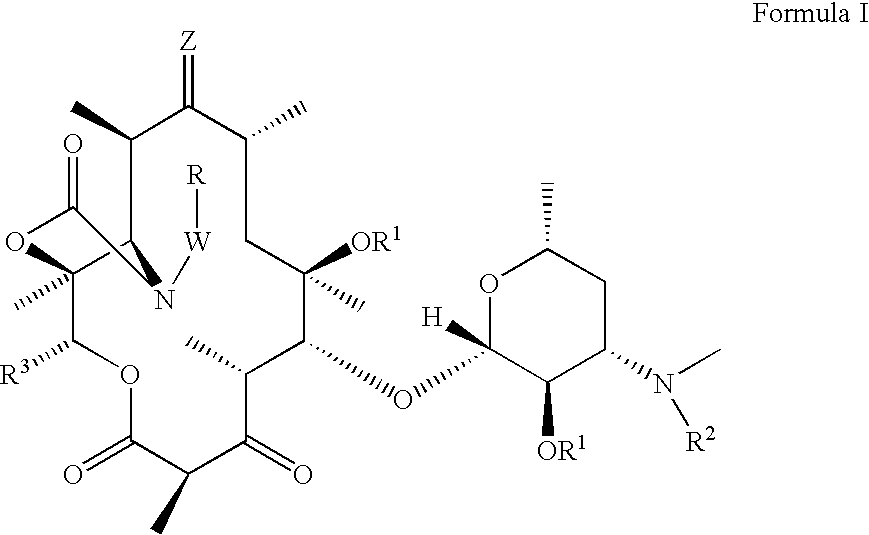
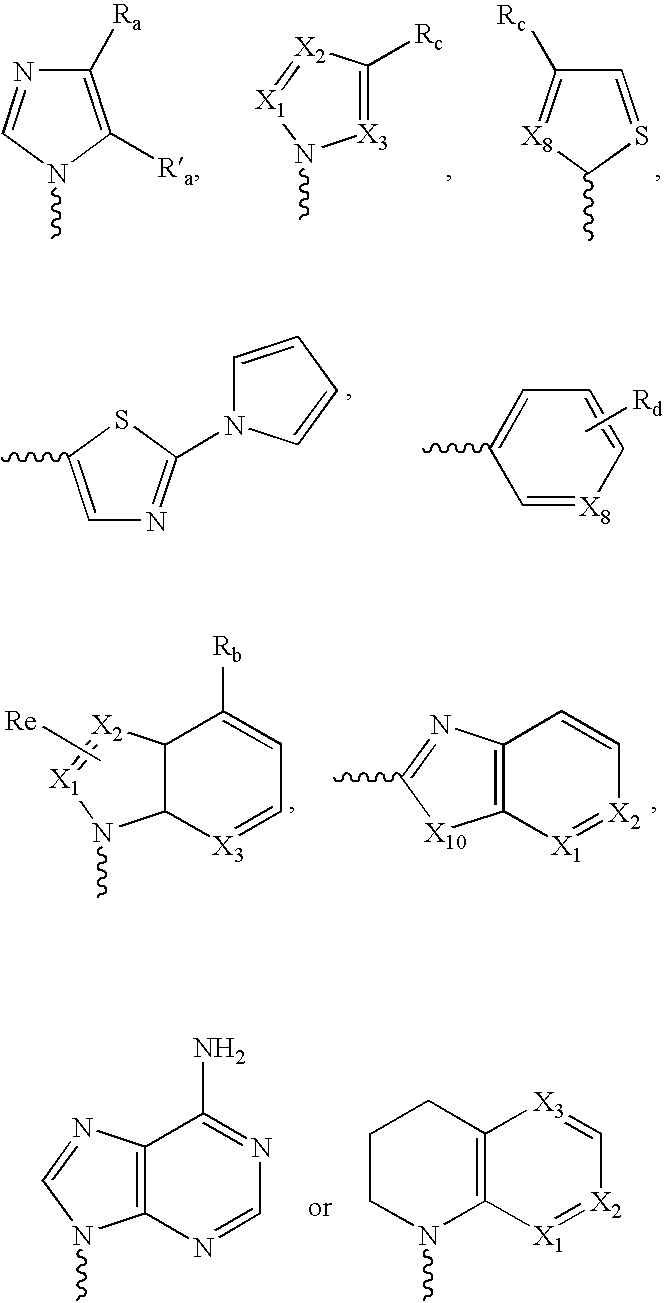
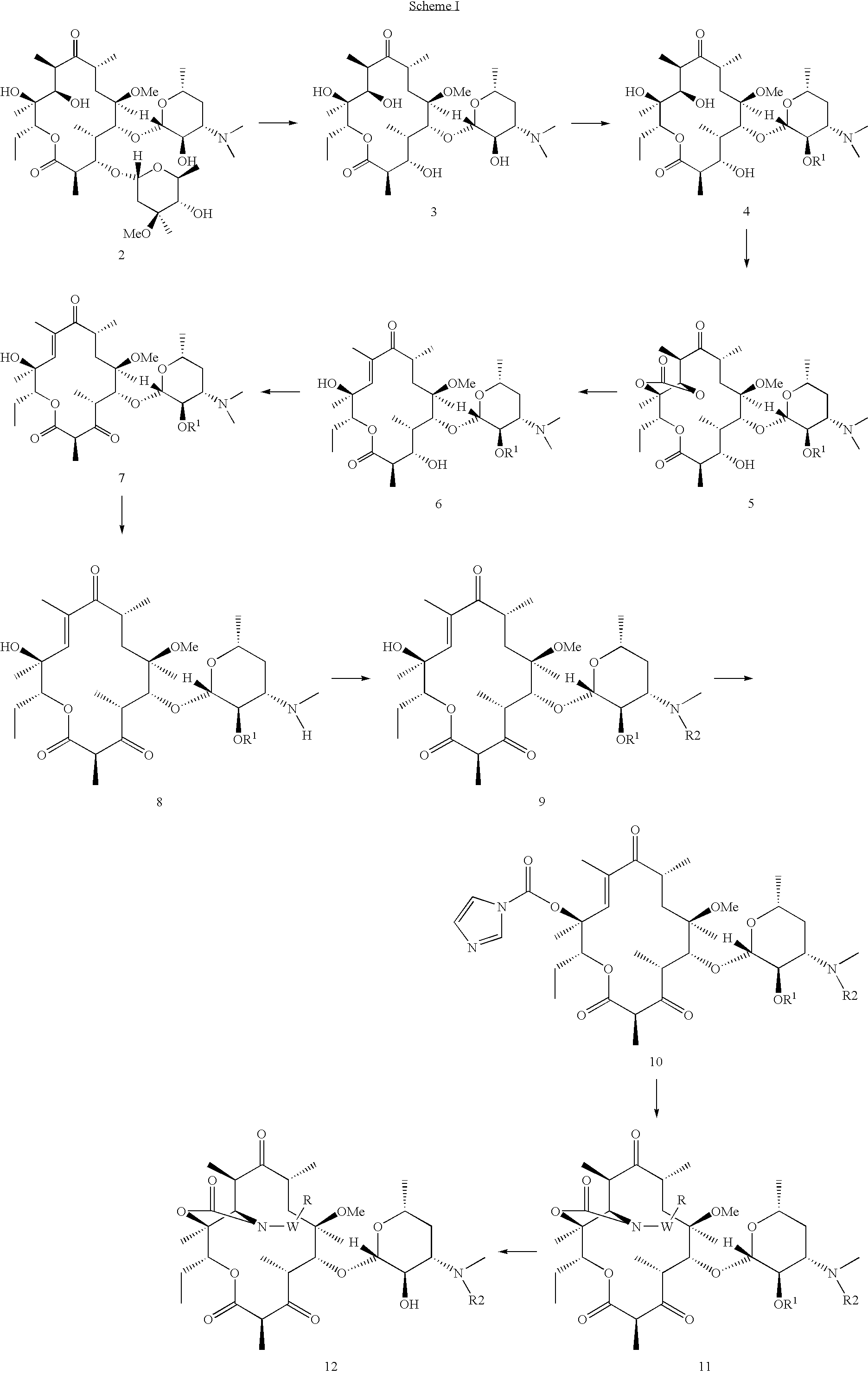
[0094]In another aspect, provided herein are methods for treating or preventing acne vulgaris and inflammatory conditions thereof comprising administering to a mammal in need thereof therapeutically effective amounts of one or more compounds of Formula I in combination with one or more therapeutic agents selected from alcohol, benzoyl peroxide, clindamycin, tretinoin, vitamin E, vitamin A and its derivatives, tetracycline, isotretinoin, vitamin C, vitamin D, chaparral, dandelion root, licoric root, Echinacea, kelp, cayenine, sassafras, elder flowers, pantothenic acid, para amino benzoic acid, biotin, cholin, inositol, folic acid, calcium, magnesium, potassium, vitamin B6, zinc, carotenoid, azelaic acid, and other therapeutic agents, which can be used to treat acne or condition the skin.
