Patents
Literature
59 results about "Isotachophoresis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
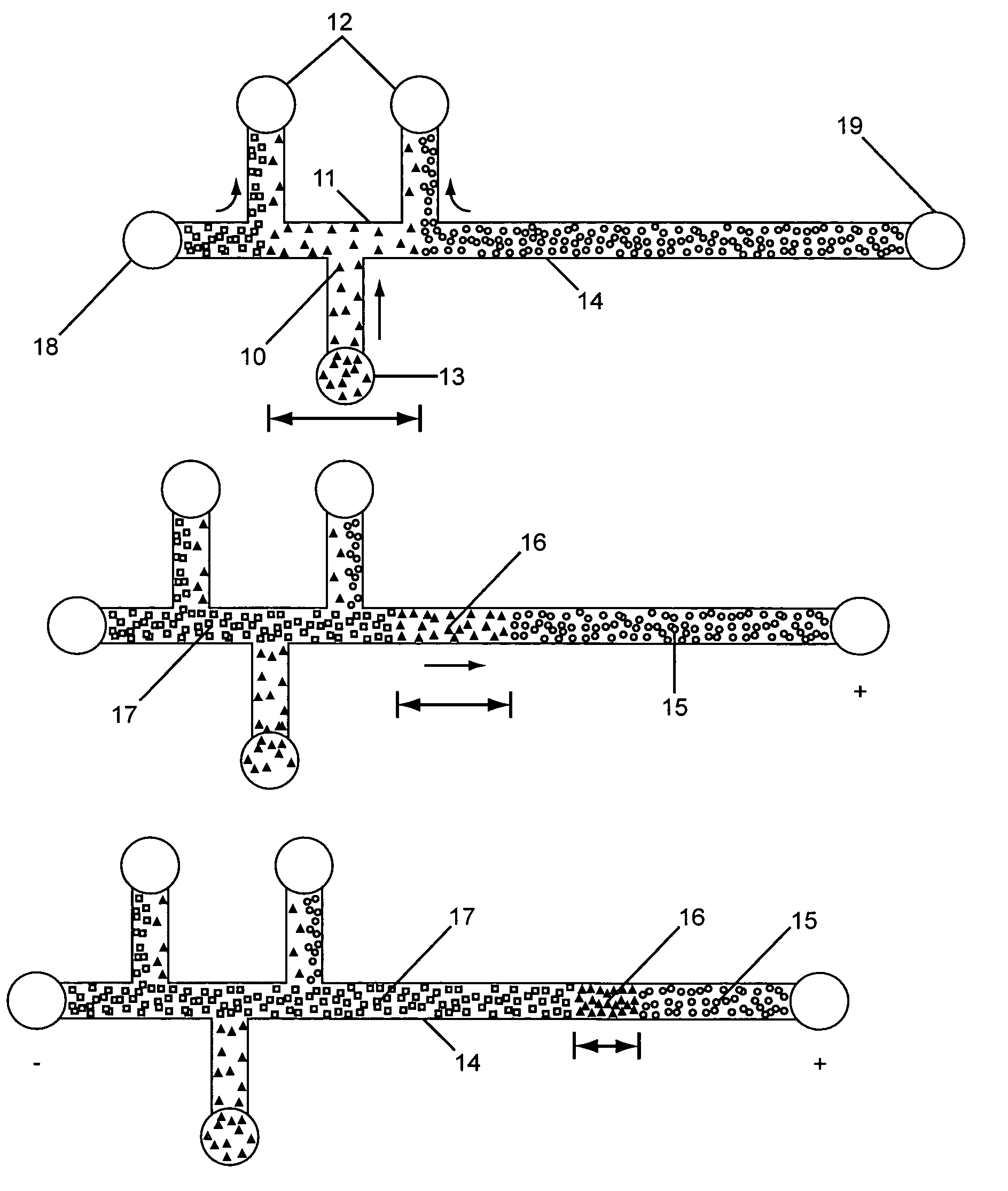
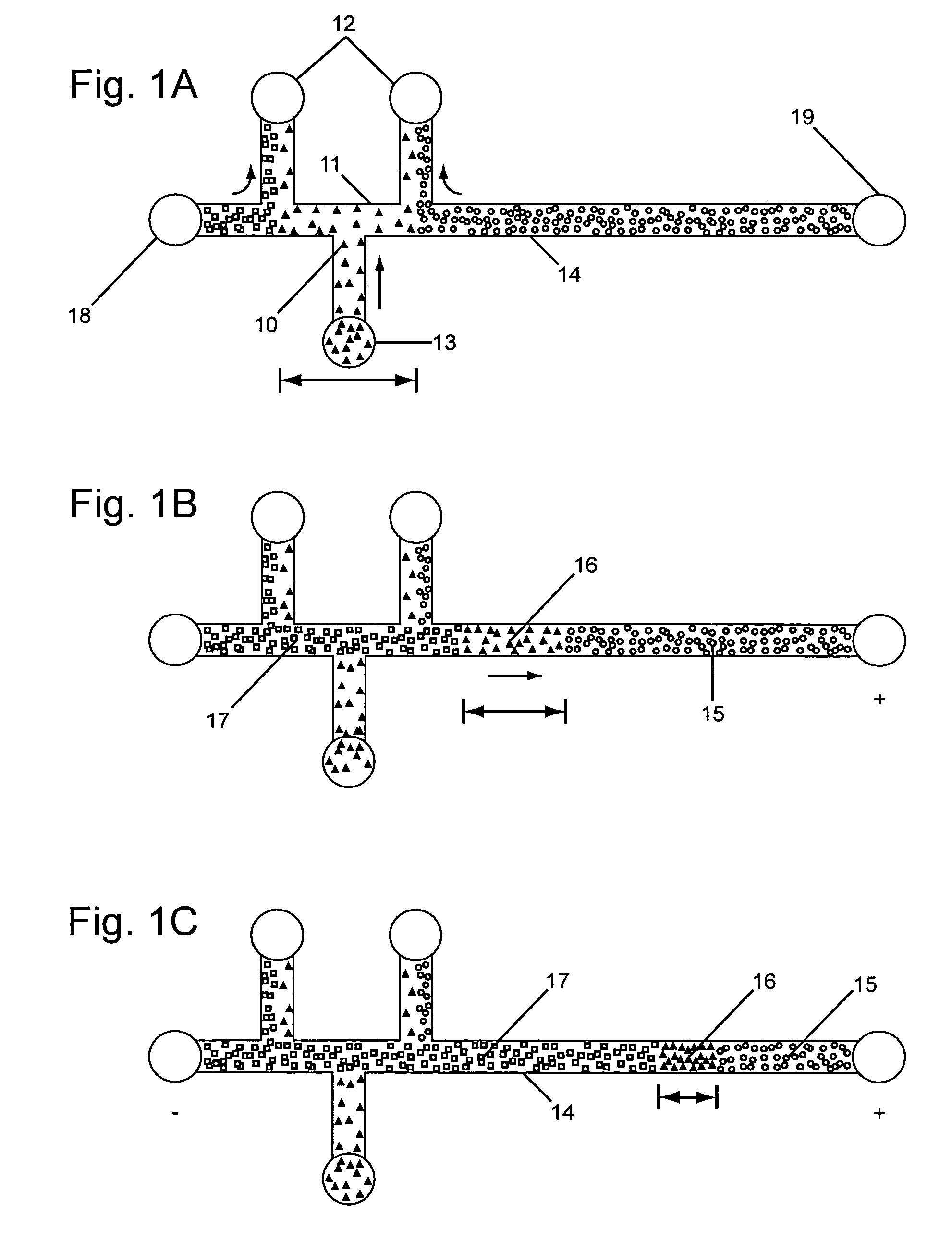
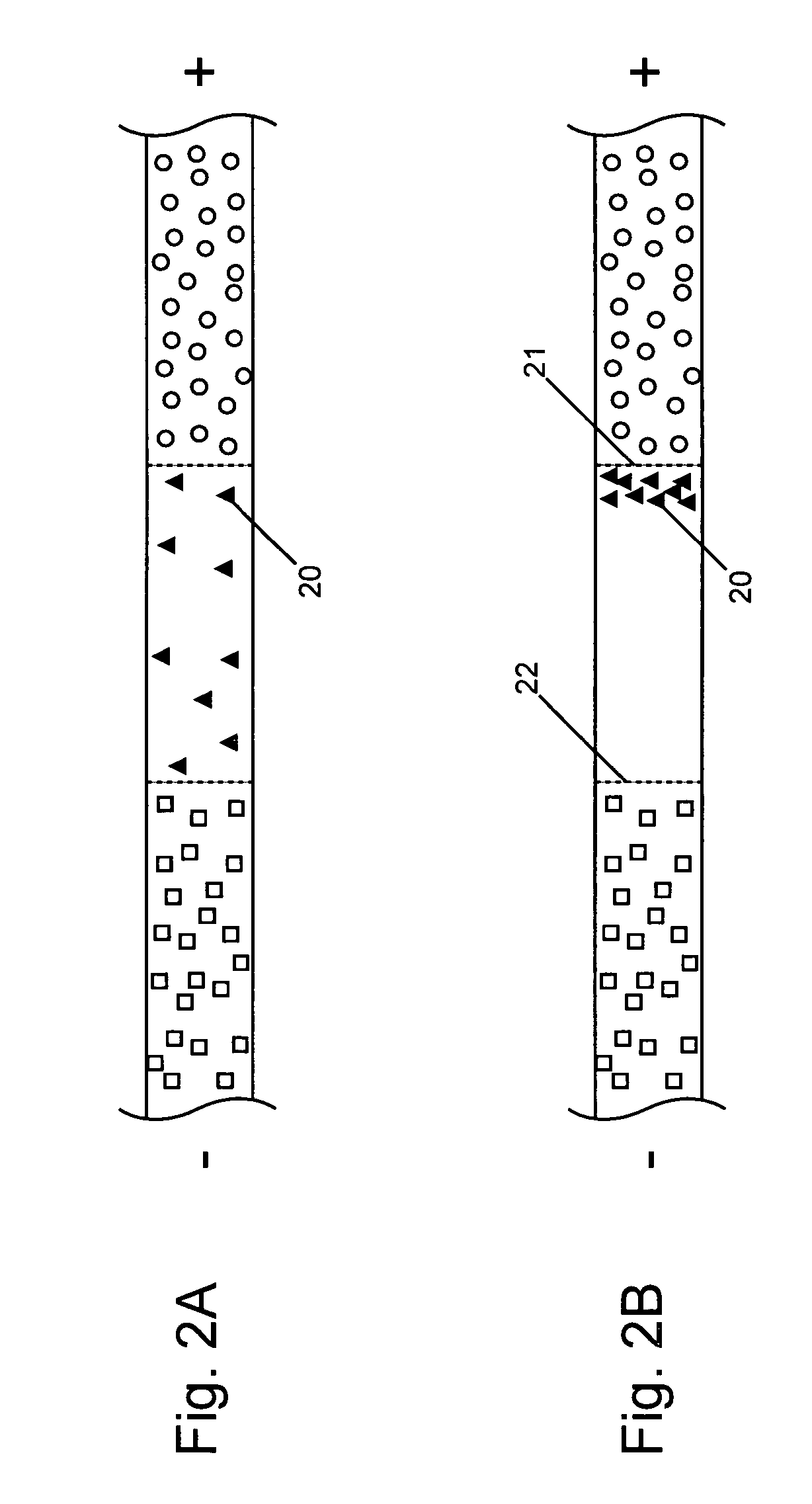
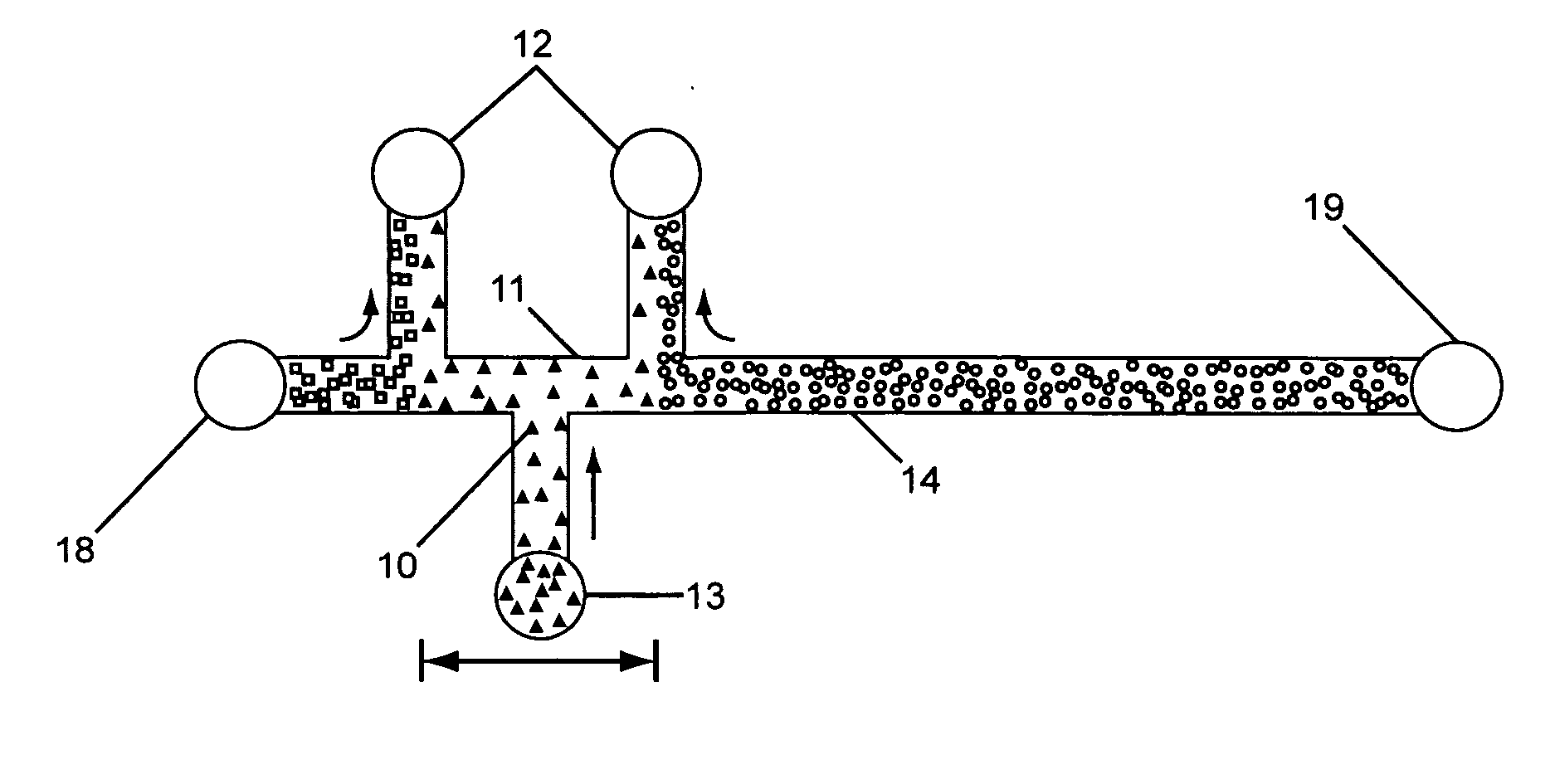
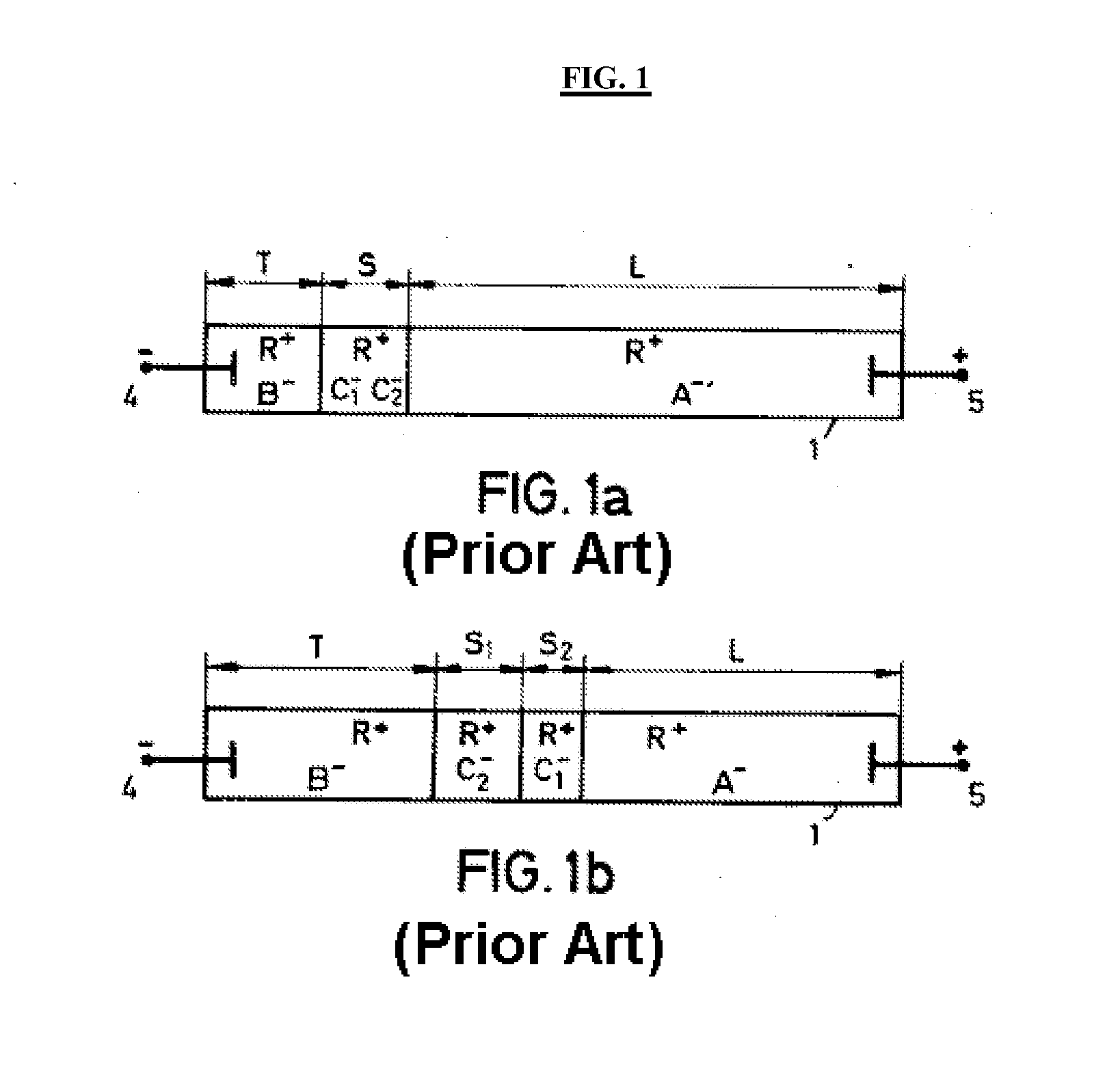
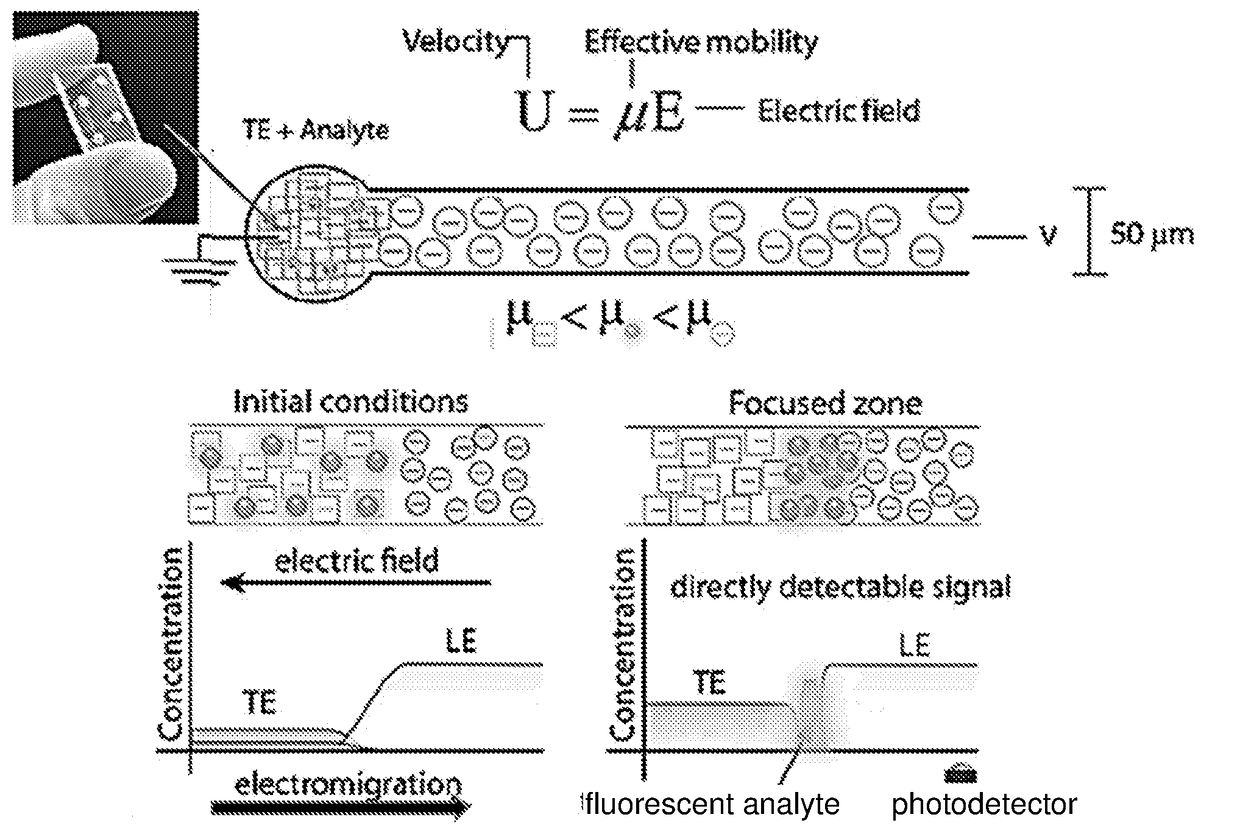
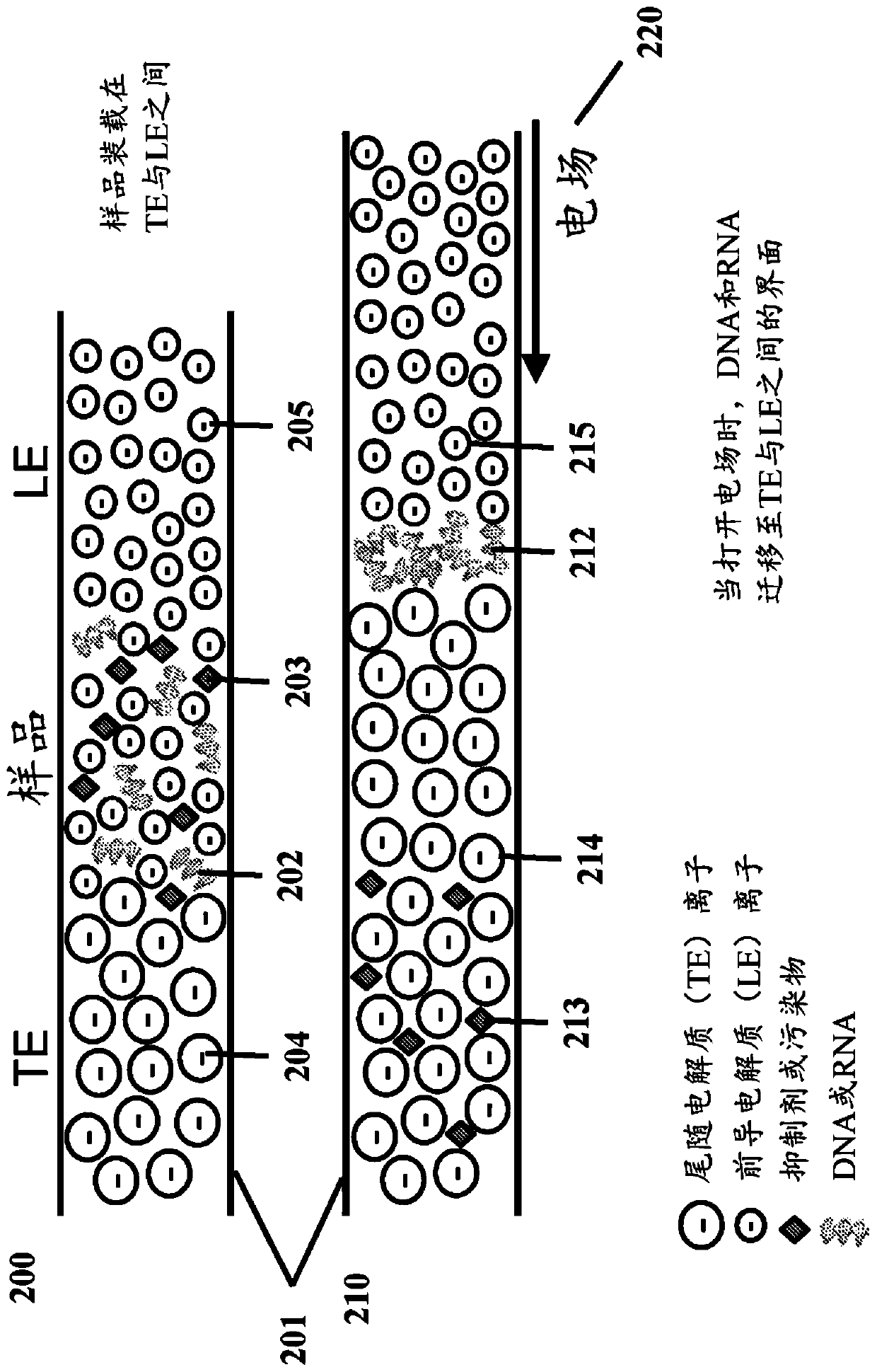
Isotachophoresis (ITP) is a technique in analytical chemistry used for selective separation and concentration of ionic analytes. It is a form of