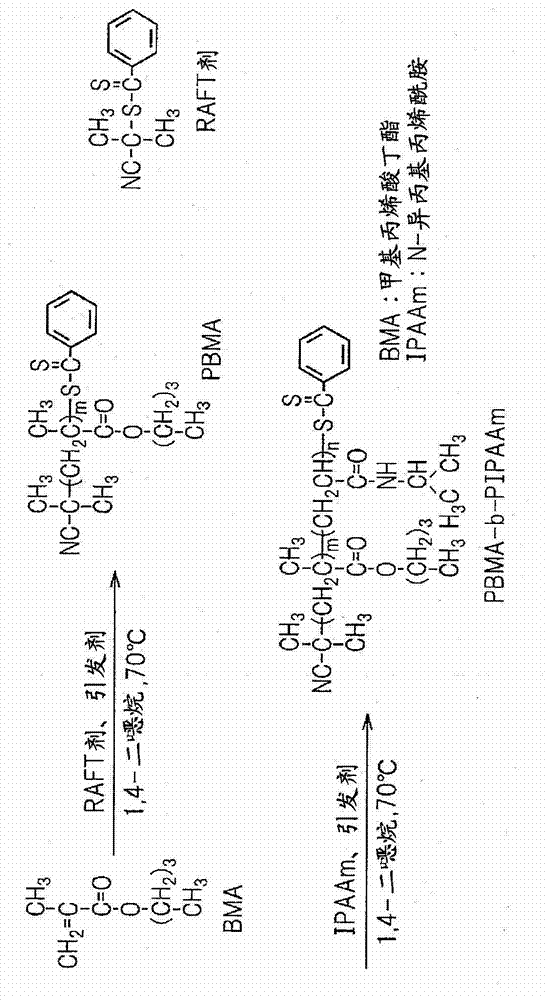
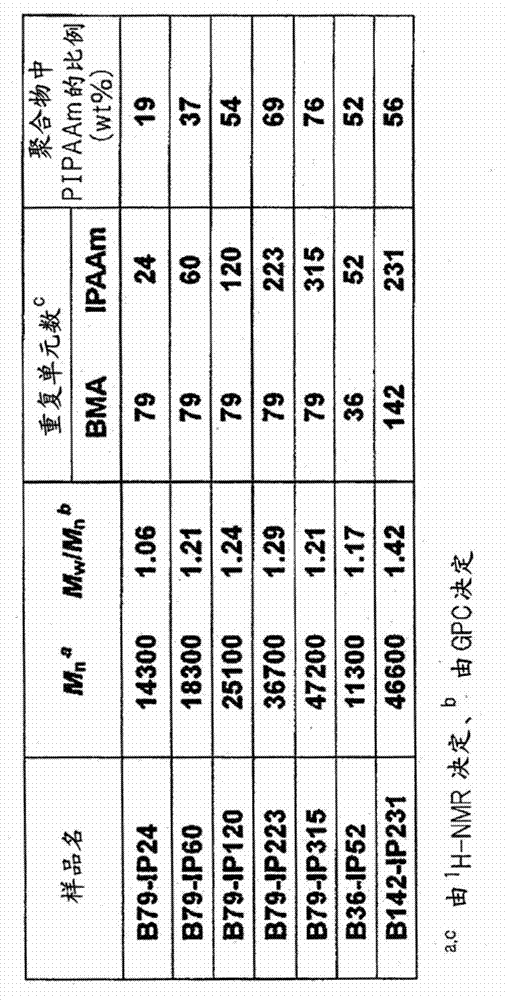
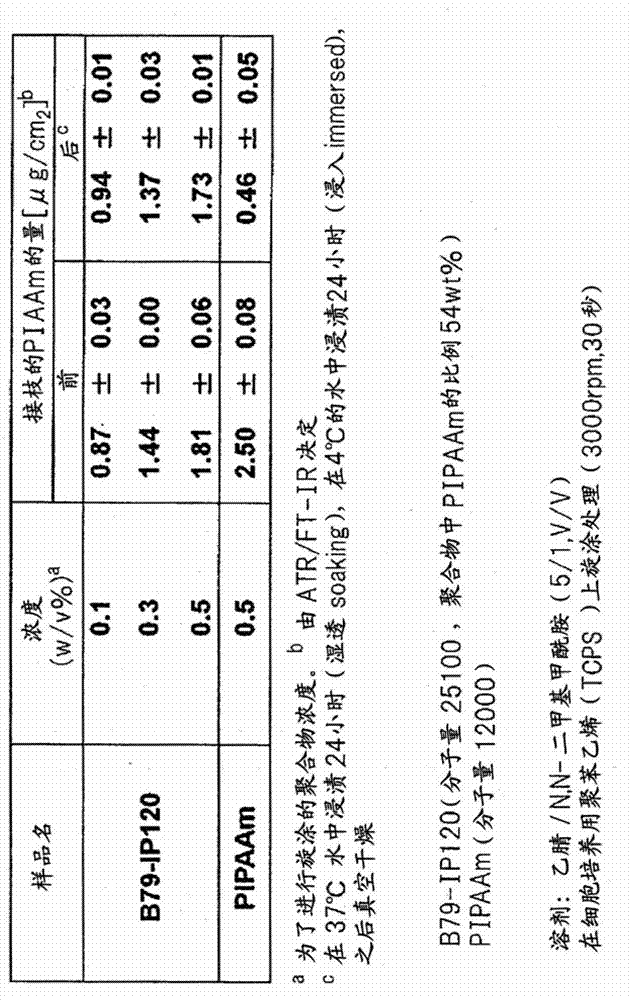
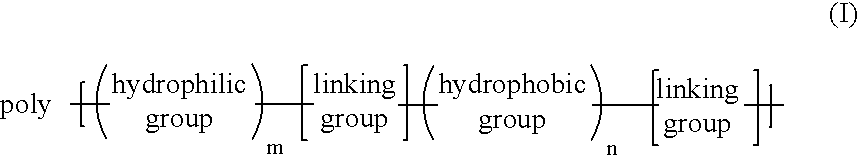Patents
Literature
84 results about "Temperature-responsive polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
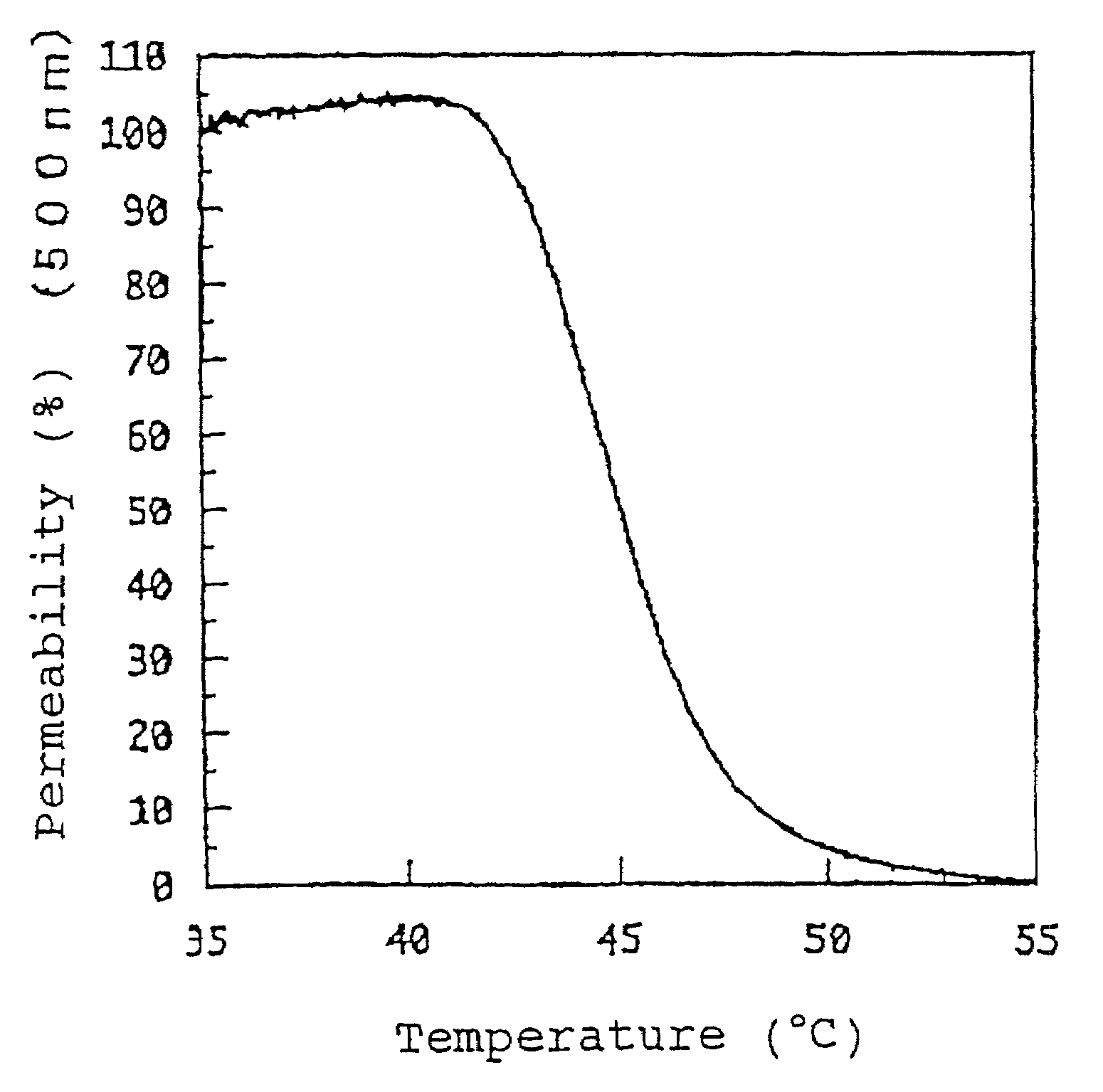
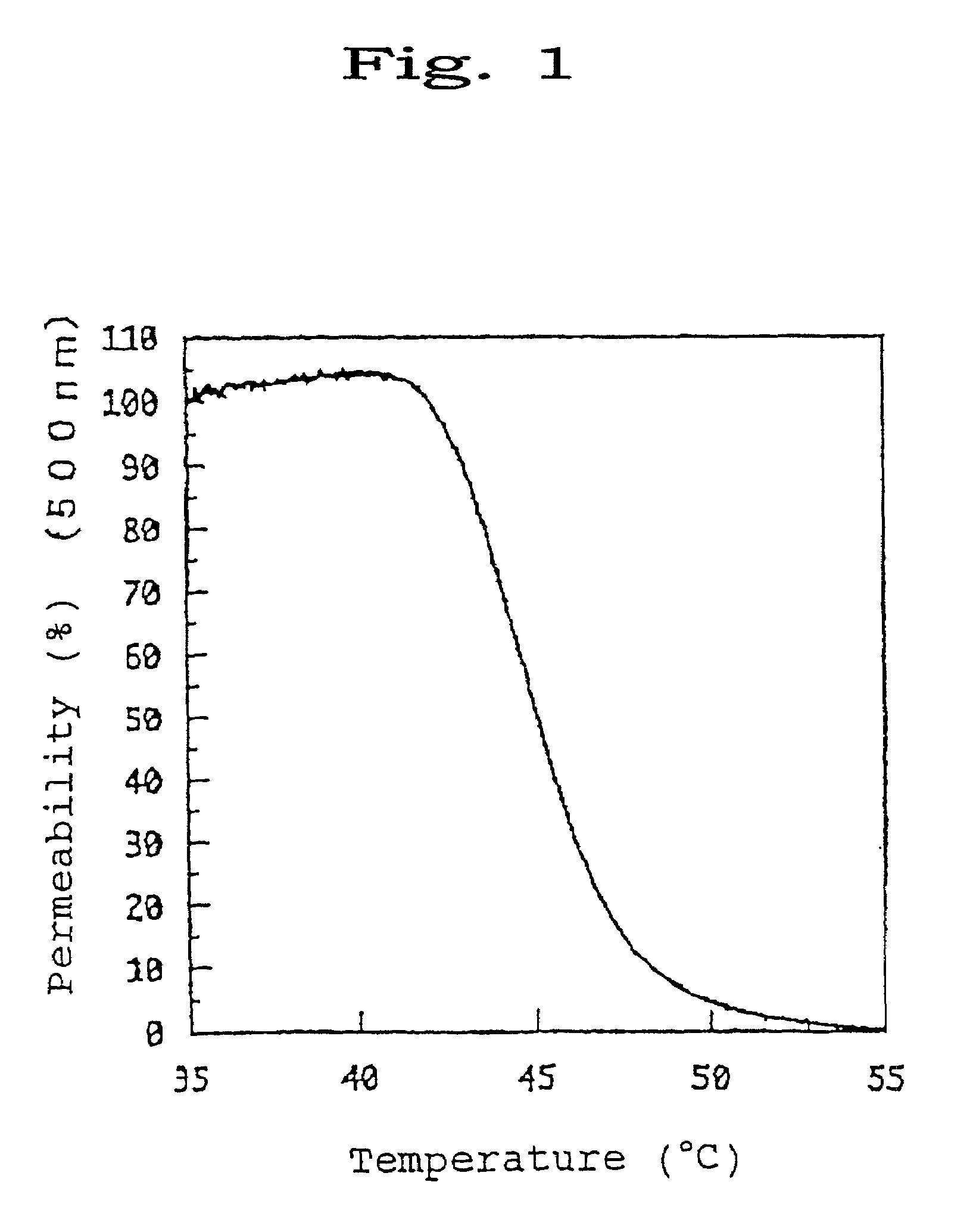
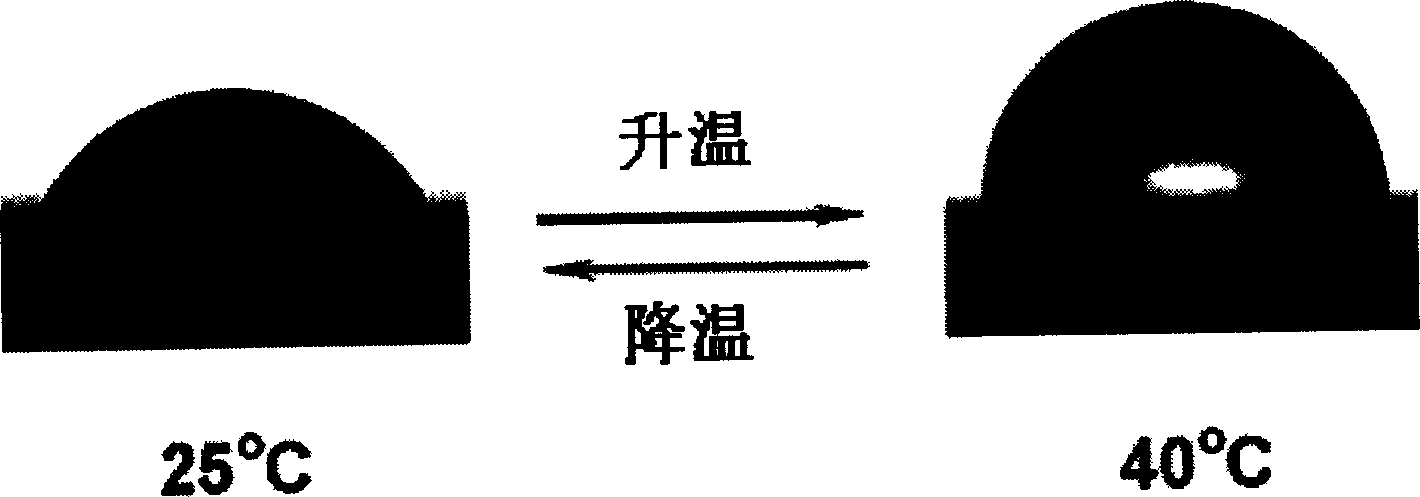
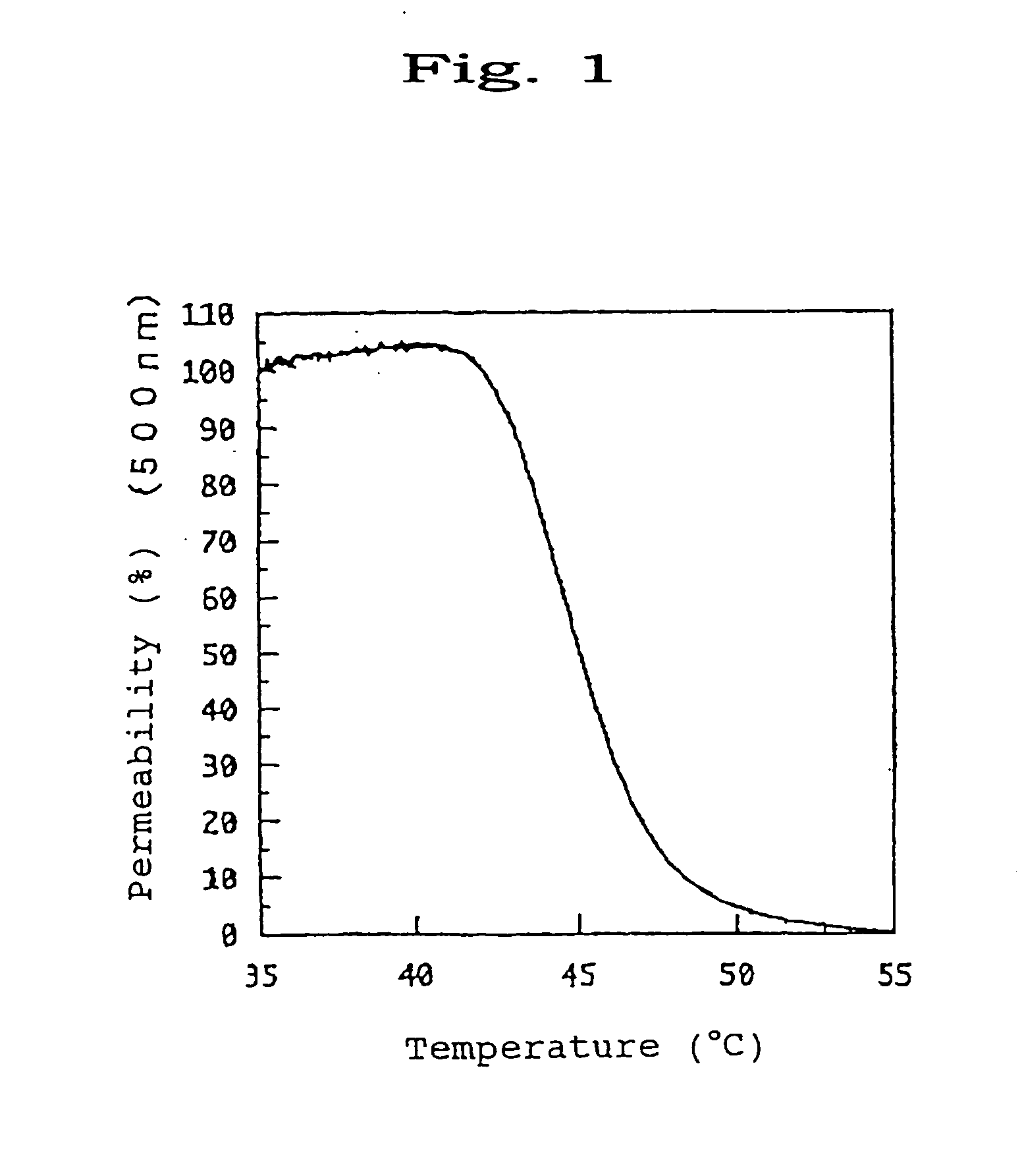
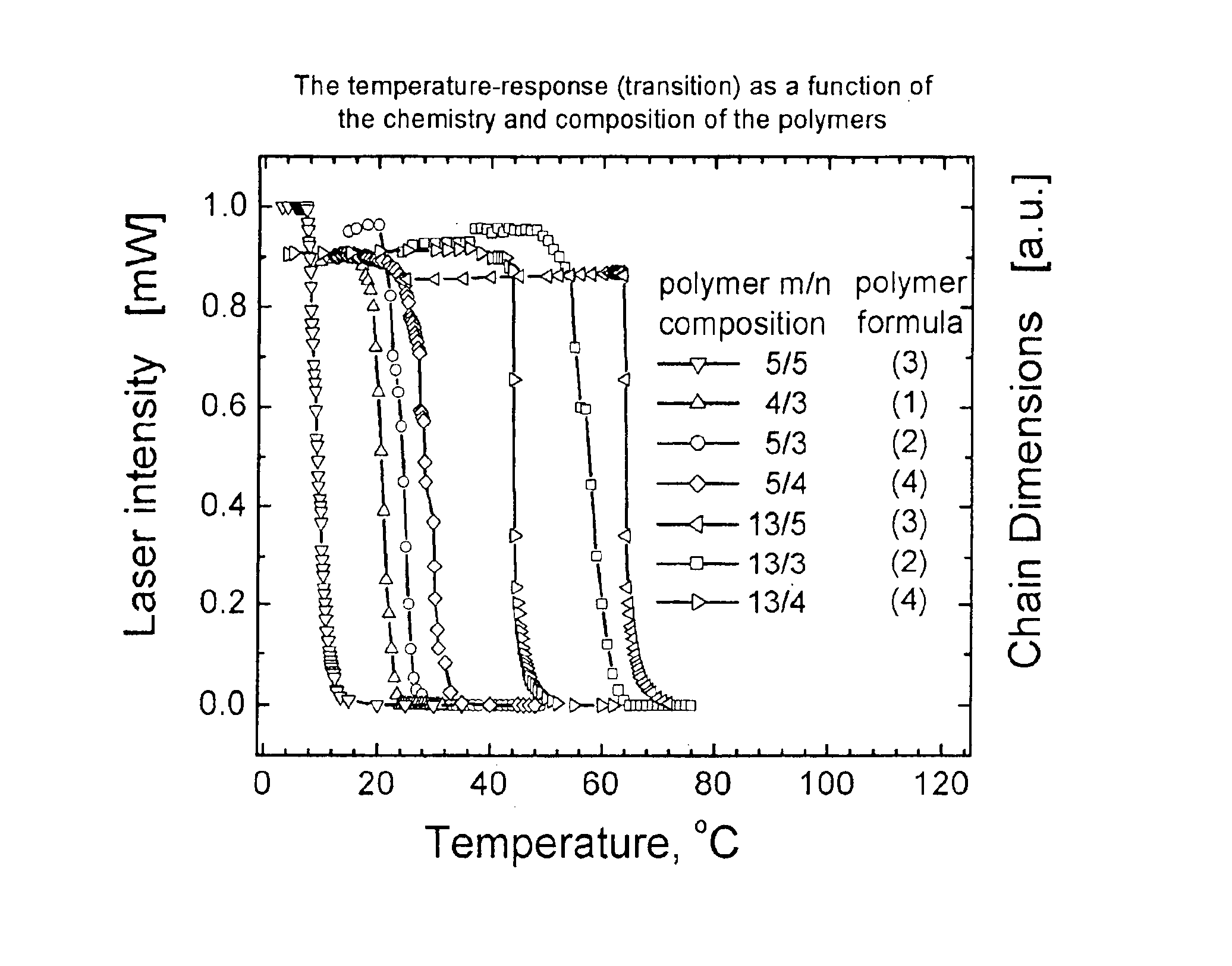
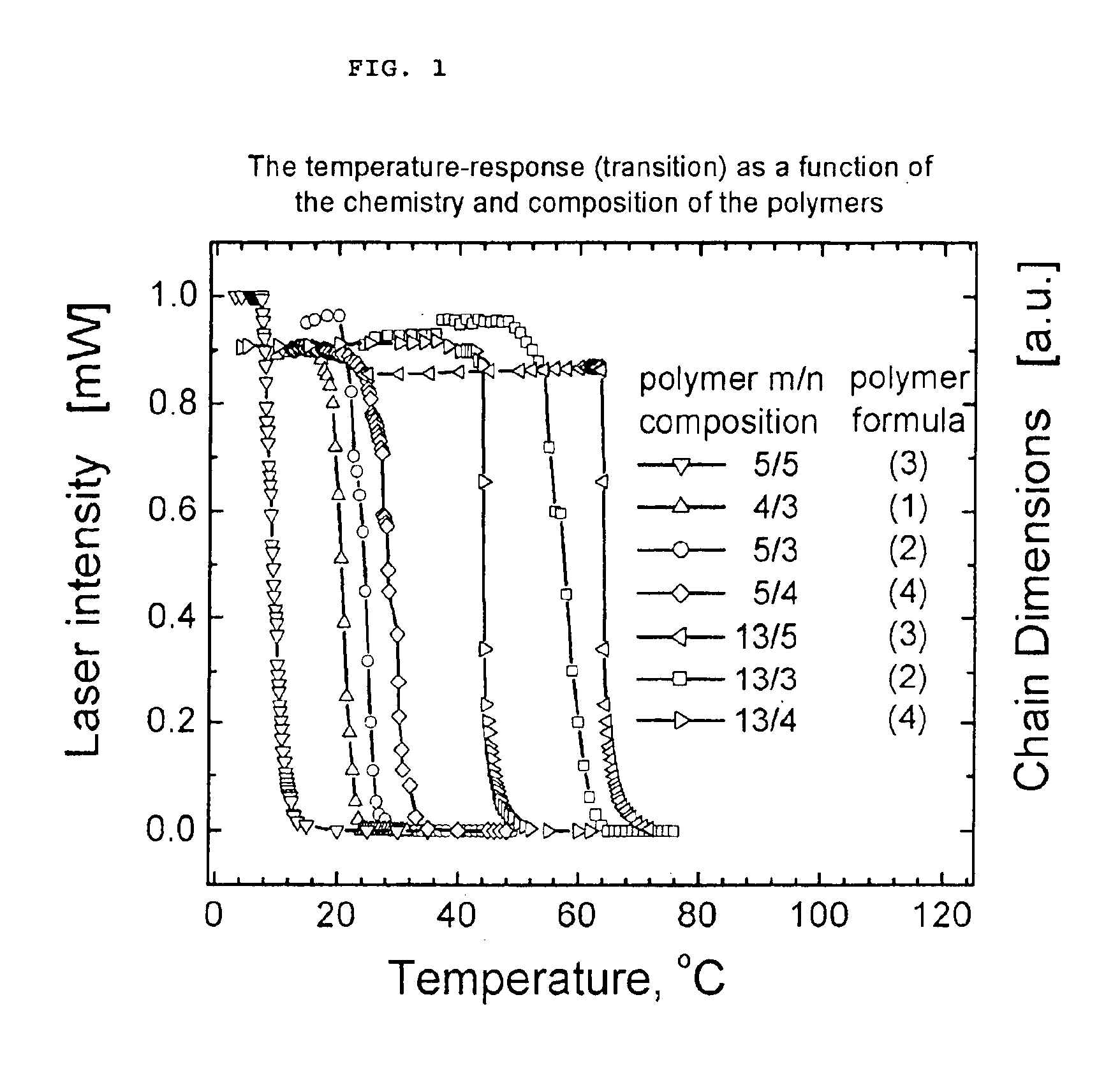
Temperature-responsive polymers or thermoresponsive polymers are polymers that exhibit a drastic and discontinuous change of their physical properties with temperature. The term is commonly used when the property concerned is solubility in a given solvent, but it may also be used when other properties are affected. Thermoresponsive polymers belong to the class of stimuli-responsive materials, in contrast to temperature-sensitive (for short, thermosensitive) materials, which change their properties continuously with environmental conditions. In a stricter sense, thermoresponsive polymers display a miscibility gap in their temperature-composition diagram. Depending on whether the miscibility gap is found at high or low temperatures, an upper or lower critical solution temperature exists, respectively (abbreviated UCST or LCST).
