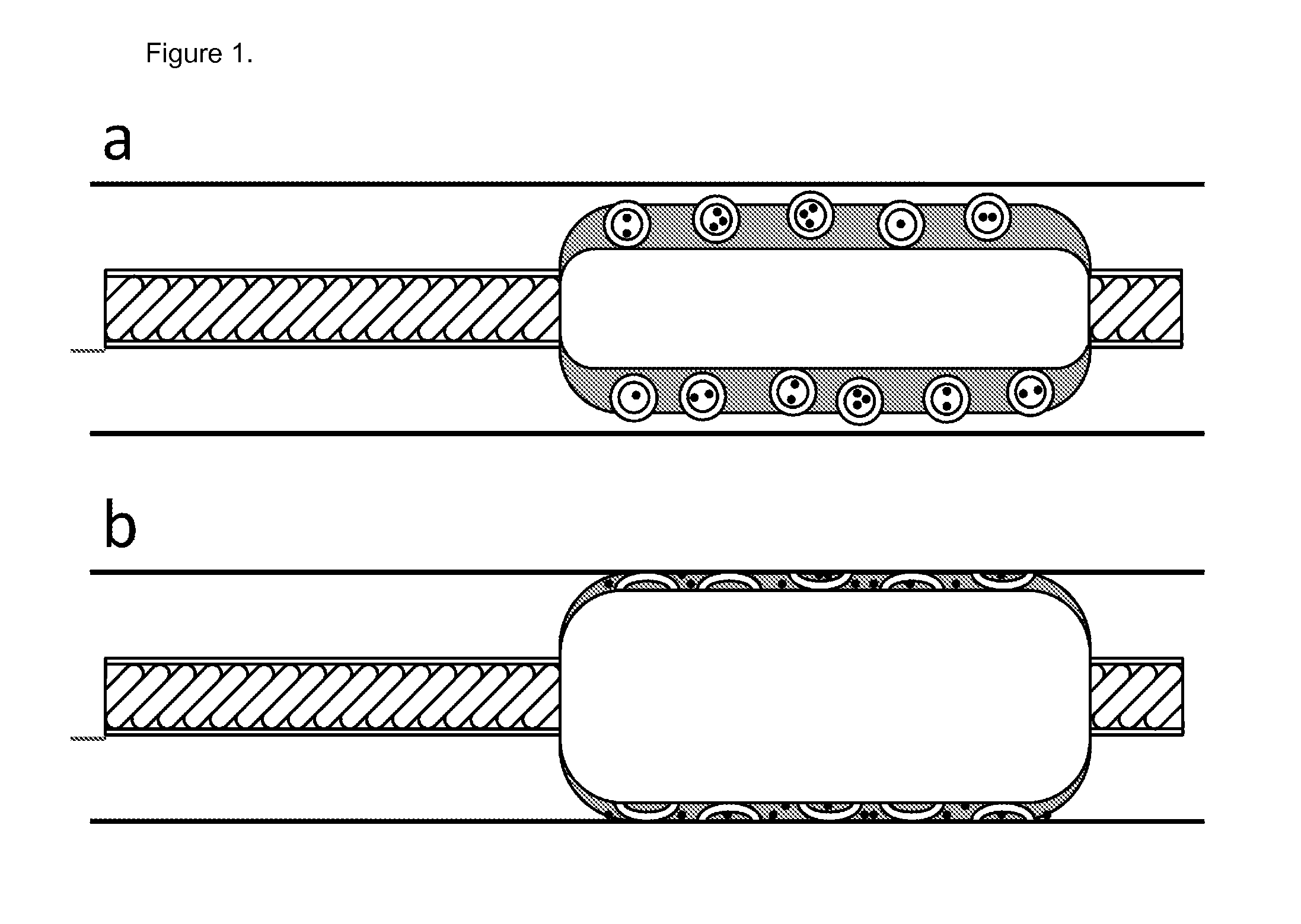
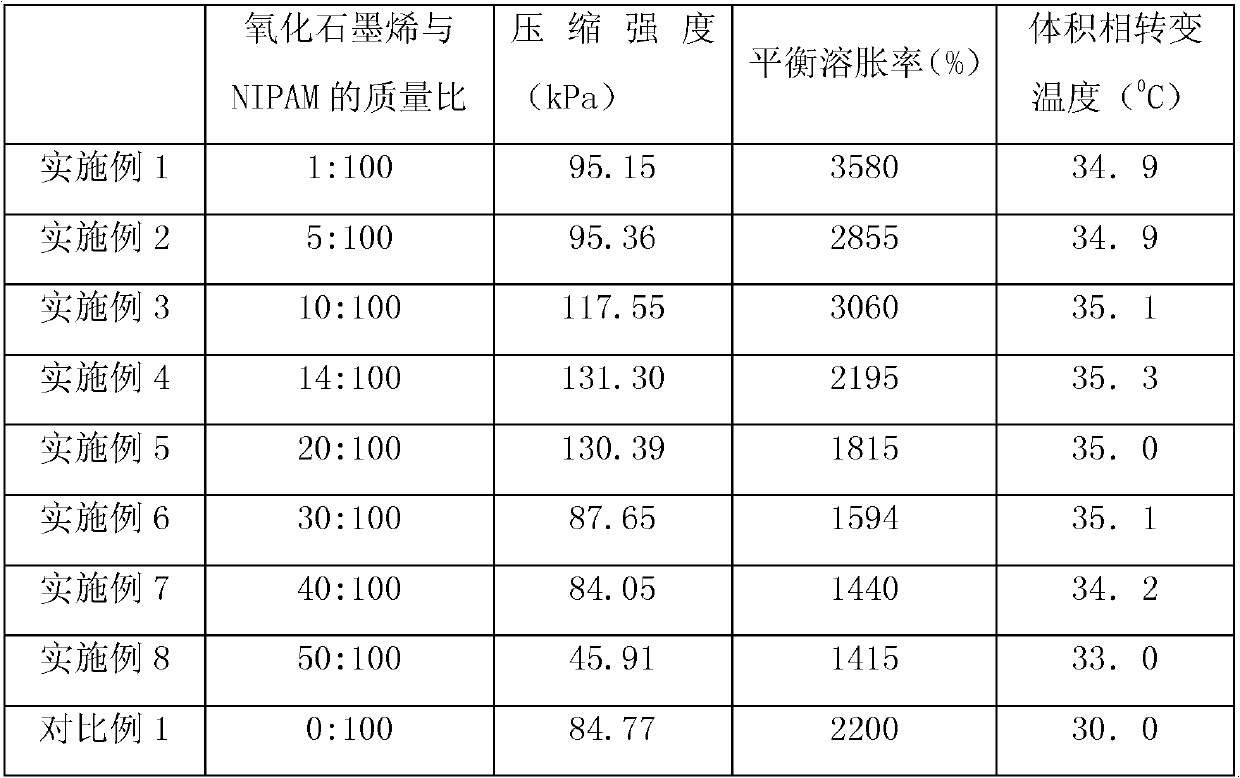
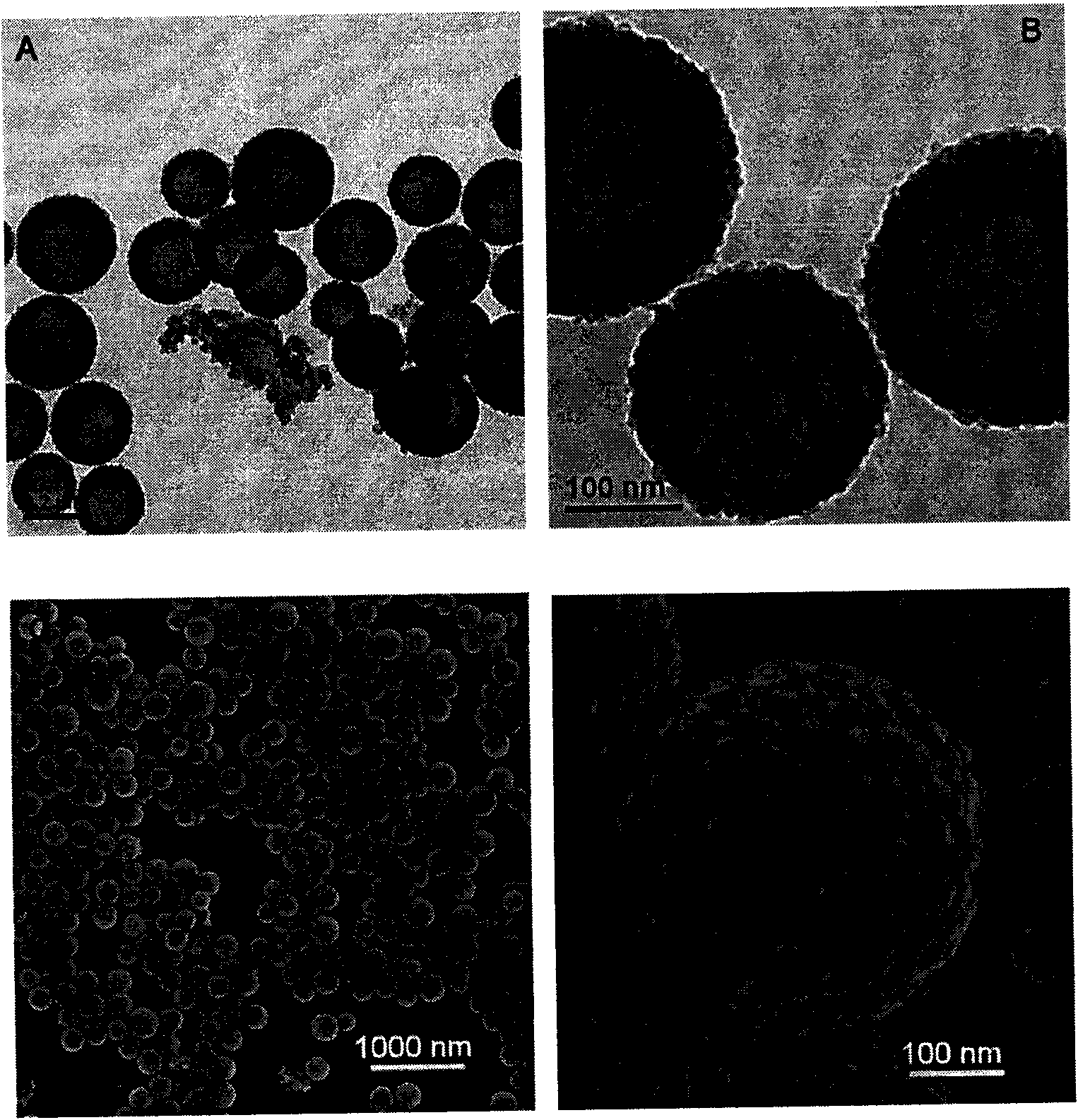
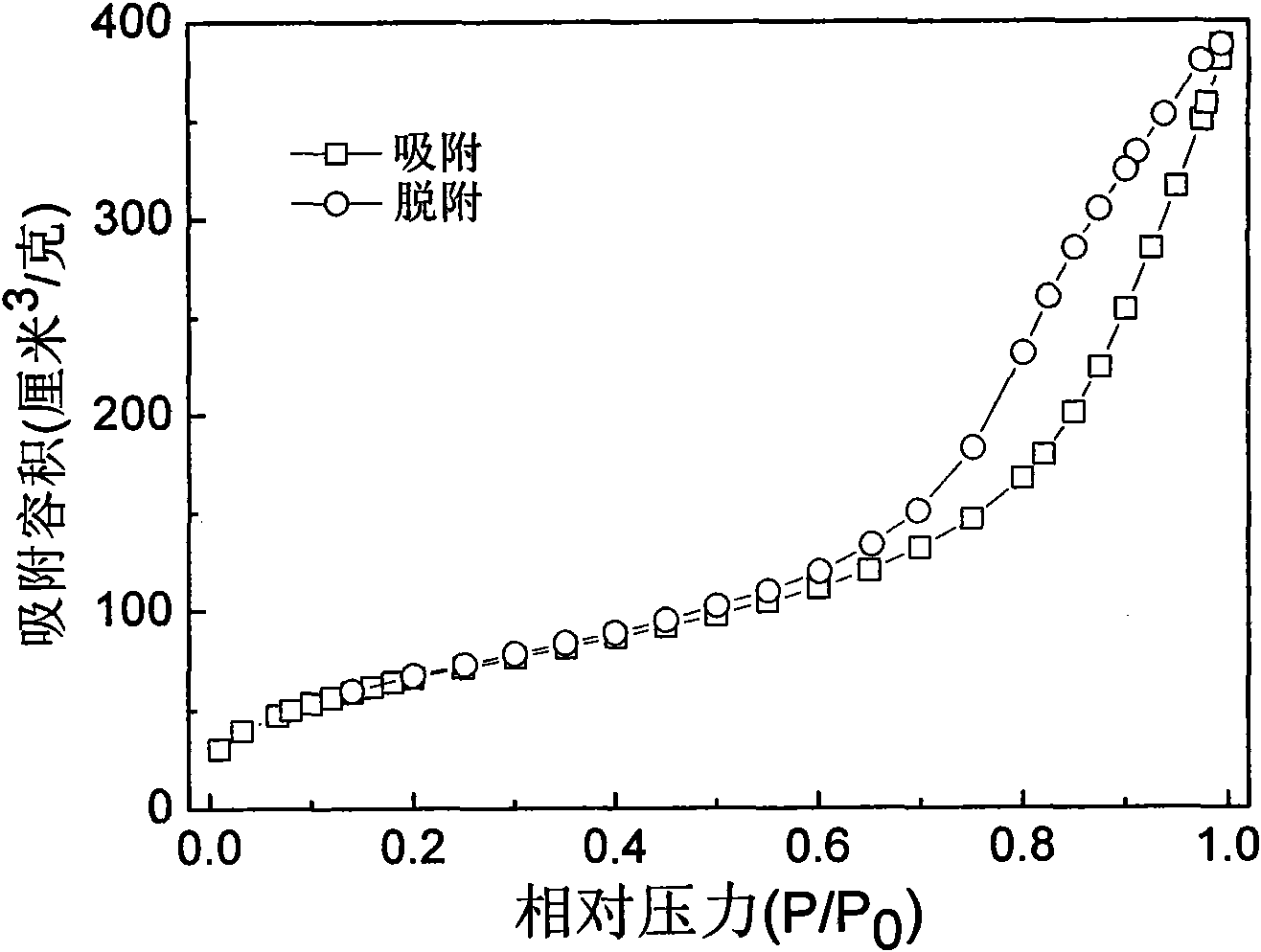
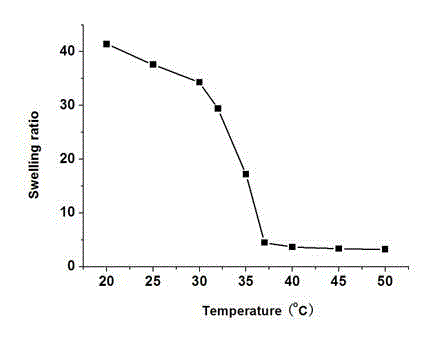
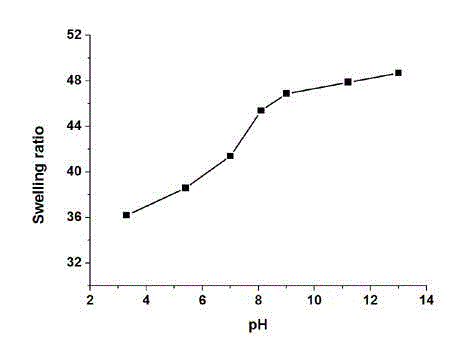
Patents
Literature
977 results about "N-n-propylacrylamide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Water-dispersible oral, parenteral, and topical formulations for poorly water soluble drugs using smart polymeric nanoparticles
ActiveUS8313777B2Control releaseImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderWater dispersibleSmart polymer
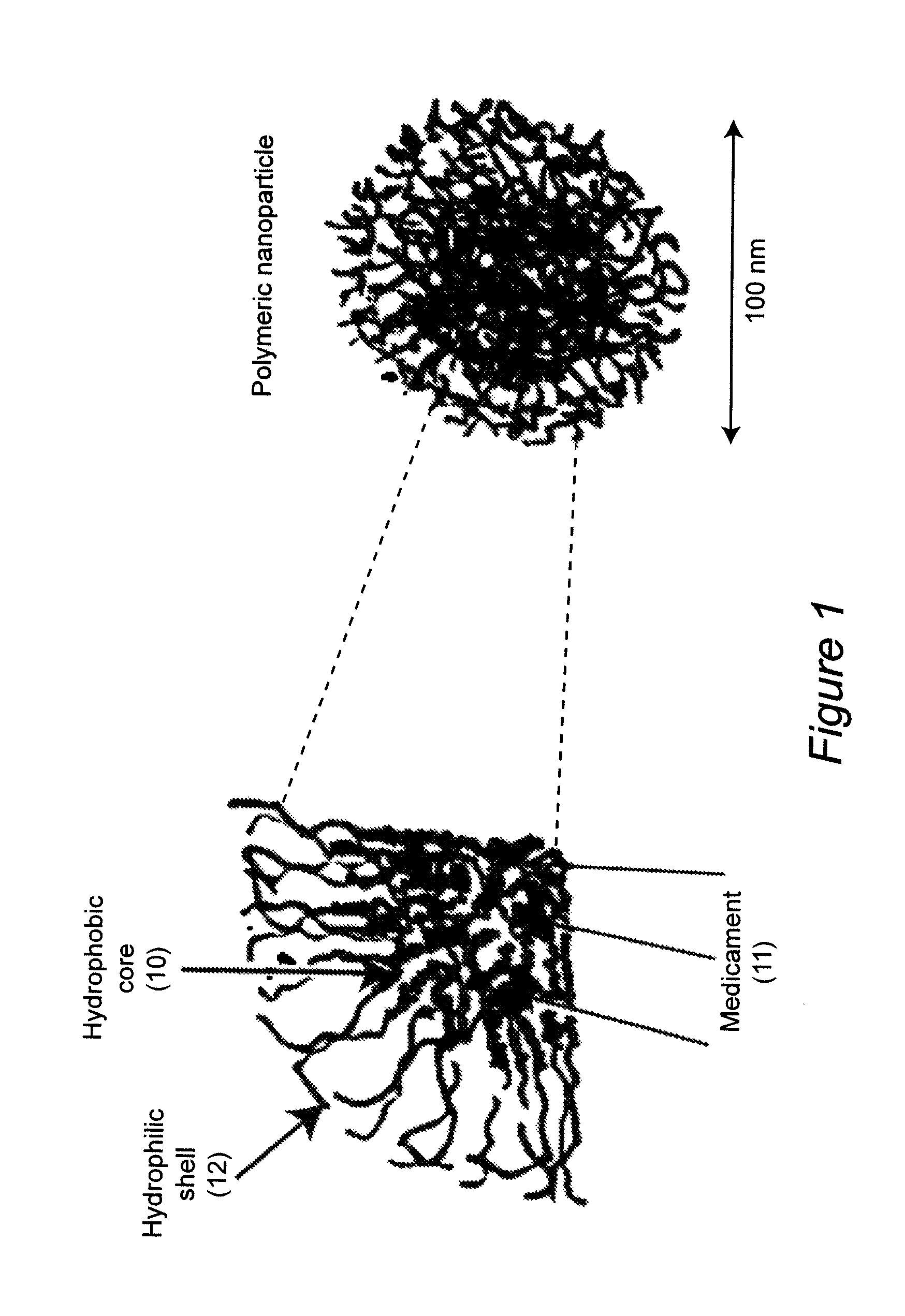
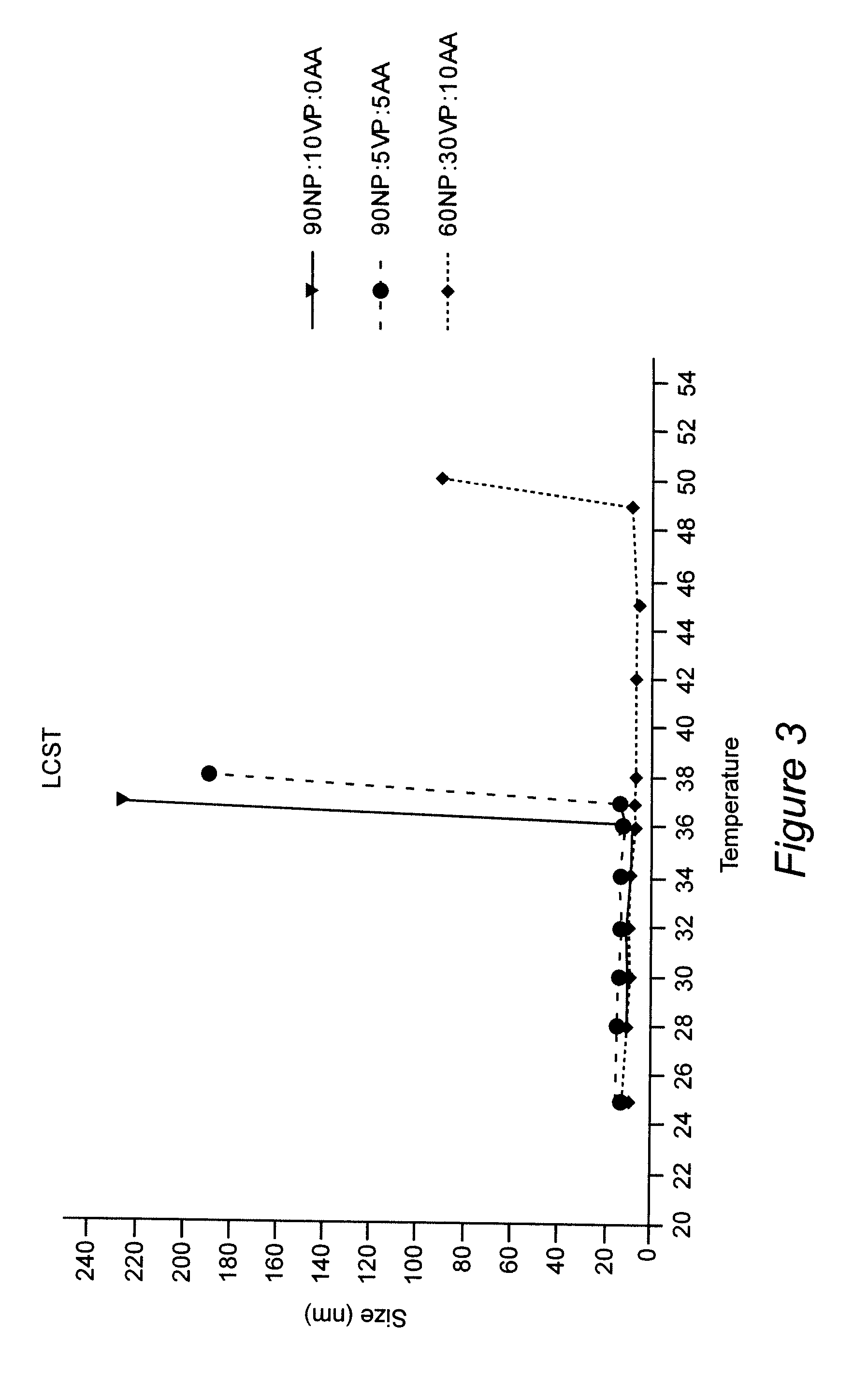
Polymeric nanoparticles with a hydrophobic core and a hydrophilic shell are formed from: 1) N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAAM), at a molar ratio of about 50% to about 90%, and preferably 60% for specific delivery routes such as oral or parenteral; either water-soluble vinyl derivatives like vinylpyrolidone (VP) or vinyl acetate (VA), or water insoluble vinyl derivatives like methyl methacrylate (MMA) or styrene (ST), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%; and acrylic acid (AA), at a molar ratio of about 10% to about 30%. The formed nanoparticles may be optionally surface functionalized using reactive groups present in AA, including PEGylation, or conjugation of moieties such as chemotherapeutics, contrasting agents, antibodies, radionucleides, ligands, and sugars, for diagnostic, therapeutic, and imaging purposes. The polymeric nanoparticles are preferably dispersed in aqueous solutions. The polymeric nanoparticles incorporate one or more types of medicines or bioactive agents in the hydrophobic core; on occasion, the medicine or bioactive agent may be conjugated to the nanoparticle surface via reactive functional groups. The polymeric nanoparticles are capable of delivering the said medicines or bioactive agents through oral, parenteral, or topical routes. The polymeric nanoparticles allow poorly water soluble medicines or bioactive agents, or those with poor oral bioavailability, to be formulated in an aqueous solution, and enable their convenient delivery into the systemic circulation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Preparing method for infrared response high-strength hydrogel for cartilago articularis repair
InactiveCN105107019AImprove mechanical propertiesEfficient photothermal conversion effectProsthesisCross-linkSide chain
