Device for synchronously measuring granularity of dynamic light scattering nanometer particles of multi-particles and method thereof
A dynamic light scattering and nano-particle technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, particle size analysis, particle and sedimentation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of complex instrument structure, long sampling time requirements, and low concentration of measured particles, so as to reduce the measurement time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
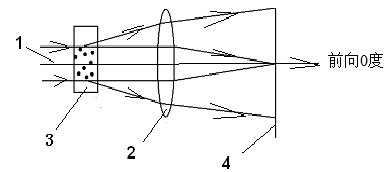
[0058] Depend on figure 1 As shown, the laser beam emitted by the laser source 1 is incident on the sample cell 3, and the particle sample to be measured is placed in the sample cell 3, the particles will scatter the incident laser light, and the scattered light of the particles is collected by the lens 2 and formed on the focal plane of the lens 2 Spatially distributed scattered light points, due to the different sizes of particles and the effect of Brownian motion, the spatially distributed scattered light points will have random changes in intensity and position over time, and this random change in light point intensity and position can be continuously measured An area array photosensitive device 4, such as a CCD or CMOS camera or video camera records, and obtains a sequence of spatially distributed images of continuously changing scattered light points. Due to the Brownian motion and the different sizes of the particles, the scattered light spots at the corresponding posi...
Embodiment 2
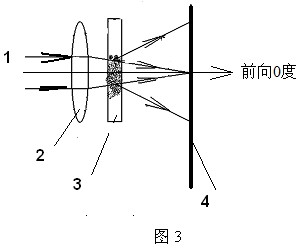
[0062] Such as image 3 As shown, the difference from Example 1 is that the sample cell 3 is arranged behind the receiving lens 2, the laser beam emitted by the laser source 1 first passes through the lens 2 and then enters the sample cell 3, and the dynamic scattered light of the particles is then captured The area array photosensitive device 4, such as a CCD or CMOS camera or video camera, continuously receives and records, and obtains a moving image sequence of continuously changing spatial distribution of scattered light points.
Embodiment 3
[0064] In the optical path where the laser beam 1 , the sample cell 4 , the lens 2 , and the area array photosensitive device 4 are coaxially arranged in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, the size of the entire device is relatively long. To reduce the size of the measuring device, such as Figure 4 As shown, the laser light source 1 is equipped with a Dove prism behind it to reduce the size of the measuring device. The laser beam emitted by the laser light source 1 is rotated 90 degrees by the corner prism, and then enters the lens 2 or the sample cell 3 . Such as Figure 4 As shown, the sample cell 3 is arranged behind the lens 2 . The sample cell 3 can also be arranged in front of the lens 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com