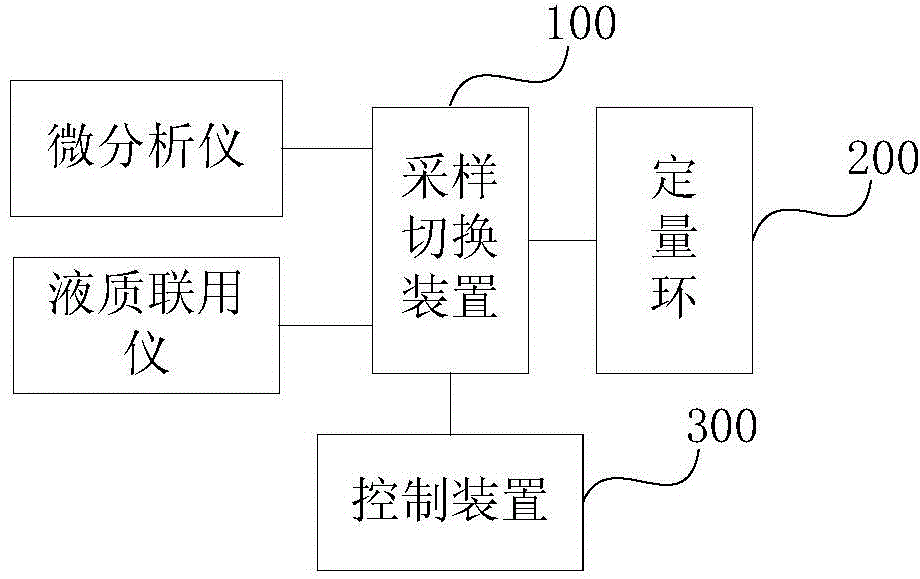
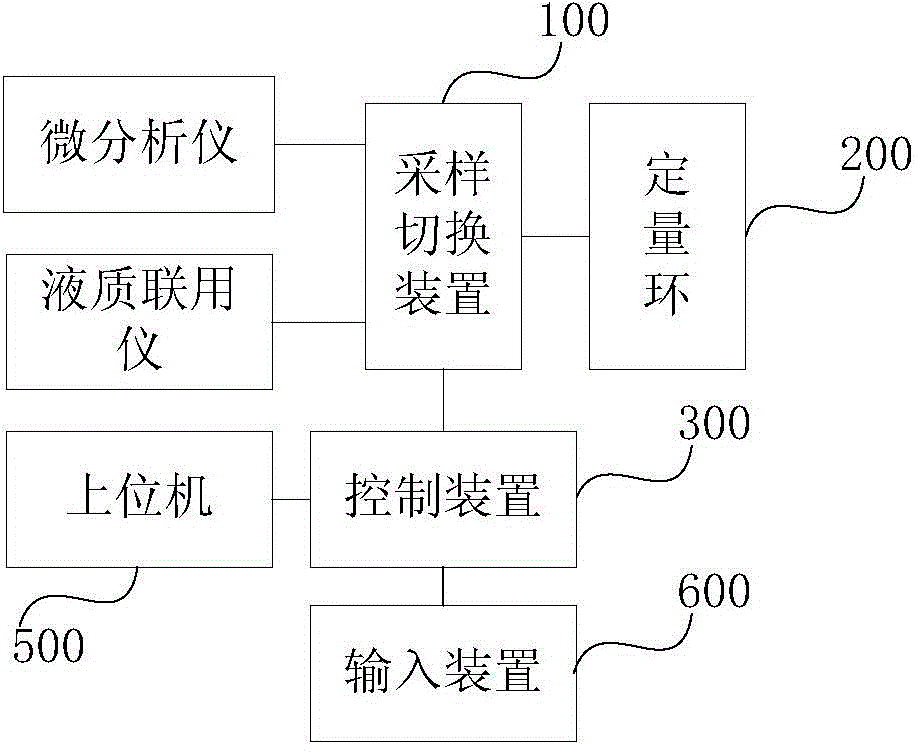
Microdialysis analyzer and HPLC-MS combined equipment
InactiveCN104374851AFast analysisRealize online useComponent separationBiochemical engineeringLive organisms
The present invention provides microdialysis analyzer and HPLC-MS combined equipment. According to the microdialysis analyzer and HPLC-MS combined equipment, a control device is adopted to control a sampling switch device so as to achieve guide communication between the quantitative ring and the microdialysis analyzer or the HPLC-MS, such that the purpose that the sample is collected or the sample enters the HPLC-MS to separate and analyze is achieved; when the quantitative ring and the microdialysis analyzer form the guide communication through the sampling switch device, the sample collected from living organisms by the microdialysis analyzer enters the quantitative ring and is enriched, the control device controls the sampling switch device to achieve the guide communication between the quantitative ring and the HPLC-MS and the HPLC-MS is triggered to inject the sample after the first preset time, and the control device controls the sampling switch device again to achieve the guide communication between the quantitative ring and the microdialysis analyzer so as to enter the next time sample enrichment and analysis after the second preset time, such that the online combination of the microdialysis analyzer and the HPLC-MS, and the automated treatment on the dialyzate are achieved, the labor amount is reduced, and the analysis speed of the dialyzate is accelerated.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
