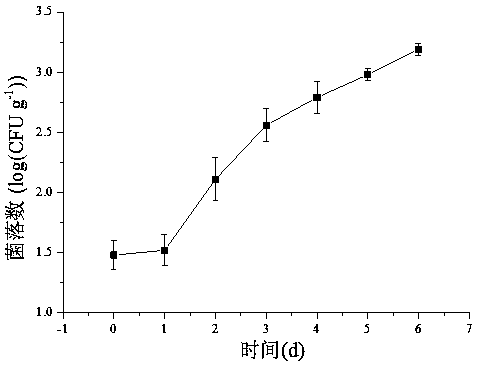
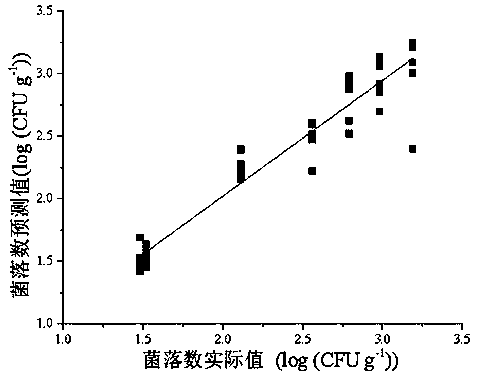
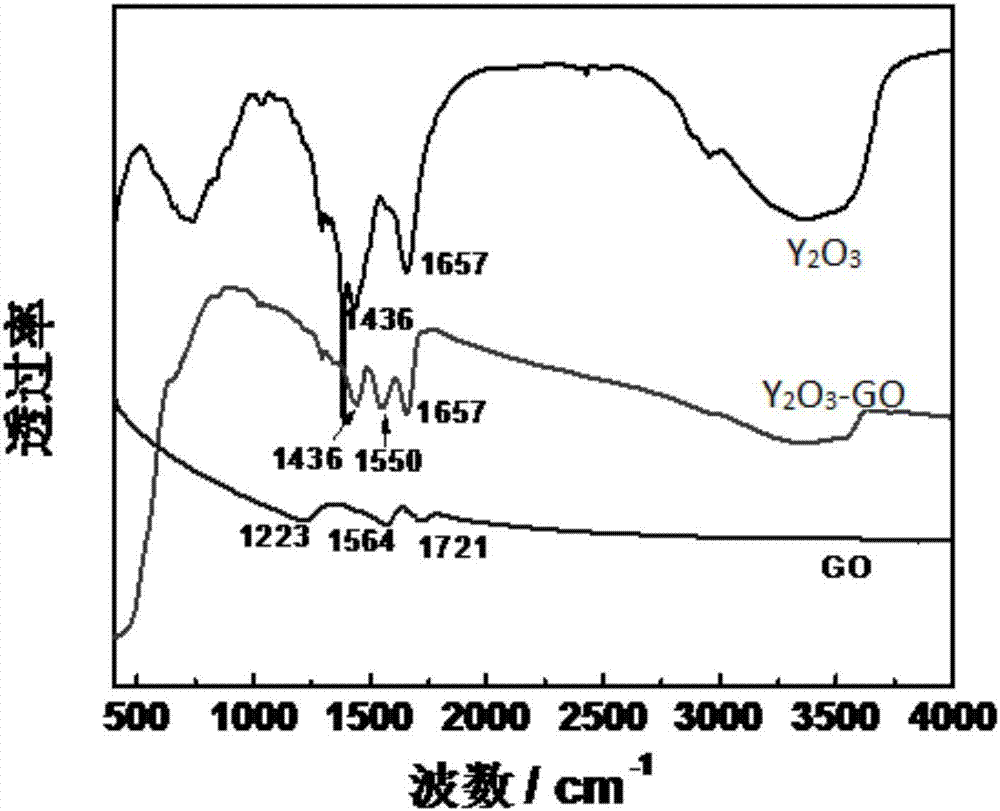
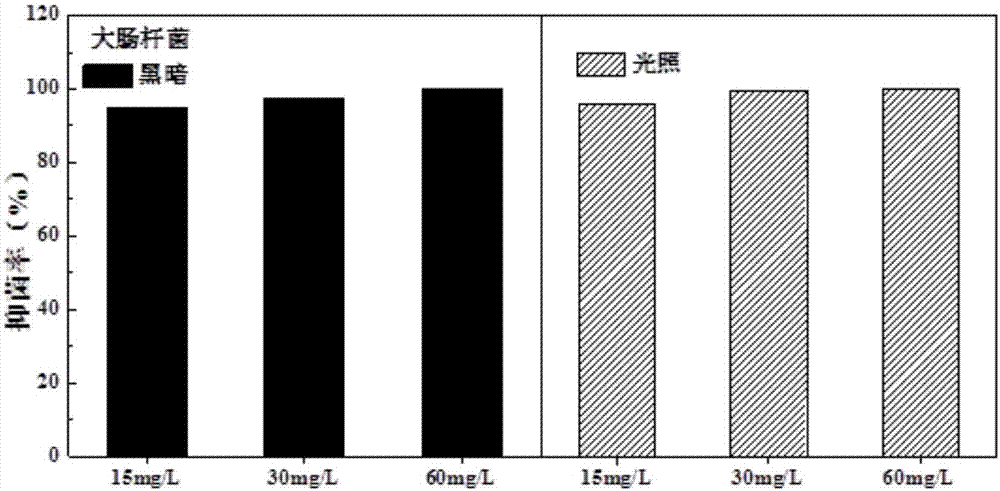
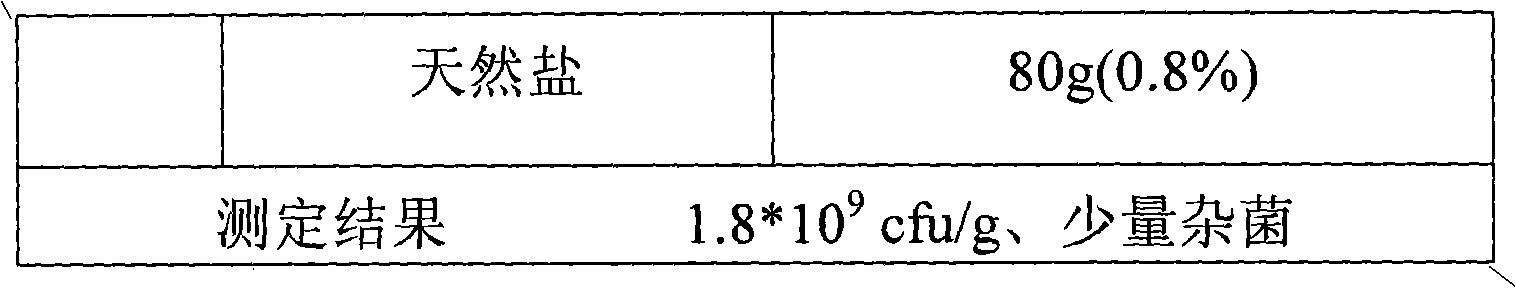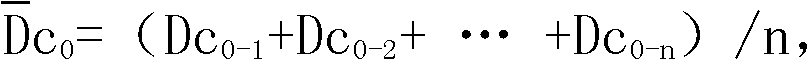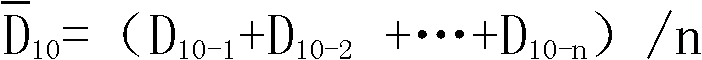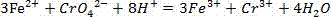Patents
Literature
91 results about "Plate count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plate count. noun. : a determination of the degree of bacterial contamination of a sample (as of milk or semen) made by enumeration after a period of incubation of the colonies appearing in a plate that has been inoculated with a suitable dilution of the sample.
Preparation of freeze-dried Lactobacillus acidophilus powder
ActiveCN101486986AActivity is not affectedStability is not affectedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of freeze dried microbial powder of Lactobacillus acidophilus, which comprises the technical processes of fermented cultivation of Lactobacillus acidophilus, separation of a fermented fluid, emulsification of microbial soil and vacuum freeze drying of an emulsified solution. The preparation method is characterized in that the strain fermented cultivation comprises the steps as follows: a lactobacillus strain is inoculated into a fluid culture medium in a triangular flask, cultivated at the temperature of 30 to 40 DEG C for 10 to 30 hours, inoculated into a large fermentation flask and fermentation cultivated at the temperature of 35 to 40 DEG C for 10 to 30 hours, and sterilized at the temperature of 115 DEG C for 15 minutes; and fermentation and augmentation cultivation is carried out for 10 to 30 hours, the pH value of the fermented fluid is 5.5 to 6.5, and OD600 is over 2.0; the vacuum freeze drying of the emulsified solution comprises the steps: the emulsified solution is pre-frozen at the temperature of minus 60 to minus 40 DEG C for 1 to 5 hours, and then vacuum frozen and dried at the temperature of minus 60 DEG C and with the vacuum degree of 1 to 8 Pa for 10 to 30 hours. The freeze dried microbial powder of Lactobacillus acidophilus with the total plate count of 1.0 multiplied by 10 cfu / g can be preserved for 18 months at the temperature of minus 18 DEG C with unaffected liveness and stability.
Owner:方曙光
Rapid and automated electrochemical method for detection of viable microbial pathogens
InactiveUS20040175780A1Quick checkImprove automationMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementBiotechnologyMicrobial disease
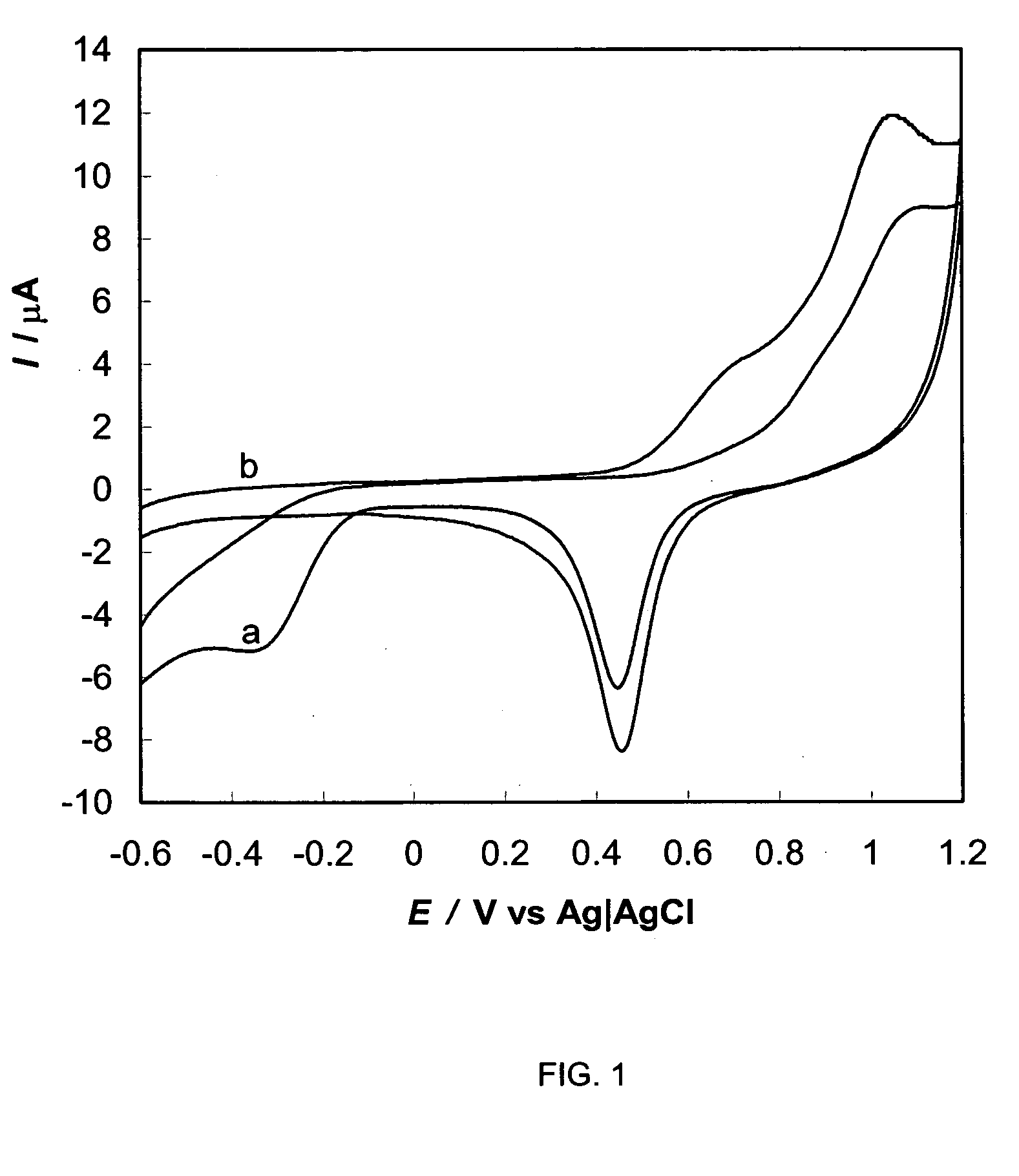
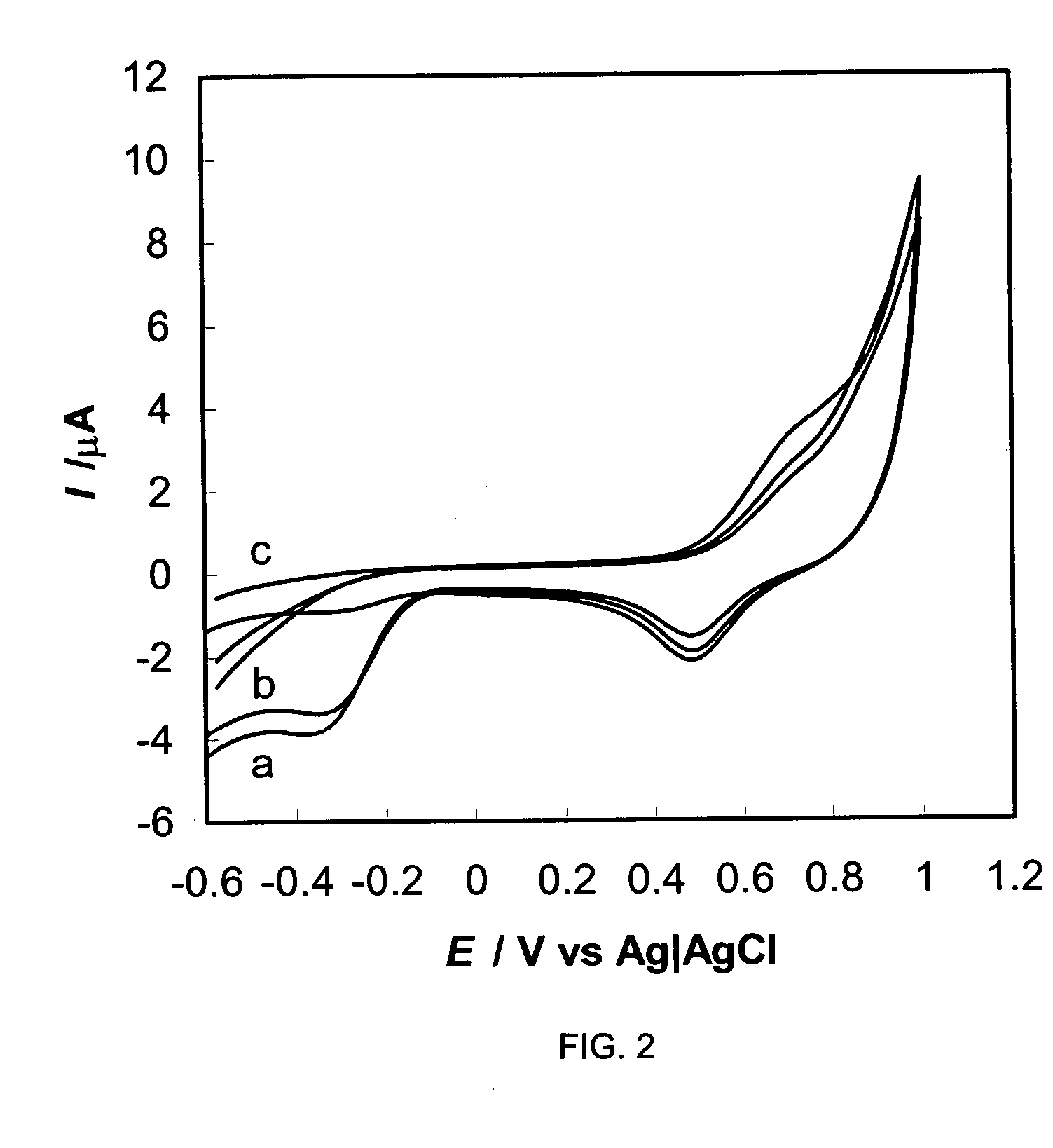
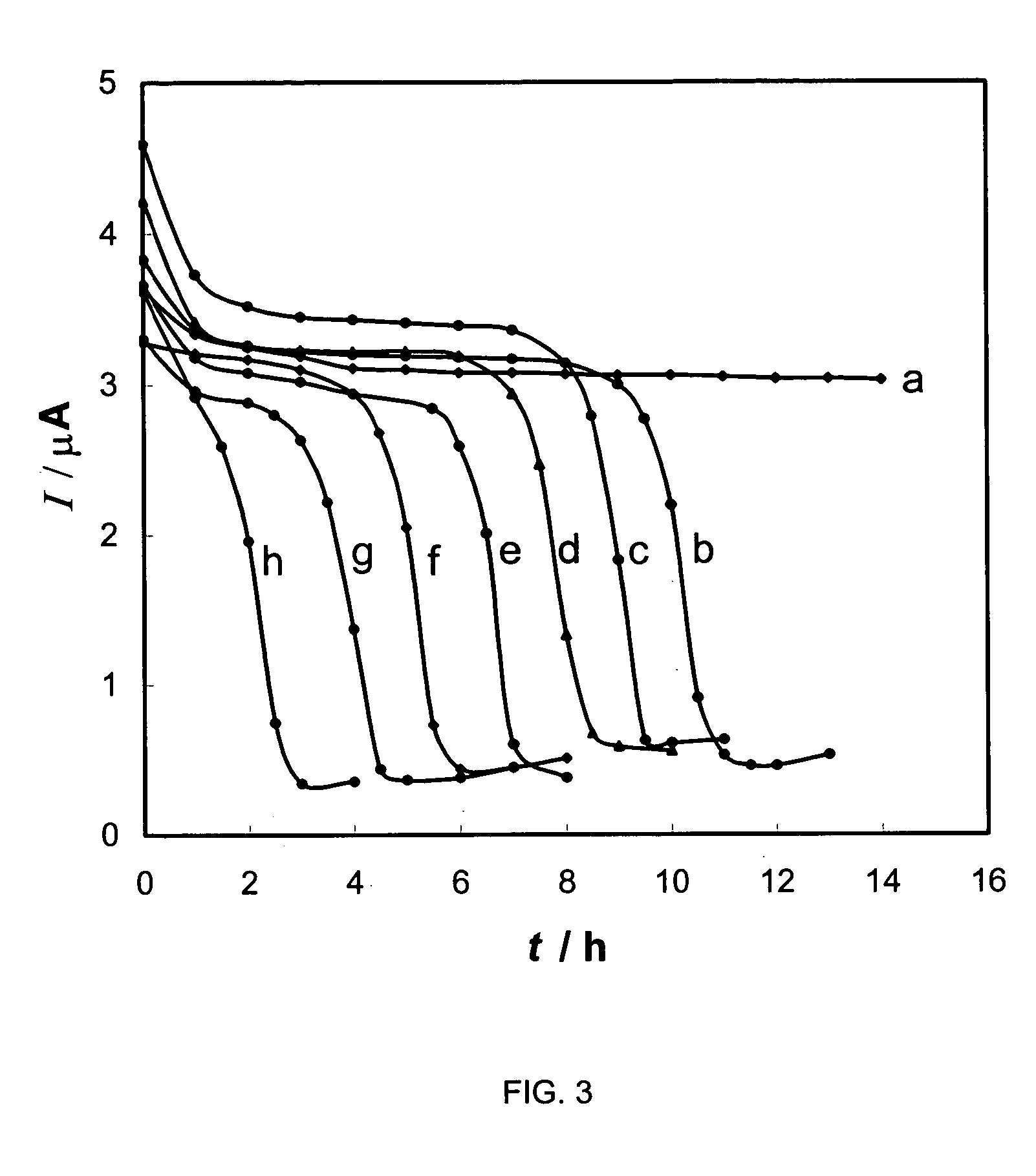