[0095]The term “alkyl,” unless otherwise specified, refers to a monoradical branched or unbranched saturated hydrocarbon chain having from 1 to 20 carbon atoms. Alkyl groups can be optionally interrupted by atom(s) or group(s) independently selected from oxygen, sulfur, a phenylene, sulfinyl, sulfonyl group or —NRa—, wherein Ra can be hydrogen, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl cycloalkyl or aryl. This term can be exemplified by groups such as methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, iso-butyl, sec-butyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, isopentyl, neopentyl, n-hexyl, n-decyl, tetradecyl, and the like. Alkyl groups may be substituted further (referred herein as “substituted alkyl”) with one or more substituents selected from alkenyl, alkynyl, alkoxy, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, acyl, acylamino, acyloxy, alkoxycarbonylamino, azido, cyano, halogen, hydroxy, keto, oxo, thiocarbonyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, aryl (for R6-R9, alkyl is not substituted with aryl), heterocyclyl, heteroaryl, arylthio, thiol, alkylthio, aryloxy, nitro, aminosulfonyl, aminocarbonylamino, —NHC(═O)Rk, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —NHC(═O)NRpRq, —C(═O)heteroaryl, C(═O)heterocyclyl, —O—C(═O)NRpRq {wherein Rp and Rq are independently selected from alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, aryl, aralkyl, heterocyclyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclylalkyl, heteroarylalkyl}, nitro, hydroxyamino, alkoxyamino or S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, aralkyl, aryl, heterocyclyl, heteroaryl, heteroarylalkyl or heterocyclylalkyl). Unless otherwise constrained by the definition, alkyl substituents may be further substituted by 1-3 substituents selected from alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, carboxy, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —OC(═O)NRpRq, —NHC(═O)NRfpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier), hydroxy, alkoxy, halogen, CF3, cyano, and S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 are the same as defined earlier); or an alkyl group also may be interrupted by 1-5 atoms of groups independently selected from oxygen, sulfur or —NRa— {wherein Ra is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, acyl, aralkyl,—C(═O)ORp (wherein Rp is the same as defined earlier), S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is as defined earlier), or —C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are as defined earlier)}. Unless otherwise constrained by the definition, all substituents may be substituted further by 1-3 substituents selected from alkyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —O —C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier) hydroxy, alkoxy, halogen, CF3, cyano, and S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is same as defined earlier); or an alkyl group as defined above that has both substituents as defined above and is also interrupted by 1-5 atoms or groups as defined above.
