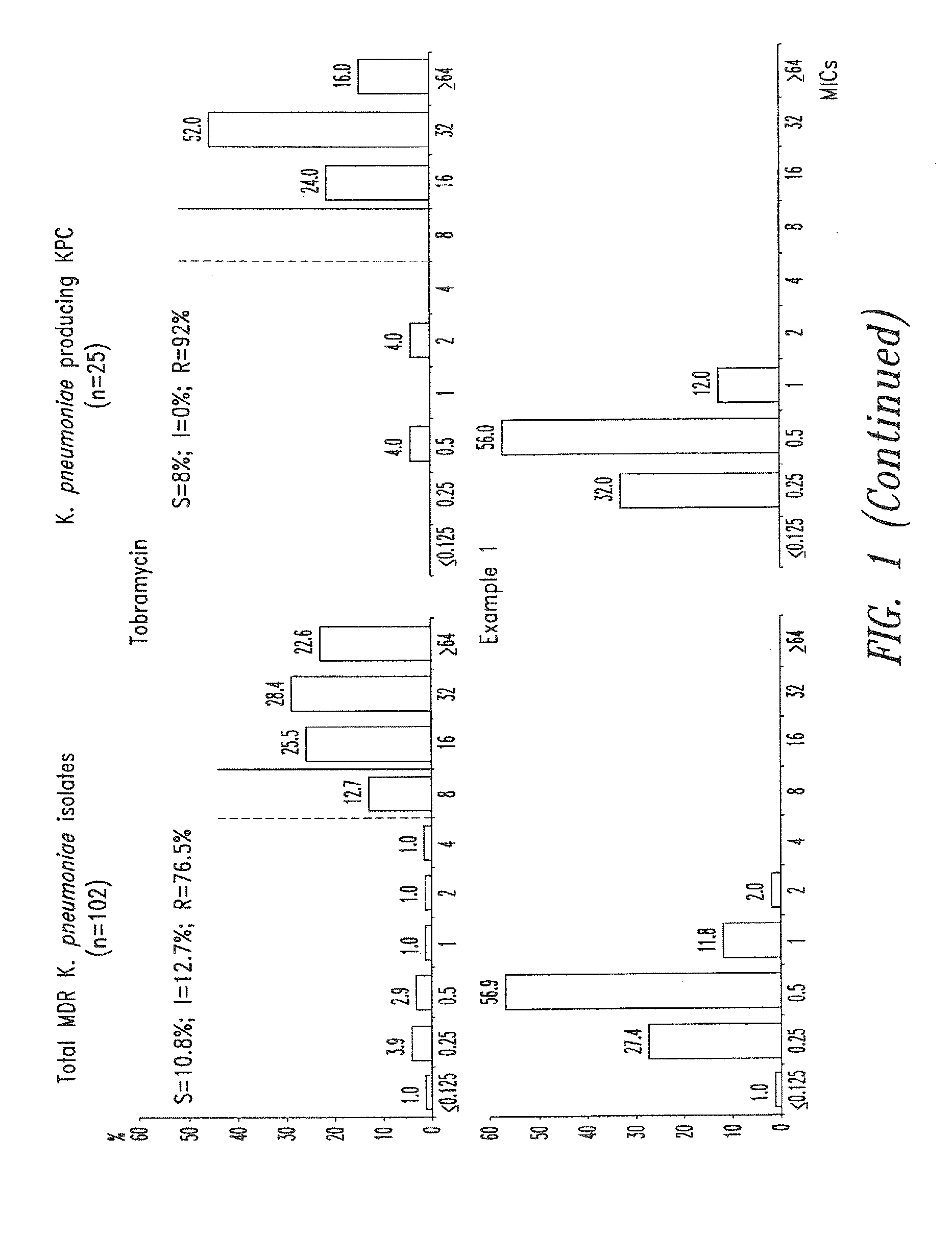
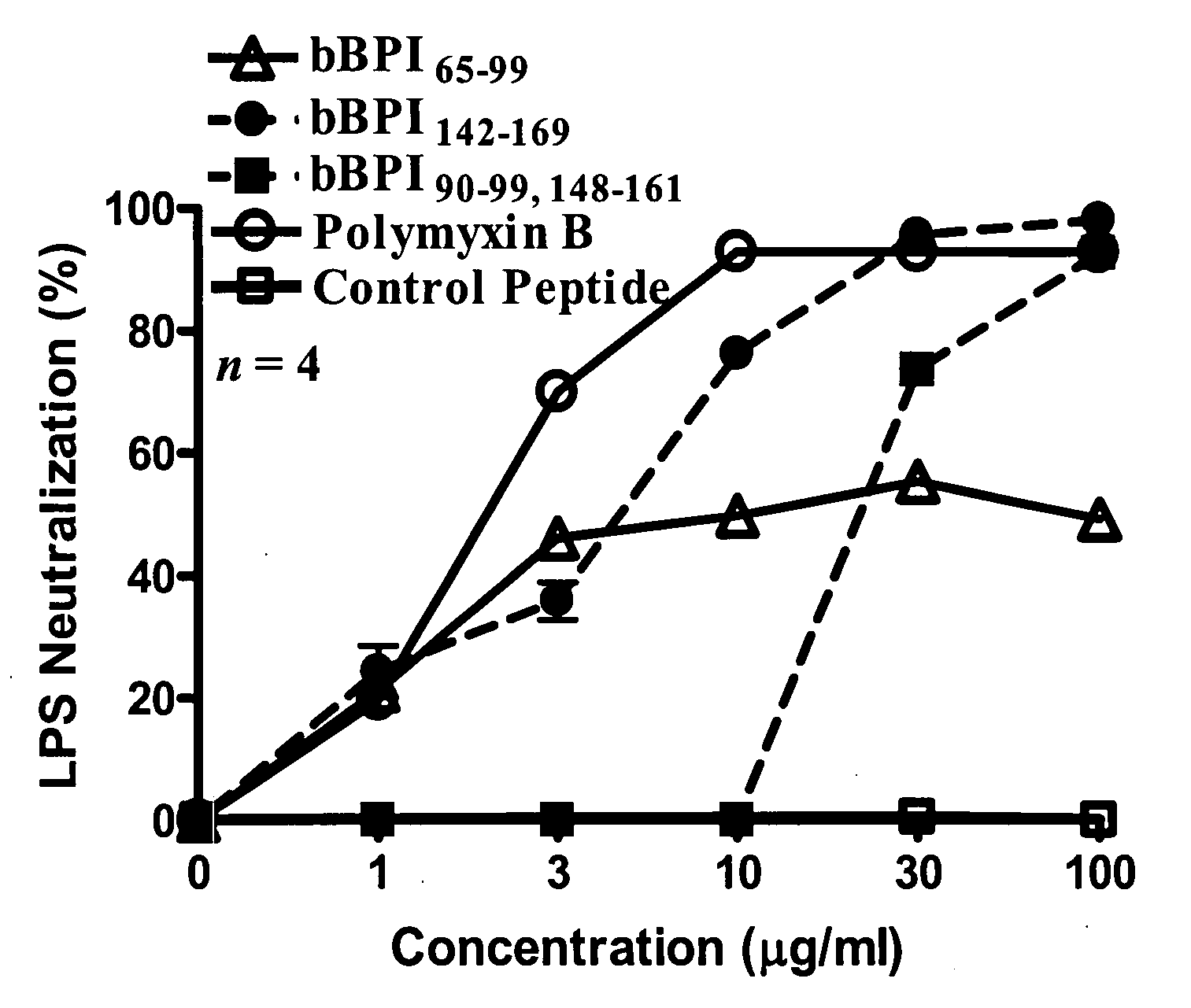
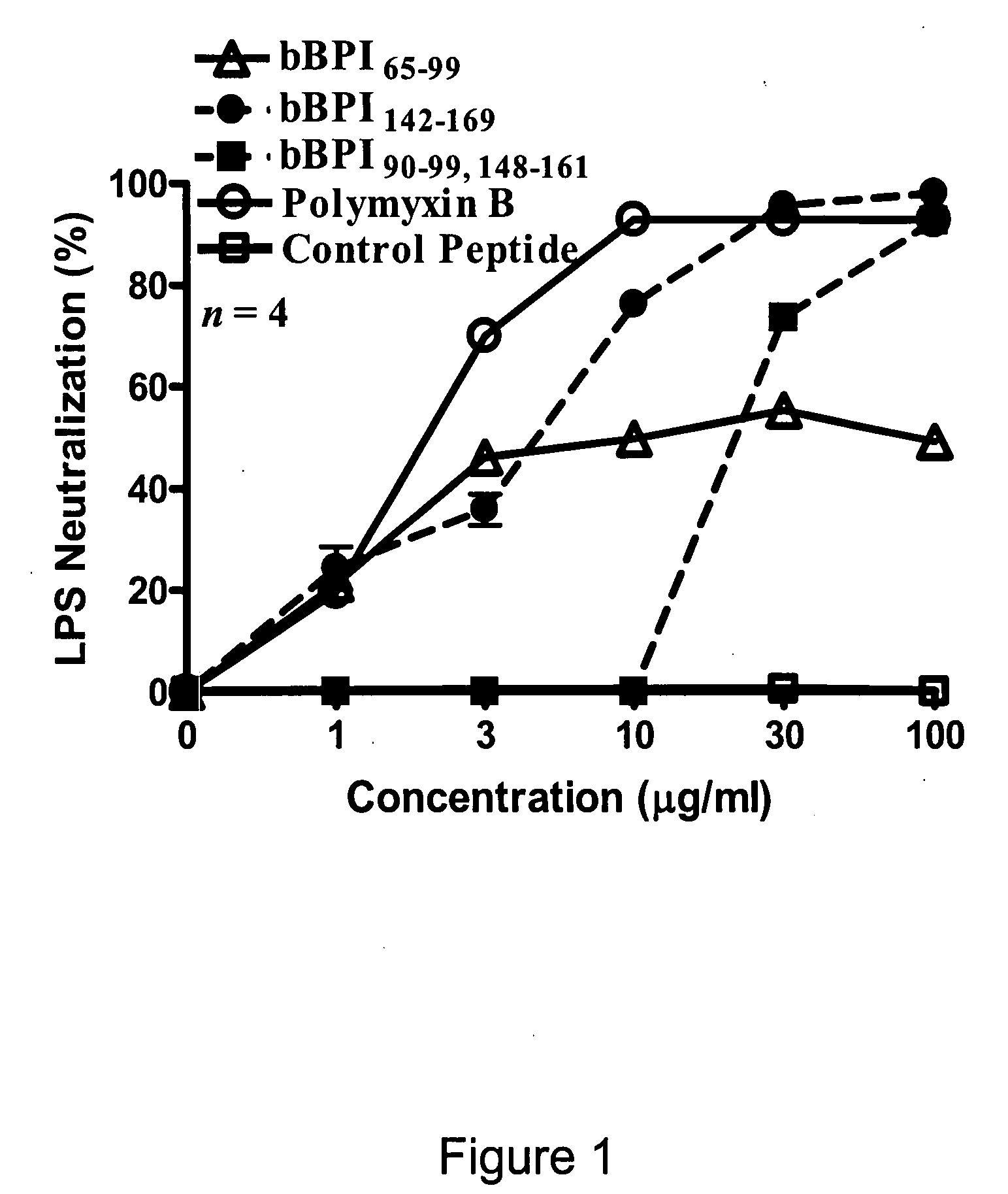
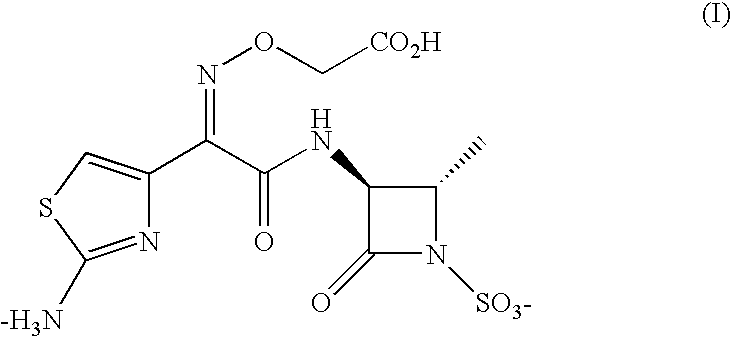
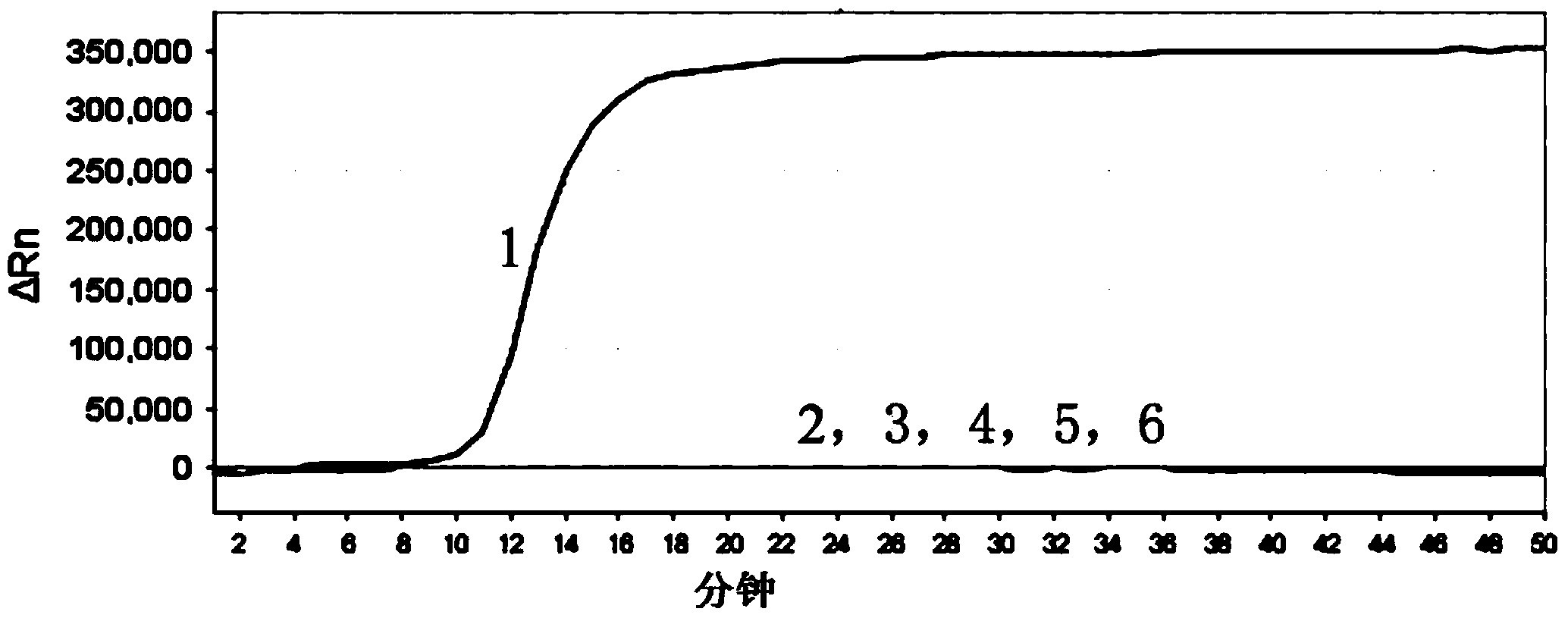