The invention discloses a preparing method for infrared response high-strength hydrogel for cartilago articularis repair. The preparing method mainly includes the operation steps that polysaccharide or protein is modified in a double bond forming mode through methacrylic acid, methacrylic anhydride and methacrylate substances, so that the polysaccharide or the protein has a double-bond group in a side chain and is capable of being polymerized to form the hydrogel. Under the action of an initiator and a cross-linking agent, N-isopropyl acrylamide and the polysaccharide or the protein modified in the double bond forming mode form the double-network high-strength hydrogel through in-situ polymerization. The prepared infrared response high-strength hydrogel is high in biocompatibility and excellent in mechanical property and has good application prospects in the field of cartilago articularis repair.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Nanometer plural gel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a nanometer plural gel and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a polymer into a film in a mould, and then solidifying or cross-linking to obtain a polymer gel film; and (2) adding a nanometer material, N-isopropylacrylamide, a cross-linking agent and an initiating agent to water to obtain a mixed solution, adding the mixed solution to the mould with the polymer gel film, and carrying out polymerization reaction and cross-linking reaction under the irradiation of an ultraviolet lamp to obtain the nanometer plural gel. The nanometer plural gel provided by the invention has a double-layer structure; and PNIPAAm gel which contains nanometer particles can generate the temperature and volume change of a specific area under illumination due to photothermal effect and can integrally generate response behaviors, such as bending and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polymeric wood preservative compositions
The present invention relates to a method and a wood preserving composition which comprises mixtures of a metal compound, complexing agents selected from ethanolamines, polyethylenimine, ammonia or a mixture of these compounds, and a vinyl based polymer selected from poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), poly(acrylamide) (PA), poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) and poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAM). The resulting metal amine solution can then be used to formulate a variety of metal-based cellulosic material preserving products.