A method for in situ detection of viable pathogenic bacteria in a selective medium by measuring cathodic peak current of oxygen on cyclic voltammograms during bacterial proliferation with an electrochemical voltammetric analyzer. The rapid oxygen consumption at a time during the growth of bacteria resulted in a sharp decline of the cathodic peak current curves. The detection times (threshold values) obtained from the cathodic peak current curve were inversely related to the concentrations of the pathogenic bacteria in the medium. This method for detection of pathogenic bacteria is more sensitive than nucleic acid-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods and any of antibody-based methods such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technology, electrochemical immunoassays, immunosensors, and it has a sensitivity similar to conventional culture methods and impedimetric methods but is more rapid than both of them. A calibration curve was obtained by plotting initial cell concentrations (CFU / ml) determined by conventional plate counting, as a function of the detection time.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
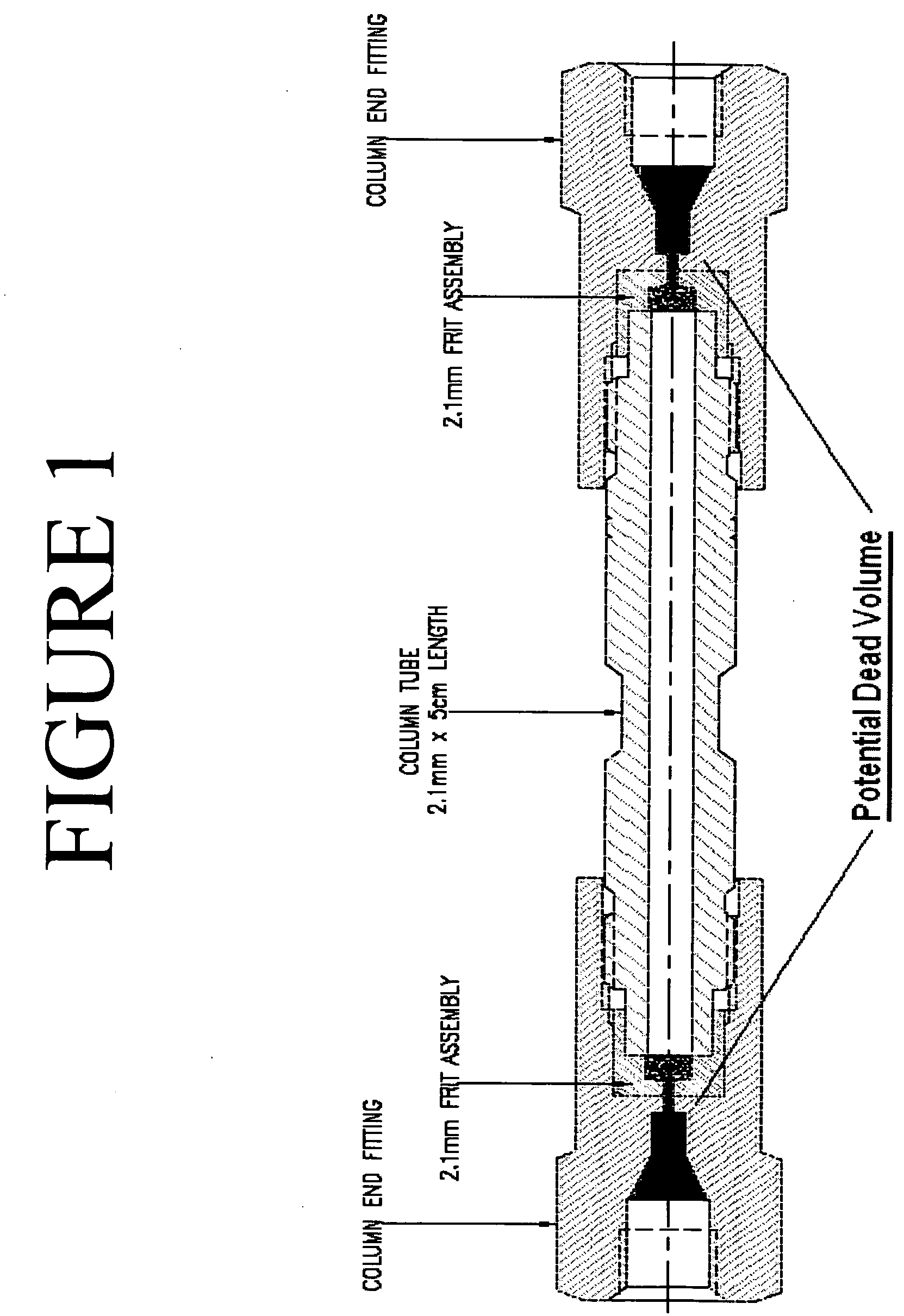
Accel-X™ HPLC column hardware
InactiveUS20060213823A1Avoid disruptionIncreased riskIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationPlate countEngineering
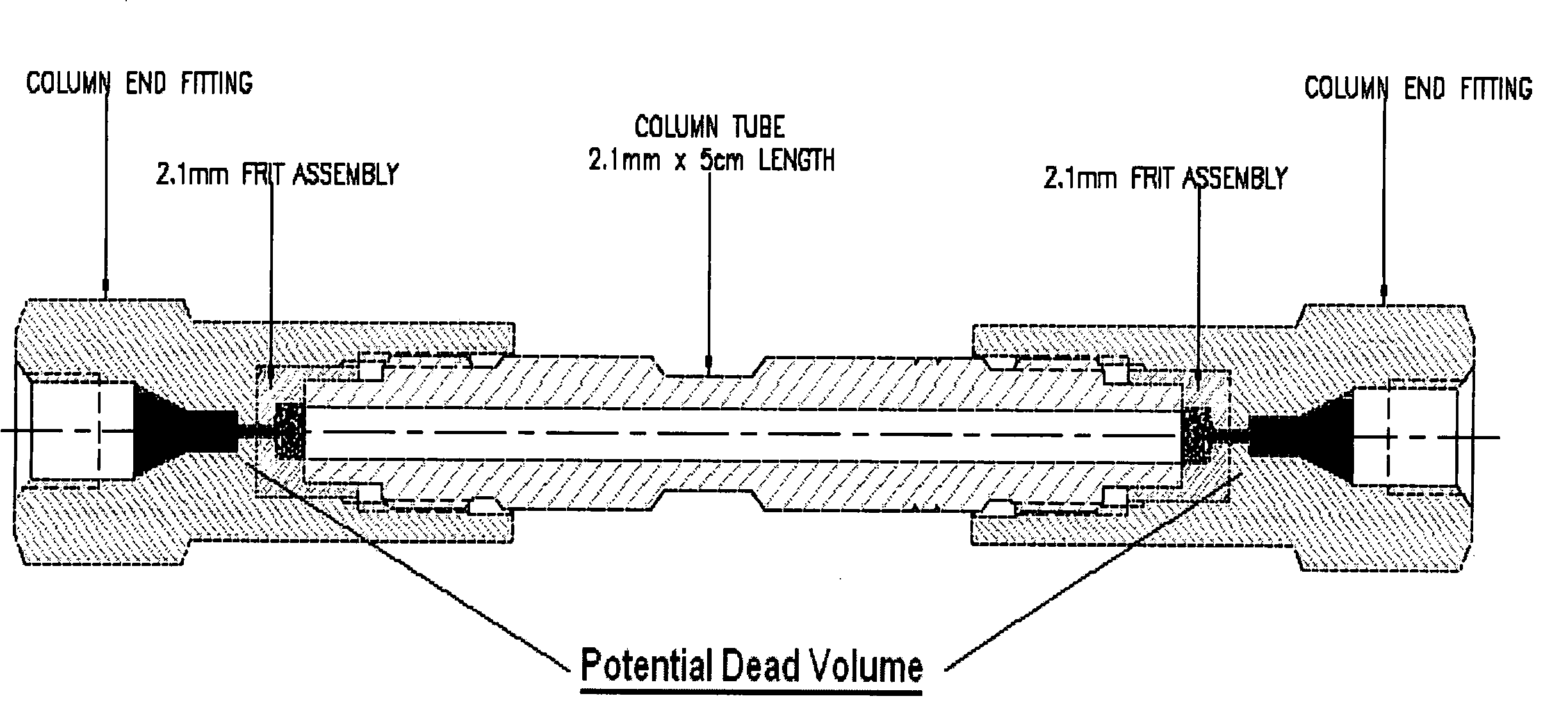
The present invention comprises the next generation of narrow bore HPLC Column Hardware. The inventors have developed and designed narrow bore column hardware that provides the ultimate configuration to obtain optimum peak shape, improved sensitivity and reduced backpressure. The improvements of the present invention comprise a new HPLC column hardware design that can be utilized to improve chromatographic performance as follows: reduced backpressure, reduced band broadening, and increased plate count.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENG
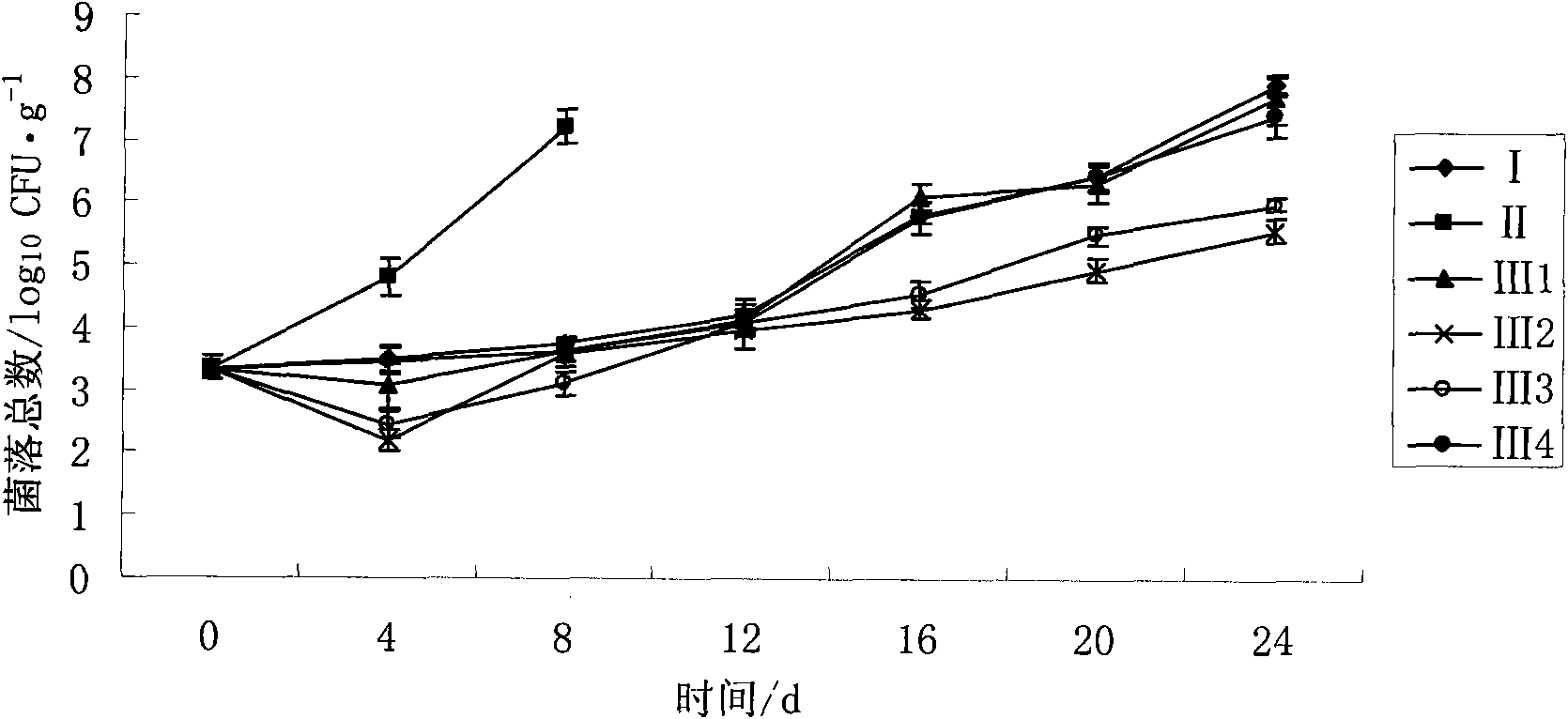
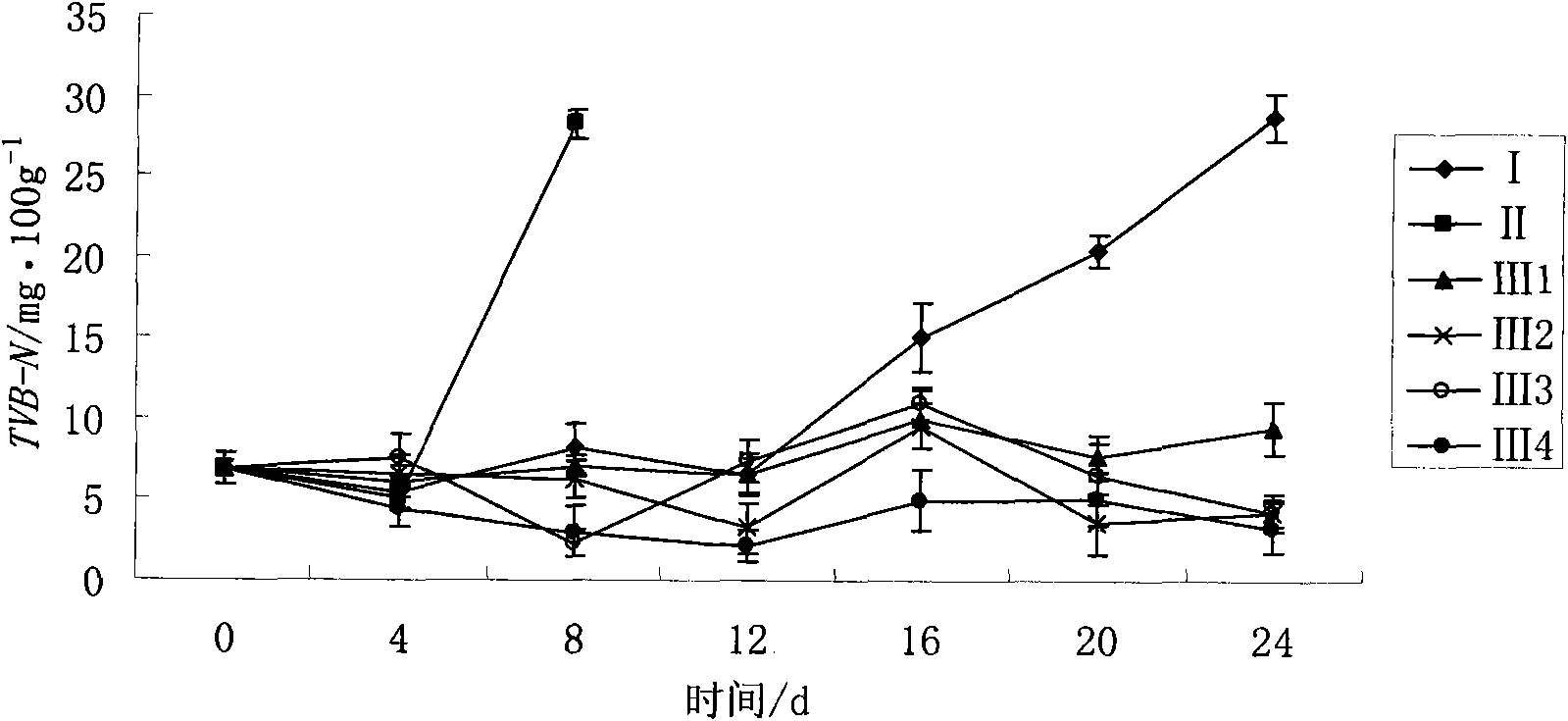
Method for prolonging cooled meat shelf period by combination of chilling and high concentration oxygen modified atmospheric packaging
InactiveCN101536706AMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsHigh concentrationLoss rate
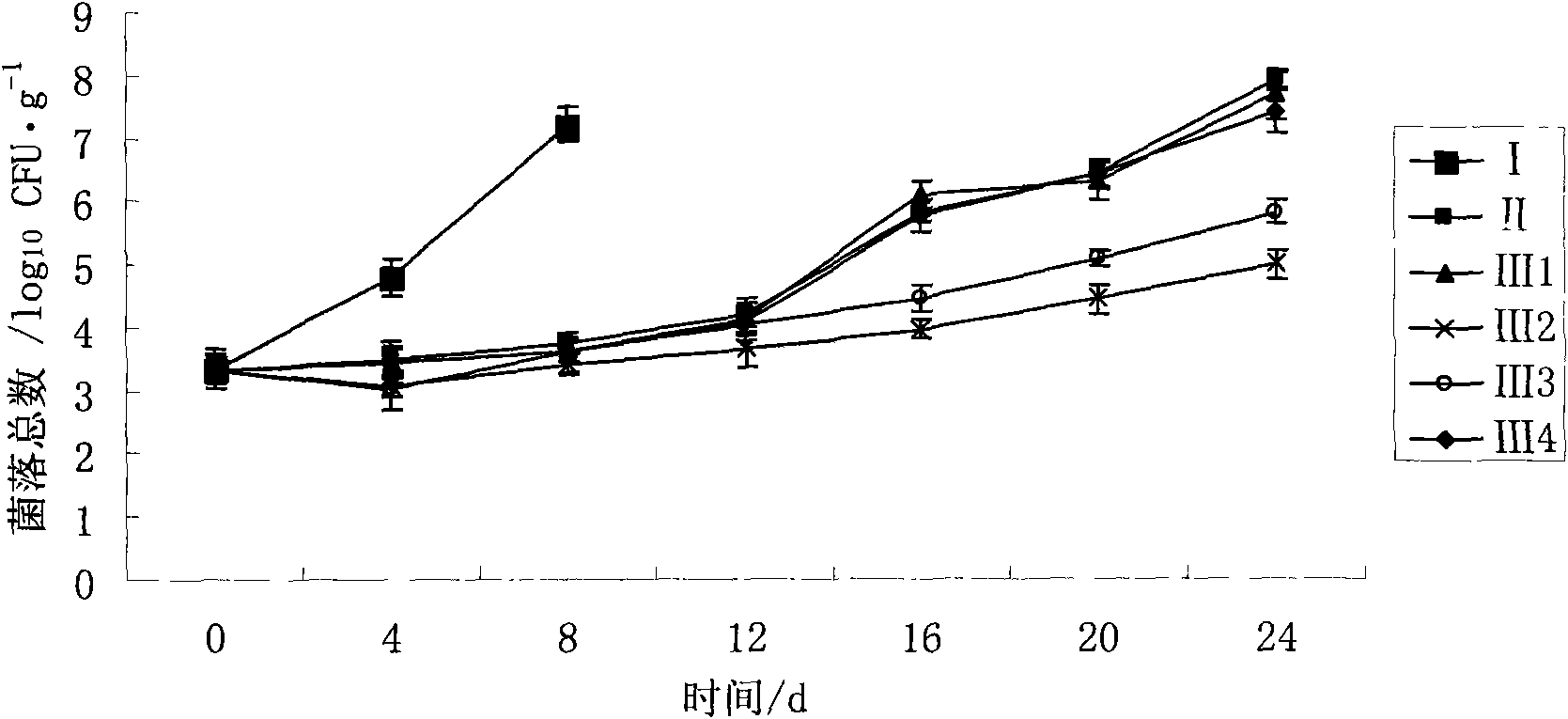
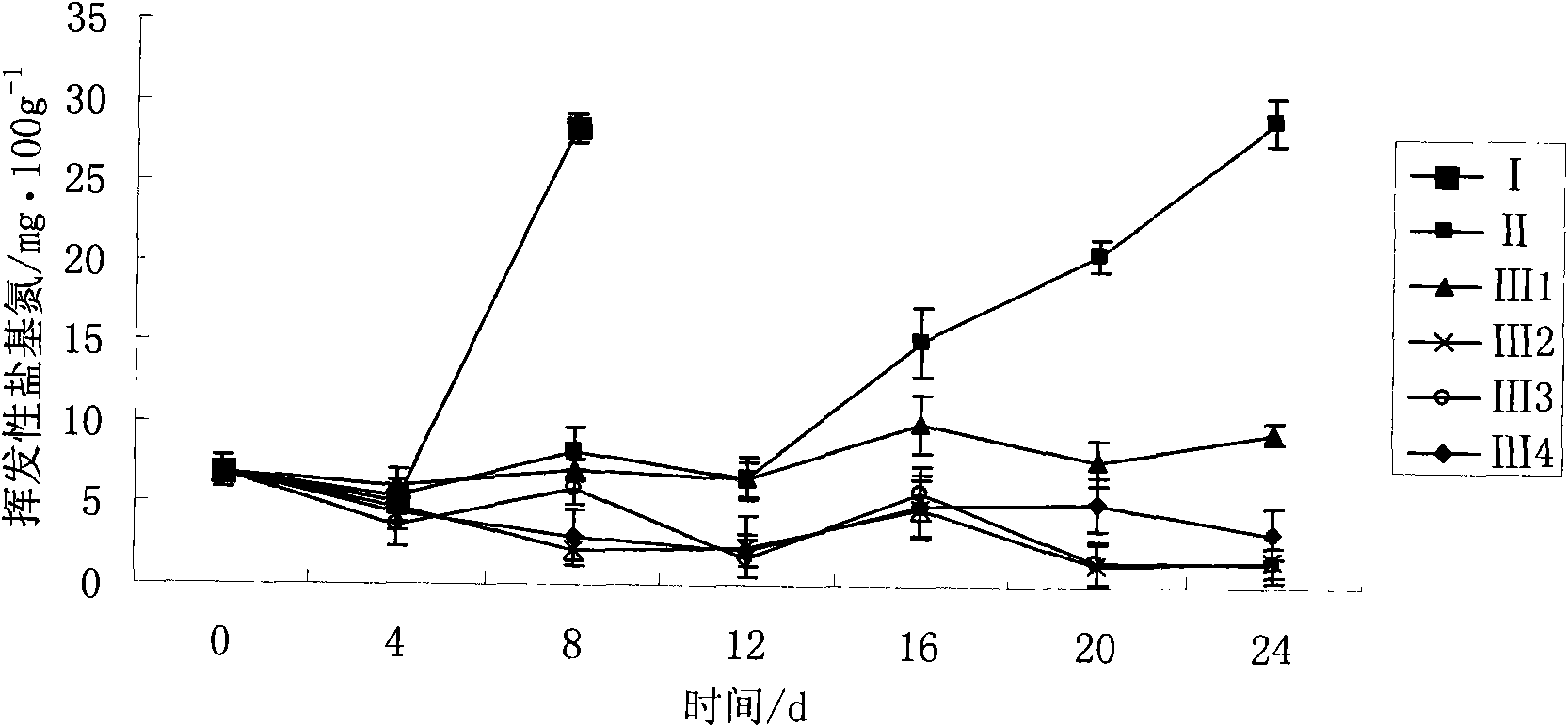
The invention discloses a method for prolonging cooled meat shelf period by combination of chilling and high concentration oxygen modified atmospheric packaging; the method is based on the study of the preservative effect of cooled meat by the combination of chilling and oxygen modified atmospheric of different concentration; the method sets up six experimental groups, comprising chilling, freezing(4 DEG C), vacuum packing and chilling, 20%CO2, 80%O2(hyperoxia) and chilling, 20%CO2, 20%O2, 60%N2 and chilling and 20%CO2, 80%N2(oxygen free) and chilling and measures total plate count, TVBN, drip loss rate, water retaining capacity and color difference. The invention has the following advantages: the total plate count 24d under the condition of chilling and high concentration oxygen does not exceed the health standard of cooled meat; high concentration oxygen modified atmospheric can maintain the color of cooled meat to change in a small range during the whole storage period; by using the method combining chilling and high concentration oxygen modified atmospheric packaging, the shelf period cooled meat can be prolonged and color of cooled meat can be maintained, and cooled meat can be kept fresh for above twenty four days.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method of identifying prebiotics and compositions containing the same