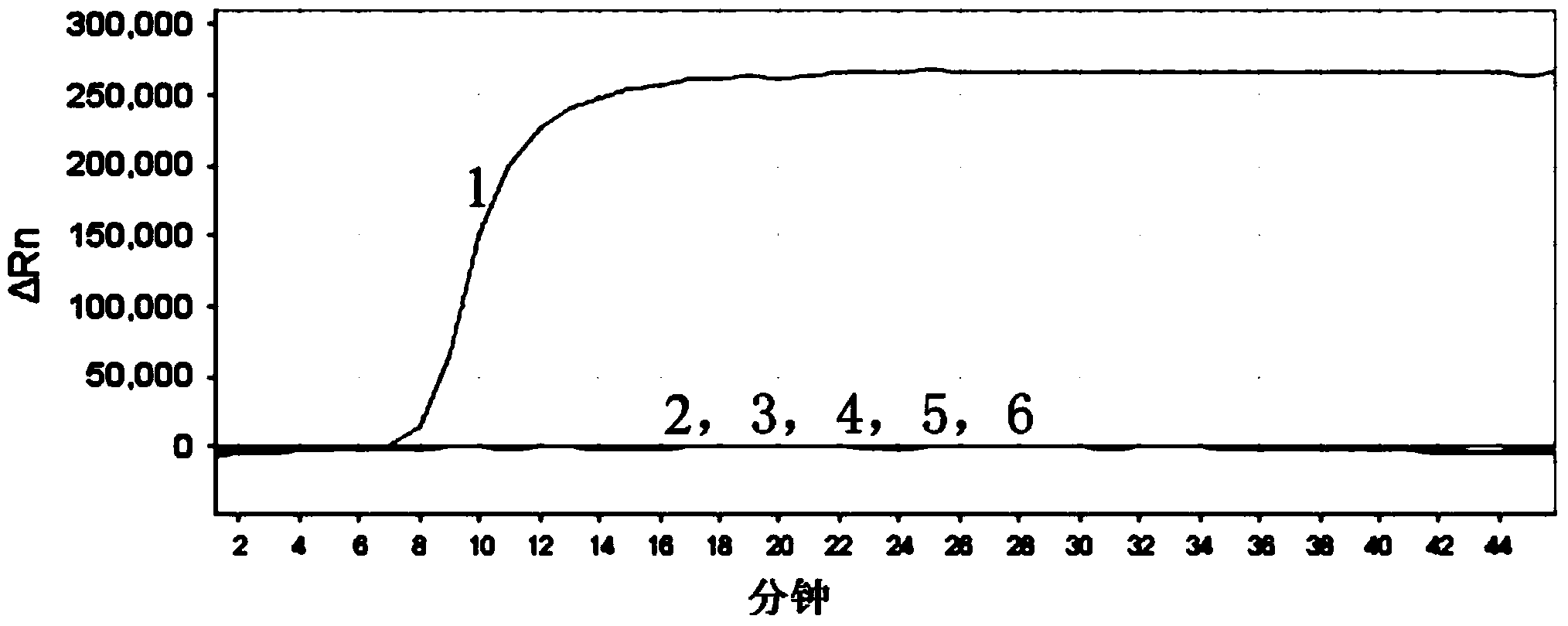
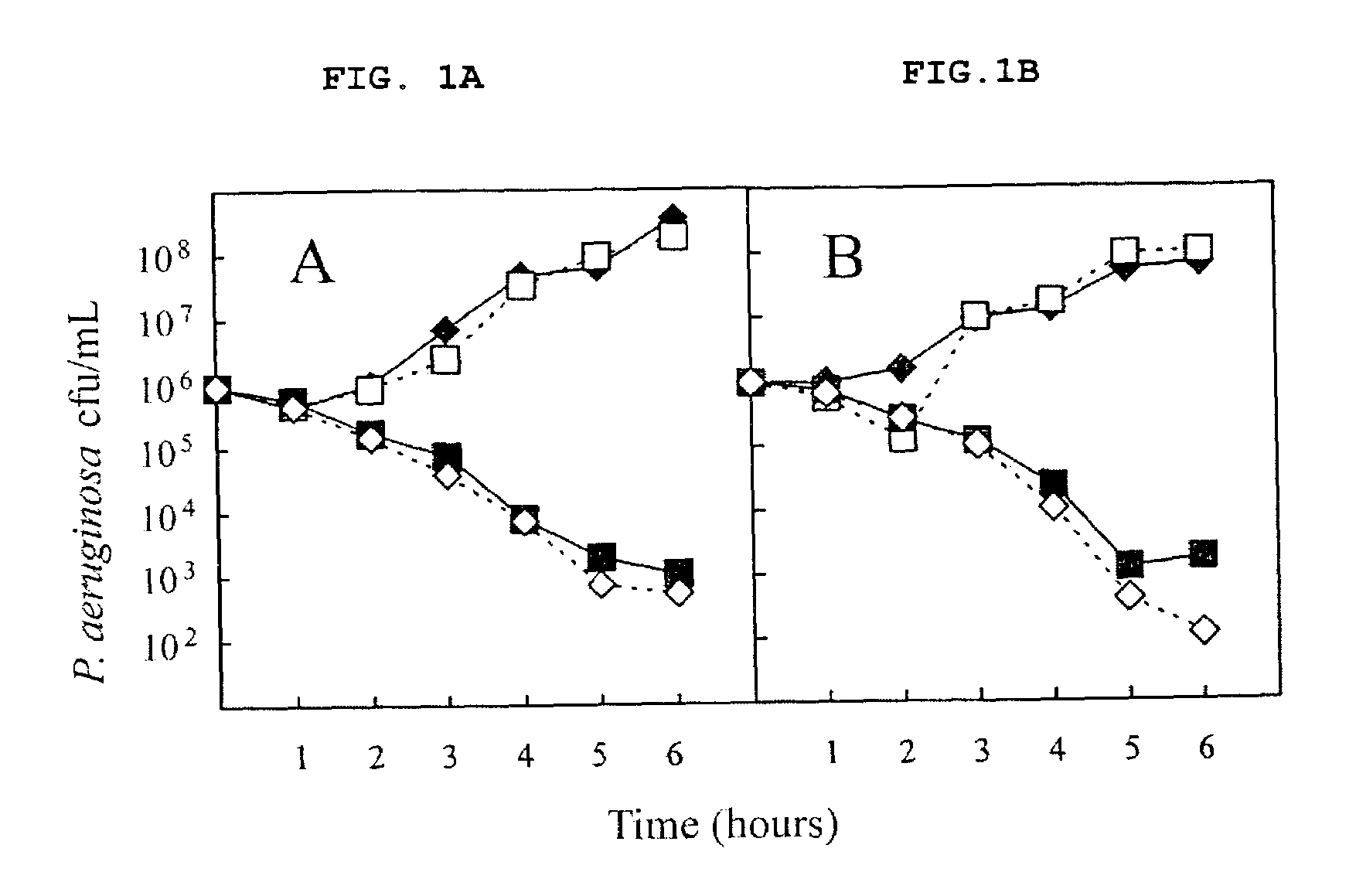
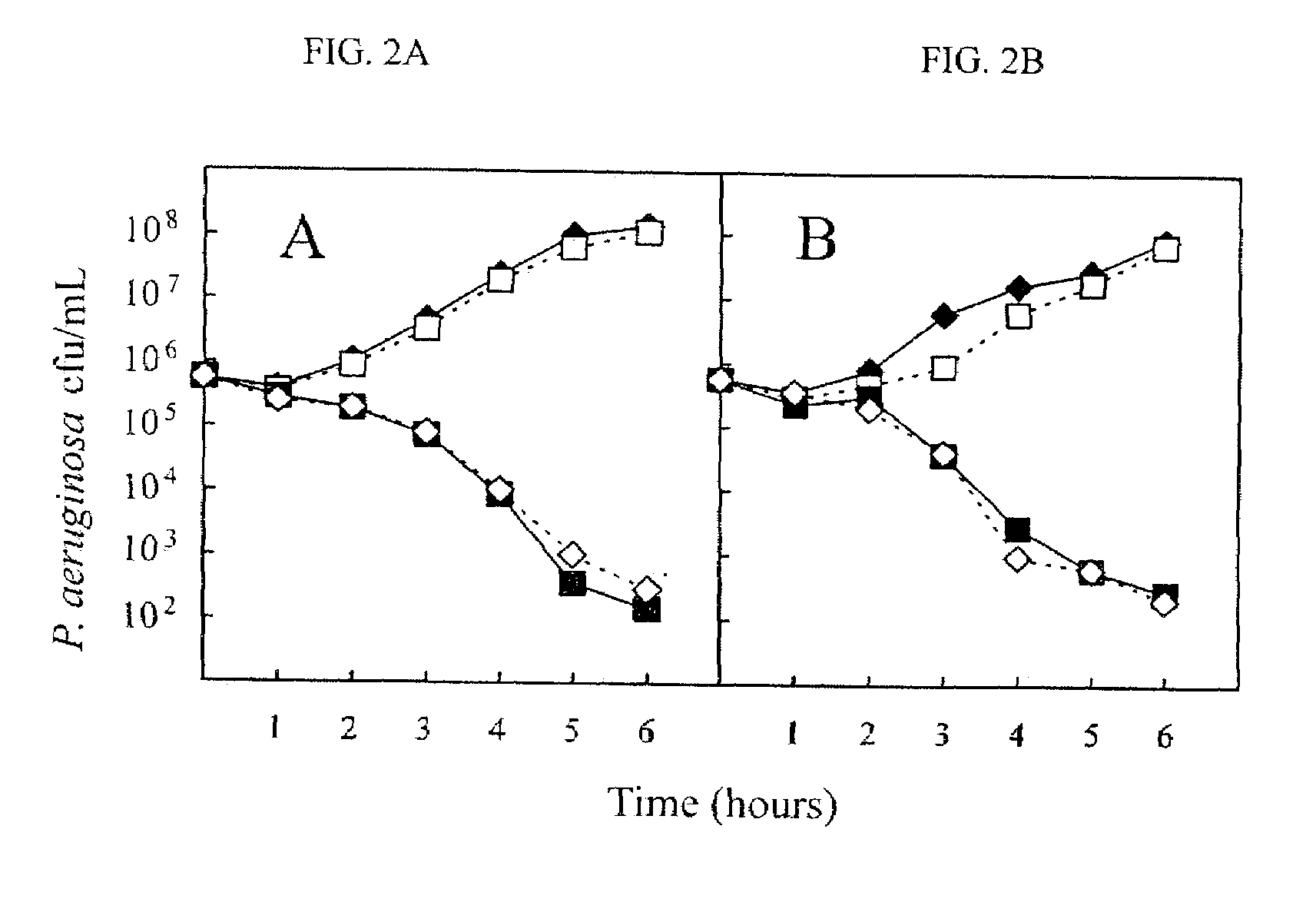
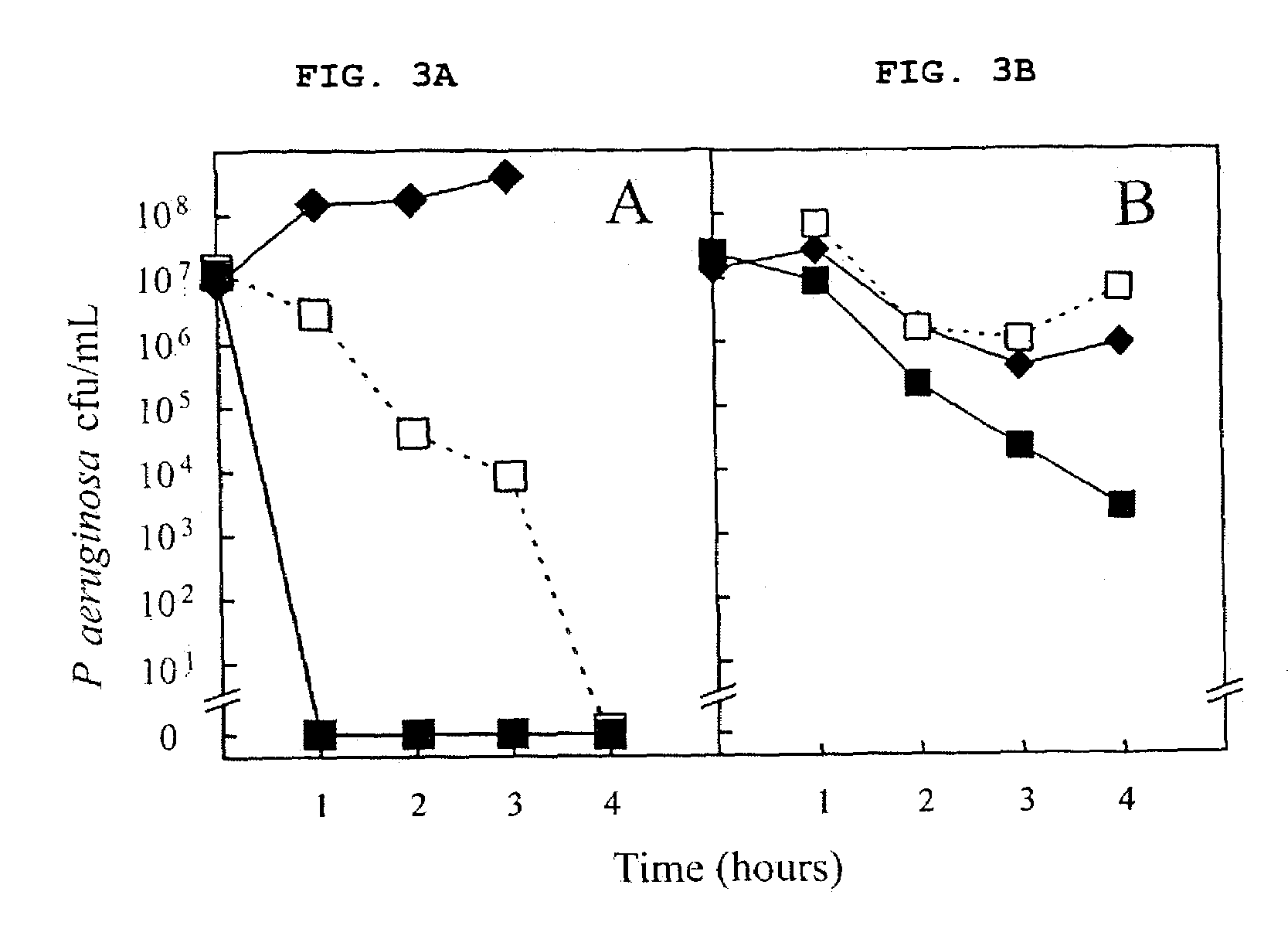
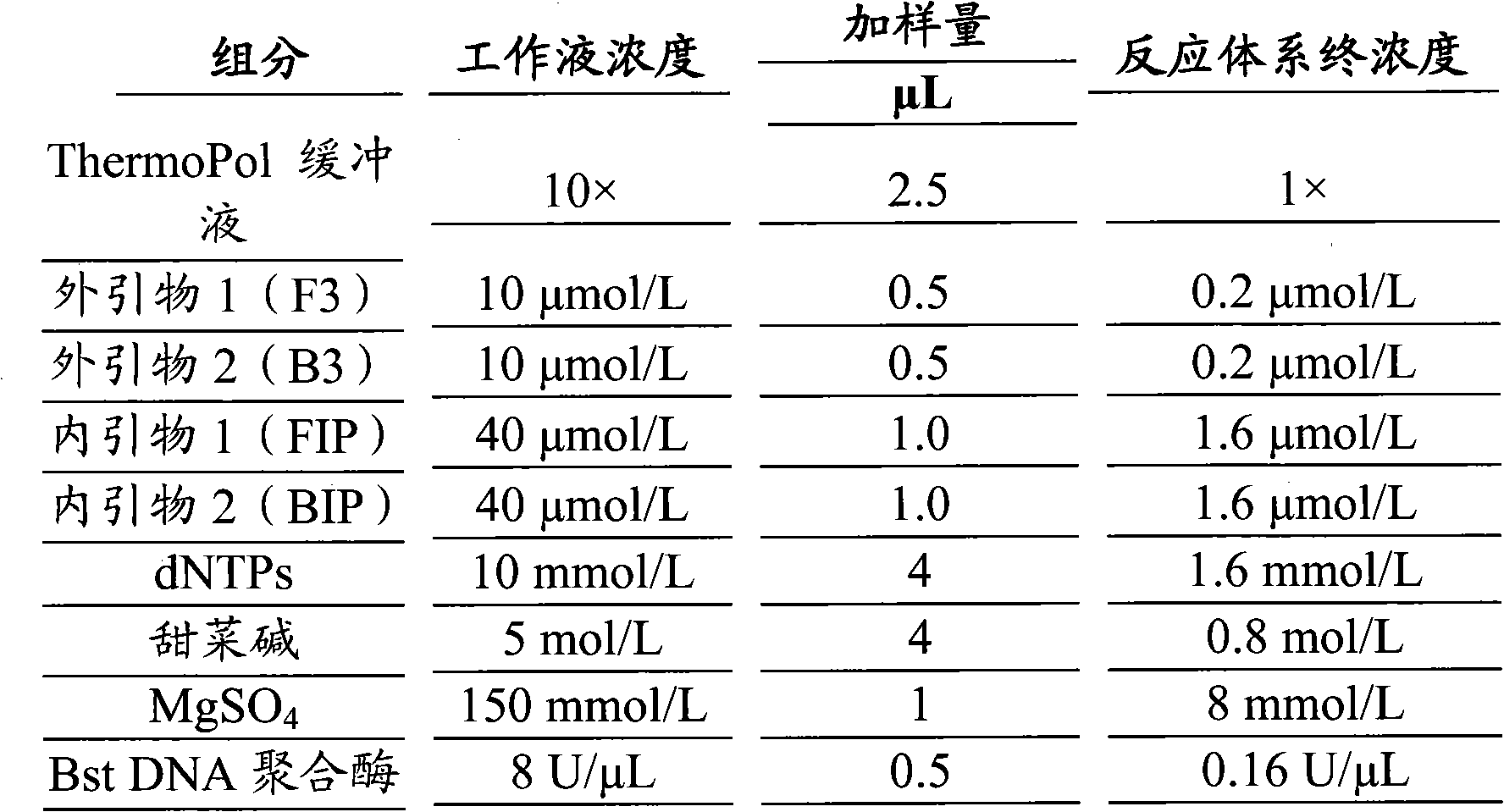
Patents
Literature
636 results about "Pneumonia klebsiella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a bacterium in the genus Klebsiella. It is a major cause of pneumonia, found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines.