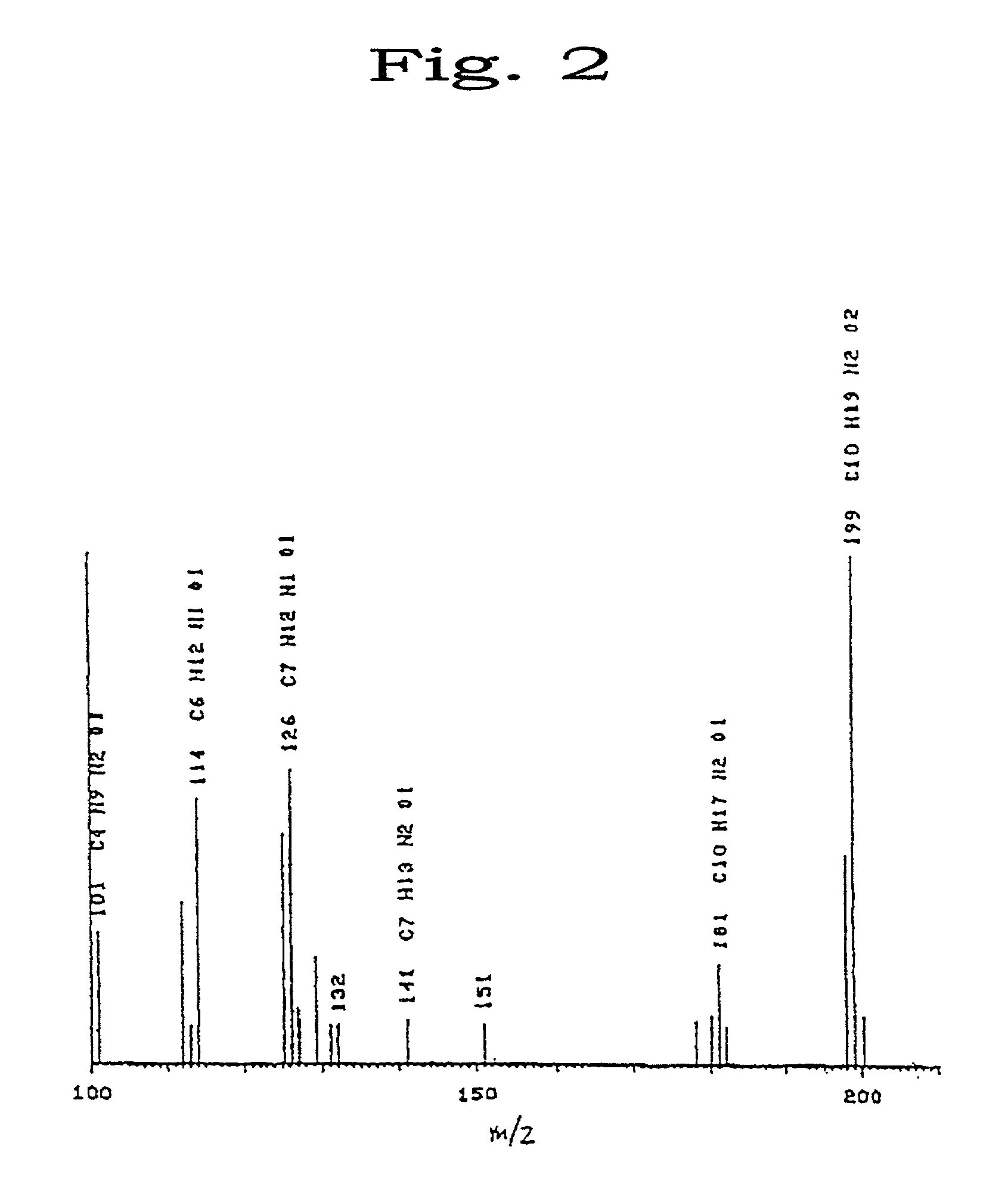
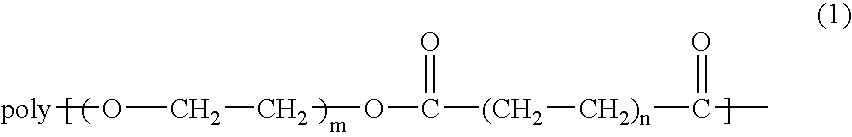
Temperature-responsive polymer compound and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6956077B1Improve hydrophobicityComponent separationOther chemical processesChemical compoundSide chain
A temperature-responsive polymer and polymer material which has ester bond(s) and / or acid amide bond(s) respectively at one or more sites in the side chain and can be arbitrarily controlled by varying the side chain is provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Cell cultivation-support material, method of cocultivation of cells and cocultivated cell sheet obtained therefrom
InactiveUS20030036196A1Rapid responseA large amountNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
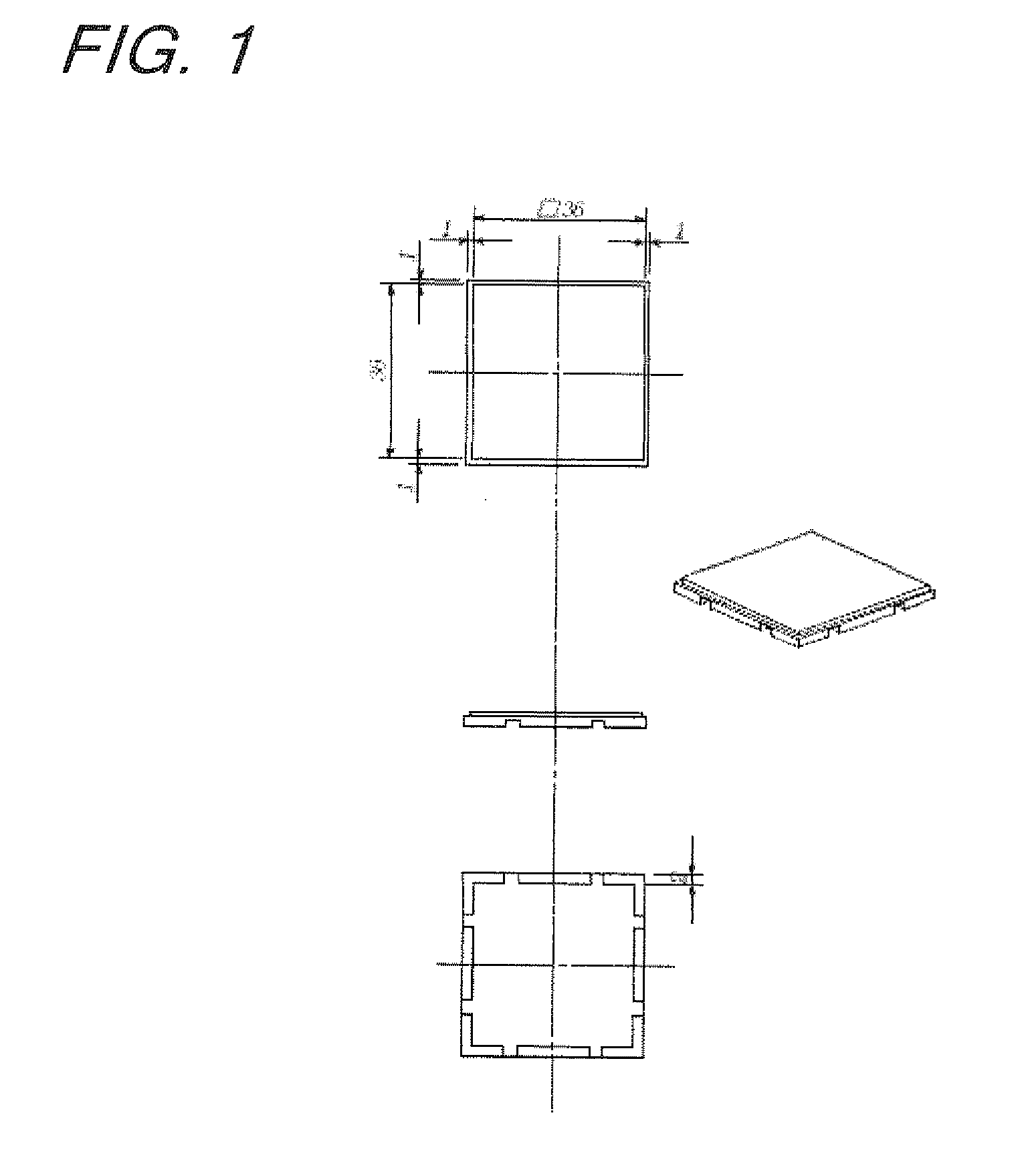
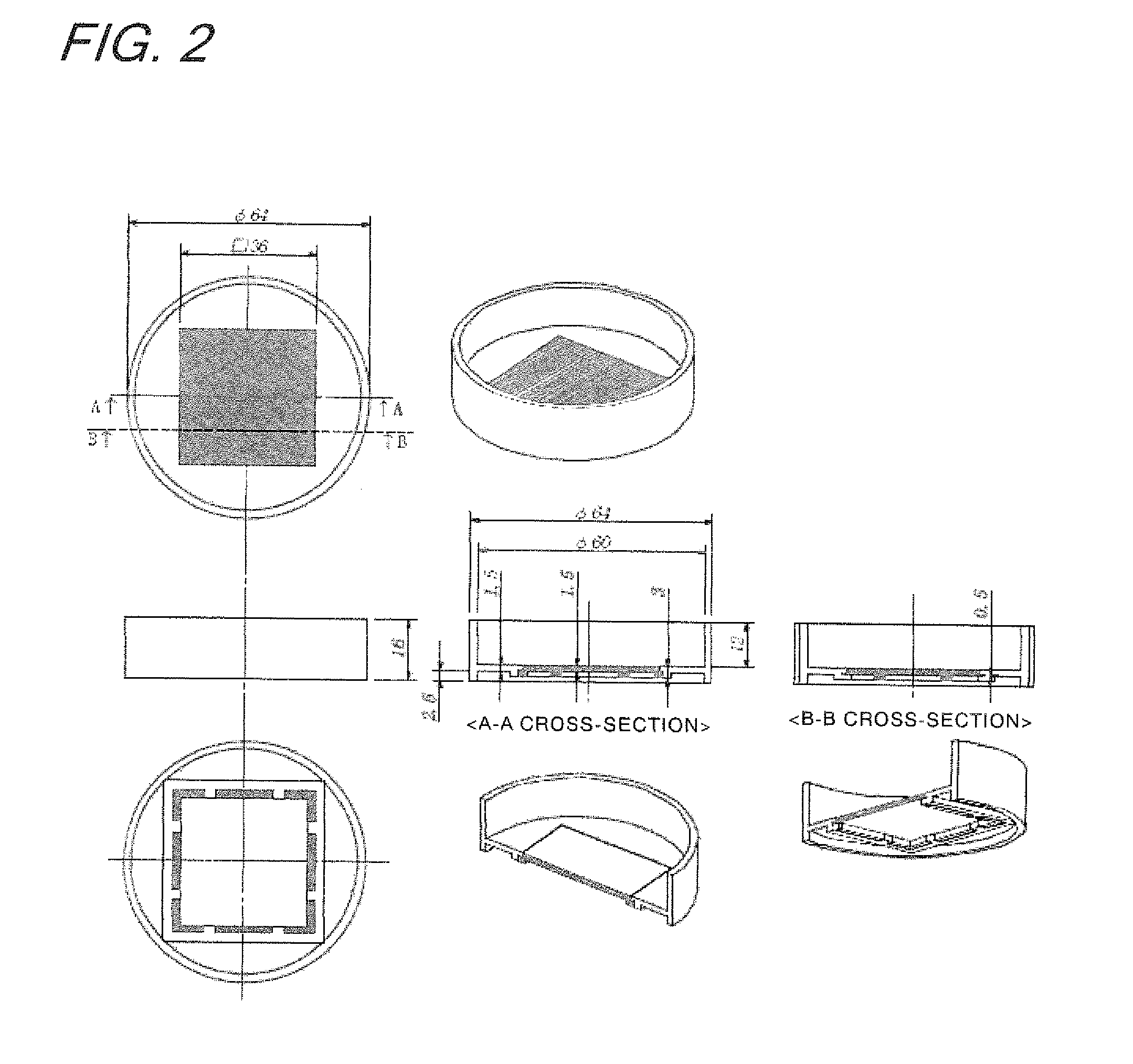
By using a bed material for cell culture having a surface composed of two domains of domain A coated with a temperature-responsive polymer and domain B composed of any one or a combination of a domain coated with a polymer having high affinity with cells, a domain coated with the temperature-responsive polymer in an amount different from the amount of the temperature-responsive polymer of domain A, and a domain coated with a polymer which responds to a temperature different from the temperature to which domain A responds, a method for the co-culture of a plurality of kinds of cells which has heretofore been difficult becomes possible.
