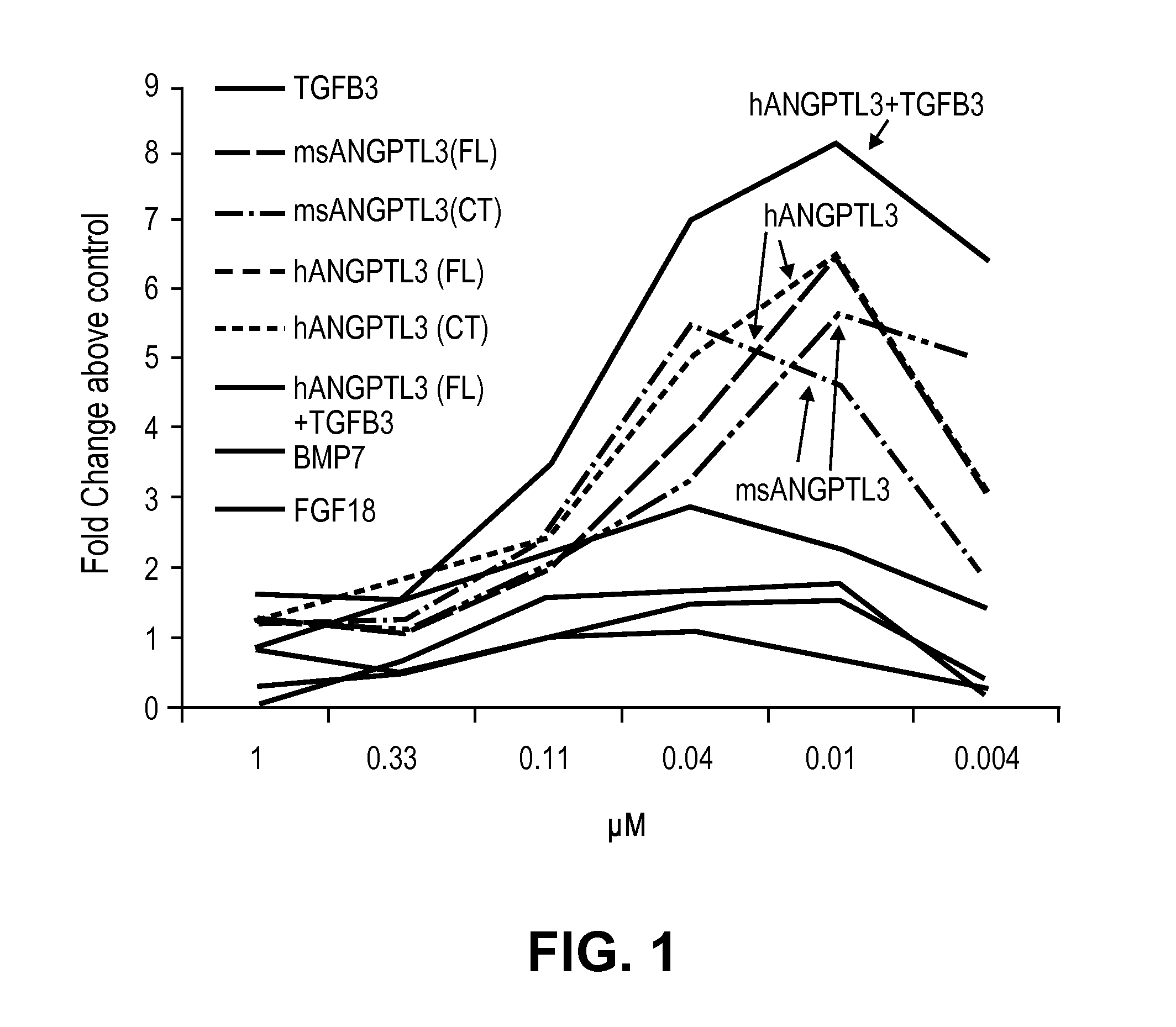
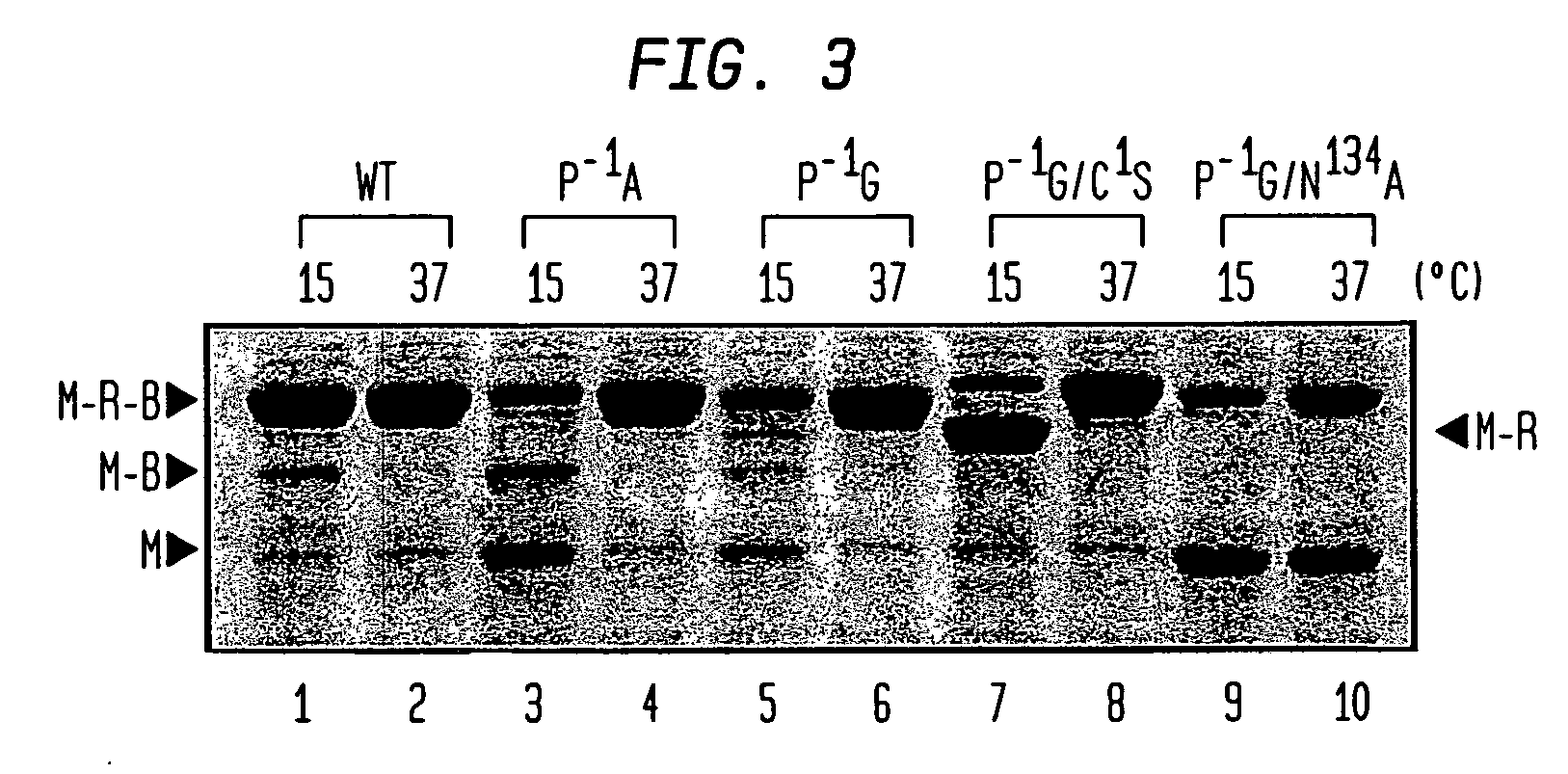
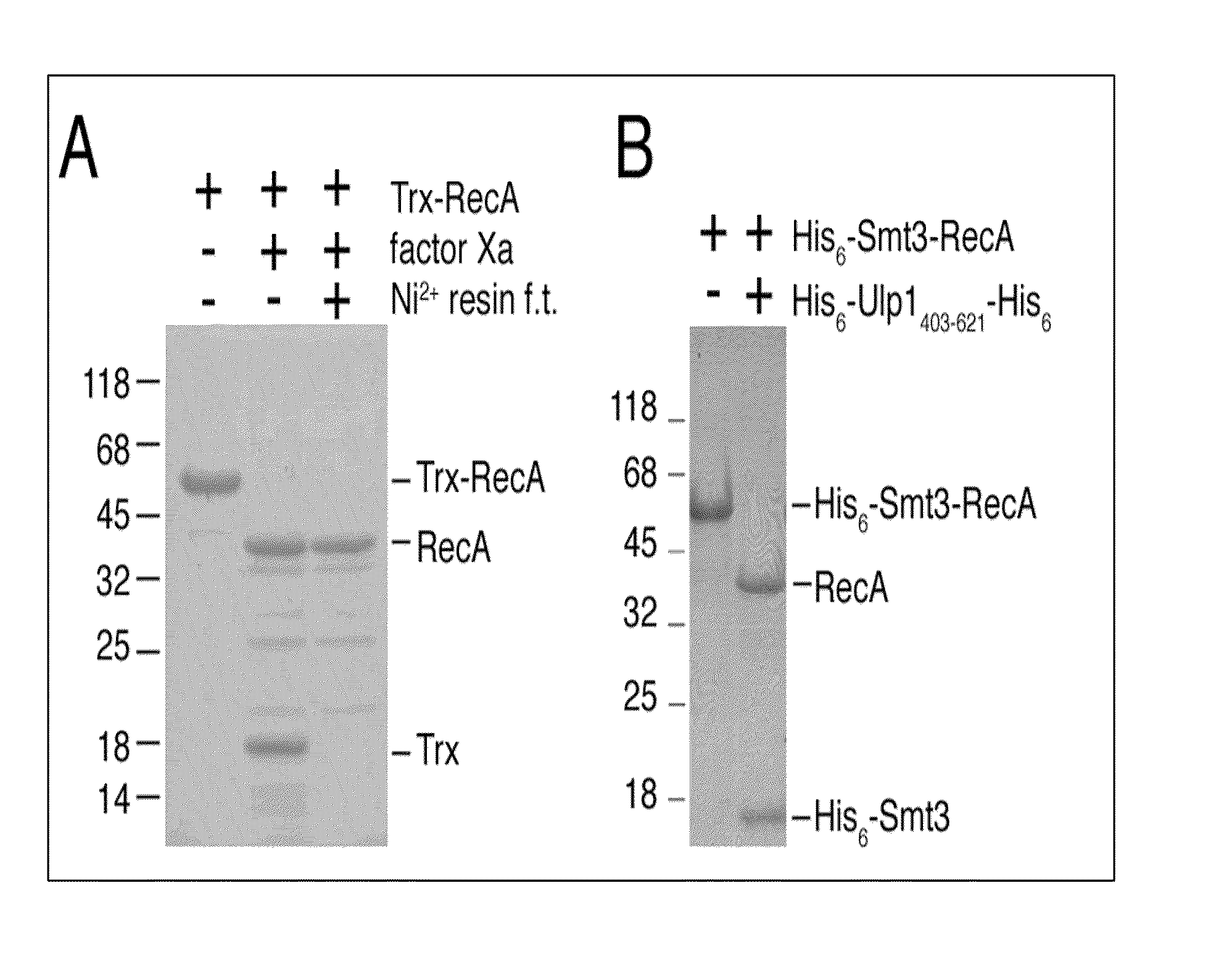
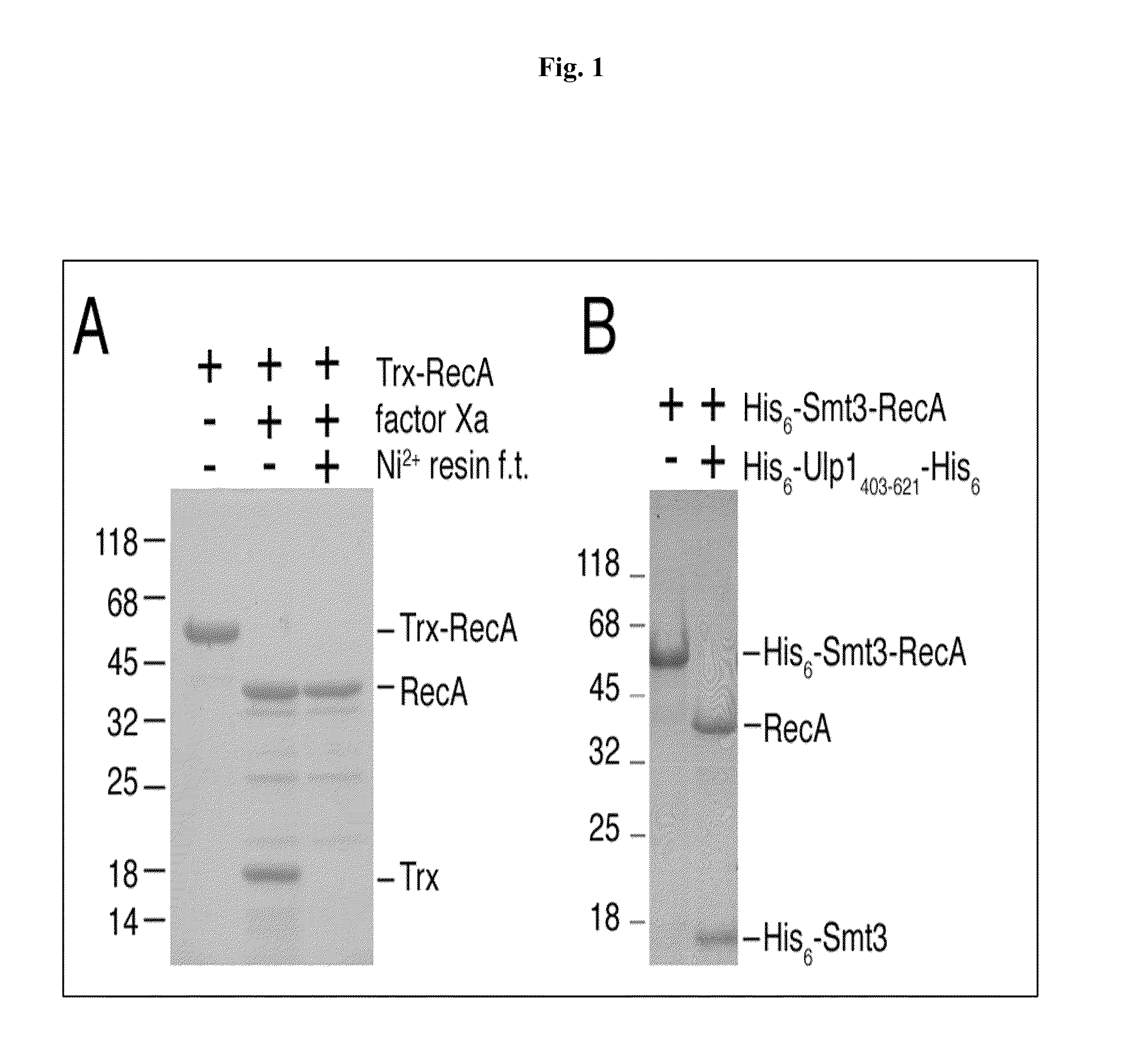
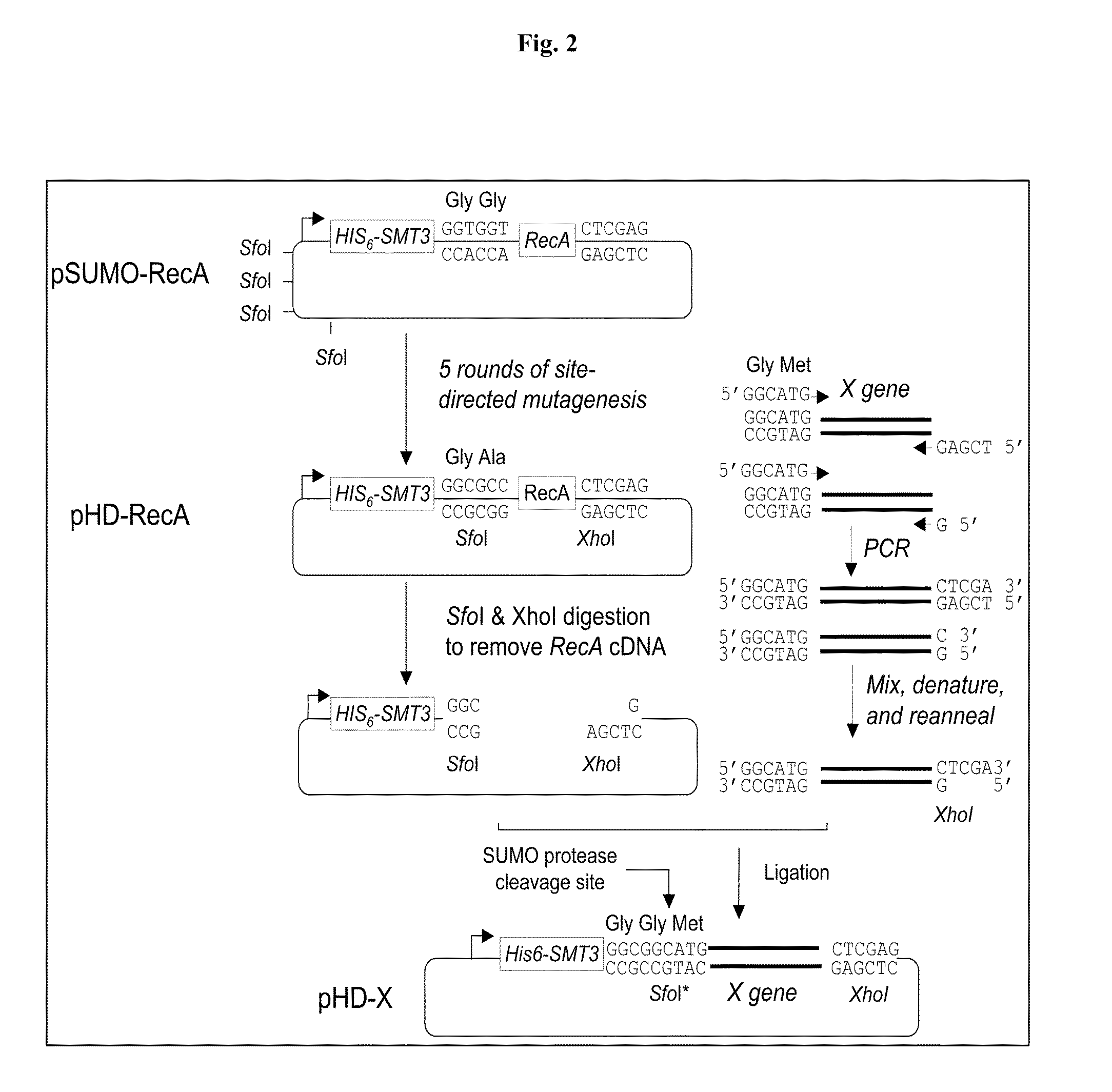
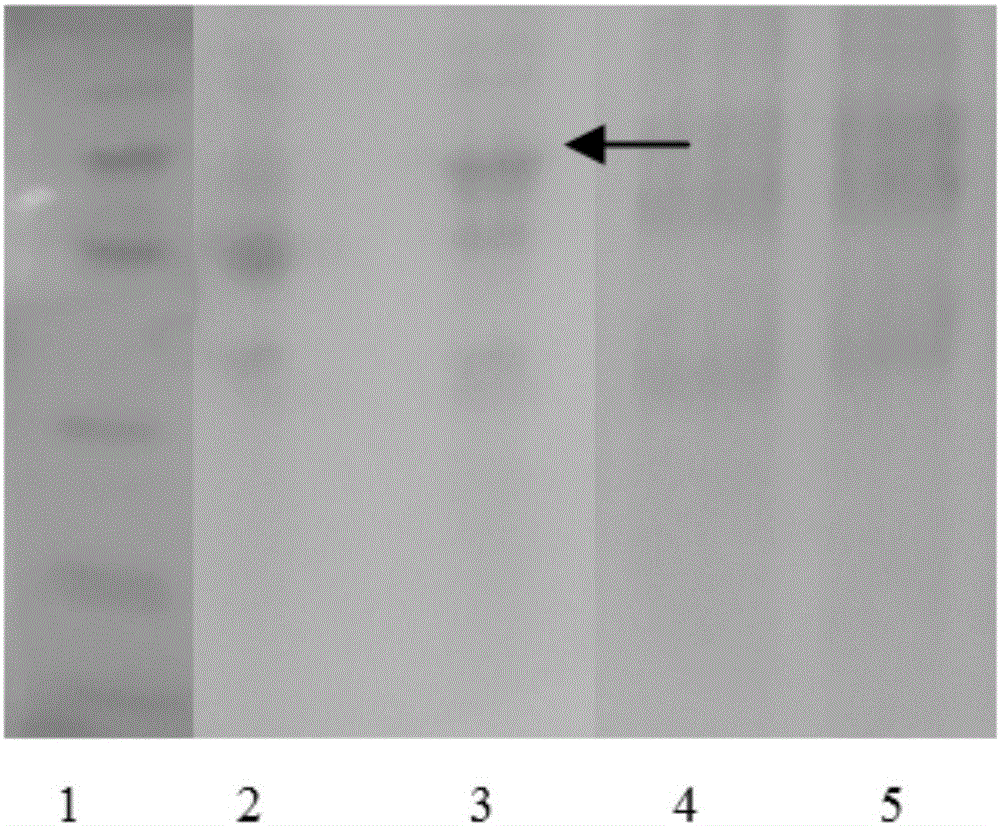
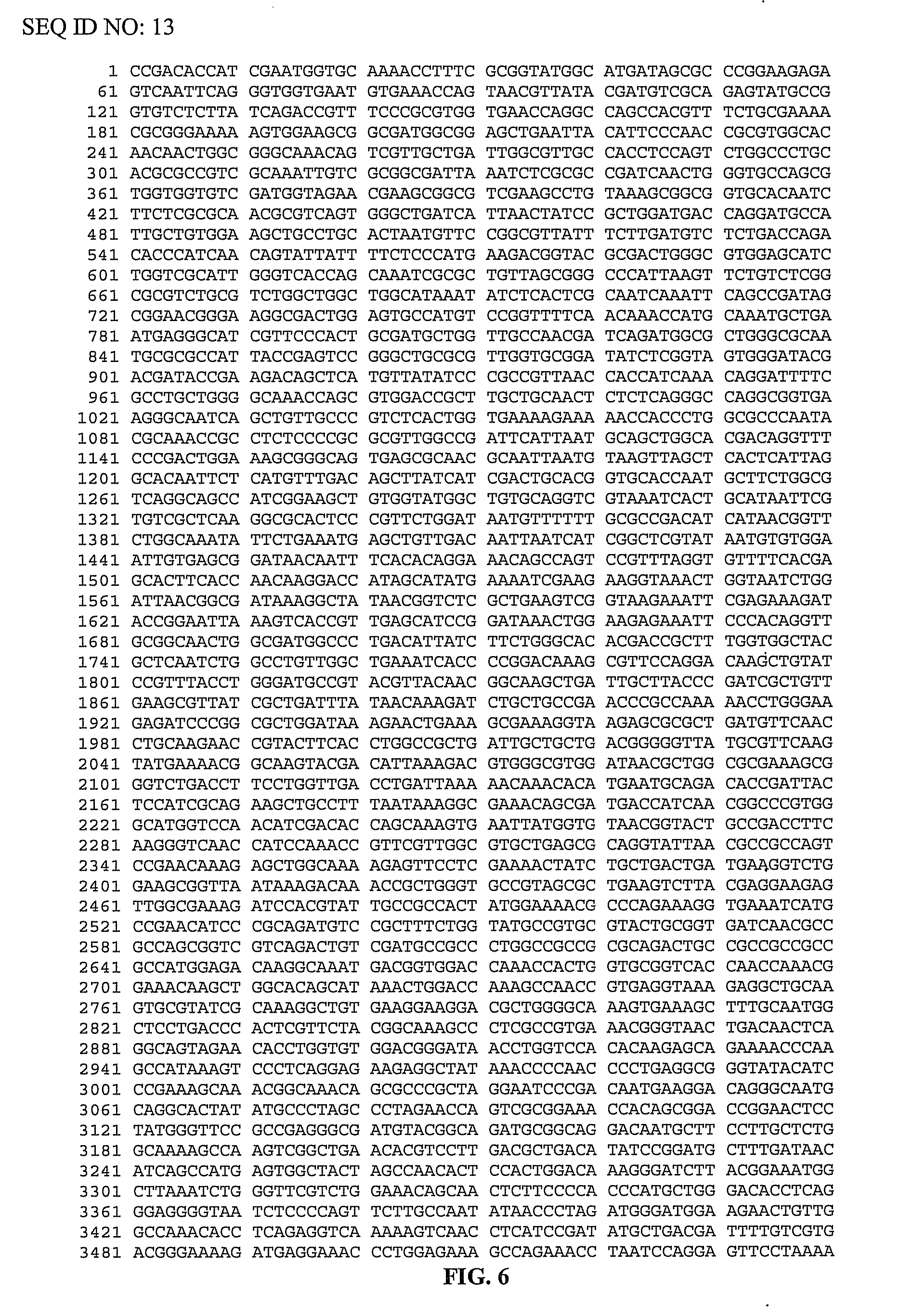
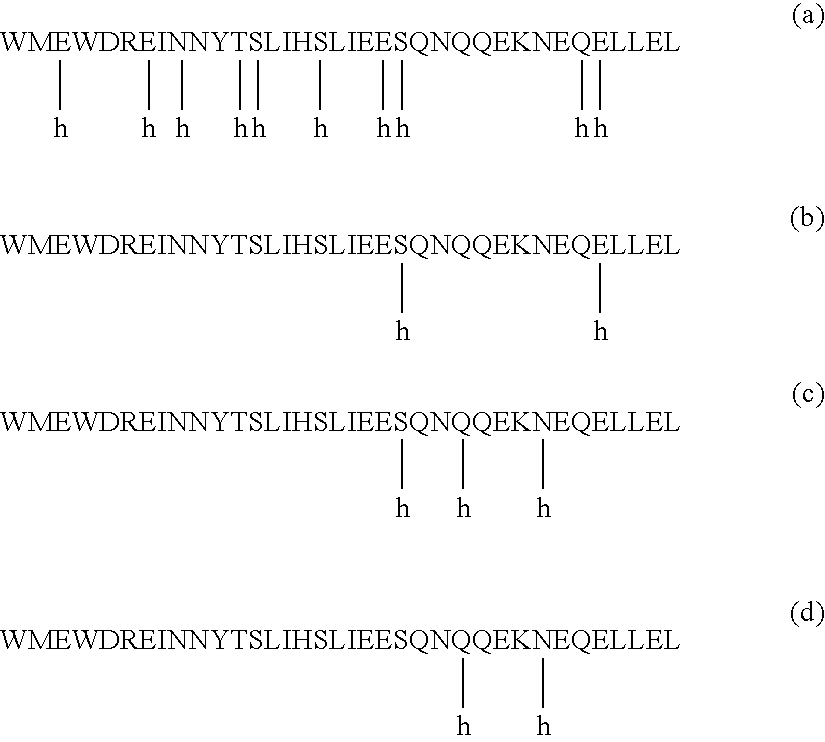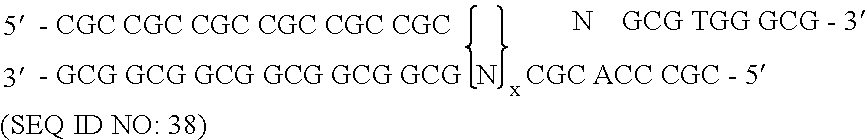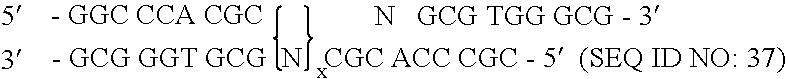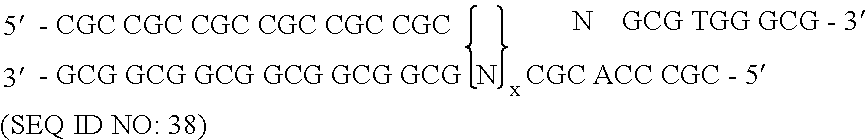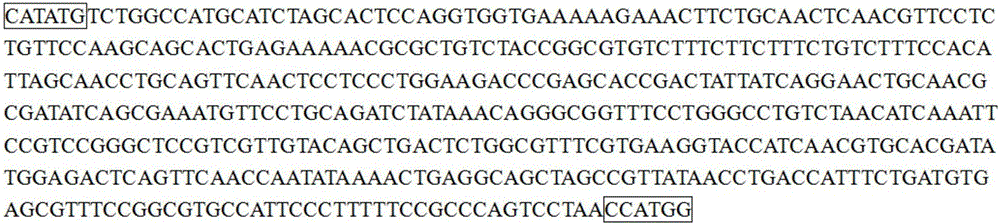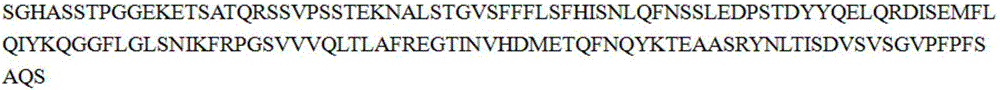Patents
Literature
184results about "Polypeptide with MBP-tag" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The insecticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing lepidopteran, coleopteran, dipteran, fungal, hemipteran, and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
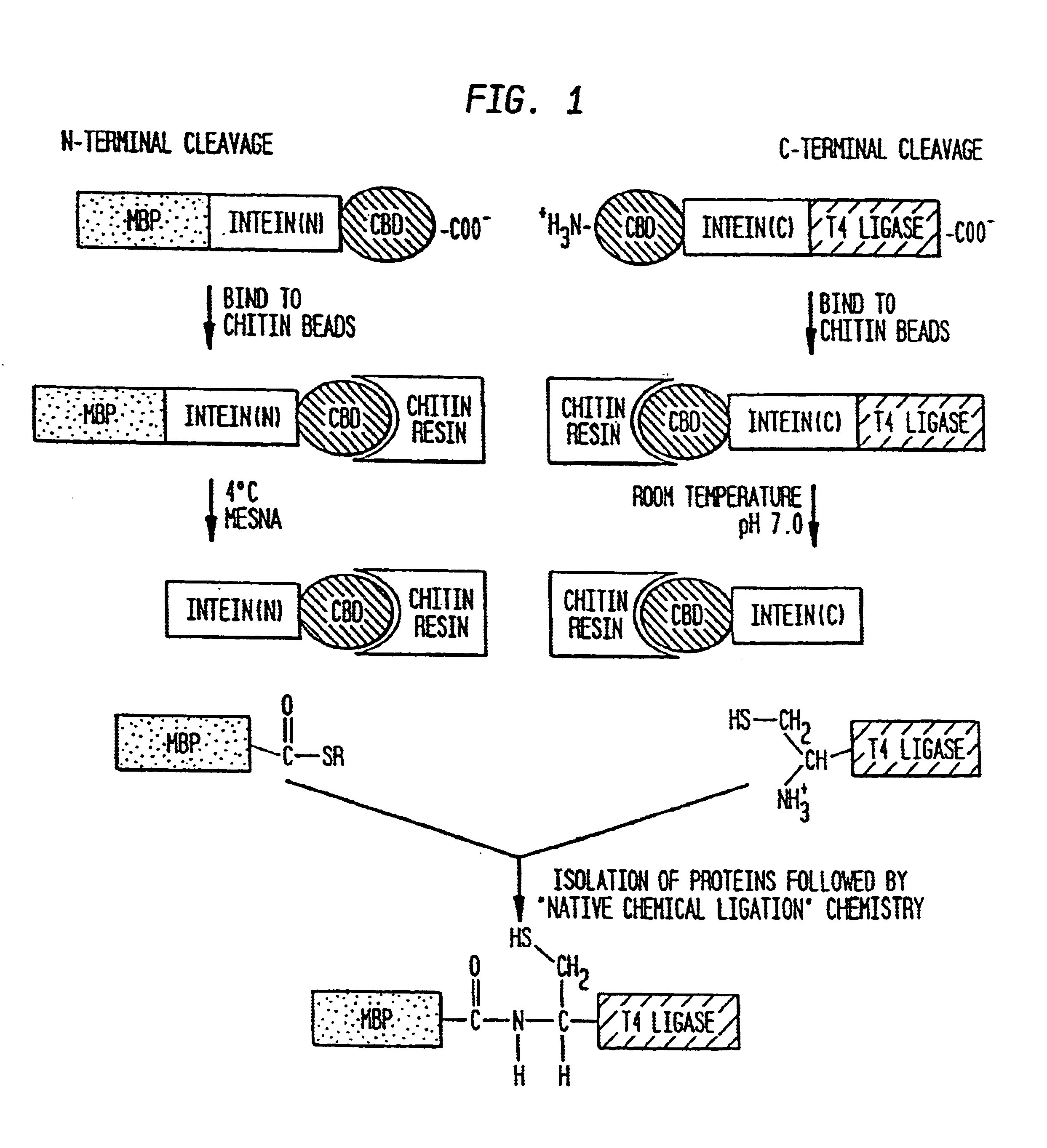
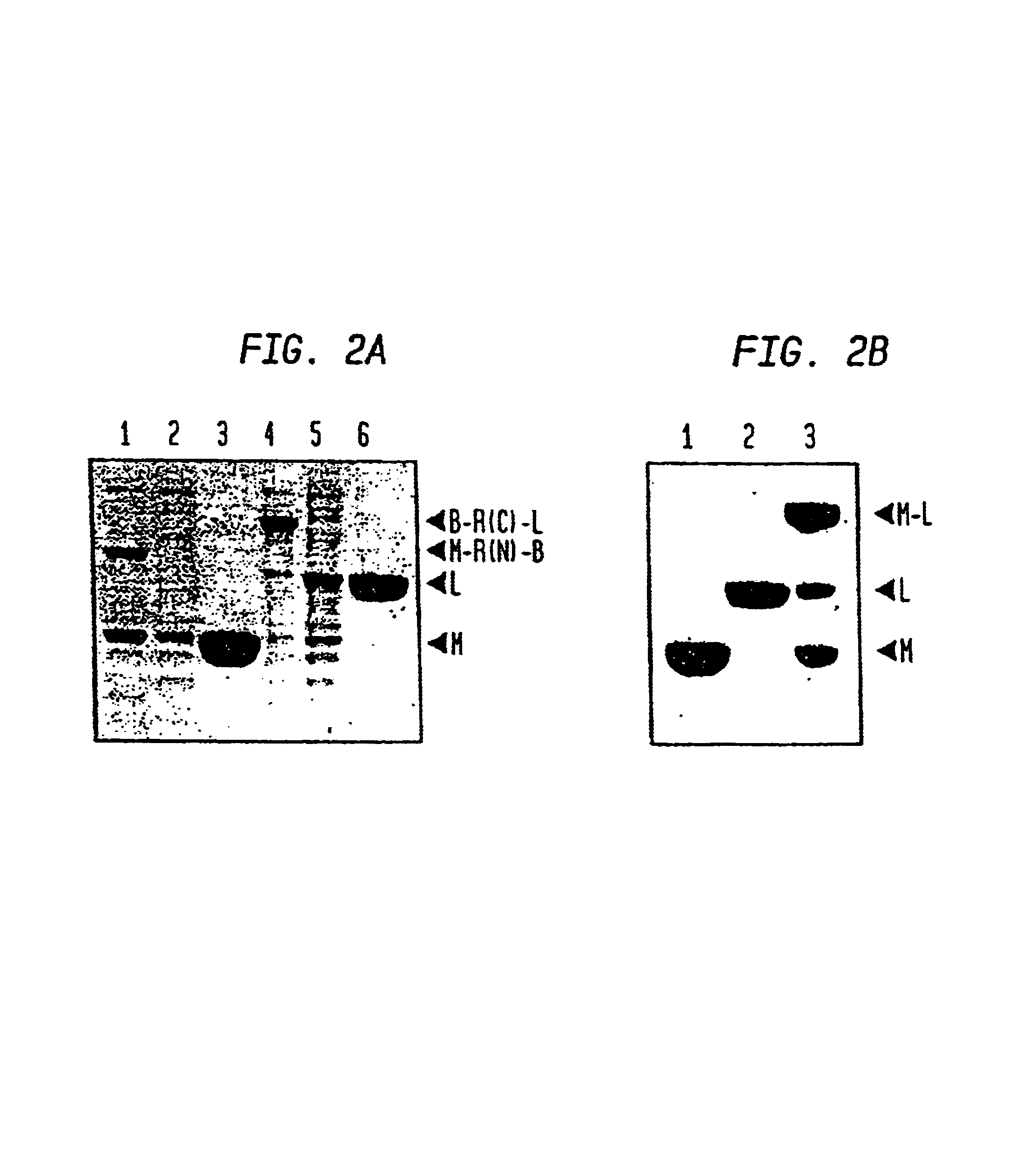
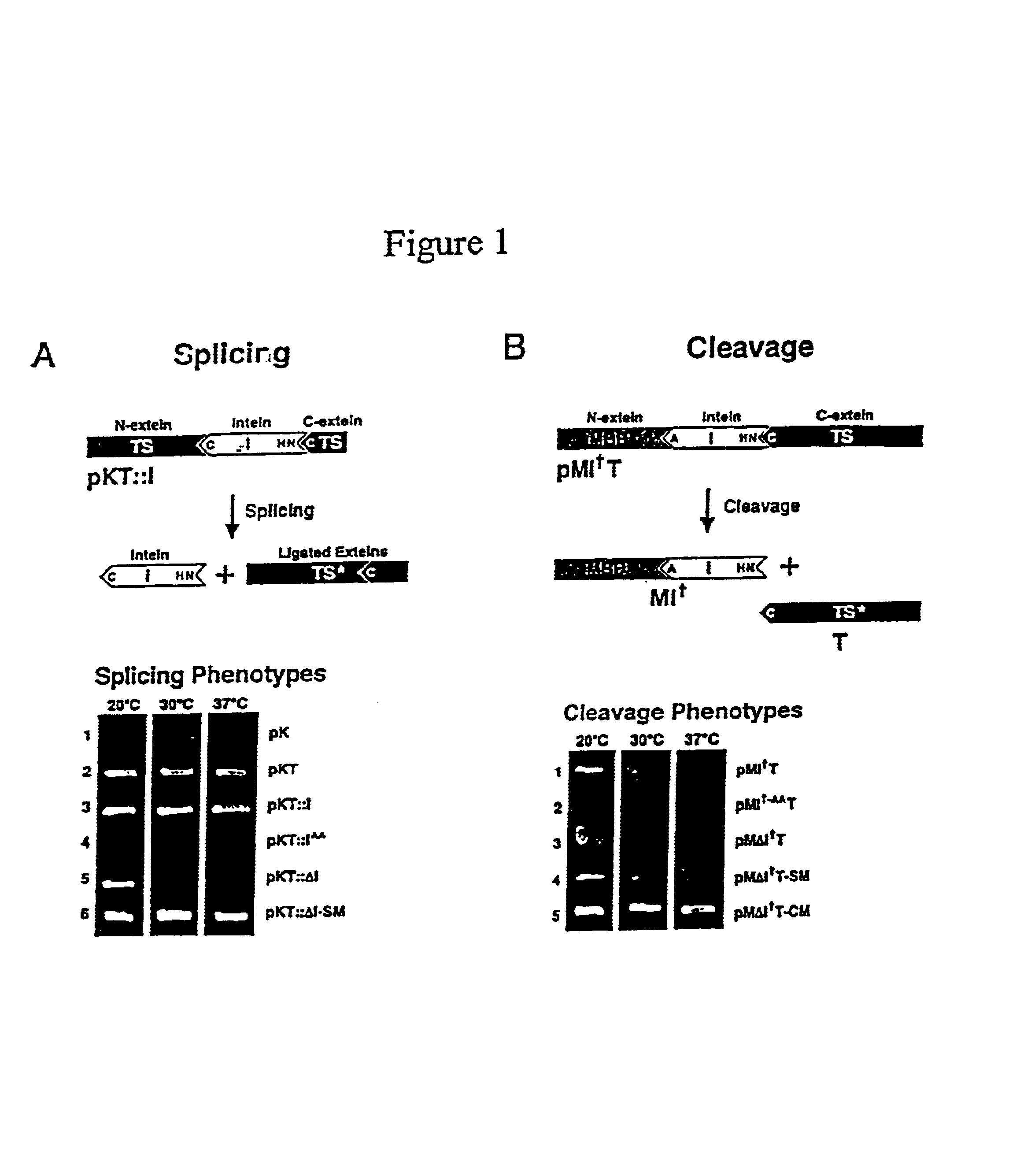
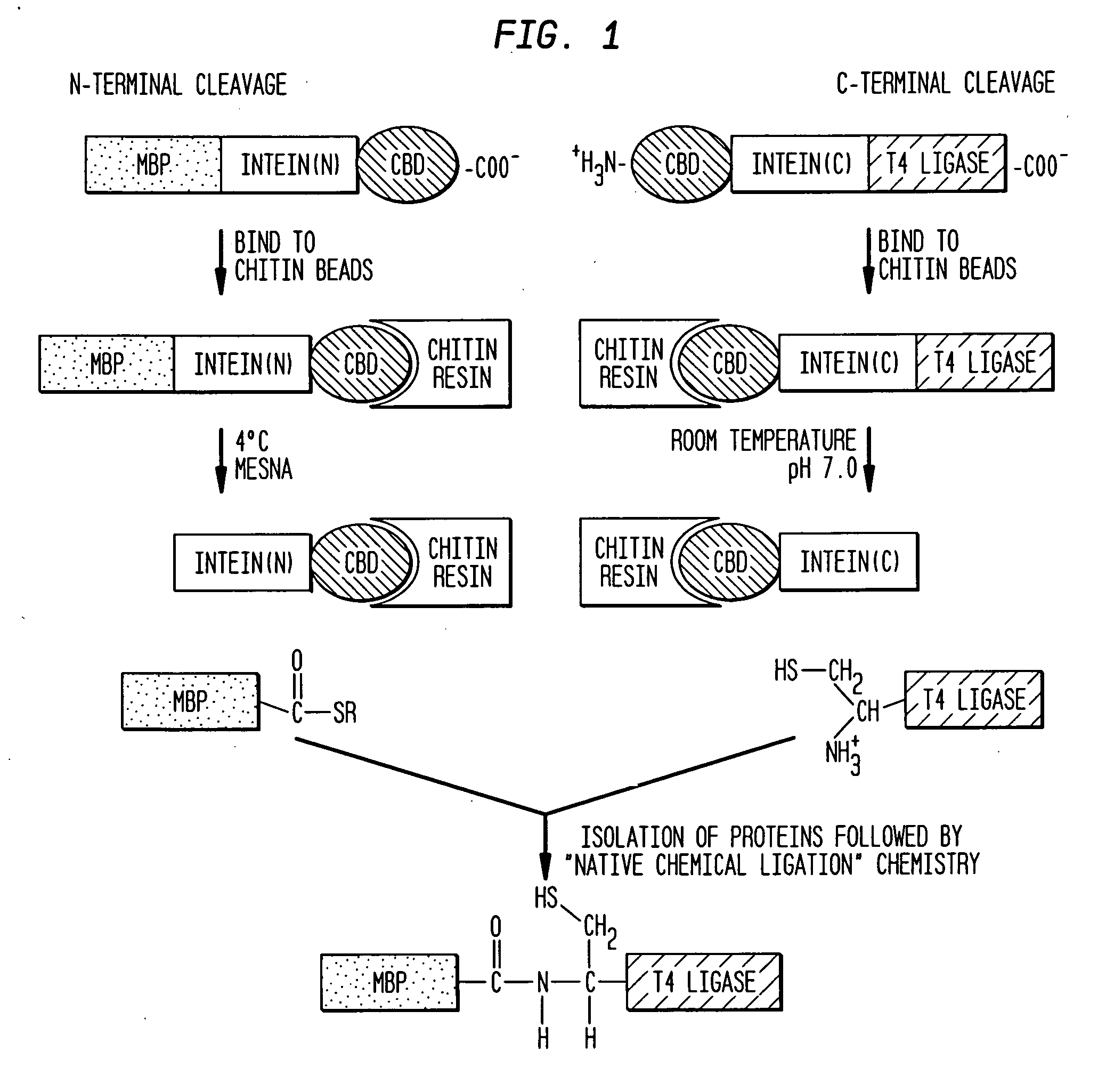
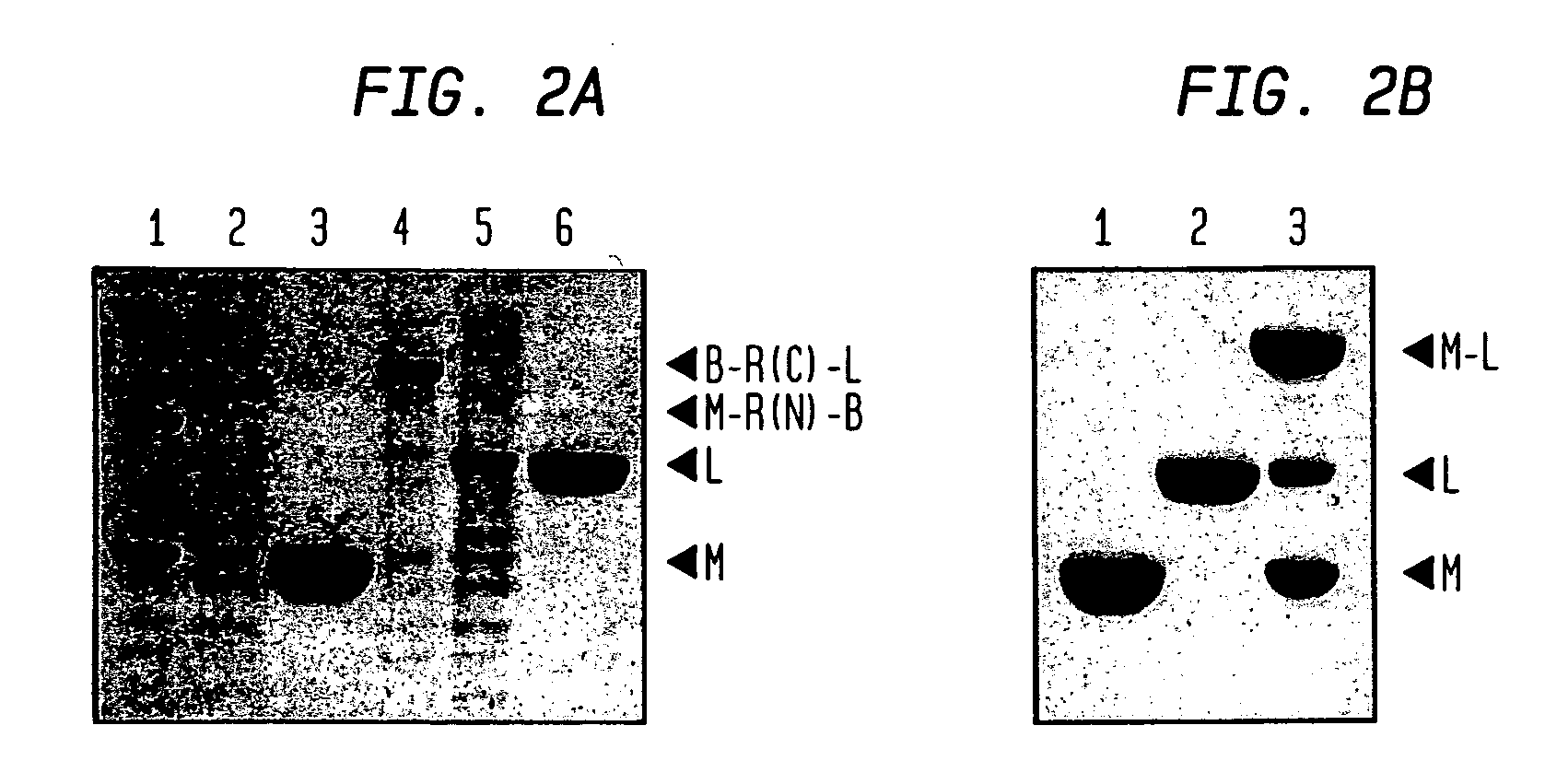
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
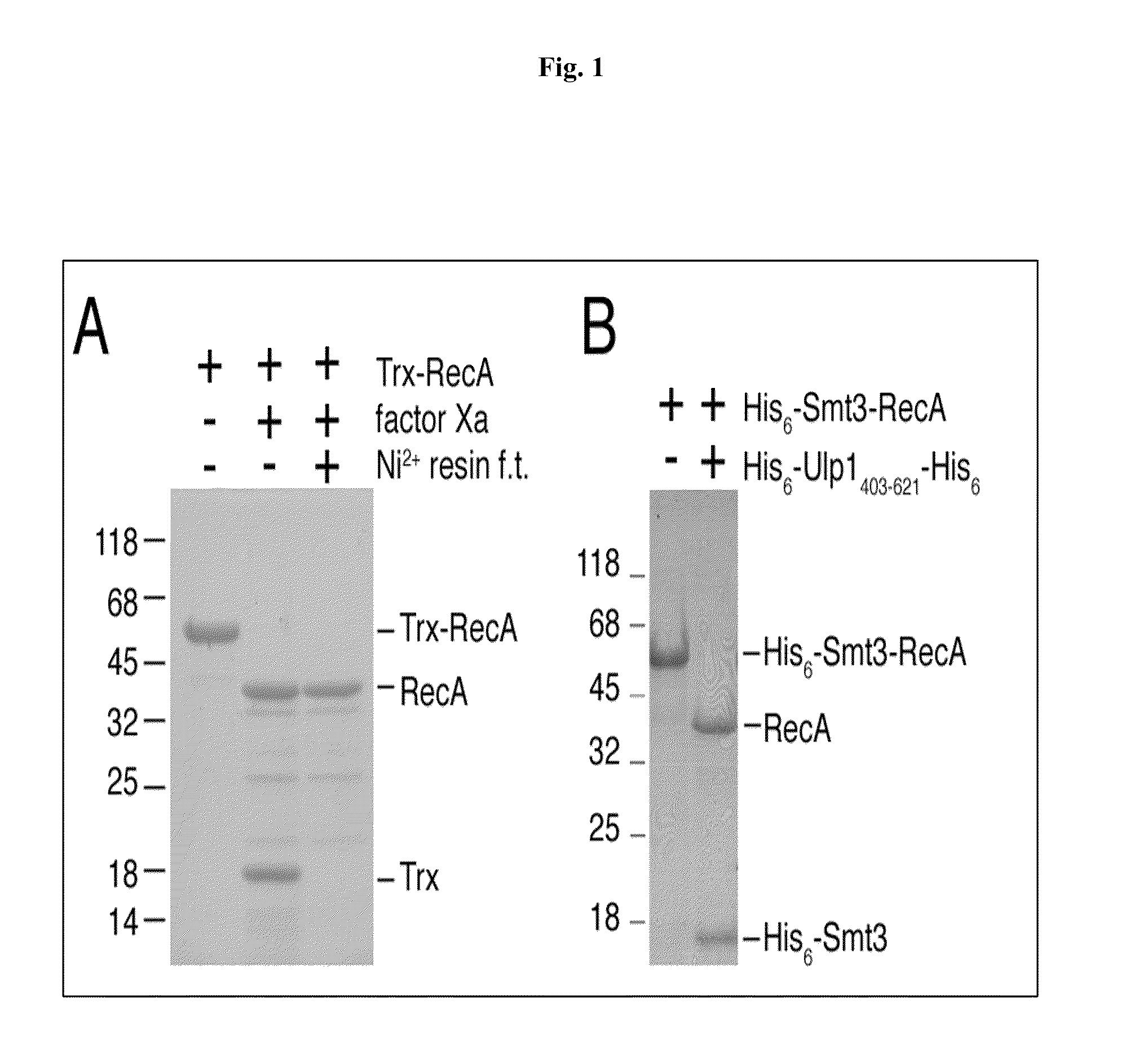
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
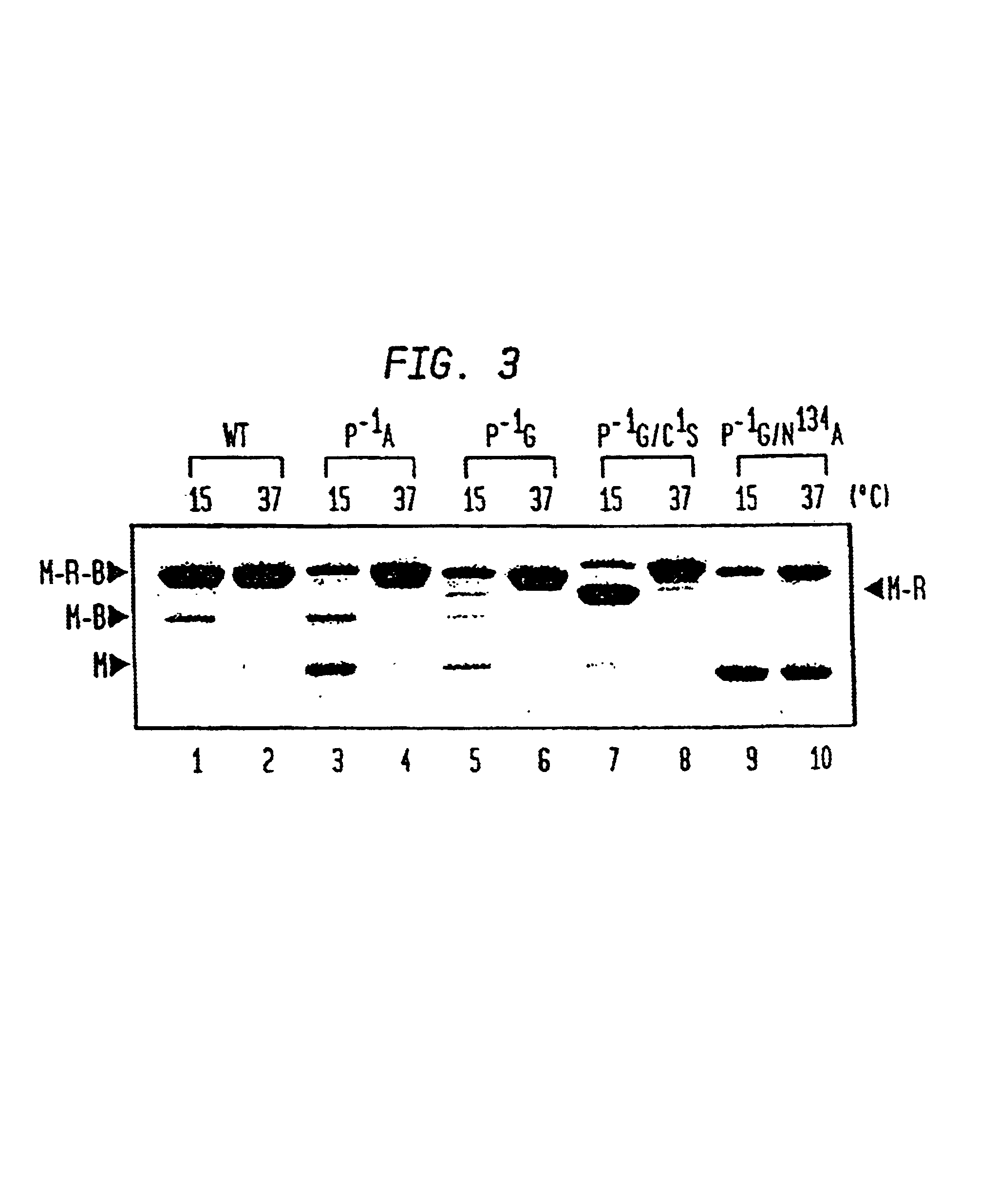