Process for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol with high titer
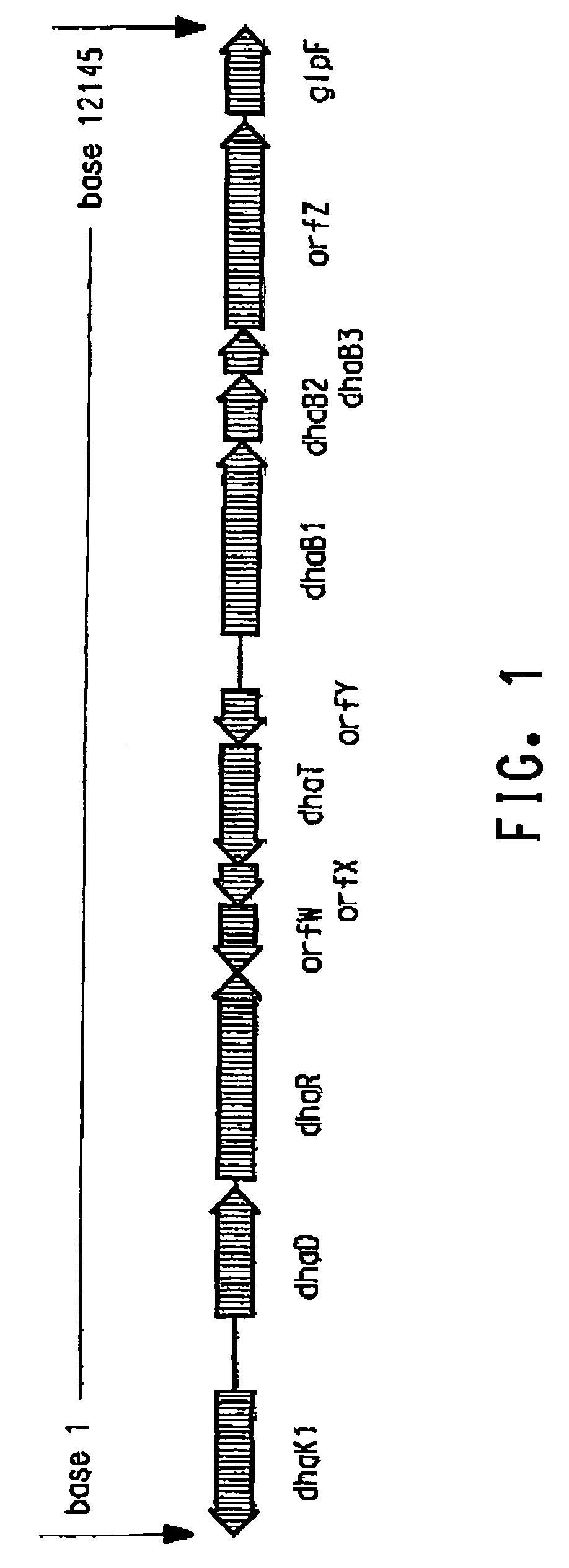
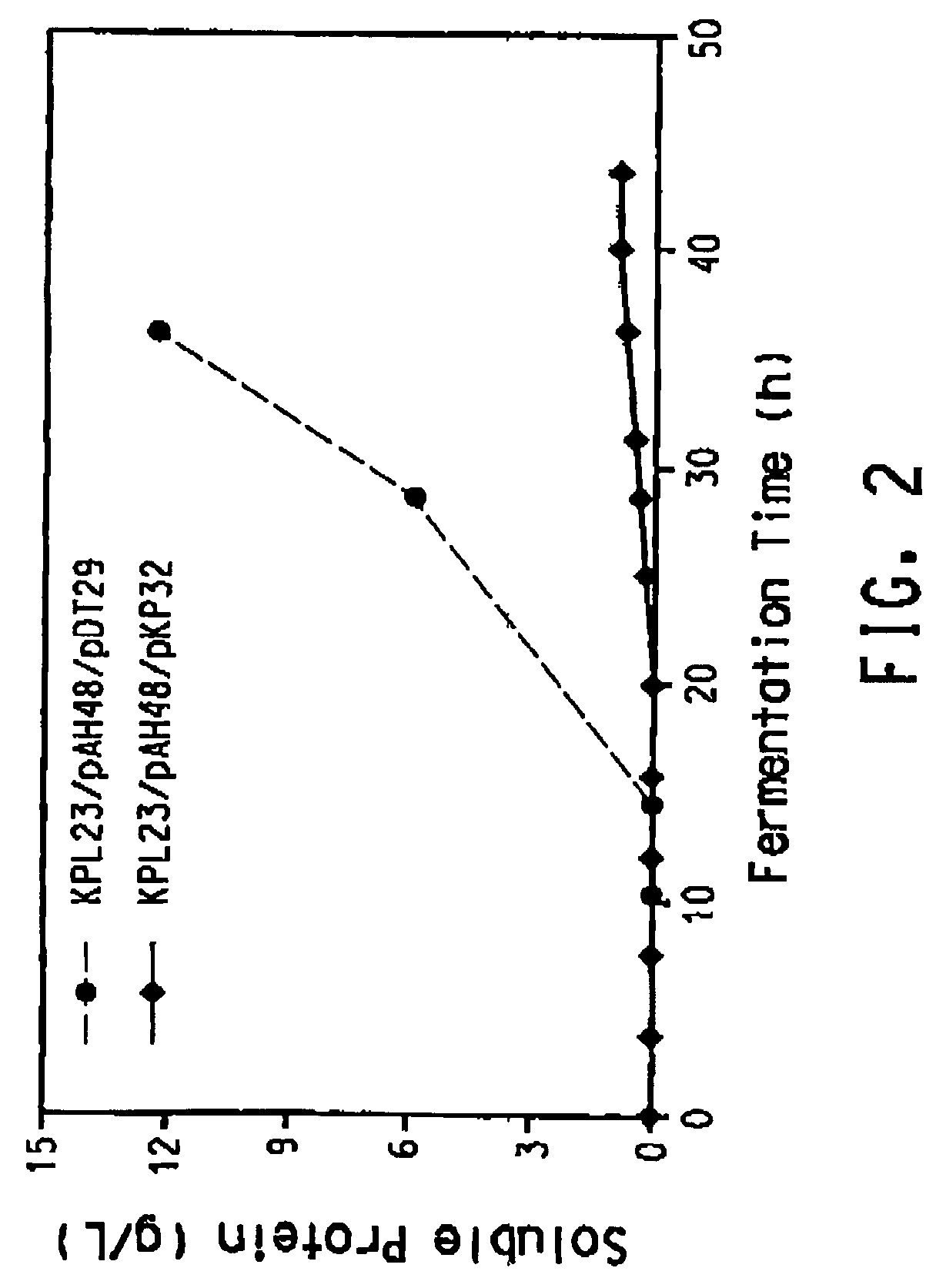
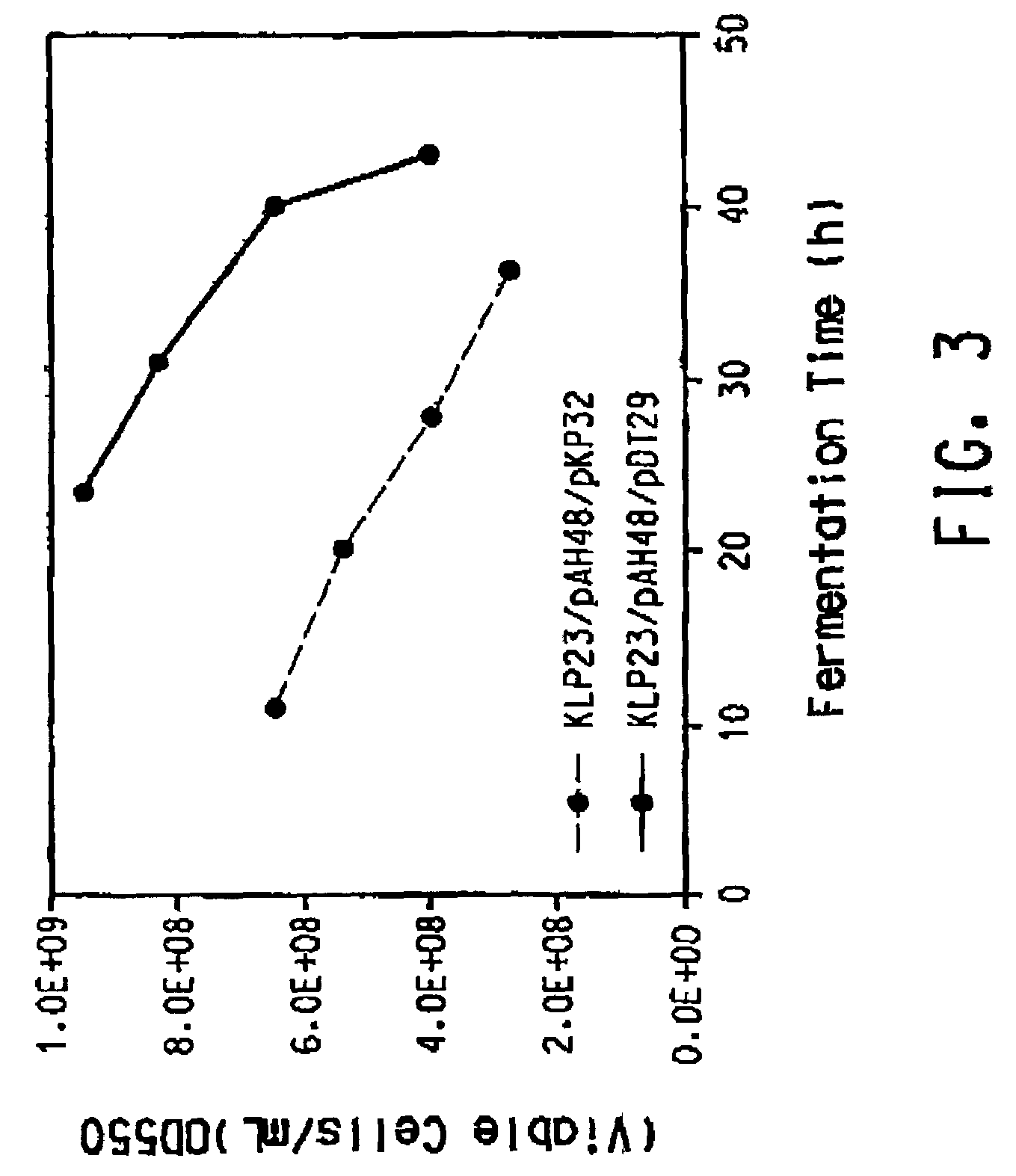
The present invention provides an improved method for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol from a fermentable carbon source in a single microorganism. In one aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the conversion of glucose to 1,3-propanediol is achieved by the use of an E. coli transformed with the Klebsiella pneumoniae dha regulon genes dhaR, orfY, dhaT, orfX, orfW, dhaB1, dhaB2, dhaB3, and orfZ, all these genes arranged in the same genetic organization as found in wild type Klebsiella pneumoniae. In another aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the production of 1,3-propanediol from glucose using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, and a dehydratase reactivation factor compared to an identical process using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, a dehydratase reactivation factor and a 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase (dhaT). The dramatically improved process relies on the presence in E. coli of a gene encoding a non-specific catalytic activity sufficient to convert 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde to 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
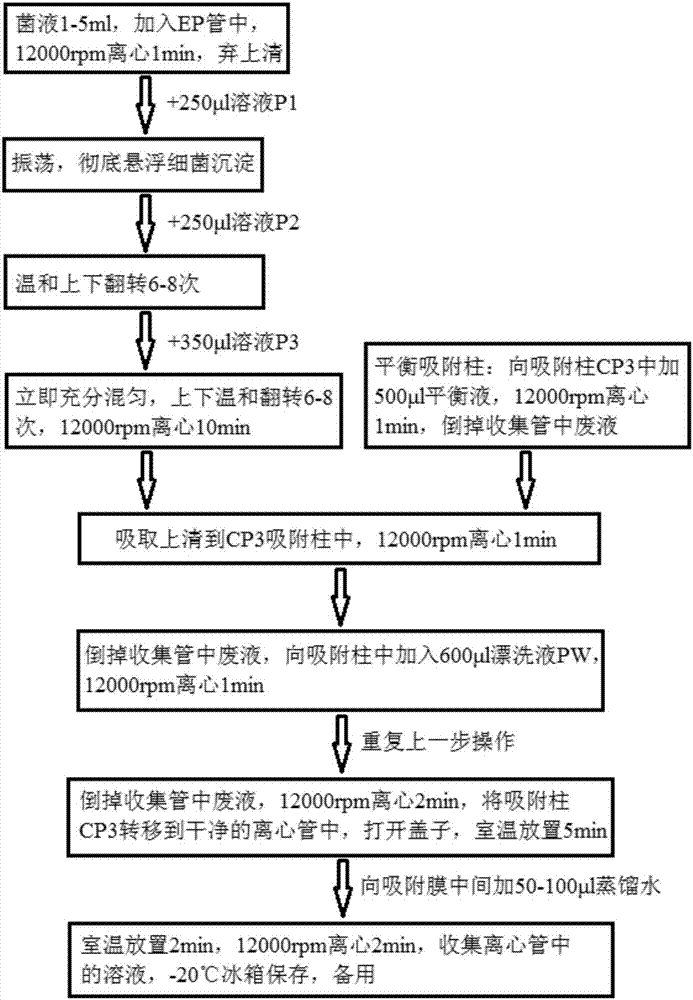
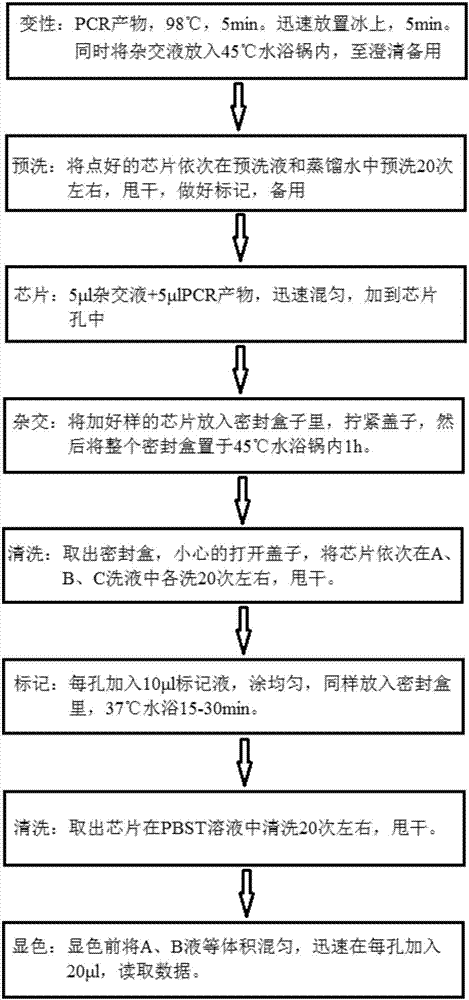
Kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN107338315AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention discloses a kit for quickly detecting 15 pneumonia pathogenic bacteria. The kit can detect streptococcus pneumoniae, staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae, mycoplasma pneumoniae, pseudomonas aeruginosa, baumanii, enterococcus faecalis, enterococcus faecium, klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli, enterobacter cloacae, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, burkholderia cepacia, legionella pneumophila and chlamydia pneumoniae which cover clinically common pneumonia pathogenic bacteria difficult to culture. 16S rDNA and specific gene sequences corresponding to the pneumonia pathogenic bacteria are detected by combining gene chips with multiple asymmetric PCR reactions, and the categories of the bacteria in a to-be-detected sample are identified in genus and species. The kit makes up for the defect that current clinical detection of pneumonia pathogenic bacteria is not in time or comprehensive and a novel detection means for early diagnosis and early treatment of patients suffering from pneumonia is provided.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
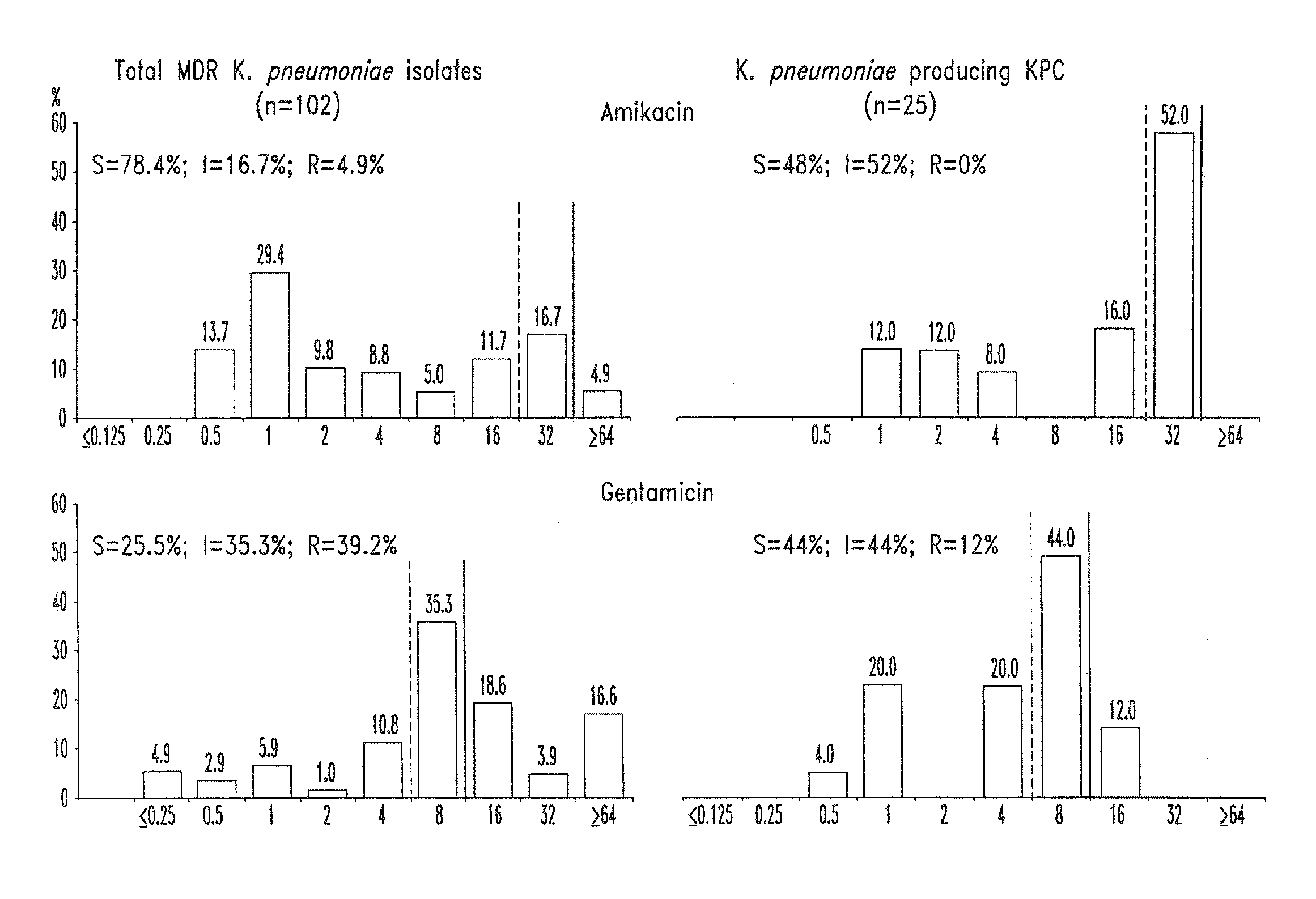
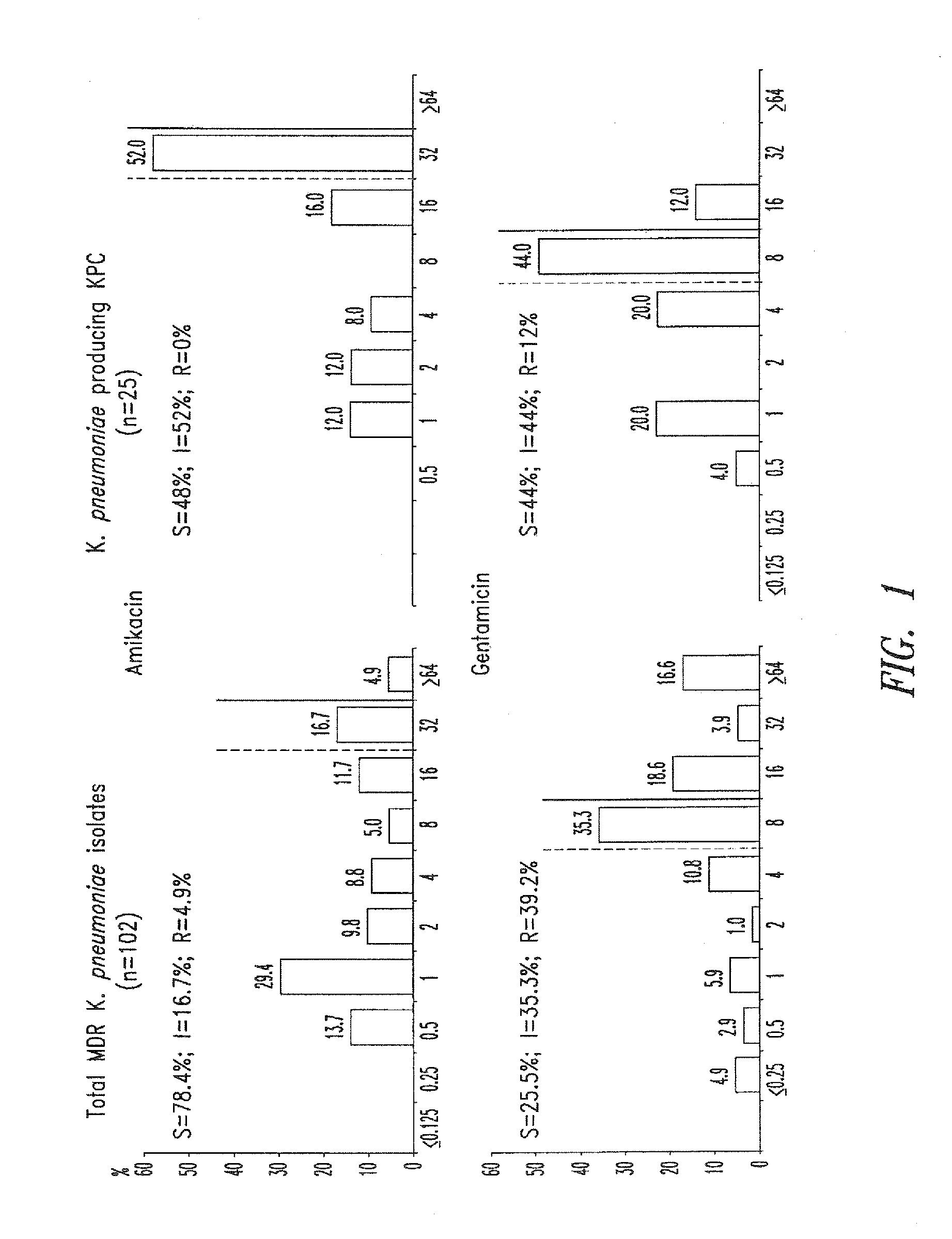
Treatment of klebsiella pneumoniae infections with antibacterial aminoglycoside compounds
A method for treating a Klebsiella pneumonia infection in a mammal in need thereof is disclosed, the method comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of an antibacterial aminoglycoside compound.
Owner:CIPLA USA INC
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20050042606A9Rapid bacterial identificationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesGenomic SegmentMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Antimicrobial activity of bovine bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI)-derived peptides against Gram-negative bacterial mastitis isolates
The antimicrobial activity of bovine bactericidal / permeability-increasing protein (bBPI)-derived synthetic peptides against mastitis-causing Gram-negative bacteria was evaluated. Three peptides were synthesized with sequences corresponding to amino acids 65-99 (bBPI65-99), 142-169 (bBPI142-169), or the combination of amino acids 90-99 and 148-161 (bBPI90-99,148-161) of bBPI. The bBPI90-99,148-161 peptide demonstrated the widest spectrum of antimicrobial activity, with minimum inhibitory (MIC) and bactericidal (MBC) concentration values ranging from 16-64 μg / ml against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterobacter spp, and 64-128 μg / ml against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. None of the peptides exhibited any growth inhibitory effect on Serratia marcescens. The antimicrobial activity of bBPI90-99,148-161 was inhibited in milk, but preserved in serum. Finally, both bBPI142-169 and bBPI90-99,148-161 were demonstrated to completely neutralize LPS. The peptide bBPI90-99,148-161 is a potent neutralizer of the highly pro-inflammatory molecule bacterial LPS and has antimicrobial activity against a variety of Gram-negative bacteria.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Inhalable aztreonam aerosol for treatment and prevention of pulmonary bacterial infections