Owner:OSMOSE
Multifunctional organic-inorganic composite polymeric microball and preparing method thereof
The present invention relates to an organic-inorganic composite high-molecular microsphere with multiple response property and its preparation method. Said method includes the following steps: using alkyl metasilicate as precursor, utilizing gel-sol process to prepare magnetic nano granules covered with silicon dioxide, and using silicane coupling agent to make surface modification, then adopting template polymerization process, using the above-mentioned magnetic nano granules as seed and using isopropyl acrylamide or its derivative as main monomer, and using acrylic acid or its salt as functional monomer and controlling the dose of main monomer, functional monomer and crosslinking agent to prepare the organic-inorganic composite high-molecular microsphere with different swelling ratios.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Balloon catheter comprising pressure sensitive microparticles
InactiveUS20120083734A1Improve brittlenessEffective treatmentSurgeryDilatorsPolyesterPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention provides a solution to the above mentioned problem in that it provides a catheter balloon comprising a flexible coating on its outer surface wherein a plurality of microparticles are contained wherein said coating comprises a material selected from the group consisting of poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone, poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone-co-butylacrylate), poly(-vinyl pyridine), polyacrylamides, e.g. poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(amido-amines), poly(ethylene imine), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide-block-ethylene oxide), poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene), poly(hydroxystyrene-block-isobutylene-block-hydroxystyrene), polydialkylsiloxanes, polysaccharides, polyacrylates and polyalkylmethacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein said microparticles comprise a material selected from the group consisting of polyesters, e.g. poly(lactic acid), poly(lactic-co-glycol acid), poly(glycolic acid), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxyvalerate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and polycaprolactone, polyamides, polysaccharides, polyurethanes, polyalkylmethacrylates and polyacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein the microparticles comprise a pharmaceutically active compound.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Preparation method of graphene oxide/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogel
InactiveCN102580633AIncrease temperatureImprove mechanical propertiesColloidal chemistry detailsWater bathsCross-link
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene oxide / poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogel. The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly, placing the graphene oxide in water and ultrasonically dispersing the graphene oxide for 30-60 min to obtain a graphene oxide colloidal solution; then adding N-isopropylacrylamide, a cross-linking agent and an initiator 1 in the graphene oxide colloidal solution; stirring for dissolving so as to obtain a mixed solution; then inflating nitrogen in the mixed solution to deoxidize fully, then adding an initiator 2 in the deoxidized mixed solution, mixing uniformly and placing the mixture in a thermostatic water bath at 25+ / -1 DEG C so as to obtain the graphene oxide / poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogel. The graphene oxide / poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite hydrogel prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good temperature responsiveness and mechanical property and wide application prospect in the biomedical field (such as tissue engineering and drug controlled release).
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Polymeric Microgels for Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP) Processing
ActiveUS20090013609A1Reduce mechanical stressDesirable removal ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCross-linkPolymer network
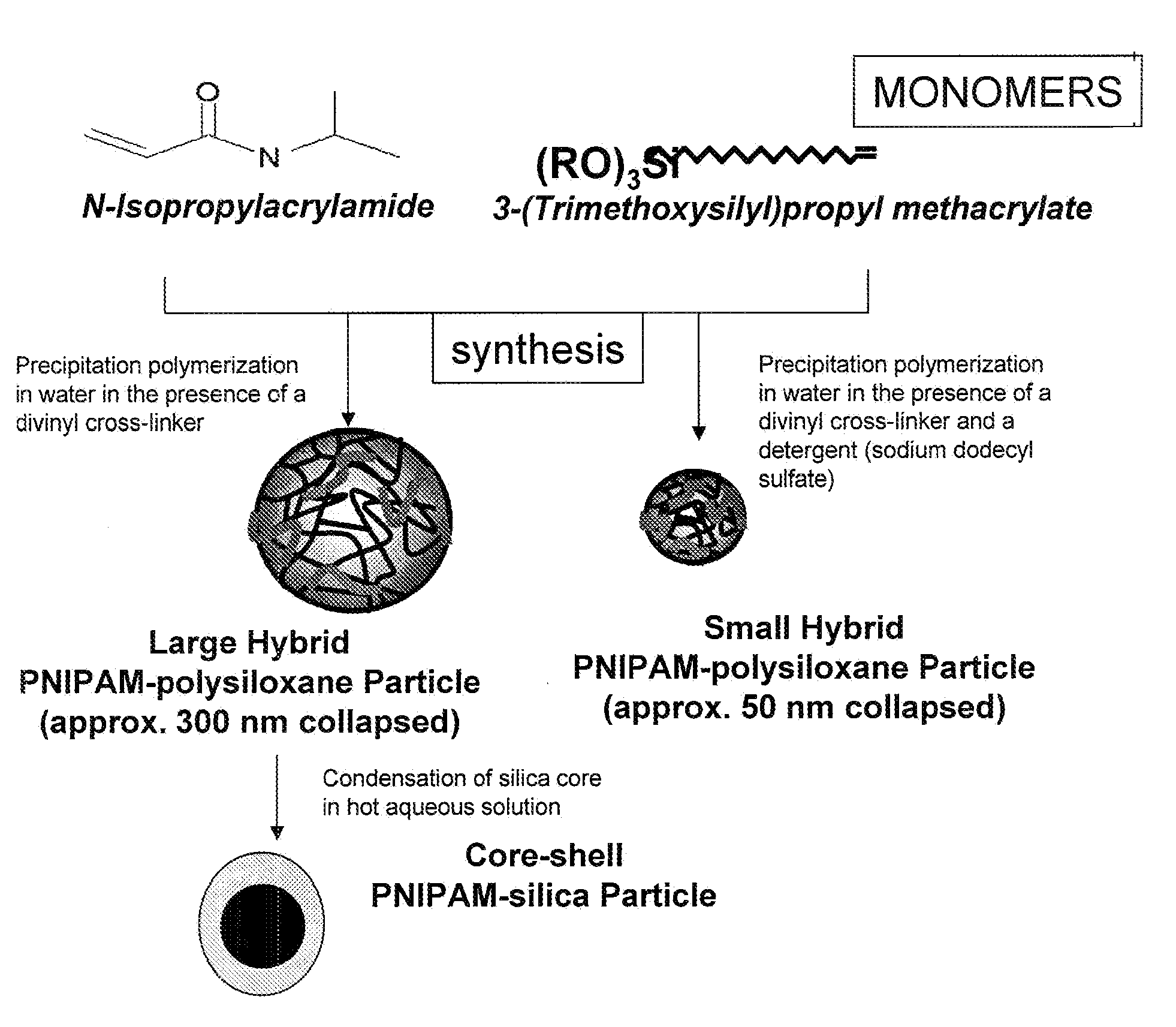
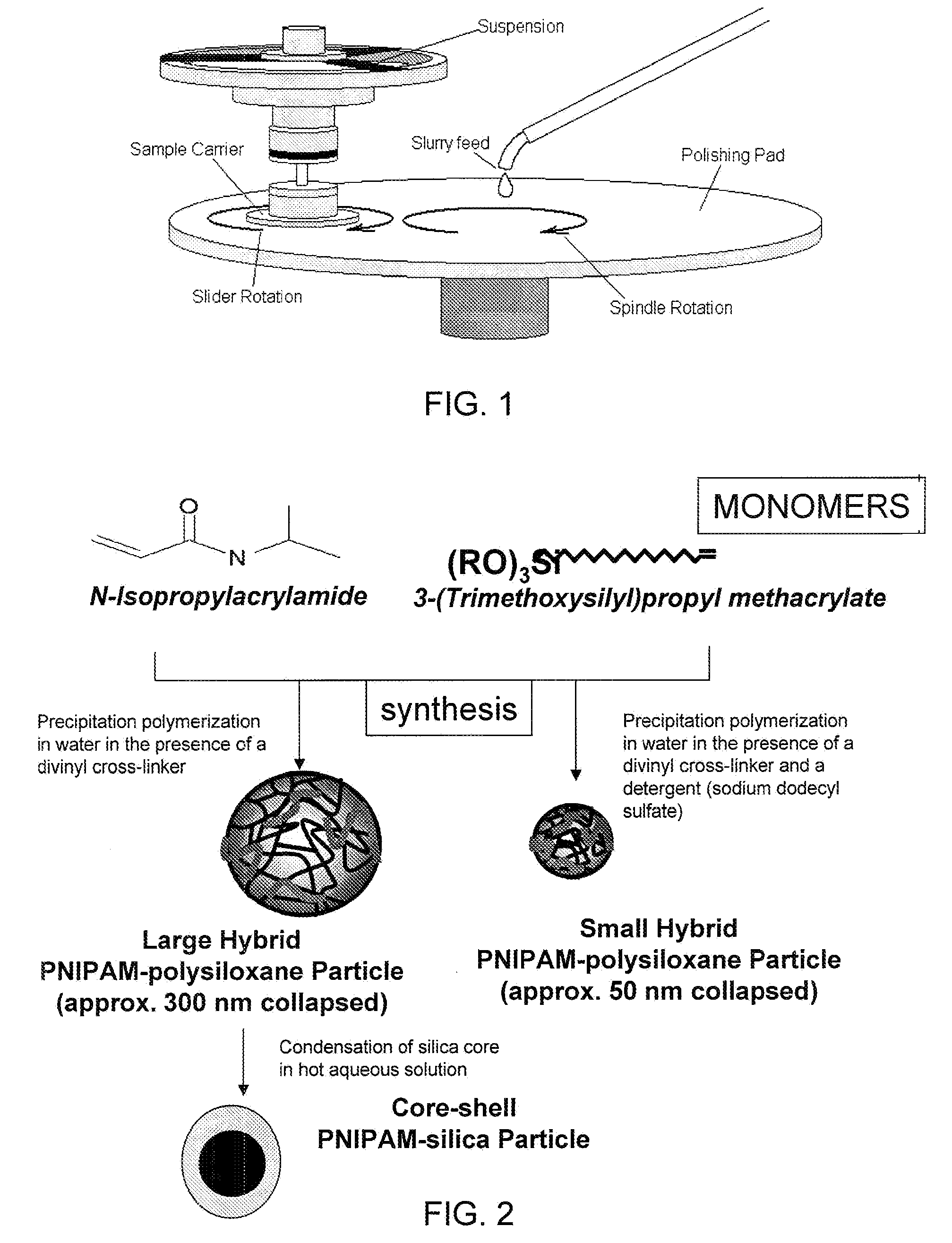
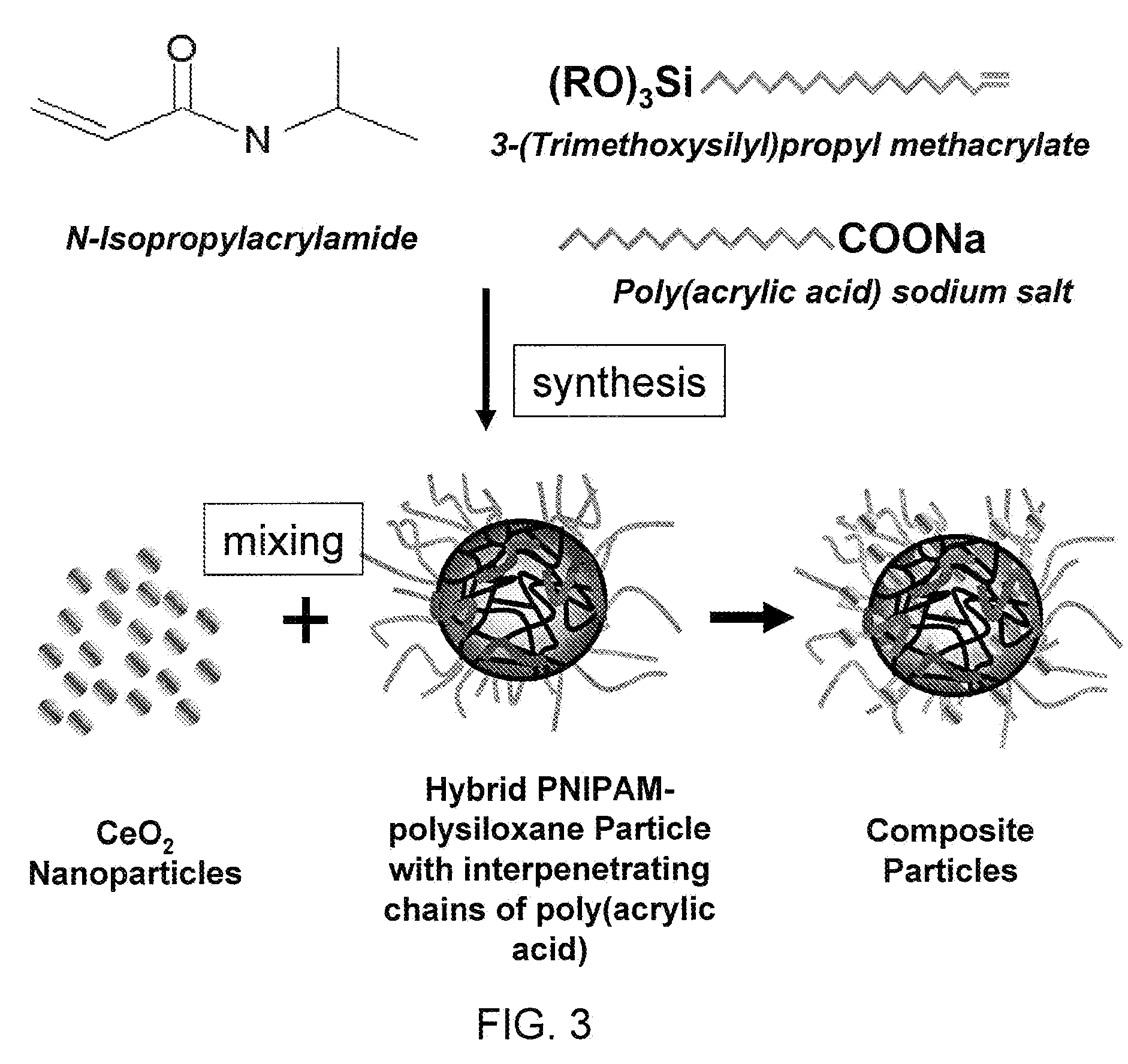
Organic-inorganic composites were prepared as colloidal particles of a cross-linked, thermally responsive polymer. Hybrid PNIPAM-polysiloxane particles and composite polymeric particles with embedded nanoparticles of an inorganic metal-oxide (MOx) such as CeO2 and TiO2 were formed. To promote the incorporation of unaggregated nanoparticles, temperature responsive microspherical gels (microgels) of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) with interpenetrating (IP) linear chains of poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) were used. The organic-inorganic composition of the hybrid polymer network was controlled by changing the time for condensation and hydrolysis of the siloxane monomer during synthesis. Experimental results indicated that the planarization of silicon oxide wafers using these hybrid particles and composites exhibited lower topographical variations and surface roughness as compared to slurries consisting of only silica or ceria nanoparticles while achieving similar removal rates and better or similar frictional characteristics.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Biological preconcentrator
