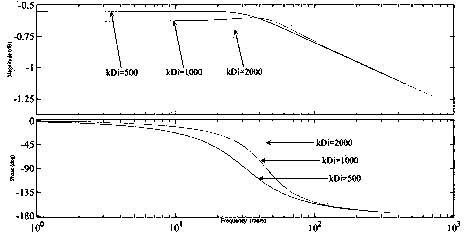
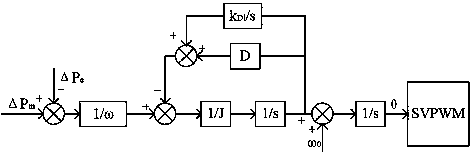
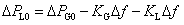Patents
Literature
100 results about "Root locus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
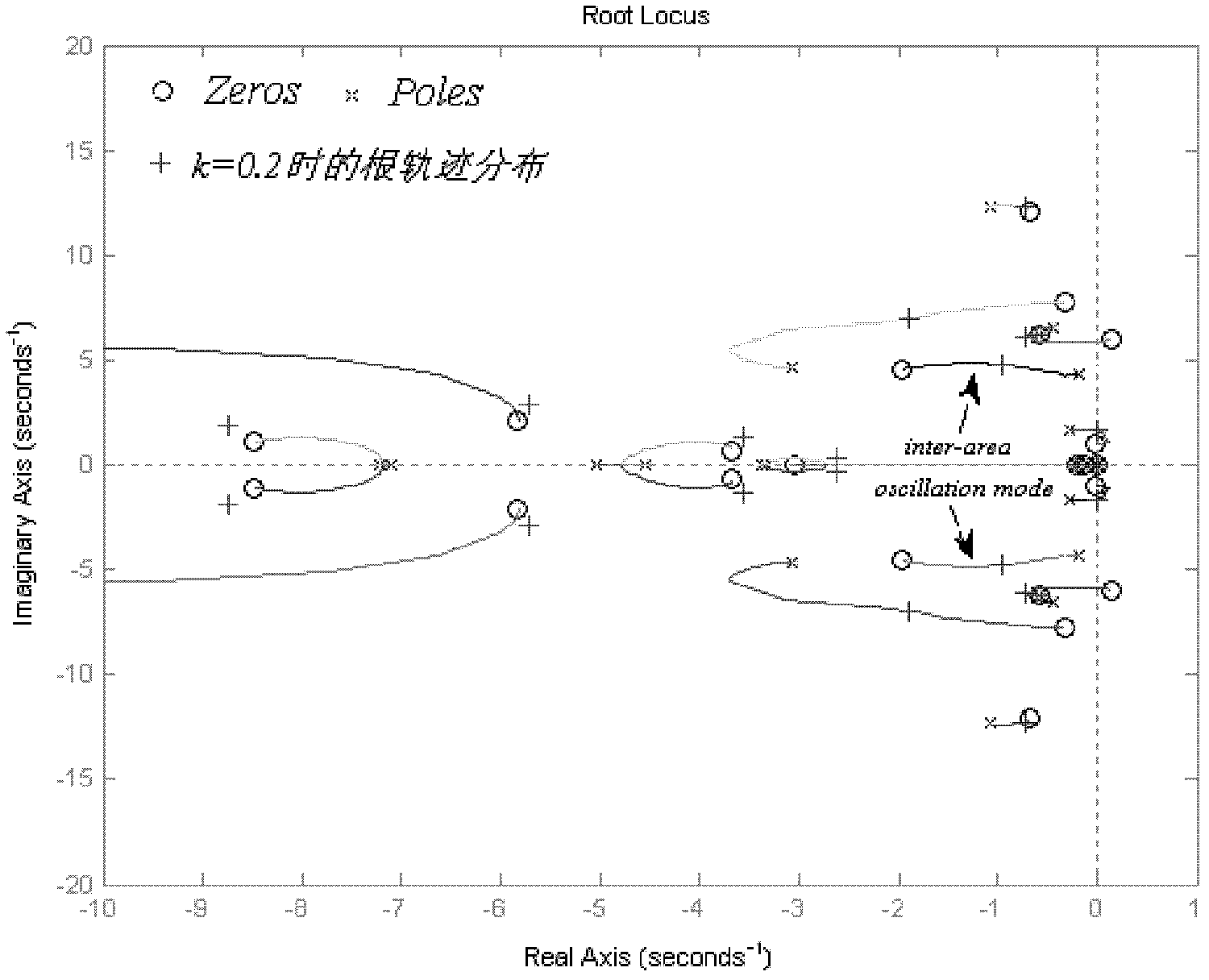
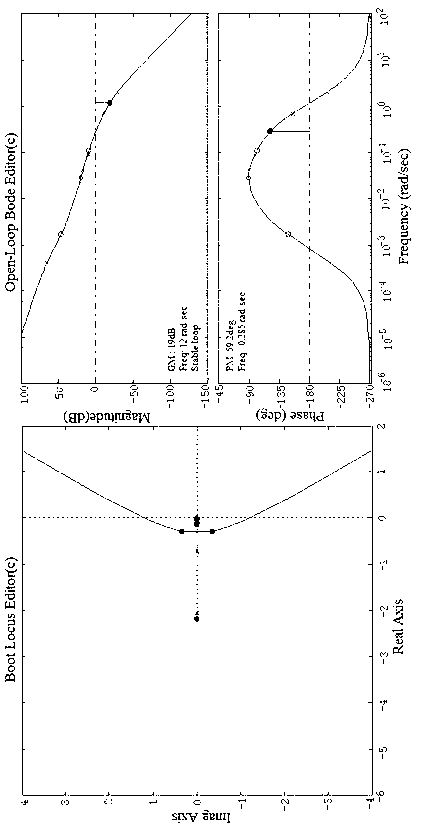
In control theory and stability theory, root locus analysis is a graphical method for examining how the roots of a system change with variation of a certain system parameter, commonly a gain within a feedback system. This is a technique used as a stability criterion in the field of classical control theory developed by Walter R. Evans which can determine stability of the system. The root locus plots the poles of the closed loop transfer function in the complex s-plane as a function of a gain parameter (see pole–zero plot).
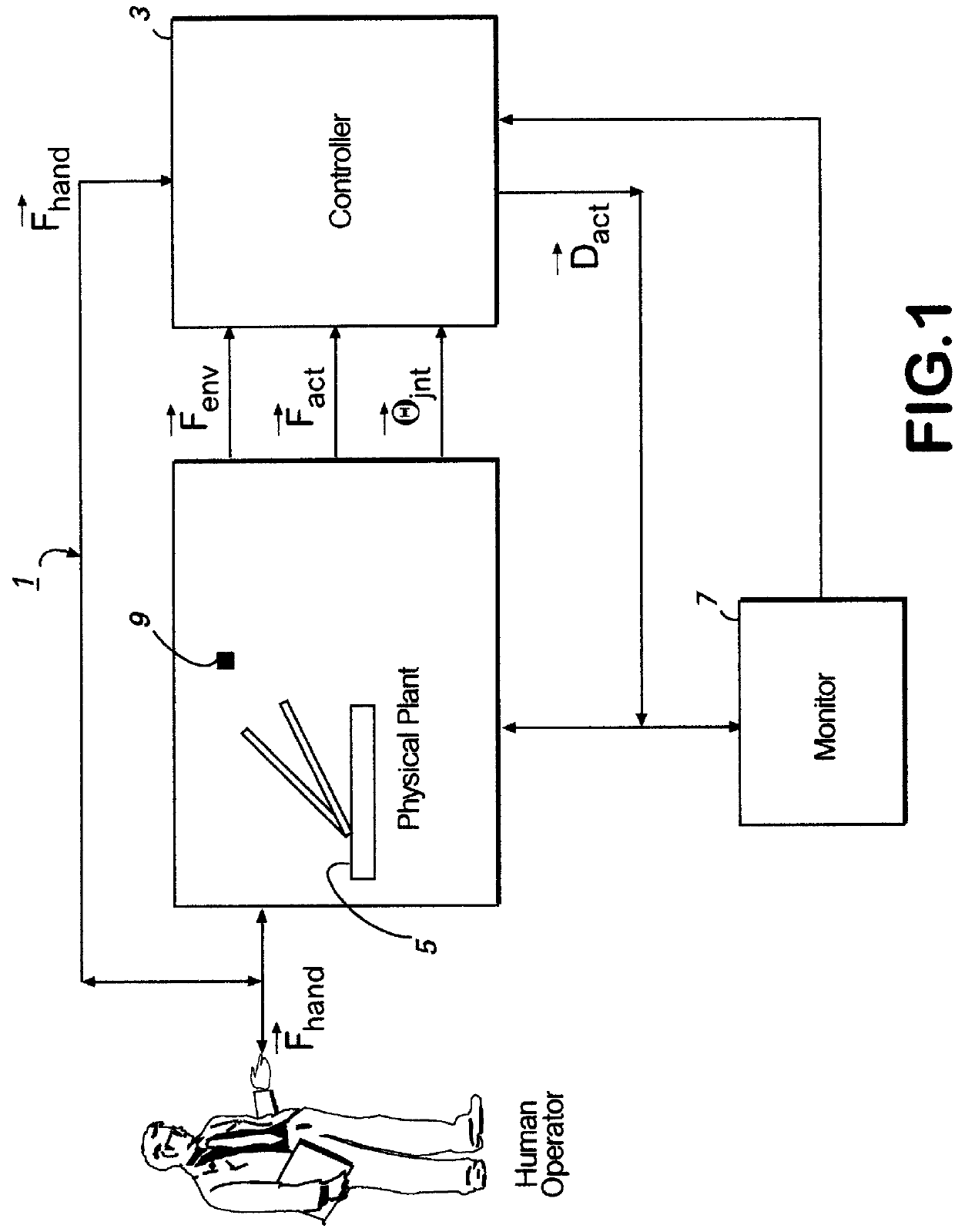
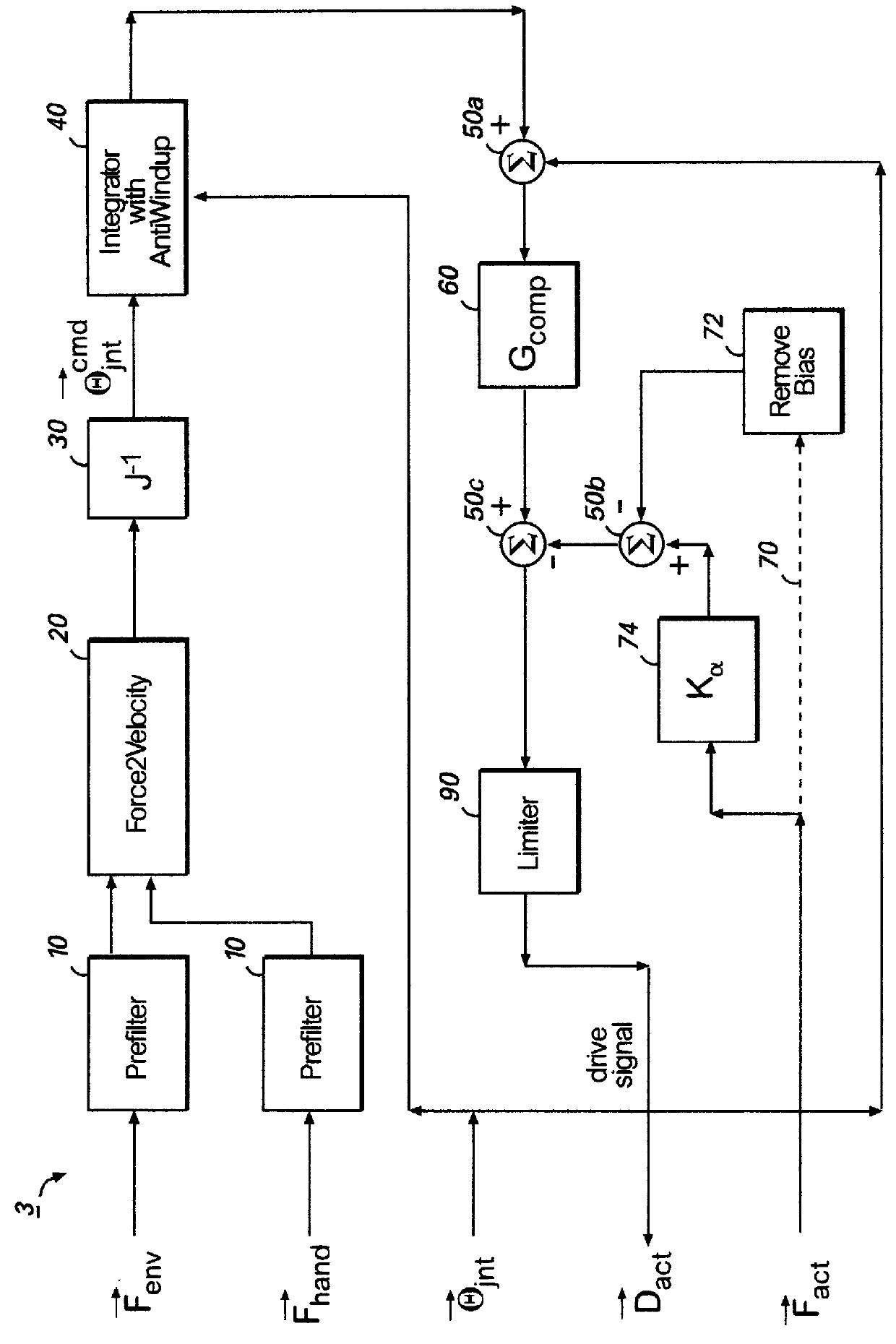
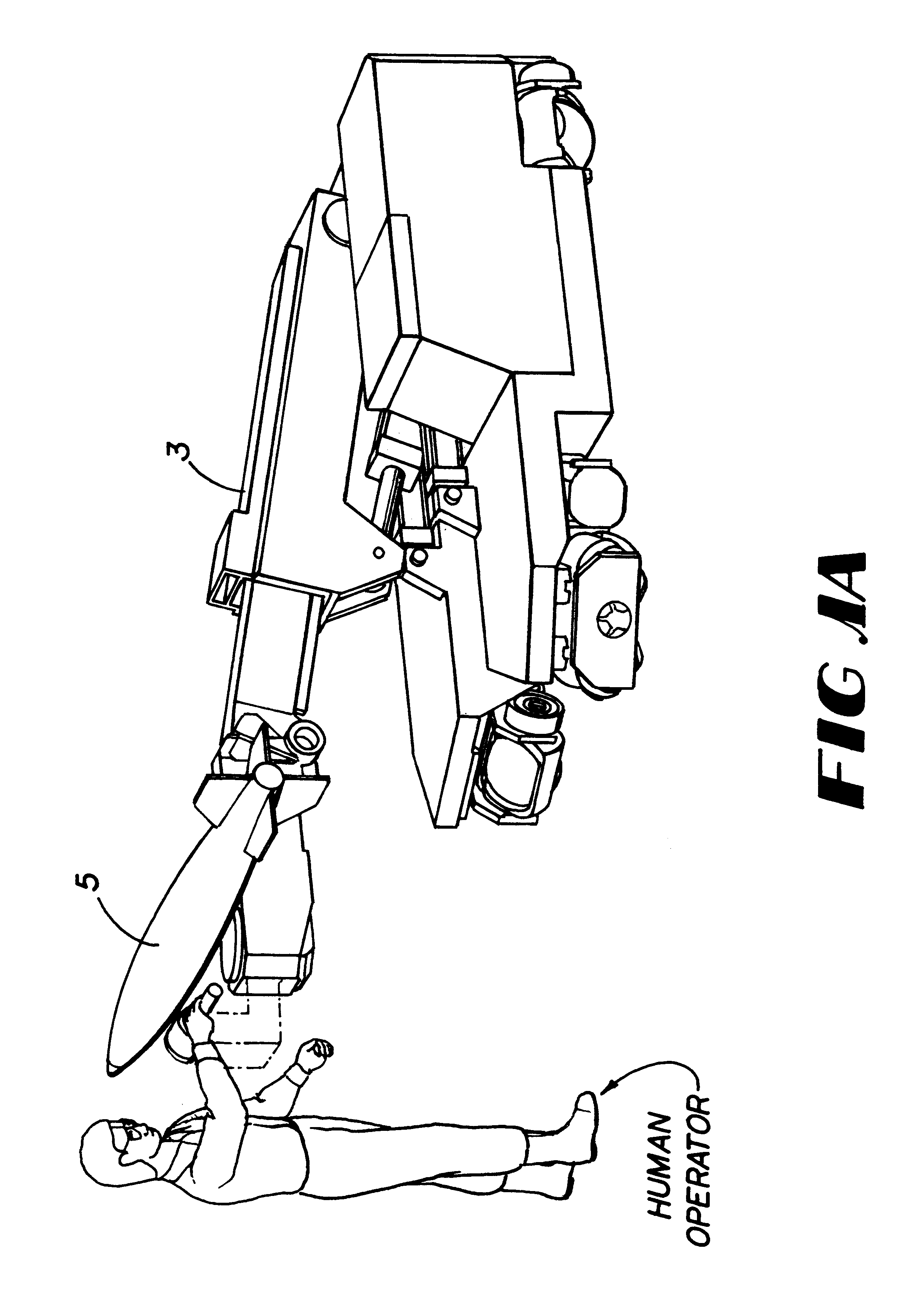
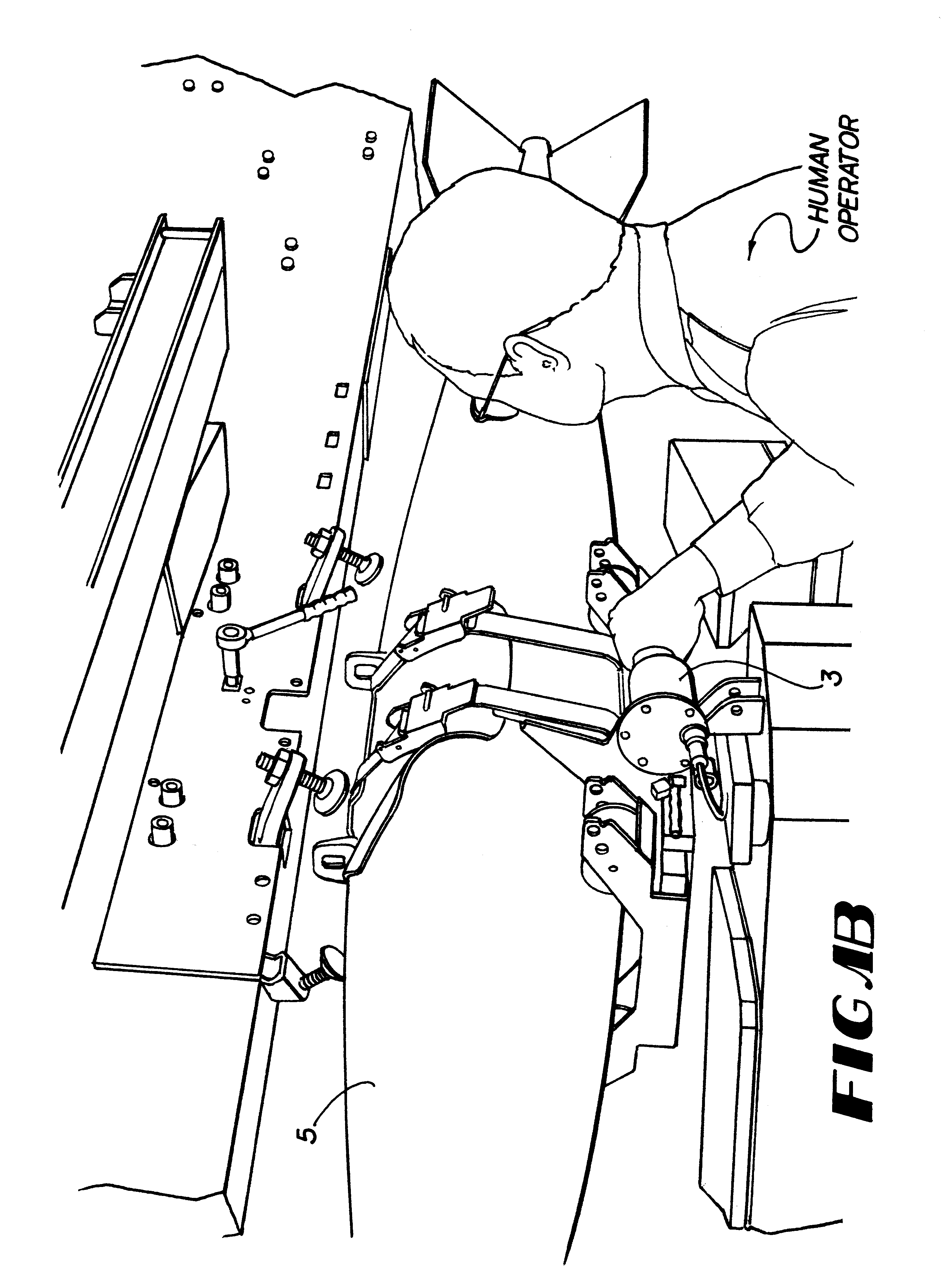
Apparatus and methods for a human de-amplifier system
InactiveUS6084371AProgramme-controlled manipulatorMicromanipulatorOperational systemAudio power amplifier
A human de-amplifier system for interfacing a human operator and a physical object through a physical plant, wherein the physical object has dimensions in the range of 1 micrometer to 1 mm. The human de-amplifier system uses an inner-feedback loop to increases the equivalent damping of the operating system to stabilize the system when it contacts with the environment and reduces the impact of the environment variation by utilizing a high feedback gain, determined by a root locus sketch. Because the stability of the human de-amplifier system of the present invention is greatly enhanced over that of the prior art, the de-amplifier system is able to manipulate the physical object has dimensions in the range of 1 micrometer to 1 mm with high stability and accuracy. The system also has a monitoring device to monitor the motion of the physical object under manipulation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
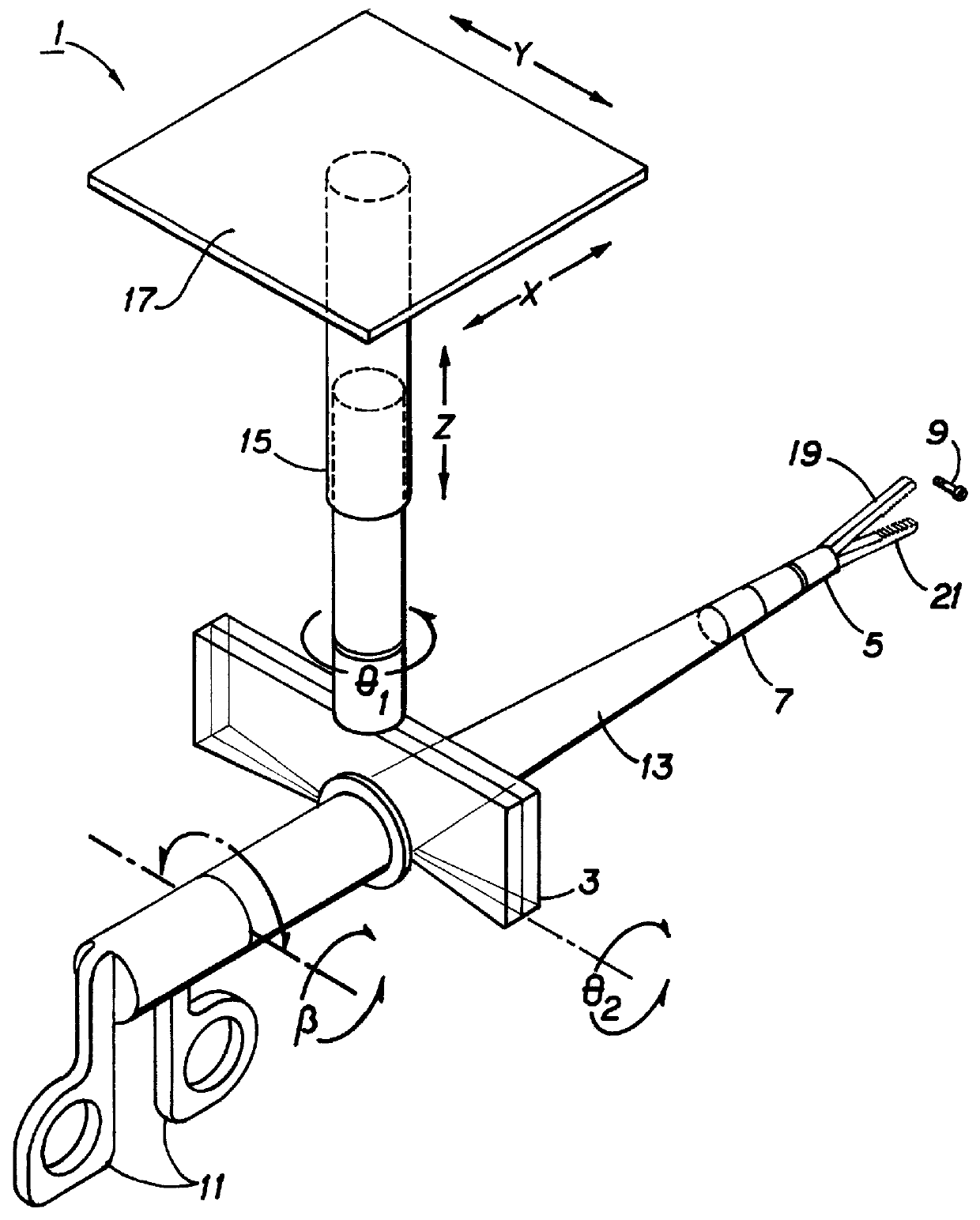
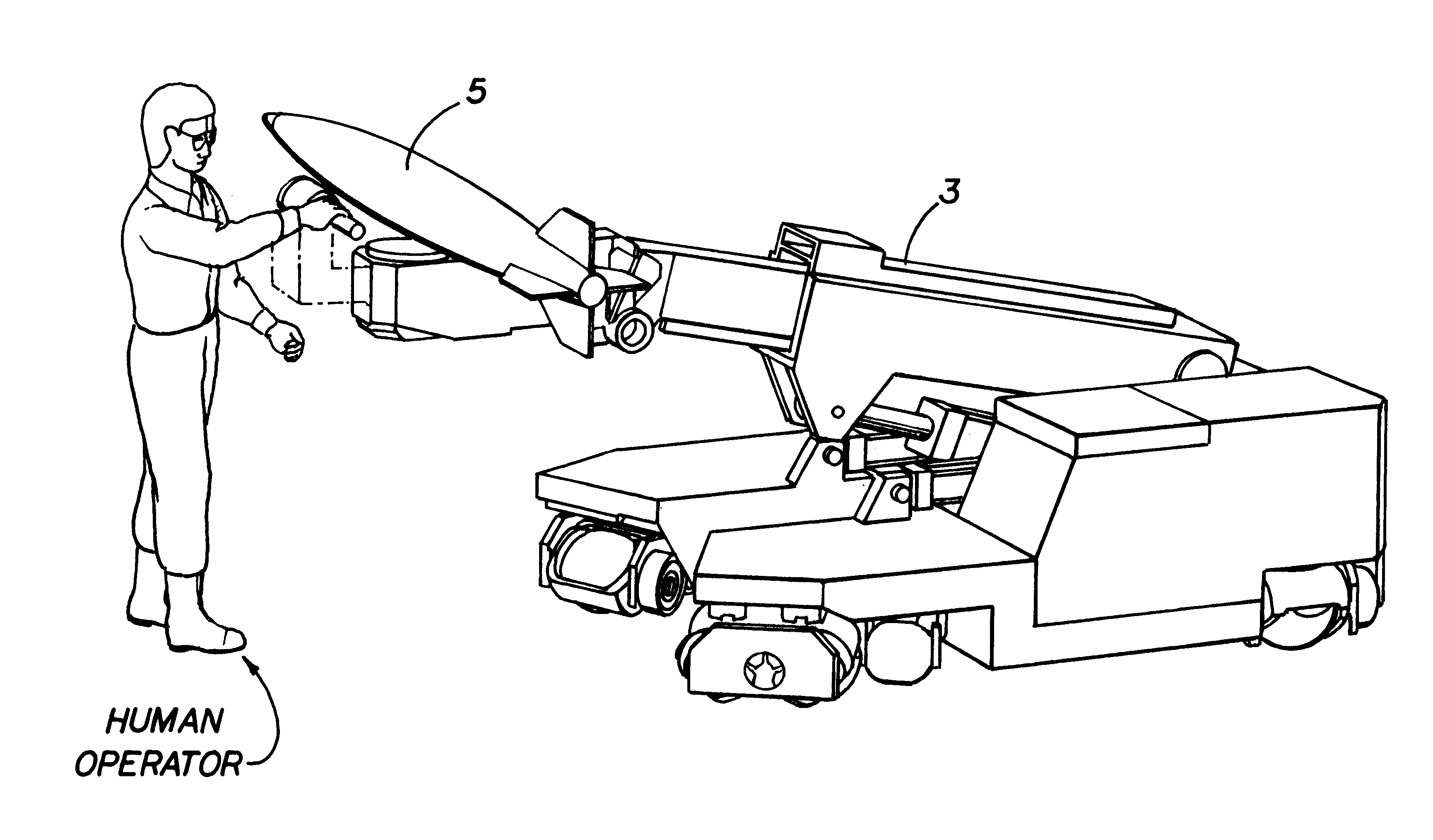
Apparatus and methods for a human extender
A human extender controller for interface between a human operator and a physical object through a physical plant. The human extender controller uses an inner-feedback loop to increase the equivalent damping of the operating system to stabilize the system when it contacts with the environment and reduces the impact of the environment variation by utilizing a high feedback gain, determined by a root locus sketch. Because the stability of the human extender controller of the present invention is greatly enhanced over that of the prior art, the present invention is able to achieve a force reflection ratio 500 to 1 and capable of handling loads above the two (2) ton range.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
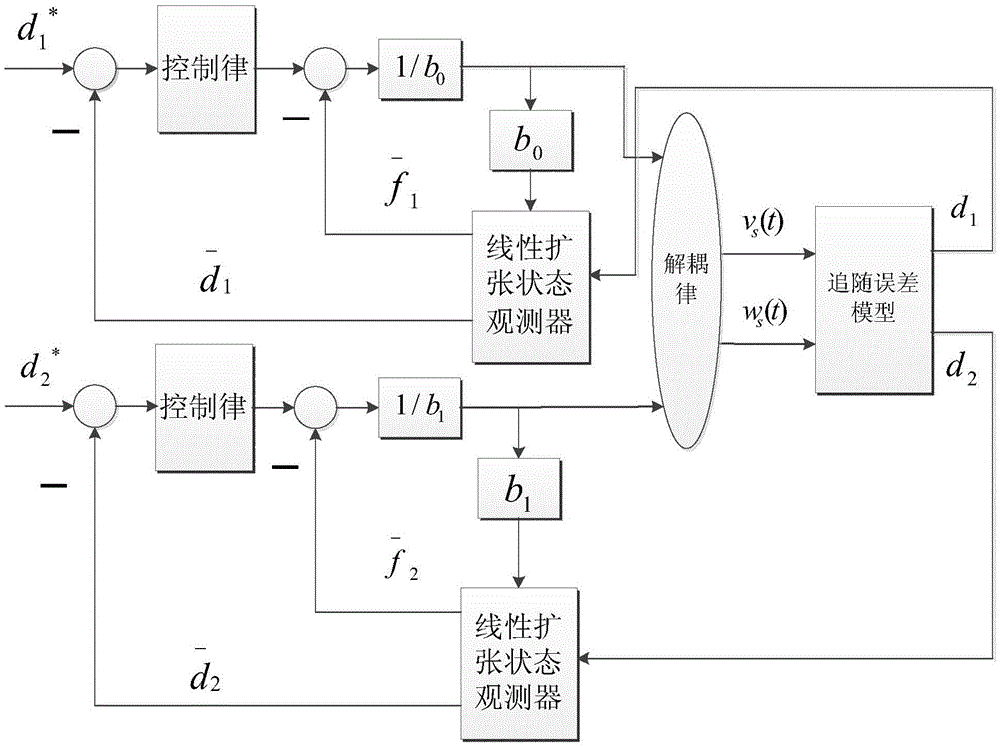
Network mobile robot locus tracking control method based on linearity auto-disturbance rejection
The invention discloses a network mobile robot locus tracking control method based on linearity auto-disturbance rejection, comprising steps of establishing the moving robot locus tracking control system model containing communication delay, describing the uncertainty dynamic condition caused by the time delay as the uncertainty of the system model, designing an extended state observer for estimating the uncertainty of the locus tracking control system which is caused by the network time delay, designing a moving robot locus tracking linearity auto-disturbance rejection controller with the extended state observer to perform dynamic linearity compensation on the uncertainty dynamic condition caused by the time delay. As a result, the invention eliminates affects on the system performance which are caused by the network time delay and realizes the real-time compensation of the network time delay and the high accuracy locus tracking.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
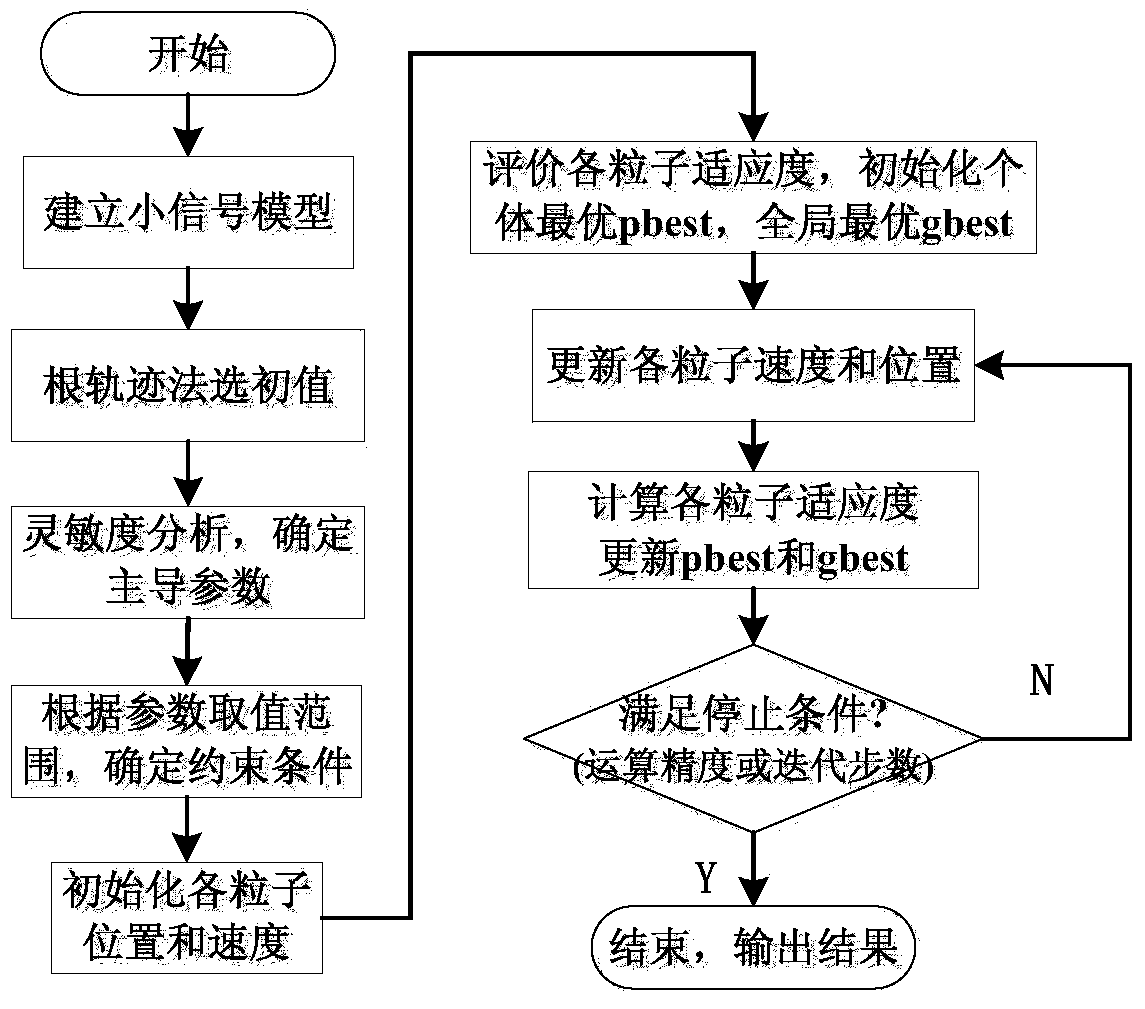
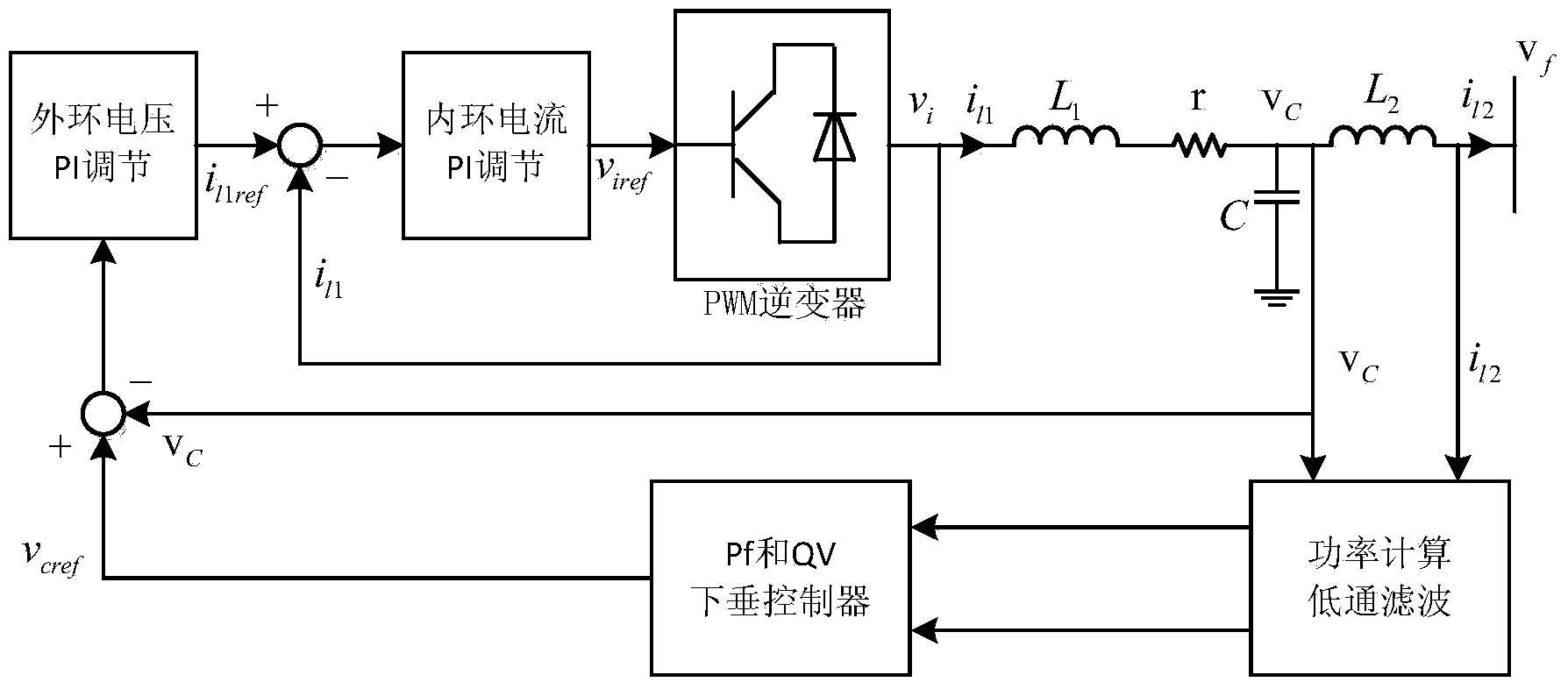
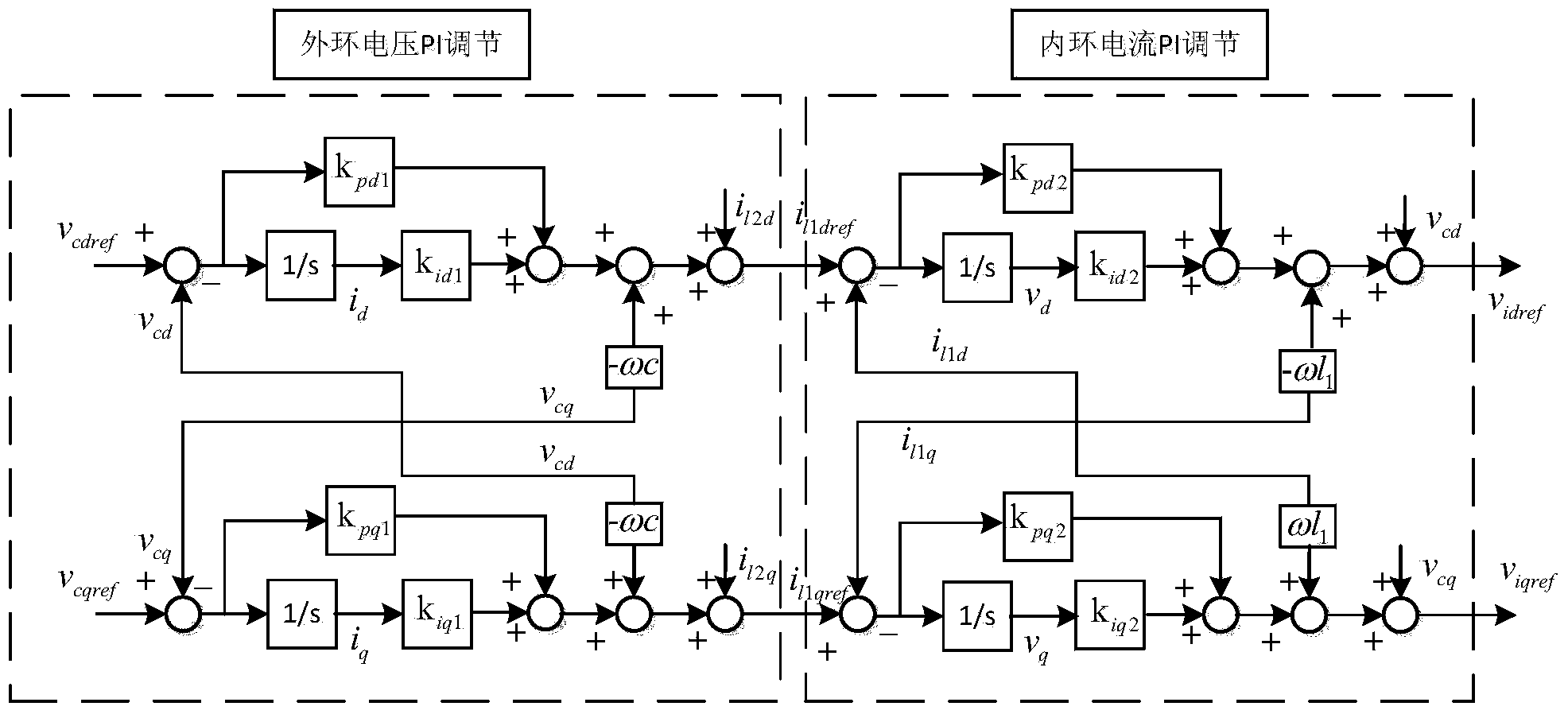
Micro-grid small signal stability analyzing and parameter coordinated setting method
The invention discloses a micro-grid small signal stability analyzing and parameter coordinated setting method, and belongs to the technical field of power system micro-grid operation and control. The micro-grid small signal stability analyzing and parameter coordinated setting method comprises the steps of establishing micro-grid mathematical models which comprise a network and load small signal model and an inverter small signal model and are in need of parameterized design, determining each parameter of the micro-grid according to the root-locus method and using the parameters as initial values of the particle swarm algorithm, conducting sensitivity analyzing through a characteristic value, determining a leading parameter, determining the value range of all the parameters or the mathematical relationships among all the parameters, solving the constraint