Owner:CELLSEED
Soakage reversibly variable temperature-responsive copolymer film preparation method
InactiveCN1569933AEasy to prepareWide applicabilityPolymer scienceAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention relates to a process for preparing temperature-responsive polymeric thin films which consists of, carrying out free radical polymerization reaction through surface triggering atom transition on smooth surfaces or rough surfaces with micrometer or nano structure, thus making the material surface have reversible soakage.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cultured Cell Sheet, Production Method Thereof, and Application Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080226692A1Expand the scope ofIncrease stickinessBiocideSkeletal disorderUpper critical solution temperatureCultured cell
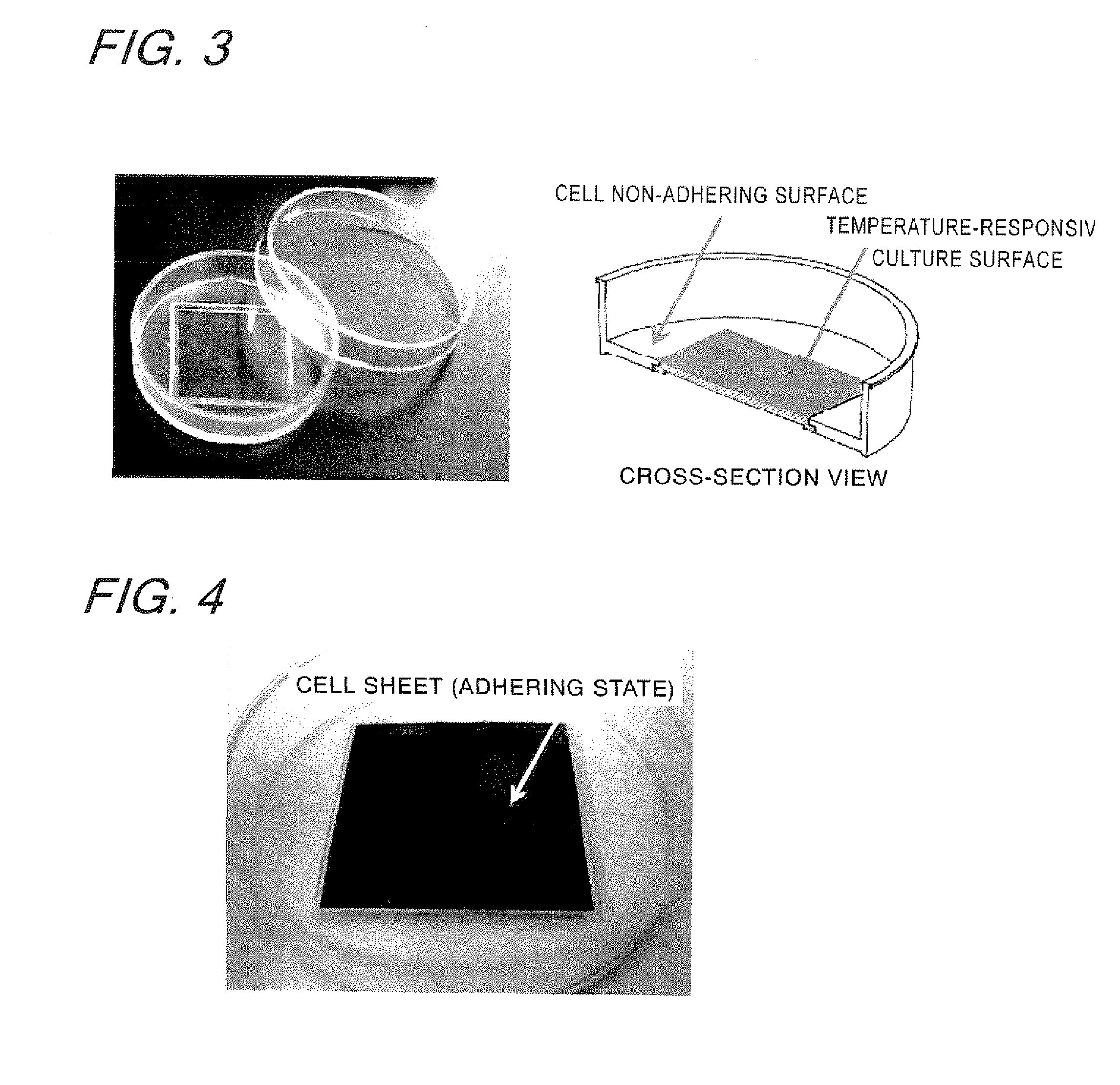
The problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a cultured cell sheet that expresses phenotypes of the chondroid tissue. The problems can be solved by producing the cultured cell sheet in which cells are cultured on a surface of a cell culture support that is coated with a temperature responsive polymer having an upper or lower critical solution temperature ranging from 0° C. to 80° C. in water, including steps of: adjusting the temperature of the culture medium to a temperature below the lower critical solution temperature or above the upper critical solution temperature; bringing the cultured cell sheet in close contact with the carrier; and detaching the cultured cell sheet together with the carrier.
Owner:TOKAI UNIV +1
Cultured Cell Sheet, Production Method and Tissue Repair Method Using Thereof
InactiveUS20080131476A1Good flexibilitySuppress air leakage and blood leakage and bodily fluid leakageDigestive systemSurgeryTissue repairUpper critical solution temperature
It is intended to provide a cultured cell sheet with excellent tissue adherence and flexibility. The above object can be achieved by culturing cells on a support for cell culture in which a surface of a substrate is coated with a temperature-responsive polymer whose lower or upper critical solution temperature against water is in the range of 0 and 80° C. along with a surfactant protein or a crosslinking inhibitor and producing a cultured cell sheet by detaching it by setting the temperature of the culture to the upper critical solution temperature or higher or to the lower critical solution temperature or lower.
Owner:CELLSEED
Temperature-responsive polymer compound and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20050224415A1Improve hydrophobicityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesChemical compoundSide chain
A temperature-responsive polymer and polymer material which has ester bond(s) and / or acid amide bond(s) respectively at one or more sites in the side chain and can be arbitrarily controlled by varying the side chain is provided. The process for production thereof and the use thereof are also provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Preparation method of double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer
InactiveCN102659979ARich sourcesLow priceGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHydrophilic monomerTemperature response
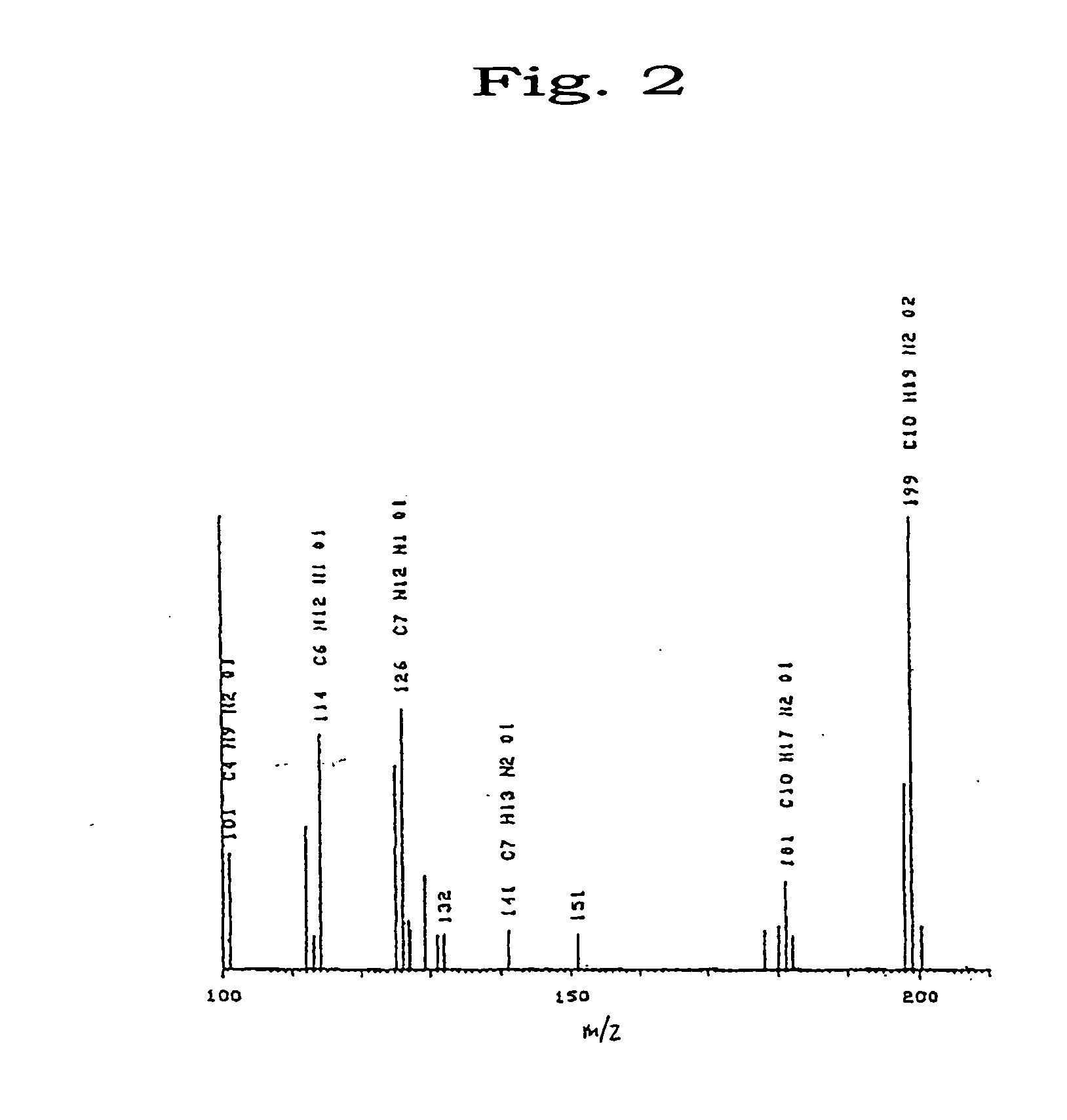
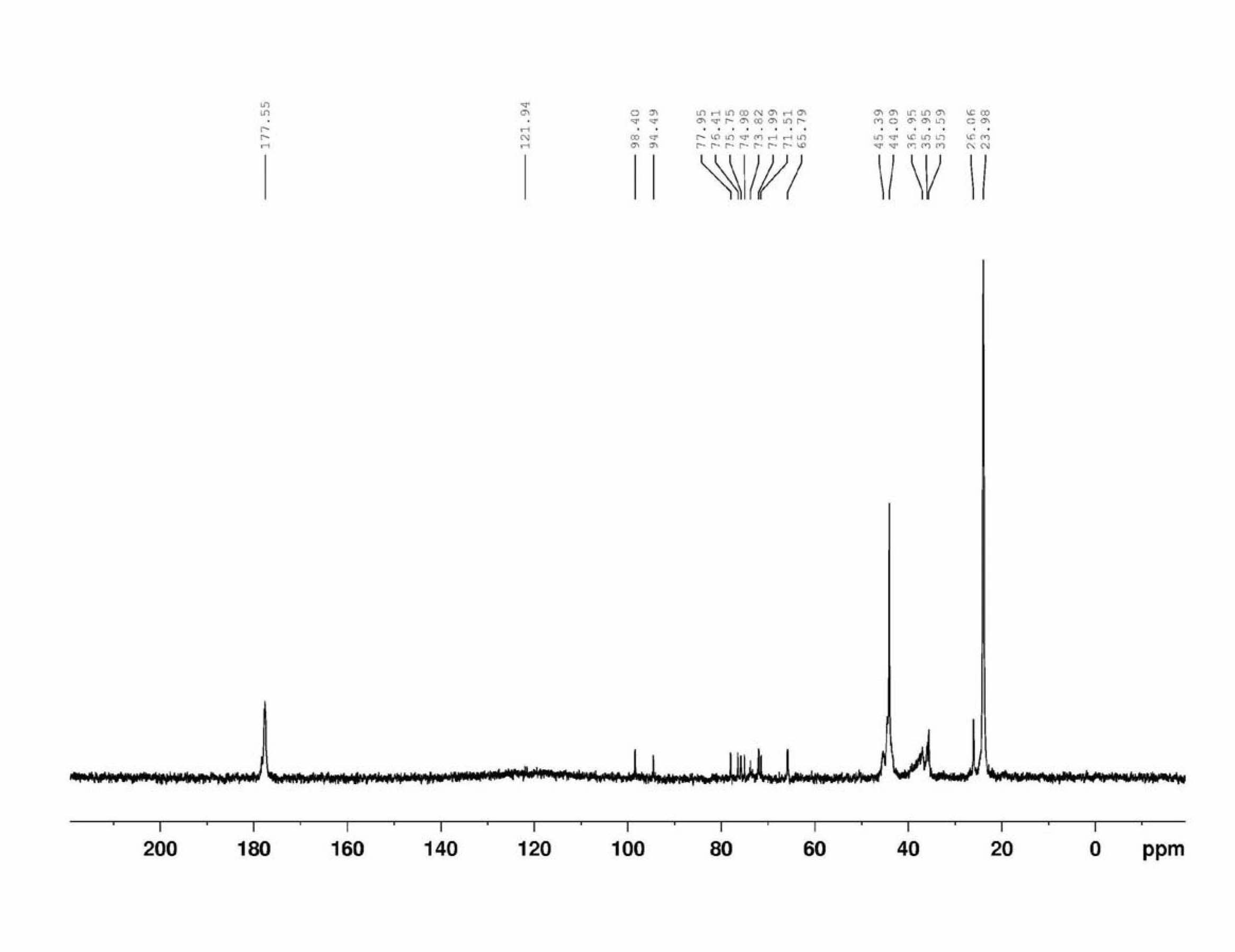