A method and a composition for treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections caused by gram-negative bacteria suitable for treatment of infection caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens as well as those caused by Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a concentrated formulation of aztreonam, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, delivered as an aerosol or dry powder formulation.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
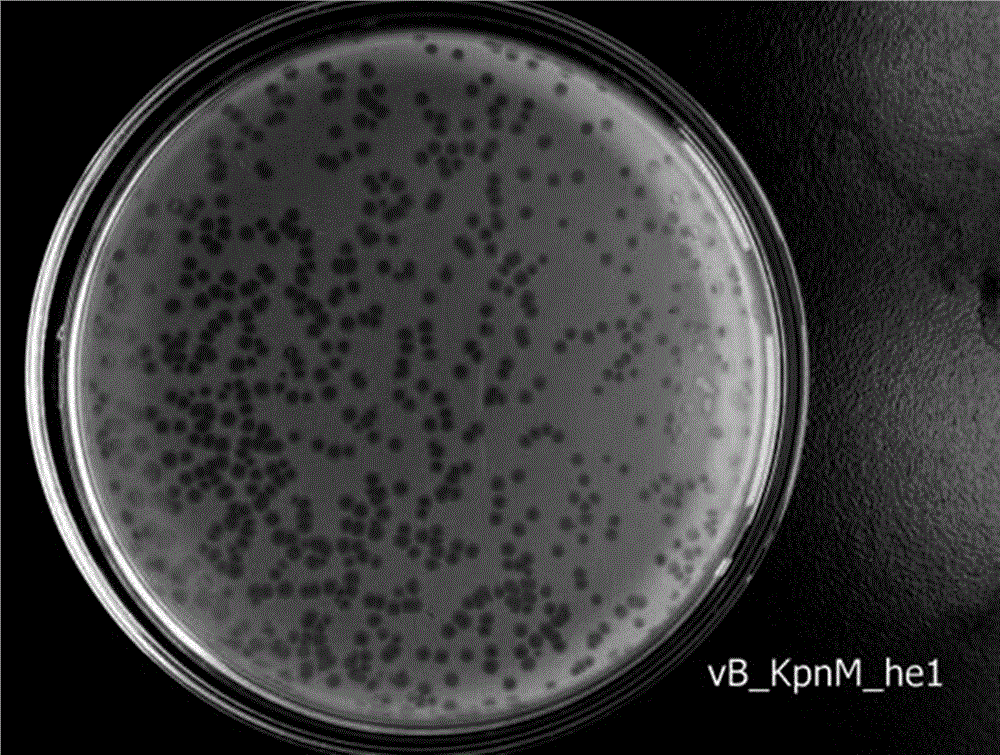
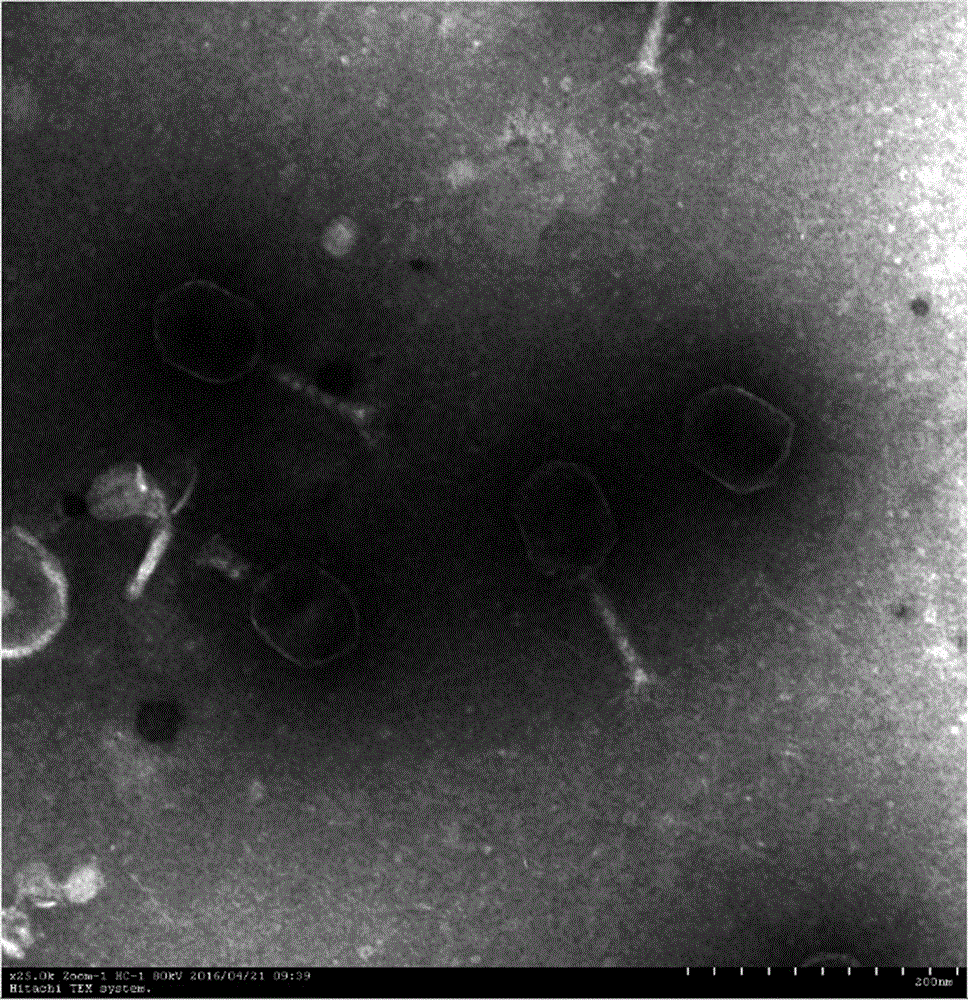
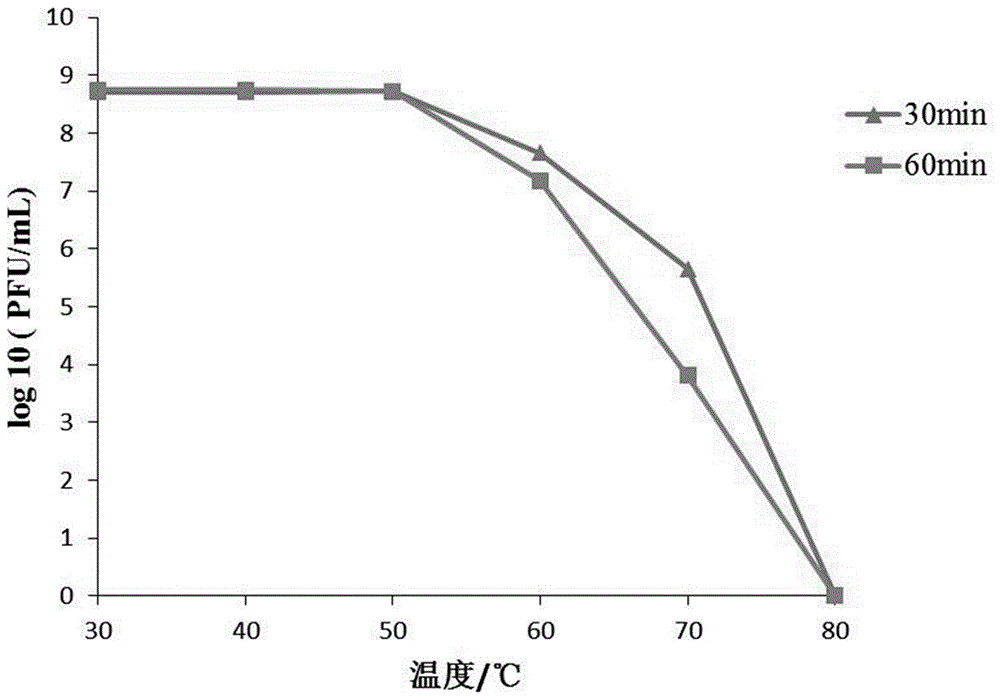
Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophage and application thereof
ActiveCN106754745AEnhance killing activityBroad cracking spectrumAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsK pneumoniaeInduced infections
The invention discloses a strong lysis bacteriophage for splitting NDM-1 positive Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates, and an application of the strong lysis bacteriophage used as a biological preparation in the prevention and treatment of NDM-1 Klebsiella pneumoniae induced infection and pollution. The preservation number of the bacteriophage is CCTCC M 2015760, and the bacteriophage has a regularly icosahedral head and a telescopic tail, and belongs to a Myoviridae double-stranded DNA bacteriophage. The bacteriophage has strong kilign activity and wide bacteriophage lysis spectrum, can be used for preparing medicines for preventing and treating NDM-1 Klebsiella pneumoniae induced bacterium infection, and also can be used for killing NDM-1 positive Klebsiella pneumoniae in culture environment and medical environment.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, kit and detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli
ActiveCN103614465APrecise screeningSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The invention discloses loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, a kit and a detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli. In the LAMP primers disclosed by the invention, klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and new delhi metallo-b-lactamase (NDM) primer groups can detect all subtypes except for NDM-10; hypoxanthine nucleotide (IMP) and vimentin (VIM) primer groups can detect common subtypes at home and abroad. The LAMP kit built by the invention is applied to joint detection of KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes, can cover the common carbapenemase genes of non-fermentative bacteria and enterobacteriaceae, can accurately and quickly screen the common carbapenemase genes, and has great clinical significance for timely detecting and further controlling fulminant epidemic caused by propagation of the carbapenemase genes in enterobacteriaceae. The kit disclosed by the invention is high in detection sensitivity and the minimum detection limits of the KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes can reach 100 CFU / reaction.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Inhalable aztreonam lysinate formulation for treatment and prevention of pulmonary bacterial infections
InactiveUS7214364B2Improve stabilityHigh purityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryK pneumoniaeKlebsiella oxytoca
A method and a composition for treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections caused by gram-negative bacteria suitable for treatment of infection caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens as well as those caused by Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a concentrated formulation of aztreonam lysinate delivered as an aerosol or dry powder formulation.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Oligonucleotide primer for detecting common pathogenic bacteria by adopting fluorescent quantitation PCR (Rich Client Platform) technology, method thereof for detecting common pathogenic bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN101928773AEfficient and wideWide range of applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyFood poisoning
