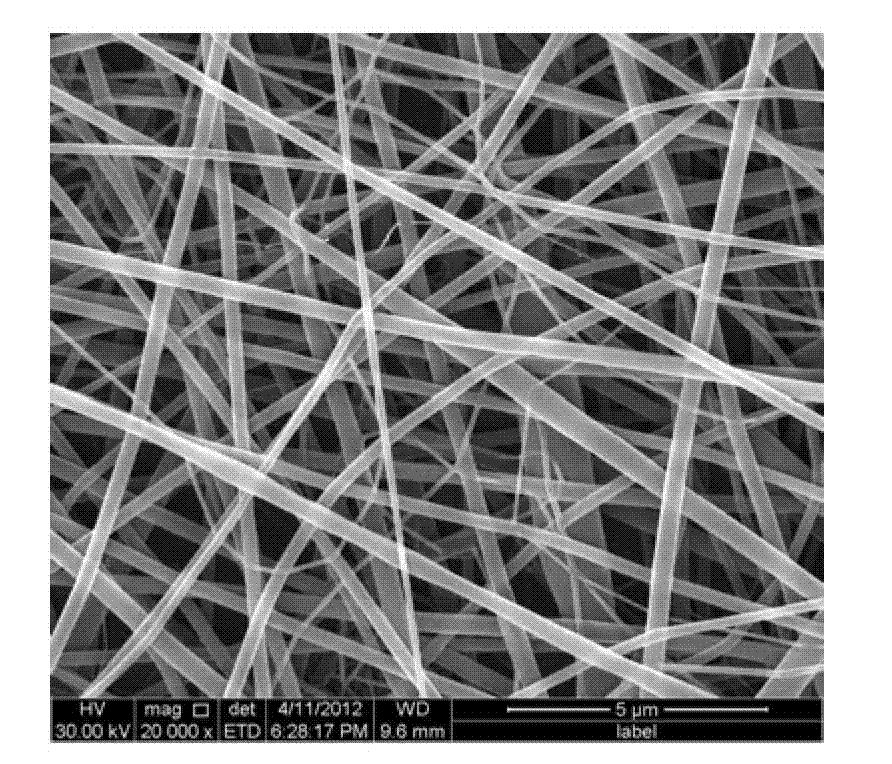
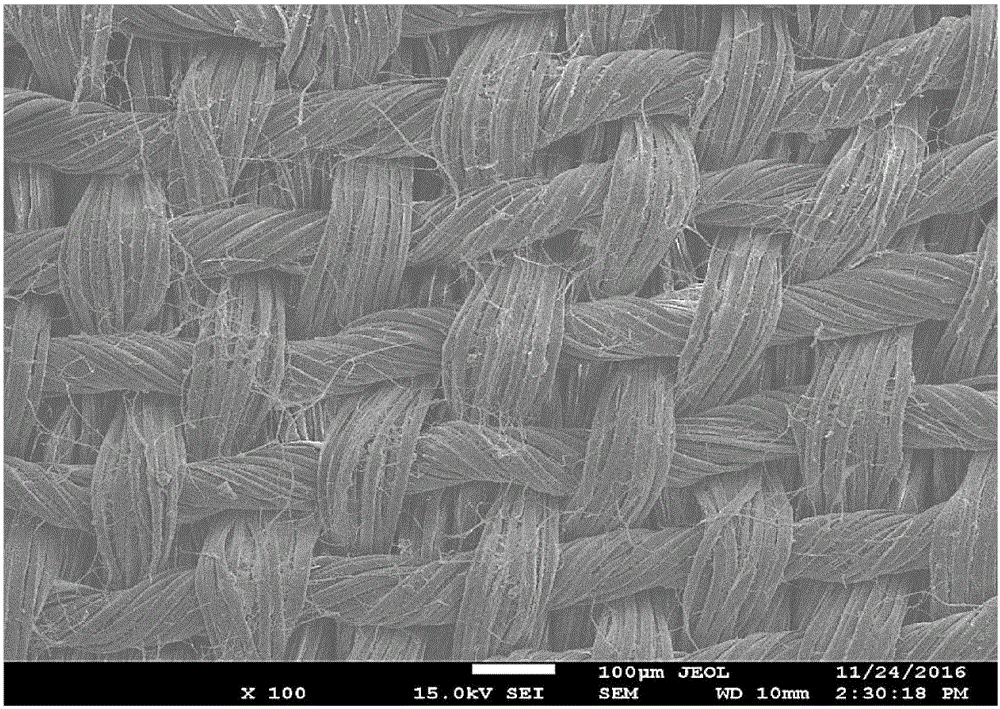
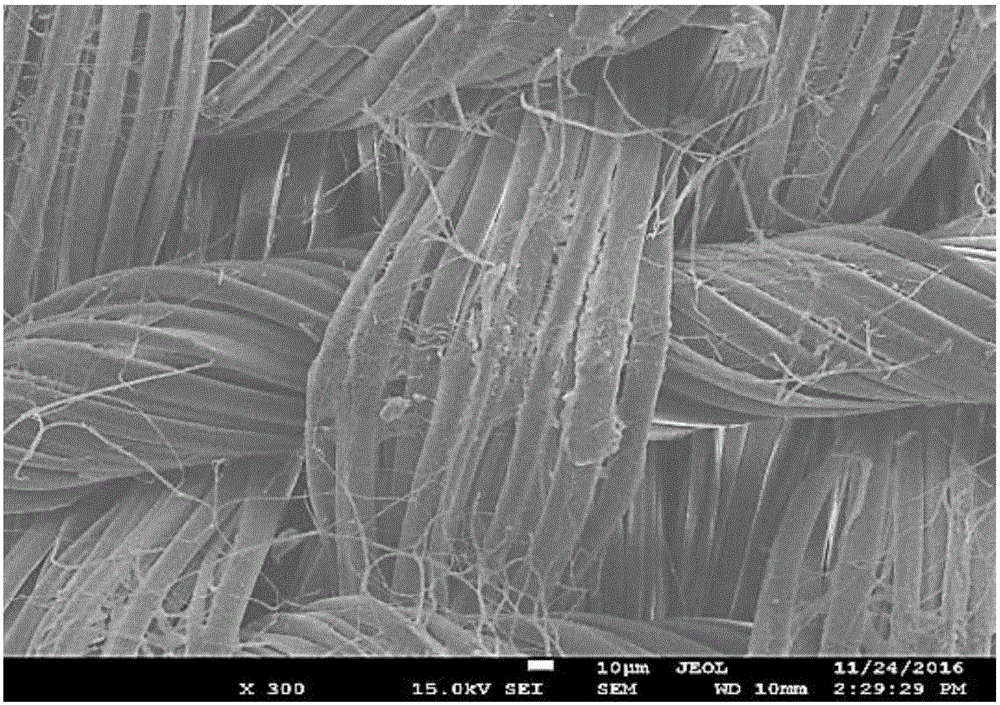
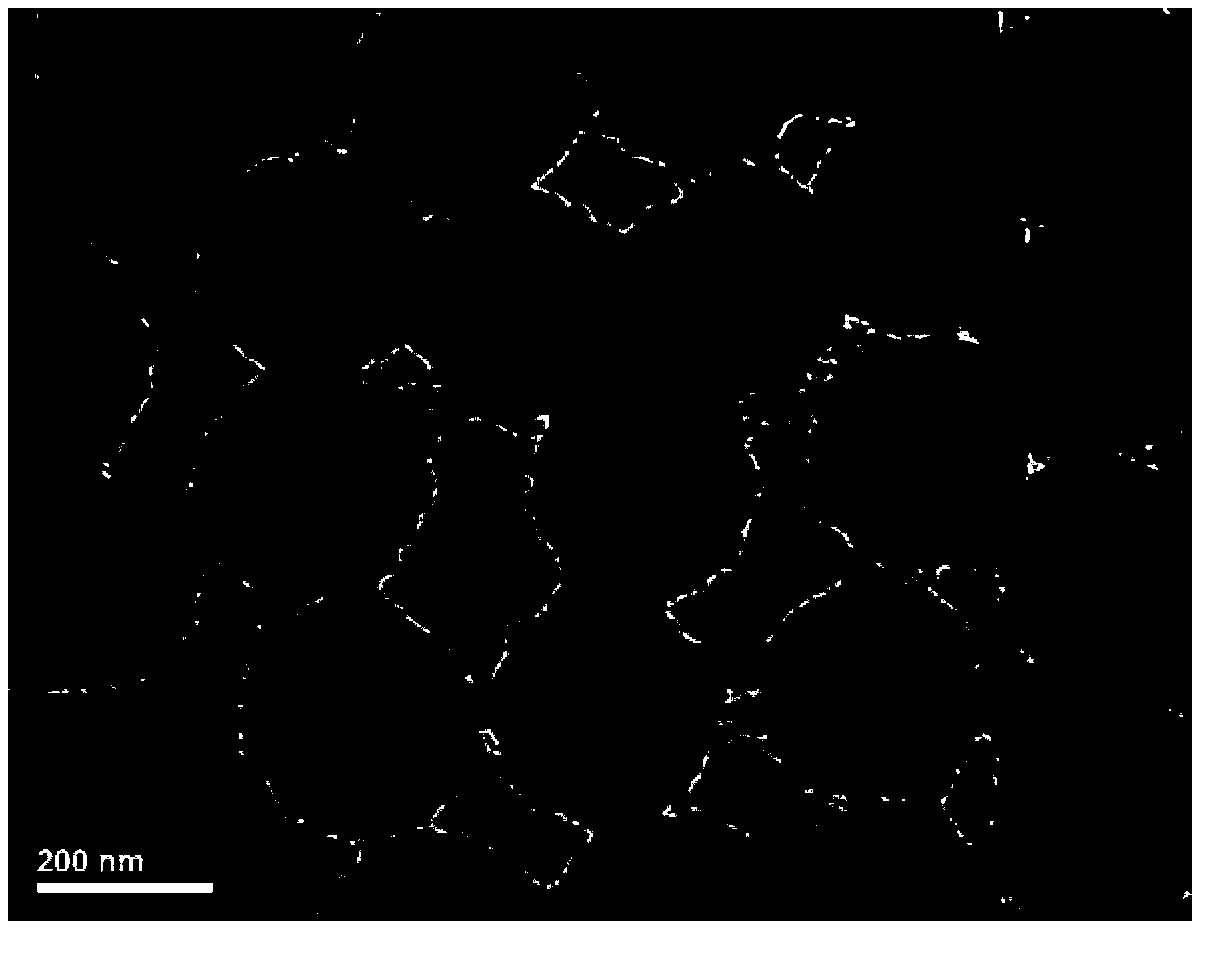
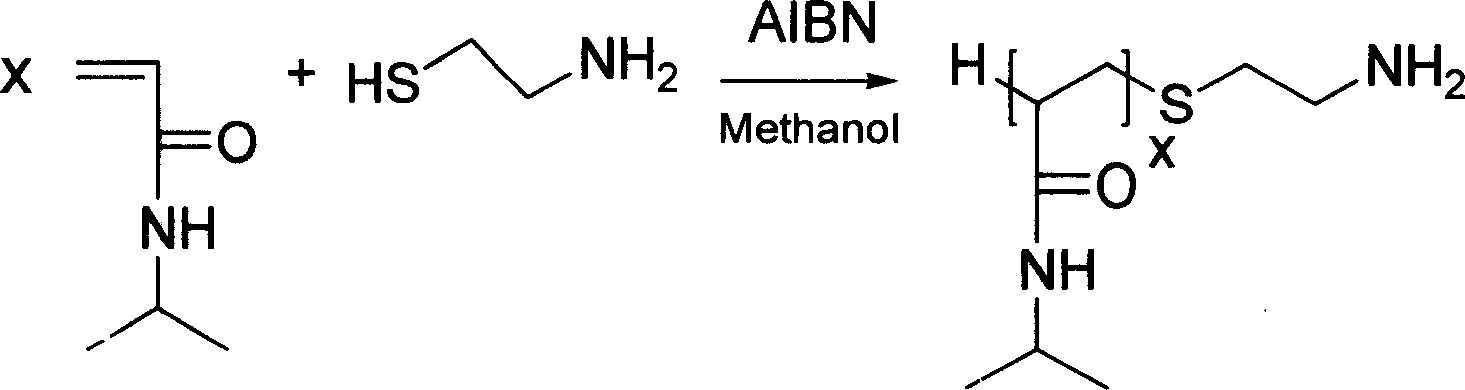
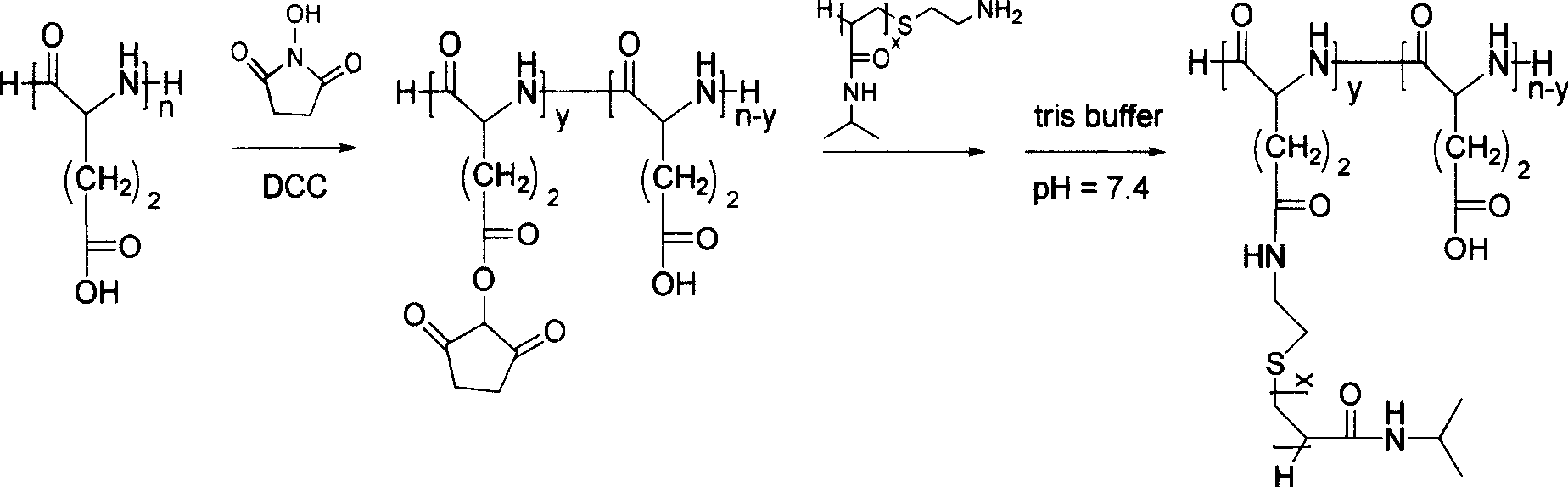
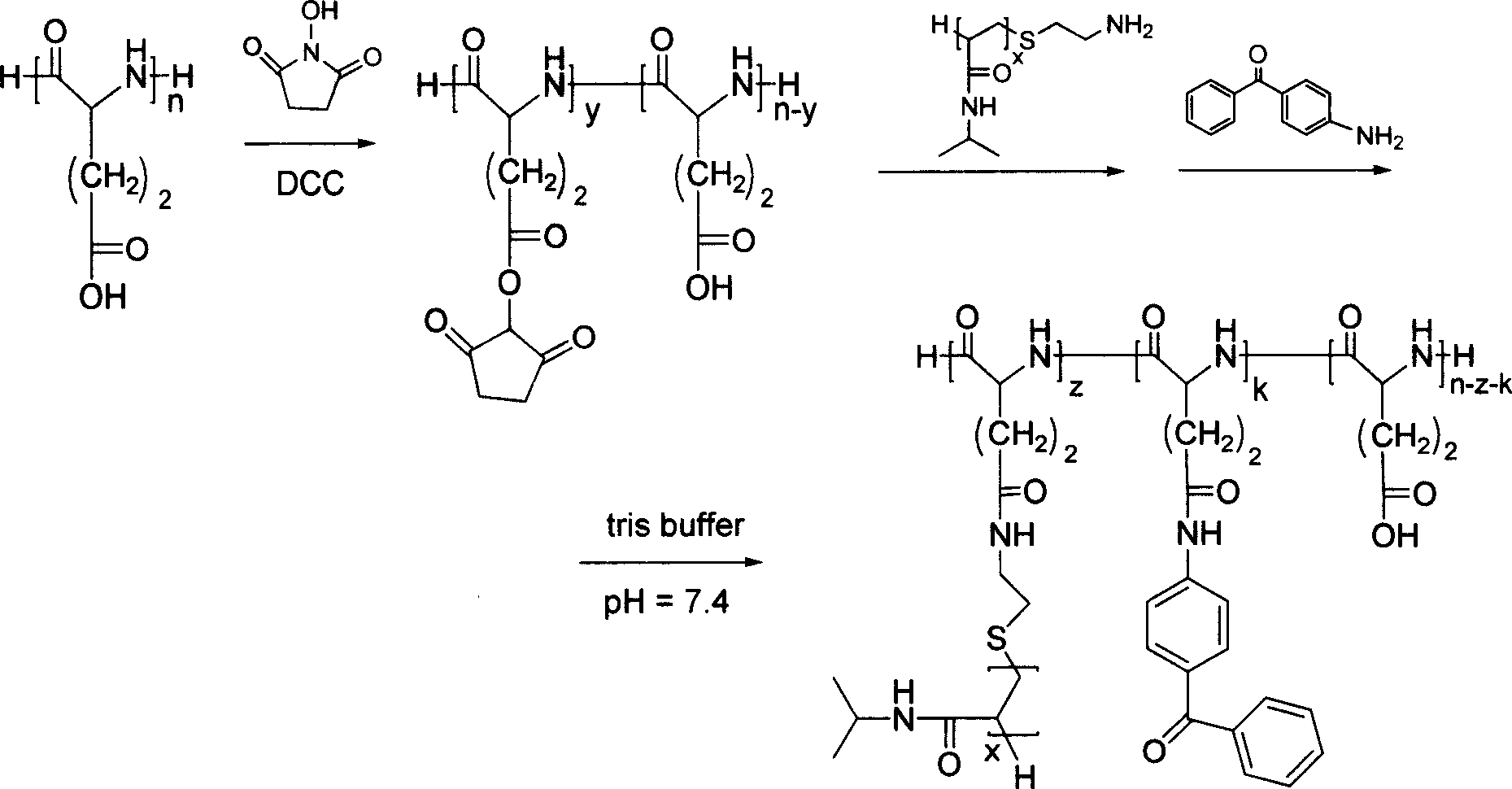
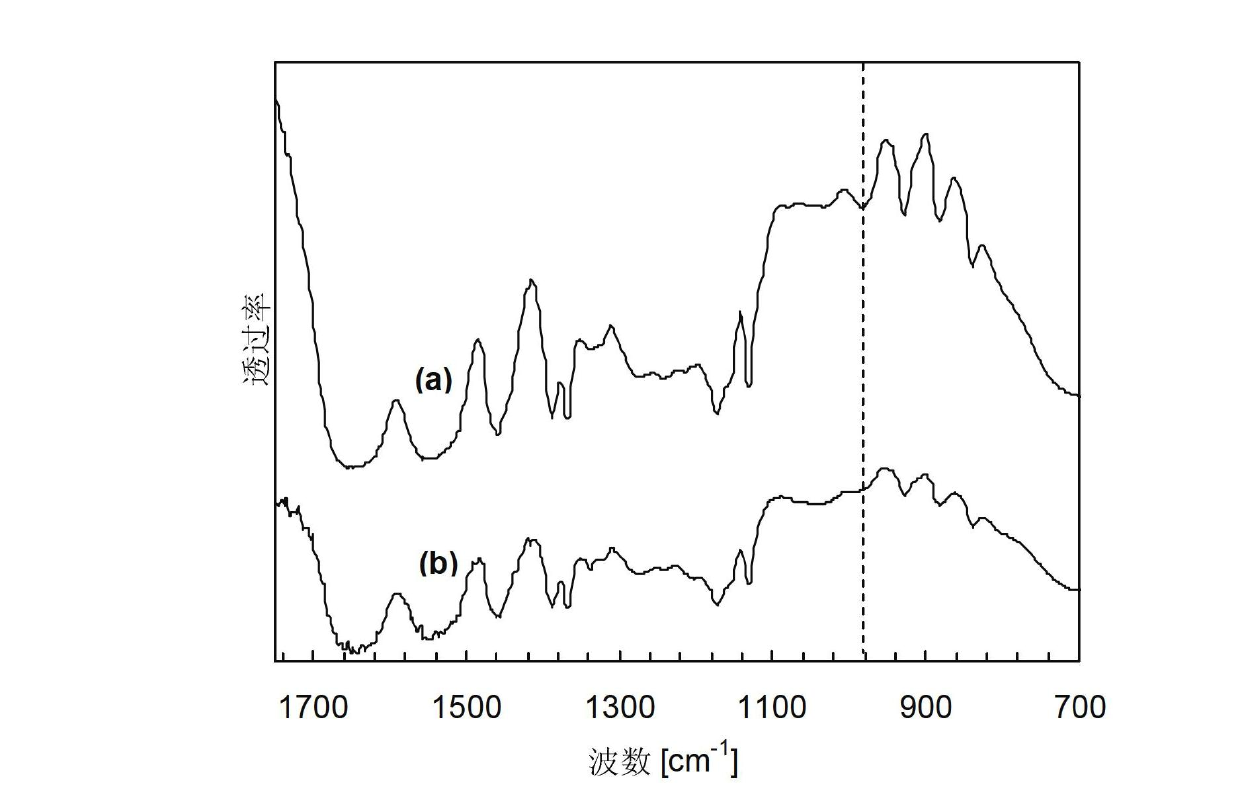
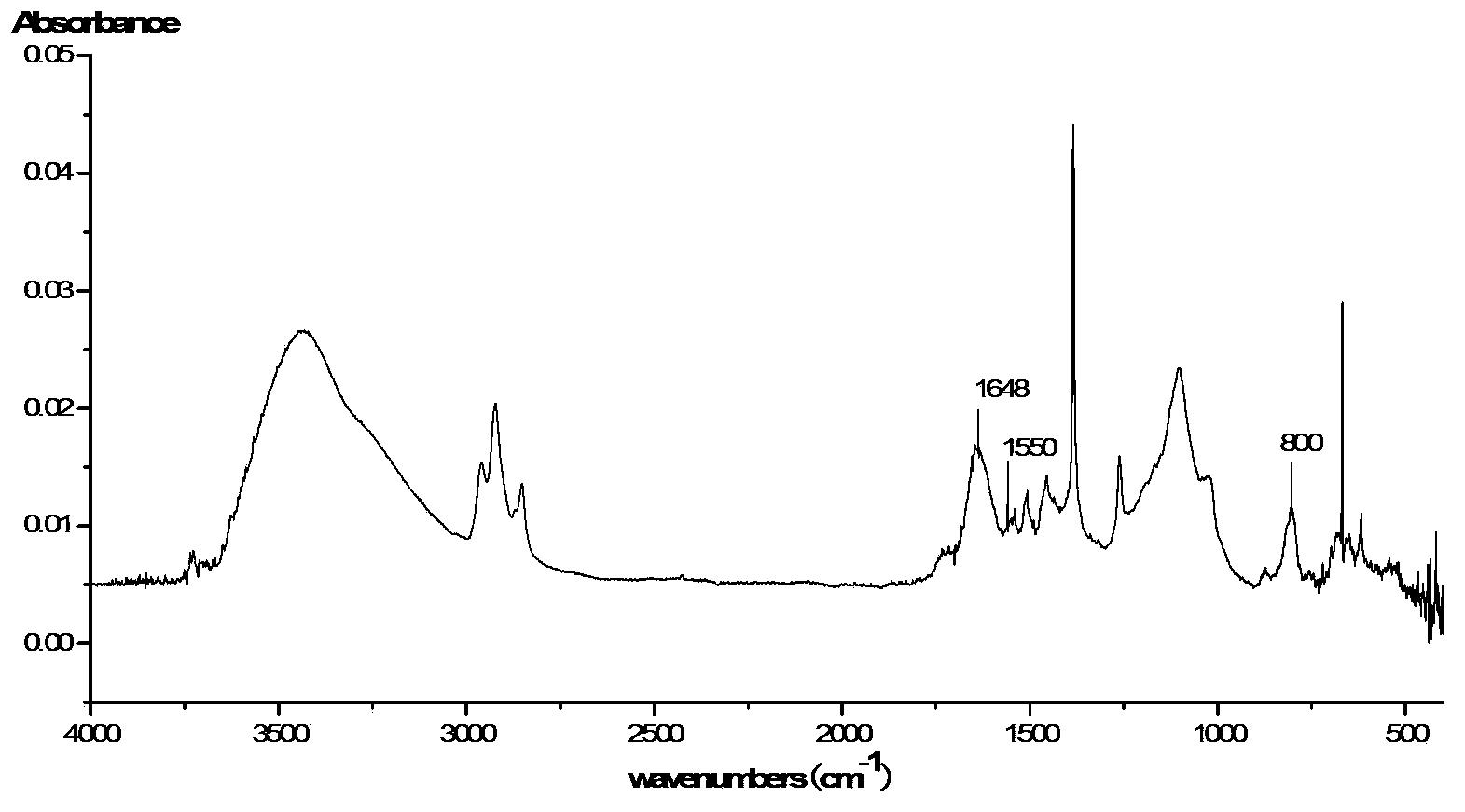
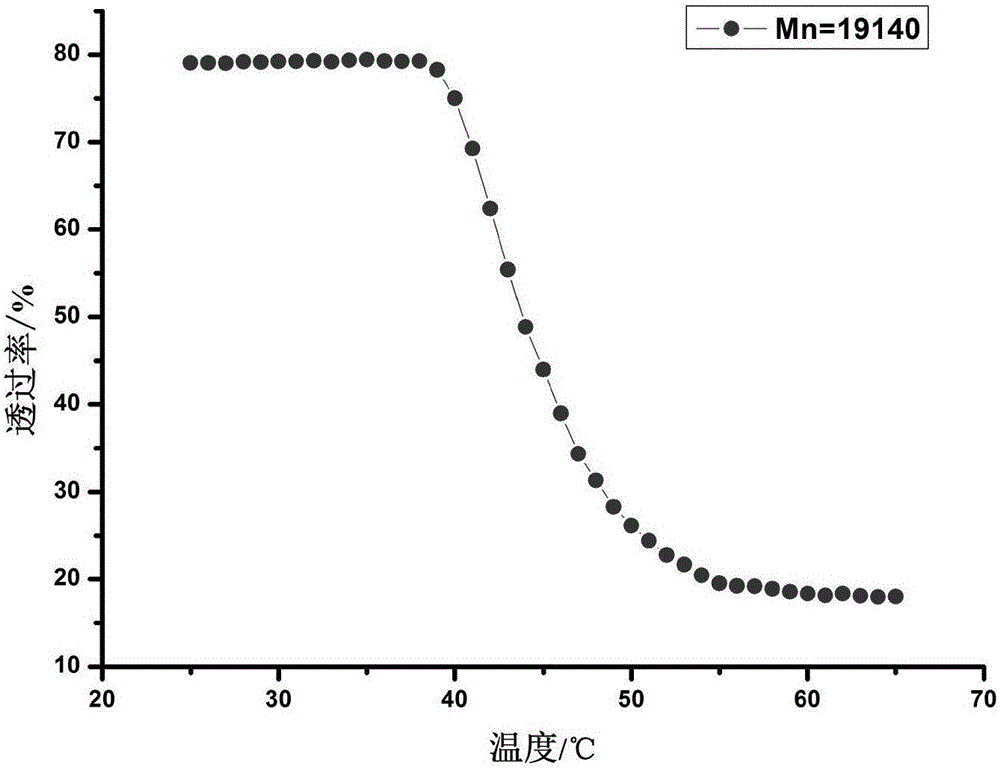
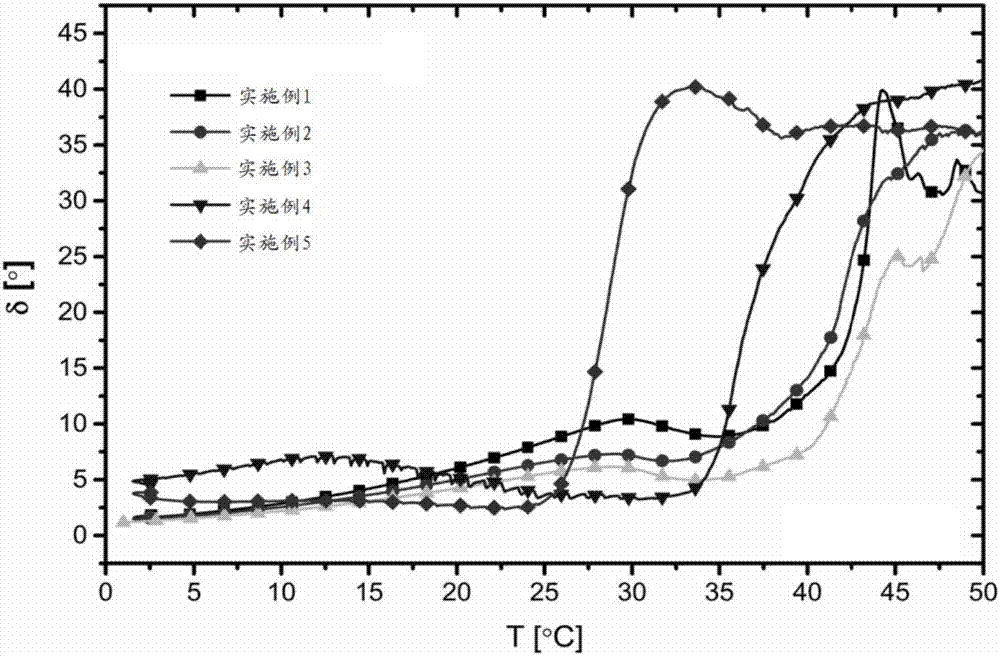