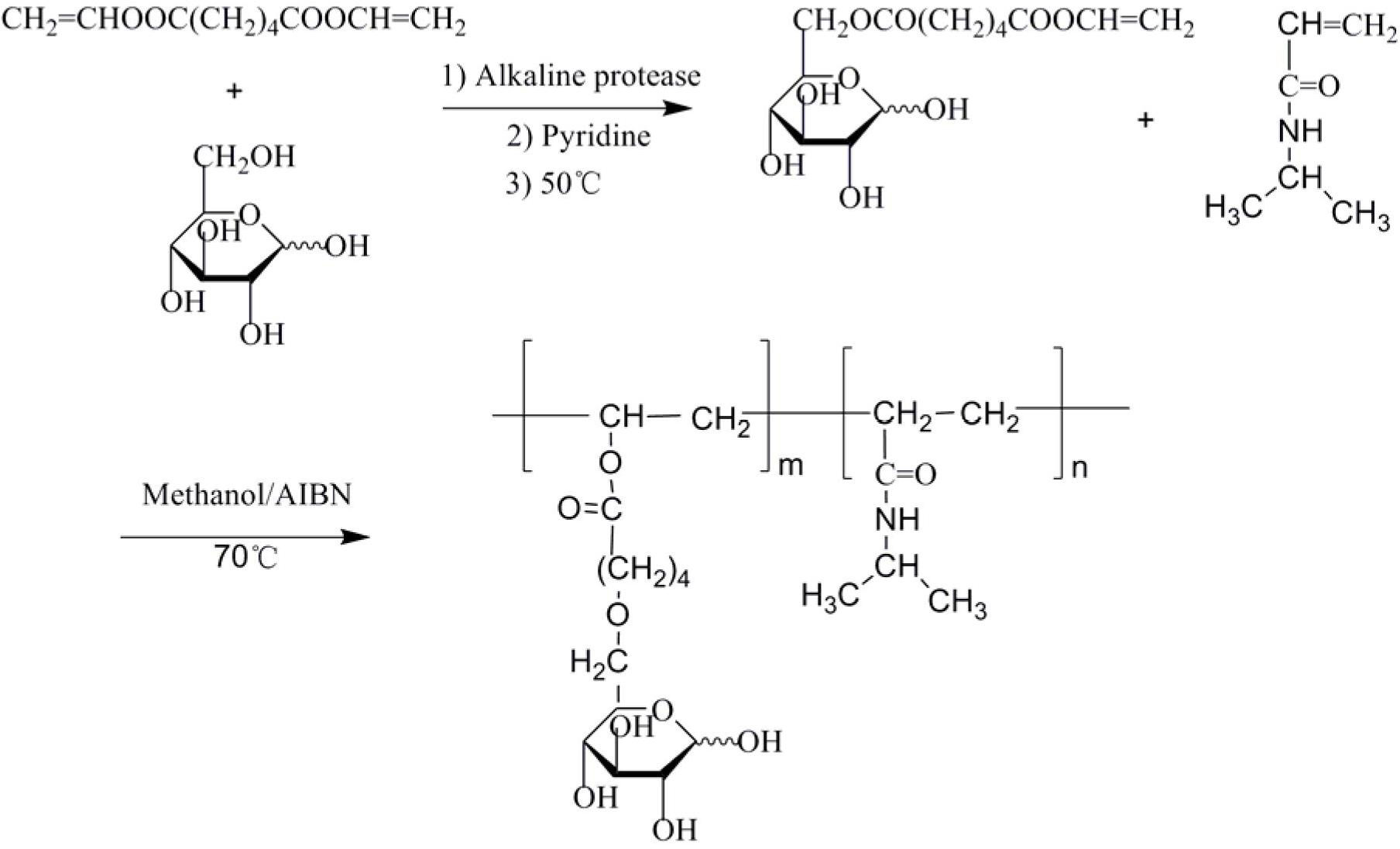
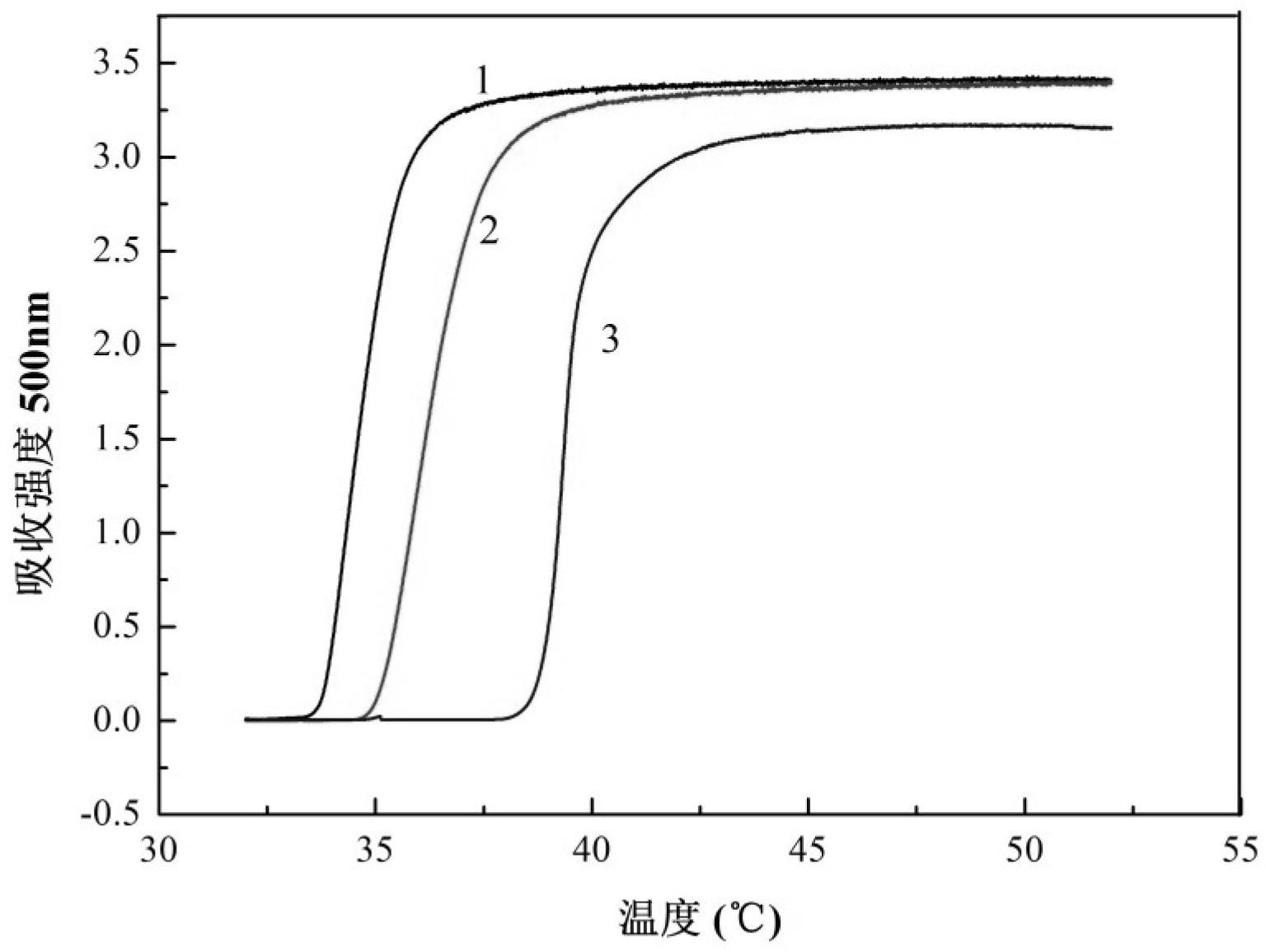
The invention relates to a preparation method of a double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing aliphatic diacid divinyl ester; (2) dissolving the aliphatic diacid divinyl ester and glucose into an organic solvent, and adding bacillus subtilis alkali protease or lipase AY30 to obtain a polymerizable saccharine hydrophilic monomer; and (3) dissolving the polymerizable saccharine hydrophilic monomer, an N-isopropylacrylamide monomer and an initiator into an organic solvent, performing a polymerization reaction under the protection of nitrogen gas at the temperature of 50-80 DEG C to obtain a polymer, repeatedly precipitating, and performing vacuum drying on an obtained precipitant to obtain the double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer. The method is simple, has mild reaction conditions, is easy, convenient and practicable for operating, and is easy for industrializing; and the obtained double-hydrophilic temperature response polymer can be applied in the fields of medicament targeted conveying, gene delivery, biological separation, membrane science and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Temperature-responsive polymer/polymer complex
The problem of the invention is to find a polymer mixture which forms an inter-polymer complex by being responsive to temperature even under neutral to alkaline conditions. According to the invention, a temperature responsive inter-polymer complex capable of showing thermal responsiveness in an aqueous solution, which contains a poly-N-acetylacrylamide or polyvinyl alcohol and polyethylene glycol, polyacrylamide or polymethacylamide, is applied to separating agents, immobilized enzymes, denatured protein modifiers, separation method or concentration of microorganisms, purification or concentration of nucleic acids, drug-releasing microcapsules and the like.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Anterior ocular-associated cell sheet, three-dimensional construct and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060240552A1Few structuresNervous system cellsMammal material medical ingredientsDissolutionCultured cell
An anterior ocular segment related cell sheet or three-dimensional structure that have only a few structural defects as they have been recovered retaining the intercellular desmosome structure and the basement membrane-like protein between cell and substrate. The anterior ocular segment related cell sheet or three-dimensional structure is produced by a process comprising the steps of cultivating cells on a cell culture support comprising a substrate having its surface covered with a temperature responsive polymer having an upper or lower critical dissolution temperature of 0-80° C. with respect to water, optionally stratifying the layer of cultured cells by the usual method, and thereafter, (1) adjusting the temperature of the culture solution to either above the upper critical dissolution temperature or below the lower critical dissolution temperature, and further optionally (2) bringing the cultured anterior ocular segment related cell sheet or three-dimensional structure into close contact with a polymer membrane, and (3) detaching the sheet or three-dimensional structure together with the polymer membrane.
