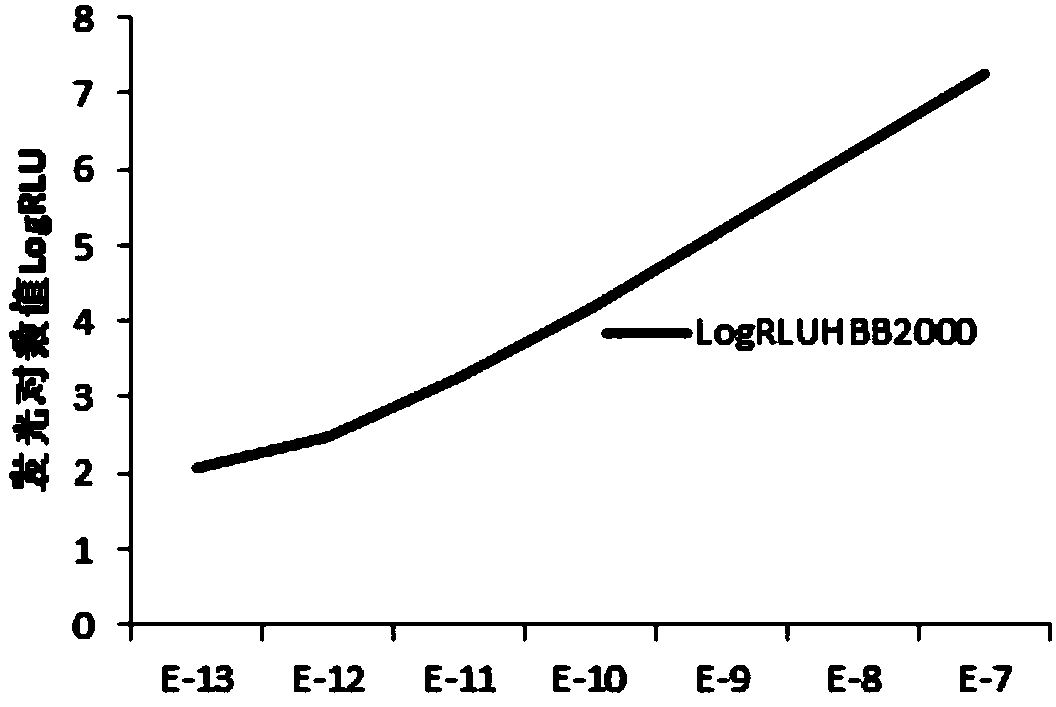
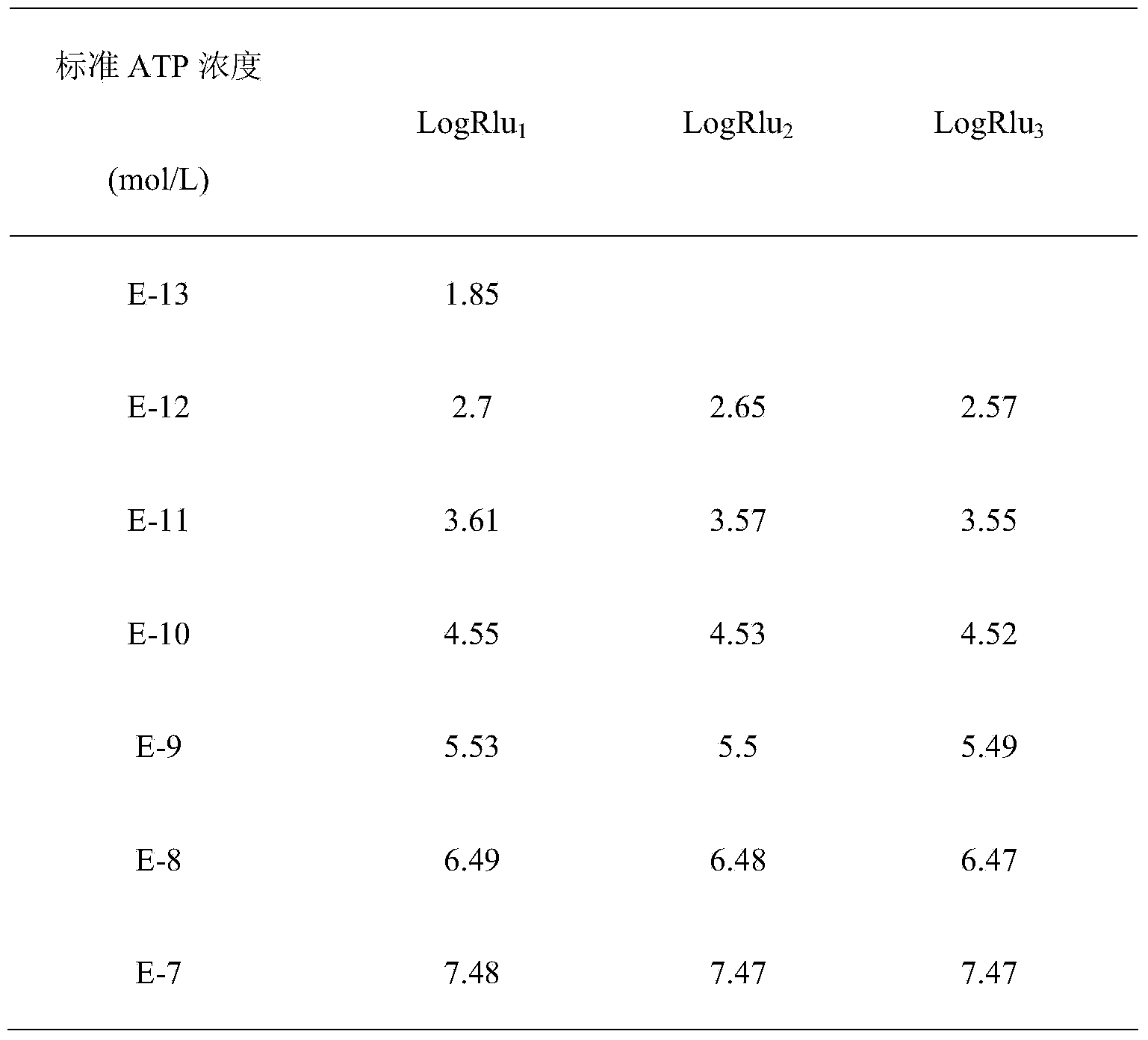
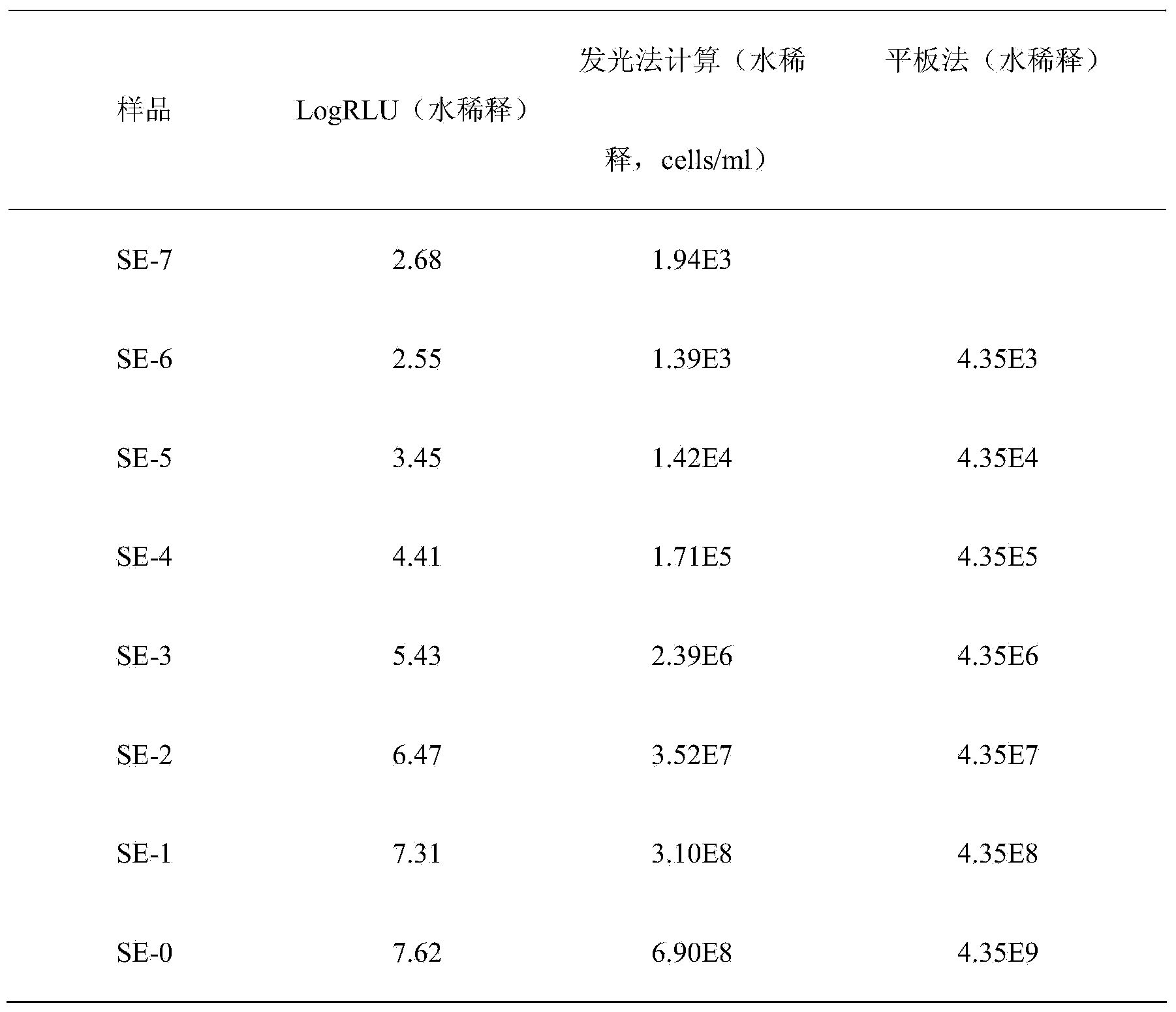
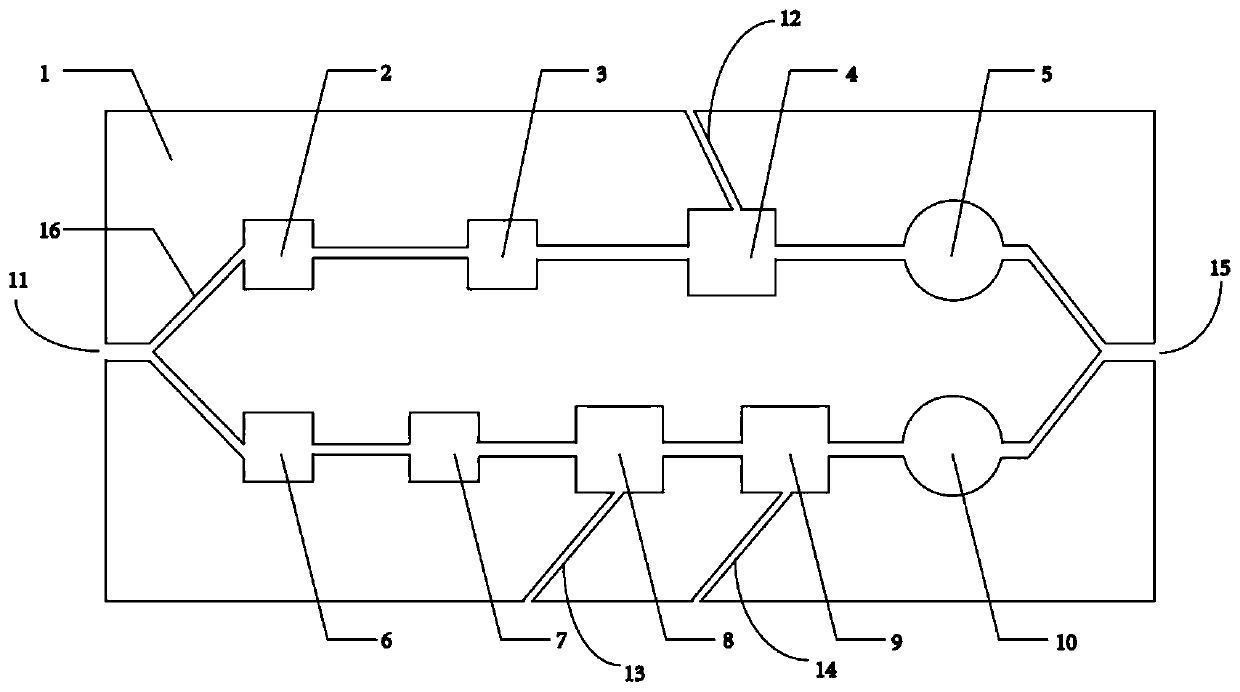
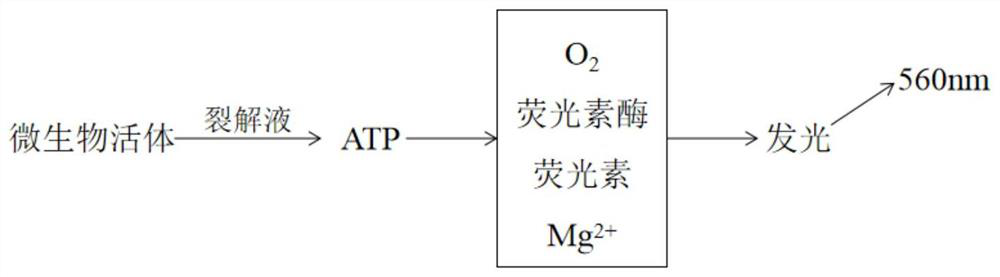
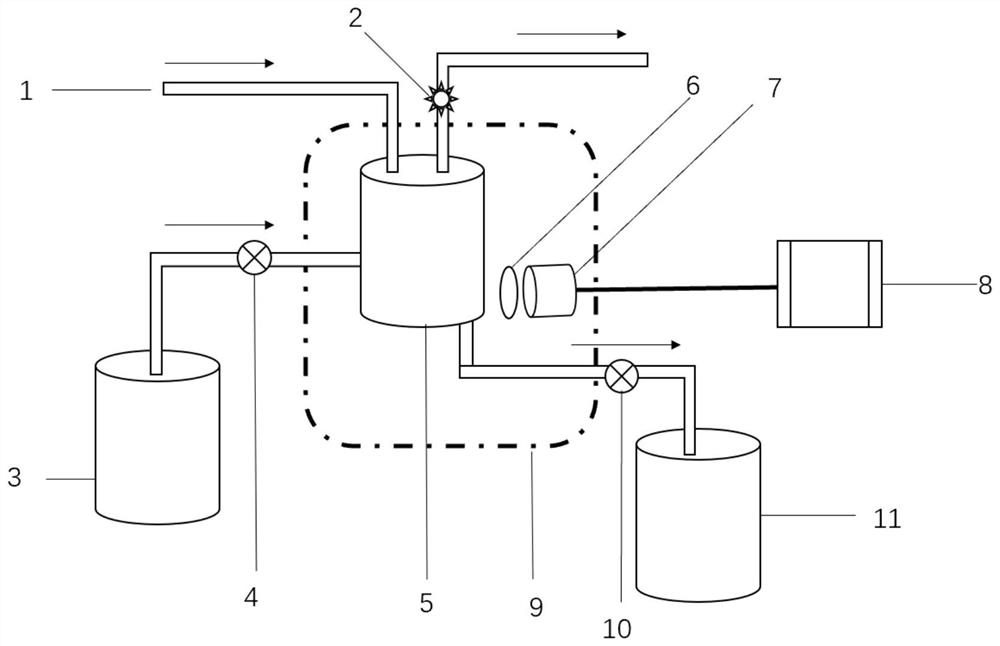
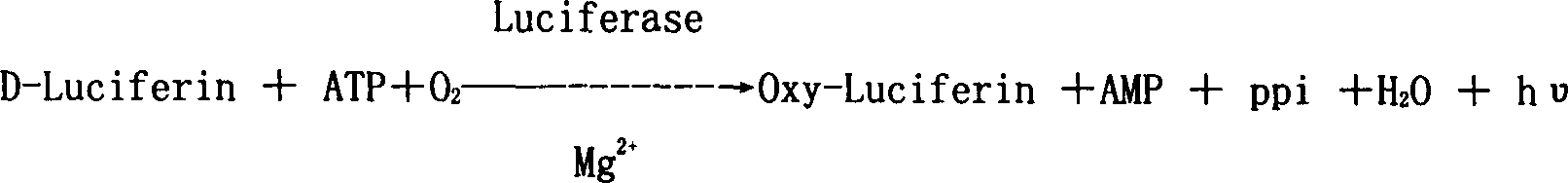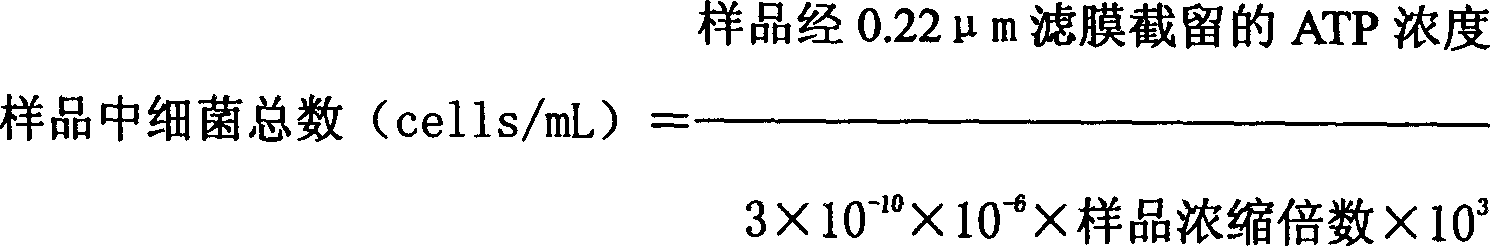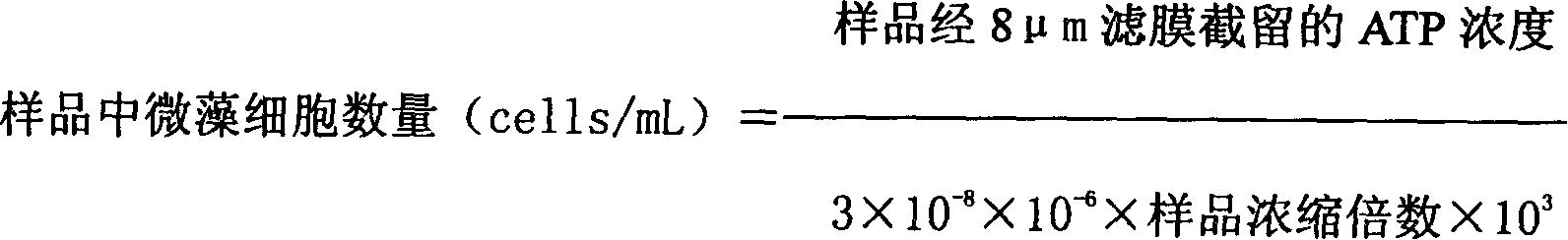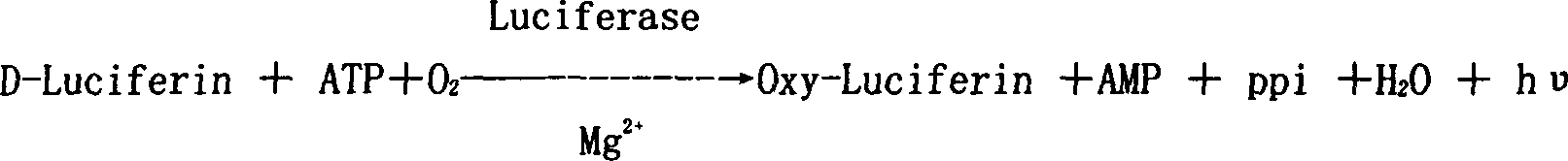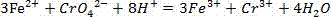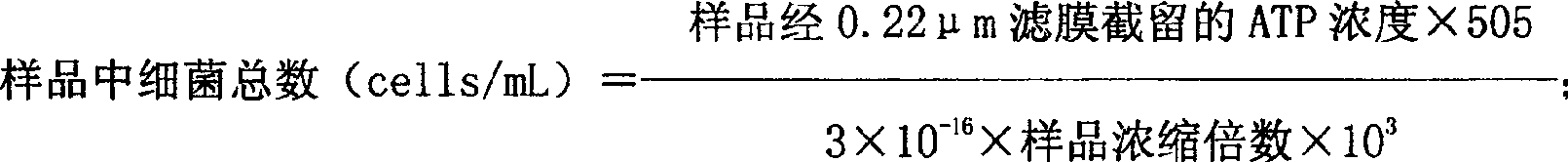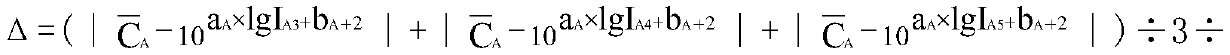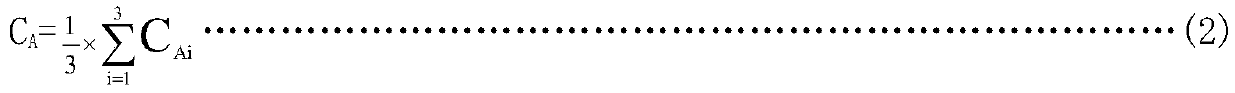Patents
Literature
51 results about "Atp bioluminescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Use of ATP Bioluminescence for Rapid Detection and Enumeration of Contaminants: The Milliflex Rapid Microbiology Detection and Enumeration System. 109 An easy protocol was developed to quickly enumerate spore contamination in artificially inoculated products with RMDS.