ActiveUS7422724B1Analysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationActive polymerSemiconductor materials
A biological preconcentrator comprises a stimulus-responsive active film on a stimulus-producing microfabricated platform. The active film can comprise a thermally switchable polymer film that can be used to selectively absorb and desorb proteins from a protein mixture. The biological microfabricated platform can comprise a thin membrane suspended on a substrate with an integral resistive heater and / or thermoelectric cooler for thermal switching of the active polymer film disposed on the membrane. The active polymer film can comprise hydrogel-like polymers, such as poly(ethylene oxide) or poly(n-isopropylacrylamide), that are tethered to the membrane. The biological preconcentrator can be fabricated with semiconductor materials and technologies.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Temperature responsive intelligent facial mask and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1883438AInhibit high temperature dehydrationAct as a supportCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSmart hydrogelsCellulose fiber
A temperature responsive intelligent face mask and preparation method thereof wherein a chitosan modified temperature sensitive isopropyl acryl amide / polyurethane copolymer hydrogel is grafted to a cellulose fiber. The advantages lie in that the intelligent hydrogel can swell and contract reversibly near body temperature, and the high-temperature dehydration phenomenon may be inhibited by the introduction of the polyurethane, the non-woven fabric exerts a supporter function by grafting the isopropyl acryl amide / polyurethane copolymer hydrogel thereto and as a result the strength of the gel is increased, the coupling of the natural chitosan to external surface of the gel film not only improves the face mask comfort, the skin affinity, but also offers the bacteria resistant ability. The gel face mask carries multiple nutrients and the carried nutrient and moisture may release intelligently through gel contraction under body temperature, meanwhile the temperature responsive intelligent face mask can be utilized in a plurality of times to satisfy the personalized requirement.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Graphene hydrogel and method for using the same
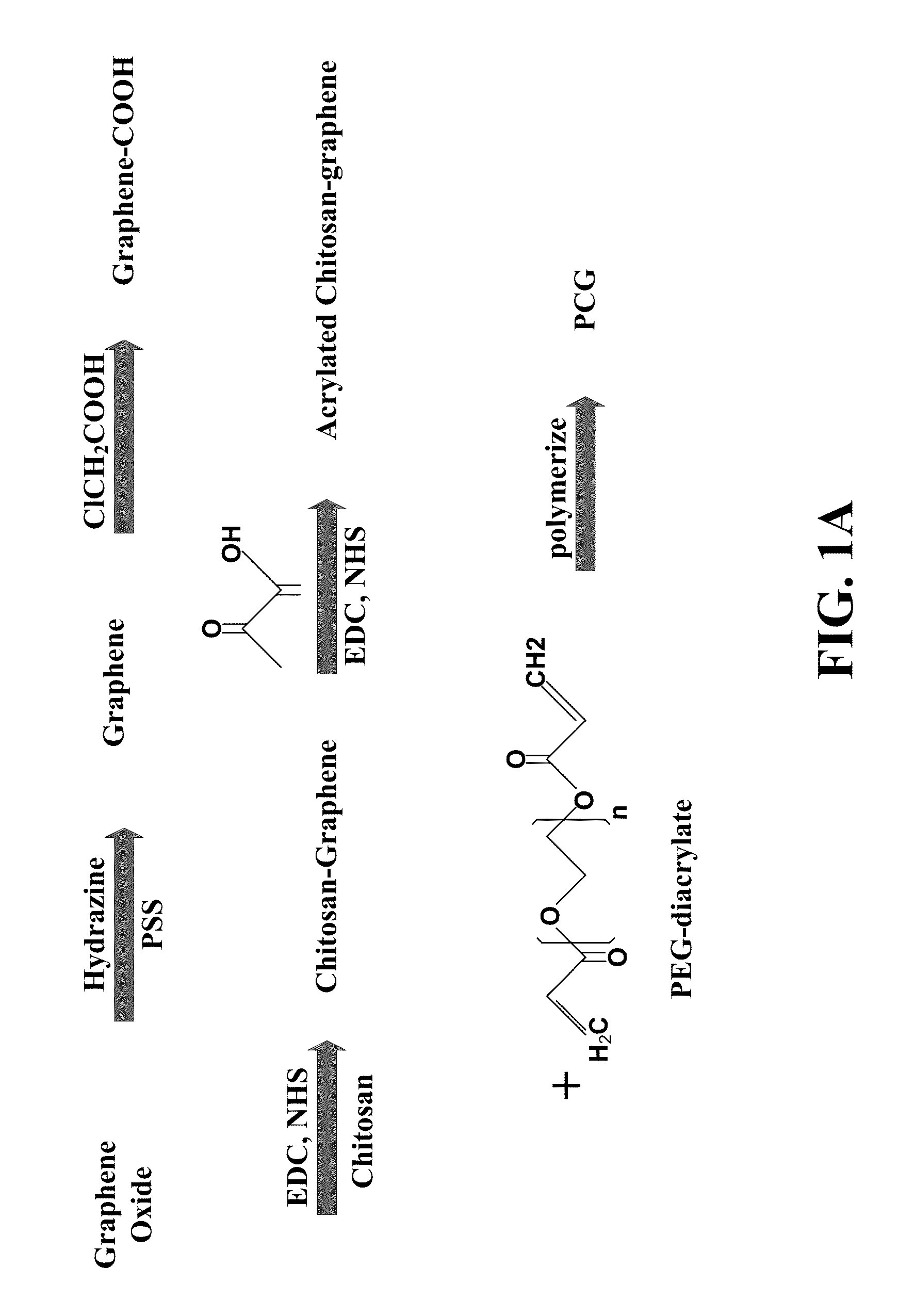
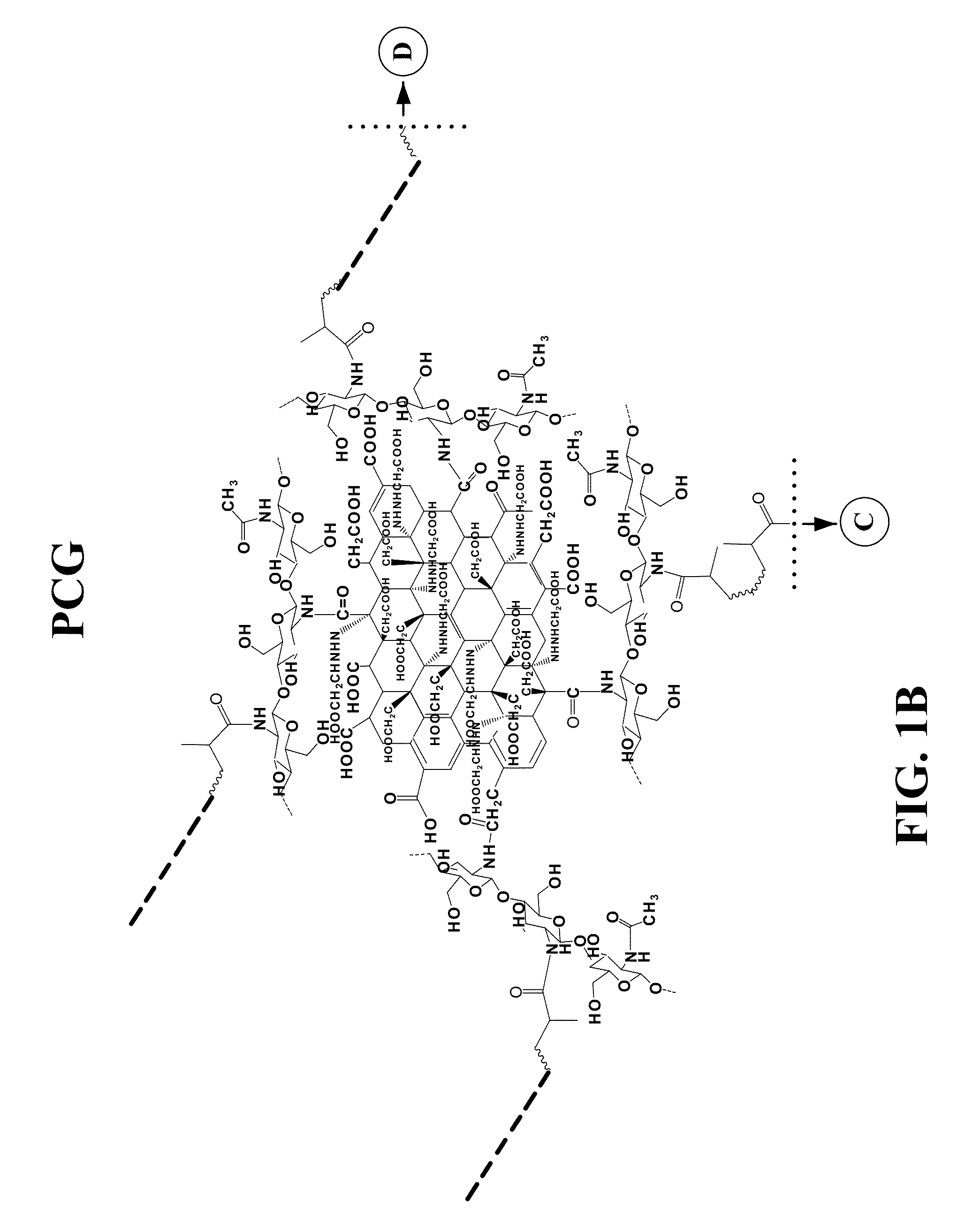
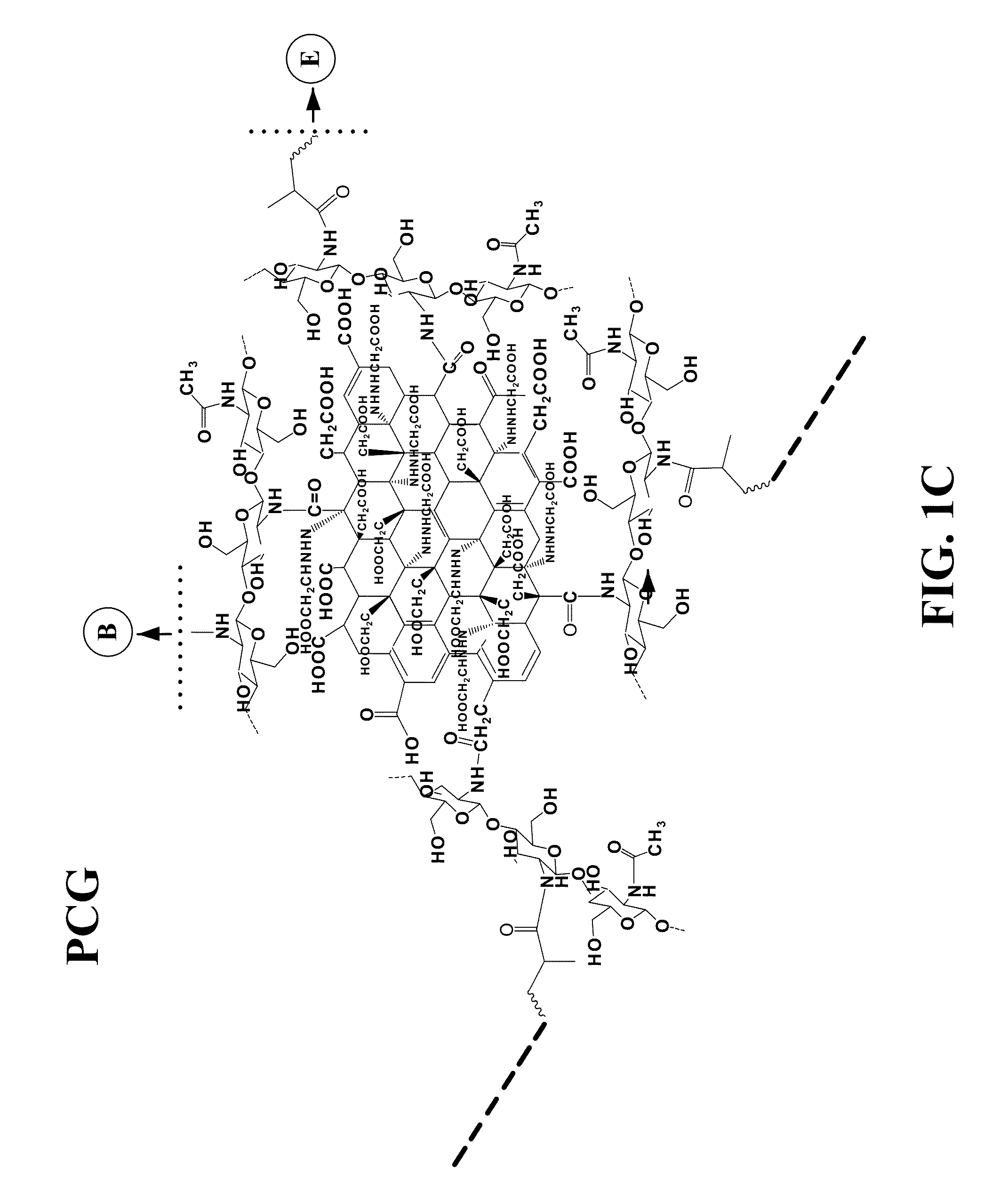
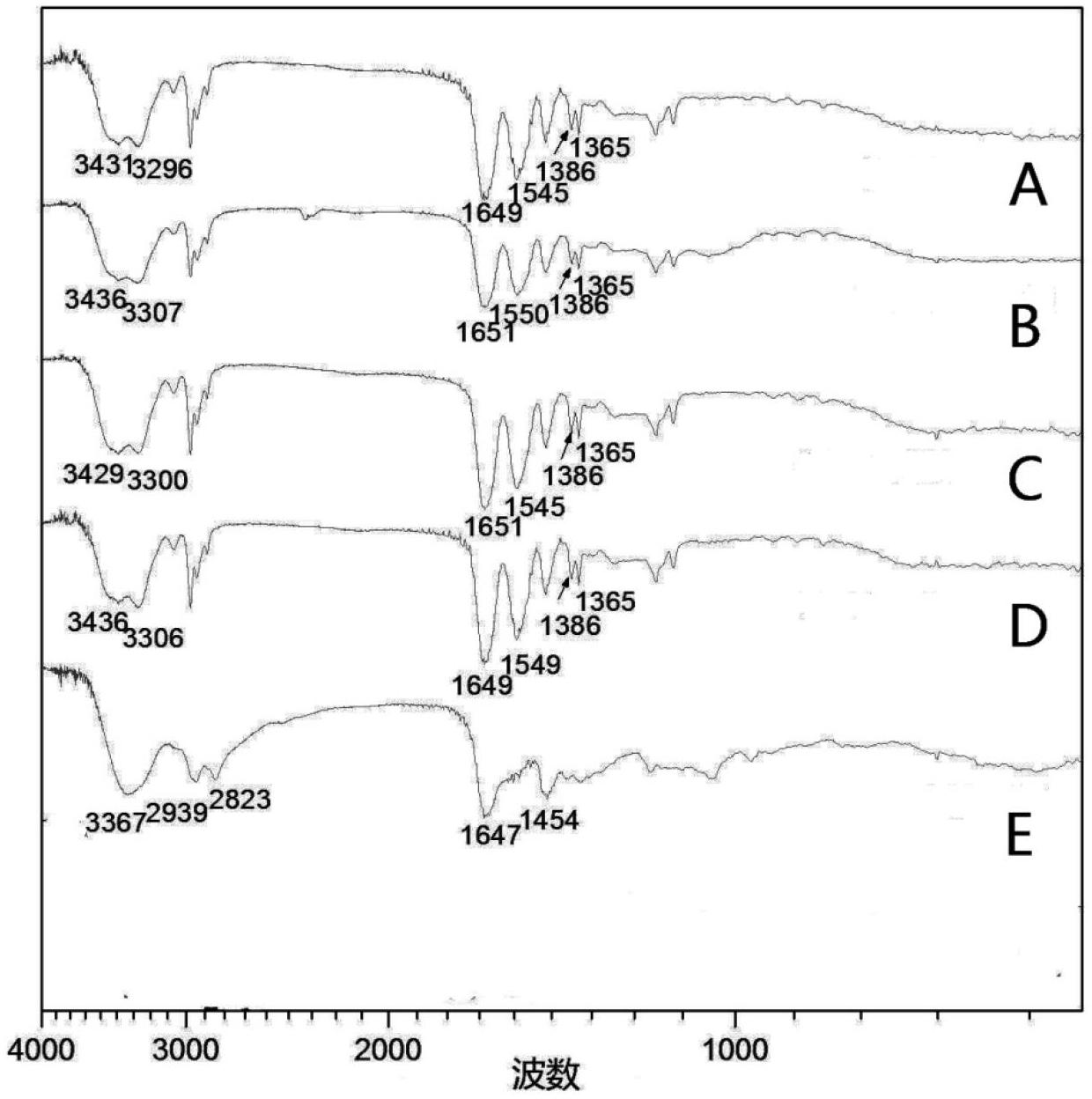
Provided herein is a hydrogel composition comprising a graphene, a chitosan, and a polyethylene (glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) (PCG hydrogel). In some embodiments, the hydrogel further comprises a N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) (TPCG hydrogel). Also provided is a method for differentiating a mesenchymal stem cell comprising contacting the cell with the PCG hydrogel. Further provided herein is a method for delivering a pharmaceutical composition to a cell comprising administering to the cell a TPCG hydrogel and the pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Graphene oxide nano composite organic hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses graphene oxide nano composite organic hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The graphene oxide nano composite organic hydrogel is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 0.1 to 1.5 percent of graphene oxide, 5 to 17 percent of organic monomer, 0.4 to 0.9 percent of initiating agent, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of catalyst and the balance of deionized water; and the organic monomer is one or any combination of acrylamide, acrylic acid, and N-isopropylacrylamide. According to the graphene oxide nano composite organic hydrogel, the added graphene oxide has the lamellar structure which is similar to that of lithium diatomite, and the surface of graphene oxide has abundant hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups, so that the graphene oxide can be combined with acrylic acid, acylic acid amide and water; and therefore, the strength and mechanical properties of the hydrogel can be improved, and the defects that the ion type monomers cannot be used by a lithium diatomite system can be overcome.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
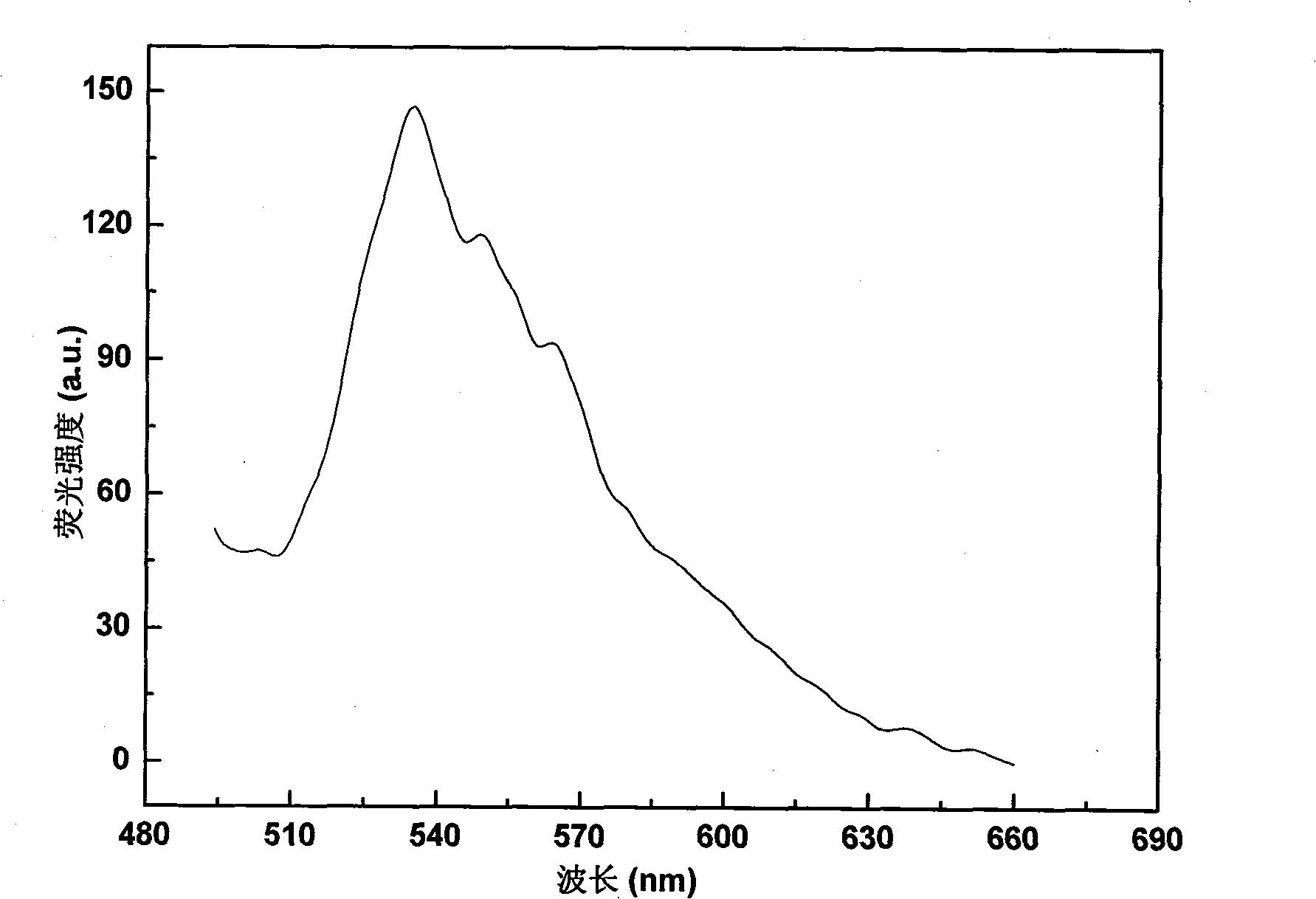
Carbon quantum dot-poly N-isopropylacrylamide composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102675565AStrong fluorescenceImprove performanceSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrowaveModified carbon
The invention discloses a carbon quantum dot-poly N-isopropylacrylamide composite material and a preparation method thereof. An N-isopropylacrylamide polymer is grafted to the surface of carbon quantum dots obtained by microwave treatment by adopting an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATPR) method. The preparation method is simple, convenient and mild in conditions. Modified carbon nano particles have fluorescence property and temperature sensitivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Injectable hydrogel microspheres from aqueous two-phase system
InactiveUS7776240B2Big lossSustained releaseLiquid surface applicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityEmulsion
