Ovarian-cancer-targeted polypeptide
An ovarian cancer and targeting technology, applied in the field of protein polypeptides, can solve the problems of few reports on screening ovarian cancer targeting ligands, and the ability to use the in vivo targeting properties of polypeptides to deliver drugs, etc., and achieve good targeting. Ability, small molecular weight of polypeptide, good tissue penetration effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
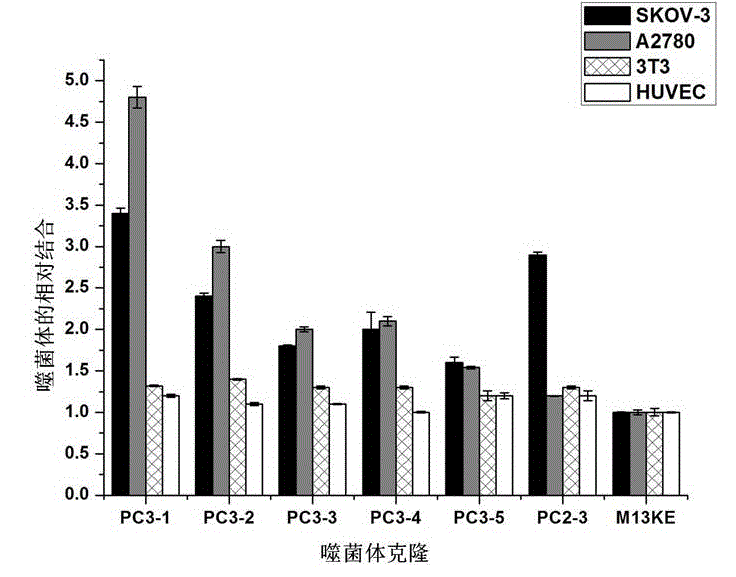
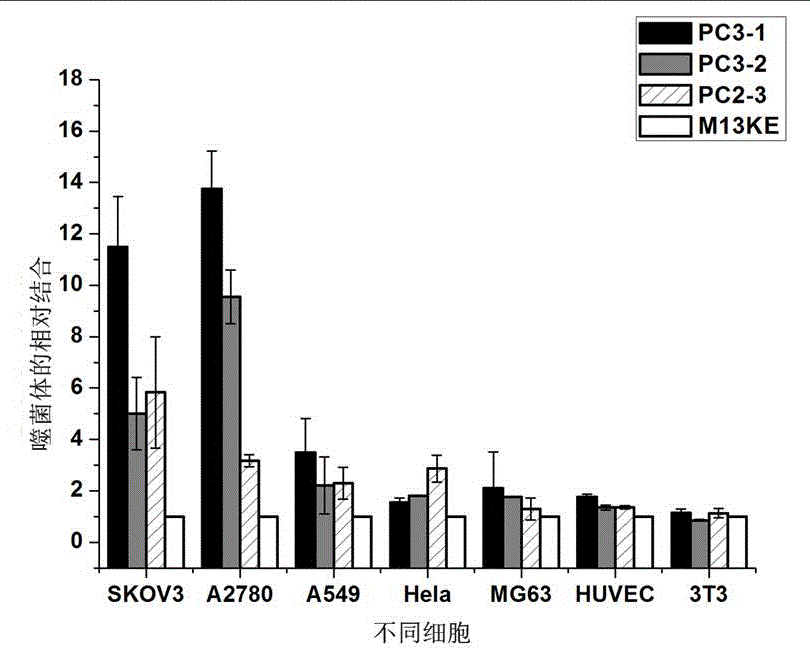
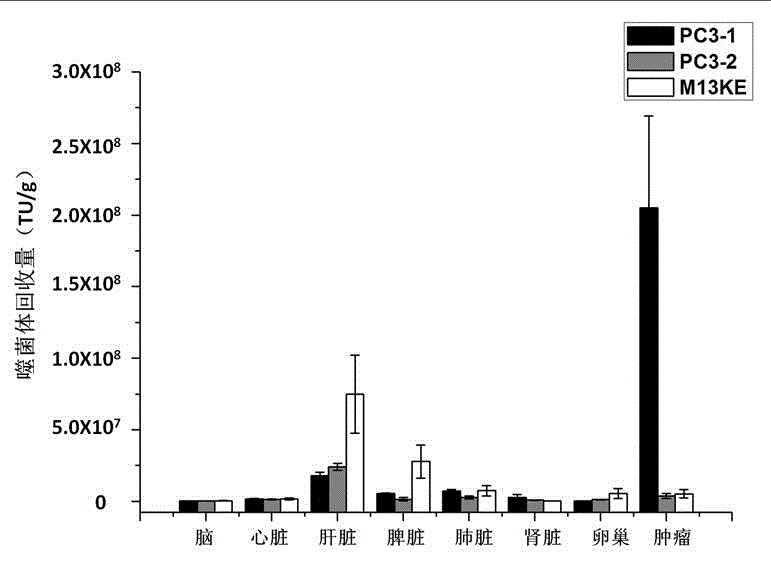
[0022] (1) In vivo screening of phage display random dodecapeptide library and sequencing and analysis of phage monoclonal DNA
[0023] BALB / c nude mice aged 4-6 weeks were selected and inoculated with human ovarian epithelial cancer cells SKOV-3 in the armpit of their right forelimbs to establish a human ovarian cancer tumor model. Choose Ph.D-12 from New England Biolabs TM The peptide library, diluted in PBS, was injected into the tumor model and circulated for 15 minutes. After heart perfusion, the tumor tissue was recovered, homogenized, weighed, and the cells were lysed to recover the phages, which were amplified and put into the next round of in vivo screening. At the same time, the titer of the phages recovered in each round of screening was determined by the method described in the New England Biolabs company's experimental guide, and the monoclonal DNA of the phages randomly selected and amplified in the second and third rounds of screening results was extracted an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com