ATP biological luminous method use for rapid estimating effect of antiseptics
InactiveCN1680803AImprove evaluation efficiencyShorten assessment timeChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceScavengerDisinfectant
A method for evaluating sterilization effect of disinfectant by means of ATP bioluminescence includes preparing standard bacterial suspension, processing it with cell ATP release agent Ec and adding luciferase - luciferin reagent to detect out luminous value or filtering it with microhole film in combination with ATP scavenger and detecting out luminous value of filtering film, then carrying out equation calculation and utilizing conversion coefficient K to derive out live bacteria number in suspension for evaluation.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM +1
Rapid microbiological detection and reagent for environmental water body
InactiveCN1680805AChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationLinear regressionIndustrial water
A fast detection method of water microbe includes filtering water sample by microhole filtering film with different hole diameter, carrying out ATP luminous detection for used filtering film and for ATP standard solution and new microhole filtering film, calculating linear regression equation of Lg [ATP] = A+ BLg [CPM] based on logarithmic relation of ATP concentration to its luminous pulse counts and calculating out microbe content in water as well as ATP concentration in sample according CPM value of filtering film.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
Method for specific detection of staphylococcus aureus
ActiveCN104655839AHave specific recognitionEasy to synthesizeBiological material analysisLuminous intensityMagnetite Nanoparticles
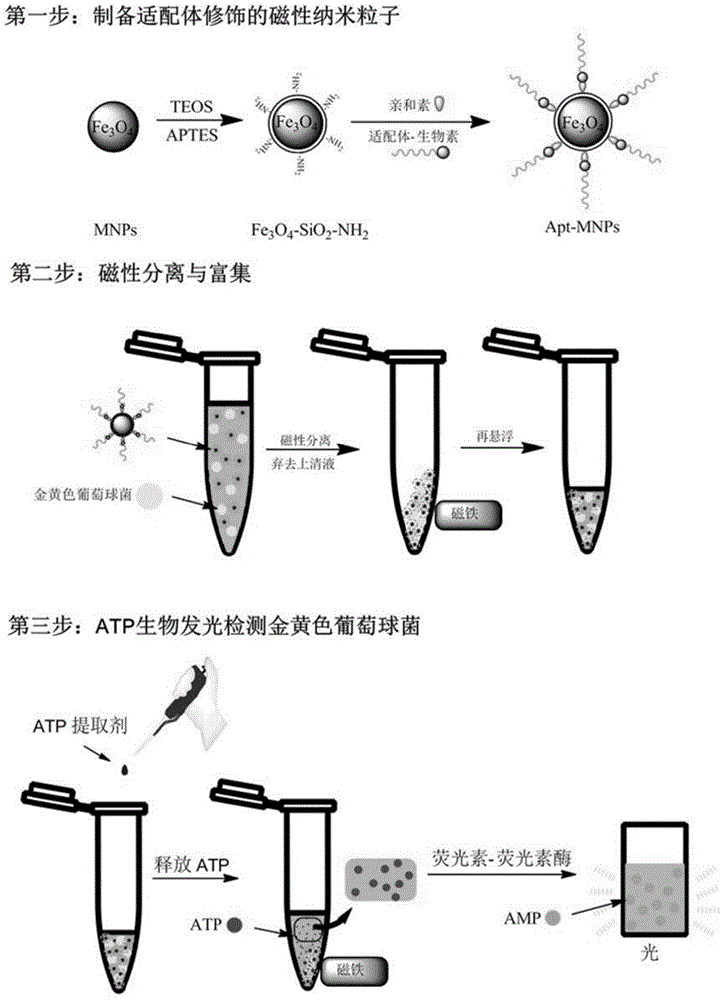
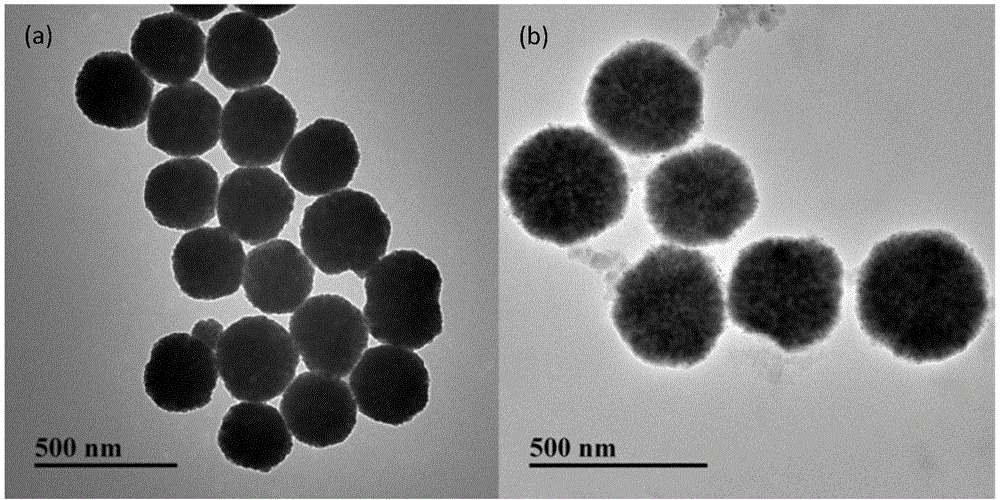
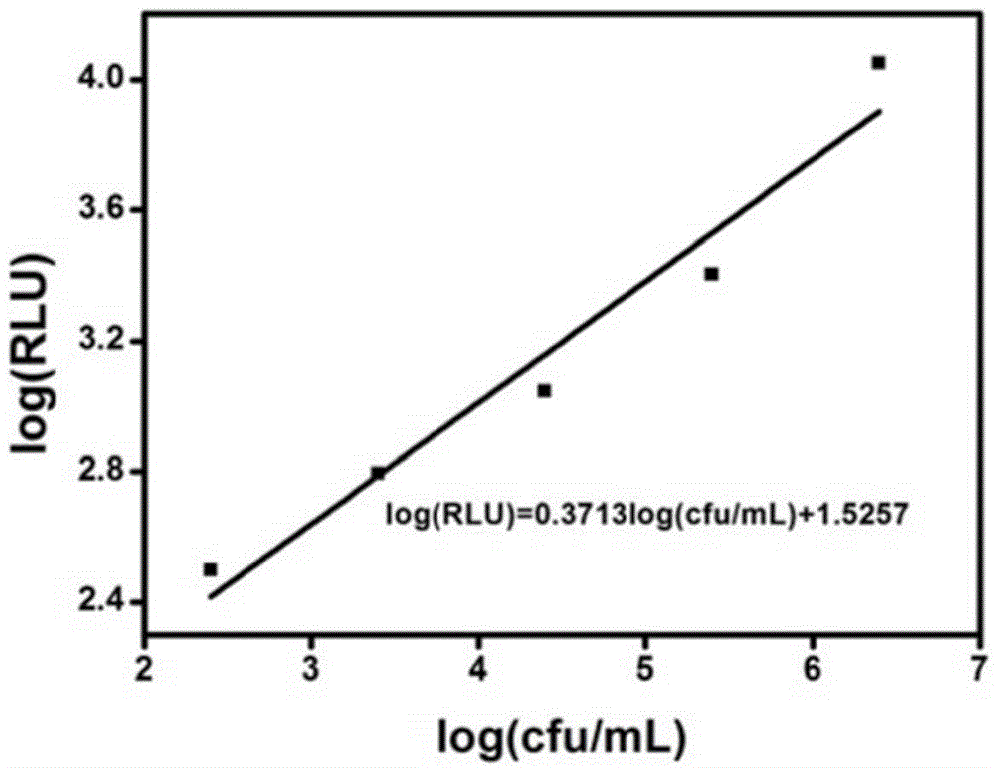
The invention provides a method for specific detection of staphylococcus aureus. The method is characterized in that a nucleic acid aptamer is modified on the surfaces of magnetic nano particles, quickly recognizes, and is combined with staphylococcus aureus in a solution sample; target fungi combined with the magnetic nano particles are separated and enriched by using a magnetic field; captured fungi are suspended in a lysate with a certain volume; ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) extracting staphylococcus aureus is released and used; and as the amount of ATP is directly proportional to the concentration of fungi liquid, after a linearity curve of the fungi concentration and the luminous intensity is obtained by an ATP bioluminescence method, staphylococcus aureus can be detected quantitatively. The method has the advantages that the aptamer is easy to synthesize, modify and fix, and can be kept for a long time; by performing combination, separation, enrichment and concentration on the target fungi, sample matrices and other interference fungi are removed effectively; and the detection sensitivity is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
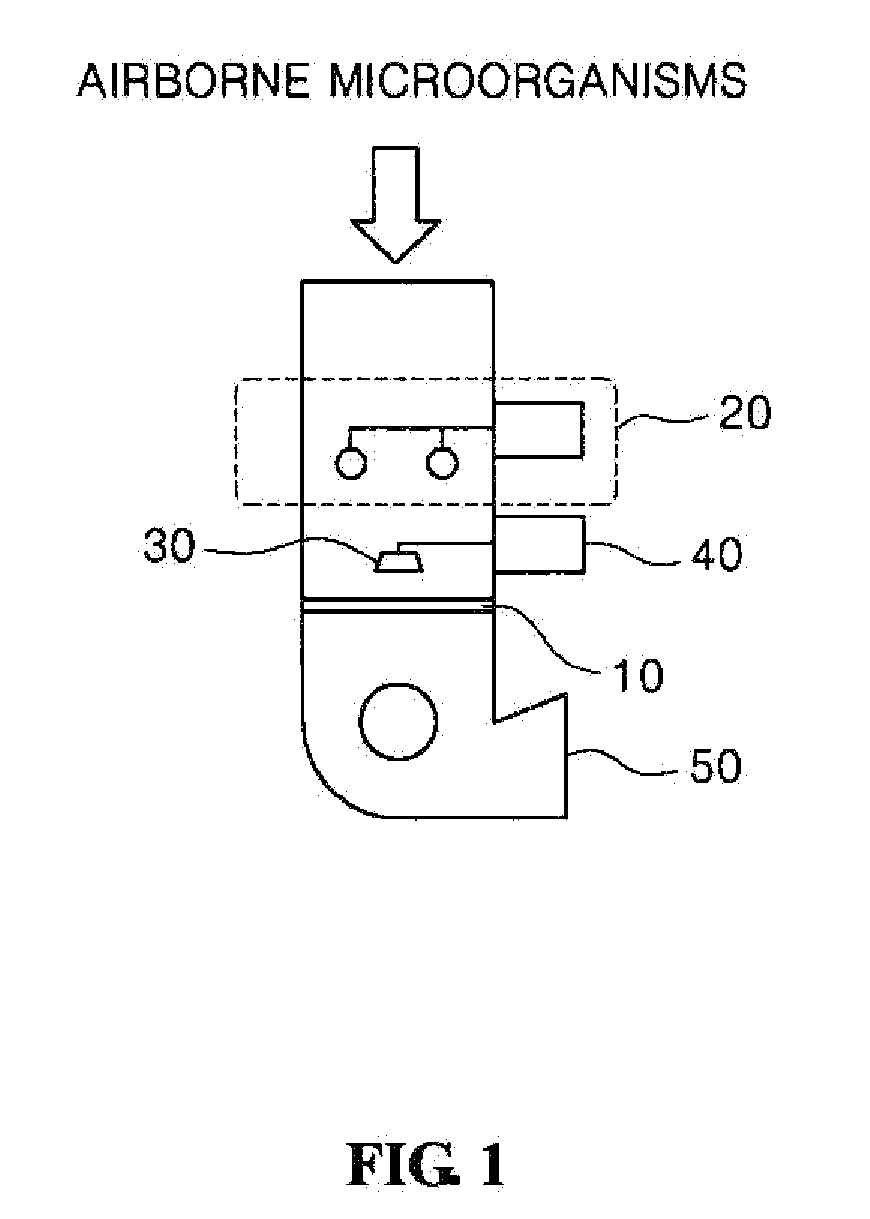
Apparatus for measuring floating microorganisms in a gas phase in real time using a system for dissolving microorganisms and ATP illumination, and method for detecting same
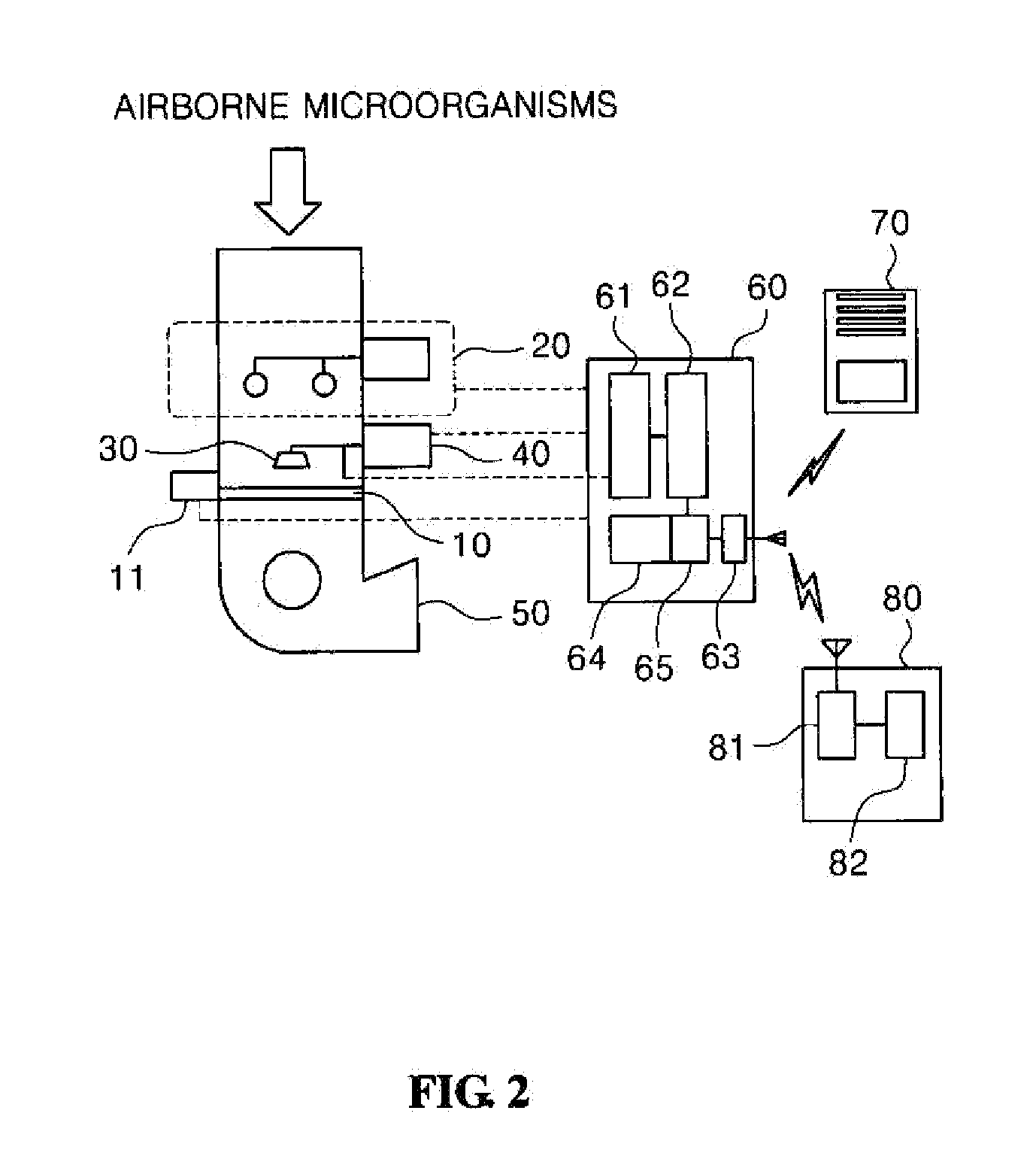
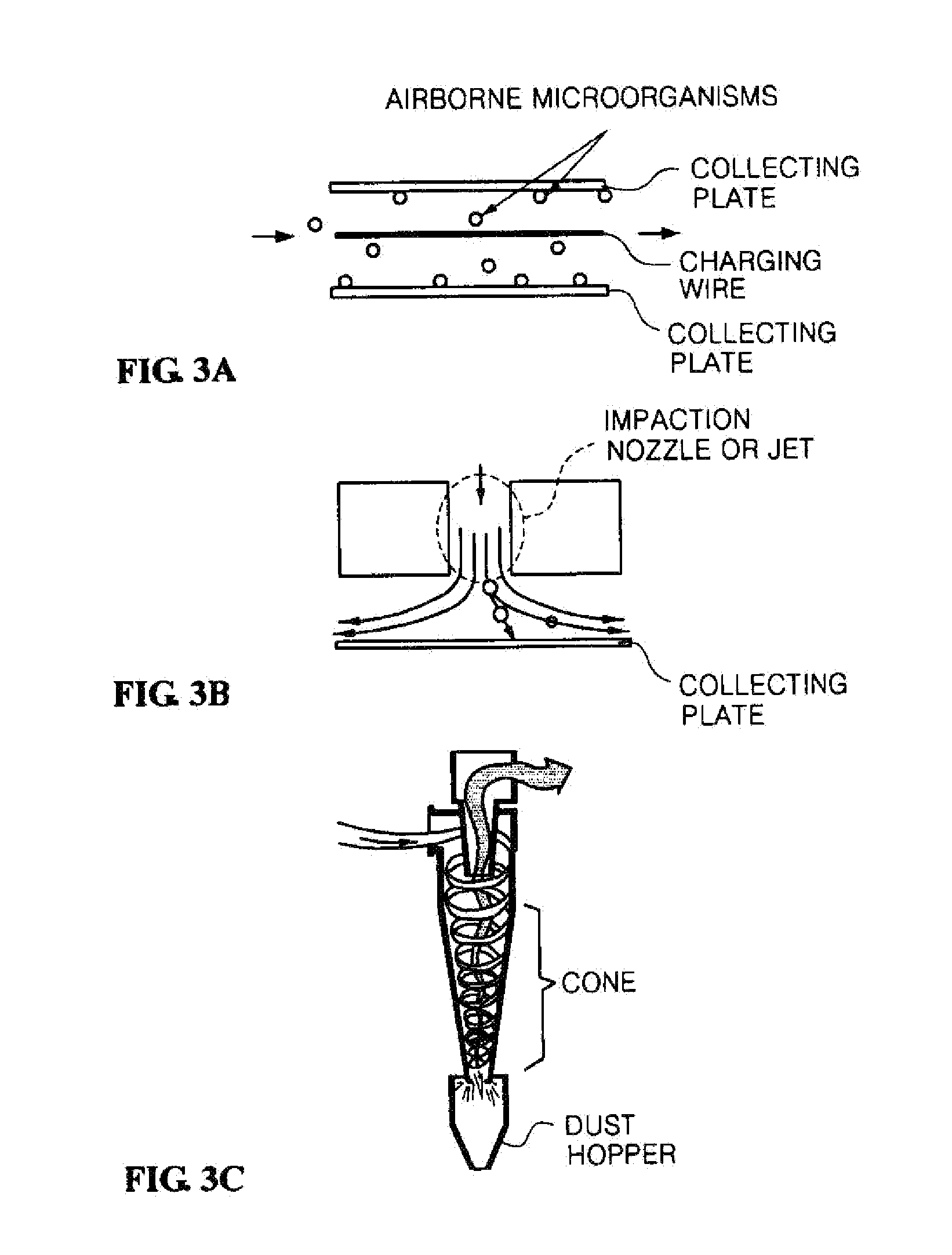
The present invention relates to a method for measuring airborne microorganisms in real time using a microorganism lysis system and ATP bioluminescence, the method including sampling the airborne microorganisms in a particle classification device to which an ATP-reactive luminescent agent is applied and, at the same time, lysing the microorganisms in a microorganism lysis system under continuous operation to extract adenosine triphosphate (ATP) of the microorganisms sampled in the particle classification device, thus inducing a luminescent reaction between the ATP-reactive luminescent agent and the ATP of the particle classification device in real time; and measuring the concentration of microorganisms using a light receiving device. According to the detection method using ATP organism illumination, the floating microorganisms in the gas phase can be readily detected and the detection can be automatically conducted in real time without manual labor.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV +1
