Method for increasing butanol-acetone ratio and butanol yield of clostridia ABE fermentation
A technology of Clostridium acetobutylicum and butanol fermentation, which is applied in the field of ABE fermentation, can solve the problems of increasing difficulty, butanol production does not reach the inhibitory concentration of Clostridium acetobutylicum, and the ratio of butanol/acetone does not increase significantly, so as to improve the comprehensive performance , simple implementation, effective use of waste water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
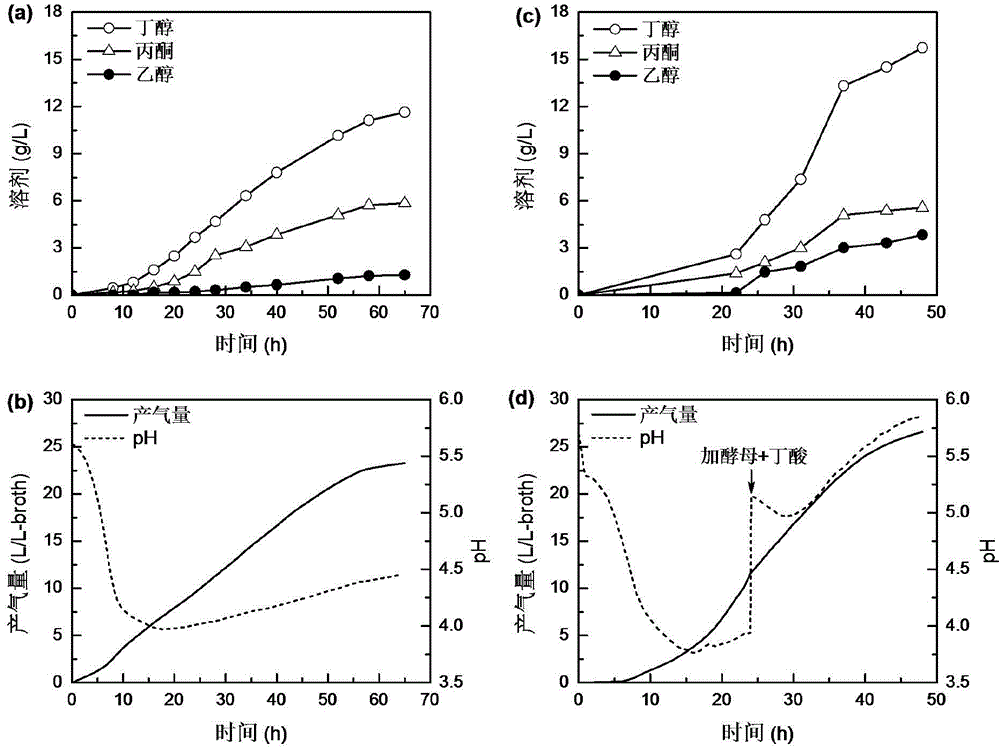
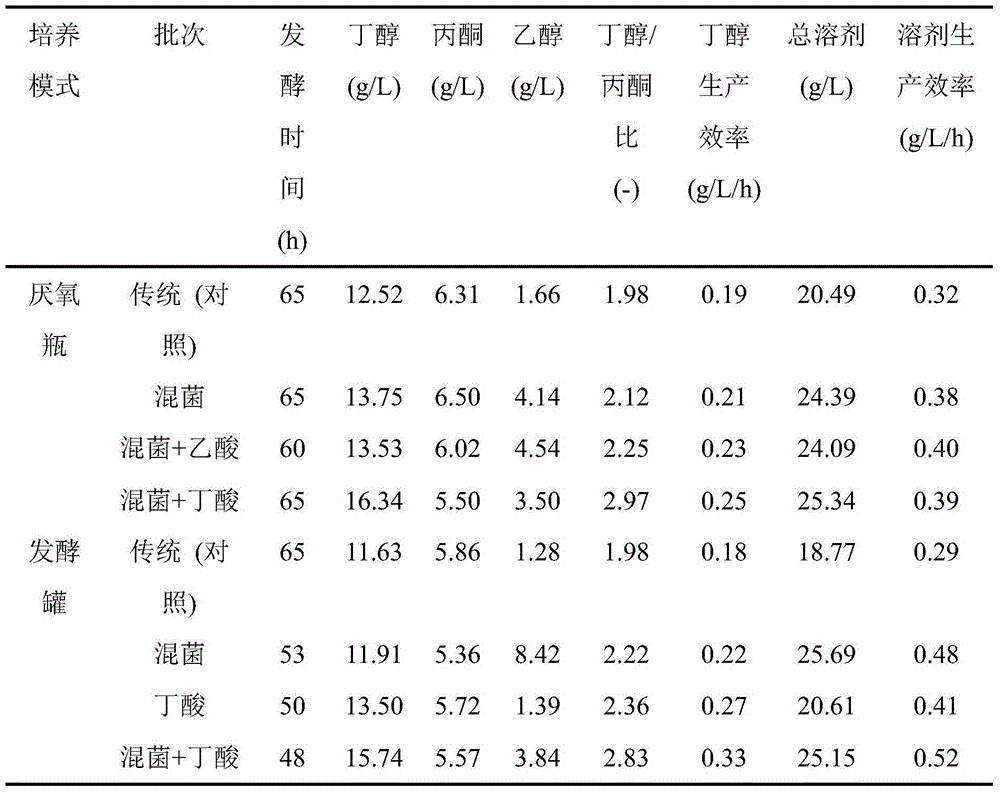
[0022] Embodiment 1 corn butanol traditional fermentation
[0023] Strain activation: inoculate Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824 stored in a refrigerator at 4°C in 5% (w / v) corn mash seed medium, remove the air with a vacuum pump, and culture it statically in a water bath at 37°C for 27 hours as Fermented inoculum. Wherein, the preparation process of corn mash seed culture medium is as follows: take 25g corn flour and dissolve in 2L water, gelatinize in boiling water at high temperature until the volume of corn mash solution is 500mL, which is 5% (w / v) corn seed Culture medium, the sterilization condition is 121°C, 50min.
