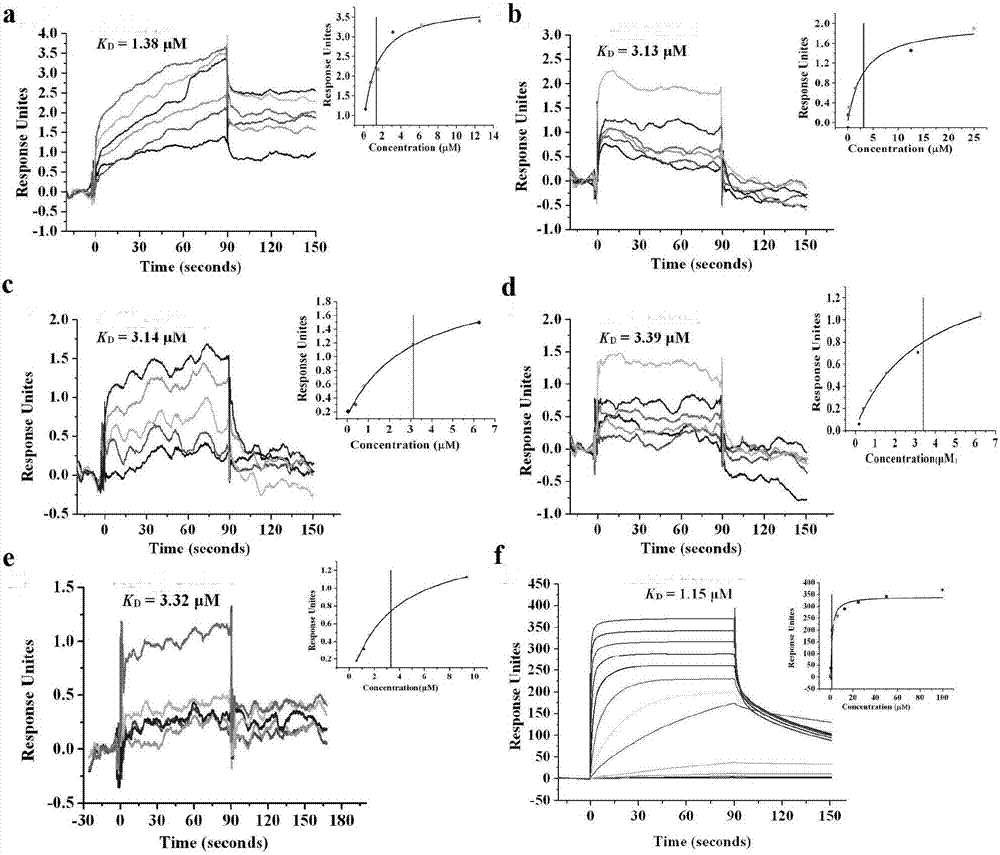
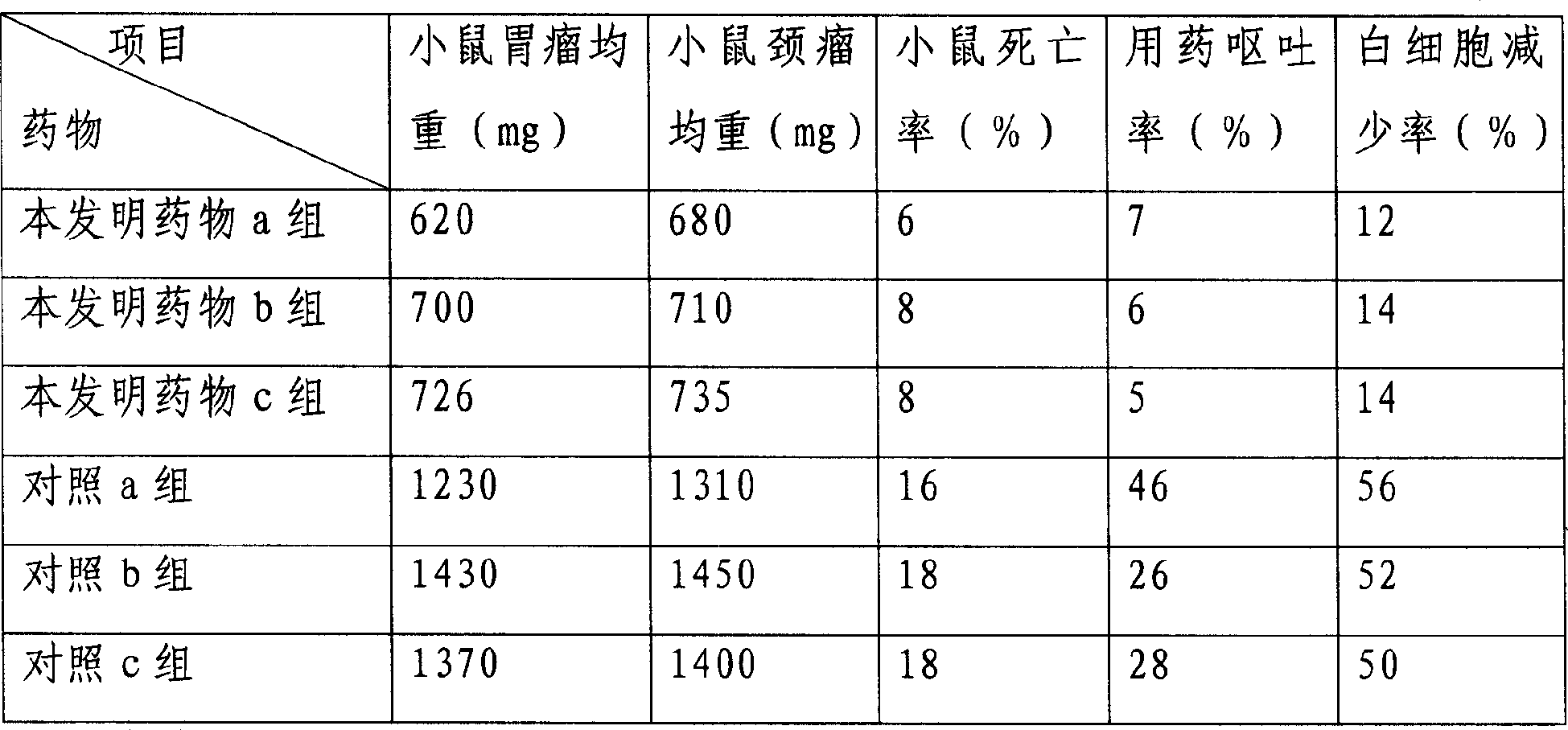
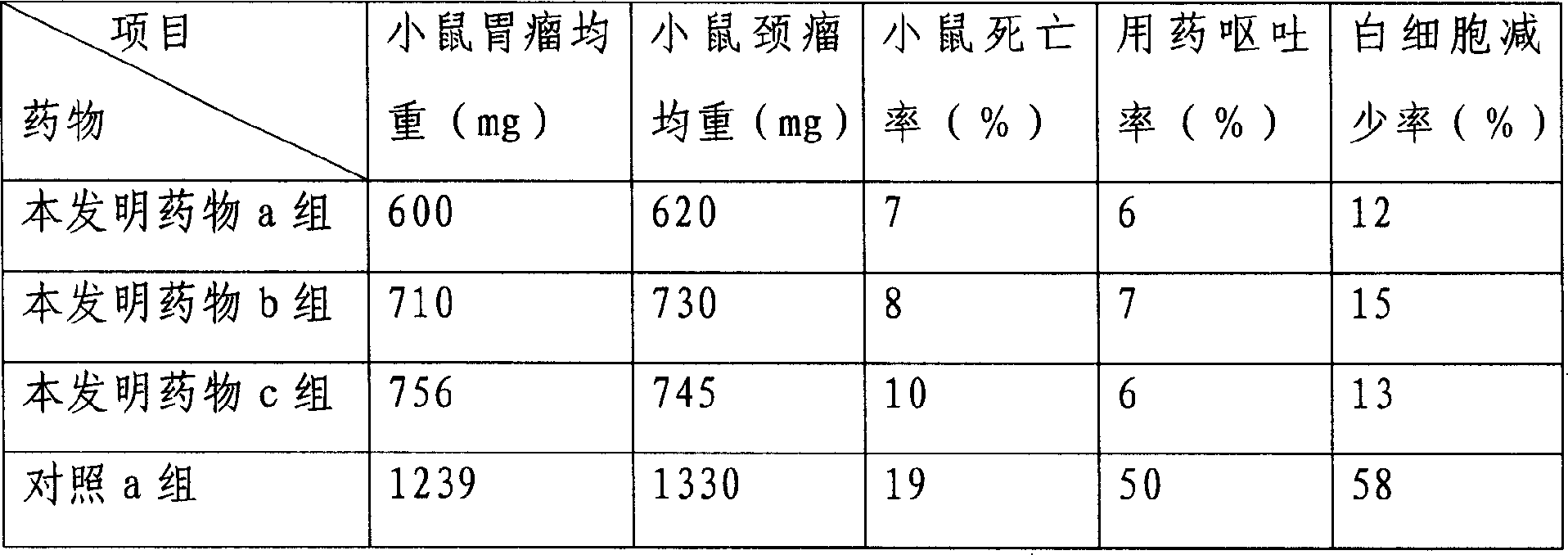
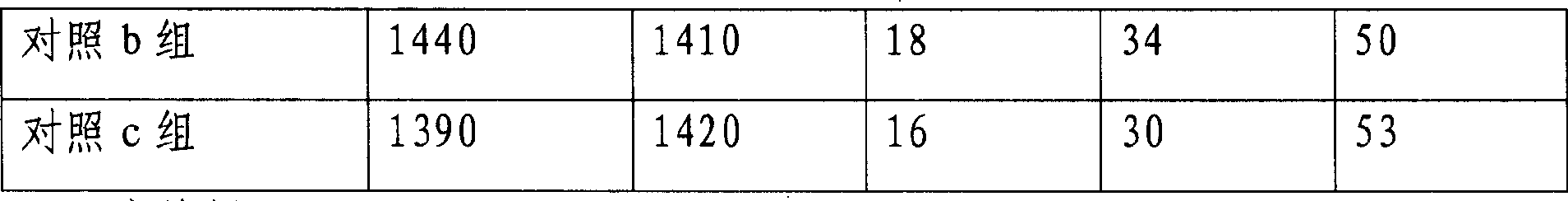
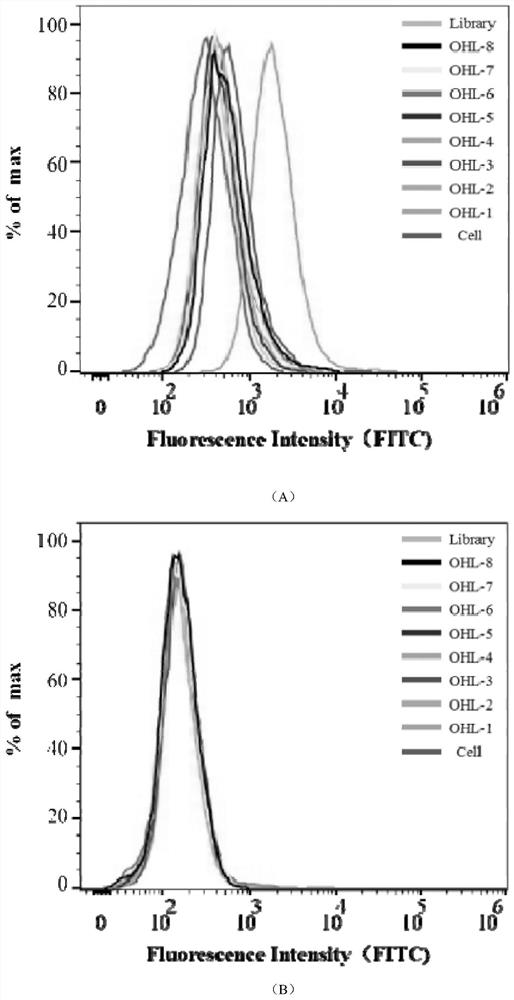
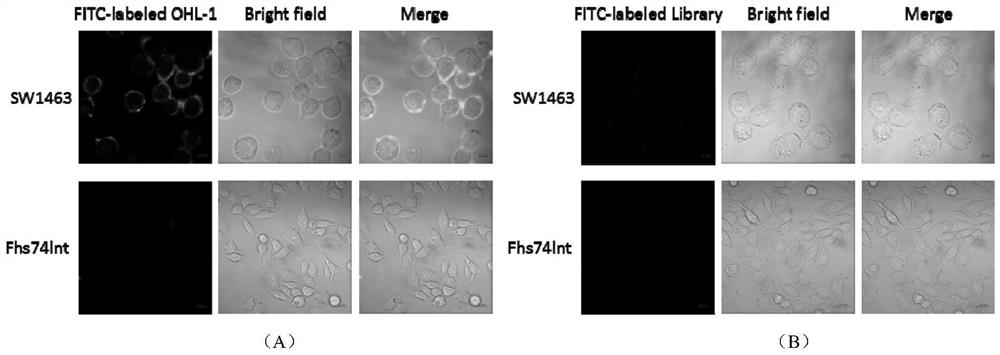
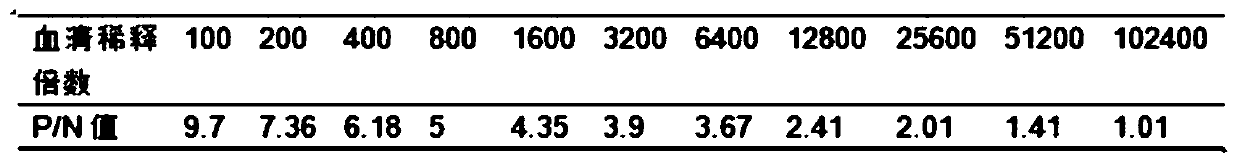
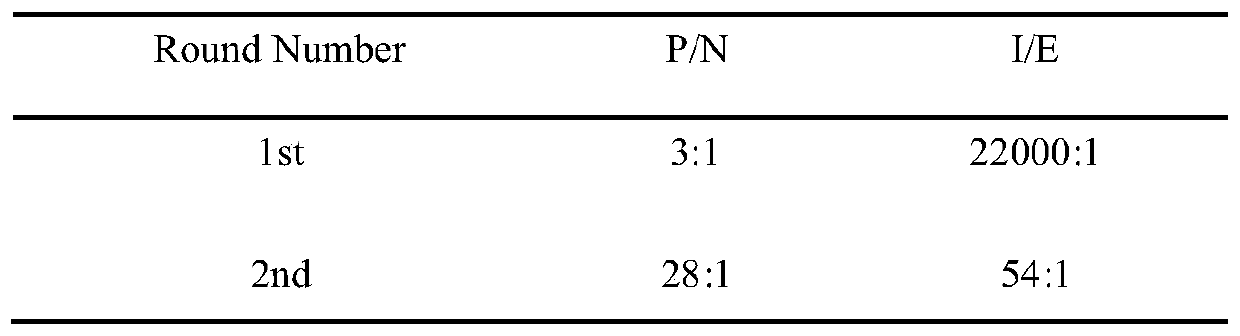
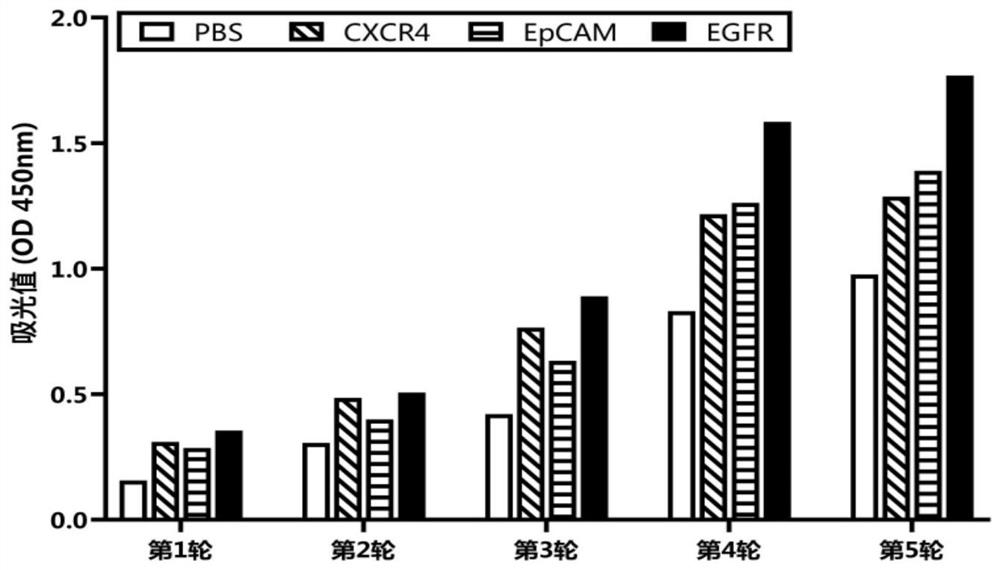
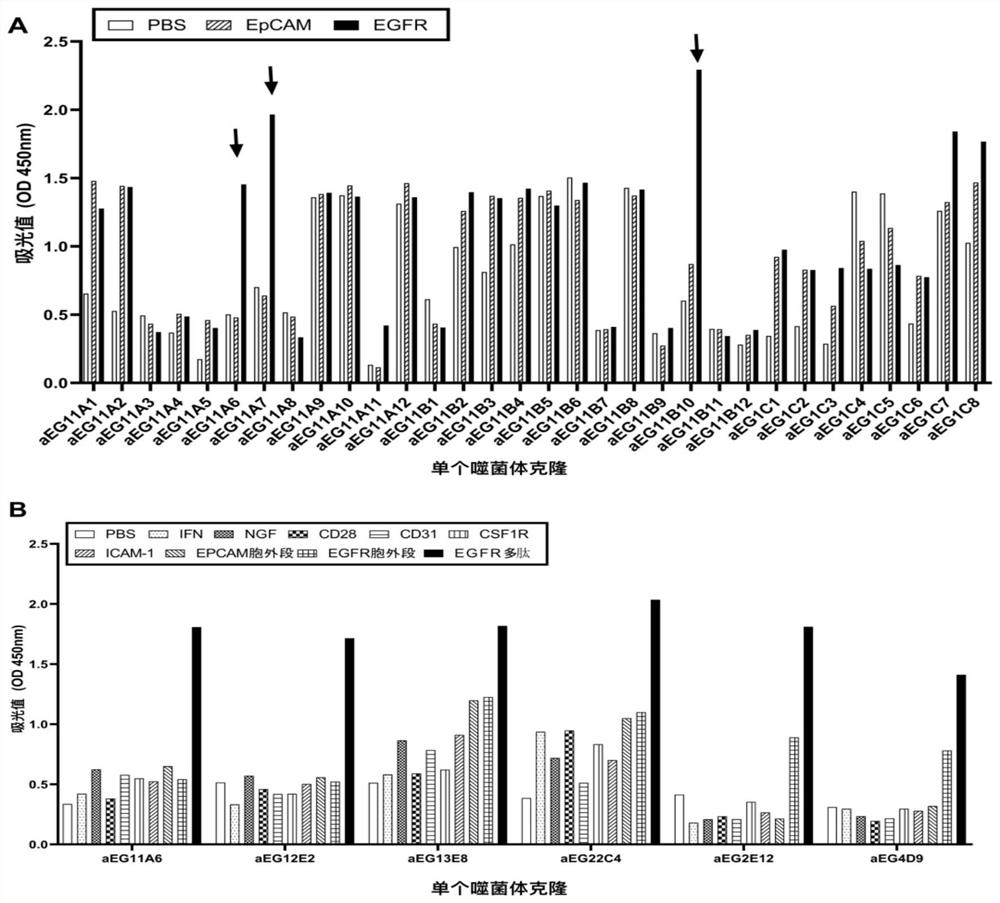
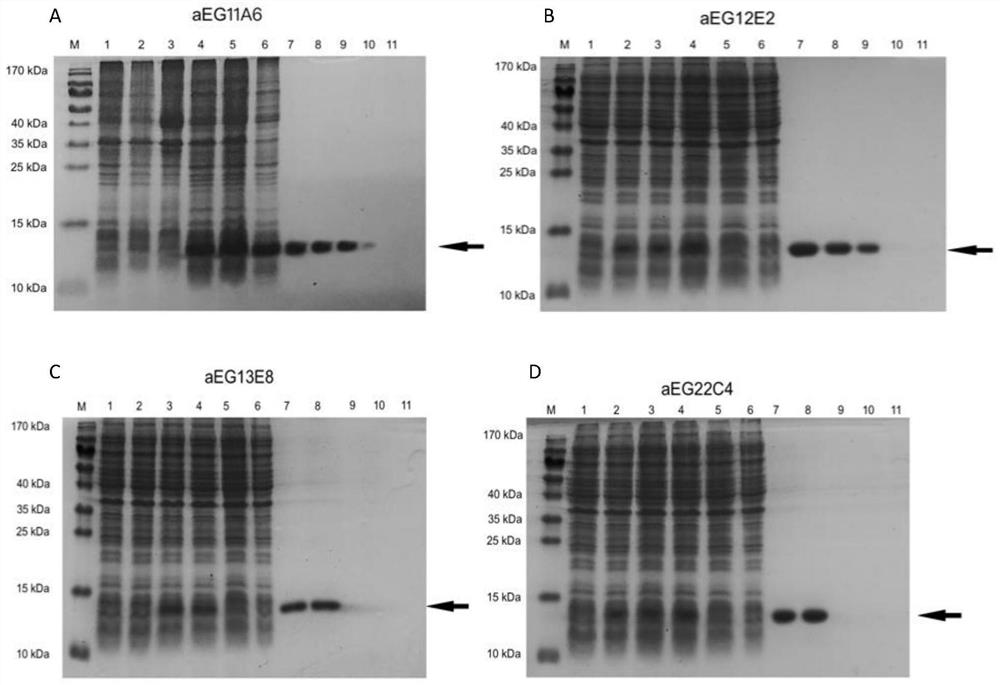
Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Good tissue permeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel PD-1 inhibitor and application thereof
PendingCN108727453AImprove bindingHigh binding affinityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseasePharmacology
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Treatment for diabetes and obesity as well as method of screening compounds useful for such treatments
InactiveUS20060293325A1Speed up the conversion processHighly cell membrane permeableBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusAlcohol
The present invention relates to a compound having the formula where Z is an amine, alcohol, or thiol-containing group, and Y is an alkyl-containing amine. Methods of producing such compounds and using them to treat patients with diabetes and obesity are also disclosed. The present invention also relates to treating such conditions with GADPH inhibitors and screening compounds useful for treating such conditions by using GADPH inhibitors. Compounds can also be screened for their effectiveness in modulating diabetes and obesity with a C. elegans strain.