[0096]The term “alkenyl,” unless otherwise specified, refers to a monoradical of a branched or unbranched unsaturated hydrocarbon group having from 2 to 20 carbon atoms with cis, trans, or geminal geometry. It can be optionally interrupted by atom(s) or group(s) independently chosen from oxygen, sulfur, phenylene, sulfinyl, sulfonyl and —NRa—, wherein Ra can be hydrogen, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl or aryl. In the event that alkenyl is attached to a heteroatom, the double bond cannot be alpha to the heteroatom. Alkenyl groups may be substituted further (referred to herein as “substituted alkenyl”) with one or more substituents selected from alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkoxy, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, acyl, acylamino, acyloxy, —NHC(═O)Rp, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —NHC(═O)NRpRq, —O—C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier), alkoxycarbonylamino, azido, cyano, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, keto, carboxyalkyl, thiocarbonyl, carboxy, arylthio, thiol, alkylthio, aryl, aralkyl, aryloxy, heterocyclyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclyl alkyl, heteroaryl alkyl, aminosulfonyl, aminocarbonylamino, alkoxyamino, hydroxyamino, alkoxyamino, nitro, or SO2R66 (wherein R66 are is same as defined earlier). Unless otherwise constrained by the definition, alkenyl substituents optionally may be substituted further by 1-3 substituents selected from alkyl, carboxy, hydroxy, alkoxy, halogen, —CF3, cyano, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —O—C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier) and —SO2R66 (where R66 is same as defined earlier). Groups such as ethenyl or vinyl (CH═CH2), 1-propylene or allyl (—CH2CH═CH2), iso-propylene (—C(CH3)═CH2), bicyclo[2.2.1]heptene, and the like, exemplify this term.
[0097]The term “alkynyl,” unless otherwise specified, refers to a monoradical of an unsaturated hydrocarbon, having from 2 to 20 carbon atoms. It can be optionally interrupted by atom(s) or group(s) independently chosen from oxygen, sulfur, phenylene, sulfinyl, sulfonyl and —NRa—, where Ra can be hydrogen, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl or aryl. In the event that alkynyl is attached to a heteroatom, the triple bond cannot be alpha to the heteroatom. Alkynyl groups may be substituted further (referred to herein as “substituted alkynyl”) with one or more substituents selected from alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkoxy, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, acyl, acylamino, acyloxy, alkoxycarbonylamino, azido, cyano, halogen, hydroxy, keto, oxo, thiocarbonyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, arylthio, thiol, alkylthio, aryl, aralkyl, aryloxy, aminosulfonyl, aminocarbonylamino, hydroxyamino, alkoxyamino, nitro, heterocyclyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclylalkyl, heteroarylalkyl, —NHC(═O)Rp, —NRpRq, —NHC(═O)NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier), S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is as defined earlier). Unless otherwise constrained by the definition, alkynyl substituents optionally may be substituted further by 1-3 substituents selected from alkyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, halogen, CF3, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, NHC(═O)NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier), cyano, or S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is same as defined earlier). Groups such as ethynyl, (—C≡CH), propargyl (or propynyl, —CH2C≡CH), and the like exemplify this term.
[0098]The term “cycloalkyl,” unless otherwise specified, refers to cyclic alkyl groups of from 3 to 20 carbon atoms having a single cyclic ring or multiple condensed rings, which may optionally contain one or more olefinic bonds, unless otherwise constrained by the definition. Such cycloalkyl groups can include, for example, single ring structures, including cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclooctyl, cyclopentenyl, and the like, or multiple ring structures, including adamantanyl, and bicyclo [2.2.1] heptane, or cyclic alkyl groups to which is fused an aryl group, for example, indane, and the like. Spiro and fused ring structures can also be included. Cycloalkyl groups may be substituted further with one or more substituents selected from alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, alkoxy, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, acyl, acylamino, acyloxy, alkoxycarbonylamino, azido, cyano, halogen, hydroxy, oxo, thiocarbonyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, arylthio, thiol, alkylthio, aryl, aralkyl, aryloxy, aminosulfonyl, aminocarbonylamino, —NRpRq, —NHC(═O)NRpRq, —NHC(═O)Rp, —C(═O)NRpRq, —O—C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier), nitro, heterocyclyl, heteroaryl, heterocyclylalkyl, heteroarylalkyl, or S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is same as defined earlier). Unless otherwise constrained by the definition, cycloalkyl substituents optionally may be substituted further by 1-3 substituents selected from alkyl, carboxy, hydroxy, alkoxy, halogen, CF3, —NRpRq, —C(═O)NRpRq, —NHC(═O)NRpRq, —O—C(═O)NRpRq (wherein Rp and Rq are the same as defined earlier), cyano or S(O)mR66 (wherein m is an integer from 0-2 and R66 is same as defined earlier). As used herein the term “halogen or halo” refers to fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine.
 Login to View More
Login to View More