Straw in-situ decomposition microbial agent and application thereof
A technology of bacteria agent and straw, which is applied in the direction of application, bacteria, fixed on or in the inorganic carrier, can solve the problems of difficult to ensure the moisture of microbial proliferation, unclear composition of straw, etc., and achieve rapid decomposition, low cost, and wide The effect of applying the foreground
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1, the preparation of straw decomposing bacterial agent in situ
[0043] 1. Experimental materials
[0044] 1. The strains used for the preparation of bacterial agents
[0045] Clostridium xylanolyticum (Clostridium xylanolyticum) DSM No.6555T: This strain is preserved in the German Culture Collection of Microorganisms (DSMZ), and the preservation number is DSM No.6555T;
[0046] Cellulolytic Xylanomonas (Xylanimonas cellulosilytica) DSM No.15894: This strain is preserved in the German Microorganism Culture Collection (DSMZ), and the preservation number is DSM No.15894;
[0047] Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas sp.) ACCC No.11691: This strain is preserved in the China Agricultural Microorganism Culture Collection Center (ACCC), and the preservation number is ACCC No.11691;
[0048] Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) ACCC No.03189: This strain is preserved in the China Agricultural Microorganism Culture Collection Center (ACCC), and the preservation number is ACC...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2, Analysis of the decomposing effect of straw in-situ decomposing bacteria agent on straw in culture medium
[0063] 1. Analysis of the decomposing effect of straw in-situ decomposing bacterial agent I prepared in Example 1 on corn stalks in the culture medium
[0064] Inoculate the straw in situ decomposing bacterial agent I prepared in Example 1 into a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 50mL medium with 10g / L corn stalk as a carbon source, and culture it statically at 30°C with an initial pH of 8.0 After 15 days, the removal rate of cellulose and hemicellulose in corn stalks was measured after the cultivation.
[0065] Among them, the specific formula of the medium with 10g / L corn stalk as carbon source is as follows: peptone 5g / L, yeast extract 1g / L, NaCl 5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.35g / L, CaCO 3 3g / L, corn straw 10g / L, pH=7.2±0.1. The particle size of corn stalks is 2-10 cm.
[0066] The method for determining the removal rate of cellulose...
Embodiment 3
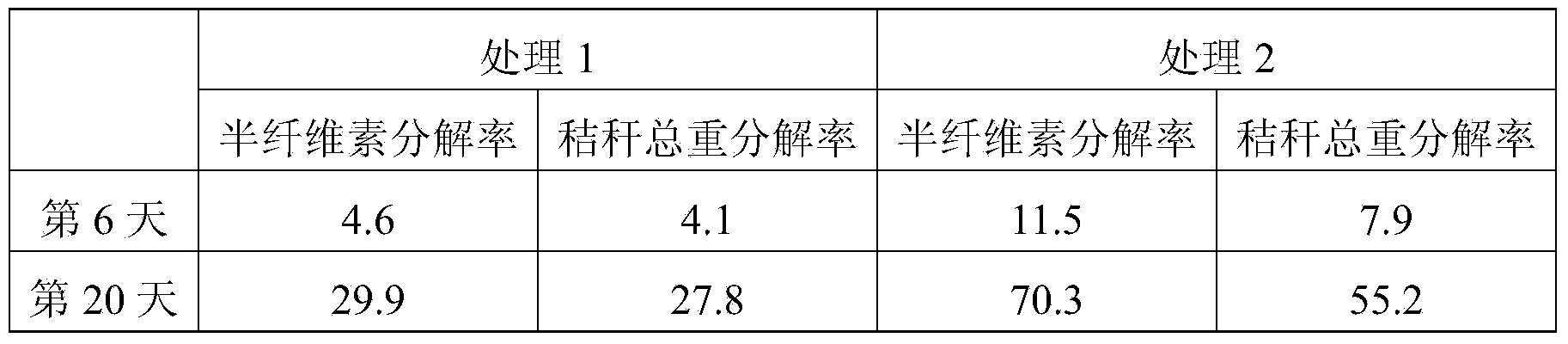
[0079] Example 3. Straw in-situ decomposing bacteria agent I is applied to the direct return of corn stalks to the field
[0080] Experimental location: Shangzhuang Experimental Station of China Agricultural University, Haidian District, Beijing.
[0081] Experimental materials: corn stalks, straw in situ decomposing bacterial agent I prepared in Example 1.
[0082] Experimental design: set up two experimental points, each experimental point has two treatments, each treatment takes an area of not less than 0.5 mu, and the treatments are randomly arranged to ensure that the experimental conditions are basically the same.
[0083] Treatment 1: Without adding fungicides, the corn stalks were directly returned to the field.
[0084] Treatment 2: Using the in-situ straw decomposing bacterial agent I prepared in Example 1, the corn straw was directly returned to the field.
[0085] Application method: After crushing corn stalks (with a particle size of 2-5cm), sprinkle them even...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com