A high-throughput, tiered screening method of indentifying test agents that exhibit prebiotic activity on human skin commensal microorganisms and cosmetic compositions that include such agents. The method includes determining the metabolite level of a culture and comparing the metabolite level to a control value. The assay further comprises performing a plate count using the culture when the metabolite level of the culture is greater than its corresponding control value. The plate count results are compared to another control value, and the test agent is identified as a prebiotic agent when the number of colonies present in the plate count assay of the culture is greater than the second control value.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Pasteurized uncooked batters and refrigerated ready-to-bake batters, and the methods of manufacturing
Described are uncooked batters that have been effectively pasteurized and have no gelatinized starch. These batters are characterized as having low viscosity, a water activity of greater than 0.90, the absence of an active leavening agent, and a total plate count of less than 1000 per gram. There are two methods of manufacturing these pasteurized uncooked batters. One method uses irradiated flour and sterile aqueous liquid to make a pasteurized flour slurry; the other method uses a process of treating the whole grain at temperature and time conditions such that the exterior of grain is pasteurized followed by wet milling of the whole grain in a sterile aqueous liquid such that the slurry passes through a 20 mesh screen. In both methods, the farinaceous material remains uncooked and the starch has not been gelatinized. The pasteurized aqueous flour slurries, are then added to the pasteurized remaining ingredients of the batter in a sterile environment. Refrigerated Ready-to-Bake batters can be made by the addition of gas upon dispensing the batter from a container having the batter and a compressed gas such as carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, or nitrogen.
Owner:MITCHELL CHERYL R +1
Selective culture medium used for quantitative detection of bacillus
ActiveCN102127518AHigh selectivityFast and accurate quantitative detectionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a selective culture medium used for the quantitative detection of bacillus. Each litre of the selective culture medium comprises the following components: 1-10g of glucose, 1-5g of yeast extract, 5-10g of tryptone, 0.2-2g of calcium chloride, 0.1-1g of magnesium sulfate, 15-20g of agar and 100-500IU of bacteriostatic agent. Through variable temperature cultivation, the selective culture medium adopts can be used to increase the selectivity of the conventional plate counting method to bacillus, eliminate the influences of other microorganisms or impurities in s sample to be detected and achieve the aim of detecting bacillus fast and quantitatively.
