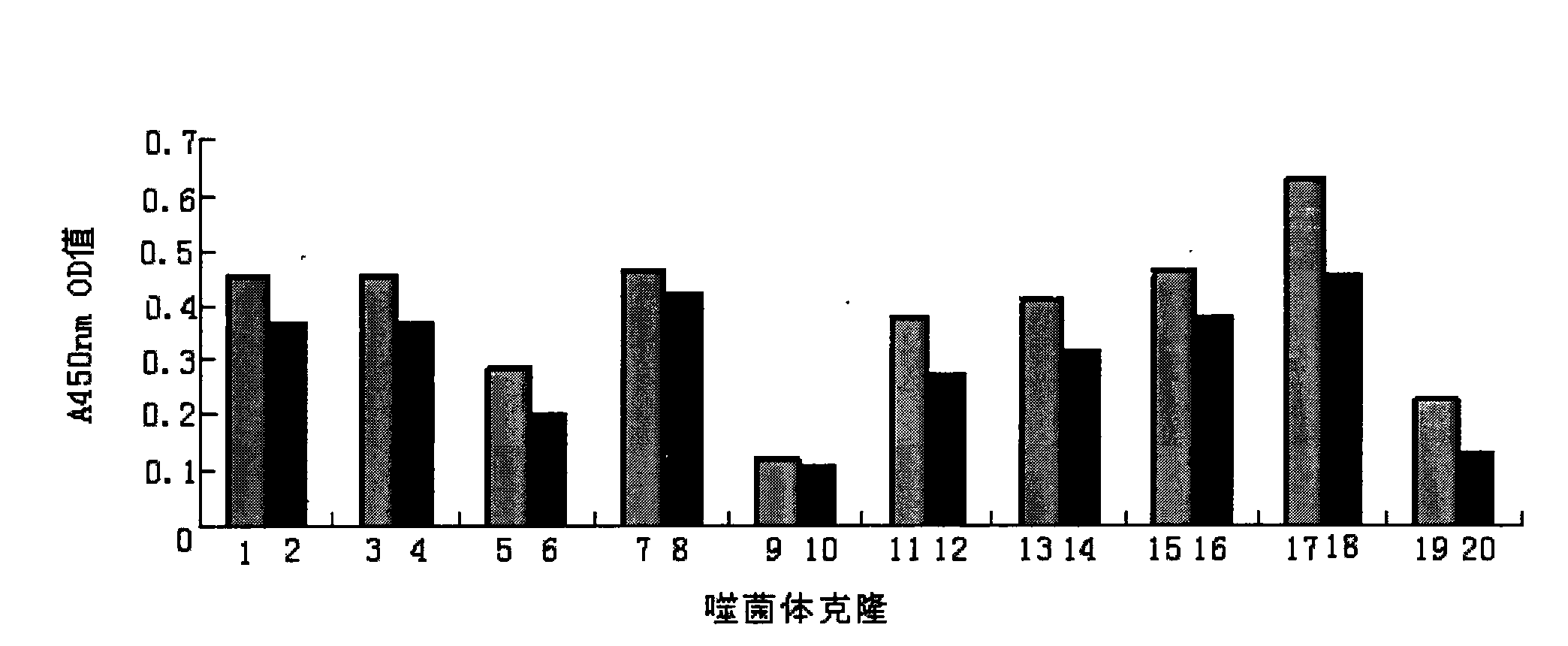
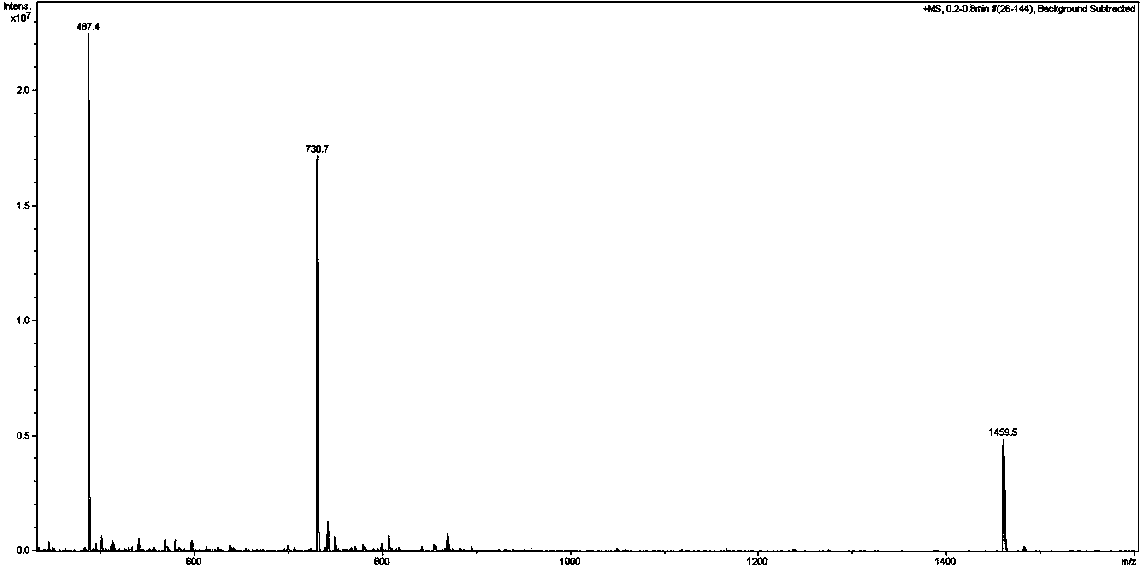
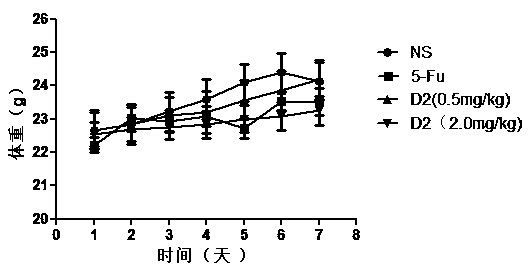
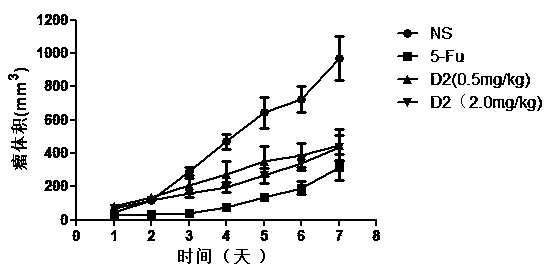
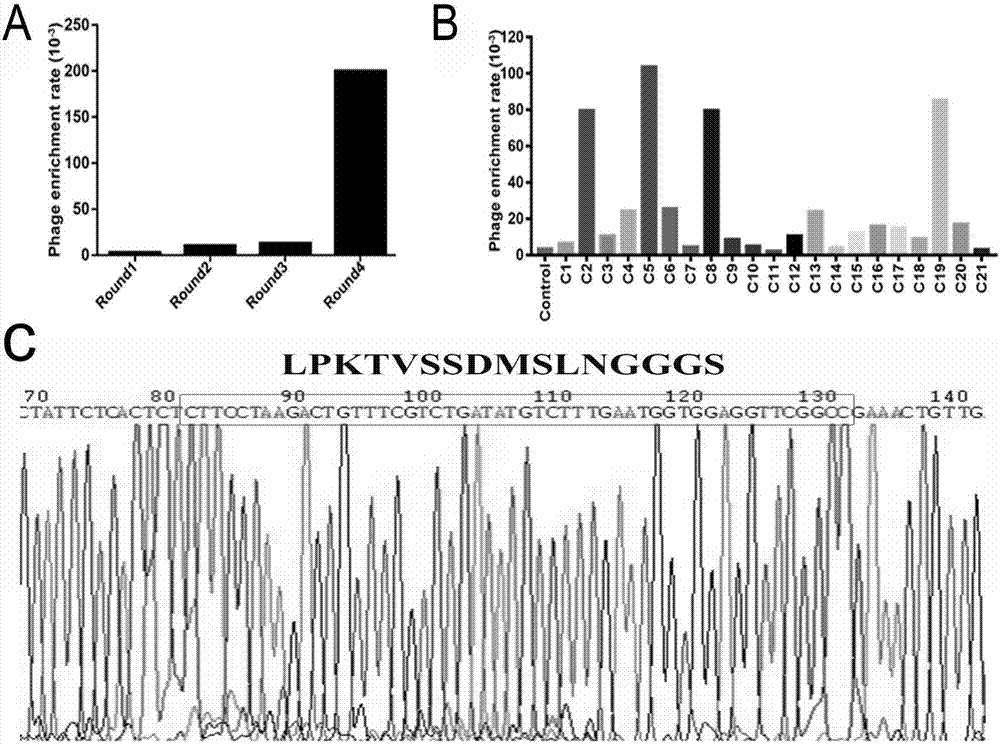
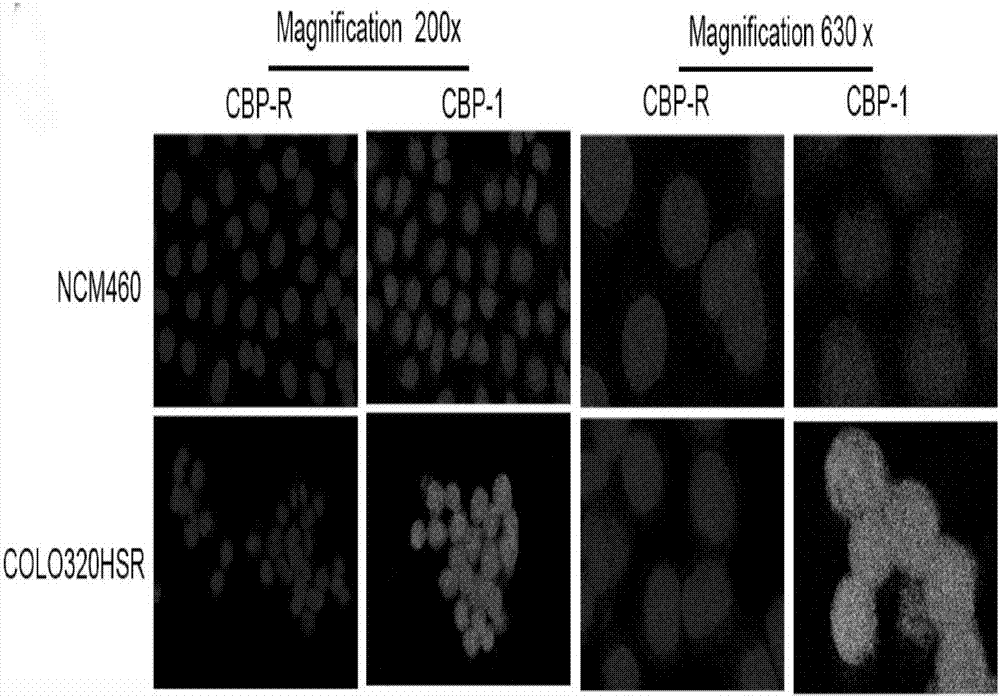
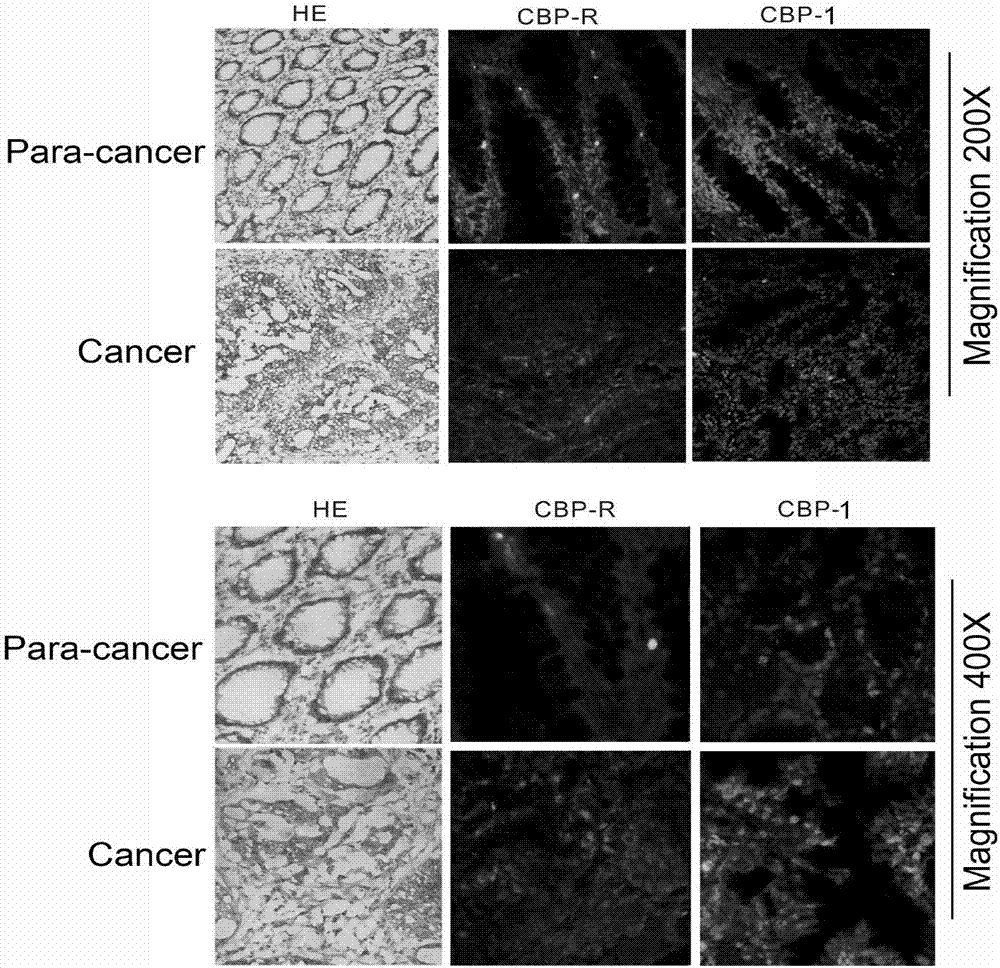
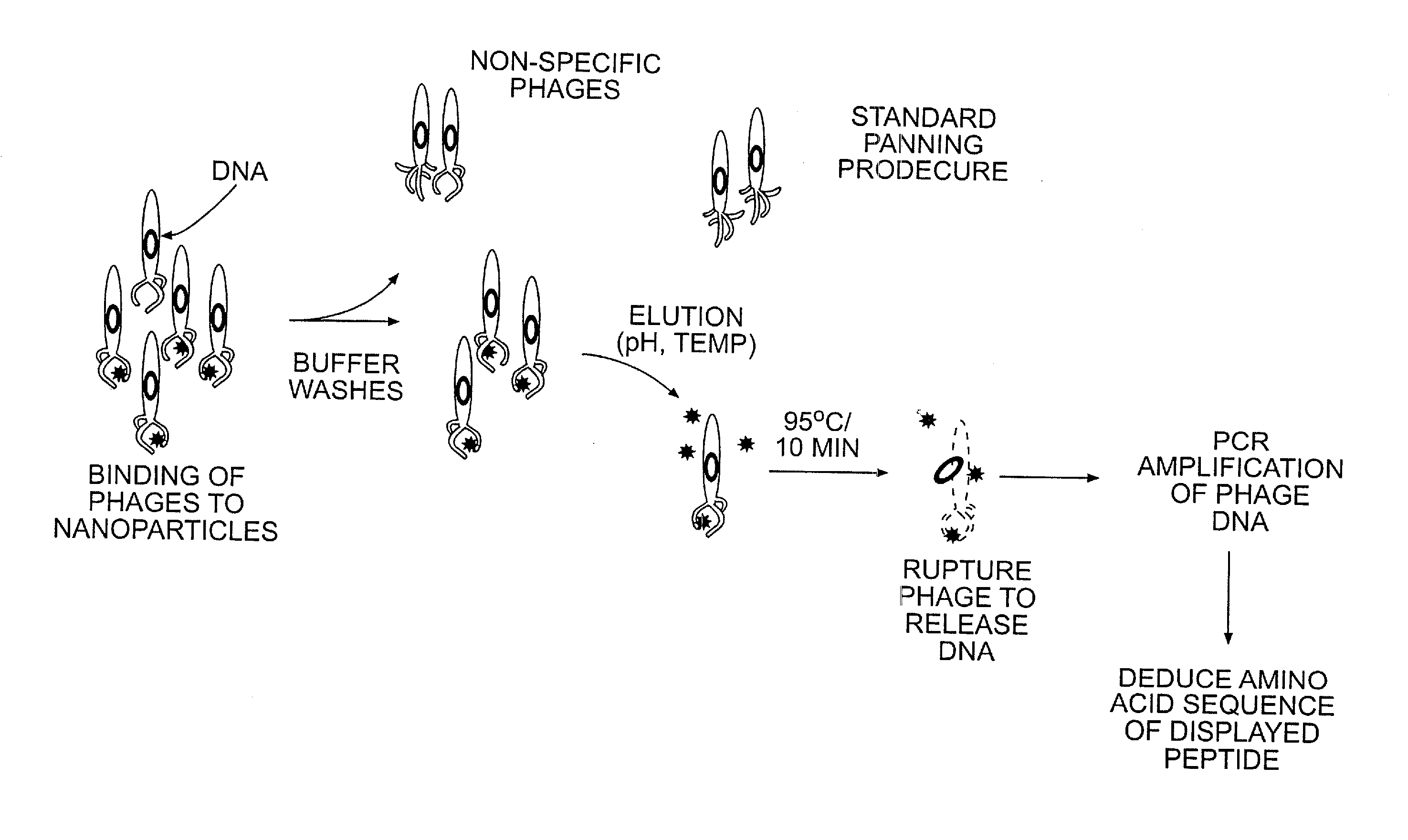
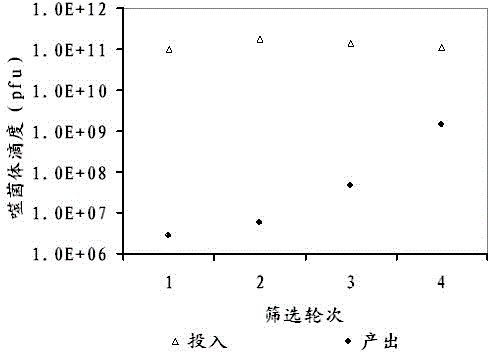
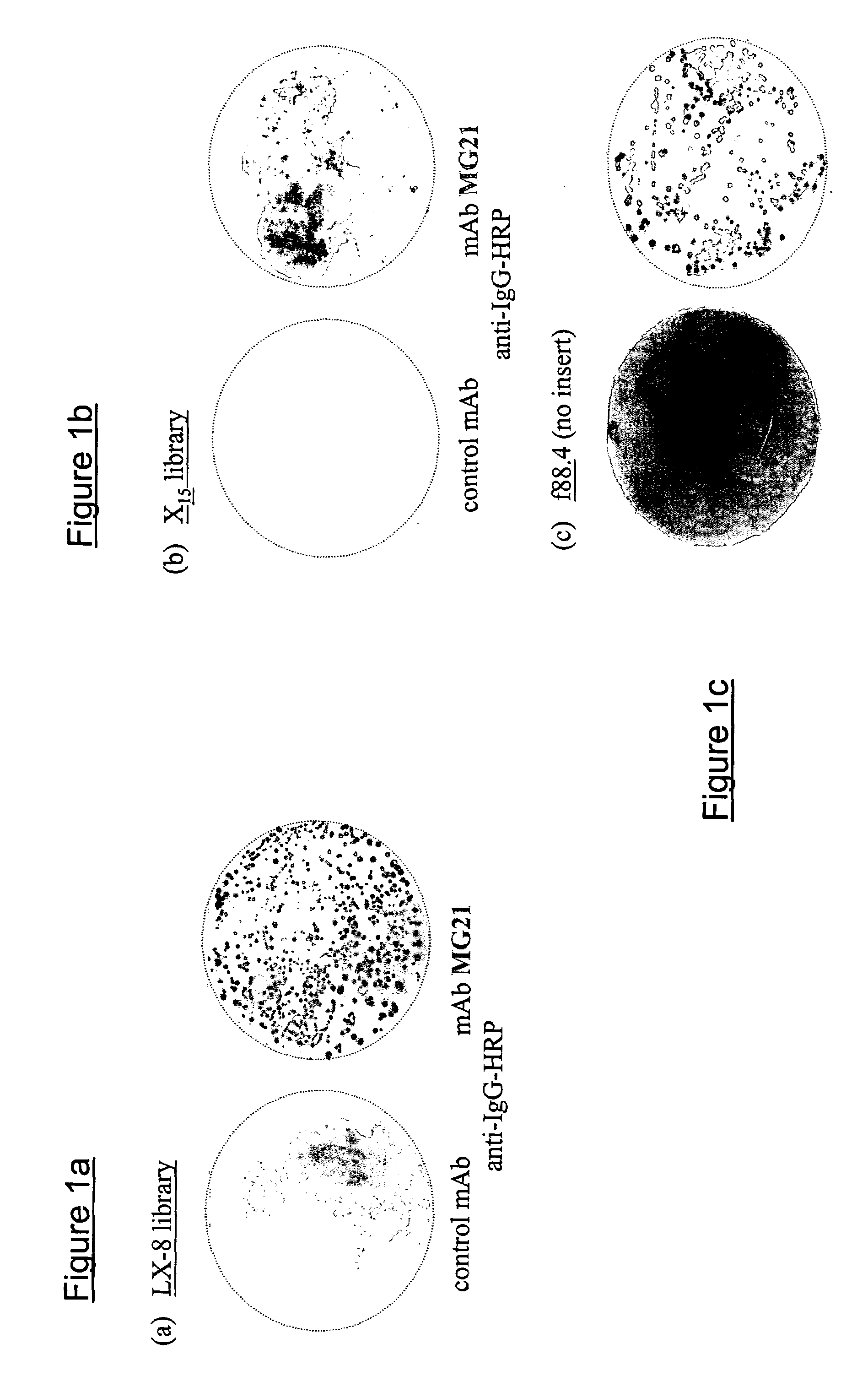
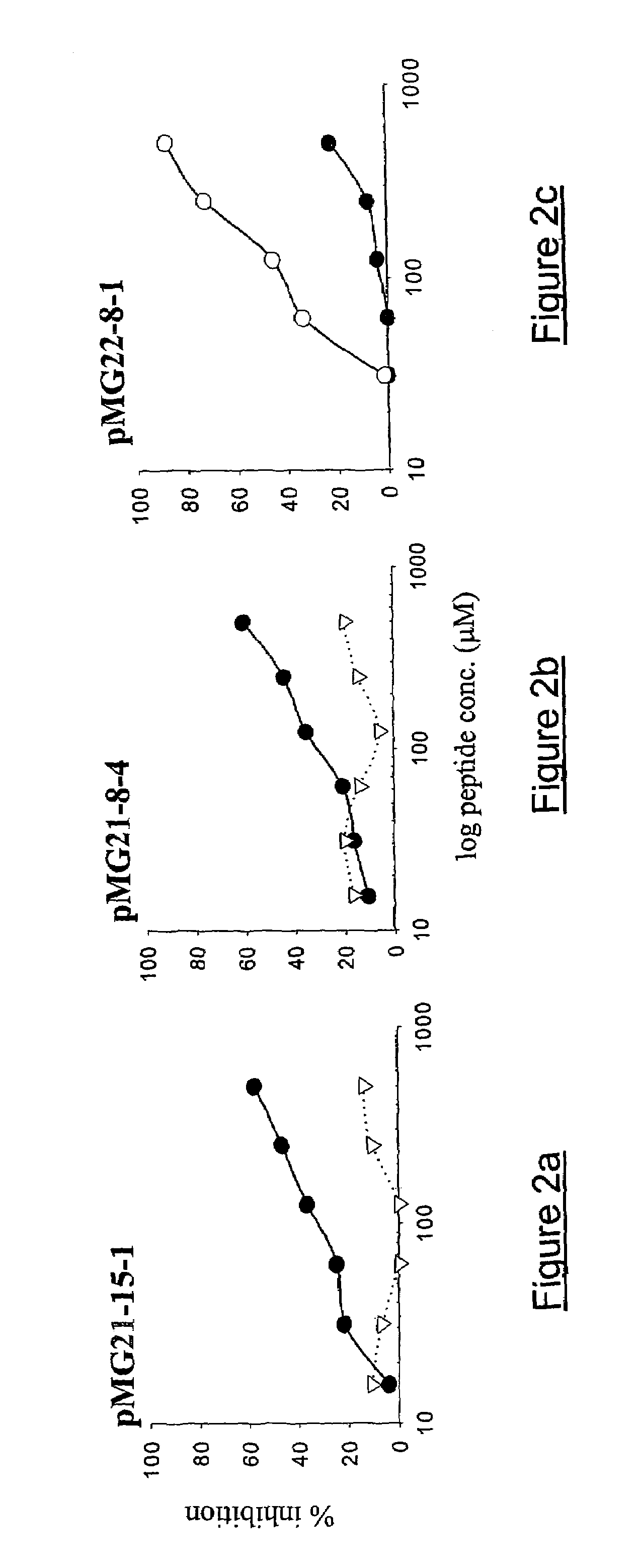
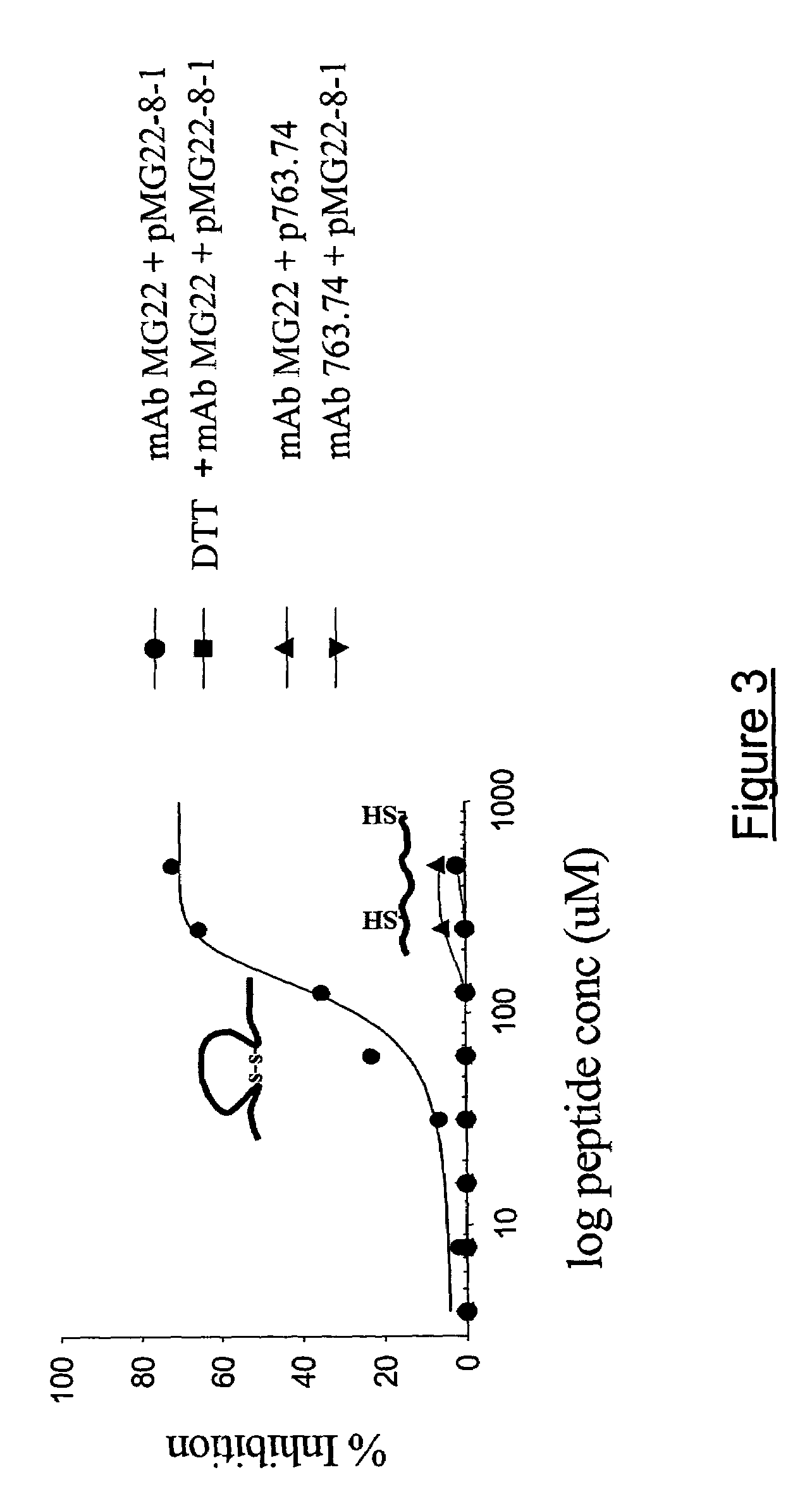
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Phage Display Peptide Library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
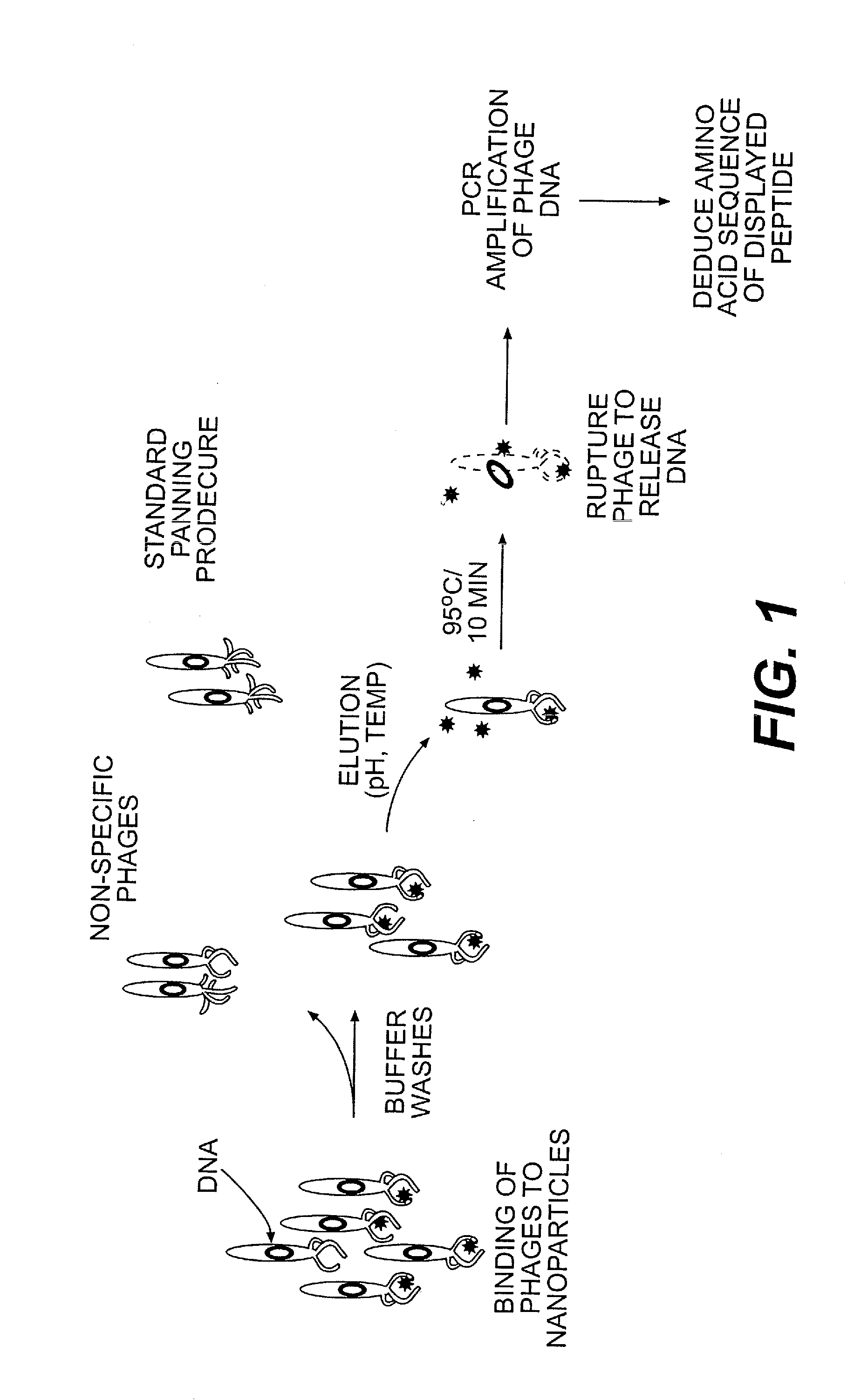
Peptide templates for nanoparticle synthesis obtained through PCR-driven phage display method
InactiveUS20060172282A1Efficient mannerEliminate labor-intensive and inefficient procedureMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementCarbon nanotubeBinding peptide
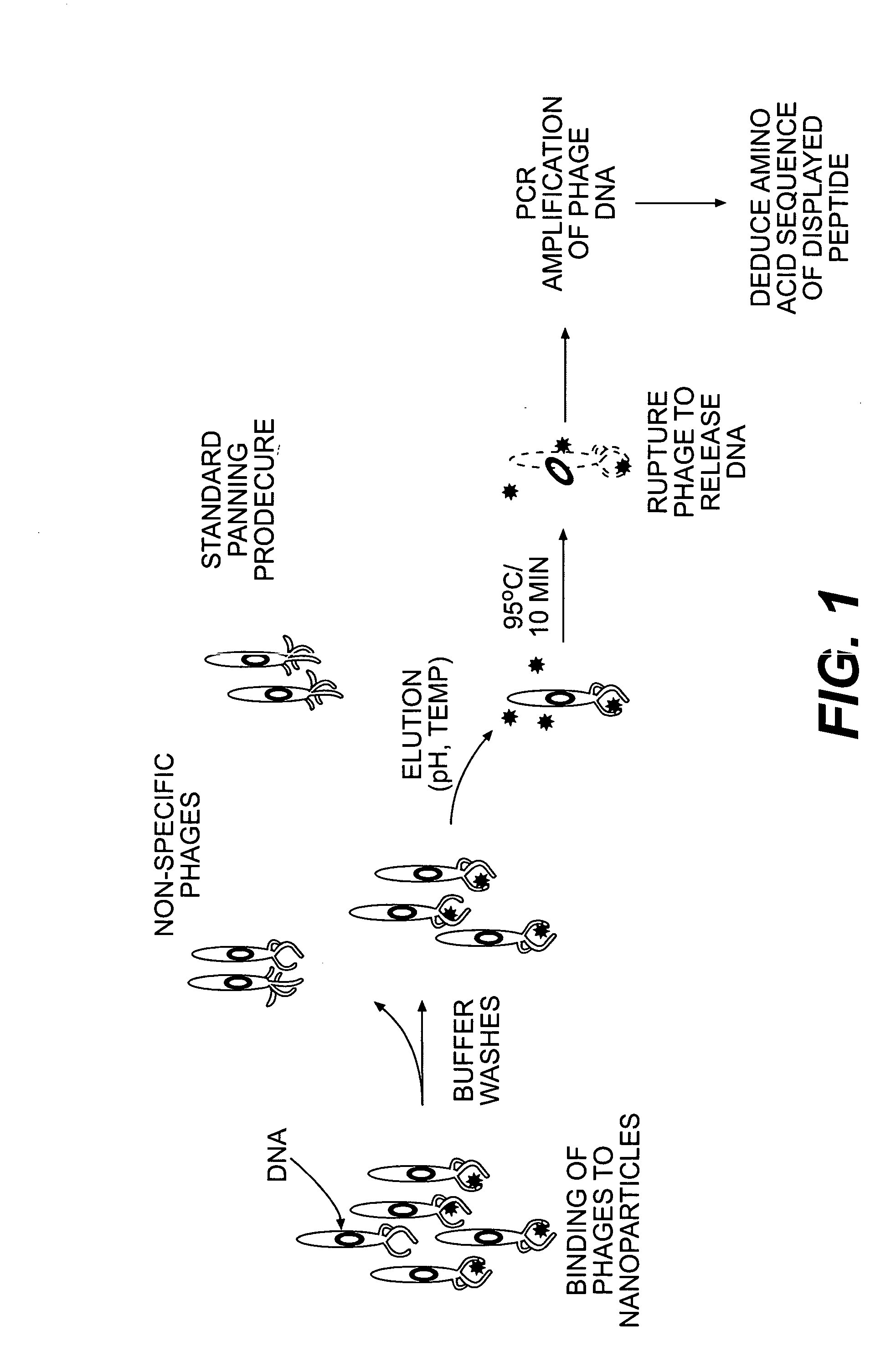
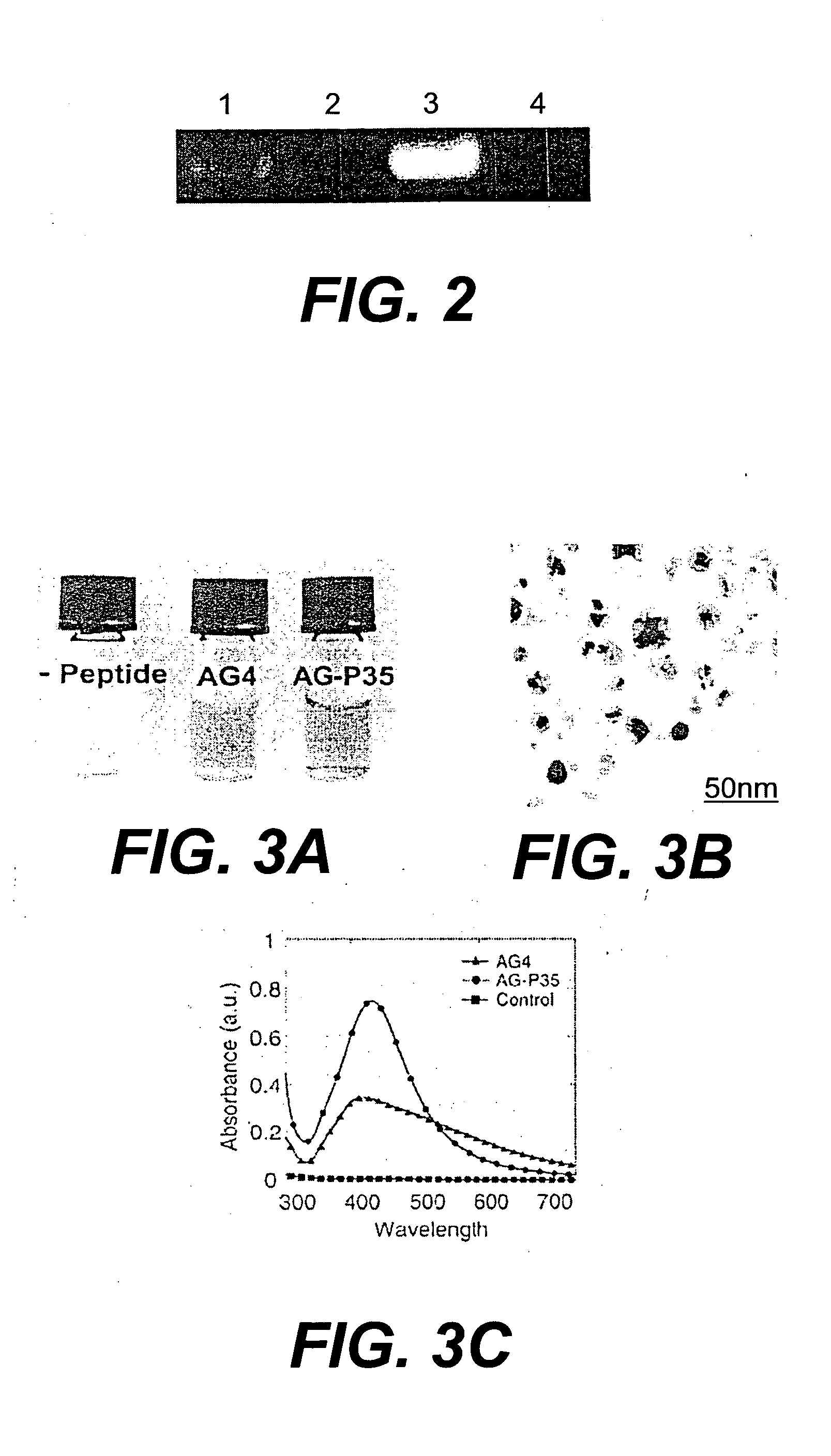