electrophoresis: charged analytes are separated based on ionic mobility, a factor which tells how fast an ion migrates through an electric field.
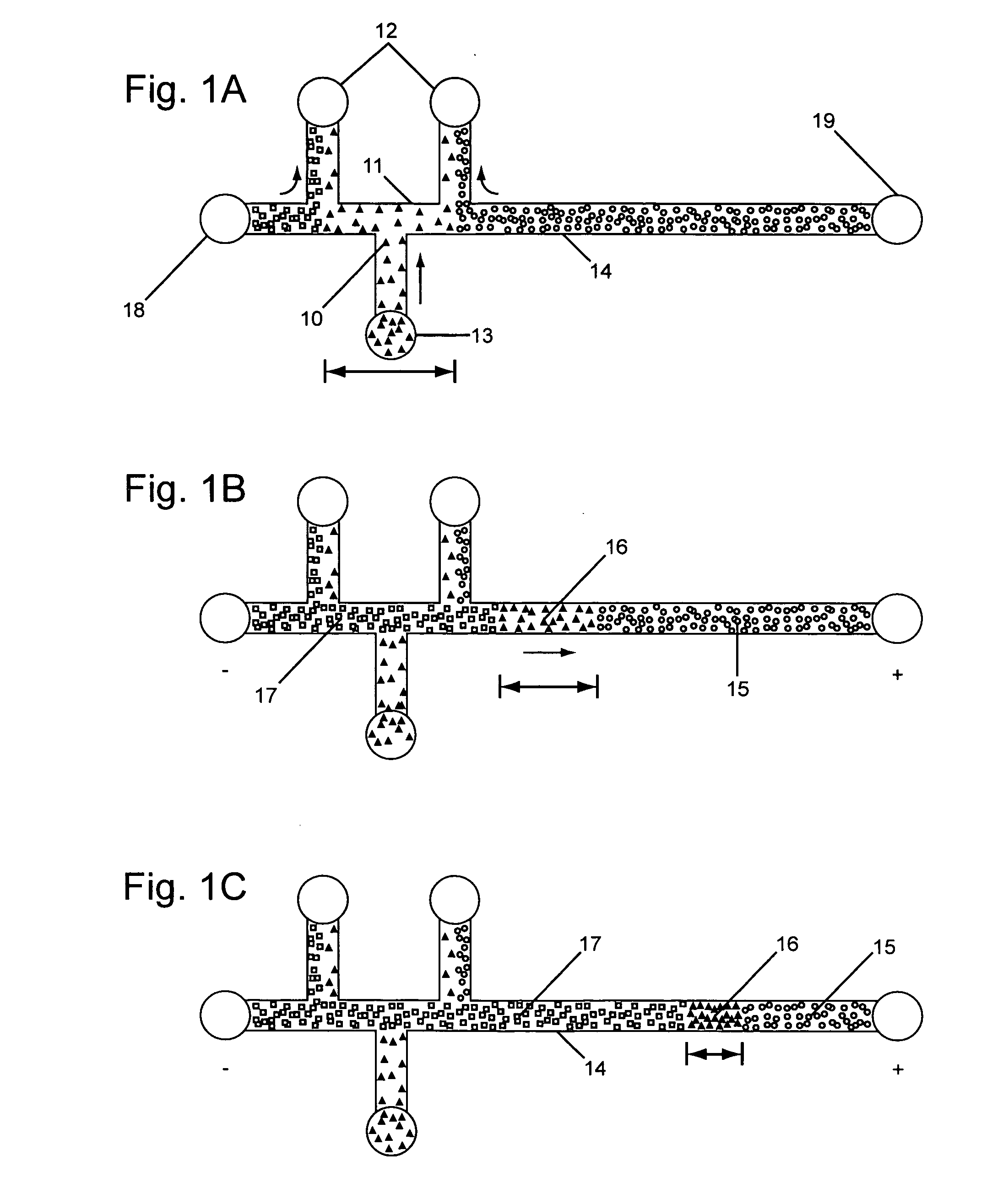
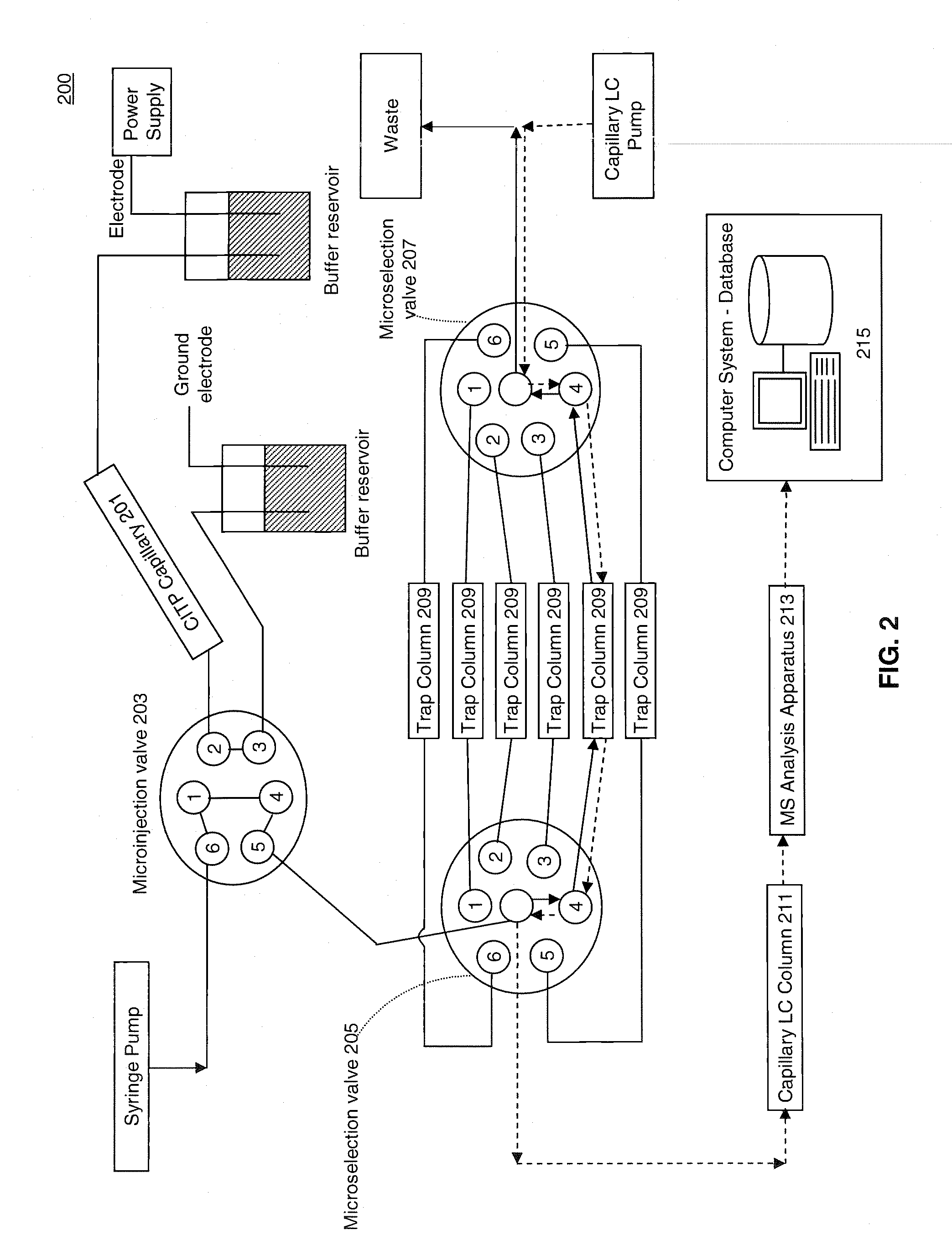
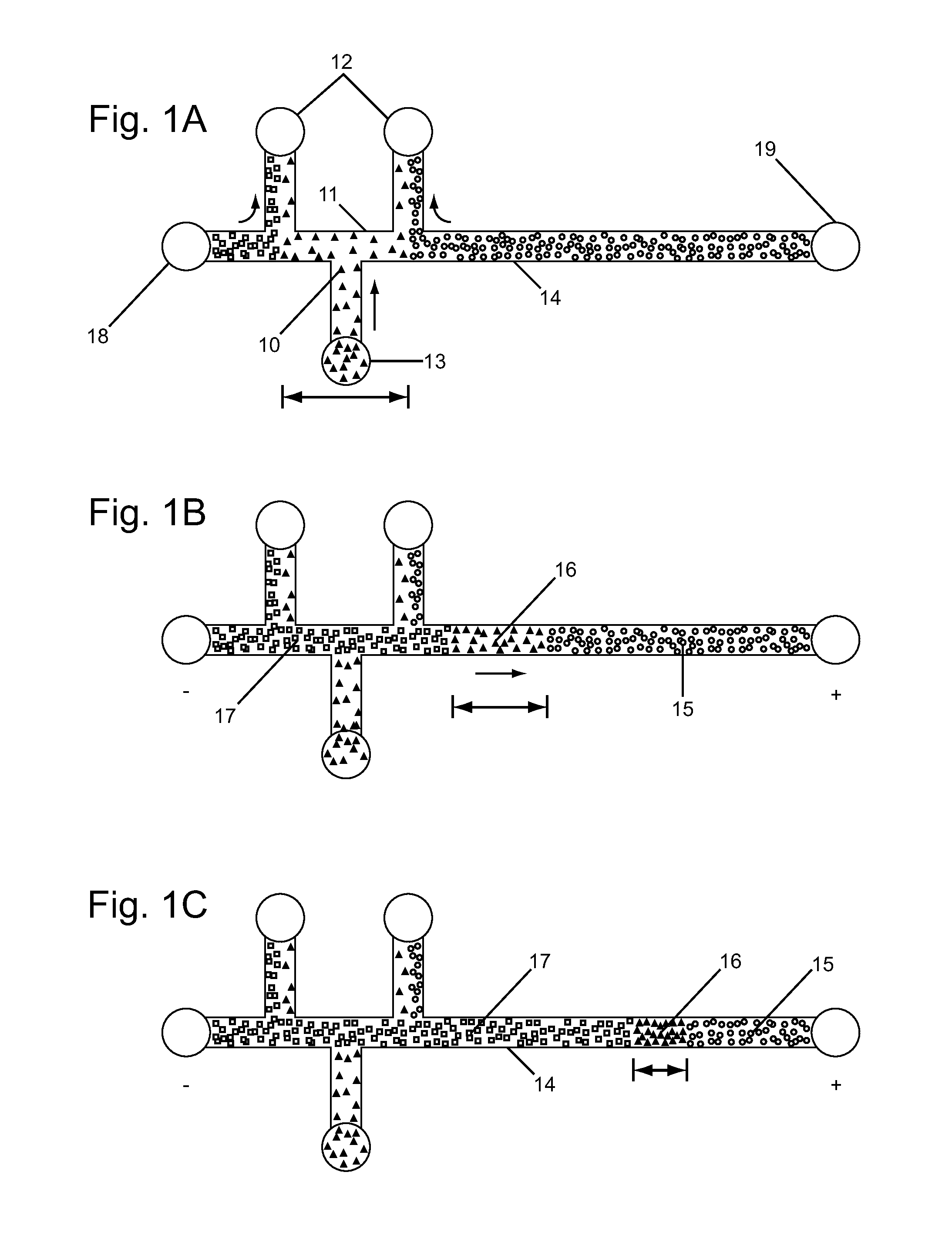
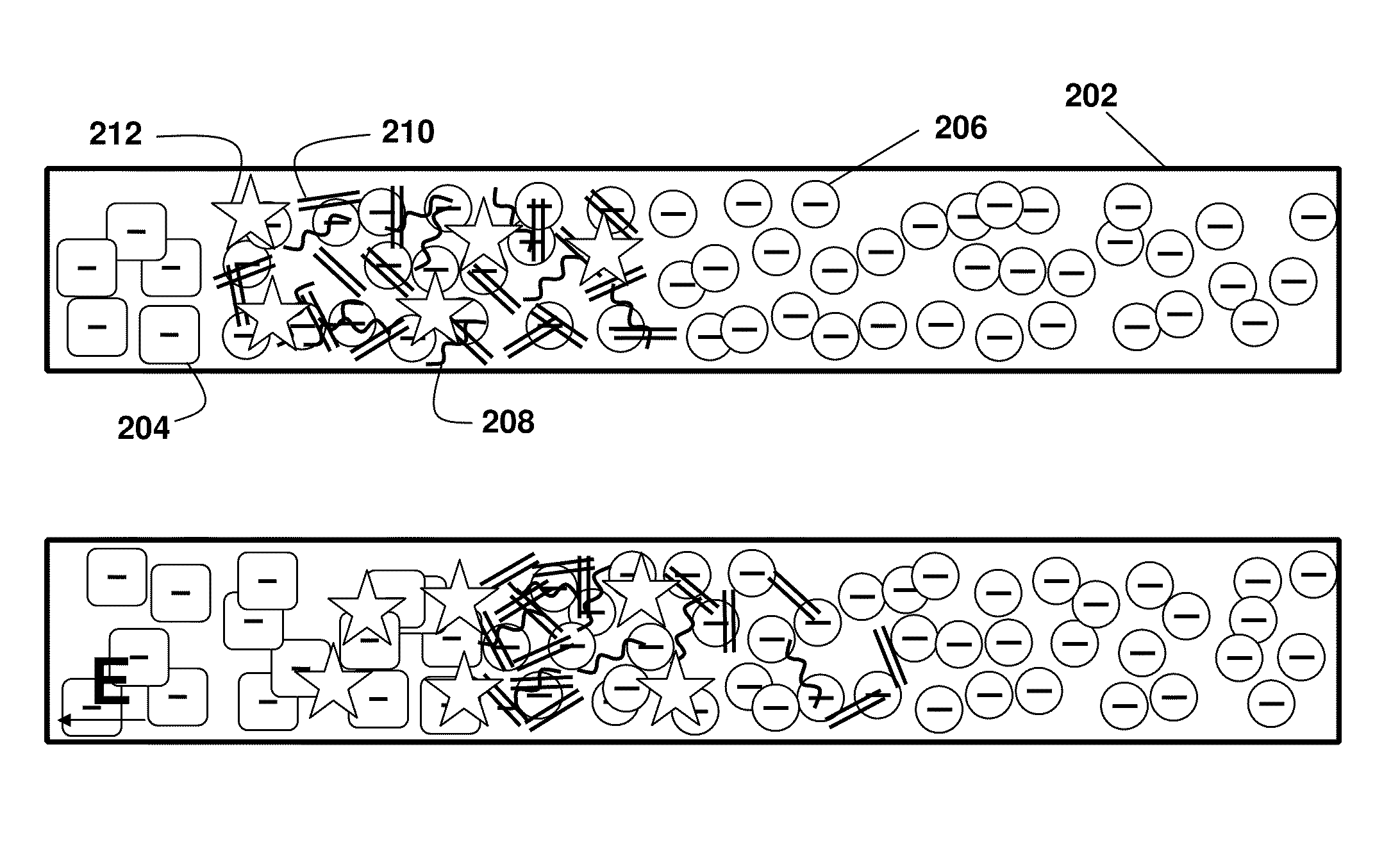
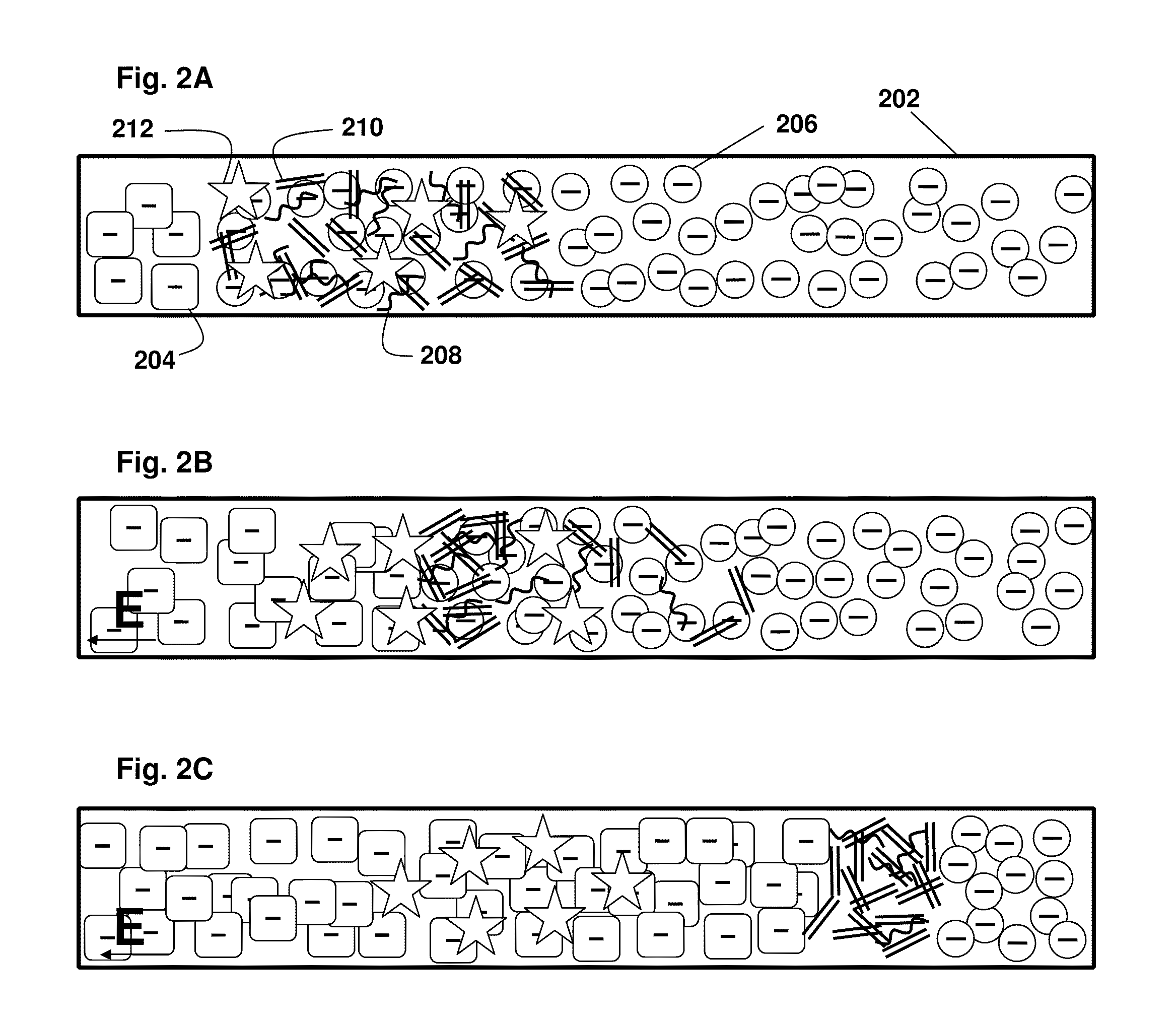
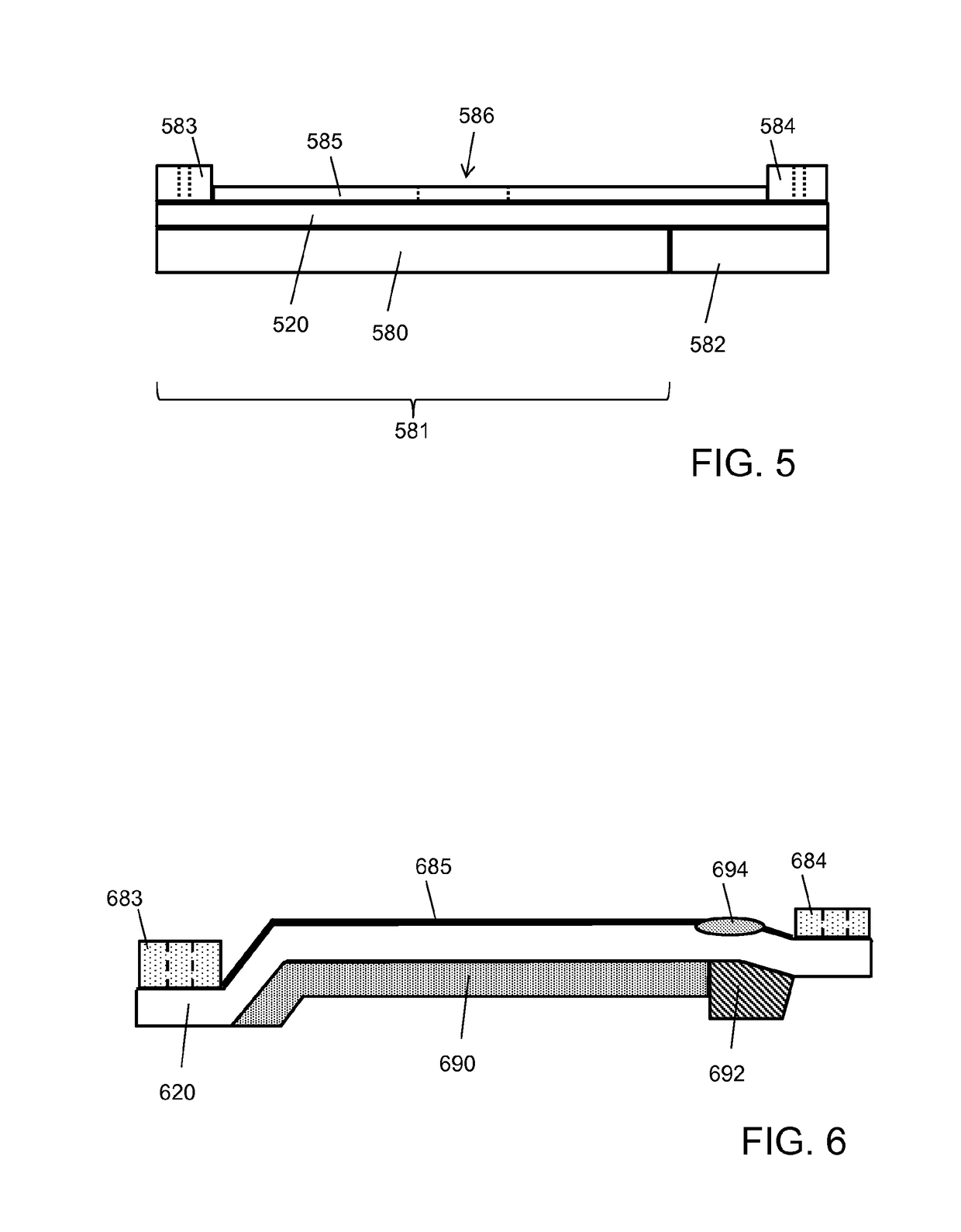
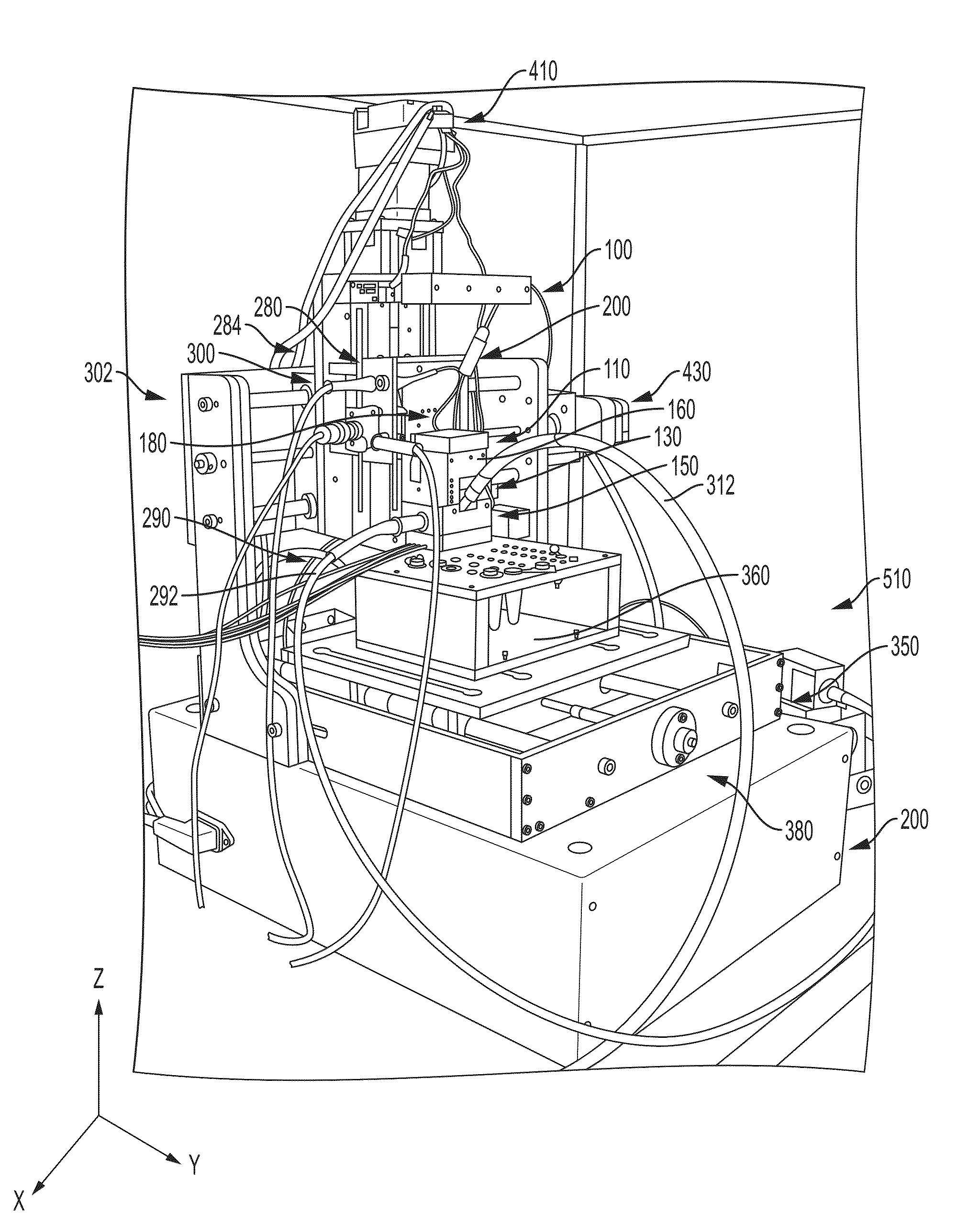
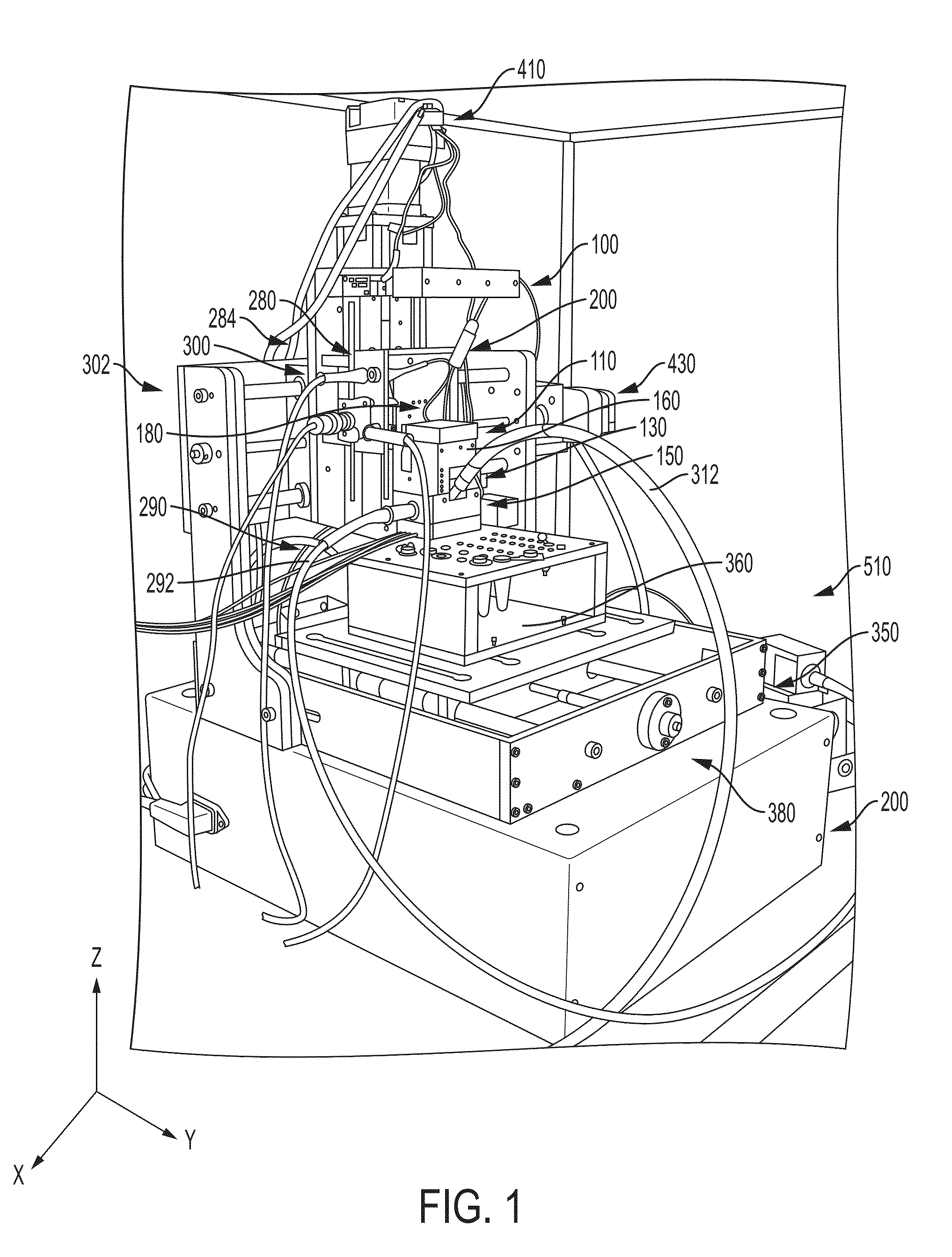
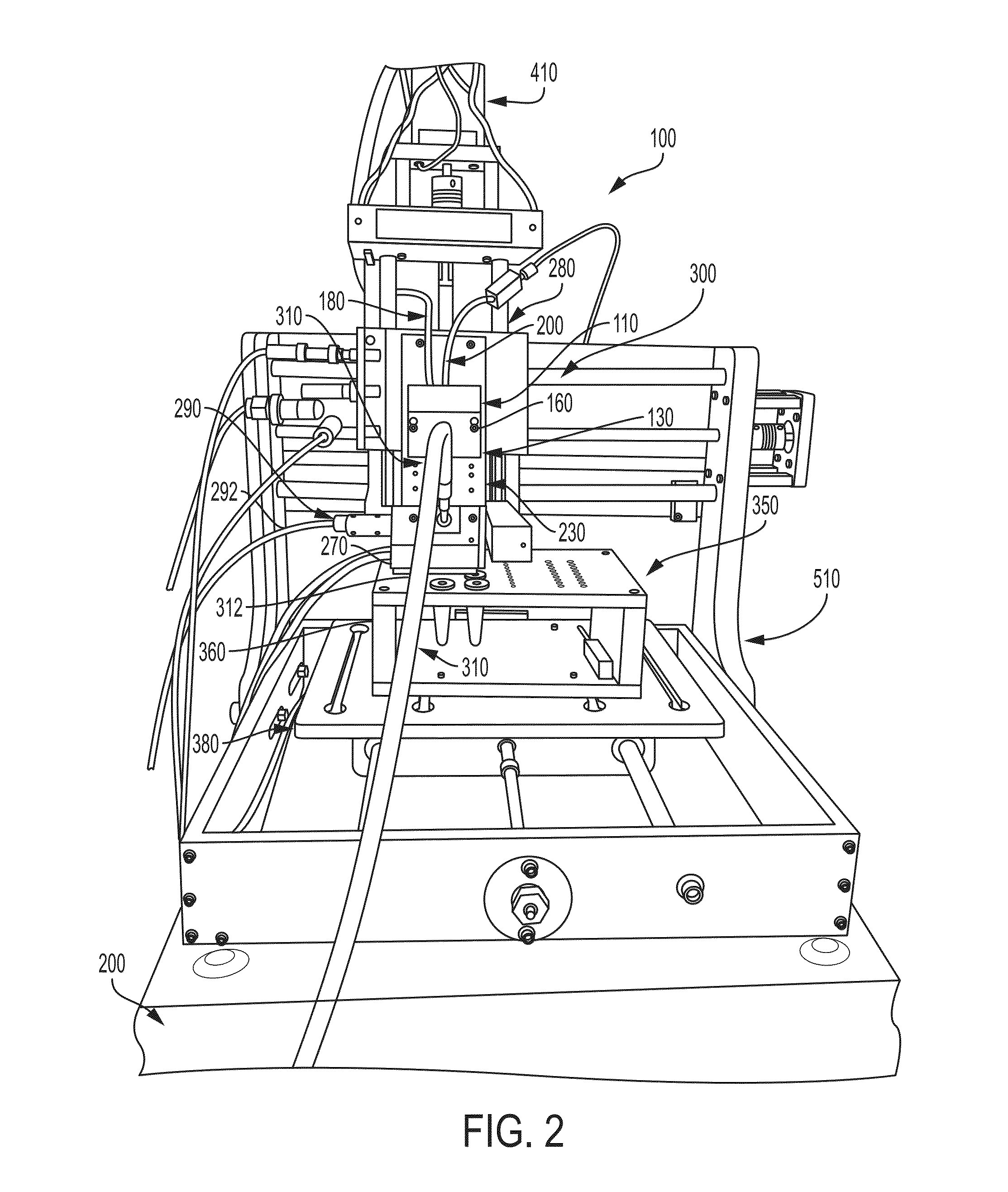
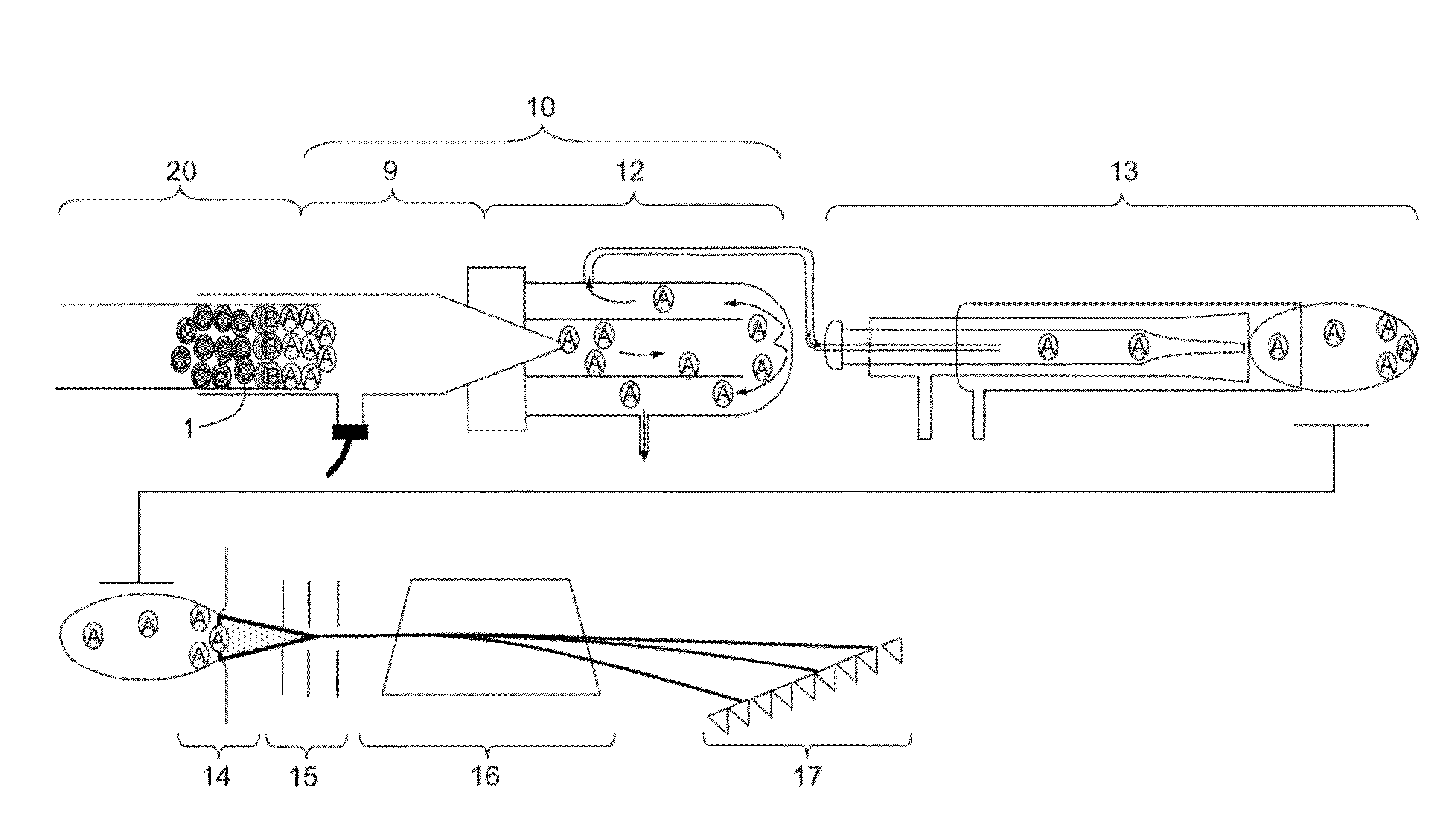