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
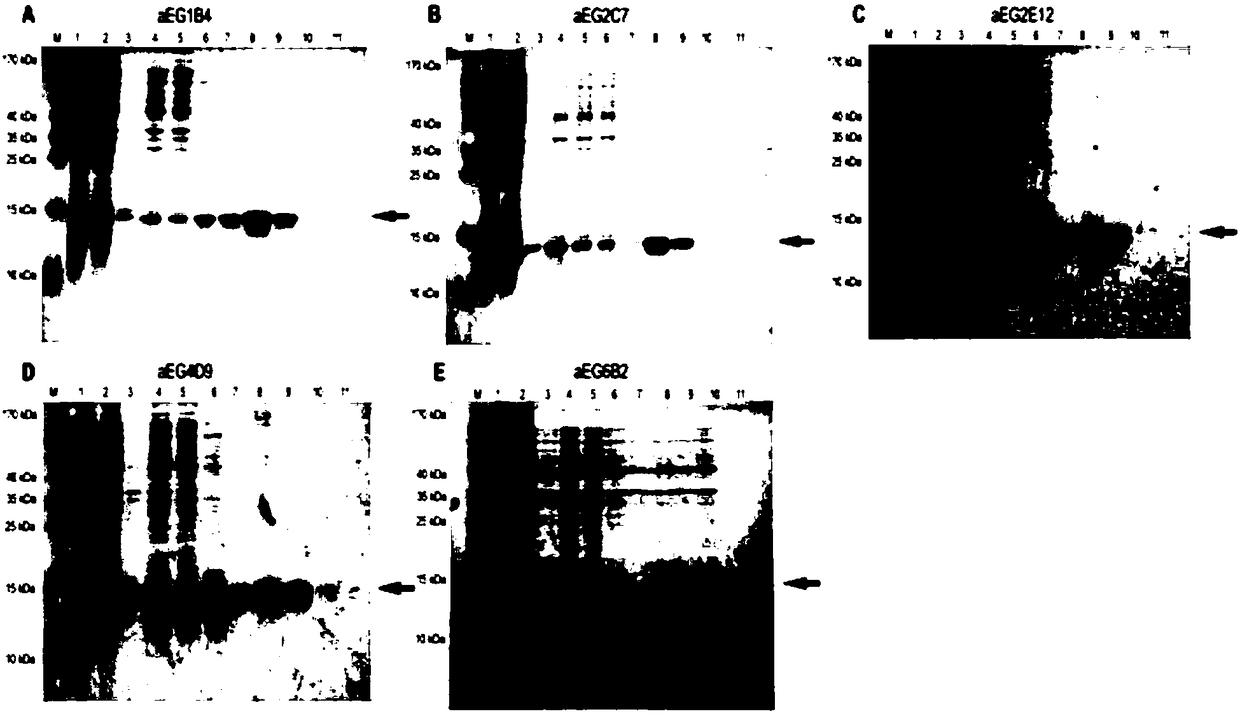
Anti-human EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) nano antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN109336976AReduce manufacturing costGood stabilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDrugAntibody
The invention discloses an anti-human EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) nano antibody and an application of the nano antibody. The nano antibody is one or a combination of at least two of an aEG1B4 nano antibody with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: (sequence identifier number) 1, an aEG2C7 nano antibody with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, an aEG2E12 nano antibody with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 3, an aEG4D9 nano antibody with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 4 and an aEG6B2 nano antibody with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 5. The nano antibody has high affinity, specificity and low immunogenicity and the advantages of better stability, simple structure and easy engineering transformation, and can be better applied to development of antibody medicines.