conditions in the process by the utilization of the particle swarm algorithm, determining the initial values, the parameters in need of optimization and the constraint conditions, and conducting parameter optimization and coordinated setting by the utilization of the particle swarm algorithm. By means of the micro-grid small signal stability analyzing and parameter coordinated setting method, determining of each parameter can be realized quickly and accurately in a coordinated mode, the complexity of setting the parameters one by one is avoided, and the system is made to be more stable on the basis of small signal stability; target functions and boundary conditions are flexibly adjusted, the working time is greatly shortened and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +2
Parameter tuning method of damping controller of wind farm side based on wide area measurement system signal
InactiveCN102545247AIncreased power transfer capabilityImprove voltage controlPower oscillations reduction/preventionWide areaEngineering
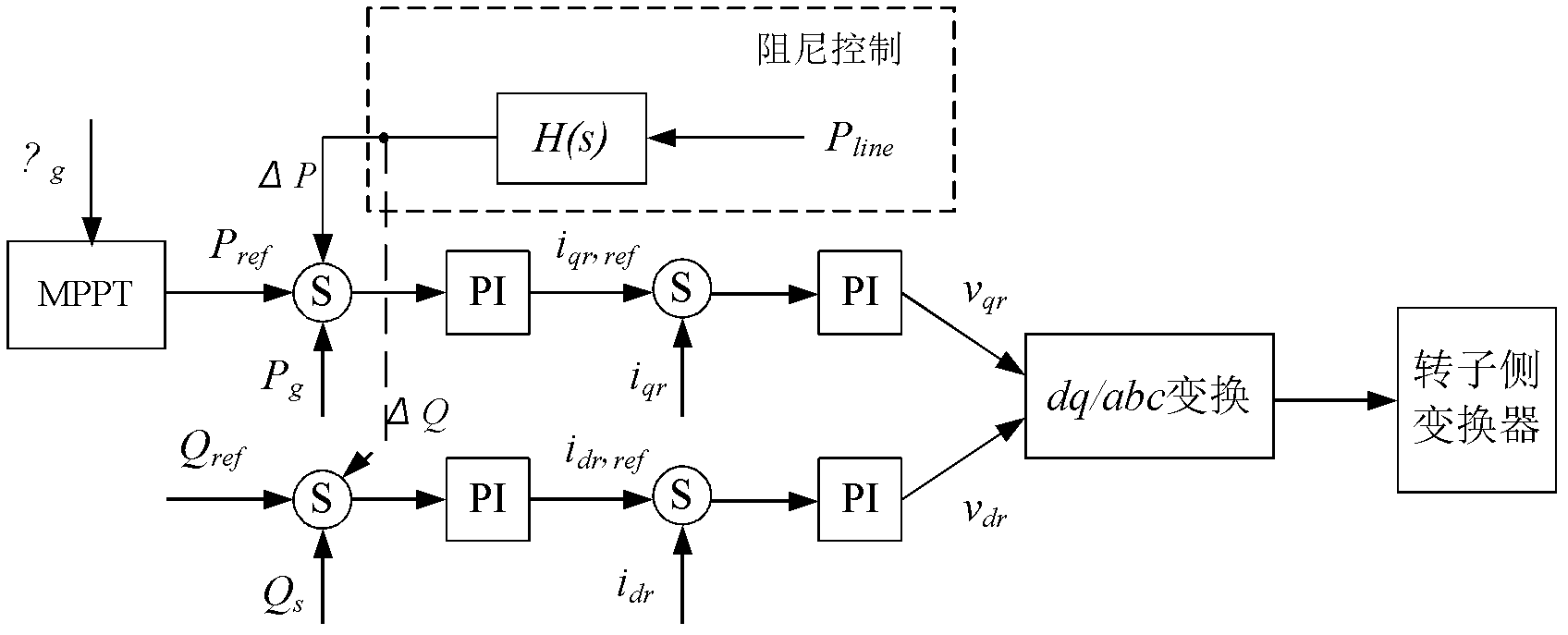
The invention discloses a parameter tuning method of a damping controller of a wind farm side based on a wide area measurement system signal, and can effectively inhibit the interval low-frequency oscillation in a system, improve a transmission capacity of a call wire, replace a traditional synchronous generator PSS (Power System Stabilizator) and improve the voltage control. The parameter tuning method comprises the following steps of: 1) adding an excitation signal at the input end of the system and carrying out signal collection at the output end for system identification; 2) utilizing a Prony analysis method to carry out identification on a power transmission system containing a double-fed wind electric field and determining an open-loop transfer function which is not introduced with an additional damping control; 3) on basis of the step 2), utilizing a retention index to select a feedback signal utilized by the additional damping control and a mounting position of the additional damping control; and 4) on basis of the steps 2) and 3), utilizing the open-loop transfer function of the system to tune phase compensation link parameters in an additional damping control link; and drawing a root locus picture of a closed-loop transfer function and determining a gain value K of an additional damping controller.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +3
Multichannel direct current added damping control device capable of simultaneously restraining sub-synchronization and low frequency oscillation, and parameter setting method of multichannel direct current added damping control device
InactiveCN103795070ASuppress low frequency oscillationPower oscillations reduction/preventionMatrix pencilHigh pressure
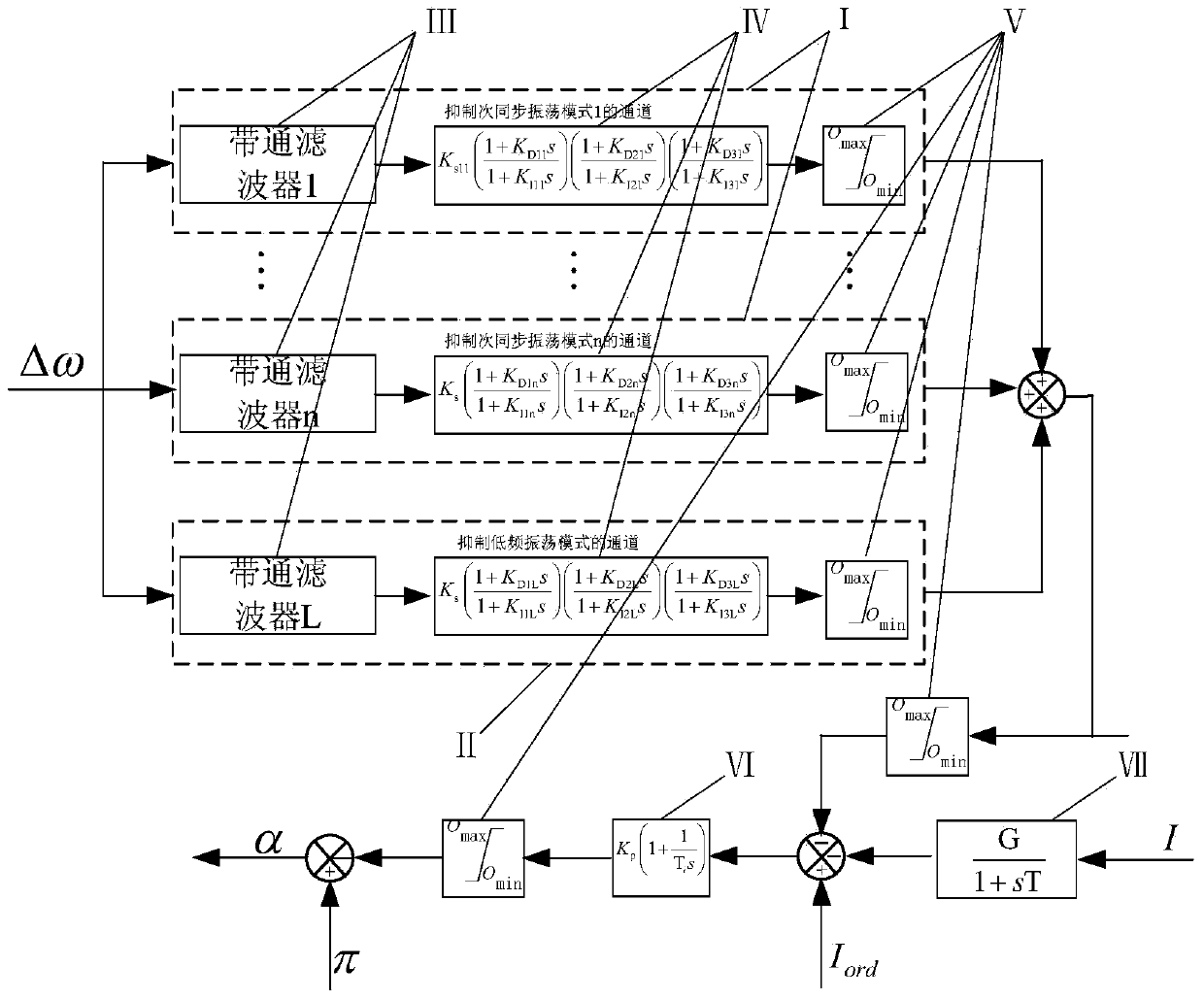
The invention discloses a multichannel direct current added damping control device capable of simultaneously restraining sub-synchronization and low frequency oscillation, and a parameter setting method of the multichannel direct current added damping control device. The device is characterized in that the device identifies the subsynchronous oscillation, the low frequency oscilation frequency and the damping of a direct current under island running and a system reduced-order model on the basis of a matrix pencil algorithm which has high operation efficiency and anti-interference capacity, a multichannel direct current added damping controller is designed through a root locus method so as to reduce mutual effects between oscillation modes, and sub-synchronization and low frequency oscillation can be simultaneously restrained. Electric generator rotating speed signals are divided into multiple frequency bands according to results of analysis conducted on characteristics of system oscillation through the matrix pencil algorithm, a passageway corresponding to each frequency band can independently adjust the gain, the phase position, the output amplitude limit and the filter parameters, and therefore appropriate damping can be provided for sub-synchronization and low frequency oscillation in different frequency bands. The device is efficient and easy to obtain, and the function of simultaneously restraining sub-synchronization and low frequency oscillation through the direct current added damping controller is achieved for the first time in the high voltage direct current transmission field.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Subsynchronous source-network combination damping inhibition method for offshore wind plant
ActiveCN108270240AReduce interactionLess investmentSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectricityNew energy
