Temperature-responsive substrate for cell culture and method for producing same
A technology for cell culture and manufacturing methods, applied in general culture methods, cell culture supports/coatings, tissue cell/virus culture devices, etc., to achieve the effect of simple production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Preparation and Characterization of Temperature Responsive Surfaces
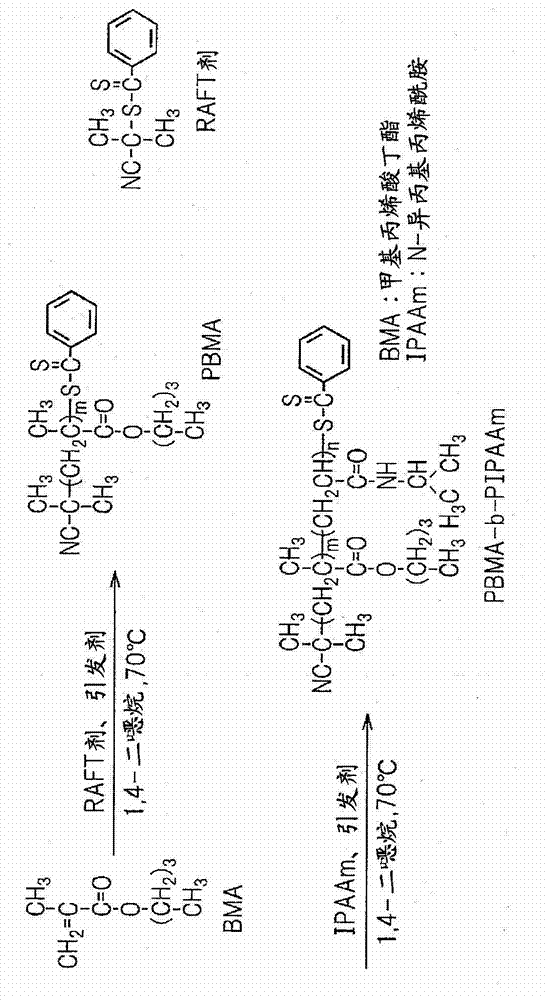
[0066] In this example, a temperature-responsive block copolymer comprising segments of poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (PIPAAm) as a temperature-responsive polymer and a water-insoluble Polymer segments of poly(n-butyl methacrylate) (PBMA) are spin-coated on the substrate surface. For the produced temperature-responsive block copolymer-coated surface, physical properties such as the amount of polymer incorporated into the surface and surface wettability were evaluated, and differences in cell adhesion to the substrate surface due to temperature changes were studied.
[0067] (1) Preparation of temperature-responsive block copolymers
[0068] Specifically, PBMA as a water-insoluble polymer synthesized by RAFT polymerization was used as a macromolecular RAFT agent to prepare a PBMA-b-PIPAAm block copolymer ( figure 1 ). In addition, the analysis values of PBMA and PBMA-b-PIPAAm synthesized ...
Embodiment 2
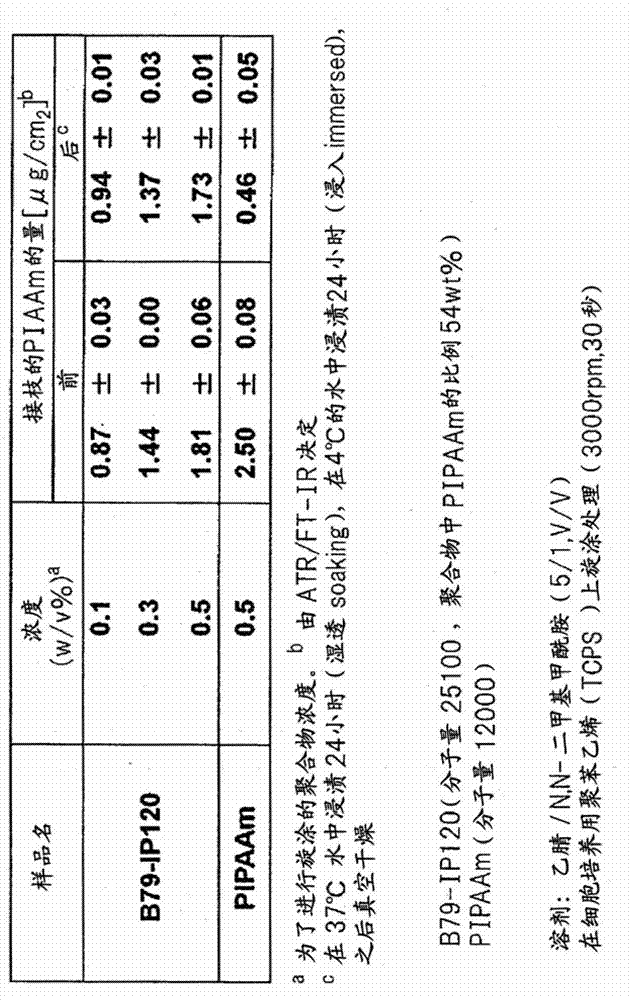
[0072] Example 2: Research on grafting amount and cell behavior
[0073] According to the description of Example 1, the substrates coated with TCPS with various concentrations of B79-IP120 were prepared, and on the prepared substrates, 1.0×10 4 cells / cm 2 Vascular endothelial cells (BAEC) derived from bovine carotid artery were seeded at a