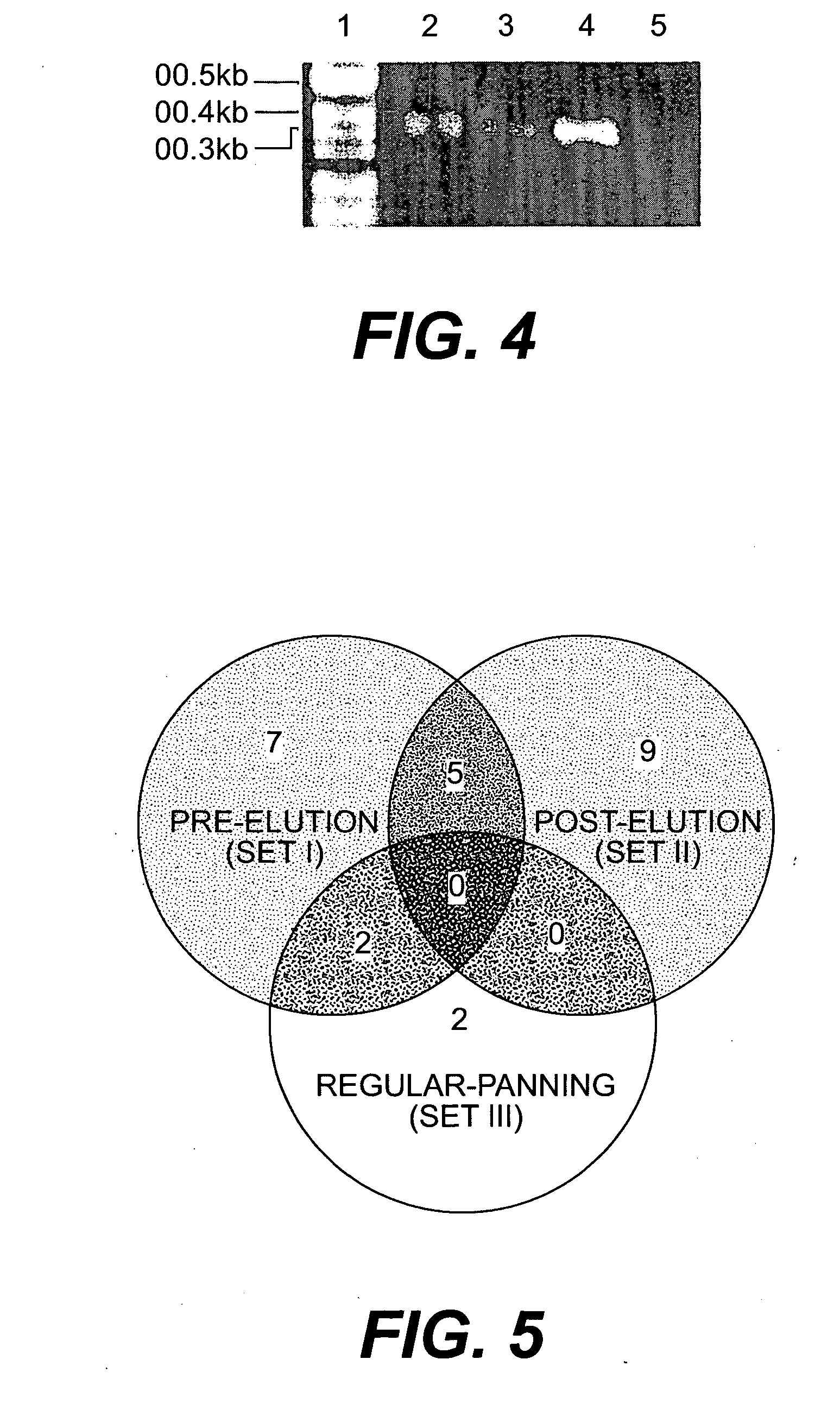
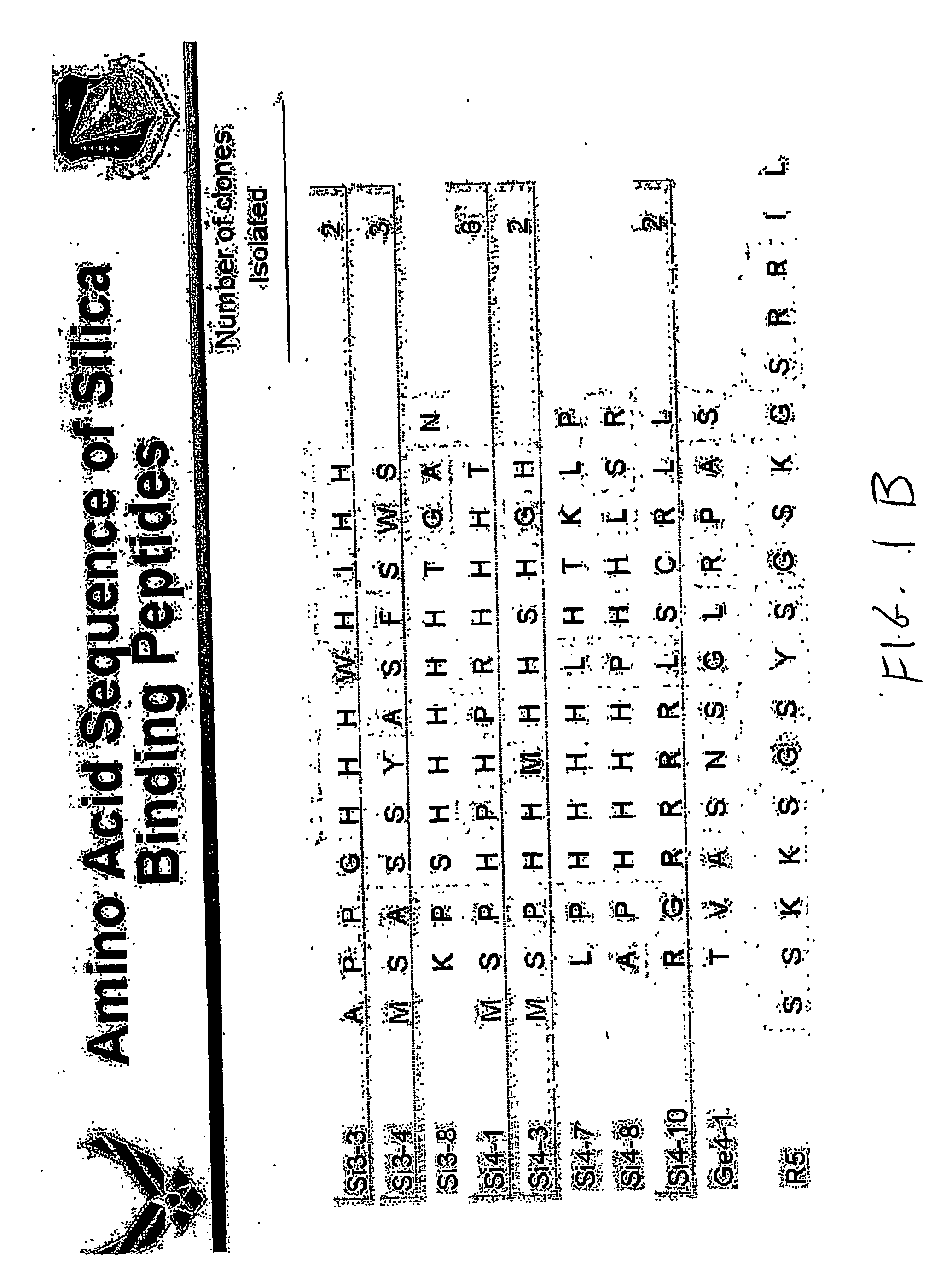
A method is provided for identifying and isolating peptides capable of binding of inorganic materials such as silica, silver, germanium, cobalt, iron, or oxides thereof, or other materials on a nanometric scale such as carbon nanotubes, using a combinatorial phage display peptide library and a polymerase-chain reaction (PCR) step to obtain specific amino acids sequences. In the method of the invention, a combinatorial phage display library is used to isolate and select the desired binding peptides by a series of steps of target binding of phage with the nanometric material of interest, elution and purification of the bound phages, and amplification using PCR to determine the sequences of phages producing the desired binding peptides. The binding peptides of the invention are particularly advantageous in that they may be used as templates to guide the development of useful structures on a nanometric scale.