Injectable hydrogel microspheres are prepared by forming an emulsion where hydrogel precursors are in a disperse aqueous phase and polymerizing the hydrogel precursors. In a preferred case, the hydrogel precursors are poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate and N-isopropylacrylamide and the continuous phase of the emulsion is an aqueous solution of dextran and a dextran solubility reducer. The microspheres will load protein, e.g., cytokines, from aqueous solution.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Porous temperature-sensitive hydrogel slow release formulation and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a porous temperature-sensitive hydrogel slow release formulation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of taking poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) porous temperature-sensitive hydrogel as a carrier, loading drugs in the hydrogel, thereby realizing controlled release of the drug by utilizing the temperature sensitivity characteristic of the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). When the temperature is lower than the LCST (Lower Critical Solution Temperature) of the hydrogel, the drug release is slow, and when the temperature is higher than the LCST, the release speed is accelerated. The preparation method can be used for preparing temperature-sensitive sustained-release pesticide and insecticide, the drug use frequency can be reduced by utilizing the temperature-sensitive sustained-release property, and the effects of improving the pesticide effect and reducing the toxicity can be achieved. The porous temperature-sensitive hydrogel sustained-release inhibitor is fast to react, and simple in technique, has good temperature-sensitive characteristic and sustained-release property, is convenient to use, safe and efficient, thereby having wide application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Environment responding aquogel copolymer and its prepn
The present invention relates to one kind of environment responding aquogel copolymer and its preparation process. The aquogel consists of: N-isopropyl acrylamide 10-90 wt% and methacrylate dextran derivative 10-90 wt%. The preparation process of the environment responding aquogel copolymer includes chemical modification of dextran with GMA to synthesize methacrylate dextran derivative, MA-Dex, with reaction activity; and subsequent copolymerization of MA-Dex and NIPA to obtain the said environment responding aquogel copolymer P(NIPA-co-MA-Dex). The aquogel copolymer has high temperature sensitivity and quick responding speed as well as high strength and excellent biocompatibility. The preparation process is simple, needs no special apparatus and is easy to realize in industry.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Nano-particle compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101250313AGood weather resistanceGood acid and alkali resistanceNanoparticle ComplexHydrogel microspheres
The invention discloses a nano particle compound and a preparation process thereof. The nano particle compound which is provided by the invention is formed by aquogel microsphere and inorganic nano particles, wherein the inorganic nano particles are jogged in the aquogel microsphere, the aquogel microsphere is isopropyl acrylamide and acroleic acid copolymer aquogel microsphere. The preparation process of nano particle compound comprises following steps that firstly preparing isopropyl acrylamide and acroleic acid copolymer aquogel microsphere, and dispersing aquogel microsphere into water, and dispersing inorganic nano particles into water, secondly mixing two kinds water solution which are obtained in first step, wherein the mass ratio of isopropyl acrylamide and acroleic acid copolymer aquogel microsphere and inorganic nano particle in mixing solution is 1:10-1:20, stirring mixing solution for 5-10 minutes under the conditions of temperature is 25-35 DEG C, and pH is 5-7, thereby obtaining nano particle compound.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with copper metal organic skeleton nanoparticles and preparation method of thermosensitive hydrogel
InactiveCN109513038AAggregation is simpleStable in naturePharmaceutical delivery mechanismBandagesMetal-organic frameworkDouble bond
The invention discloses thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with copper metal organic skeleton nanoparticles and a preparation method of the thermosensitive hydrogel. The preparation method comprises thesteps that an amino group on gelatin and methacrylic anhydride are subjected to acylation reaction to synthesize methylacrylic esterified gelatin with a branch containing a carbon-carbon double bond,the carbon-carbon double bond on the branch and N-isopropyl acrylamide are subjected to free radical polymerization, and methylacrylic esterified gelatin-g-poly N-isopropyl acrylamide is prepared; 1,3,5-benzene tricarbonic acid and copper acetate monohydrate are used for preparing copper-based MOF nanoparticles; the copper-based MOF nanoparticles are added to a methylacrylic esterified gelatin-g-poly N-isopropyl acrylamide solution, and a product is prepared. Copper ions are embedded in the biodegradable thermosensitive hydrogel in the form of HKUST-1 NPs, controlled slow release of the copperions is achieved, cytotoxicity is effectively reduced, migration of in-vitro dermal cells is promoted, angiogenesis is induced, and wound healing is promoted.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