Owner:深圳新锐基因科技有限公司
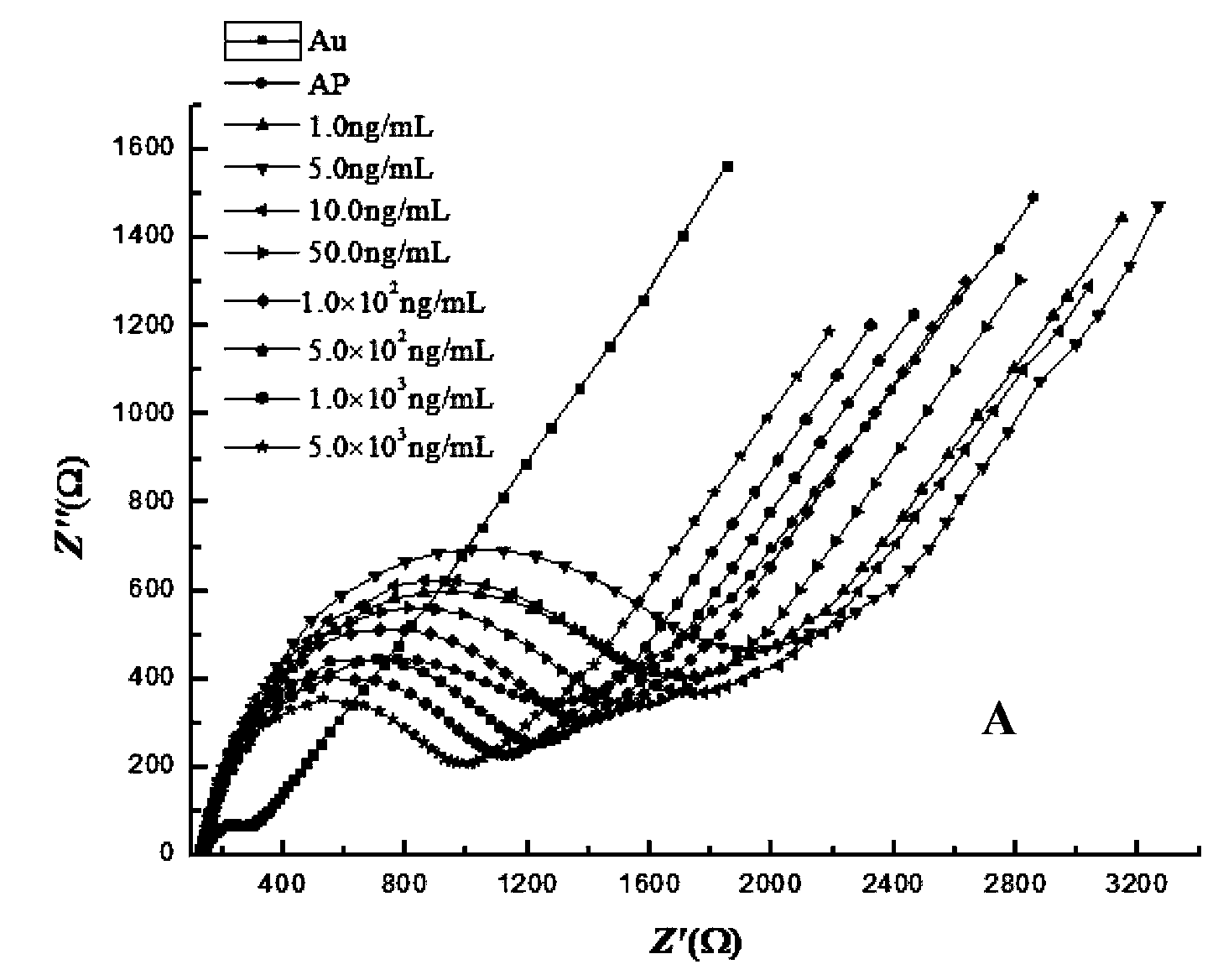
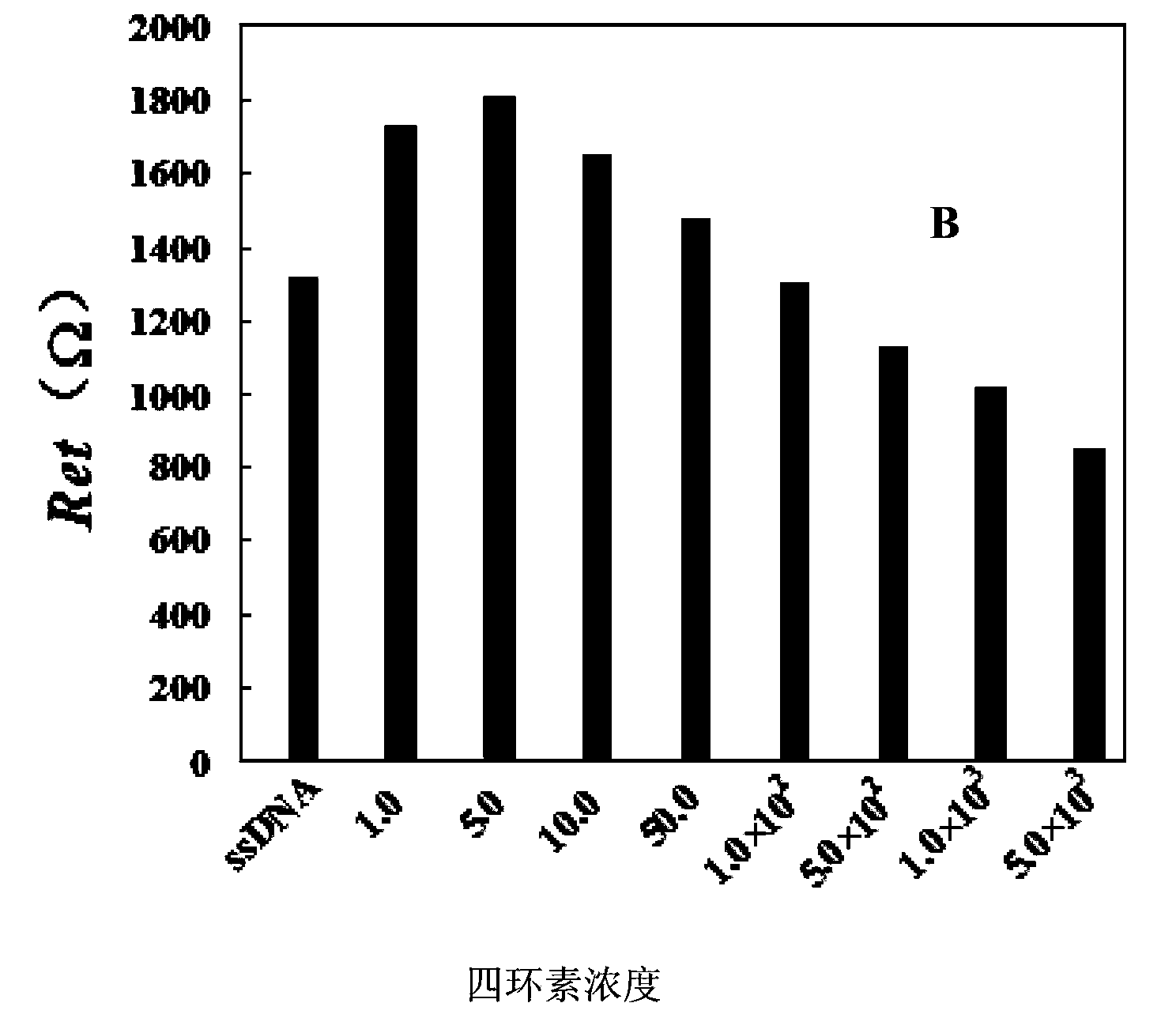
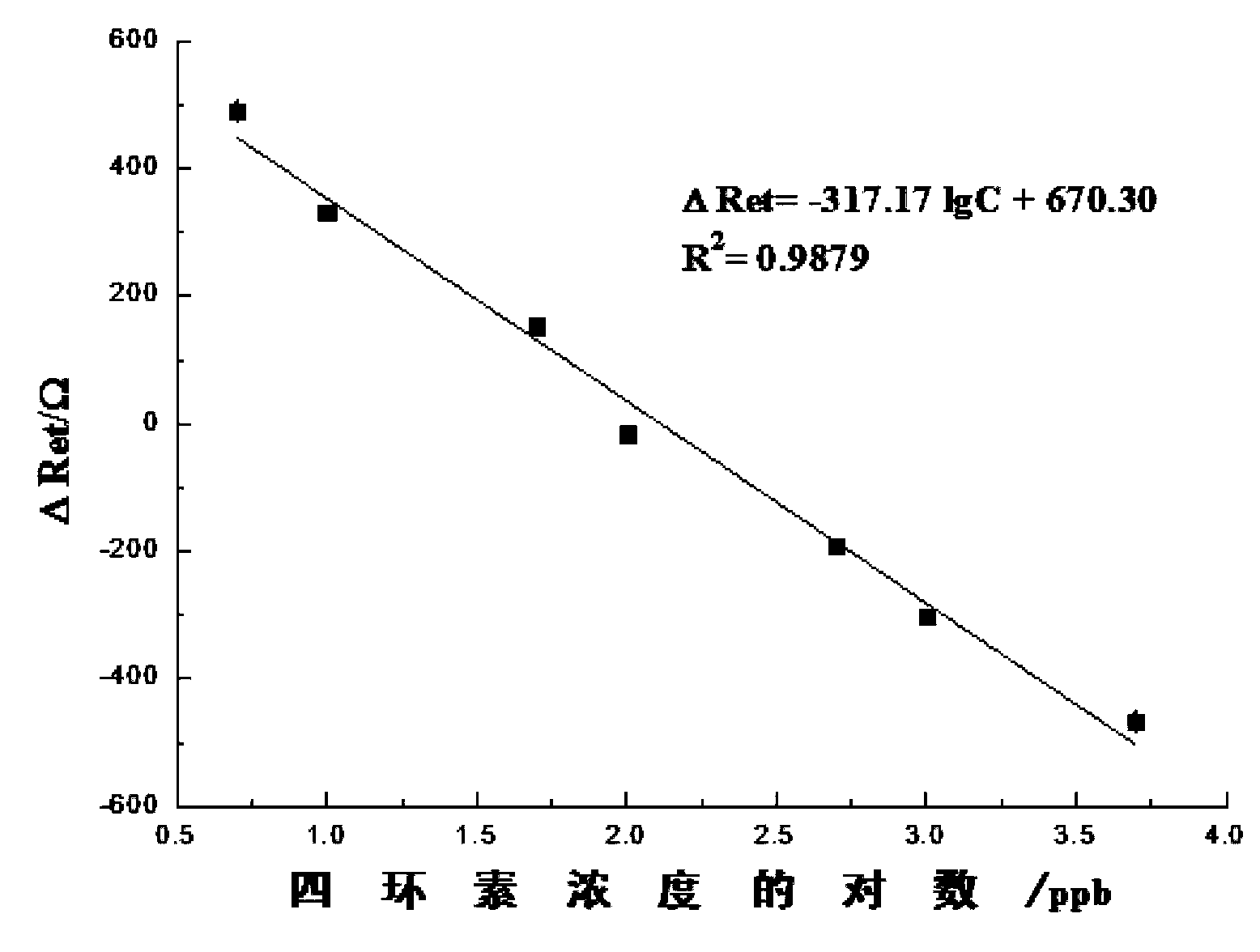
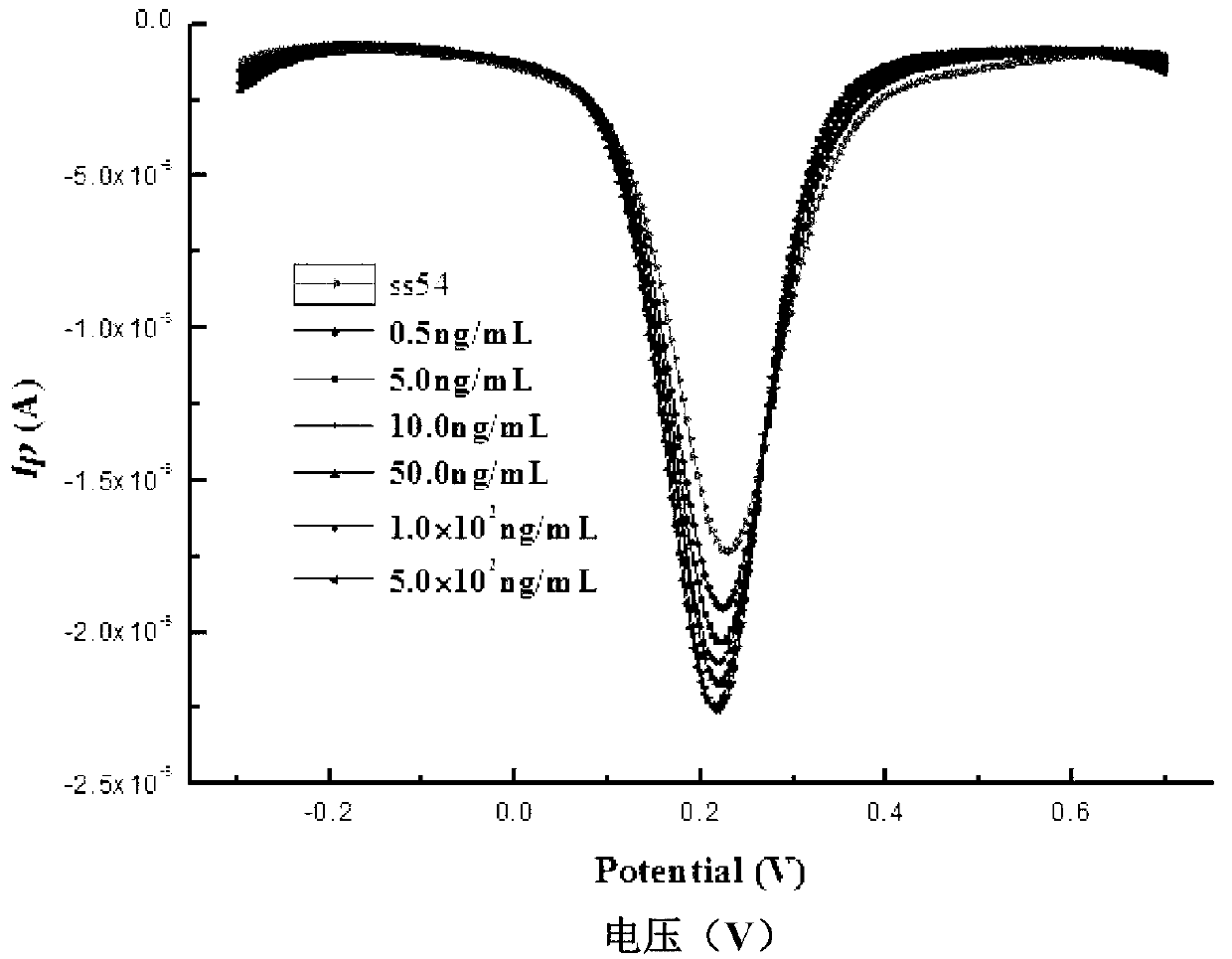
Tetracyclines aptamer and aptamer electrochemical biological sensor for detection of tetracyclines
ActiveCN103361353AWide range of target moleculesHigh affinityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerElectrochemical biosensor
The invention relates to a tetracyclines aptamer, an aptamer electrochemical biological sensor for detection of tetracyclines, and a preparation method and a detection method of the sensor. The tetracyclines aptamer is a single strand DNA probe containing a TTGAGCCCT sequence and having the length of 13-20 bp, and an amino is modified by a 5' end, namely 5'-NH2-(CH2)6-. The aptamer electrochemical biological sensor for the detection of the tetracyclines contains the tetracyclines aptamer. The sensor improves the sensitivity of the detection of the tetracyclines, and can detect the tetracyclines in a minimum concentration of 1.0 ng / mL; and the sensor greatly reduces the cost of the detection of the tetracyclines, has simple and convenient operation, and can rapidly detecting the tetracyclines.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Ractopamine aptamer and electrochemical biosensor for detecting same
ActiveCN103343126AWide range of target moleculesHigh affinityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorSingle strand dna
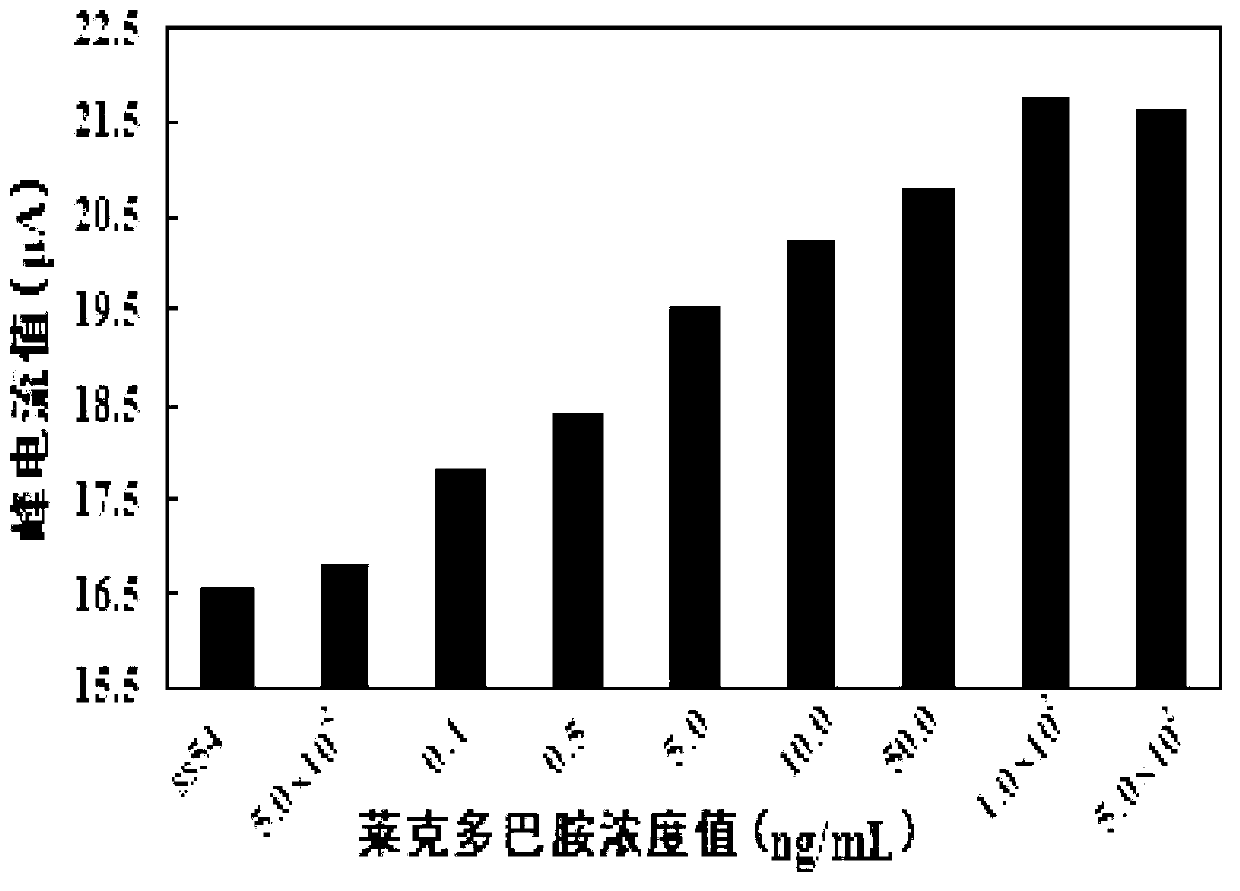
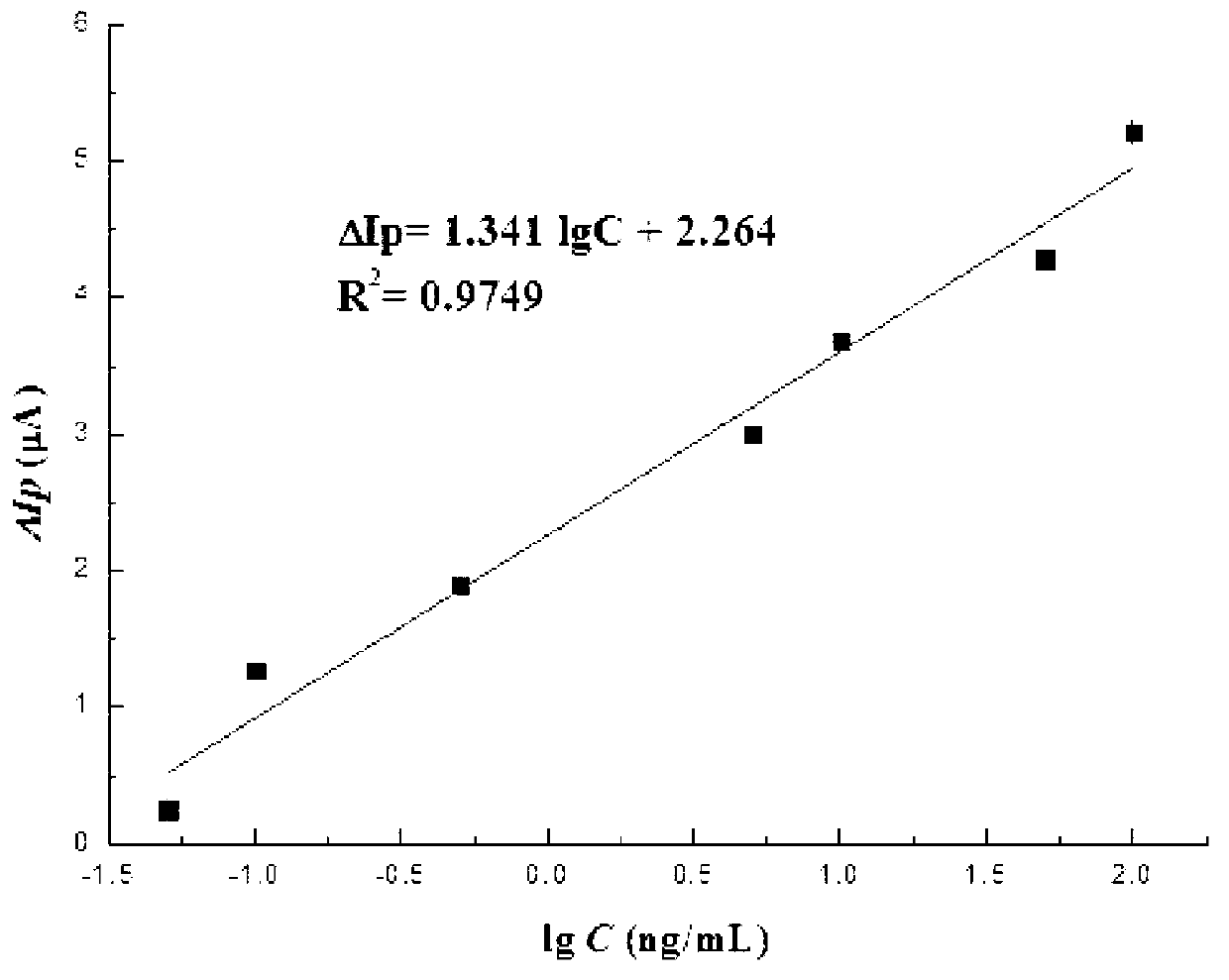
The invention relates to a ractopamine aptamer, an electrochemical biosensor for detecting the ractopamine aptamer same, a method for manufacturing the electrochemical biosensor and a method for detecting the ractopamine aptamer by using the electrochemical biosensor. The ractopamine aptamer is a single-chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probe which contains an AGTGCGGGC sequence and has a length of 13-20bp, and the amino group of 5'-NH2-(CH2)6- is modified on the 5' terminal. The electrochemical biosensor for detecting the ractopamine aptamer comprises the ractopamine aptamer, has higher ractopamine detection sensitivity, can be used for detecting 0.1ng / mL of ractopamine at least, ensures that the ractopamine detection cost is lowered greatly, is easy and convenient to operate and can realize the rapid detection of the ractopamine.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Aptamer-modified nanogold colorimetric detection-based analysis method of ibuprofen
InactiveCN104914099AWide range of target moleculesHigh affinityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAptamerQuantitative determination
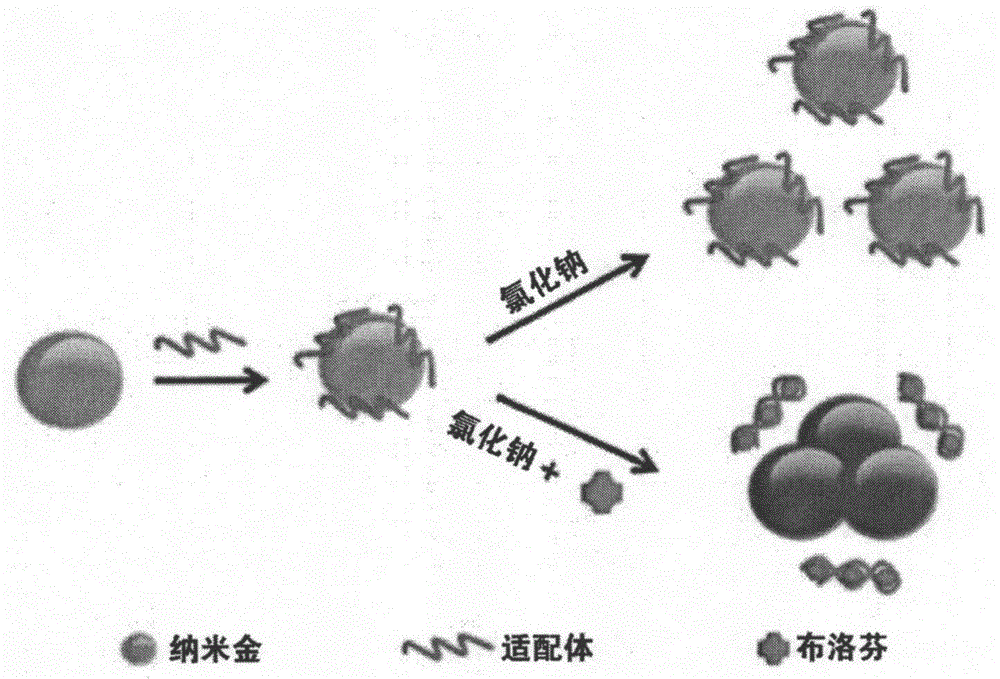
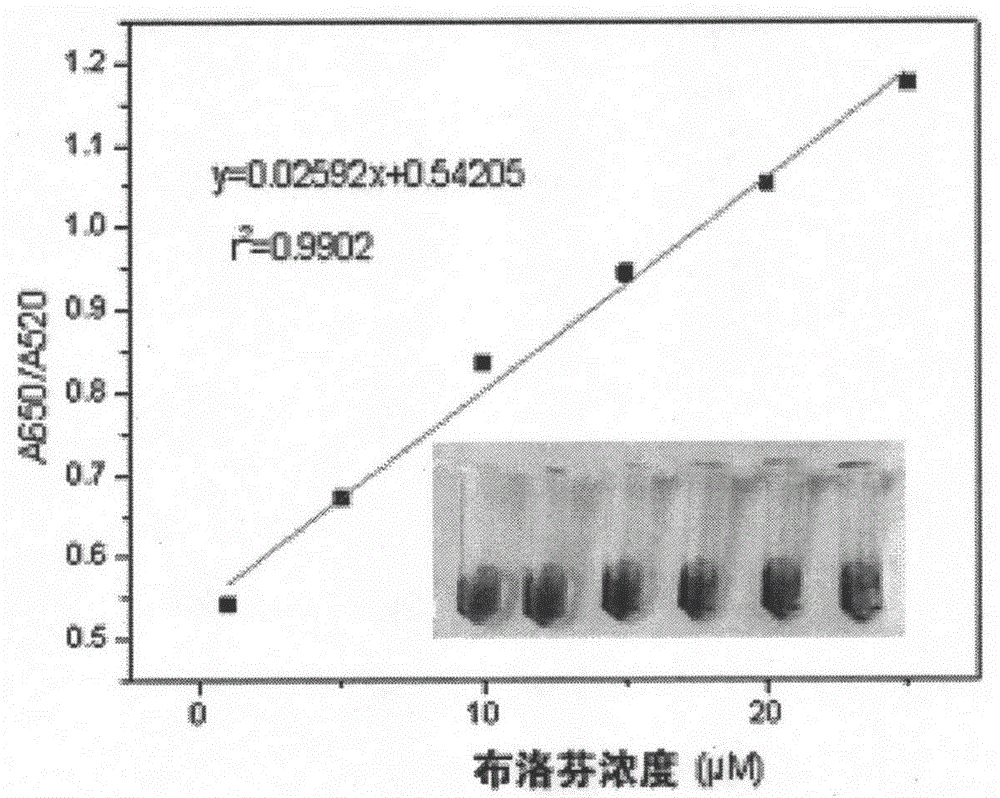
The invention provides an aptamer-modified nanogold colorimetric detection-based analysis method of ibuprofen. The aptamer-modified nanogold colorimetric detection-based analysis method comprises following steps: single strand nucleic acid ibuprofen aptamer is taken as an identification probe of ibuprofen, ibuprofen standard solutions with different concentrations are mixed with gold nanoparticle solutions, single strand nucleic acid ibuprofen aptamer solutions, and salt solutions so as to obtain standard detection solutions of different concentrations; after reaction, an ultraviolet spectrophotometer is adopted to detect light absorption values of obtained systems based on different discoloration degrees of the systems caused by gold nanoparticle coagulation, a standard curve is drawn, and the concentration of ibuprofen of a sample to be detected is determined according to the standard curve. According to the aptamer-modified nanogold colorimetric detection-based analysis method, detection can be finished in a short time, and qualitative detection and quantitative determination results can be obtained; and the aptamer-modified nanogold colorimetric detection-based analysis method is high in specificity and stability, wide in application range, and low in cost, and is convenient for popularization and routine application.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Fusion polypeptide against eb virus-induced tumor and colicin ia mutant
InactiveUS20130066051A1Highly specific targetingHighly specific safetyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesEscherichia coliMutant
The present invention provides a fusion polypeptide against EB virus-induced tumor, which comprises an antibody or a mimetic antibody against EB virus and an ion channel forming colicin selected form E1, Ia, Ib, A, B, N and their mutants. The present invention also provides a colicin Ia mutant, which comprises mutations of G11A, H22G, A26G, V31L, and H40D. The present invention also provides a gene, vector, preparation method and use of the fusion polypeptide, and provides a gene and use of the mutant.