Owner:NEW CENTURY PHARMA INC
PD-L1 affinity peptide with anti-tumour activity and application for same
ActiveCN103304638AGood antitumor activityInduce apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesPhage Display Peptide LibraryPD-L1
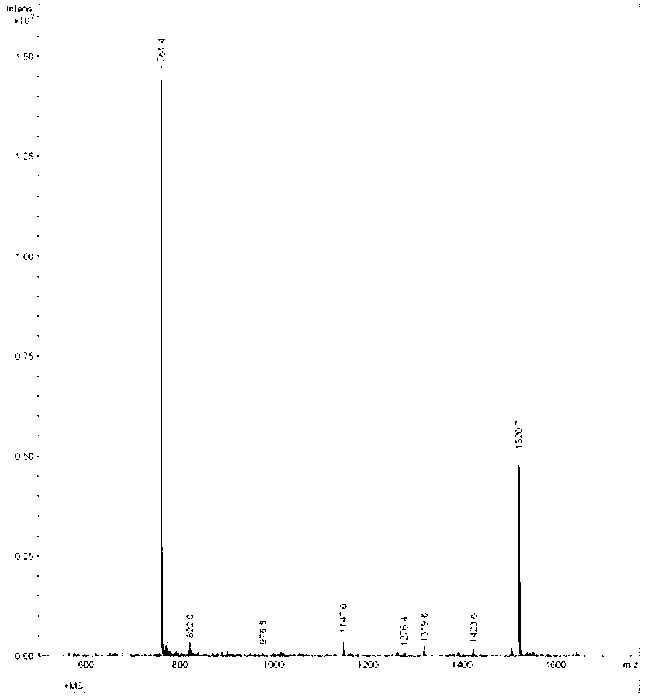
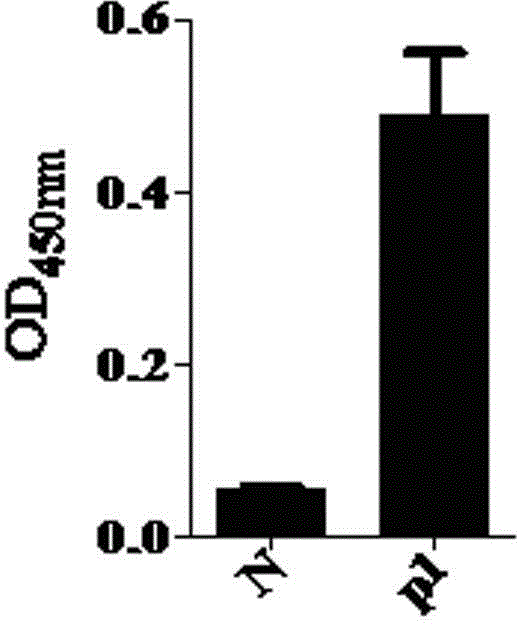
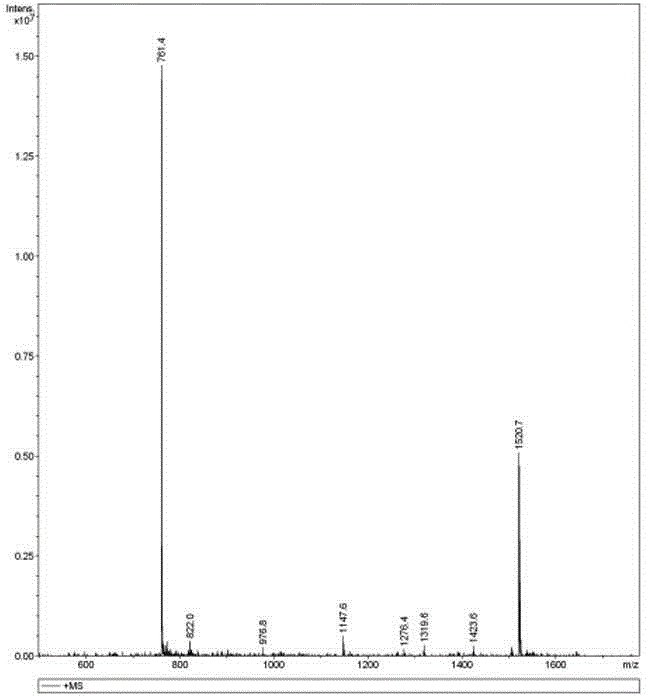
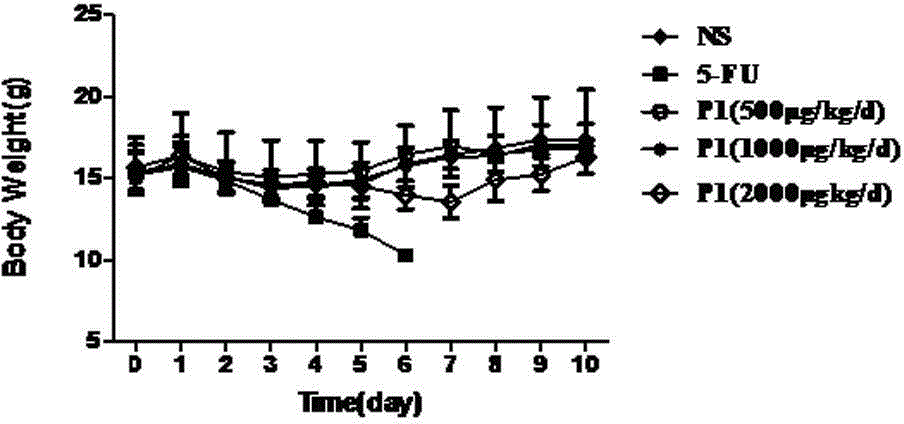
The invention discloses a PD-L1 affinity peptide P1 with anti-tumour activity, which is the polypeptide obtained by phage display peptide library screening, wherein the amino acid sequence thereof is FPNWSLRPMNQM, and the molecular weight thereof is1520.7. The affinity peptide P1 with anti-tumour activity and aiming at a PD-L1 target disclosed by the invention has the advantage of being screened with a high flux by utilizing a phage display peptide library screening technology for the first time; and via an in-vivo tumour-bearing experiment for Kunming mice, the affinity peptide P1 disclosed by the invention is proved to have a great anti-tumour activity, can induce the internal tumour cell apoptosis of mice, and have an extremely high killing capacity for tumour cells. Via the affinity peptide P1 disclosed by the invention, new thoughts and theoretical basis are provided for research and development on medicines based on PD-L1.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
PD-L1IgV-targeting affinity peptide D1 with anti-tumor activity
ActiveCN103936835AGood antitumor activityInhibit growthPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTHigh-throughput screening
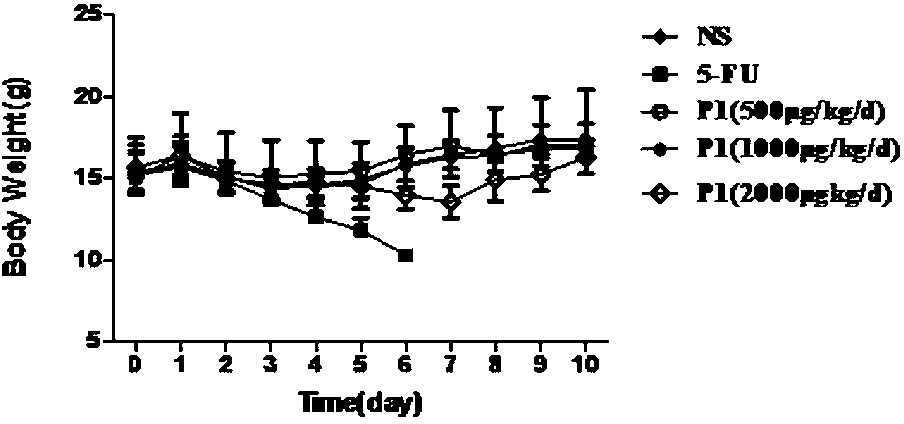
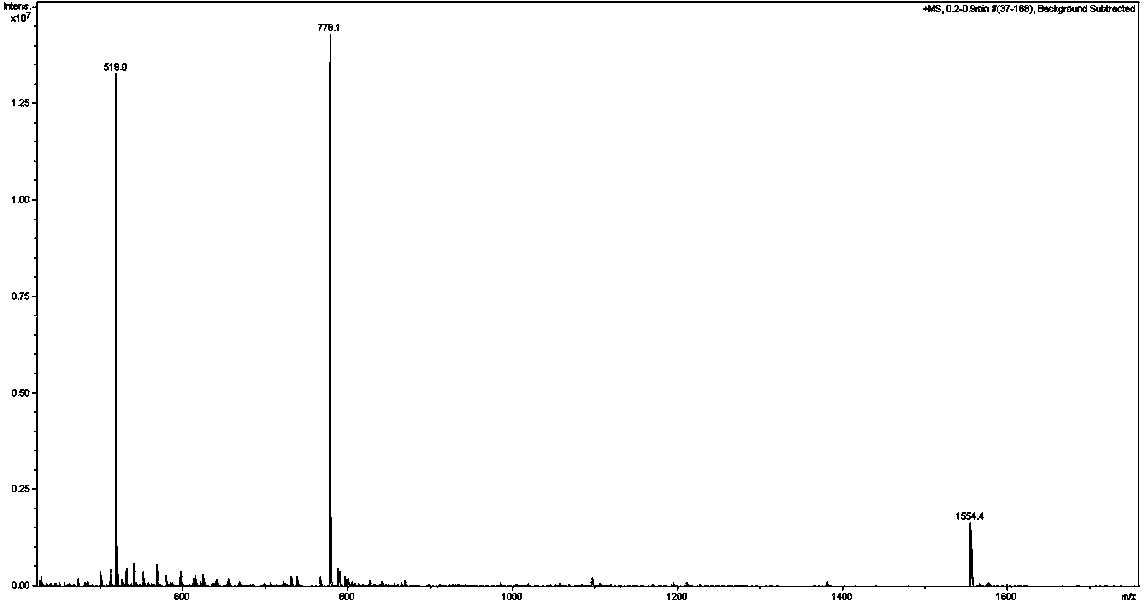
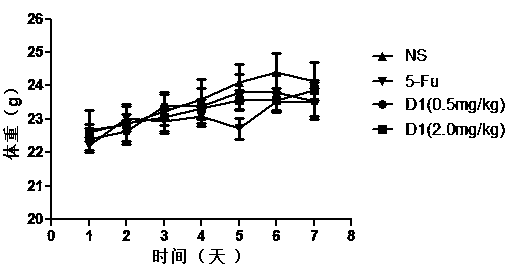
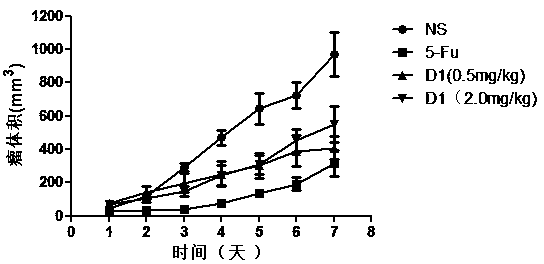
The invention belongs to the technical field of bio-pharmacy and specifically relates to a PD-L1IgV-targeting D-configuration affinity peptide D1 product with anti-tumor activity, as well as preparation and application thereof. The affinity peptide D1 is specifically bound to a PD-L1IgV region, the amino acid sequence is NYSKPTDRQYHF, and the molecular weight is 1554.7. The affinity peptide D1 is prepared through a Fomc solid-phase polypeptide synthesis method, and plays a role in preparation of anti-colon cancer medicaments as a main active ingredient. The affinity peptide D1 provided by the invention is obtained by utilizing a mirroring bacteriophage display peptide library screening technology and performing high-throughput screening by taking PD-L1IgV as a target point. Through tumor-bearing experiments in mouse bodies, the inventor proves that the affinity peptide D1 has better anti-tumor activity and can obviously inhibit the growth of tumors in the mouse bodies, so that a new idea and theoretical basis are provided for researching and developing PD-L1-based medicaments.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
HGG (Human Gammaglobulin) polypeptide in combination with tissue specificity of cerebral arterial thrombosis and application thereof
ActiveCN104592352ASmall molecular weightHigh activityPeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsTissue targetingNeuroprotective Drugs
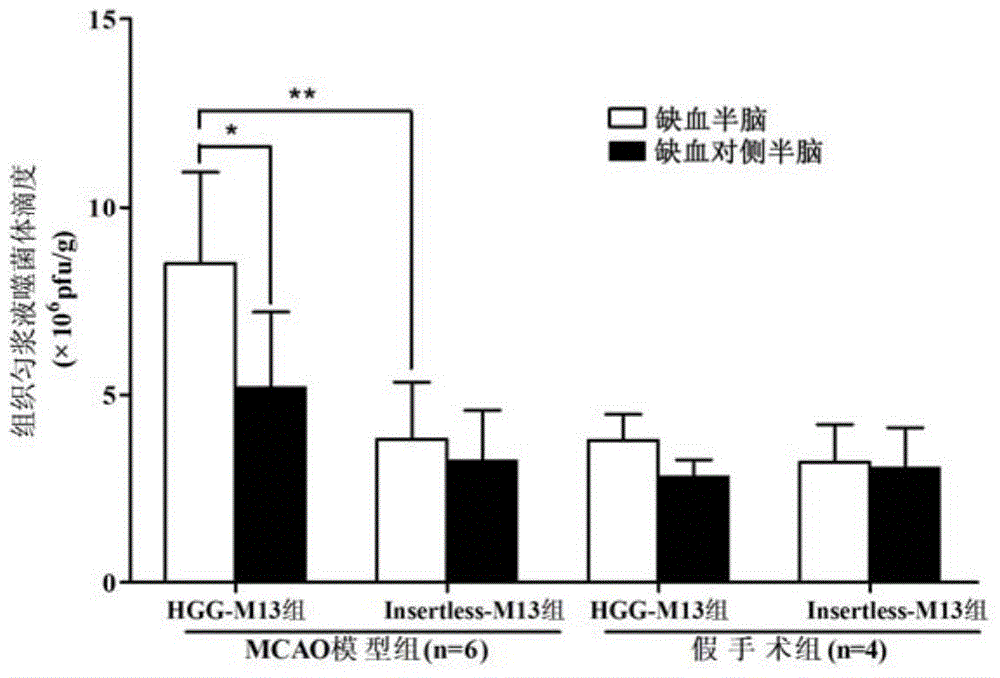
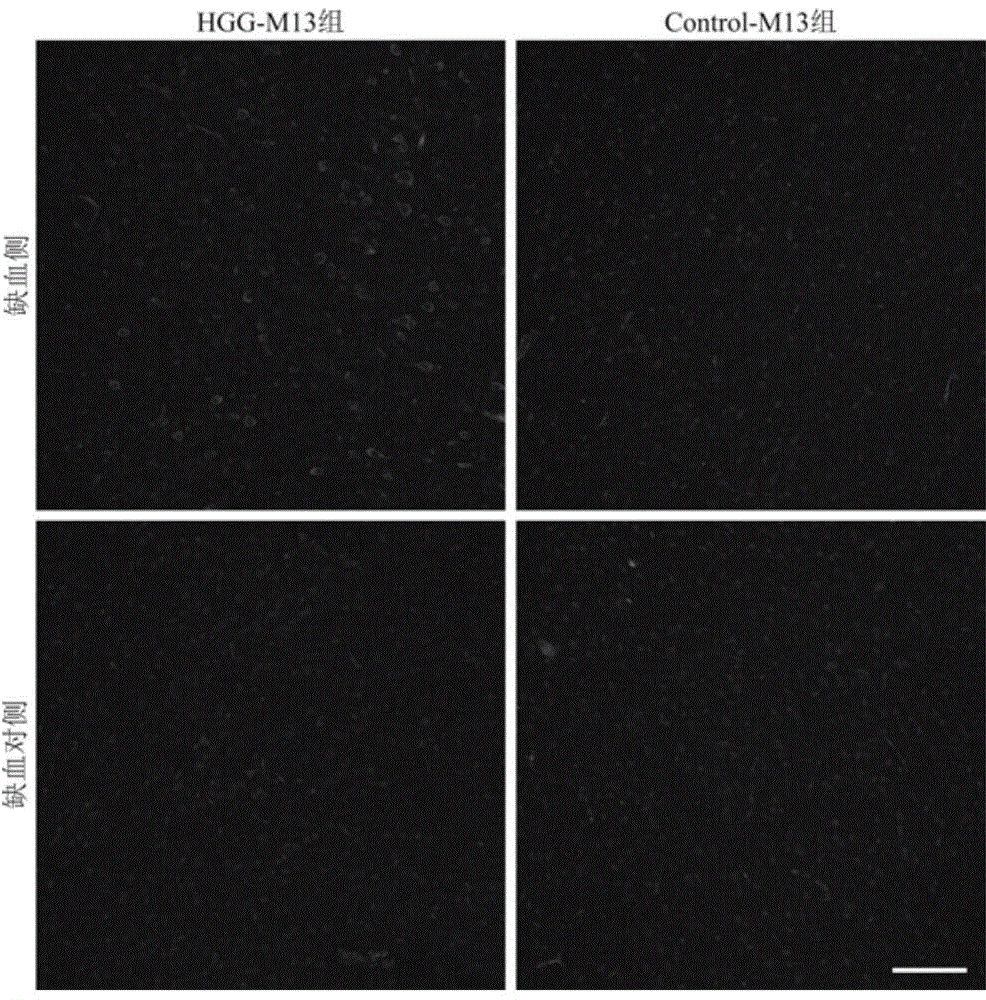
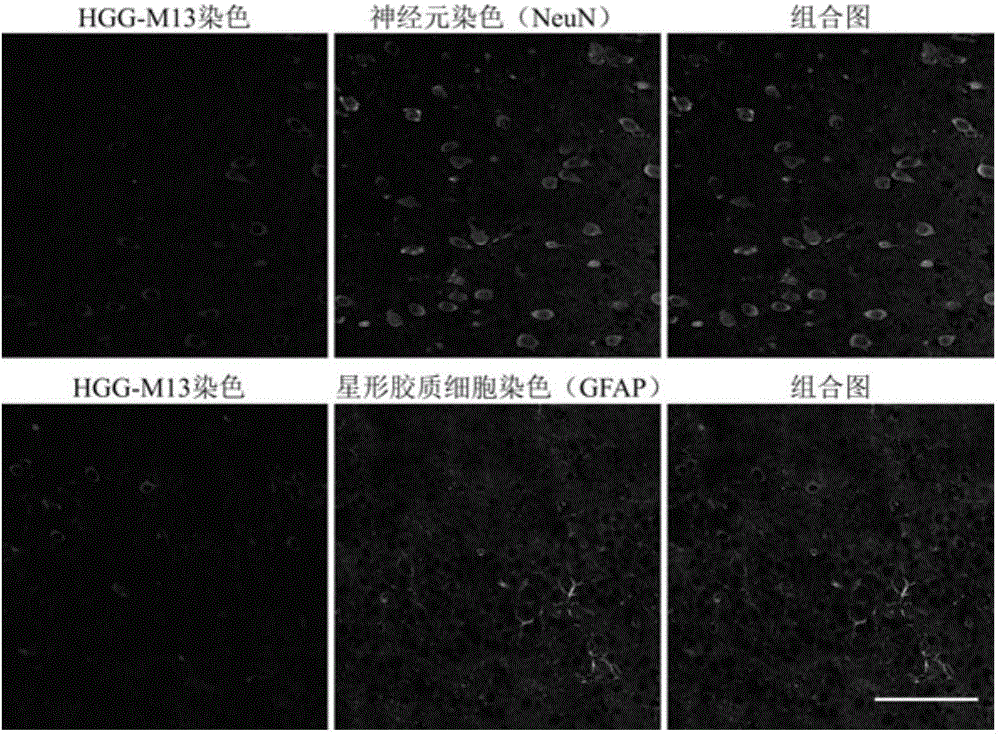
The invention discloses HGG (Human Gammaglobulin) polypeptide in combination with the tissue specificity of cerebral arterial thrombosis. The invention relates to a method for obtaining the polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out in-vivo selection of a mouse MCAO (Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion) cerebral arterial thrombosis model by adopting an in-vivo phage display peptide library screening technology so as to obtain phage clones in combination with cerebral arterial thrombosis tissue; and randomly selecting the plurality of phage clones to sequence, and authenticating the in-vivo combination specificity of HGG peptide and coded phage clones HGG-M13 thereof. The invention further relates to application of the polypeptide in preparation of a high-sensitivity imaging molecular probe and a targeting delivery neuroprotective drug for cerebral stroke. The polypeptide can be synthesized through an artificial method; the polypeptide is low in molecular weight, high in activity and penetrating power, good in specificity and low in toxicity, and has good tissue targeting of cerebral arterial thrombosis in vivo; and therefore, the polypeptide is applicable to serving as a carrier of the high-sensitivity imaging molecular probe and the targeting delivery neuroprotective drug.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of isolating binding peptides from a combinatorial phage display library and peptides produced thereby
InactiveUS20060035223A1Quick and efficientEfficient mannerCompound screeningPeptide librariesPhage Display Peptide LibraryBinding peptide
A method is provided for identifying and isolating peptides capable of binding of inorganic materials such as silica, cobalt, iron, or oxides thereof using a combinatorial phage display peptide library. In the method of the invention, a combinatorial phage display library is used to isolate and select the desired binding peptides by a series of steps of target binding of phage with the inorganic material of interest, elution and purification of the bound phages, and amplification to determine the sequences of phages producing the desired binding peptides. The binding peptides of the invention are particularly advantageous in that they may be used as templates to guide the development of useful structures on a nanometric scale.