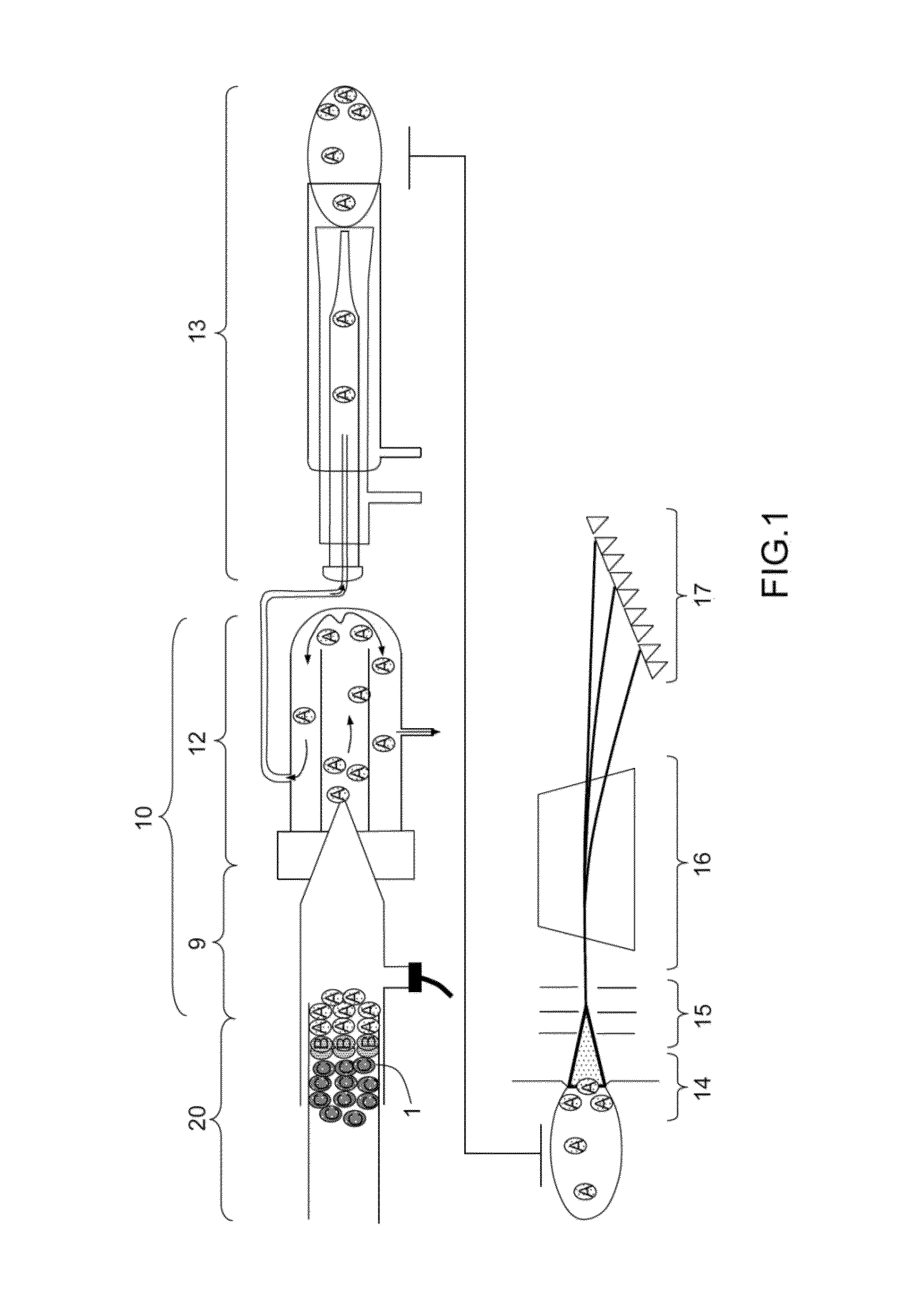
Analyte injection system
InactiveUS20050133370A1Increase in sizeShort amount of timeSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementGlutaric acidAntibody conjugate
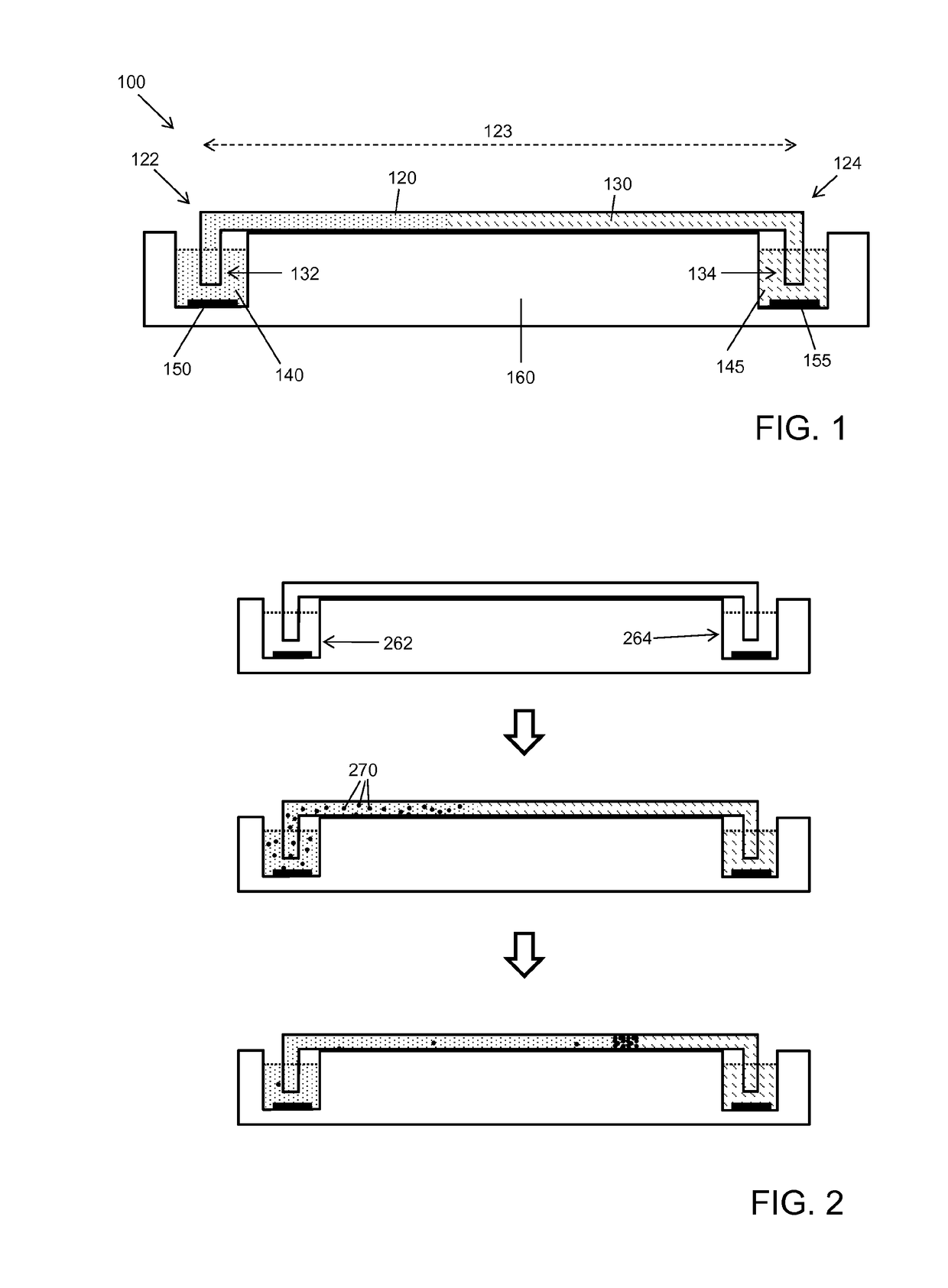
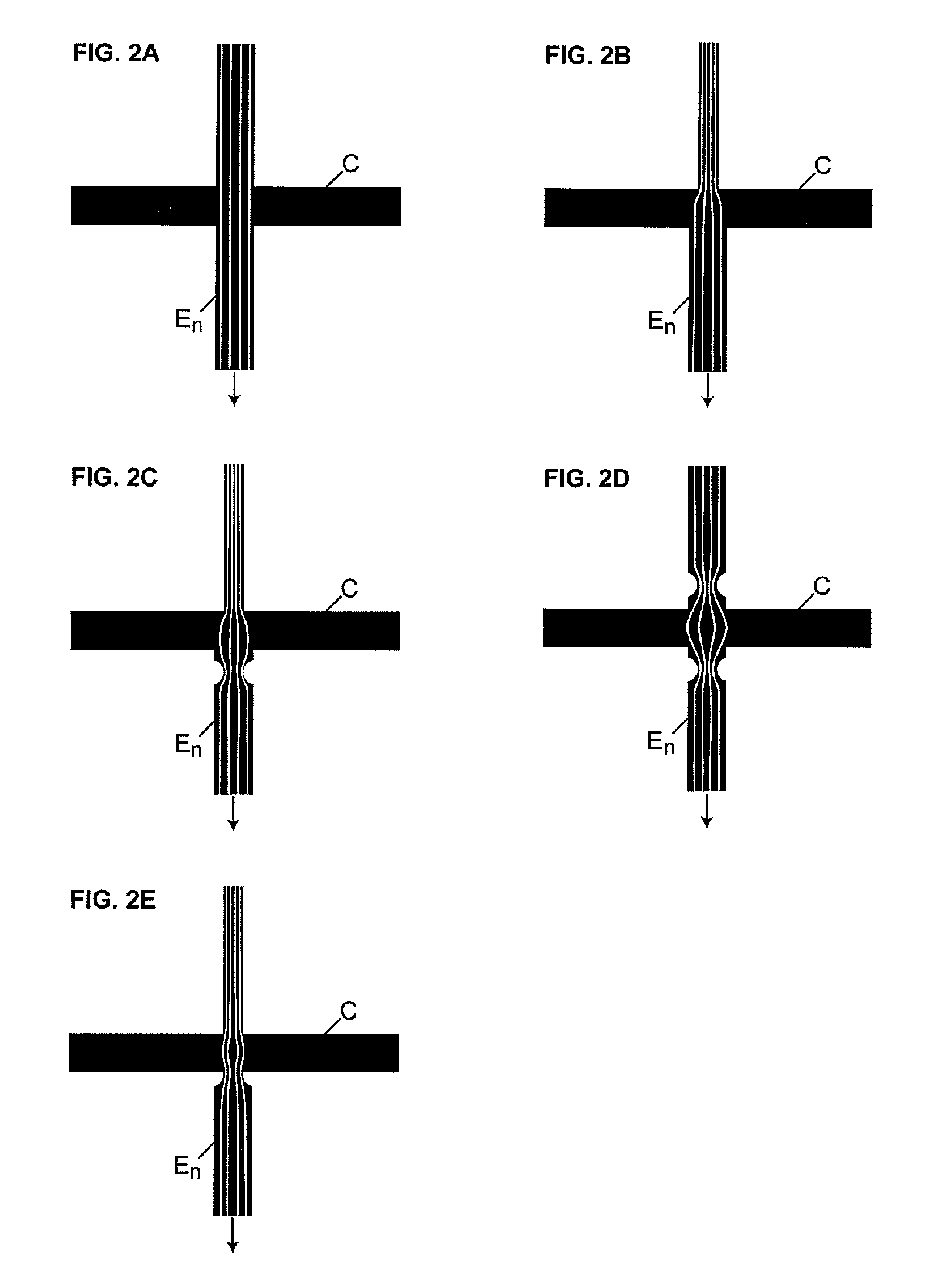
This invention provides methods and devices for spatially separating at least first and second components in a sample which in one exemplary embodiment comprises introducing the first and second components into a first microfluidic channel of a microfluidic device in a carrier fluid comprising a spacer electrolyte solution and stacking the first and second components by isotachophoresis between a leading electrolyte solution and a trailing electrolyte solution, wherein the spacer electrolyte solution comprises ions which have an intermediate mobility in an electric field between the mobility of the ions present in the leading and trailing electrolyte solutions and wherein the spacer electrolyte solution comprises at least one of the following spacer ions MOPS, MES, Nonanoic acid, D-Glucuronic acid, Acetylsalicyclic acid, 4-Ethoxybenzoic acid, Glutaric acid, 3-Phenylpropionic acid, Phenoxyacetic acid, Cysteine, hippuric acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, isopropylmalonic acid, itaconic acid, citraconic acid, 3,5-dimethylbenzoic acid, 2,3-dimethylbenzoic acid, p-hydroxycinnamic acid, and 5-br-2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and wherein the first component comprises a DNA-antibody conjugate and the second component comprises a complex of the DNA-antibody conjugate and an analyte.