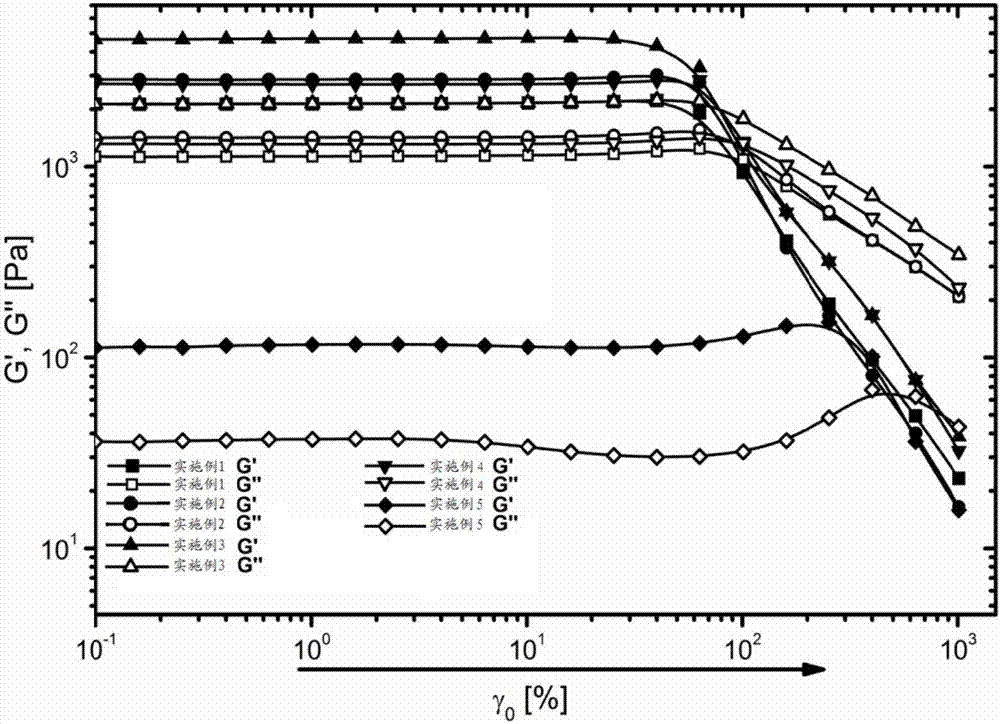
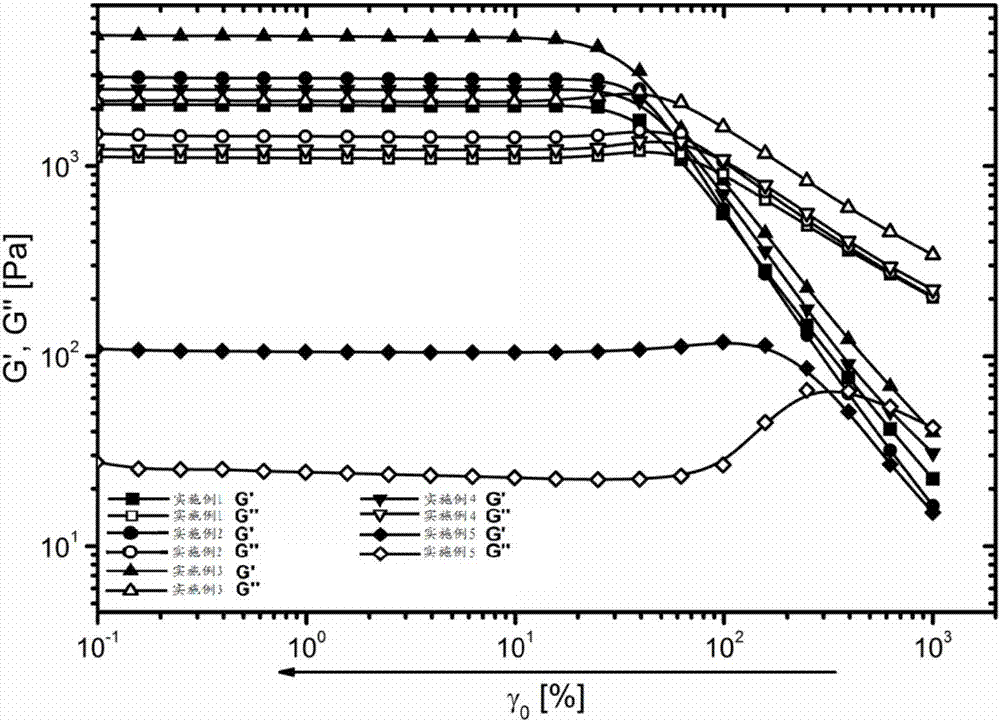
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (variously abbreviated PNIPA, PNIPAAm, NIPA, PNIPAA or PNIPAm) is a temperature-responsive polymer that was first synthesized in the 1950s. It can be synthesized from N-isopropylacrylamide which is commercially available. It is synthesized via free-radical polymerization and is readily functionalized making it useful in a variety of applications.
