Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application
A technology for staphylococcus and staphylococcus infection, which is applied to Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophages and application fields, and can solve the problems of high specificity requirements of host bacteria and unpopularized bacteriophages.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Isolation and screening of phage SH-St 15644
[0027] Add a small amount of chloroform to the sewage samples from Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University and Shanghai Huashan Hospital, centrifuge at 4°C and 3500rpm for 10 minutes, take the supernatant, dilute it with SM Buffer appropriately, and take 10μl and 400μl of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria liquid (OD 600 =0.6) to mix, add the upper medium to mix, and pour the bottom medium to make a double-layer LB plate. Inverted after solidification, and incubated overnight in a 37°C incubator. If there are phage plaques on the plate, use a syringe needle to pick a typical, clear single phage plaque, add it to 1mL SM Buffer and crush it, place it on a shaker at 4°C for more than 4 hours, add 0.1mL chloroform to the tube, and centrifuge Take the supernatant and store it at 4°C. After repeated purification at least 3 times by the double-layer plate method (the shape and size...
Embodiment 2
[0028]Example 2 Purification of phage SH-St 15644
[0029] The phage SH-St 15644 culture fluid (10 6 PFU / mL) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (OD 600 =0.6,10 8 CFU / mL) were mixed and cultured at 37°C. On the next day, add 2% chloroform and let stand at 4°C for 1 hour, then centrifuge at 6500r / min for 15min at 4°C. DNase1 enzyme and RNase1 enzyme were added to the supernatant at a final concentration of 1 