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Axmi238 toxin gene and methods for its use
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a toxin polypeptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also comprise transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated toxin nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the polynucleotides are encompassed, and antibodies specifically binding to those amino acid sequences. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2-5, or the nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Anti-cd40 antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140093497A1Reduce the frequency of occurrenceReduce severityOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismsEpitopeTransplant rejection
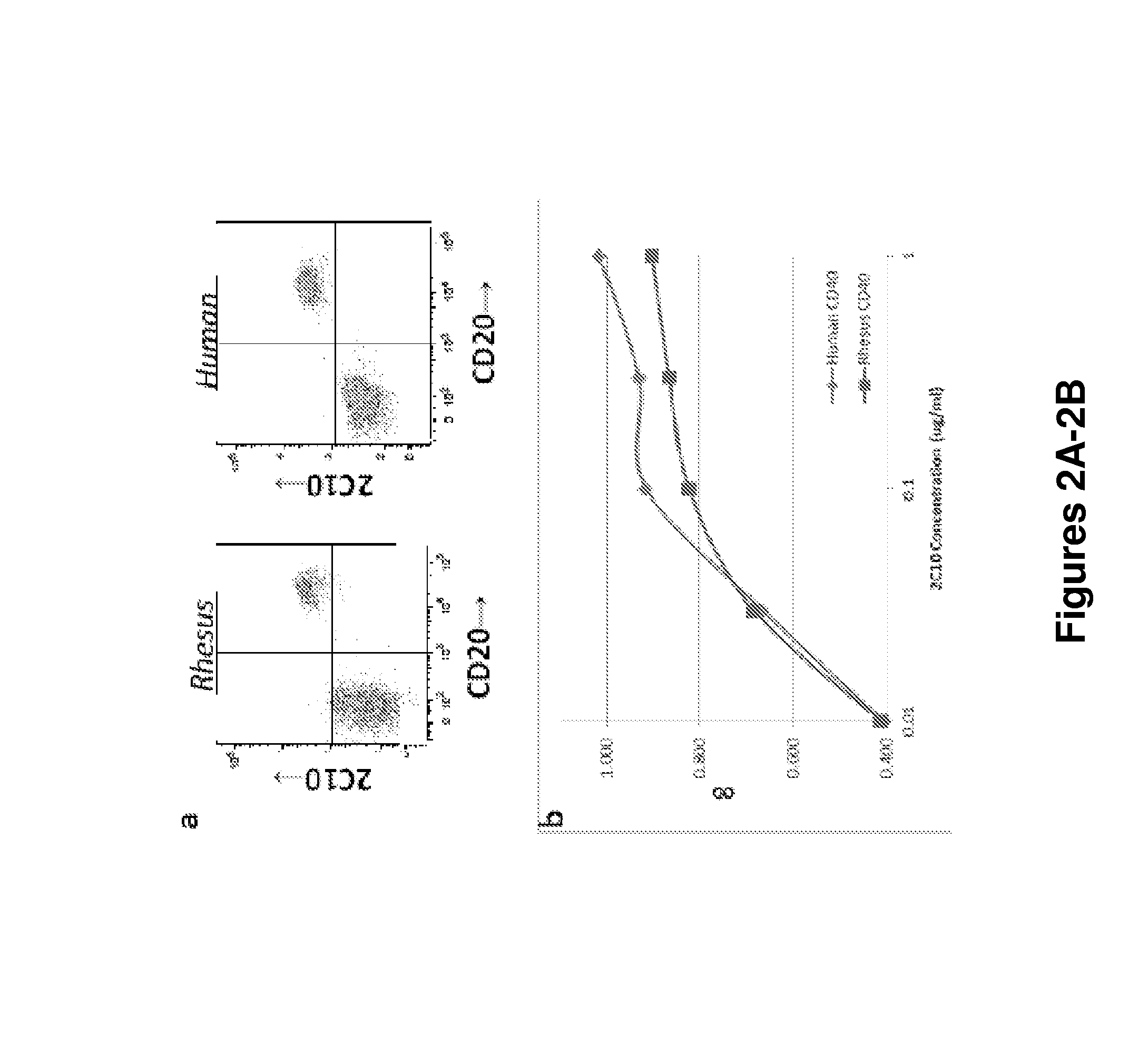
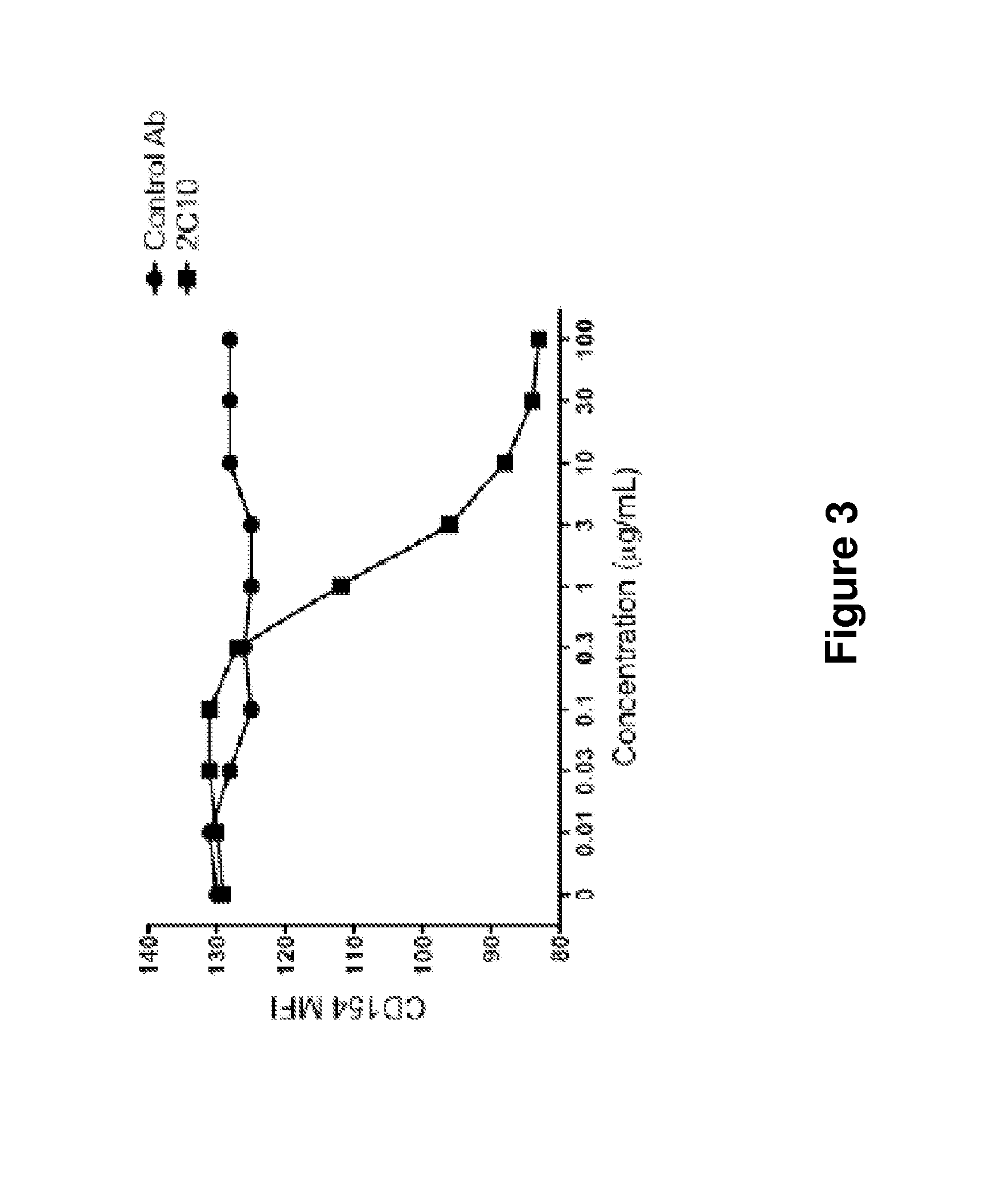
The present invention relates to antibodies specific for a particular epitope on CD40 and antibodies that bind CD40 and have particular functional characteristics. The present invention also relates to fragments of these antibodies, uses of the antibodies for reduction or treatment of transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease, and methods for making the antibodies.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
