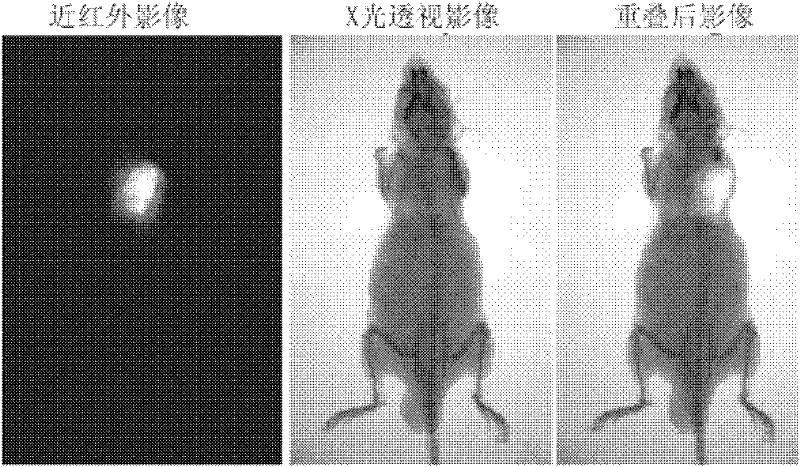
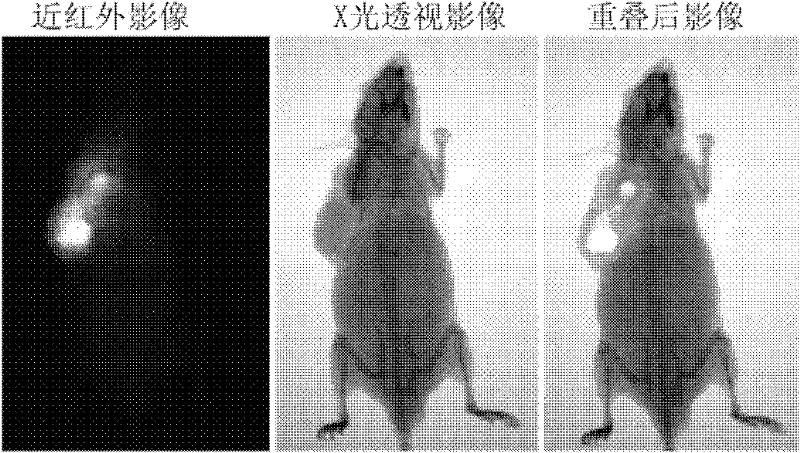
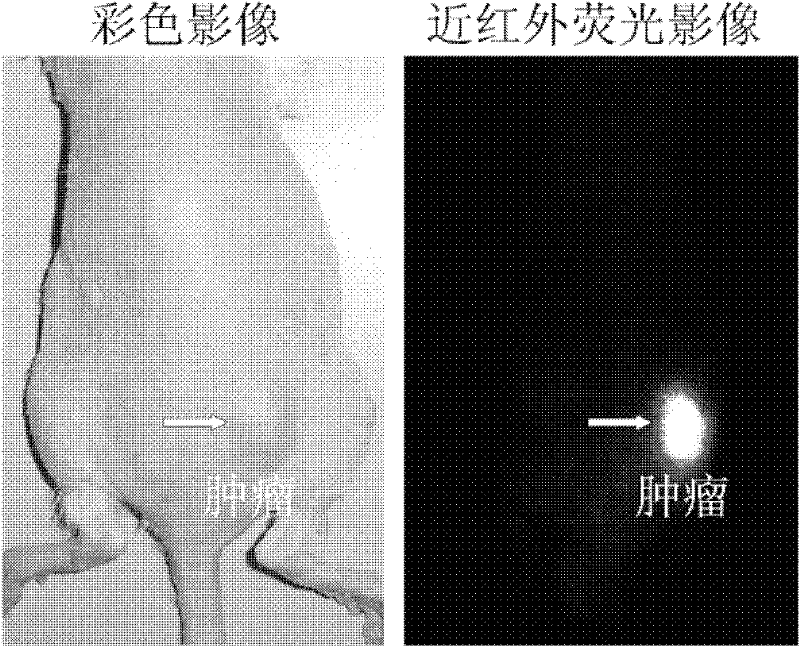
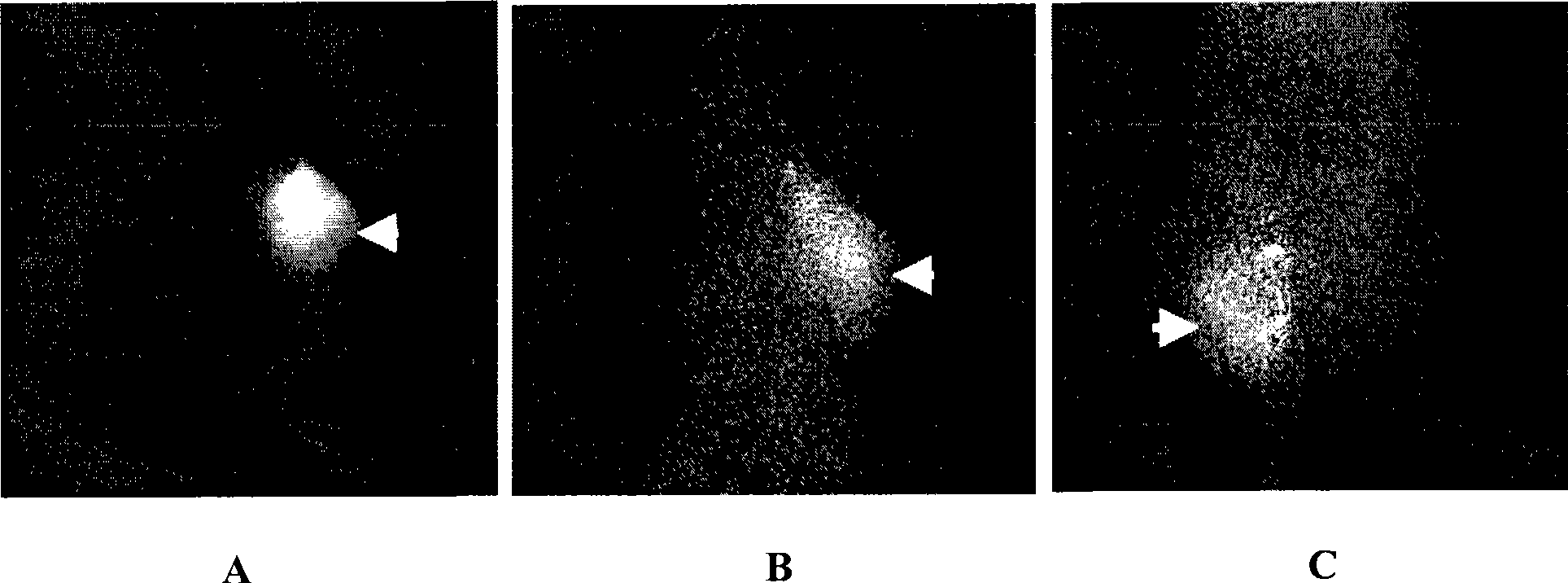
Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Good tissue penetration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heptamethanindocyanine dye and its synthesis method and application
ActiveCN102268191AEasy post-processingHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsMethine/polymethine dyesCyanineSide chain
The invention relates to a heptamethine indocyanine dye containing N-fatty esters or N-fatty amide side chains, a synthetic method thereof and applications thereof in tumor targeting imaging and treatment. The heptamethine indocyanine dye which possesses or individually possesses near infrared absorption, fluorography and antineoplastic activity allows present research and development ideas and treatment levels of tumor targeting treatment medicaments to be greatly improved, and has great significances to aspects of early discovery, control and the like of various tumors.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Application of carbocyanine dye near infrared fluorescent compound
ActiveCN101518528AGood light stabilityGood tissue penetrationOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsArylCarboxyl radical
The invention discloses an application of a carbocyanine dye near infrared fluorescent compound in the preparation of a photosencitizer used for treating tumors or abnormal hyperplasia tissues, shown in formula I or II, wherein X is selected from iodine, chlorine, bromine, alkyl sulfide (OSO2-alkyl), BF4 or ClO4; R1 is selected from chlorine or bromine; R2 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxyl group (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), aryl, aromatic alkyl, alkyl sulfonate, alkyl carbonate and alkyl amine; and n is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, l1 or 12.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Application of pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc in killing staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN102755647AAvoid damageEasy to makeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityBacteroides
The invention relates to an application of pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc in killing staphylococcus aureus. The pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc are taken as the main component for killing staphylococcus, and a phosphate buffer solution and a medical surfactant are added as auxiliary agents to prepare a drug for killing staphylococcus aureus. The drug has the advantages that the main component has a definite structure with the purity reaching more than 98 percent, and has a good water solubility; the drug can be specially combined with cell membranes of bacteria, is low in use concentration, and has small toxicity on human embryonic lung fibroblast and skin; and when the concentration of the pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc is greater than 5 mu M, as long as a light source with excitation wavelength of 670 nm is used to radiate for 2 minutes, more than 99.99 percent of staphylococcus aureus can be killed. Thepentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc has a good application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic composite nano material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111388668AHigh saturation magnetizationProlong circulation time in the bodyEnergy modified materialsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsTumor tissueMacromolecule
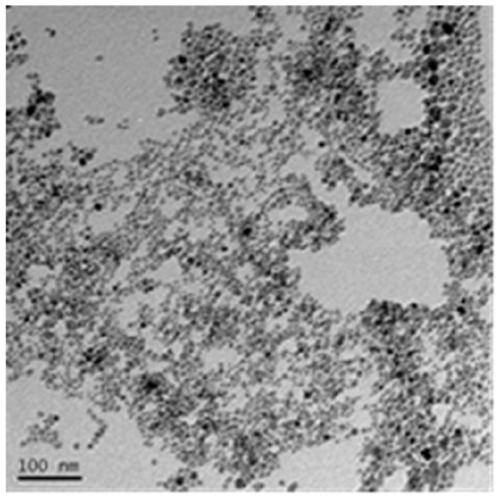
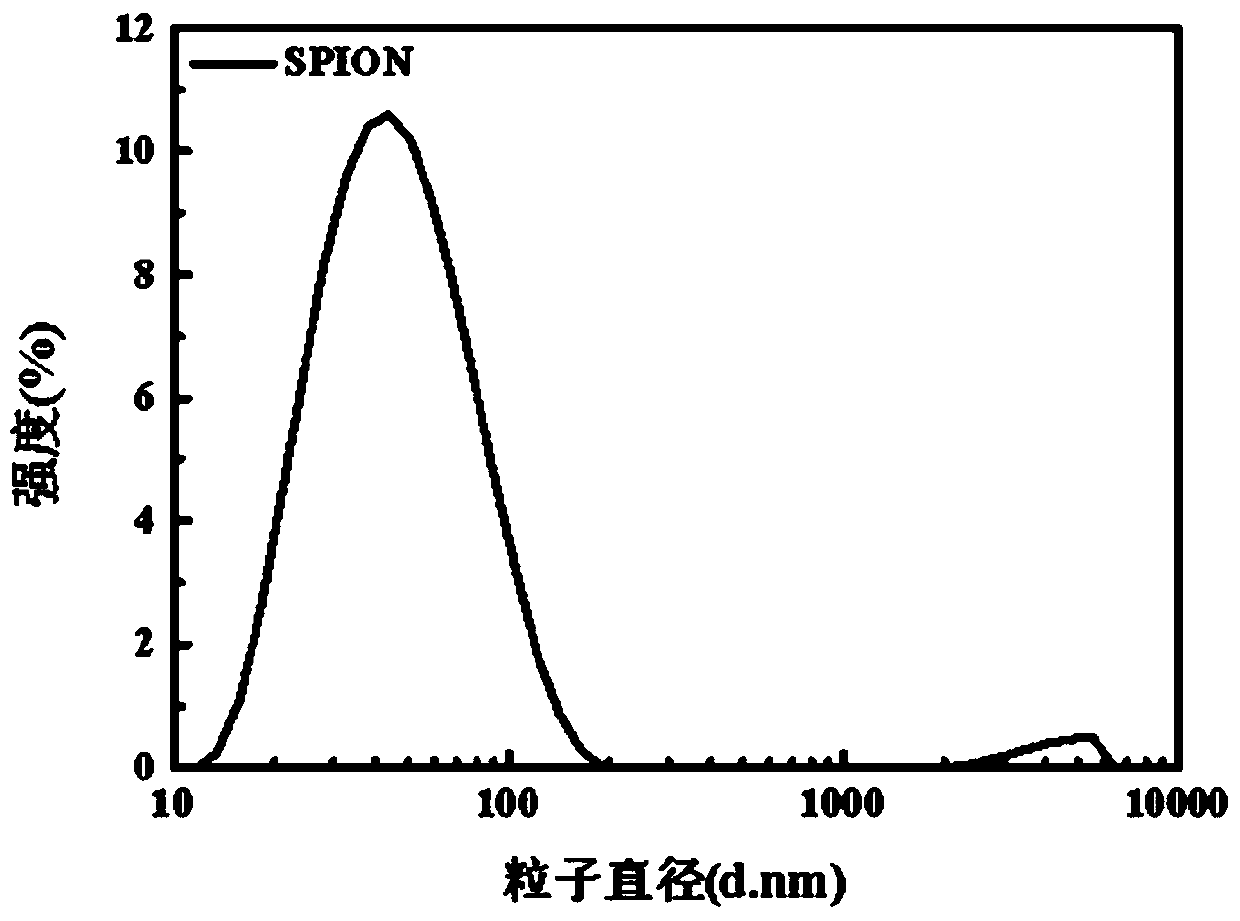