Owner:PROTEIN DESIGN LAB LTD
Individualized beautifying skin care product and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106943338ADredge microcirculationDredge anti-microthrombosisCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFreeze-dryingCutaneous microcirculation
The invention discloses an individualized beautifying skin care product and a preparation method thereof. The individualized beautifying skin care product is prepared by mixing the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 1 to 20 percent of individualized human-derived immune cell culture supernatant fluid freeze-dried powder expressing hirudin, 1 to 15 percent of grease, 1 to 27 percent of aliphatic ester, 1 to 8 percent of organic solvent, 0.1 to 1 percent of perfume, 5 to 30 percent of nutrient and the balance of ultrapure water. The beautifying skin care product containing individualized immune cell culture supernatant fluid freeze-dried powder expressing the hirudin, disclosed by the invention contains most of purely natural and individualized growth factors which are required by cell growth as well as the hirudin which is transfected by genes and expressed by individualized immune cell secretion, so that immunological rejection can be avoided when the individualized beautifying skin care product is used for beautifying, and the individualized beautifying skin care product has comprehensive effects of dredging skin microcirculation, resisting microthrombus, removing spot and acne, moisturizing skin, whitening, preventing skin ageing and increasing skin elasticity, and is an individualized, efficient and green beautifying skin care product.
Owner:江苏赛拉纳生物医药有限公司
Nucleic-acid composite nano-drug self-assembled and constructed based on coordination of metal ions, and preparation method and application of nucleic-acid composite nano-drug
ActiveCN111317826AIncrease load factorEasy to makePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a nucleic-acid composite nano-drug self-assembled and constructed based on coordination of metal ions, and a preparation method and application of the nucleic-acid composite nano-drug. The nucleic-acid composite nano-drug can be applied to drugs for treating skin; the nucleic-acid composite nano-drug is formed through driving a nucleic acid nano-material with relatively goodbiocompatibility to assemble a nucleic acid nano-carrier with uniform size and controllable particle size and loading a drug based on the coordination of the metal ions; or the nucleic-acid compositenano-drug is formed through driving assembling of a conjugate of a chemotherapy drug and nucleic acid; or the nucleic-acid composite nano-drug is formed through driving a gene drug or a gene drug ofan embedded drug. According to the method provided by the invention, the complexity of a design and synthesis process of a nucleic acid nano-material by a nucleic acid nanotechnology is improved, thebiotoxicity of the nano-material is effectively lowered, the hydrophobic problem of the drug can be solved, and the treatment effect of the drug is improved; and in addition, the nano-composite nano-system has relatively good skin tissue permeability and provides a novel way of think for the field of local drug administration.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Formula and preparation technology of nano antibacterial brush hair
ActiveCN106360959AImprove antibacterial propertiesHelps cleanlinessBristlePolyesterBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a formula of a nano antibacterial brush hair. The formula comprises the following components in weight: 20-60g of thermoplastic polyester particles, 20-30g of nanosilver antibacterial liquid, 1-10g of a coupling agent, 1-5g of nano magnetic powder, 1-2g of coral nano powder and 1-3g of nano pearl powder. The nano antibacterial brush hair is simple in preparation technology and low in manufacturing cost; The statistics prove that the probability that the antibacterial effect of the nano antibacterial brush hair is higher than that of a common brush hair is more than 99%, and antibacterial property is superior; and the nano antibacterial brush hair contains a silver ion active ingredient, can be widely applied to medical treatment and is proved to be safe, efficient, non-irritant to skin and non-toxic, no allergic reaction is caused, and an efficient broad-spectrum antibacterial effect can be obtained by low concentration.
