Method for measuring content of live spores in fungal microbial pesticide quickly
A microbial pesticide, rapid determination technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as cumbersome operations, inability to distinguish target colonies and colonies of miscellaneous bacteria, affecting measurement results, etc., to achieve accurate detection. High accuracy, simple and rapid measurement, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
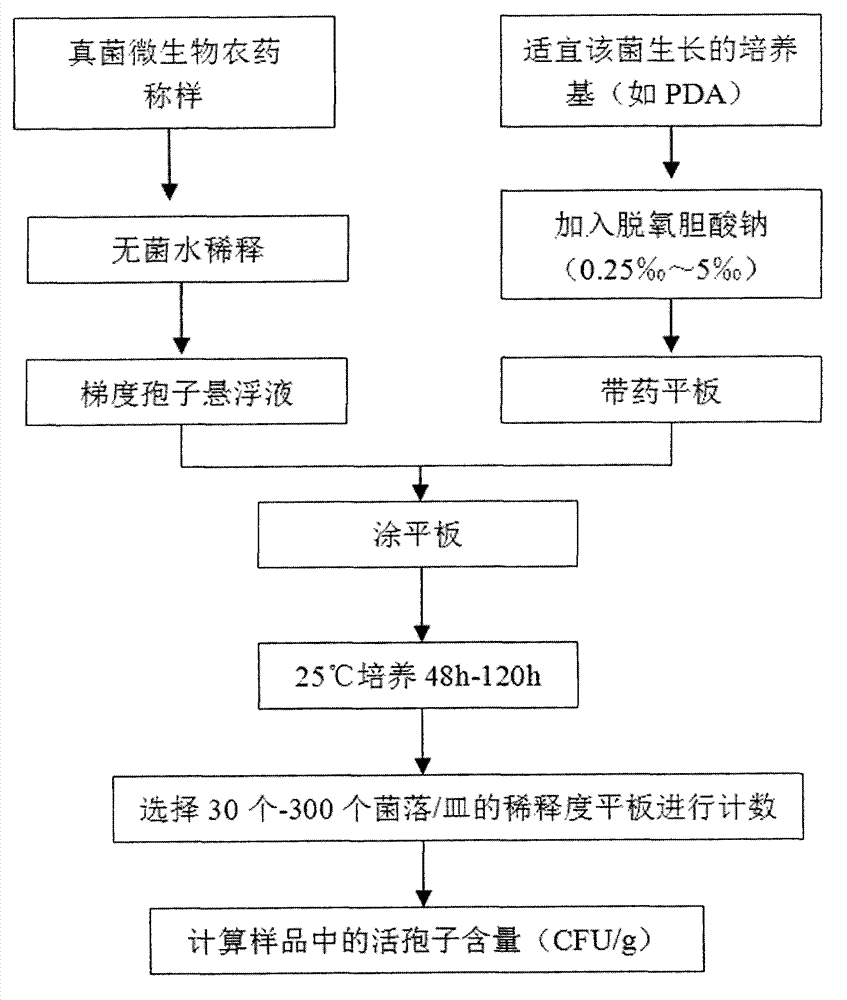
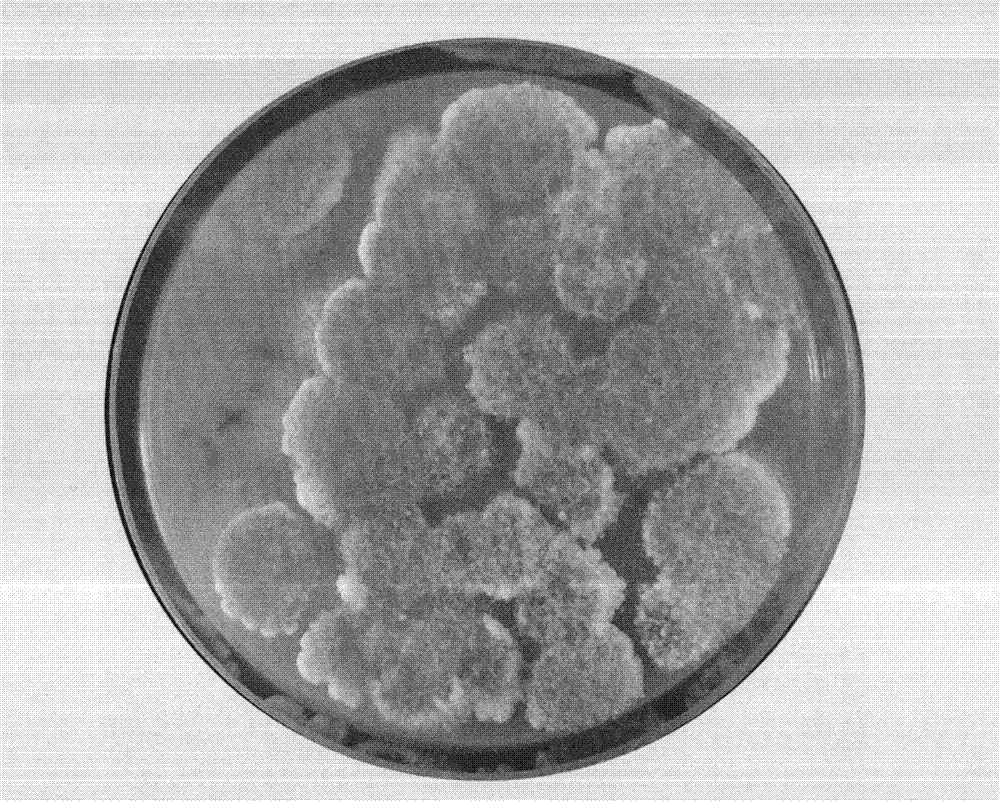
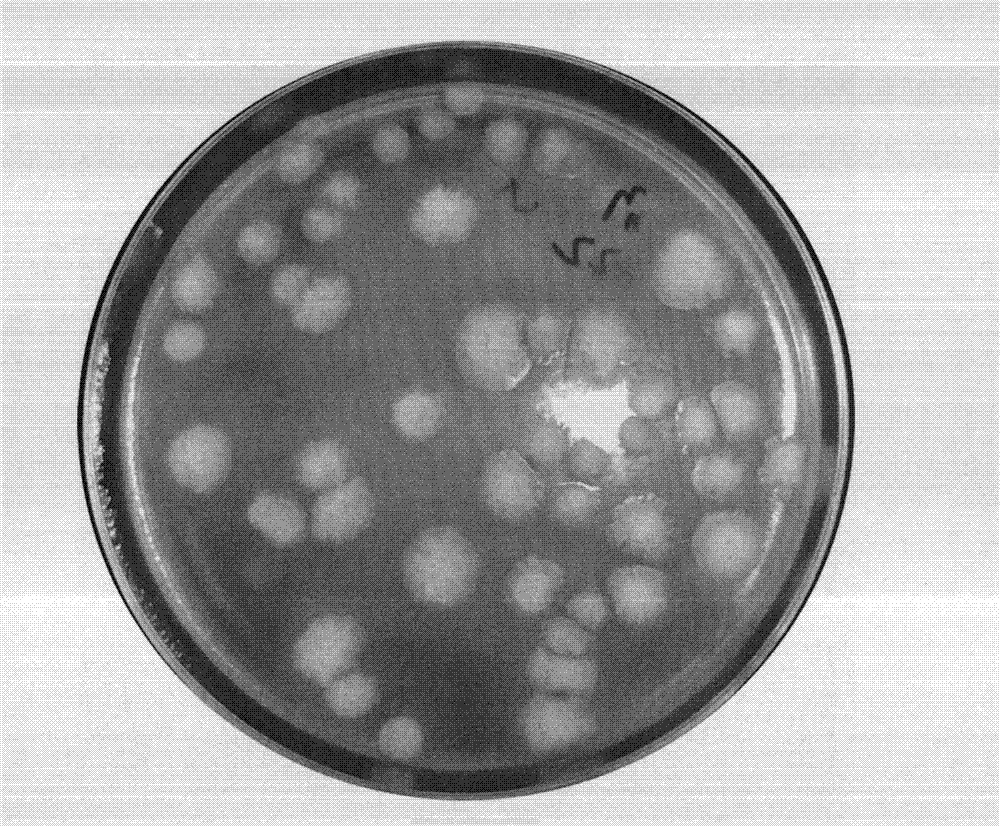
[0031] Example: using figure 1 According to the method shown, the viable spore content of Trichoderma wettable powder, Paecilomyces lilacinus wettable powder, Paecilomyces lilacinus liquid, and Beauveria bassiana parent drug were respectively determined. As embodiment 1 to embodiment 4.
[0032] The determination steps are as follows:
[0033] (1) Add 38g of potato dextrose agar powder (PDA) into 1000mL of distilled water, heat to boil, divide into 500mL Erlenmeyer flasks, after autoclaving, cool to about 60°C and prepare 0.25‰, 0.5‰, Sodium deoxycholate PDA plates with 1%, 2%, 5‰ content;
[0034] (2) Under aseptic conditions, stir the sample evenly, accurately weigh 3.0 g of the sample, dissolve it in 27.0 mL of sterile water containing 0.05% Tween20, soak it for 30 min, shake it for 30 min, and obtain a 10-fold diluted sample solution, Mark it as No. 0, and then perform serial dilutions, and set 3 replicate samples for each dilution;
[0035] (3) Take 100 μL of the abov...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com