Sanitary status on-site rapid detection device and detecting method
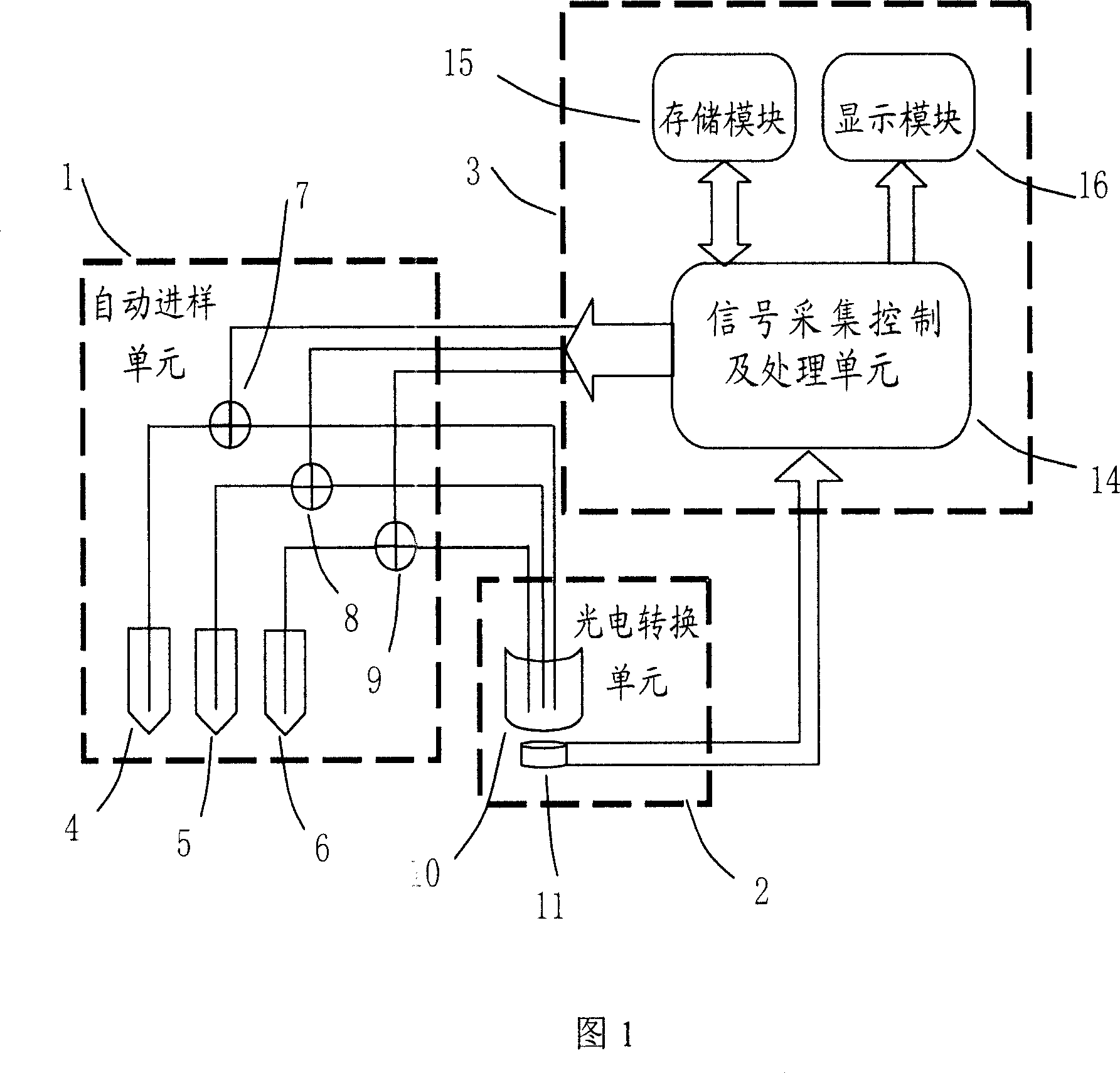
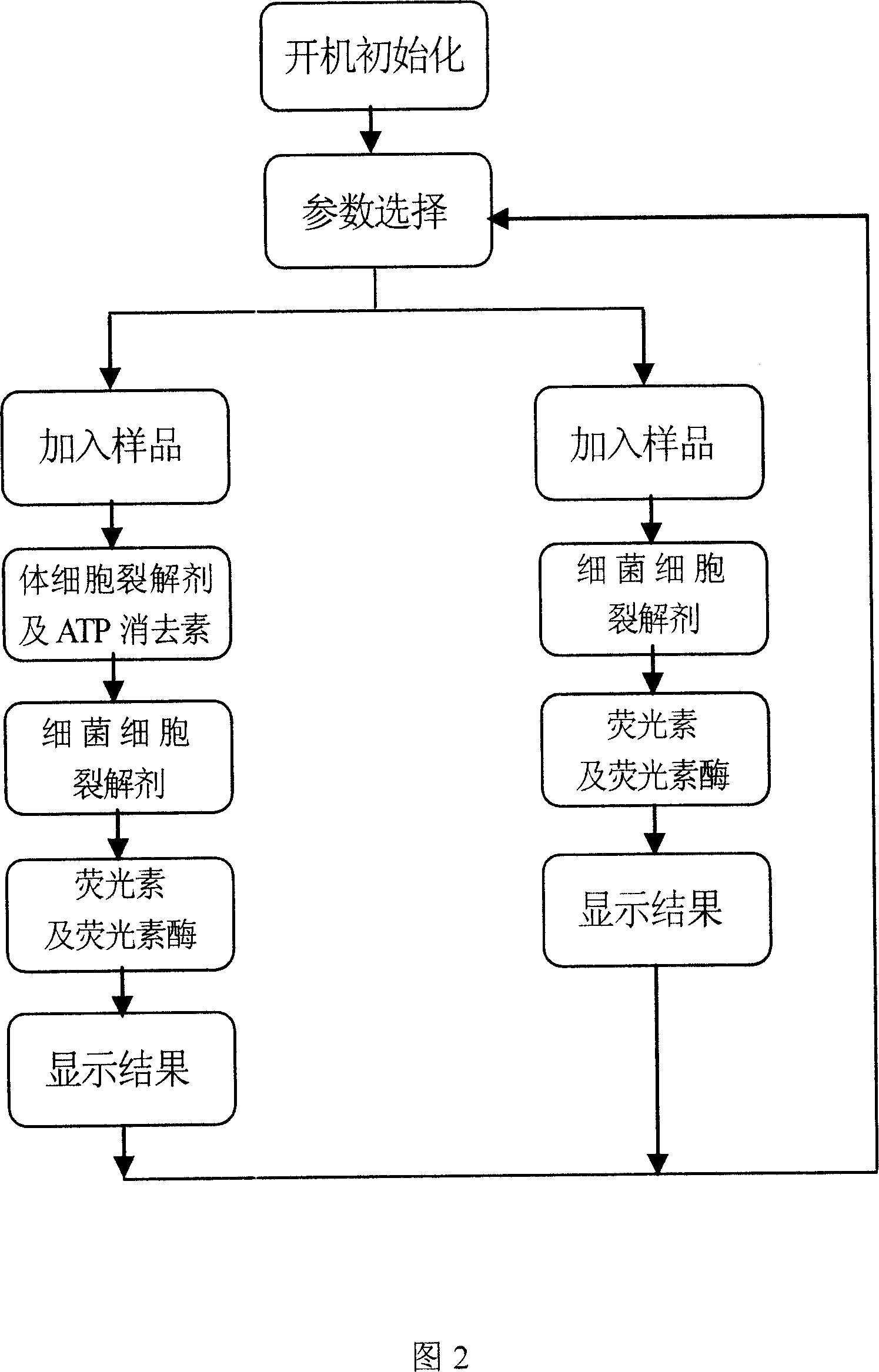
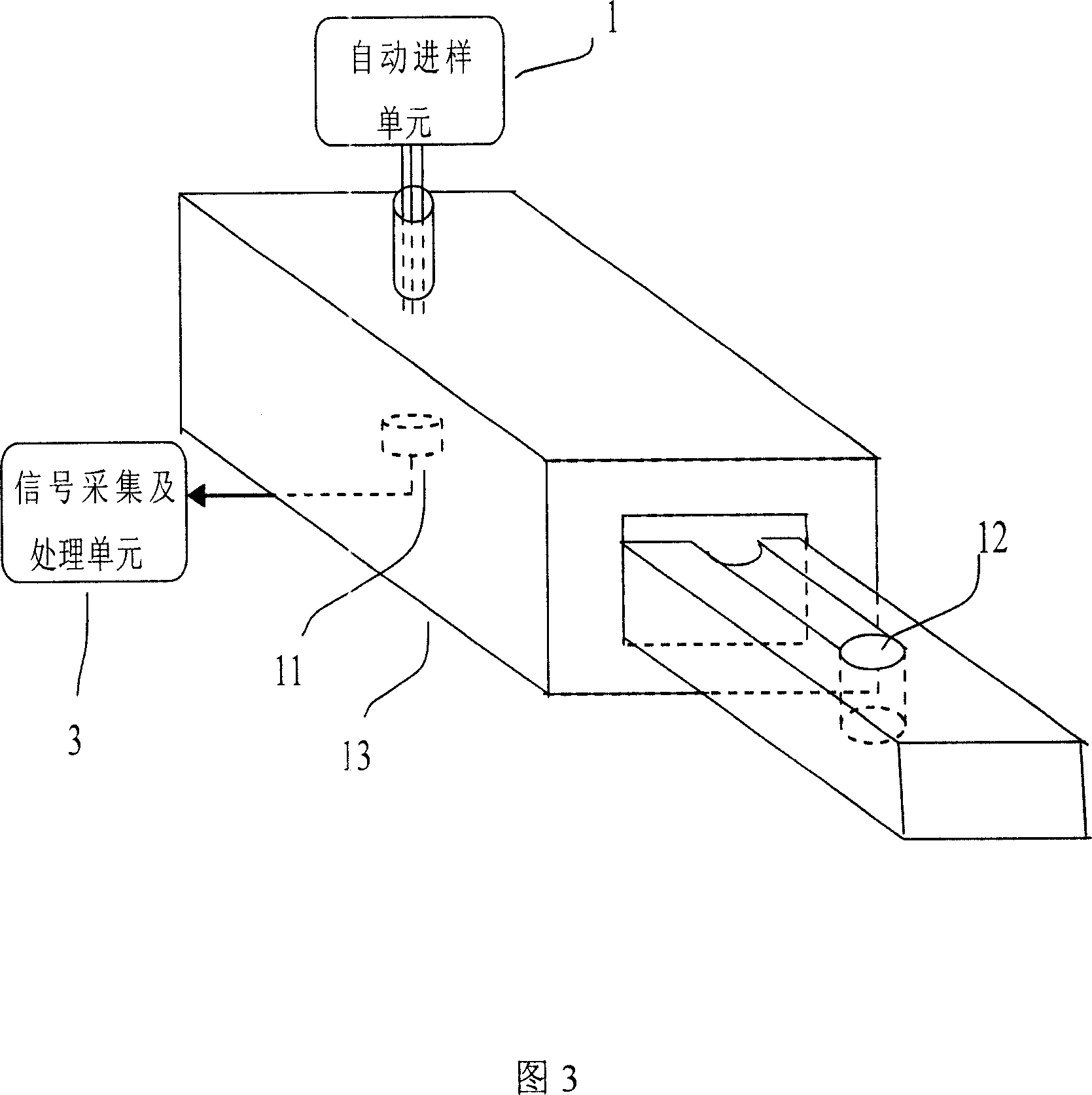
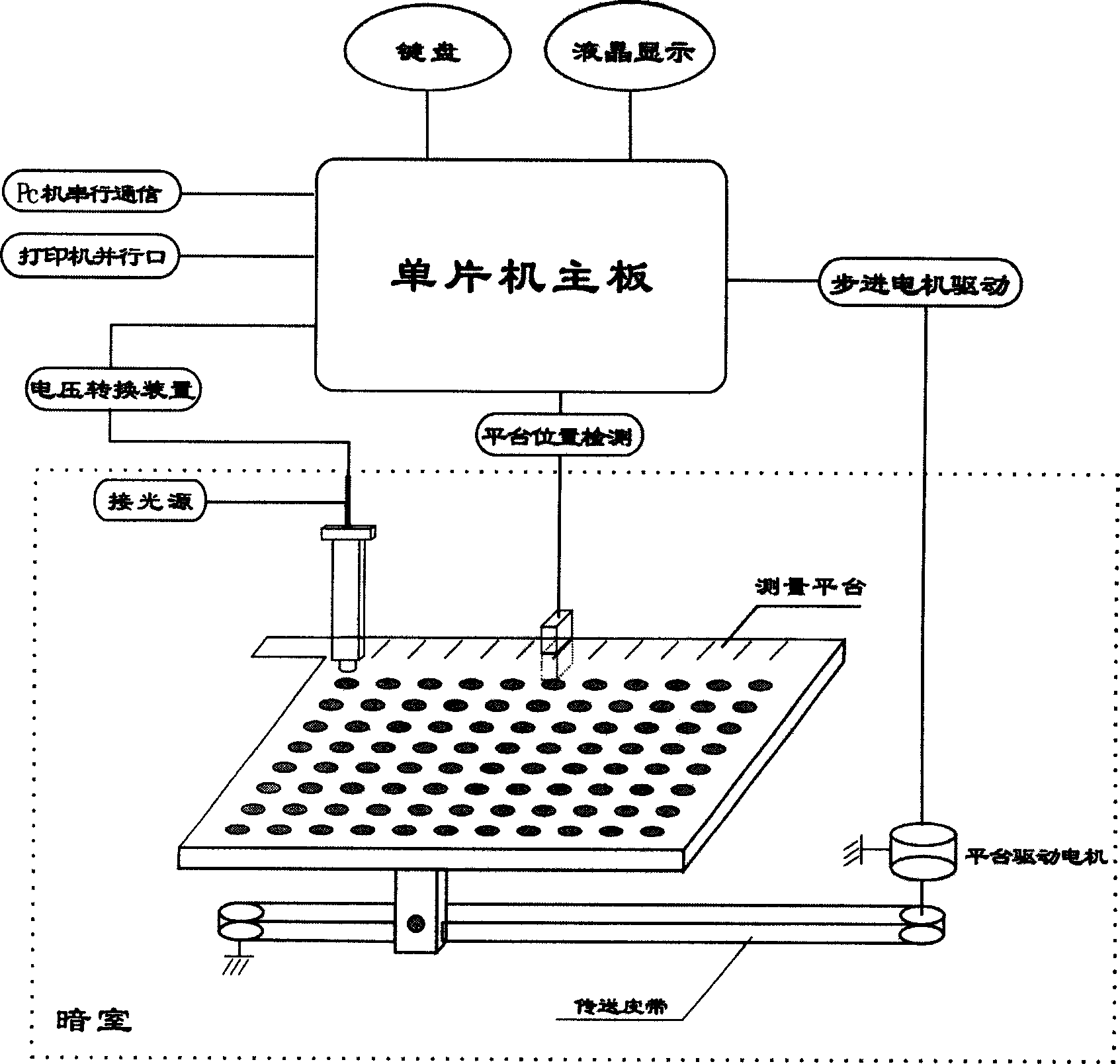
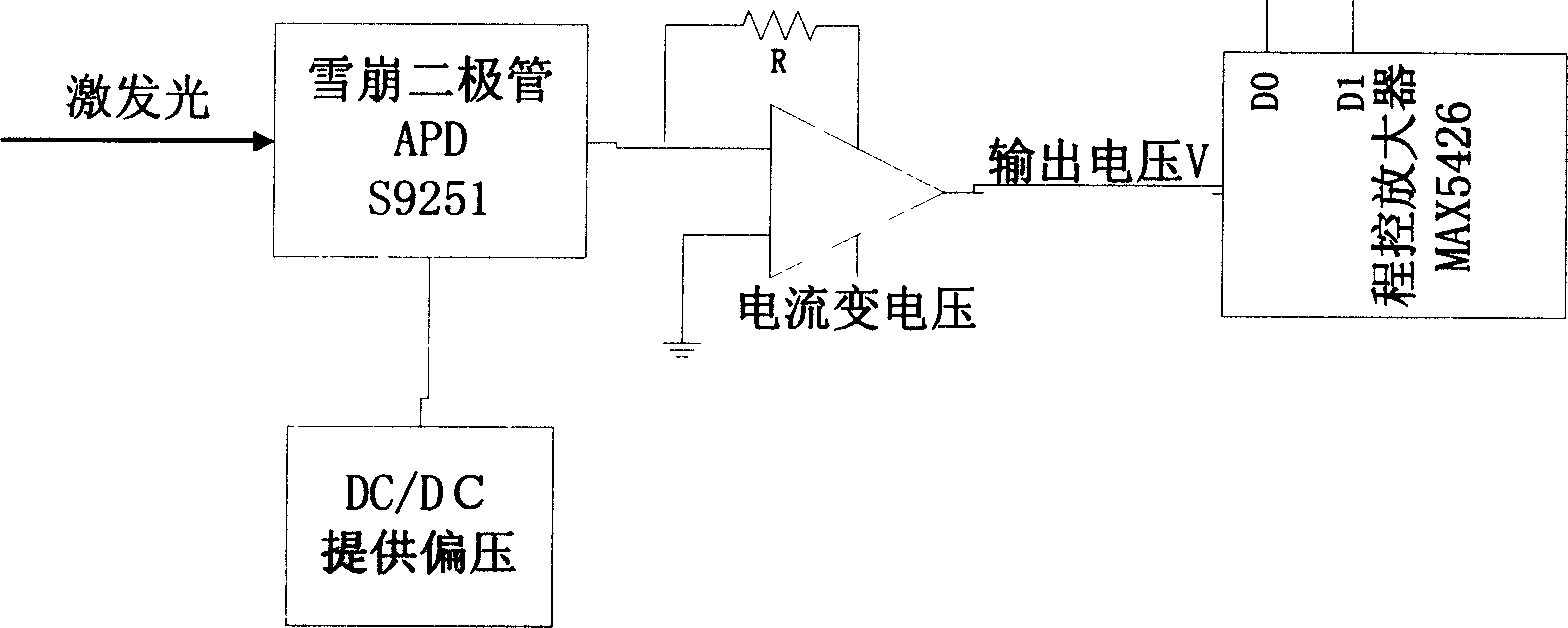
ActiveCN101113985AShort detection timeHigh degree of automationChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAtp contentEngineering
The invention discloses a sanitary quality locale rapid detection device and a detection method, the device comprises an auto sampling element, a photoelectricity conversion element and a control, operation and storage display circuit element. The method comprises that: the detected parameters are selected, based on an ATP bioluminescence theory, the detected sample and three groups detection reagents of a body cell lysates agent, a bacterial cell lysates agent and a luciferase-luciferase luminescence reagent are added to a sample pool, each reagent is provided with an auto sample adding device connected with the sample pool, the auto sample adding device controls to inject different reagents to the sample pool according to the detection requirement, the sample surface cleanliness condition is gained by measuring the total ATP content, the bacteria quantity in the sample is quantitatively detected by measuring the ATP content in the bacteria cell. Compared with the traditional device, the detection speed of the invention is fast, the detection time is less than 30 minutes, the degree of automation is high, and the maneuverability is good, the invention can be applicable to the locale rapid detection of health quality in the food, cosmetics, medical, environmental, and other fields.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting acute toxicity of water environment by using ATP bioluminescence
InactiveCN101865850AResponsiveImprove test performanceChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryAcute toxicity testingLuminescent bacteria
The invention discloses a method for detecting the acute toxicity of water environment by using ATP bioluminescence. The method comprises the following steps: an ATP reaction reagent, luciferase, an ATP standard sample, and a water body to be detected are sequentially added in a reaction test tube, placing the reaction test tube in an ATP fluoroscope testing instrument to detect fluorescence intensity, the detection response time is 30s and the detection is served as an experimental group; the standard sample is replaced by distilled water, the detection is served as a control group; the experimental group and the control group are repeatedly detected for three times; and the toxicity of the water body is judged by calculating relative luminance K. The method of the invention has the characteristic of stable and sensitive test effect; and the effect of a luminescent bacteria test can be reached within 3 min of the testing time at most; and the response on organic toxic substances is more sensitive than the luminescent bacteria. In the invention, a portable ATP handholding instrument with a direct current power supply is adopted, thus the ATP handholding instrument is convenient to be carried and is suitable for site test.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) bioluminescent reagent for detecting hygienic quality of drinking water and surface sanitation of GMP factory, method and kit
The invention discloses an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) bioluminescent reagent for detecting hygienic quality of drinking water and surface sanitation of a GMP factory, a method and a kit. The ATP bioluminescent reagent disclosed by the invention comprises luciferase, fluorescein and a luminous stability buffer system for sterile treatment to remove ATP; the luciferase is necessary to be purified; the dynamic background ratio of the purified luciferase can be up to 50-3,000; the lighting specific activity of the ATP bioluminescent reagent is in 0.4mL of luminescent system; the relative lighting log value can be up to 6.5-7.5 in ATP measurement; the luciferase, the fluorescein and the luminous stability buffer system for sterile treatment to remove ATP are frozen after being mixed, so as to obtain freeze-dried powder. Rapid detection on the hygienic quality of the drinking water and the surface sanitation of the GMP factory is carried out by adopting the ATP bioluminescent reagent with the sensitivity and a stable lighting function; sampling and rapid detection can be finished within half an hour.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM +1