The invention relates to a subsynchronous source-network combination damping inhibition method for an offshore wind plant, and the method comprises the steps: S1, building a linearized state space model of an offshore wind plant based on a double-feed wind turbine generator through a VSC-HVDC grid-connected system; S2, recognizing the subsynchronous oscillation modal of a system; S3, calculating aparticipation factor through modal analysis, and screening a state variable which is strongly correlated with the subsynchronous oscillation modal at each order; S4, analyzing the impact on the subsynchronous oscillation modal damping from the strongly correlated state variable through a root-locus method; S5, designing the parameters of DFIG_SEDC and VSC_SSDC according to a locus analysis result, and reducing the mutual impact between the subsynchronous oscillation modals at all orders, and inhibiting the plurality of subsynchronous oscillation modals. Compared with the prior art, the methodsolves a problem of cost in adding a FACTS device, and a designed source-network combination damping controller can inhibit the plurality of subsynchronous oscillation modals, improves the subsynchronous stability of a system, and guarantees the safe and stable operation of the transmission of new energy power.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Power electronic transformer enabling high quality of electric energy output, and control method thereof
ActiveCN105006825AAddresses issues with limited AC volume gainSmall steady state errorPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionAc network voltage adjustmentPower qualityTransformer
The invention provides a power electronic transformer enabling the high quality of electric energy output, and a control method thereof. A topologic structure of the power electronic transformer includes an input stage, an intermediate isolation stage and an output stage. The output stage is an inverter of a three-phase four-leg structure, wherein the previous three phase legs adopts a dual-closed loop control strategy based on an output voltage outer loop of a PIR controller and an inductance current inner loop of a PI controller, and the fourth leg adopts a neutral current independent control method based on proportion resonance. The frequency characteristic curve and root locus of the frequency domain theory and other relevant methods are utilized to carrying out frequency division setting for dual-closed loop PIR-PI controller parameters. Therefore, the stability is effectively improved, and stable errors and robustness requirements of a system are also taken into consideration.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD +1
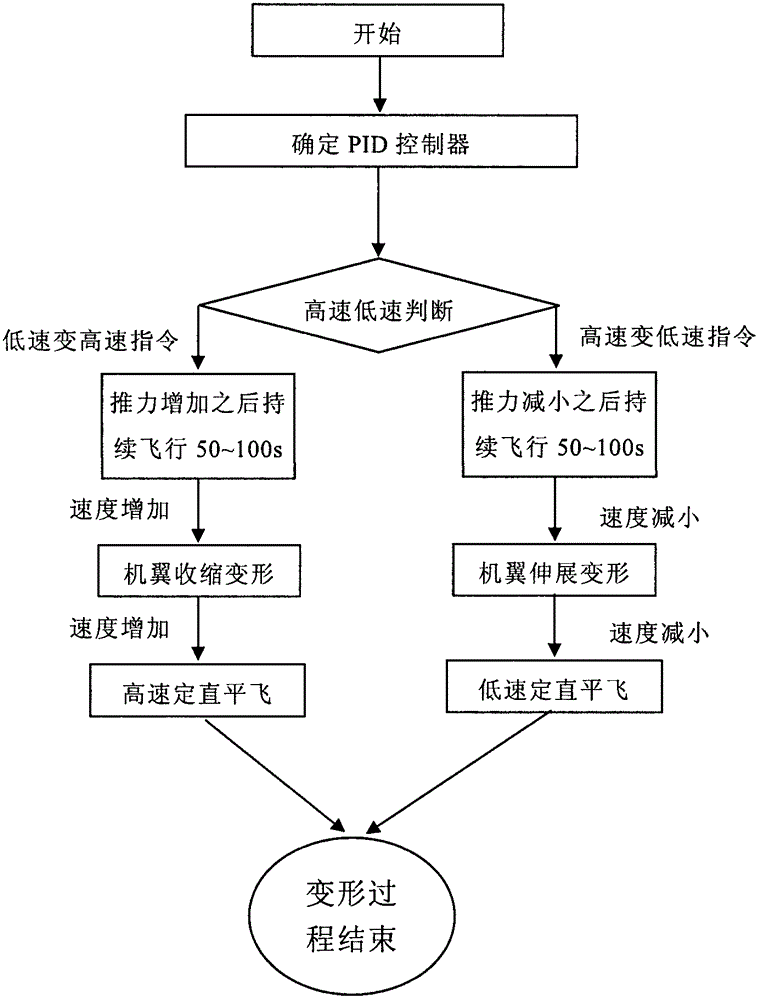
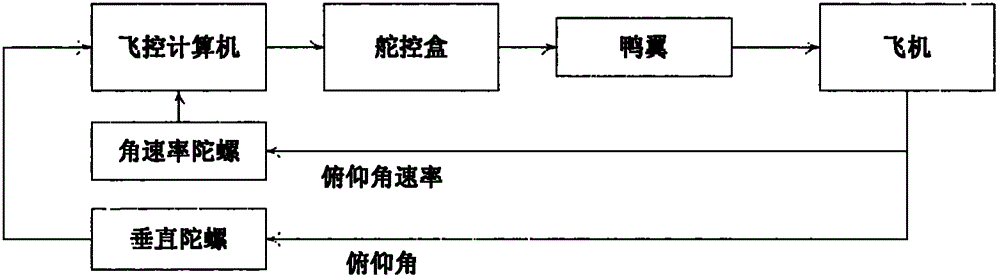
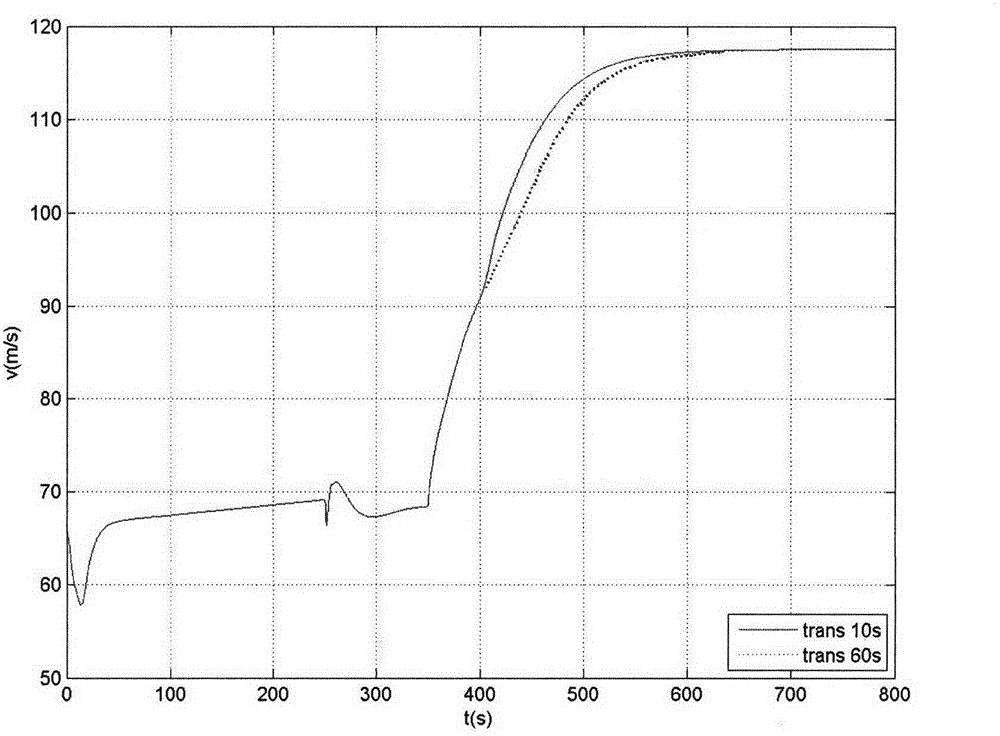
Flight control method of deformable unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN102722176AStable flightPosition/course control in three dimensionsLow speedFlight control modes
The invention provides a flight control method of a deformable unmanned aerial vehicle. The deformable unmanned aerial vehicle has a canard type telescopic forward-swept wing and single vertical fin aerodynamic arrangement; according to the adjustment and analysis of a root-locus method, a high-low speed deformable unmanned aerial vehicle can perform the adjustment on parameters of a controller through a design method of a low-speed controller, and therefore the design requirement on the controllers under two flight speeds can be met. Matching the deformation time and the control time of an engine is part of a control strategy of the deformable unmanned aerial vehicle; and as shown in the analysis of the flight mechanics design, the thrust of the engine is changed prior to implementing the process and the strategy under the deformation time.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
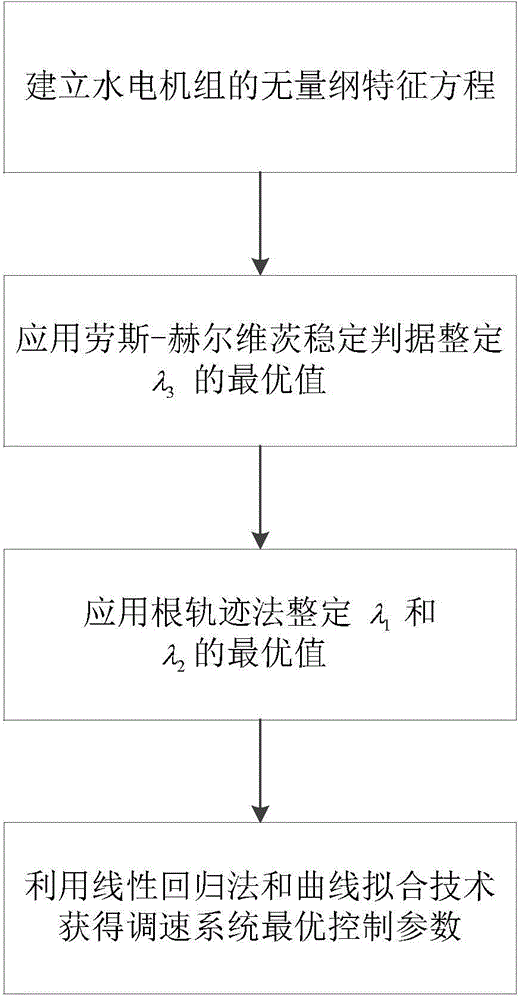
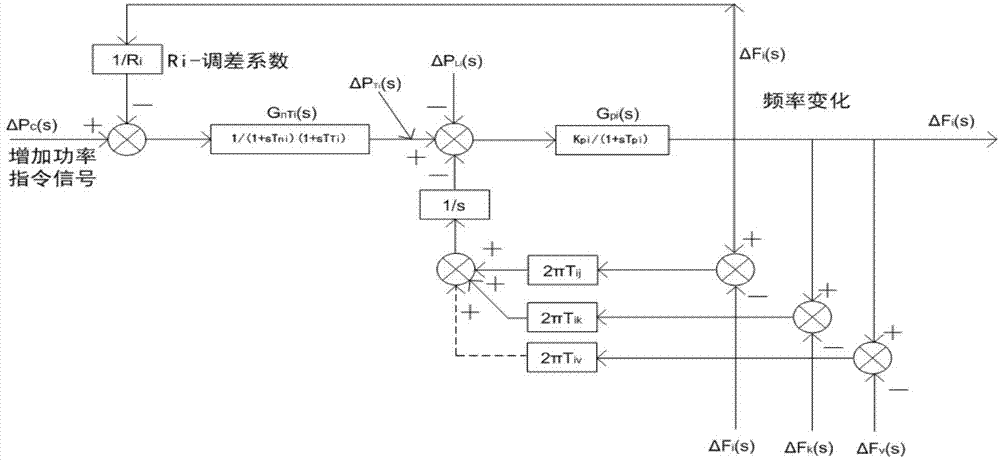
Hydroelectric generating set speed regulating system control parameter setting method based on characteristic parameters
InactiveCN104808705ASpeed/accelaration control using electric meansAdaptive controlWater turbineCurve fitting
The invention discloses a hydroelectric generating set speed regulating system control parameter setting method based on characteristic parameters and belongs to the technical field of optimization of water turbine speed regulators. The hydroelectric generating set speed regulating system control parameter setting method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a hydroelectric generating set non-dimensional characteristic equation through non-dimensional processing; (2) applying Routh-Hurwitz stable criterion and a root-locus method to solve speed regulating system optimal control parameters; and (3) utilizing a linear regression method and a curve fitting technology to obtain an optimal value of speed regulating system control parameters. The hydroelectric generating set speed regulating system control parameter setting method has the advantages of simple setting process, small calculation amount, easiness for realization and the like; the speed regulating system optimal control parameters are directly set according to five characteristic parameters (including a water flow inertia time constant, a set inertia time constant, a servomotor responding time constant, a perpetual state rotary difference coefficient and a power generator comprehensive self-adjusting coefficient).