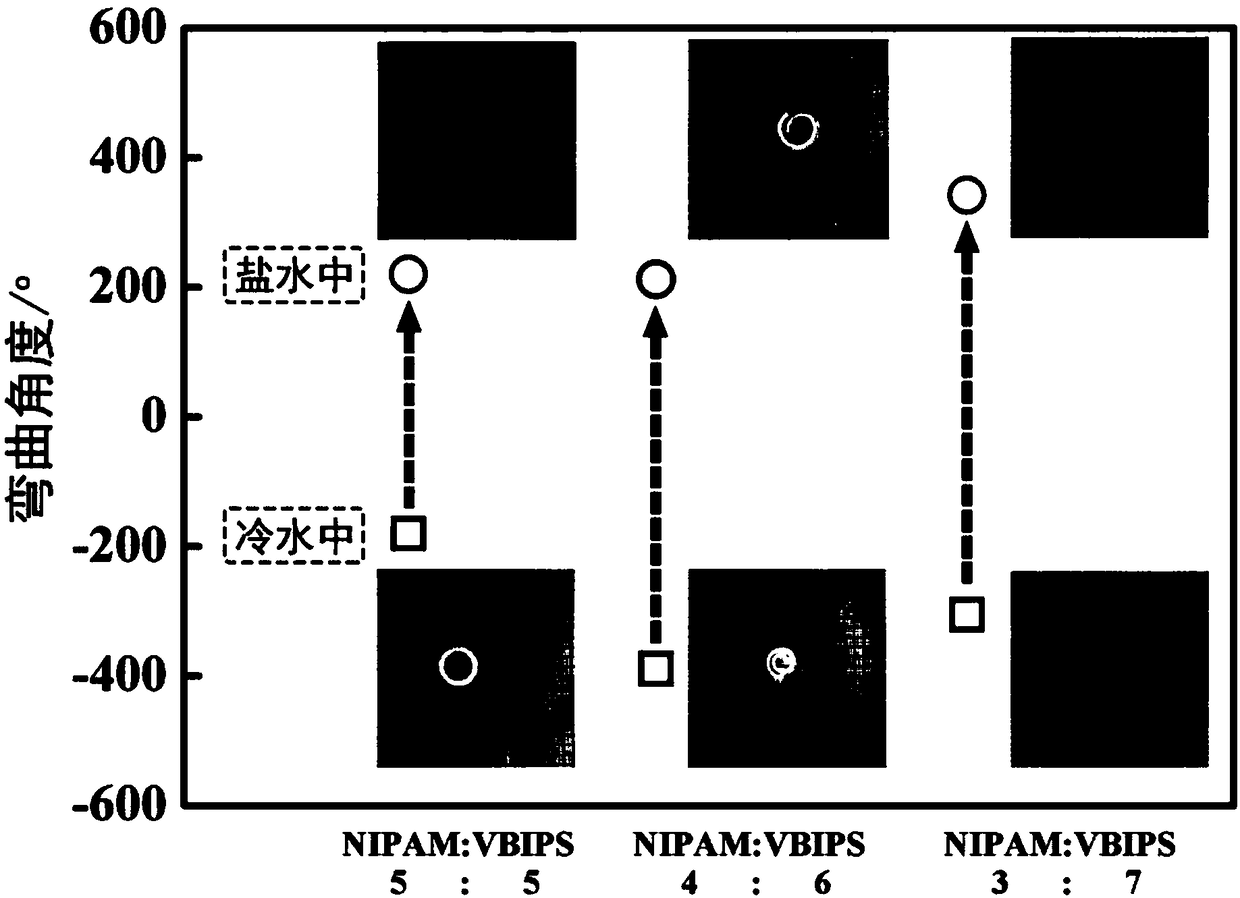
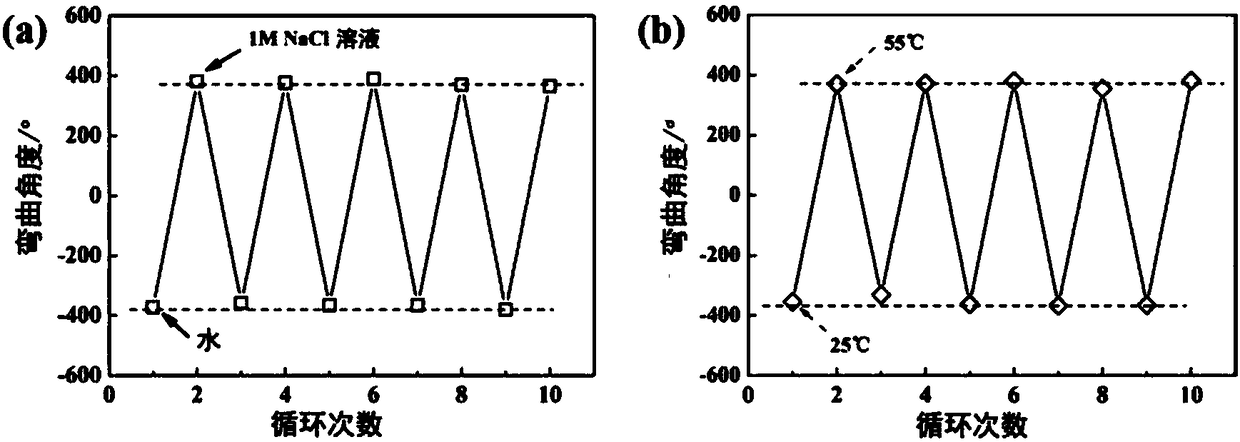
Preparation method, product and application of double-layer water gel with salt-temperature dual response
ActiveCN108395548AUniversalHigh sensitivity of spontaneous bending behaviorCross-linkFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a preparation method of double-layer water gel with salt-temperature dual response. The method comprises the following steps of adding N-isopropylacrylamide, amphoteric ion monomers, cross-linking agents, photoinitiators, radical initiators and catalysts into water; performing stirring dissolution to obtain reaction liquid; performing polymerization reaction on the reactionliquid under inert gas protection and UV-irradiation; performing crosslinking for 1 to 5 hours to obtain poly-N-isopropylacrylamide and amphoteric ion polymer double-layer water gel. Great differences of two kinds of functional monomers in aspects of polarity and polymerization speed are utilized; the double-layer water gel with the salt-temperature dual response is prepared by a one-step method;the double-layer water gel can realize fast great-amplitude self periodic deformation in water-slat solution and low-temperature / high-temperature environment. The water gel can be used for being madeinto a soft body robot or sensor element realizing the salt-temperature dual response.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing fluorescent composite microgel hypersensitive to temperature and pH
The invention discloses a preparation method of fluorescent complex microgel which is sensitive to temperature and pH. The method comprises the technical steps of preparing a mixed surface active agent, preparing the oil phase of a template, preparing an emulsive liquid, preparing a water phase, preparing N-isopropyl acryl amide copolymerized methacrylic acid microgel, preparing turgid N-isopropyl acryl amide copolymerized methacrylic acid microgel, preparing a mixed liquid of Gamma-aminopropyl triethoxy silane and normal heptane, preparing a silicon dioxide polymer complex microballoon decorated by a surface deposited amino group, preparing a mixed liquid of fluorescein isothiocyanate and absolute ethyl alcohol as well as preparing the fluorescent complex microgel. In the invention, the fluorescein isothiocyanate with high quantum yield and good optical stability is adopted as fluorescent matter; the prepared fluorescent complex microgel is sensitive to temperature and pH; and the size of the prepared fluorescent complex microgel is in a micron range and is hard to be aggregated. The method has the advantages of reasonable design, practical technique and easy operation; moreover, reactions are carried out under normal temperature and the like; the method can be applied to the fields of controlled release of medicament, biological probe, chemical separation, and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Nanogels and their production using liposomes as reactors
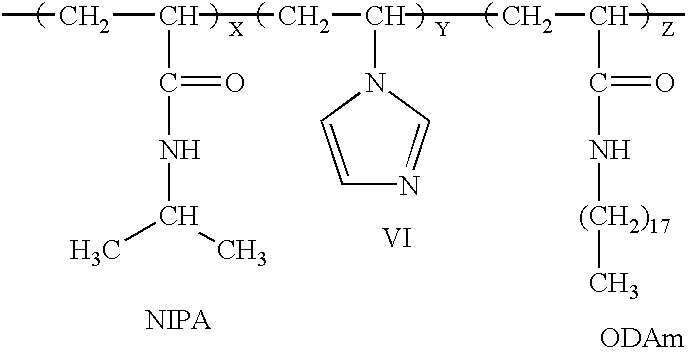
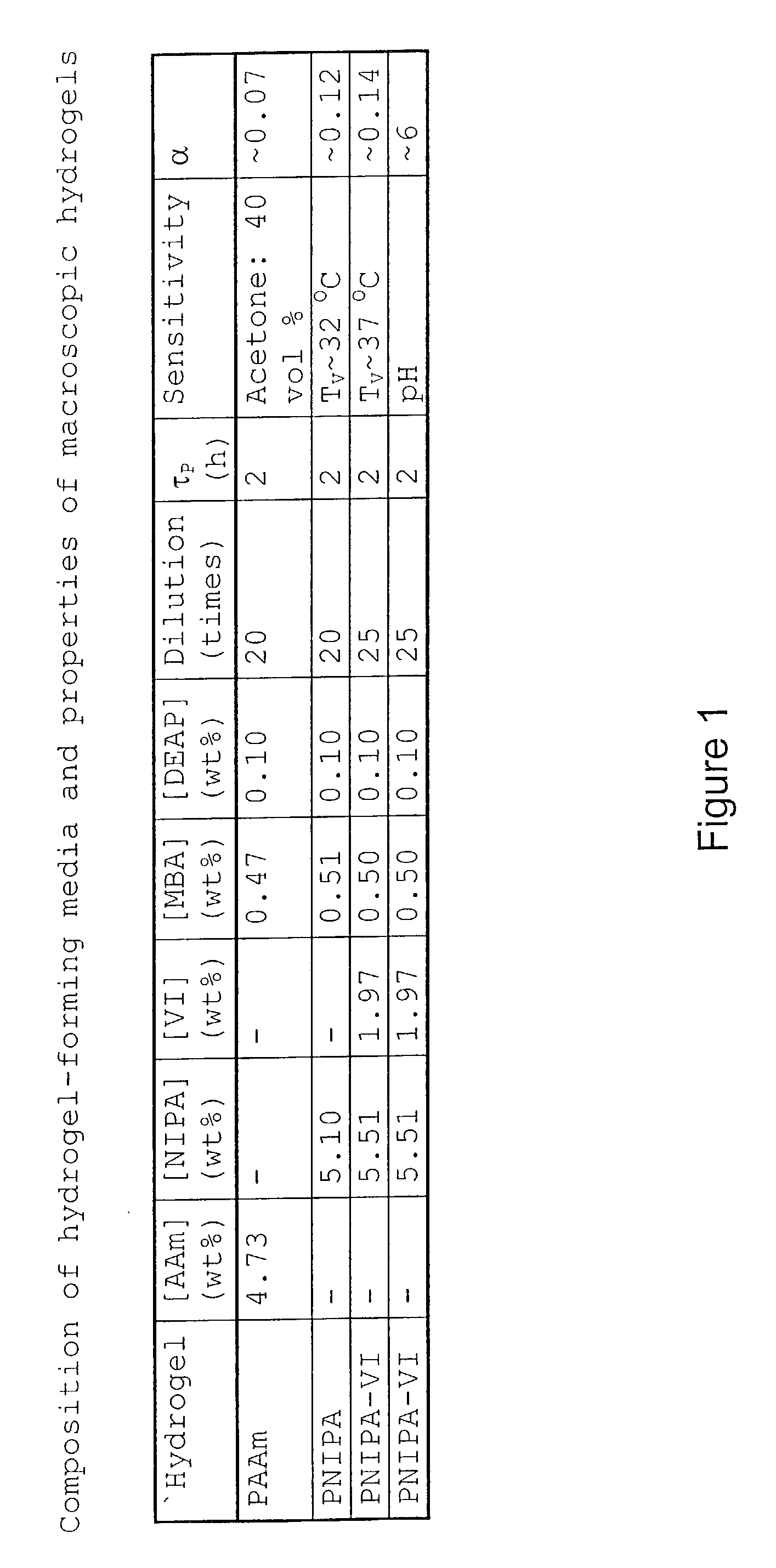
The present invention includes a method for preparing polymer hydrogel spherical particles on a nanometer scale (nanogels). The method includes encapsulating hydrogel-forming components into liposomes, diluting the large unilamellar liposomes suspension to prevent polymerization outside the liposomes, and polymerizing the encapsulated hydrogel-forming components. The lipid bilayer may be solubilized with detergent. The phospholipid and detergent molecules and their micelles may then be removed by dialysis. The resulting nanogels may then be dried by evaporation in a temperature gradient. Poly(acrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-1-vinylimidazole) hydrogel particles with a diameter from 30 to 300 nm were detected and characterized by dynamic light scattering technique. The solvent, temperature, pH, and ionic sensitivities of the nanogels were studied.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
High-strength temperature-sensitive hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101824123AImprove mechanical propertiesAvoid damageVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCross-linkBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to high-strength temperature-sensitive hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The high-strength temperature-sensitive hydrogel is prepared by copolymerizing 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine and N-isopropyl acrylamide as raw materials in the presence of a cross-linking agent and an initiator, wherein the mass ratio of the 2-vinyl-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine as a monomer to the N-isopropyl acrylamide is 0.2-2:1. The high-strength temperature-sensitive hydrogel has high stretching and compression resistance and favorable biocompatibility and optical property, and the surface of the hydrogel has the capacities of adsorbing DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) transfection cells and regulating the attaching and disattaching behaviors of the cells through temperature. The preparation method of the hydrogel is simple, and the hydrogel is easy to store for a long term and transport for a long distance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of thermosensitive microgel asymmetric supported nano silver catalyst