Integrated micro-fluidic chip for detecting bacteria total amount and bacterial spore amount
PendingCN110437978AImprove analysis efficiencyAccurately drawBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDecompositionFluorescence
The invention discloses an integrated micro-fluidic chip for detecting the bacteria total amount and the bacterial spore amount and application thereof. The integrated micro-fluidic chip for detectingthe bacteria total amount and the bacterial spore amount comprises two independent channels which are separately used for an ATP bioluminescence method and DPA fluorescence detection, a sample is divided into two parts after entering the channels, one part passes through a splitting decomposition area, a washing area and a reaction area, the other part passes through a splitting decomposition area, a washing area, a reaction area and a fluorescence excitation area, and finally the bacteria total amount and the bacterial spore amount are measured and determined by an optical detection system.The integrated micro-fluidic chip for detecting the bacteria total amount and the bacterial spore amount can be operated in a one-button mode, has the advantages of integration, high sensitivity and the like, and can rapidly, conveniently and simultaneously detect the bacteria total amount and the bacterial spore amount.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for rapidly detecting mycobacterium
InactiveCN101639479AOvercome the disadvantage of slow cultivation speedMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAcid-fastMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting mycobacterium. In the method, ATP bioluminescence technology is used for detection, and the growth condition of the mycobacterium is judged by comparing the initial ATP value with the ATP value measured after a cultivation period and by adding acid-fast stain. Compared with the prior art, the method uses the rapid and sensitive ATP bioluminescence technology for detecting the growth condition of the mycobacterium in a liquid culture medium, and simultaneously combines the acid-fast stain to primarily judge whether the growth of the mycobacterium exists to achieve the characteristics of high speed, high sensitivity, and the like. Generally, the report time of the positive detection result is no more than 2 to 3 weeks.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEIQUAN SCI & BIOTECH
Multi-sample microbial pollution fast screening method
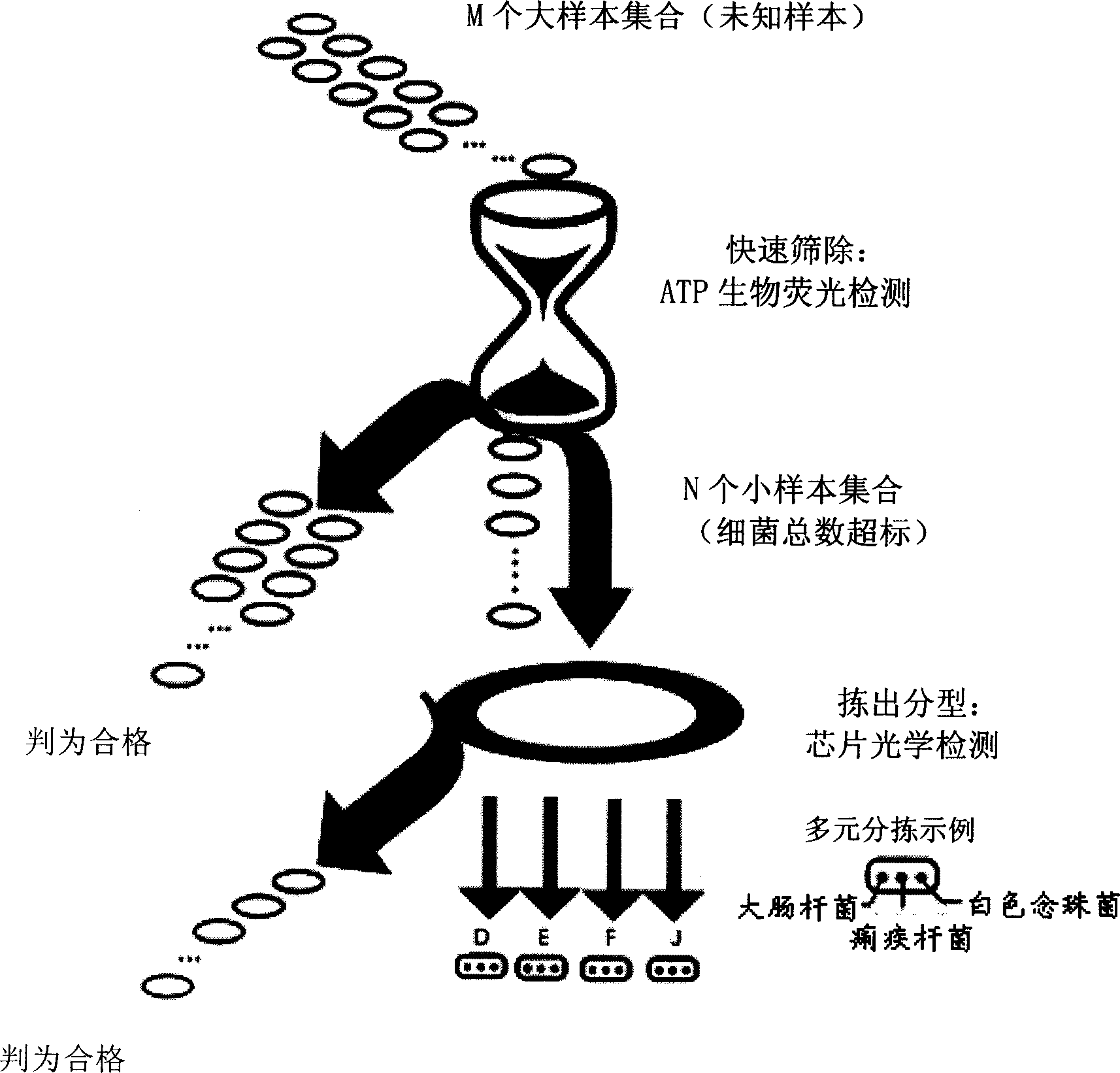
InactiveCN1743834AMake up for deficienciesQuick screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSmall sampleFluorescence
This invention discloses a method for quick screening multi sample microbial contamination, which utilizes ATP bioluminescence test to complete large sample test, then utilizing biochip technology making identification and classification of harmful microbial to small sample group with exceeded bacteria sum, overcoming the shortage of ATP bioluminescence test in specificity and test quantity.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for quick detection of microbe
InactiveCN1828303AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenMicroorganism
The provided method comprises: with specific immune magnetic pearl to capture the special microbe in sample; releasing the ATP in microbe cell with cracking agent; finally, detecting the ATP to decide the target and opposite amount with the fluorescein-luciferase bioluminescence system. Compared with prior art, this invention has high sensitivity and strong specificity to complete whole process within 8h.