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST OF GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD +1
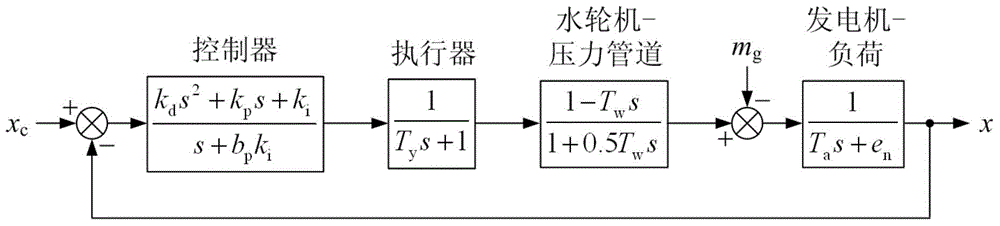
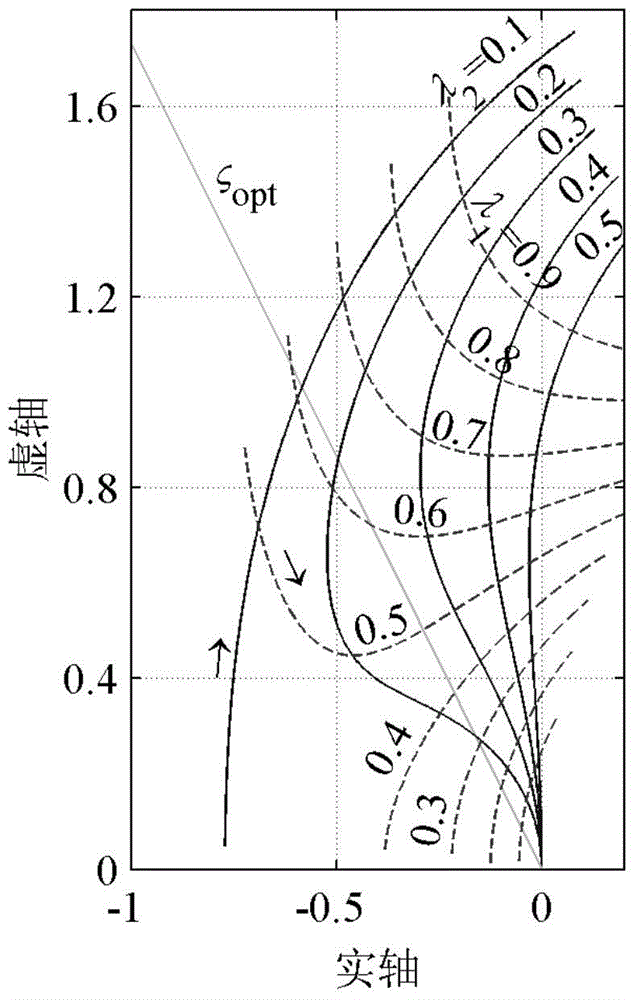
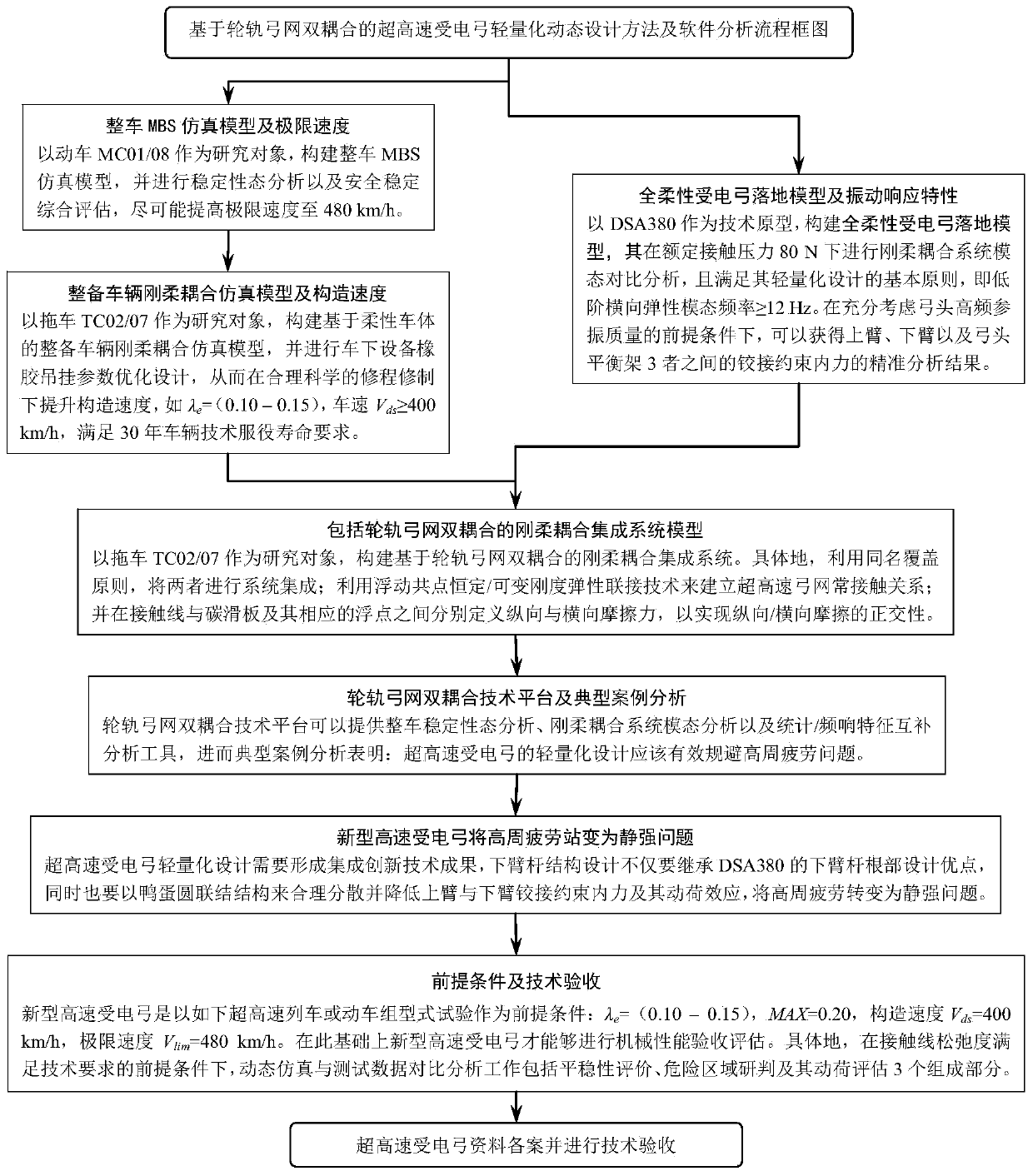
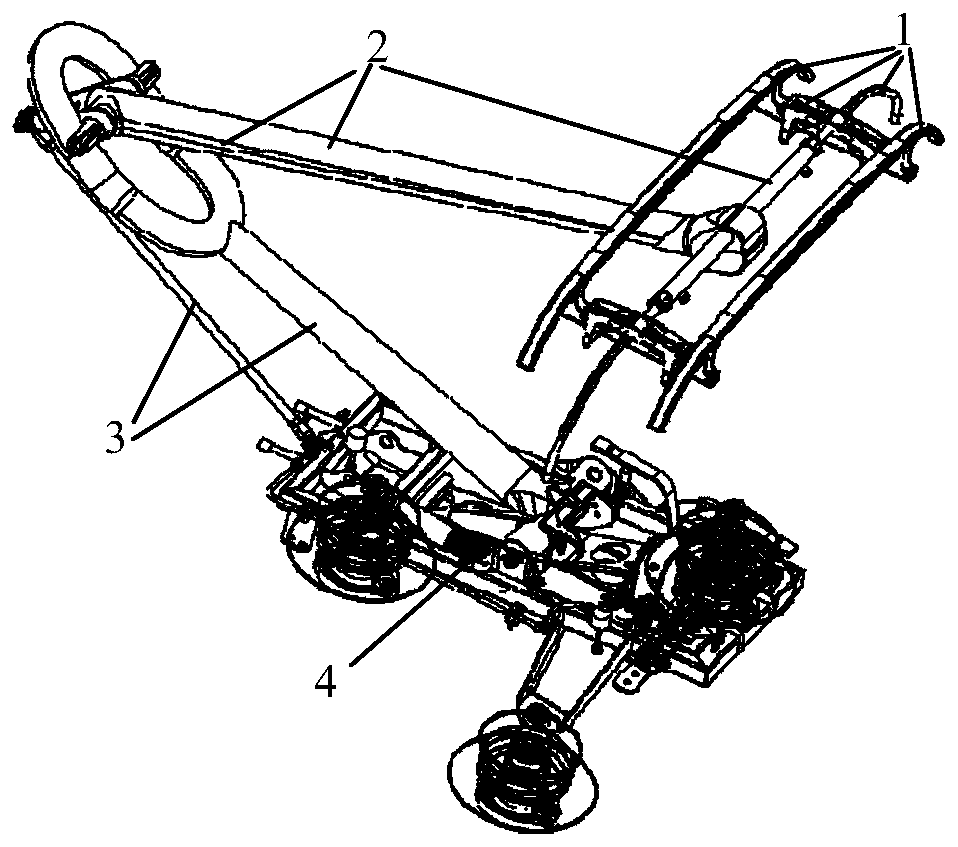
Novel high speed pantograph and lightweight dynamic design method thereof
InactiveCN110126625AReduce contact dynamicsAvoid implicating sports relationshipsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationBogieRail profile
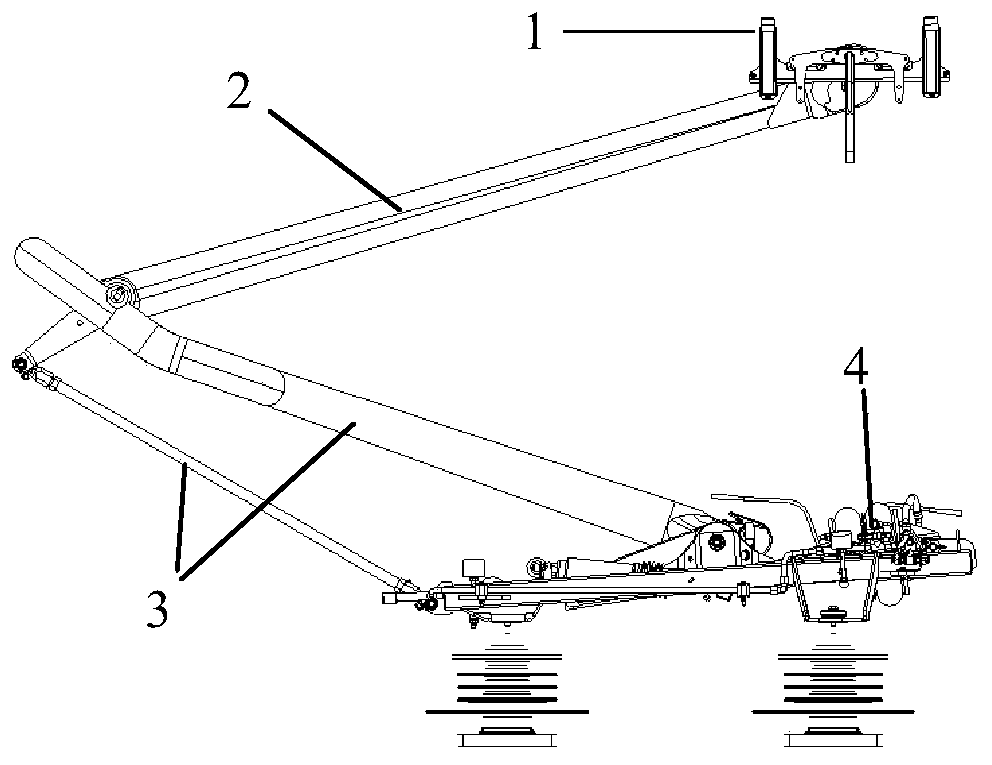
The invention discloses a novel high speed pantograph and lightweight dynamic design method thereof. Optimization of bogie parameters is led according to a root locus diagram, the dynamic action of the contact rail of an abrasion wheel is lowered, under the condition of uniform / normative wheel rail profile matching, the limiting speed is improved up to 480 km / h; through optimal design of rubber suspension parameters of equipment under a vehicle, the transverse vibration mass of hostling flexible vehicle body is decreased, and under reasonable and scientific repair program and repair system, the construction speed is increased up to 400 km / h. In order to better count input stimulus formed by high speed pantograph net contact, a fully flexible pantograph landing model and a hostling vehiclerigid flexible coupling simulation model are systematically integrated to construct a wheel rail pantograph net double coupling simulation technology platform. According to complex constraint and accurate analyze of internal force, analysis of a typical case indicates that a novel lightweight design form is needed by an ultra-high speed pantograph, namely the hinging constraint force between an upper arm and a lower arm and the dynamic load effect are reasonably dispersed and reduced through a duck-egg-shaped joint structure, and thus high cycle fatigue is transformed to a static strength problem.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Frequency domain analysis method for ship autopilot system
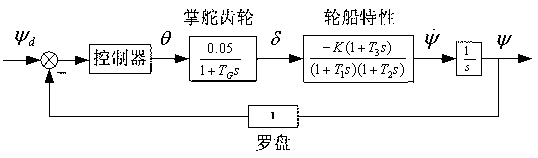
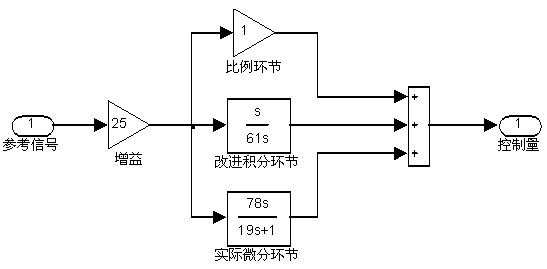
The invention relates to a frequency domain analysis method for a ship autopilot system, which includes the following steps: building a math model of a controlled object of the ship autopilot system, and establishing an autopilot control system; confirming a closed loop predominant pole of the control system as per expected response overshoot and adjusting time of the closed loop system; confirming the zero pole of the controller based on a root locus diagram and a Bode diagram of the autopilot control system; designing a ship autopilot second-order ahead controller based on the frequency domain method; drawing a simulation block diagram of the helm autopilot control system; and verifying the effectiveness and feasibility through carrying out simulation comparison and analysis of the ship autopilot control system and the traditional PID control system. According to the method, good stability and fewer frequency in auto-steering are realized, helm blades are rotated in a reasonable range, abrasion and leakage of a steering engine system as well as thrust consumption during helm steering can be reduced, so that energy consumption is saved, the heading of the ship can be automatically kept or changed with high accuracy, safe shipping at ordinary times and collision prevention of ships under a severe environment can be guaranteed, and the method has reference value in the practical engineering application.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Control method for realizing overload autopilot by using accelerometer
ActiveCN102425980AImprove dynamic characteristicsReduce the numberSelf-propelled projectilesAccelerometerMathematical simulation
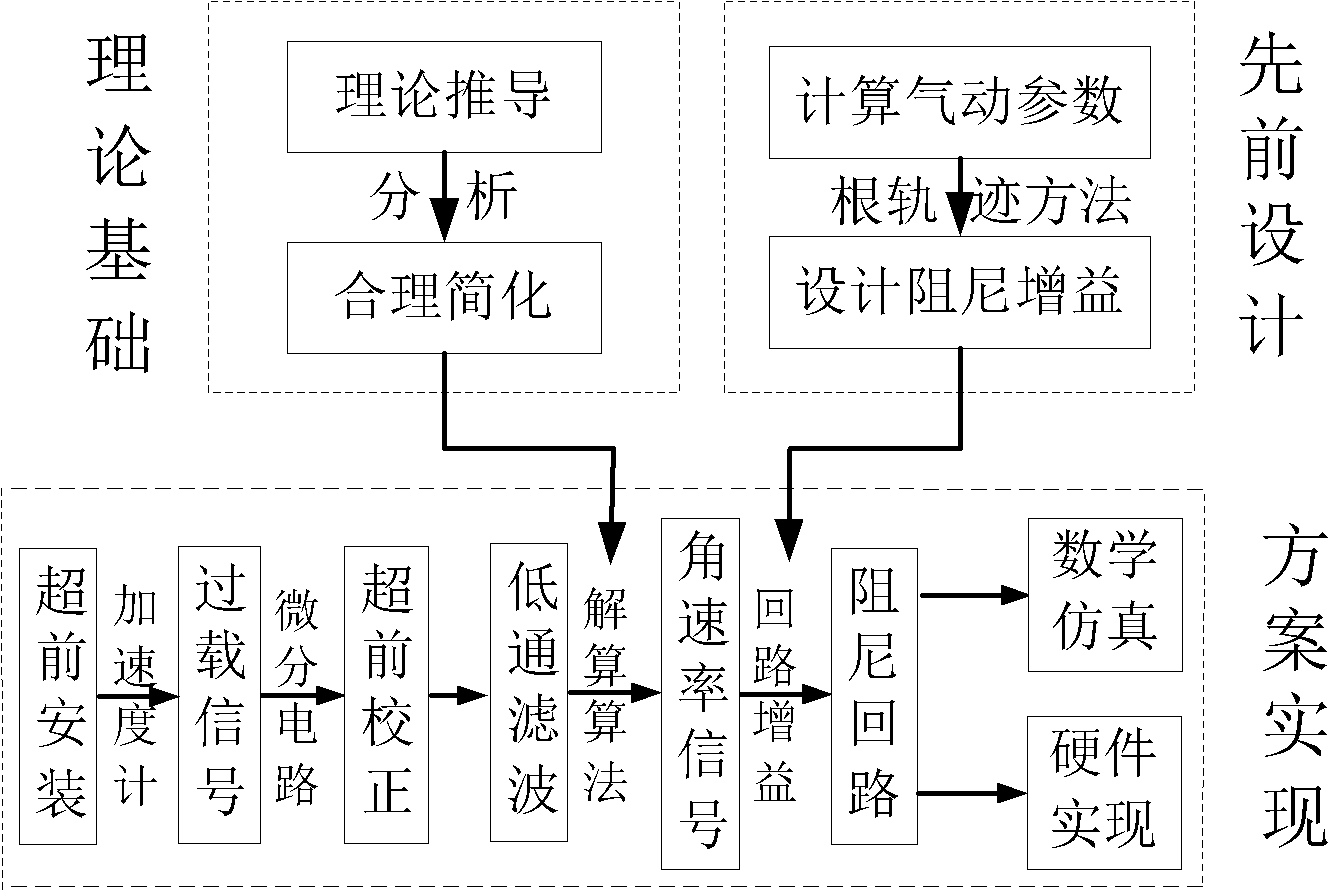
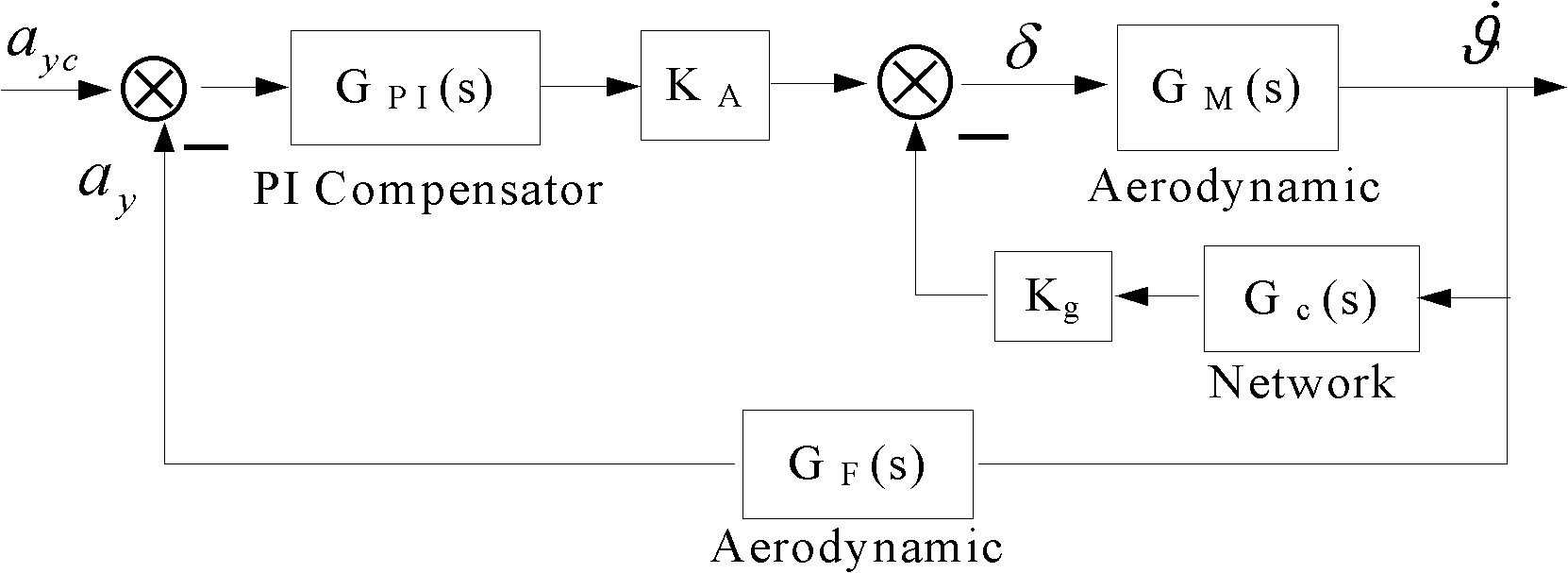
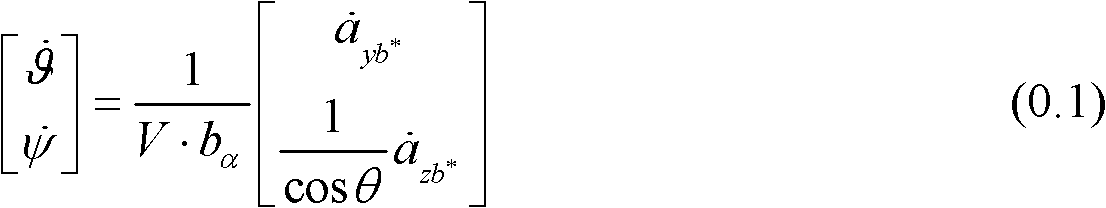
The invention relates to a control method for realizing an overload autopilot by using an accelerometer. The control method comprises the following steps of: firstly, calculating a functional relation between the attitude angular rate and the overload of a missile body under an inertial coordinate system; secondly, obtaining a damping circuit grain Kg and a stable circuit gain KA of the overload autopilot at a characteristic point of a missile track by adopting a root locus method of a classical control theory; and finally, constructing a damping circuit by using an accelerometer signal under the missile body coordinate system according to the result obtained in the first step and realizing the overload autopilot by using the accelerometer. According to the control method disclosed by the invention, aiming at the dynamic characteristic of a guide missile, by using the function relation between the overload and the angular rate and using a method of constructing the damping circuit by repeatedly using the accelerometer through the overload autopilot, the mathematical simulation validation can be carried out and a corresponding engineering realization scheme is provided.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Position control method of single-joint flexible manipulator based on state feedback
ActiveCN107290956ASolve the clipping problemStable controlControllers with particular characteristicsPosition controlFeedback control
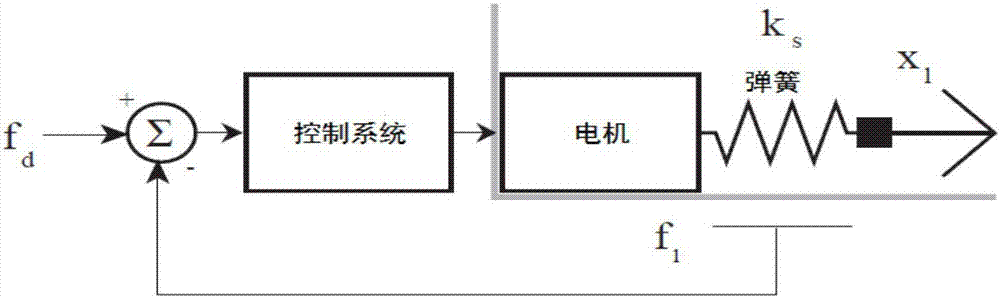
The invention discloses a position control method of a single-joint flexible manipulator based on state feedback. Firstly the time variation effect of SEA load movement on a motor end kinetic model is considered, the load moment acts as disturbance to be fed back to the motor end through a speed reducer and modeling of the motor and the SEA overall system is performed in comparison with the method of separately establishing a motor model and an SEA module; then the state space and the root locus are combined, and a SEA single-joint position controller design method based on state feedback is given so that coordinated optimization of stable, fast, static difference and parameter insensitive performance of the control system can be visually performed; and finally the situation that the full-state feedback method cannot meet the current requirements is considered, and the SEA single-joint position controller design method based on combination of state feedback and PI is put forward to perform PI control on the current, and state feedback control is still performed on other variables so as to achieve a great control effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
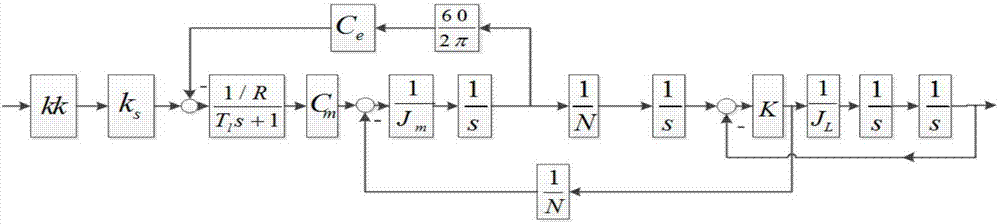
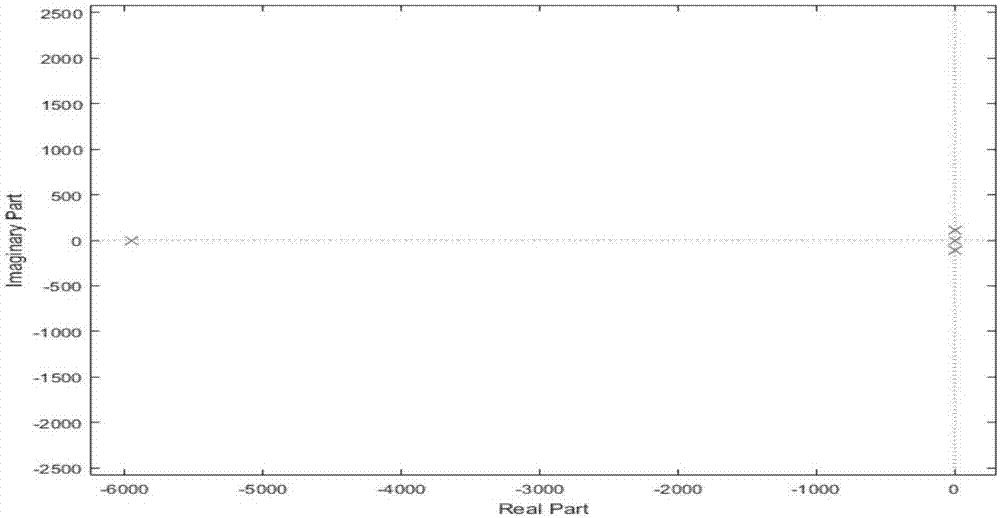
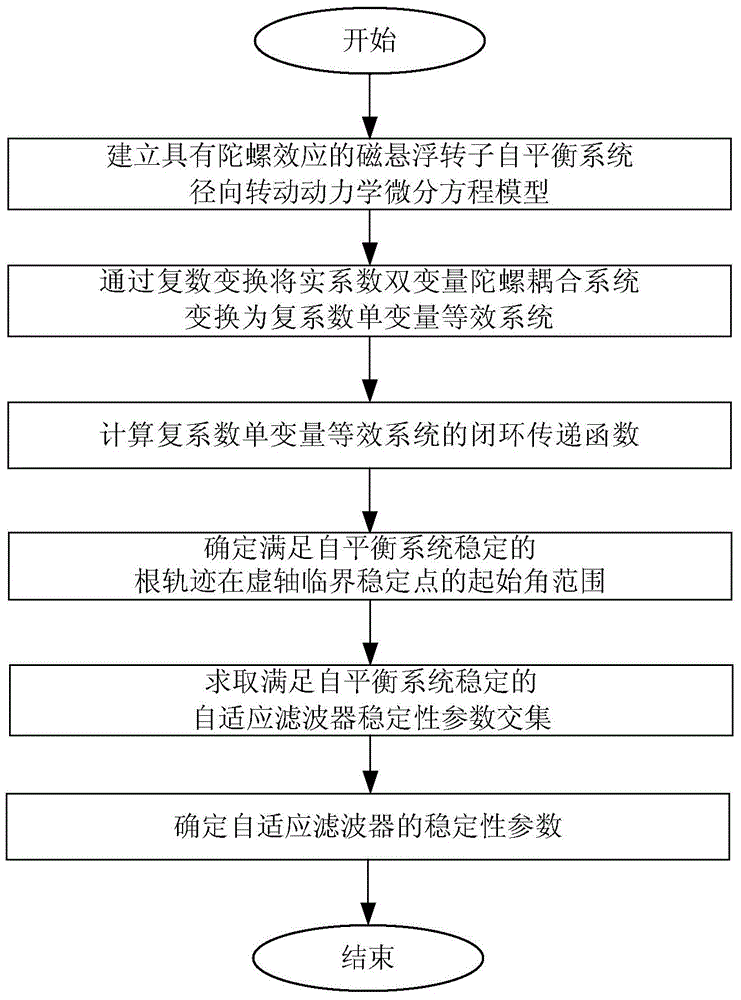
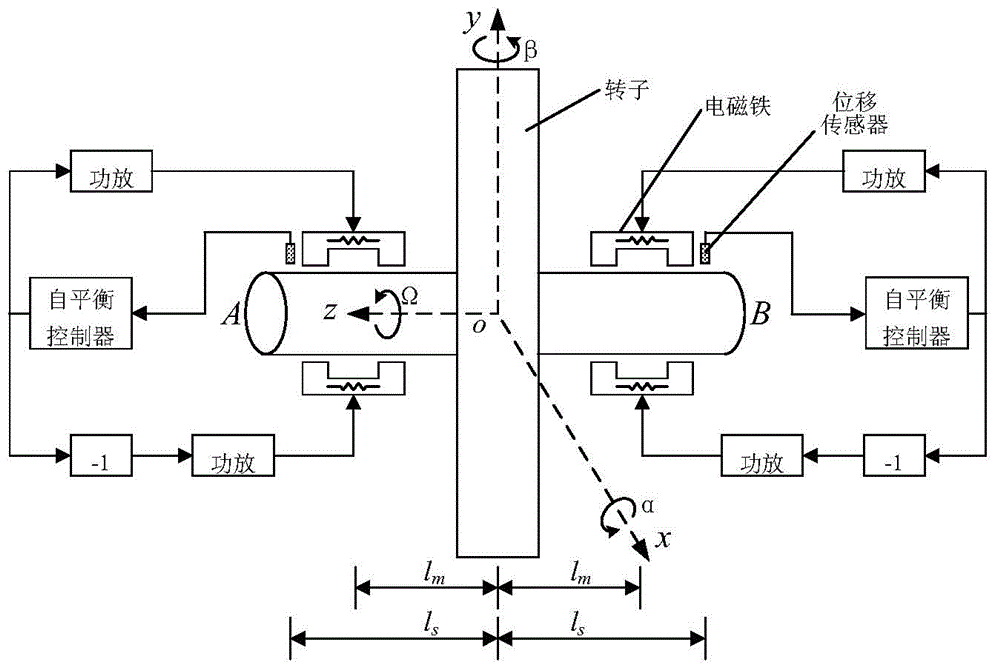
Method for designing stability parameters of self-adapting filter of self-balancing system of magnetic suspension rotor
ActiveCN104950919AGuaranteed stabilityImprove self-balancing accuracyAdaptive networkControl using feedbackStability parameterAdaptive filter
The invention discloses a method for designing stability parameters of a self-adapting filter of a self-balancing system of a magnetic suspension rotor. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a radial rotation dynamics differential equation model of the self-balancing system of the magnetic suspension rotor with a gyroscopic effect; converting a real coefficient bivariate gyroscopic coupling system into a complex coefficient univariate equivalent system through complex transformation; calculating a closed-loop transfer function of the complex coefficient univariate equivalent system; determining a start angle range of a root locus, which meets the stability requirement of the self-balancing system, at a critical stable point of an imaginary axis; resolving a stability parameter intersection of the self-adapting filter; finally, determining the stability parameters of the self-adapting filter. While the rotor speed is estimated and tracked in real time so as to improve the self-balancing precision, the stability of the self-balancing system of the magnetic suspension rotor with the gyroscopic effect within a full speed range is ensured. The method disclosed by the invention is simpler and more convenient than other methods, and is especially suitable for practical magnetic suspension rotor systems.