Owner:DONGGUAN ZHENGHE DAILY USE PROD CO LTD
LRPPRC (leucine rich pentatricopeptide repeat containing) specific nucleic acid aptamer and application thereof
ActiveCN108410878AEffective treatmentGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsKinase activityAptamer
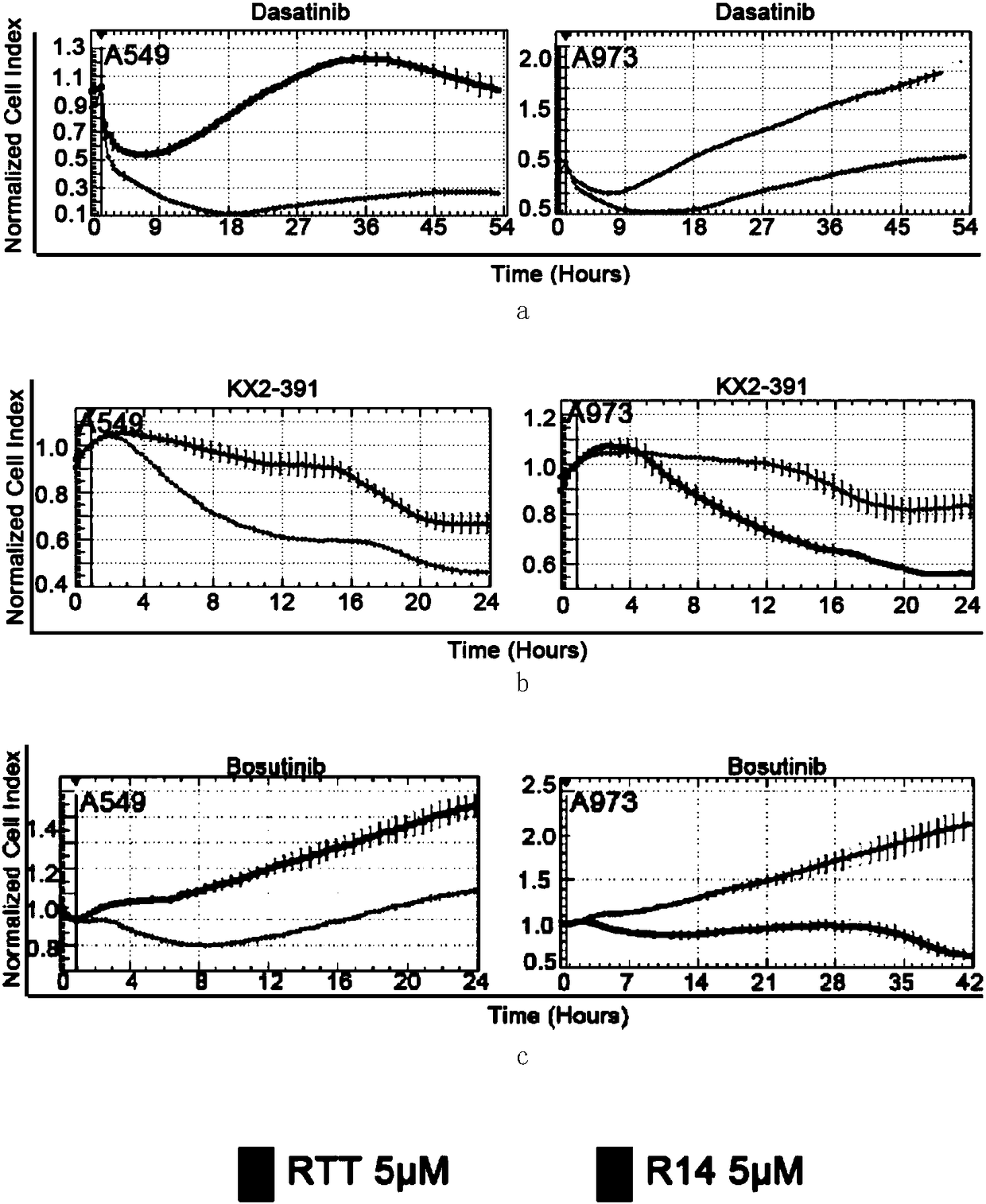
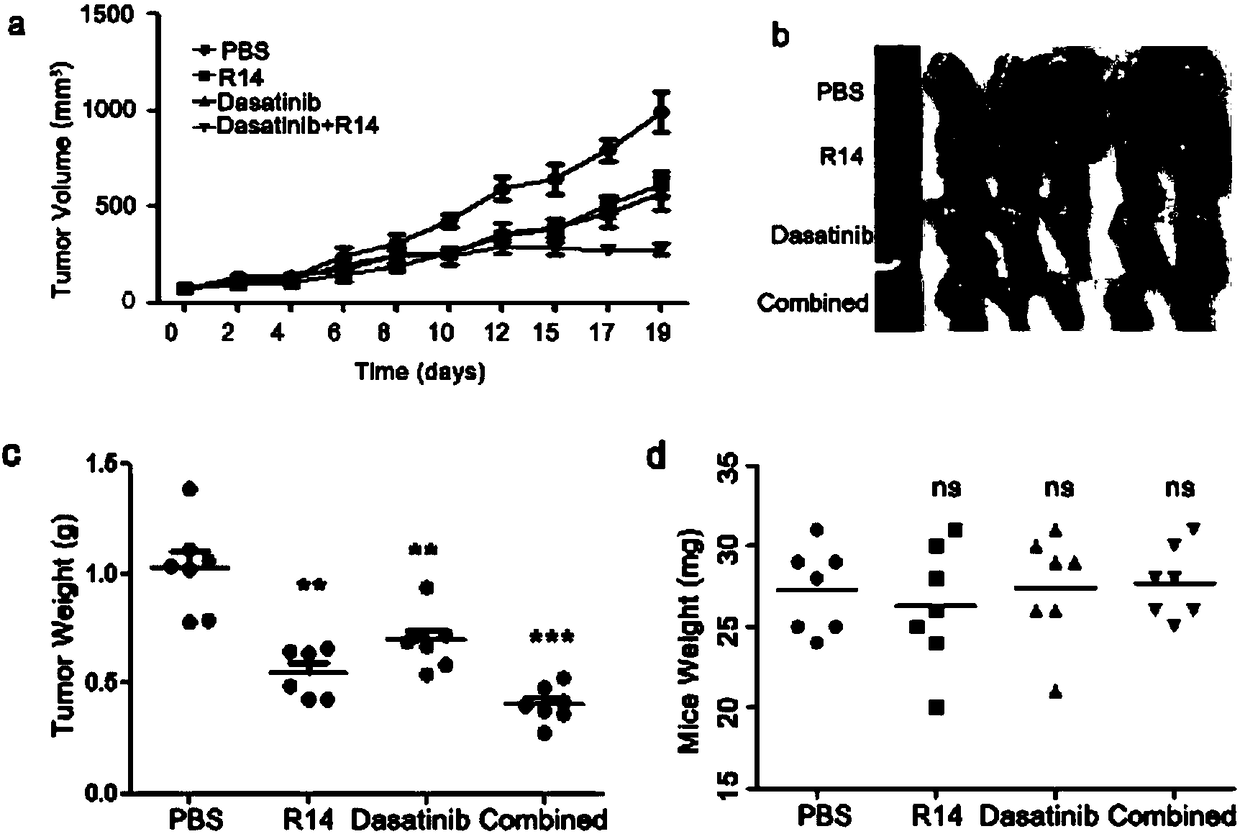
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer R14 which can specifically recognizing LRPPRC (leucine rich pentatricopeptide repeat containing), and the sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer R14 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The nucleic acid aptamer R14 is capable of inhibiting tumor cell proliferation by blocking the normal tissue function of the LRPPRC and interfering the cell cycle progression. Theinvention further provides application of the nucleic acid aptamer R14 specifically recognizing the LRPPRC and SRC kinase inhibitor in combined treatment of tumour. The nucleic acid aptamer R14 is capable of enhancing the sensitivity of tumour to the SRC kinase inhibitor, and the SRC kinase inhibitor can be used for eliminating SRC kinase activity abnormal activation caused by the nucleic acid aptamer R14.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
PD-1 targeted polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveCN107226842AImprove bindingHigh binding affinityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsChemical synthesisPeptide
The invention discloses a PD-1 targeted polypeptide and an application thereof. The invention further discloses a preparation method for polypeptides and pharmaceutical compositions containing the polypeptides. The polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be bonded to a human PD-1 protein, so that the polypeptide can serve as a leader peptide for developing human PD-1 receptor inhibitors, and a foundation is provided for the development of antitumor drugs. The polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be prepared by adopting a chemical synthesis method and has the advantages of high purity, small molecular weight, safety, reliability and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nanometer particle target preparation of hydroxycamptothecine, and its preparing method
InactiveCN101002772AGood tissue permeabilityImprove targetingOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCarboxymethyl celluloseMedicine
A targeting nanoparticle of 10-hydroxy camptothecine for treating tumor is proportionally prepared from gelatin, 10-hydroxy camptothecine, tert-butanol, VC, chitosan, carboxymethyl cellulose sodium, and the water for injection. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:HUNAN KANGDU PHARMA
Sodium fusidate powder-injection pharmaceutical composition for injection and preparation method
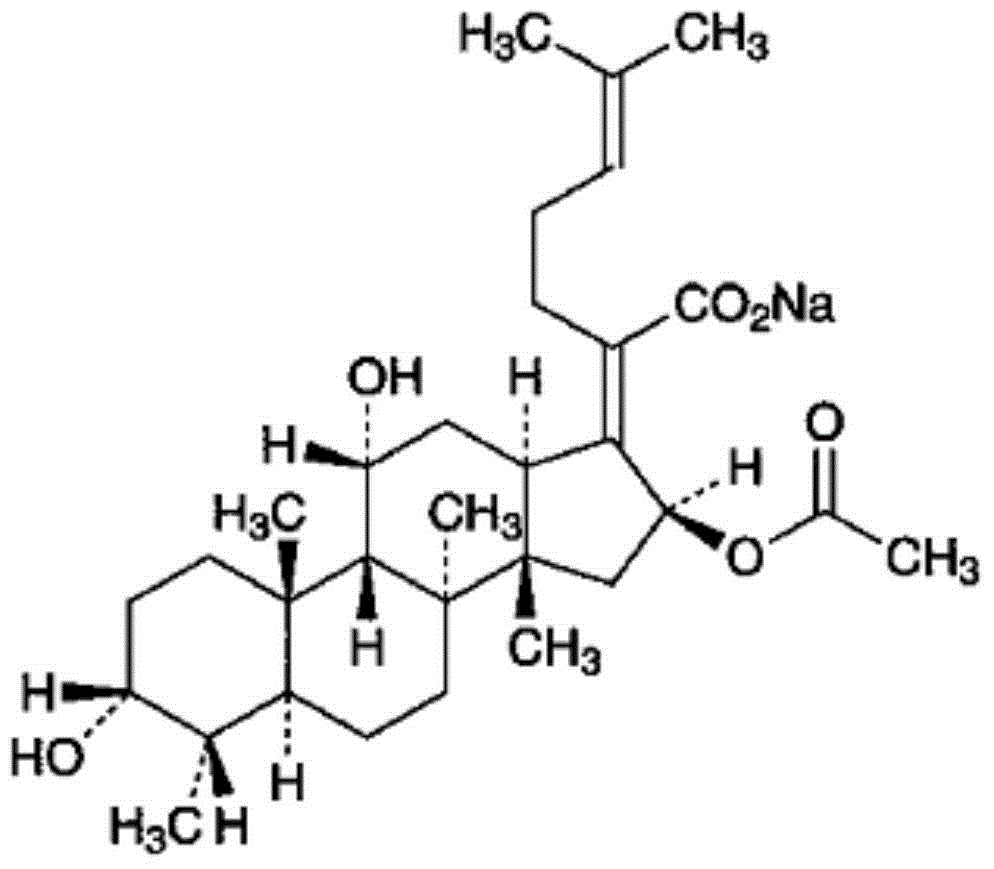
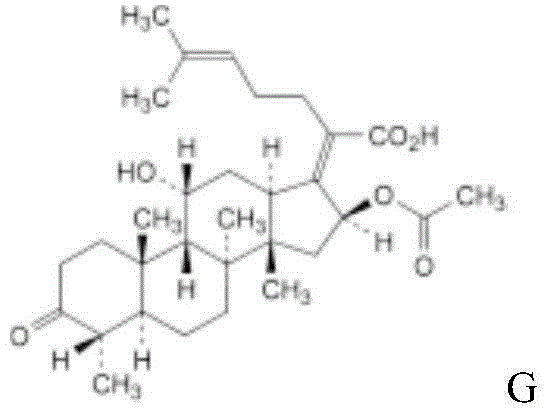
ActiveCN104352454AGood tissue permeabilityWidely distributedAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryNeutral Amino AcidsFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a sodium fusidate powder-injection pharmaceutical composition for injection and a preparation method. Specifically, the invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, relates to a medicine which can be used for treating various infections such as osteomyelitis, sepsis, endocarditis, repeatedly infected cystic fibrosis, pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections, surgical and traumatic infections and the like caused by various sensitive bacteria, especially staphylococcus, and particularly relates to a pharmaceutical composition such as a freeze-dried powder injection prepared by taking sodium fusidate as an active component. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the pharmaceutical composition. In an implementation scheme, the invention relates to a sodium fusidate powder-injection pharmaceutical composition for injection, which comprises sodium fusidate, a neutral amino acid and an alkaline amino acid. The pharmaceutical composition has excellent pharmaceutical properties.