Owner:WAKO PURE CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES +1
Analyte injection system
InactiveUS20050121324A1Improve analysis resultsHigh resolutionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteIsotachophoresis
This invention provides methods and systems for injection of analytes into a separation channel for resolution and detection. Samples can be preconditioned and concentrated by isotachophoresis (ITP) before the injection is triggered by a detected voltage event. Separation of analytes from other sample constituents can be enhanced using skewing channel ITP.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
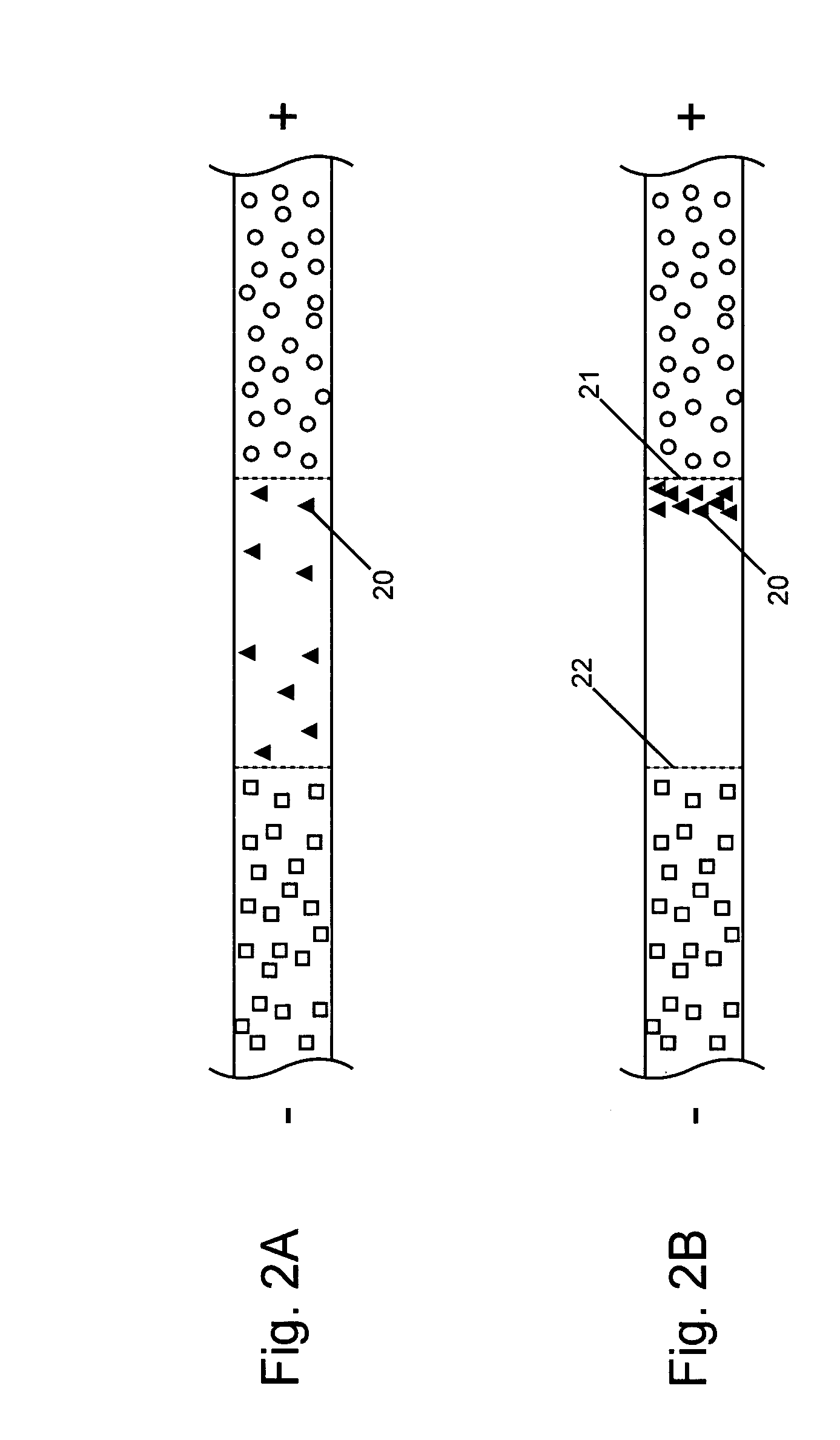
Tandem isotachophoresis/zone electrophoresis method and system
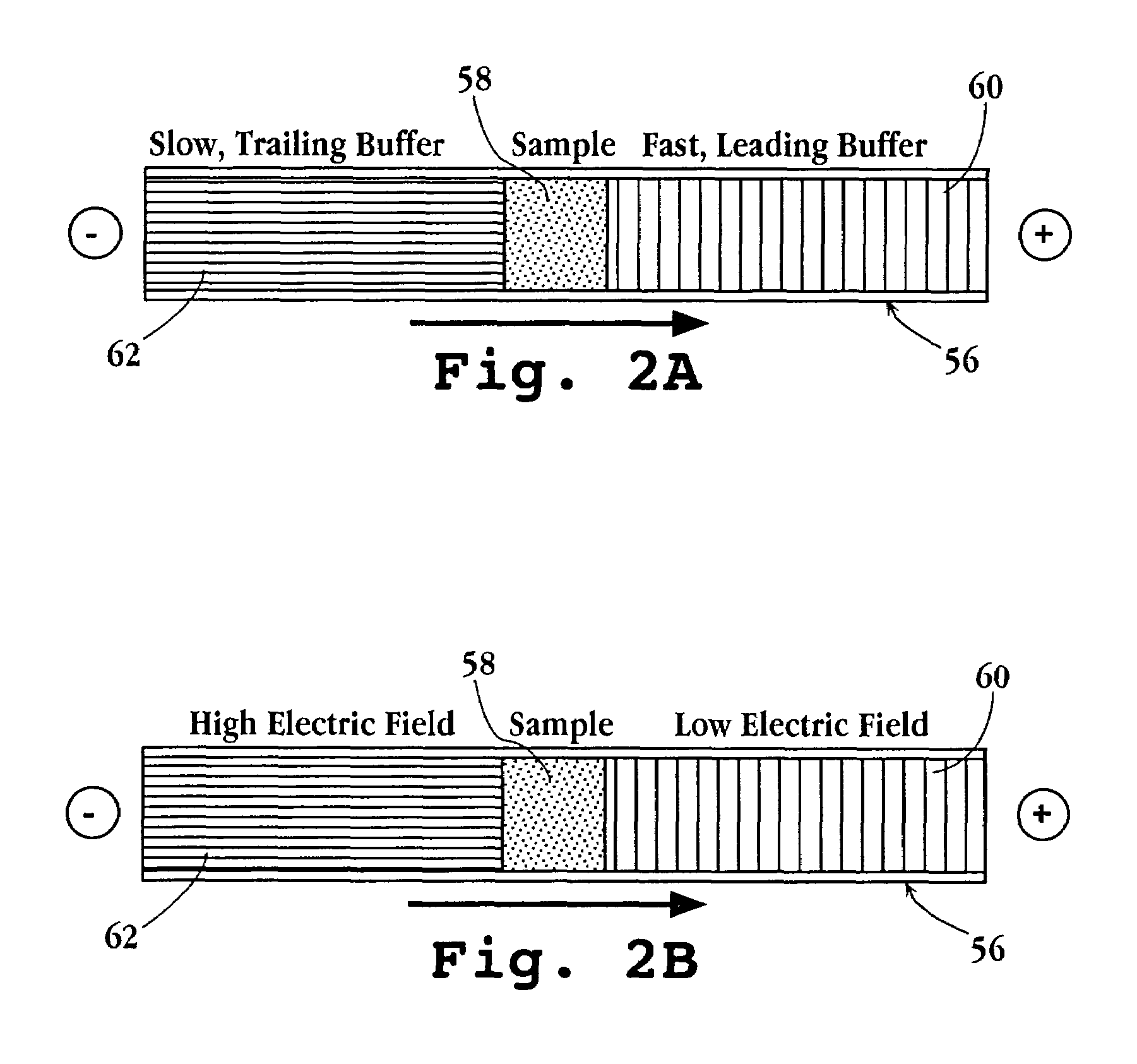
A method of separating components having a given negative or positive charge and contained in a sample is disclosed. The method involves, in one embodiment, loading a microchannel with a sample, placed between a trailing-edge electrolyte having a selected concentration of a titratable species, and a leading-edge electrolyte. With the application of a voltage potential across the microchannel, charged components in the sample stack by isotachophoresis, and electrolytic hydroxyl or hydrogen ions formed by electrolysis at the upstream-end electrode migrate into the trailing-edge ion buffer, titrating the titratable species therein, where the concentration of the titratable species in the trailing-edge electrolyte is selected , in relation to the lengths of the upstream channel region and sample-loading volume, to permit the sample to stack into a relatively small sample volume before electrolytic-ion migration from the upstream electrode into and through the sample-volume region is effective to overtake the charge sample components. With continued application of an electric potential across the channel ends, charged sample components in the stacked sample volume separated by zone electrophoresis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
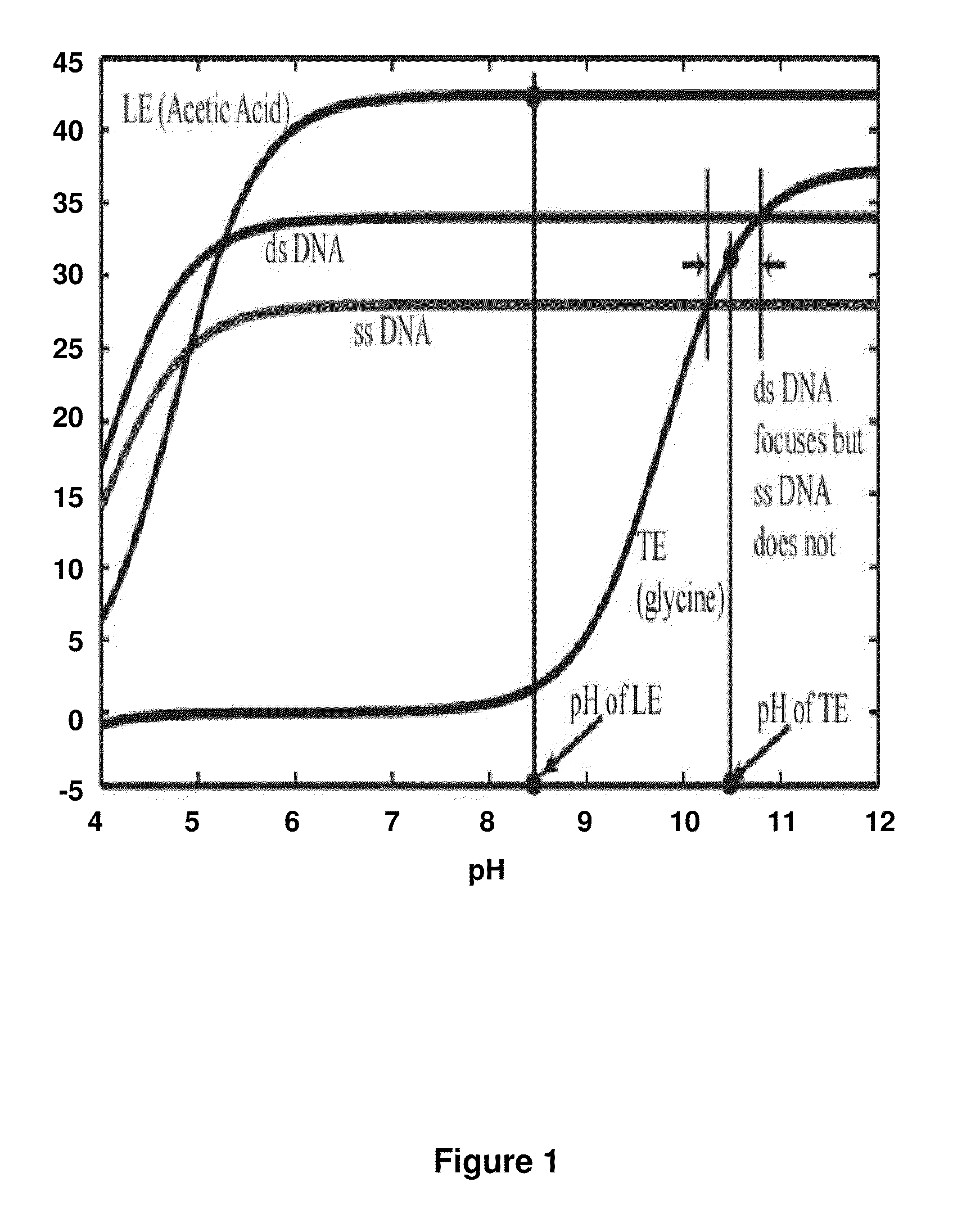
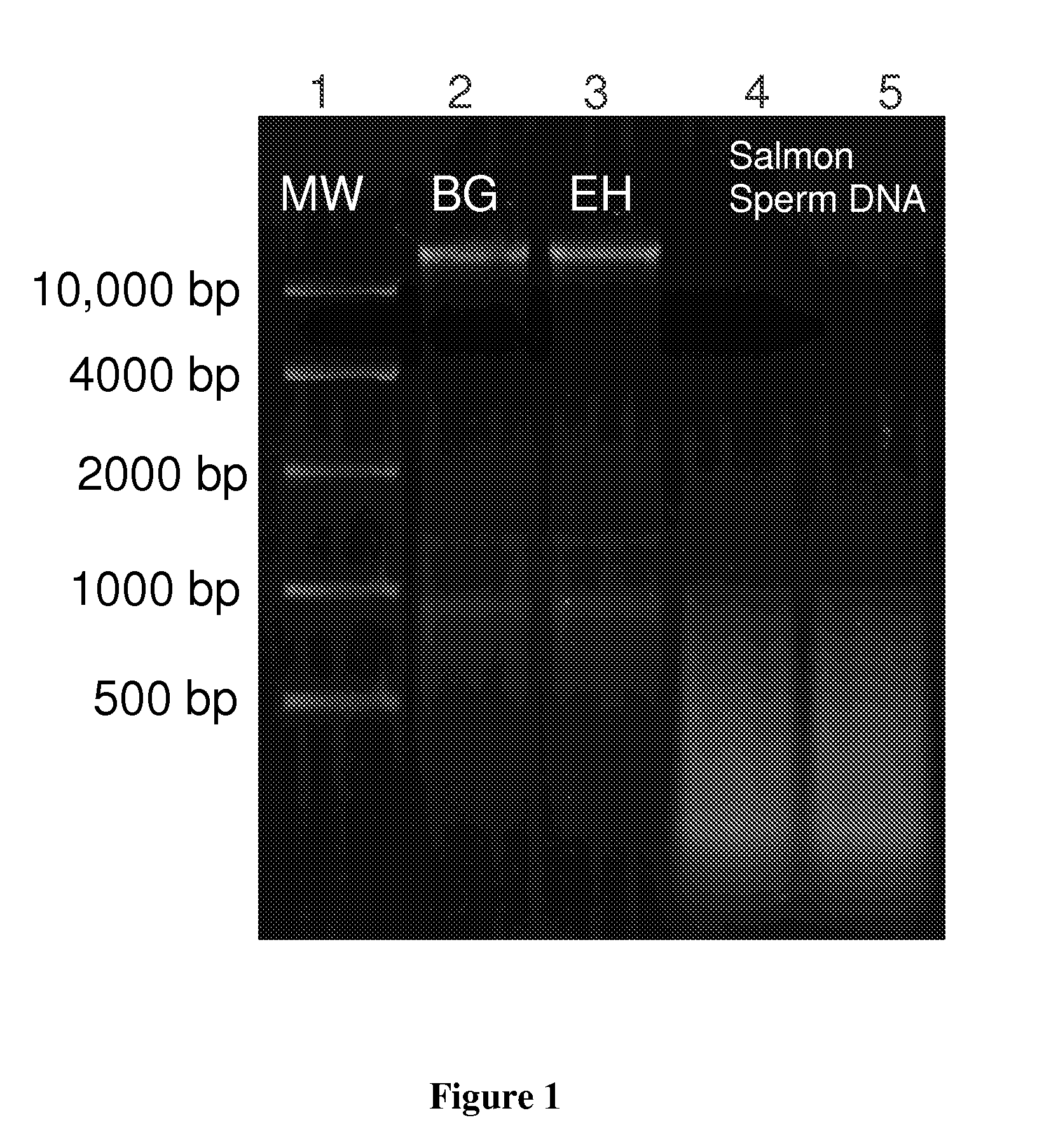
Isotachophoretic Focusing of Nucleic Acids
ActiveUS20100224494A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementIsotachophoresisNucleic acid detection
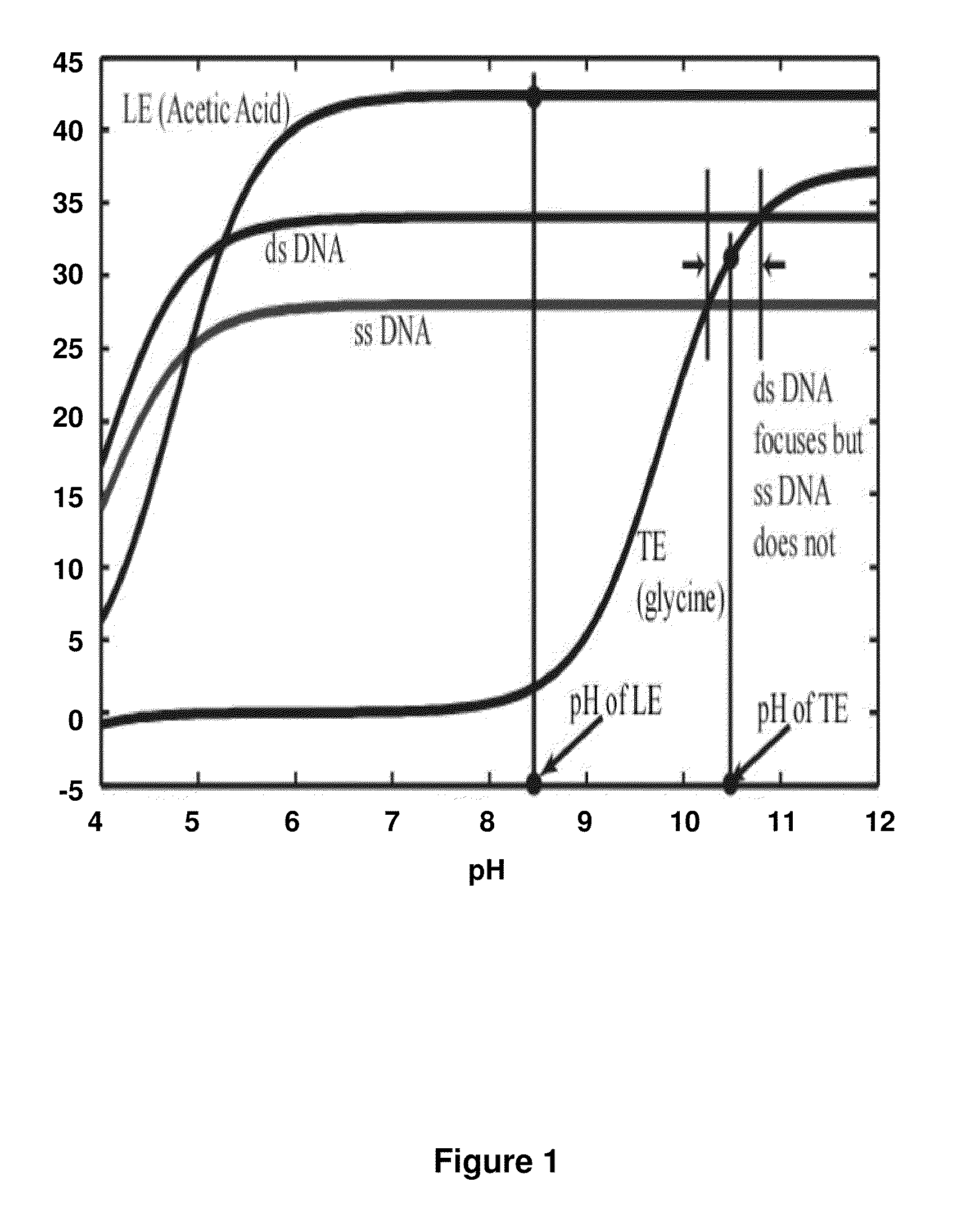
A method and system are presented for fast and efficient isolation, purification and quantitation of nucleic acids from complex biological samples using isotachophoresis in microchannels. In an embodiment, a sieving medium may be used to enhance selectivity. In another embodiment, PCR-friendly chemistries are used to purify nucleic acids from complex biological samples and yield nucleic acids ready for further analysis including for PCR. In another embodiment, small RNAs from biological samples are extracted, isolated, preconcentrated and quantitated using on-chip ITP with a high efficiency sieving medium. The invention enables fast concentration and separation (takes 10s to 100s of seconds) of nucleic acids with high selectivity and using lower volumes of reagents (order of 10s of μL to focus less than 1 pg / μL of nucleic acid).