Owner:清远海贝生物技术有限公司
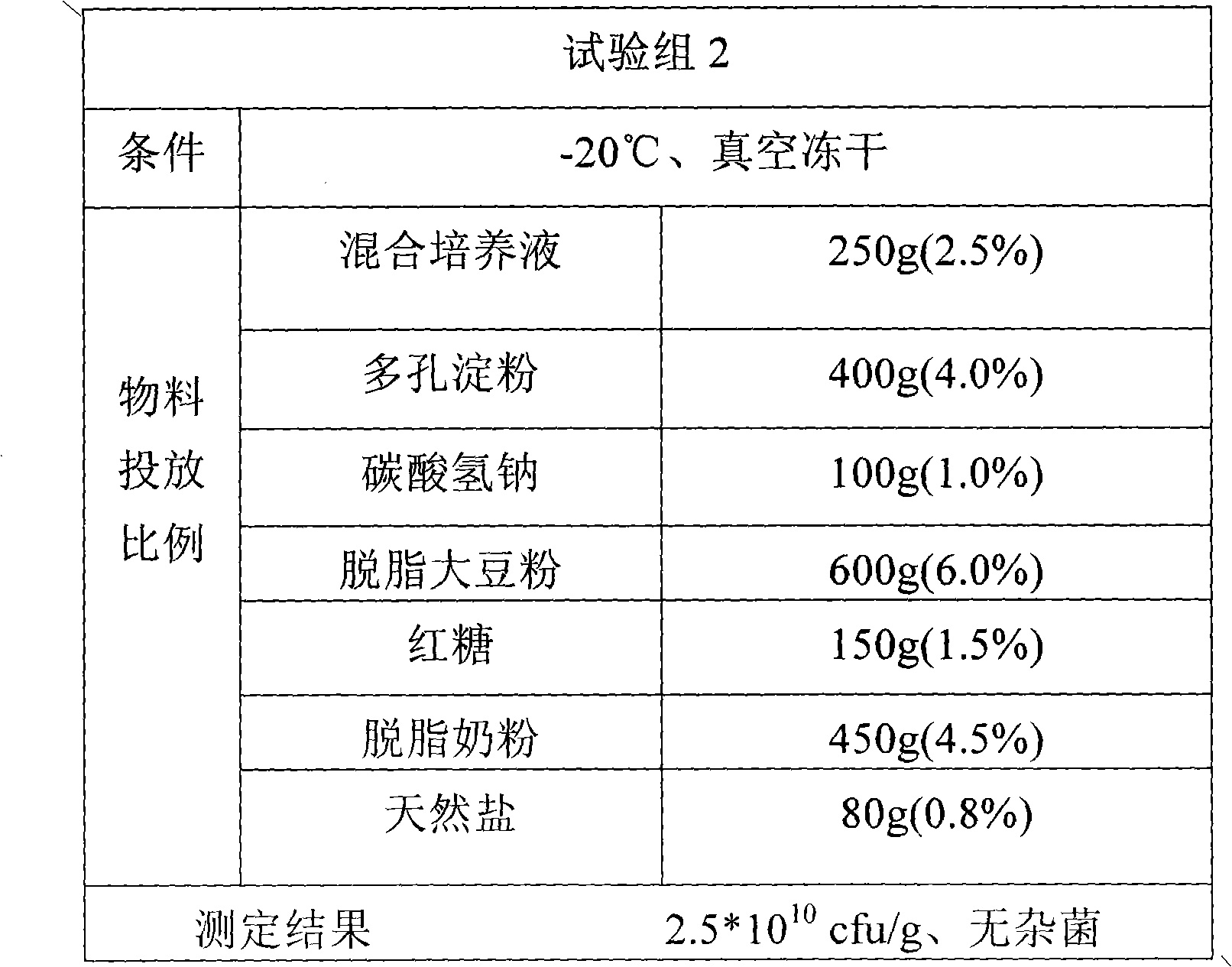
Probiotic powder and preparation method
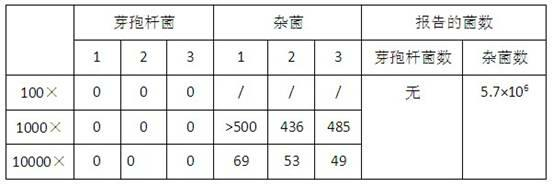
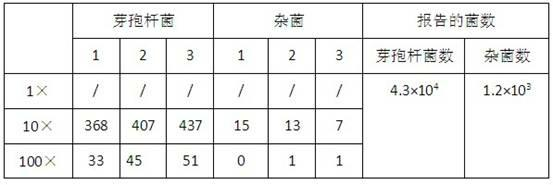
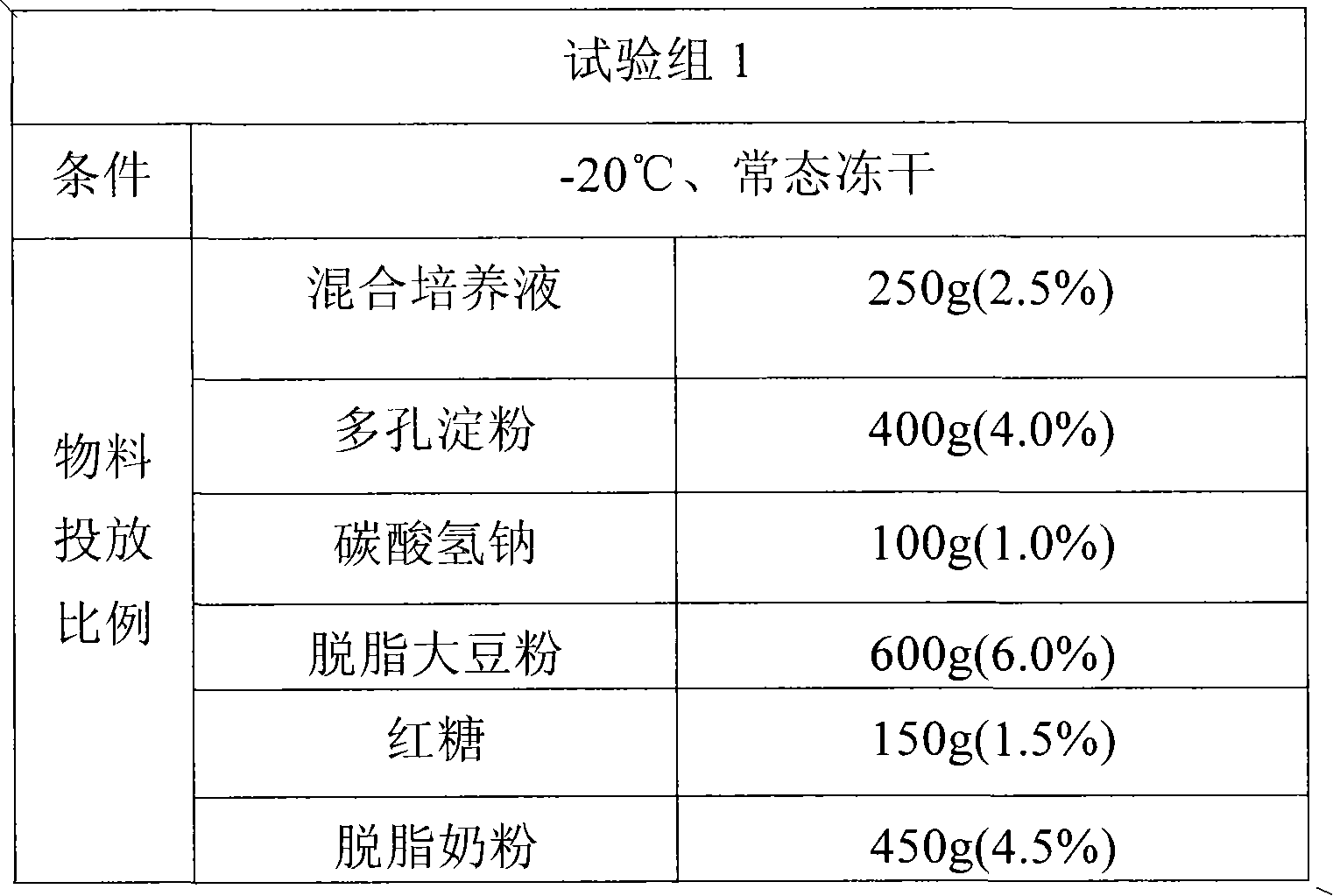
The invention provides dry probiotic powder. The probiotic powder is a probiotic mixture of microzyme, lactic acid bacteria and photosynthetic bacteria, wherein the mixing ratio of the microzyme, the lactic acid bacteria to the photosynthetic bacteria is 1-2:1-3:1; the total plate count is 1.5*109 to 1.2*1,010cfu / g; and the average grain size of the probiotic powder is 1 to 9um m. The invention relates to a process for culturing and preparing the probiotic mixture. A method for preparing the probiotic powder of which the average grain size is 1 to 9um m comprises the following steps of: preparing mixing probiotic culture by using three different kinds of probiotic culture solution, adding purified water, defatted milk powder, sodium bicarbonate, porous starch, defatted soybean powder, brown sugar and the like into the mixing probiotic culture, mixing and stirring the mixture, and performing propagation culture; and then performing freeze drying by using an ultralow temperature vacuum freeze drying machine to obtain the finished product. The preparation method has the advantages of simple production process and low production cost. The dry probiotic powder can be added into products such as foods and nutritional supplements and has a wide application range.
Owner:何黎明 +1
Preparation method of Bacillus strain and microbial inoculant thereof
ActiveCN104371954AImprove survival rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationHigh survival rateTemperature resistance
The invention provides a preparation method of a Bacillus strain and a microbial inoculant thereof. The strain is Bacillus FZUL-33 (Bacillus sp.), and was registered and collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 15th, 2014; and the collection number is CGMCC No.9523. The preparation method of the microbial inoculant comprises the following steps: activating and fermenting the strain to obtain a fermentation culture solution, mixing with additives, and carrying out spray drying to obtain the microbial inoculant. The microbial inoculant is used for degrading soil persistent pesticides. By using the characteristics of high temperature resistance and desiccation resistance of the Bacillus, the strain still has higher survival rate after being subjected to the microbial inoculant preparation process of spray drying; and a plate count process detects that the survival rate of the microbial inoculant is up to higher than 70% and the viable count is greater than 10<10> cfu / g.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV +1
Method for judging irradiation of product and dosage thereof
InactiveCN102012378AExpand the species that can be detectedReduce incidenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimetersAquatic productQuarantine
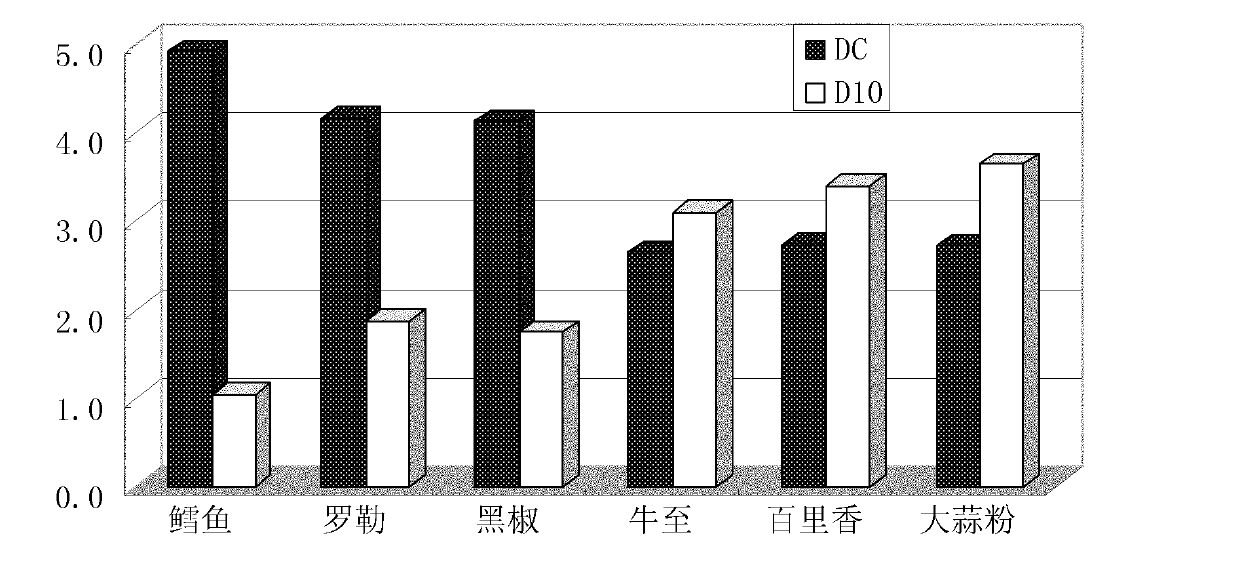
The invention relates to a method for judging the irradiation of a product and the dosage thereof, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly acquiring the mean value D0 of an unirradiated product with a direct epifluorescent filter technique (DEFT) and an aerobic plate count (APC) method, and meanwhile, determining the mean value D10 of same class products, wherein the mean value D0 is equal (Dc(0-1)+Dc(0-2)+......Dc(0-n)) / n, and the mean value D10 is equal to (Dc(10-1)+Dc(10-2)+......Dc(10-n)) / n; and setting four classes of judging standards by taking the difference value between Dc and the mean value of Dc0 of a detected sample as a judging reference, thereby achieving the purpose of detecting the irradiation of an actual product and the dosage thereof. The method can enhance the sensitivity and the accuracy of the traditional DEFT / APC method on detecting irradiated products and has important application value for an irradiation enterprise on daily controlling the quality of the irradiated product and a food production enterprise, a food sanitation supervision department and an import and export quarantine department on monitoring the quality safety of irradiated agricultural products (seasonings, dehydrated vegetables, aquatic products, and the like).
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
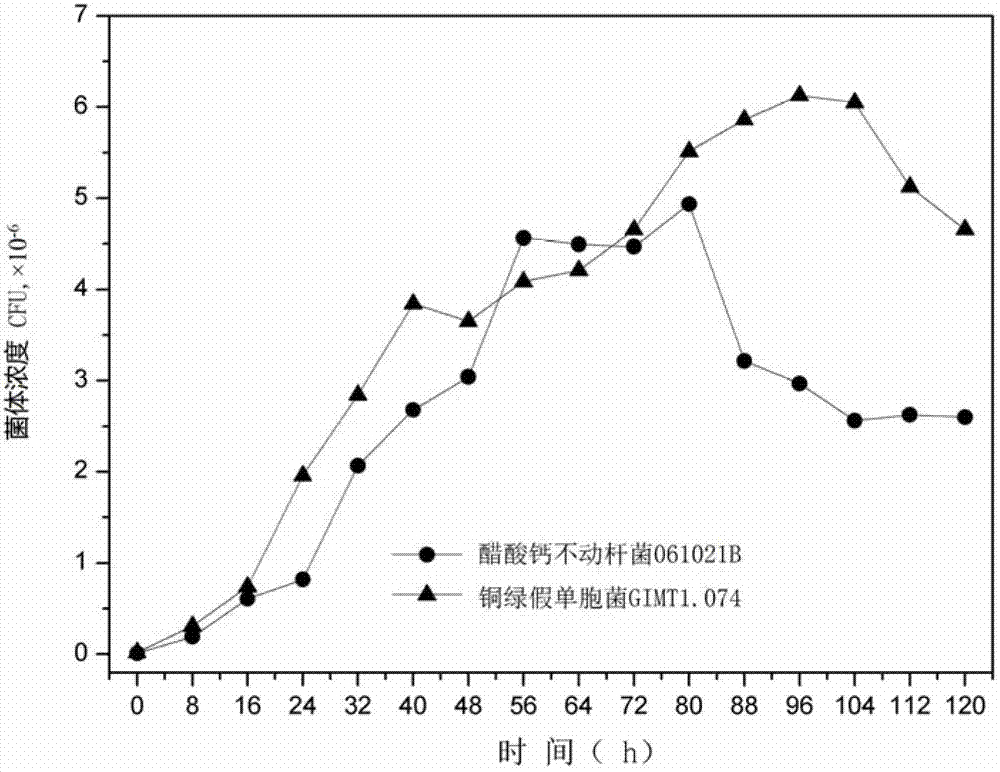
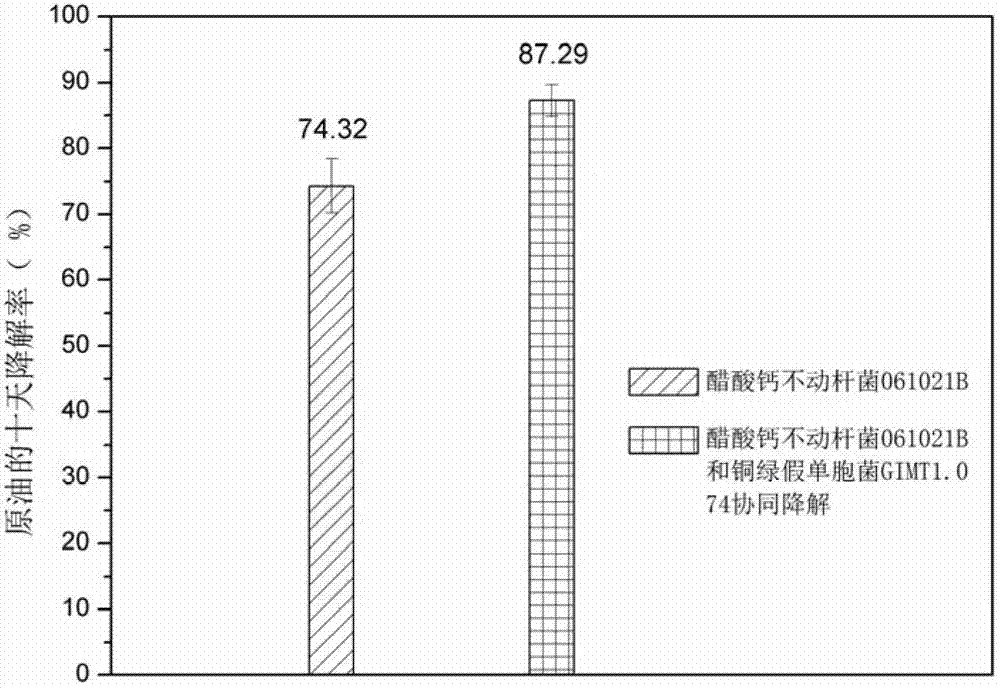
Method for studying synergistic effect of surfactant producing bacteria on petroleum degradation
InactiveCN102899381AImprove degradation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGlycerolPlate count
The invention relates to a method for studying synergistic effect of surfactant producing bacteria on petroleum degradation. According to the method, a mineral culture medium for use in degradation experiments is prepared; and Pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074 is capable of producing surfactant in a mineral culture medium with glycerol as the only carbon source. Pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074 and acinetobacter calcoaceticus 061021B are inoculated with the initial OD600 being 0.01, and three groups of parallel tests are carried out respectively; according to the distinct phenotype of pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074 and acinetobacter calcoaceticus 061021B in a panel, the number of each kind of bacteria at corresponding moment is obtained by a plate count method, and the synergistic effect of pseudomonas aeruginosa GIMT1.074 and acinetobacter calcoaceticus 061021B in petroleum degradation is studied. The degradation rate of petroleum pollutants is improved by 12.83% due to the synergistic effect of the two strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of biological preservative for Penaeus vannamei