Owner:NEW CENTURY PHARMA INC
Chitosan affine heptapeptide and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN106518968AImprove stabilityHigh affinityLibrary screeningPeptidesSequence analysisScreening method
The invention discloses chitosan affine heptapeptide. The amino acid sequence of the chitosan affine heptapeptide is shown as any of SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6. Screening includes the steps that nanoparticles wrapped by chitosan are prepared through the ion gelation method, then the nanoparticles are mixed with a phage displayed peptide library, the peptide library is screened through centrifugal separation, and finally a phage clone obtained through screening is subjected to ELISA identification and sequence analysis. The provided short peptide has high affinity and can be bound to the surface of a chitosan material, surface properties of the mesoporous silicon nanoparticles wrapped by chitosan can be changed, and accordingly the application range is widened. More materials, methods and means are provided for developing nano materials, especially nanoparticle medicine carriers, with chitosan as the basis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Specific combined polypeptide for lung cancer, preparation and uses thereof
InactiveCN101492505AEasy to detectReliable detectionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsTumor targetBacterial virus
The invention discloses a polypeptide that can be specifically combined with lung cancer cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The polypeptide specifically combined with lung cancer cells shows peptide library reducing screening by a bacterial virus so as to obtain bacterial virus clone specifically with lung cancer; the bacterial virus clone having stronger affinity with lung cancer is identified by Elisa and an immunohistochemical method; and sequencing is sent so as to obtain a 12 polypeptide, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The 12 polypeptide screened by the invention not only has the advantages of traditional antibody molecule but also has small molecular weight, strong penetrating power and easy arriving to tumor tissue; the 12 polypeptide has good tumor targeting effect and more sensibility of tumor diagnosis, and can be used for preparing a kit for tumor diagnosis and drug for curing tumors.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Targeted PD-L1IgV affinity peptide D2 with anti-tumor activity
ActiveCN103936836AGood antitumor activityInhibit growthPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsHigh-throughput screeningAnti neoplastic
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy, and in particular relates to a targeted PD-L1IgV D-configured affinity peptide D2 product with anti-tumor activity, and a preparation method and application of the targeted PD-L1IgV D-configured affinity peptide D2 product. The affinity peptide D2 is specifically bonded in a PD-L1IgV region; the amino acid sequence of the affinity peptide D2 is KHAHHTHNLRLP; the molecular weight of the affinity peptide D2 is 1459.8; the affinity peptide D2 is prepared by virtue of a Fomc solid-phase polypeptide synthesis method; the affinity peptide D2 serving as the main active component plays a role in preparation of anti-colon-cancer drugs. The affinity peptide D2 provided by the invention is obtained by displaying the peptide library screening technology by utilizing mirrored phage and carrying out high-throughput screening by taking D-PD-L1IgV as the target spot. The tumor-burdened experiments in mice prove that the affinity peptide D2 has better anti-tumor activity and is capable of obviously inhibiting the growth of tumor in mice, and therefore, a novel idea and a theoretical basis are provided for researching and developing PH-L1-based drugs.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Method for constructing expression library of cell penetrating peptide by utilizing bacteriophage display technology
InactiveCN108752425APeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionExpression LibraryCell membrane
The invention relates to a method for constructing an expression library of cell penetrating peptide by utilizing bacteriophage display technology. The method comprises the following steps of adoptingthe bacteriophage display technology, combining with a whole-cell screening mode, and screening polypeptide with cytomembrane penetrating activity; then constructing pronucleus expression library ofcell penetrating peptide by utilizing the screened cell penetrating peptide; selecting and using a Ph.D.-c7c bacteriophage display peptide library, inserting the gene sequence of random heptapeptide into a bacteriophage capsid protein coding gene pIII, and enabling an expression product, which is corresponding to the random heptapeptide, and the capsid protein terminal of bacteriophage to form fusion protein, so as to form a combinatorial library. The positive cloning efficiency of the library constructed by the method is far higher than that of a random polypeptide library, the time period required for screening and verification is greatly shortened, and the method has the advantage of high flux.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
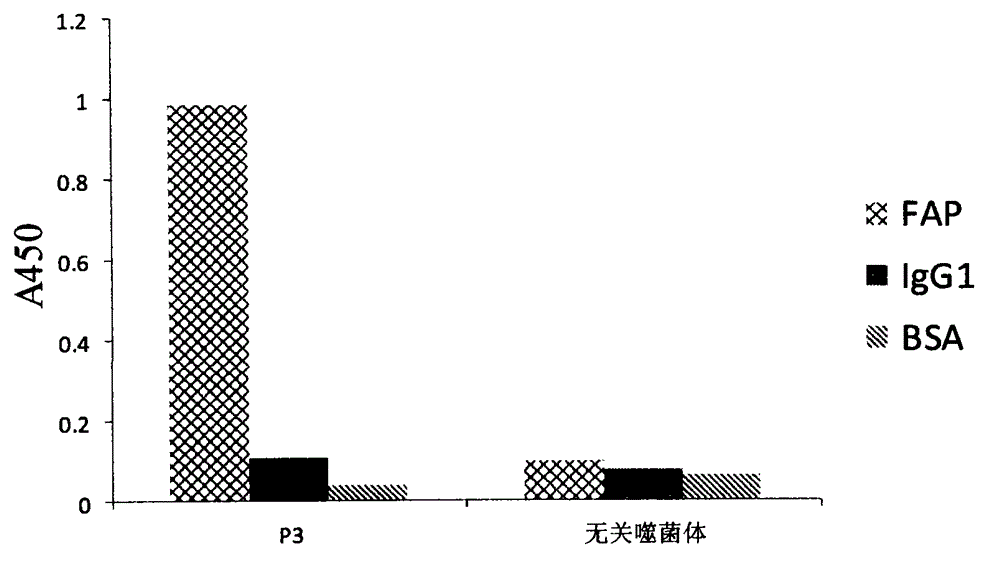
Polypeptide combined with FAP (Fibroblast Activation Protein)
InactiveCN102977189ARadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsAbnormal tissue growthTumor stroma
The invention discloses a polypeptide combined with an FAP (Fibroblast Activation Protein). The polypeptide is obtained by screening from a phage display peptide library, can be specifically combined with the FAP, has high activity and has a sequence of SCDYNHHWC. The polypeptide can be used for preparing a broad spectrum probe aiming at a tumor matrix, and can meet the application requirement on the aspects of molecular imaging of tumors, targeting therapy of tumors, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING CHAOYANG HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Method for screening polypeptide specifically bound with human colon cancer cells and application of polypeptide
ActiveCN106967154ASmall molecular weightOvercoming immune allergic reactionsPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesCancer cellScreening method
