Indoor identification method for resistance of peanut pods to Aspergillus flavus infection and application of indoor identification method
An indoor identification and Aspergillus flavus technology, applied in the direction of material inspection, food testing, etc., can solve the problems of microbial pollution, a large amount of labor, difficult peanut resistance level, etc., and achieve the effect of easy implementation and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
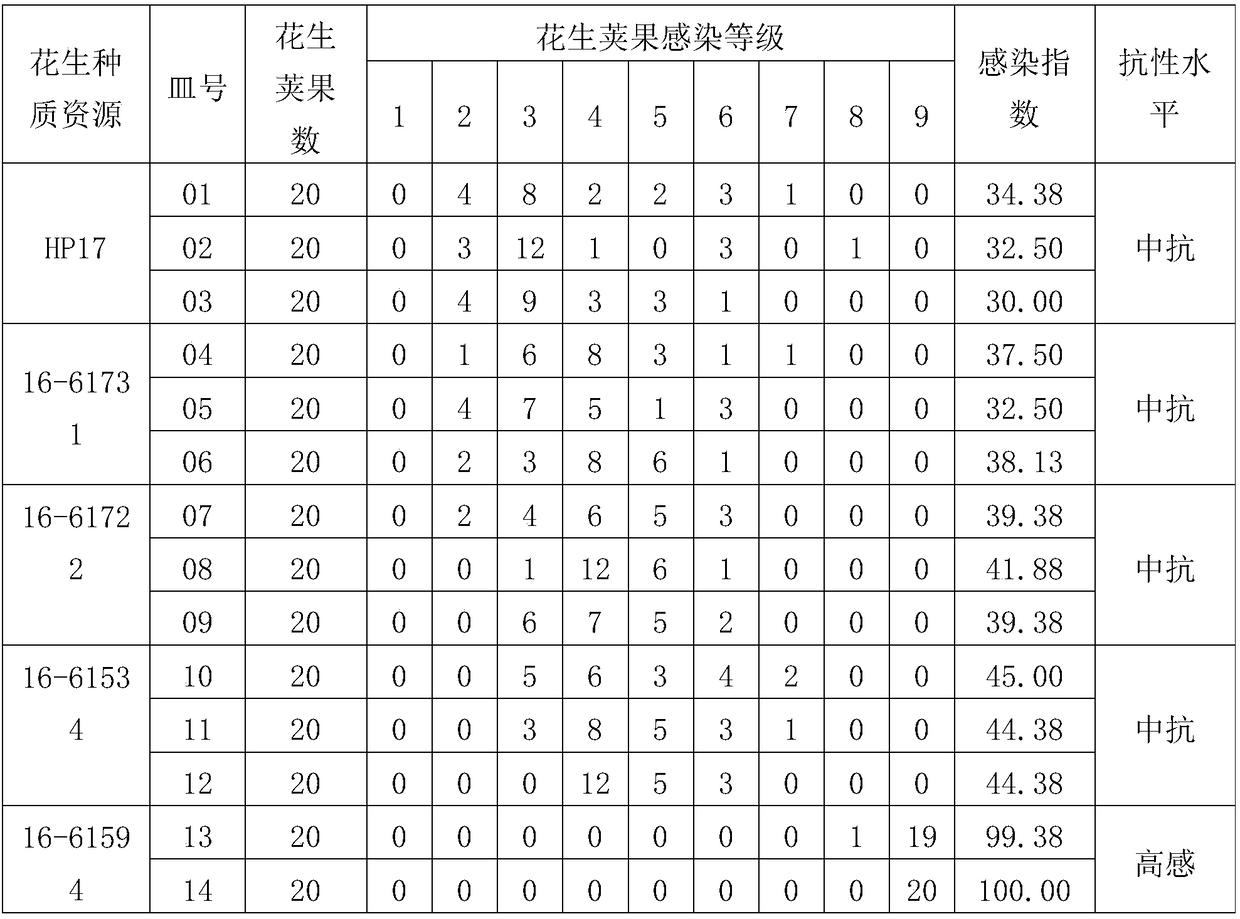
[0058] (1) Select the Aspergillus flavus strain: use the Aspergillus flavus strain AF2202 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) as the inoculation strain with high toxin production and strong infectivity; inoculate the Aspergillus flavus strain AF2202 in PDA medium, 30 ℃ dark Cultivate for 7 days, collect conidia with sterile mass concentration of 0.1% Tween 80 solution when inoculating, and resuspend conidia, adjust the concentration of spores to 2×10 6 spore / mL to obtain the Aspergillus flavus spore suspension (as the Aspergillus flavus spore inoculation suspension for subsequent use);
[0059] (2) Selection, sterilization and rehydration of peanut pods: Peanut germplasm resources HP17, 16-61731, 16-61722, 16-61534 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) were selected as test materials (ie peanut varieties) , high-sensitivity peanut germplasm resource 16-61594 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sci...
Embodiment 2
[0071](1) Select the Aspergillus flavus strain: use the Aspergillus flavus strain AF2202 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) as the inoculation strain with high toxin production and strong infectivity; inoculate the Aspergillus flavus strain AF2202 in PDA medium, 30 ℃ dark Cultivate for 7 days, collect conidia with sterile mass concentration of 0.1% Tween 80 solution when inoculating, and resuspend conidia, adjust the concentration of spores to 2×10 6 spore / mL to obtain the Aspergillus flavus spore suspension (as the Aspergillus flavus spore inoculation suspension for subsequent use);
[0072] (2) Selection, sterilization and rehydration of peanut pods: Peanut germplasm resources 16-61730, 16-61714, 16-61639, 16-61689 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) were selected as test materials. Peanut germplasm resource 16-61594 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) was used as a control. 60 hea...
Embodiment 3
[0082] (1) Select the Aspergillus flavus strain: use the Aspergillus flavus strain AF2202 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) as the inoculation strain with high toxin production and strong infectivity; inoculate the Aspergillus flavus strain AF2202 in PDA medium, 30 ℃ dark Cultivate for 7 days, collect conidia with sterile mass concentration of 0.1% Tween 80 solution when inoculating, and resuspend conidia, adjust the concentration of spores to 2×10 6 spore / mL to obtain the Aspergillus flavus spore suspension (as the Aspergillus flavus spore inoculation suspension for subsequent use);
[0083] (2) Selection, sterilization and rehydration of peanut pods: Peanut germplasm resources 16-61602, 16-61600, 16-61601, 16-61598 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) were selected as test materials. Peanut germplasm resource 16-61594 (Institute of Oil Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) was used as a control. 60 he...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com