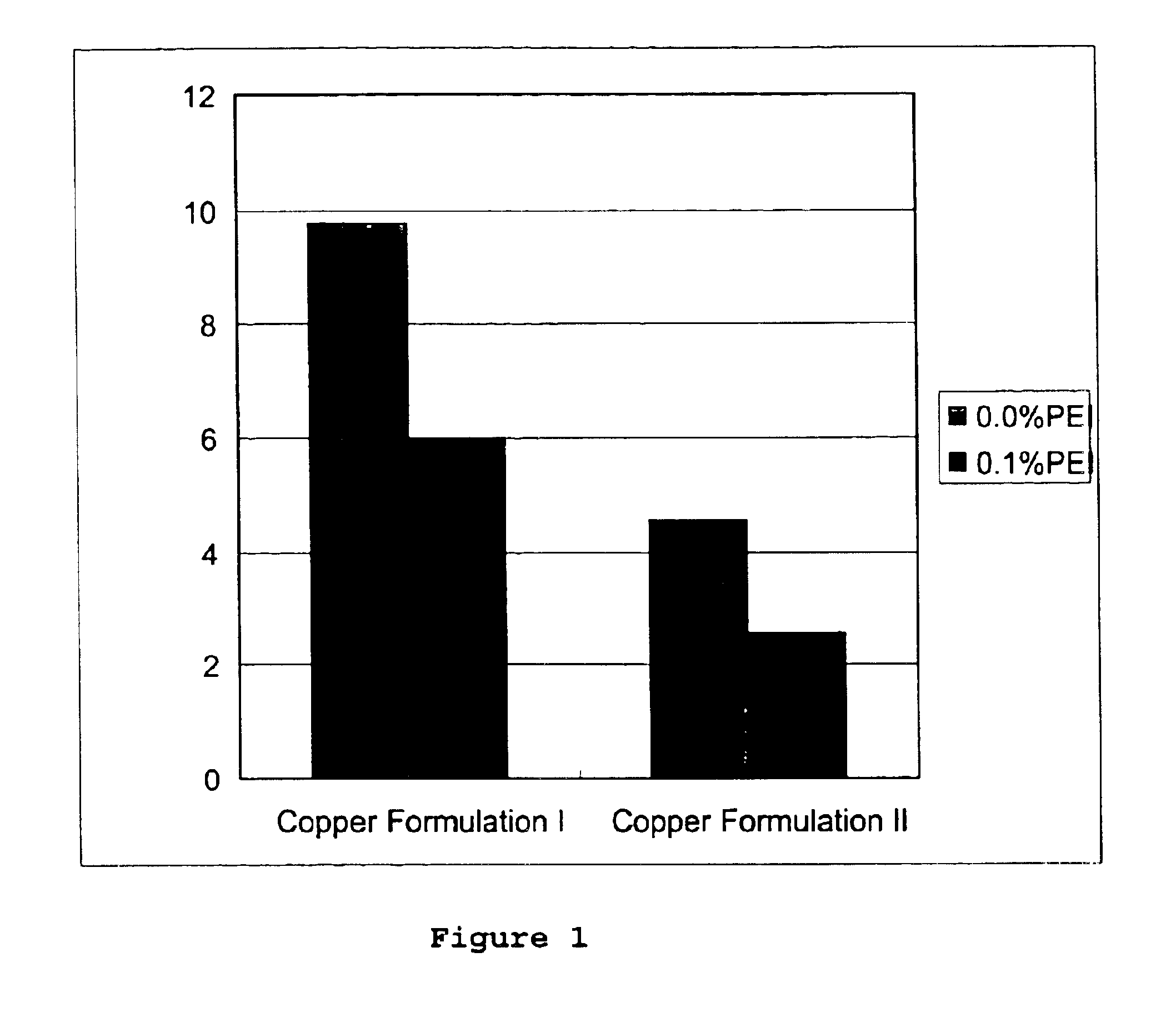
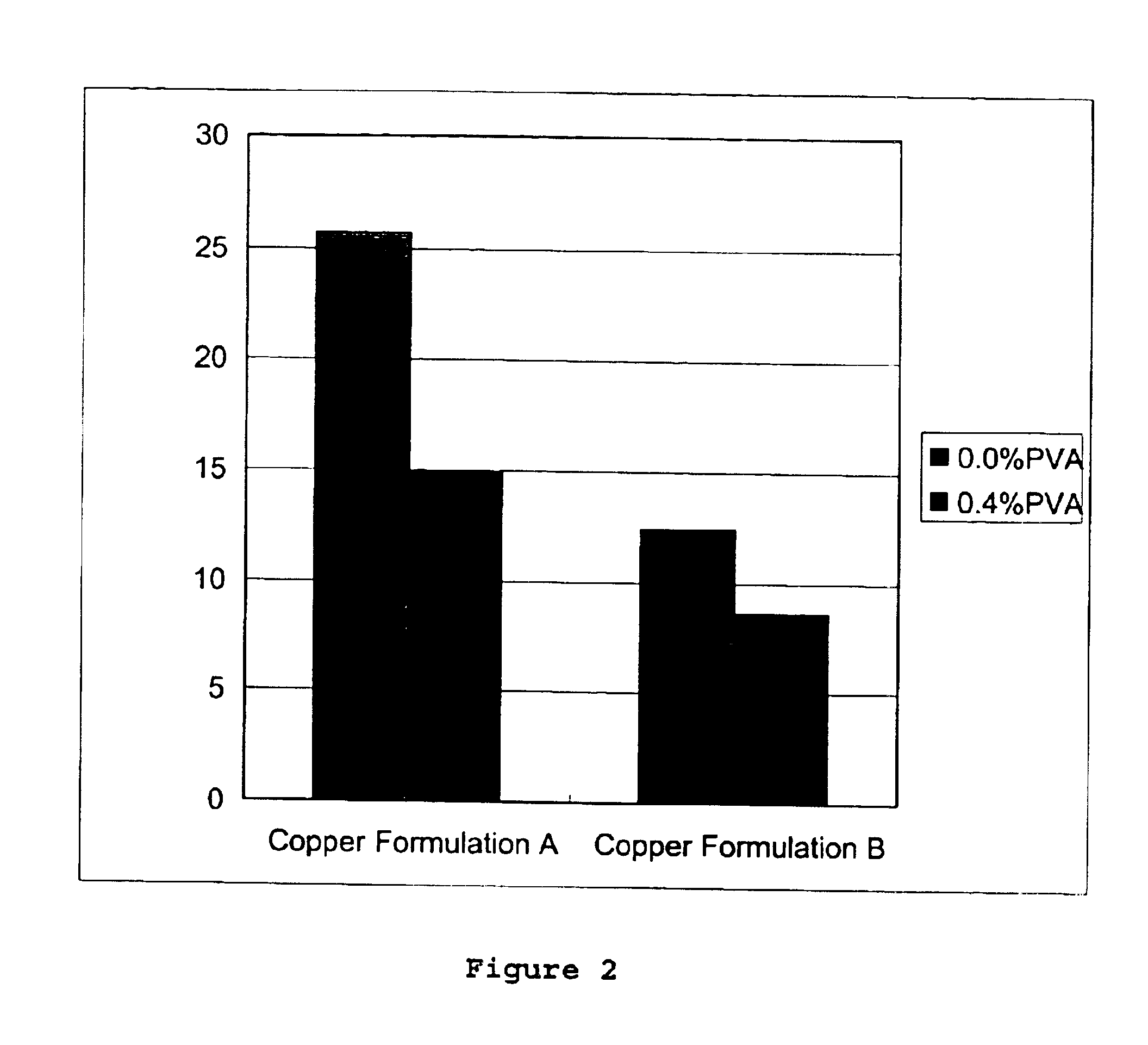
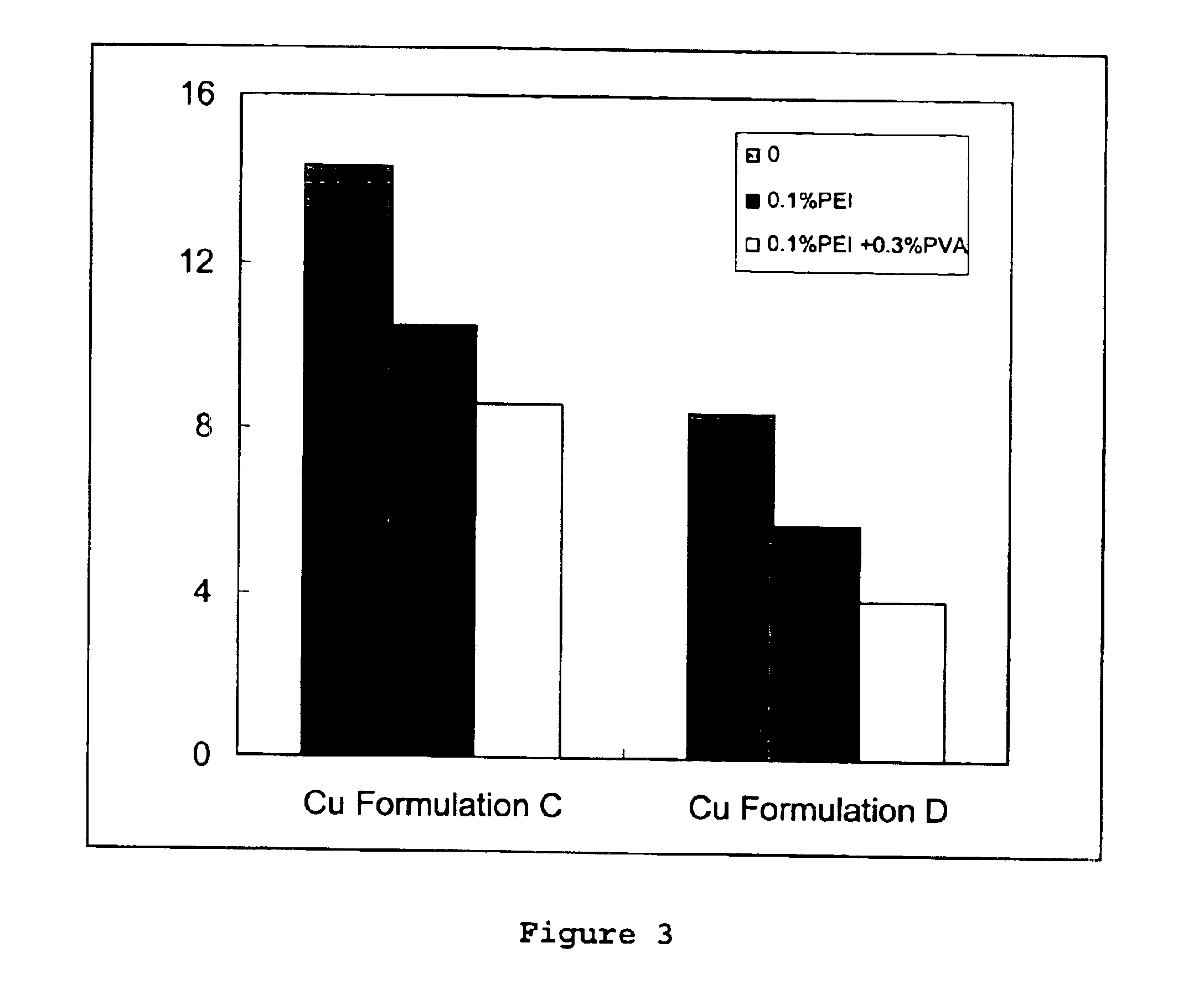
Polymeric wood preservative compositions
The present invention relates to a method and a wood preserving composition which comprises mixtures of a metal compound, complexing agents selected from ethanolamines, polyethylenimine, ammonia or a mixture of these compounds, and a vinyl based polymer selected from poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), poly(acrylamide) (PA), poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) and poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAM). The resulting metal amine solution can then be used to formulate a variety of metal-based cellulosic material preserving products.