μg / mL, and left at room temperature for 30 minutes. Add NaCl to a final concentration of 0.5 M, and after 1 hour of ice-bath, centrifuge at 11,000 g for 10 minutes at 4°C. Take the supernatant, add solid PEG8000 to a final concentration of 10% (w / v), mix well and let stand at 4°C overnight. Take the mixture from the previous day, centrifuge at 4°C, 8500r / min for 20min, discard the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet with SM Buffer. Add an equal amount of chloroform and mix lightly for 30 seconds, centrifuge at 4000g for 10 minutes, and take the supernatan...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 Determination of phage SH-St 15644 titer
[0031] The titer of phage refers to the number of live phage contained in 1 mL of culture medium. The phage SH-St 15644 prepared in Example 2 was diluted to 10 with SM Buffer -7 、10 -8 、10 -9 After three gradients, take 10 μl and 400 μl of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria solution (OD 600 =0.6,10 8 CFU / mL) were mixed and added to the upper medium, then poured into the bottom medium to form a double-layer plate, and placed in a 37°C incubator overnight after it solidified. On the second day, count the number of plaques (calculation formula: titer (pfu / mL)=number of plaques×dilution factor×100).
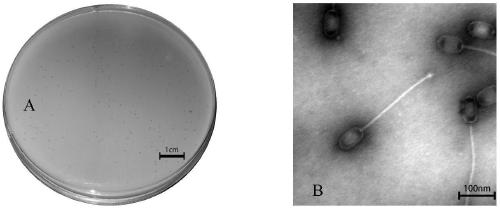
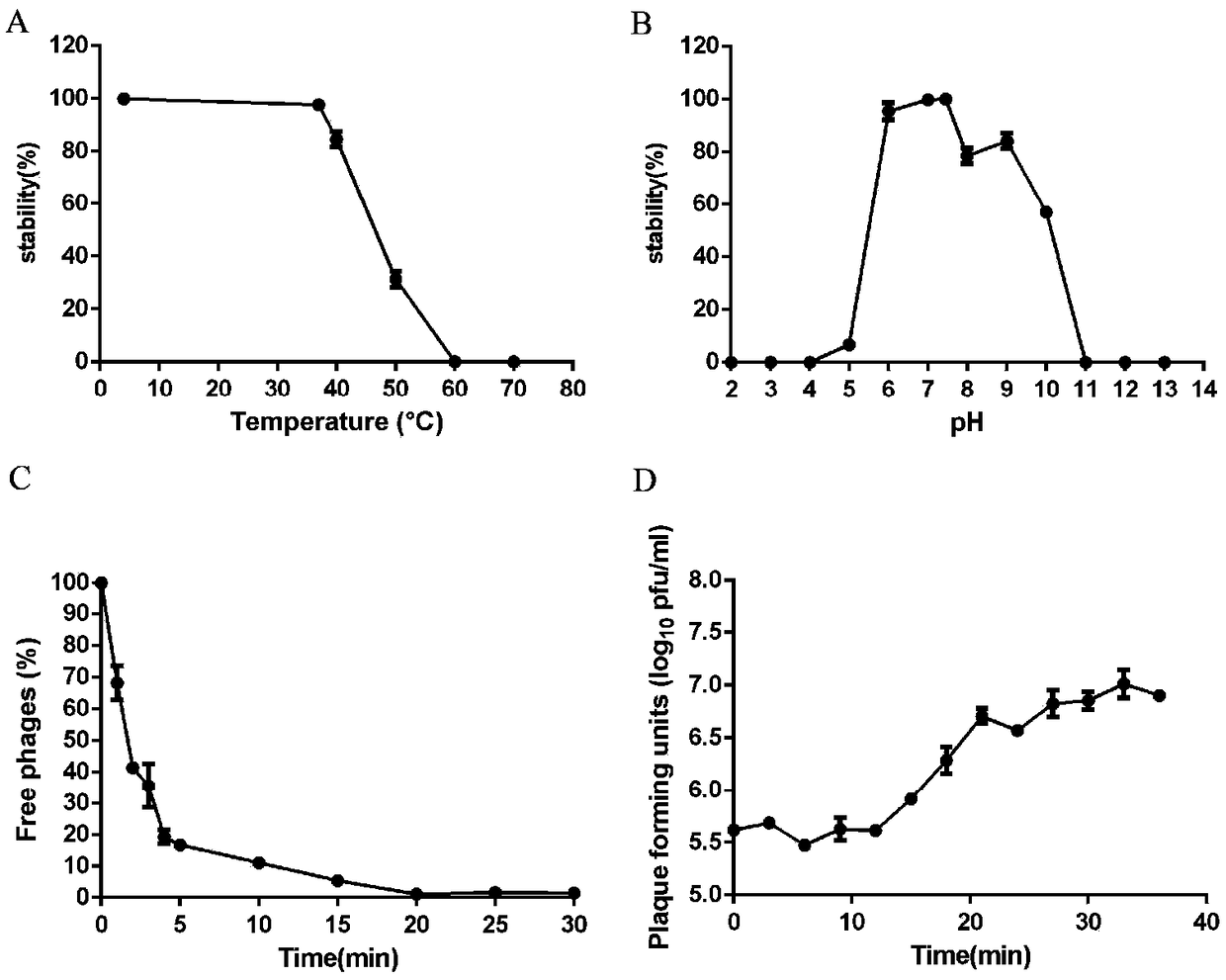
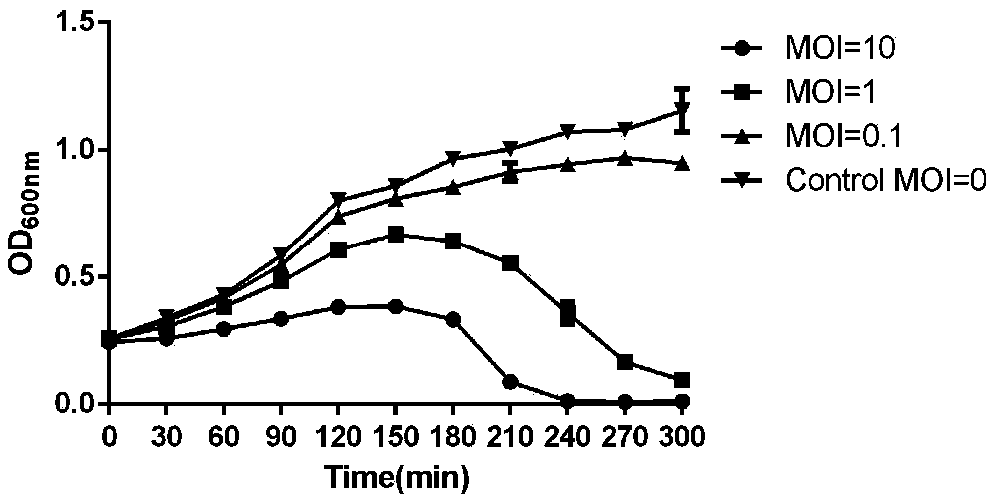
[0032] The diameter of plaques formed by SH-St 15644 infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus was about 0.5-1mm. Spots are round and transparent. see figure 1 In A, the titer of phage SH-St 15644 prepared in Example 2 was 2×10 11 pfu / mL.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Incubation period | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com