Owner:北京高孚动力科技有限公司
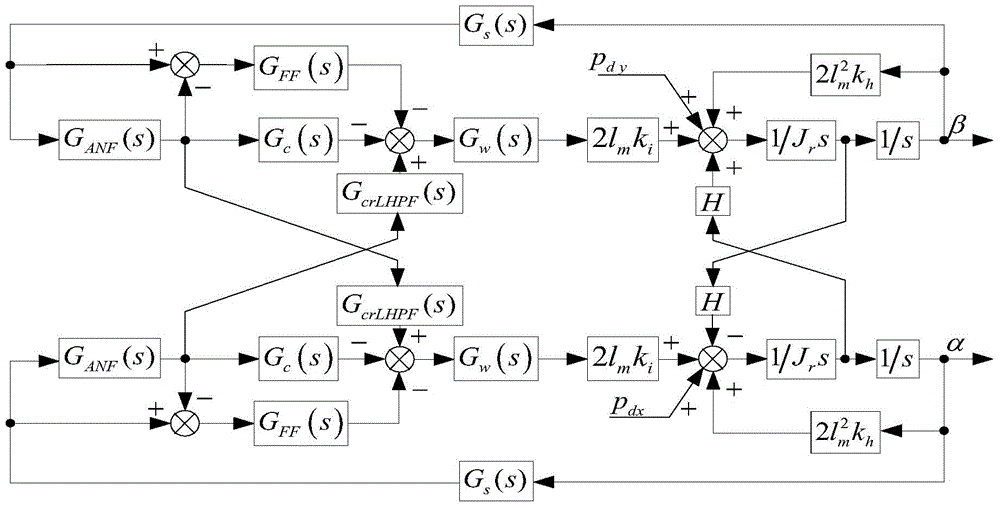
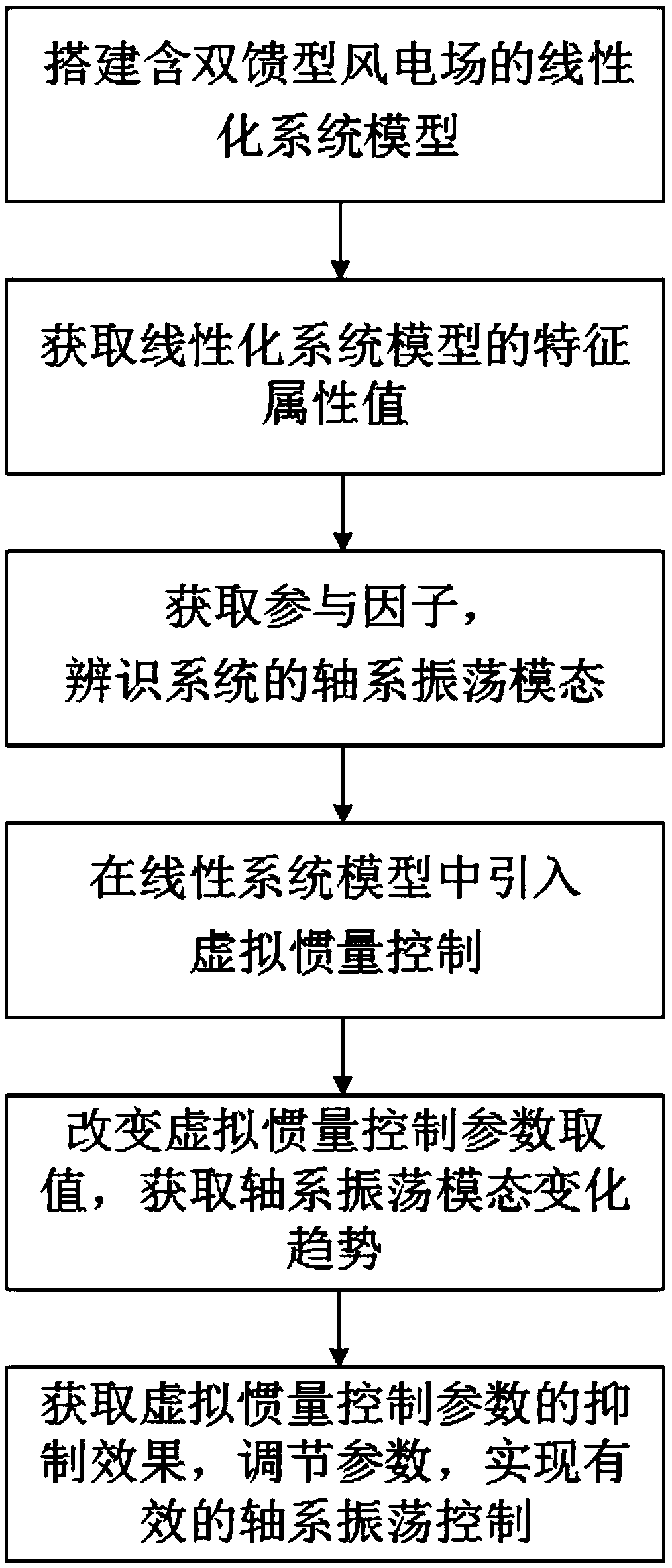
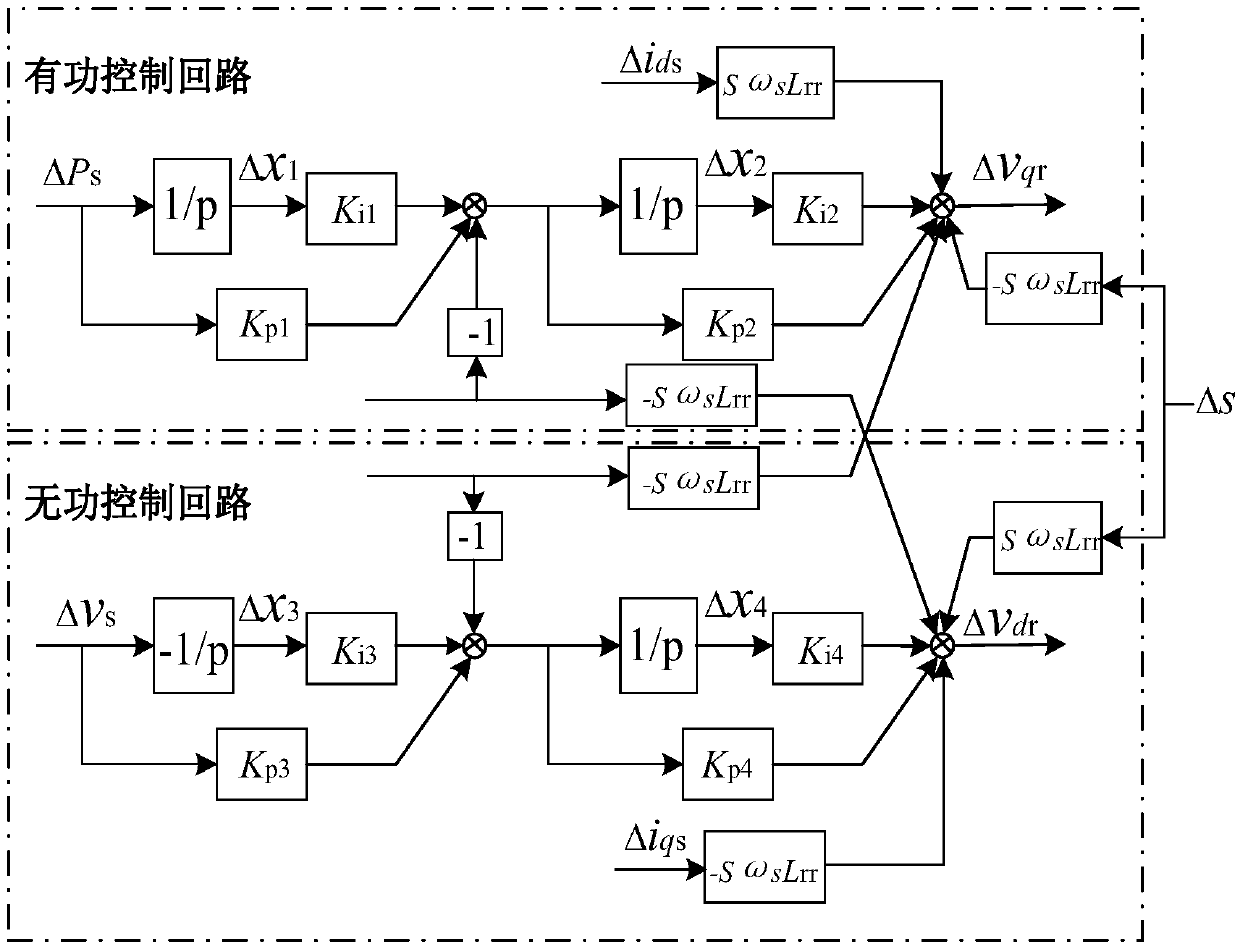
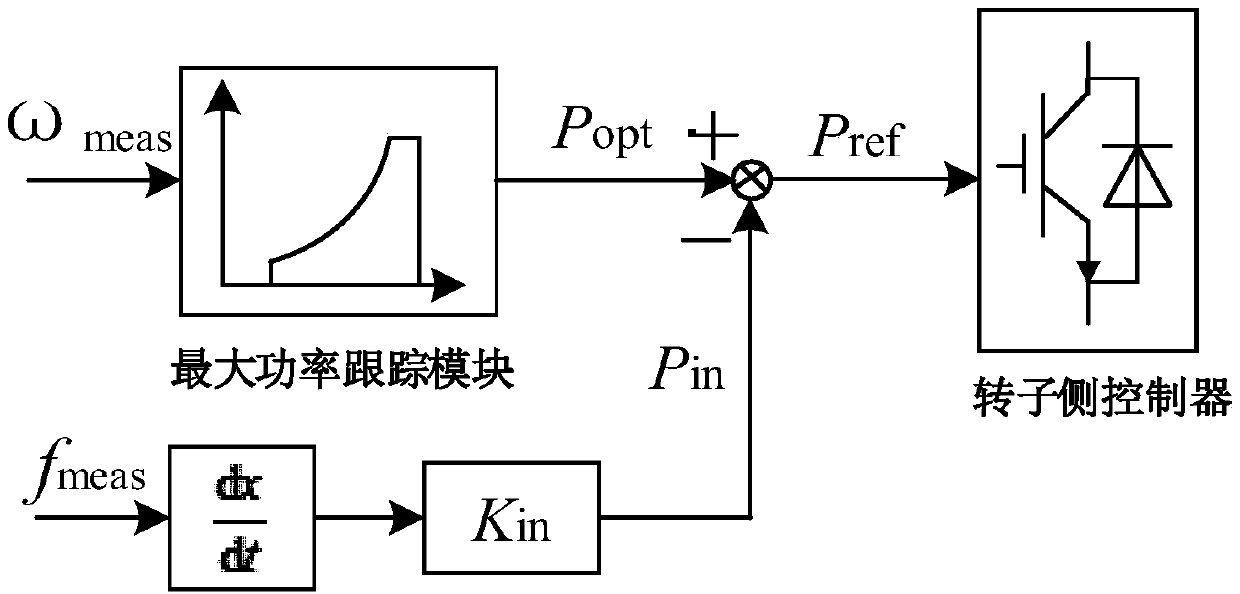
A control method of DFIG shafting oscillation based on virtual inertia control
ActiveCN109038649ALarge inertiaImprove vibrationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping ratioVirtual inertia
The invention relates to a control method of DFIG shafting oscillation based on virtual inertia control, which comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a linearized system model containing a doubly-fed wind farm; S2, obtaining the characteristic attribute value of the linearized system model, obtaining the participation factor by using the characteristic attribute value to the conjugate characteristic root, and identifying the shafting oscillation mode according to the participation factor; 3, introducing virtual inertia control, changing values of the virtual inertia control parameters, and obtaining root locus curves of the shafting oscillation mode and the change trend of the damping ratio under different values; and S4: acquiring the suppression effect of the virtual inertia control parameters on the shafting oscillation of the doubly-fed fan in a certain range according to the changing trend, adjusting the appropriate virtual inertia control parameters, and realizing the effective DFIG shafting oscillation control. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of increasing the inertia of the electric power system, ensuring the safe and stable operationof the fan, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
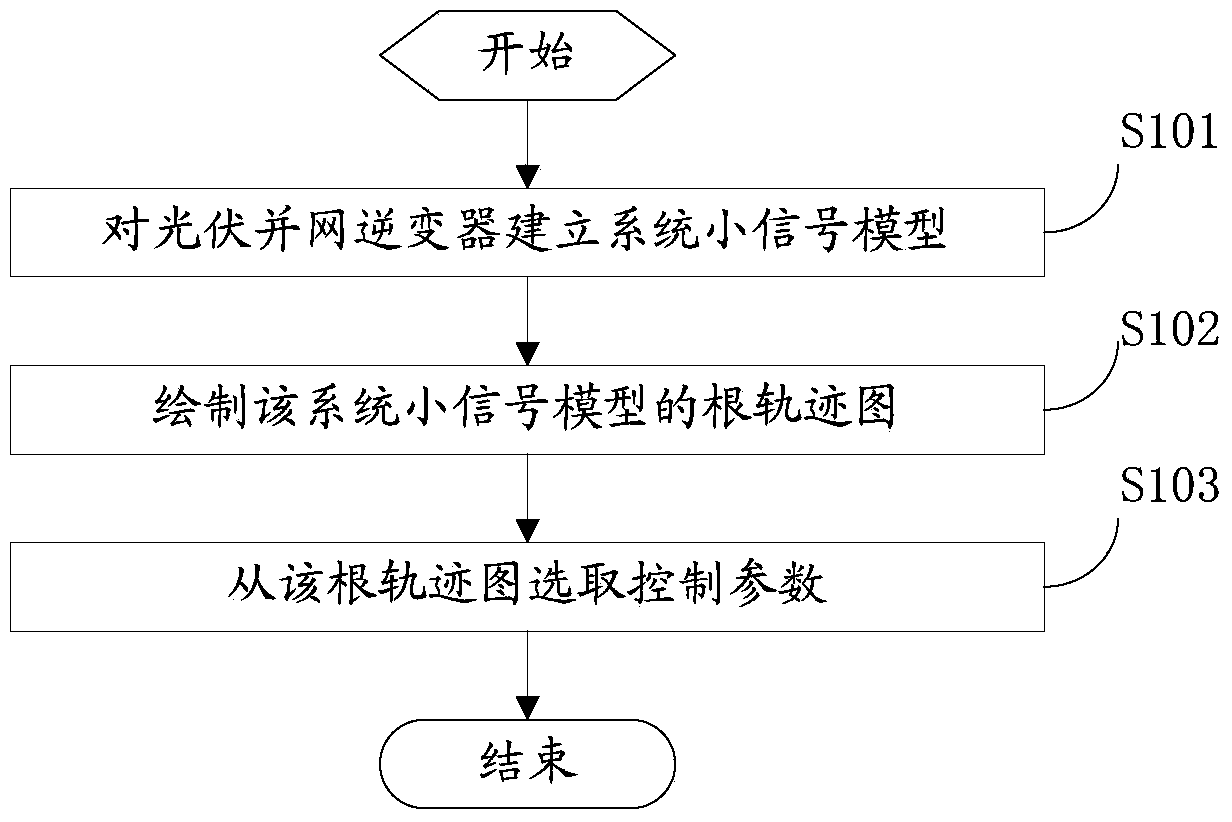
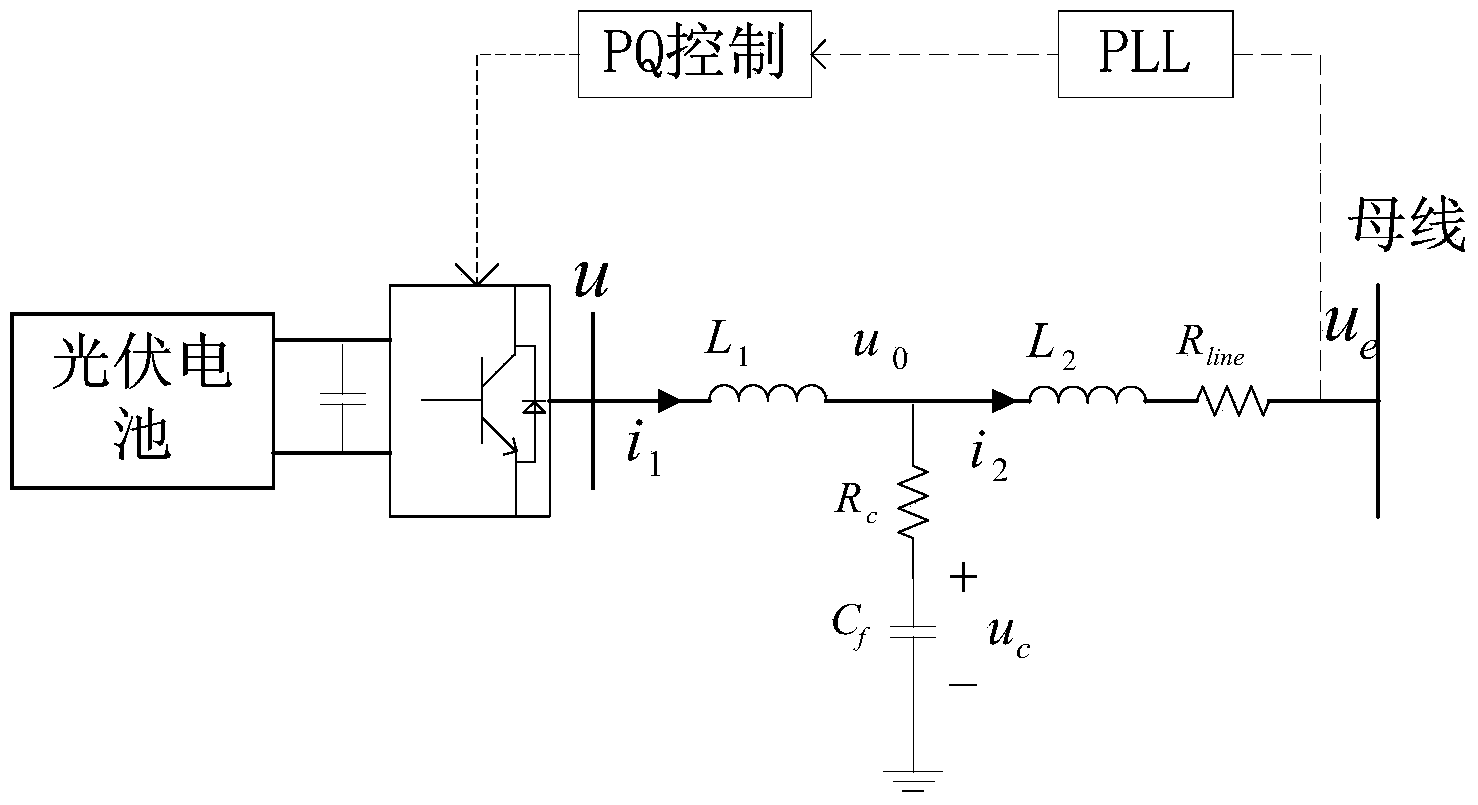
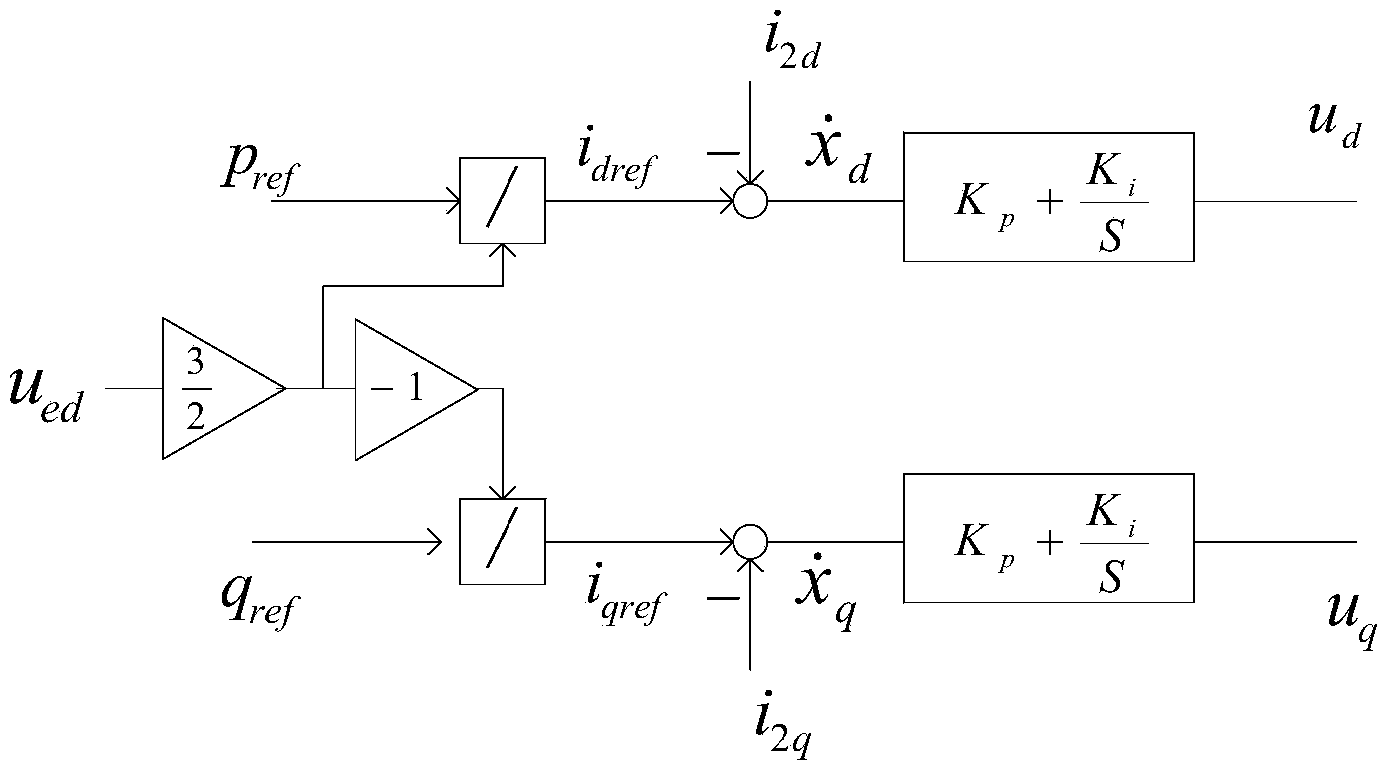
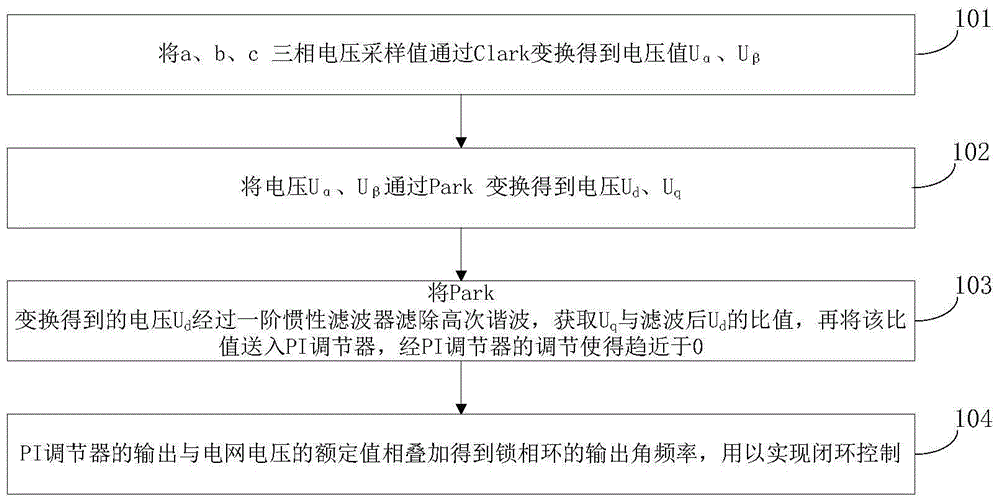
Method and system for determining control parameters of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN104319814ASingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationSmall-signal modelGrid connected inverter
The invention provides a method and system for determining control parameters of a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. According to the method and system, firstly, a system small-signal model is established for the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter; then, a root locus diagram of the system small-signal model is drawn; finally, according to the root locus diagram, a group of parameter values capable of enabling main system characteristic values to be away from an imaginary axis are selected as the control parameters. Due to the fact that according to the method and system, the control parameters are directly selected through a root locus method without repeated tests, the problems that repeated tests are needed in an existing method for determining the control parameters, time and labor are saved, and work efficiency is low can be solved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
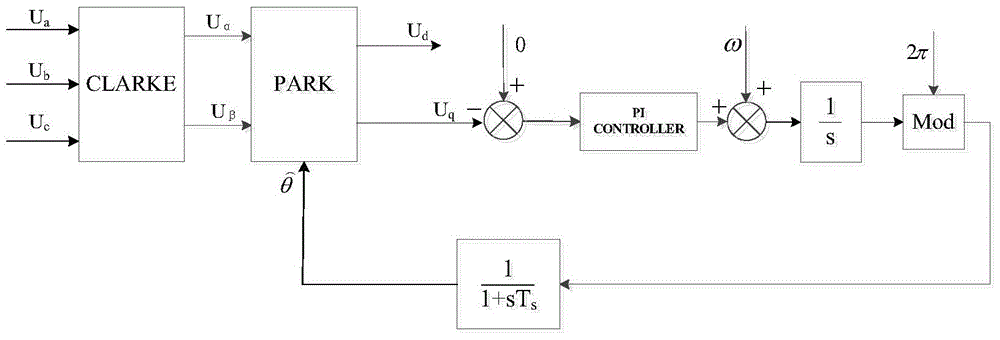
Rapid three-phase voltage phase-locked loop method and dynamic response performance analyzing method thereof
The invention discloses a rapid three-phase voltage phase-locked loop method and a dynamic response performance analyzing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of electric power and electronic control. The analyzing method comprises the following steps: establishing a simplified model of a phase-locked loop, obtaining an open-loop transfer function of a traditional three-phase voltage phase-locked loop and a high-speed three-phase voltage phase-locked loop based on the simplified model, and obtaining a root locus of the changes of a PI regulator parameter Kp based on the open-loop transfer function, a sampling frequency and a fundamental wave angular frequency; drawing two root loci in the same coordinate system, performing equivalent simplification on a high-order system to a typical second order system through the method of closed loop dominant apices, and obtaining convergence time t1 and t2 of the typical second order system in correspondence to the traditional three-phase voltage phase-closed loop and the high-speed three phase voltage phase-locked loop. The analyzing method begins with a simplified mathematics model from a rapid three-phase voltage phase-closed loop structure, conducts separate and detailed discussion on time domain and frequency domain mathematics models, and at the same time demonstrates a theory analysis based on a relevant simulation platform and a hardware experiment platform.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
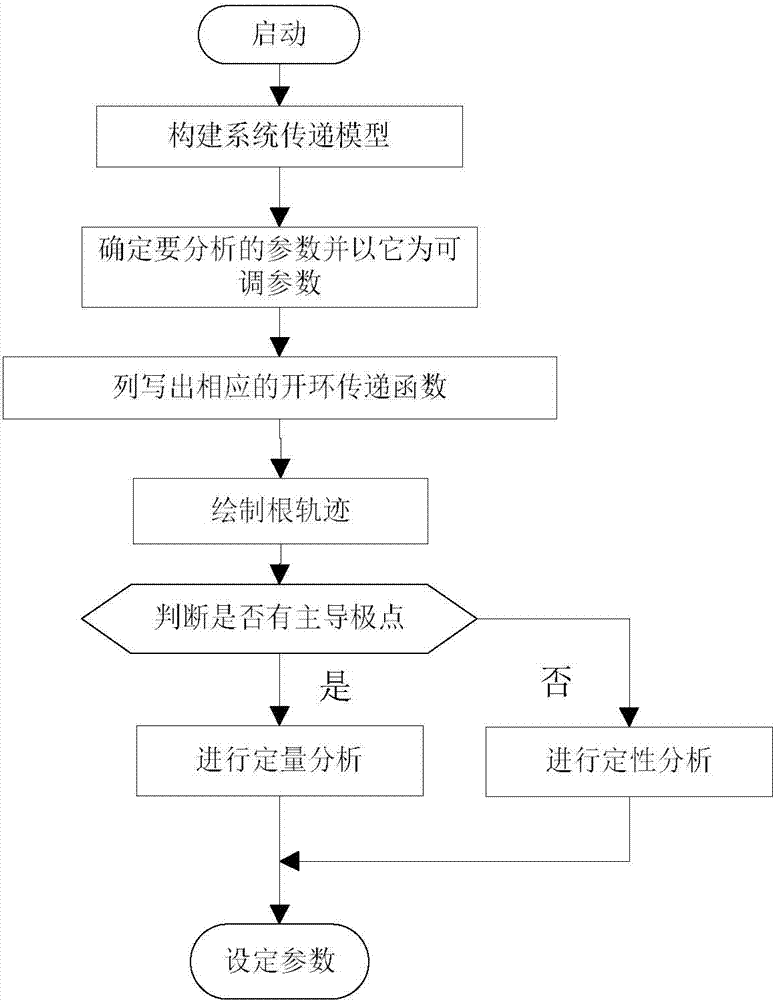
Method and device for setting speed regulator parameters
ActiveCN104503260AAvoid inaccuraciesIntuitive impact resultsSimulator controlTransfer modelEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for setting speed regulator parameters. The method for setting the speed regulator parameters comprises the following steps of A, building a transfer model of a system; B, determining the speed regulator parameters needing to be analyzed, , wherein the speed regulator parameters are adjustable parameters; C, listing a corresponding open-loop transfer function, and drawing a root locus of a corresponding system characteristic equation; D, judging whether a dominant pole exists in the root locus, when the dominant pole exists, performing quantitative analysis on the frequency modulation performance of the system based on the adjustable parameters, and otherwise, performing qualitative analysis on the frequency modulation performance of the system based on the adjustable parameters; E, setting the speed regulator parameters by utilizing an analysis result. By utilizing the method and the device for setting the speed regulator parameters, influence on the stability and the transient performance of the system caused by the speed regulator parameters can be taken into consideration, so that the stability of the system is improved, and the performance of the system is improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