Owner:OSMOSE
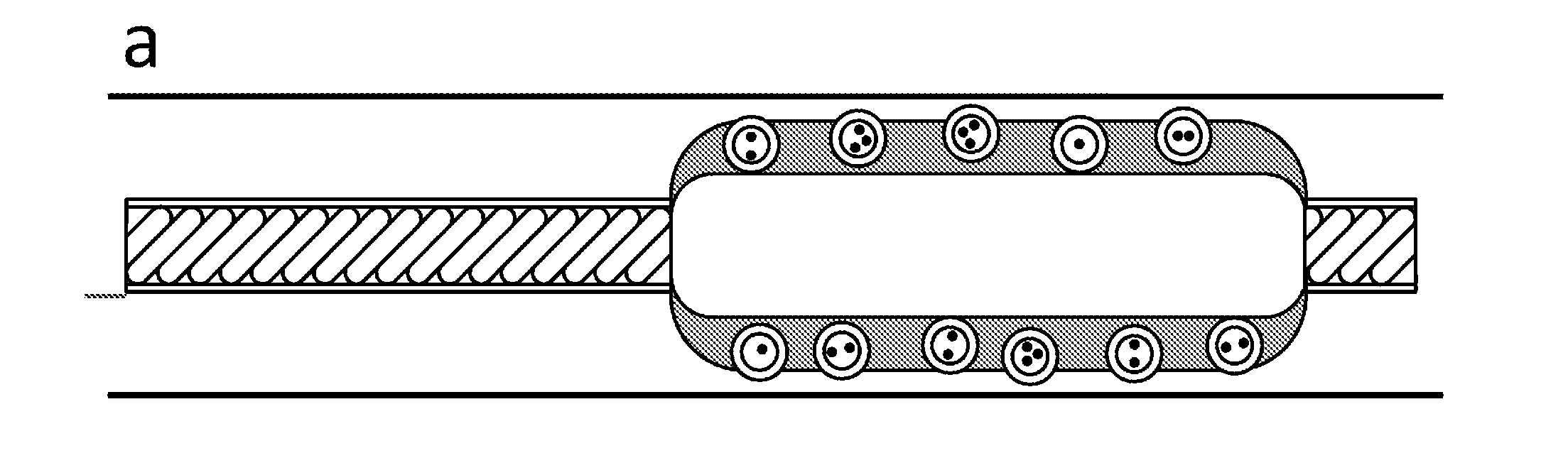
Balloon catheter comprising pressure sensitive microparticles
InactiveUS20120083734A1Improve brittlenessEffective treatmentSurgeryDilatorsPolyesterPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention provides a solution to the above mentioned problem in that it provides a catheter balloon comprising a flexible coating on its outer surface wherein a plurality of microparticles are contained wherein said coating comprises a material selected from the group consisting of poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone, poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone-co-butylacrylate), poly(-vinyl pyridine), polyacrylamides, e.g. poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(amido-amines), poly(ethylene imine), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide-block-ethylene oxide), poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene), poly(hydroxystyrene-block-isobutylene-block-hydroxystyrene), polydialkylsiloxanes, polysaccharides, polyacrylates and polyalkylmethacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein said microparticles comprise a material selected from the group consisting of polyesters, e.g. poly(lactic acid), poly(lactic-co-glycol acid), poly(glycolic acid), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxyvalerate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and polycaprolactone, polyamides, polysaccharides, polyurethanes, polyalkylmethacrylates and polyacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein the microparticles comprise a pharmaceutically active compound.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Carbon quantum dot-poly N-isopropylacrylamide composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102675565AStrong fluorescenceImprove performanceSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrowaveModified carbon
The invention discloses a carbon quantum dot-poly N-isopropylacrylamide composite material and a preparation method thereof. An N-isopropylacrylamide polymer is grafted to the surface of carbon quantum dots obtained by microwave treatment by adopting an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATPR) method. The preparation method is simple, convenient and mild in conditions. Modified carbon nano particles have fluorescence property and temperature sensitivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method, product and application of double-layer water gel with salt-temperature dual response
ActiveCN108395548AUniversalHigh sensitivity of spontaneous bending behaviorCross-linkFunctional monomer
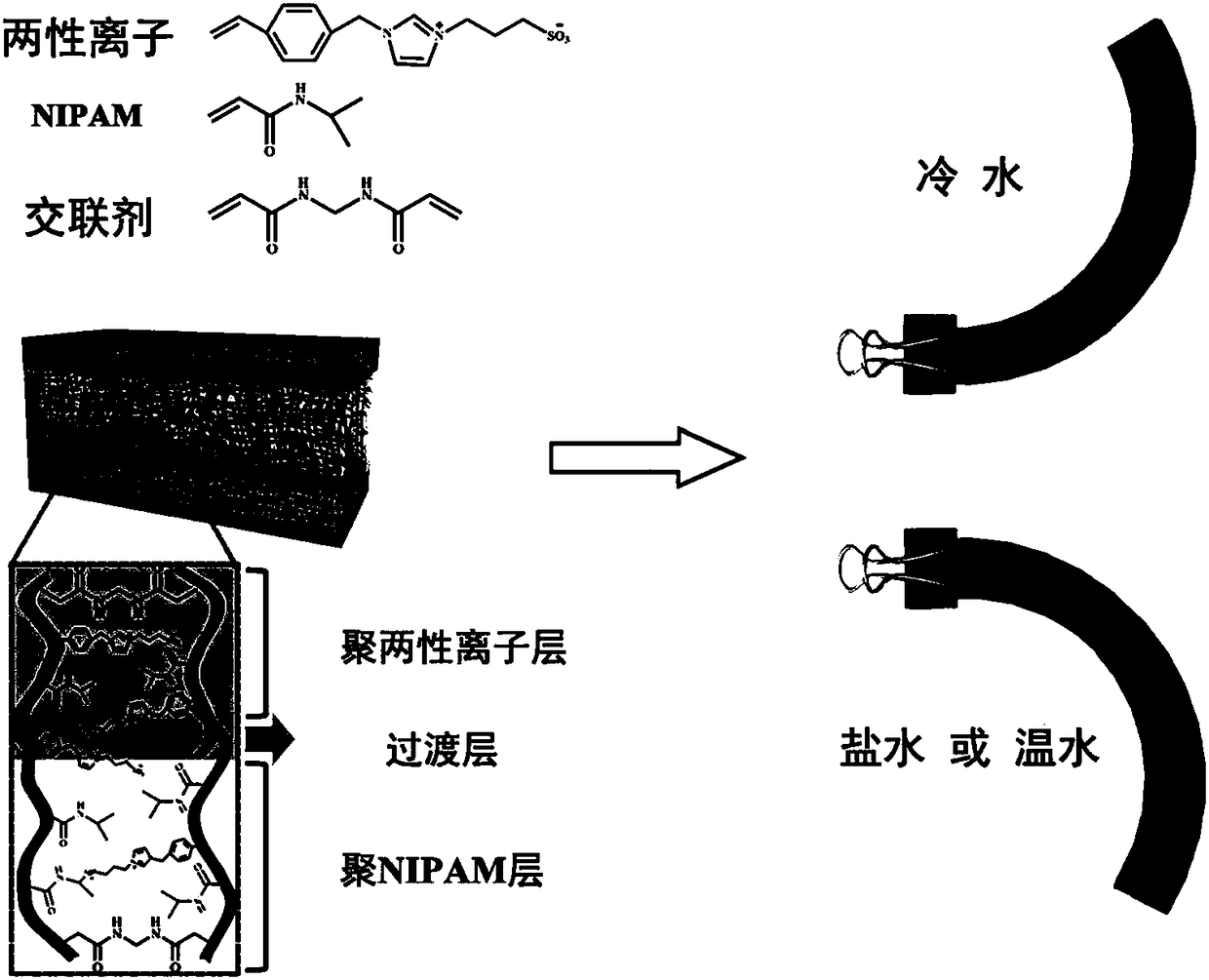
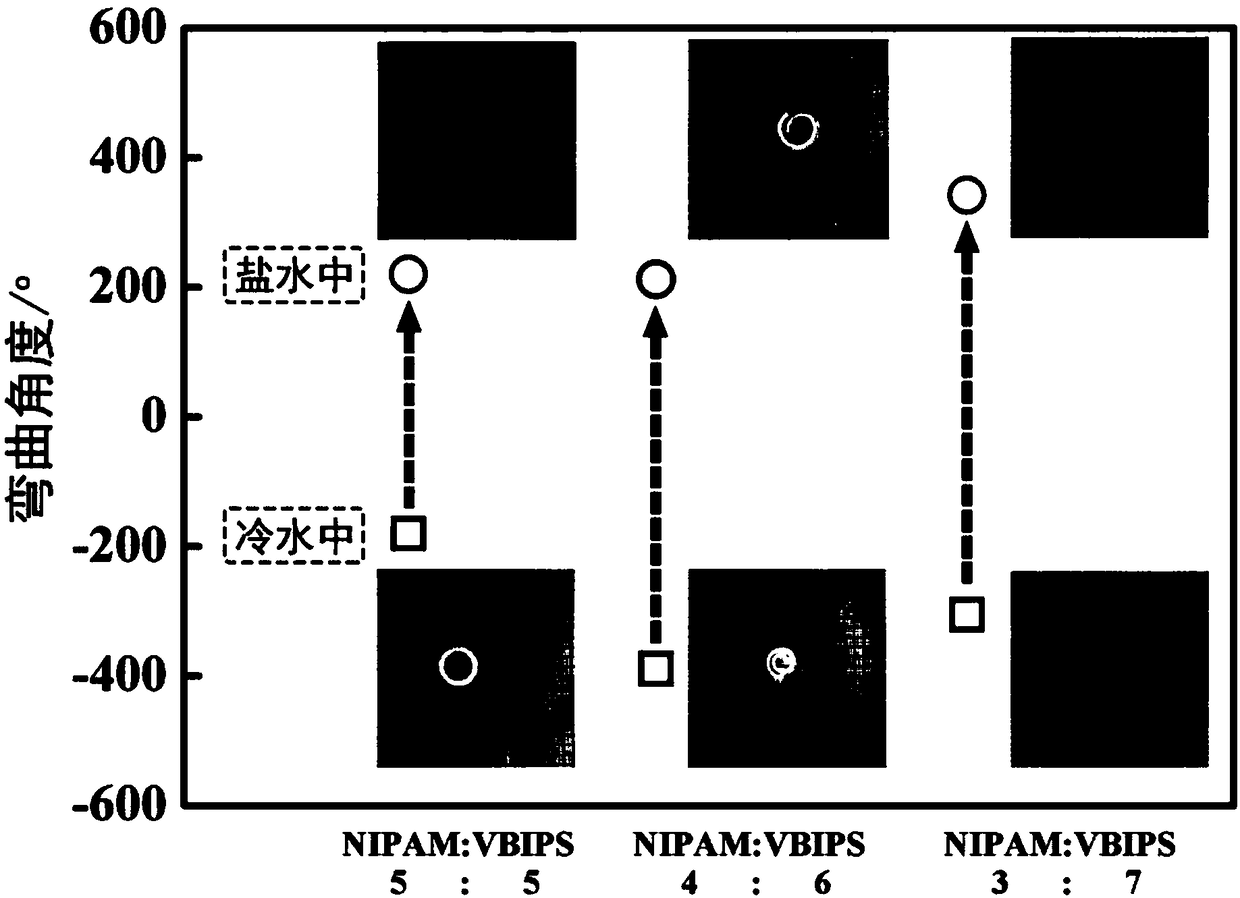
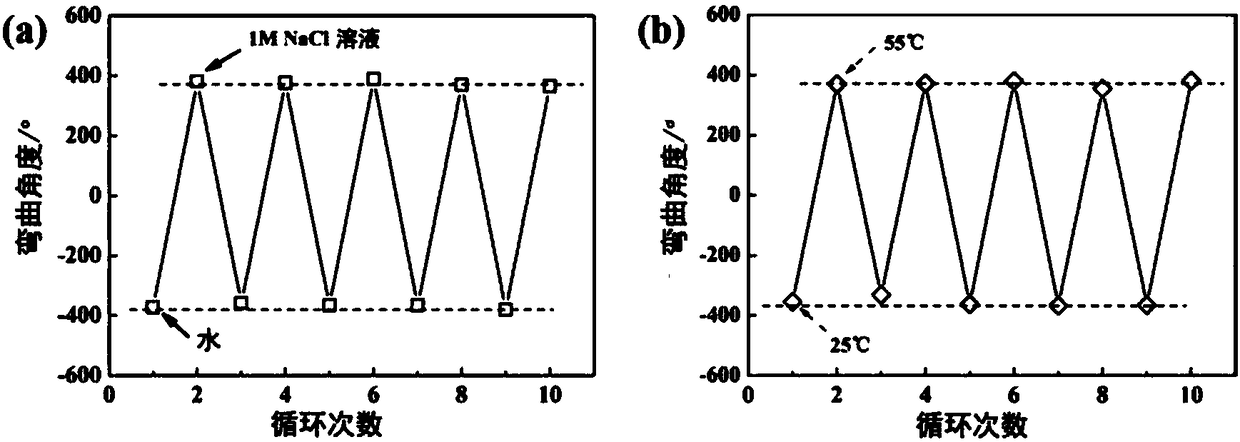
The invention discloses a preparation method of double-layer water gel with salt-temperature dual response. The method comprises the following steps of adding N-isopropylacrylamide, amphoteric ion monomers, cross-linking agents, photoinitiators, radical initiators and catalysts into water; performing stirring dissolution to obtain reaction liquid; performing polymerization reaction on the reactionliquid under inert gas protection and UV-irradiation; performing crosslinking for 1 to 5 hours to obtain poly-N-isopropylacrylamide and amphoteric ion polymer double-layer water gel. Great differences of two kinds of functional monomers in aspects of polarity and polymerization speed are utilized; the double-layer water gel with the salt-temperature dual response is prepared by a one-step method;the double-layer water gel can realize fast great-amplitude self periodic deformation in water-slat solution and low-temperature / high-temperature environment. The water gel can be used for being madeinto a soft body robot or sensor element realizing the salt-temperature dual response.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nanogels and their production using liposomes as reactors
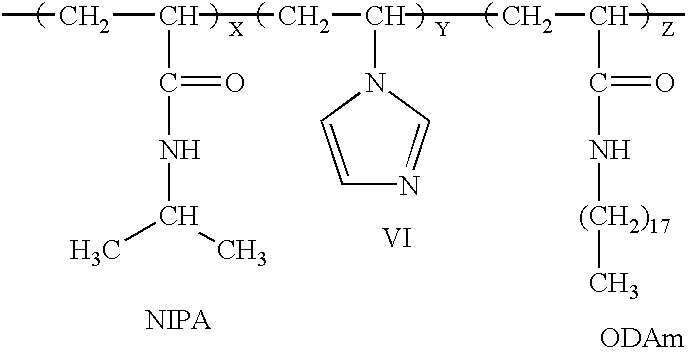
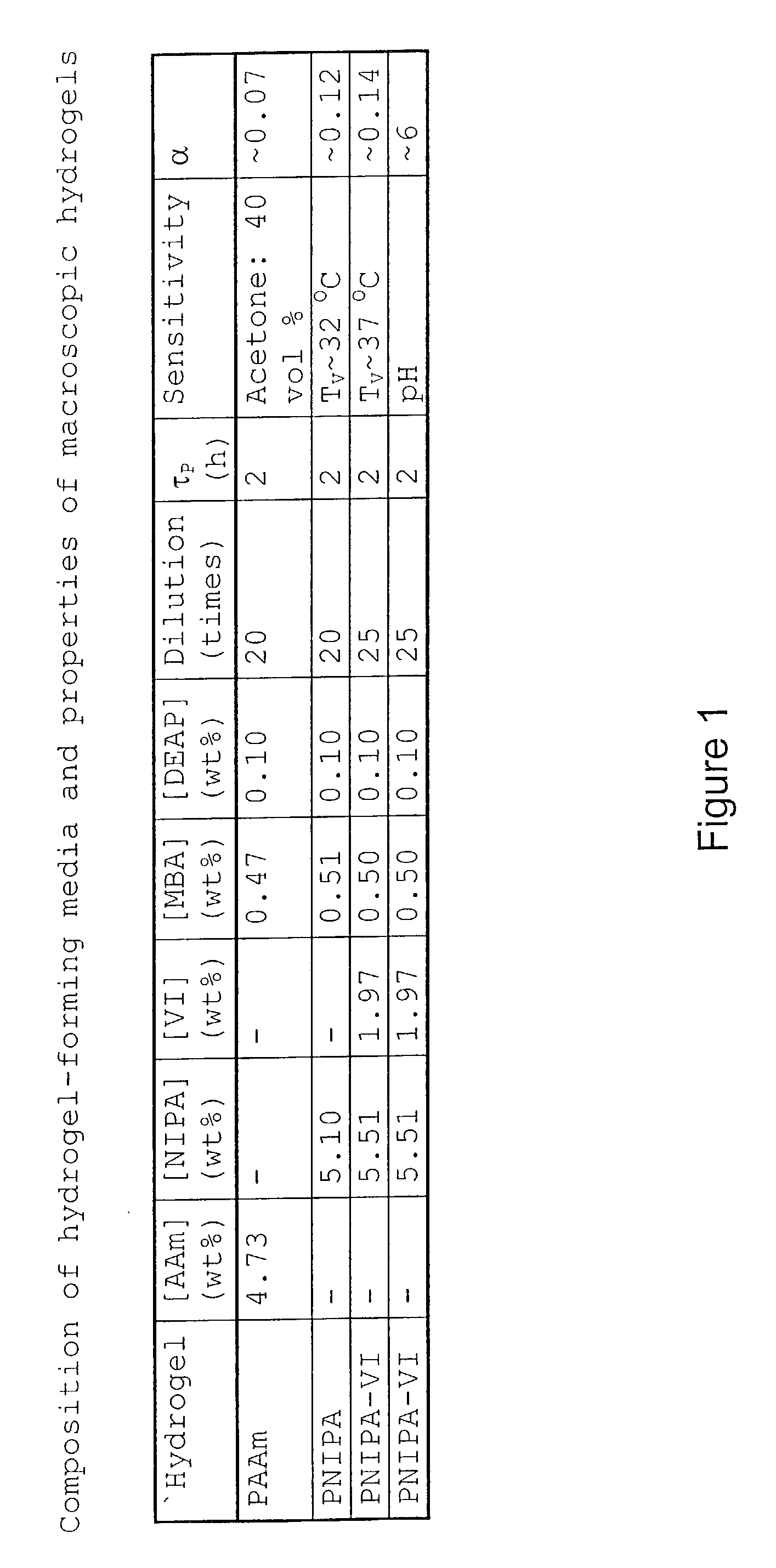
The present invention includes a method for preparing polymer hydrogel spherical particles on a nanometer scale (nanogels). The method includes encapsulating hydrogel-forming components into liposomes, diluting the large unilamellar liposomes suspension to prevent polymerization outside the liposomes, and polymerizing the encapsulated hydrogel-forming components. The lipid bilayer may be solubilized with detergent. The phospholipid and detergent molecules and their micelles may then be removed by dialysis. The resulting nanogels may then be dried by evaporation in a temperature gradient. Poly(acrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-1-vinylimidazole) hydrogel particles with a diameter from 30 to 300 nm were detected and characterized by dynamic light scattering technique. The solvent, temperature, pH, and ionic sensitivities of the nanogels were studied.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