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Purification and Concentration of Proteins and DNA from a Complex Sample Using Isotachophoresis and a Device to Perform the Purification
A method of simultaneously co-purifying and concentrating nucleic acid and protein targets is described. The method includes automation of the entire sample preparation process, performed by having an analyst add a sample into a device that performs all of the steps necessary to prepare a sample for analysis. The method provides for samples that are not split during the sample preparation process and where common purification methods can be used for purifying multiple analytes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
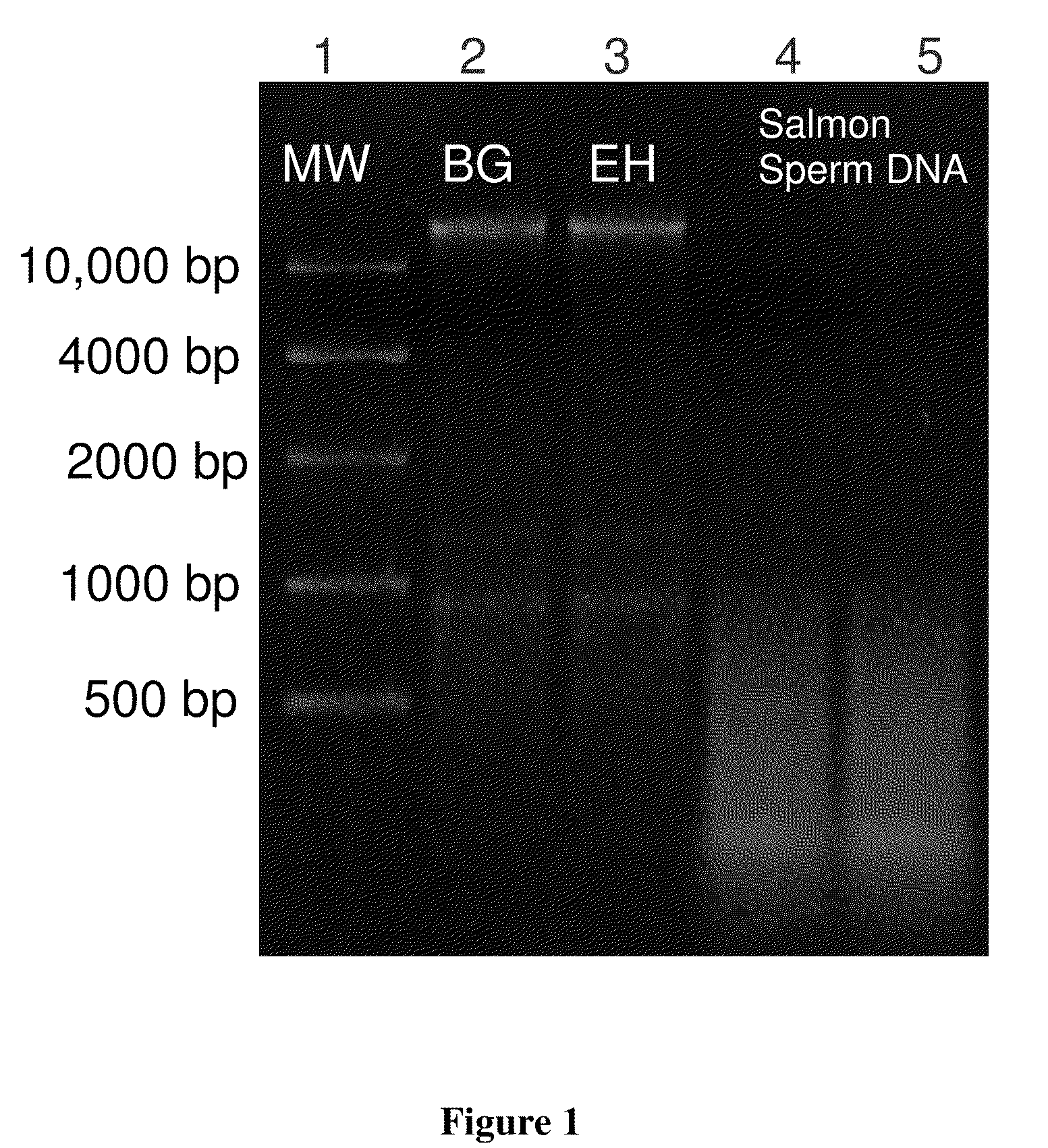
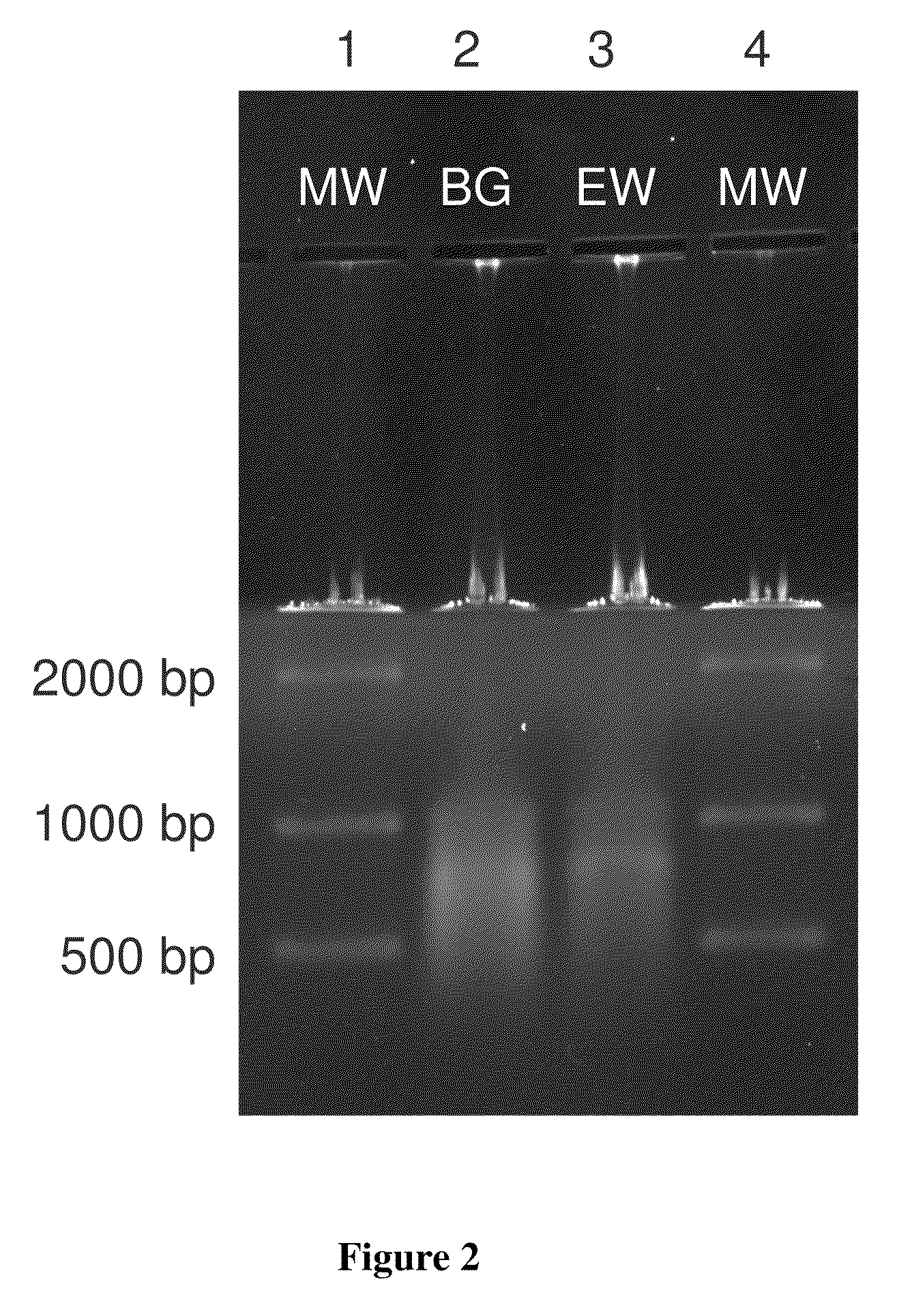
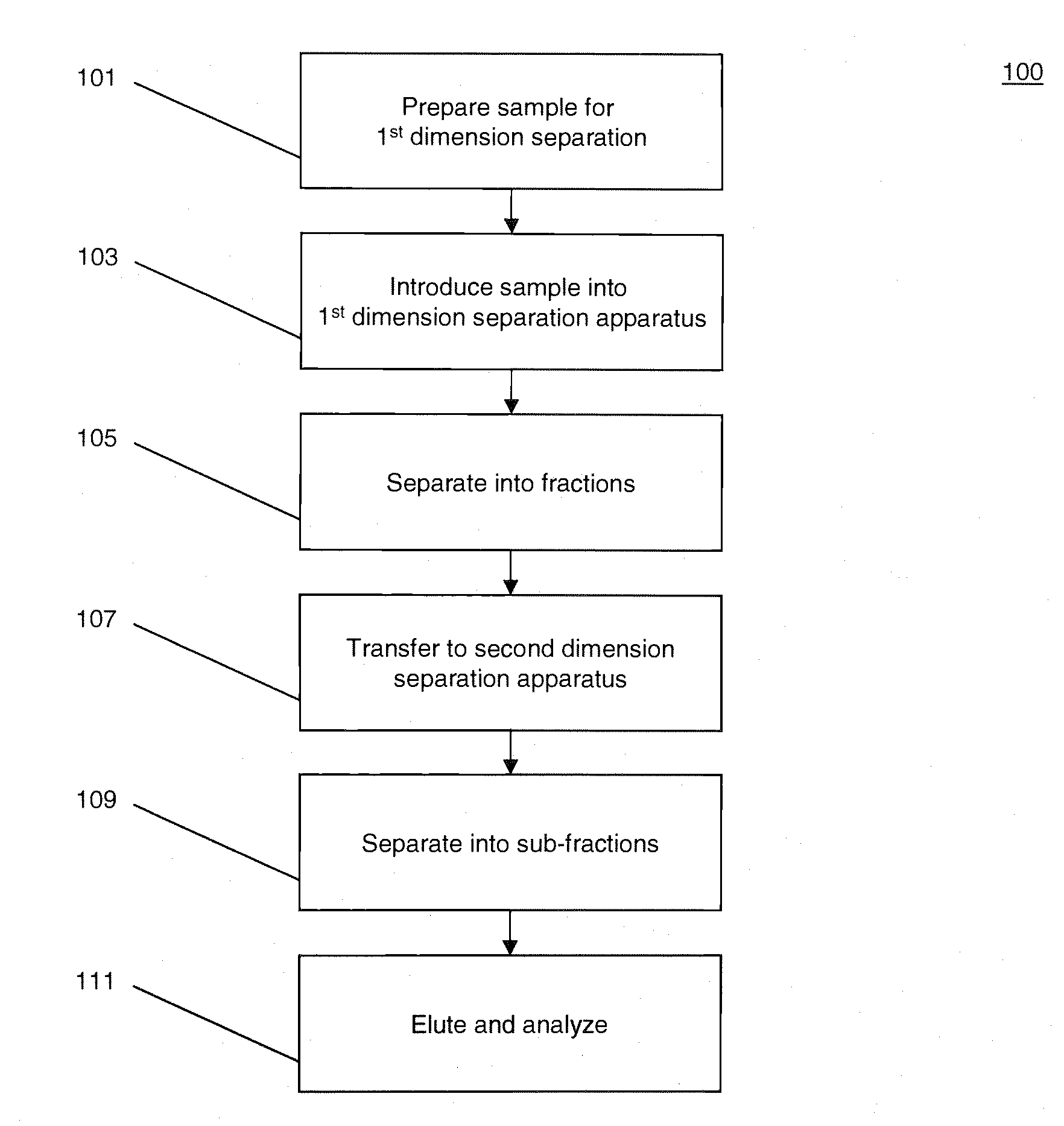
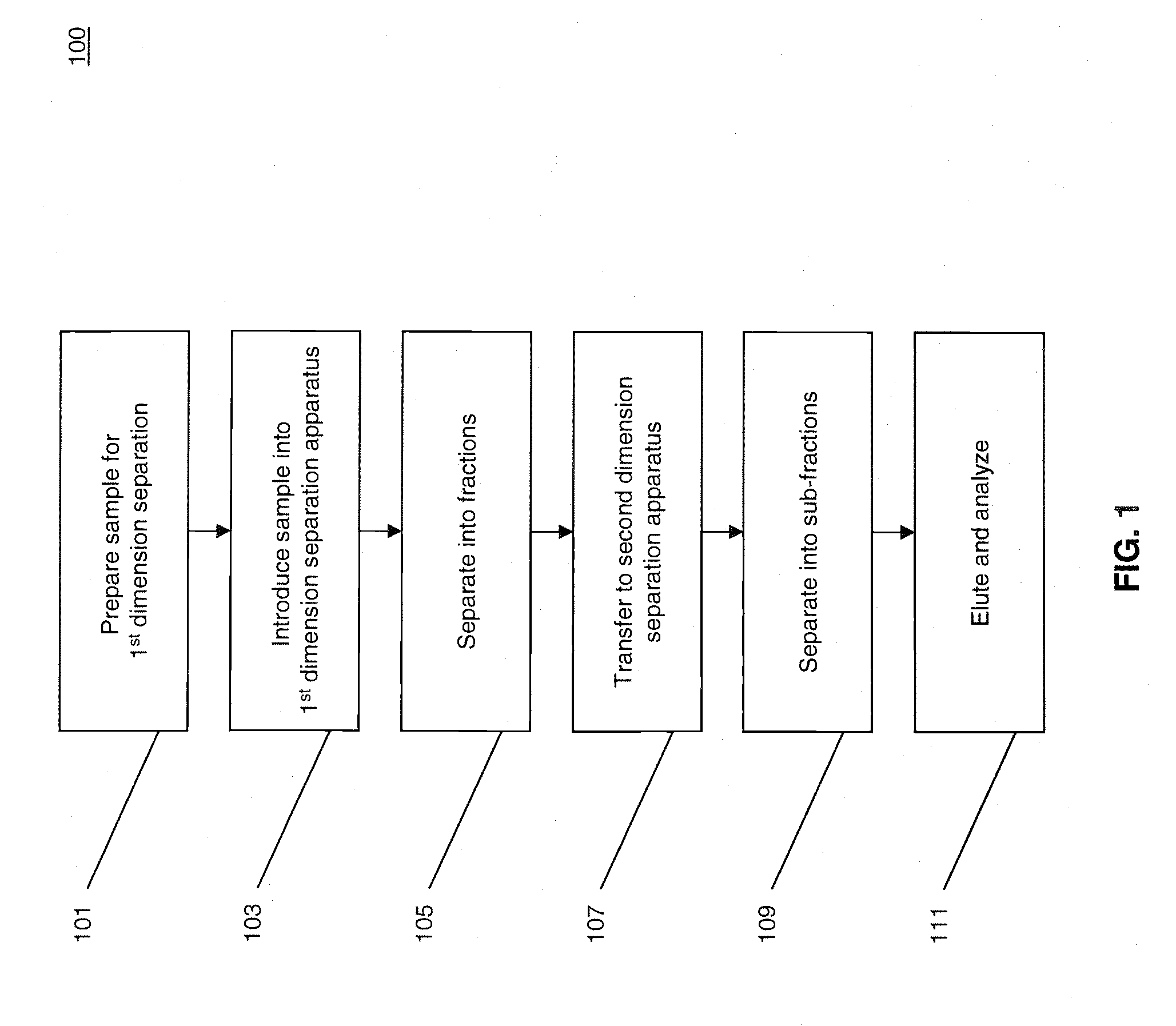
Methods and systems for multidimensional concentration and separation of biomolecules using capillary isotachophoresis
InactiveUS20080156080A1Enhanced low abundance protein analysisLess sensitivityComponent separationSurface/boundary effectIsotachophoresisElectrophoresis
The invention provides a method for performing off-line multi-dimensional separation and analysis of a heterogeneous biomolecular sample. The method includes separating the heterogeneous biomolecular sample into a plurality of fractions using an, at least partially, capillary isotachophoresis mechanism. The plurality of fractions are then transferred to a liquid chromatography apparatus where they are each separated into a plurality of sub-fractions. The sub-fractions are then analyzed to determine their constituent molecules.
