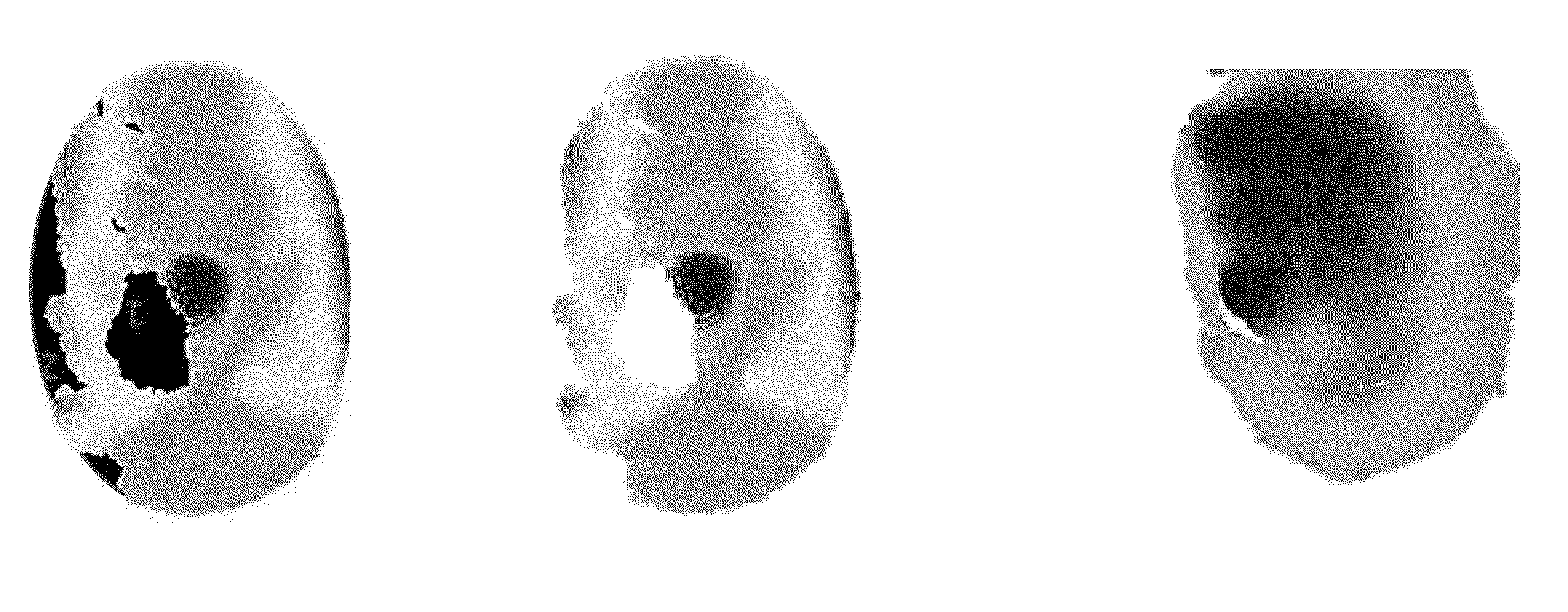System and Method for Off Angle Three-Dimensional Face Standardization for Robust Performance
a three-dimensional face and robust technology, applied in the field of system and method for robust performance of three-dimensional face standardization, can solve the problems of two scans, complex process, and 3d face alignmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