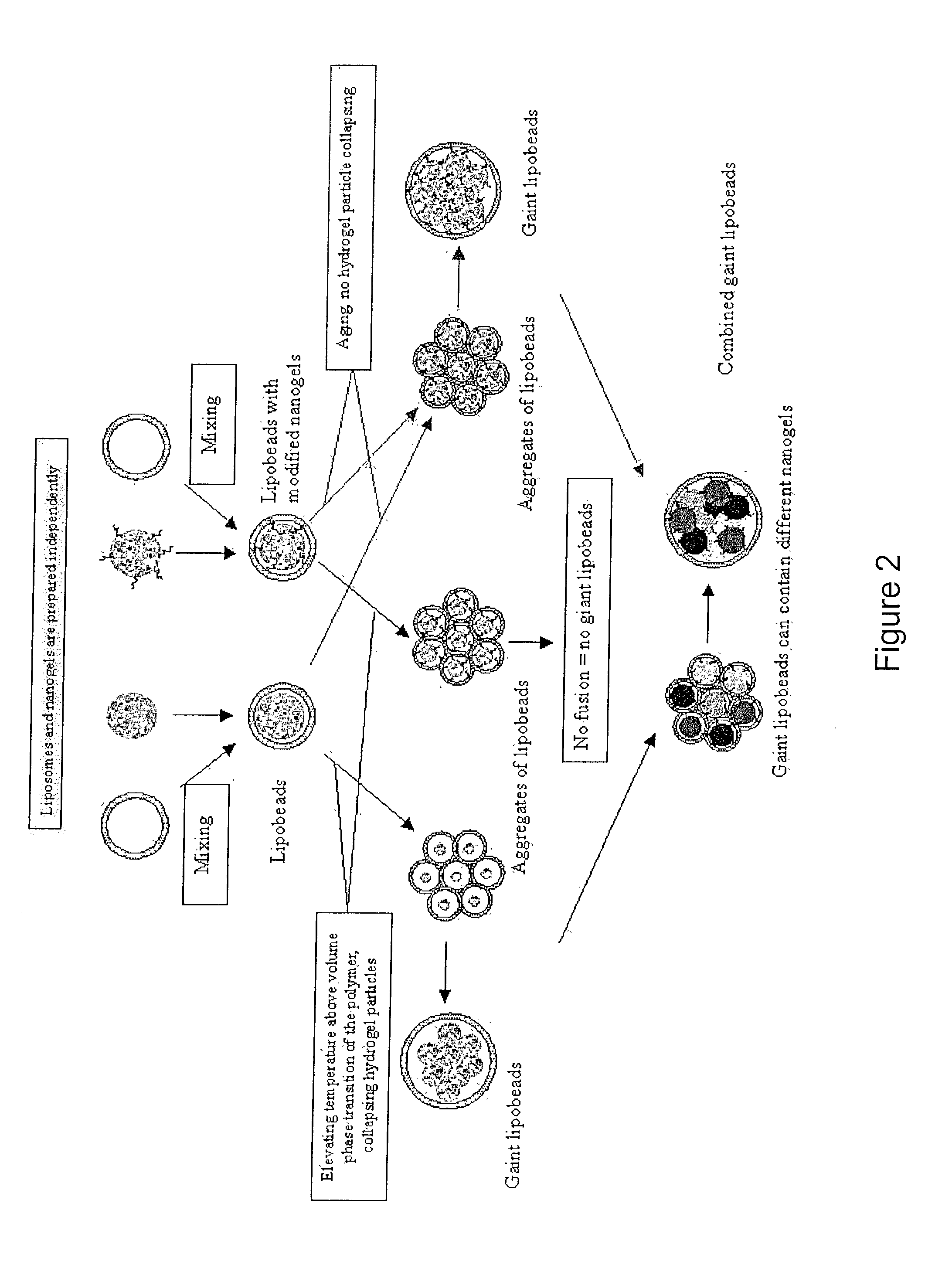
Lipobeads and their production
InactiveUS20030035842A1Easy to understandImpression capsLiquid surface applicatorsPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)Liposome
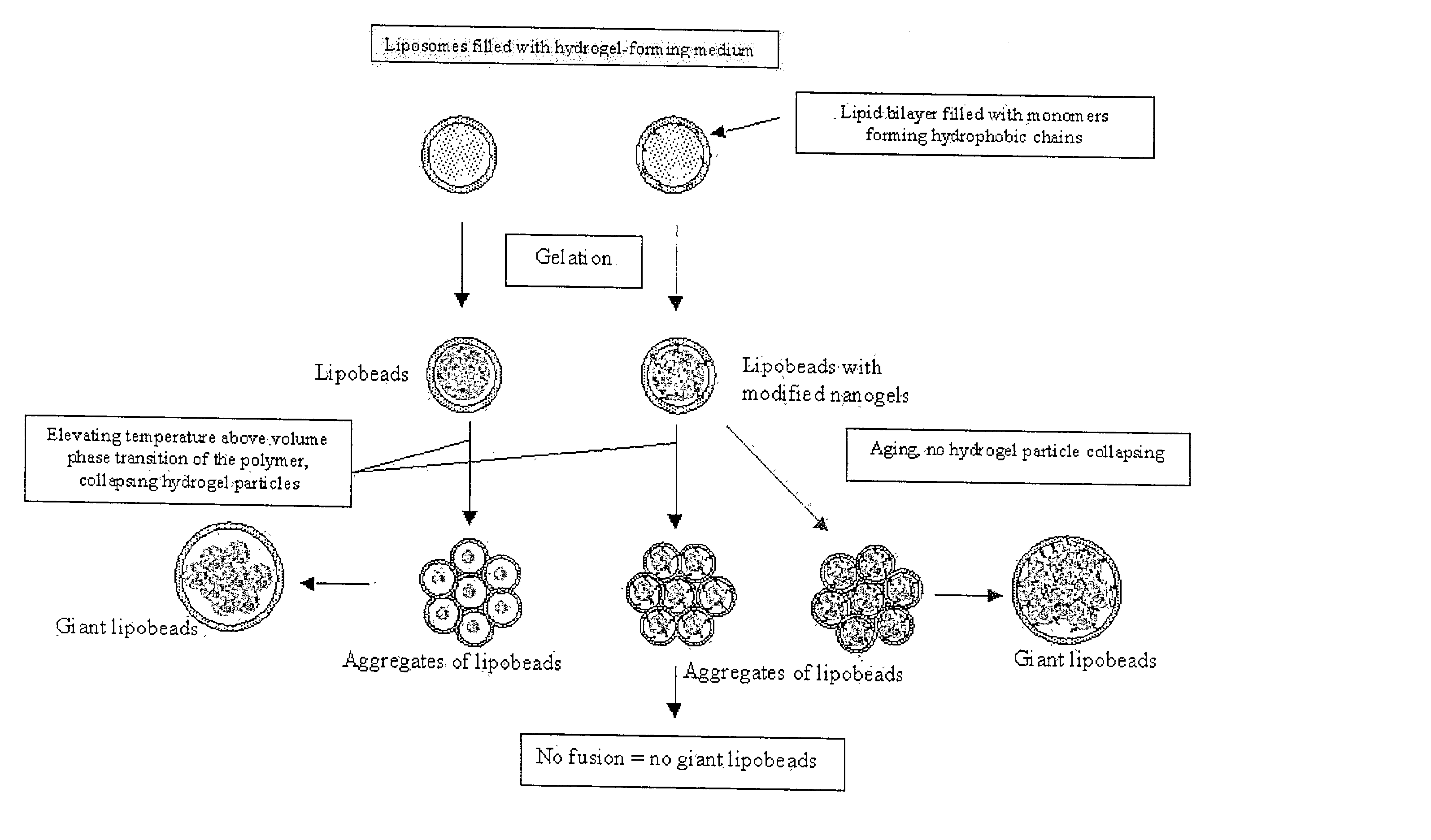
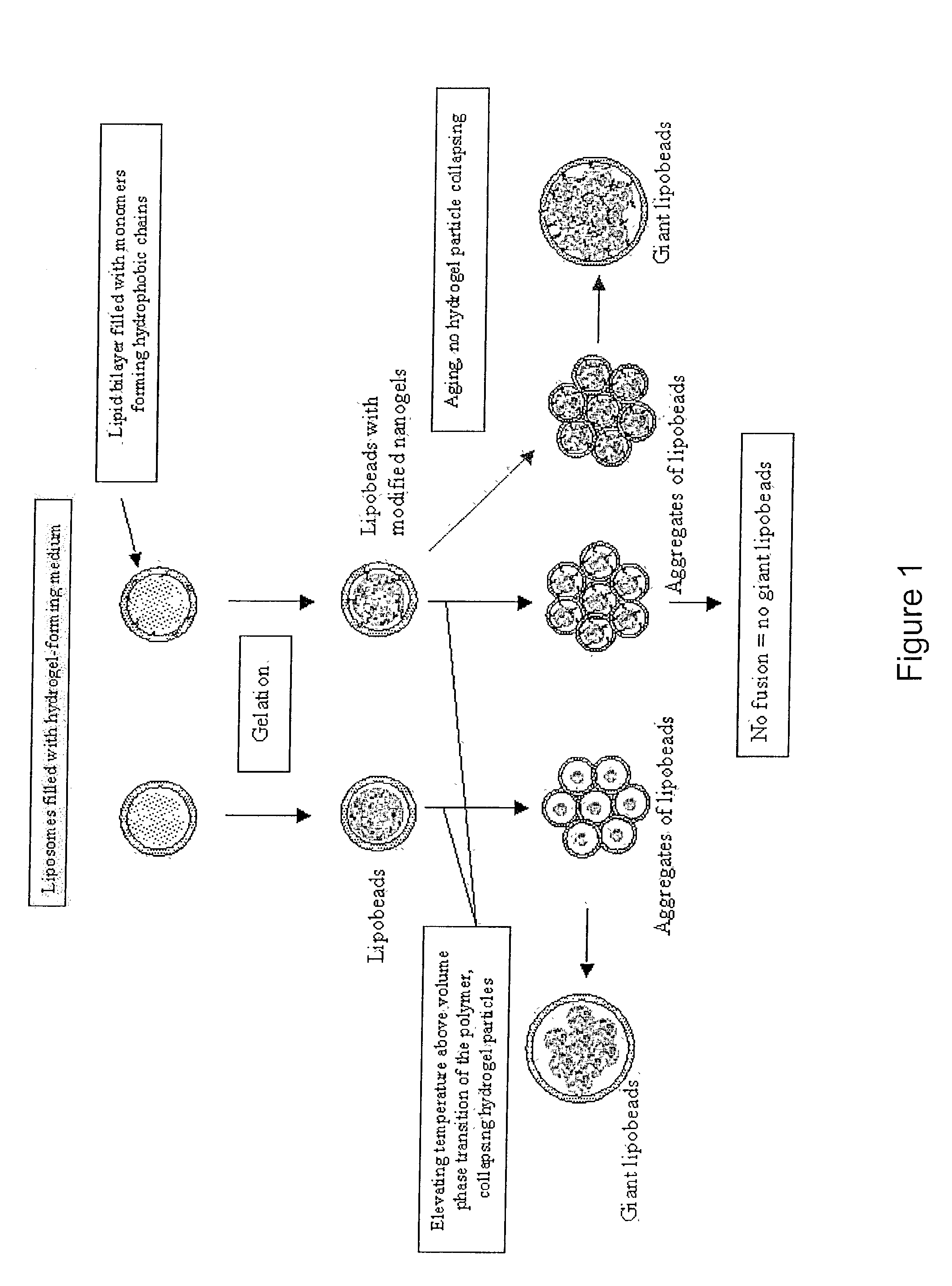
Lipobeads (liposome-encapsulated hydrogels) combine properties of hydrogels and liposomes to create systems that are sensitive to environmental conditions and respond to changes in those conditions in a fast time scale. Lipobeads may be produced by polymerizing anchored or unanchored hydrogels within liposomes or by mixing anchored or unanchored hydrogels with liposomes. Giant lipobeads may be produced by shrinking unanchored nanogels in lipobeads and fusing the resulting lipobead aggregates, long-term aging of anchored or unanchored lipobeads, or mixing anchored or unanchored aggregated nanogels with liposomes. Poly(acrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-1-vinylimidazole) lipobeads were produced and characterized.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
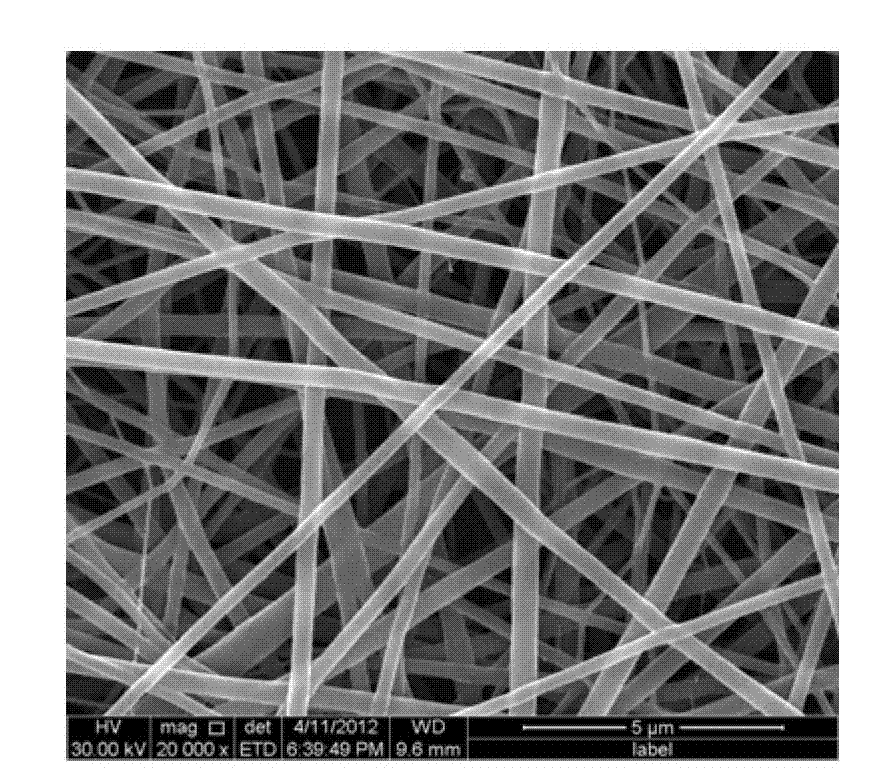
Thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropylacrylamide/polyurethane medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102733088ALarge specific surface areaHigh drug loadingOrganic active ingredientsFilament/thread formingN dimethylformamideElectrospinning
The invention relates to a thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropylacrylamide / polyurethane medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane and a preparation method thereof, relating to a medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane and a preparation method thereof and aiming to solve problems of poor mechanical property of existing poly N-isopropylacrylamide medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane and no temperature sensitivity of a polyurethane medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane. The thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropylacrylamide / polyurethane medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane is prepared by poly N-isopropylacrylamide, polyurethane, N,N-dimethylformamide and a medicine; the preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing static spinning solution; 2, dissolving the medicine so as to obtain the static spinning solution containing the medicine; 3, carrying out electrospinning; and 4, carrying out dry treatment to obtain the thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropylacrylamide / polyurethane medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane. According to the invention, the preparation method is mainly used for preparing the thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropylacrylamide / polyurethane medicine-loading electro-spun fibrous membrane.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
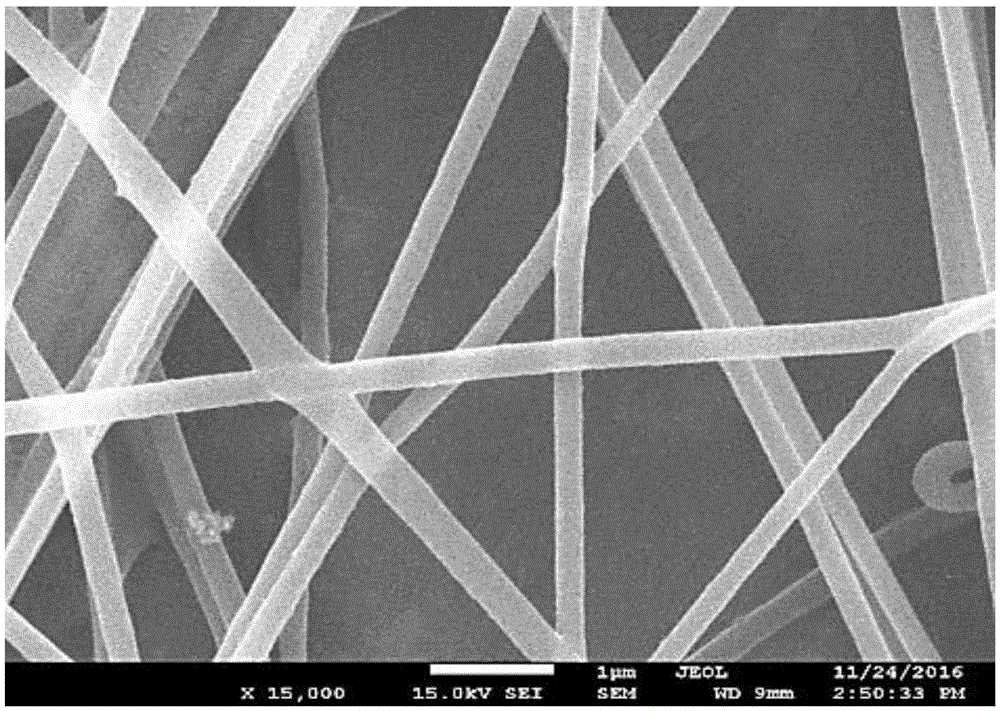
Temperature-sensitive antibacterial nanofiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106757520AImprove breathabilityImprove thermal performanceConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsAnimal fibresPolyethylene oxidePoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention provides temperature-sensitive antibacterial nanofiber. The temperature-sensitive antibacterial nanofiber is prepared by the following steps: adding N-isopropylacrylamide, chitosan, N,N-methylene bisacrylamide, an initiator and N,N,N,N-tetramethylethylenediamine into an acetic acid solution and performing free radical polymerization reaction to obtain chitosan / poly-N-isopropylacrylamide interpenetrating network hydrogel; mixing the chitosan / poly-N-isopropylacrylamide interpenetrating network hydrogen and an aqueous solution of polyethylene oxide to obtain electrostatic spinning liquid; performing electrostatic spinning on the electrostatic spinning liquid to obtain the temperature-sensitive antibacterial nanofiber. The temperature-sensitive antibacterial nanofiber provided by the invention has excellent antibacterial property and heat sensitivity.