InactiveCN103464203AHigh catalytic activityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEmulsion polymerizationPickering emulsion
A preparation method of a thermosensitive microgel asymmetric supported nano silver catalyst comprises the steps of preparing poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide-styrene) / poly-(N-isopropylacrylamide-methacrylic acid) core-shell microgel by a soap-free emulsion polymerization method and a seed emulsion polymerization method, and then synthesizing the asymmetric supported nano silver catalyst taking the microgel as a template by a pickering emulsion template method. The thermosensitive microgel asymmetric supported nano silver catalyst prepared by the method shows good thermosensitivity, and good catalytic activity as the catalytic reaction efficiency is regulated and controlled by temperature and the thermosensitivity of the microgel simultaneously during catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of double-sensitivity cyclodextrin supermolecule aggregate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-sensitivity cyclodextrin supermolecule aggregate, belonging to the technical field of functional materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing a host molecule-photosensitive 4-hydroxycinnamic acid-cyclodextrin (4HCA-CD) by using 4-hydroxycinnamic acid (4HCA) to modify beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD); using trithioester with adamantine (AD) at tail end as a chain transfer agent, and preparing temperature-sensitive object polymer-double-arm adamantine-poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-adamantine (AD-PNIPAM-AD) by using a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer free radical polymerization (RAFT) method; constructing a double-sensitivity supermolecule inclusion complex 4HCA-CD / AD-PNIPAM-AD by utilizing comprehensive performance of a beta-CD dewatering cavity and AD; and self-assembling the 4HCA-CD / AD-PNIPAM-AD to form the supermolecule aggregate which is capable of realizing reversible conversion in shape and size by changing light and temperature. The supermolecule aggregate prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has good light / temperature double sensitivities and is capable of carrying out smart response onto external stimulus, so that the supermolecule aggregate has a wide application prospect in the fields of drug loading, controlled release, and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation and application of metal ion directly induced fluorescent supramolecular gel
ActiveCN103374132AShort gel timeStrong fluorescent emissionLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceBiopolymer
The invention discloses preparation and application of a metal ion directly induced fluorescent supramolecular gel, which belongs to the field of functional materials. According to the invention, combined action of coordination bonds formed between metal ions and terpyridyl units in a polymer, and intermolecular hydrogen bonds formed by amide bonds in N-isopropylacrylamide units in the polymer are utilized for induction preparation of the fluorescence supramolecular gel. The preparation method is simple and easy for mass production; meanwhile, because coordination bonded hydrogen bonds are employed to assemble the supramolecular gel, the prepared supramolecular gel overcomes the defects of a general supramolecular gel, such as long preparation time, industrial complex and instability; besides, the supramolecular gel with fluorescence characteristics expands its application to fields of diffusion process tracking, control of transition of biological polymer phase, environmental stimuli induction and bioluminescence imaging.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane-polypeptide block-graft copolymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102336913AEasy to preparePrecise control of relative contentPolypropylene glycolN isopropyl acrylamide
The invention relates to a poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane-polypeptide block-graft copolymer and a preparation method thereof. In the copolymer, the molecular weight of polyurethane is 10000-60000; the molecular weight of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) is 3000-10000; and the molecular weight of polypeptide is 500-4000. The preparation method comprises the steps: 1) synthesis of polyurethane containing side carboxyl group and terminal double-bond group: adding diisocyanate, polypropylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, a catalyst and a solvent to a reaction bottle and reacting, then sequentially adding bis(hydroxymethyl) propanoic acid, butylene glycol and hydroxypropyl acrylate and reacting; 2) synthesis of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane block copolymer: adding polyurethane containing side carboxyl group and terminal double-bond group, a solvent and an initiator, and isopropyl acrylamide to a reactor and reacting; and 3) adding poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane block copolymer, a solvent, a condensing agent, and a polypeptide homopolymer to a reactor and reacting to obtain a target product with temperature and pH dual responsibility.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