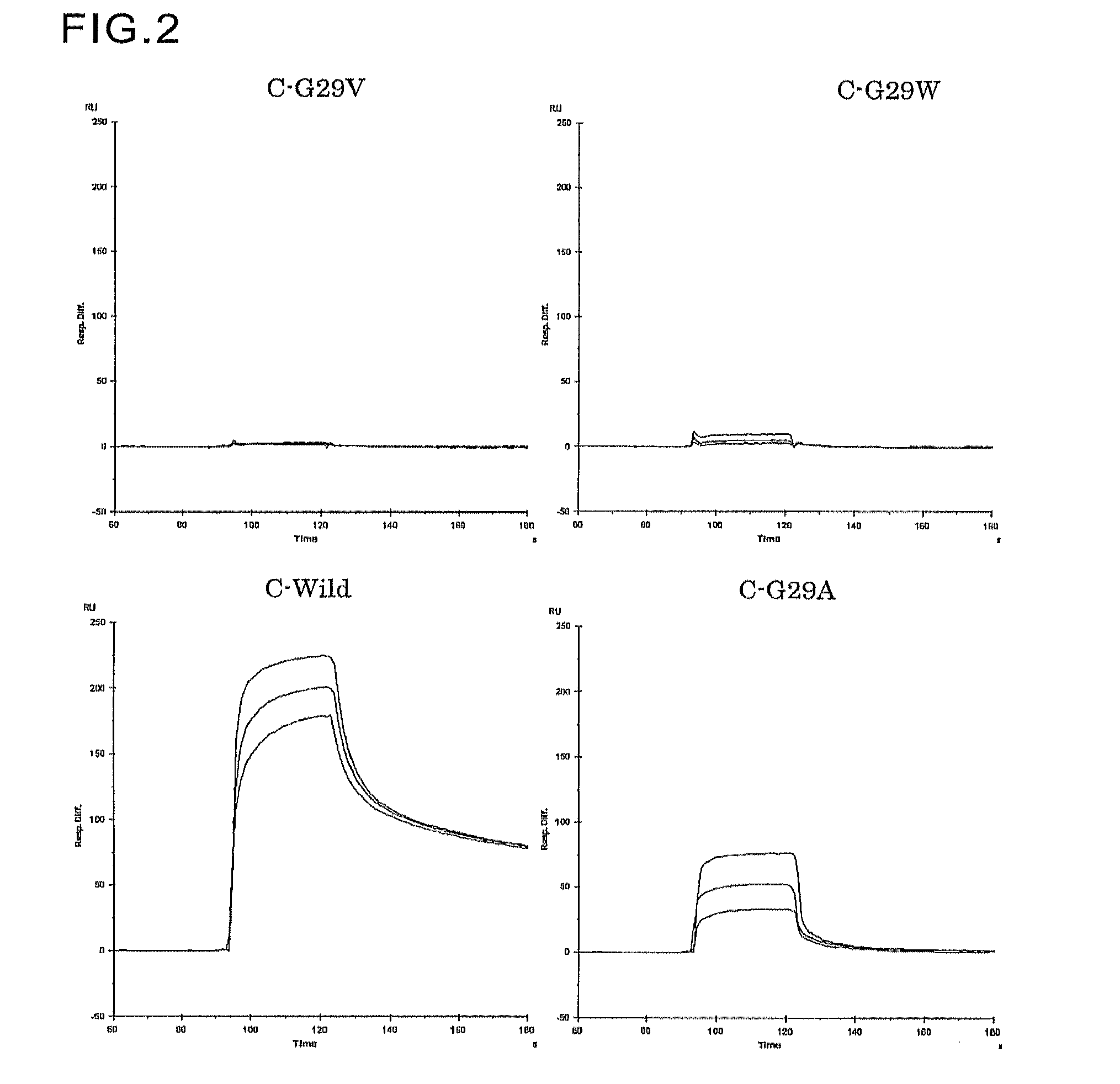
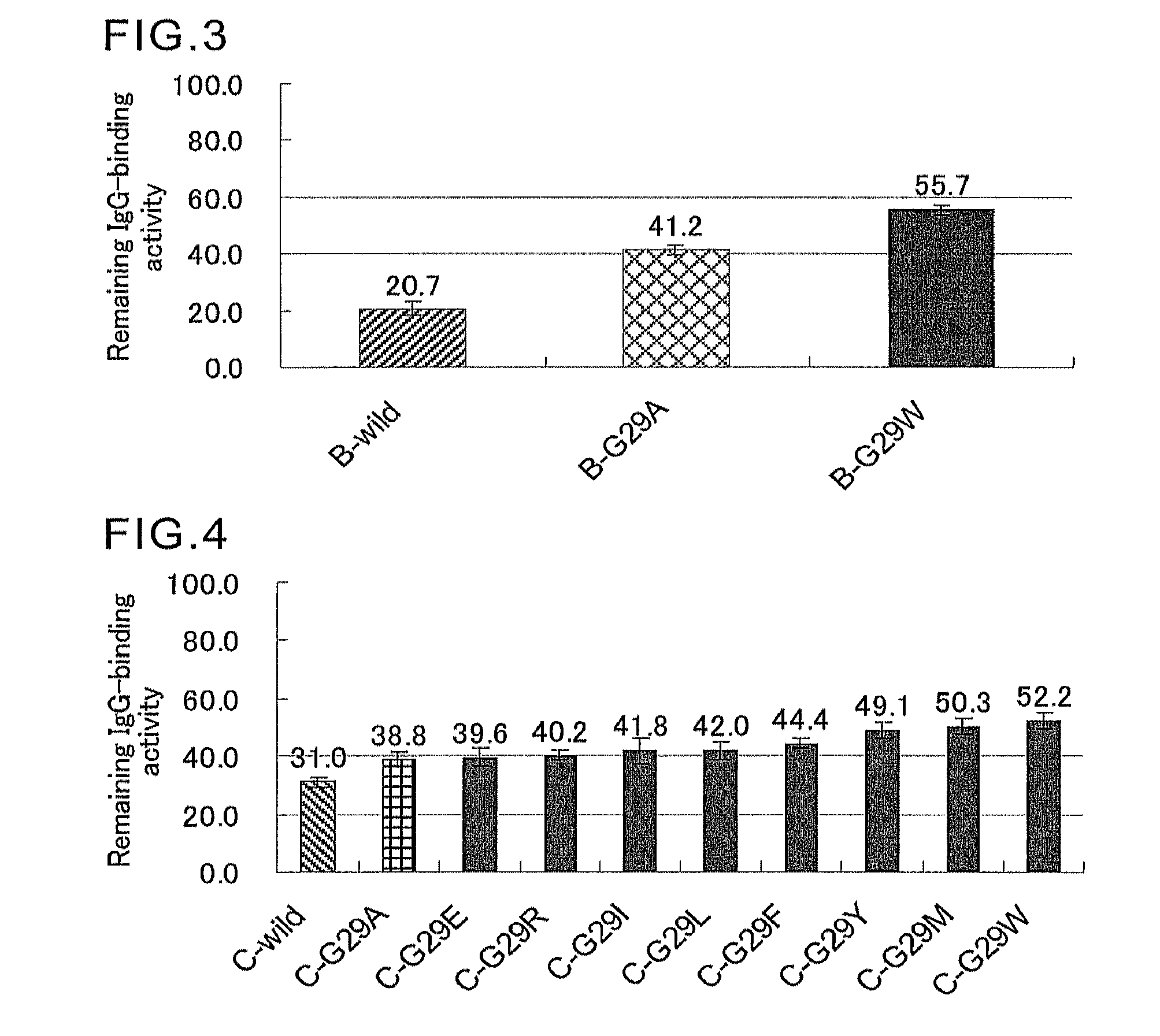
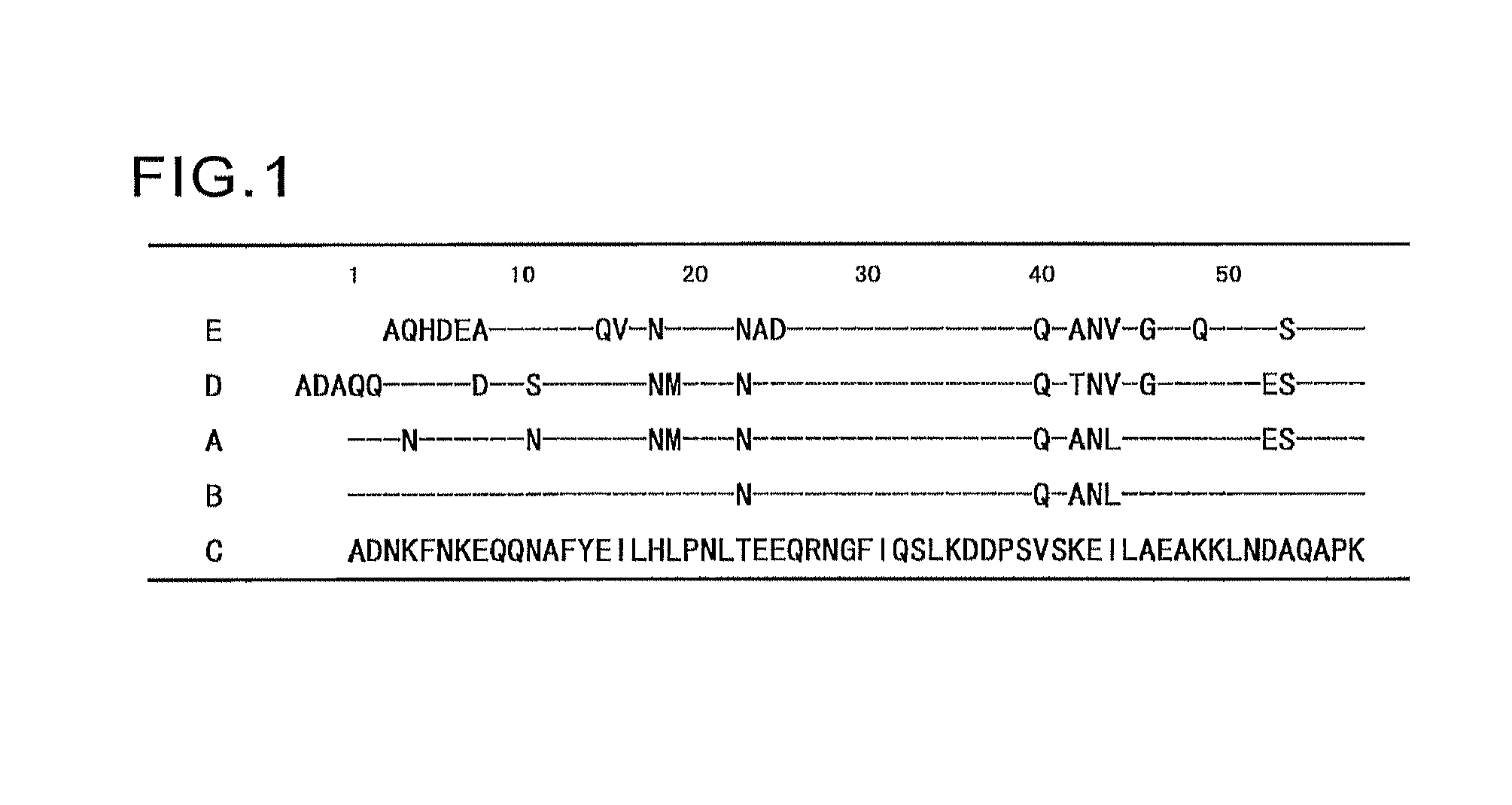
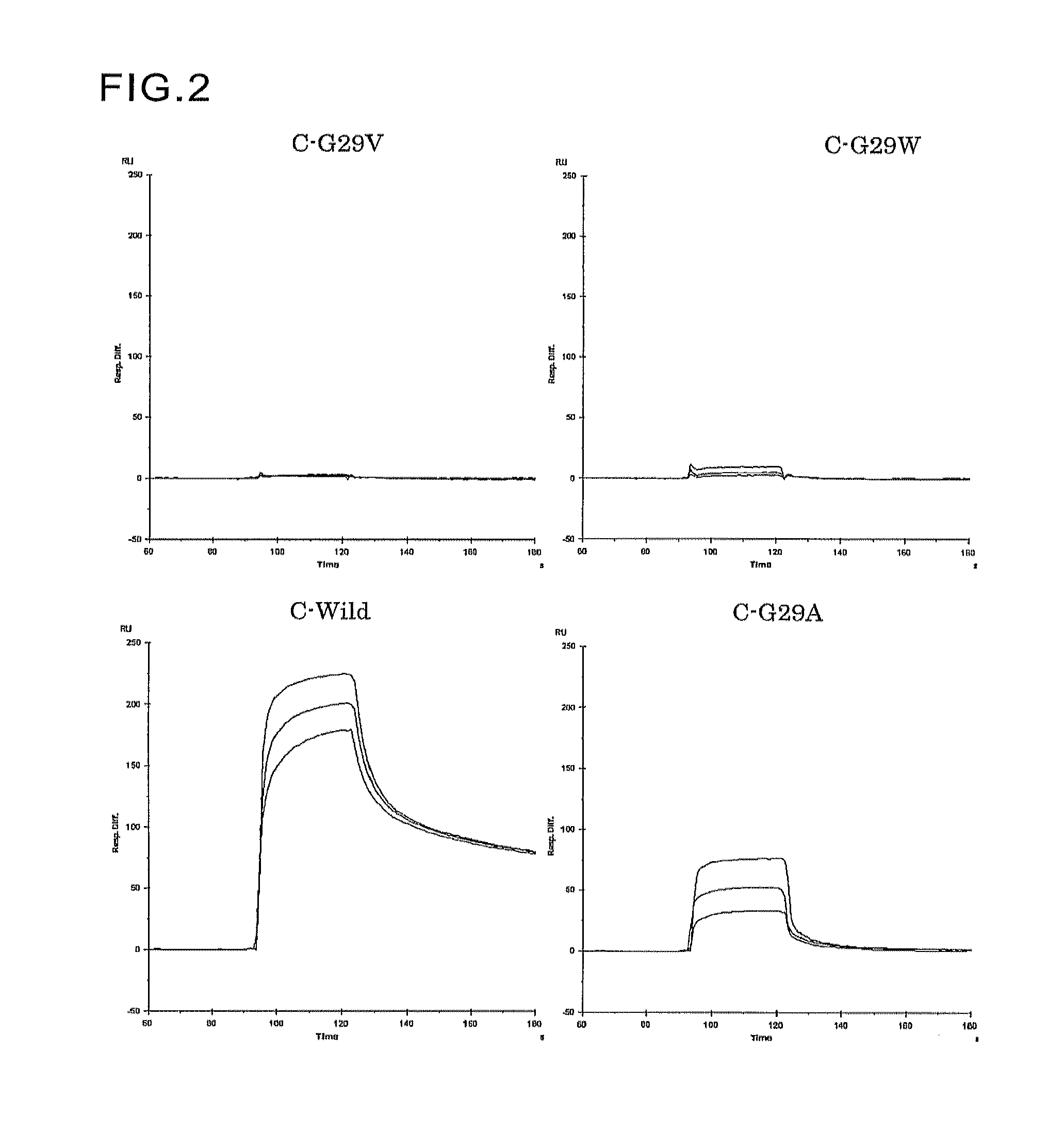
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS20120208234A1Good chemical stabilityImprove identityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityADAMTS Proteins
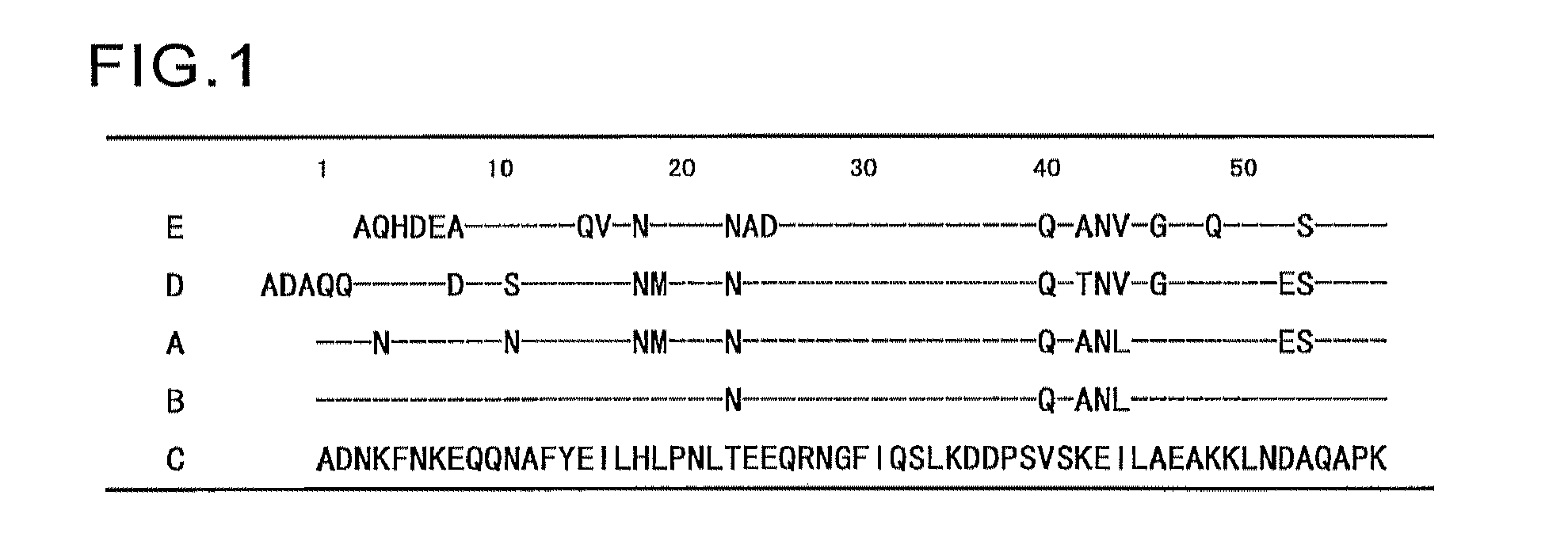
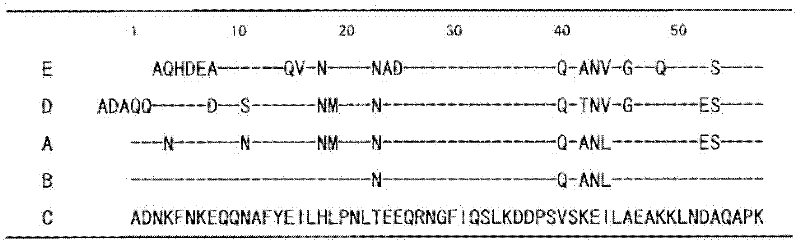
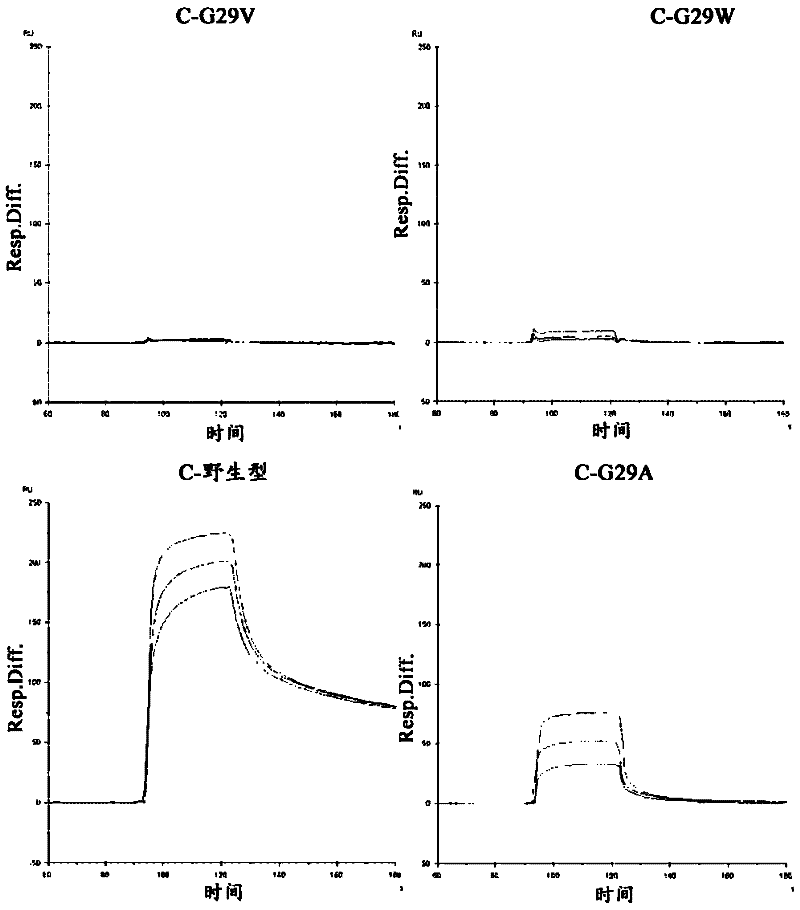
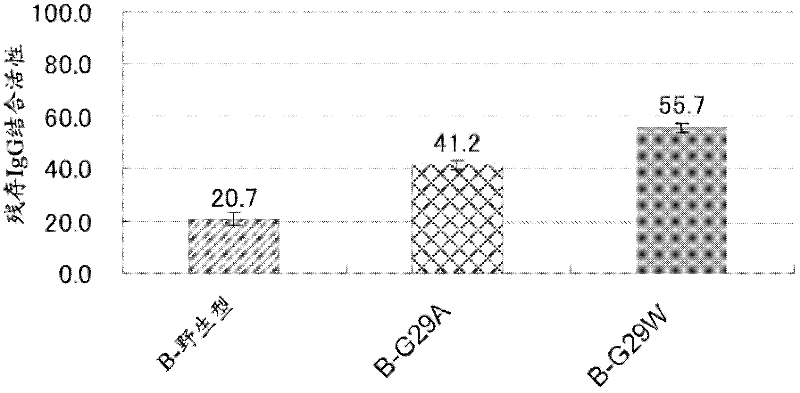
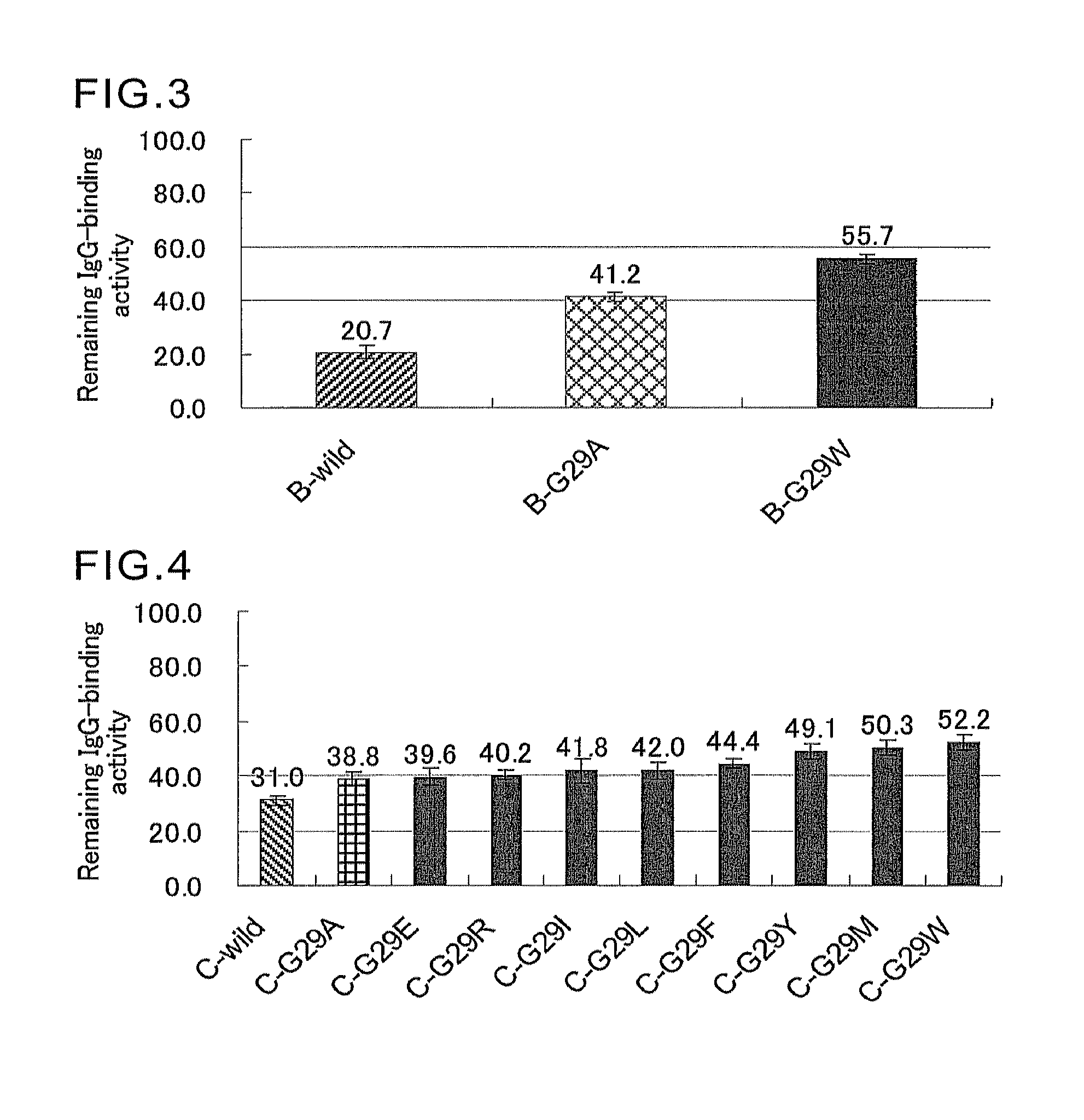
An object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having better antibody dissociation properties in the presence of an acid than conventional engineered Protein A ligands and a further object of the present invention is to create a novel engineered Protein A ligand having higher alkali resistance. The present invention is to provide a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, including an amino acid sequence derived from any of E, D, A, B and C domains of Protein A, wherein at least one Gly residue in the amino acid sequence is replaced with an amino acid other than Ala, and the protein has a lower affinity for an Fab region of an immunoglobulin than a protein including an amino acid sequence in which the Gly residue is replaced with Ala. Also, the present invention is to provide the protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, which has improved chemical stability in an alkaline condition compared to the corresponding domain.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Engineered stimulus-responsive switches
InactiveUS20070196816A1Useful in detectionReduce riskFusion with DNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsScientific domainStimuli responsive
Ligand-responsive chimeric proteins are engineered to cause a detectable output in response to a preselected stimulus. The engineered chimeric proteins are useful in industrial, commercial, medical, and scientific fields as a tool for programming a cellular response to a stimulus of choice and for use with in vitro assays. The engineered chimeric proteins include a detection domain and an interaction domain. Interaction of the engineered chimeric protein with a target biomolecule is modulated by the presence or absence of the preselected stimulus.