Owner:EASTERN LIAONING UNIV
Poly L-glutamic acid-poly N-isopropylacrylamide graft copolymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101058641AGood biocompatibilityControl releasePoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)N isopropyl acrylamide
The invention discloses a two-block copolymer of poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide-polyamino acid and making method, which is characterized by the following: the number average molecular weight of poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide-polyamino acid is 1000-10000; the polyamino acid is poly-L-glutamic acid or poly-L-aspartic acid with number average molecular weight at 1000-30000; the molar percentage of amino acid carbobenzoxy is 0-90%; the invention uses hydrogen bromide or reducing method to strip benzyl through catalyzing and hydrogenating to obtain the product, which possesses double response for temperature and pH value in the solution; the copolymer can be biological decomposed to be discharged out of body through kidney directly, which can be carrier of target drug release and injectable intellectual response aquagel.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Method for preparing high-strength hydrogel with macromolecular microgel composite structure
ActiveCN102675549ASimple processEase of industrial productionPolymer sciencePoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-strength hydrogel with a macromolecular microgel composite structure. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding 10 to 20 mmol of N-isopropylacrylamide serving as a first monomer, 0.4 to 0.8 mmol of cross linker, 0.5 to 1.0 g of surfactant and 0.1 to 0.2 mmol of initiator into every 100 mL of water; adding the N-isopropylacrylamide, the cross linker, the surfactant, the initiator and the water into a reaction container, mixing uniformly, charging nitrogen to remove oxygen, sealing the reaction container, reacting for 10 to 60 minutes with stirring at the temperature of between 40 and 60 DEG C, and cooling the reaction product to the temperature of below 20 DEG C by using cooling water of below 15 DEG C; and (2) adding poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel aqueous dispersion prepared in the step (1) and a second monomer into the reaction container, charging nitrogen to remove oxygen after the second monomer is dissolved and mixed uniformly, sealing the reaction container, reacting for 24 to 48 hours at the temperature of between 0 and 25 DEG C, and thus obtaining the high-strength hydrogel with the macromolecular microgel composite structure, wherein the ratio of the volume of the poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel aqueous dispersion to the mass of the second monomer is 2: (0.1-0.5).
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation of easily stripped off temporary wound dressing materials by radiation grafting
InactiveUS6022330APromote absorptionGood compatibilityPlaster of paris bandagesAbsorbent padsWound dressingPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
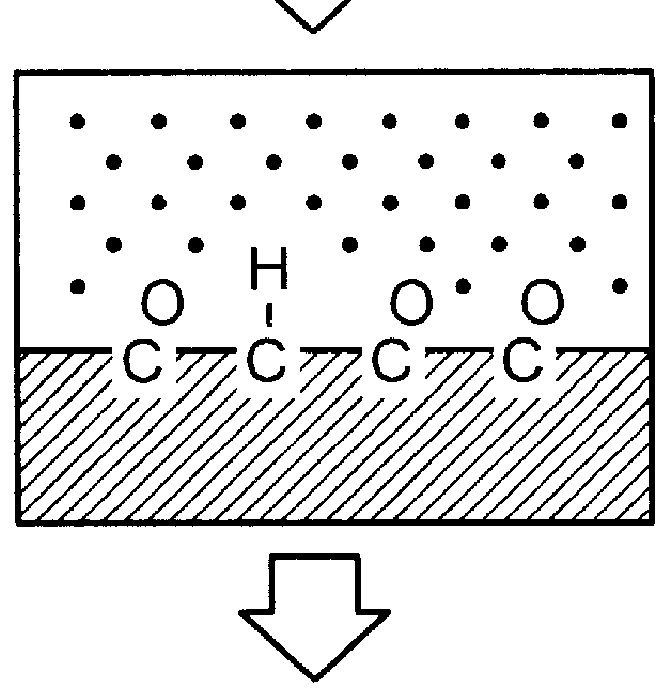
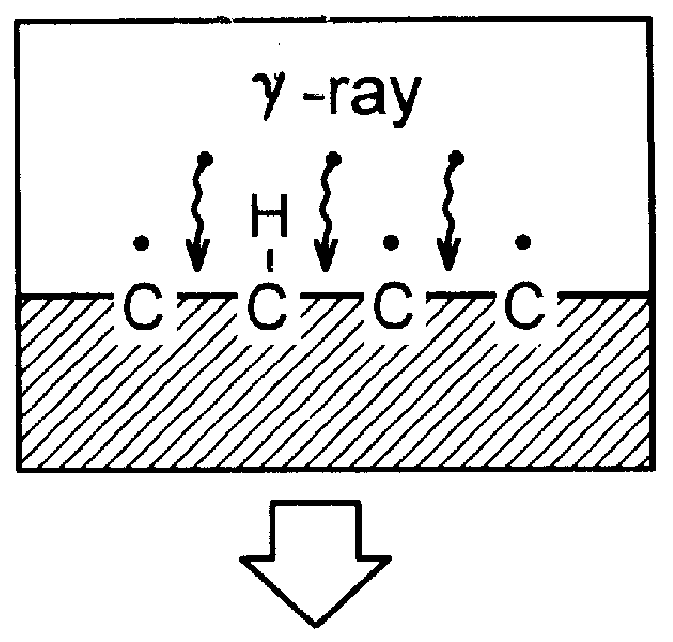
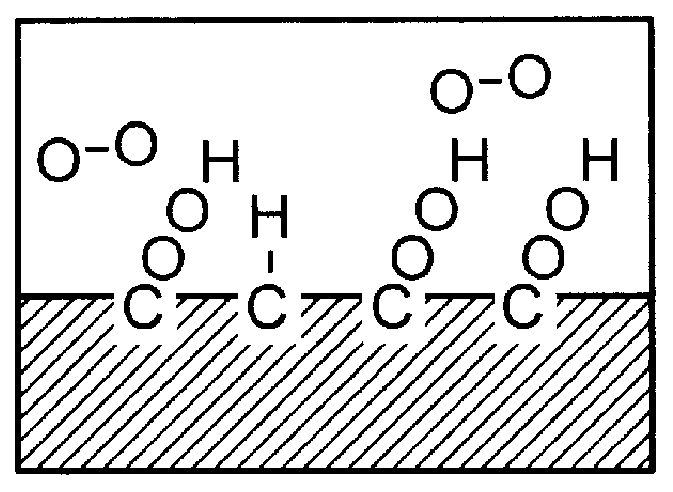
A novel method of preparation of easily stripped off temporary wound dressing material is disclosed. In this process, the-N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAAm) monomer is successfully grafted on the non-woven cloths by copolymerization. It is initiated by gamma -ray irradiation to activate the surface of the non-woven cloth. NIPAAm is then grafted onto the surface of the non-woven cloth. The free radical or peroxide is produced by Co-60 gamma -ray, then grafted on the non-woven cloths. The lower critical solution temperature (LCST) in thermoresponsive poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm) is still retained after the grafting. This will make the dressing cloth stripped off easily and without hurting the tissue. The material process is very simple and has medically applicable value.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
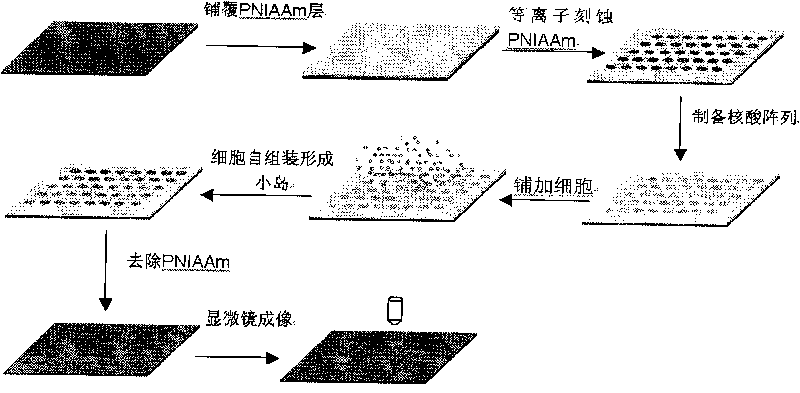
Nucleic acid chip, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101696449ASolve the real problemLow costSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)Apoptosis
The invention relates to a nucleic acid chip and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the detection field of enzymes, microorganisms or nucleic acid molecules. The nucleic acid chip comprises a substrate, nucleic acid molecules are attached to a part of the surface of the substrate; a region of the substrate without the nucleic acid molecules is covered with a material capable of inhibiting cell growth; the material can be a non-biocompatible material, such as poly-N-isopropylacrylamide, polyvinyl caprolactam, polyacrylic acid, chitosan, sodium alginate, and the like or be DNA, siRNA, esiRNA, plasmid, and the like. The nucleic acid chip is particularly suitable for researching functional gene screening aspects, such as cell proliferation, cell differentiation, apoptosis, cell migration, and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU GENOARRAY
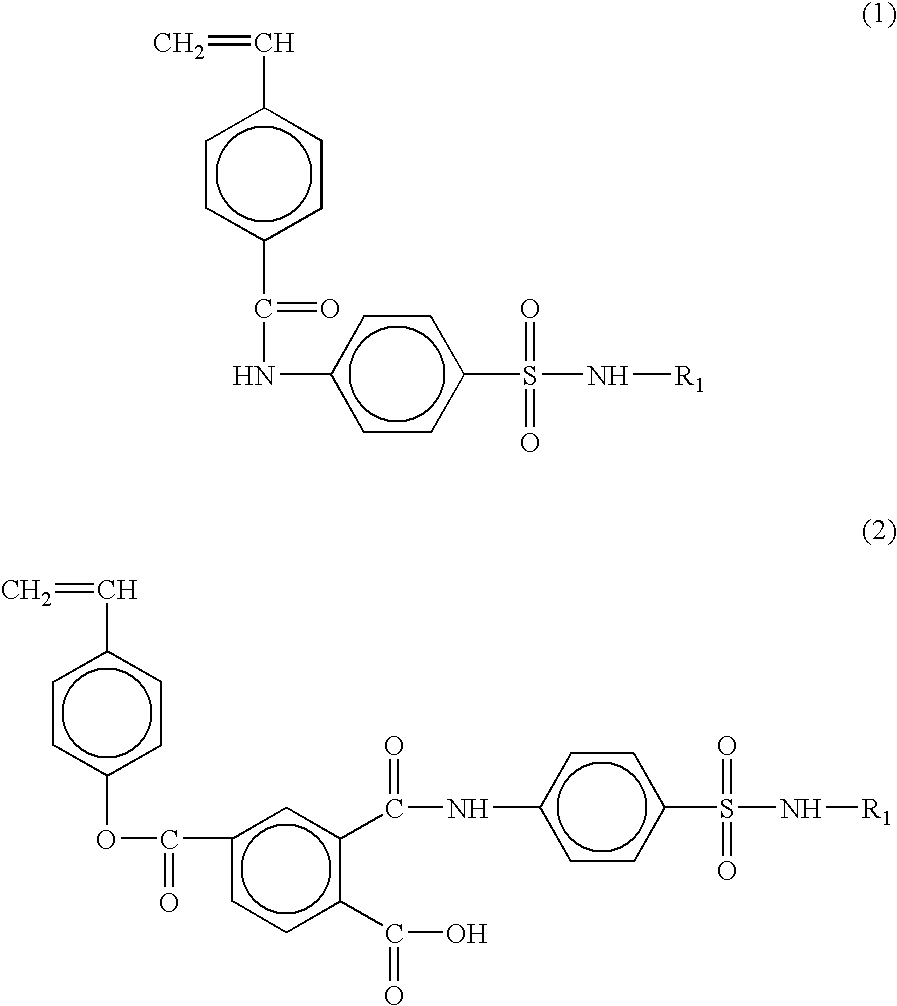
Dual stimuli-responsive hydrogels and their synthetic methods
The present invention relates to a process for preparing copolymer hydrogels with controlled molecular weights and having both thermo- and pH-responsive properties, wherein the process comprises the steps of (a) providing sulfonamide type styrenic or (meth)acrylamide-based monomers exhibiting different pKa values; (b) providing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) or crosslinked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methylene bisacrylamide) hydrogels having thermo-responsive properties; and (c) providing several hydrogels exhibiting pH-sensitive properties and random or block copolymerizations of the sulfonamide type styrenic or (meth)acrylamide-based monomers prepared in step (a) with N-isopropylacrylamide and / or methylene bisacrylamide monomers used in step (b) in a polar or non-polar solvent; wherein said steps (b) and (c) are carried out by controlled / living radical polymerization using alkyl halides as the initiators and the transition metals with phosphine or amine ligands as the catalysts. The present invention also relates to the copolymer hydrogels made by the aforesaid process.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Preparation method for monodisperse hollow silicon dioxide nanosphere with controllable size and shell thickness
InactiveCN103359743AThickness is easy to controlEasy to prepareMaterial nanotechnologySilicaEmulsionEmulsion polymerization
The invention discloses a preparation method for a monodisperse hollow silicon dioxide nanosphere with the controllable size and shell thickness. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing poly-N-isopropylacrylamide by polymerizing an N-isopropylacrylamide monomer with soap-free emulsion under an oxygen-free condition at 60-80 DEG C; after mixing the prepared poly-N-isopropylacrylamide emulsion with prehydrolysis solution of tetraethoxysilane at 40-60 DEG C, carrying out a thermostatic reaction for 48-96 hours, and obtaining the monodisperse hollow silicon dioxide nanosphere after separating and calcining. The preparation method is simple and controllable, and the water is taken as the solvent in each reaction, so that the preparation method is green and environment-friendly; the obtained hollow silicon dioxide nanosphere is of a monodisperse structure, the size is 100-500 nm, the shell thickness is 30-100 nm, and the size and the thickness are both controllable, so that the method can be widely applied to the fields of medical controllable slow release, catalysis, microcapsules and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for adsorbing uranium by using macroporous poly-N-isopropylacrylamide/chitosan semi-interpenetrating network temperature-sensitive hydrogel
InactiveCN104645946AImprove adsorption capacityLarge adsorption surface areaOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCross-linkDesorption
The invention relates to a method for adsorbing uranium by using macroporous poly-N-isopropylacrylamide / chitosan semi-interpenetrating network temperature-sensitive hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: by utilizing emulsion polymerization means, taking Span-80 as an emulsifier, taking N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide (MBA) as a cross-linking agent, taking ammonium persulfate (APS) as an initiator, and taking N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) as an accelerant, preparing the macroporous poly-N-isopropylacrylamide / chitosan semi-interpenetrating network temperature-sensitive hydrogel under certain conditions, and researching and measuring the adsorption performance of the hydrogel on uranium. Compared with the traditional gel and pore-free gel, the hydrogel disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high mechanical strength, good swelling properties, large adsorption surface area, controllable adsorption and desorption processes, high uranium adsorption quantity and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Cell sheet engineering and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101629162AGet the effect of graftingNo deformation damageTissue cultureProsthesisPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)Cell sheet
The invention belongs to the field of tissue engineering, in particular to a cell sheet engineering and a preparation method thereof. The cell sheet is prepared with the following methods: firstly, an electron accelerator is used for radiating on the surface of the cell culture supporter for synthesizing poly-N-isopropylacrylamide; then, temperature is controlled to cause the poly-N-isopropylacrylamide to be hydrophobicity phase, and cells are cultured on the phase; temperature is changed to cause hydrogel to be hydrophilic phase; with the method that a polymeric membrane is used for adsorbing or a clamp is used for clamping to separate the cell sheet engineering. Obtained cell sheets are cultivated by multiple stratification, or protein adhering liquid is used for adhering to obtain multiple layers of cell sheets. The cell sheet obtained by the invention can keep desmosome structure between cells, ZO-1 tight connection structure and the connection structure between other cells, can keep basement membrane protein and a plurality of components thereof relative to adhesion, such as integrin and the like and has certain strength.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Culture apparatus used for temperature sensitive cells, preparation method thereof and cell culturing method
InactiveCN103436444AReduce deathAvoid damageSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTissue/virus culture apparatusCell-Extracellular MatrixCulture cell
The invention provides a culture apparatus used for temperature sensitive cells, a preparation method thereof and a cell cultureing method. The culture apparatus used for temperature sensitive cells comprises a polystyrene body; and the polystyrene body is grafted with a polystyrene-poly N-isopropylacrylamide block polymer. Compared with existing technologies, when the culture apparatus used for temperature sensitive cells is used for cell culturing, it is possible to obtain complete cultured cell layers and extracellular matrixes from deposition of the culture cell layers without damage by simple temperature variation, digestion by pancreatic enzyme or dissociation by chemical reagents is avoided, the death of cells is reduced, damages to the extracellular matrixes are lessened, and quality and activity of the cultured cells are improved.
