Colon cancer nucleic acid aptamer obtained by rapid screening of tissue samples and application of colon cancer nucleic acid aptamer to detection preparation
A nucleic acid aptamer and colon cancer technology, which is applied in the preparation of colon cancer clinical diagnosis and treatment reagents, can solve the problems of low patient acceptance, unsatisfactory sensitivity and specificity, and the risk of bleeding and perforation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Nucleic acid aptamer screening of clinical colon cancer tissue
[0021] Based on the Tissue-SELEX technology, clinical colon cancer tissues were used as positive screening samples, and colon cancer paracancerous tissues were used as negative screening samples for screening. Firstly, the X-Aptamer library with affinity group modification was synthesized, and then the initial library was incubated with colon cancer paracancerous tissue, and the nucleic acid sequence combined with the paracancerous tissue was retained and isolated after incubation. Simultaneously, the nonbinding nucleic acid sequences were incubated with clinical colon cancer tissue. Nucleic acid sequences bound to colon cancer tissue were retained and isolated after incubation. Then, in the second round of screening, the positive screening and negative screening libraries retained in the previous round were divided into three groups, respectively, and sterilized water (blank control group), co...
Embodiment 2
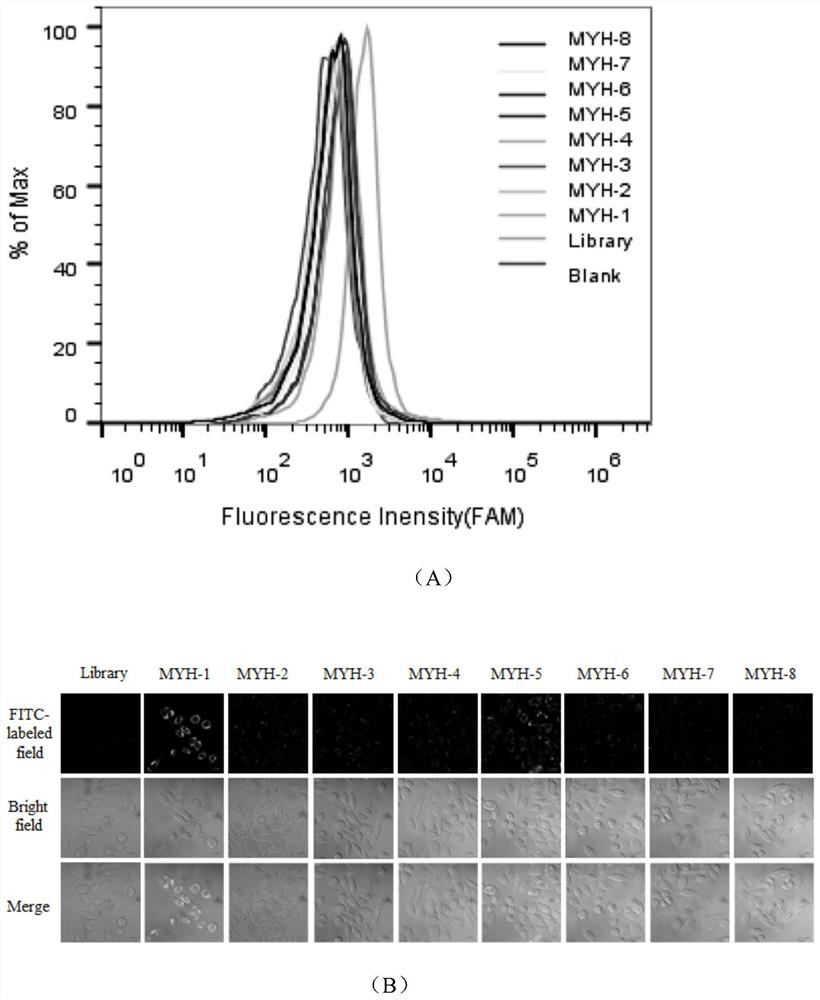
[0025] Example 2: Determining the sequence with the strongest specific binding ability to colon cancer cell line SW480
[0026] First, the 8 candidate sequences and the reference library strands were preprocessed. The candidate sequence and the control library were diluted with sterilized water to a final concentration of 250 nM, then denatured in a 95°C metal bath for 5 minutes, refolded on ice for 10 minutes, and then placed at room temperature. Second, colon cancer cells SW480 were pretreated. Wash the cells 2-3 times with DPBS; then digest the adherent colon cancer cells SW480 from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA, and then pass through the washing buffer (Washing buffer, containing 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride) Cells were pipetted and collected into centrifuge tubes. Finally, candidate sequences and binding buffer (Binding Buffer: DPBS, 0.45% glucose, 5 mM magnesium chloride, 100mg / LtRNA, 1g / L BSA) were added to the treated cells. After shaking and mixing, pla...