Owner:益思美诠生物科技(上海)有限公司
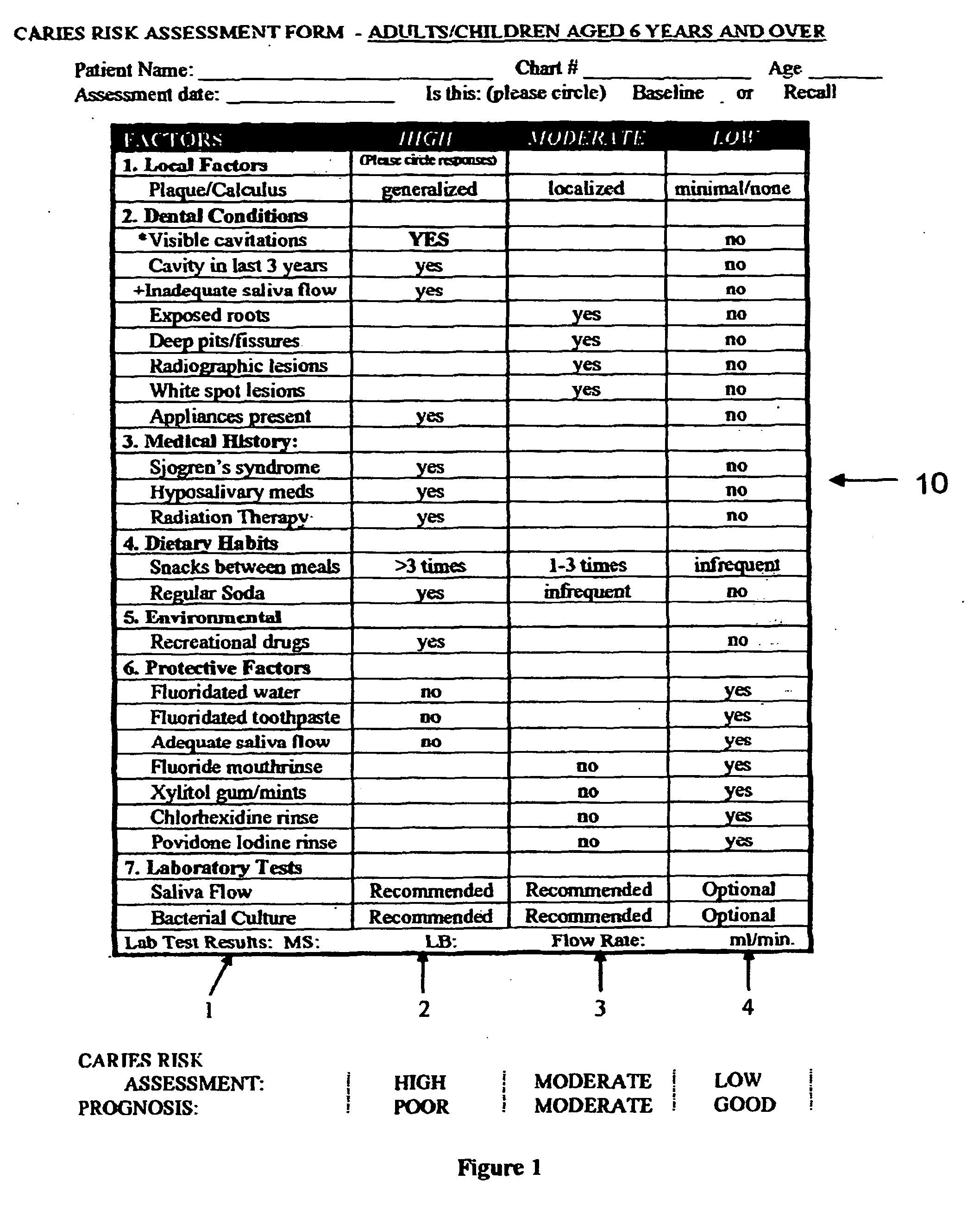
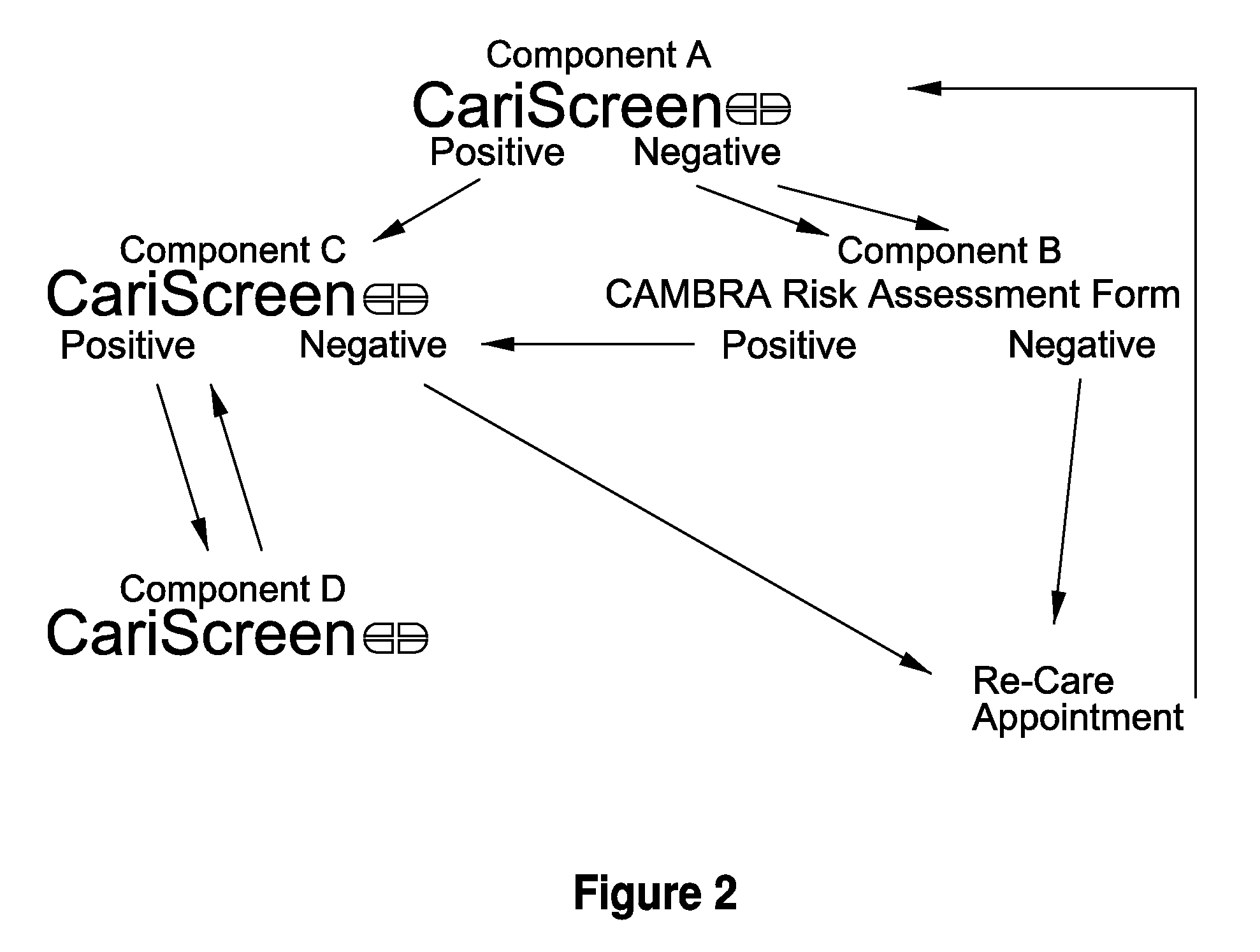
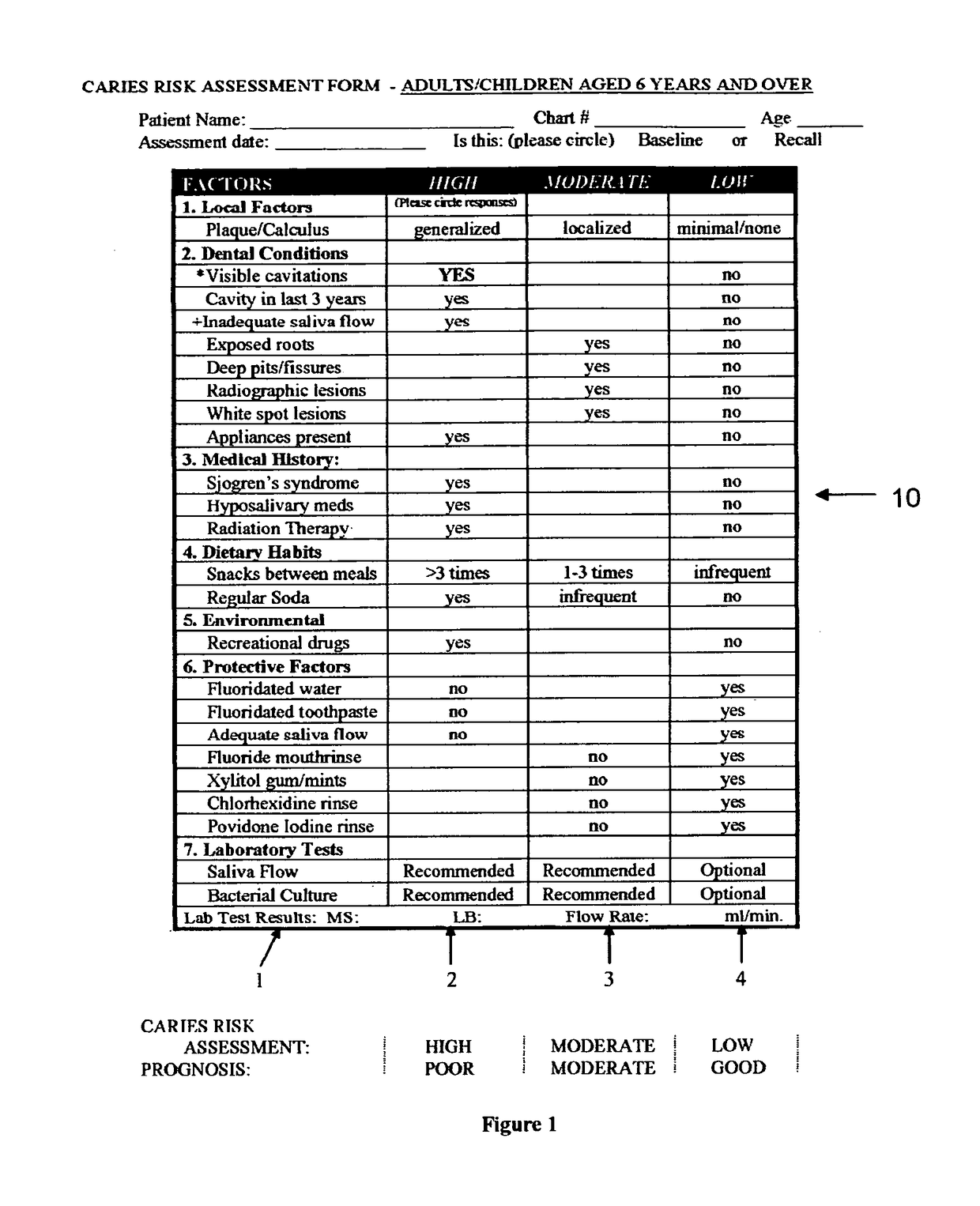
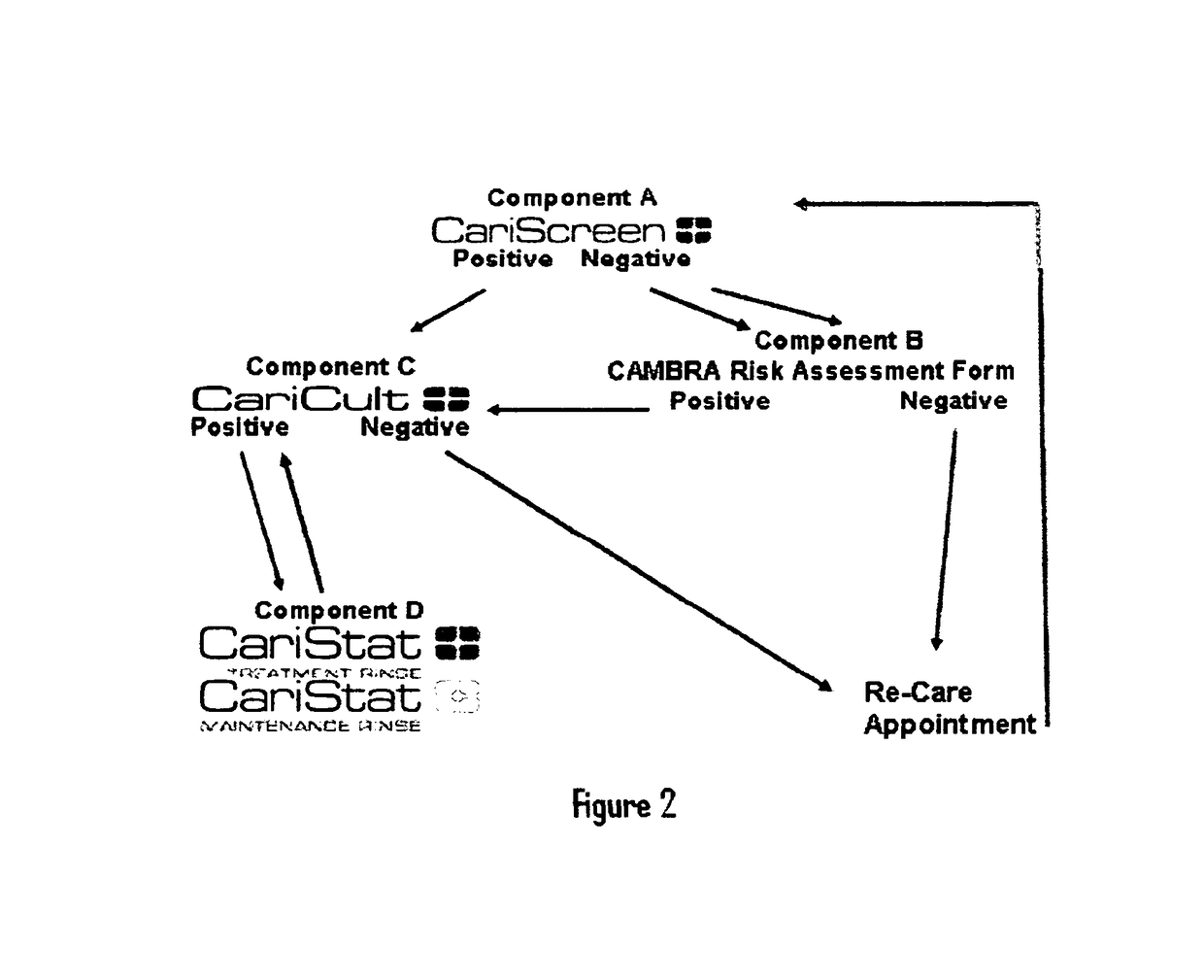
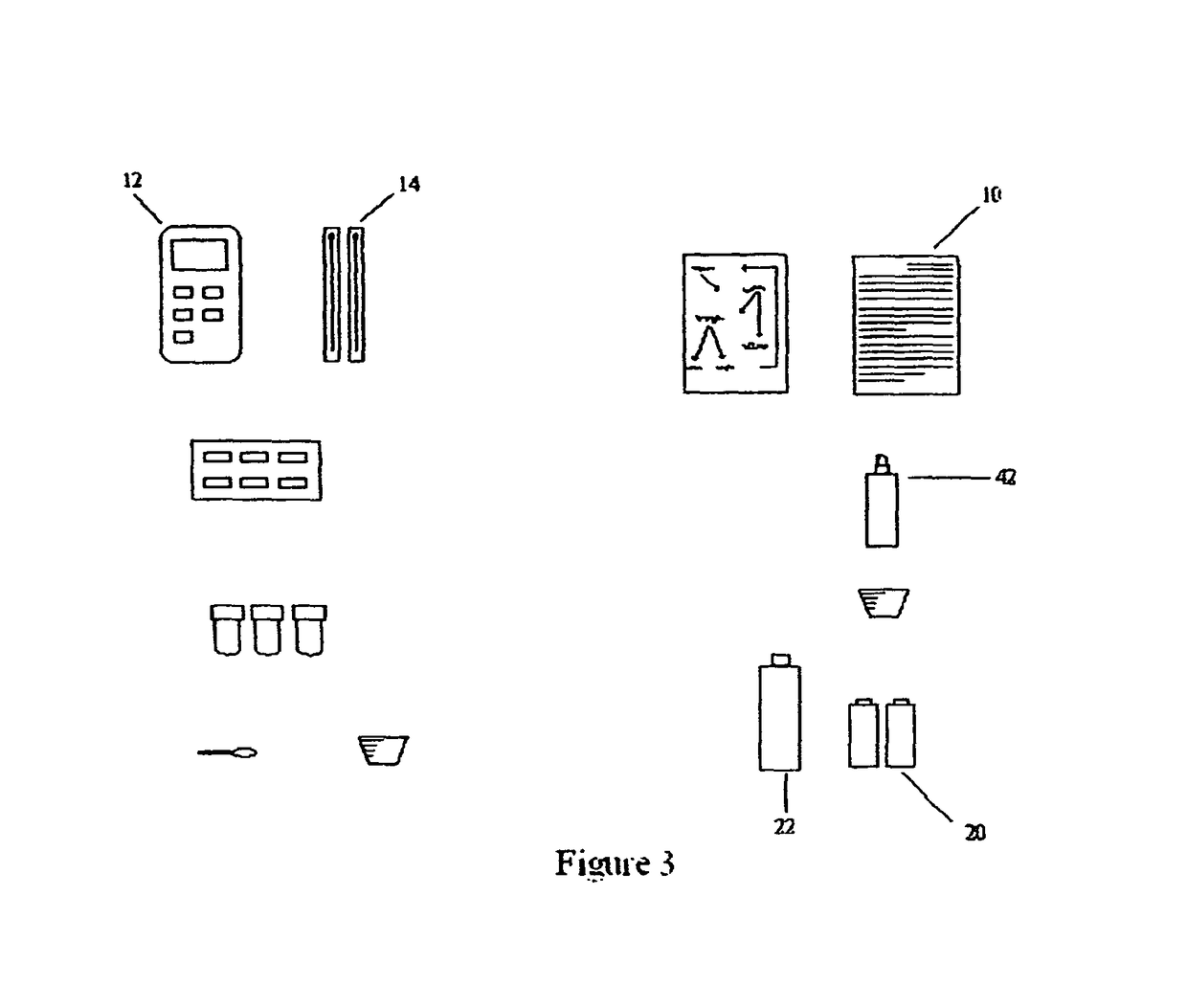
System for caries management by risk assessment
ActiveUS20120321570A1The process is simple and effectiveAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsDental patientsShort term treatment
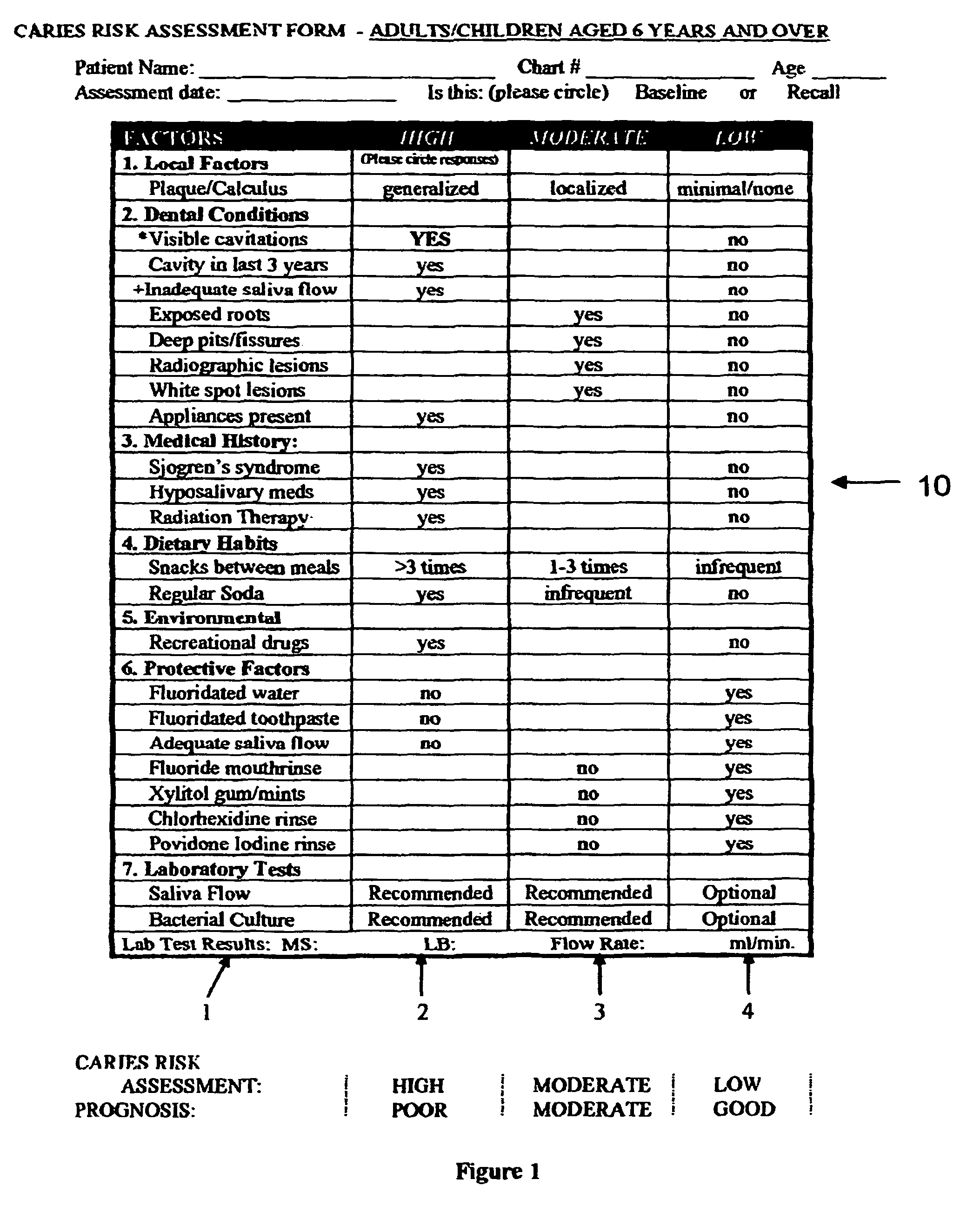
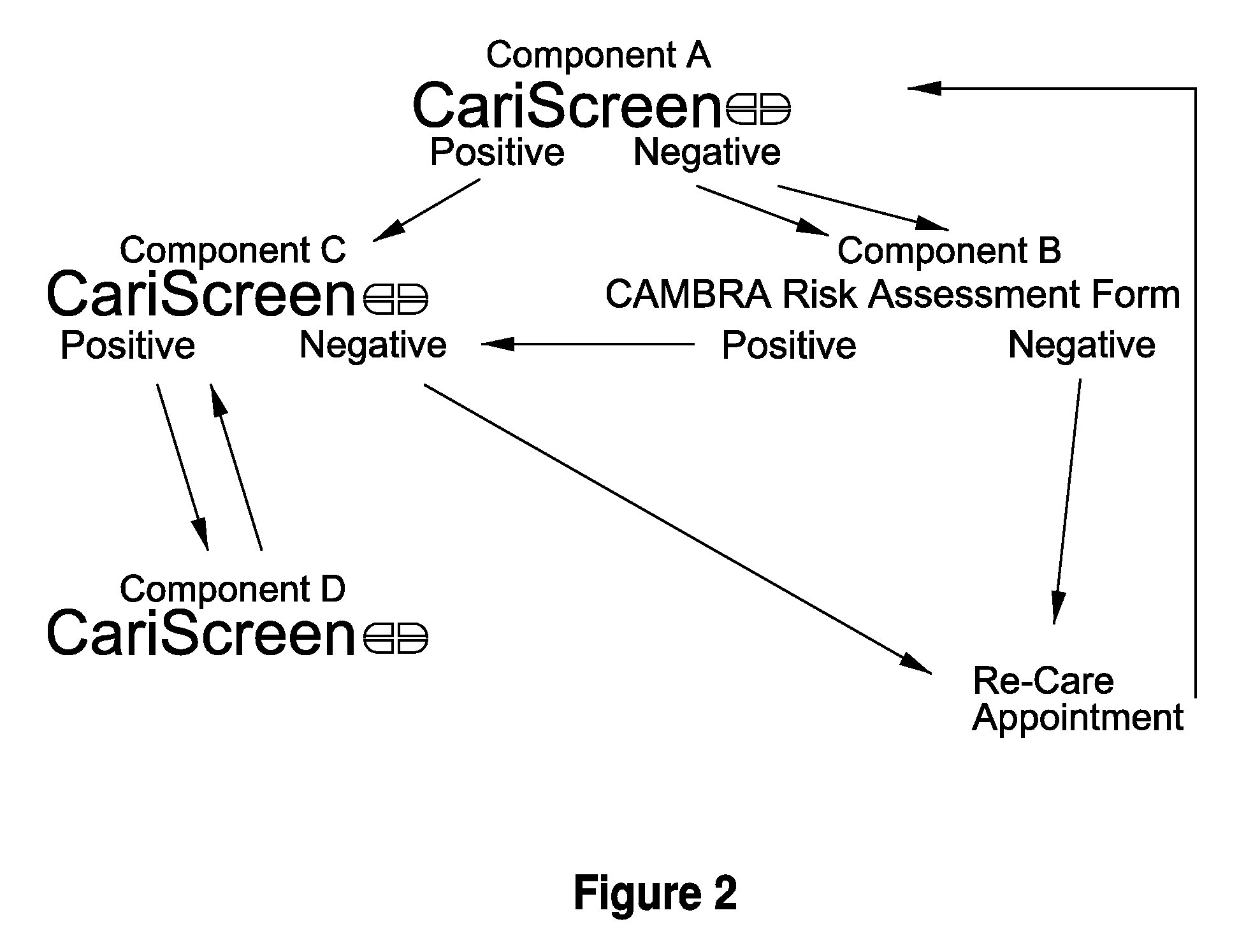
The invention provides the tools needed for a dental patient's caries risk assessment. Included is a complete turnkey system for caries risk assessment and treatment, including an ATP test and a plurality of rinses and educational and diagnostic materials. The system for the detection and treatment of the bacterial infection that causes dental caries in a patient comprises a disposable ATP Bioluminescence sampler to swab areas of the patient's mouth, a bioluminescent light meter which measures the amount of ATP present in the patient's mouth, a rapid culture test for the detection of Mutans streptococci and lactobacilli, a diagnostic testing component that includes a caries risk assessment questionnaire, a treatment component that includes a short term therapeutic oral rinse of at least two components, and a long term maintenance rinse.
Owner:DENTAL ALLIANCE HLDG LLC
Method for preparing firefly luciferase
InactiveCN101302502AImprove developmentSimple processOxidoreductasesFermentationMicroorganismFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for making firefly luciferase, comprising the following steps of: inserting the firefly luciferase gene into multiple cloning sites of a prokaryotic expression vector; obtaining a recombinant expression vector containing the firefly luciferase gene; introducing the recombinant expression vector into a colon bacillus cell to obtain a recombinant cell containing the recombinant expression vector; culturing the recombinant cell to obtain the firefly luciferase from the expression. The method for making the firefly luciferase has the advantages of simple process, short growth period, low cost, easy purification, high enzyme activity and stable performance and so on. The method can relieve a situation that the firefly luciferase mainly depends on import, and can promote the development of a fluorescent microorganism rapid detection system and the application of the firefly luciferase in medicine and environment science and so on, thereby providing excellent enzyme preparation for the rapid detection and applications in other aspects of ATP bioluminescence microorganism.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Metering method for rapid measurement of mould in stored grain through ATP bioluminescence method and applications
InactiveCN103336000AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFiltrationSterile water
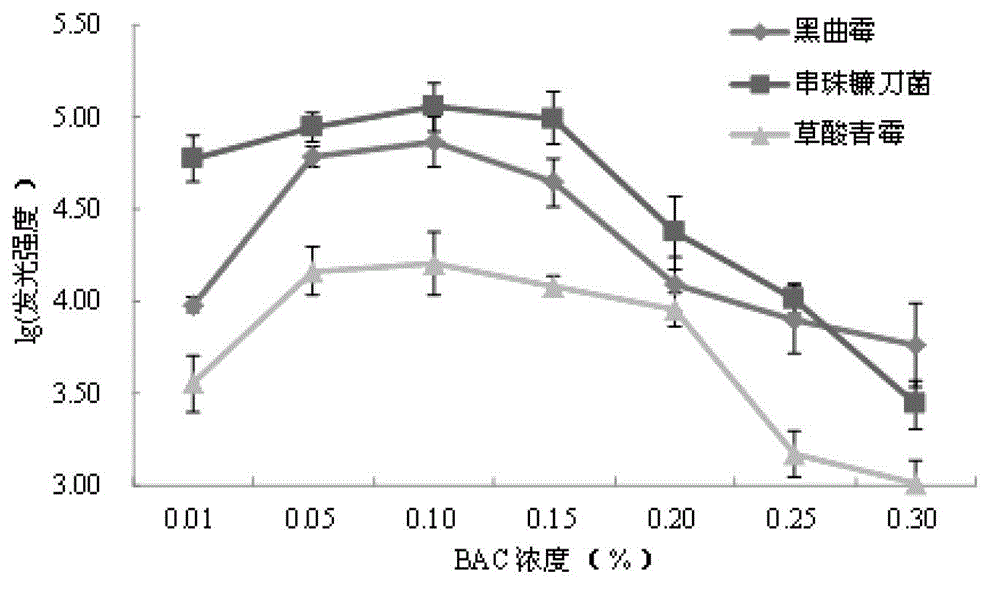
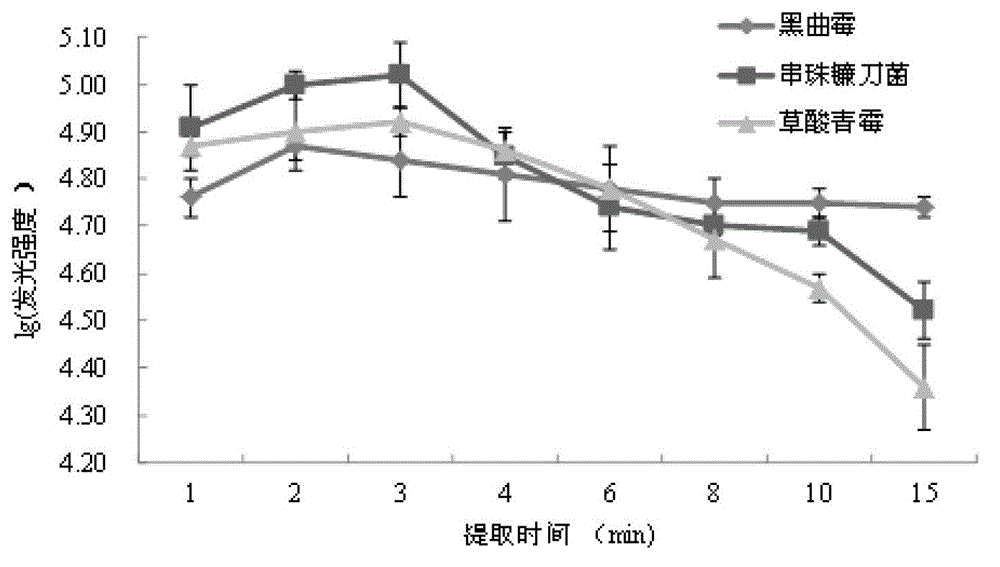
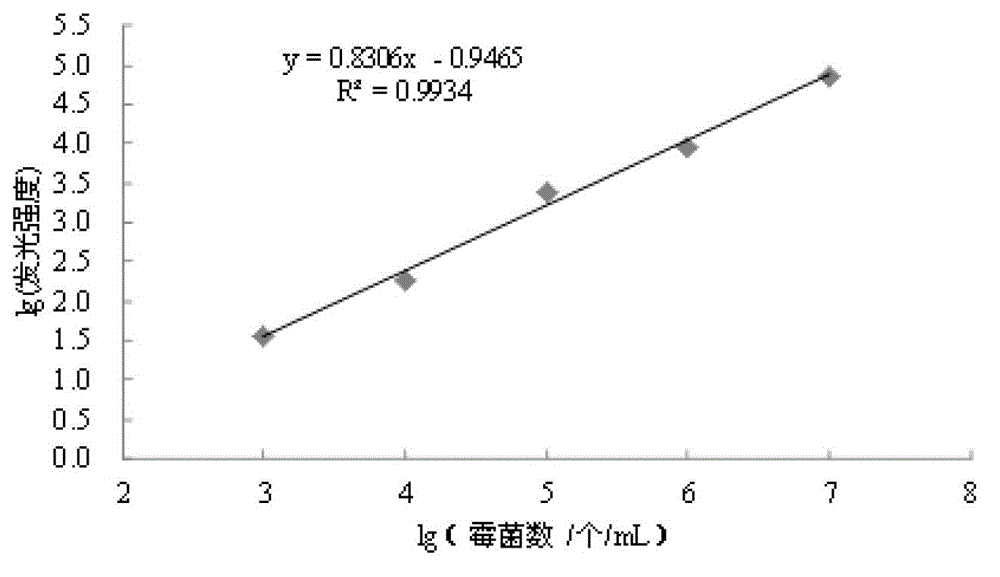