Owner:上海瀚正生物技术有限公司
SERS (surface enhanced Raman scattering) device, as well as preparing method and application thereof
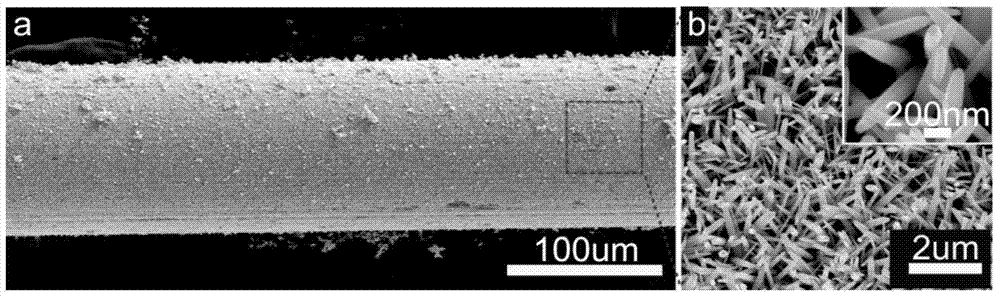
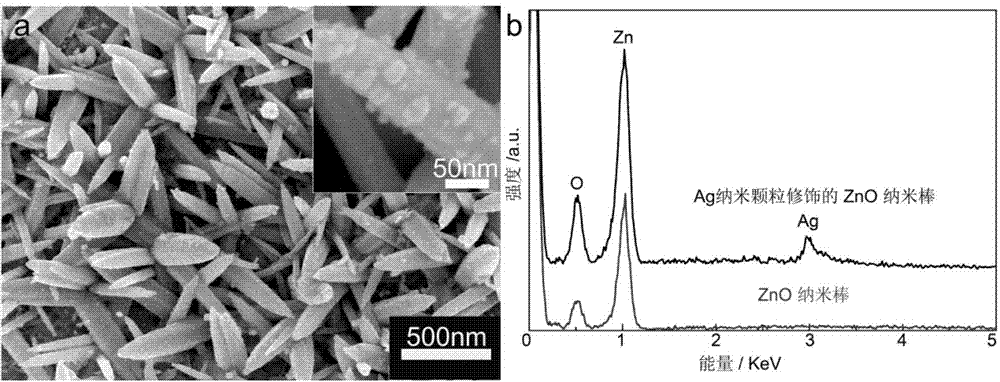
InactiveCN103674928AEfficient detectionAdjustable spacingRaman scatteringPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)Zinc oxide nanorod
The invention discloses an SERS (surface enhanced Raman scattering) device, as well as a preparing method and application thereof. The device comprises a capillary tube with a mixing colloid and an active substrate both arranged therein, wherein the mixing colloid consists of poly-(N-isopropyl acrylamide), gold nanorods and water with the weight ratio of (1.8-2.2):(0.001-0.003):(100); the active substrate adopts the structure that tapered zinc oxide nanorods with silver nanoparticles modified surfaces are stood on the surface of a heating wire. The method includes the following steps: adding ammonia water in a zinc nitrate hexahydrate solution, and obtaining an electric precipitating solution after the ammonia water is completely dissolved; using the heating wire as a cathode and placing the heating wire in the solution for electric precipitation, so as to obtain the heating wire with tapered nanorods stood on the surface; then immersing the heating wire with the tapered nanorods stood on the surface in a silver nitrate solution and irradiating the heating wire by ultraviolet light, so as to obtain an active substrate; then placing the active substrate and the mixing colloid in the capillary tube, so as to prepare the target product. According to the invention, the SERS device can be widely applied in real-time detection of pollutants in water solutions in environmental, chemical, biological fields and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermal response-type ultrafine fiber film material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101704933AGood biocompatibilityImprove breathabilityFilament/thread formingMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentTemperature responseFiber
The invention discloses a thermal response-type ultrafine fiber film material and a preparation method thereof. The formula of the material comprises the following components in mol percentage content: 93-98% of poly-N-isopropylacrylamide, and 2-7% of long chain alkyl acrylate. The preparation method of the thermal response-type ultrafine fiber film material comprises the following steps: a) dissolving the polymer with the above proportion in methanol, stirring at room temperature, and preparing into uniform transparent solution; and b) injecting the above uniform transparent solution in an electrostatic spinning device for electrostatic spinning. The invention has the advantages that the method can control the density of physical crosslink points in fibers after electro spinning, and obtain thermal response-type ultrafine fiber film materials with different temperature response ranges and different volume changing scale. The material has the advantage of good biological compatibility, light weight and softness, good permeability and the like, and can be used as a carrier of temperature sensitive medicines. The preparation method is effective, adopts conventional radical polymerization to synthesize polymer with a dewatering side chain, effectively enlarges the temperature range of LCST, and leads the thermal respond process to be more controllable.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Polymer, preparation method and poly-N-isopropylacrylamide europium complex micelle
InactiveCN105085845AEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer sciencePoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
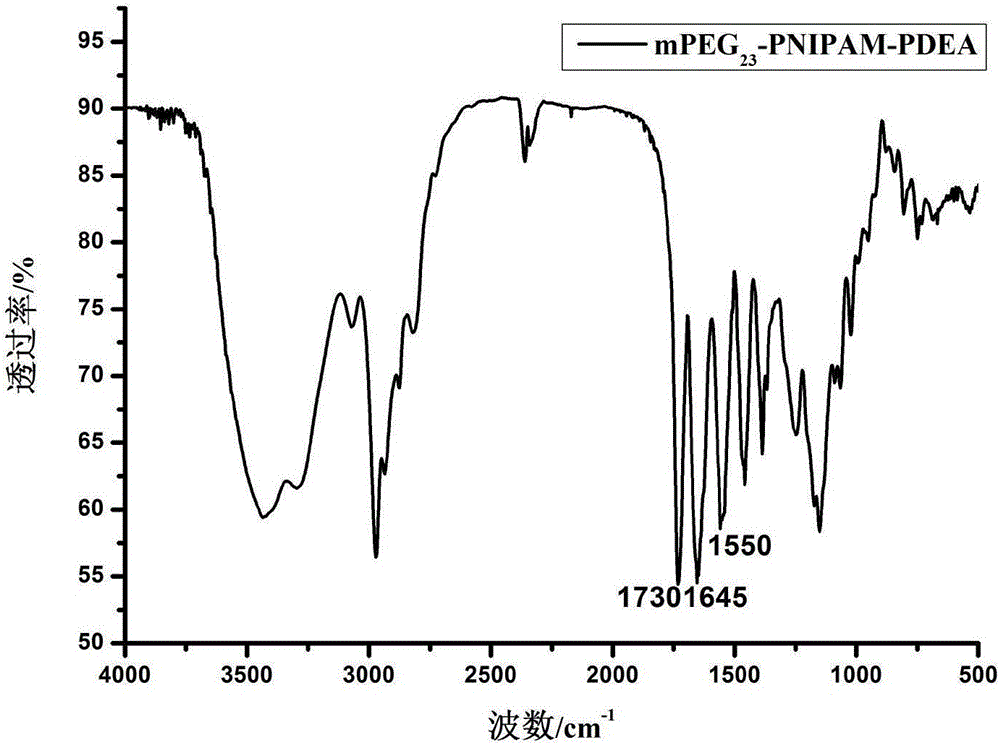
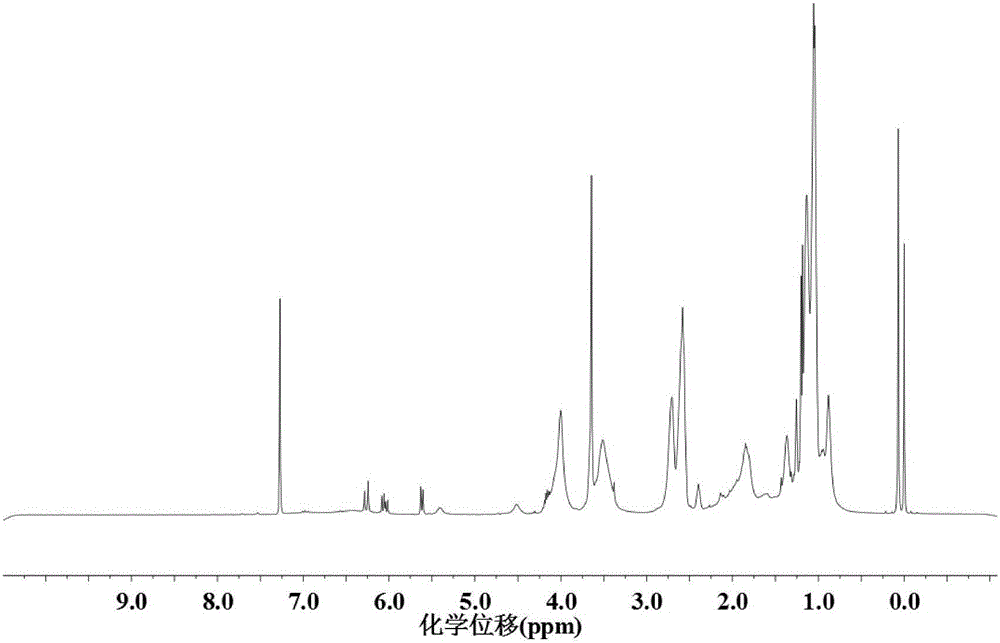
The invention provides a polymer, a preparation method and a poly-N-isopropylacrylamide europium complex micelle, and belongs to the field of europoium complexes. The polymer is methoxypolyethylene glycol-poly-N-isopropylacrylamide-polymethylacrylic acid N,N-diethylaminoethyl, the structural formula is shown as the formula I, and the abbreviate formula is mPEG23-PNIPAM-PDEA, wherein mPEG23 is methoxypolyethylene glycol, PNIPAM is poly-N-isopropylacrylamide, and PDEA is polymethylacrylic acid N,N-diethylaminoethyl. The structural formula of the europium complex micelle is shown as the formula II. Due to the fact that the polymer (mPEG23-PNIPAM-PDEA) has good thermosensitivity and pH sensibility, the polymer can be used as a chemical conveying carrier after being prepared into the europium complex micelle.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multiple-response type self-repair hydrogel material and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a multiple-response type self-repair hydrogel material and a preparation method and application thereof. The multiple-response type self-repair hydrogel material is prepared from polydopamine methacrylate-N-isopropylacrylamide, poly-N-isopropylacrylamide-4-vinyl benzeneboronic acid and water. The multiple-response type self-repair hydrogel material has the characteristics that the effects of pH (potential of hydrogen) response and temperature response are realized, the self-repair property is realized, and the application prospect is broad in the fields of biomedical materials, nanometer materials and photoelectric materials.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Dual stimuli-responsive hydrogels and their synthetic methods
InactiveUS20040024096A1Controlled molecular weightAffect propertyAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryPolymer scienceMeth-
The present invention relates to a process for preparing copolymer hydrogels with controlled molecular weights and having both thermo- and pH-responsive properties, wherein the process comprises the steps of (a) providing sulfonamide type styrenic or (meth)acrylamide-based monomers exhibiting different pKa values; (b) providing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) or crosslinked poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methylene bisacrylamide) hydrogels having thermo-responsive properties; and (c) providing several hydrogels exhibiting pH-sensitive properties and random or block copolymerizations of the sulfonamide type styrenic or (meth)acrylamide-based monomers prepared in step (a) with N-isopropylacrylamide and / or methylene bisacrylamide monomers used in step (b) in a polar or non-polar solvent; wherein said steps (b) and (c) are carried out by controlled / living radical polymerization using alkyl halides as the initiators and the transition metals with phosphine or amine ligands as the catalysts. The present invention also relates to the copolymer hydrogels made by the aforesaid process.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Device for Water Collection from Atmospheric Moisture
ActiveUS20150020687A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useIsotope separationWater conservationAtmospheric airPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
A device for collecting water from atmospheric moisture comprises water absorbing material, a protection wall and a water container. The protection wall is in a porous form. The water absorbing material is made of the temperature responsive polymer with a phase separation temperature, including Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), Poly(vinylphosphonate) and etc. when its temperature is below phase separation temperature, the temperature responsive polymer is in a swollen hydrated state, forming hydrogen bond with water molecules; so as to absorb water from the air. When its temperature is above said phase separation temperature, the temperature responsive polymer is in a shrunken dehydrated state, forming hydrogen bond with other temperature responsive polymer molecules; so as to expel the water to the water container.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particle for emulsion stabilization and preparation method of hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particle
The invention provides a hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particle for emulsion stabilization. The hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particles are gel microspheres composed of network gel hemispheres obtained fromcalcium ion crosslinked sodium alginate and chemically crosslinked polymer network hemispheres having thermosensitivity, and have hydrophilic and hydrophobic high anisotropy. The preparation method of the hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particles comprises the following steps: dissolving sodium alginate, a calcium salt, a crosslinking agent and a thermosensitive polymer into water to serve as an aqueous phase; preparing an oil phase containing a nonionic surfactant; mixing the aqueous phase and the oil phase, and sharply stirring to prepare monodispersed emulsion; performing solvent replacement toremove the surfactant; raising the temperature of the emulsion, precipitating poly-N-isopropylacrylamide from the gel, forming hydrogel hemispheres from the sodium alginate and calcium ions, and forming the hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particle. The hydrogel-solid amphiphilic particle has an effect of stabilizing the emulsion at a high temperature of higher than 37 DEG C, so that the emulsion can be stored for a long time at the high temperature.
Owner:常州晶丽光学科技有限公司
Composite material film containing poly N-isopropylacrylamide component and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101812211AGood temperature sensitivityUniform film formationComposite filmPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention relates to a composite material film containing a poly N-isopropylacrylamide component and a preparation method thereof. A film forming material of the composite film is poly N-isopropylacrylamide and chitosan components, wherein the mass content of the chitosan components is from 10% to 70%, and the balance of the poly N-isopropylacrylamide components. The preparation method comprises the steps of: fully mixing a solution containing the poly N-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAAm) with the proportion ratio and a cross-linking chitosan solution for reaction under stirring; paving and drying the reactants; neutralizing the reactants by an alkaline solution until the pH of the solution is from 6 to 7; and cleaning by water to remove impurities and obtain the composite material film product. The composite material film has good thermosensitivity and uniform film forming property, improves the property of poor mechanical performance under a swelling state of the PNIPAAm (poly N-isopropylacrylamide), greatly widens the application range, and has more convenient application in the aspects of drug slow release, material separation and purification as well as medical materials. The preparation method is simple and convenient.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
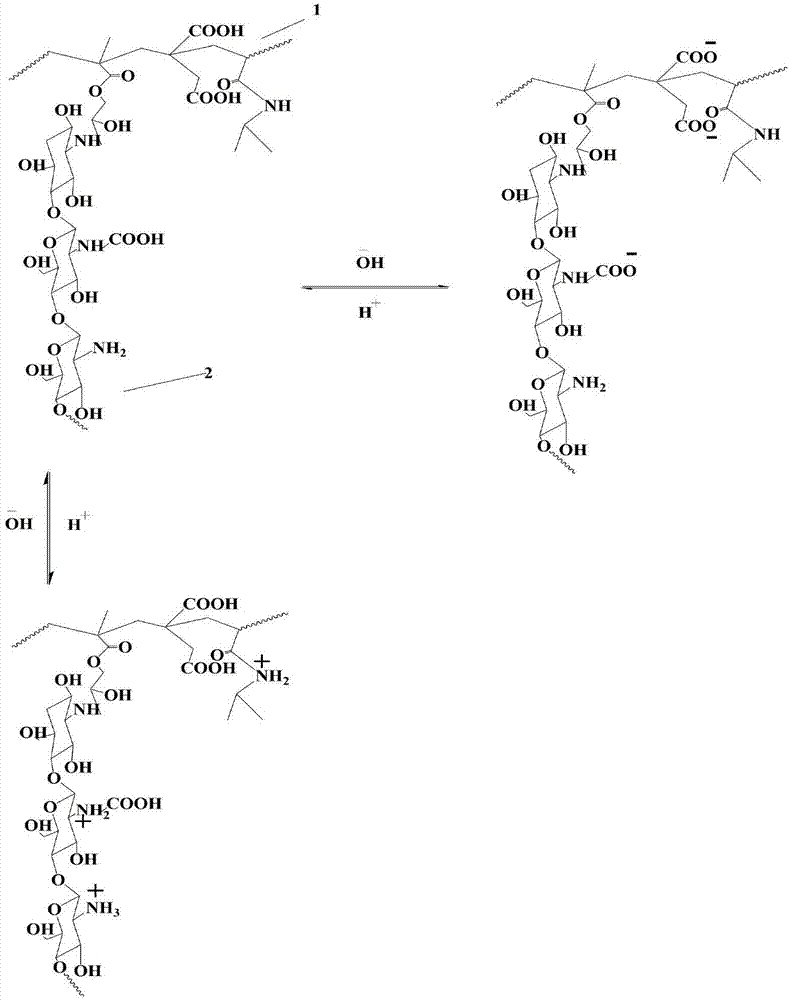
Novel pH sensitive type hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107540851AQuick responsePromote swellingOintment deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsWater basedSwelling ratio
The invention relates to novel pH sensitive type hydrogel and a preparation method and an application thereof. According to the hydrogel, selected pH response main polymer monomer raw materials of carboxymethyl chitosan and itaconic acid both come from natural product chemical compounds and are water-based environmentally friendly and good in biocompatibility; the polyvinyl modified carboxymethylchitosan and polyitaconic acid in the hydrogel are subjected to carboxyl ionization at a high pH value, meanwhile the polyvinyl modified carboxymethyl chitosan and poly N-isopropylacrylamide are subjected to amino absorption hydrogen ion ionization at a low pH value, and due to existence of different polymer units, the hydrogel has pH sensitivity. The hydrogel has higher swelling ratio at relatively mild pH and has low swelling ratio at relatively drastic pH so that the hydrogel can be used for drug release, achieves effectiveness of drug administration through the gastrointestinal tract and has wide application prospects.