The invention relates to a polypeptide specifically bound with the surfaces of colon cancer cells and application of the polypeptide. A method for screening the polypeptide includes steps of (1), incubating clone strains with amplified bacteriophage dodecapeptide libraries and the colon cancer cells together, discarding the clone strains which are not bound with the colon cancer cells, screening the clone strains and then amplifying the screened clone strains which are bound with the colon cancer cells; (2), repeatedly carrying out the step (1) by four times, continuously enriching bacteriophage clone strains to obtain clone strains with high colon cancer cell affinity and repeatedly verifying the binding capacity of the bacteriophage clone strains in liquid phases; (3), incubating the bacteriophage clone strain obtained at the step (2) and normal colonic epithelial cells and removing non-specifically bound clone strains; (4), carrying out sequencing on positive clone strains; (5), verifying the specificity of the polypeptide on the clone cancer cells and tissues by the aid of immunofluorescence. The polypeptide and the application have the advantages that short peptides which are specifically bound with the colon cancer cells are screened by the aid of technologies for displaying peptide libraries by the aid of bacteriophage, and the polypeptide can be used as a molecular marker or targeted carrier or the like for targeted therapeutic medicines.
Owner:孟祥军
Peptide templates for nanoparticle synthesis obtained through pcr-driven phage display method
InactiveUS20080176760A1Quick and efficientMinimum of stepsMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesCarbon nanotubeBinding peptide
A method is provided for identifying and isolating peptides capable of binding of inorganic materials such as silica, silver, germanium, cobalt, iron, or oxides thereof, or other materials on a nanometric scale such as carbon nanotubes, using a combinatorial phage display peptide library and a polymerase-chain reaction (PCR) step to obtain specific amino acids sequences. In the method of the invention, a combinatorial phage display library is used to isolate and select the desired binding peptides by a series of steps of target binding of phage with the nanometric material of interest, elution and purification of the bound phages, and amplification using PCR to determine the sequences of phages producing the desired binding peptides. The binding peptides of the invention are particularly advantageous in that they may be used as templates to guide the development of useful structures on a nanometric scale.
Owner:NAIK RAJESH R +2
Clec9a-targeting affinity peptide WH peptide
ActiveCN105924501AImprove permeabilityEasy to synthesizePeptidesCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsAntigenIn vivo
The invention belongs to the technical field of tumor prevention and treatment and concretely relates to a Clec9a-targeting affinity peptide WH peptide and its preparation method and use. The peptide comprises 12 amino acids, has an amino acid sequence of WPRFHSSVFHTH and can be prepared through an Fmoc solid-phase synthesis method. The peptide can be used in tumor prevention and treatment. The peptide can be obtained through phage-displayed peptide library technology screening. The result of the research on an in-vivo and in-vitro foreign antigen cross presentation capacity and induction cases of specific CTL reaction shows that the WH peptide as a targeting carrier can well induce specific CTL response, improve IFN-gamma and related cell killing molecule expression quantity and improve tumor resistance. Through a computer simulated molecular docking technology, a possible docking area between the WH peptide and the Clec9a protein and action sites of the possible docking area can be researched. The peptide provides good reference and reference significance for related research.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Ovarian-cancer-targeted polypeptide
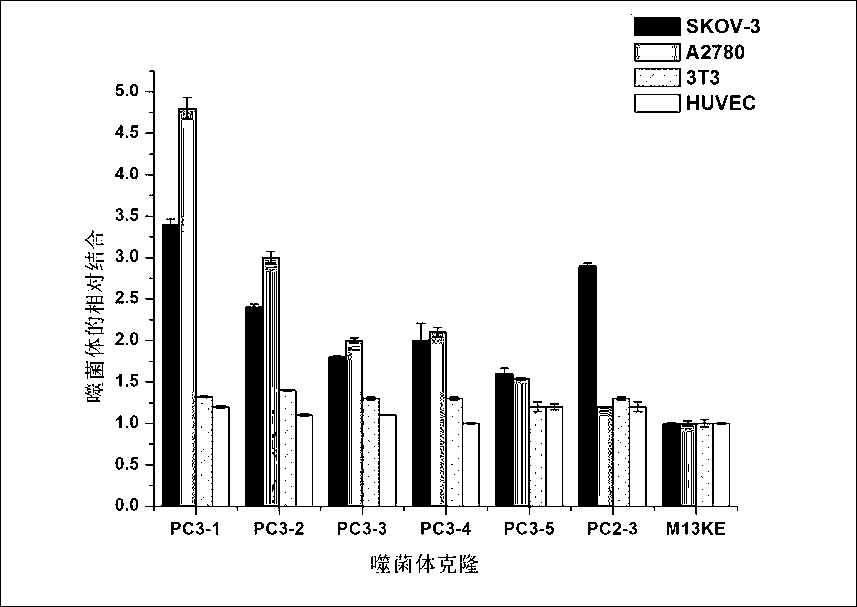
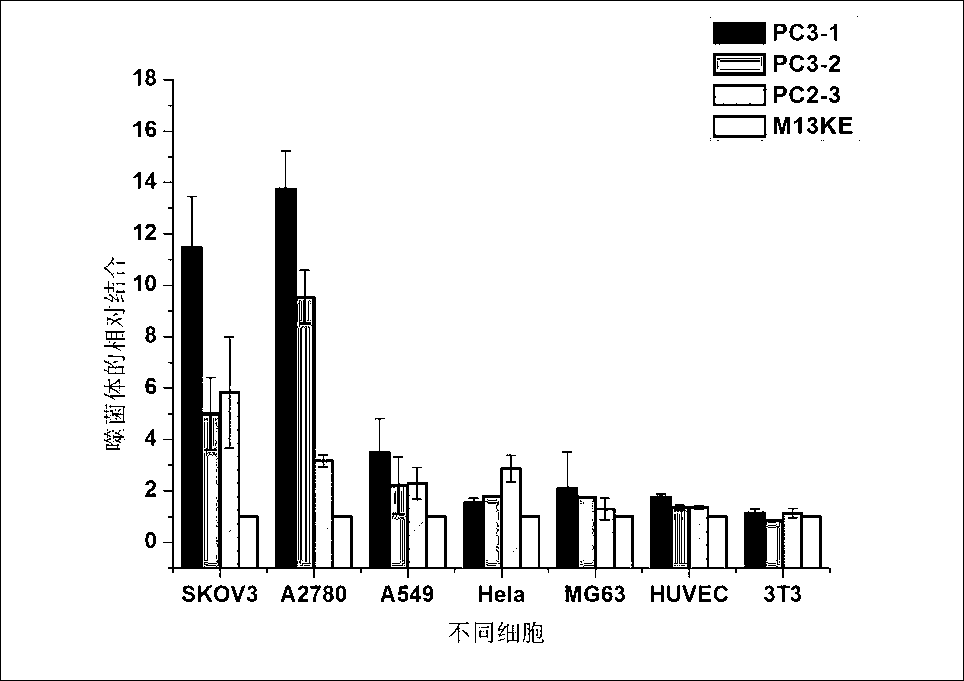
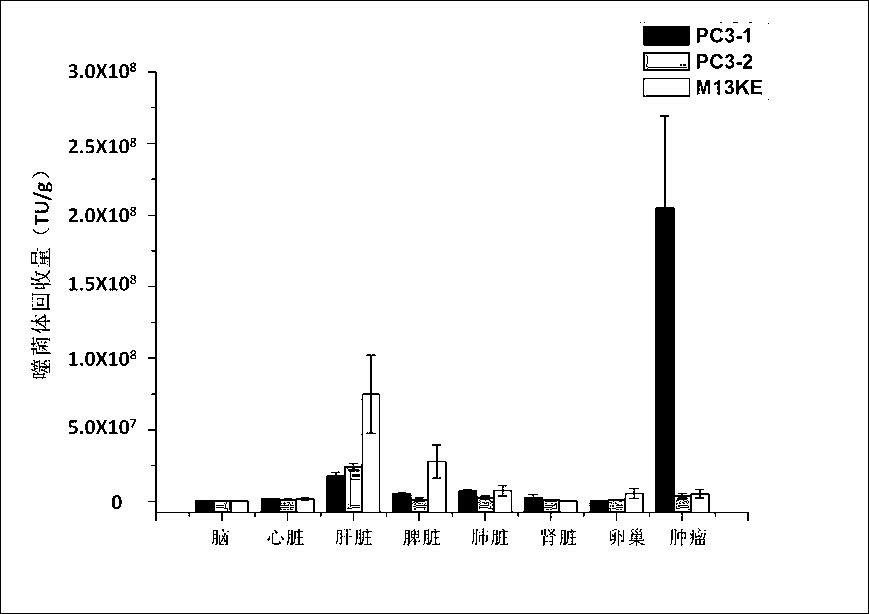
The invention discloses an ovarian-cancer-targeted polypeptide. The polypeptide is screened from a tumor model of ovarian cancer by using phage display peptide library technology and the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is WSGPGVWGASUK. Identification proves that the polypeptide can distinguish ovarian cancer cells from normal cells and ovarian cancer cells from other cancer cells, and thus can be combined with ovarian cancer cells specifically and be effectively internalized by the ovarian cancer cells. Serving as a medicine carrier, the polypeptide can improve the absorption of medicines. After being injected into the tumor model through vines, the polypeptide can be enriched in the tumor area of the ovarian cancer. The polypeptide is a totally new polypeptide with invivo targeting capacity proved, and the polypeptide can be used as an ideal ligand to construct a targeting carrier for transmitting anticancer medicines.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Defense peptides against fungal infection and method of their use
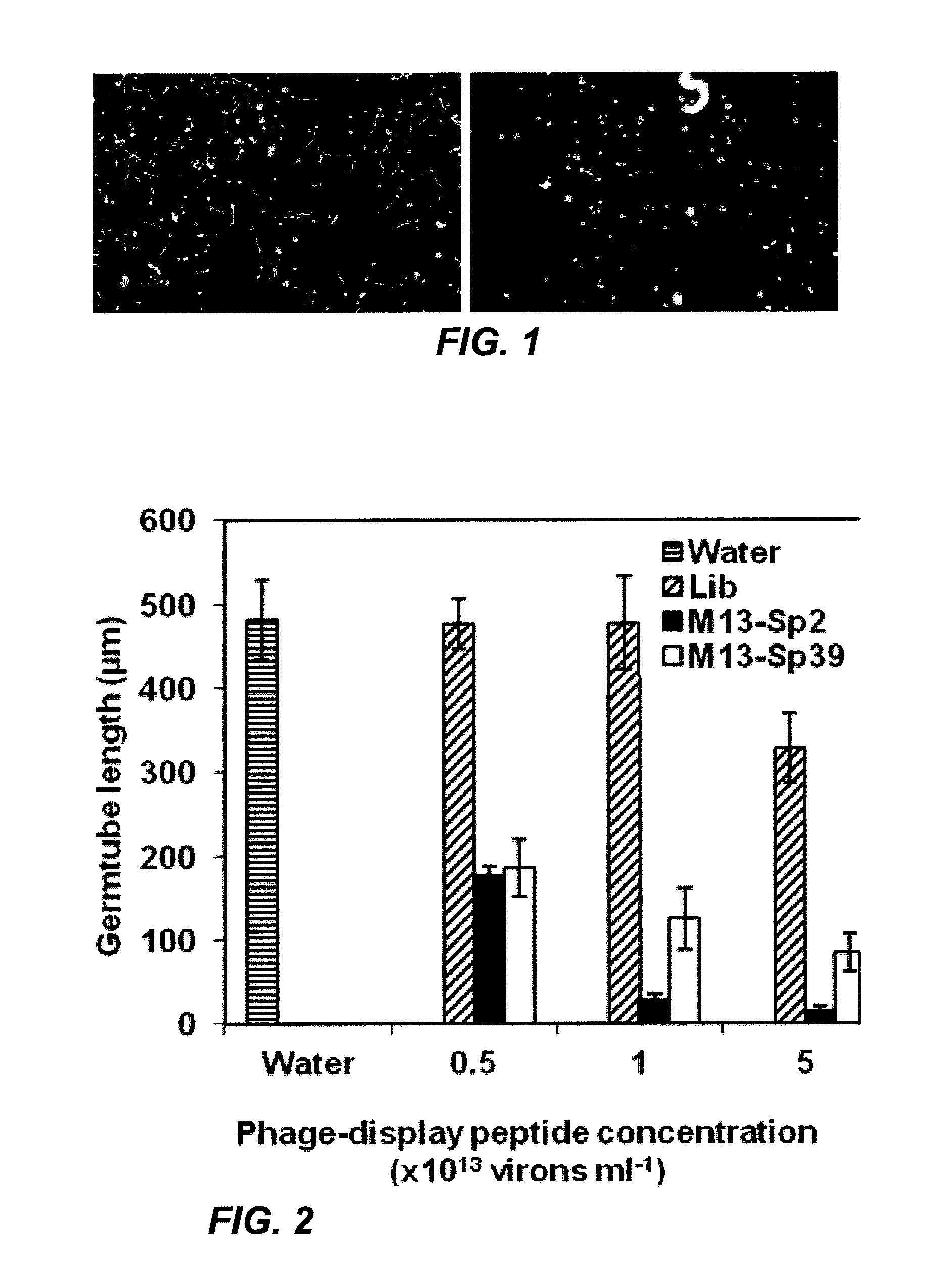
InactiveUS9051581B2High recovery rateRapidly identify new defense peptidesSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyAsian soybean rust
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
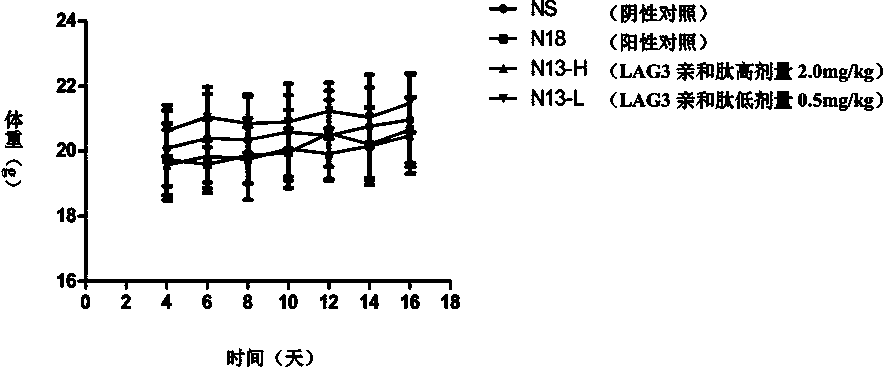
lag-3 affinity peptide n13, preparation method and application thereof
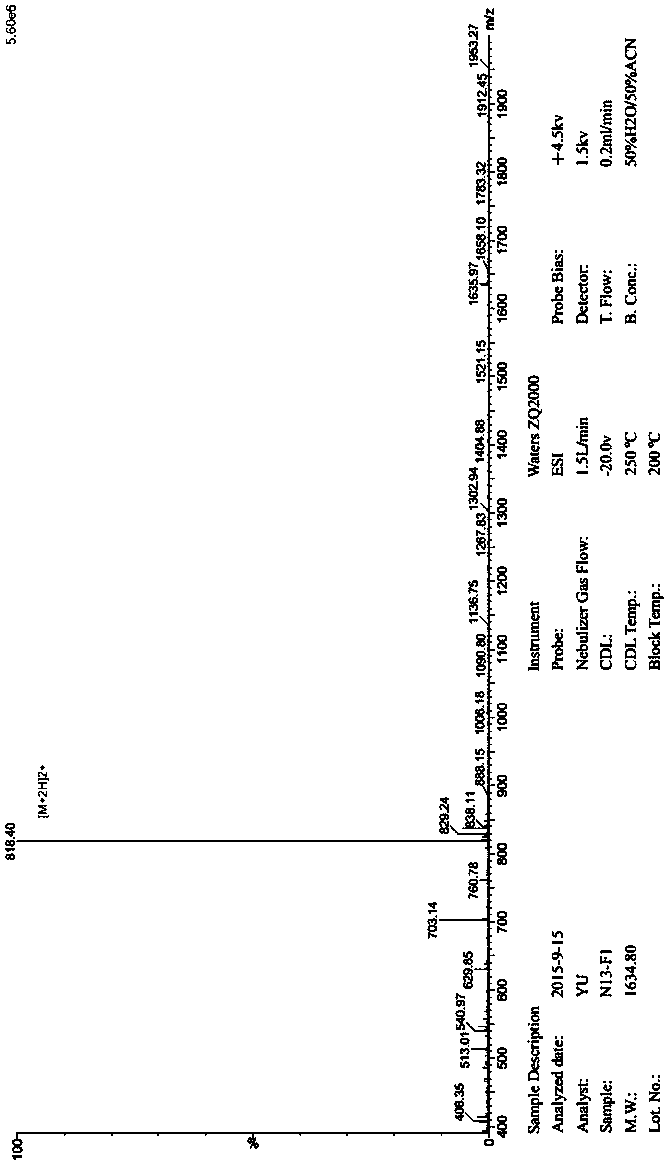
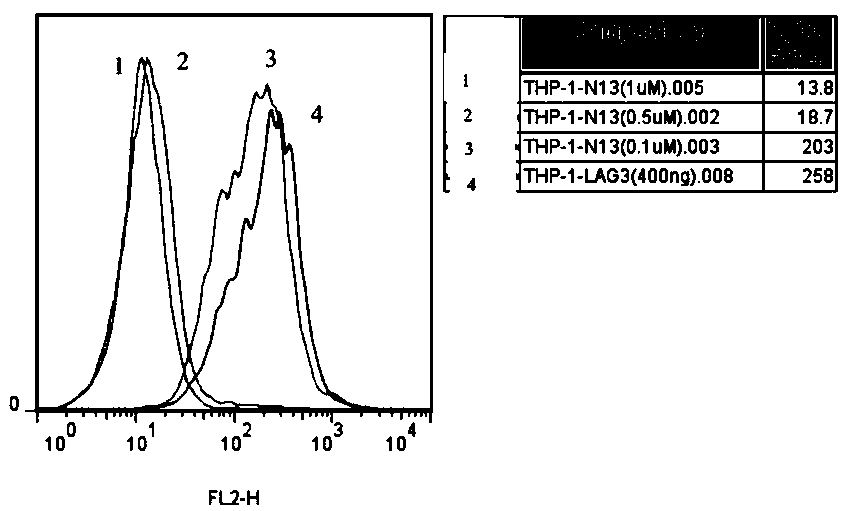
ActiveCN105504018BProlong lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSynthesis methodsMouse tumor
The invention belongs to the technical field of biopharmaceuticals, and in particular relates to a LAG‑3 affinity peptide N13, a preparation method and an antitumor application thereof. The affinity peptide includes 12 amino acids, the molecular weight is 1634.8 Da, and its sequence is DDFRVWWPNFPR. The peptide can be prepared by the Fmoc solid-phase polypeptide synthesis method, and at the same time, the peptide can be used as a drug in tumor treatment. In this application, the eukaryotic protein rhLAG3-Fc is used as the target molecule, hIgG1-Fc is used as the tag protein, and the affinity peptide N13 of the extracellular segment of LAG-3 is screened out through the high-throughput technology of phage display peptide library. For this peptide, further in vitro signal pathway blocking experiments and mouse tumor-bearing experiments showed that this peptide has good application prospects in tumor treatment and prolonging the survival of organisms, and provides a new method for the immunotherapy of organism tumors. possible.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
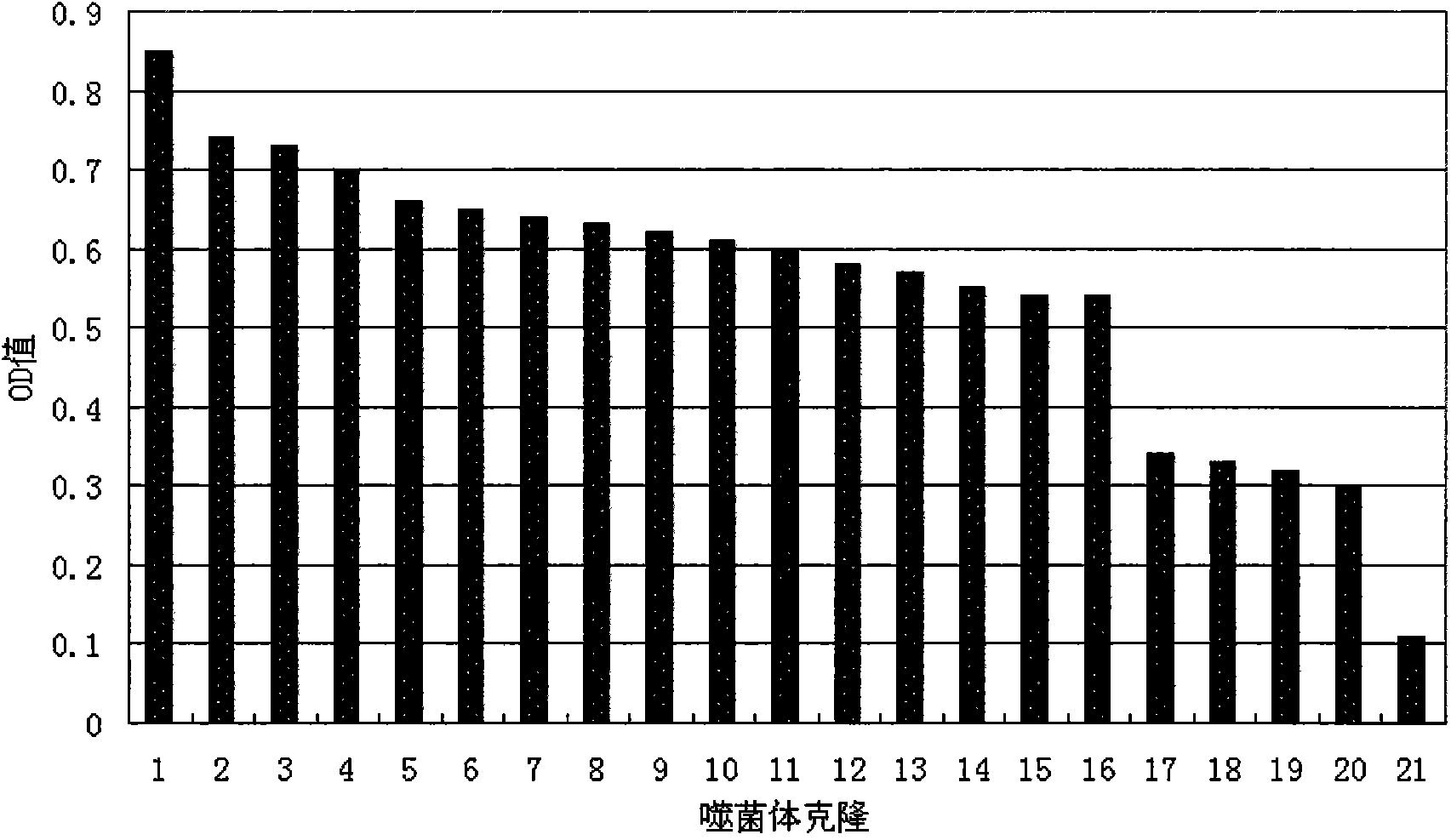
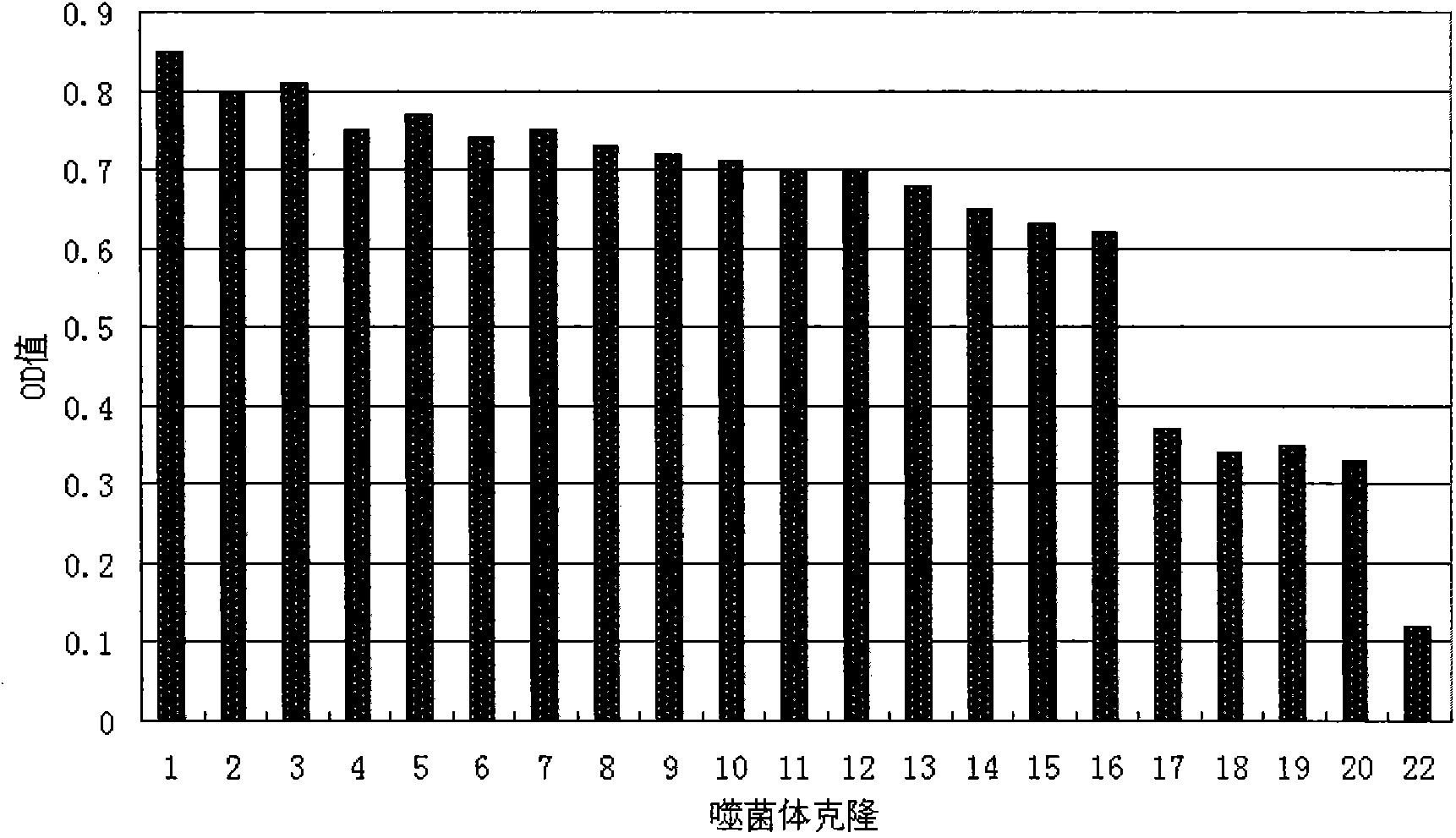
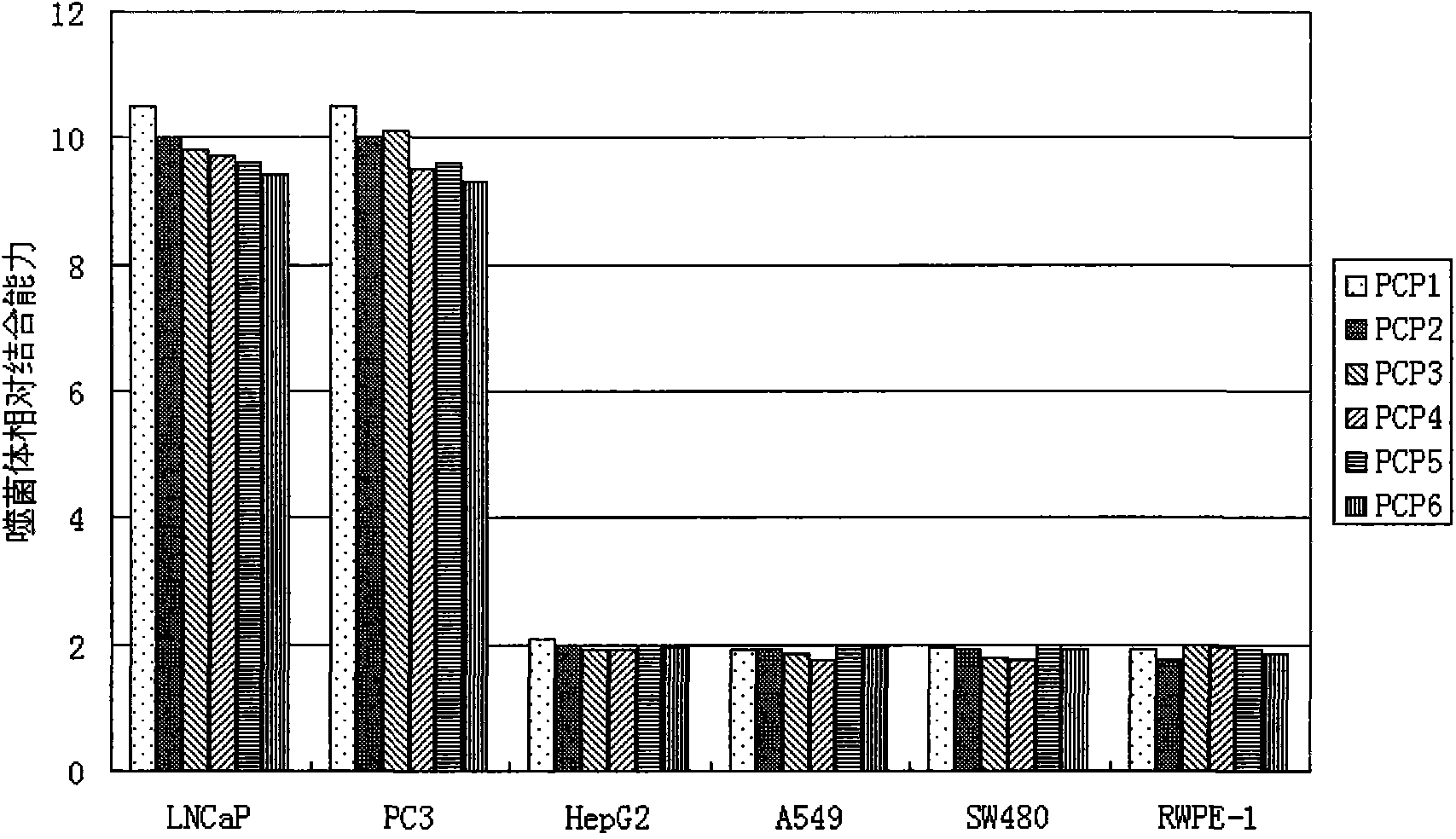
Oligopeptide of specifically combined prostate cancers and application of oligopeptide
ActiveCN103897037ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingTreatment effectPhage Display Peptide Library
The invention provides a series of polypeptides with characteristics of targeted prostate cancers, which are obtained by screening with a phage display peptide library technology. The combined polypeptides are high in specificity and can be used for general investigation of high-risk people with the prostate cancers, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancers and assessment of prostate cancer treatment effects.