Owner:CHENGDU TIANTAISHAN PHARMA
Fluorescent probe
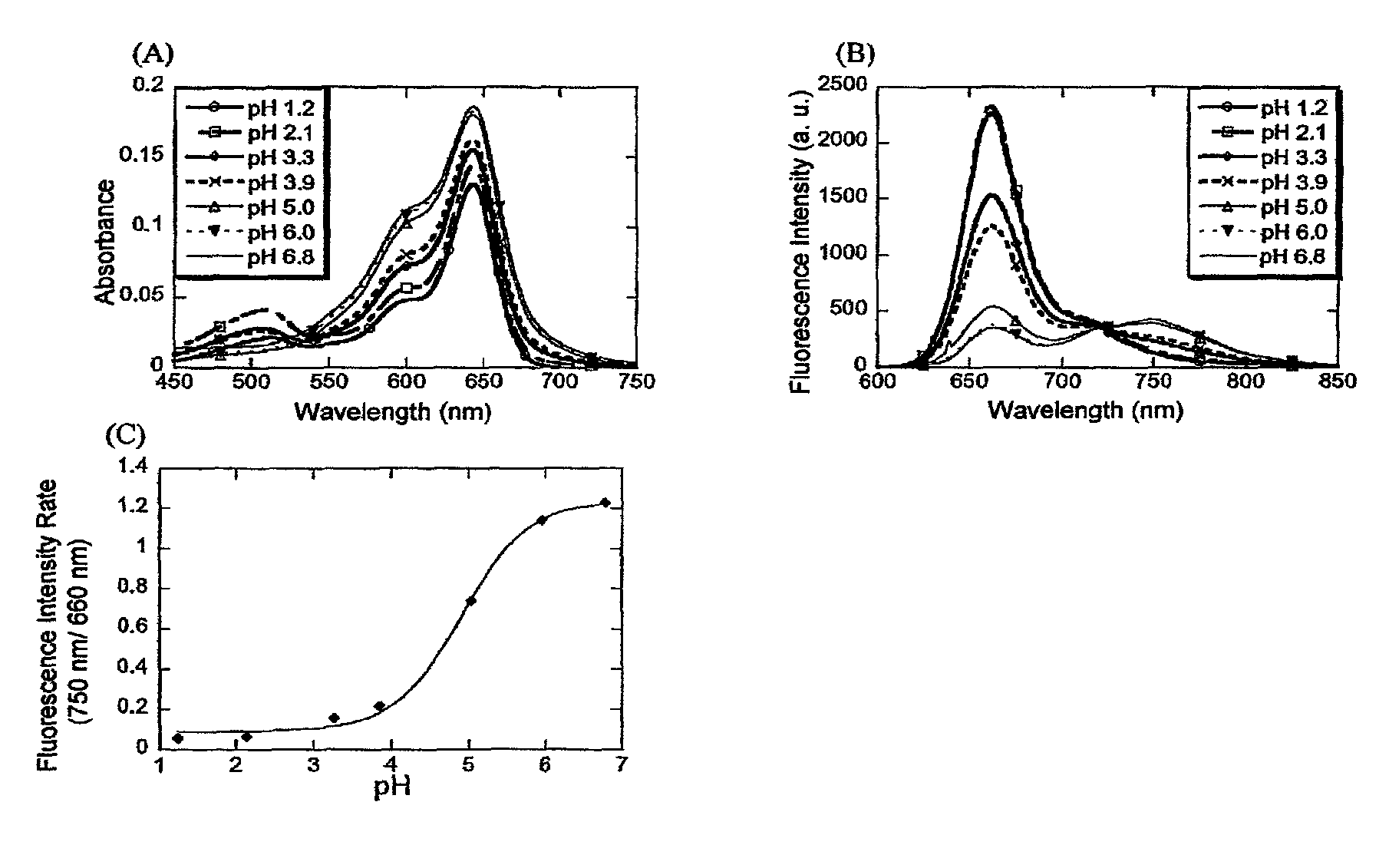
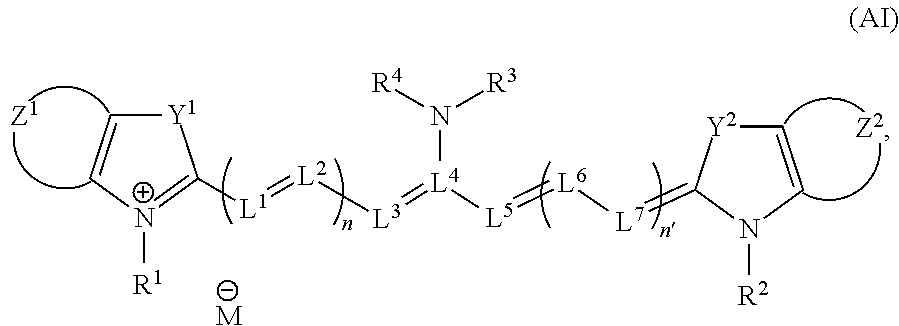
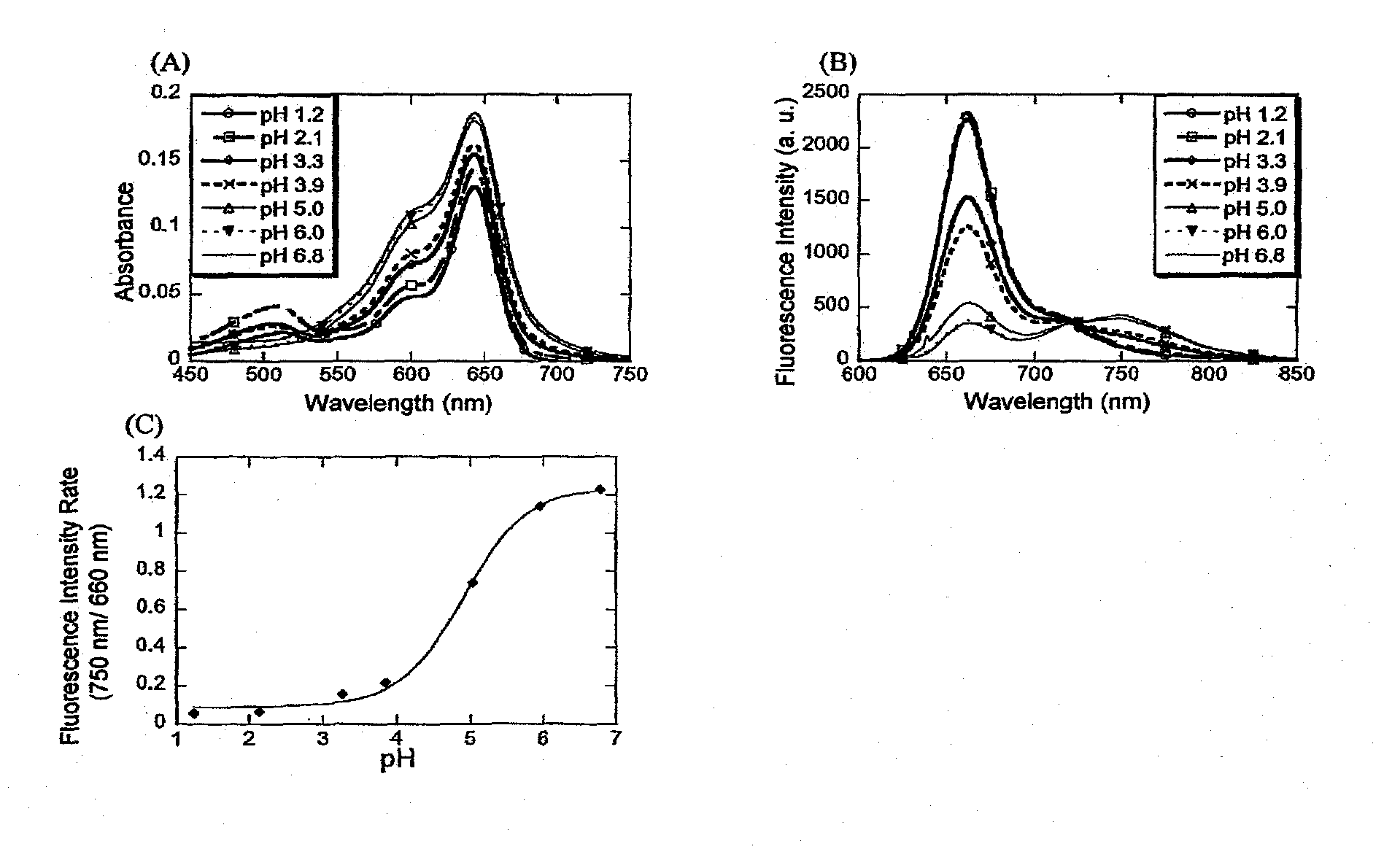
InactiveUS8465985B2Superior biological tissue permeabilityGood tissue permeabilityOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEnergy transferResonance
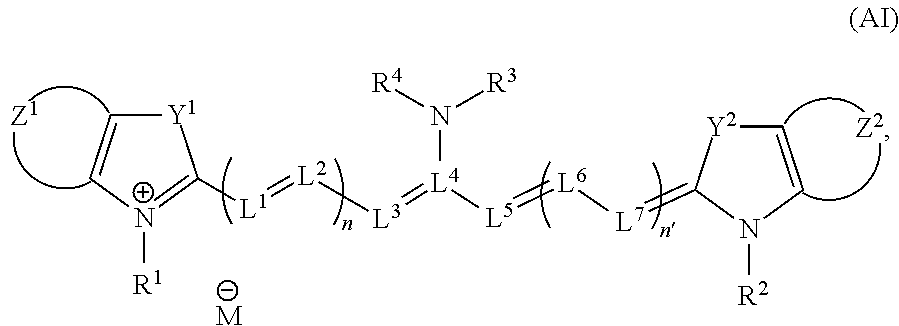
A fluorescent probe comprising a compound represented as (Fluorophore A)-S-(Fluorophore B) (Fluorophore A and Fluorophore B are fluorophores which emit fluorescence when they are irradiated with an excitation light of a wavelength of 600 to 950 nm, Fluorophore A has a property that it shows change of fluorescence characteristic before and after a specific reaction with an substance to be measured, and S represents a spacer which connects Fluorophore A and Fluorophore B), which compound shows substantial change in efficiency of fluorescence resonance energy transfer between Fluorophore A and Fluorophore B before and after the specific reaction with the objective substance, wherein Fluorophore A is represented by the following formula (AI):which uses and shows an excitation light wavelength / fluorescence wavelength in the near infrared region, lights of which region show superior biological tissue permeability, and enables measurement of an substance to be measured by the ratio method.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Method for detecting chiral compound based on aptamer modified nanogold
InactiveCN104897596AWide range of target moleculesHigh affinityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsAptamerNanoparticle
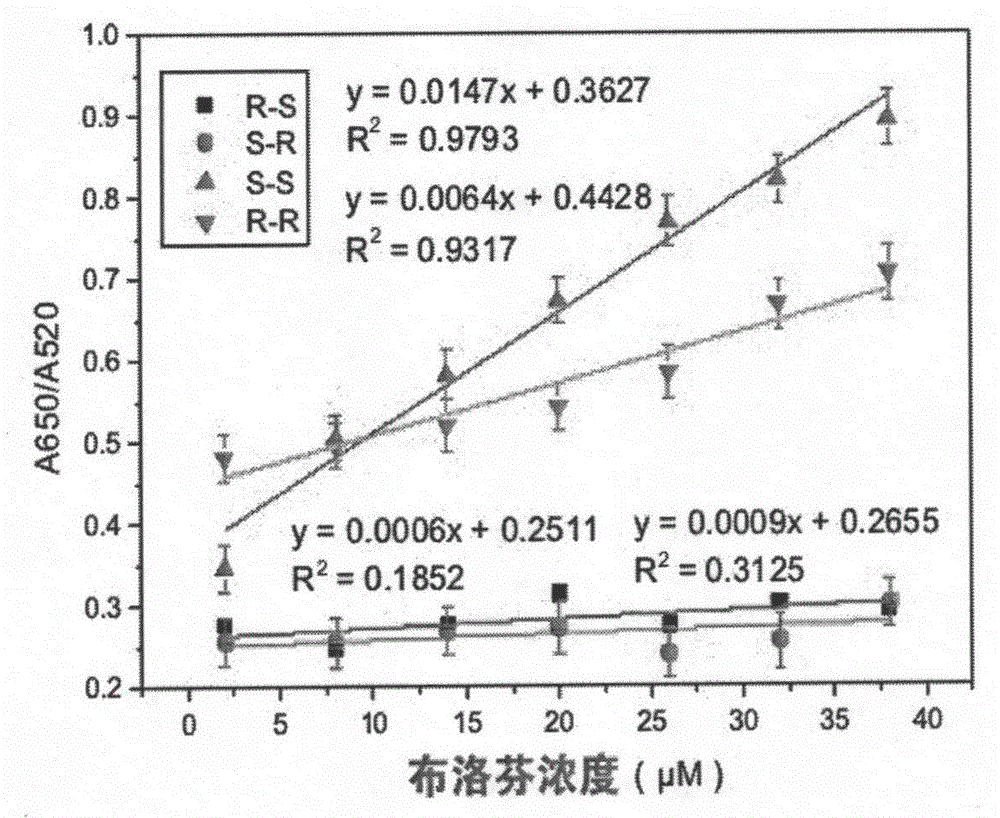
The invention provides a method for detecting chiral compound based on aptamer modified nanogold. The method is characterized by specifically comprising the following steps: step 1, preparing a gold nanoparticle solution; step 2, preparing at least one of an S-ibuprofen aptamer and an R-ibuprofen aptamer; and step 3, by taking the S-ibuprofen aptamer as a recognition probe of S-ibuprofen, mixing the gold nanoparticle solution, S-ibuprofen aptamer solution, sodium chloride solution and S-ibuprofen standard solution, making the volume constant, reacting for 30 minutes, detecting the light absorption values A650 and A520 of the detection system at 650nm and 520nm by virtue of an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and obtaining a standard curve by taking the ibuprofen concentration as a horizontal coordinate and taking the A650 / A520 as a vertical coordinate; and detecting the S-ibuprofen concentration in a to-be-detected sample by utilizing the standard curve. The method disclosed by the invention can be finished in a short time, qualitative and quantitative detection results are obtained, the method has the advantages of high specificity, high stability, wide application range, low cost and the like, and the conventional application of chiral recognition is easily popularized.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Colon cancer nucleic acid aptamer obtained by rapid screening of tissue samples and application of colon cancer nucleic acid aptamer to detection preparation
PendingCN111944821AImprove the status of diagnosis and treatmentLow toxicityDNA preparationMaterial analysisAptamerTissue sample
The invention discloses a colon cancer nucleic acid aptamer obtained by rapid screening of tissue samples and an application of the colon cancer nucleic acid aptamer to a detection preparation. The sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer is selected from any one of sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.8, or the sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer is marked and modified. The nucleic acid aptamer has the characteristics similar to or even superior to those of a biological antibody, and is mainly reflected in that the nucleic acid aptamer has specificity, high substantivity, low toxicity andlow immunogenicity, can be synthesized in vitro, and is convenient to store and transport. When the nucleic acid aptamer provided by the invention is used for early colon cancer tissue detection after being labeled by a fluorophore, the operation is simple and feasible, and the detection result is more intuitive. Besides, the nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention is a short-chain nucleic acid sequence, and the in-vitro synthesis cost of the nucleic acid aptamer is relatively low.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Cerebral cancer suppressing phycocyanin-polylactic acid-adriamycin micelle and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105476956AHas inhibitory effectOvercome influenceOrganic active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryCancer cellCerebral cancer
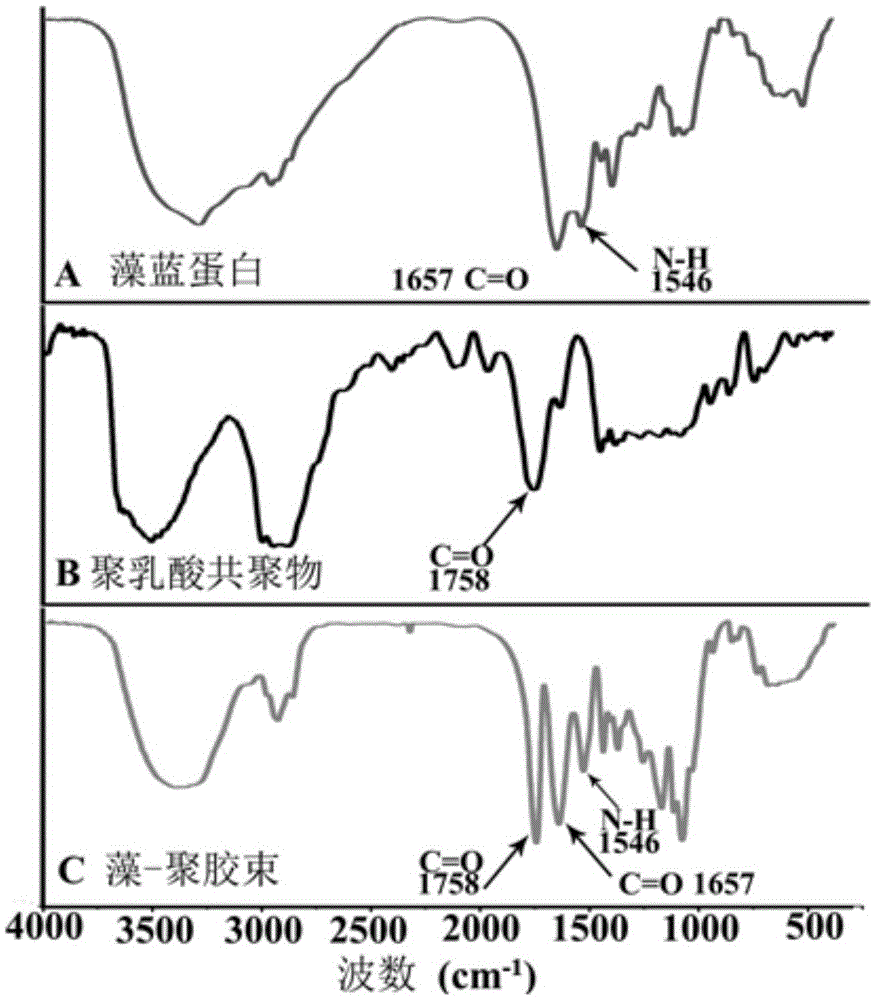
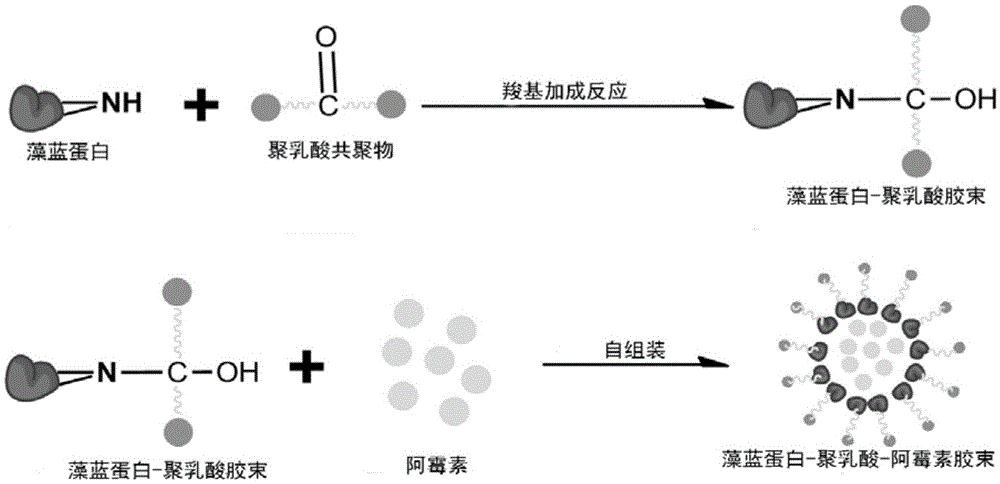
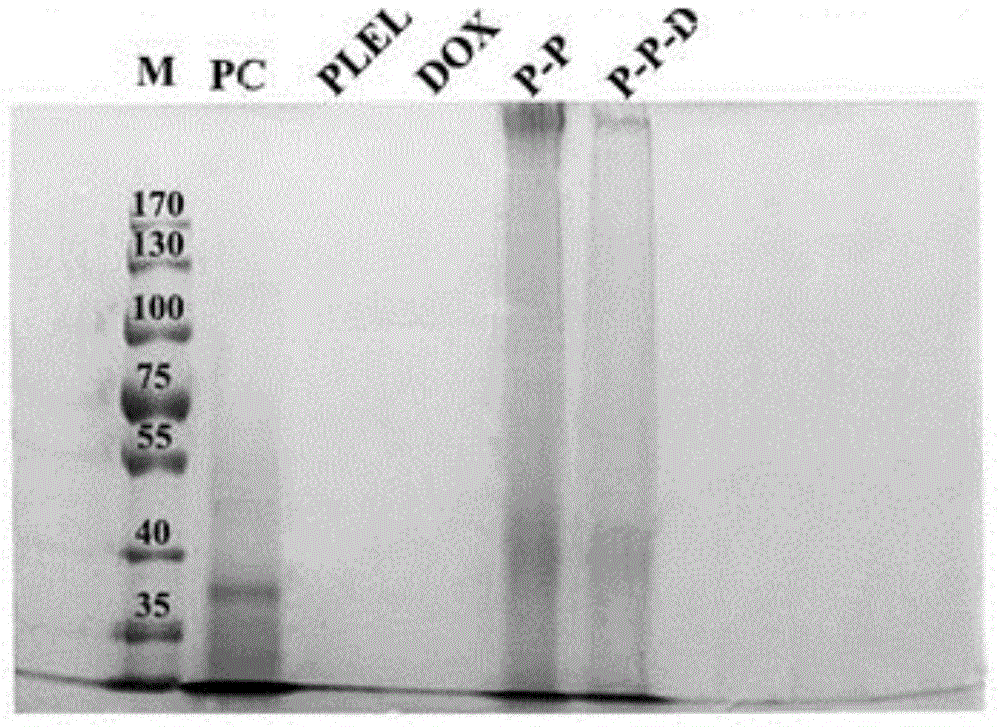
The invention discloses a cerebral cancer suppressing phycocyanin-polylactic acid-adriamycin micelle. Phycocyanin and PLA-PEG-PLA are utilized as raw materials, and a phycocyanin-polylactic acid no-load micelle is formed according to addition reaction of carboxyl and self-assembly principle based on hydrophilia and hydrophobicity. According to the self-assembly principle, adriamycin is coated in the no-load micelle to assemble by itself to form the micelle. The phycocyanin-polylactic acid-adriamycin micelle is a novel nano medicine capable of directly acting on tumor through blood-brain barrier to suppress cerebral cancer cells and capable of releasing slowly to retain in blood for a long time, thereby overcoming influence and limit of the blood-brain barrier to drug treatment effect. Besides, the micelle is prepared from natural or degradable components which are not involved with organic solvents during synthesis, has the advantages such as good biocompatibility, biodegradability, hypotoxicity, high loading capacity, and accordingly has high application potential in treating cerebral cancer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Ligands that bind il-4 and/or il-13
InactiveCN101578298AGood tissue permeabilityImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntibody ingredientsAllergic asthmaInterleukin 13
Disclosed are ligands that have binding specificity for interleukin-4 (IL-4), for interleukin-13 (IL-13), or for IL-4 and IL-13. Also disclosed are methods of using these ligands. In particular, the use of these ligands for treating allergic asthma is described.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Rapid screening of tissue sample of rectal cancer aptamer and application of rectal cancer aptamer to preparation of detection preparation
InactiveCN112760323ALow immunogenicityLow toxicityDNA preparationMaterial analysisImmunogenicityCancer research