The invention relates to a metering method for rapid measurement of mould in stored grain through the ATP bioluminescence method. The metering method comprises the following steps. (1) 25 g grain and 10-20 glass beads are put into 225 mL sterile water and oscillated to obtain a bacterial suspension, standby. (2) 50-200 mL of the bacterial suspension is subjected to suction filtration through filter membranes with a pore size of 0.22 mum, the filter membranes are then transferred to a BAC solution which is 0.1 times the bacterial suspension in volume, the BAC solution is oscillated to extract ATP, and a reaction solution to be measured is obtained. (3) 100 muL of the reaction solution from step (2) is added into 100 muL of the rL / L reagent and mixed evenly, and luminescence values are measured. The metering method does not need cultivation processes to measure mould quantity through the ATP bioluminescence method and has simple operations and high sensitivity. Measurement results can be obtained in short time, and the metering method has obvious advantages compared with other measurement methods for microorganisms.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Distinctive method for quantitatively detecting staphylococcal bacteria
The invention discloses a distinctive method for quantitatively detecting staphylococcal bacteria. The invention discloses recombinant lysostaphin shown as the following (1) or (2): (1) a protein shown as N-terminal amino acids (13-258 positions) in SEQ ID No. 2; (2) a protein formed by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence (1) and having the same function. The distinctive method for quantitatively detecting staphylococcal bacteria, disclosed by the invention, is recombinant lysostaphin-integrated ATP bioluminescence method. The method disclosed by the invention is rapid and easy to operate, provides a theoretical support for on-site or clinical quantitative detection of staphylococcal bacteria, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
System for caries management by risk assessment
ActiveUS9427384B2The process is simple and effectiveAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsDental patientsLight meter
The invention provides the tools needed for a dental patient's caries risk assessment. Included is a complete turnkey system for caries risk assessment and treatment, including an ATP test and a plurality of rinses and educational and diagnostic materials. The system for the detection and treatment of the bacterial infection that causes dental caries in a patient comprises a disposable ATP Bioluminescence sampler to swab areas of the patient's mouth, a bioluminescent light meter which measures the amount of ATP present in the patient's mouth, a rapid culture test for the detection of Mutans streptococci and lactobacilli, a diagnostic testing component that includes a caries risk assessment questionnaire, a treatment component that includes a short term therapeutic oral rinse of at least two components, and a long term maintenance rinse.