Owner:汉恒生物科技(上海)有限公司
Antigen mimic epitope of SARS-COV-2 coronavirus and immunochromatographic test strip
ActiveCN113388039AStrong specificityHigh sensitivitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesNitrocelluloseAmino acid
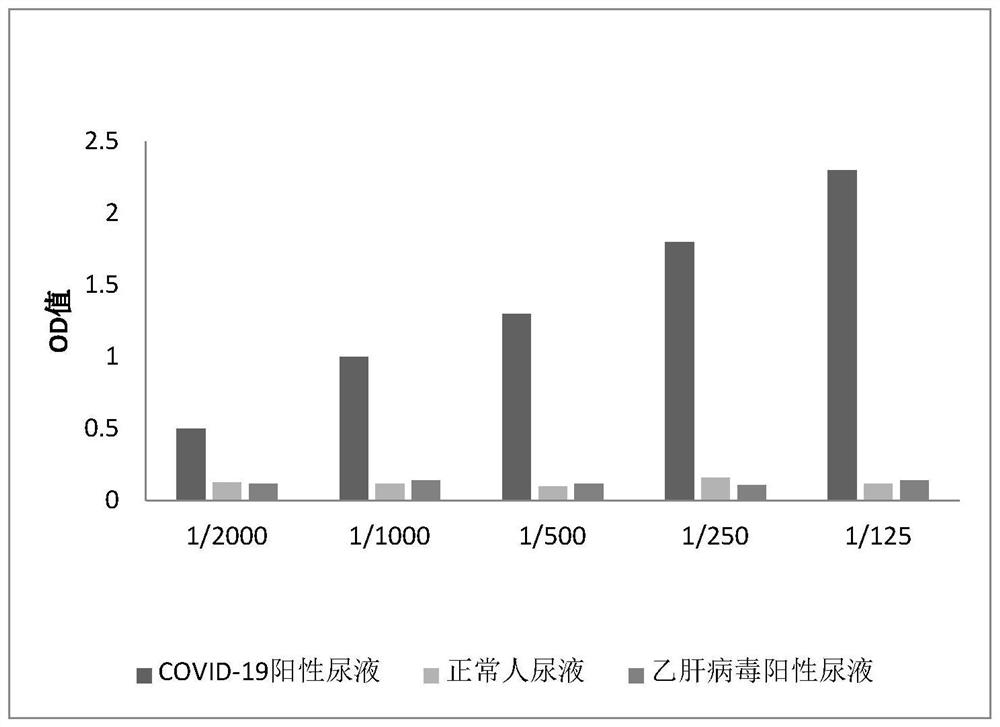
The invention discloses an antigen mimic epitope of SARS-COV-2 with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, application of the antigen mimic epitope, and an SARS-COV-2 coronavirus detection immunochromatographic test strip. The test strip comprises a sample pad, a binding pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and a water absorption pad which are sequentially bonded on a bottom plate in a lap joint manner, wherein a colloidal gold labeled anti-human IgG antibody is sprayed on the binding pad; and a detection line for coating the antigen mimic epitope or fusion protein thereof and a quality control line for coating the human IgG antibody are arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane. A polypeptide capable of being specifically bound with the SARS-COV-2 antibody is screened from a peptide library from the SARS-COV-2 antibody in urine from a COVID-19 rehabilitative person by using a phage display peptide library technology. According to the screened SARS-COV-2 antigen mimic epitope, the novel coronavirus detection immunochromatographic test strip with high specificity and good sensitivity is prepared, and the test strip has the advantages of simplicity, convenience and rapidness in operation.
Owner:浙江佳米生物医药科技有限公司
Diethylstilbestrol mimic antigenic epitope peptide, and preparation method and application thereof
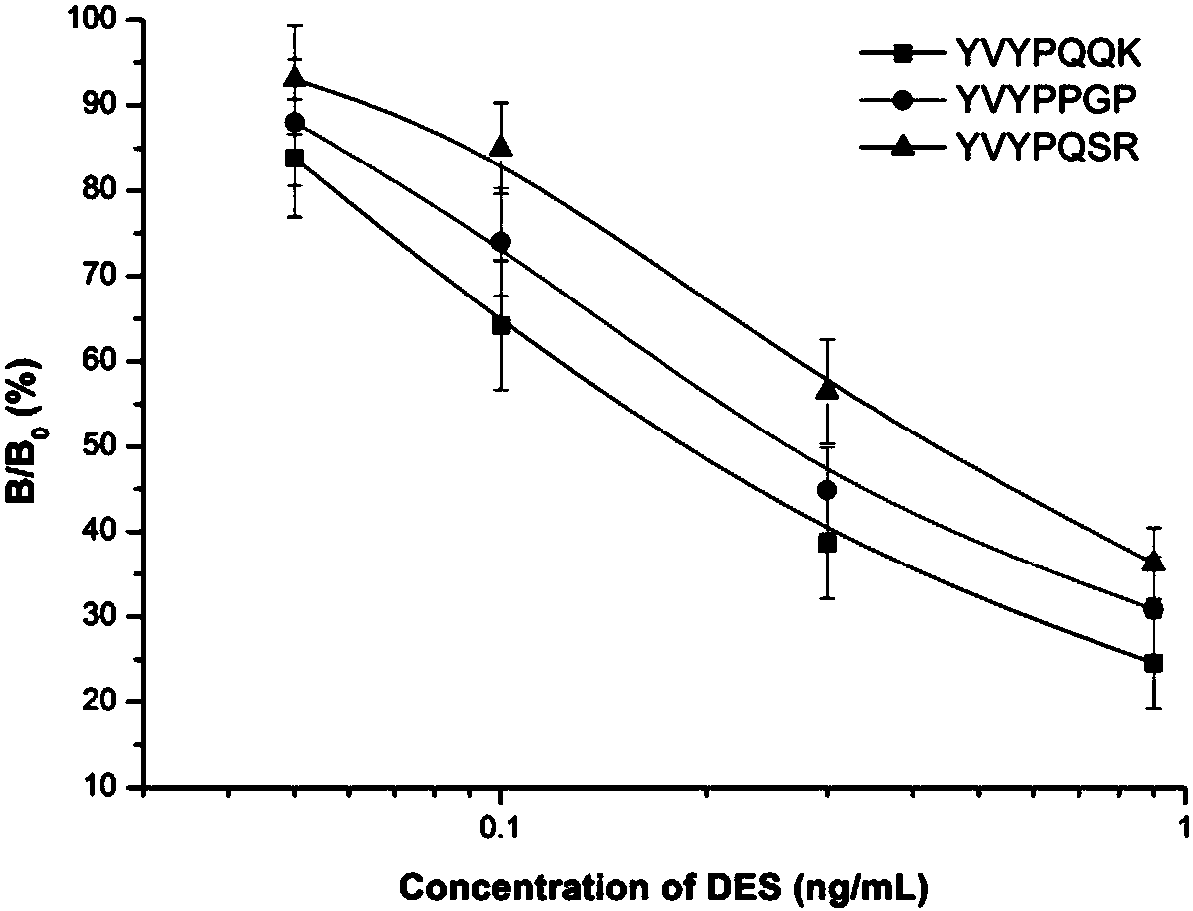
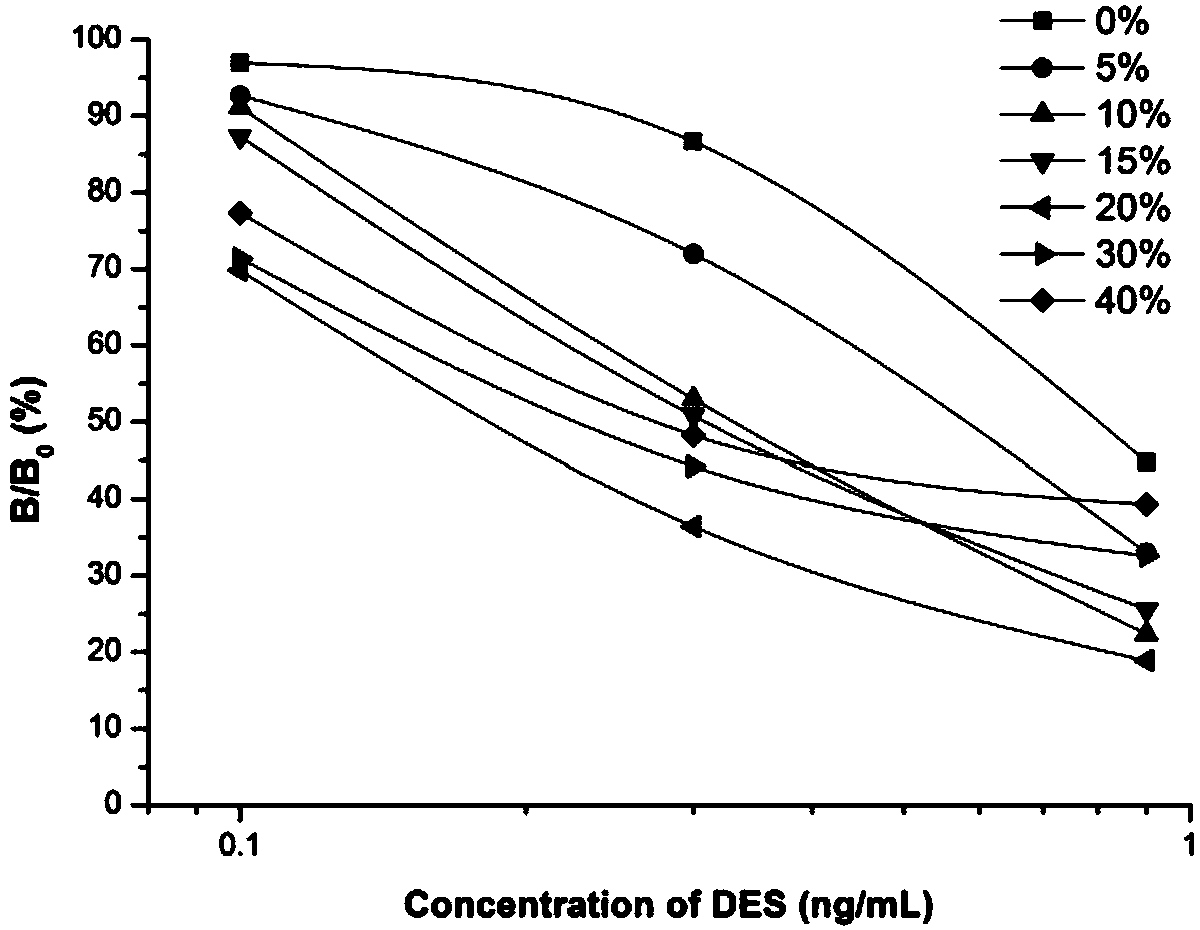
ActiveCN108358996AHarm reductionThe test result is accurateVector-based foreign material introductionPolypeptide with MBP-tagDiethylstilbestrolImmune reaction
The invention provides a diethylstilbestrol (DES) mimic antigenic epitope peptide, and a preparation method and an application thereof. Firstly, based on a phage display peptide library technology, ananti-DES monoclonal antibody is used as a target, and a DES antigen mimic epitope having the sequence of YVYPQQK, YVYPPGP or YVYPQSR is selected from a phage random display heptapeptide library. Centering on immune binding characteristics of the antigen mimic epitope, a specific detection method is designed based on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, colloidal gold immunochromatography and fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography. The antigenic mimic epitope has similar immunoreactivity characteristics to those of natural DES molecules, can replace an expensive DES standard substance having teratogenic and carcinogenic effects to be used in immunological detection of DES; the detection results are accurate and the sensitivity is high. The harm to human body health in the DES detectionprocess is effectively reduced, and meanwhile, the cost is saved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
PD-L1 affinity peptide with anti-tumour activity and application for same
ActiveCN103304638BGood antitumor activityInduce apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesPD-L1In vivo
The invention discloses a PD-L1 affinity peptide P1 with anti-tumour activity, which is the polypeptide obtained by phage display peptide library screening, wherein the amino acid sequence thereof is FPNWSLRPMNQM, and the molecular weight thereof is1520.7. The affinity peptide P1 with anti-tumour activity and aiming at a PD-L1 target disclosed by the invention has the advantage of being screened with a high flux by utilizing a phage display peptide library screening technology for the first time; and via an in-vivo tumour-bearing experiment for Kunming mice, the affinity peptide P1 disclosed by the invention is proved to have a great anti-tumour activity, can induce the internal tumour cell apoptosis of mice, and have an extremely high killing capacity for tumour cells. Via the affinity peptide P1 disclosed by the invention, new thoughts and theoretical basis are provided for research and development on medicines based on PD-L1.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
PD-l1 IgV affinity peptide S10 with antitumor activity
ActiveCN104086627BGood antitumor activityInhibit growthPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsScreening techniquesHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
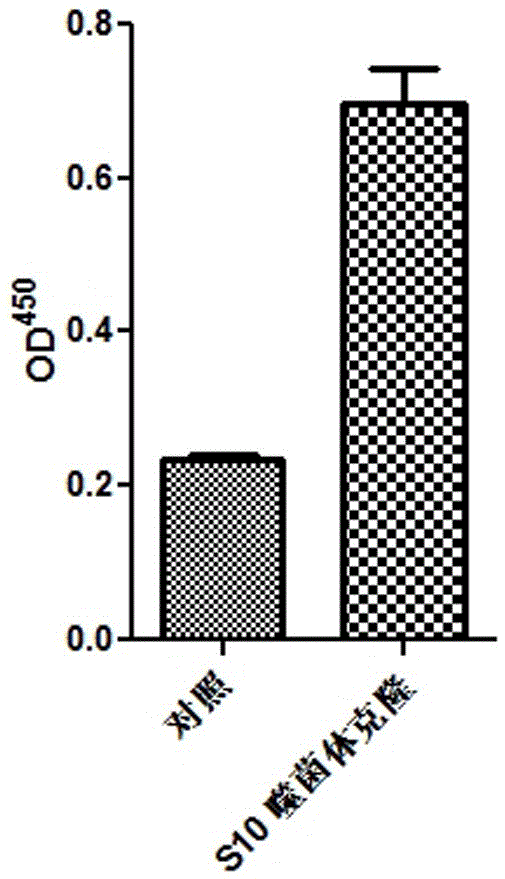
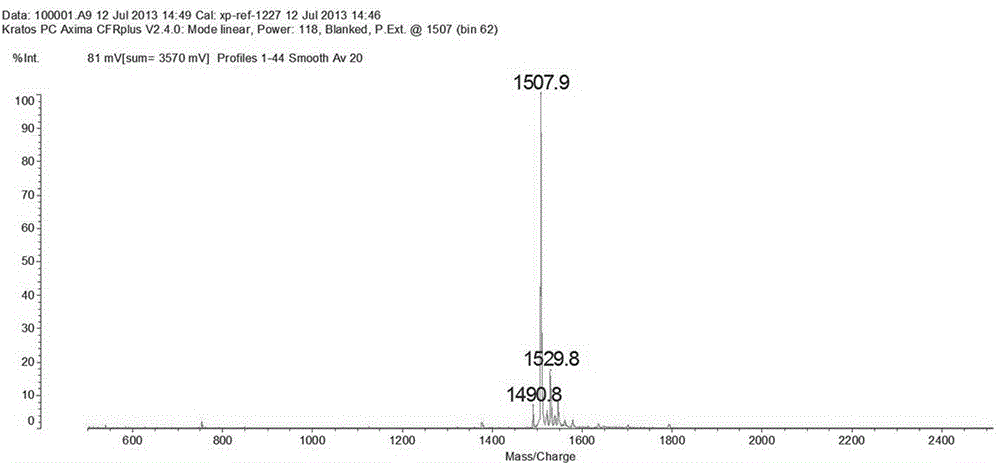
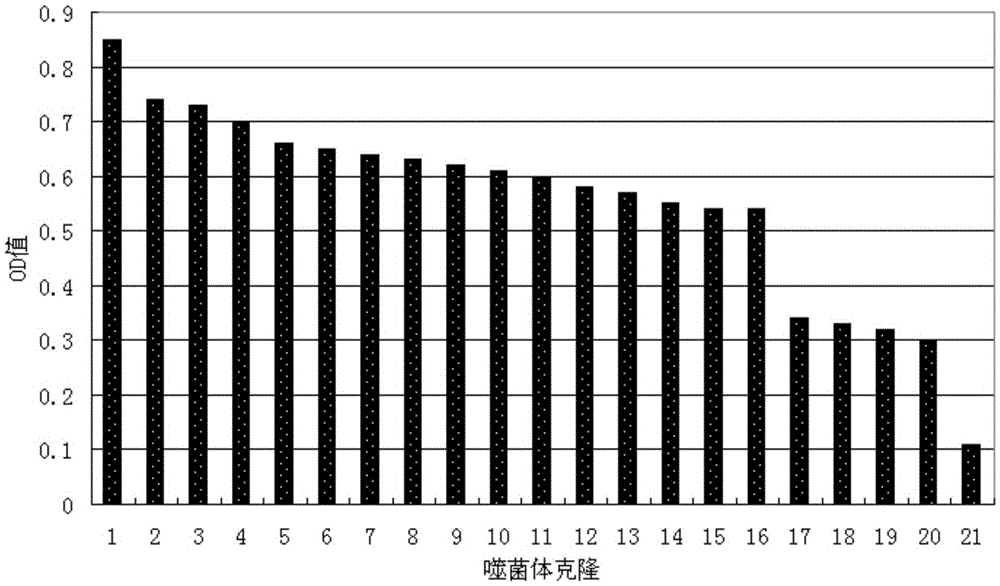
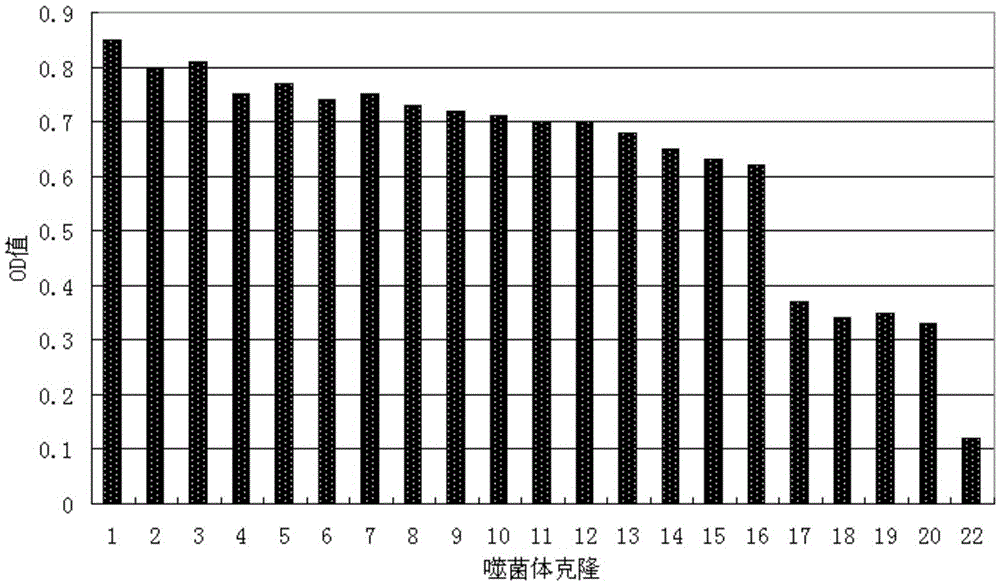