Owner:SCHWARTZ JOHN JACOB +2
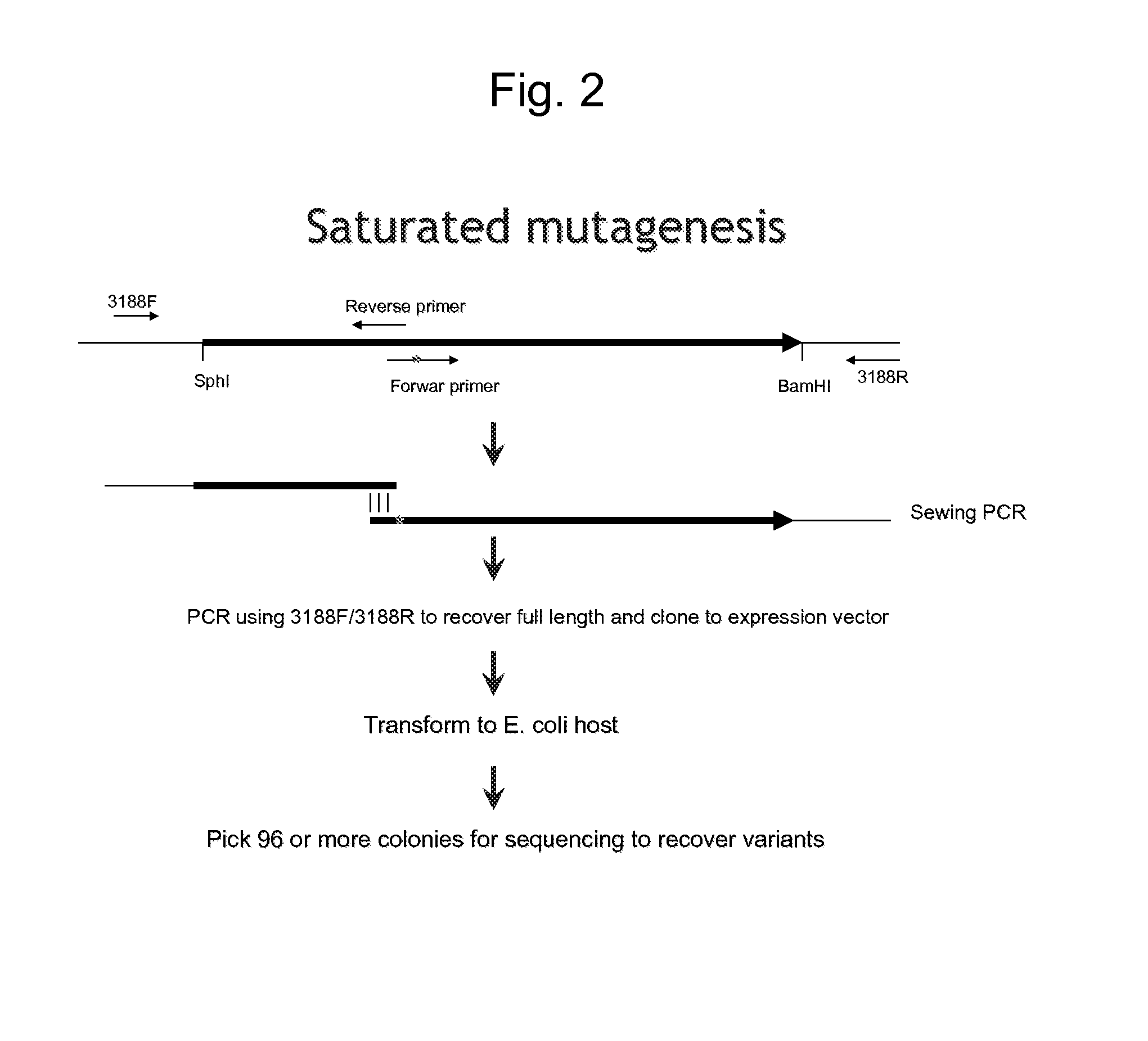
Genetic system and self-cleaving inteins derived therefrom, bioseparations and protein purification employing same, and methods for determining critical, generalizable amino acid residues for varying intein activity
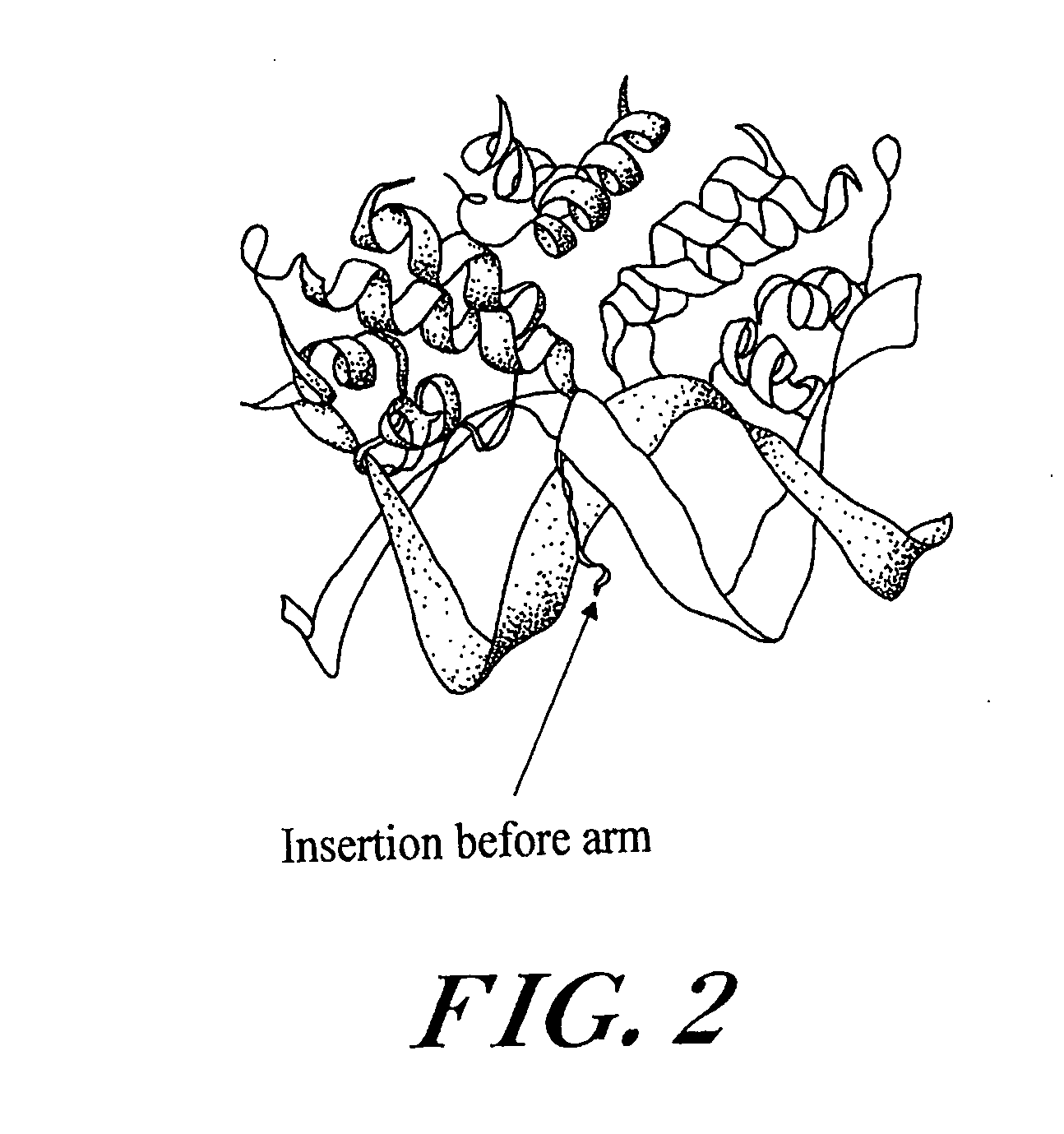
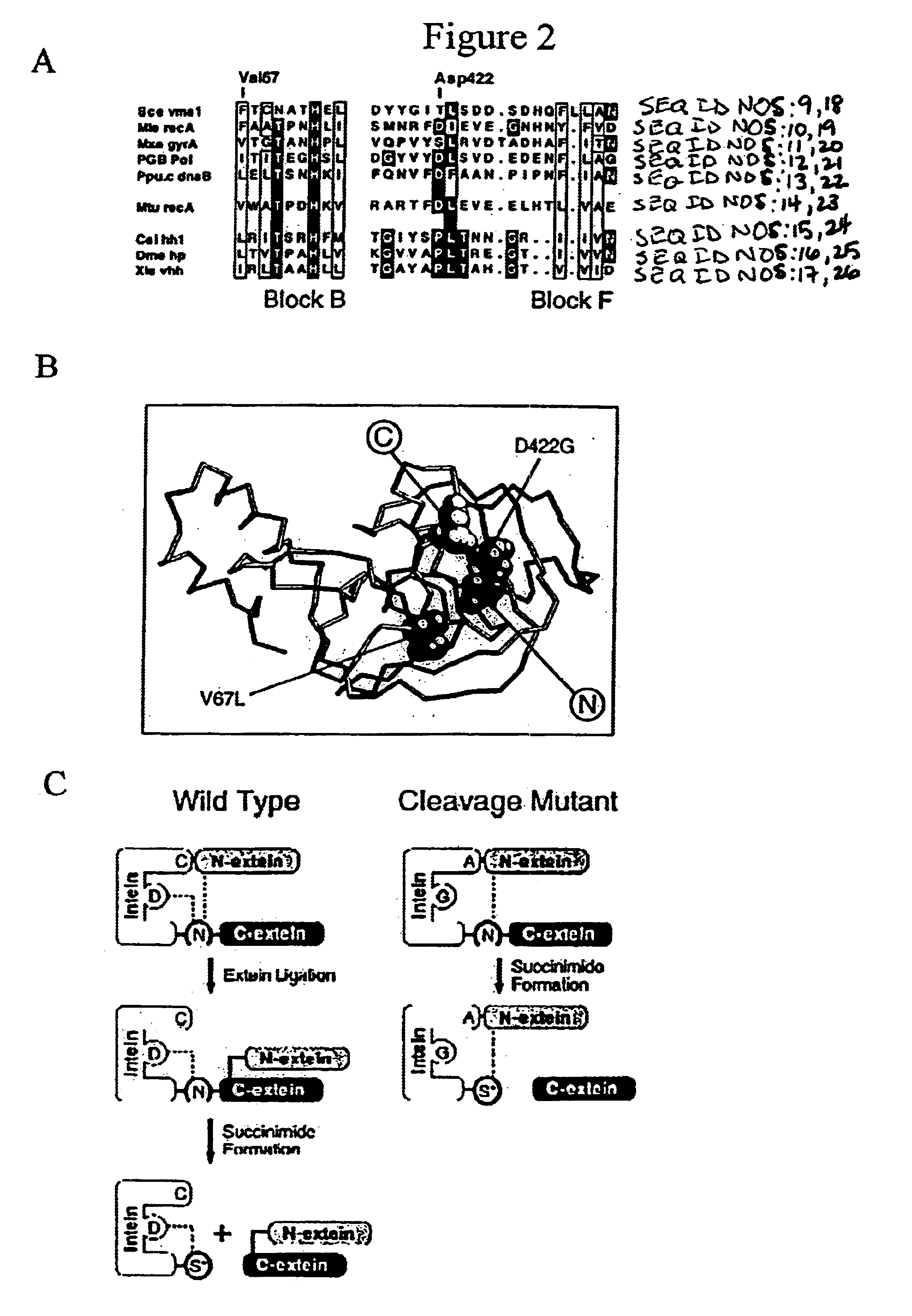
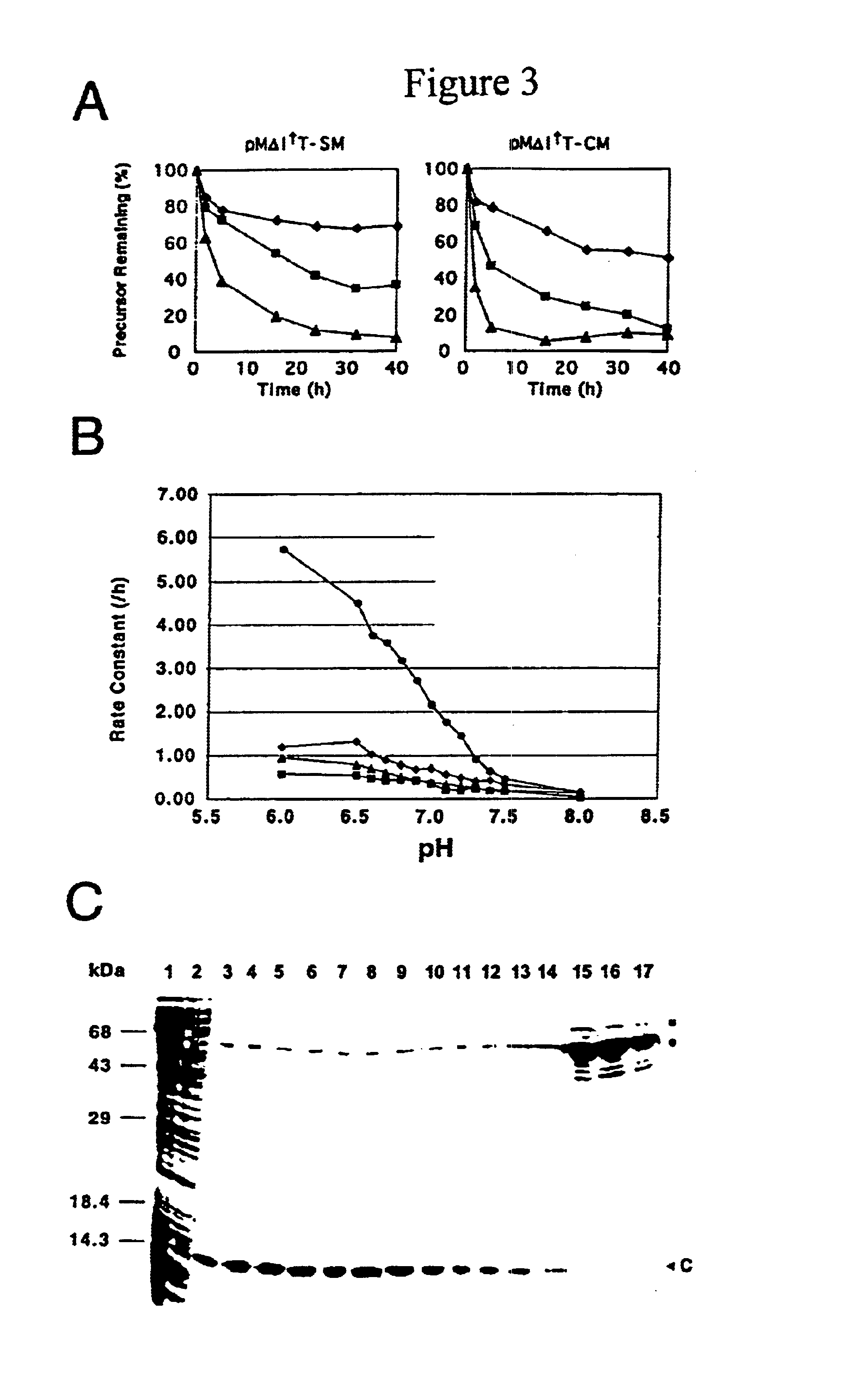
A self-cleaving element for use in bioseparations has been derived from a naturally occurring, 43 kDa protein splicing element (intein) through a combination of protein engineering and random mutagenesis. A mini-intein (18 kDa) previously engineered for reduced size had compromised activity and was therefore subjected to random mutagenesis and genetic selection. In one selection a mini-intein was isolated with restored splicing activity, while in another, a mutant was isolated with enhanced, pH-sensitive C-terminal cleavage activity. The enhanced cleavage mutant has utility in affinity fusion-based protein purification. The enhanced splicing mutant has utility in purification of proteins such as toxic proteins, for example, by inactivation with the intein in a specific region and controllable splicing. These mutants also provide new insights into the structural and functional roles of some conserved residues in protein splicing. Thus, disclosed and claimed are: a genetic system and self-cleaving inteins therefrom; bioseparations employing same; protein purification by inactivation with inteins in specific regions and controllable intein splicing; methods for determining critical, generalizable residues for varying intein activity; and products.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
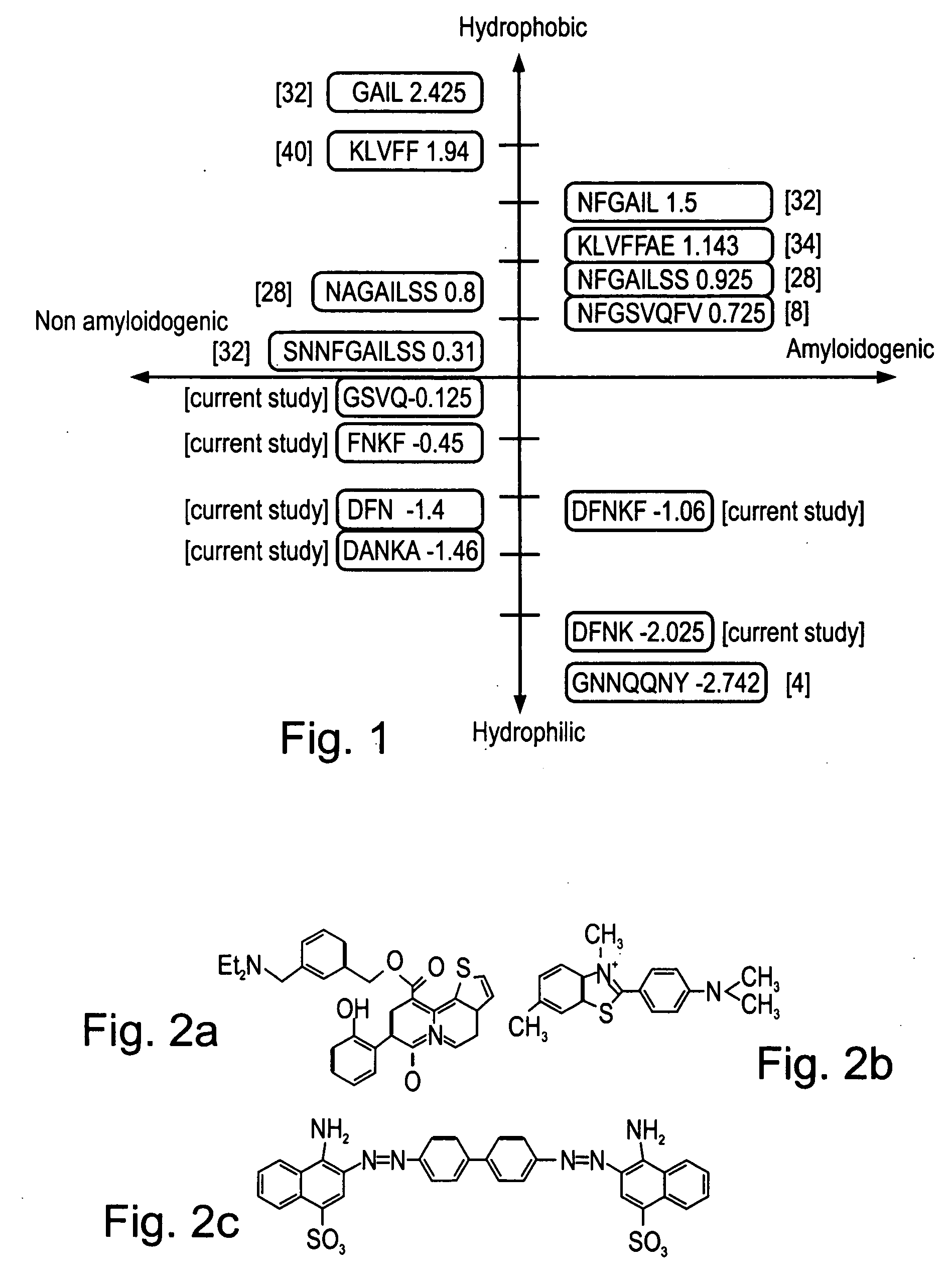
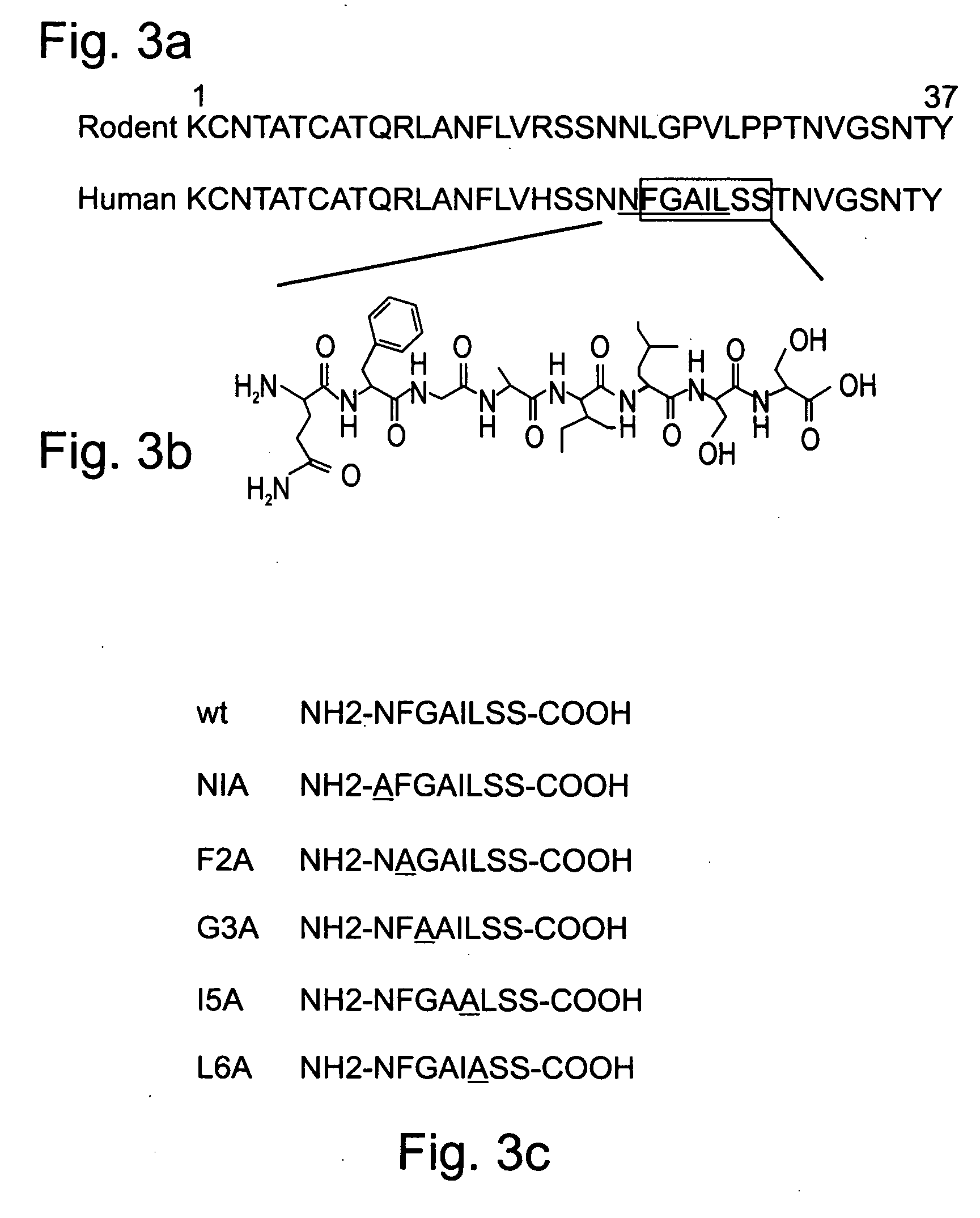
Peptides antibodies directed thereagainst and methods using same for diagnosing and treating amyloid-associated diseases
Peptides having at least 2 amino acid residues and no more than 15 amino acid residues are provided. The peptides comprise amino acid sequence X-Y or Y-X, wherein X is an aromatic amino acid and Y is any amino acid other than glycine. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions and kits including such peptides as well as methods using same for diagnosing and treating amyloid associated diseases.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
Cell-directed synthesis of multifunctional nanopatterns and nanomaterials
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Insecticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS9688730B2Increase productionEnhance the imageBiocideClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The insecticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing lepidopteran, coleopteran, dipteran, fungal, hemipteran, and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
Disclosed are: a novel modified protein A ligand having a superior property of causing the acid dissociation of antibodies compared to those of existing modified protein A ligands; and a novel modified protein A ligand having high alkali resistance. Specifically disclosed are: a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, which is characterized by comprising an amino acid sequence produced by substituting at least one Gly residue by an amino acid residue other than an Ala residue in an amino acid sequence derived from any one of E-domain, D-domain, A-domain, B-domain and C-domain of protein A, and which is also characterized by having a reduced affinity for an Fab region contained in the immunoglobulin compared to a protein comprising an amino acid sequence produced by substituting the Gly residue by an Ala residue in the amino acid sequence derived from any one of E-domain, D-domain, A-domain, B-domain and C-domain of protein A; and a protein having an affinity for an immunoglobulin, which is characterized by having improved chemical stability under alkaline conditions compared to a corresponding domain.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