Owner:CELLSEED
Temperature-responsive cell culture substrate and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20110229962A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMulti materialCell adhesion
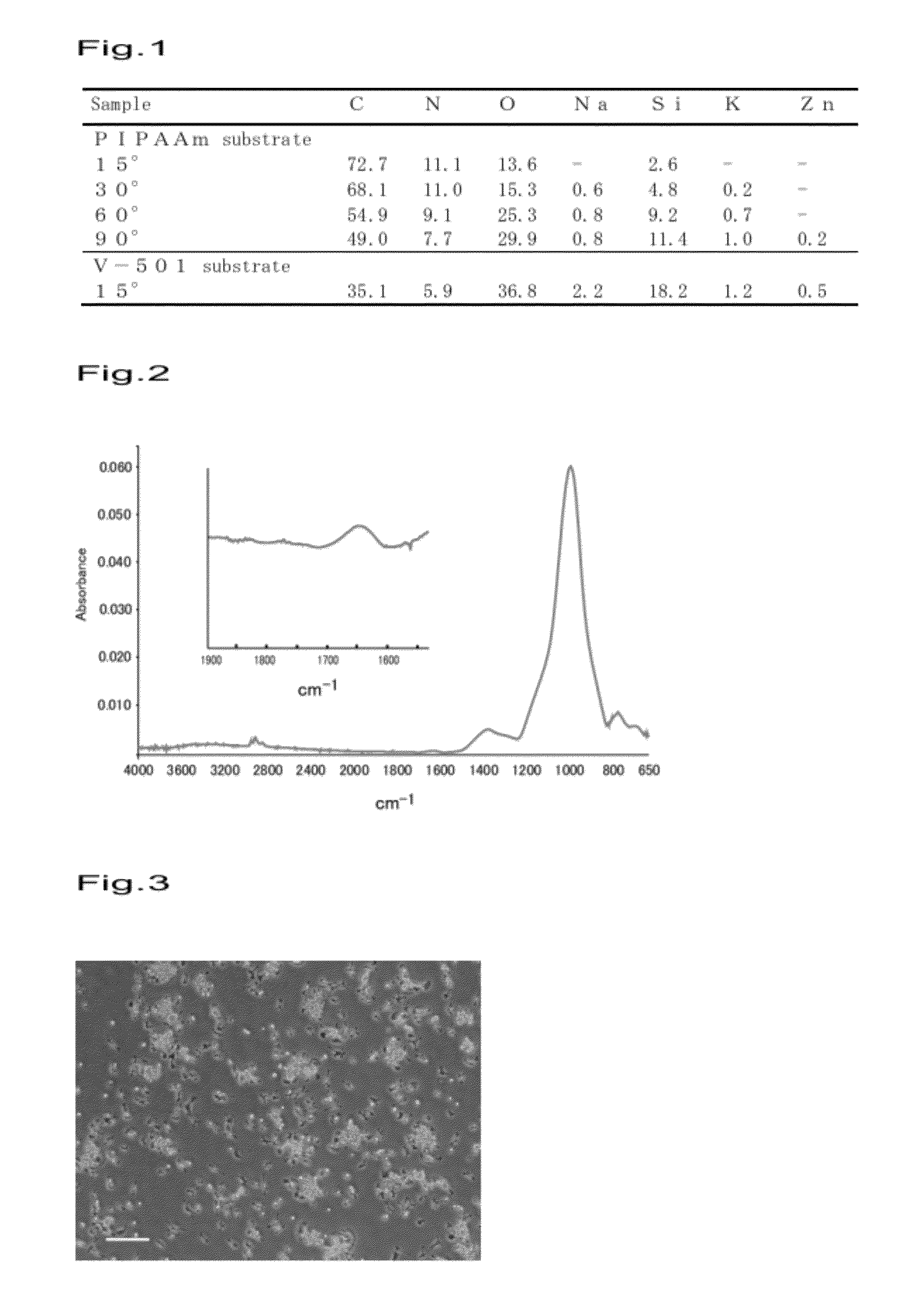
A substrate having a pattern of two or more materials exhibiting different grafting efficiencies for a temperature-responsive polymer that varies its interaction with water in a temperature range of 0 to 80° C. by electron beam irradiation under the same conditions is grafted with the temperature-responsive polymer by simultaneously irradiating the surfaces of the materials with electron beams to obtain a temperature-responsive cell culture substrate. According to this method, a temperature-responsive cell culture substrate having a surface (1) that allows cells to adhere thereto and to grow thereon during cell culturing and that allows the adhering and grown cells to be detached therefrom by changing the culturing temperature and a surface (2) that does not allow the cells to adhere thereto at all can be obtained by a simple process.
Owner:CELLSEED
Method for preparing temperature-responsive adhesive injectable hydrogel
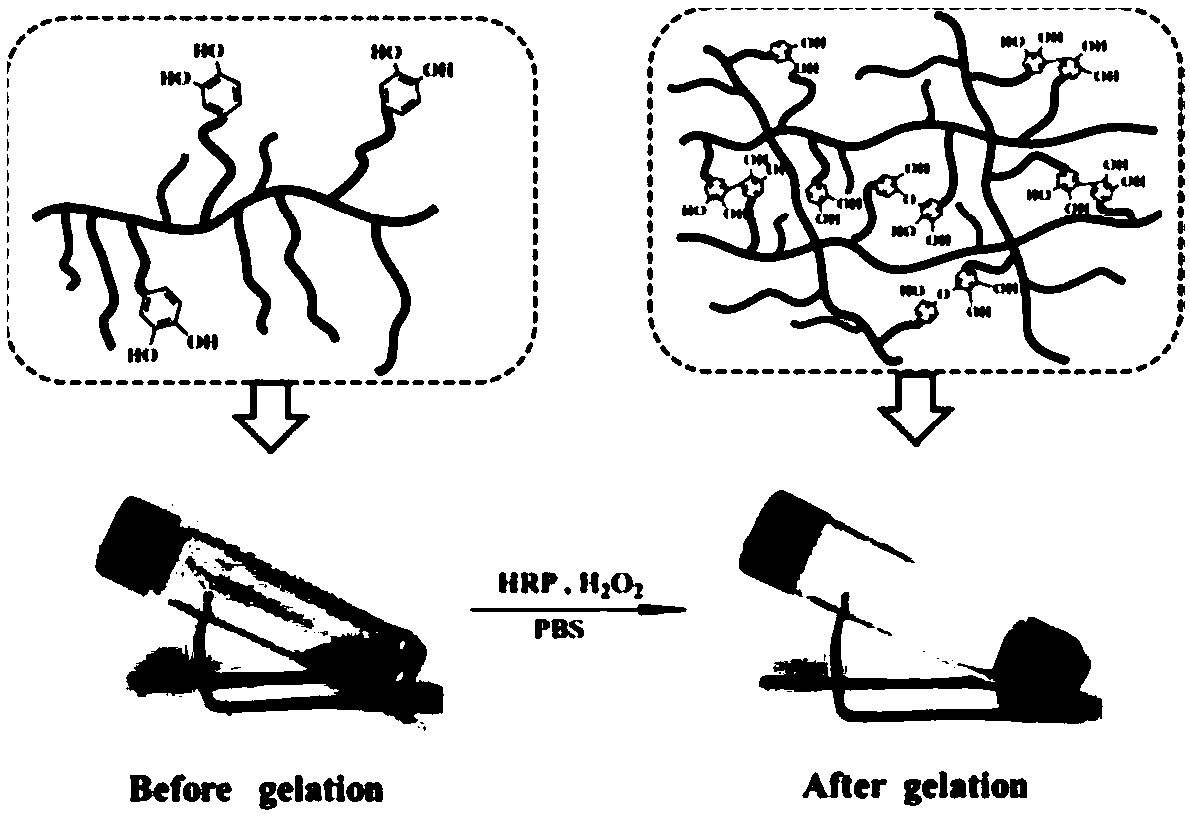
ActiveCN108929412AGel time controlImprove adhesion strengthSurgical adhesivesAerosol deliveryMethacrylateWound dressing
The invention provides a method for preparing a temperature-responsive adhesive injectable hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a temperature-responsive polymer with different dopamine contents from dopamine methacrylamide used as an adhesive monomer and ethyl 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)methacrylate and oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate as temperature-sensitive monomers, and carrying out enzyme catalytic crosslinking on the polymer and a dopamine group under the catalysis of horseradish peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide to prepare the temperature-responsive adhesive hydrogel. The hydrogel prepared in the invention has the characteristics of fastness in gel formation, realization of in-situ injection molding, realization of regulating the gelation time and the gel strength by regulating the concentrations of the polymer, horseradish peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide, and convenience in use; and the adhesion strength of the hydrogel is enhanced with the rising of the temperature, so the temperature-responsive characteristic makes the obtained hydrogel applied to fields of tissue adhesives, wound dressings, cell culture media and drug controlled releasecarriers.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Temperature-responsive cell culture substrate on which a straight-chain temperature-responsive polymer is immobilized, and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20120156781A1Effective trainingEffective peelingAnimal cellsCell culture supports/coatingTemperature responseCell culture media