The invention belongs to the technical field of biopharmaceuticals, and in particular relates to an affinity peptide S10 product targeting PD-L1 IgV with anti-tumor activity and its preparation and application. The affinity peptide S10 specifically binds to the PD-L1 IgV region, its amino acid sequence is WSHGGHQHFIRF, and its molecular weight is 1507.7. The affinity peptide S10 is prepared by the Fomc solid-phase peptide synthesis method, and plays a role as the main active ingredient in the preparation of anti-colon cancer drugs. The affinity peptide S10 provided by the present invention is obtained by high-throughput screening with PD-L1 IgV as the target by using phage display peptide library screening technology. Through tumor-bearing experiments in mice, the inventors proved that the affinity peptide S10 has good anti-tumor activity and can significantly inhibit the growth of tumors in mice, thereby providing new ideas and ideas for the research and development of drugs based on PD-L1. theoretical basis.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
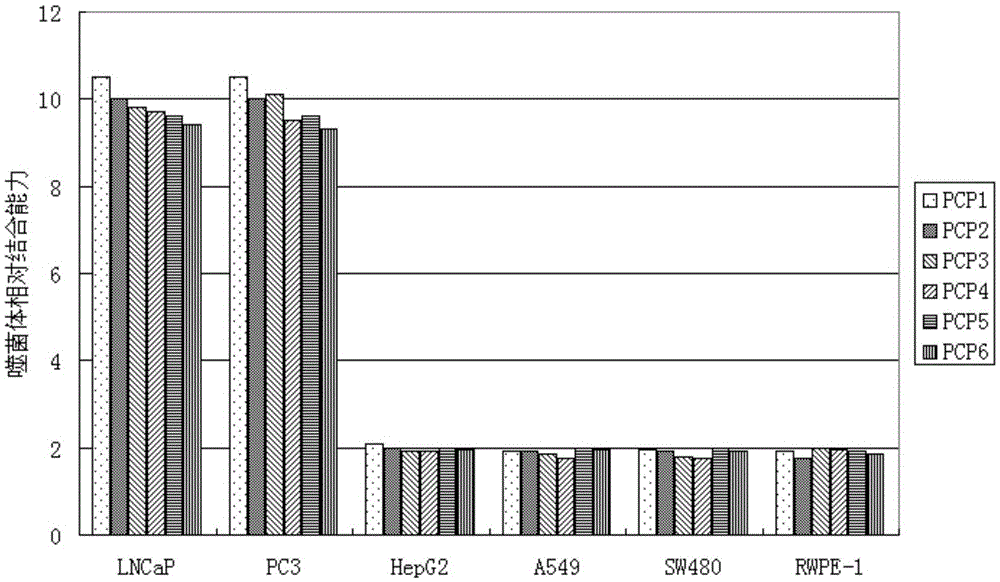
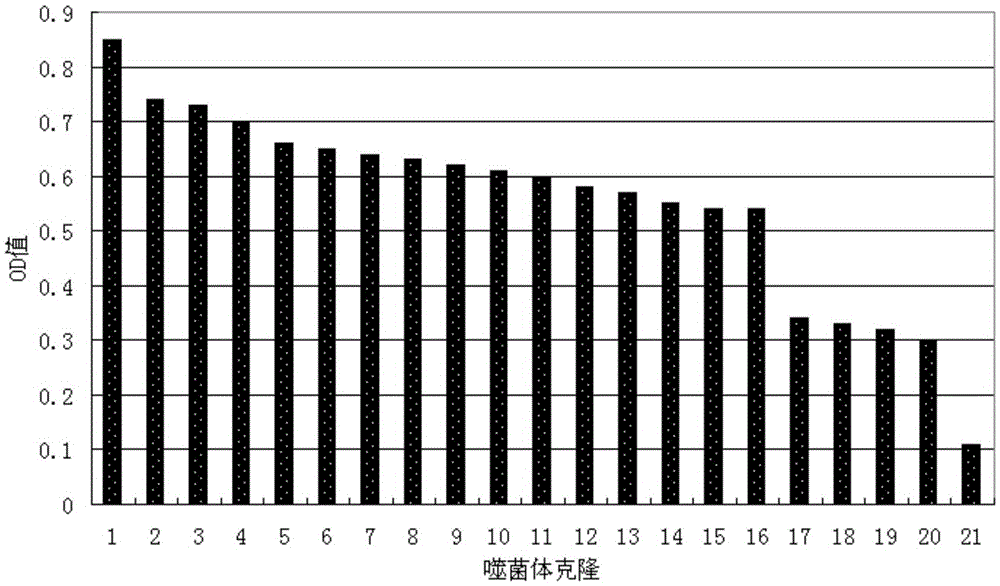
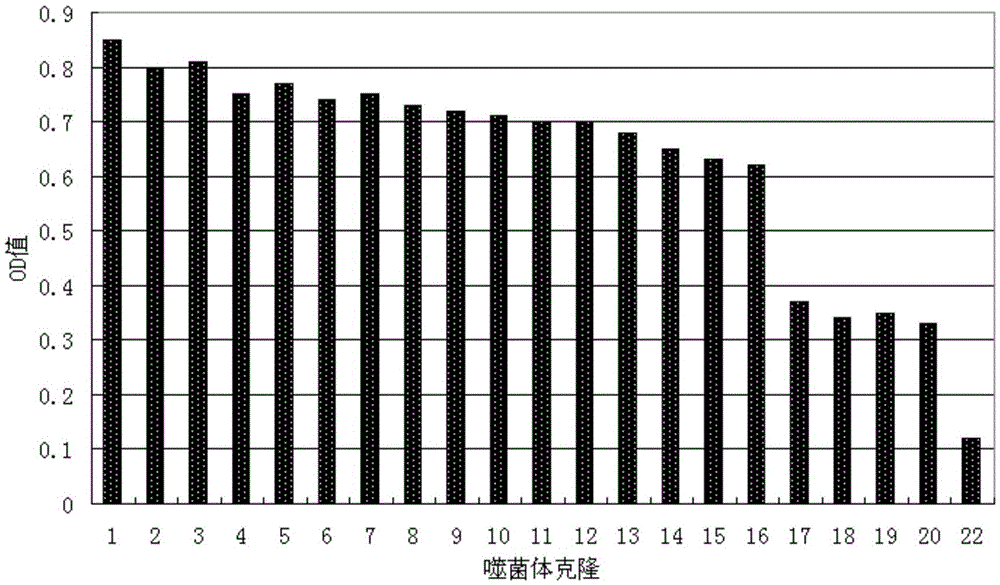
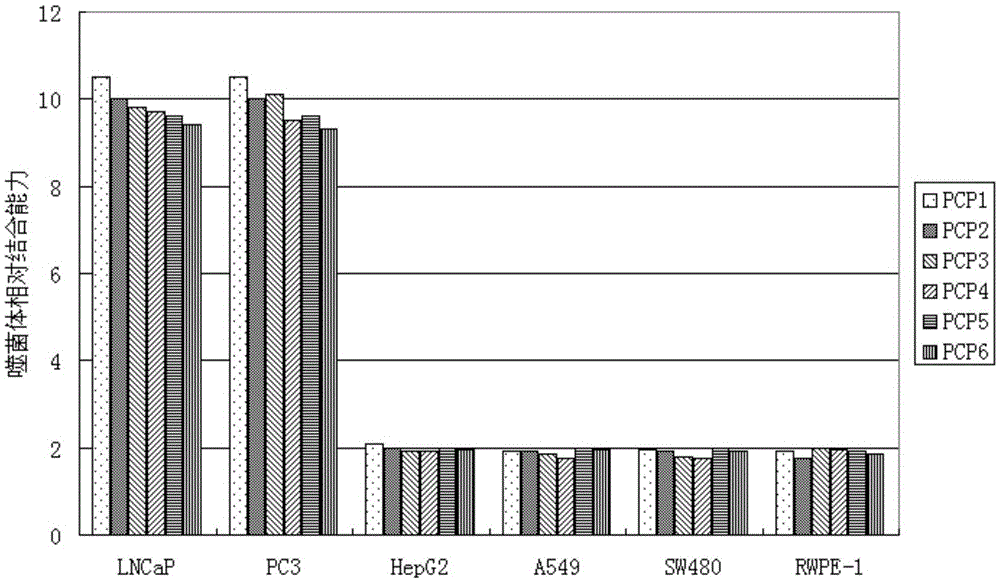
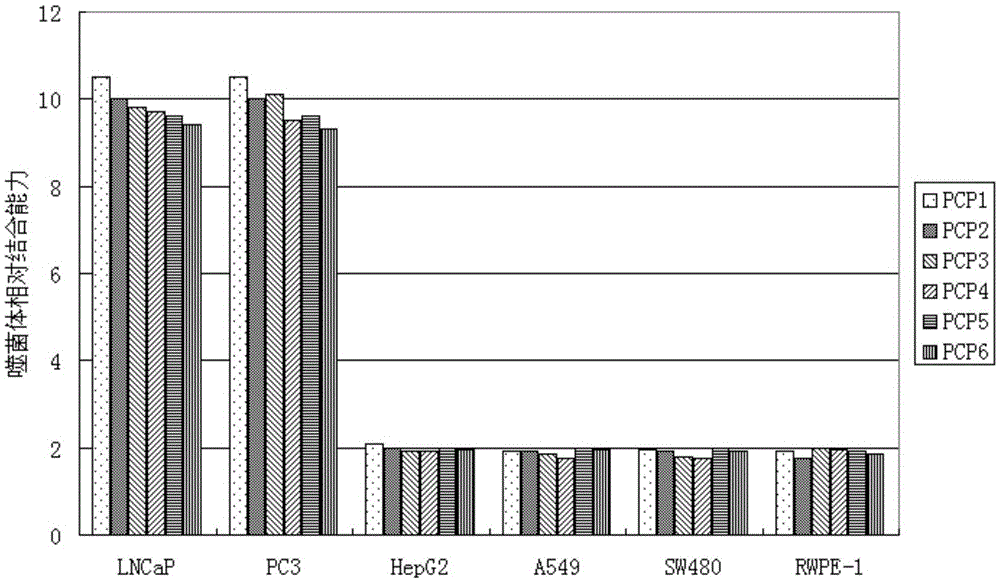
Short-chain polypeptides PCP14 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and application of short-chain polypeptides PCP14
InactiveCN105646665ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingProstate cancer cellPhage Display Peptide Library
The invention provides a series of polypeptides obtained through screening with a phage display peptide library technology and having a prostate cancer targeting characteristic. The binding polypeptides have high specificity and can be applied to general survey of high risk groups of the prostate cancer, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancer and evaluation of a treatment effect.
Owner:朱育盼
Short-chain polypeptides PCP4 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and application of short-chain polypeptides PCP4
InactiveCN105646663ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingProstate cancer cellPhage Display Peptide Library
The invention relates to short-chain polypeptides PCP4 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and an application of the short-chain polypeptides PCP4 and provides a series of polypeptides obtained through screening with a phage display peptide library technology and having a prostate cancer targeting characteristic. The binding polypeptides have high specificity and can be applied to general survey of high risk groups of the prostate cancer, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancer and evaluation of a treatment effect.
Owner:朱育盼
Defense peptides against fungal infection and method of their use
InactiveUS20110271400A1High expressionHigh recovery rateFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyAsian soybean rust
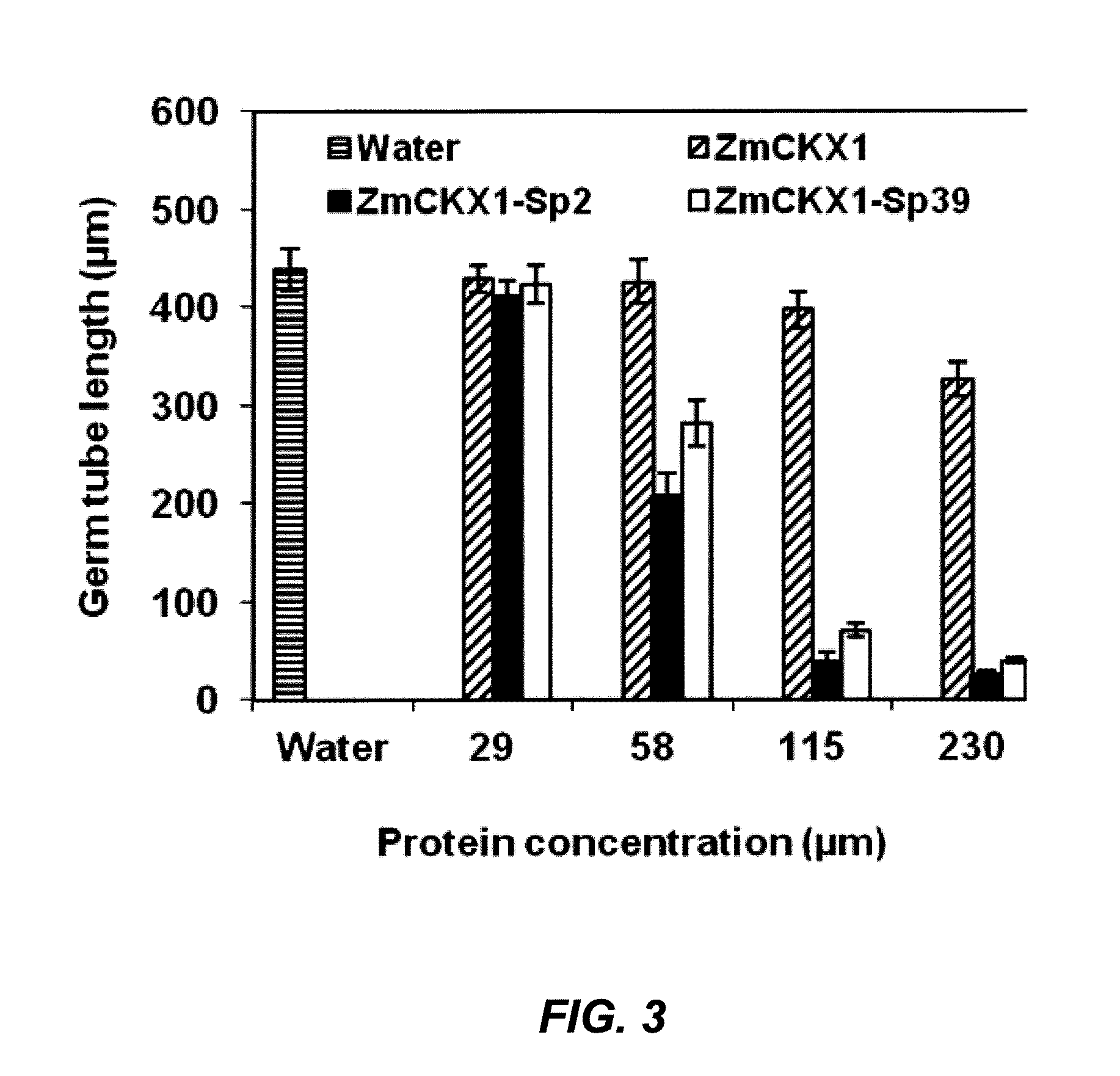
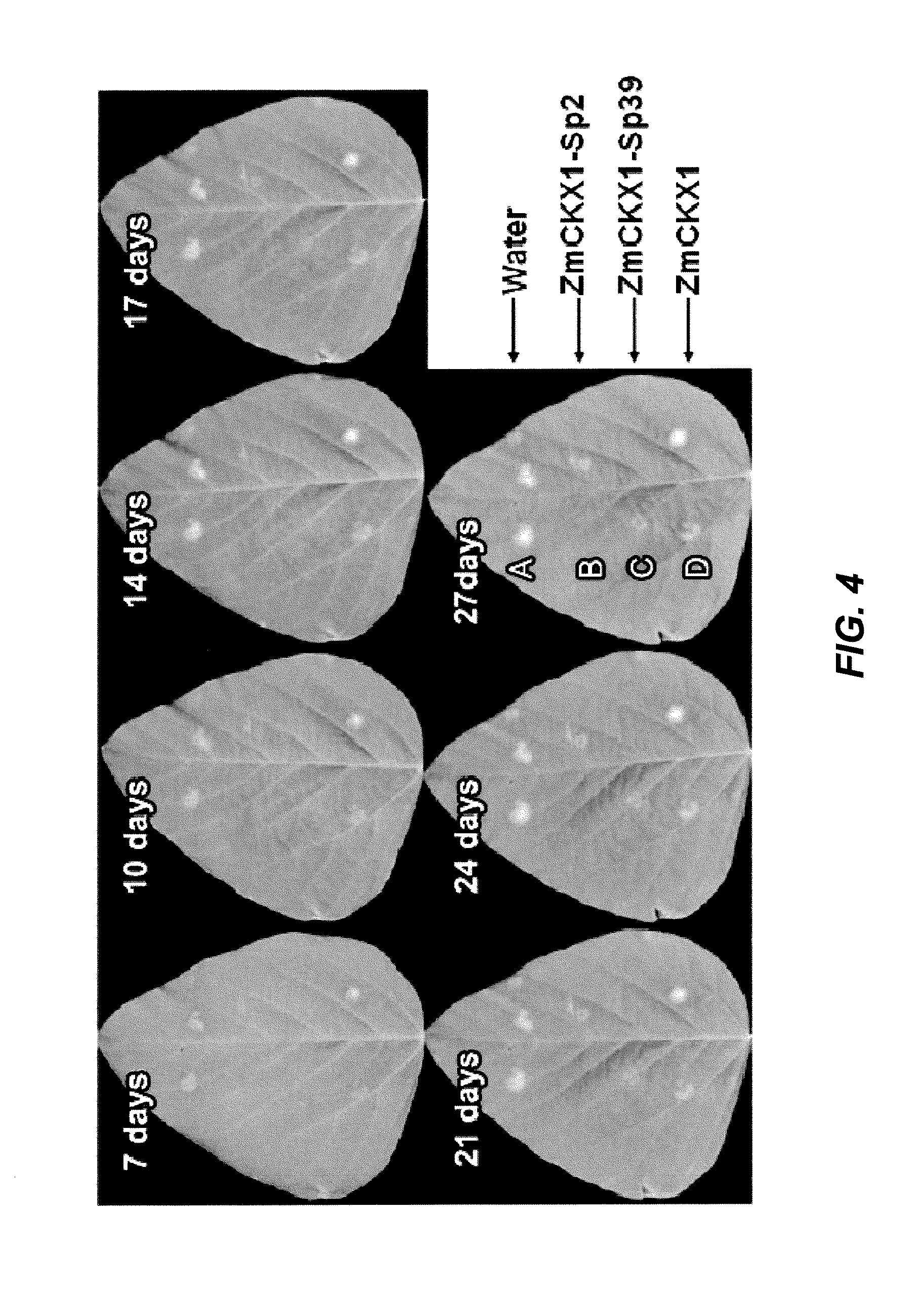
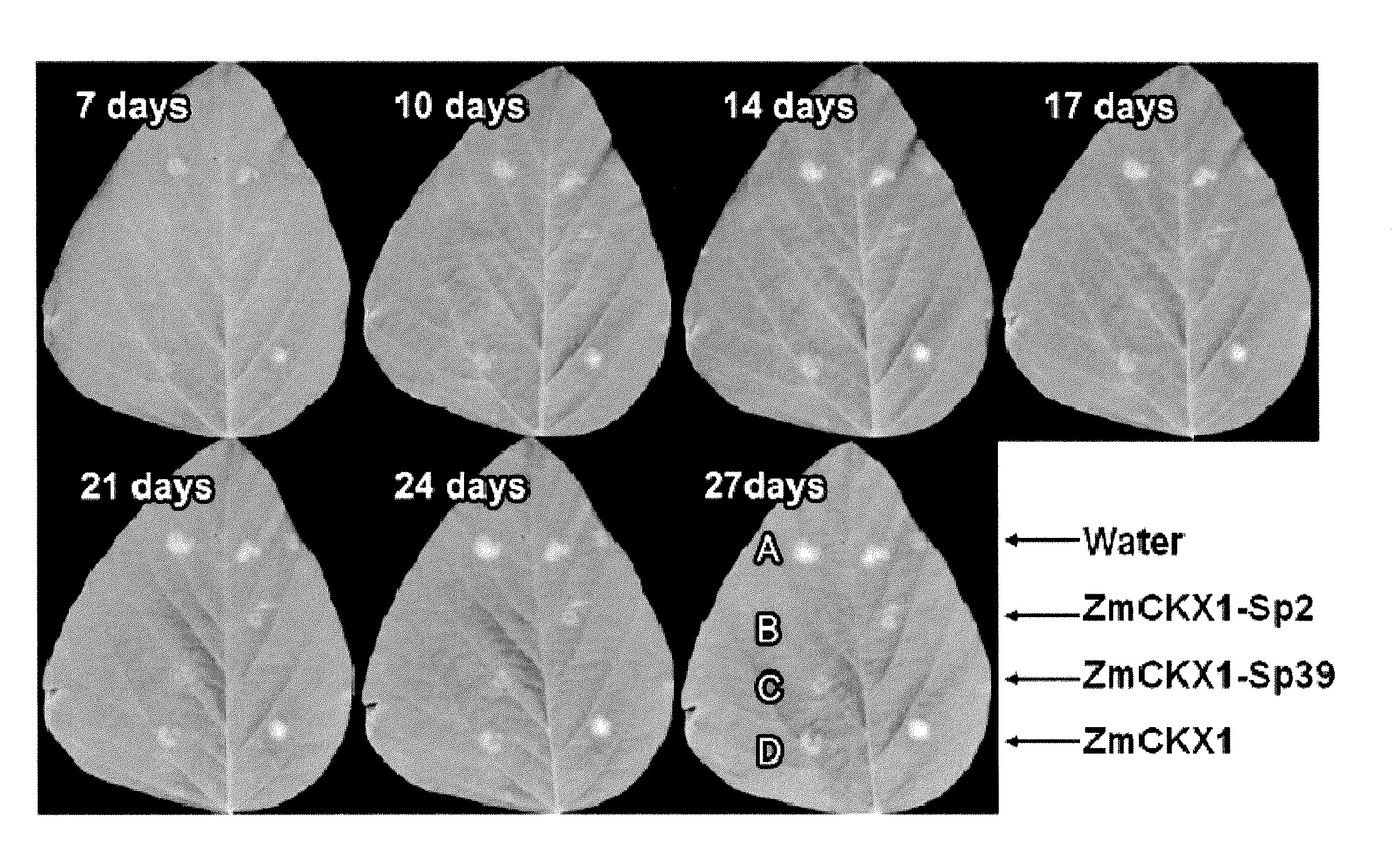
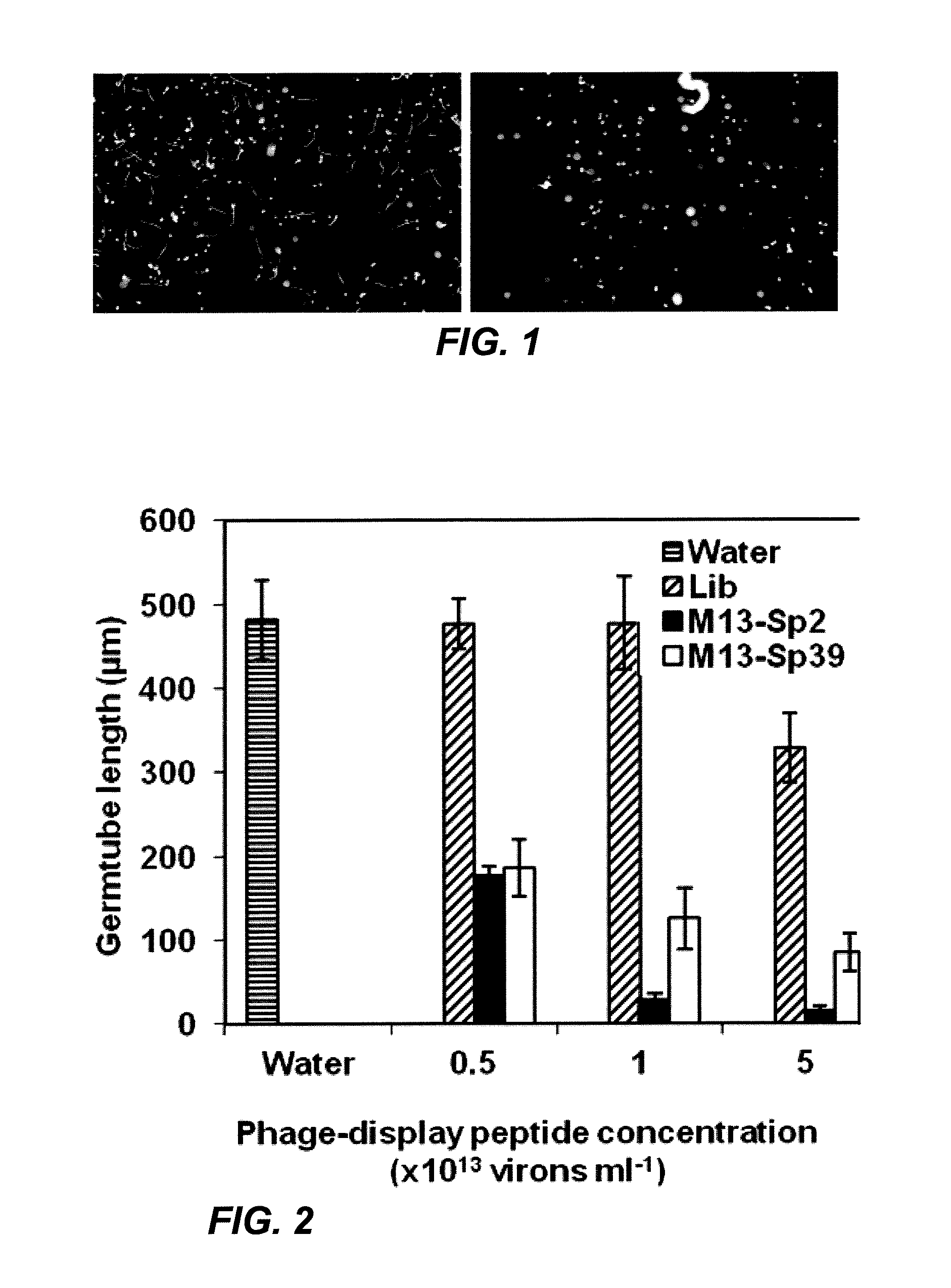
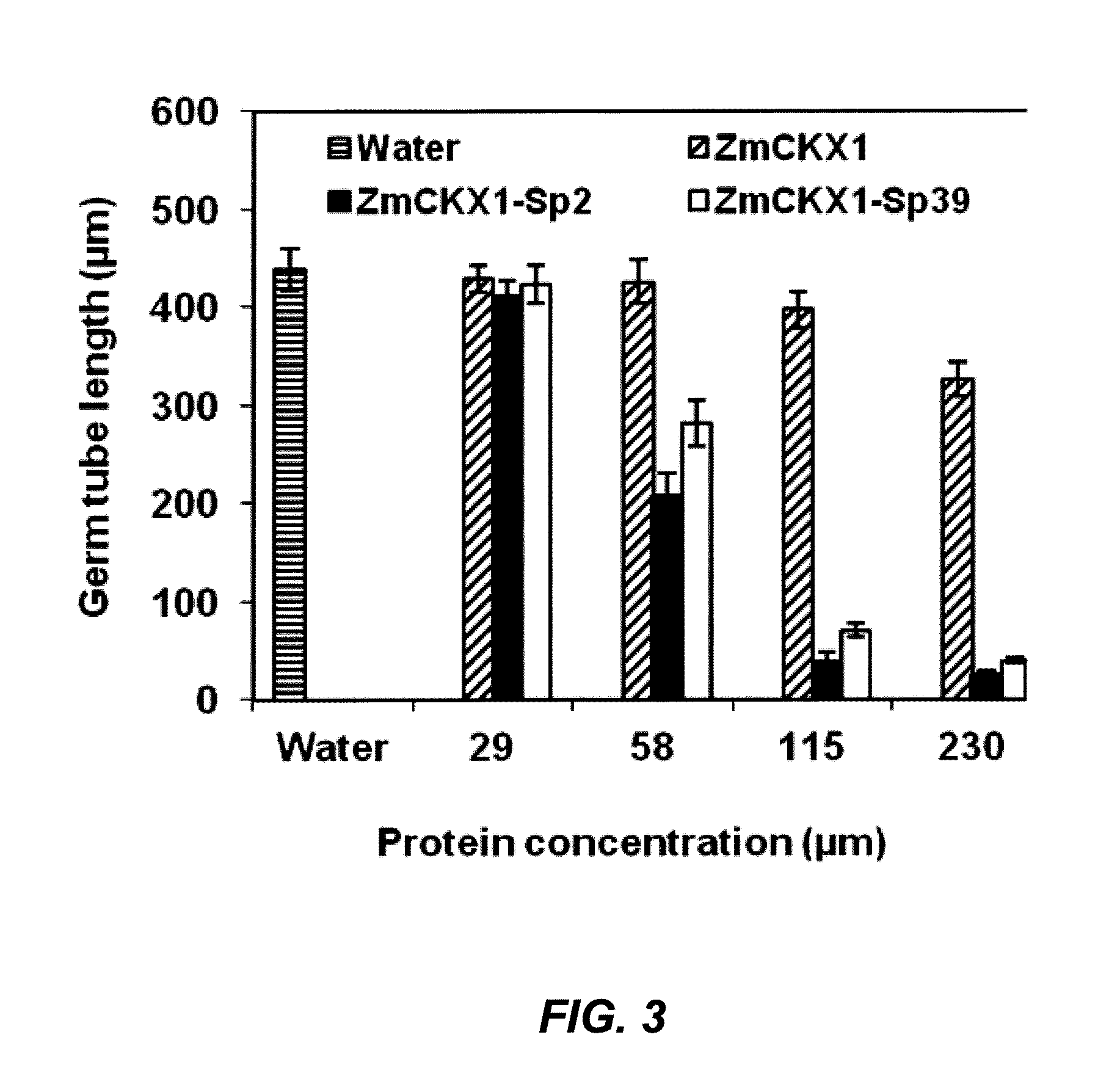
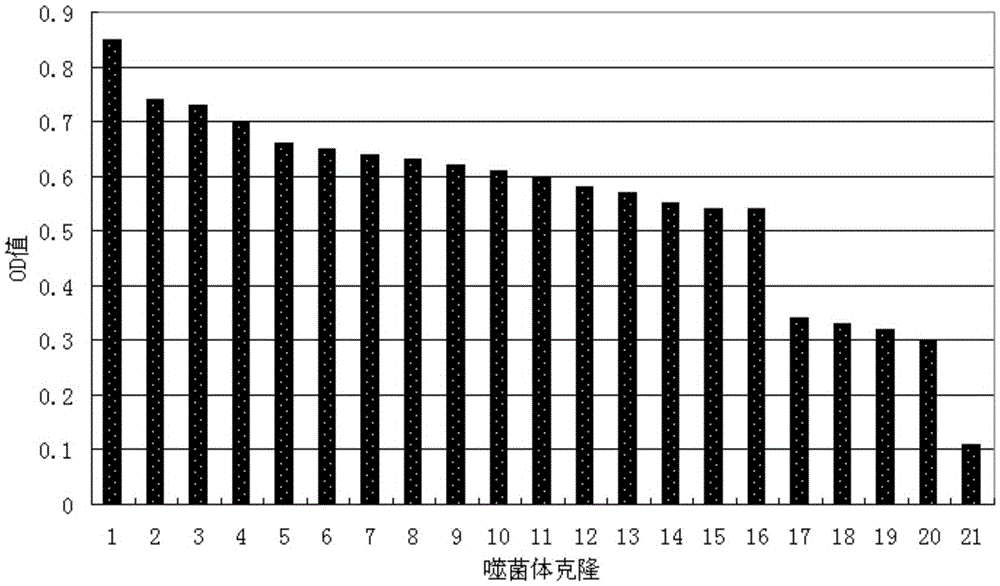
Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the fungal pathogen that causes Asian soybean rust, has the potential to cause significant losses in soybean yield in many production regions of the U.S. To assist the development of new modes of soybean resistance to fungal infection, peptides were identified from combinatorial phage-display peptide libraries which inhibit germ tube growth from urediniospores of P. pachyrhizi. Two peptides, Sp2 and Sp39, were identified that inhibit germ tube development when displayed as fusions with the coat protein of M13 phage or as fusions with maize cytokinin oxidase / dehydrogenase (ZmCKX1). These peptides may be used in vitro to help control fungal infection. These peptides may also be expressed as transgenes in a plant to help the resulting transgenic plant defend against the fungi
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Short-chain polypeptides PCP9 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and application of short-chain polypeptides PCP9
InactiveCN105646662ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingProstate cancer cellTreatment effect
The invention provides a series of polypeptides obtained through screening with a phage display peptide library technology and having a prostate cancer targeting characteristic. The binding polypeptides have high specificity and can be applied to general survey of high risk groups of the prostate cancer, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancer and evaluation of a treatment effect.
Owner:朱育盼
Preparation method of peptide ligand for non-competitive detection of water-soluble pesticide residues
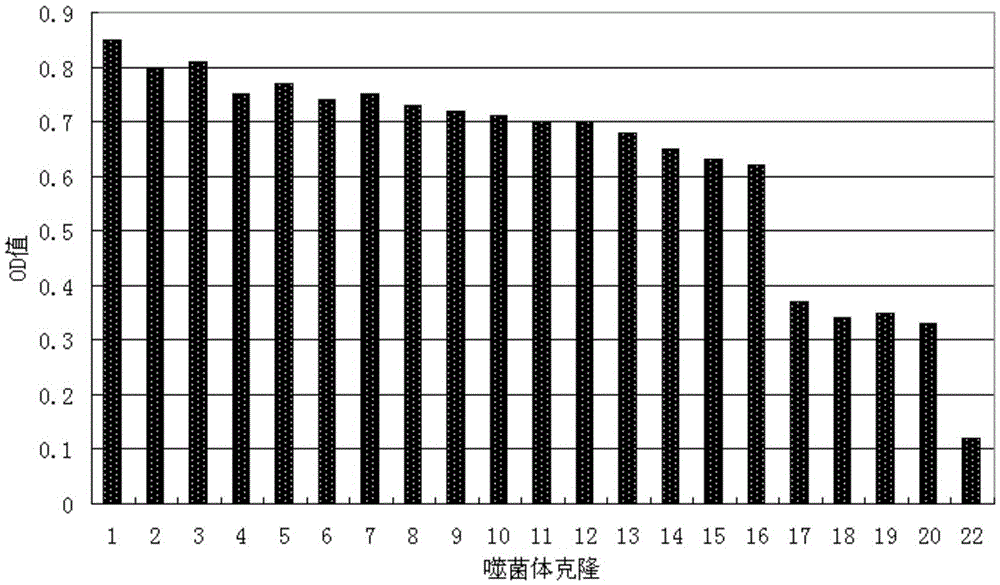
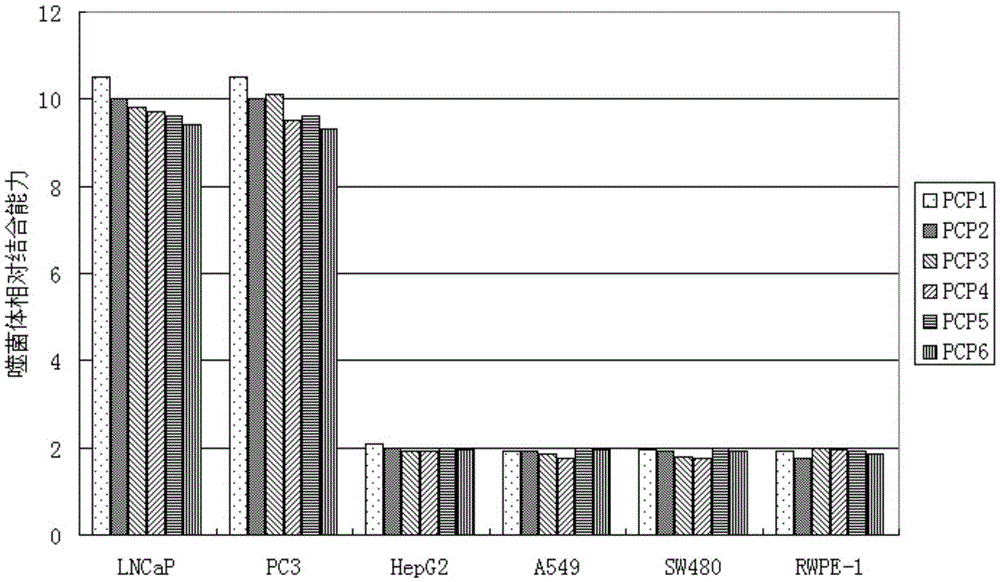
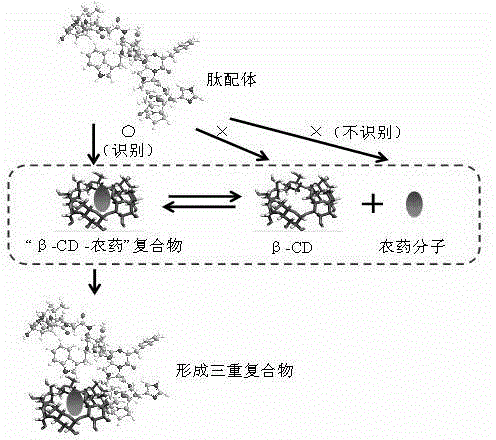
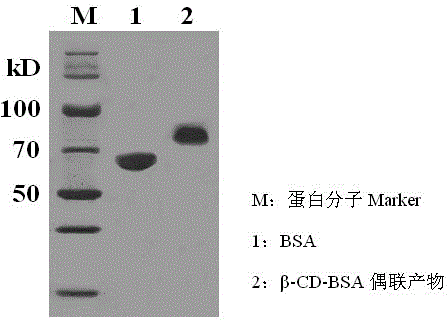