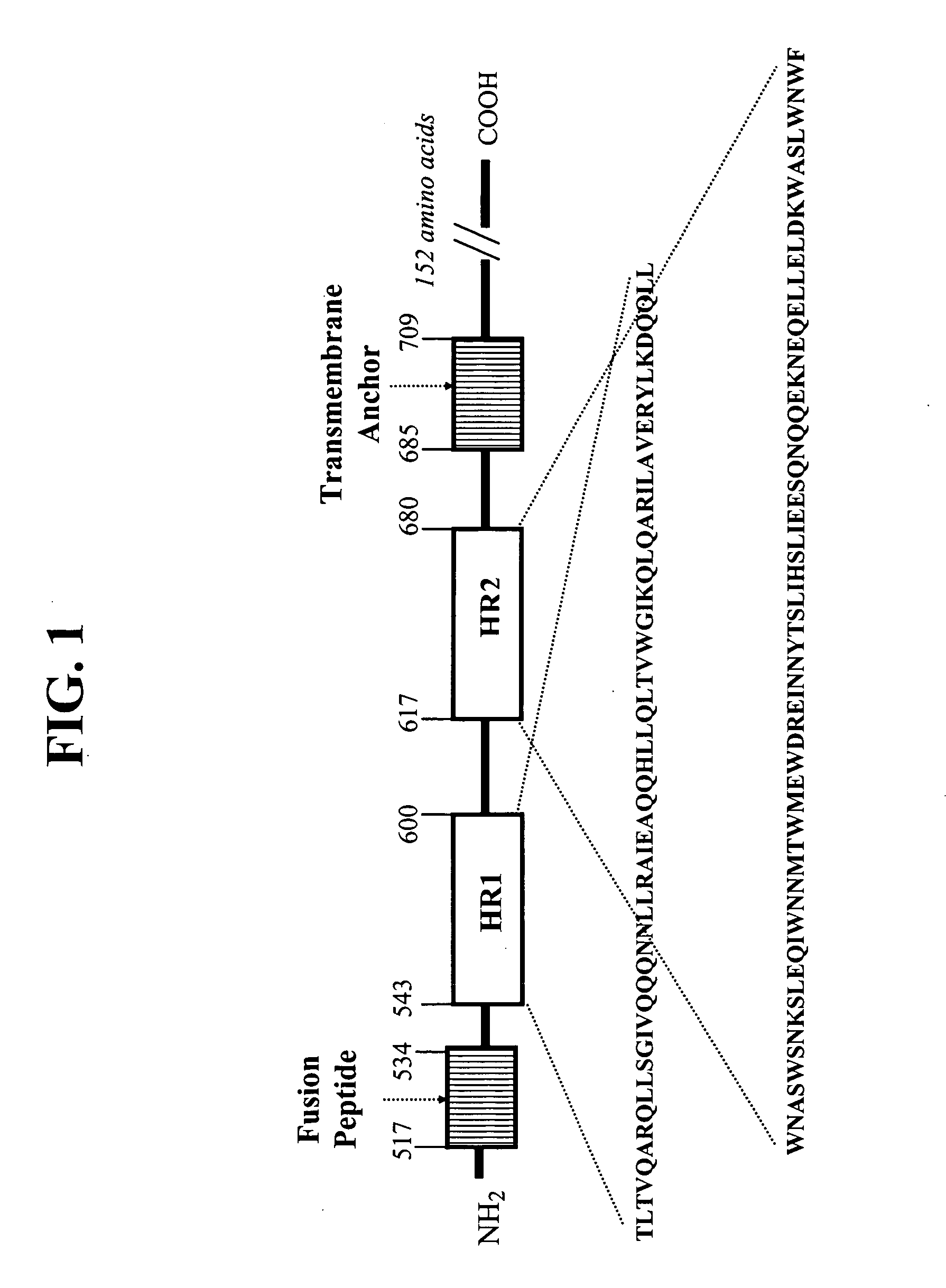
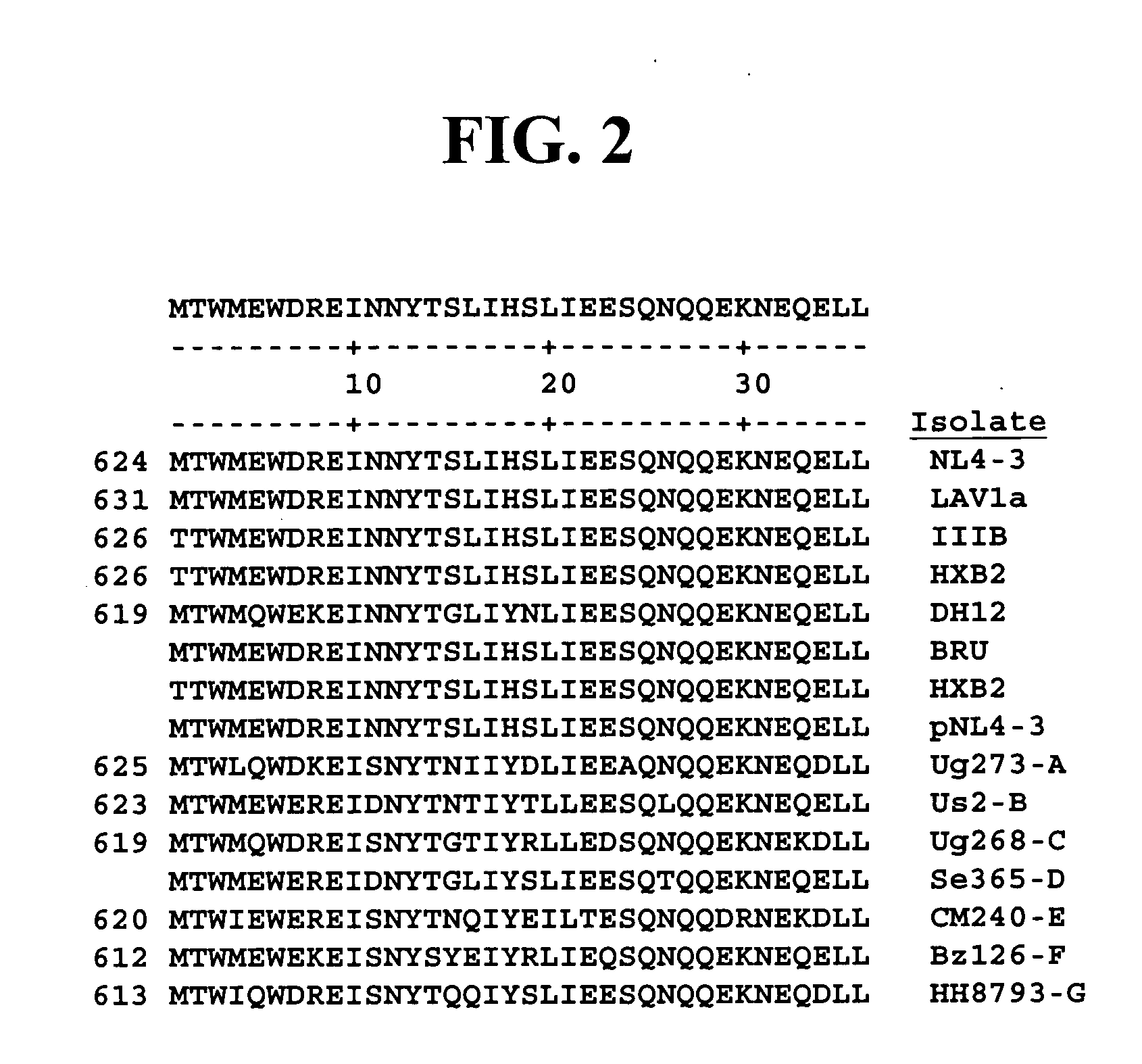
HIV gp41 HR2-derived synthetic peptides, and their use in therapy to inhibit transmission of human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20060247416A1Improve biological activityStrong antiviral activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesImmunodeficiency virusAmino acid substitution
Provided are synthetic peptides based on a native sequence of HIV gp41 HR2 except that the synthetic peptides have a plurality of amino acid replacements comprising (a) a helix-promoting amino acid, or (b) a combination of helix-promoting amino acids, and charged amino acids introduced to form ion pairs in the synthetic peptide; wherein the synthetic peptides demonstrate an unexpected, improved biological activity, as compared to a peptide having an amino acid sequence without the plurality of amino acid substitutions. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding synthetic peptide, and methods of using these synthetic peptides in inhibition of, or as compositions to inhibit, transmission of HIV to a target cell.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS9403883B2Good chemical stabilityImprove identityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityLower affinity
Owner:KANEKA CORP
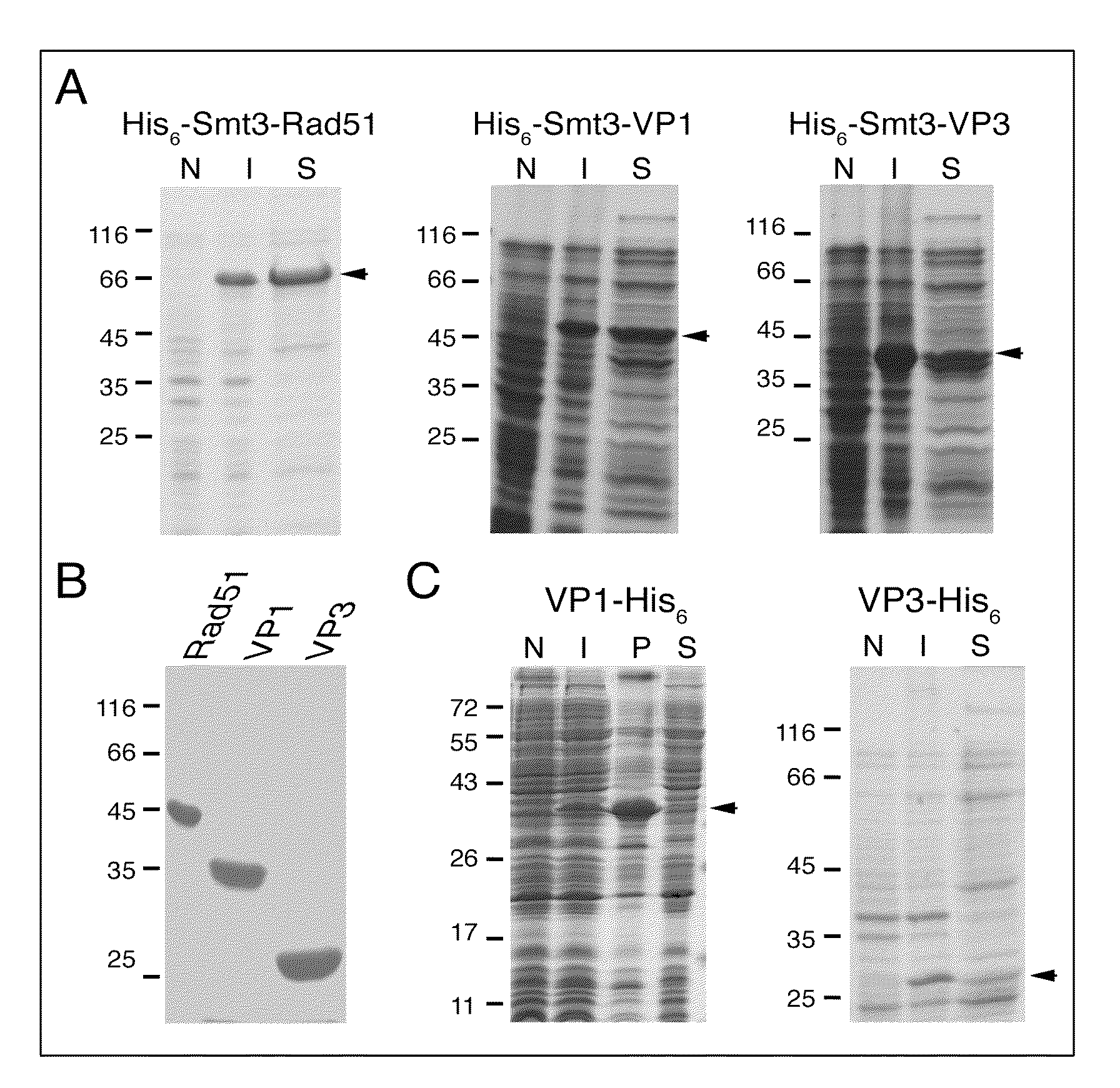
SUMO Fusion Protein Expression System for Producing Native Proteins
ActiveUS20090280535A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsFusion Protein ExpressionProtein formation
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Zinc finger protein derivatives and methods therefor
InactiveUS20050084885A1Modulate it functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainBiological activationTransgene
Zinc finger proteins of the Cys2His2 type represent a class of malleable DNA binding proteins which may be selected to bind diverse sequences. Typically, zinc finger proteins containing three zinc finger domains, like the murine transcription factor Zif268 and the human transcription factor Spl, bind nine contiguous base pairs (bp). To create a class of proteins which would be generally applicable to target unique sites within complex genomes, the present invention provides a polypeptide linker that fuses two three-finger proteins. Two six-fingered proteins were created and demonstrated to bind 18 contiguous bp of DNA in a sequence specific fashion. Expression of these proteins as fusions to activation or repression domains allows transcription to be specifically up or down modulated within cells. Polydactyl zinc finger proteins are broadly applicable as genome-specific transcriptional switches in gene therapy strategies and the development of novel transgenic plants and animals. Such proteins are useful for inhibiting, activating or enhancing gene expression from a zinc finger-nucleotide binding motif containing promoter or other transcriptional control element, as well as a structural gene or RNA sequence.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
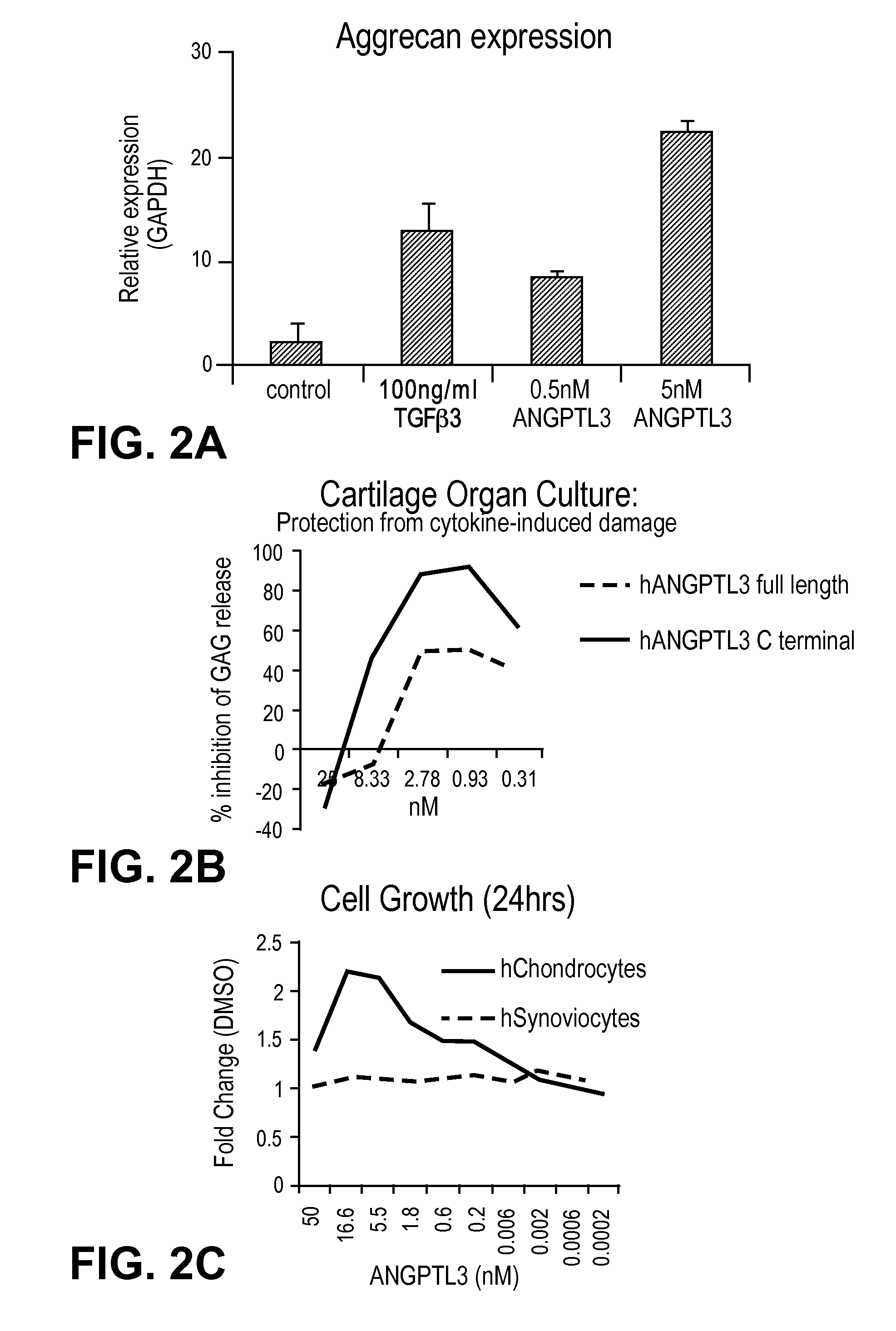
Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation
The present invention provides for methods and compositions for treating or preventing arthritis and joint injury.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +2
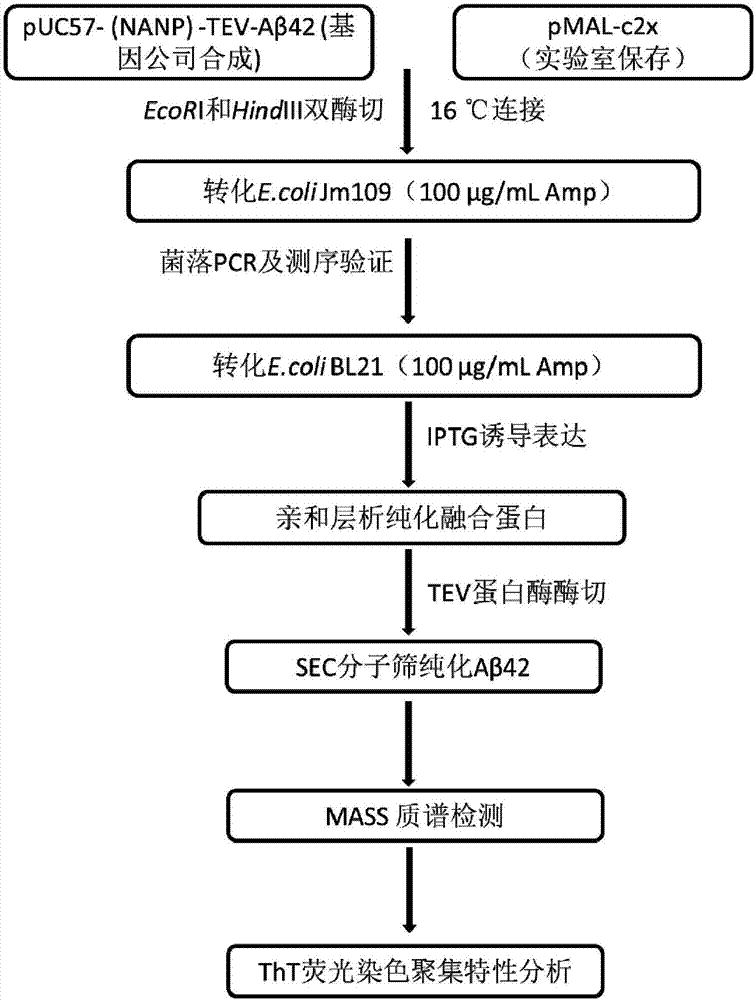
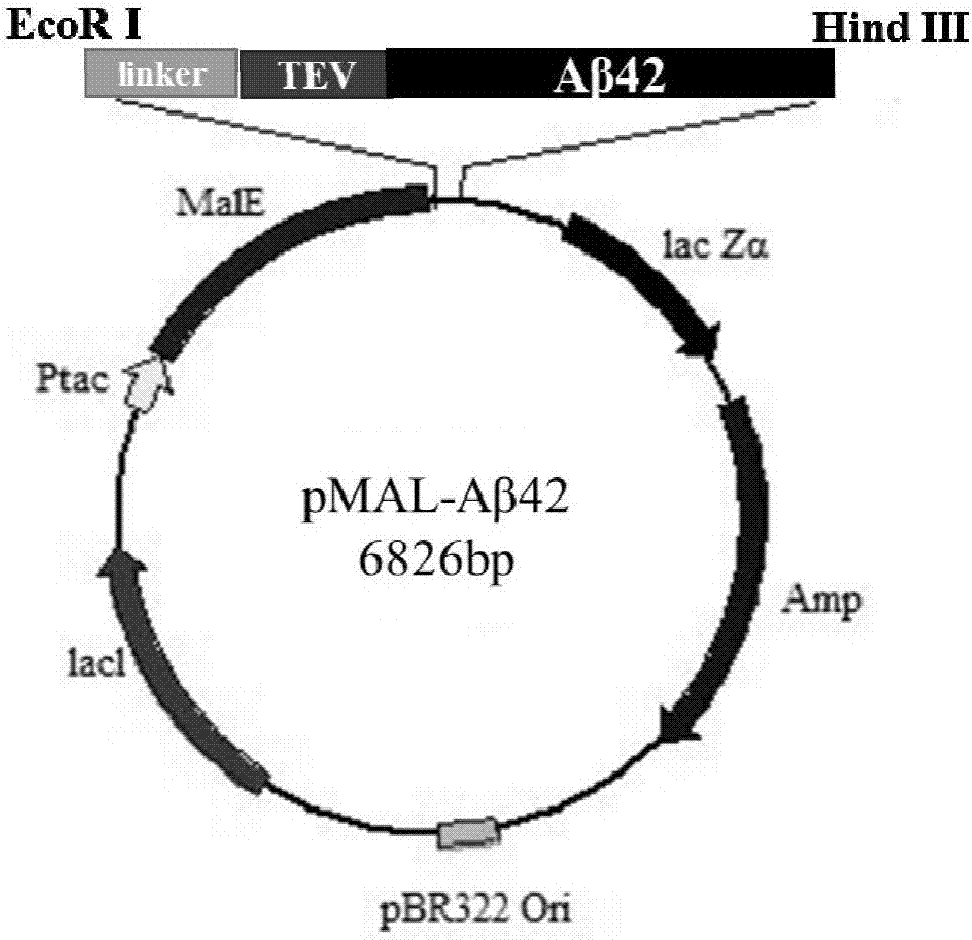
Efficient soluble expression and purification method of Abeta42 in escherichia coli