[0024] The fermentation medium is a dual-enzyme hydrolyzate of 15% (w / v) corn flour, and the preparation process is as follows: the first step is to add high-temperature amylase in an environment of 95°C, the addition amount is 8U / g-starch, and liquefy for 45min; Cool the enzymatic hydrolyzate obtained in the first step of hydrolysis to 62°C, add glucoa...
Embodiment 2
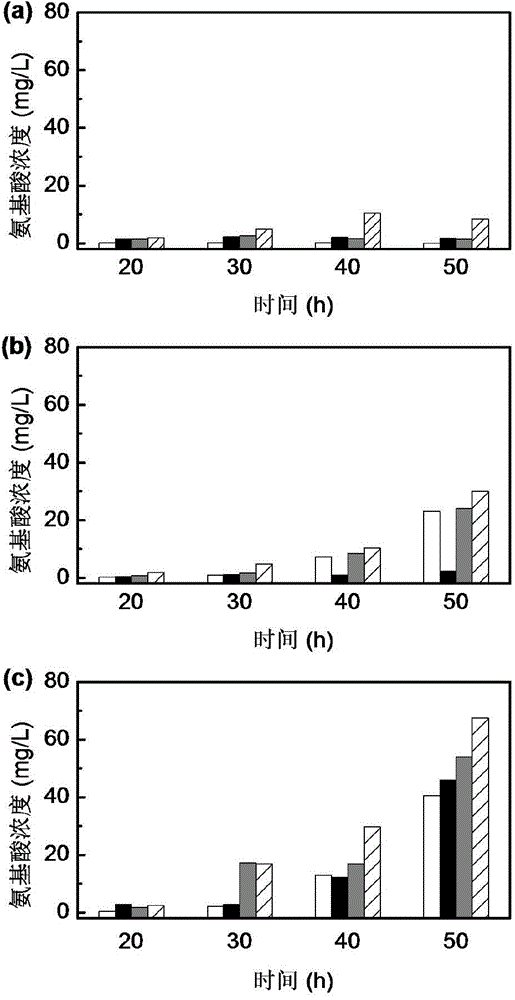
[0030] Embodiment 2 single adding Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0031] In Example 2, the strain activation and fermentation conditions were the same as in Example 1. When the fermentation was carried out to 24h, the pH of the butanol fermentation broth was adjusted to 5.0 with 3mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, and then 10 % (v / v) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae broth until the end of fermentation. The medium formula of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is: glucose 20g / L, yeast extract 8.5g / L, ammonium sulfate 1.3g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.1g / L, calcium chloride dihydrate 0.06g / L, sterilized The conditions were 121°C, 20min; at the beginning of ABE fermentation, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae slant stored in the refrigerator at 4°C was transferred to a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100mL yeast medium, cultured at 30°C, 200r / min for 24h, then When entering the ABE fermentation broth, the yeast culture broth OD 600 8.5-9.5, pH 4.4-4.8.
[0032] The operating conditions of the ana...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3 single addition of butyric acid
[0035] The strain activation and fermentation conditions in Example 3 were the same as in Example 1, and when the fermentation was carried out to 24 hours, the butyric acid solution (pH 3.8) was added in pulses. An organic acid was added every 3 hours until the pH dropped by 0.1 each time. And record the balance readings before and after the addition to calculate the amount of organic acid added. The addition process is accompanied by slight stirring (the rotation speed of the stirring paddle is 100r / min), so that the added organic acid solution and the fermentation broth are mixed quickly to ensure that the pH of each part of the fermentation broth is uniform. After the addition process, the stirring is turned off. The total amount of butyric acid added is 4g / L.
[0036] The operating conditions of the fermenter were the same as in Example 1. The mensuration of parameter: the mensuration of relevant parameter is the sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com