The invention discloses a preparation method of a peptide ligand for non-competitive detection of water-soluble pesticide residues. The preparation method comprises the following steps: coupling beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) with bovine serum albumin (BSA), enveloping the coupling products with a solid phase carrier to complex with chlorpyrifos; performing four-round screening on commercialized phage display peptide libraries by using 'positive and negative alternative screening' strategy; separating and selecting mono phage clones from the fourth-round screening elution products, identifying the mono phage clone capable of specifically recognizing 'beta-CD-pesticide' complex; finally sequencing the identified phage clone to determine the insertion of polypeptide fragment and obtain the amino acid sequence information of the polypeptide. The preparation method has the advantages that the molecular modification of the detection object is not needed, and the obtained peptide ligand is used for constructing the non-competitive detection of water-soluble pesticide residues.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF ARTS & SCI +1
GD3 peptide mimics
InactiveUS6998237B1Easy to controlSymptoms improvedPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGd3 gangliosidePhage Display Peptide Library
The present invention provides peptide mimics for GD3 ganglioside. The peptide mimics were identified by panning phage display peptide libraries with an anti-GD3 monoclonal antibody. The peptide mimics inhibit the binding of an anti-GD3 antibody to GD3 positive cells and also elicit antibodies which can bind to GD3 positive cells. The identified peptide mimics can be used as immunogens for cancer therapy.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
A kind of epitope peptide simulating dienestrol, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108373495BHarm reductionThe test result is accurateVector-based foreign material introductionPolypeptide with MBP-tagDienestrolElisa method
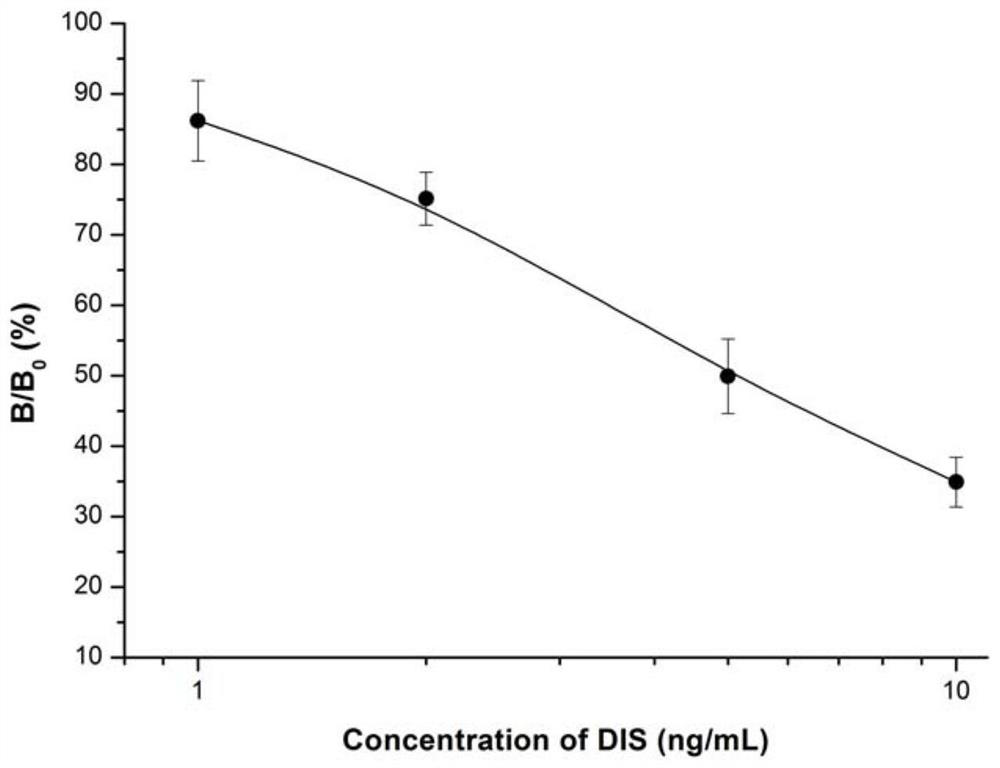
The invention provides an epitope peptide simulating dienestrol, its preparation method and application. The technical solution is firstly based on the phage display peptide library technology, with the anti-DIS monoclonal antibody as the target, and panning from the phage random display heptapeptide library to obtain a DIS antigen mimic epitope whose sequence is CTLNWAC. The present invention respectively provides methods for preparing the antigen mimetic epitope by means of phage amplification and gene recombination. The present invention designs specific detection methods based on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, colloidal gold immunochromatography and fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography around the immunological binding characteristics of the antigen mimic epitope. The antigen mimic epitope has similar immune response characteristics to the natural DIS molecule, and can replace the expensive DIS standard substance with teratogenic and carcinogenic effects for the immunological detection of DIS, with accurate detection results and high sensitivity.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Ovarian-cancer-targeted polypeptide
The invention discloses an ovarian-cancer-targeted polypeptide. The polypeptide is screened from a tumor model of ovarian cancer by using phage display peptide library technology and the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is WSGPGVWGASUK. Identification proves that the polypeptide can distinguish ovarian cancer cells from normal cells and ovarian cancer cells from other cancer cells, and thus can be combined with ovarian cancer cells specifically and be effectively internalized by the ovarian cancer cells. Serving as a medicine carrier, the polypeptide can improve the absorption of medicines. After being injected into the tumor model through vines, the polypeptide can be enriched in the tumor area of the ovarian cancer. The polypeptide is a totally new polypeptide with invivo targeting capacity proved, and the polypeptide can be used as an ideal ligand to construct a targeting carrier for transmitting anticancer medicines.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Short-chain polypeptides PCP2 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and application of short-chain polypeptides PCP2
InactiveCN105646661ASmall molecular weightNon-immunogenicPeptidesBiological testingProstate cancer cellTreatment effect
The invention relates to short-chain polypeptides PCP2 capable of being specifically bound to prostate cancer cells and an application of the short-chain polypeptides PCP2 and provides a series of polypeptides obtained through screening with a phage display peptide library technology and having a prostate cancer targeting characteristic. The binding polypeptides have high specificity and can be applied to general survey of high risk groups of the prostate cancer, early clinical diagnosis of the prostate cancer and evaluation of a treatment effect.
Owner:朱育盼
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com