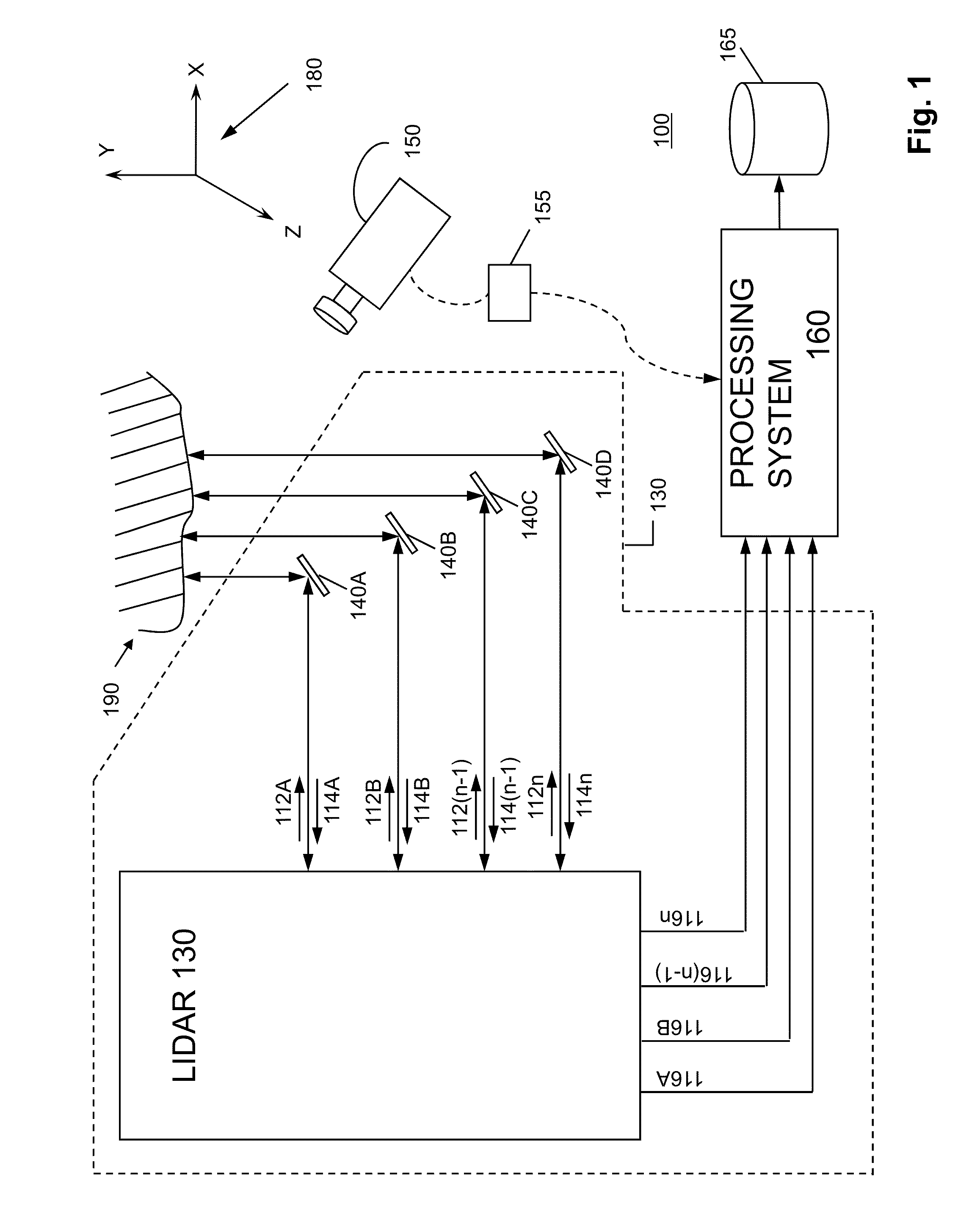
[0030]FIG. 1 illustrates a combined lidar and video camera system 100 (three dimensional measurement system 100) according to various implementations of the invention. Various implementations of the invention utilize synergies between lidar measurements and video images to resolve six degrees of freedom for motion of a target to a degree not otherwise possible with either a lidar or video camera alone.