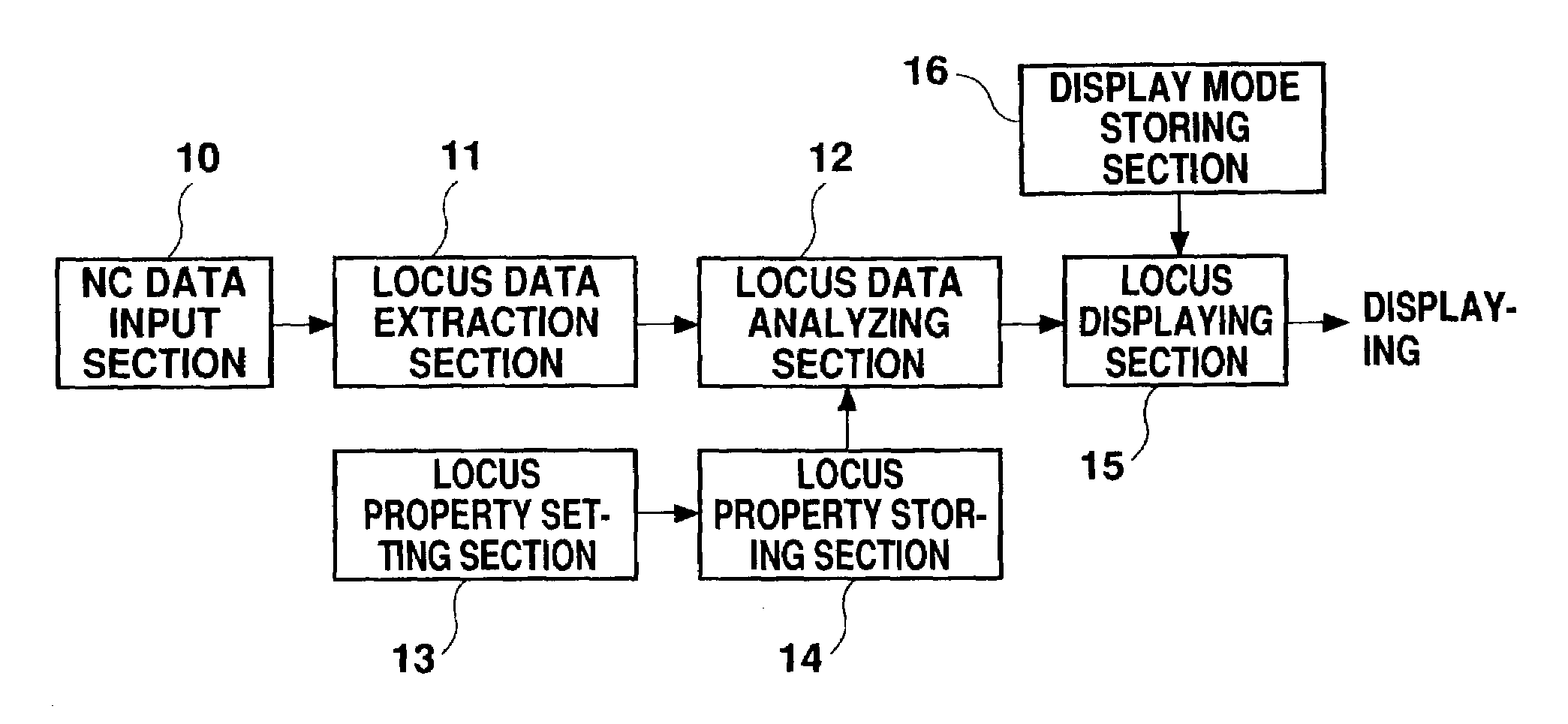
Method for displaying tool locus in NC data and method for analyzing NC data
InactiveUS7062352B2Easy to detectEasy defect detectionComputer controlSimulator controlRoot locusComputer science
With respect to two or more NC data points among a group of dots together representing a tool locus, a curvature radius of the tool locus is determined. Then, the NC data point and its succession with other points is displayed in a display color determined according to the magnitude of the curvature radius. Alternatively, a movement direction of each minute segment relative to a specific axis selected from the three (XYZ) axes is determined as either positive, negative, or zero, and the minute segment or an end point thereof is display with the display property determined according to the movement direction. Still alternatively, after a specific axis is selected from the three (XYZ) axes, a region relative to the selected region is divided along the selected axis, for predetermined dividing width, first beginning with a predetermined reference point, and the resultant divided regions are given predetermined display properties. Then, a tool locus is displayed in the three-axial (XYZ) system according to the display properties given to the respective divided regions.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Composite PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) neural network control method based on nonlinear dynamic factor
InactiveCN101900991ARealize online real-time intelligent controlPrediction freeAdaptive controlZiegler–Nichols methodNerve network
The invention discloses a composite PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) neural network control method based on a nonlinear dynamic factor. In the method, creative improved research is carried out on the basis of stabilizing a PID controller based on a dynamic nonlinear factor by adopting a Ziegler-Nichols method abroad, and the defect of learning a mathematical model of a controlled object by confirming a PID gain parameter through utilizing a root locus method according to the Ziegler-Nichols method is effectively overcome. The invention aims to recombine three gain parameters and three factors in the prior art abroad to obtain six weight factors so as to obtain a composite PID neural network control law based on the nonlinear dynamic factor, which has six neural network weight factors, constructs a neural network model according to the nonlinear control law, and trains the weight factors in the composite PID controller based on the nonlinear dynamic factor on line in real time by using a neural network method to realize intelligent control on a nonlinear system. The invention can rapidly and accurately control a nonlinear object and has high robustness.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Incomplete constraint wheeled robot locus tracking control method based on look-up table method
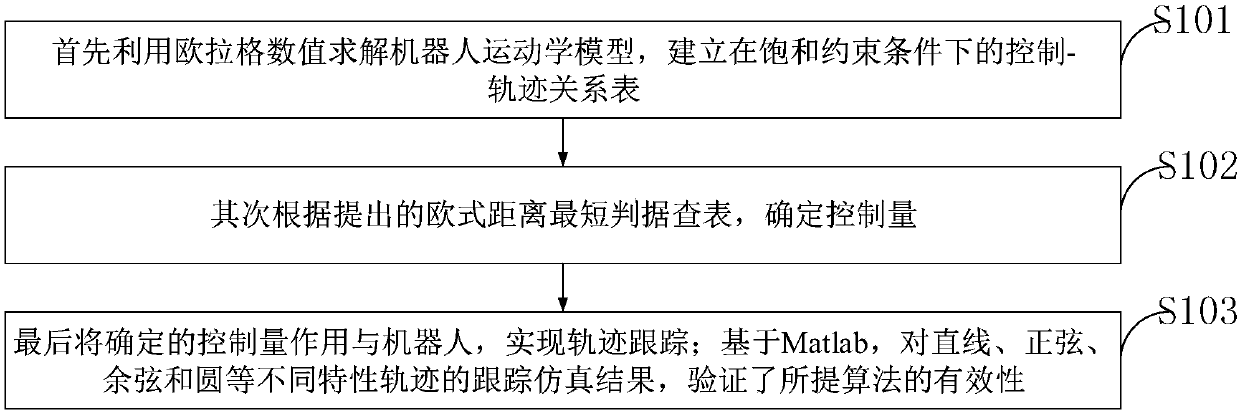
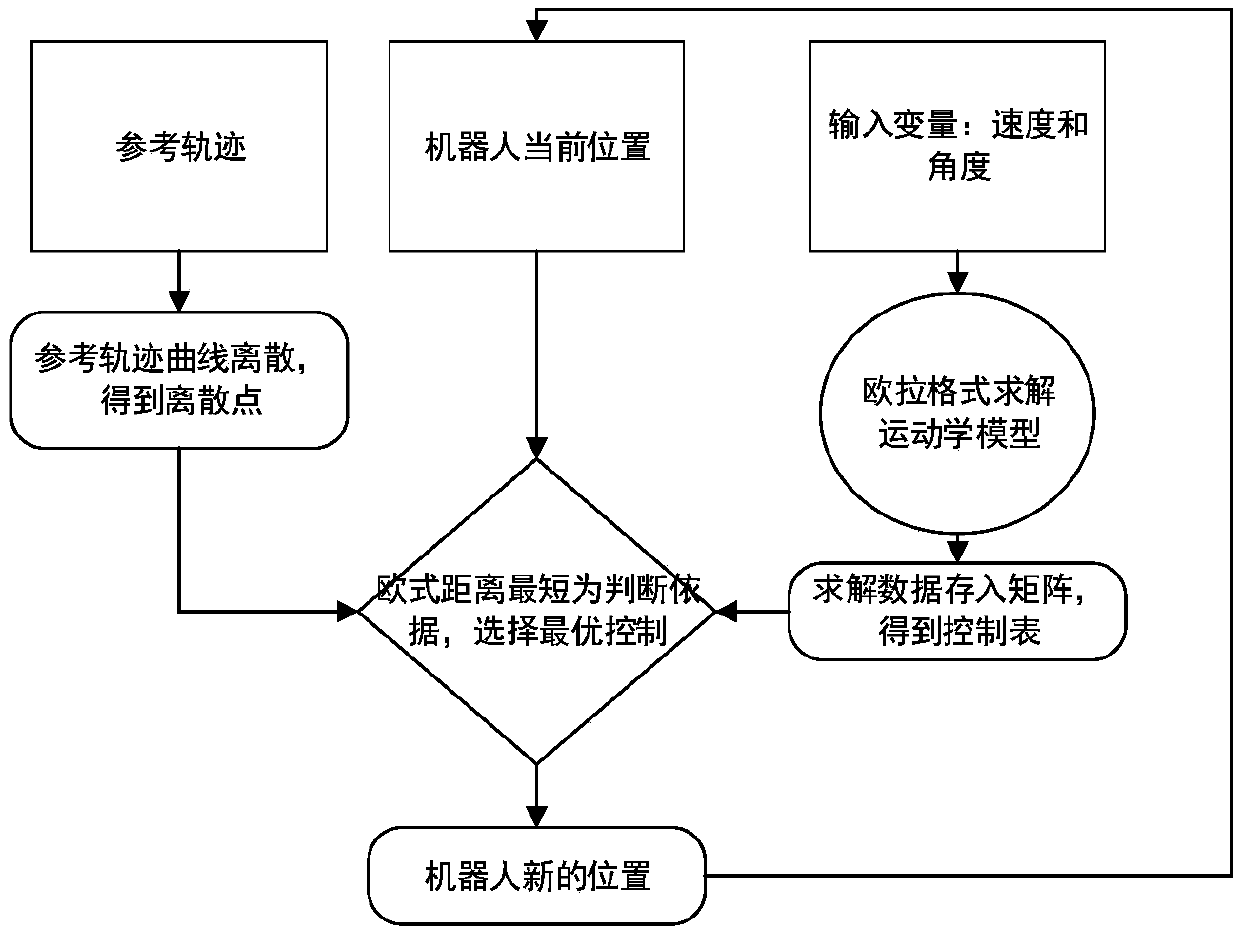
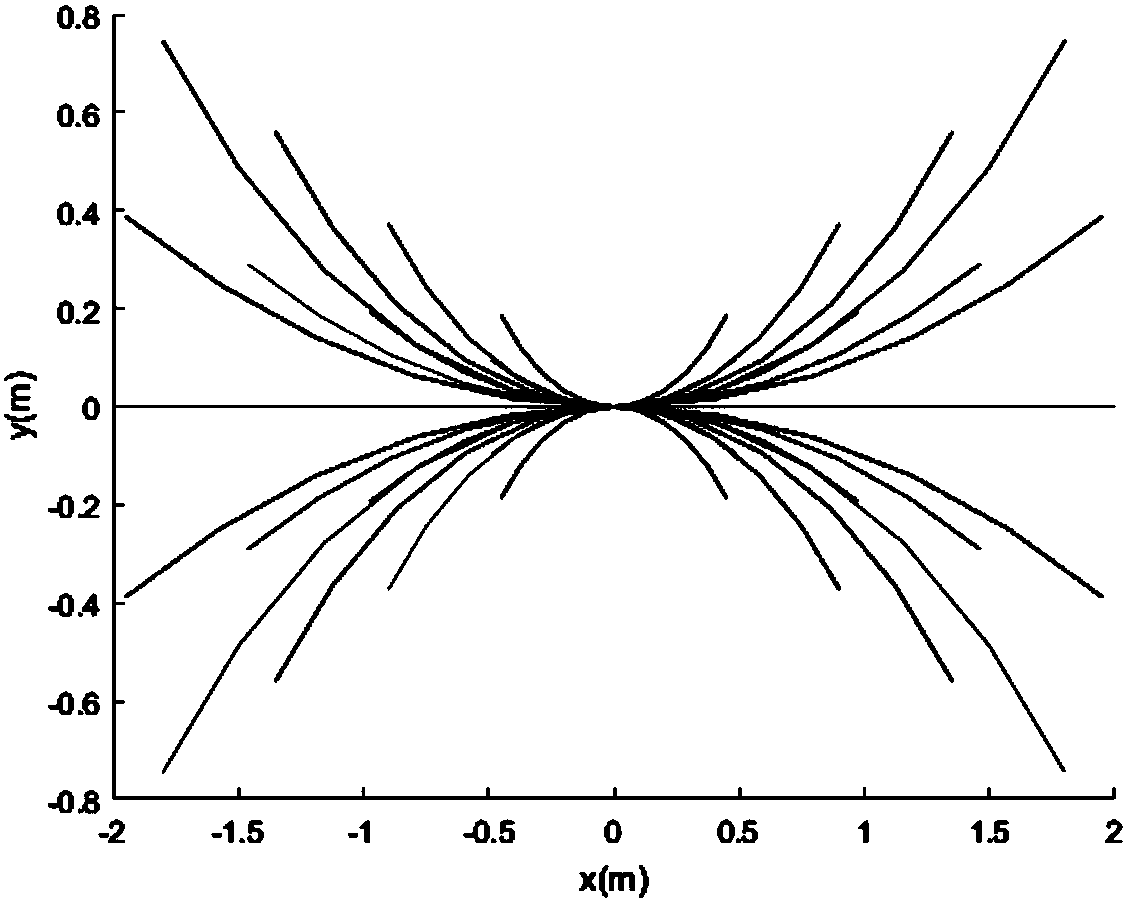
ActiveCN107943056AVerify validityRealize trajectory trackingPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematicsSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and discloses an incomplete constraint wheeled robot locus tracking control method based on a look-up table method. The method comprises the steps: solving a robot kinematic model through an Euler numerical value, and building a movement locus (x, y) relation table between system input (v, omega) and the robot under the condition of saturation constraint; determining a control input quantity according to a proposed shortest Euclidean distance criterion look-up table; finally employing the determined control input quantity for the robot, and enabling the movement locus of the robot to be tracked to a specific reference locus. The effectiveness of the method provided by the invention is verified based on Matlab through the tracking simulation results of linear, sine, cosine and circular loci.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Virtual automatic control experimental system and design method of virtual automatic control experimental system
InactiveCN103995474AExperiment content is flexibleEasy to operateSimulator controlAutomatic controlSimulation
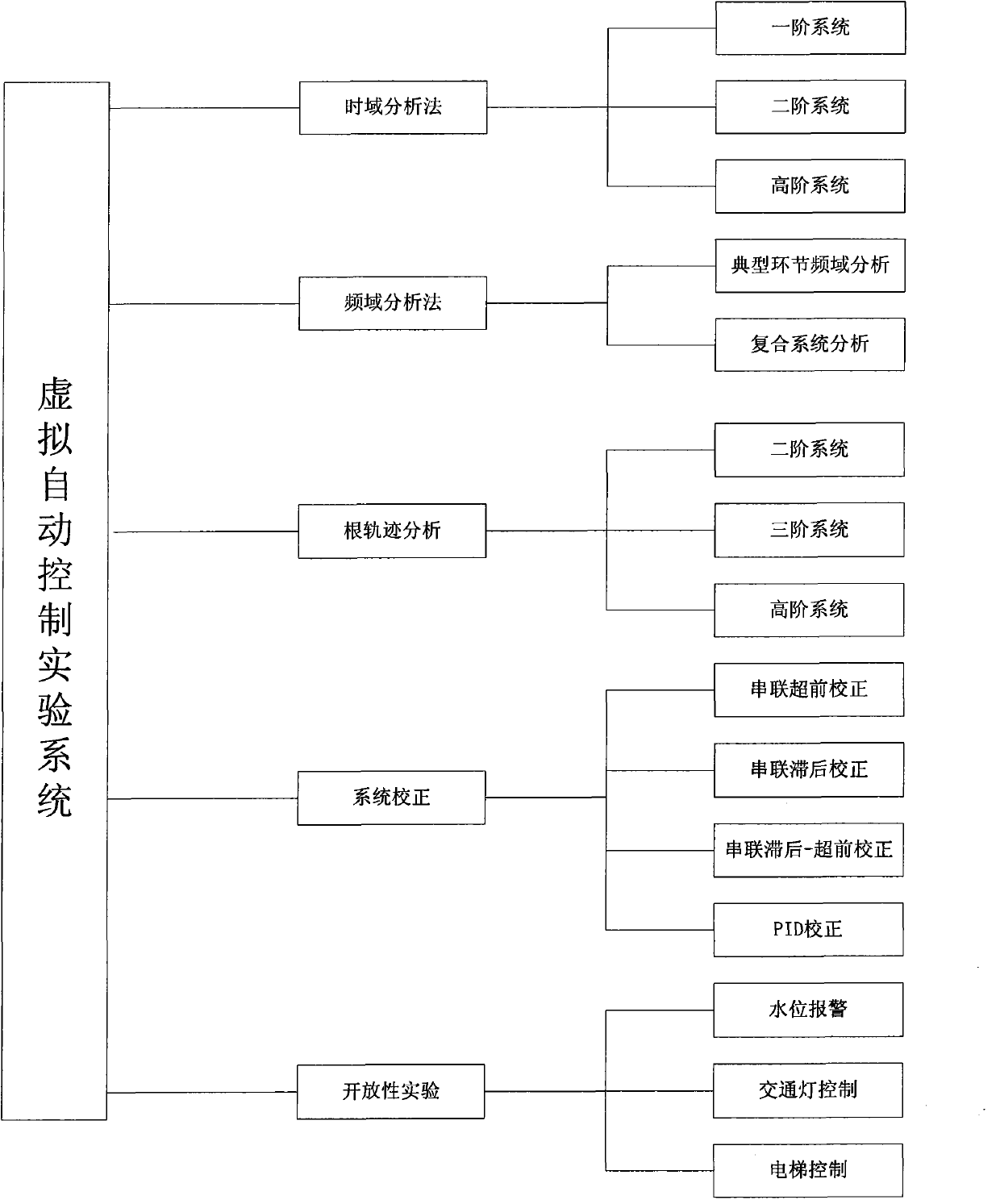
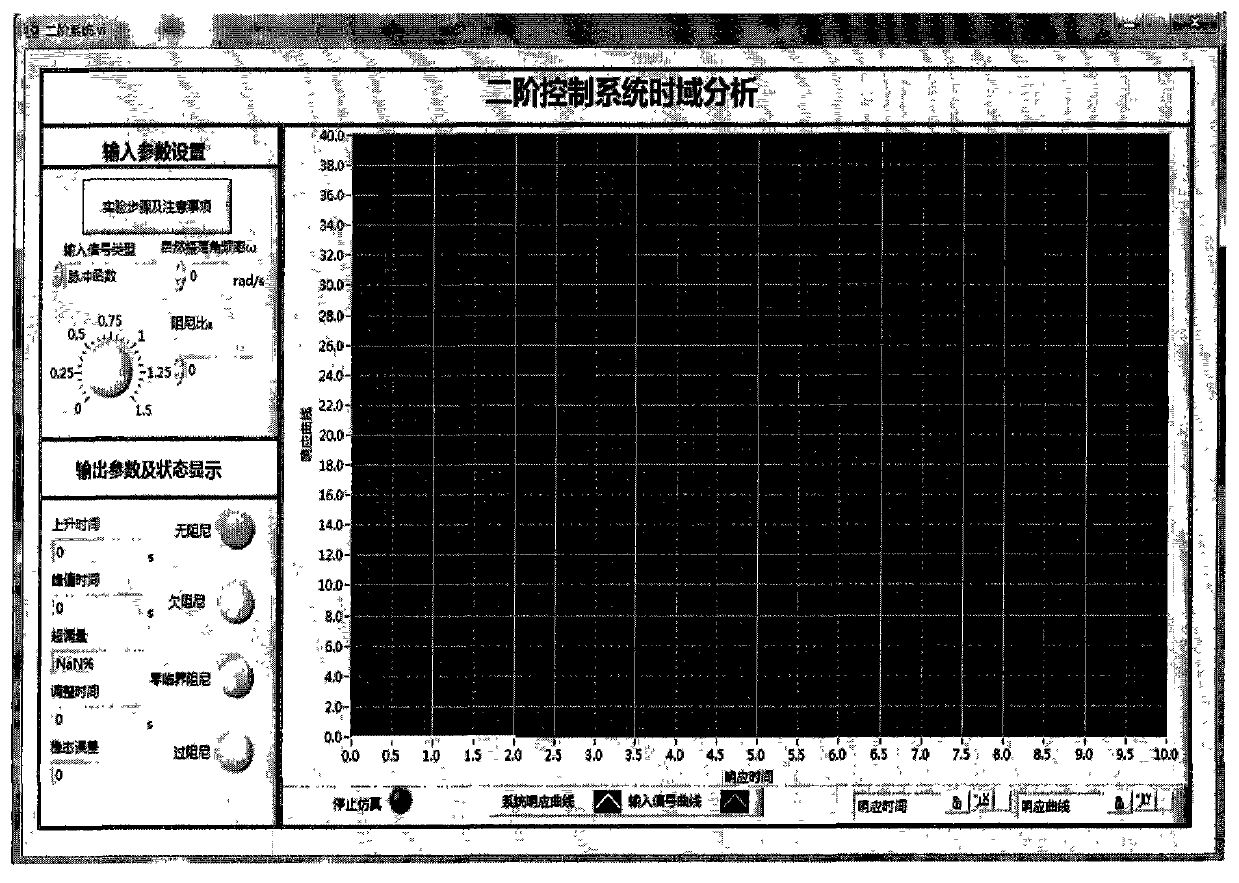
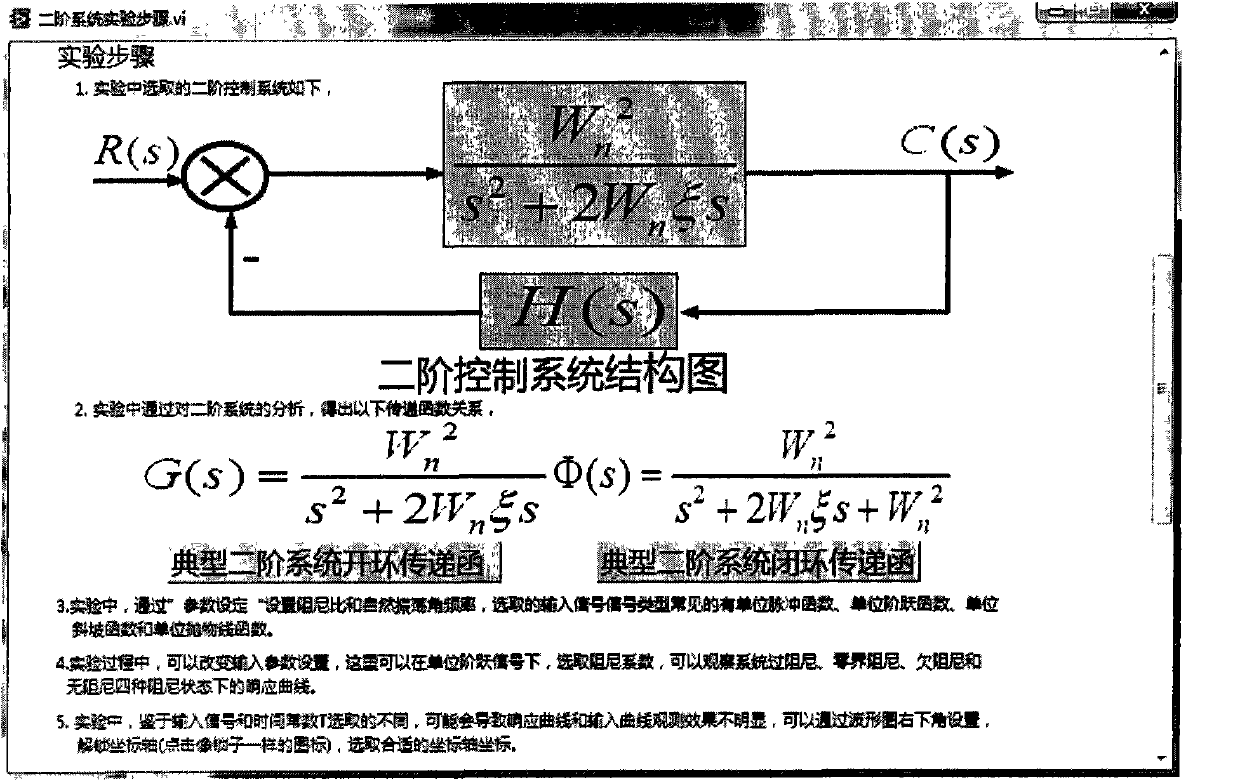