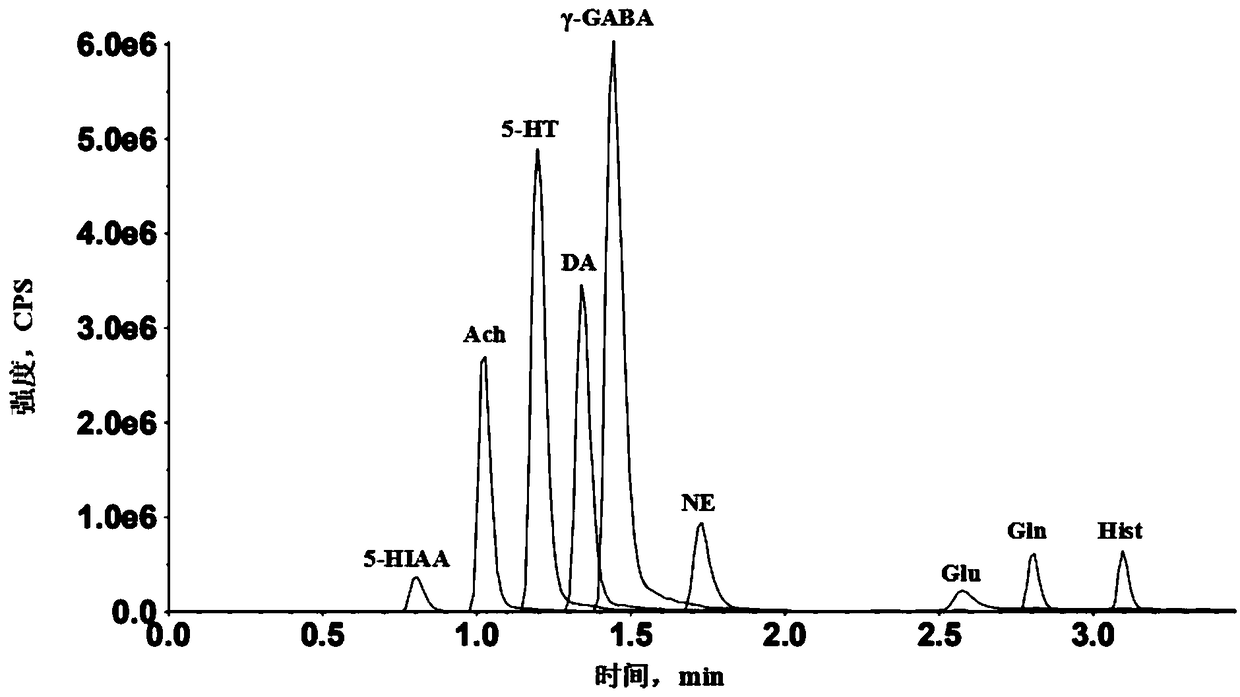
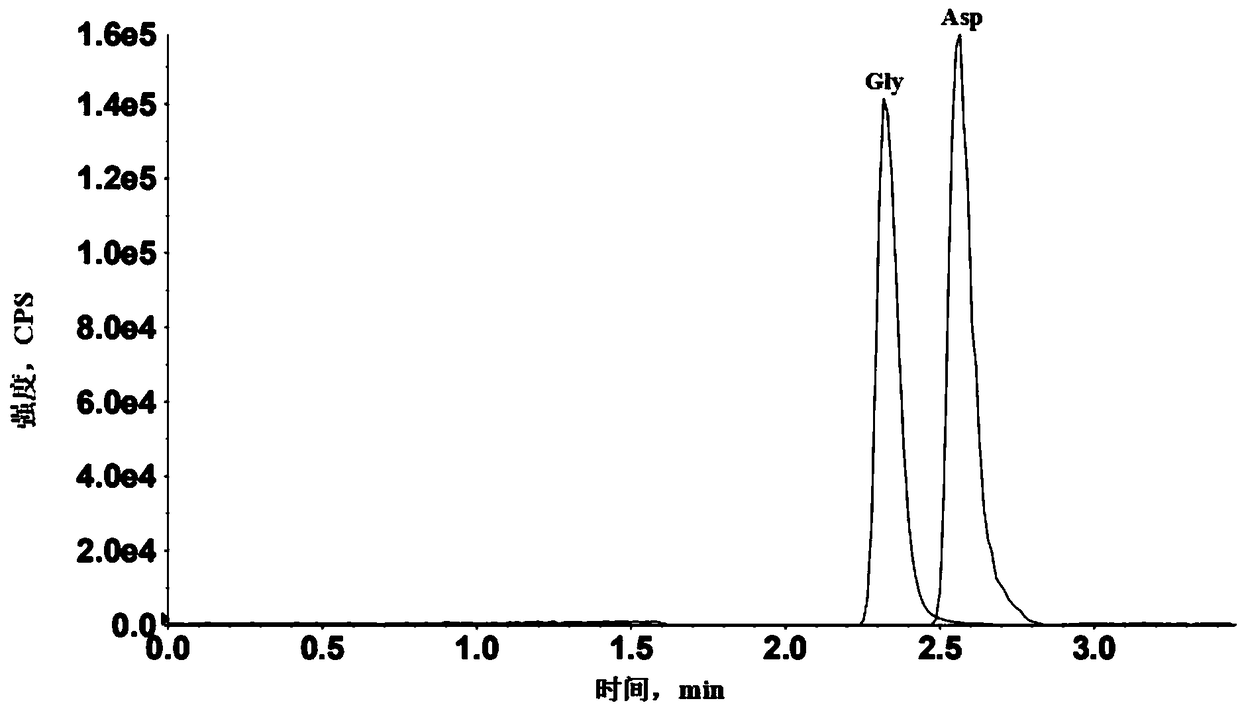
Method for detecting 11 neurotransmitters in brain microdialysis fluid by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveCN108802250AQualitatively accurateAccurate detectionComponent separationUsabilityMass spectrometry imaging
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and particularly relates to a method for detecting 11 neurotransmitters in brain microdialysis fluid by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a brain microdialysis sample solution by diluting brain microdialysis fluid with an acetonitrile-water solution or an acetonitrile-formic acid solution, and performing qualitative and / or quantitative detection by using the ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry / mass spectrometry. The method canrealize real-time qualitative and quantitative detection of 11 neurotransmitters by one time through an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry / mass spectrometry system only bysimply diluting the brain microdialysis fluid, the detection result is controllable, accurate and stable, and the method has good usability, and is short in analysis time. The method overcomes the defects of complicated processing, long time consuming, low accuracy and single data caused by various neurotransmitter types, low neurotransmitter content, large matrix effect and the like, and has a prospective clinical application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Methods for drug delivery