The invention discloses a magnetic composite nano material and a preparation method and application thereof. The magnetic composite nano material comprises modified magnetic nano particles and a modified macromolecular layer located on the outer surfaces of the modified magnetic nano particles, wherein the modified macromolecular layer comprises macromolecules and polymers connected with the macromolecules through pH response groups, and the response pH value of the pH response groups is smaller than 6.8. The magnetic composite nano material exists in a cluster form before reaching a tumor part, and due to the large particle size, the magnetic composite nano material is not likely to be rapidly removed by kidney metabolism; after the magnetic composite nano material reaches the tumor part,an assembly (the magnetic composite nano material) is gradually dispersed under the tumor subacid condition, the magnetic composite nano material exists in the tumor part in a small-particle-size magnetic nano particle form, and therefore the penetration depth of tumor tissue is increased; and due to falling of the surface modification polymers, surface positive charges are increased, and the nano particles are more easily taken by cells. Therefore, the pH response type magnetic composite nano material cluster enhances the MRI imaging contrast effect and improves the tissue penetration.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Cell nucleolus imaging red fluorescent carbon dot and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113881429AEasy to prepareSmall sizeLuminescence/biological staining preparationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsP-PhenylenediamineBiophysics
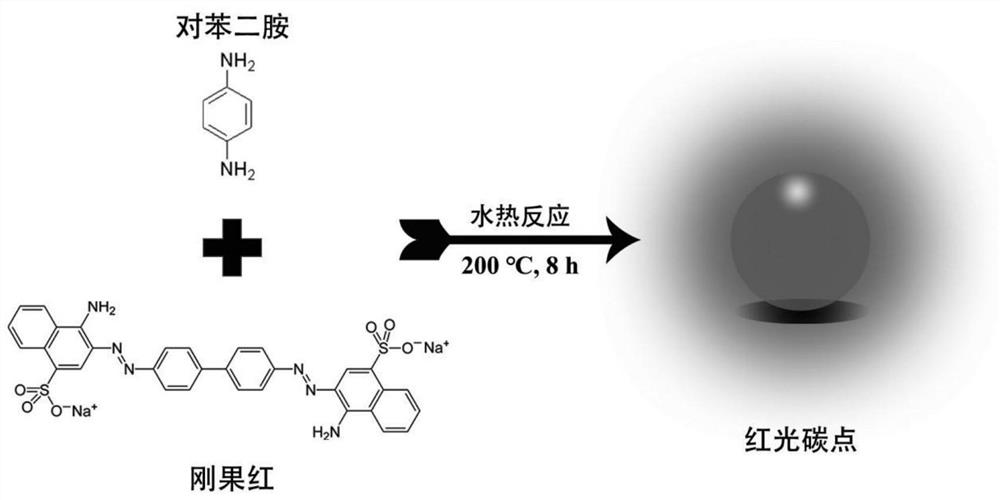
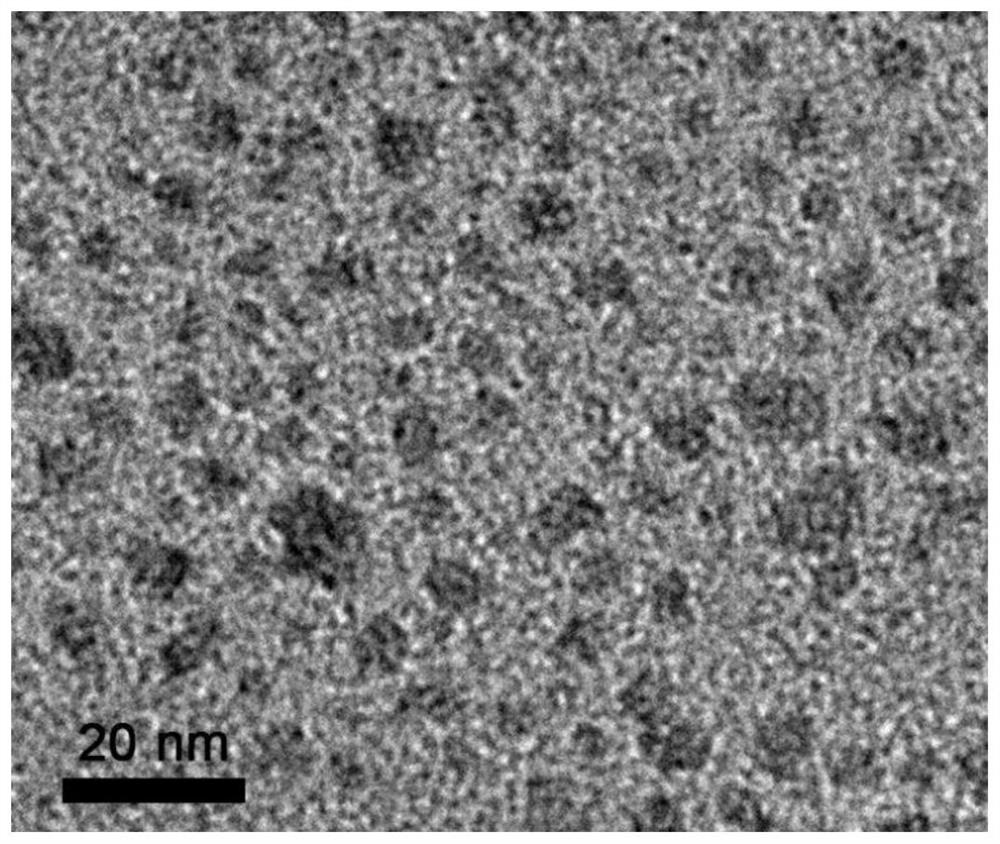
The invention discloses a cell nucleolus imaging red fluorescent carbon dot and a preparation method and application thereof. The red fluorescent carbon dot is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1 part of Congo red and 1-10 parts of p-phenylenediamine. The fluorescent carbon dot is prepared by taking p-phenylenediamine and Congo red as raw materials and adopting a one-step hydrothermal method, and the carbon dot prepared by the invention can realize rapid, no-clean, long-time and light-stable (anti-bleaching) imaging of cell nucleuses and nucleuses of mammalian cells, and can also be applied to living cell nucleolus fluorescence imaging of model animals (such as zebra fish and nematodes). In addition, the carbon dot also has the advantages of low preparation cost, good water dispersibility, low cytotoxicity, large Stokes shift and the like, and can replace the commercialized nucleolus fluorescent probe which is widely used at present.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Nitrogen-sulfur-doped efficient red light emission carbon dot, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112980437AHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsBiocompatibilityBiomedicine
The invention discloses a nitrogen-sulfur-doped efficient red light emission carbon dot, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) by taking phenylenediamine as a carbon source and a nitrogen source and thiocyanic acid and a derivative thereof as a sulfur source, dissolving the phenylenediamine and the sulfur source in a water solution according to a certain proportion; (2) transferring the mixed solution into a high-pressure reaction kettle, putting the high-pressure reaction kettle into a drying oven, preserving heat for 6-18 hours at 120-220 DEG C, and carrying out hydrothermal reaction treatment; and (3) cooling to room temperature, centrifuging the original solution of the carbon dots, dialyzing and purifying to obtain the carbon dots. According to the invention, the synthesis route is simple, the raw materials are wide in source and low in price, purification is easy, and the obtained red light carbon dots have the characteristics of good biocompatibility, good water solubility, high stability, low toxicity and the like, have excellent tissue penetrability and have unique advantages in biological cell, in-vivo imaging and other related biomedical applications.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Lung carcinoma cell specificity conjugation oligopeptide and application thereof