The invention discloses a virtual automatic control experimental system and a design method of the virtual automatic control experimental system. The virtual automatic control experimental system comprises a time domain analysis method experiment module, a root-locus method experiment module, a frequency domain analysis method experiment module, a system correction experiment module and an open experiment module, wherein the time domain analysis method experiment module comprises a first-order system time domain analysis module, a second-order system time domain analysis module and a high-order system time domain analysis module; the root-locus method experiment module comprises a second-order system root-locus analysis module, a third-order system root-locus analysis module and a high-order system root-locus analysis module; the frequency domain analysis method experiment module comprises a typical link frequency response characteristic analysis module and a composite system frequency response analysis module; the system correction experiment module comprises a series connection lead correction module, a series connection lag correction module, a series connection lag-lead correction module and a PID correction module; the open experiment module comprises a water level control module, an elevator control module and a traffic lamp control module. By means of the virtual automatic control experimental system and the design method, a user can design and simulate an automatic control experiment, the efficiency of the automatic control experiment is improved, limitation of hardware equipment is avoided, an experimenter can conveniently have a study, and shortcomings in a traditional experiment are overcome.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Controller parameter setting method and device and electronic equipment
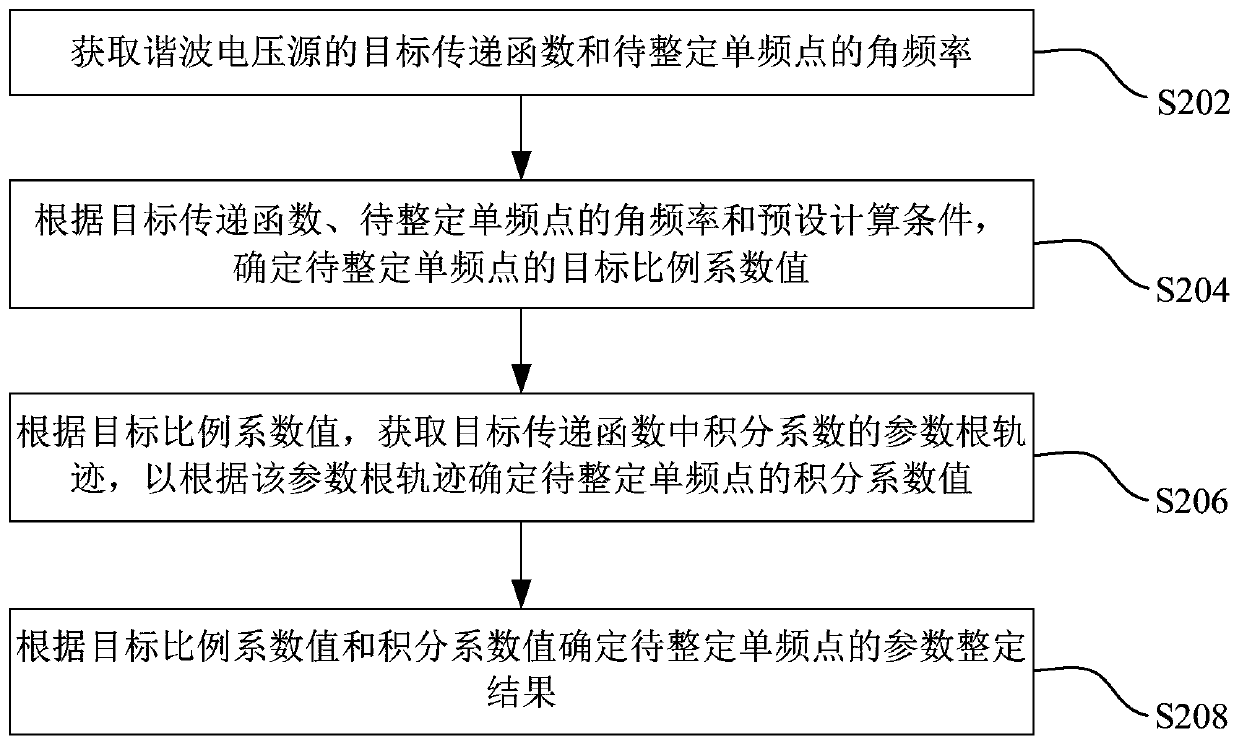
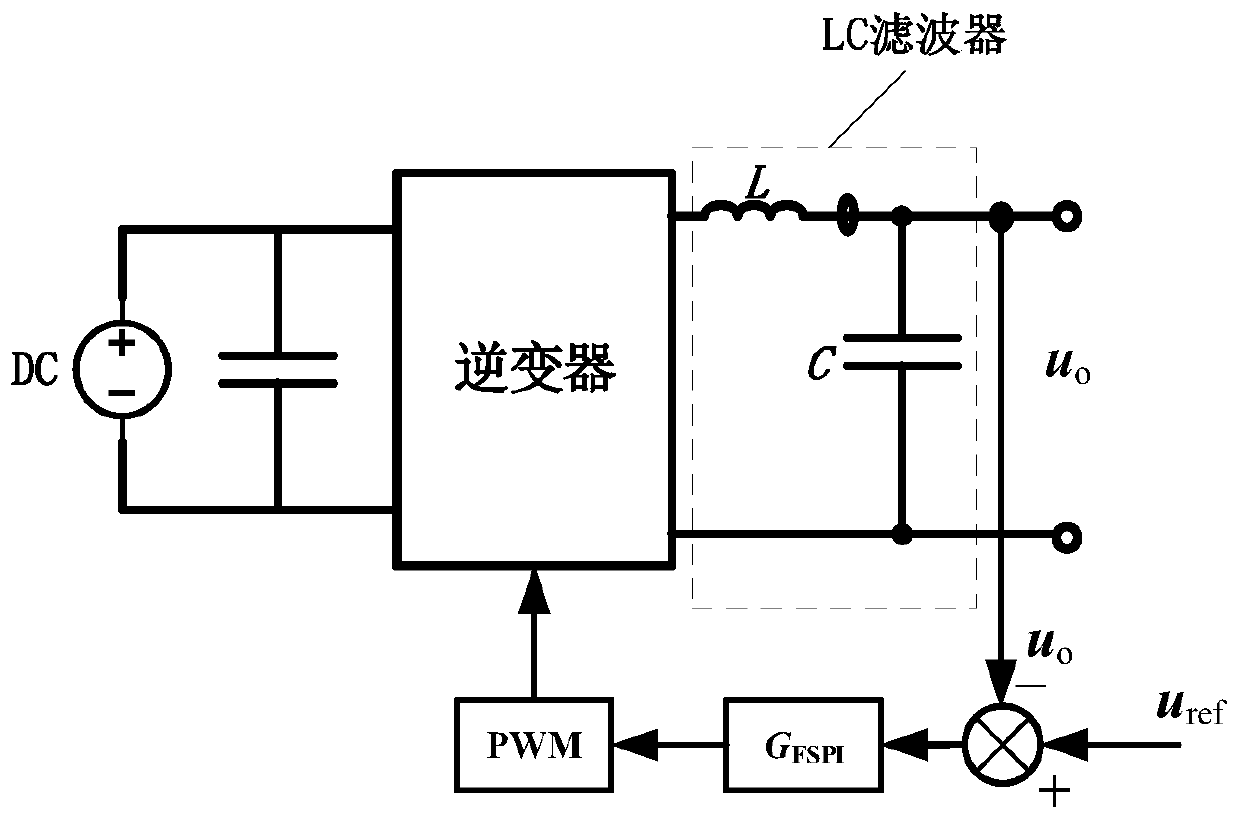
The invention provides a controller parameter setting method and device and electronic equipment, which relates to the technical field of electrical energy detection. The method includes the followingsteps: the target transfer function of a harmonic voltage source and the angular frequency of a single frequency point to be set are obtained; according to the target transfer function, the angular frequency of the single frequency point to be set and preset calculation conditions, the target proportional coefficient value of the single frequency point to be set is determined, wherein, the presetcalculation conditions include that, the integral coefficient of the target transfer function is 0, and the first amplitude frequency gain of the target transfer function away from the single frequency point to be set for the first preset angular frequency is 0dB; based on the target proportional coefficient value, the parameter root locus of the integral coefficient in the target transfer function is obtained, and the integral coefficient value of the single frequency point to be set is determined according to the parameter root locus; and according to the target proportional coefficient value and the integral coefficient value, the parameter setting result of the single frequency point to be set is determined. In this way, the controller parameters can be set quickly, which reduces thewaste of time and energy, and improves the work efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
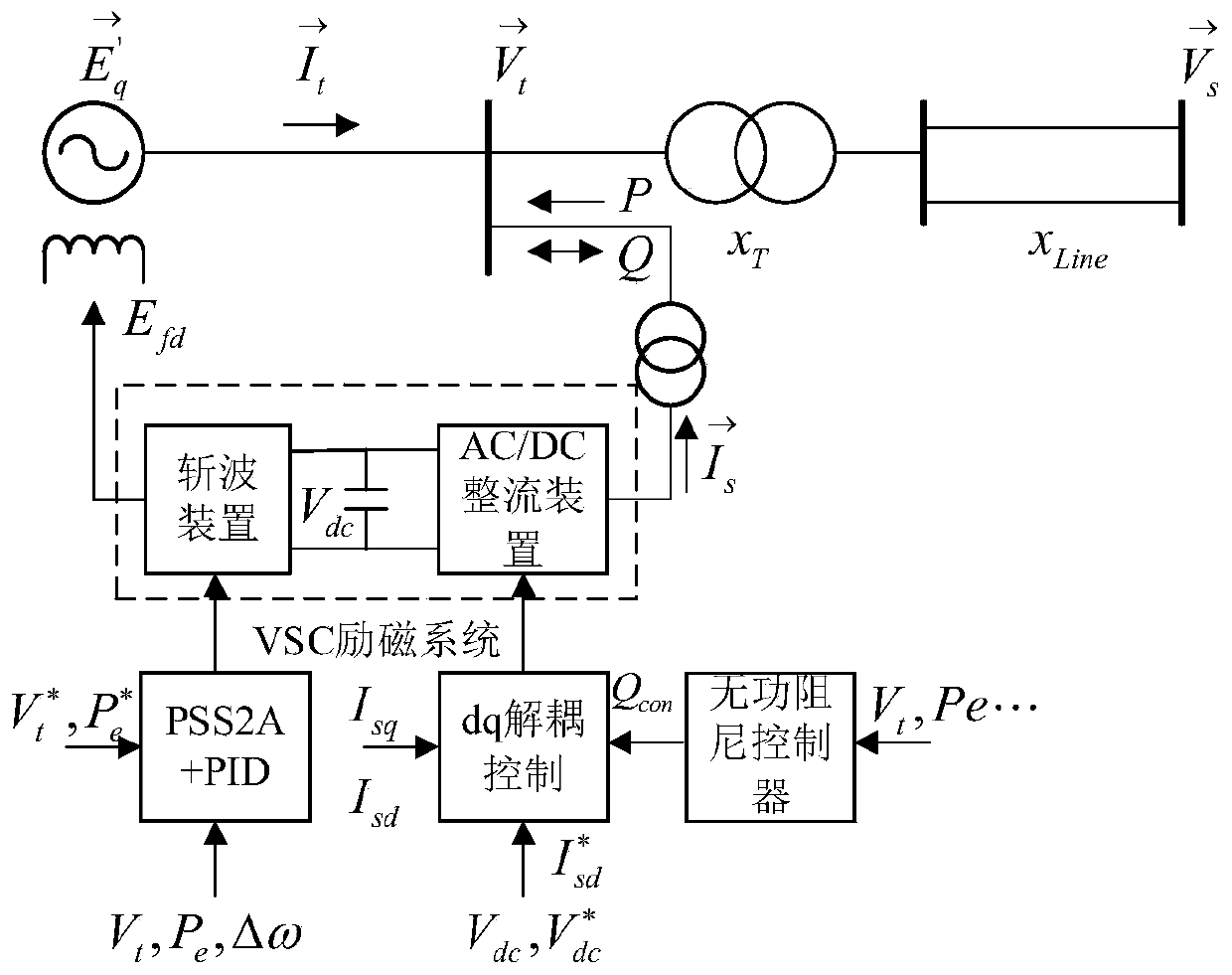
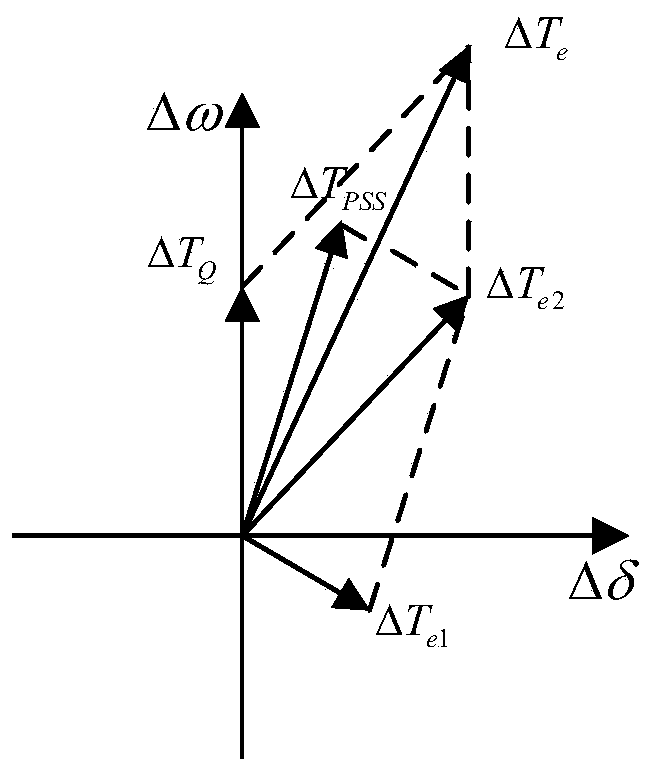
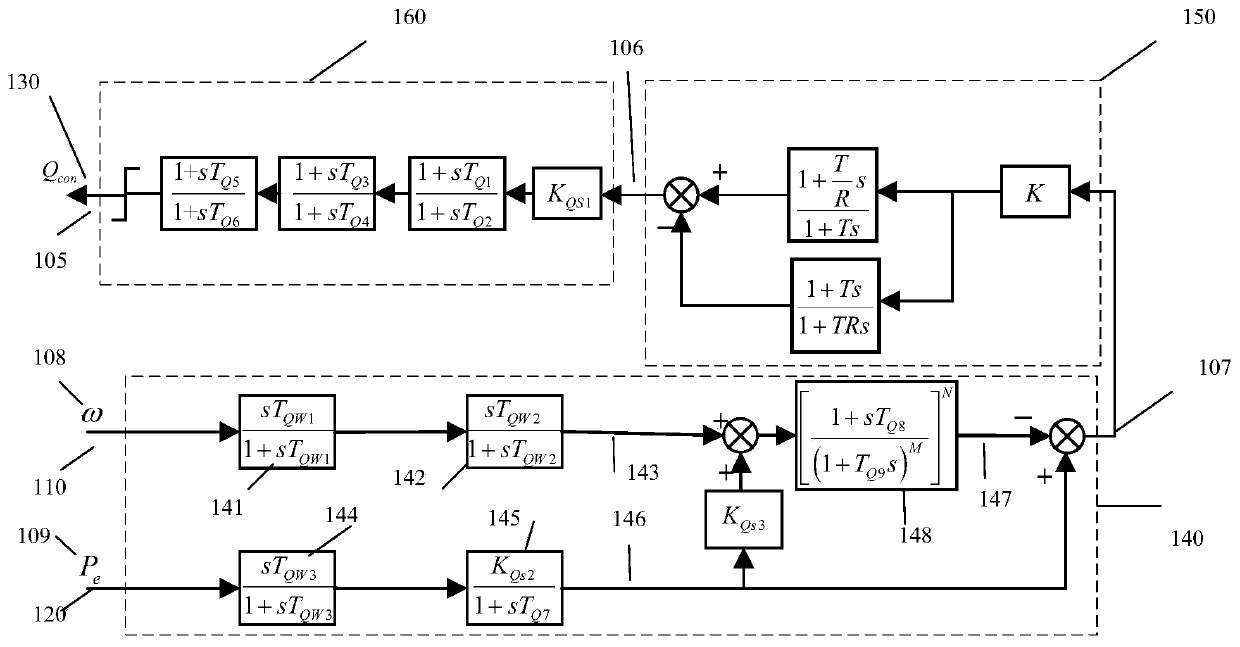
Reactive damping controller based on flexible excitation system and parameter setting method
ActiveCN110707727ADoes not affect the damping effectIncrease dampingPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectric generator controlControl signalMathematical model
The invention discloses a reactive damping controller based on a flexible excitation system and a parameter setting method. The controller is composed of a double-channel signal input end, an acceleration power signal synthesis link, a phase shift gain and output amplitude limiting link and a control signal output end. The parameter setting method comprises the following steps of setting the parameters of the acceleration power signal synthesis link; establishing a theoretical uncompensated characteristic mathematical model of a reactive damping channel of a flexible excitation system; and establishing a reactive damping controller compensation characteristic mathematical model, solving an optimal solution of the control parameters of a phase shift link of a reactive damping controller byusing an intelligent optimization algorithm, solving a critical gain by using a root locus method, and finally setting the gain of the reactive damping controller according to a damping calculation formula. The controller can replace a power system stabilizer to provide damping for a full frequency band of low-frequency oscillation, and can also independently design a damping strengthening strategy for a specific frequency band by utilizing the advantage of channel independence, so that the full-effect suppression effect of excitation control on the multi-mode low-frequency oscillation of a power system is improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +2
Ultra-low frequency oscillation inhibition method based on root locus group
ActiveCN110224416AReduce negative damping effectClear math foundationFlicker reduction in ac networkPower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping torqueDamping ratio
The invention discloses an ultra-low frequency oscillation inhibition method based on root locus group. The method comprises the following steps of S1, constructing a detailed model of a hydroelectricgeneration system; S2, carrying out derivation to obtain an analysis expression of the damping torque coefficient of an original moving system; S3, analyzing the influence of the damping torque coefficient on system damping; S4, analyzing the influence of PID parameters of a speed regulator on the damping torque coefficient; S5, constructing a two-machine equivalent system model, drawing a systemroot locus group to obtain the position of a dominant pole of a system generating ultralow frequency oscillation on the root locus group, and determining the PI parameter range of the speed regulatorwhen the system is stable; S6, according to an introduced equal-damping ratio line, determining an ideal reset point of the dominant pole, and replacing the PI parameter value of the speed regulatorcorresponding to the rest point with the original PI parameter value of the speed regulator, optimizing the parameters of the speed regulator and suppressing ultra-low frequency oscillation; and S7, based on the PSD-BPA software, performing off-line simulation on a power grid large system, analyzing the ultralow-frequency oscillation problem and verifying the correctness of the extraction method.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