concentration, and the adhesiveness of the cells on the surface of the polymer-coated substrate at 37°C and the detachment behavior of the cells by low temperature treatment at 20°C were evaluated. Figure 5 The black dots in the figure represent the TCPS substrate without polymer coating, and the black diamonds and white diamonds represent the changes of cell behavior on the substrates coated with B79-IP120 on TCPS at 0.3 and 0.5w / v%, respectively. Figure 5 BAEC cells are seeded on each substrate and cultured for 72 hours, and the change in the cell adhesion rate (%) is shown when the culture temperature is changed from 37°C to 20°C. Mor...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3: Detailed Analysis of Cell Behavior Changes Caused by Block Copolymers
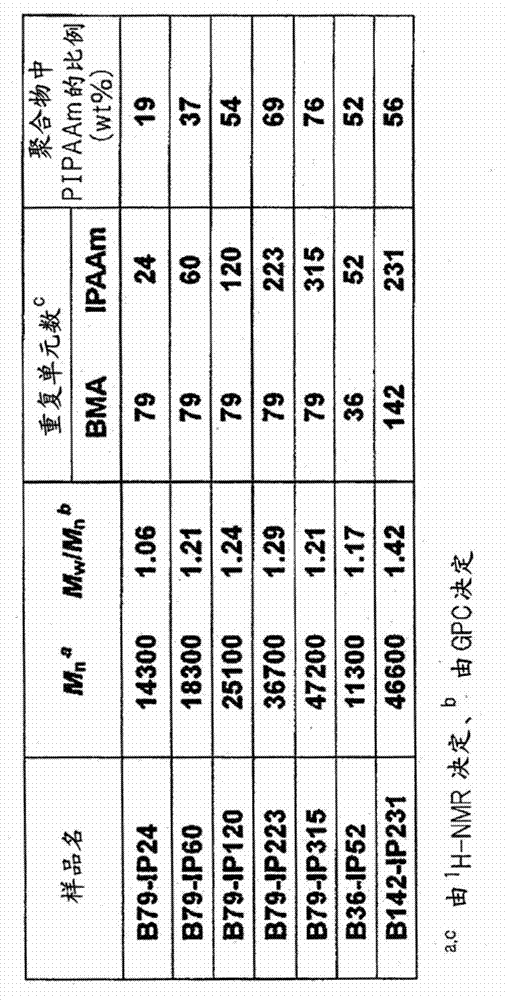
[0076] (1) Relationship between PIPAAm molecular chain length and cell behavior
[0077] The number of monomer units (number of repeating units) of BMA in the block copolymer was kept constant, and a block copolymer in which the monomer unit of IPAAm was changed was prepared according to the production method of Example 1. In the same manner as in Example 1, the block copolymer was coated with TCPS, and the change in the adhesion rate of BAEC cells accompanying the temperature change was examined ( Figure 7 ). As in Example 2 above, the cell adhesion rate increased as the amount of PIPAAm coated decreased. In addition, regarding the detachment of cells caused by temperature changes, it can be seen that the substrate with a low coating amount of PIPAAm (1.18 μg / cm 2 ), and substrates with higher coatings (1.44, 1.60, 1.63μg / cm 2 ) compared with the slow removal, the substrate with hig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com