ActiveCN107245494AHigh expressionHigh purityNucleic acid vectorFusion with protease siteBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the fields of biotechnologies and genetic engineering technologies and in particular relates to an efficient soluble expression and purification method of Abeta42 in escherichia coli. An Abeta42 expression system constructed by the invention provides a construction method of an expression vector of prokaryote for soluble fusion expression of human amyloid protein Abeta42 and the expression vector is introduced into an escherichia coli expression host; target Abeta42 with high-purity bioactivity is obtained through induced expression, protein enzyme digestion, two-step purification and identification. According to the method provided by the invention, an escherichia coli expression system and fusion protein have the characteristics of high expression efficiency, large expression amount, low cost, easiness for operation and the like; an expressed Abeta42 polypeptide has the advantages of no residues, high purity, high productivity and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
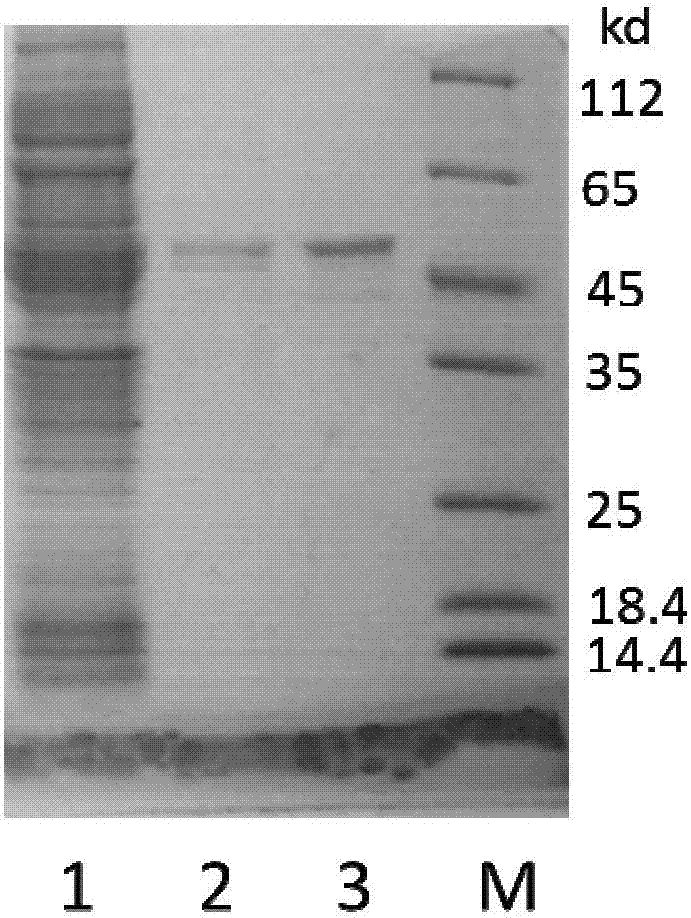
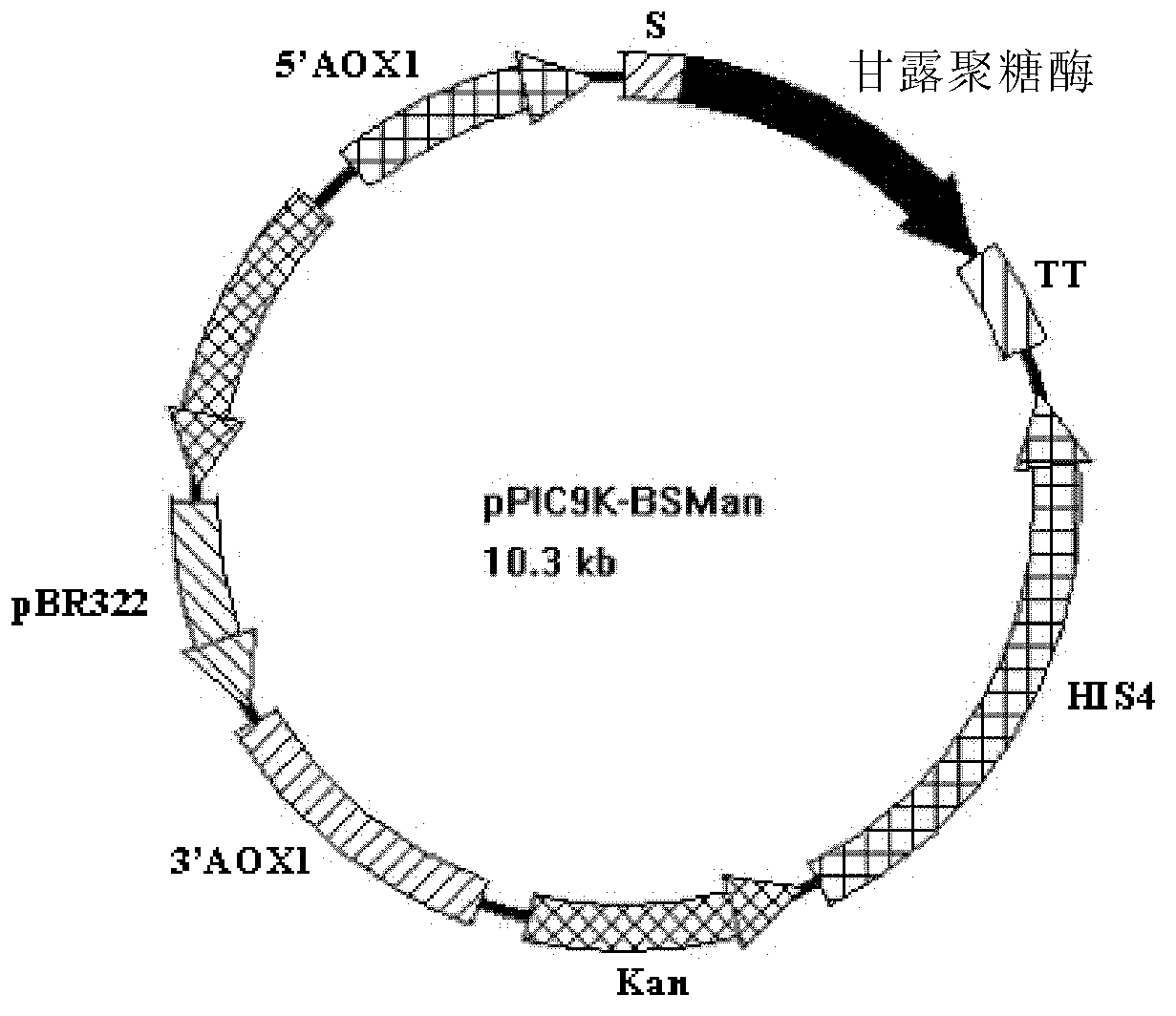
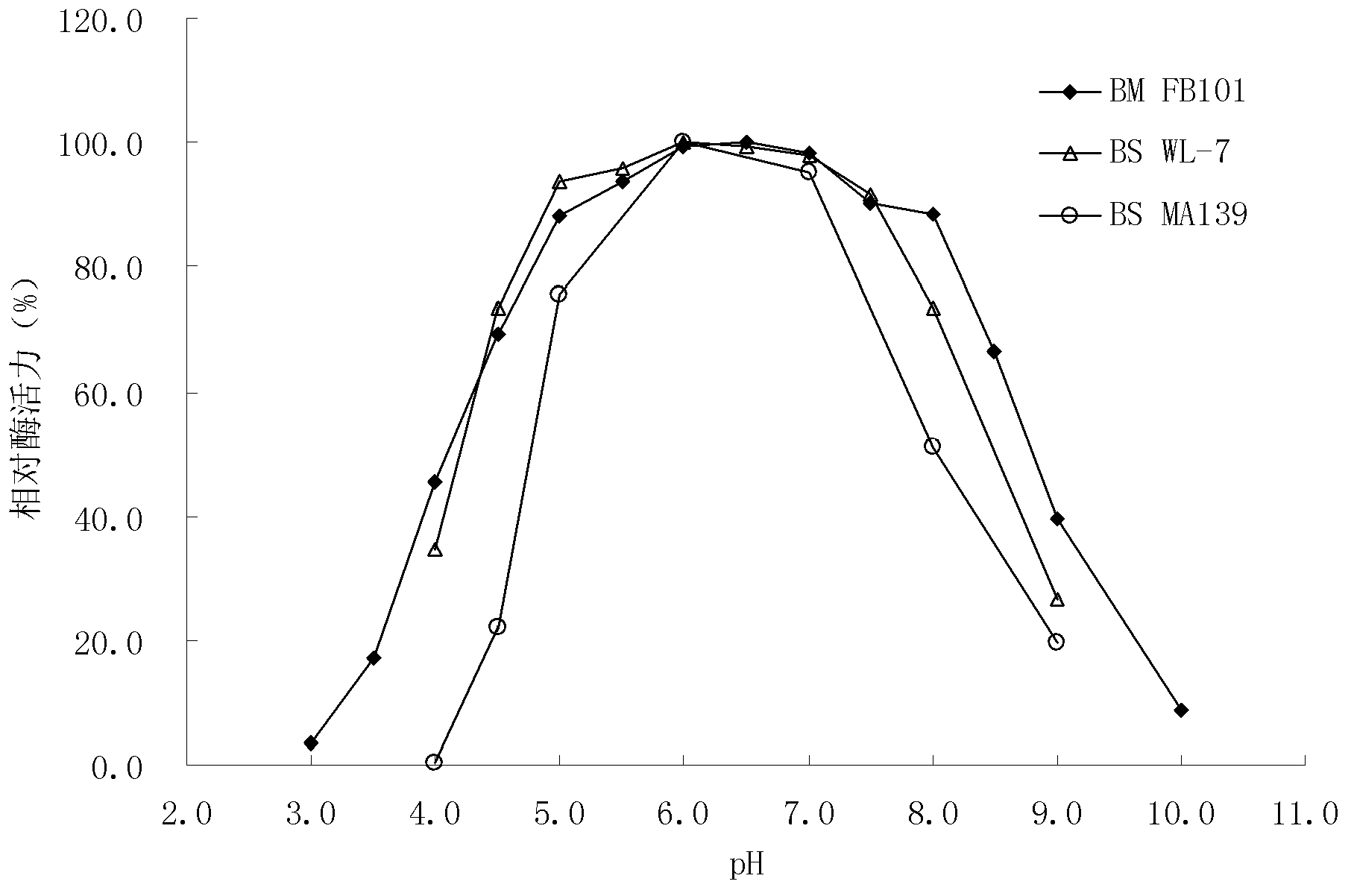
Mannanase, coding gene and production thereof
ActiveCN103261409AAchieve mass productionGood pH stabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses a mannanase and the coding gene, a recombinant vector and a host cell comprising the gene, and expression of the recombinant vector in E.coli and production of the enzyme in yeast cells by using the recombinant vector. The present invention also provides a new wild type subspecies of Bacillus Megaterium, in particular, Bacillus Megaterium FB101.
Owner:FUJIAN FUDA BIOTECH
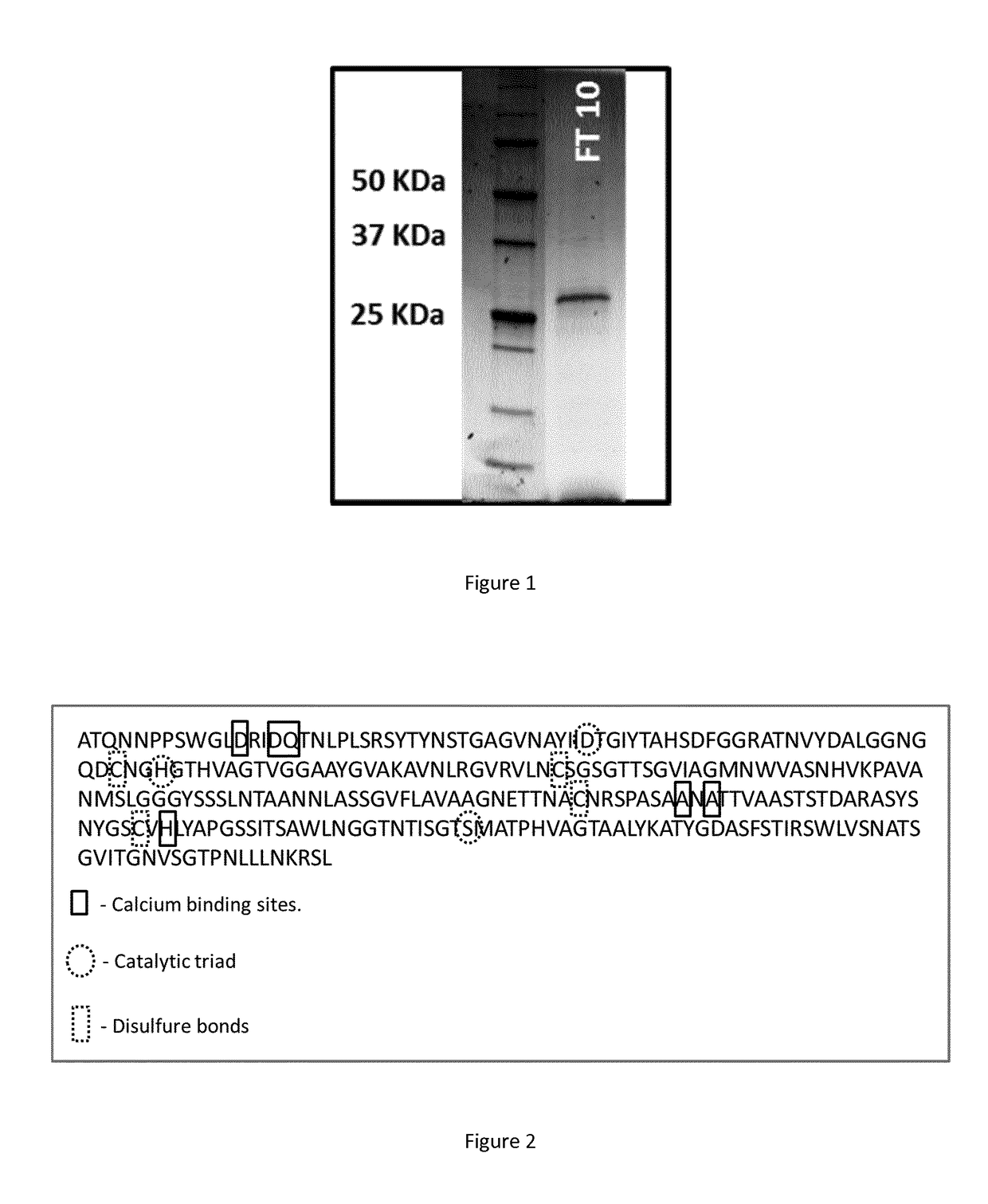
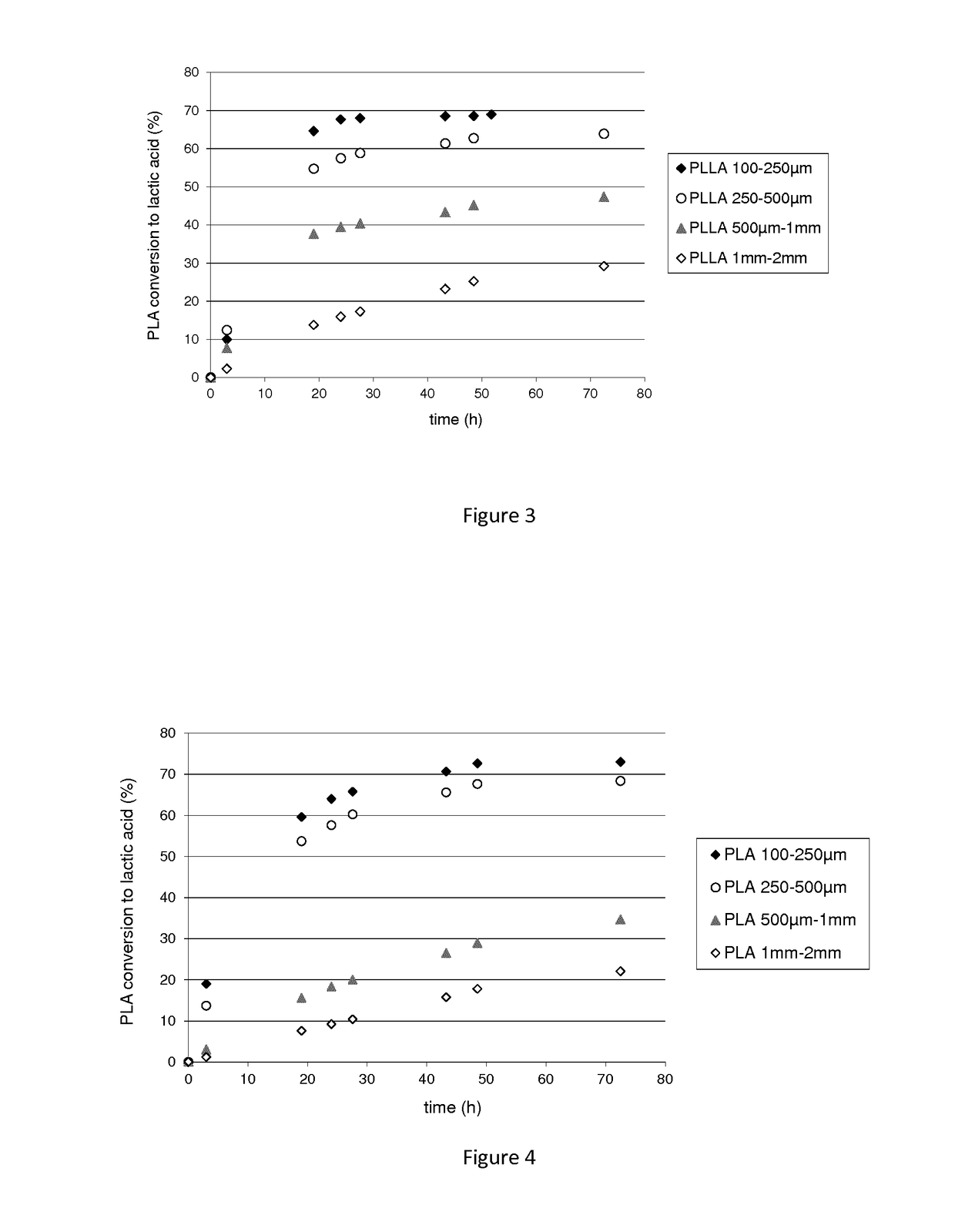
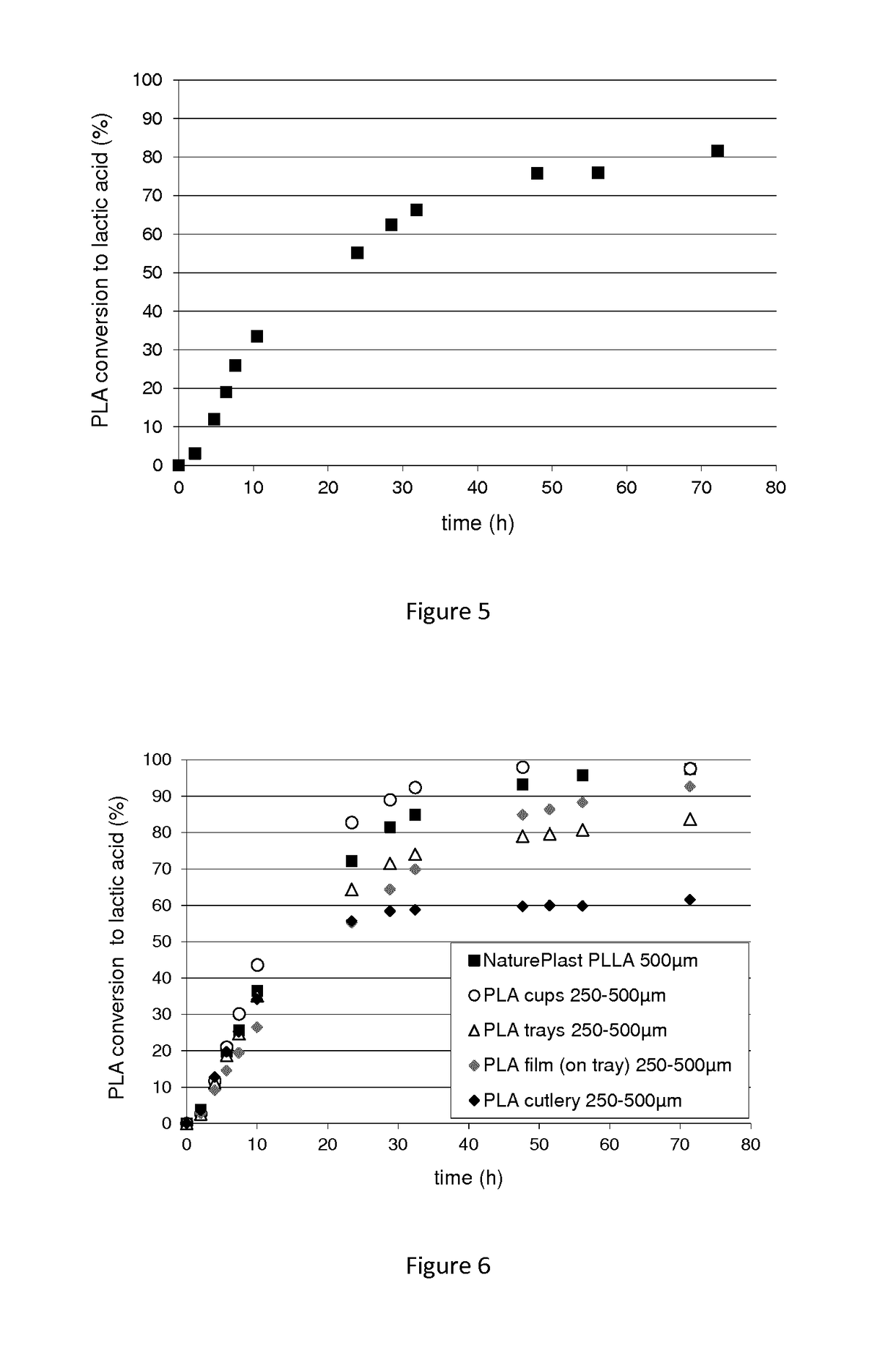
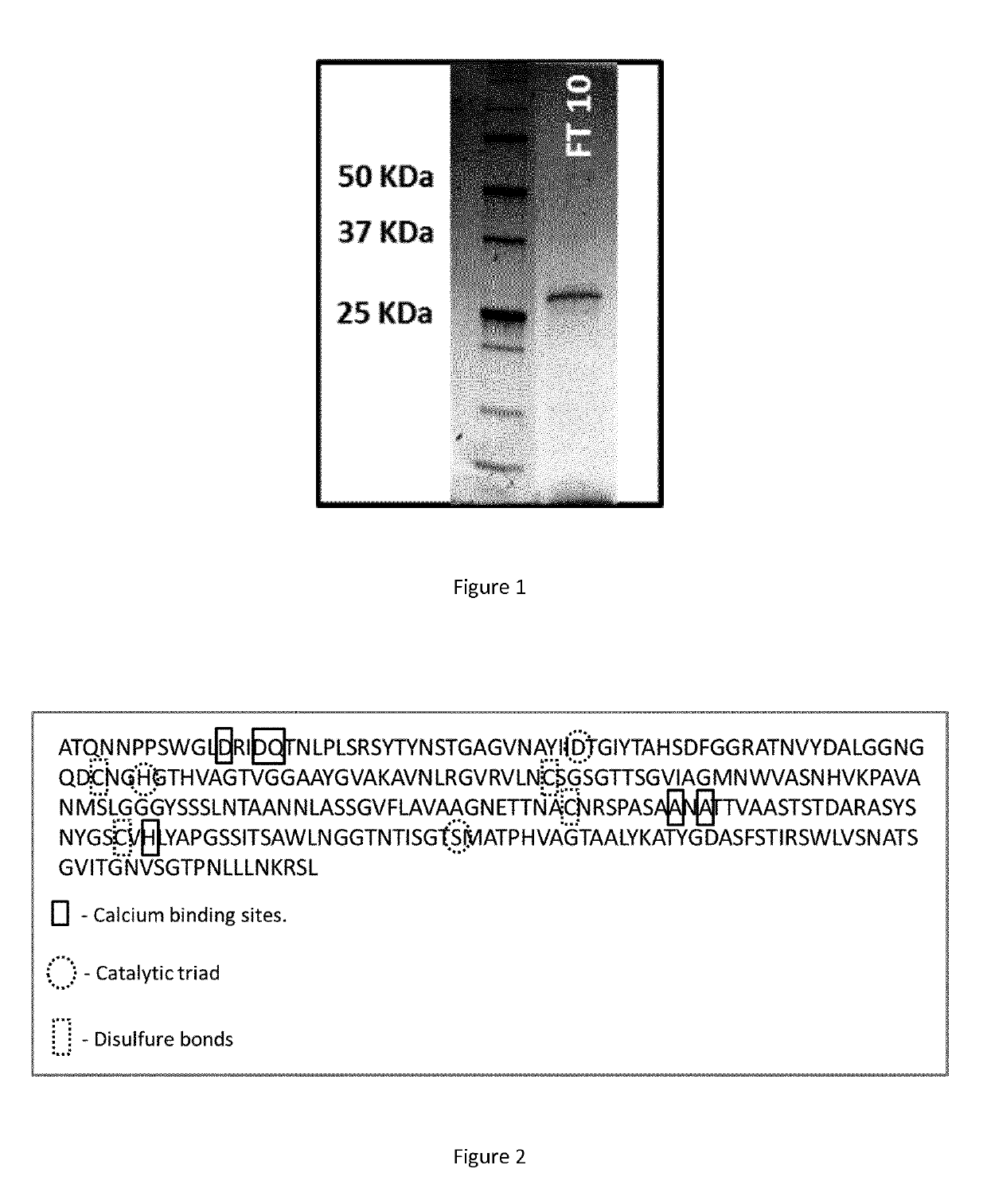
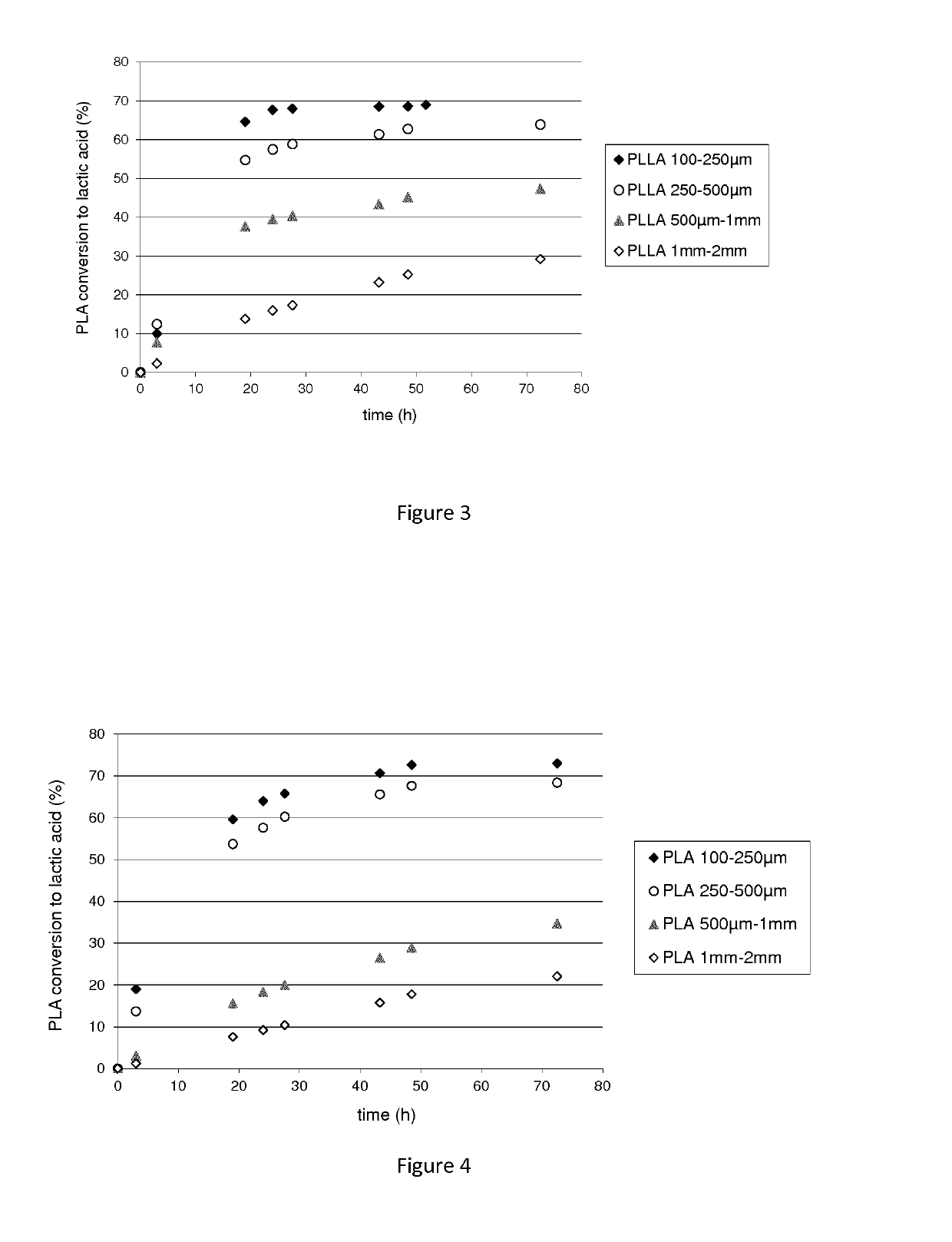
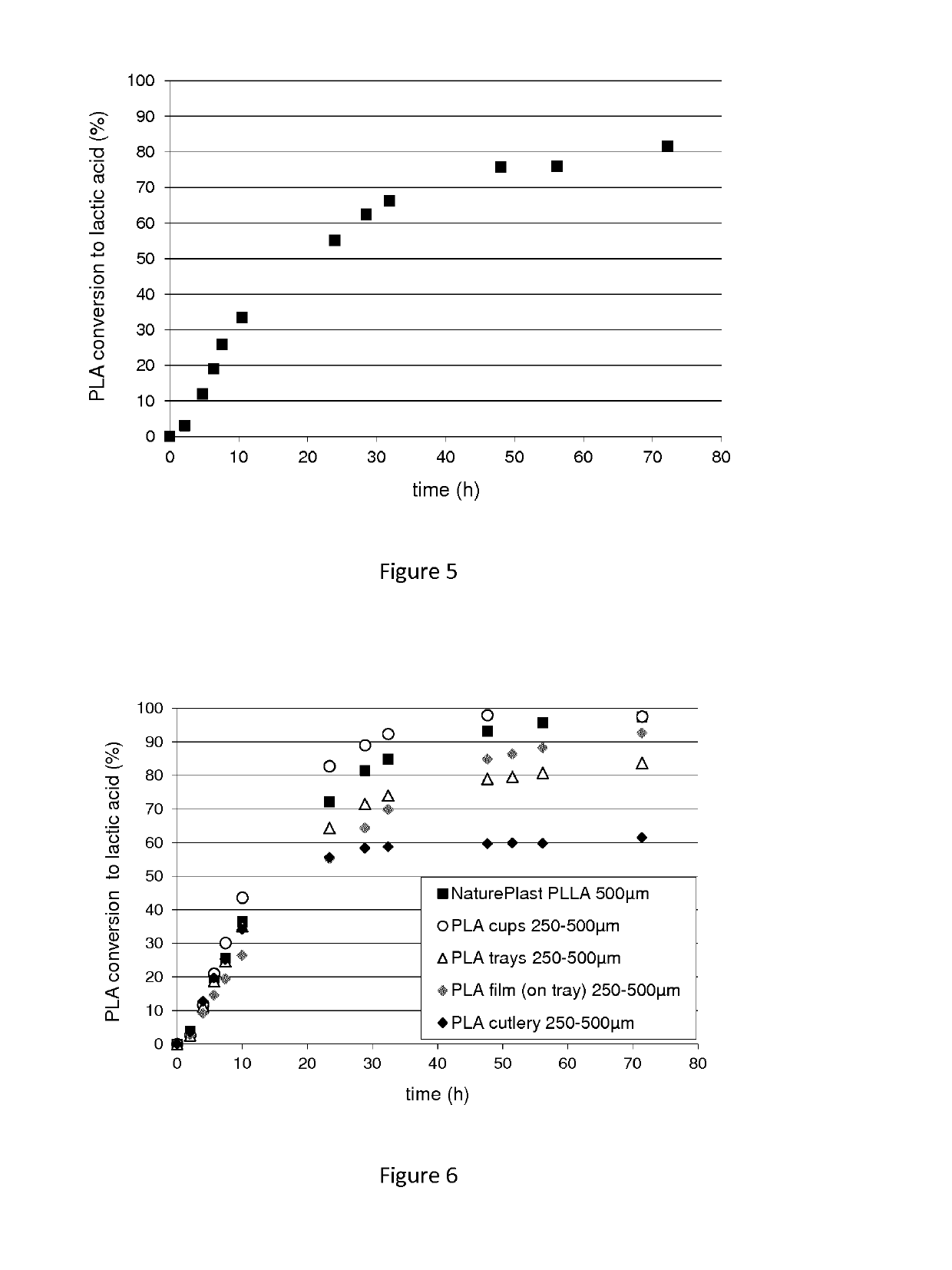
Polypeptide having a polyester degrading activity and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170313998A1Improve thermal stabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesPolyesterAmino acid
The present invention relates to a new isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 94%, 95%, 99% or 100% identity to the full length amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, and having a polyester degrading activity, and uses thereof.
Owner:CARBIOS +3
Polypeptide having a polyester degrading activity and uses thereof
ActiveUS10287561B2Improve thermal stabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention relates to a new isolated polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 94%, 95%, 99% or 100% identity to the full length amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, and having a polyester degrading activity, and uses thereof.
Owner:CARBIOS +3
Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation
ActiveUS20120177644A1Ameliorating and preventing arthritisAmeliorating and preventing and joint injuryOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineArthritis
The present invention provides for methods and compositions for treating or preventing arthritis and joint injury.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +2
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum , is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:EVANS THOMAS +2
Tumor antigen protein and tumor vaccine
InactiveCN106432460AImproving immunogenicityProlong the action timeTumor rejection antigen precursorsTumor specific antigensMelanomaHuman tumor
The invention discloses a tumor antigen protein and a tumor vaccine. The tumor antigen protein comprises a human tumor cell membrane MUC1-Xex peptide fragment, and an amino acid sequence of the MUC1-Xex peptide fragment is as shown in SEQ ID No: 1. The tumor vaccine contains the tumor antigen protein. The tumor antigen protein selects MUC1-Xex peptide fragment with an MUC1 target point as an antigen, thus having very good safety; more preferentially, an adjuvant immune stimulating protein is directly coupled with the MUC1-Xex peptide fragment by means of gene fusion recombinant expression, so that the immunogenicity is improved. The tumor vaccine selects a clinical commonly used aluminum adjuvant as an auxiliary material, so that the action time of the vaccine is prolonged. Finally, animal experiments prove that after being intramuscularly injected, the obtained tumor vaccine has good safety and effectiveness. The tumor vaccine has a good treatment effect on malignant tumors, especially for lung cancer, melanoma and colon cancer.