Provided is a temperature-responsive cell culture substrate. A non-crosslinked temperature-responsive polymer having a molecular weight between 10,000 and 150,000 is immobilized on the substrate surface with a density of 0.02 to 0.3 molecular chain per square nanometer. Using the provided temperature-responsive cell culture substrate, cells obtained from various tissues can be efficiently cultured. This culturing method makes it possible to efficiently peel off a cell sheet by just changing the temperature, without causing damage.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Method for control of temperature-sensitivity of polymers in solution
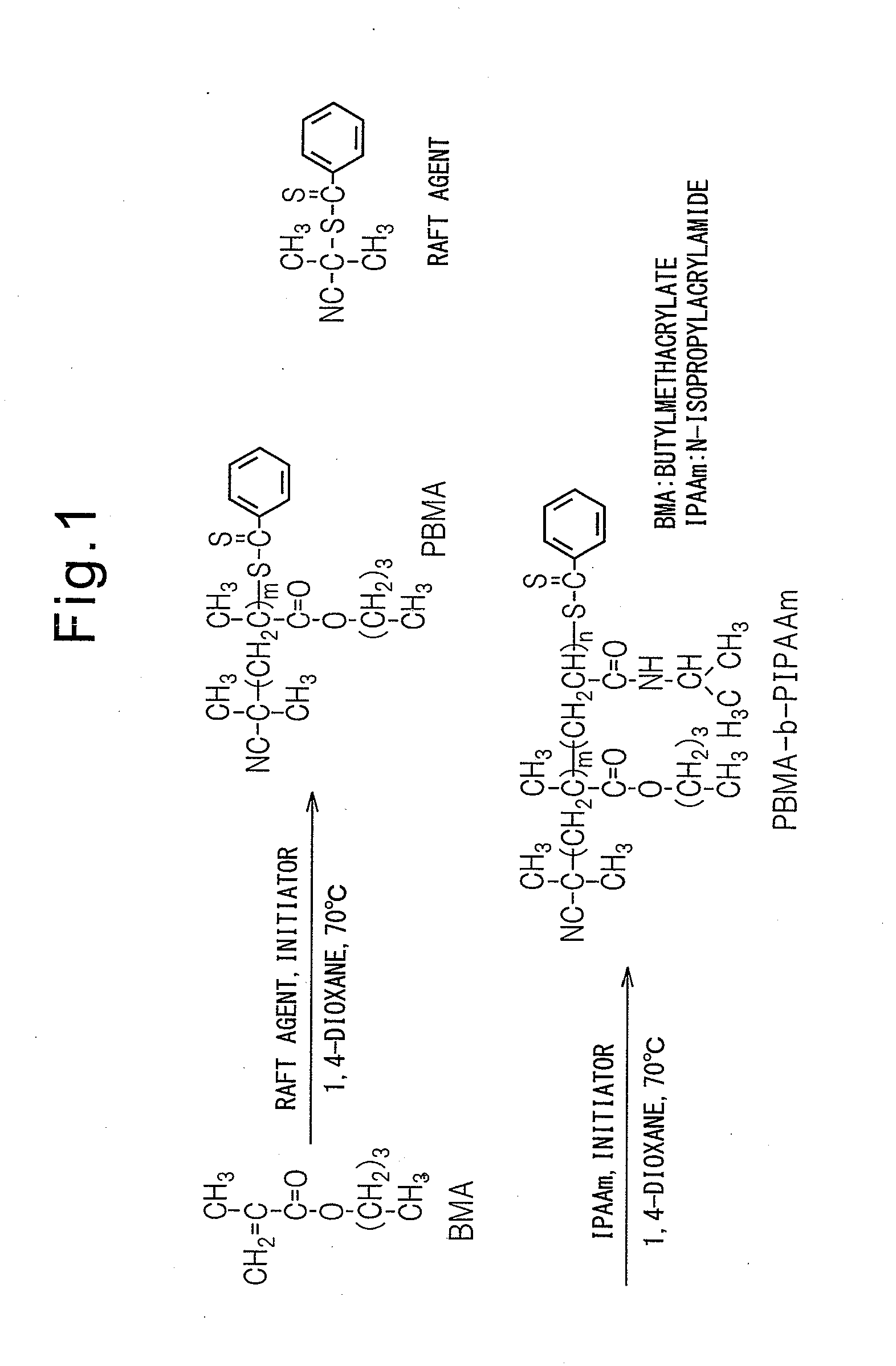
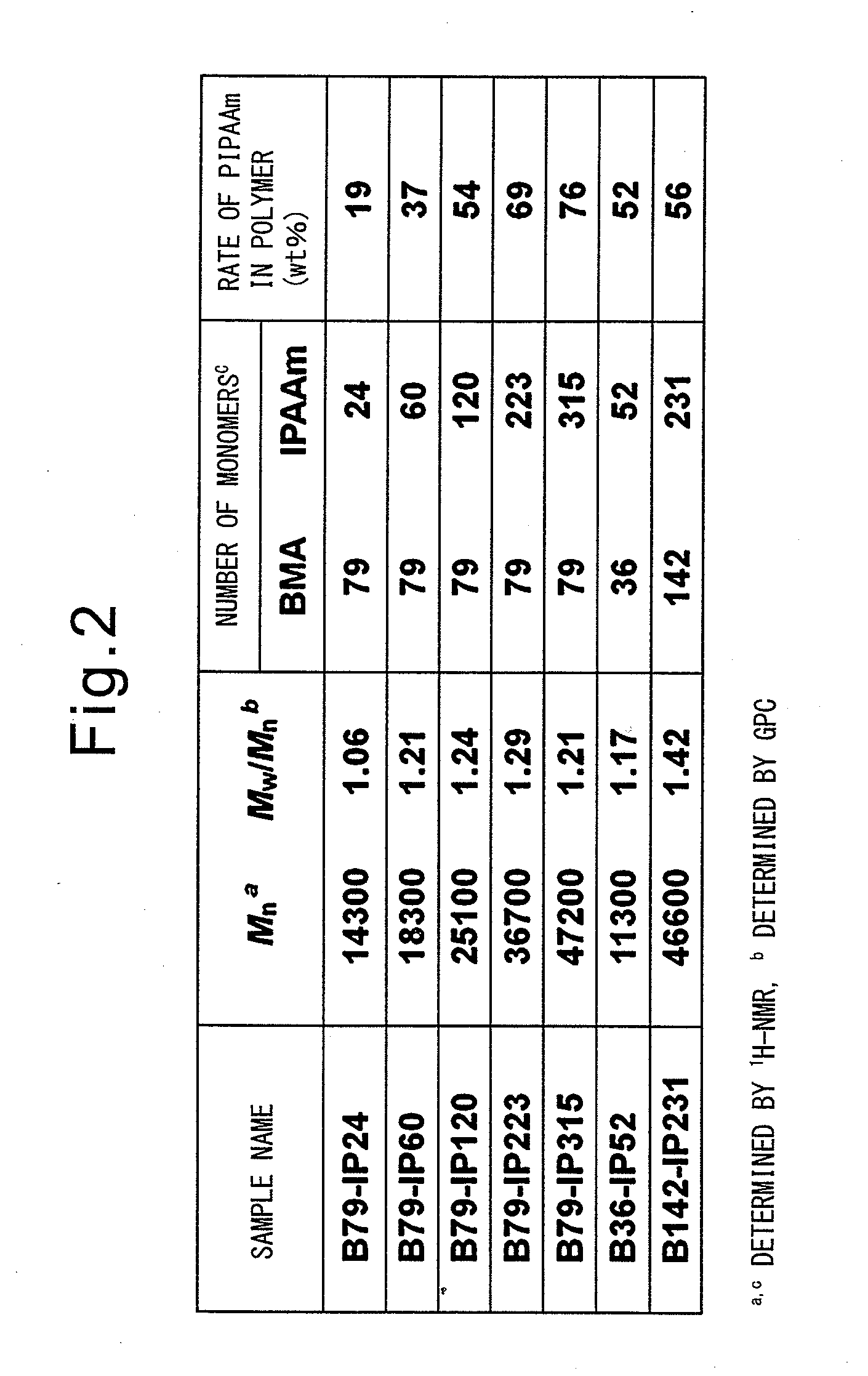
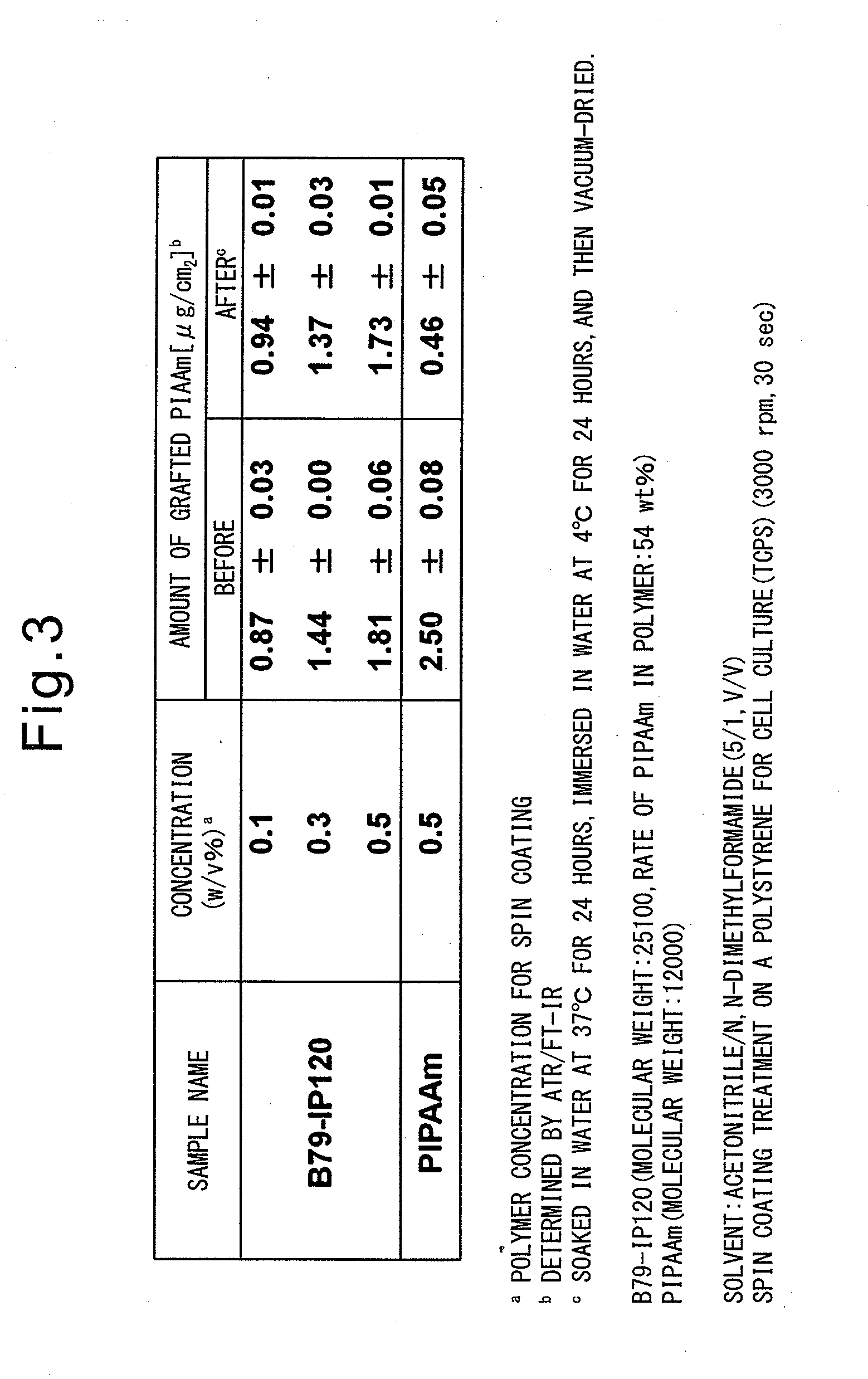
Temperature sensitive, water soluble polymers are disclosed, together with a method for control the LCST of the polymer. The polymers include hydrophillic components and hydrophobic components joined by linking groups such as ester or amide groups wherein the hydrophilic components includes m ethylene oxide groups, the hydrophobic components consist of aliphatic groups such as n ethylenes and / or n cycloaliphatic groups, and where 1≦m≦30 and 1≦n≦30. Substrates bearing the grafted temperature responsive polymers also are disclosed. Microfluidic devices which include the temperature responsive polymers also are disclosed.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Cultured Periodontal Membrane Cell Sheet, Process for Producing the Same and Method of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20080118474A1Efficient reconstructionGood bioadhesionDental implantsBiocideCulture fluidLigament structure
A cultured periodontal ligament cell sheet is produced by a process comprising culturing cells on a cell culture support composed of a base material whose surface is coated with a temperature-responsive polymer having an upper limit or lower limit critical dissolution temperature in water of 0 to 80° C. under specified conditions, (1) regulating the temperature of a culture fluid to the upper limit critical dissolution temperature or higher or to the lower limit critical temperature or lower, (2) allowing a cultured periodontal ligament cell sheet resulting from the culturing to adhere to a carrier and (3) detaching the sheet intact together with the carrier. This cultured periodontal ligament cell sheet has a syndesmotic microstructure, exhibits extremely high bioadherence to the dental root surface and realizes high density transplantation of target cells and positive reconstruction of periodontal tissues. Moreover, through lamination of cell sheets to be transplanted and donation of a three-dimensional polarity, highly efficient reconstruction of an adhesion apparatus can be accomplished and clinical application thereof to moderate periodontitis, severe peridontitis, gingival recession and the like is highly promising.