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide primer for detecting common pathogenic bacteria by adopting a fluorescent quantitation PCR (Rich Client Platform) technology, a method thereof for detecting common pathogenic bacteria and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: providing 10 pairs of specific oligonucleotide primer sequences at annealing temperature of 50-60 DEG C without differing 5 DEG C; and simultaneously, quickly, accurately and effectively identifying and quantificationally detecting various pathogenic bacteria at the same time. A detection range comprises bacillus cereus, enterobacter sakazakii, vibrio parahaemolyticus, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157, salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, Shigella, campylobacter jejuni, pseudomonas aeruginosa, klebsiella pneumoniae, and the like. The invention also can be used for the fields of disease diagnosis, environmental monitoring, water-quality and food supervision and detection, food poisoning pathogenicbacteria detection, bacteriological classification, epidemiological investigation, biological agent detection, and the like, is convenient, quick, accurate and effective and has wide application range.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit and use method thereof
ActiveCN101892300AHigh yieldHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementK pneumoniaeKlebsiella
The invention provides a klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit. The klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit comprises two pairs of primers, i.e., an inner primer FIP / BIP and an outer primer F3 / B3, which use oppA gene of klebsiella pneumoniae as the target gene and is designed based on the loop-mediated constant-temperature amplification technology. The klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit has more comprehensive detection effect and low omission ratio.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAFENG BIOTECH
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20070009947A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesBacteroidesMoraxella catarrhalis
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony. The above bacterial species can account for as much as 80% of bacterial pathogens isolated in routine microbiology laboratories. The core of this invention consists primarily of the DNA sequences from all species-specific genomic DNA fragments selected by hybridization from genomic libraries or, alternatively, selected from data banks as well as any oligonucleotide sequences derived from these sequences which can be used as probes or amplification primers for PCR or any other nucleic acid amplification methods. This invention also includes DNA sequences from the selected clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes. With these methods, bacteria can be detected (universal primers and / or probes) and identified (species-specific primers and / or probes) directly from the clinical specimens or from an isolated bacterial colony. Bacteria are further evaluated for their putative susceptibility to antibiotics by resistance gene detection (antibiotic resistance gene specific primers and / or probes). Diagnostic kits for the detection of the presence, for the bacterial identification of the above-mentioned bacterial species and for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed. These kits for the rapid (one hour or less) and accurate diagnosis of bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance will gradually replace conventional methods currently used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. They should provide tools to clinicians to help prescribe promptly optimal treatments when necessary. Consequently, these tests should contribute to saving human lives, rationalizing treatment, reducing the development of antibiotic resistance and avoid unnecessary hospitalizations.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Specific and universal probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for routine diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20090053702A1Rapid and exponential in vitro replicationQuick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStreptococcus pyogenes