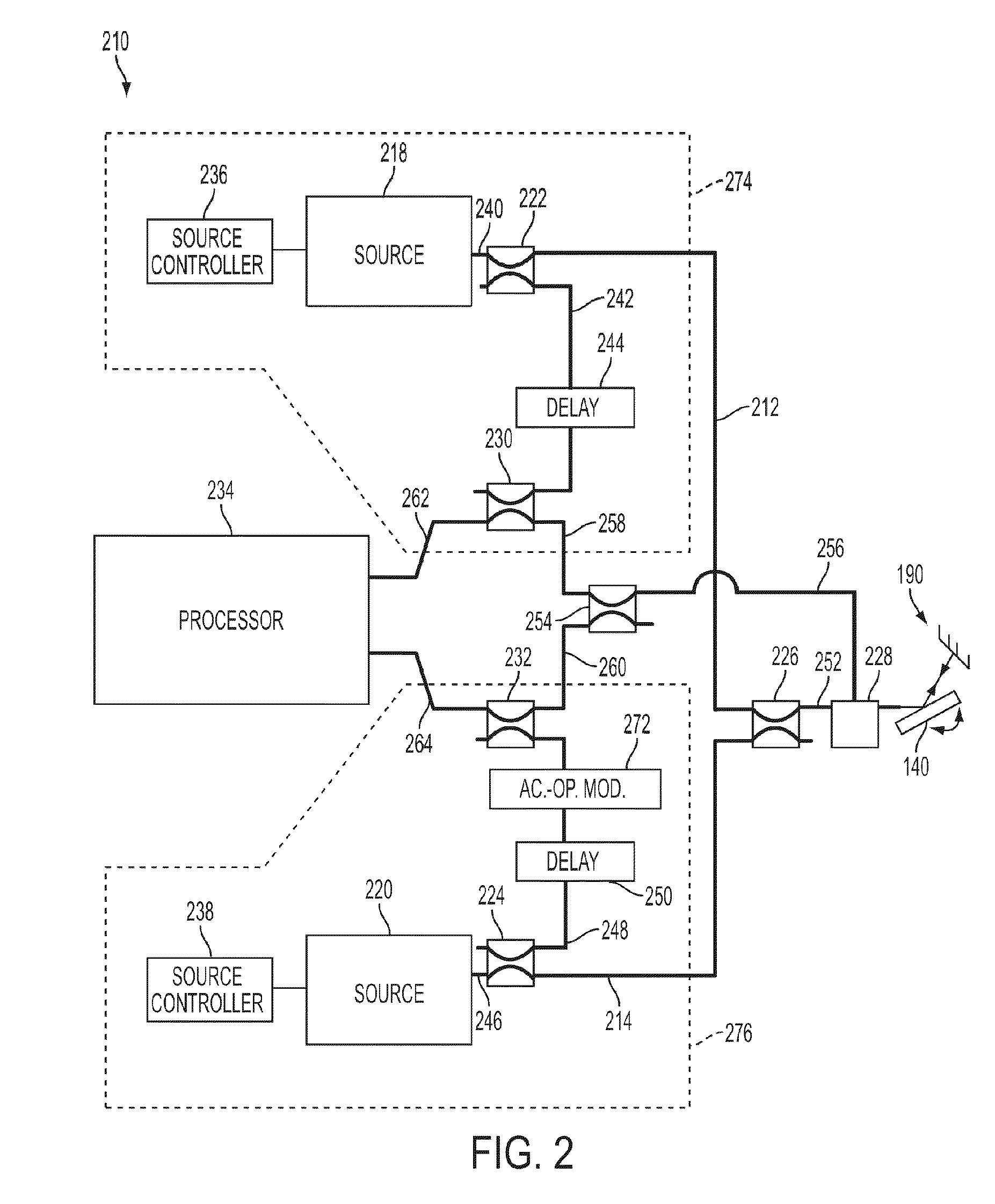
[0031]Combined system 100 includes a lidar subsystem 130, a video subsystem 150, and a processing system 160. As illustrated, lidar subsystem 130 includes two or more lidar beam outputs 112 (illustrated as a beam 112A, a beam 112B, a beam 112(n−1), and a beam 112n); two or more reflected beam inputs 114 each corresponding to one of beams 112 (illustrated as a reflected beam 114A, a reflected beam 1148, a reflected beam 114(n−1), and a reflected beam 114n); two or more lidar outputs 116 each associated with a pair of beam 112 / reflected beam 114 (illustrated as a lidar output 116A associ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com