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer which can be used for detecting early rectal cancer tissue and application of the nucleic acid aptamer to clinical diagnosis and treatment of rectal cancer. The sequence of the nucleic acid aptamer is selected from any one of sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.8, or the nucleic acid aptamer is subjected to label modification or transformation. The nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention has similar or even more superior characteristics to a protein antibody, and the characteristics are mainly reflected in that the nucleic acid aptamer has specificity, high affinity, low toxicity and low immunogenicity, can be synthesized in vitro and modified, is convenient to store and transport, and the like. When the nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention is used for early rectal cancer tissue detection after being labeled by a fluorophore, the operation is simple and easy to implement, and the detection result is more visual. Meanwhile, the nucleic acid aptamer disclosed by the invention has a short-chain nucleic acid sequence, the in-vitro synthesis cost of the nucleic acid aptamer is low, the period is short, and the reproducibility is good.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Nano antibody for HDAC6-cat 1 region and application thereof
InactiveCN109734808AImprove bindingStrong specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliComplementarity determining region
The invention discloses a nano antibody for an HDAC6-cat 1 region and application thereof, particularly relates to a nano antibody for a histone deacetylase 6 catalase 1 region (HDAC6-cat1)and application thereof, discloses an amino acid sequence of a framework region FR and a complementarity determining region CDR of a VHH chain of the nano antibody, and also discloses a gene sequence encoding the heavy-chain nano antibody and a host cell expressing the nano antibody. By means of the gene sequence and the host cell of the single-region heavy-chain nano antibody, the nano antibody can be efficiently expressed in escherichia coli, can be recognized and specifically identified with a target antigen after being expressed and purified, and can be used for analyzing the epitope of the target antigen. Meanwhile, a pcDNA5 / FRT recombinant plasmid is constructed, so that the influence of the nano antibody on the biological function of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is explored.
Owner:REGENECORE BIOTECH CO LTD
Affinity mature binding protein of EGFR and application
ActiveCN112646035AReduce manufacturing costStrong specificityMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsChemistryProteinogenic amino acid
The invention discloses an affinity mature binding protein of an anti-human EGFR and an application. The affinity mature binding protein is an aEG22C4 affinity mature binding protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 4, or a binding protein formed by combining at least one of an aEG12E2 affinity mature binding protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, an aEG13E8 affinity mature binding protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 3 and an aEG11A6 affinity mature binding protein with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 with the aEG22C4 affinity mature binding protein. The affinity mature binding protein has the advantages of high affinity, high specificity, low immunogenicity, better stability, simple structure, easiness in engineering transformation and the like, and can be better applied to development of binding protein drugs.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and applications of triblock polymer micelle
ActiveCN107412159AGood biocompatibilityGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNanocarriersPolymer science
The invention provides a preparation method of a triblock polymer micelle. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling chitosan oligosaccharide and dithiodipropionic acid to react under the effect of an activating agent, thus obtaining a first intermediate; (2) enabling the first intermediate and polyethyleneimine to react under the effect of the activating agent, thus obtaining a second intermediate; (3) enabling the second intermediate and urocanic acid to react under the effect of the activating agent, thus obtaining a triblock polymer; and (4) dissolving the triblock polymer obtained in the step (3) in water, thus obtaining the triblock polymer micelle. The triblock polymer micelle has the excellent tissue permeability and enhanced penetration and retention effects, so that a natural passive targeting effect is achieved, and a new candidate system is provided for the development of nanocarriers.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
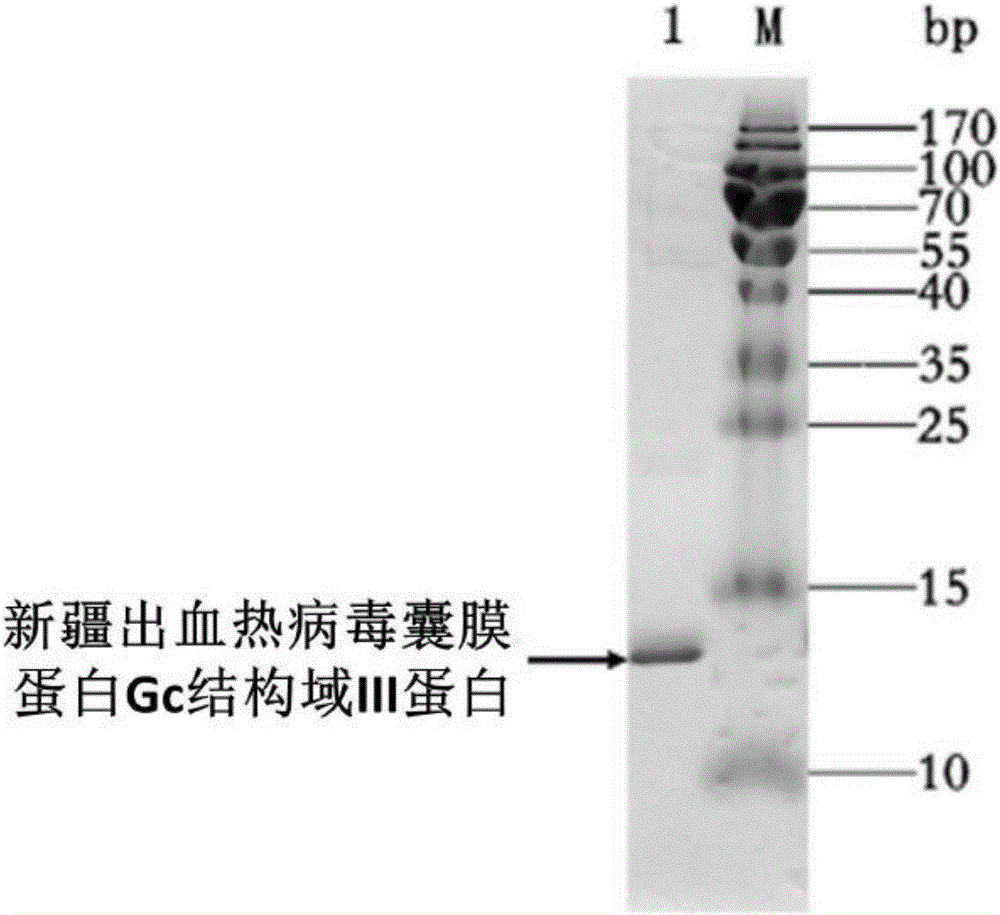
Single-domain antibody for neutralizing Xinjiang hemorrhagic fever virus
ActiveCN106188285AGood tissue permeabilityReduce manufacturing costAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological material analysisProduction cycleSteric effects
The invention provides a single-domain antibody XHF4RC8 for neutralizing the Xinjiang hemorrhagic fever virus and application thereof in preparing medicine for preventing or treating Xinjiang hemorrhagic fever virus infection. The amino acid sequence of the single-domain antibody XHF4RC8 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the nucleotide sequence of a gene for coding XHF4RC8 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The VH structural domain m0 of a human antibody IgG1 serves as the framework of the single-domain antibody. XHF4RC8 can be bound with the structural domain III of Xinjiang hemorrhagic fever virus envelope protein Gc and has the virus neutralizing effect. XHF4RC8 is small in molecular weight and has higher tissue penetration and higher capability for being bound with epitope with the steric effect. XHF4RC8 can be expressed in a prokaryotic expression system and is low in production cost and short in production cycle. XHF4RC8 has the potential function of treating the Xinjiang hemorrhagic fever virus clinically or can be used in combination with other antibodies to achieve an ideal treatment effect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
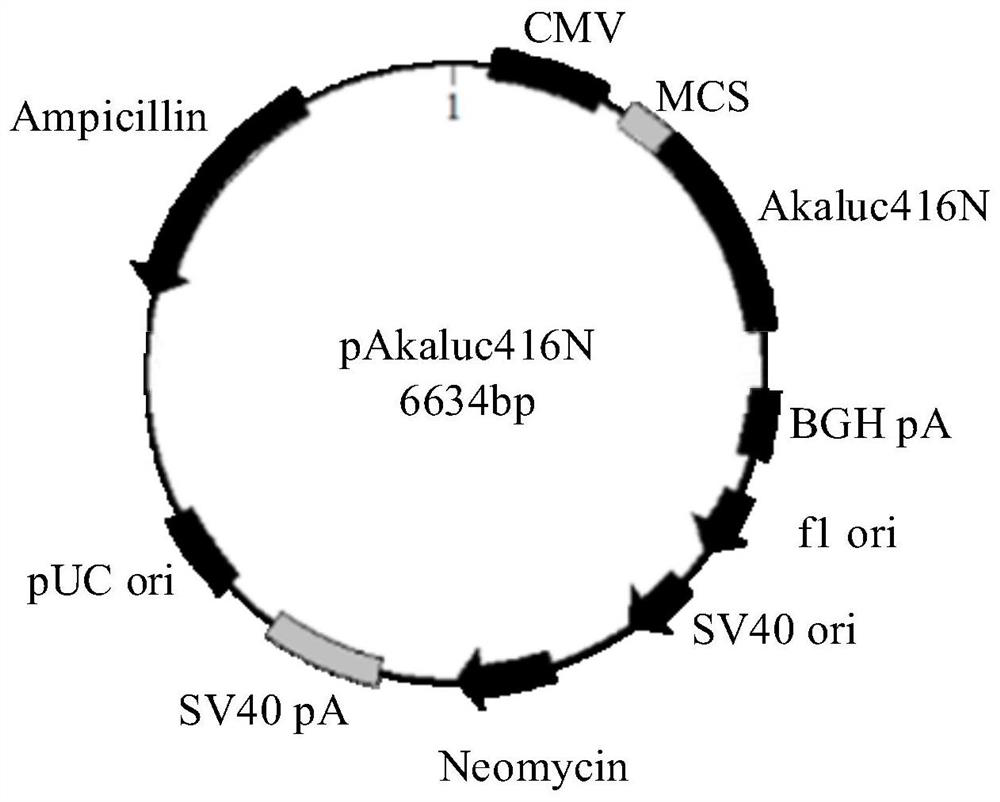
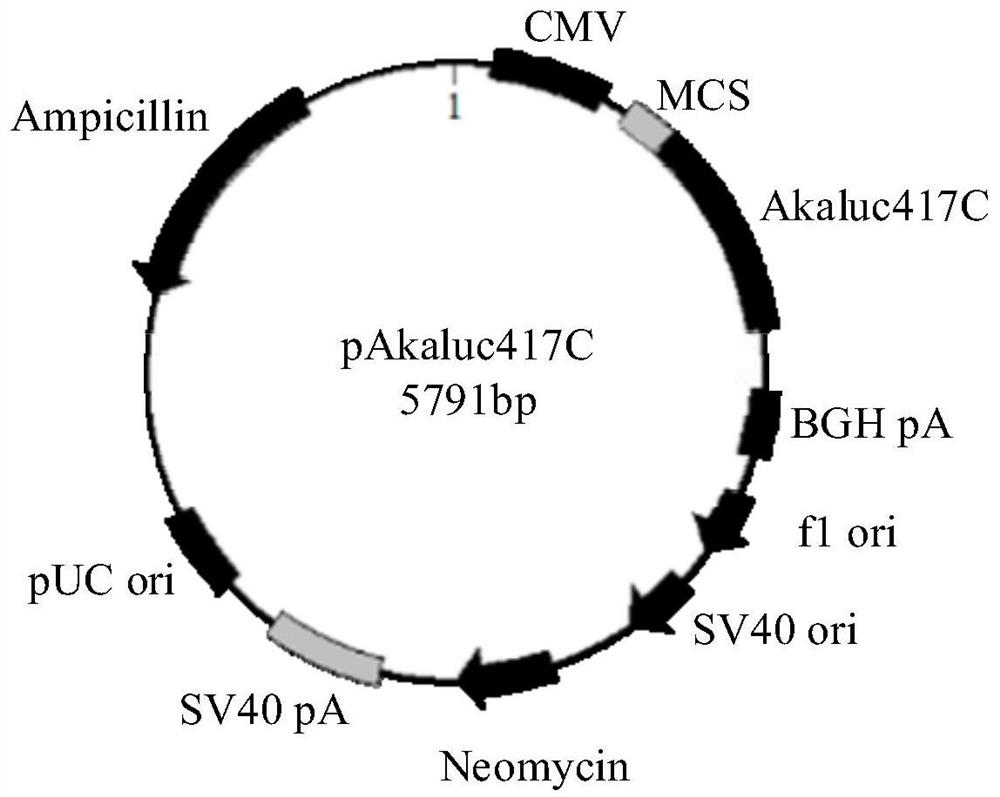
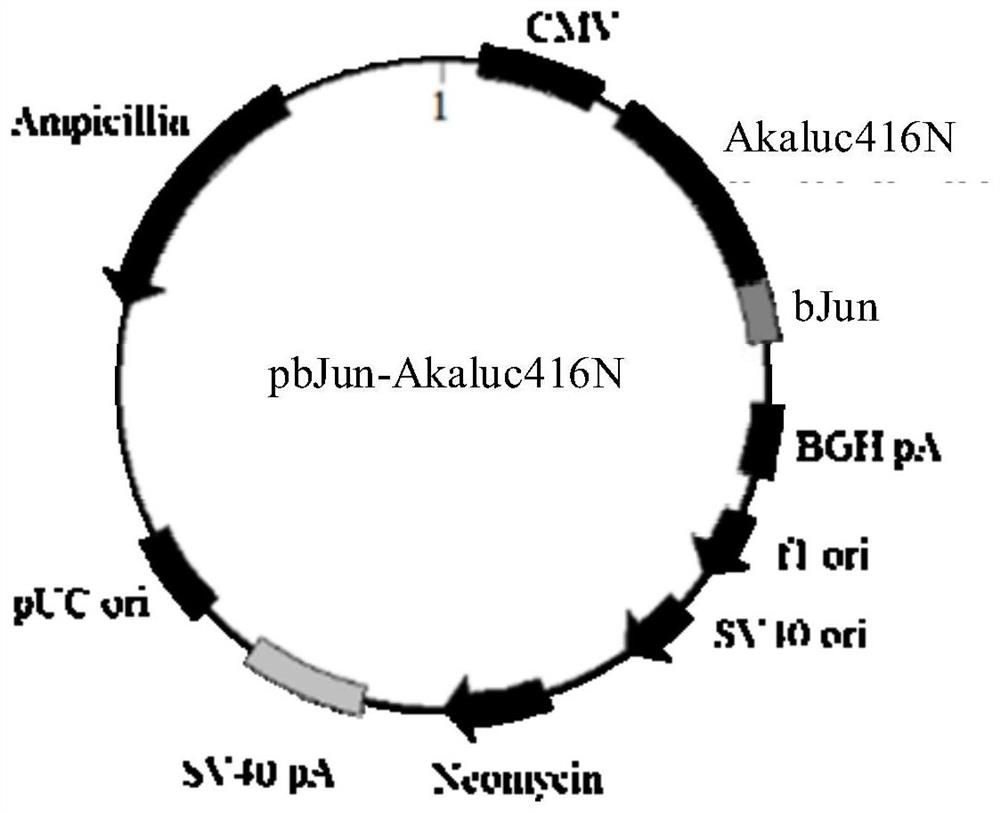
Protein fragment complementary system based on split luciferase Akaluc and construction method thereof
ActiveCN113717986AGood tissue permeabilityLong wavelengthMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesLuciferasesProtein Fragment