Owner:蔡炯
Stabilized reverse transcriptase fusion proteins
ActiveUS20120009630A1Substantial RT activityImprove synthesis abilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesReverse transcriptaseReverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
Stabilized reverse transcriptase fusion proteins including a thermostable reverse transcriptase connected to a stabilizer protein are described. Attaching the stabilizer protein to the thermostable reverse transcriptase stabilizes the fusion protein and can aid in its purification, provide increased solubility, allow for longer storage, or allow the fusion protein to be used under more rigorous conditions such as higher temperature. The stabilized reverse transcriptase fusion protein can also include a linker between the stabilizer protein and the thermostable reverse transcriptase. The stabilized reverse transcriptase fusion proteins are suitable for use in nucleic acid amplification methods such as the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and other applications involving cDNA synthesis.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compositions and methods for delivering biotherapeutics
InactiveUS20180346531A1Facilitates detection and isolation and purificationImprove solubilityNervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainDiseaseEpitope
Provided herein are compositions and methods relating to cell-penetrating conjugates for the delivery of therapeutic polypeptides or polynucleotides to cells or tissues of the body. The delivery conjugate comprises a cell-penetrating peptide and a nuclear localization signal sequence plus an effector moiety (such as a polypeptide or polynucleotide) as the payload, optionally further including an epitope tag as well as a solubility peptide and a configurating peptide. The delivery conjugate can also include a component capable of specifically directing the conjugate to a target cell or tissue, making the conjugate effective for treating diseases in the target tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
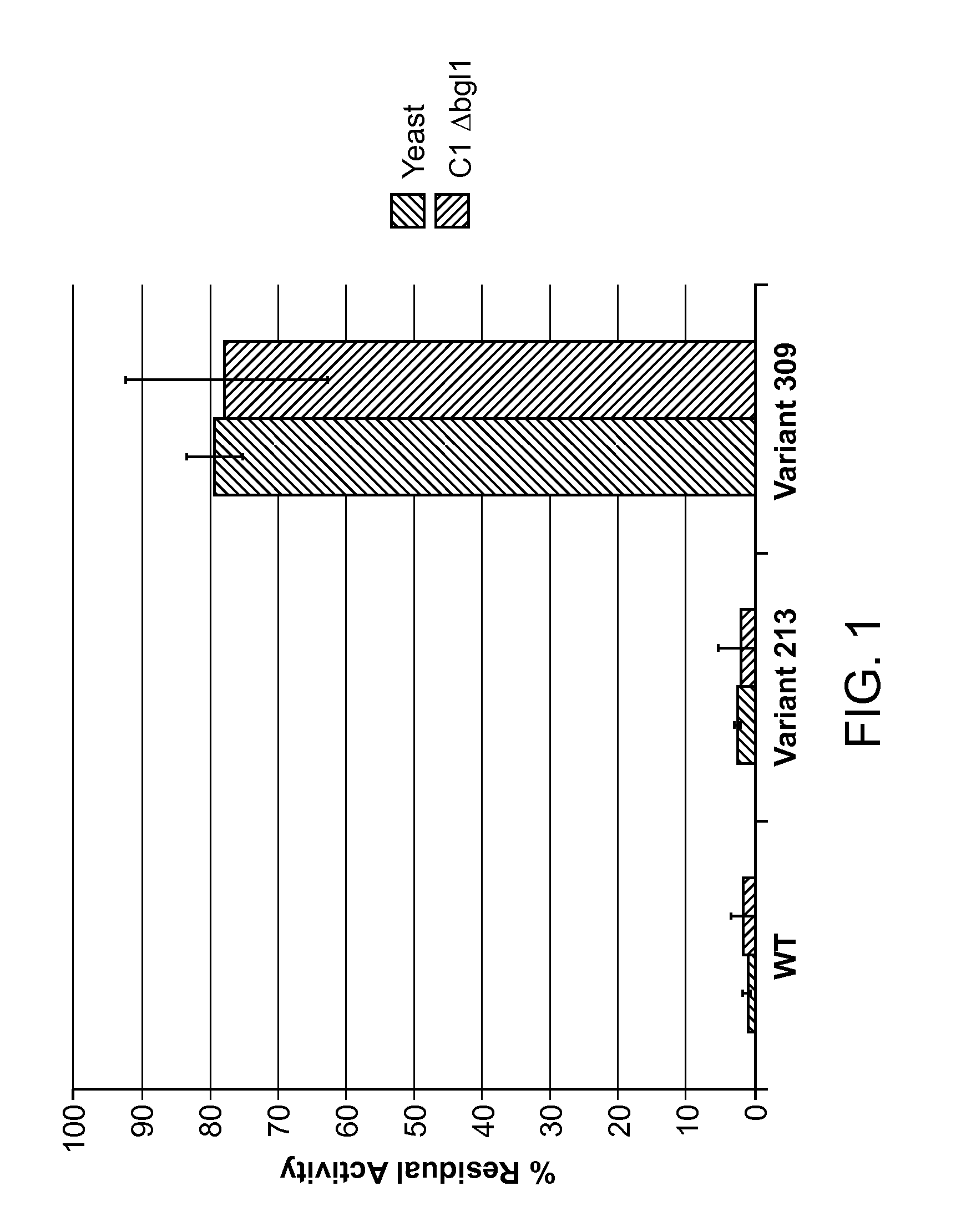
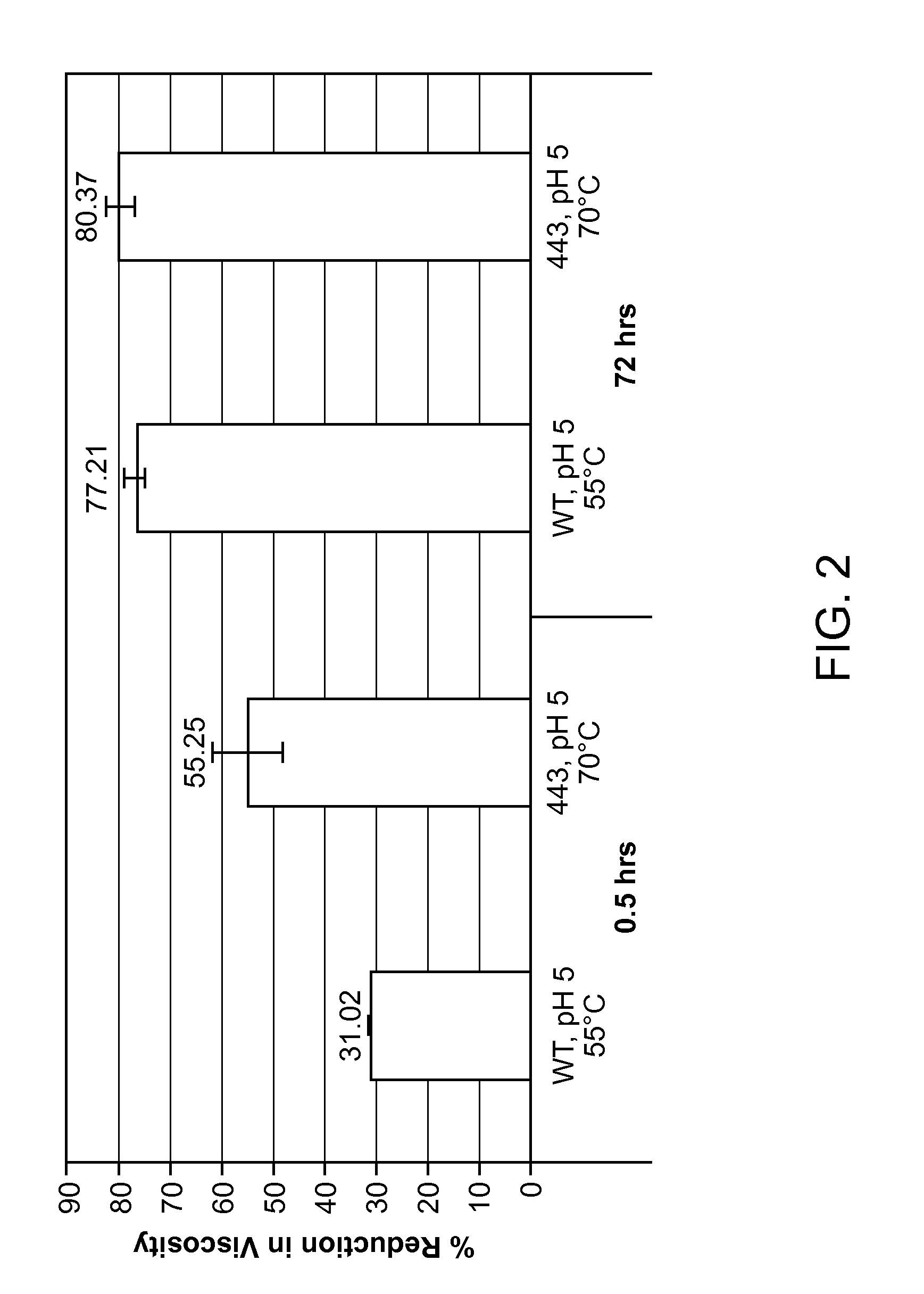
Endoglucanase variants
InactiveUS20120208235A1Improve propertiesIncreased thermoactivitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGlucanaseGenetics
The present invention relates to variant endoglucanases having improved thermoactivity, improved thermostability, and improved viscosity reduction activity over wild-type M. thermophila endoglucanase.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
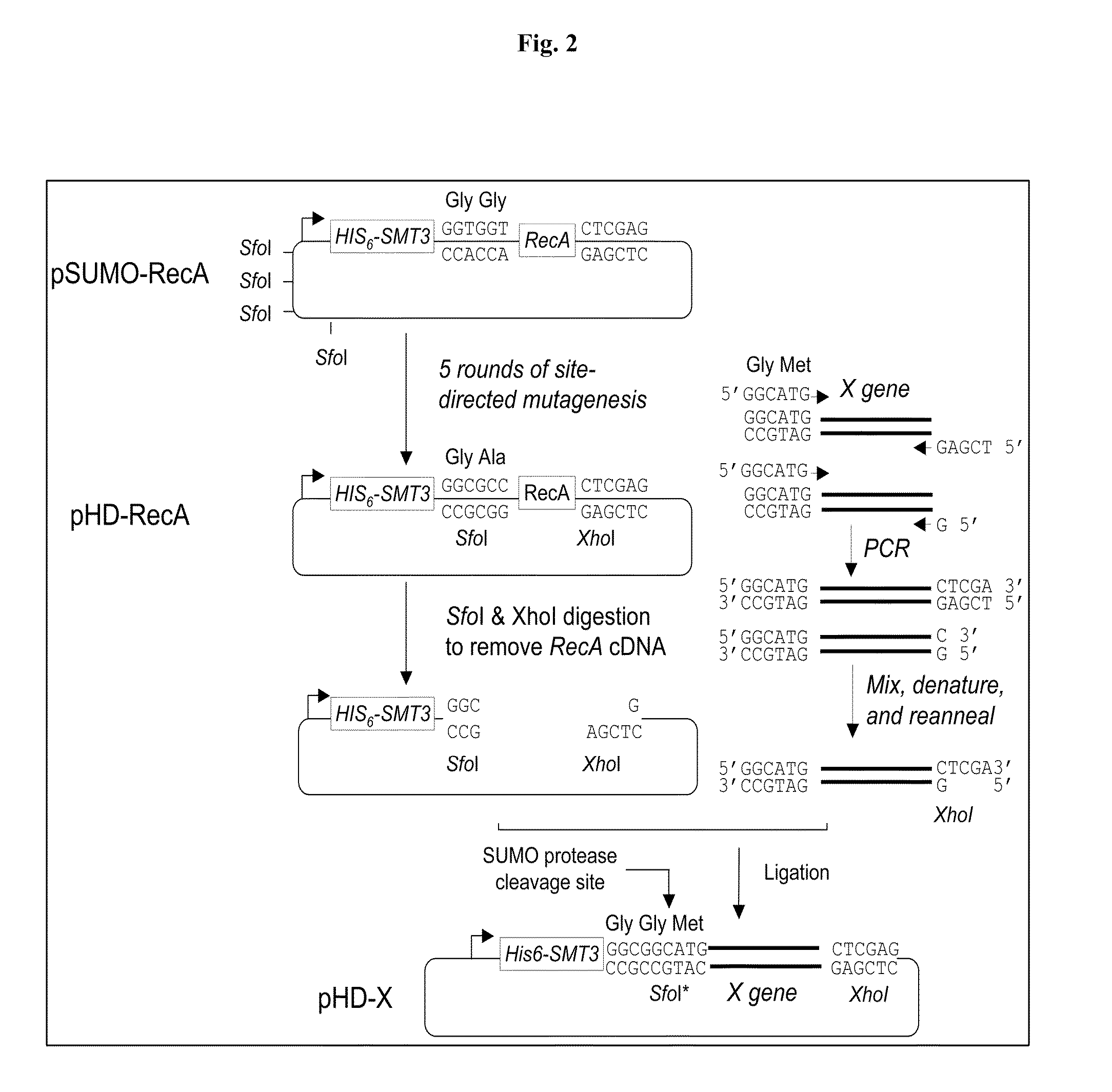
Sumo-specific affinity tag
InactiveUS20130017554A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsFluorescence/phosphorescenceProteinase activityCombinatorial chemistry
A new SUMO-specific affinity tag is described herein, based on the amino acid sequence from 403-621 of the SUMO protease Ulp1, and containing a crucial substitution of serine for cysteine. This affinity tag is particularly useful for a range of applications, including detection and affinity purification of sumoylated proteins from cell extracts.
Owner:COLLEGE OF WILLIAM & MARY
Method for producing serratia marcescens nuclease using a bacillus expression host
ActiveUS9796994B2Reduce decreaseContamination of the process product by endotoxins can be avoidedBacteriaHydrolasesMicrobiologySecretion
Owner:C LECTA GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com