ActiveCN102389151AExtended shelf lifeSlow down the speed of blackeningFood preservationAdditive ingredientPhytic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of a biological preservative for Penaeus vannamei. The compound biological preservative contains the following ingredients in percentage by weight: 0.06% of phytic acid, 0.15% of glucose oxidase, 0.02% of lysozyme and the balance of water. The solution of the compound biological preservative is processed into ice cubes by using an ice-making machine, the volume of the ice cube is 1 cm*1 cm*1 cm, and the ice cubes made of the preservative solution are used for keeping Penaeus vannamei fresh. According to the sensory evaluation of Penaeus vannamei and the detections of pH, total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N), total plate count and trimethylamine indices, the biological preservative is proved to effectively prevent spoilage and deterioration of Penaeus vannamei and prevent browning due to oxidation. Compared with the cold-storage using pure-water ice cubes, the shelf life of Penaeus vannamei is increased by 7 to 8 days. The preparation of the preservative solution is simple and feasible, the storage using the ice cubes is well controlled within the ice-temperature range, and the method has a certain value for application and promotion.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
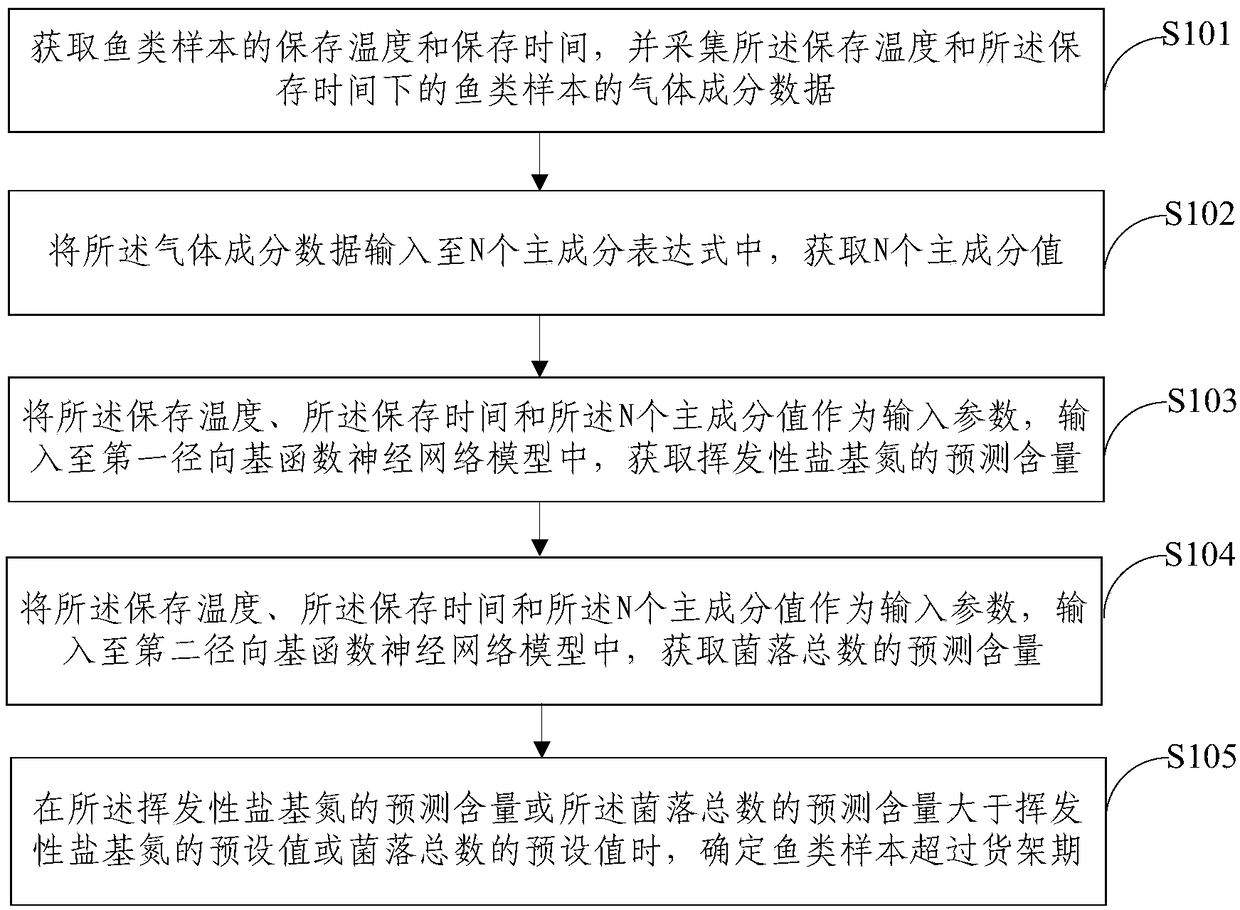
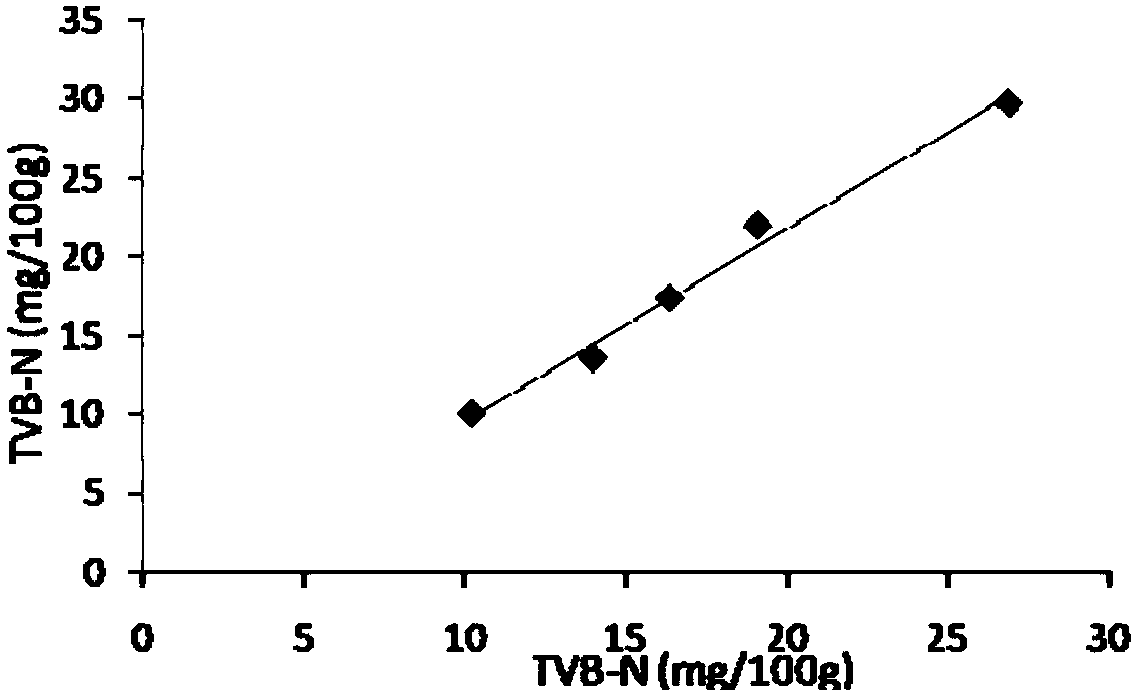
Method and device for judging fish shelf life
ActiveCN108254513AFast freshnessFast shelf lifeTesting foodNeural learning methodsNon destructiveLogistics management
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Method for predicting the shelf period of fresh pomfret
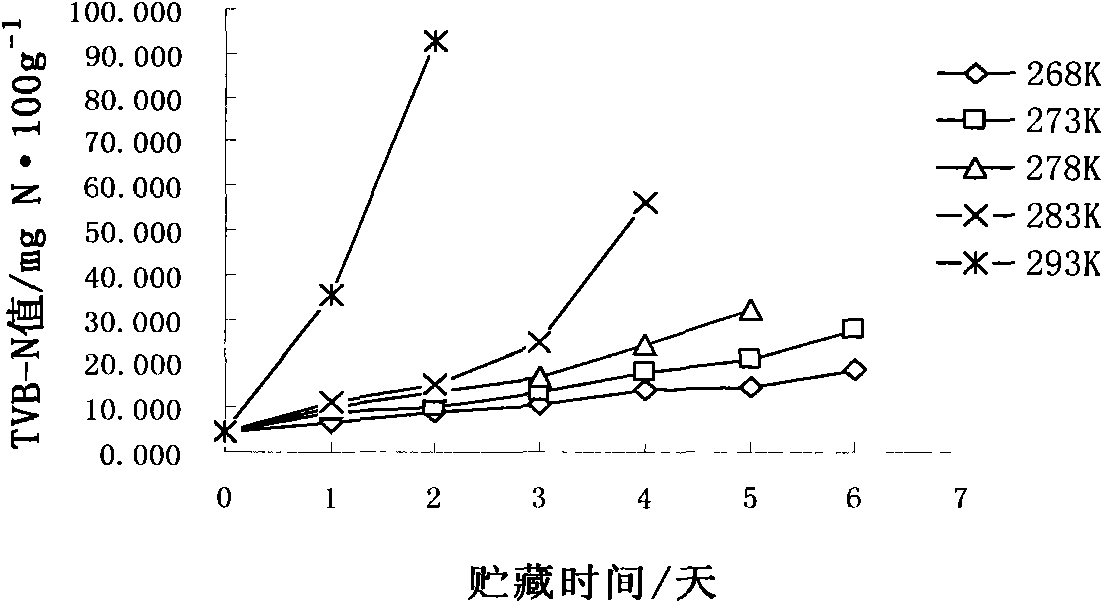
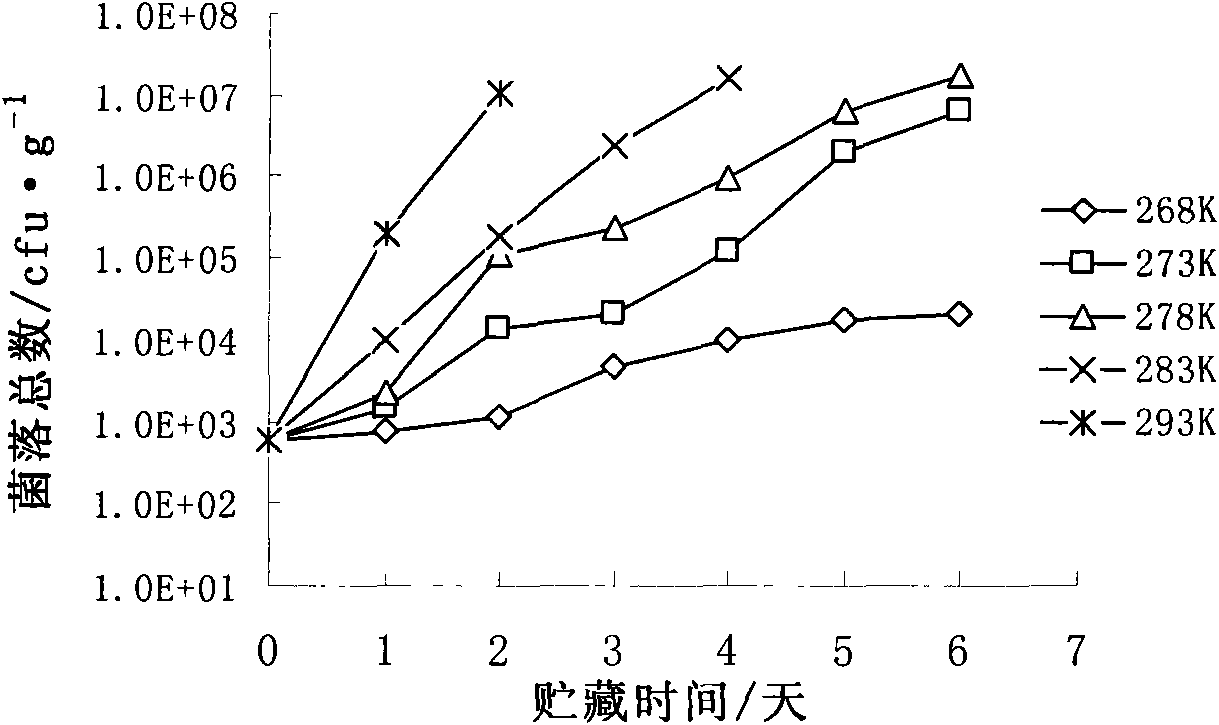
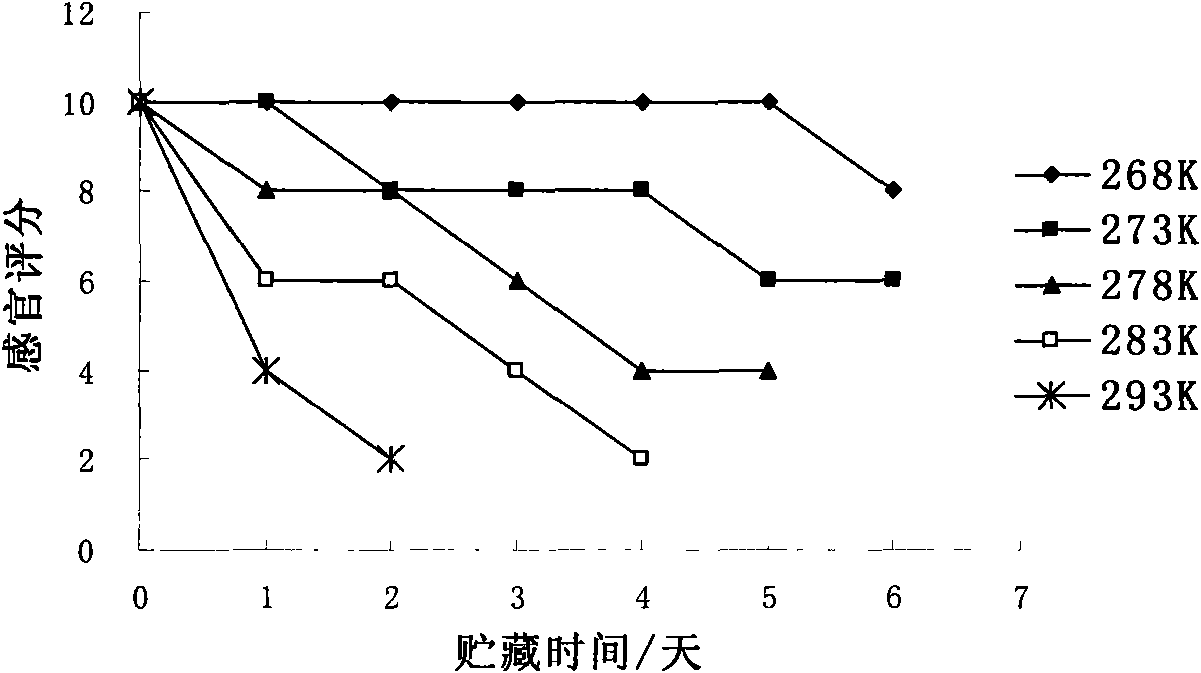
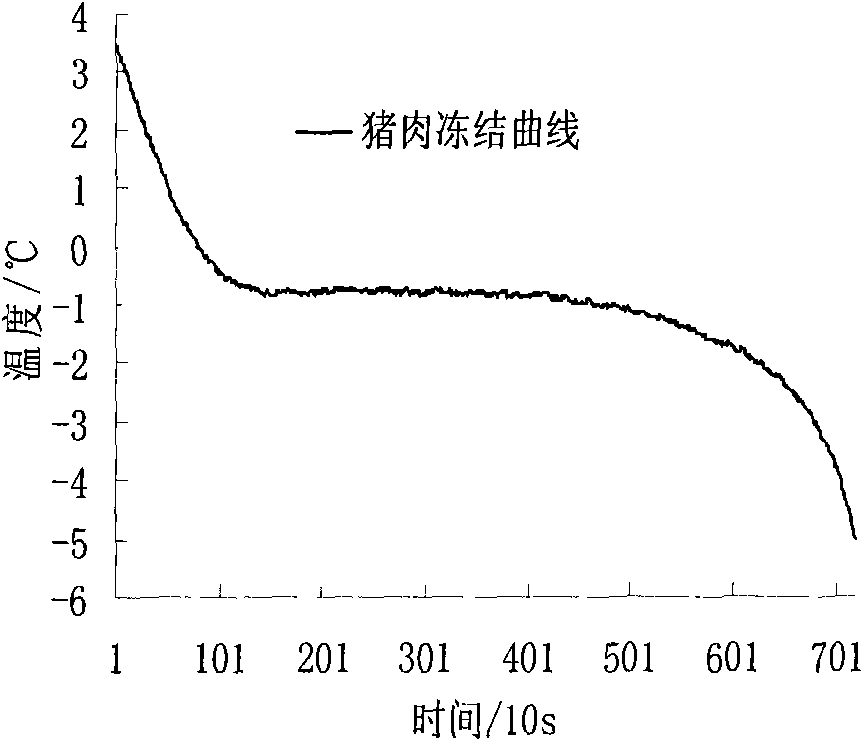
The invention relates to a method for predicting the shelf period of fresh pomfret; the invention studies the total plate count, TVBN and sensory quality changes of fresh pomfret at different storage temperatures and builds a Q10 shelf period prediction model of the quality changes of pomfret according to every index, thus being beneficial to distinguish accurately dynamically the quality of pomfret.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Bio-control bacterium nutritional tablet
The invention discloses a bio-control bacterium nutritional tablet, which comprises the following components in percentage: diatomite (determined as a carrier, and m (diatomite): V (fermentation liquor) = 2:1), 15% of sucrose (as a carbon source), 15% of peanut meal (as a nitrogen source), and 6% of corn starch or polyethylene glycol 6000 (as an adhesive). Moreover, the storage stability of strain 0116 nutritional tablets is determined by periodically measuring the viable count by using a plate count method, and results show that the viable count of the strain 0116 nutritional tablets after being stored for 4 months at a temperature of 4 DEG C is greater than or equal to 10<5>cfu / g. The bio-control bacterium nutritional tablet disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of short development cycle, low cost, simple process and long lasting period, and can be subjected to mass production. Because strain 0116 propagules are taken as the main components of the nutritional tablet, the nutritional tablet can be subjected to mass production, so that compared with the fermentation liquor of strains 0116, the field usage is greatly reduced, thereby reducing the packaging and transportation costs.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method for prolonging cooled meat shelf period by combination of chilling and high concentration carbon dioxide modified atmospheric packaging
InactiveCN101536707AStable temperatureSmall temperature fluctuationsMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsHigh concentrationLoss rate
The invention discloses a method for prolonging cooled meat shelf period by combination of chilling and high concentration carbon dioxide modified atmospheric packaging; the method studies the preservative effect of cooled meat by the combination of chilling and oxygen modified atmospheric of different concentration; the method sets up six experimental groups, comprising chilling(-1+ / -0.5 DEG C), freezing(4 DEG C), vacuum packing, 80%CO2, 20%N2 and chilling, 50%CO2, 50%N2 and chilling and 20%CO2, 80%N2 and chilling and measures total plate count, TVBN, drip loss rate, water retaining capacity and color difference. The invention has the following advantages: the higher the concentration of carbon dioxide is, the more obvious the antibacterial effect is and the total plate count of the 80%CO2 experimental group is least during the whole storage period; the TVBN of the experimental groups of modified atmospheric packaging always remains a lower level; by using the method combining chilling and high concentration carbon dioxide modified atmospheric packaging, the shelf period cooled meat can be prolonged and cooled meat can be kept fresh for twenty four days.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for rapidly quantitating Microcystis aeruginosa in water
InactiveCN107727556AThe pre-processing process is simpleReduce lossesColor/spectral properties measurementsIndividual particle analysisLinear regressionAbsorbance
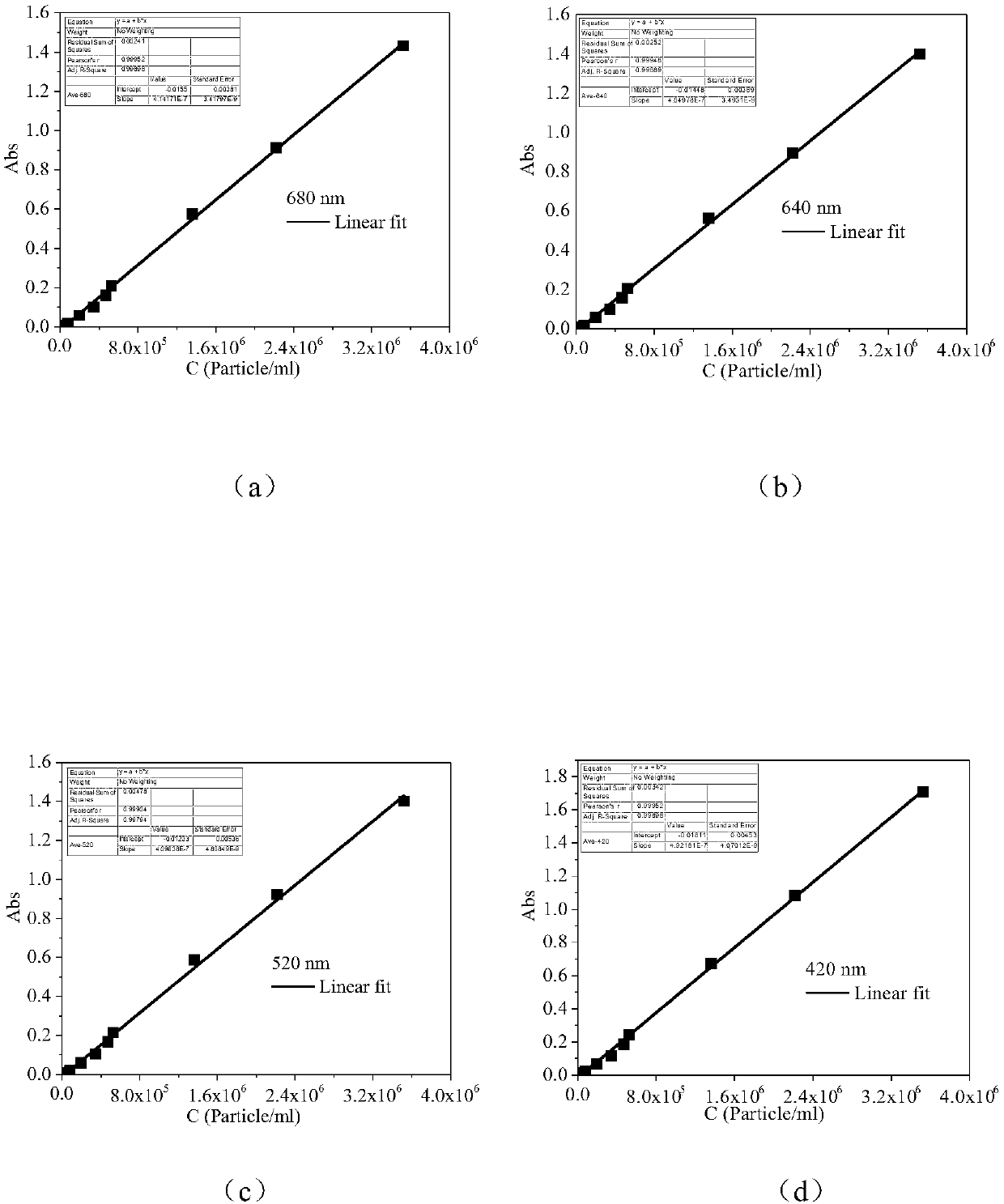
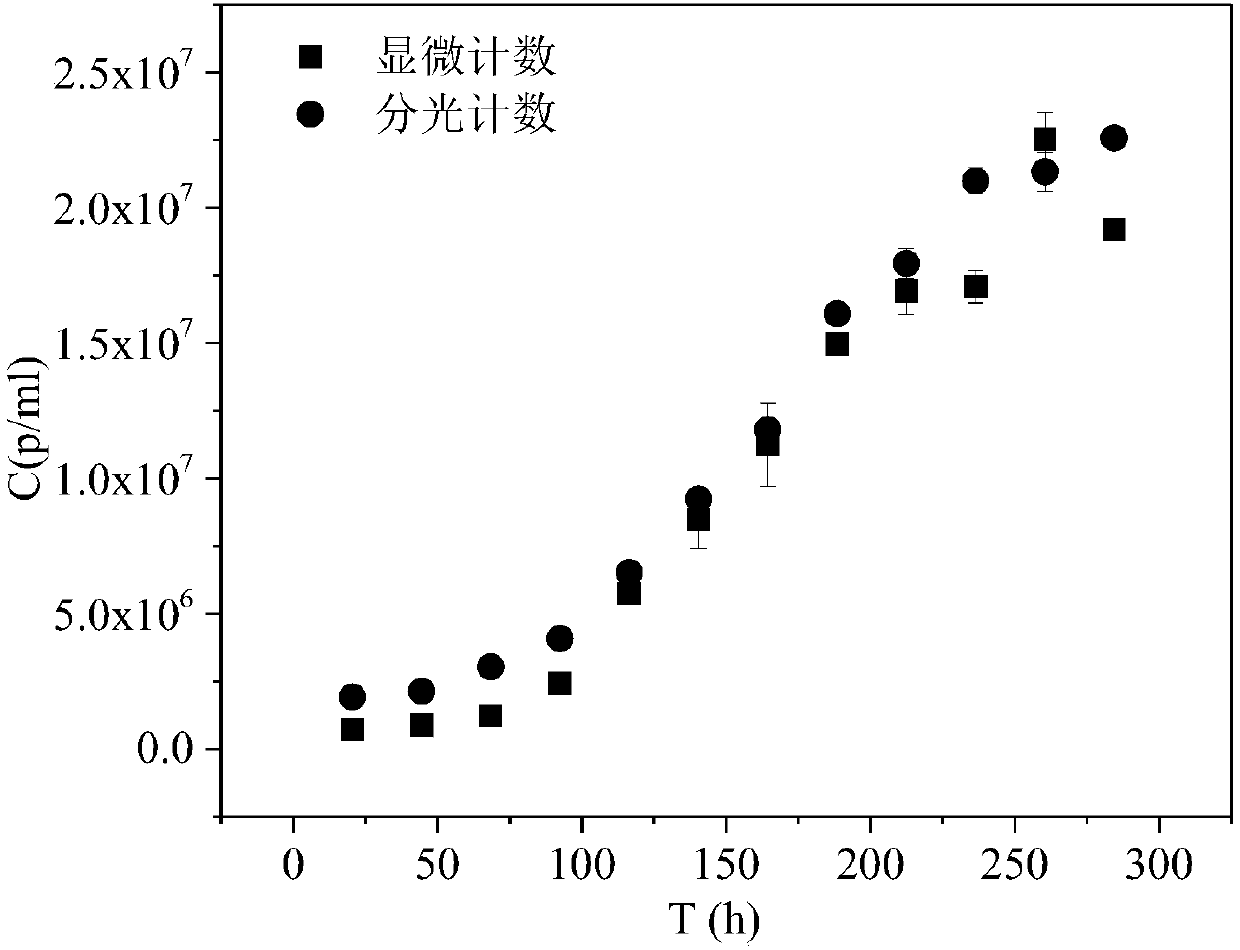