Owner:DENTAL ALLIANCE HLDG LLC
Screening method of nutritive salt for pollutant enhanced bioremediation and application
InactiveCN107377614AImprove long-term stabilityLiquid phase reaction is fastContaminated soil reclamationFluorescenceScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of nutritive salt for pollutant enhanced bioremediation. The screening method comprises the steps of 1) adding a culture medium into liquid samples containing pollutants, then, observing the growing situation of floras, and carrying out baseline screening; 2) adding different varieties of nutritive salt of different proportions into the liquid samples containing the pollutants, carrying out shake-flask culture, and testing the amount of microorganism colonies through plate count and an ATP bioluminescence detector; and 3) detecting concentration of the pollutants in the pollutant-containing liquid samples cultured through adding of nutritive salt, evaluating the pollutant enhanced bioremediation effect of nutritive salt according to a result, and acquiring an optimal nutritive salt formula.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Kit for anti-interference quick detection of microbe quantity by bioluminescence method
InactiveCN100532568CMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAtp contentLinear regression
The invention relates to a method and a detection kit for rapidly detecting the number of microorganisms using ATP bioluminescence method. The rapid detection kit includes luciferase and its protective agent, D-luciferin, standard ATP, luminescent detection buffer, acellular ATP remover, microbial cell ATP extractant and other reagents. The standard method for using this detection kit to quickly determine the number of microorganisms is to make an ATP standard curve in a selected bioluminescence instrument and a selected system, and obtain a linear regression equation after taking the logarithm. After removing non-target ATP and microbial The sample solution extracted by ATP is detected in the same instrument and system with the same batch of enzymes for ATP bioluminescence detection, and a blank control is made at the same time to obtain the CPM or RLU value of the sample and the blank, and the net relative luminescence value after removing the blank is taken as logarithm Finally, the ATP concentration of the sample is obtained through the established regression equation. According to the ATP content of microorganisms such as bacteria, yeast, mold and unicellular microalgae, it can be converted into the number of cells of bacteria, yeast, mold spores or unicellular microalgae, or only calculated Equivalent to the number of bacteria.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
ATP-bioluminescence immunoassay
InactiveUS8518658B1Wide applicationWeak matrixMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSalmonella entericaBacteroides
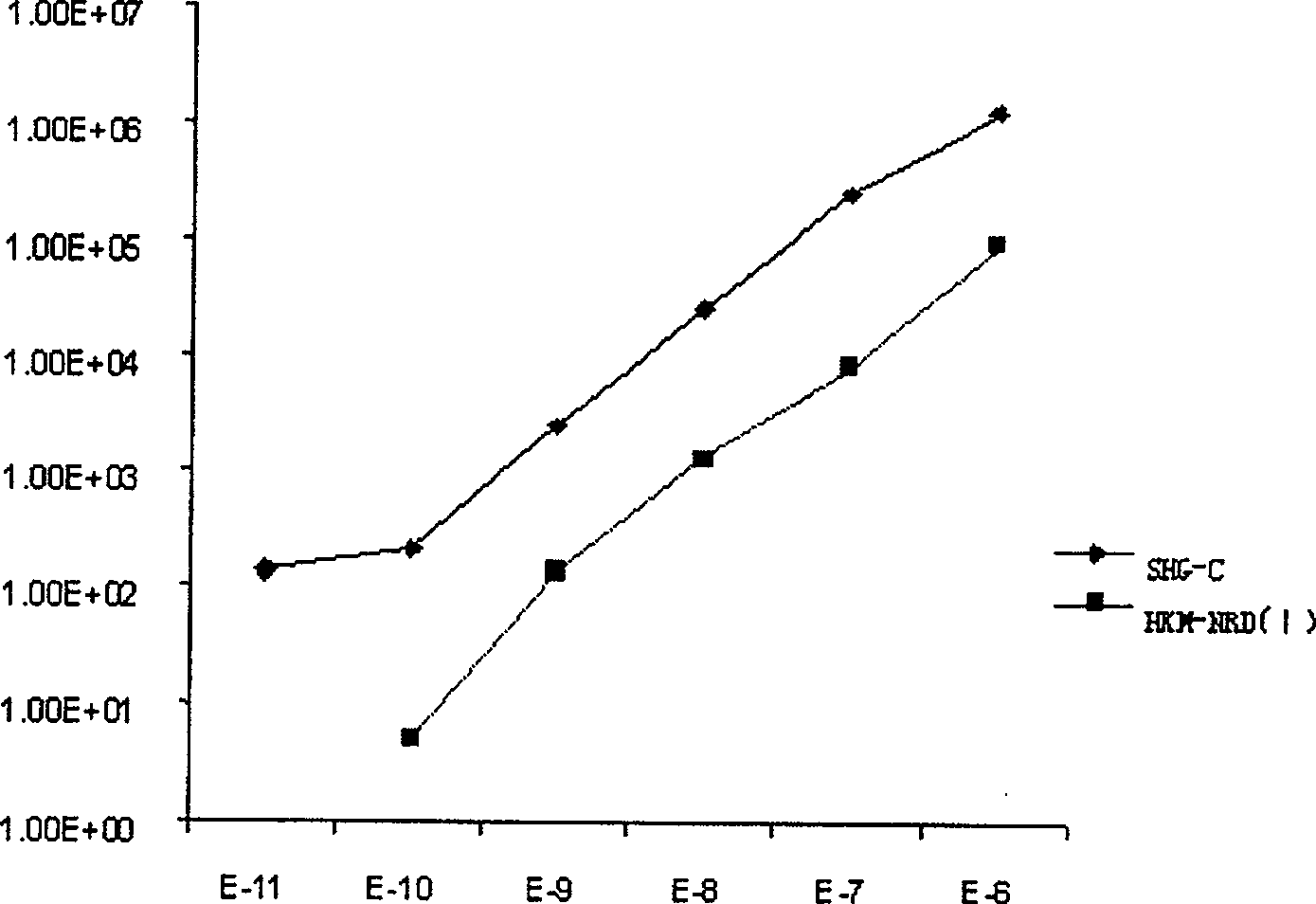
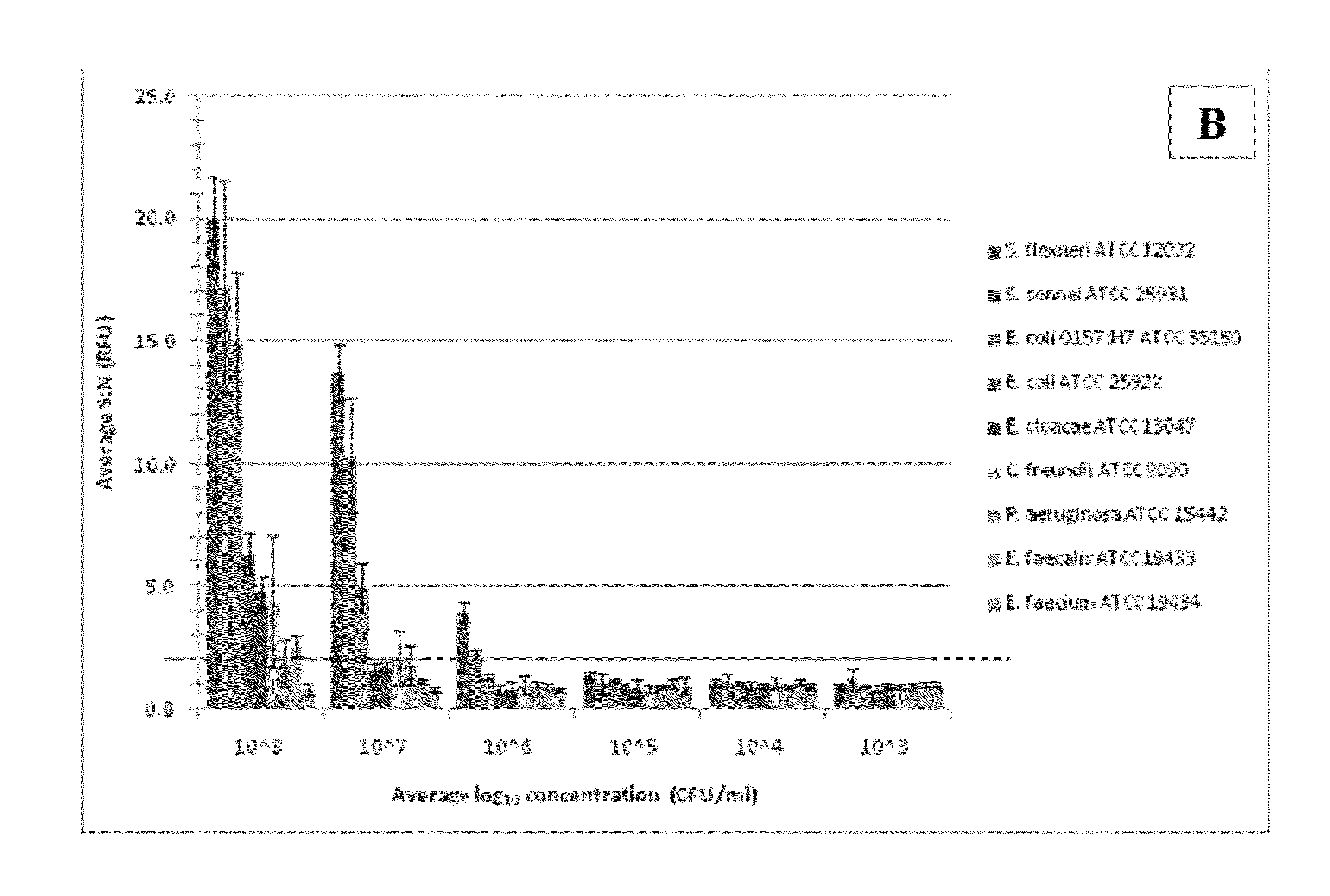
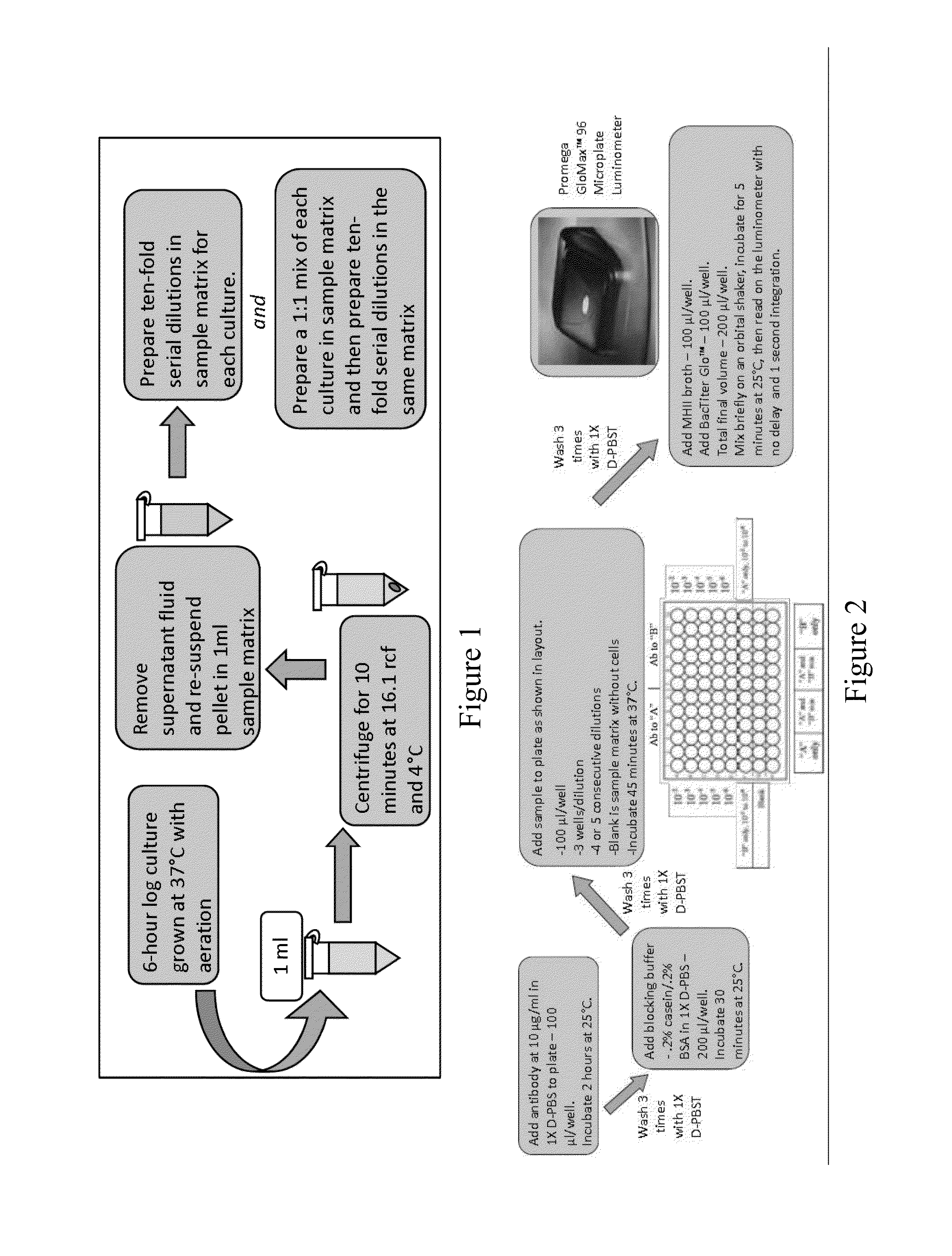
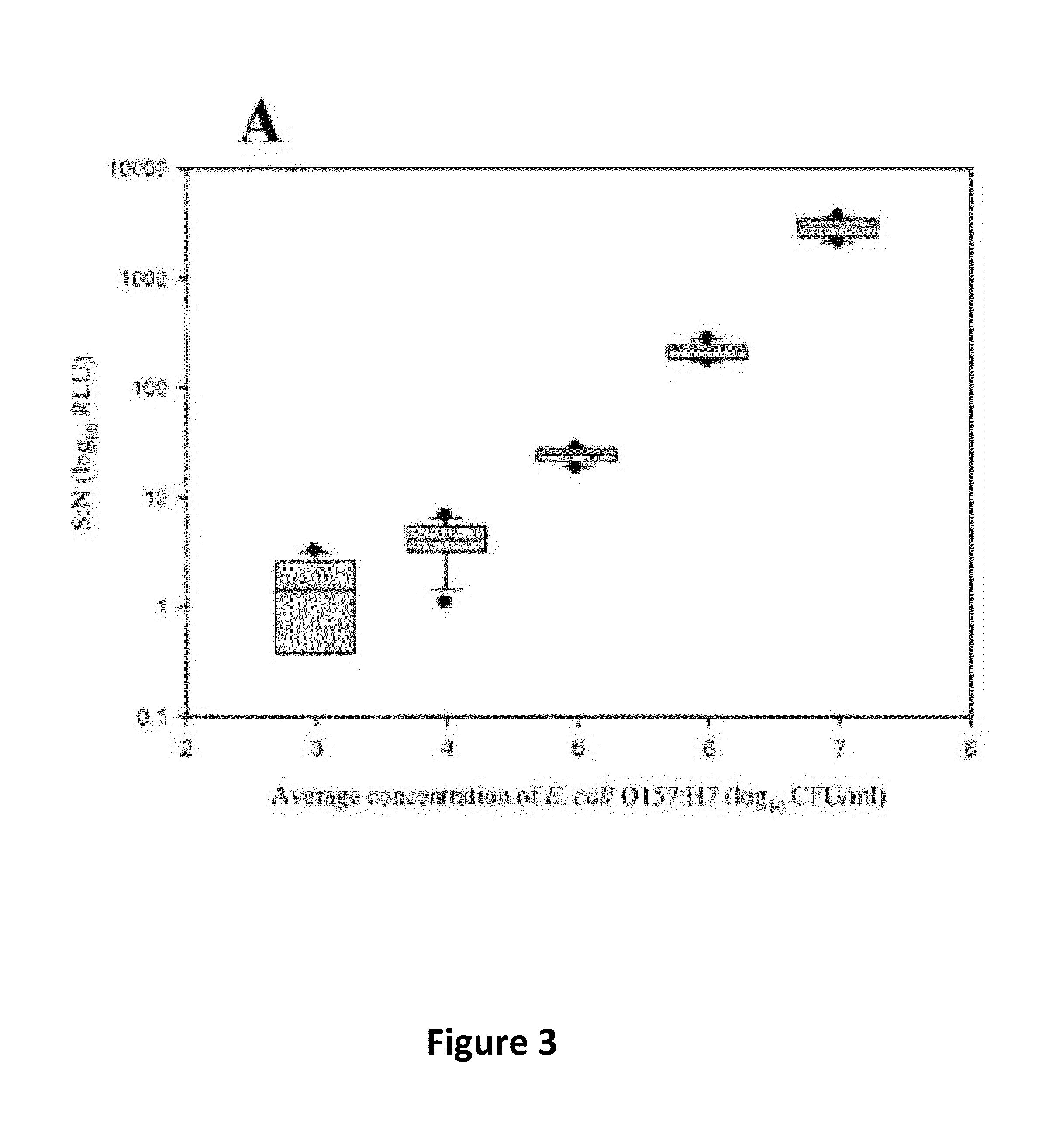
Disclosed is a method and associated device for the rapid identification of viable bacterial contaminants in food products. The method detects viable microbes by using a combined ATP-bioluminescence immunoassay. Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium were selected as target organisms in various matrices including ground beef homogenate, apple juice, milk, and phosphate-buffered saline. Specific antibodies were immobilized on the surface of well plates in which the sample matrices were incubated. The plates were washed, and the wells were incubated with BacTiter-Glo reagent in Mueller-Hinton II broth. Bioluminescent output was measured with a luminometer and signal-to-noise ratios were calculated. The LOD was not affected by the presence of non-target cells. A strong linear correlation was observed between the number of cells and luminescent output over 4 orders of magnitude. This method provides a means of simultaneously detecting and identifying viable pathogens in complex matrices.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method for detecting botulinum in food through ATP bioluminescence reaction
InactiveCN109932359AHigh sensitivityAccurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWater bathsFood safety
The invention discloses a method for detecting botulinum in food by using an ATP bioluminescence reaction. According to the method, a sample to be detected is mixed with PBS, and an obtained mixture is centrifuged, so that an initial supernatant can be obtained; a digestive solution is added to the initial supernatant, so that a water-bath heating reaction can be carried out; an obtained mixture is centrifuged again, so that a digestion supernatant is obtained and filtered; and a filter membrane is immersed in an ATP release solution, and an obtained mixture is subjected to oscillation extraction, so that an ATP extract can be obtained; a prepared luminescent reaction solution and the ATP extract are mixed in a luminous reaction tube; the luminous reaction tube is arranged in an ATP luminescence detector for detecting illumination intensity; and therefore, the rapid detection of botulinum in food can be realized. The method for detecting botulinum in food through the ATP bioluminescence reaction of the invention is simple, rapid and highly sensitive, can accurately detect whether food contains botulinum and the relative content of the botulinum, and greatly promote the improvementof food safety detection technologies.
