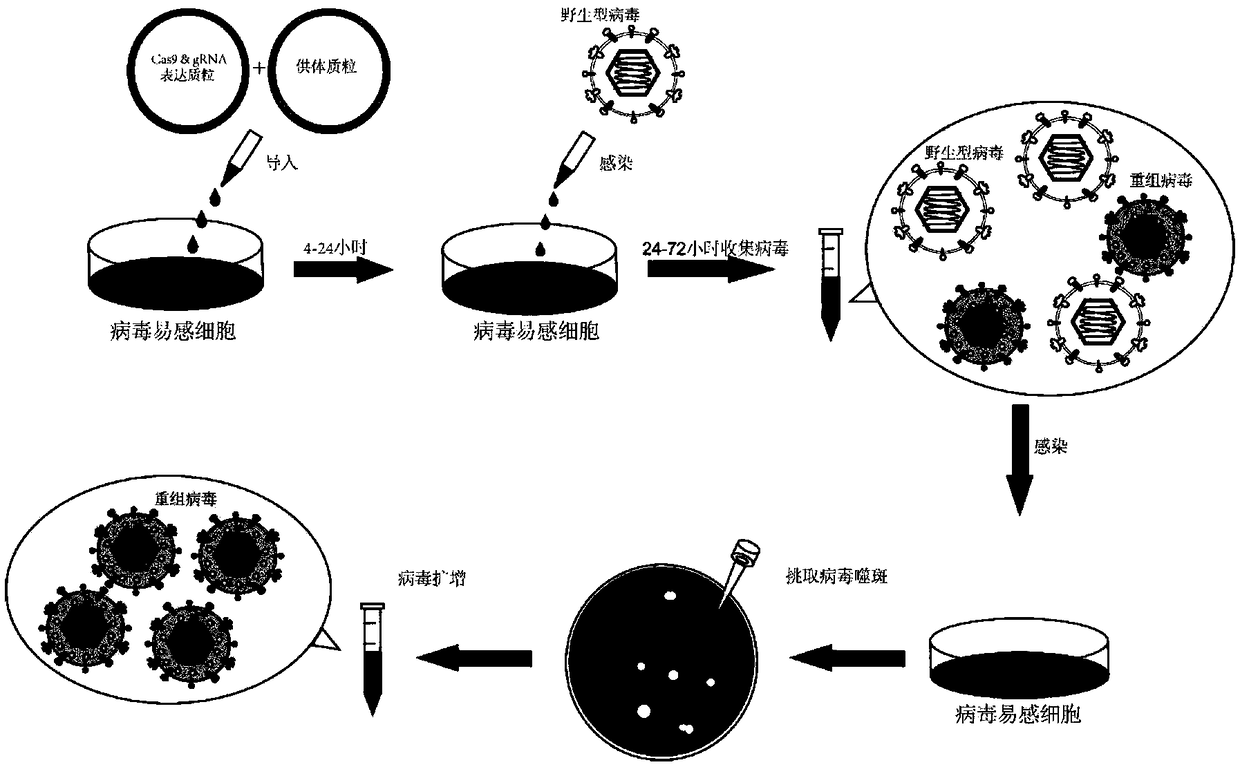
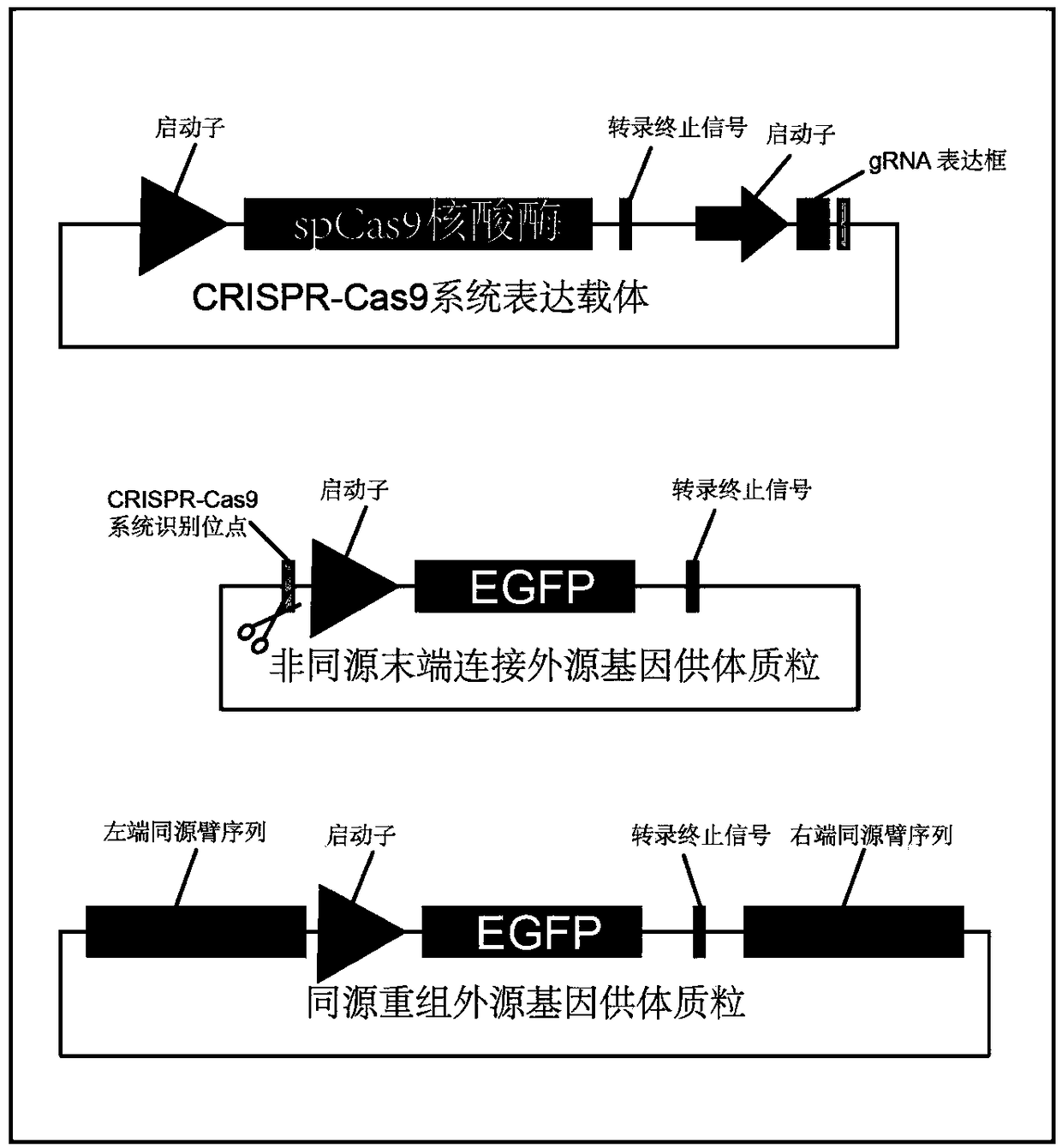
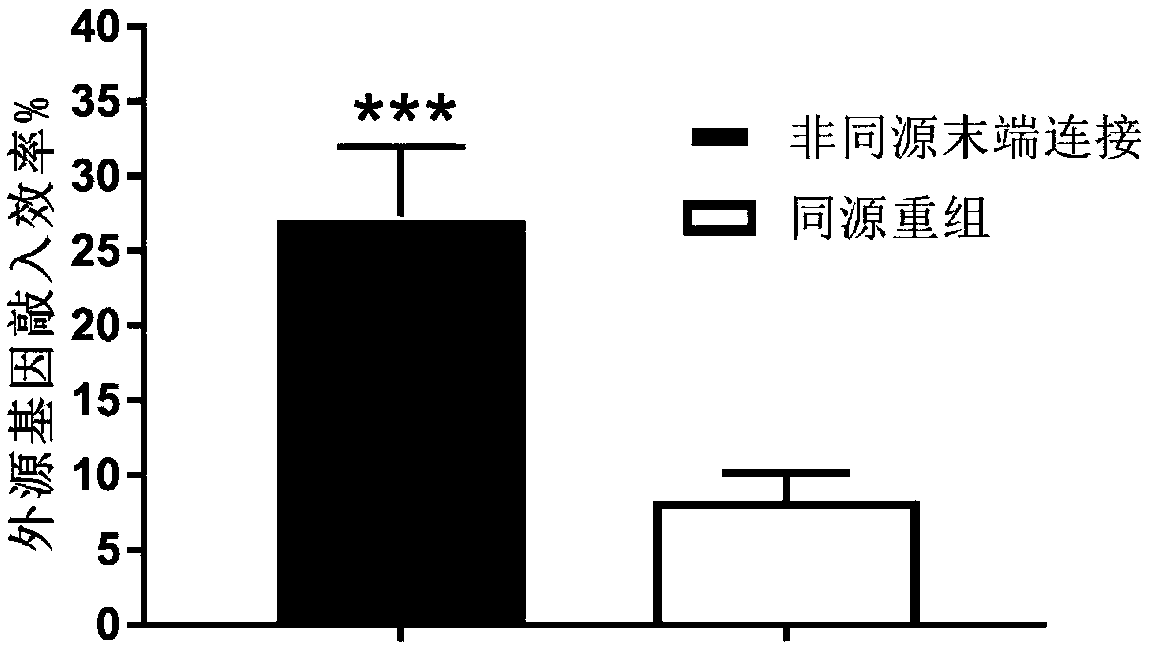
Method for inserting exogenous fragments into DNA virus genome in efficient, fixed-point and directional manner
A DNA virus and exogenous gene technology, applied in the field of efficient site-directed insertion of exogenous fragments into DNA virus genomes, can solve the problems of low occurrence frequency, large workload and low efficiency of mutants or recombinant viruses, and achieve high fidelity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example as Figure 2-Figure 3 Shown:
[0057] The enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter gene with promoter and transcription termination signal was inserted into the UL23 gene (thymidine kinase, TK) site of the type I herpes simplex virus genome to compare homology based on the CRISPR-Cas9 system The difference between recombination and non-homologous end joining in the integration efficiency of foreign genes:
[0058] 1. Selection of gene loci and construction of plasmids