The present invention relates to DNA-based methods for universal bacterial detection, for specific detection of the common bacterial pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis as well as for specific detection of commonly encountered and clinically relevant bacterial antibiotic resistance genes directly from clinical specimens or, alternatively, from a bacterial colony.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogen in dairy products
ActiveCN101240335AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsKlebsiella oxytocaStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention provides a gene chip for detecting common pathogen in dairy, which comprises a solid-phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase vector, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes DNA fragment or its complementary DNA or RNA sequence selected from E. sakazakii, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Listeria monocytogenes, salmonella and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region of Bacillus cereus, as well as ipaH gene of Shigella or gyrB gene of citrobacter freundii. The invention further provides a reagent box which uses the gene chip to detect pathogen in dairy. The gene chip and the reagent box of the invention for detecting pathogen in dairy are easy to operate, highly precise and greatly repeatable.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD +1
Combined nitrogen fixing phosphorus disintegrating potassium disintegrating micro organism composite fertilizer
InactiveCN1904035AIncreased kinetin contentIncreased mitogensBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeMicroorganism
The present invention discloses a composite microbial fertilizer. It is characterized by utilizing three bacterial powders of Bacillus mucilaginosus CGMCC, No.1641, Klebsiella pneumoniae subsp pneumonaiae CGMCC, No.1642 and Bacillus megaterium CGMCC, No.1640, mixing them according to weight ratio of 1:1:1 to obtain their mixture and mixing said mixture with a synergistic agent according to a certain mixing ratio so as to obtain the invented microbial fertilizer.
Owner:新疆惠森生物技术有限公司
Klebsiella pneumoniae inoculants for enhancing plant growth
A biological inoculant for enhancing the growth of plants is disclosed. The inoculant includes the bacterial strains Herbaspirillum seropedicae 2A, Pantoea agglomerans P101, Pantoea agglomerans P102, Klebsiella pneumoniae 342, Klebsiella pneumoniae zmvsy, Herbaspirillum seropedicae Z152, Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus PA15, with or without a carrier. The inoculant also includes strains of the bacterium Pantoea agglomerans and K. pneumoniae which are able to enhance the growth of cereal grasses. Also disclosed are the novel bacterial strains Herbaspirillum seropedicae 2A, Pantoea agglomerans P101 and P102, and Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 and zmvsy.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Kit for detecting klebsiella pneumoniae
ActiveCN104946762ASimplify testing proceduresShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationK pneumoniaeNucleotide
The invention discloses a kit for detecting klebsiella pneumoniae, and belongs to the technical field of PCR detection. The kit comprises specific primers and a probe for detecting klebsiella pneumoniae; the nucleotide sequences of the specific primers and the probe are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3; a detected target gene is a sequence of a pho gene, and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.4. The kit has the advantages of being accurate in detection, high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, and simple and quick to operate, has a favorable sample detection capacity, can replace a traditional bacterial isolated cultivation and diagnosis method, and the novel kit for quick detection is provided for klebsiella pneumoniae.