Owner:CELLSEED
Temperature-responsive three-dimensional ordered macroporous controlled-release material
InactiveCN102120854AReduce sizeGood controllable releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOn/in organic carrierControlled releaseActive enzyme
The invention relates to a temperature-responsive three-dimensional ordered macroporous controlled-release material. The apertures of a macropore and a communicating window of the controlled-release material are uniform, wherein the aperture of the macropore is 100-1000nm, the communicating window has a size of 40-120nm and the pore volume is 1.3-2.8cm<3> / g; and a substrate of the controlled-release material is monodisperse three-dimensional ordered macroporous crosslinked polystyrene with mutually communicated windows, a polymer chain segment with temperature responsiveness is introduced onto the substrate through an atom transfer radical activity-controlled graft polymerization method, and the on-off control of the communicating window between macropores is realized by utilizing the extending-curling action of the temperature-responsive polymer chain segment under different temperatures: a macroporous chain gradually shrinks along with the temperature rise, the pore window gradually opens, and furthermore, the controlled-release action on filled and packaged substances is achieved. The temperature-responsive three-dimensional ordered macroporous controlled-release material has extensive application values in the fields of controlled-release of biomedicines, drug controlled-release systems, controlled release-embedding of active enzyme and catalysts, and the like.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Cell culture support and manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20080227203A1Shorten washing timeCell adhesion cell facilitatedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRadiation exposureCell sheet
An object of the present invention is to provide a cell culture support making the detachment of a cell sheet easy as well as enabling the formation of a uniform cell sheet. The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a cell culture support having a temperature responsive polymer immobilized onto the surface thereof via covalent bonding, the method including a coating step in which a composition including a monomer that can form the polymer by polymerization by radiation irradiation, an organic solvent and, in some cases, a prepolymer formed by polymerization of the monomer is coated onto the substrate having a surface containing a material which can be covalently bonded to the temperature responsive polymer by radiation irradiation to form a film on the surface of the substrate, a radiation irradiation step in which a polymerization reaction and a binding reaction between the substrate surface and the temperature responsive polymer are allowed to proceed by irradiating radiation to the film, and a drying step to dry the film.
Owner:CELLSEED +2
Hydrogel system nano-scale phase change-based temperature-sensitive intelligent glass
ActiveCN102248722ALow light transmissionGood light transmissionGlass/slag layered productsCross-linkSolubility
The invention discloses hydrogel system nano-scale phase change-based temperature-sensitive intelligent glass. The intelligent glass can produce a transition between a transparent appearance and an opaque appearance at a critical temperature. The intelligent glass is composed of glass sheets and temperature responsive hydrogel with an interpenetrating network structure, wherein the hydrogel is arranged between two of the glass sheets at least. The hydrogel is composed of a water-soluble cross-linked polymer network, temperature responsive polymers and water or inorganic salt aqueous solution, wherein the temperature responsive polymers run through the water-soluble cross-linked polymer network. The hydrogel can form a homogeneous system at a temperature below a critical temperature, and the temperature responsive polymers and the water-soluble cross-linked polymer network carry out a nano-scale phase separation at a temperature above the critical temperature. In the invention, temperature responsive polymers run through a cross-linked polymer network to form an interpenetrating network structure thus a molecular-scale uniform distribution is realized. Through a hydrogel system nano-scale phase change produced through a solubility change of temperature responsive polymers, a transition from a transparent appearance to an opaque appearance is realized, wherein the solubility change is produced when temperature changes.
Owner:青岛至慧新材料科技有限公司
Method for control of temperature-sensitivity of polymers in solution
Temperature sensitive, water soluble polymers are disclosed, together with a method for control the LCST of the polymer. The polymers include hydrophillic components and hydrophobic components joined by linking groups such as ester or amide groups wherein the hydrophilic components includes m ethylene oxide groups, the hydrophobic components consist of aliphatic groups such as n ethylenes and / or n cycloaliphatic groups, and where 1≦m≦30 and 1≦n≦30. Substrates bearing the grafted temperature responsive polymers also are disclosed. Microfluidic devices which include the temperature responsive polymers also are disclosed.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Temperature-responsive substrate for cell culture and production method thereof
ActiveUS20140212973A1Efficient detachmentEasy to preparePretreated surfacesCell culture supports/coatingCulture cellWater insoluble
To form a temperature-responsive surface for cell culture by simple processes, said temperature-responsive surface for cell culture being capable of efficiently culturing cells. Cultured cells or a cell sheet can be efficiently removed from the temperature-responsive surface for cell culture by merely changing the temperature of the substrate surface. To coat the substrate surface with a block copolymer, in which a water insoluble polymer segment is coupled with a temperature-responsive polymer segment, in an amount of 0.8 to 3.0 μg / cm2 of the temperature-responsive polymer.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Galactosyl temperature-responsive polymer hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101293943AImprove mechanical propertiesTemperature-sensitive polymer hydrogel has better comprehensive performanceTemperature responseBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a galactosyl-based temperature-sensitive polymer hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The hydrogel is a Poly (NIPAAm-co-GAC) copolymerized hydrogel. The preparation method comprises three steps of: (1) synthesizing an intermediate L-NH2 with an aminogalactose group; (2) synthesizing an intermediate monomer GAC with galactosyl group and double bonds; and (3) preparing the Poly (NIPAAm-co-GAC) copolymerized hydrogel by using the NIPAAm (N-isopropylacrylamide) and the intermediate monomer GAC. The hydrogel has good temperature response and biocompatibility, and has good identification effect on hepatocytes; and can be used as a matrix material in tissue engineering for promoting cell adhension and growth in cell culture, and the cells can be automatically detached due to the temperature sensitivity of the hydrogel.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Temperature-responsive substrate for cell culture and method for producing same
ActiveCN103080295AEffective trainingEfficient strippingCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusCulture cell3D cell culture
To form a temperature-responsive surface for cell culture by simple processes, said temperature-responsive surface for cell culture being capable of efficiently culturing cells. Cultured cells or a cell sheet can be efficiently removed from the temperature-responsive surface for cell culture by merely changing the temperature of a substrate surface. To cover a substrate surface with a block copolymer, which functions as a temperature-responsive polymer component, in an amount of 0.8-3.0 [mu]g / cm2, said block copolymer having a structure wherein a water-insoluble polymer segment and a temperature-responsive polymer segment are bonded with each other.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
End-group functionalized comb structure polycarboxylic acid and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20200216619A1Good application prospectImprove market competitivenessPolymer scienceHalohydrocarbon
A method for preparing comb structure temperature / pH-responsive polycarboxylic acid by end-group functionalization adopts temperature / pH-responsive monomer, unsaturated halogenated hydrocarbon, small monomer of carboxylic acid and other raw materials to prepare polycarboxylic acid material via self-polymerization, substitution and copolymerization. Temperature / pH-responsive monomers are first self-polymerized to obtain temperature / pH-responsive polymer chain with end-group functionalization, and then substitution with unsaturated halogenated hydrocarbons is conducted to obtain temperature / pH-responsive macromonomers with end-group functionalization, finally the obtained product is copolymerized with small carboxylic acid monomers to prepare comb structure polymer with polycarboxylic acid main chain and temperature / pH-responsive side chain.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device for Water Collection from Atmospheric Moisture
ActiveUS20150020687A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useIsotope separationWater conservationAtmospheric airPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
A device for collecting water from atmospheric moisture comprises water absorbing material, a protection wall and a water container. The protection wall is in a porous form. The water absorbing material is made of the temperature responsive polymer with a phase separation temperature, including Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), Poly(vinylphosphonate) and etc. when its temperature is below phase separation temperature, the temperature responsive polymer is in a swollen hydrated state, forming hydrogen bond with water molecules; so as to absorb water from the air. When its temperature is above said phase separation temperature, the temperature responsive polymer is in a shrunken dehydrated state, forming hydrogen bond with other temperature responsive polymer molecules; so as to expel the water to the water container.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bed material for cell culture, method for co-culture of cell and co-cultured cell sheet obtainable therefrom
By using a bed material for cell culture having a surface composed of two domains of domain A coated with a temperature-responsive polymer and domain B composed of any one or a combination of a domain coated with a polymer having high affinity with cells, a domain coated with the temperature-responsive polymer in an amount different from the amount of the temperature-responsive polymer of domain A, and a domain coated with a polymer which responds to a temperature different from the temperature to which domain A responds, a method for the co-culture of a plurality of kinds of cells which has heretofore been difficult becomes possible.
Owner:CELLSEED
Temperature-responsive polymer particles in protein separation applications
InactiveUS8877477B2Chromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsChromatographic separationCopolymer
The present invention relates to a method for isolating proteins from a solution containing the proteins. The invention also relates to a method for the chromatographic separation of proteins. The present invention also relates to crosslinked hydroxylic polymer particles functionalized with temperature-responsive copolymer, and to methods of preparing such particles.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Method for preparing temperature-sensitive stereocomplex polylactic acid copolymer drug-loaded micell
InactiveCN105030672AGood sustained release effectEfficient releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryPolymer scienceAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention belongs to the fields of high polymer materials and biomedical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a temperature-sensitive stereocomplex polylactic acid copolymer drug-loaded micelle. The method includes the specific steps that poly L polylactic acid and poly D polylactic acid are bromized, and a temperature-sensitive polylactic acid segmented copolymer is obtained through atom transfer radical polymerization; then stereocomplex is performed, drugs are loaded, and thus a drug-loaded micelle which uses hydrophobic stereocomplex polylactic acid as the core and a hydrophilic chain temperature-sensitive polymer as the shell layer is formed. The nano drug-loaded micelle has the advantages of being compact in core structure, low in drug release speed, responsive to temperatures and the like; the stability of drug carriers can be improved easily, and drug release can be effectively controlled.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Infrared shielding film, method for producing infrared shielding film, and infrared shielding body
InactiveUS20140092468A1Increase flexibilityMaintain stable propertiesMirrorsOptical filtersPolyvinyl alcoholRefractive index
The objects of the present invention is to provide an infrared shielding film, a method for producing same, and an infrared shielding body provided with the infrared shielding film, whereby it is possible to maintain stable infrared shielding property, visible light transmittance, flexibility, and transparency over time. This infrared shielding film having at least one unit consisting of a high refractive index layer having metal oxide particles and a low refractive index layer on a substrate is achieved when (i) at least one layer of the high refractive index layer and the low refractive index layer contains a temperature responsive polymer as a binder component or (ii) the high refractive index layer has any one of a cellulose compound or polyvinyl acetal resin as a binder component, and the low refractive index layer contains a binder component different from that of the high refractive index layer.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Temperature-responsive polymer particles in protein separation applications
InactiveUS20120052550A1Chromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsChromatographic separationCopolymer
The present invention relates to a method for isolating proteins from a solution containing the proteins. The invention also relates to a method for the chromatographic separation of proteins. The present invention also relates to crosslinked hydroxylic polymer particles functionalized with temperature-responsive copolymer, and to methods of preparing such particles.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Temperature-responsive oil-water separation filter paper and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105926366AImprove stabilityLow costNon-macromolecular organic additionPaper/cardboardSilica particleOrganic solvent
The invention discloses temperature-responsive oil-water separation filter paper and a preparation method thereof. By means of a dip-coating method, the filter paper is dipped in a solution formed by evenly mixing nano silica particles, a temperature-responsive polymer, a catalyst and organic solvent, ultrasonic dispersion is conducted, the filter paper is taken out and subjected to natural drying, vacuum drying is conducted, and temperature-responsive oil-water separation filter paper is obtained. The preparation method is simple, low in cost and good in stability, the prepared filter paper has a temperature-responsive property, oil-water separation can be conducted selectively, a good separating effect is achieved for different oil-water mixtures, and the industrial application prospect is wide.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
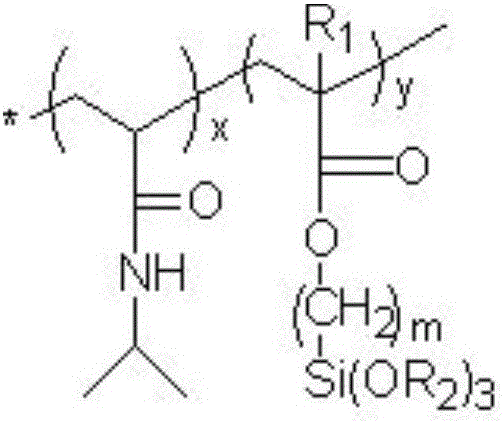
Temperature and enzyme responsive protein polymer conjugate, and preparation method and application of conjugate
ActiveCN110179994AStrong specificityGood tissue permeabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseControlled release
The invention relates to the technical field of controlled release and target delivery of protein medicines, in particular to a temperature and enzyme responsive protein polymer conjugate, and a preparation method and an application of the conjugate. The temperature and enzyme responsive protein polymer conjugate comprises a protein medicine, and enzyme responsive polypeptide and a temperature responsive polymer that are sequentially coupled with the protein medicine. On the one hand, due to temperature responsivity of the protein polymer conjugate, a half life of the protein medicine is significantly prolonged, pharmacokinetic parameters are improved, and the conjugate has the significant advantages in improving drug metabolism performance; on the other hand, due to enzyme responsivity ofthe conjugate, tissue permeability and activity of the protein medicine are effectively improved after enzyme digestion release; the efficacy of the medicine is improved; toxic and side effects of the medicine are reduced; and the conjugate is applicable to administration of various pharmaceutical protein substances and treatment of diseases and has excellent popularization and application valuesand potentials.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com