[0059] (1). The selection of Cas9 protease cleavage site: in HSV1-8F strain (using the strain of type I herpes simplex virus (HSV1) to operate, this strain adopts existing method to separate and preserve, for example, use experiment The HSV1-8F virus subculture strain preserved in the laboratory is used for infection, and 8F is the code name of the virus strain.) In the whole genome sequence, the UL23 gene sequence is found, with NGG (N is any nucleotide sequence, G represents guanine...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example two such as Figure 4-Figure 8 Shown:
[0078] Using CRISPR / Cas9 technology to insert the firefly luciferin reporter gene with promoter into the UL23 gene (thymidine kinase, ThymidineKinease, TK) site of type I herpes simplex virus genome:
[0079] 1. Selection of gene loci and construction of plasmids
[0080] (1). The selection of Cas9 protease cleavage site: in HSV1-8F strain (using the strain of type I herpes simplex virus (HSV1) to operate, this strain adopts existing method to separate and preserve, for example, use experiment The HSV1-8F virus subculture strain preserved in the laboratory is used for infection, and 8F is the code name of the virus strain.) In the whole genome sequence, the UL23 gene sequence is found, with NGG (N is any nucleotide sequence, G represents guanine) Gene locus, and then find the sequence of 20 bases at the end of the gene locus, which is the gRNA sequence. The sequence selected in this example is GAGGGCGCAACGCCGTACGTCGG;
...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Embodiment three, such as Figure 9-Figure 14 Shown:
[0105] Using CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) was inserted into the C-terminus of the UL23 gene (thymidine kinase, TK) site of the clinically isolated type I herpes simplex virus genome for protein fusion expression:
[0106] 1. Selection of gene loci and construction of plasmids
[0107] (1). Selection of Cas9 protease cleavage site: in the HSV1-ZW6A strain (using the strain of type I herpes simplex virus (HSV1) to infect, this strain can be isolated and preserved by existing methods, for example, clinical isolation The clinical isolate of HSV1-ZW6A virus that was saved later was infected, and ZW6A is the code name of the virus strain.) The UL23 gene sequence was found in the whole genome sequence, with NGG (N is any nucleotide sequence, G represents guanine) The gene locus, and then find the sequence of 20 bases at the fifth end of the gene locus, which is the gRNA sequence. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com