Owner:BIOSINO BIO TECH & SCI
Bamboo forest biological fertilizer
InactiveCN1443729AIncrease nitrogen fixation intensityIncrease productionBacteriaHorticulture methodsBacillus licheniformisK pneumoniae
The bamboo forest biolgoical fertilizer capable of meeting the requirements for biological organic fertilizer in production of nuisance-free green bamboo shoots and organic bamboo shoots for reducingor substituting chemical fertilizer is formed from matrix and bamboo plant rhizospheric combined nitrogen-fixing bacteria which are separated from bamboo plant rhizosphere, can be used for fixing molecular nitrogen in atmosphere and are any one strain or combination of any two kinds of strains or more than two kinds of (Bacillus polymyxa mace) WG-1 strain, (Bacillus polymyxa mace) WG-2 strain, (Bacillus licheniformis Chester) WG-3 strain and (Klebsiella pneumoniae (Schroeter) Trevisan) WG-4 strain. Said fertilizer can be used for cultivating bamboo forest.
Owner:吴晓丽 +1
Method for eliminating capability of klebsiella pneumoniae in synthesizing 2,3-butanediol and acetoin
ActiveCN102952826AEliminate generationReduce separation and extraction stepsBacteriaStable introduction of DNA2,3-ButanediolGlycerol
The invention discloses a method for eliminating capability of klebsiella pneumoniae in synthesizing 2,3-butanediol and acetoin, comprising the following step of inactivating acetolacetate decearboxylase gene in a synthesis route of 2,3-butanediol by lebsiella pneumoniae to cut off the catalytic reaction that acetolactic acid is converted into acetoin. According to the method, when 1,3-propylene glycol is synthesized from glycerol by the klebsiella pneumoniae, the synthesis of byproducts, i.e. 2,3-butanediol and acetoin, can be eliminated, and the conversation rate of glycerol to 1,3-propylene glycol can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for producing 1,3-propylene glycol by microorganism aerobic fermentation
The present invention provides microbial aerobic fermentation process of producing 1, 3-propylene glycol, and belongs to the field of biochemical technology. Seed liquid is first added into industrial glycerin or initial fermentation culture medium of glycerin fermenting liquid with glycerin concentration of 20-50 g / L, and under fermentation condition of 30-40 deg.c, the culture medium is fermented with PDO producing Klebsiella pneumoniae or acid producing Klebsiella pneumoniae to produce PDO. During fermentation, air in 0.2-1.0 vvm is led in, the fermented matter is stirred in 50-250 rpm, glycerin and sodium hydroxide in certain amount are added to maintain certain glycerin concentration. The present invention has the advantages of lowered investment and power consumption, raised final PDO concentration, raised production strength and increased bacteria biomass.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Primer probe combination and kit for combined inspection of 15 kinds of respiratory tract infection pathogens
ActiveCN107937578ARapid combined detectionGuaranteed matchMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStreptococcus pyogenesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a pathogen inspection reagent, and concretely discloses a primer probe combination and a kit for combined inspection of 15 kinds of respiratory tract infection pathogens. By aiming at specific target sequences of the gene sequence conserved region of klebsiella pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, chlamydia pneumoniae, mycobacterium tuberculosis, stenotrophomonas maltophilia, baumanii, mycoplasma pneumoniae, enterococcus faecalis, ligionella pneumohpillia, streptococcus pneumoniae, bacillus pyocyaneus and mycobacterium abscessus, primers and probes which do not have mutual crossed reaction are designed, so that the problem that detection probes of different pathogens can easily generate mutual influenceor interference is solved; the combination and matching of different primers and probes are ensured; the goal of simultaneously performing efficient specific inspection at the same temperature can also be achieved.
Owner:西安九安生物技术有限公司
New klebsiella pneumoniae phage and application thereof
ActiveCN110438091AImprove disinfection effectBroad spectrum antibacterialAntibacterial agentsBiocideK pneumoniaeMultidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
The invention discloses new klebsiella pneumoniae phage vB_KpnM_Bp5. The klebsiella pneumoniae phage (klebsiella pneumoniae phage) phage ) vB_KpnM_Bp5 is preserved in the China Center for Type CultureCollection (CCTCC) on June 13, 2019, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2019452. The phage has better disinfecting and sterilizing effects on host multidrug resistant klebsiella pneumoniae separated from piggery sewage, also has good disinfecting and sterilizing effects on other two multidrug resistant klebsiella pneumoniae separated from hospitals, is wide in antimicrobial spectrum, and can be applied to preparation of medicines for preventing and treating multidrug resistant klebsiella pneumoniae.
Owner:南宁鑫创生物科技有限公司
Ascendant bacterium and application for lead waste water treatment
InactiveCN101134945AHigh selectivityImprove toleranceBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPolypropyleneWater treatment
The present invention relates to the tolerance and adsorbability of microbe in biomembrane for treating low concentration lead-containing waste water, and discloses one kind of dominant bacterium, named as klebsiella pneumoniae CGMCC No.2016, shortly as Z-KAE15. Z-KAE15 has unheard-of high lead tolerance, high lead adsorbability and industrial practicability, and Z-KAE15 membrane can reach lead and COD removing rate of 95 % and 90 % separately. Z-KAE15 is obtained through the domestication on biomembrane in natural water, purifying, separating, repeated screening and 16s rDNA sequencing verification. The dominant bacterium Z-KAE15 is applied in environmental bioengineering to expand biomembrane process for continuous treatment of lead-containing sewage.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY +3
Heavy metal-resistant polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) degrading bacteria and application thereof in remediation of composite contaminated soil
ActiveCN102943052APromote degradationResistant to heavy metalsBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicroorganism
The present invention belongs to the technical field of environmental engineering and microbial engineering, and especially relates to klebsiella pneumoniae tzyx1 for degradation of PAHs and application thereof in remediation of composite contaminated soil. The accession number of klebsiella pneumoniae tzyx1 strain in the center of the Chinese Typical Culture Collection Center is CCTCC M2012239. The klebsiella pneumoniae tzyx1 strain has the ability to degrade PAHs. The strain can be applied in the governance of PAHs and heavy metal-contaminated soils.
Owner:北京霖孚科技集团有限公司
Gene engineering bacterium for producing 1,3-propanediol and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101260379AImprove stabilityHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymeGlycerol
The invention belongs to the biochemical field and discloses a 1, 3-propylene glycol genetic engineering bacterium and a preparation method and application thereof. The strain is classified and named as Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955-pUC18-yqhD-Tet<R>, and is obtained by connection of a 3-propylene redoxase isozyme gene yqhD from Escherichia coli and a tetracycline resistant gene Tet<R> from a plasmid pHY300PLK, insertion of a carrier pUC18 and conversion of Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955. The bacterium can obviously improve the capacity for conversion of glycerol into 1, 3-propylene glycol, improve the utilization ability and the conversion rate of the substrate glycerol and the final concentration of the final offspring 1, 3-propylene glycol, simultaneously shorten the fermentation time, and is convenient for industrial production of the 1, 3-propylene glycol through the microbial fermentation method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Detection method for drug resistant genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae against belta-lactamase
InactiveCN101519688AReduce infection rateReduce mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisBacteria identification
The invention discloses a detection method for drug resistant genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae against belta-lactamase, pertaining to the technical field of gene detection methods. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1. Klebsiella pneumoniae strains of inpatients are selected and sampling for backup is carried out after strain identification is carried out to all strains using bacteria identifying apparatus; 2. the sensitivity of antibacterials is determined by adopting the micro dilution method so as to judge the sensitivity of antibiotic; and 3. drug resistant genes are detected by adopting a PCR method and belta-lactamase drug resistant genes are checked and DNA positive strains are selected for carrying out sequencing analysis. The detection method finds the drug resistant genes resulting in the resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to belta lactam drugs by carrying out a systematical and complete research on the drug resistant mechanism of the Klebsiella pneumoniae, thus having important value for instructing the clinical and reasonable use of antibacterials, being capable of reducing the infection rate in a hospital, reducing mortality rate and saving social medical resources, and having good social and economic benefits.
Owner:钟建平
Gene chip for detecting pathogens of lower respiratory tract and reagent kit
ActiveCN101748193AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesK pneumoniaeStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a gene chip for detecting pathogens of lower respiratory tract, which comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises a sequence selected from one or more DNA sequences of staphylococcus aureus, 16s-23s rDNA intergenic spacer region of Klebsiella pneumoniae or Acinetobacter baumannii, 16S gene of pseudomonas aeruginosa or haemophilus influenzae, gyrB gene of streptococcus pneumoniae or legionella pneumophila and copB gene of moraxella catarrhalis or the complementary DNA or RNA sequence. The invention further provides a reagent kit containing the gene chip. The utilization of the gene chip and the reagent kit can detect the pathogens of the lower respiratory tract; furthermore, the operation is simple, the accuracy is high and the repeatability is strong.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Inhalable aztreonam lysinate formulation for treatment and prevention of pulmonary bacterial infections
A method and a composition for treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections caused by gram-negative bacteria suitable for treatment of infection caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, Serratia marcescens as well as those caused by Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Alcaligenes xylosoxidans, and multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, using a concentrated formulation of aztreonam lysinate delivered as an aerosol or dry powder formulation.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Insect antimicrobial peptide Thanatin derivant, producing method and uses of the same
InactiveCN101173005AIncrease varietyHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsK pneumoniaeHemolysis
The invention relates to a group of insect Thanatin ramifications with antibacterial action and the salt which is applicable for medicinal use, as well as a preparation method and the use thereof. Approved by the results of a sterilization experiment, a hemolysis experiment and an irritable partial stimulation experiment, the insect Thanatin ramification has bigger antibacterial activity than Thanatin to colon bacillus, Candida albicans, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and staphylococcus aureus. The hemolysis reaction is not incurred when the concentration is 2.5mg / ml without acute toxicity stimulation reaction.
Owner:沈子龙
Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application in preparing 2,3-butanediol
ActiveCN101457211AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeProduction rate
The invention discloses a Klebsiella pneumoniae SDM CCTCC M 208097 and applications in preparing 2, 3-butanediol. The Klebsiella pneumoniae SDM CCTCC M 208097 has features of wide nutritional requirement range, high outcome concentration and short production period or the like. The culture medium and the operation method are simple, the cost is low. The outcome of the 2, 3-butanediol prepared by a fermenter feeding batch fermentation can reach 120-160g / L, the conversion can reach 90-940f the theoretic conversion, the most production rate of the 2, 3-butanediol is 4. 05g / (L. h). The invention has very large commercial use prospect.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com