The present invention discloses a method for rapidly quantitating Microcystis aeruginosa in water. The method comprises: preparing a group of Microcystis aeruginosa liquids with different concentrations, determining the absorbance respectively at wavelengths of 220 nm, 360 nm, 420 nm, 520 nm, 640 nm and 680 nm through a spectrophotometer, and counting the algae cells of each sample by using a blood cell plate counting method to obtain the number of the algae cells per unit volume of the algae liquid; determining the absorbance of a blank sample at wavelengths of 220 nm, 360 nm, 420 nm, 520 nm,640 nm and 680 nm, and drawing a calibration curve according to the absorbance and the cell concentration, or obtaining regression equations corresponding to the wavelengths through linear regression; and diluting a Microcystis aeruginosa-containing sample to be measured, determining the absorbance of the algae liquid at the specific wavelengths by using the spectrophotometer, and calculating thecell concentration of the Microcystis aeruginosa in the sample to be measured according to the established calibration curve or regression equation. According to the present invention, with the method, the biomass is determined, such that the important significance is provided for the monitoring and early warning of algal bloom.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation of freeze-dried Lactobacillus acidophilus powder
ActiveCN101486986BActivity is not affectedStability is not affectedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingPlate count
The present invention discloses a preparation method of freeze dried microbial powder of Lactobacillus acidophilus, which comprises the technical processes of fermented cultivation of Lactobacillus acidophilus, separation of a fermented fluid, emulsification of microbial soil and vacuum freeze drying of an emulsified solution. The preparation method is characterized in that the strain fermented cultivation comprises the steps as follows: a lactobacillus strain is inoculated into a fluid culture medium in a triangular flask, cultivated at the temperature of 30 to 40 DEG C for 10 to 30 hours, inoculated into a large fermentation flask and fermentation cultivated at the temperature of 35 to 40 DEG C for 10 to 30 hours, and sterilized at the temperature of 115 DEG C for 15 minutes; and fermentation and augmentation cultivation is carried out for 10 to 30 hours, the pH value of the fermented fluid is 5.5 to 6.5, and OD600 is over 2.0; the vacuum freeze drying of the emulsified solution comprises the steps: the emulsified solution is pre-frozen at the temperature of minus 60 to minus 40 DEG C for 1 to 5 hours, and then vacuum frozen and dried at the temperature of minus 60 DEG C and with the vacuum degree of 1 to 8 Pa for 10 to 30 hours. The freeze dried microbial powder of Lactobacillus acidophilus with the total plate count of 1.0 multiplied by 10<11> cfu / g can be preserved for 18 months at the temperature of minus 18 DEG C with unaffected liveness and stability.
Owner:方曙光
Waste plastic and molten salt cracking tower
ActiveCN105505426AWell mixedFully lysedPlastic recyclingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMolten saltPlate count
The invention discloses a waste plastic and molten salt cracking tower. The waste plastic and molten salt cracking tower comprises a molten salt furnace and a cracking tower body connected with the molten salt furnace through a salt conveying pipe, wherein the top part of the cracking tower body is provided with a rotor feeder, the upper part of the cracking tower body is provided with a molten salt inlet, the lower part is provided with a molten salt outlet, a plurality of tower plates are arranged between the molten salt inlet and the molten salt outlet in the cracking tower body, the cracking tower body is also provided with a cracking gas outlet, the cracking gas outlet is located below a second tower plate counted from top to bottom, the bottom part of the cracking tower body is provided with a tapered molten salt sedimentation basin, the bottom part of the sedimentation basin is provided with a lower deslagging device, and the lower part of the cracking tower body is provided with an upper deslagging device. According to the waste plastic and molten salt cracking tower provided by the invention, when waste plastic floats on the surface of molten salt for being heated, a part of molten salt dropping from the tower plates impacts the waste plastic, so that the molten salt can be fully mixed with the waste plastic to improve a heat transfer effect, gasified plastic then passes through molten salt pillars dropping from openings of the tower plates, so that the heat transfer area is further increased and a cracking process is more sufficient.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Detection method of microbiological indexes of xanthan gum and similar gum
The invention discloses a detection method of microbiological indexes of xanthan gum and similar gum. The detection method comprises the following steps: making a plate count agar (PCA) culture medium, making a phosphate buffer solution, adding a sample to be tested into the phosphate buffer solution for diluting to prepare a sample plate, culturing the plate in a constant-temperature culture box, counting bacterial colonies on the plate, calculating the total number of bacterial colonies, expressing the total number of bacterial colonies, and forming a report. The detection method overcomes the shortcoming that xanthan gum in GB / T4789 cannot be dissolved, is simple and feasible, is relatively suitable for actual operations of labs in enterprises, and has relatively high values and progressive meanings on the aspect of xanthan gum detection.