Embodiment 3
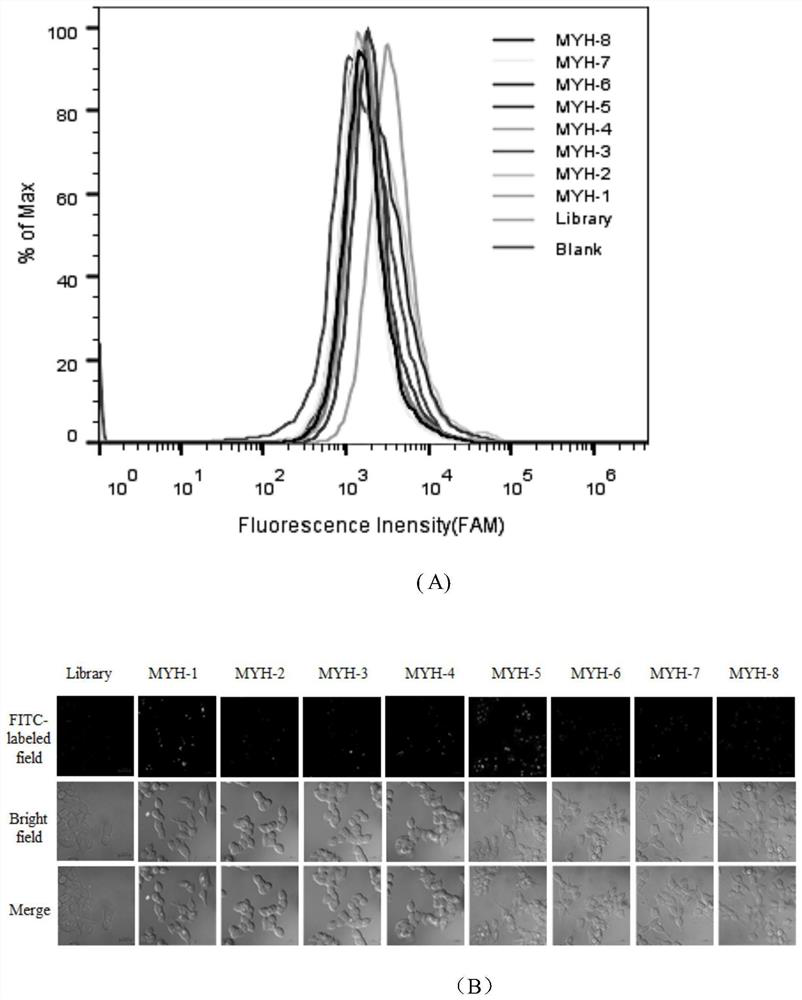
[0029] Example 3: Determining the sequence with the strongest specific binding ability to colon cancer cell HCT116
[0030] First, the 8 candidate sequences and the reference library strands were preprocessed. The candidate sequence and control library were diluted to a final concentration of 250 nM, then denatured in a 95°C metal bath for 5 minutes, refolded on ice for 10 minutes, and then placed at room temperature. Second, colon cancer cells HCT116 were pretreated. The cells were washed 2-3 times with DPBS; the colon cancer cells HCT116 in the adherent state were digested from the culture dish with 0.2% EDTA, and then the cells were collected by blowing through the washing buffer. Finally, the prepared nucleic acid sequence and binding buffer are added to the treated cells. After shaking and mixing, place on a shaker at 4°C and incubate for 1 h. After the incubation was completed, centrifuge and wash 3 times with washing buffer, and then perform fluorescence detection by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com