InactiveUS20140378944A1Eliminating many of the microfluidic engineering hurdlesAvoiding central regionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid tissueMedicine
Methods and devices for delivering an agent to a solid tissue in vivo for assessment of efficacy are described. One method involves withdrawing of a needle from and injecting of the agent into the solid tissue; another method involves delivering the agent using a plurality of microdialysis probes to a solid tissue.
Owner:PRESAGE BIOSCI
Method for use of microdialysis
ActiveUS20100021932A1Accurately permeabilityAccurate measurementSensorsBiological testingWarfarinContinuous flow
Very accurate measurements of mass transfer can be made rapidly by permitting diffusion of an agent desired to be measured into or out of a small, very precisely known volume of a microdialysis probe, then rapidly pumping or flushing (“pulsing”) the probe with a known volume of fluid as a single pulse. The diffusion and pulsing may be repeated. The method, hereinafter called pulsatile microdialysis (PMD) to distinguish it from prior art continuous flow microdialysis, is useful for measurements in a number of processes, including protein binding, adsorption to binding agents such as activated charcoal, release from microemulsion drug delivery systems, determination of drug diffusion coefficients and concentrations, and for various other purposes.The method is based on mathematical manipulation of Fick's Laws. Resulting equations were verified against experimental data using methazolamide, warfarin and benzocaine as test drugs.