InactiveCN103788181ASmall molecular weightGood tissue penetrationPeptidesBiological testingLung cancerTreatment effect
The invention provides an oligopeptide capable of performing specificity conjugation with lung carcinoma cells. The oligopeptide provided by the invention is high in conjugation specificity with the lung carcinoma cells, and can be used for early-phase clinical diagnosis and evaluation and prognostic judgment of a treatment effect.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Near-infrared quantum dot probe for brain glioma tracing
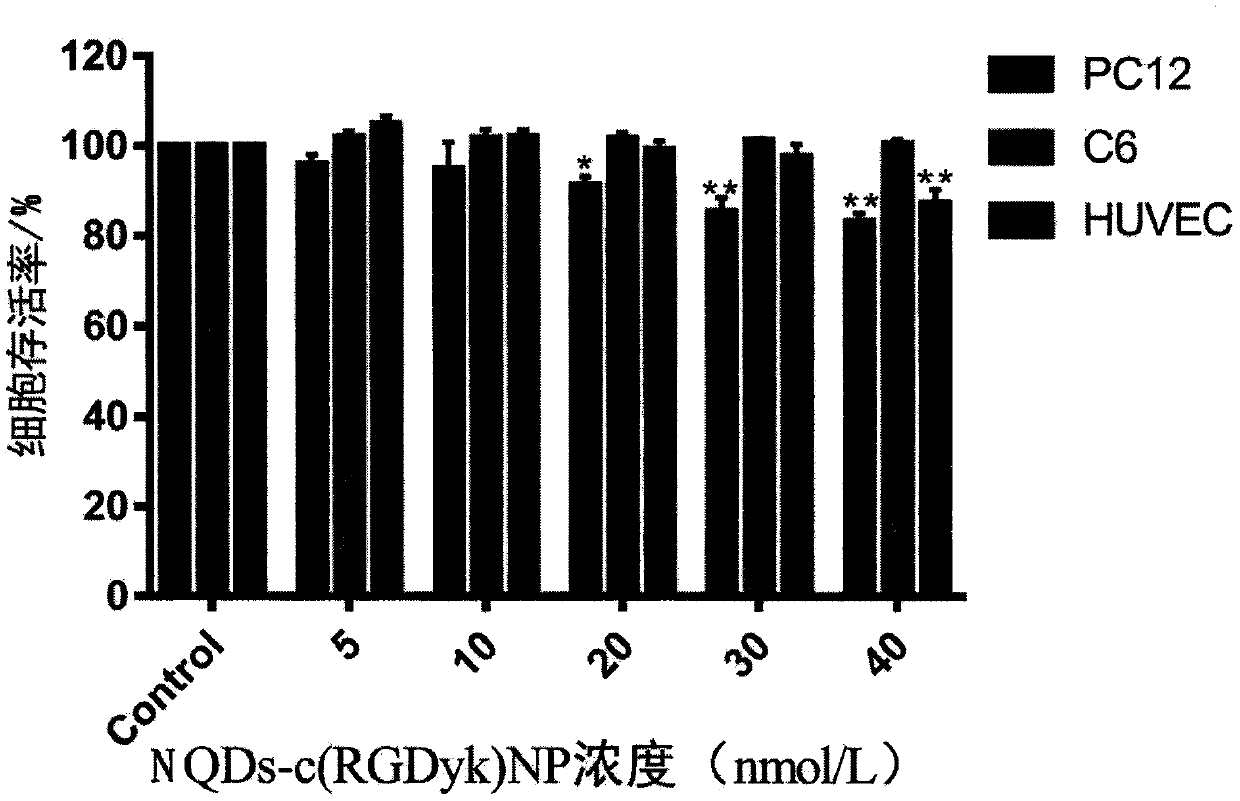
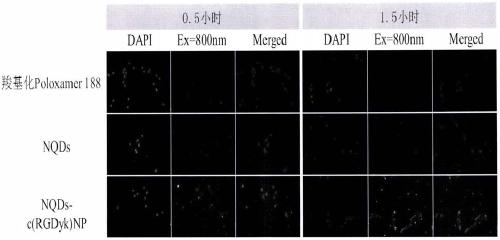
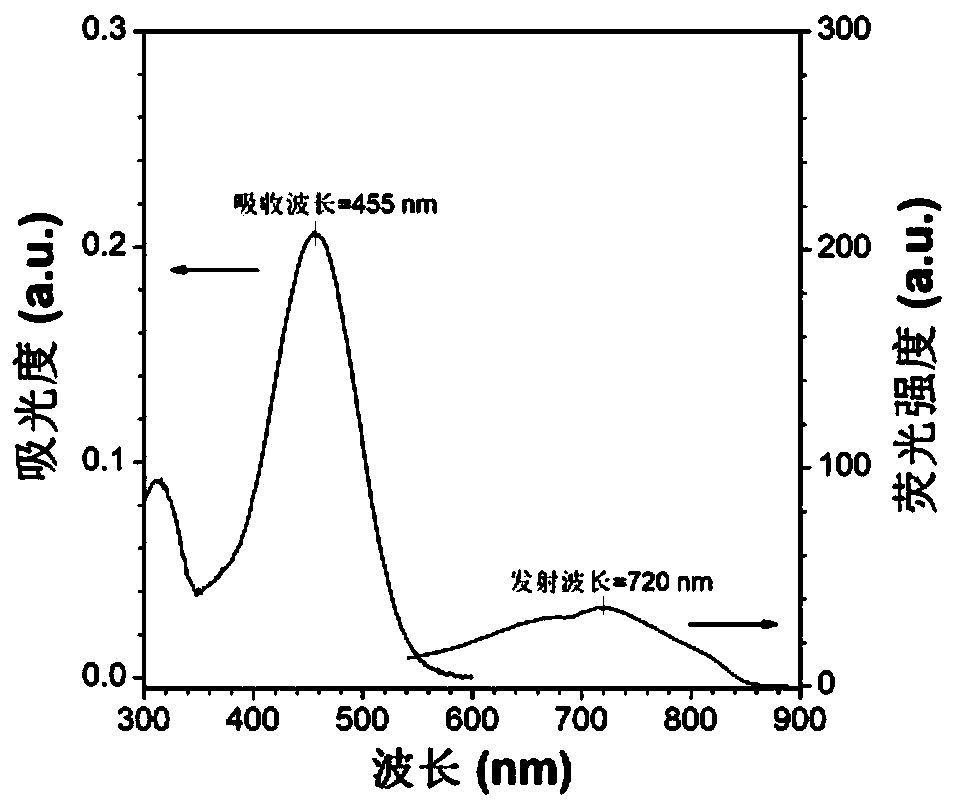
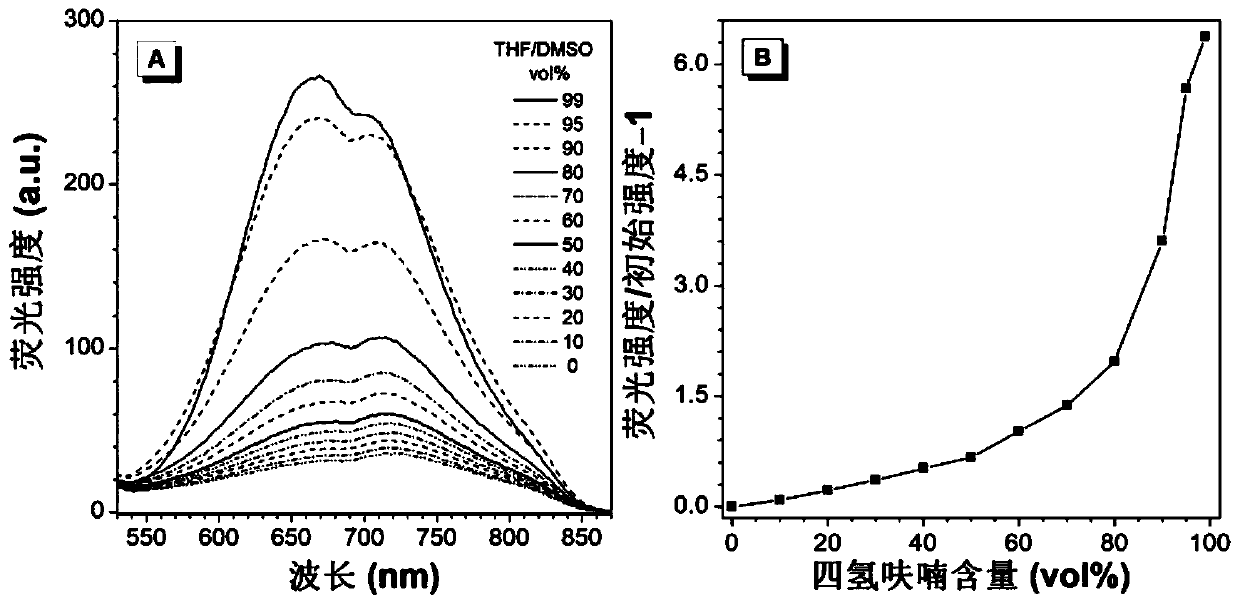
ActiveCN110157406AUniform particle sizeImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsTumor targetingGlutamine
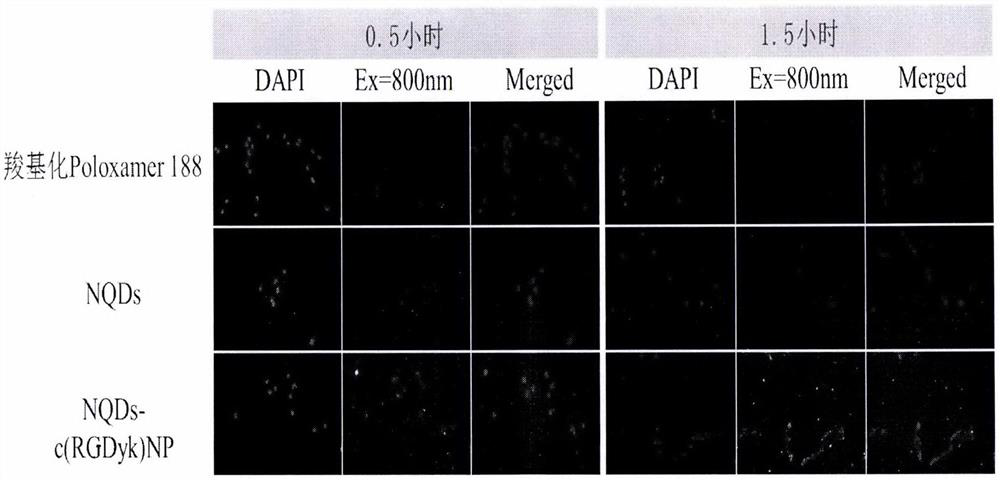
The invention provides a near-infrared quantum dot probe for the brain glioma tracing. The probe uses a carboxylated poloxamer, and a cyclic glycyl-arginyl-glycyl-aspartyl-asparaginyl-proline short peptide grafted poloxamer as materials, near-infrared quantum dots and a cysteine-alanine-glutamine-lysine tetrapeptide are encapsulated, nanomicelles are formed by the self-assembly in an aqueous solution, and a solution of the near-infrared quantum dot probe that specifically binds to integrin alpha v beta 3 overexpressed by glioma cells is formed. The near-infrared quantum dot probe has the characteristics of uniform particle size, high stability, good tumor targeting, and strong tissue penetration. The brain glioma tracing with high efficiency, targeting and specificity can be realized by combining the ultrasound-targeted micro-bubble blasting technology to reversibly open the blood-brain barrier.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Red/near-infrared AIE probe and preparation method thereof, and application of red/near-infrared AIE probe in detection of Abeta aggregate and fibrotic plaques of Abeta aggregate
ActiveCN111574438ALow Background Fluorescent NoiseReduce signal to noise ratioOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological imagingBoronic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological imaging, and relates to a red / near-infrared AIE probe, a preparation method thereof and an application of the red / near-infrared AIE probe indetection of Abeta aggregates and fibrotic plaques of the Abeta aggregates. The probe has a general formula, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out Suzuki reaction on bromine-substituted aryl acetonitrile and arylboronic acid, carrying out substitution or salification reaction on the reaction product and a straight-chain halogenated compound, and finally carrying out Knoevenagel condensation reaction on the reaction product and an aldehyde-substituted aromatic compound to obtain a target compound. Compared with the prior art, the aggregation-induced emission (AIE) probe disclosed by the invention overcomes the fluorescence quenching effect caused by aggregation, so that the AIE probe has higher luminous efficiency and signal-to-noise ratio. And the probe canrealize high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection of the A beta aggregate. More importantly, the probe can realize early imaging of A beta fibrotic plaques in vivo.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Near-infrared long-afterglow luminescent material excited by biological window and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111676015ARayleigh scattering effect is smallReduce phototoxicityPhotodynamic therapyIn-vivo testing preparationsChemical structurePhotodynamic therapy
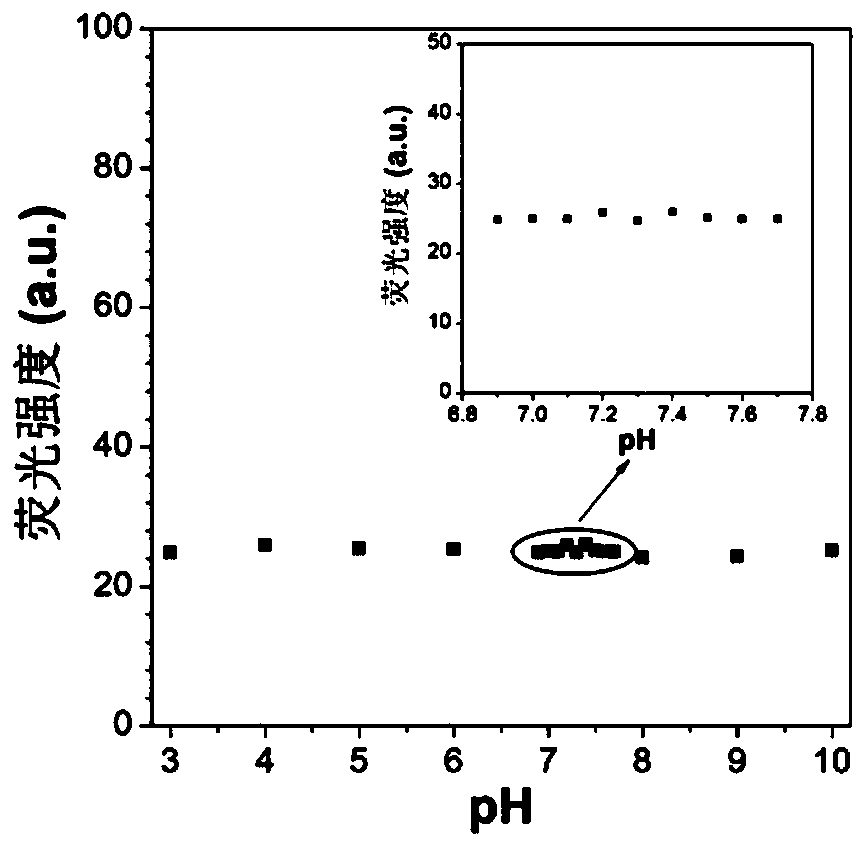
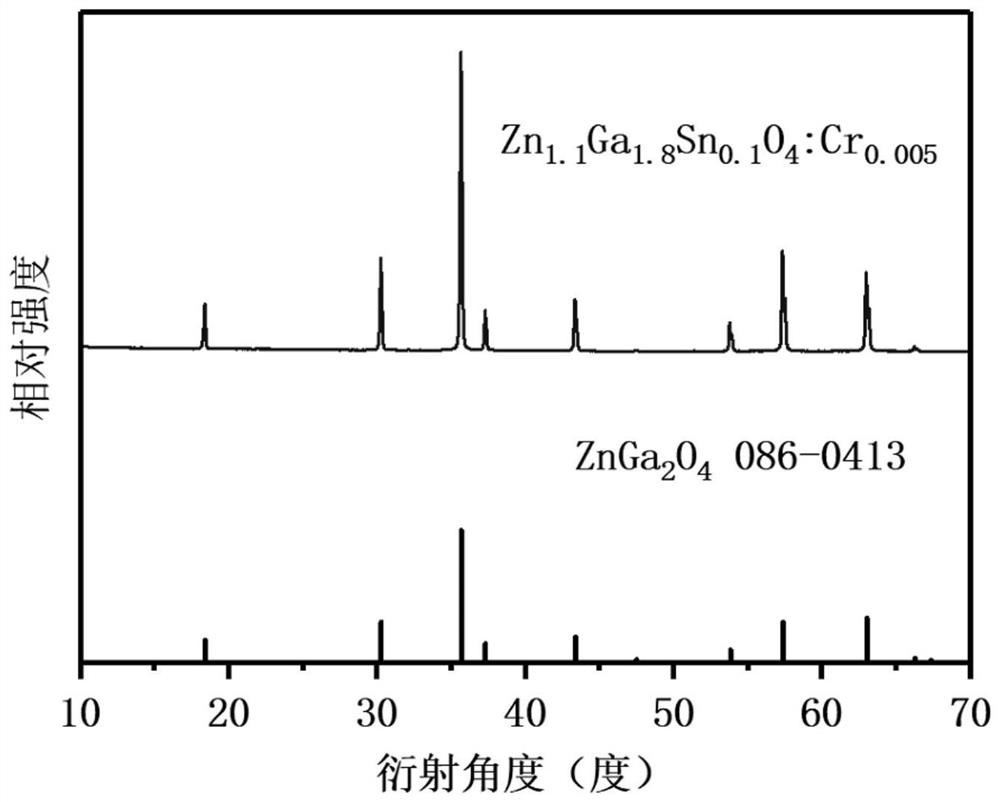
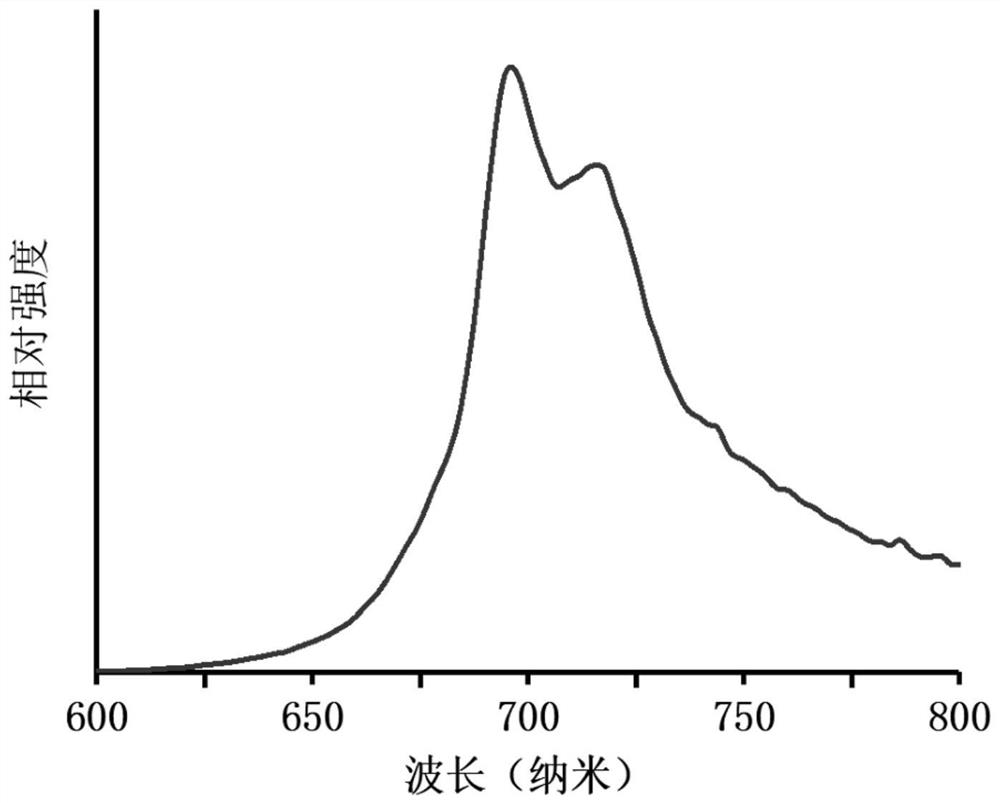
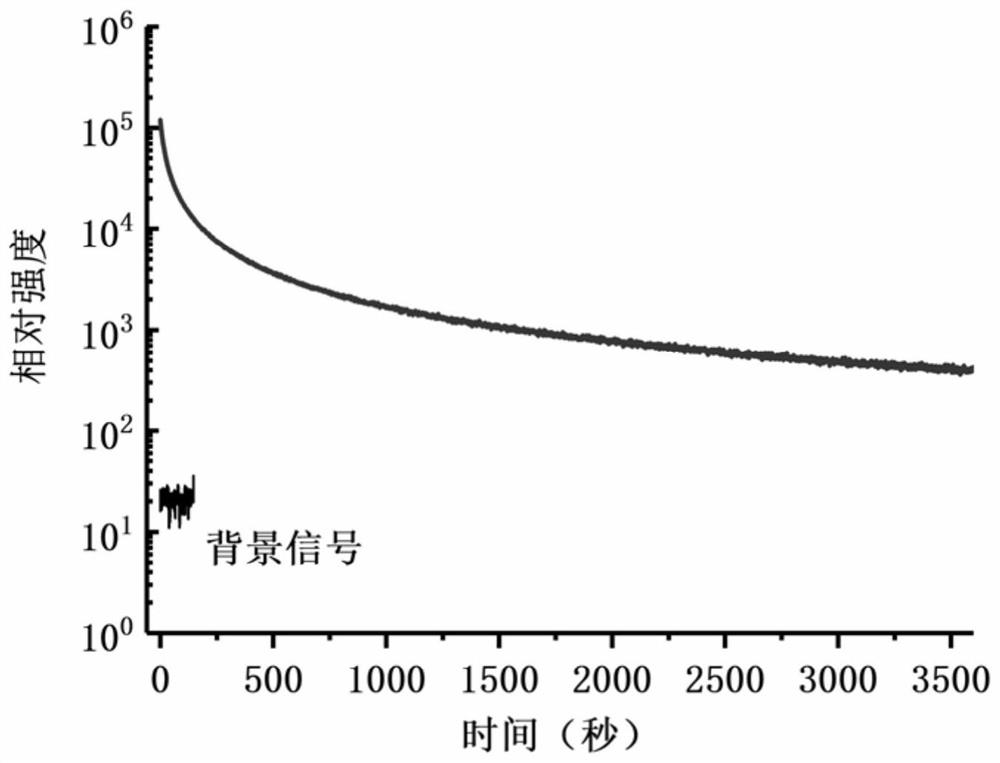