Owner:张 丽英
Method for detecting antibacterial performance of antibacterial plastics by ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method
InactiveCN110272973AAvoid errorsEnsure quantificationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementModel selectionAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a method for detecting the antibacterial performance of antibacterial plastics. The method comprises the following detection steps of: carrying out sample preparation and preprocessing; carrying out equipment model selection and reagent and culture medium preparation; carrying out culture preservation and activation, and preparing bacterial suspension; establishing an optical density (OD) value-viable bacterium content logarithm value lgC standard curve, and carrying out inoculation bacteria solution C calibration; establishing a lgC-relative fluorescence intensity logarithm value lgC standard curve; carrying out sample inoculation, culture, elution and recovery; measuring recovery liquid I, and reckoning the viable bacterium contents C and T of the recovery liquid; calculating an antibacterial ratio R or an antibacterial activity value A; and carrying out result evaluation. The method is characterized in that an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) fluorophotometer is applied to accurately and quantitatively test the plastic antibacterial performance represented by R or A. The method stipulates that control samples and antibacterial samples subjected to 0h contact and cultured for 24h are eluted and recovered, the recovery liquid I is measured, R or A is represented and calculated by lgI, and a result evaluation basis is provided. The ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method researched and developed by the invention for detecting the antibacterial performance of the plastics supports product quality improvement by a scientific and advanced detection technology.
Owner:李文杰
Method for detecting anti-fungal performance of nano inorganic material by ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method
PendingCN110272970ADetermination of precisionBreak through the limitations of qualitative analysisFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementStainingModel selection
The invention relates to a method for detecting anti-fungal performance of a nano inorganic antibacterial material. The method for detecting the anti-fungal performance of the nano inorganic antibacterial material comprises the steps that sample preparation and pretreatment are carried out; equipment model selection and reagent and culture medium preparation are carried out; culture preservation, excitation and bacterium suspension preparation are carried out; viable bacterium content C blood cell plate counting of a bacterium suspension after methylene blue staining is carried out; an ATP concentration log value lgC-relative fluorescence intensity log value lgI standard curve is established and an inoculating bacterium solution C is calibrated; sample inoculation and cultivation are carried out; recycled solution I measurement and ATP concentration C and T calculation are carried out; an antibacterial ratio R or an antibacterial activity value A is calculated; and a result is evaluated. The method for detecting the anti-fungal performance of the nano inorganic antibacterial material is characterized in that an ATP fluorophotometer is used for accurately and quantitatively testing the anti-fungal performance of the nano inorganic material represented by R or A. According to the method for detecting the anti-fungal performance of the nano inorganic antibacterial material, it is stipulated that control samples and antibacterial samples after shake cultivation are recycled, and I of the control samples and the antibacterial samples is measured and lgI is used for representing and calculating R or A; and a result evaluation basis is provided. According to an ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method for detecting the anti-fungal performance of the nano inorganic material, an advanced detection technology can be used for supporting product quality improvement.
Owner:李文杰
Method for detecting antibacterial performance of antibacterial paint by ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method
PendingCN110272978AAvoid errorsEnsure quantificationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementModel selectionAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a method for detecting the antibacterial performance of antibacterial paint. The method comprises the following detection steps of: carrying out sample extraction, preparation and preprocessing; carrying out equipment model selection and reagent and culture medium preparation; carrying out culture preservation and activation, and preparing bacterial suspension; establishing an ATP concentration logarithm value lgC-relative fluorescence intensity logarithm value lgI standard curve, and carrying out calibration on inoculation bacteria solution viable bacterium ATP concentration C; carrying out sample inoculation, culture, elution and recovery; measuring recovery liquid I, and reckoning the viable bacterium ATP concentrations C and T of the recovery liquid; calculating an antibacterial ratio R or an antibacterial activity value A; and carrying out result evaluation. The method is characterized in that an ATP fluorophotometer is applied to accurately and quantitatively test the paint antibacterial performance represented by R or A. The method stipulates that control samples and antibacterial samples subjected to 0h contact and cultured for 24h are eluted and recovered, the recovery liquid I is measured, R or A is represented and calculated by lgI, and a result evaluation basis is provided. The ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method researched and developed by the invention for detecting the antibacterial performance of the antibacterial paint supports product quality improvement by a scientific and advanced detection technology.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF QINHUANGDAO ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for detecting antibacterial performance of antibacterial coated glass with ATP (adenosine triphosphate) bioluminescence lgCB-lgIB standard curve method
InactiveCN110283877AAvoid errorsEnsure quantificationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibacterial activityBiological activation
The invention relates to a method for detecting antibacterial performance of antibacterial coated glass. The method comprises detection steps as follows: sample preparation and pretreatment; selection of equipment type and preparation of reagents and culture media; strain preservation and activation and preparation of a bacterial suspension; establishment of an OD value-viable content logarithm value lgCB standard curve and calibration of an inoculant liquid CB; establishment of an lgCB-relative fluorescence intensity logarithm value lgIB standard curve; inoculation, culture and eluting recovery of samples; IB determination of a recovery liquid and calculation of viable content CB and TB of the recovery liquid; calculation of antibacterial ratio R or antibacterial activity value A; result evaluation. The method is characterized in that an ATP fluorophotometer is applied to accurate and quantitative test of the antibacterial performance of the R or A characterized glass. According to the method, a control sample and an antibacterial sample after 0 h contact and 24 h culture are eluted and recovered, and IB of the recovery liquid is measured and R or A is characterized by lgIB and calculated; result evaluation basis is provided. According to the developed ATP bioluminescence lgCB-lgIB standard curve method for detecting the antibacterial performance of the antibacterial coated glass, product quality improvement is supported with a scientific and advanced detection technology.
Owner:李文杰
Mobile laboratory for environment detection
InactiveCN112844497AEasy to moveMove quicklyMeasurement devicesHospitalsTransceiverExperimental laboratory
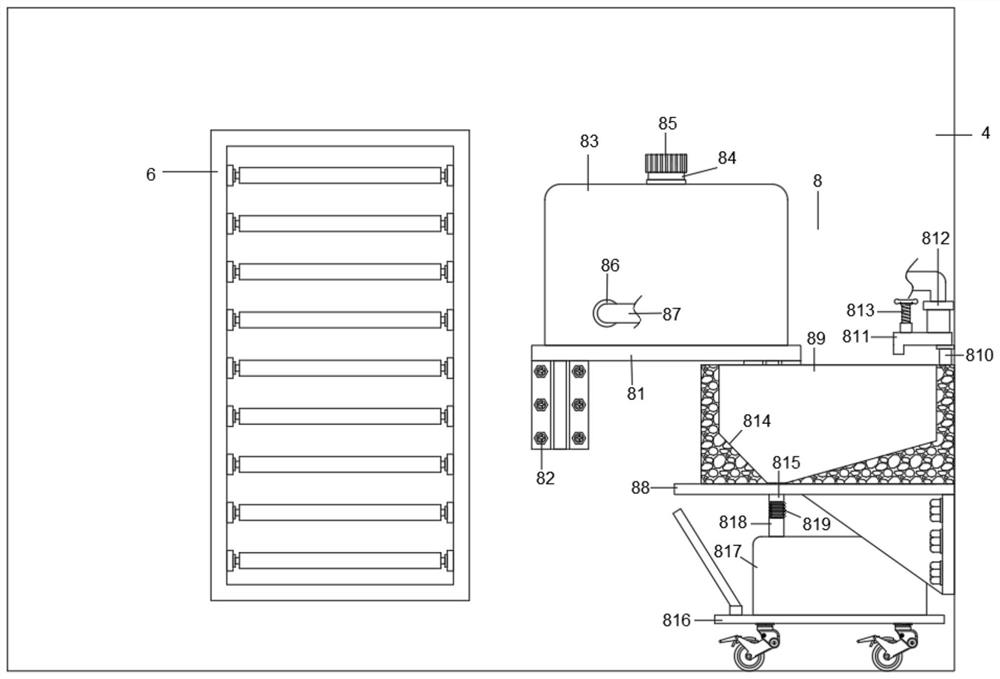
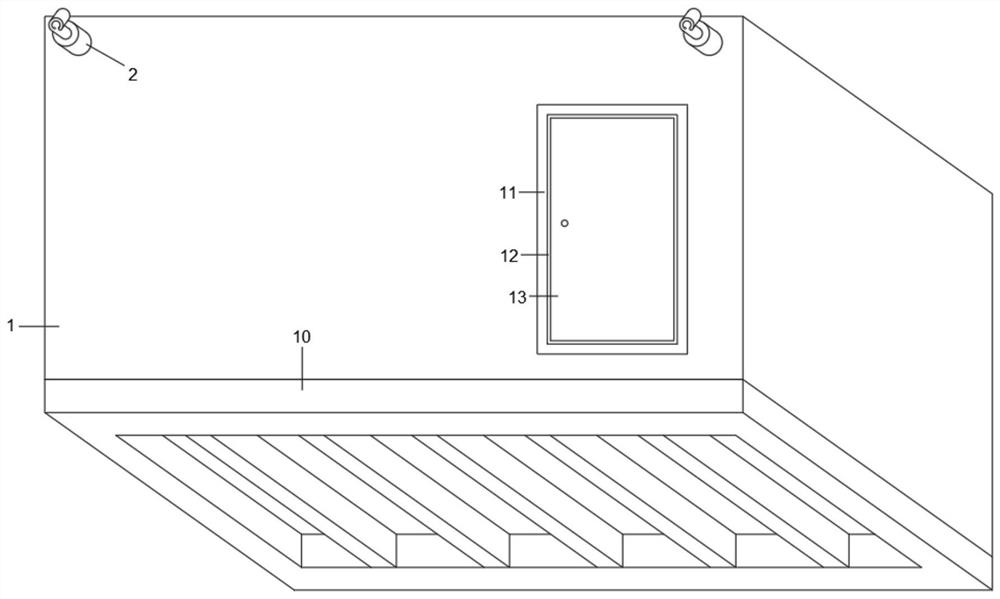
The invention discloses a mobile laboratory for environment detection, wherein the mobile laboratory comprises a laboratory box body; lifting hooks are welded at four corners of the top end of the outer wall of the laboratory box body, a support frame is fixed at the bottom of the laboratory box body, and a detection chamber is arranged at one end in the laboratory box body. The mobile laboratory has the benefit effects: through the arrangement of the lifting hook, the device can be conveniently moved after being lifted, the device can be matched with a transport vehicle to move in the direction according to the use requirement, and the mobile laboratory adaptive to the environment of an incident place can be rapidly assembled; and in the detection process, a signal transceiver completes a near infrared spectroscopy method, a biosensor technology, a biochip, an ATP bioluminescence method, an immunological analysis method and transmission of detection data of the immunological analysis method and the like through a two-dimensional code tag, an RFID tag, a camera, a temperature inductor, a sound inductor, a vibration inductor, a pressure inductor, an RFID reader-writer, a two-dimensional code reader and a single-chip microcomputer controller.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHONGHUI MOBILE LAB TESTING TECH CO LTD
Method for evaluating bacterium killing effect of daily chemical products by ATP bioluminescence lgCA-lgIA standard curve method
PendingCN110272969AAvoid errorsEnsure quantificationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementModel selectionAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a method for evaluating bacterium killing effect of daily chemical products. The method comprises detection steps as follows: sample extraction and pretreatment requirement; model selection of equipment and preparation of a reagent and a culture medium; collection and activation of strains and preparation of a bacterial suspension; construction of an ATP concentration log value lgCA-relative fluorescence intensity log value igIA standard curve and viable bacteria ATP concentration CA calibration of an inoculation bacterial solution; neutralizer identification and sterilization test; IA determination of a recovery solution and calculation of viable bacteria ATP concentration CA and TA of the recovery solution; calculation of an antibacterial rate R or antibacterial activity value A; and result evaluation. The method is characterized by applying an ATP fluorophotometer to precisely and quantitatively test the bacterium killing effect of daily chemical products represented by R or A. The method neutralizes and recovers control samples and antibacterial samples after specific time of contamination / killing, determines IA of the recovery solution and represents and calculates R or A by lgIA and provides result evaluation basis. The researched and developed ATP bioluminescence lgCA-lgIA standard curve method for detecting the bacterium killing effect of daily chemical products will support product quality improvement by the scientific and advanced detection technology.
Owner:李文杰
Method for detecting antibacterial performance of polyurethane synthetic leather by ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method
InactiveCN110272972AAvoid errorsEnsure quantificationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementModel selectionElution
The invention relates to a method for detecting antibacterial performance of polyurethane synthetic leather. The method for detecting the antibacterial performance of the polyurethane synthetic leather comprises the steps that sample preparation and pretreatment are carried out; equipment model selection and reagent and culture medium preparation are carried out; culture preservation, excitation and bacterium suspension preparation are carried out; an OD value-viable bacterium content log value lgC standard curve is established and an inoculating bacterium solution C is calibrated; an lgC relative fluorescence intensity log value lgI standard curve is established; sample inoculating, cultivating, eluting and cultivating are carried out; recycled solution I measurement and variable bacterium content C and T calculation are carried out; an antibacterial ratio R or an antibacterial activity value A is calculated; and a result is evaluated. The method for detecting the antibacterial performance of the polyurethane synthetic leather is characterized in that an ATP fluorophotometer is used for accurately and quantitatively testing the antibacterial performance of the synthetic leather represented by R or A. According to the method for detecting the antibacterial performance of the polyurethane synthetic leather, it is stipulated that control samples and antibacterial samples are recovered by elution after contact for 0h and cultivation for 24h and cycled, and a recycled solution I is measured and lgI is used for representing and calculating R or A; and a result evaluation basis is provided. According to an ATP bioluminescence lgC-lgI standard curve method for detecting antibacterial performance of the polyurethane synthetic leather, an advanced detection technology can be used for supporting product quality improvement.
Owner:李文杰
System for caries management by risk assessment
ActiveUS9968526B1The process is simple and effectiveCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsShort term treatmentDental patients
The invention provides the tools needed for a dental patient's caries risk assessment. Included is a complete turnkey system for caries risk assessment and treatment, including an ATP test and a plurality of rinses and educational and diagnostic materials. The system for the detection and treatment of the bacterial infection that causes dental caries in a patient comprises a disposable ATP Bioluminescence sampler to swab areas of the patient's mouth, a bioluminescent light meter which measures the amount of ATP present in the patient's mouth, a rapid culture test for the detection of Mutans streptococci and lactobacilli, a diagnostic testing component that includes a caries risk assessment questionnaire, a treatment component that includes a short term therapeutic oral rinse of at least two components, and a long term maintenance rinse.
Owner:DENTAL ALLIANCE HLDG LLC
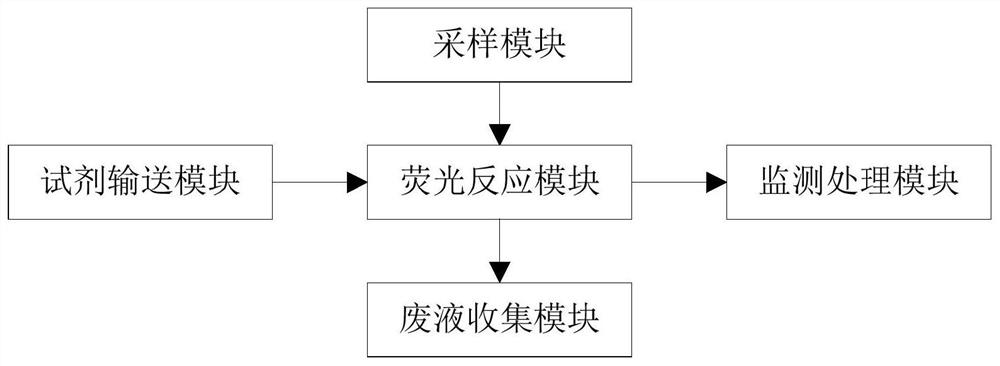
Bioaerosol early warning device based on ATP bioluminescence technology
InactiveCN112649412ASimple structureReliable functionFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiochemical engineeringEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of air microorganism monitoring, and discloses a bioaerosol early warning device based on an ATP bioluminescence technology. The device comprises a reagent conveying module used for containing a reaction reagent and conveying the reaction reagent to a fluorescence reaction module; a sampling module used for collecting and conveying microorganisms in ambient air to the fluorescence reaction module; the fluorescence reaction module used for mixing the reaction reagent with the microorganisms and generating fluorescence; a monitoring and processing module used for detecting the fluorescence change, converting the fluorescence change into an electric signal, processing the electric signal to obtain the concentration of microorganisms, and sending an early warning signal when the concentration exceeds a preset value; and a waste liquid collection module used for collecting waste liquid after reaction of the fluorescence reaction module. The change of the concentration of microorganisms in air is obtained based on the ATP bioluminescence technology, an early warning signal is sent out when the concentration exceeds a preset value, the overall structure is simple, the function is reliable, the implementation is easy, and the working efficiency of the whole device can be improved.
Owner:北京鼎蓝科技有限公司
Method for preparing firefly luciferase
InactiveCN101302502BSimple processShorten the growth cycleOxidoreductasesFermentationMicroorganismFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for making firefly luciferase, comprising the following steps of: inserting the firefly luciferase gene into multiple cloning sites of a prokaryotic expression vector; obtaining a recombinant expression vector containing the firefly luciferase gene; introducing the recombinant expression vector into a colon bacillus cell to obtain a recombinant cell containing therecombinant expression vector; culturing the recombinant cell to obtain the firefly luciferase from the expression. The method for making the firefly luciferase has the advantages of simple process, short growth period, low cost, easy purification, high enzyme activity and stable performance and so on. The method can relieve a situation that the firefly luciferase mainly depends on import, and can promote the development of a fluorescent microorganism rapid detection system and the application of the firefly luciferase in medicine and environment science and so on, thereby providing excellentenzyme preparation for the rapid detection and applications in other aspects of ATP bioluminescence microorganism.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com