The invention relates to the technical field of protein interaction imaging, and provides a protein fragment complementary system based on split luciferase Akaluc and a construction method thereof. The protein fragment complementary system comprises a first vector and a second vector, the first vector is a vector containing a sequence SEQ ID NO.2, and the second vector is a vector containing a sequence SEQ ID NO.3. The protein fragment complementary system is a complementary system based on the split luciferase Akaluc, the luciferase Akaluc can react with a substrate Akalumine, and fluorescence is generated under the condition of physiological temperature (37 DEG C). Furthermore, the fluorescence generated by the reaction of the luciferase Akaluc and the substrate Akalumine has longer wavelength, so that the fluorescence generated by the protein fragment complementary system has better tissue permeability and is beneficial to imaging observation.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineered binding proteins of EpCAM and uses thereof
ActiveCN113234165AHigh affinityReduce manufacturing costImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunogenicityPharmaceutical Substances
The invention discloses a modified binding protein of EpCAM and application of the modified binding protein. The modified binding protein is at least one of a modified binding protein of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, a modified binding protein of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, a modified binding protein of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.3 and a modified binding protein of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.4. The invention also discloses an application of the binding protein modified by the EpCAM in preparation of antitumor drugs. The binding protein has high structural stability and strong tissue permeability, is human-derived, has no immunogenicity in a human body, and can be better applied to development of antitumor drugs.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Fluorescent probe
InactiveUS20110117666A1Superior biological tissue permeabilityGood tissue permeabilityOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluoProbesFluorophore
A fluorescent probe comprising a compound represented as (Fluorophore A)-S-(Fluorophore B) (Fluorophore A and Fluorophore B are fluorophores which emit fluorescence when they are irradiated with an excitation light of a wavelength of 600 to 950 nm, Fluorophore A has a property that it shows change of fluorescence characteristic before and after a specific reaction with an substance to be measured, and S represents a spacer which connects Fluorophore A and Fluorophore B), which compound shows substantial change in efficiency of fluorescence resonance energy transfer between Fluorophore A and Fluorophore B before and after the specific reaction with the objective substance, wherein Fluorophore A is represented by the following formula (AI):which uses and shows an excitation light wavelength / fluorescence wavelength in the near infrared region, lights of which region show superior biological tissue permeability, and enables measurement of an substance to be measured by the ratio method.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
White spot disease virus single-chain variable region recombinant antibody as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114702574AStrong specificityEfficient preparationBacteriaVirus peptidesAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibodies monoclonal
The invention discloses a white spot disease virus single-chain variable region recombinant antibody as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A strain WSSV-VP28-3B7-scFv for efficiently expressing the protein is prepared by cloning an scFv gene sequence of the anti-WSSV-VP28 neutralizing monoclonal antibody 3B7, so that the single-chain variable region recombinant antibody of the WSSV-VP28 neutralizing monoclonal antibody is obtained. The recombinant single-chain variable region antibody can be specifically combined with and recognize natural protein of the envelope protein VP28 of the white spot disease virus, also can recognize white spot disease virions, and can effectively neutralize the white spot disease virus and delay prawn death caused by the virus. The prepared single-chain variable region antibody of the white spot disease virus envelope protein VP28 neutralizing monoclonal antibody provides an important tool for research on rapid detection, diagnosis and prevention of white spot disease viruses based on the single-chain variable region antibody.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Fusion polypeptide against EB virus-induced tumor and colicin Ia mutant
InactiveUS8883161B2Increase lethalityReduce the possibilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesEscherichia coliMutant
The present invention provides a fusion polypeptide against EB virus-induced tumor, which comprises an antibody or a mimetic antibody against EB virus and an ion channel forming colicin selected form E1, Ia, Ib, A, B, N and their mutants. The present invention also provides a colicin Ia mutant, which comprises mutations of G11A, H22G, A26G, V31L, and H40D. The present invention also provides a gene, vector, preparation method and use of the fusion polypeptide, and provides a gene and use of the mutant.
Owner:PROTEIN DESIGN LAB LTD
Red fluorescent probe for use in detection of peptidase activity
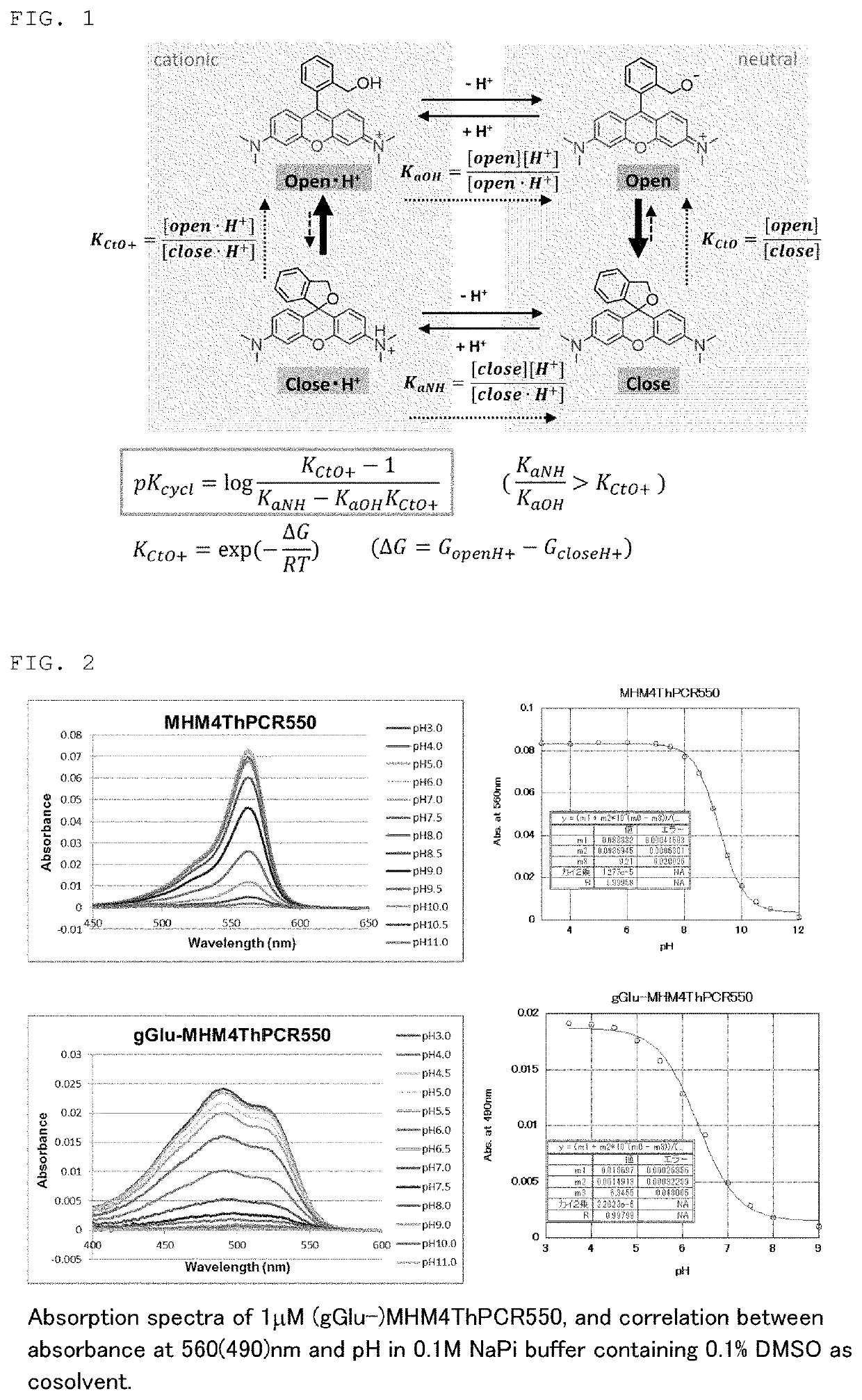
PendingUS20200087516A1Accurate detectionHigh sensitivityCompounds screening/testingGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluoProbesCyclopentene
[Problem]A problem addressed by the present invention is to provide a novel fluorescent probe having excellent tissue permeability that is capable of detecting the peptidase activity expressed at a high level in cancer cells and the like as a response of long-wavelength red fluorescence.[Solution]A compound represented by formula (I) or a salt thereof:[In the formula, A represents a ring structure selected from the group consisting of a thiophene ring, a cyclopentene ring, a cyclopentadiene ring, and a furan ring;X represents a C0-C3 alkylene group;Y represents O, S, C(═O)O, or NH,Z represents O, C(Ra) (Rb), Si(Ra) (Rb), Ge(Ra) (Rb), Sn(Ra) (Rb), Se, P(Rc), or P(Rc) (═O) (where Ra and Rb each independently represent a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group, and Rc represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, or an aryl group);R1 and R2 each independently represent from one to three of the same or different substituents selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, a halogen atom, and an alkyl group, a sulfo group, a carboxyl group, an ester group, an amide group, and an azide group each of which may be substituted;R3 represents an acyl residue derived from an amino acid (where the acyl residue is a residue obtained by removing an OH group from a carboxyl group of the amino acid);R4 and R5 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group (where when R4 or R5 is an alkyl group, the R4 or R5, together with R2, may form a ring structure comprising a nitrogen atom to which R4 and R5 are bonded).]
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com