The invention provides a near-infrared long-afterglow luminescent material excited by a biological window and a preparation method of the near-infrared long-afterglow luminescent material. The chemical structural formula of the near-infrared long-afterglow luminescent material is Zn1+xGa2-2xSnxO4: Cry, Yz, wherein x is larger than 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.5, y is larger than 0 and smallerthan 0.01, and z is larger than or equal to 0 and smaller than 0.01. Exciting light of the near-infrared long-afterglow luminescent material is located in a biological imaging window, and the wavelength of the exciting light is larger than 650 nm. The luminescent peak value is about 696nm, the long afterglow luminescent time is far longer than 1 hour, the afterglow intensity is high, the afterglowtime is long, and the material can be applied to the fields of photodynamic therapy, biological imaging and the like. In addition, the invention further relates to a preparation method of the near-infrared long-afterglow luminescent material excited by the biological window. The raw materials are wide in source and low in price. In the operation process, only all the compounds need to be mixed, ground and calcined, protective atmosphere is not needed, operation is easy, and the method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:厦门大学附属心血管病医院
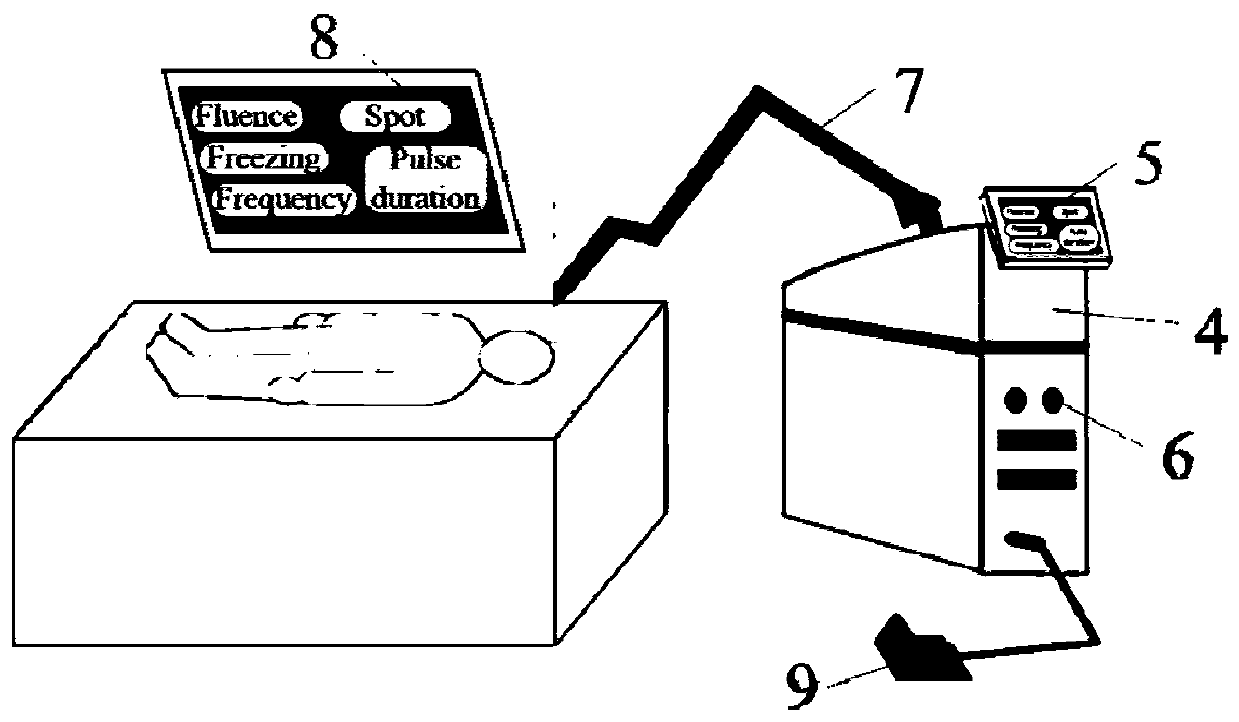
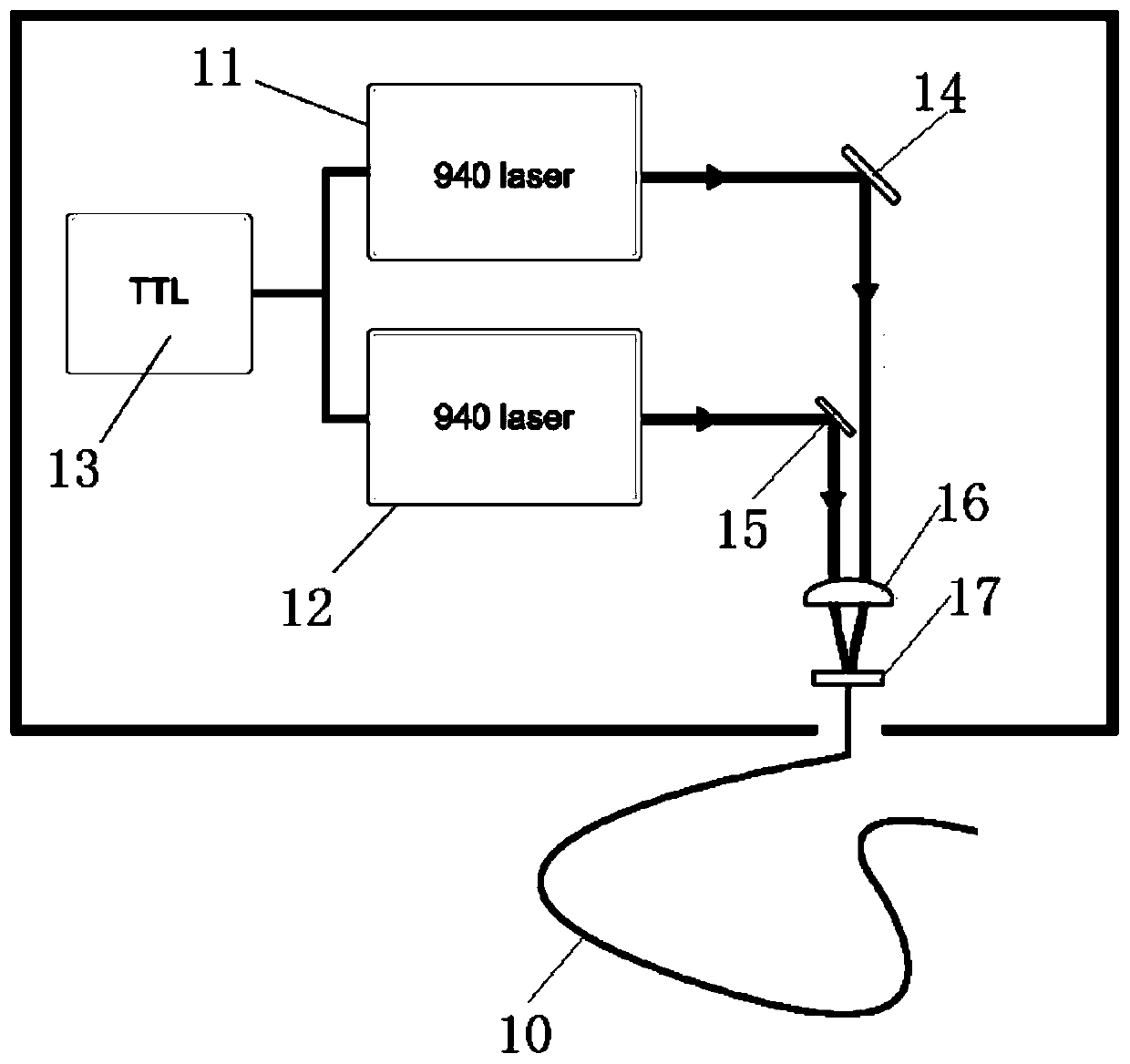
Treatment device based on laser with wavelength of 940 nm
InactiveCN111150939APromote absorptionReduce absorptionLight therapyAbsorption (skin)Therapeutic effect
The invention discloses a treatment device based on laser with wavelength of 940 nm. The treatment device is characterized by comprising a laser device, a cooling system and a probe handle, wherein the laser device is used for emitting the laser with the wavelength of 940 nm and is connected with the probe handle through a transmission optical fiber; the cooling system is used for providing a cooling working medium and is connected with the probe handle through a cooling working medium conveying pipeline; the laser with the wavelength of 940 nm emitted by the laser device has relatively good tissue penetrability; absorption of hemoglobin to the laser is increased, absorption of melanin and the like to the laser is reduced, treatment of vascular skin diseases such as fat and thick type port-wine stains with relatively large lesion blood vessels and face angiotelectasis with relatively small lesion blood vessels is realized, and the treatment device is relatively good in treatment effectand relatively good in universality; and meanwhile, a mode of coupling refrigerant surface spray cooling with cold air cooling is adopted, so that thermal injury to epidermis and dermis is effectively avoided.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Magnetocaloric-immune combined medicine and application thereof
ActiveCN113181359AGrowth inhibitionGood tissue penetrationMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismTumor therapyOncology
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicine, and discloses a magnetocaloric-immune combined medicine and an application thereof. The combined medicine comprises a magnetocaloric agent and an immunologic adjuvant, and the magnetocaloric agent is a ferromagnetic nanocrystal. The combined medicine is directly injected at a focus part, and an alternating magnetic field with specific field intensity is applied, so that tumor cells are killed, generated tumor cell fragments can be used as tumor antigens, and in combination with an immune amplification effect of an immunologic adjuvant, a tumor-like related vaccine effect can be generated, the in-situ tumors can be killed, and far-end tumor growth can be inhibited, and an efficient tumor treatment effect is provided; compared with photo-thermal therapy, the magnetic thermal therapy used in the invention has better tissue penetrability; and compared with traditional commercial Fe3O4 particles, the adopted magnetocaloric agent (ferromagnetic nanocrystals) has a better heat effect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of carbocyanine dye near infrared fluorescent compound