Owner:ORDOS ZHONGXUAN BIOCHEM
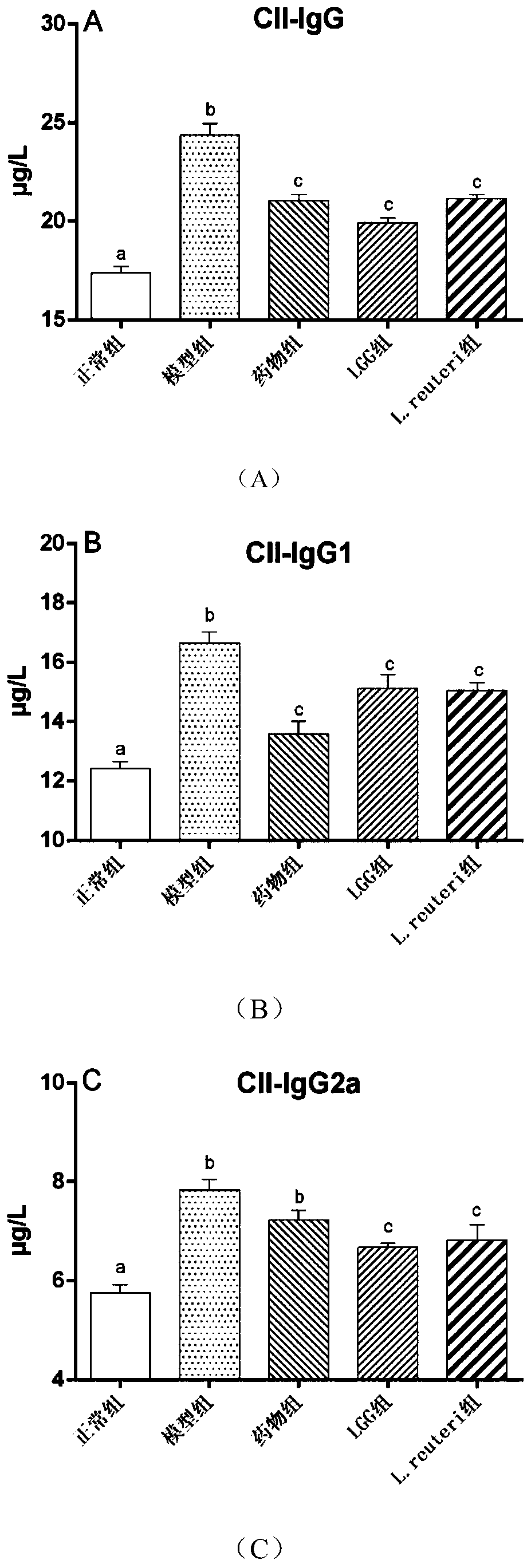
Lactobacillus reuteri composition capable of relieving rheumatoid arthritis
ActiveCN110613738AImprove adhesionInhibition levelAntipyreticAnalgesicsSaccharumProinflammatory cytokine
The invention discloses a lactobacillus reuteri composition capable of relieving rheumatoid arthritis, and belongs to the technical field of food microorganisms. The concentrated biological preparation is prepared by activating lactobacillus reuteri CCFM8631 and lactobacillus reuteri CCFM14, performing enlarge cultivation, performing centrifugation, and performing re-suspension in a 30% sucrose solution; and the numbers of viable bacteria of the lactobacillus reuteri CCFM8631 and CCFM14 obtained by a plate count process are both greater than 10<10> CFU / mL. The lactobacillus reuteri composition provided by the invention can significantly alleviate rheumatoid arthritis induced by type II collagen, relieve joint redness and swelling symptoms, inhibit the level of antibodies resisting againstthe type II collagen, reduce the content of proinflammatory cytokines and anti-inflammatory cytokines in serum, reduce the levels of Th1 and Th2 cell-related effect characteristic factors, improve anintestinal function, and has broad market application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
RVA-APC combined method for discrimination of ionizing irradiation wheat and flour
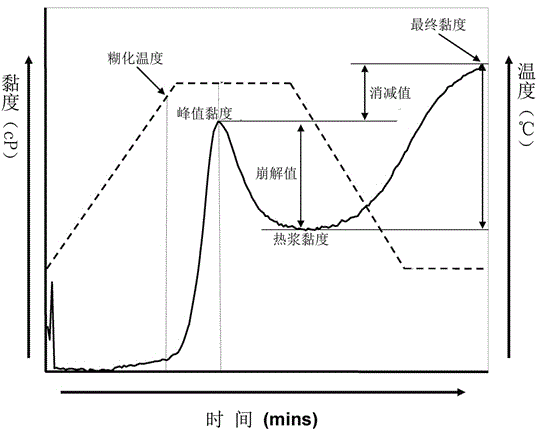
InactiveCN104535459AEasy to measureRapid determinationFlow propertiesCombined methodIonizing irradiation
The invention discloses a RVA-APC combined method for discrimination of ionizing irradiation wheat and flour. The method includes: taking test wheat raw grain or flour sample and a wheat raw grain or flour product (unirradiated) of the same variety and producing area to do contrast; conducting sample pretreatment, grinding the sample into flour and performing sieving by a 80-mesh sieve; conducting RVA test on the sample, weighing 2.0-3.5g of the sample, adding 20.0-30.0g of distilled water, and then putting the mixture into a RVA tester to carry out heating determination to obtain 6 main characteristic spectrum values in the RVA tester; performing APC determination on the sample; conducting comparison with the contrast group, if five RVA characteristic indexes, i.e. peak viscosity, through viscosity, final viscosity, breakdown and setback decrease, the pasting temperature rises and the aerobic plate count is less than 10<6> cfu / g, determining that ionizing irradiation occurs yet and the greater the difference is, the higher the received irradiation dose is. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of small detection sample amount, simple operation, fast determination process, and low cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
Culture medium composition, culture medium and viable bacteria counting method for strain
ActiveCN103911298AControl contentTo achieve the purpose of jointly counting live bacteriaFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementColony morphologyNitrogen source
The invention discloses a culture medium composition, which contains a nitrogen source. The culture medium composition is characterized in that the nitrogen source contains urea and / or amino acid, in terms of nitrogen element, urea and / or amino acid account for more than 80wt% of the total content of the nitrogen source, and based on the total weight of the culture medium composition, in terms of nitrogen element, the total content of the nitrogen source is 0.02-15wt%. The invention also discloses a culture medium, which contains the culture medium composition provided by the invention and water, wherein the culture medium composition and the water are in a weight ratio of 1:20-30. In addition, the invention discloses a viable bacteria counting method for a strain. The method includes: subjecting the strain to plate culture on the culture medium provided by the invention, and conducting plate counting on the cultured strain. By means of the method provided by the invention, viable bacteria counting on different strains can be carried out according to different colony morphologies and colors.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
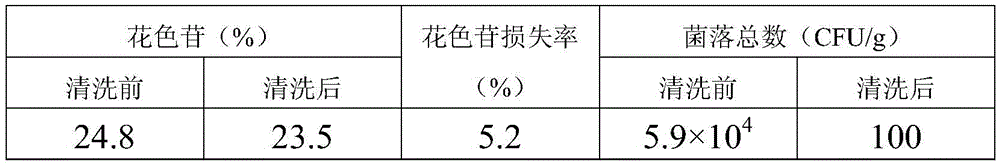
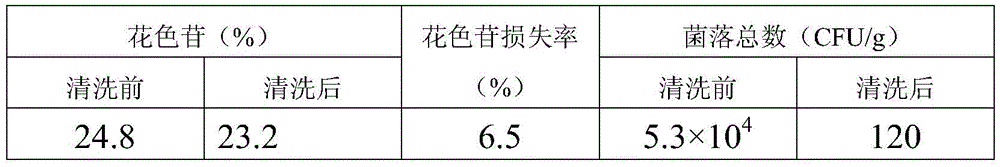
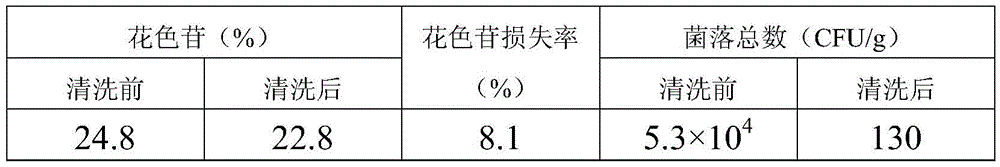
Ultrasonic cleaning method of Lycium ruthenicum
The invention discloses an ultrasonic cleaning method of Lycium ruthenicum. The ultrasonic cleaning method includes following steps: a, preparing an alcohol solution with concentration of higher than 70%v / v and temperature of minus 18-25 DEG C as cleaning liquid; b, placing Lycium ruthenicum in the cleaning liquid for ultrasonic cleaning, wherein cleaning time is 0.5-30 min, ultrasonic frequency is 20-200 kHz, and ultrasonic power is 200-500 w; c, drying Lycium ruthenicum after being cleaned until no water exists on the surface. The ultrasonic cleaning method is efficient, simple and convenient, silt, dust and impurities on the surface of Lycium ruthenicum can be removed, total plate count of Lycium ruthenicum fruits can be lowered remarkably, good sterilization effect can be realized, and loss of anthocyanin in the cleaning process of Lycium ruthenicum can be lowered greatly. Total plate count of Lycium ruthenicum cleaned by the method is less than 1.5x102 (CFU / g), loss rate of anthocyanin is maintained below 12%, and dried fruits of Lycium ruthenicum are bright in color and luster, safe and reliable to human body and environment-friendly.
Owner:青海西拙生态农业开发有限公司
Method for predicting degree that rice is contaminated by aspergilli based on electronic nose
InactiveCN109666717AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial resistanceSensor arrayPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a method for predicting the degree that rice is contaminated by aspergilli based on an electronic nose. The method comprises the steps that after the rice is subjected to ultraviolet sterilization, the aspergilli is inoculated on the rice; by using the electronic nose, samples obtained after the rice stored for different time is inoculated are subjected to headspace gas detection; by using the plate count method, the number of bacterial colonies on the rice samples is detected; according to principal component analysis, an electronic nose sensor array is optimized, andthe optimized sensor response signals are subjected to feature extraction by using the stable value method; a prediction model based on electronic nose signal feature values and the number of the bacterial colonies is built by using the modified support vector machine (GA-SVM) algorithm optimized based on the genetic algorithm, the regression model with a large correlation index and a low root-mean-square error is selected as a final prediction model for the number of the bacterial colonies, and therefore, the predicted number of the colony forming units is obtained. The method can quickly predict the degree that the rice is contaminated by the aspergilli, the rice samples are not damaged, the operation is simple, a good prediction effect si achieved, and the method is higher in practicalapplication value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