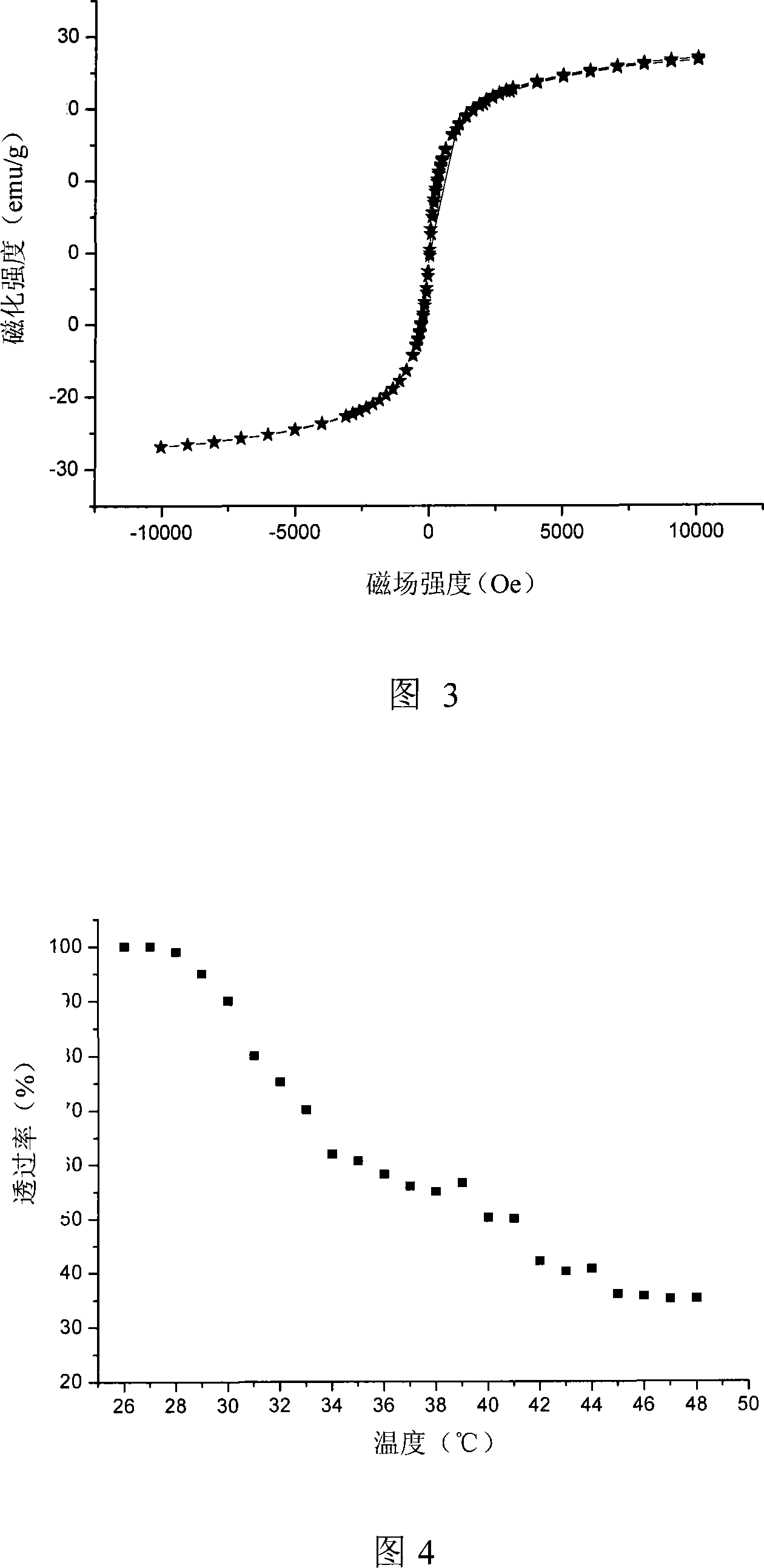
Magnetic temperature sensing nano-particle with bioavailability and synthesizing method thereof
InactiveCN101173025ABiocompatibleMagneticOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismBiocompatibility TestingDrug release
The invention relates to a magnetic thermometer nm particle with biocompatibility, which has biocompatibility, and double response properties of magnetism and thermometer property, and the particle diameter thereof is 20 to 60 nm, and the magnetic responsibility is strong, and magnetic saturation intensity is 10.0 to 27.0 emu / g. The synthetic method of the magnetic thermometer nm particle with biocompatibility comprises: firstly, adopting chemical coprecipitation method to prepare magnetic Fe3O4 nm particle, and using silane coupler to hold surface modification, and then using the modified magnetic Fe3O4 nm particle as a seed, and having polyreaction with dextran, N-isopropyl acrylamide, finally obtaining the magnetic thermometer nm particle with biocompatibility. The magnetic thermometer nm particle with biocompatibility synchronously has double responses of magnetism and thermometer property, and has wide application prospect in the fields of drug release, protein and enzyme separation.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
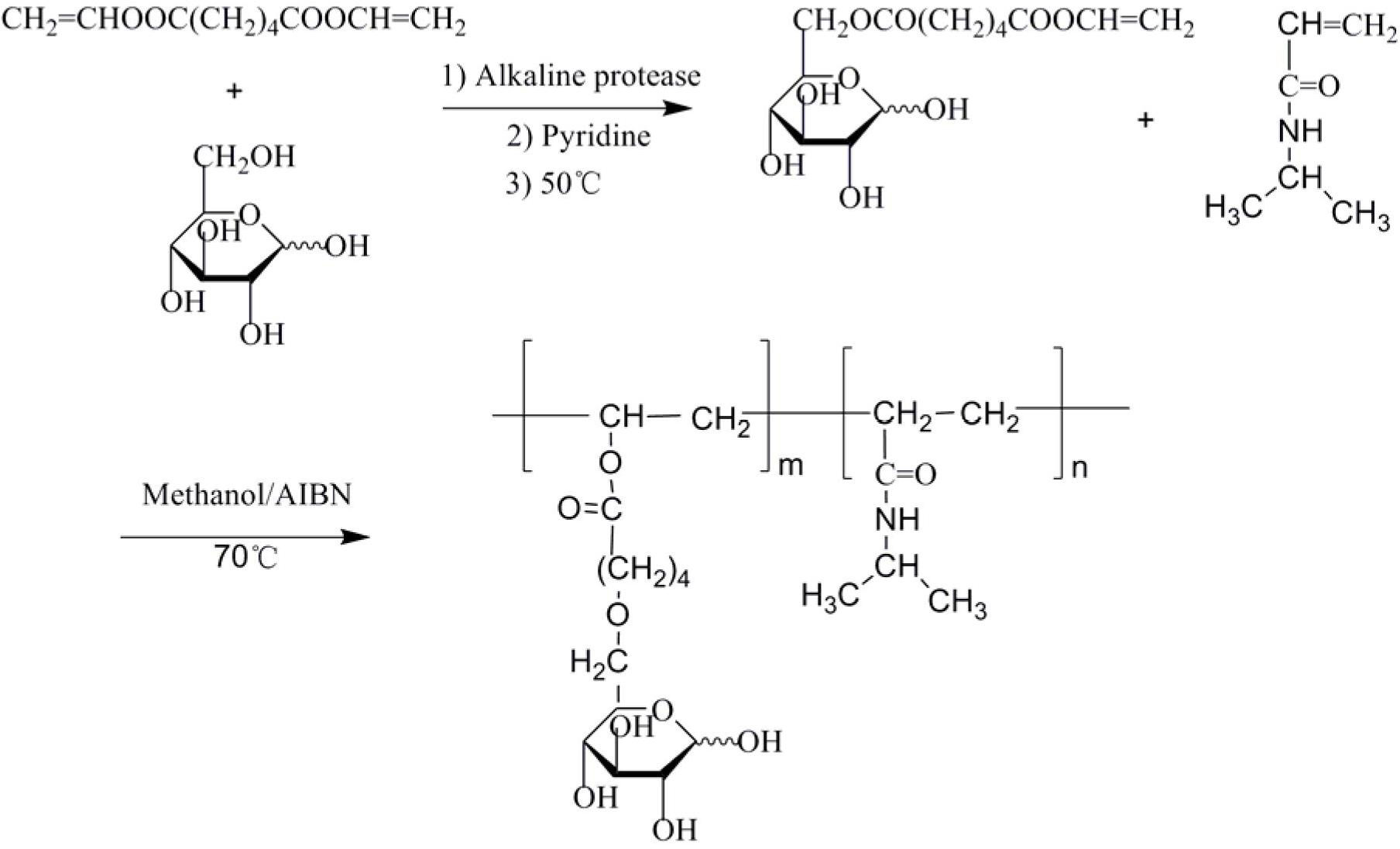
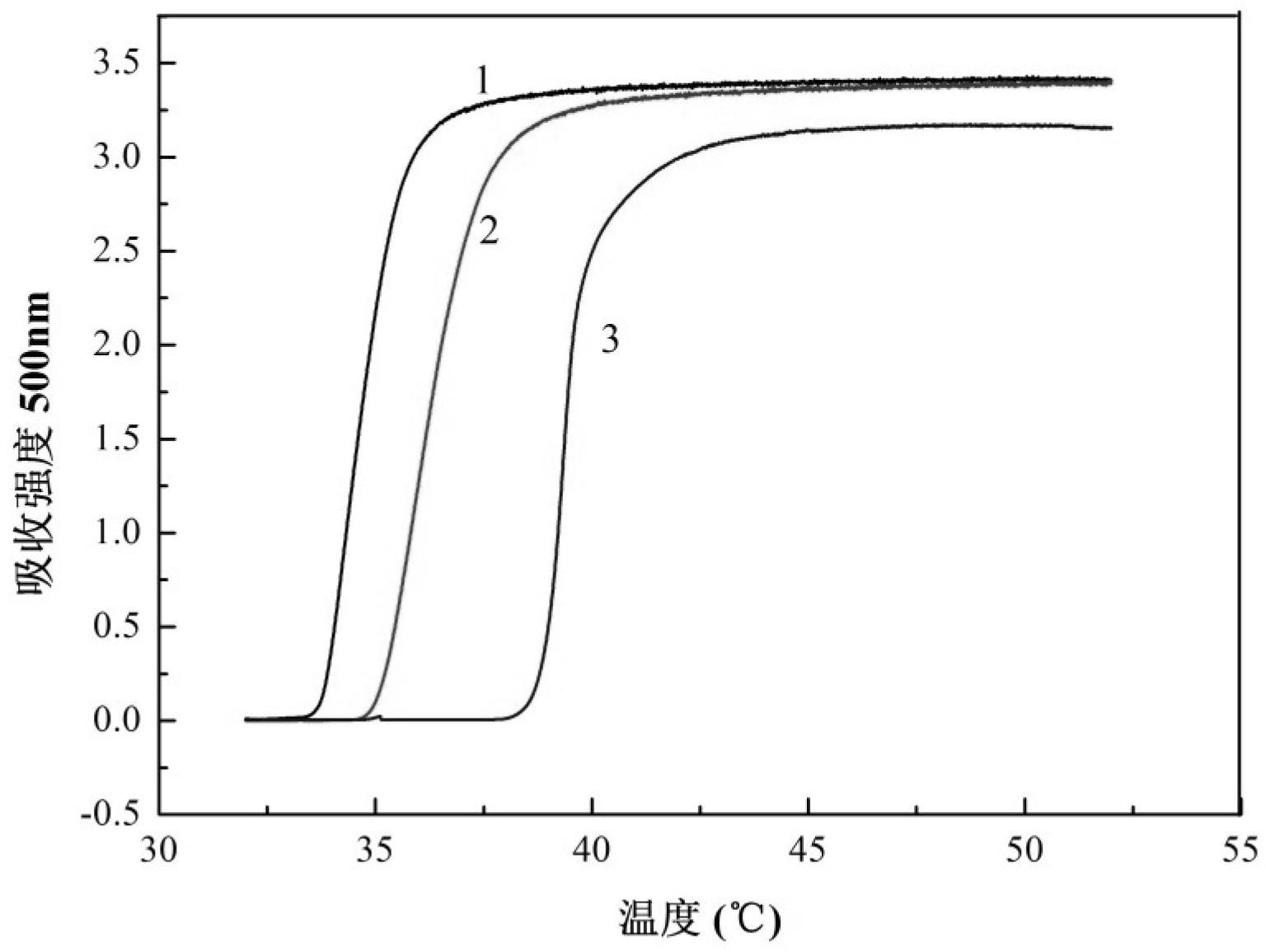
Preparation method of double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer
InactiveCN102659979ARich sourcesLow priceGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHydrophilic monomerTemperature response
The invention relates to a preparation method of a double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing aliphatic diacid divinyl ester; (2) dissolving the aliphatic diacid divinyl ester and glucose into an organic solvent, and adding bacillus subtilis alkali protease or lipase AY30 to obtain a polymerizable saccharine hydrophilic monomer; and (3) dissolving the polymerizable saccharine hydrophilic monomer, an N-isopropylacrylamide monomer and an initiator into an organic solvent, performing a polymerization reaction under the protection of nitrogen gas at the temperature of 50-80 DEG C to obtain a polymer, repeatedly precipitating, and performing vacuum drying on an obtained precipitant to obtain the double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer. The method is simple, has mild reaction conditions, is easy, convenient and practicable for operating, and is easy for industrializing; and the obtained double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer can be applied in the fields of medicament targeted conveying, gene delivery, biological separation, membrane science and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Hollow silica nanosphere and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101559950ANot destructiveThe process is simple and easy to controlSilicaMicroballoon preparationOrganic solventReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hollow silica nanosphere by one step. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a poly-N-isopropyl acrylamide aqueous solution and an ethyl orthosilicate prehydrolysis solution at a temperature of 40 to 60 DEG C to react at a constant temperature for 160 to 180 hours; and carrying out ethanol washing, ultrasonic concussion, centrifugal separation and drying on a reaction liquid, and then obtaining the hollow silica nanosphere. The hollow silica nanosphere has a hollow core and mesoporous shell structure, the particle diameter is between 200 and 600 nm, and the shell thickness is between 30 and 100 nm. The invention also discloses the hollow silica nanosphere and the application. The method does not need to use an organic solvent to catalyze or further remove a template agent by high-temperature calcination or chemical corrosion, and can control the hollow nanosphere size and the shell thickness by simply changing the reaction temperature, the reaction time and the feed ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method of temperature, pH and ultraviolet multi-stimuli-responsive semi-interpenetrating network nanocomposite hydrogel
The invention relates to a preparation method of a semi-interpenetrating network nanocomposite hydrogel which can respond to variations in temperature, pH and ultraviolet to realize volume transition. The preparation method of the gel is as follows: taking temperature-sensitive monomers, namely N-isopropylacrylamide and azo type water soluble monomers, namely 4-((4-acryloxy) phenyl azo) benzoic acid as copolymerization monomers, taking modified nano-clay as a cross-linking agent, dissolving the monomers and the cross-linking agent in a cellulose type macromolecular water solution, uniformly stirring, and then performing oxidation, reduction and catalytic free radical polymerization in an ice bath under the protection of nitrogen for preparation. The gel uses nano-laponite cross-linked monomers to constitute a framework of the gel and takes cellulose type macromolecules as semi-interpenetrating macromolecules. The obtained hydrogel has the advantages of excellent mechanical properties, high swelling rate and fast and controllable stimulus response. The gel has the potential to be applied to the field of sustained release of medicaments.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com