ActiveCN101518528BGood light stabilityGood tissue penetrationOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsCarboxyl radicalFluorescence
The invention discloses an application of a carbocyanine dye near infrared fluorescent compound in the preparation of a photosencitizer used for treating tumors or abnormal hyperplasia tissues, shown in formula I or II, wherein X is selected from iodine, chlorine, bromine, alkyl sulfide (OSO2-alkyl), BF4 or ClO4; R1 is selected from chlorine or bromine; R2 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxyl group (-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), aryl, aromatic alkyl, alkyl sulfonate, alkyl carbonate and alkyl amine; and n is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, l1 or 12.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Construction method and application of anti-PEDV (Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus) N protein VHH (variable region of heavy chain) bacteriophage display library
InactiveCN109678953ARich diversityHigh number of transformantsImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganism librariesCompetent cellHeavy chain
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an anti-PEDV (Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus) N protein VHH (variable region of heavy chain) bacteriophage display library. The construction method comprises the following steps: carrying out extraction and reverse transcription of immune two-humped camel peripheral blood lymphocyte and lymphocyte total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid); designing two pairs of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification primers to obtain a target fragment; connecting the obtained target fragment with a phagemid carrier pCANTAB-5E; converting a connection product into a TG1 competent cell, and obtaining the bacteriophage display library; successfully constructing the VHH bacteriophage display library of the anti-PEDV N protein; calculating the capacity and the diversity of the library; and carrying out quality evaluation on the constructed library. The library established with the construction method has the characteristics of large library capacity, rich diversity and the like, and lays a foundation for establishing a clinic diagnosis method of the PEDV and researching a virus infection mechanism.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
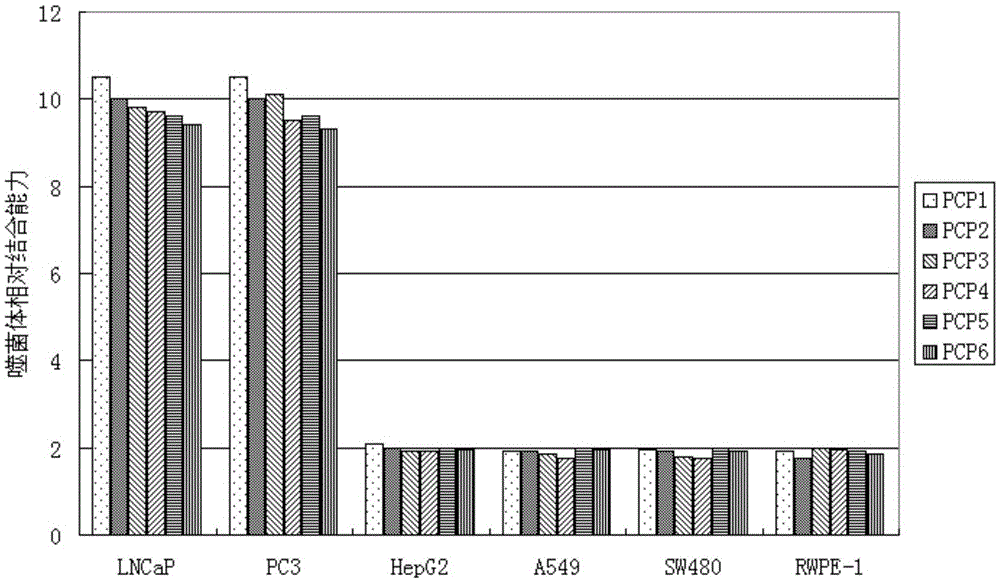
Short-chain polypeptides PCP14 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and application of short-chain polypeptides PCP14
InactiveCN105646665ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingProstate cancer cellPhage Display Peptide Library
The invention provides a series of polypeptides obtained through screening with a phage display peptide library technology and having a prostate cancer targeting characteristic. The binding polypeptides have high specificity and can be applied to general survey of high risk groups of the prostate cancer, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancer and evaluation of a treatment effect.
Owner:朱育盼
Short-chain polypeptides PCP4 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and application of short-chain polypeptides PCP4
InactiveCN105646663ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingProstate cancer cellPhage Display Peptide Library
The invention relates to short-chain polypeptides PCP4 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and an application of the short-chain polypeptides PCP4 and provides a series of polypeptides obtained through screening with a phage display peptide library technology and having a prostate cancer targeting characteristic. The binding polypeptides have high specificity and can be applied to general survey of high risk groups of the prostate cancer, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancer and evaluation of a treatment effect.