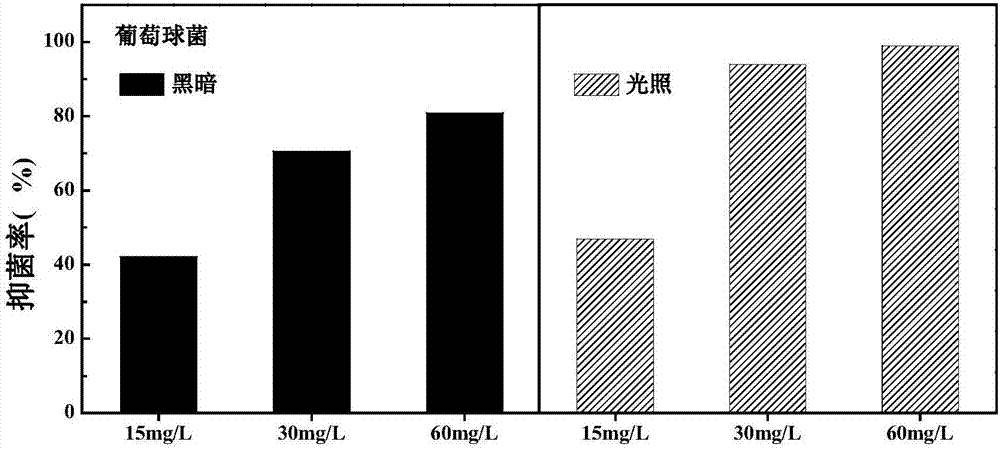
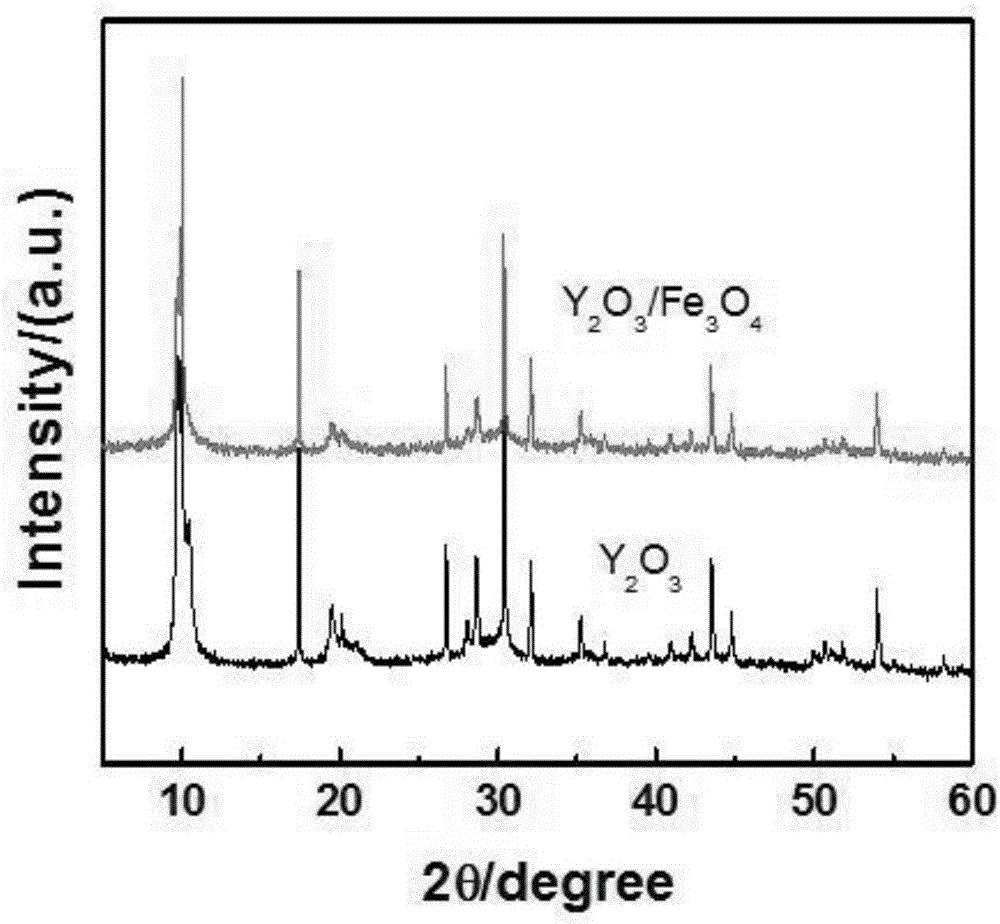
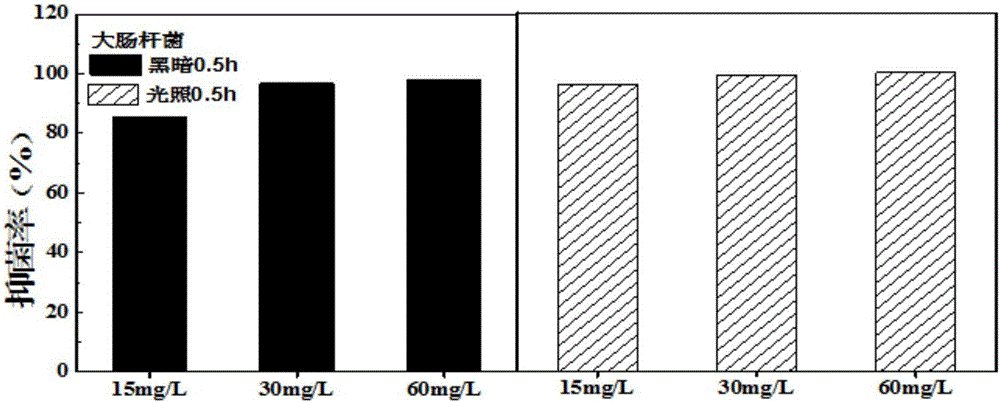
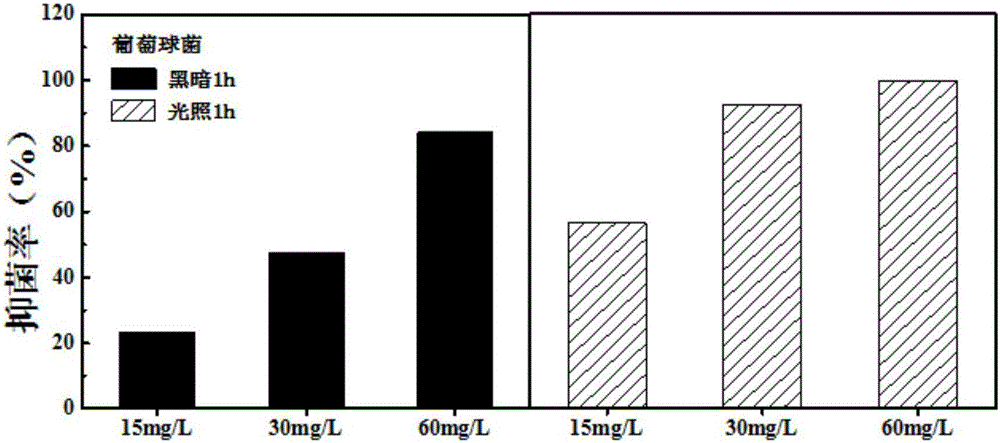
Yttrium oxide-graphene composite nanobacteriostatic material, preparation and application
InactiveCN107041378ALarge specific surface areaGood dispersionBiocideDead animal preservationEscherichia coliHigh pressure
The invention relates to a yttrium oxide-graphene composite nanobacteriostatic material, preparation and an application. The preparation comprises the steps of uniformly dispersing graphene oxide powder into a yttrium oxide synthesis system, reacting in a high-pressure reactor, centrifugally separating a sediment and drying overnight to obtain a yttrium oxide-graphene compound; sterilizing the nanomaterial through absolute ethyl alcohol, centrifuging, removing a supernatant, adding water and fully mixing evenly; adding yttrium oxide-graphene compound materials of different concentrations to test tubes of escherichia coli and staphylococcus of a certain concentration, carrying out shake cultivation in the light and darkness for a certain period of time separately; and analyzing the suppression efficiency of the nanomaterial on a gram-positive bacterium and a gram-negative bacterium by using a plate count method. The yttrium oxide-graphene composite material has a good inhibition effect on the gram-negative bacterium and the gram-positive bacterium, has very high suppression efficiency on the gram-negative bacterium, is friendly to environment and does not generate the problems, such as drug resistance of bacteria.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Screening method of nutritive salt for pollutant enhanced bioremediation and application
InactiveCN107377614AImprove long-term stabilityLiquid phase reaction is fastContaminated soil reclamationFluorescenceScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of nutritive salt for pollutant enhanced bioremediation. The screening method comprises the steps of 1) adding a culture medium into liquid samples containing pollutants, then, observing the growing situation of floras, and carrying out baseline screening; 2) adding different varieties of nutritive salt of different proportions into the liquid samples containing the pollutants, carrying out shake-flask culture, and testing the amount of microorganism colonies through plate count and an ATP bioluminescence detector; and 3) detecting concentration of the pollutants in the pollutant-containing liquid samples cultured through adding of nutritive salt, evaluating the pollutant enhanced bioremediation effect of nutritive salt according to a result, and acquiring an optimal nutritive salt formula.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
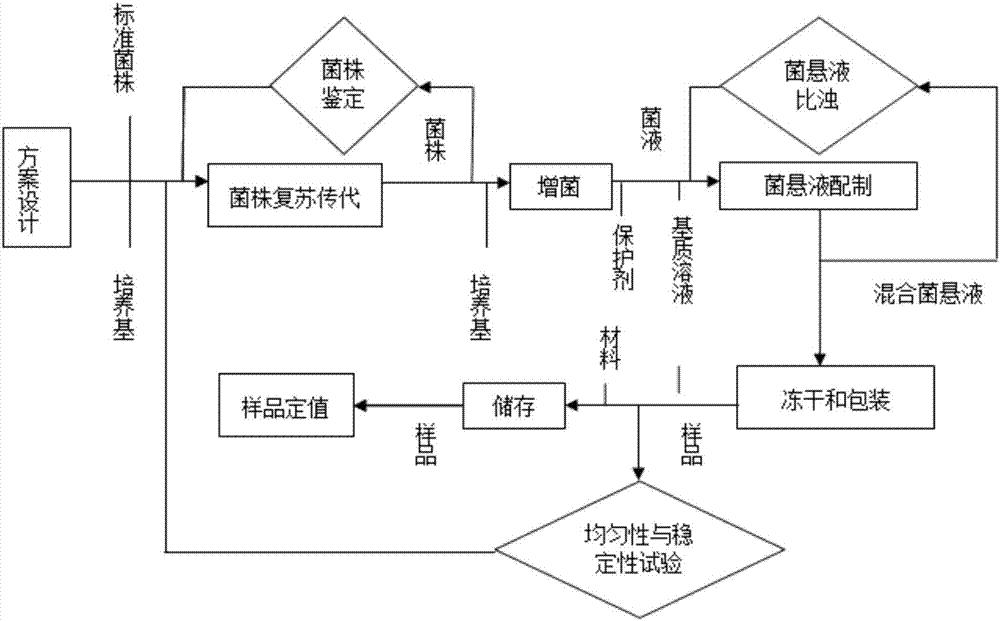
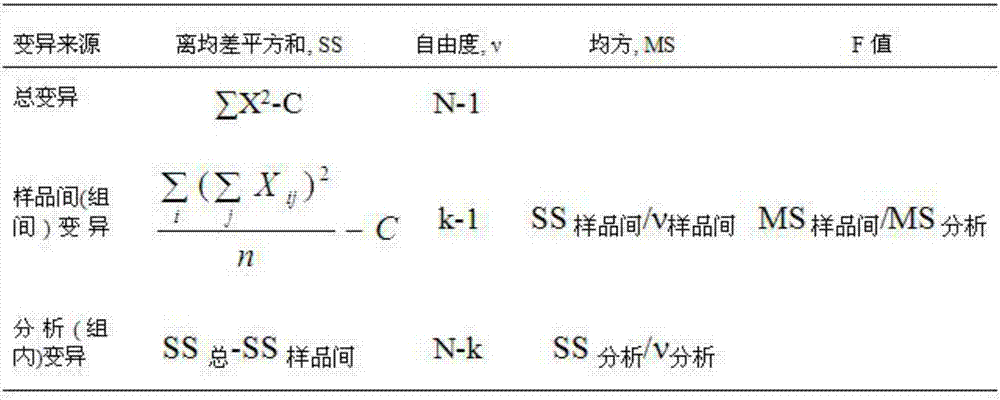
Standard sample for total plate count in milk powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107090489ASimple processIncrease success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliTest sample
The invention belongs to the field of quality control in the aspect of microbiological test, and particularly relates to a standard sample for total plate count in milk powder and a preparation method thereof. A target flora of the standard sample for total plate count in milk powder is composed of bacillus cereus, escherichia coli, klebsiella pneumonia, enterobacter cloacae and staphylococcus aureus. The uniformity and stability of the standard sample for total plate count in milk powder meet the requirements on the standard sample, the stability of the test sample can be ensured to the max, and even if the content of escherichia coli is changed during transportation and storage, the total plate count is not affected in a statistical sense; and the preparation method for the sample has the advantages of simple process and high success rate.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
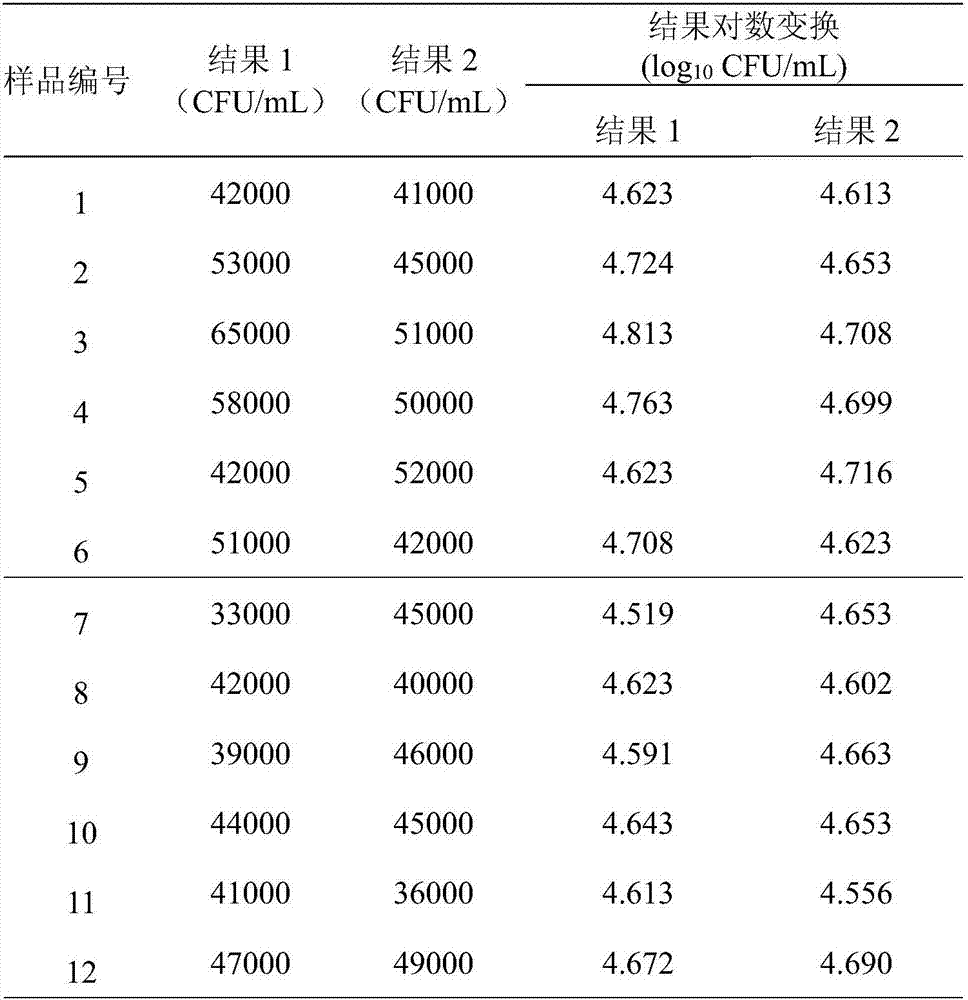
Preparation and application of yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide composite nanometer antibacterial material
ActiveCN106587291AImprove antibacterial propertiesLow costSpecific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processEscherichia coliAntibiotic resistance
The invention relates to preparation and application of an yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide composite nanometer antibacterial material. Preparation of the yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide composite nanometer antibacterial material includes the following steps that nanometer iron oxide obtained through hydro-thermal synthesis is uniformly dispersed into an yttrium oxide synthesis system, a reaction is conducted in a high-pressure reaction kettle, precipitate is subjected to centrifugal separation and dried and stays overnight, and an yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide compound is obtained; a nanometer material is subjected to sterilization with absolute ethyl alcohol, then supernatant is removed through centrifugation, then water is added, and the mixture is fully and uniformly mixed; yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide compound materials of different concentrations are added into a test tube of escherichia coli and staphylococcus of a certain concentration and subjected to shake cultivation under the light or in dark for certain time; and then inhabitation efficiency of the nanometer material to the gram-negative bacterium and the gram-positive bacterium is analyzed through a plate count method. The compound material has a good inhabitation effect on both the gram-negative bacterium and the gram-positive bacterium, particularly on the gram-negative bacterium, is environmentally friendly and cannot cause antibiotic resistance in bacteria and other problems.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
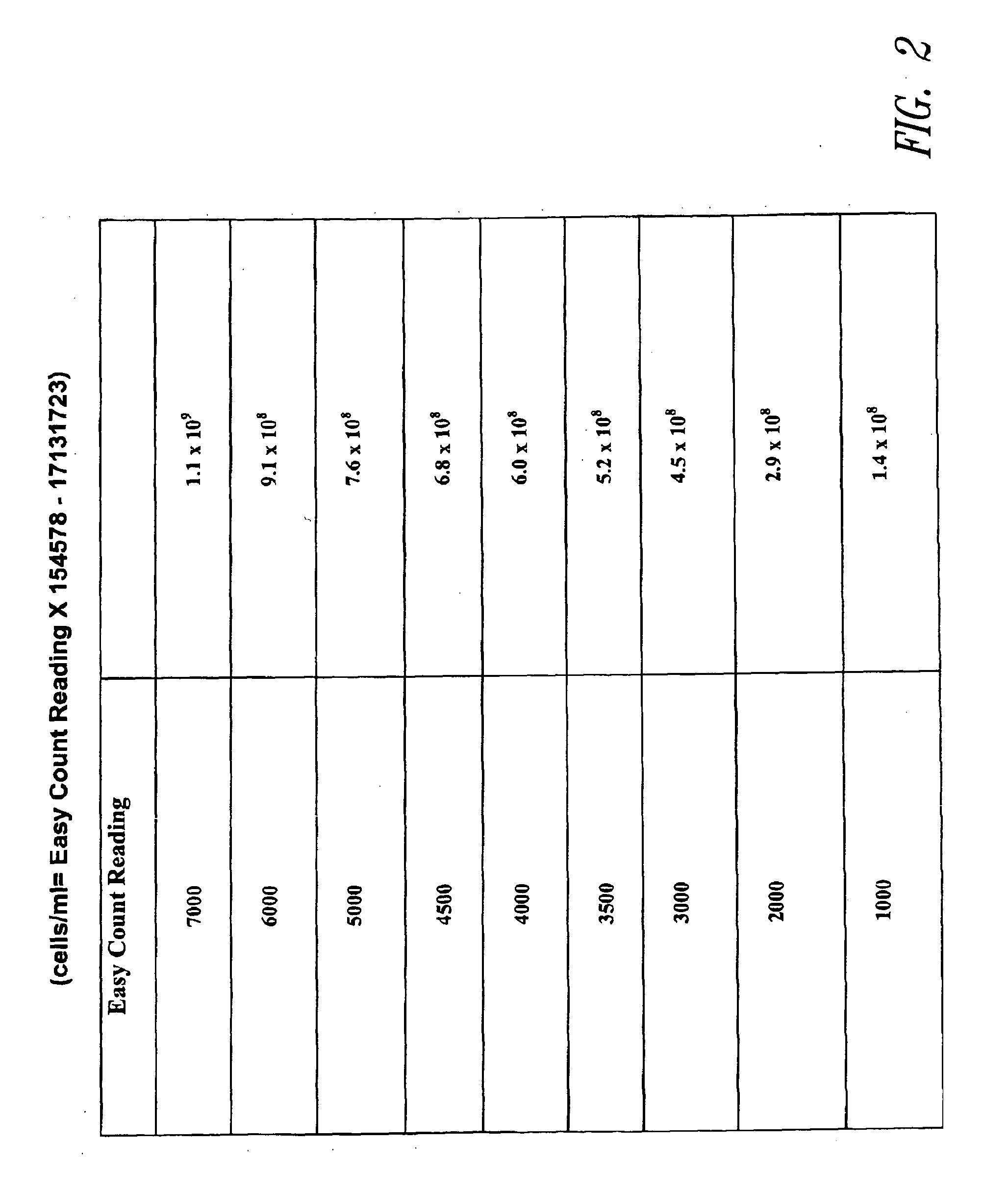
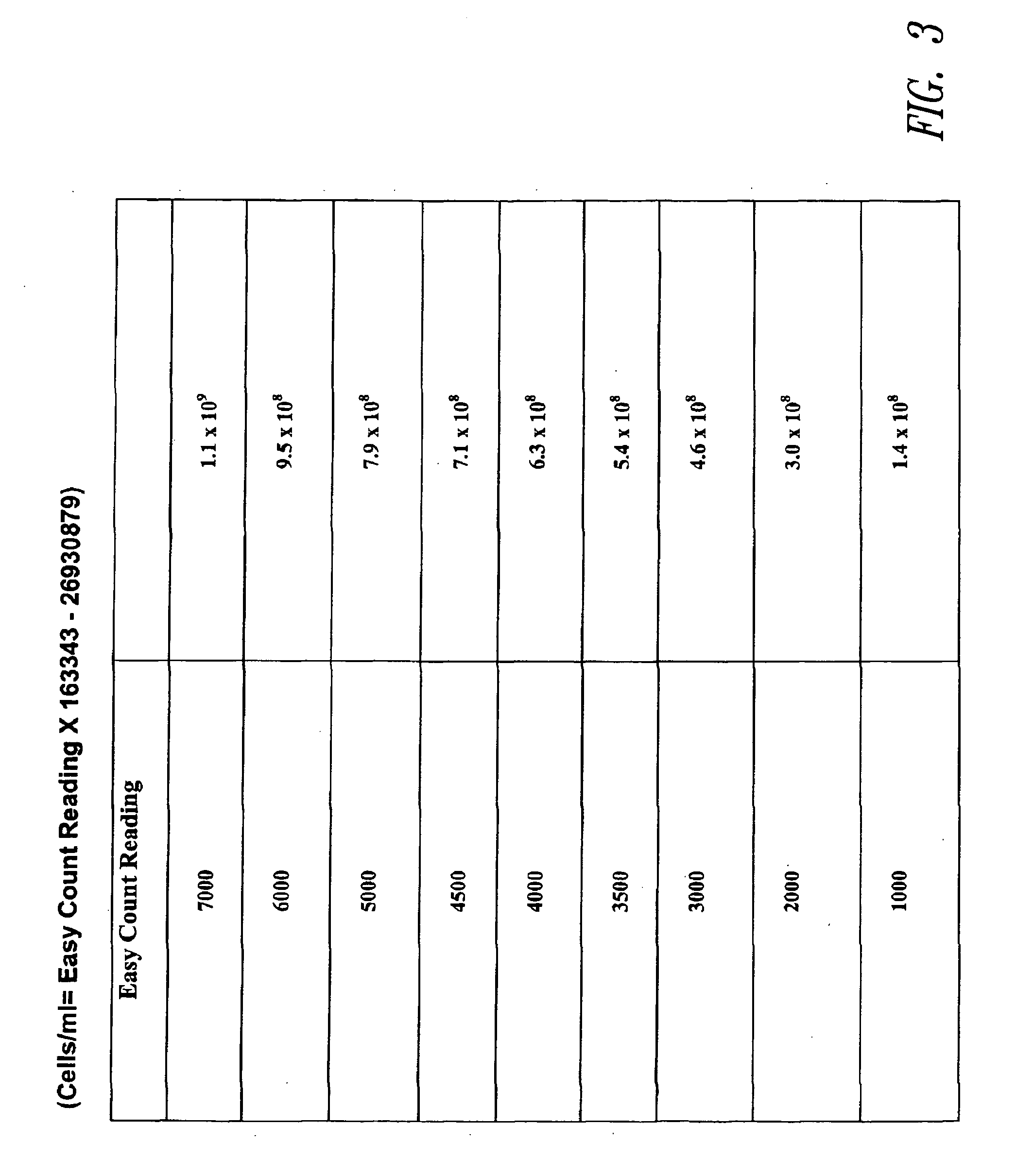
Method and apparatus for viable and nonviable prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell quantitation
InactiveUS20090104652A1Increase uptakeSpeed up rate conversionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical settingsMammal
A rapid method for the quantitation of various live cell types is described. This new cell fluorescence method correlates with other methods of enumerating cells such as the standard plate count, the methylene blue method and the slide viability technique. The method is particularly useful in several applications such as: a) quantitating bacteria in milk, yogurt, cheese, meat and other foods, b) quantitating yeast cells in brewing, fermentation and bread making, c) quantitating mammalian cells in research, food and clinical settings. The method is especially useful when both total and viable cell counts are required such as in the brewing industry. The method can also be employed to determine the metabolic activity of cells in a sample. The apparatus, device, and / or system used for cell quantitation is also disclosed.
Owner:GENPRIME
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com