Owner:HUNAN QIWEI TECH CO LTD
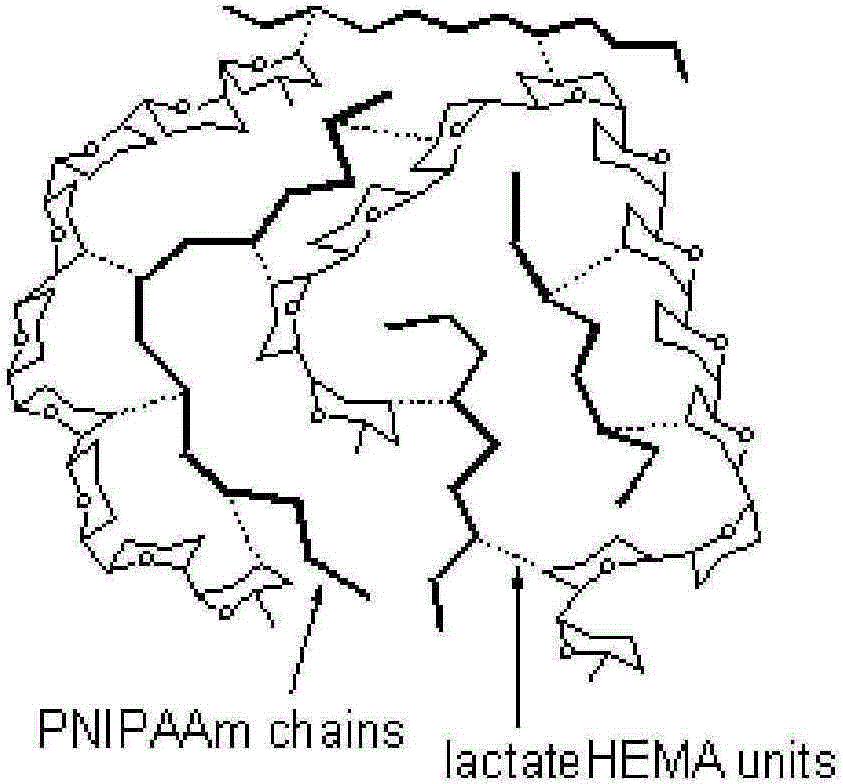
Method for synthesizing heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a biodegradable cross-linking agent, namely polymerizing lactic acid dimmer lactide and hydroxyethyl methylacrylate to form an intermediate, introducing glucosan to synthesize the biodegradable cross-linking agent by virtue of a chemical reaction; and preparing the heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel, namely dissolving N-isopropylacrylamide, an initiator and the biodegradable cross-linking agent in bovine serum albumin, adding a photoinitiator, performing light initiated polymerization, thereby obtaining the heat-sensitive and biodegradable hydrogel. The poly-N-isopropylacrylamide gel synthesized by the method is decomposed in a certain time due to the degradable structure of the cross-linking agent, and the decomposition products such as polylactic acid and glucosan can participate in human metabolism.
Owner:杨俊
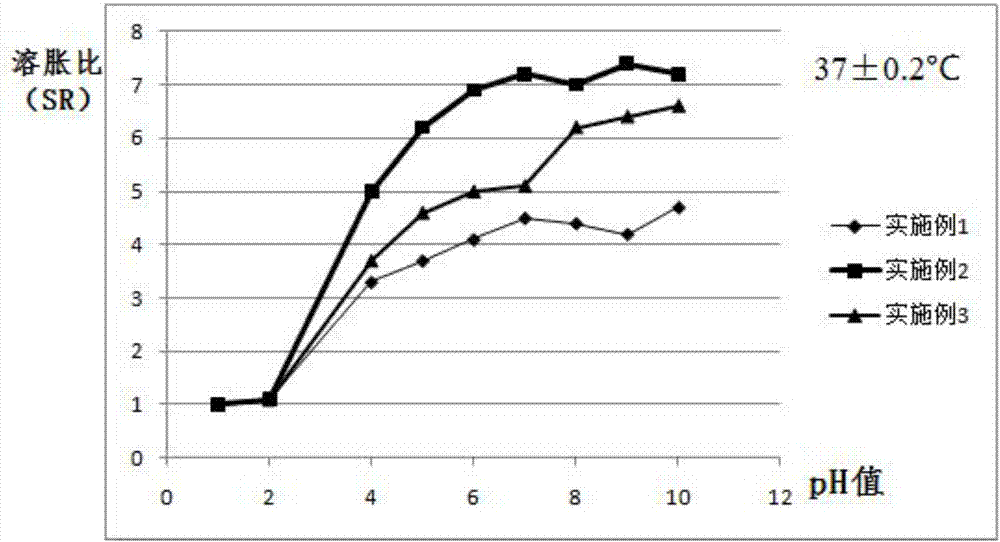
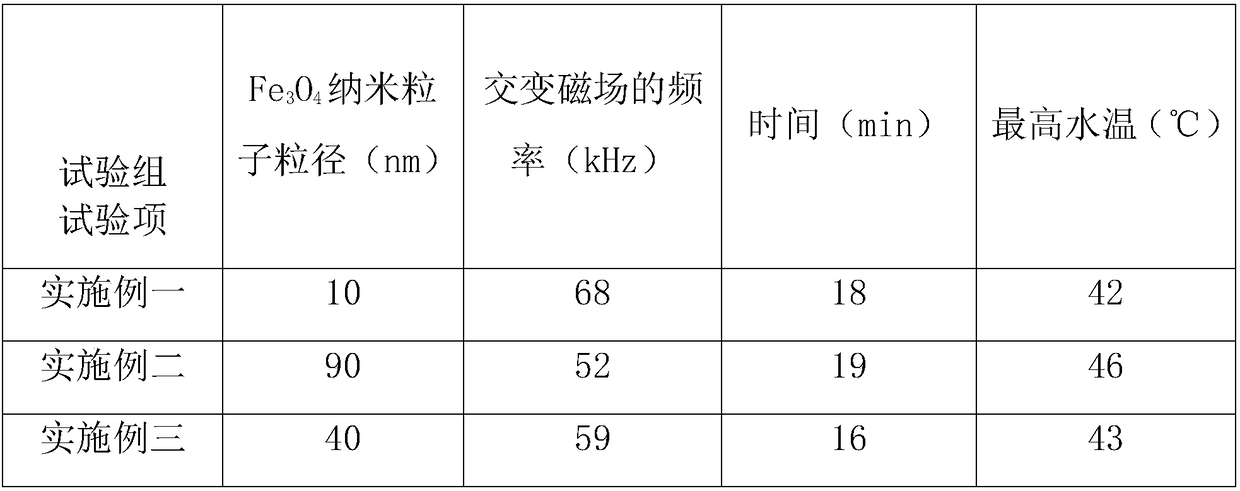
Injection type bone filling material and preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN108553687AIncrease profitImprove efficacyAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectrotherapyMicrospherePoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention discloses an injection type bone filling material and a preparation method and using method thereof, and relates to the technical field of medical materials. The material comprises beta-tricalcium phosphate bone cement, curing liquid and medicine carrying micro beads, and the curing liquid comprises, by mass, 0.5-1.8 wt% of carboxymethyl chitosan, 8-15 wt% of citric acid, 1-2 wt% ofpolyving akohol and the balance of deionized water; Fe3O4 nano particles are taken as the core material of the medicine carry micro beads, the surface of the core material is coated with a layer of core-shell structure of poly N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogel, the surfaces of the Fe3O4 nano particles are modified with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin, and medicines are loaded on the hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. By means of the material, inflammation diminishing medicines can be injected into a fractured vertebral body along with the bone cement, subsequent releasing of the medicines can be externally controlled through a manner of magnetic hyperthermia according to the inflammation situation of a patient, medicine injection is not needed, and secondary hurting on the patient is prevented.
Owner:AFFILIATED YONGCHUAN HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
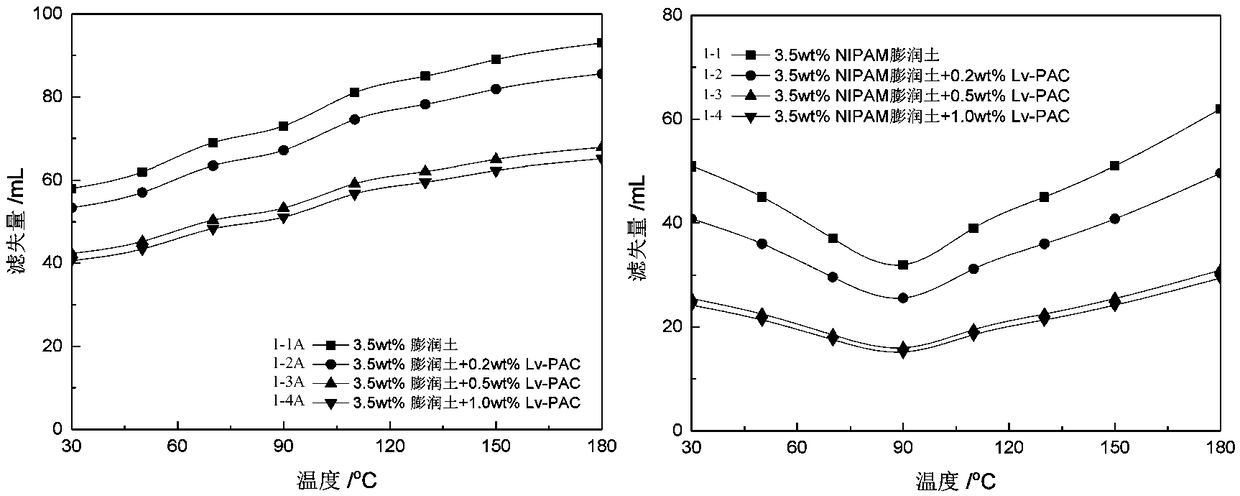
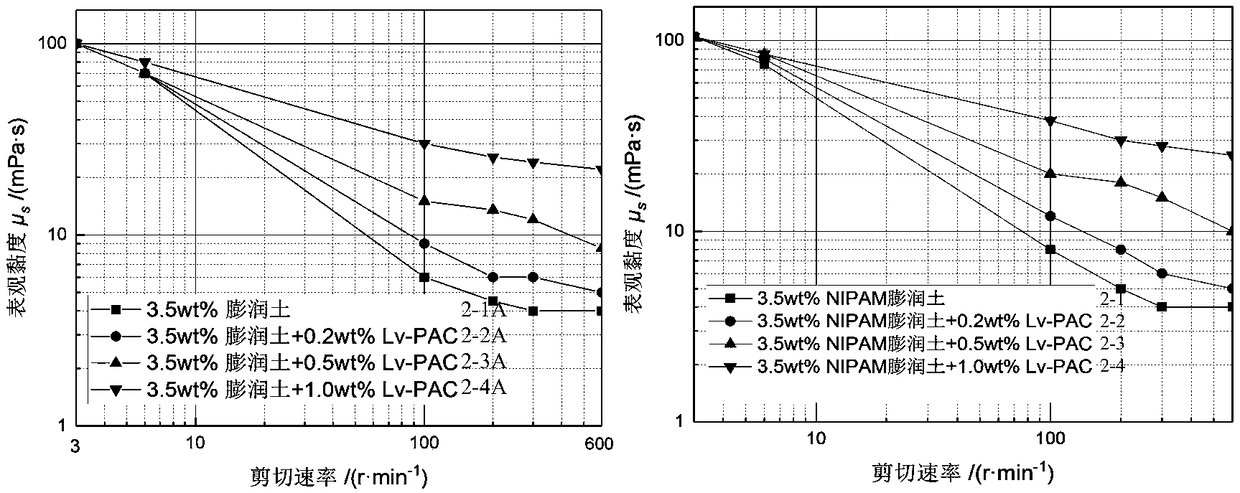
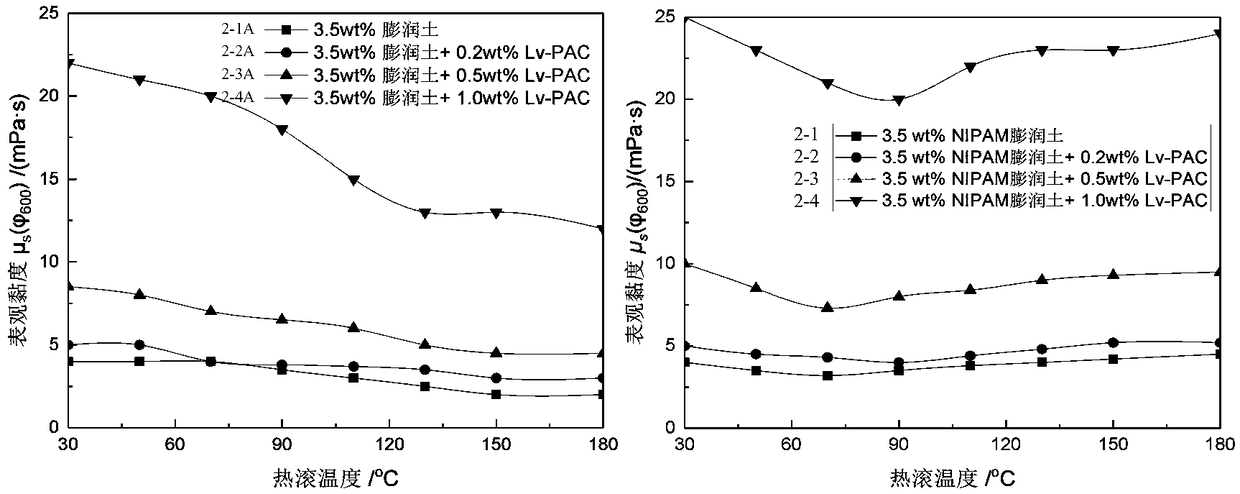
Modified thermo-sensitive NIPAM bentonite and temperature response type drilling fluid
InactiveCN109233761ASpecial temperature characteristicsReduce fluid lossDrilling compositionChemistryPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention discloses modified thermo-sensitive NIPAM bentonite. NIPAM molecules are firmly adsorbed on montmorillonite minerals, and are inserted between bentonite mineral layers or adsorbed on thesurfaces of bentonite particles, and the bentonite particles responds to the temperature. A preparation method of the modified thermo-sensitive NIPAM bentonite comprises the following steps: pre-hydrating bentonite, adding an N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAM) crystal or low molecular weight poly N-isopropylacrylamide, performing constant-temperature magnetic stirring, sufficiently reacting NIPAM with hydrated clay to obtain a mixed solution, removing NIPAM molecules not adsorbed on the surface of the bentonite, and drying and crushing to prepare the modified thermo-sensitive NIPAM bentonite. Theinvention further discloses a temperature response type drilling fluid, which is prepared from the modified thermo-sensitive NIPAM bentonite, Lv-PAC, CMC, CaCO3 and water. The modified thermo-sensitive NIPAM bentonite can enhance the plugging property of a mud cake under the formation condition, reduce the filter loss of the drilling fluid, and improve the high temperature stability of drilling fluid rheology. The temperature response type drilling fluid has temperature responsibility, and has certain self repairing ability, and under a high temperature condition, the temperature response type drilling fluid has relatively high stability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Thermoresponsive microparticle composite hydrogels for electrophoresis
ActiveUS20090127116A1Powder deliveryElectrolysis componentsElectrophoresisPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
Disclosed are thermoresponsive microparticle composite hydrogels comprising poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) and polyacrylamide, and methods regarding their manufacture and their use. The present invention provides in one aspect a thermoresponsive microparticle hydrogel, wherein the matrix morphology is controllably and selectively altered by incorporation of thermoresponsive nano / micro-particles. The particles are preferably poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) particles. The present invention also provides methods of making and using such hydrogels.
Owner:TENNESSEE TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com