Owner:朱育盼
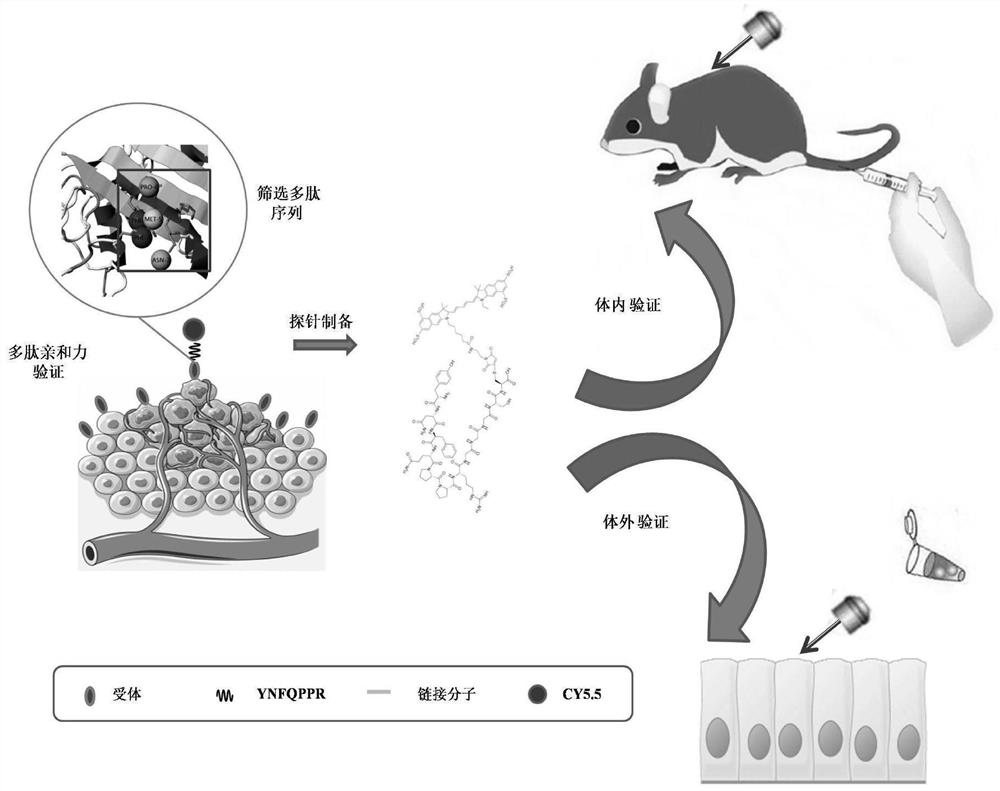
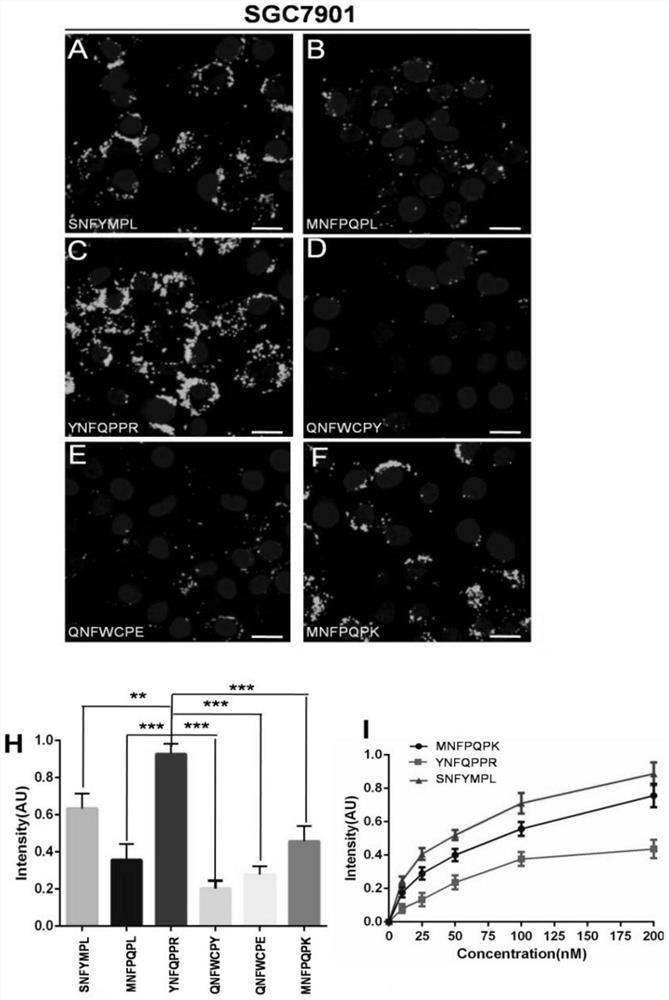
High-affinity early gastric cancer combined near-infrared probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113956332AGood tissue penetrationHigh affinityPeptide preparation methodsFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid imagingFluoProbes
The invention discloses a high-affinity early gastric cancer combined near-infrared probe and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the high-affinity early gastric cancer combined near-infrared probe comprises the steps: S1, firstly, constructing a polypeptide SNF and a three-dimensional structure thereof, obtaining a binding receptor EpCAM extracellular three-dimensional structure of the polypeptide SNF, and carrying out SNF modification and screening on a three-dimensional simulated SNF and EpCAM binding site to obtain a candidate optimized oligopeptide; S2, carrying out fluorescent staining and affinity comparison on the optimized polypeptide and EpCAM high-expression gastric cancer cell line SGC7901 cells; and S3, preparing a probe: linking the optimal oligopeptide screened out in the step S2 with CY5.5 through GGGSK to synthesize the near-infrared probe. A fluorescent probe capable of specifically targeting the early gastric cancer can be formed.The near-infrared probe has good characteristics of good stability, low immunogenicity, low production cost, capable of implementing rapid imaging after administration and the like.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A specific short peptide targeting glioma cells, its coding gene and its application
ActiveCN113480603BThe recognition effect is accurateSmall molecular weightMicroorganism based processesPeptidesPharmaceutical drugTargeting ligands
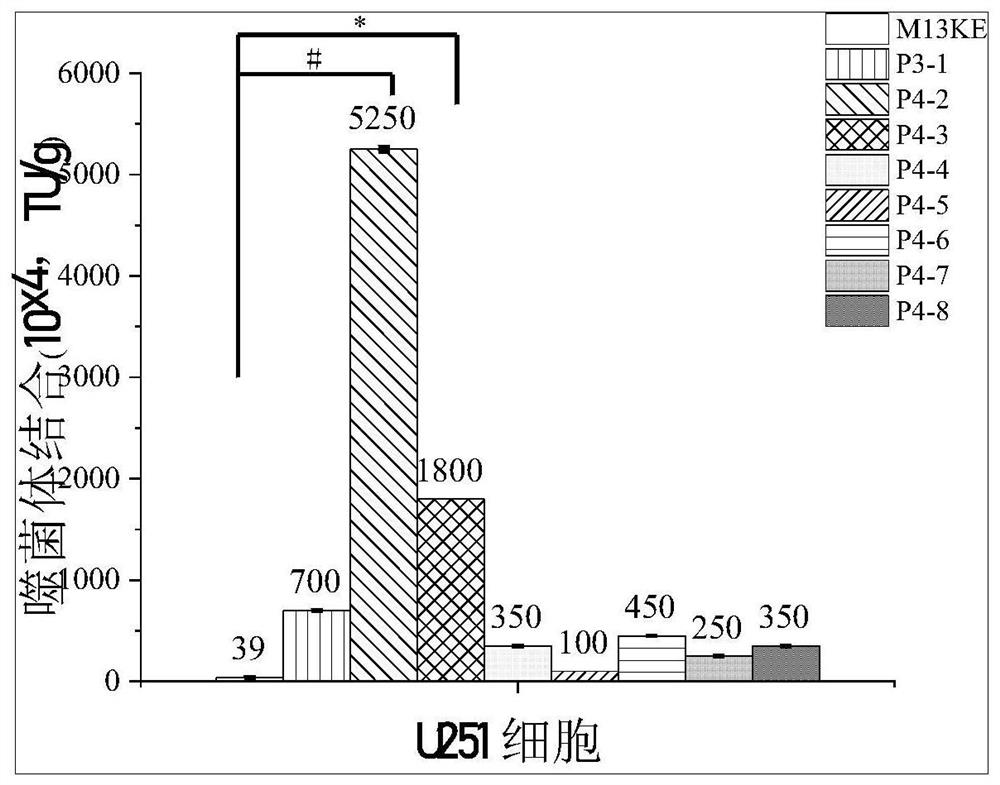
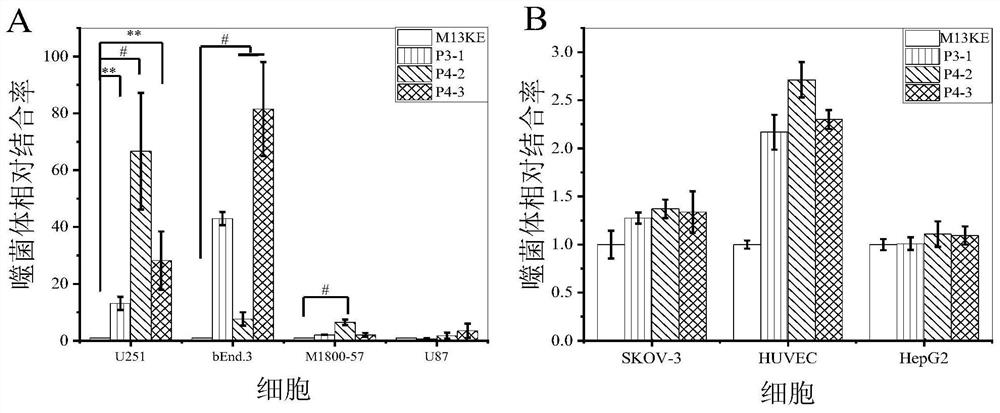
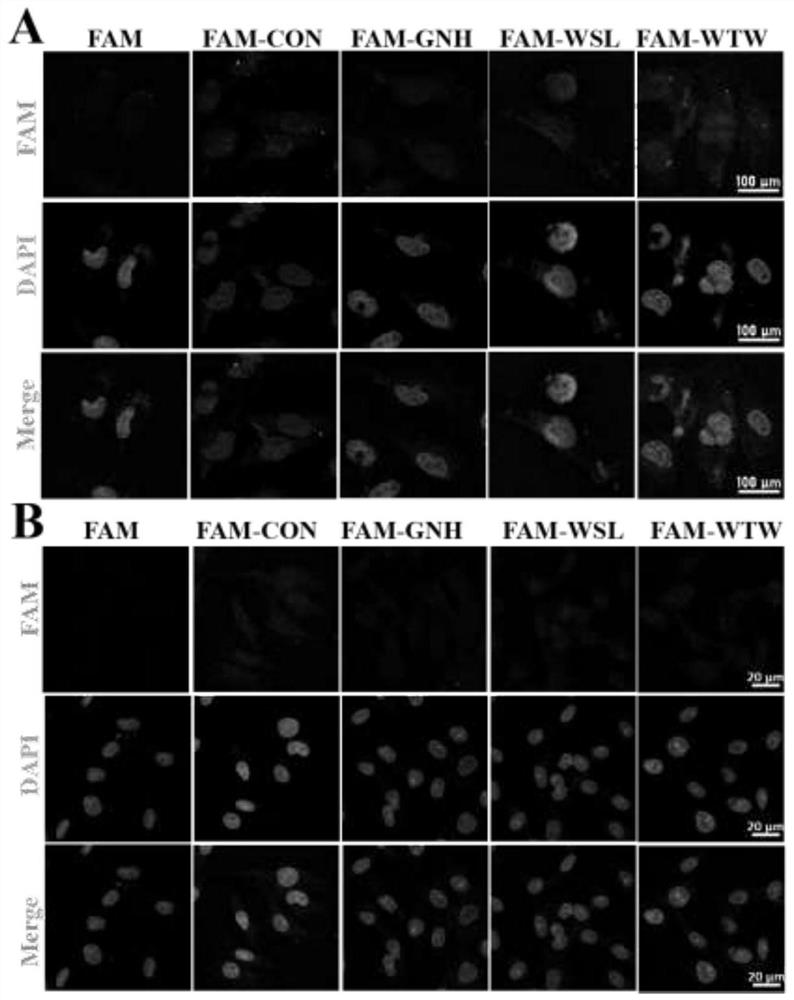
The invention provides a specific short peptide targeting brain glioma cells, which belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The amino acid sequence of the short peptide is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The short peptide can effectively recognize and specifically bind to the glioma cell line U251, and has the feasibility of being used as a targeting ligand for delivering drugs to the glioma site. The present invention also provides a coding gene of a specific short peptide targeting glioma cells and its application in the preparation of medicaments for preventing or treating glioma.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
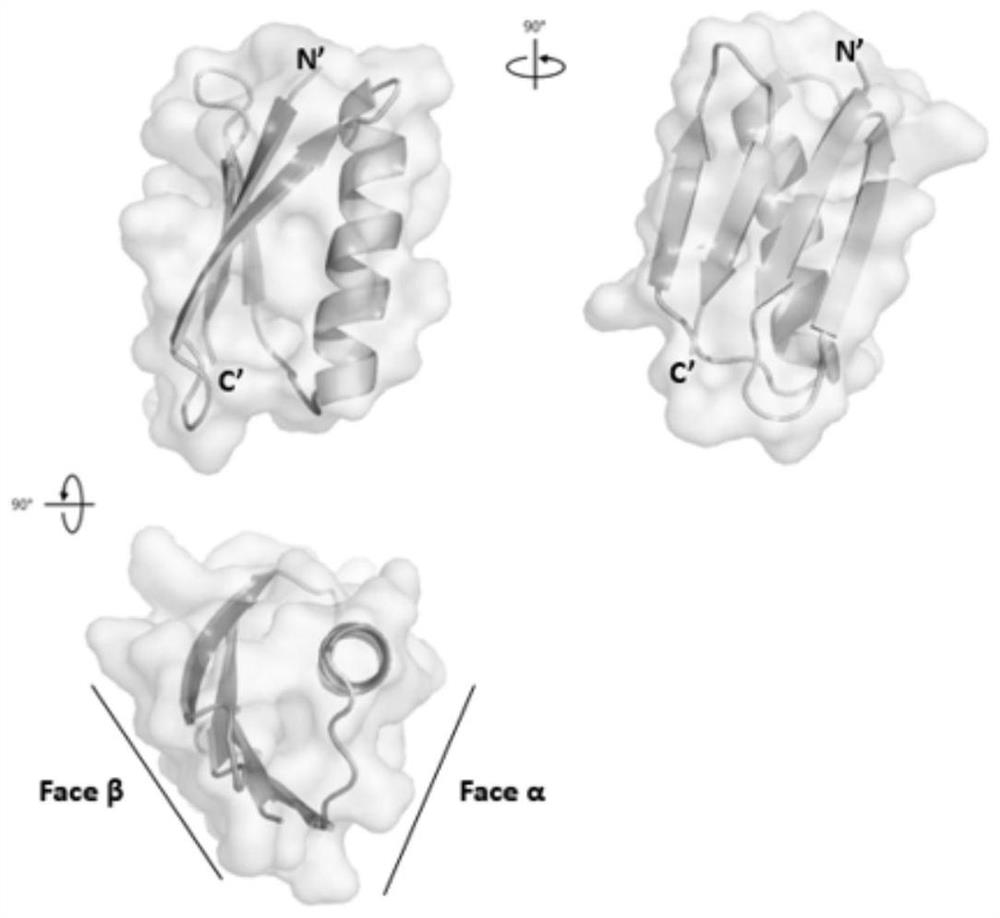
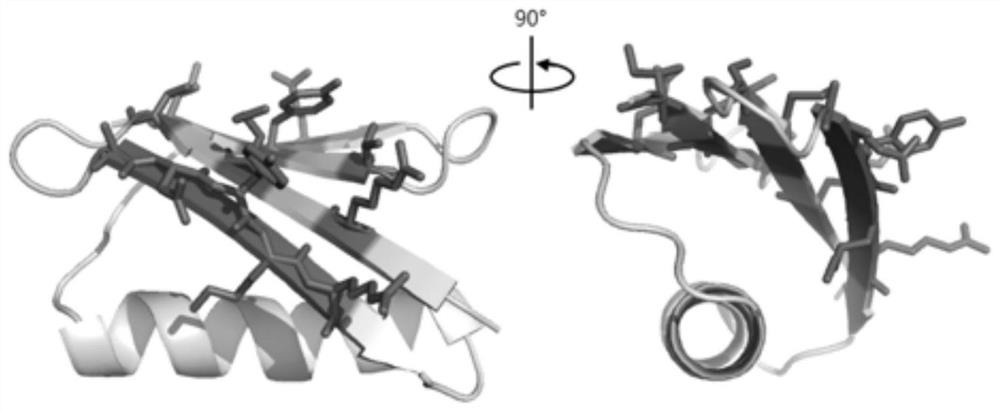
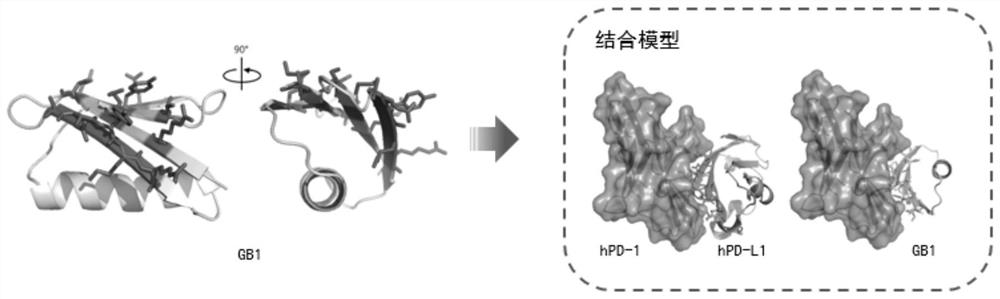
A Class of Small Proteins and Their Applications
ActiveCN110305200BImprove structural stabilityHigh structural similarityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAlpha helixProtein G
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Lung cancer cell-specific adhesion short peptide and its application
InactiveCN103788181BSmall molecular weightGood tissue penetrationPeptidesBiological testingCancer cellTherapeutic effect
The invention provides an oligopeptide capable of performing specificity conjugation with lung carcinoma cells. The oligopeptide provided by the invention is high in conjugation specificity with the lung carcinoma cells, and can be used for early-phase clinical diagnosis and evaluation and prognostic judgment of a treatment effect.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Nanobody targeting rage and its application
ActiveCN114031687BSmall molecular weightGood tissue penetrationNervous disorderBacteriaComplementarity determining regionReceptor
The present invention provides a nanobody targeting RAGE and applications thereof, wherein the complementarity determining region of the amino acid sequence of the nanobody targeting RAGE is CDR1 as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, as shown in SEQ ID NO:4 CDR2 as shown, CDR3 as shown in SEQ ID NO:6; or CDR1 as shown in SEQ ID NO:9, CDR2 as shown in SEQ ID NO:11, CDR3 as shown in SEQ ID NO:13; or CDR1 as shown in SEQ ID NO:16, CDR2 as shown in SEQ ID NO:18, CDR3 as shown in SEQ ID NO:20. The nanobody of the technical solution of the present invention has a strong combination with RAGE, can block the interaction between RAGE and various receptors, and has a therapeutic effect on AD and cancer.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
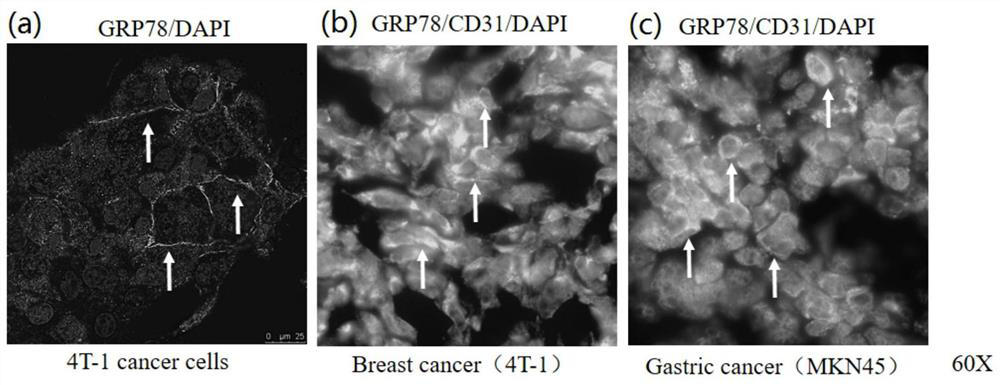
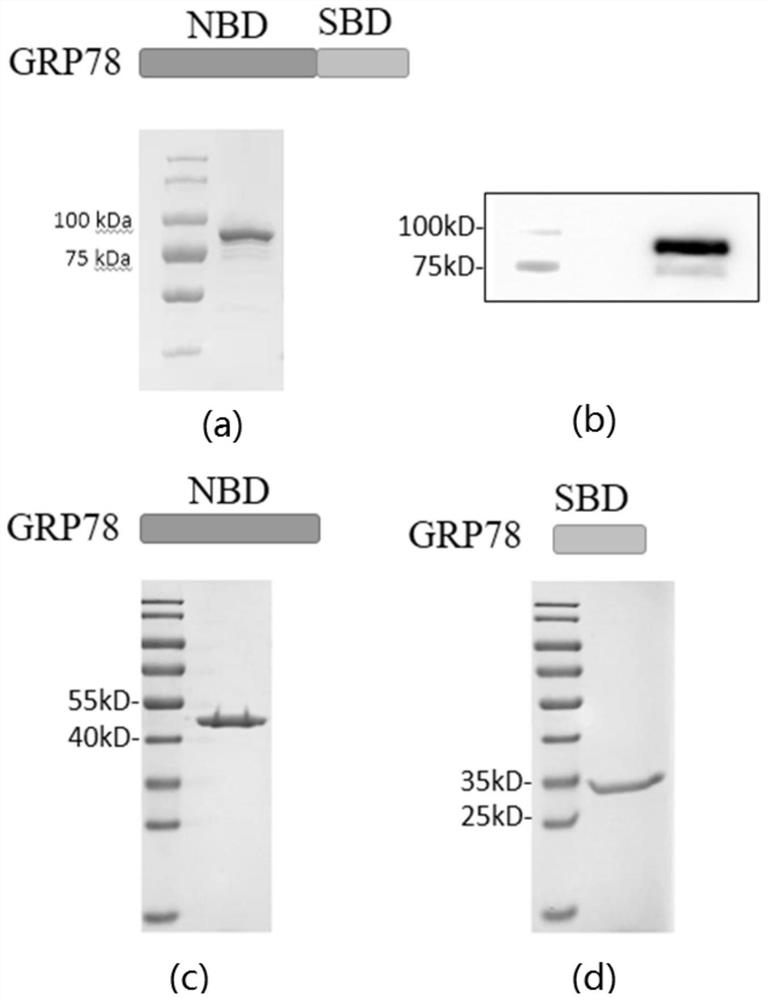
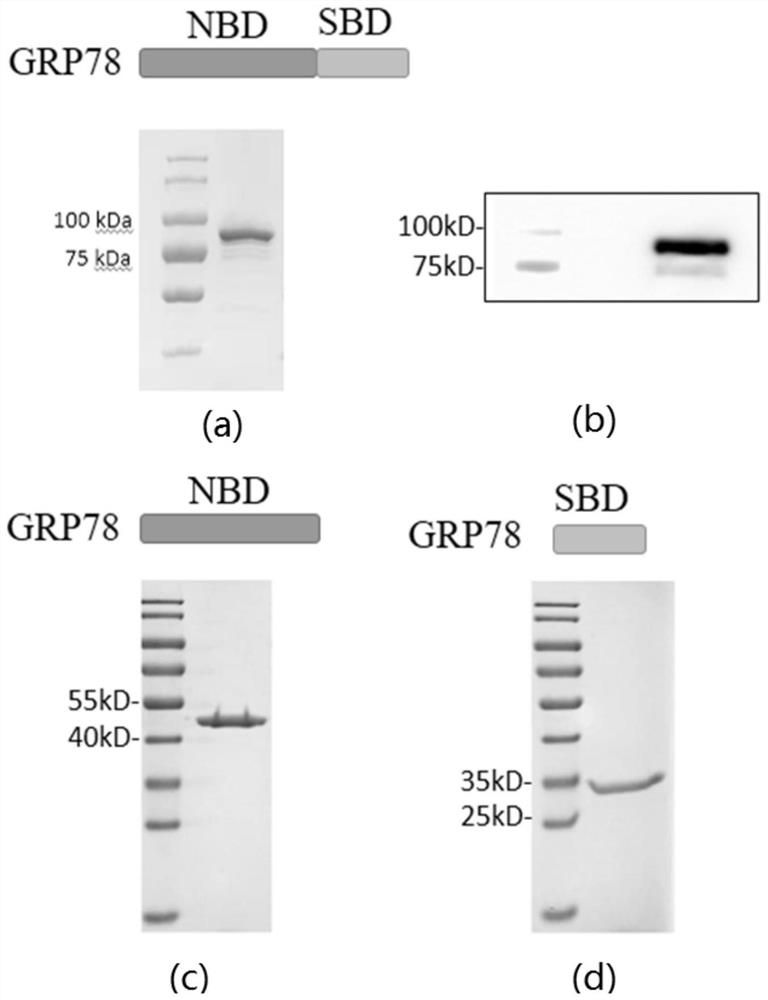