An improved VSG secondary frequency modulation controller and control method
InactiveCN108988360AReduce outputAchieve FM effectSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionConstant frequencyRoot locus
An improved VSG secondary frequency modulation controller and control method are disclosed. When constant frequency limit exceeding occurs to a systme, a PI control is automatically put into an integral link at that virtual damping part of the frequency modulation invert, The micro-power supply which is responsible for frequency modulation can automatically track the load fluctuation and make no-difference regulation, so that the secondary frequency modulation function of micro-grid can be realized, and the stability of the designed secondary frequency modulation control method is analyzed byusing small signal equivalence and root locus analysis method. And the frequency control method of VSG is designed.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF ENG
Motor train unit bogie suspension system kinetic parameter optimization method and device
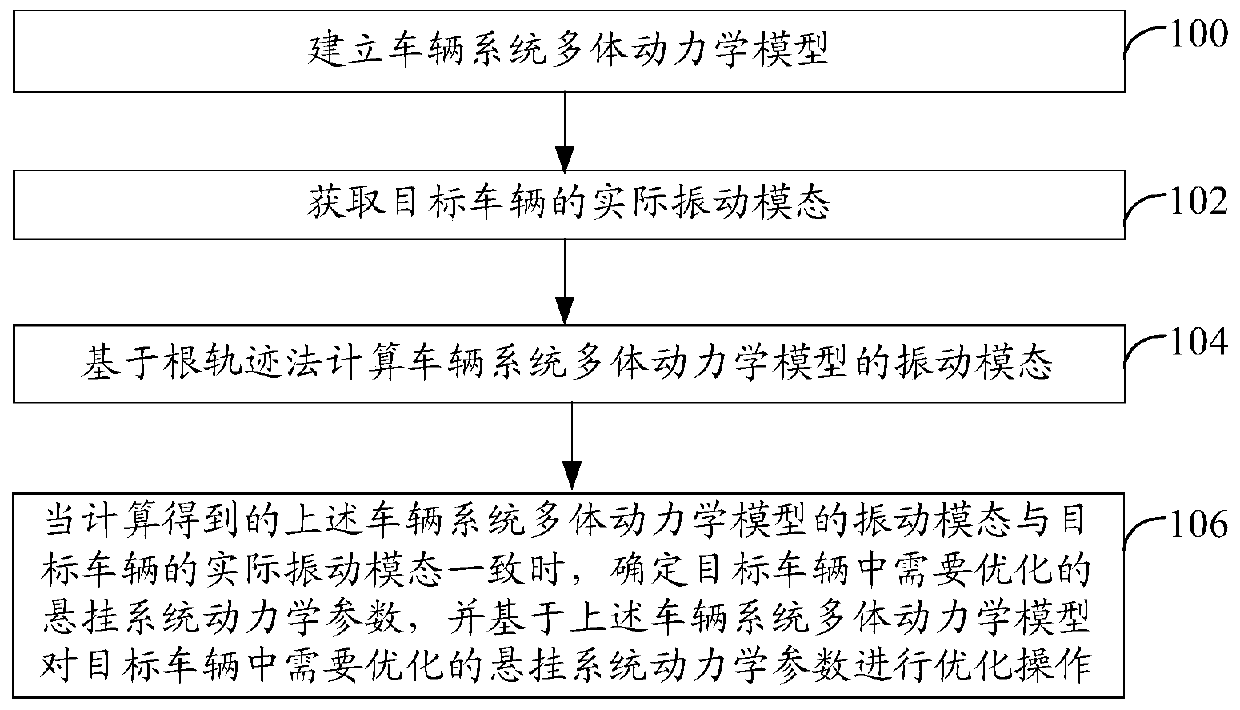
ActiveCN109858120ASimplify the optimization processImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesSustainable transportationBogieDynamic models
The invention provides a motor train unit bogie suspension system kinetic parameter optimization method and device, and the method comprises the steps: building a vehicle system multi-body kinetic model; obtaining an actual vibration mode of the target vehicle; calculating a vibration mode of the vehicle system multi-body dynamic model based on a root locus method; and when the calculated vibration mode of the vehicle system multi-body dynamic model is consistent with the actual vibration mode of the target vehicle, determining suspension system dynamic parameters needing to be optimized in the target vehicle, and carrying out optimization operation on the suspension system dynamic parameters needing to be optimized in the target vehicle based on the vehicle system multi-body dynamic model. According to the motor train unit bogie suspension system kinetic parameter optimization method and device, massive data analysis is not needed, the optimization process of the suspension system ofthe motor train unit is simplified, and the calculation speed is increased.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG CO LTD
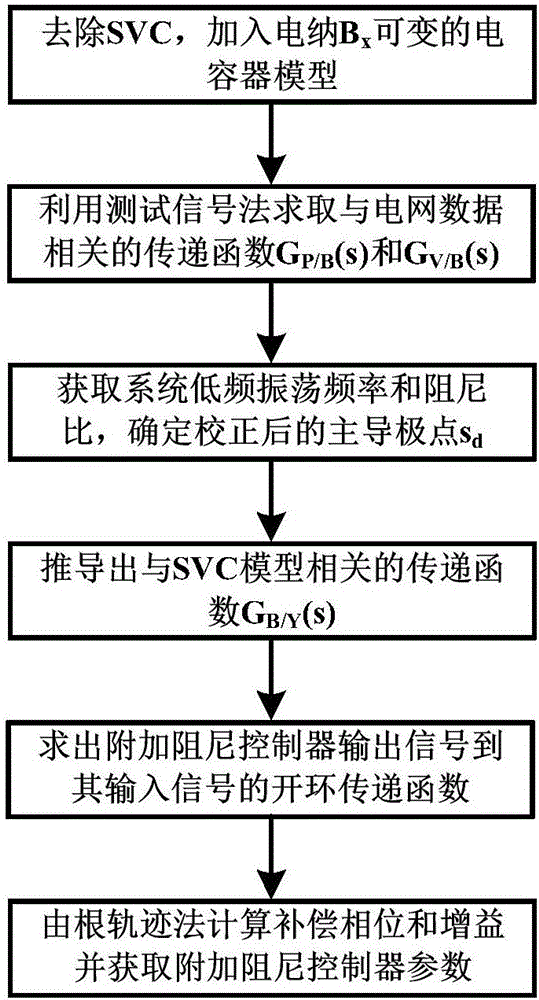
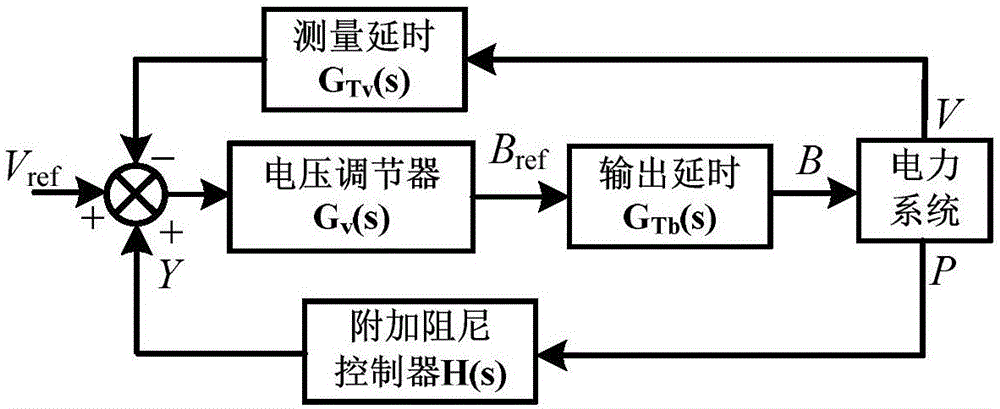
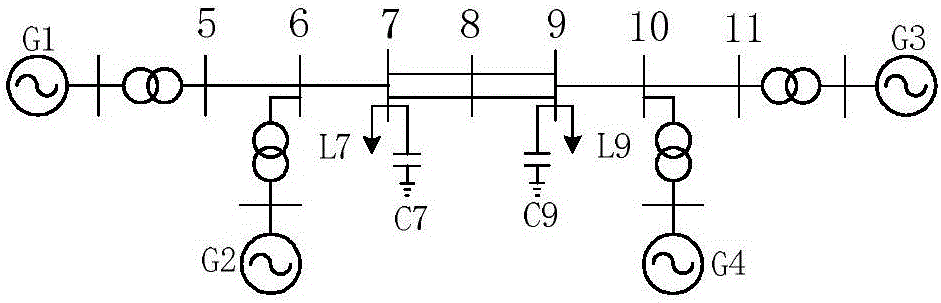
Method for setting parameters of SVC (supplementary damping controller)
ActiveCN106684886AReduce workloadFlexible AC transmissionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationElectric power systemPower grid
The invention discloses a method for setting parameters of an SVC (supplementary damping controller), and belongs to the technical field of power system control. The method comprises the steps of introducing a susceptance variable capacitor; obtaining a transfer function associated with a large power grid by using a test signal method and deducing an open-loop transfer function between an output signal injection point of the supplementary damping controller and an input signal according to an SVC model; and finally calculating the parameters of the supplementary damping controller through a root-locus method. The SVC model is not needed to provide an interface of adding small signal excitation, the application range is wider, simulation and calculation of the test signal method do not need to be carried out again when the parameters of the SVC model change, and the parameters of the supplementary damping controller can be more simply and conveniently obtained.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +4
Stability analysis method of single-phase voltage source based on Jacobi theory
InactiveCN110138241AAccurate analysisAc-dc conversion without reversalDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelNonlinear model
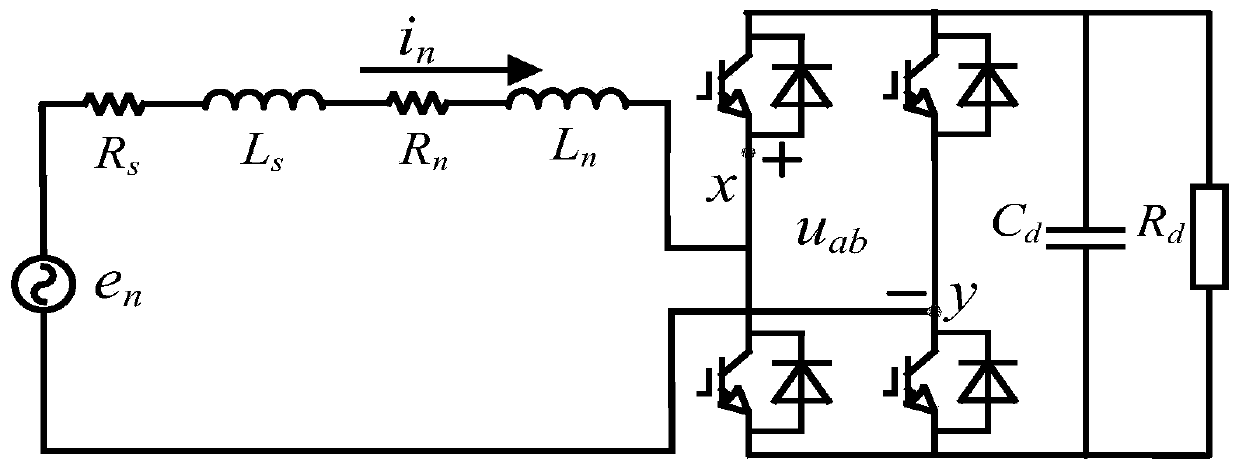
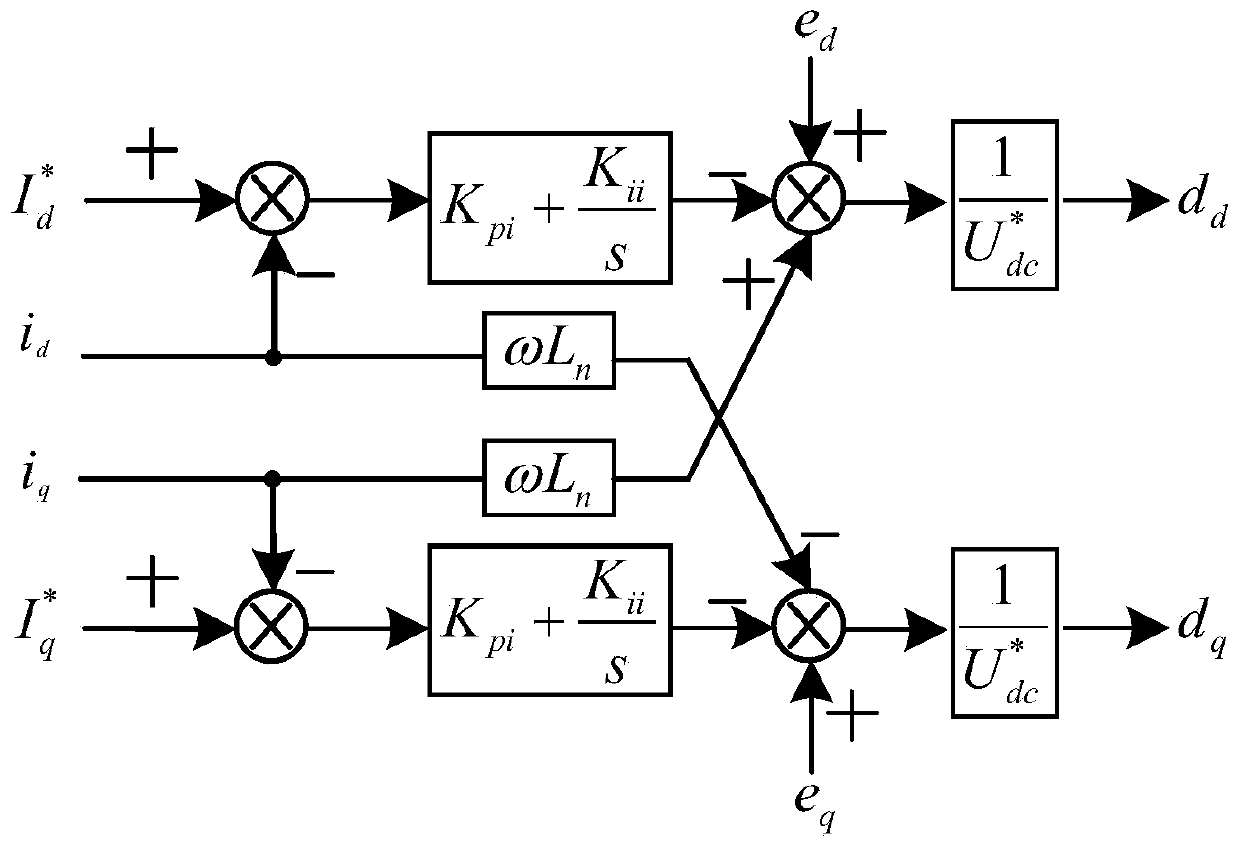
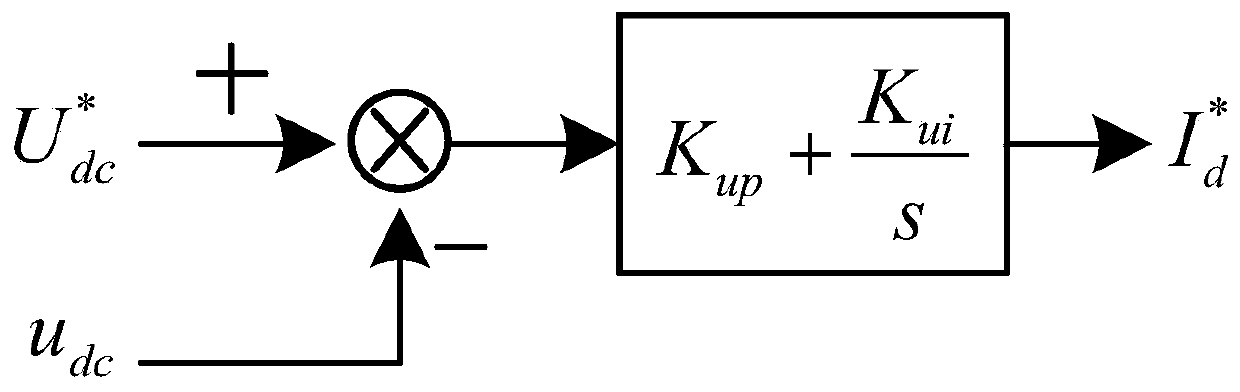
The invention discloses a stability analysis method of a single-phase voltage source based on the Jacobi theory. The method is characterized by, to begin with, establishing a mathematical model of a single-phase voltage source rectifier under a dq coordinate system; then, establishing a time domain nonlinear dynamic average model according to the mathematical model of the single-phase voltage source rectifier under the dq coordinate system; solving a steady-state operating point based on the mathematical model of the single-phase voltage source rectifier under the dq coordinate system; and finally, calculating the characteristic value of the system according to the Jacobi theory, and judging the stability of the system by utilizing a root locus method. The method adopts a time domain nonlinear model to make the system model clear and concise; and bullet train network side parameters and rectifier DC side parameters obtained based on the root locus method can affect the stability of thesystem.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com