Owner:PHYSICAL PHARMA
Microdialysis probe capable of carrying out photogenetic stimulation
ActiveCN110559499AAvoid damageAvoid reactionDialysis systemsLight therapyNeuronal damageOptical Module
The invention discloses a microdialysis probe capable of carrying out photogenetic stimulation. The probe comprises a probe shell, a limiting block and an optical fiber connector, the head of the probe shell is connected with a limiting block, the optical fiber connector is combined with the limiting block, the three structures form a main body structure of the probe, an optical fiber module and adialysis module are combined, two operations of optical genetic stimulation and micro dialysis are synchronously carried out, and molecular level change caused after specific neurons are activated byoptical waves can be synchronously detected in real time; the optical fiber can be inserted into a target brain area only when photostimulation and microdialysis operations are carried out, so that neuron damage and tissue reaction caused by a traditional method of placing the optical fiber and the brain for a long time can be avoided, and a long-term tracking experiment is facilitated. The microdialysis probe is used in the field of biomedical instruments.
Owner:陈嘉志
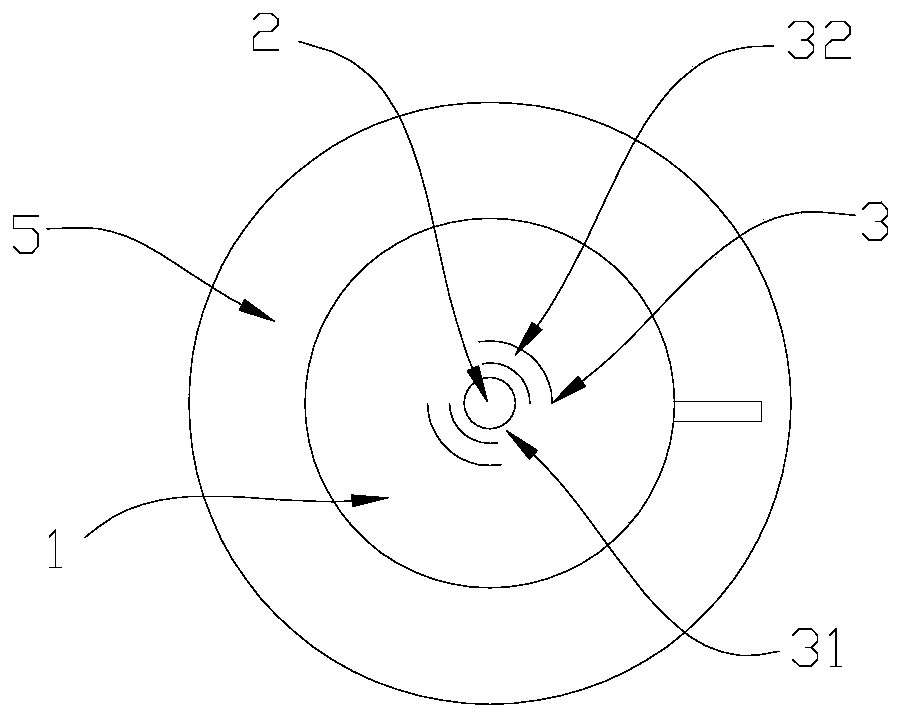
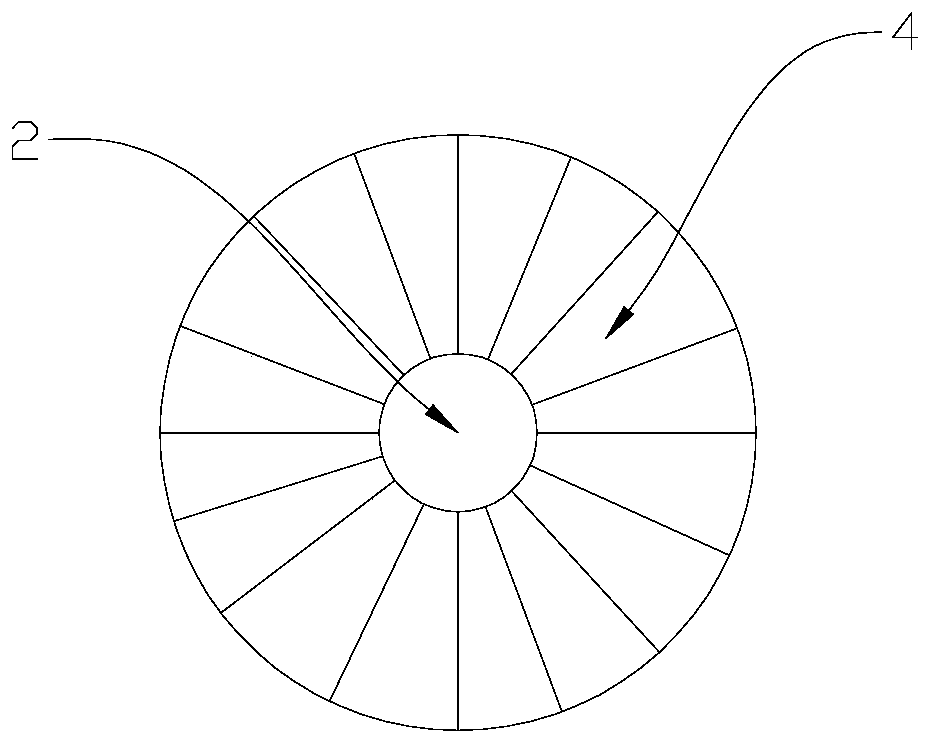
Direct implantation type microdialysis probe and preparation method thereof
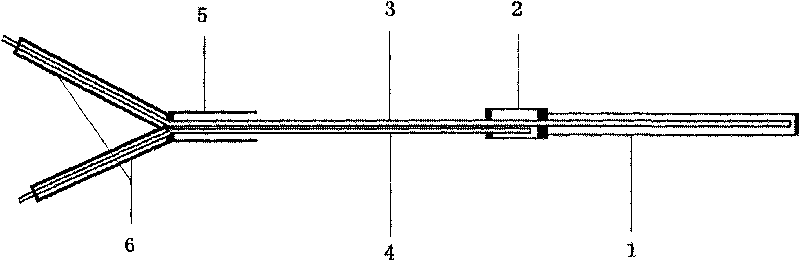
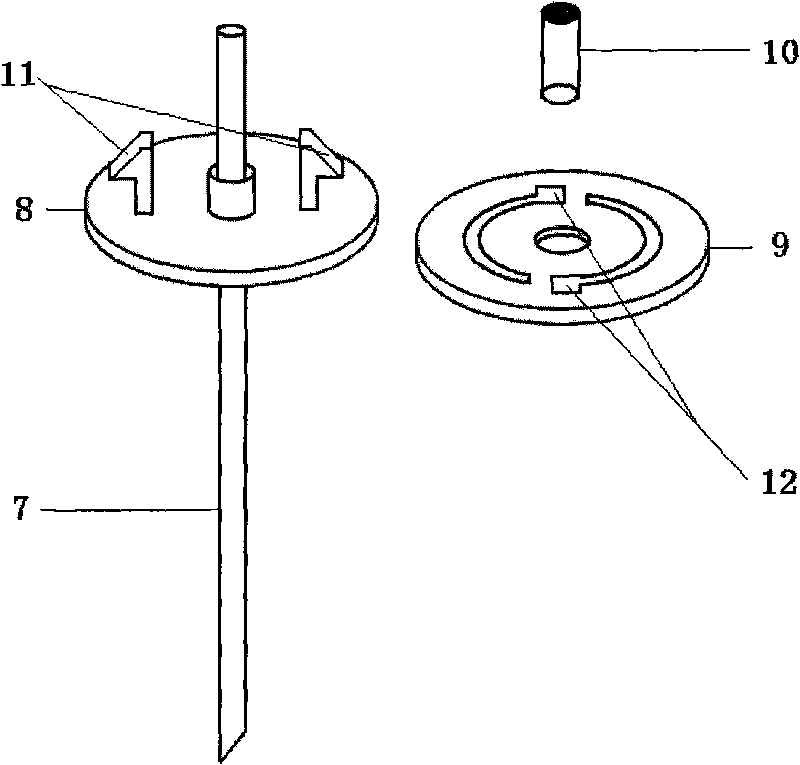
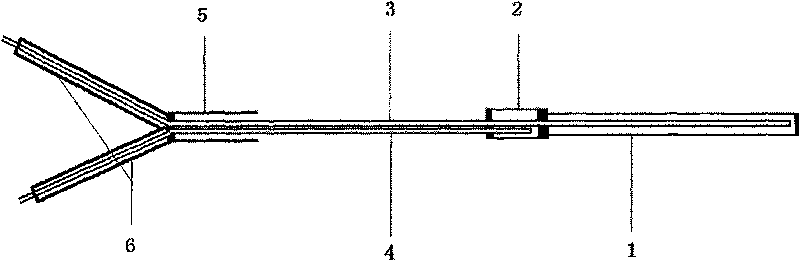
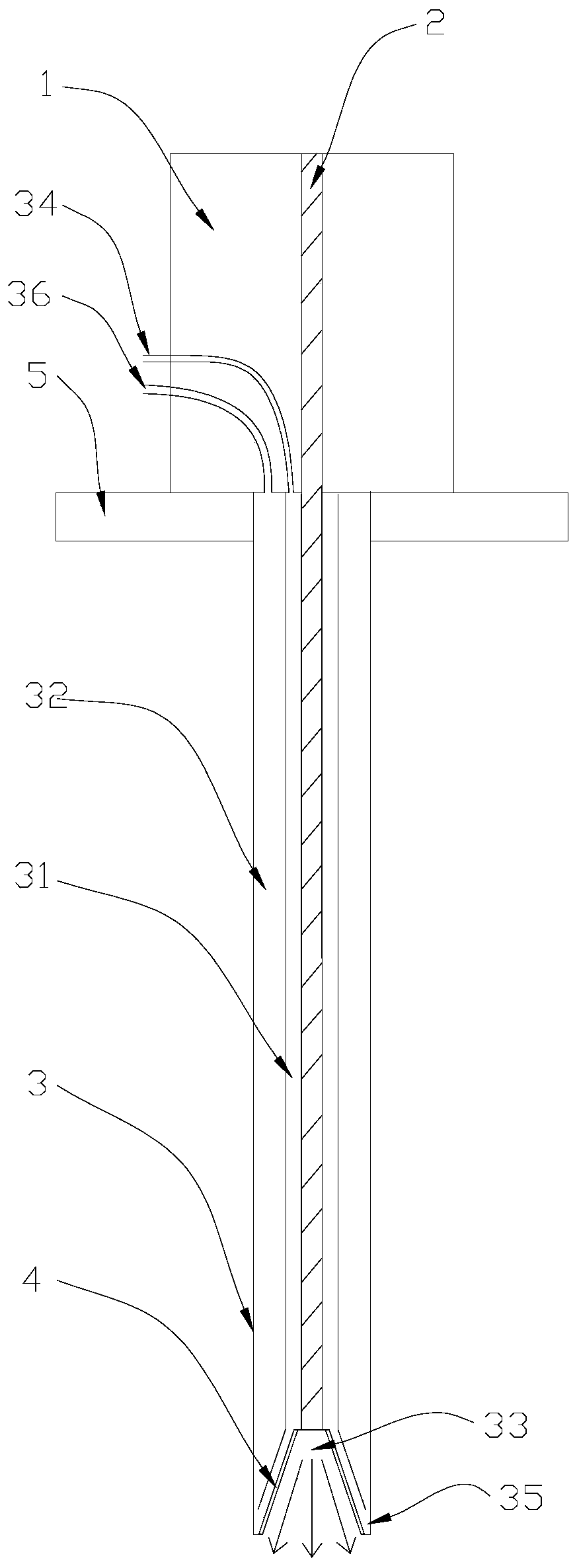
The invention relates to a direct implantation type microdialysis probe and a preparation method thereof. The probe comprises a hollow dialysis membrane and two different connecting pipes, wherein thetwo connecting pipes are respectively connected to both sides of the hollow dialysis membrane to be used as a liquid inlet pipe and a liquid outlet pipe, one end of one connecting pipe is burnt intoa pointed head so that the connecting pipe can conveniently penetrate into tissues, and connecting parts are well glued by gluewater; in the process of preparation, one metal wire penetrates through the dialysis membrane and the connecting pipes; when the probe is implanted, the dialysis membrane is supported by the metal wire and can not be bent, folded and broken; and after the probe is implanted, the metal wire is pulled out, the pointed head is nipped off, and perfusate can not be prevented from flowing. The invention has the advantage that the preparation process is simple; and when the probe is used, the thin pointed head penetrates into the tissues, the resistance force is low, and the dialysis membrane is not easily stressed to be bent and folded.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com