Glucoregulatory protein 78 targeting nano antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN114163526AGood binding activityGood tissue penetrationBacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansGlucose-regulated proteinAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention provides a nano antibody targeting glucose regulatory protein 78 and application thereof. Complementary determining regions of an amino acid sequence of the nano antibody targeting glucose regulatory protein 78 are CDR1 as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, CDR2 as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 and CDR3 as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6; the CDR1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 9, the CDR2 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 11, and the CDR3 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 13. The affinity of the nano antibody targeting the glucose regulatory protein 78 and the glucose regulatory protein 78 is at a nanomole level, the affinity is high, and the nano antibody has specific recognition capacity on the GRP78 protein on the surface of a cell membrane.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Short peptides PCP7 specifically binding to prostatic cancer cells and application of short peptides PCP7
InactiveCN105541972ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingPhage Display Peptide LibraryMedicine
The invention provides a series of polypeptides which have targeted prostatic cancer characteristics and are obtained through screening by adopting a phage display peptide library technology. The binding polypeptides have high specificity, and can be applied to general investigation of high risk groups with prostatic cancer, early clinical diagnosis of prostatic cancer and evaluation of a therapeutic effect.
Owner:朱育盼
Application of near infrared fluorescent chemical in lymphaden imaging and angiogram
ActiveCN101574529BIncreased sensitivityReduce dosageIn-vivo testing preparationsSide effectFluorescence
The invention relates to an application of near infrared fluorescent chemical in lymphaden imaging and angiogram. The application of near infrared fluorescent chemical in lymphaden imaging and angiogram has the beneficial effects of simple operation, high marking efficiency, easy resolving and non toxic side effects, thus providing powerful technical support for clinician to effectively, accurately and safely resolving the lymphaden.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Prevention of the risks associated with drug-induced qt interval prolongation by using a specific inhibitor of the production of ros of miochondrial origin
ActiveUS20210052549A1Reduce riskReduce the production of ROSPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugProlonged QT
A method of treating a subject for reducing the risk of QT space prolongation associated with the intake of a drug known to prolong QT space includes administering to the subject at least one specific inhibitor of mitochondrial ROS production selected from among anethole trithione (ATT), 4-OH-anethole trithione (ATX), and an ATX ester, and administering to the subject the drug known to prolong QT space.
Owner:CHILDS MARC +5
A near-infrared quantum dot probe for tracking glioma
ActiveCN110157406BGood tissue penetrationAvoid interferenceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsTumor targetingGlutamine
The invention provides a near-infrared quantum dot probe for glioma tracing. The probe is based on carboxylated poloxamer, cyclic glycyl-arginyl-glycyl-aspartyl- Asparagine-proline short peptide grafted poloxamer as material, wrapped near infrared quantum dots, cysteine-alanine-glutamine-lysine tetrapeptide, self-assembled in aqueous solution Nano micelles form a solution of near-infrared quantum dot probes that specifically bind to integrin αvβ3 overexpressed in brain glioma cells. The near-infrared quantum dot probe has the characteristics of uniform particle size, high stability, good tumor targeting, and strong tissue penetration. , Specific glioma tracer.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Polyamino acid for targeted delivery of mRNA vaccine and preparation method and application of polyamino acid
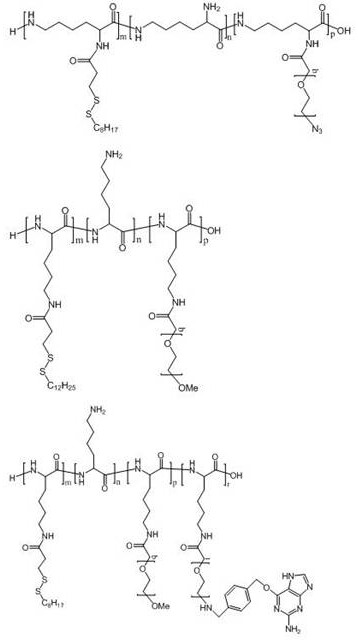
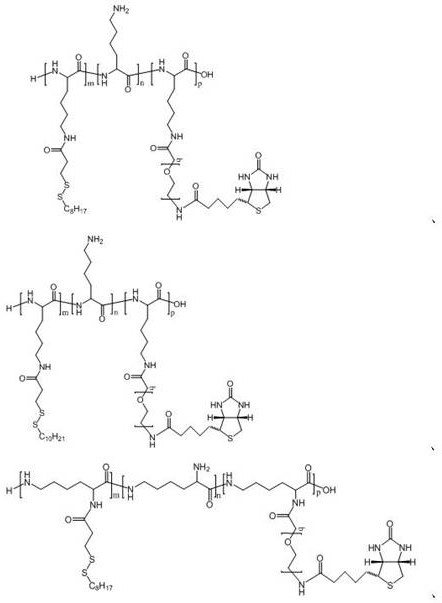
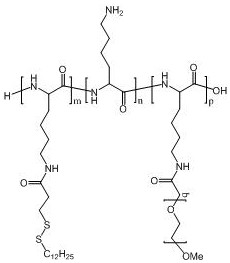
PendingCN113788951AEfficient deliveryImprove the environmentOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsNanocarriersLysosome
The invention provides polyamino acid for targeted delivery of a mRNA vaccine and a preparation method and application of the polyamino acid. The polyamino acid is side-chain-modified polyamino acid; a hydrophilic component and a hydrophobic component are introduced into the side chain of the polyamino acid, so polyamino acid micelles can be formed, and the micelles are used for efficiently delivering nucleic acid molecules. According to the side-chain-modified polyamino acid disclosed by the invention, a disulfide bond split in a reducing environment is introduced on the side chain, so the response of micelles to the reducing environment and a low pH value in cytoplasm can be promoted, and the mRNA vaccine is helped to actively escape from a lysosome trap and enter the cytoplasm. The active cleavage of a nanocarrier can more efficiently release mRNA compared to a passive osmotic pressure dominated escape process.
Owner:天津力博生物科技有限公司
A kind of magnetic composite nanomaterial and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111388668BHigh saturation magnetizationProlong circulation time in the bodyEnergy modified materialsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsMagnetite NanoparticlesPolymer
The application discloses a magnetic composite nanomaterial and its preparation method and application, including modified magnetic nanoparticles and a modified macromolecular layer located on the outer surface of the modified magnetic nanoparticle, and the modified macromolecular layer includes macromolecular Molecules and polymers linked to the macromolecules via pH responsive groups, the responsive pH value of the pH responsive groups being <6.8. The magnetic composite nanomaterial exists in the form of clusters before reaching the tumor site. Due to its large particle size, it is not easy to be cleared by rapid renal metabolism; after reaching the tumor site, the assembly (magnetic composite nanomaterial) gradually disperses under the slightly acidic condition of the tumor. The tumor site exists in the form of small-sized magnetic nanoparticles, thereby increasing its tumor tissue penetration depth, while the shedding of surface-modified polymers increases the surface positive charge, and the nanoparticles are more easily taken up by cells. Therefore, the pH-responsive magnetic composite nanomaterial cluster provided by the present application not only enhances the contrast effect of MRI imaging, but also improves its tissue penetration.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
A nanobody targeting glucose regulatory protein 78 and its application
ActiveCN114163526BSmall molecular weightGood tissue penetrationBacteriaImmunoglobulins against animals/humansComplementarity determining regionCell membrane
The present invention provides a nanobody targeting glucose-regulated protein 78 and its application. The complementarity determining region of the amino acid sequence of the nanobody targeting glucose-regulated protein 78 is CDR1 as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, such as CDR2 shown in SEQ ID NO:4, CDR3 shown in SEQ ID NO:6; or CDR1 shown in SEQ ID NO:9, CDR2 shown in SEQ ID NO:11, CDR2 shown in SEQ ID NO:13 CDR3 indicated. The nanobody targeting glucose regulatory protein 78 of the present invention has an affinity with glucose regulatory protein 78 at the nanomolar level, has relatively high affinity, and has specific recognition ability for the GRP78 protein on the cell membrane surface.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
CD40 targeted binding protein, coding nucleic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN114075290AIncrease productionGood tissue penetrationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmune activationCD40
The invention discloses a CD40 targeted binding protein, which is characterized in that the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID No.8, Xaa at the 30th site, the 32th site, the 33th site, the 35th site, the 43rd site, the 44th site, the 63rd site, the 65th site, the 66th site, the 68th site, the 76th site, the 77th site, the 96th site, the 98th site, the 99th site, the 101th site, the 109th site and the 110th site are respectively any amino acid. The multivalent CD40 targeted binding protein is formed by carrying out multivalent series connection on the CD40 targeted binding protein through a linker. According to the invention, the molecular weight of the antibody is only about 18kDa and is about one tenth of that of the antibody, and the antibody has good tissue penetrability, and is simple in production process and high in yield; and the CD40 specific targeted binding protein also has a good immune activation effect after being connected in series in a multivalent manner by using a proper linker.
Owner:NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com