Owner:CALIBRANT BIOSYST
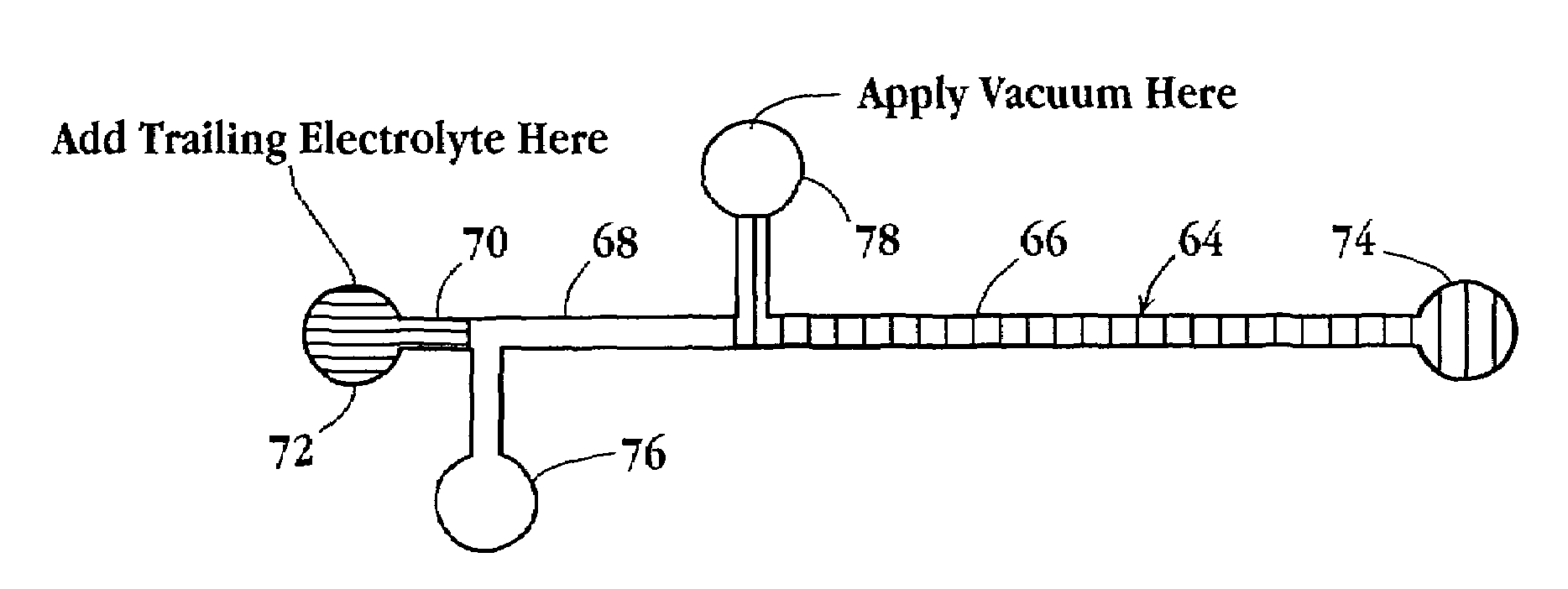
Method of detecting directly undetectable analytes using directly detectable spacer molecules
The present invention provides a method of indirectly detecting at least one directly undetectable analyte of interest. According to the method, a leading electrolyte and a trailing electrolyte are provided. In addition, a mixture of the at least one directly undetectable analyte and at least two directly detectable spacer molecules is provided. The directly detectable spacer molecules and the directly undetectable analyte are then concentrated and separated into zones using isotachophoresis. A displacement between the zones of directly detectable spacer molecules is then used to determine the presence of the directly undetectable analyte.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and devices for isotachophoresis applications
InactiveUS20100294663A1Increase heightAvoid disadvantagesSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementIsotachophoresisOperation mode
The invention relates to an operation mode of electrophoresis, which separates and / or fractionates particles of differentiated electrophoretic mobility. More specifically, the invention relates to isotachophoresis (ITP), including free-flow and capillary isotachophoresis, and provides novel electrophoresis methods, as well as kits and devices for carrying out such methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Purification and Concentration of Proteins and DNA from a Complex Sample Using Isotachophoresis and a Device to Perform the Purification
ActiveUS20100261612A1Improve automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIsotachophoresisAnalyte
A method of simultaneously co-purifying and concentrating nucleic acid and protein targets into a single volume is described. The method includes automation of the entire sample preparation process, performed by having an analyst add a sample into a device that performs all of the steps necessary to prepare a sample for analysis. The method provides for samples are not split during the sample preparation process and where common purification methods can be used for purifying multiple analytes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
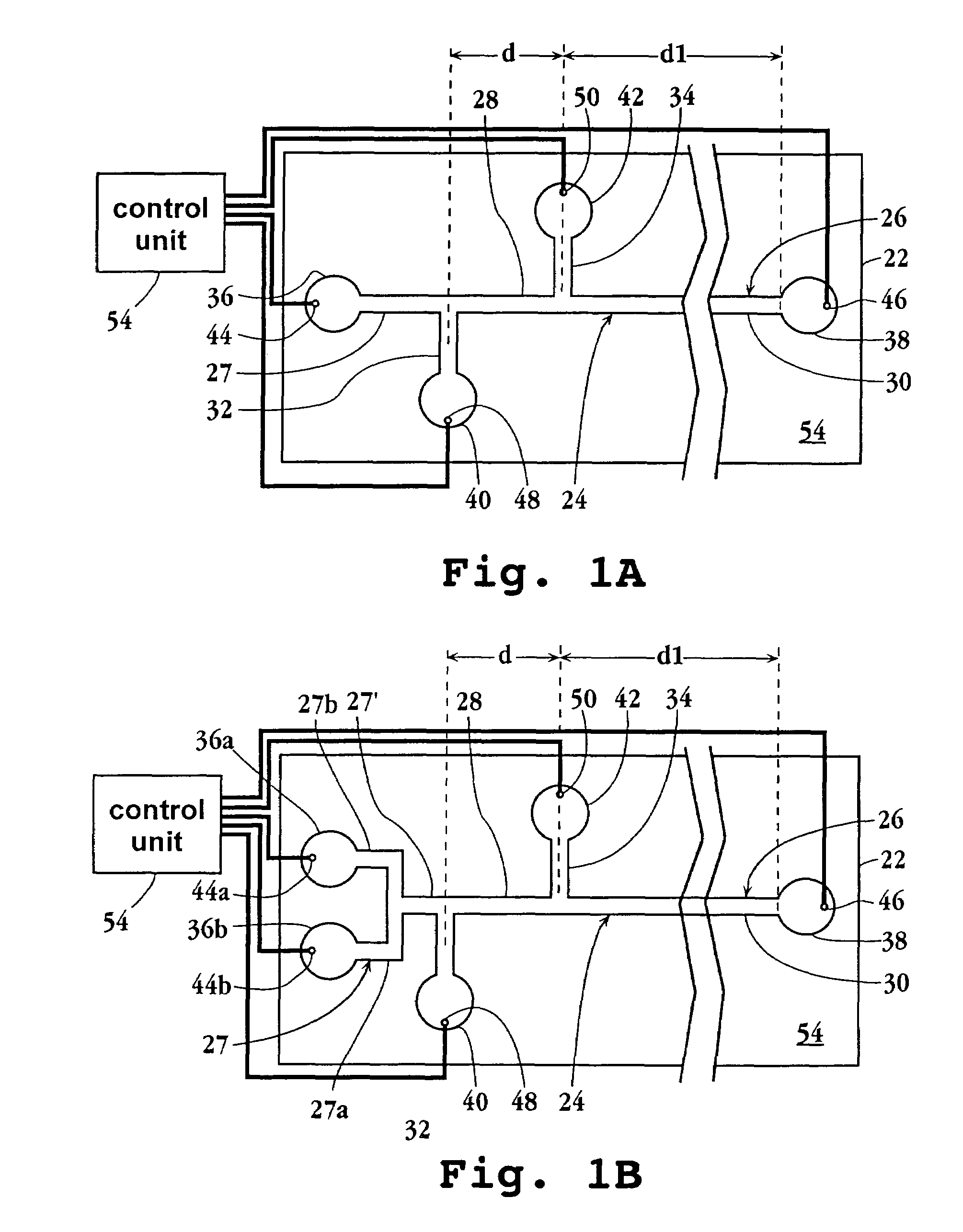
Methods and Apparatus for Carrier-Free Deflection Electrophoresis
ActiveUS20110174624A1Exclude influenceImprove separation qualitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityIsotachophoresis
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Analyte Injection System
ActiveUS20110024296A1Improve analysis resultsHigh resolutionElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteIsotachophoresis
This invention provides methods and systems for injection of analytes into a separation channel for resolution and detection. Samples can be preconditioned and concentrated by isotachophoresis (ITP) before the injection is triggered by a detected voltage event. Separation of analytes from other sample constituents can be enhanced using skewing channel ITP.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Purification and concentration of proteins and DNA from a complex sample using isotachophoresis and a device to perform the purification
ActiveUS8614059B2Improve automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein targetPurification methods
A method of simultaneously co-purifying and concentrating nucleic acid and protein targets into a single volume is described. The method includes automation of the entire sample preparation process, performed by having an analyst add a sample into a device that performs all of the steps necessary to prepare a sample for analysis. The method provides for samples are not split during the sample preparation process and where common purification methods can be used for purifying multiple analytes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Functionalization micro-flow control chip and method for PCR product analysis
ActiveCN101157952AShort reaction timeSensitive analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsA-DNAPcr dgge
The invention discloses a functionalized microflow controlled chip and a method using the functionalized microflow controlled chip to analysis the PCR products. The chip comprises a buffering liquid pool, a waste liquid pool of buffering liquid, a sample injection waste liquid pool, a sample pool, a separating channel and a sample injection channel. Two ends of the separating channel are respectively connected with the buffering liquid pool and the waste liquid pool of buffering liquid. Two ends of the sample injection channel are respectively connected with the sample pool and the sample injection waste liquid pool. The length of the effective sample injection channel is 0.5cm to 20cm. the invention combines the isotachophoresis pre concentration and the screening electrophoresis separation. The buffering liquid contains a liac dielectric medium and a DNA screening medium. The method uses the chloride ion self contained in PCR products as a leading ion. The chip is only needed to be introduced in one type of buffering liquid, which reduces the number of the needed electrode and simplify the operation and has the advantages of sensitive and fast analyzing. The chip can effectively shorten the PCR reaction time through enhancing the detecting sensitivity. The invention can sensitively, fast and simply analyze the PCR products.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Isotachophoretic focusing of nucleic acids
ActiveUS8846314B2Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementIsotachophoresisOrganic chemistry
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Purification and concentration of proteins and DNA from a complex sample using isotachophoresis and a device to perform the purification
ActiveUS8865401B2Improve automationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementPurification methodsAnalyte
A method of simultaneously co-purifying and concentrating nucleic acid and protein targets is described. The method includes automation of the entire sample preparation process, performed by having an analyst add a sample into a device that performs all of the steps necessary to prepare a sample for analysis. The method provides for samples that are not split during the sample preparation process and where common purification methods can be used for purifying multiple analytes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Isotachophoretic device and methods
InactiveUS20170184543A1Preparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMetaboliteFirst pathway
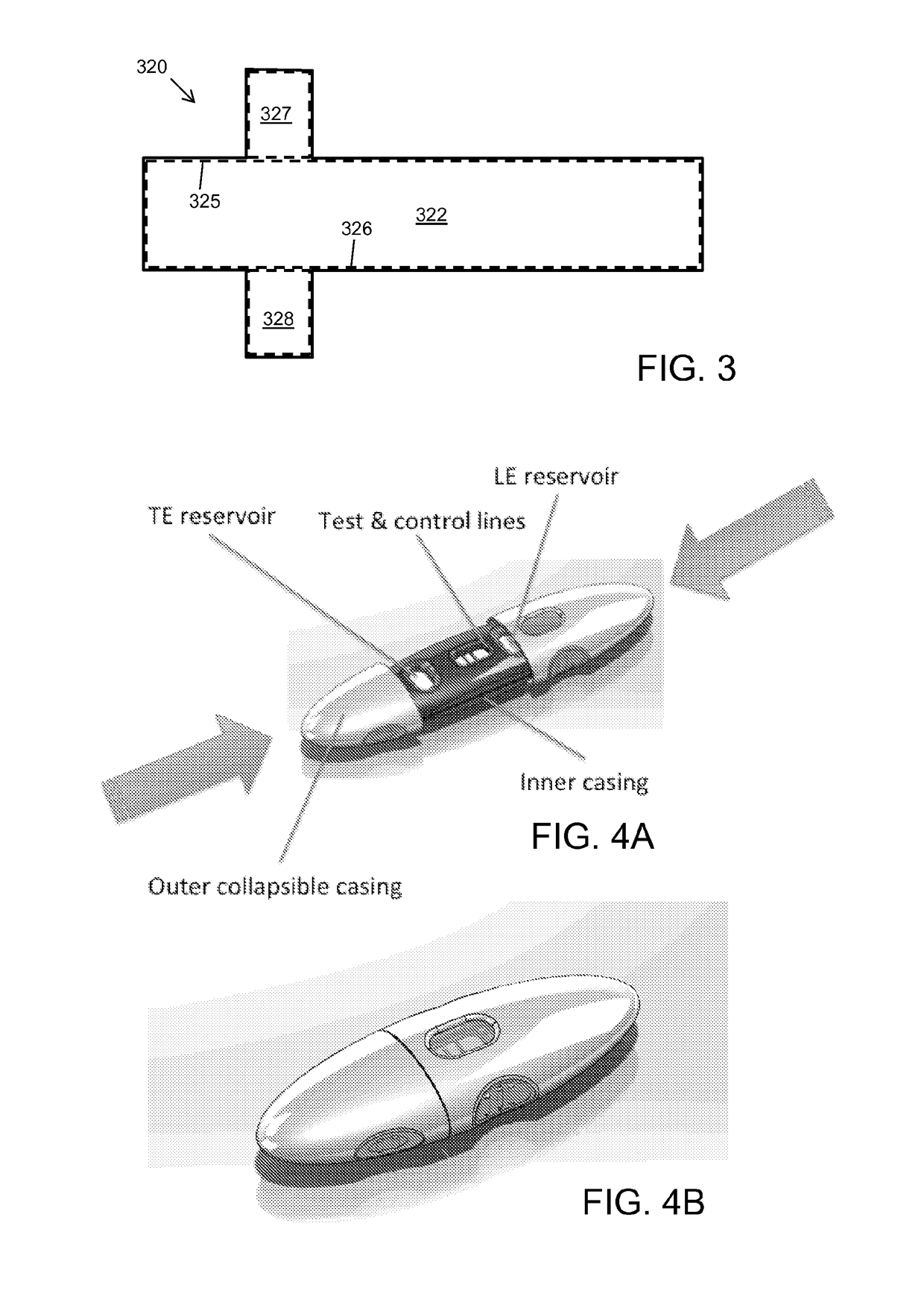
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for performing isotachophoretic concentration of analytes using a porous matrix, for example, for use in diagnostic assays such as lateral flow assays. For example, the disclosure provides a method of concentrating an analyte in a sample. The method includes providing a device comprising a porous matrix having a first fluid pathway having a first end and extending to a second end, a first electrode, and a second electrode; introducing to the first pathway a first fluid comprising a trailing electrolyte, a second fluid comprising a leading electrolyte and the analyte; and applying a voltage across the first electrode and the second electrode for a time sufficient to provide an ITP plug. As described herein, the devices and methods described herein can be used in conjunction with lateral flow assay techniques to detect and quantify a variety of biochemical and biological analytes, such as nucleic acids, proteins, cells and metabolites.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
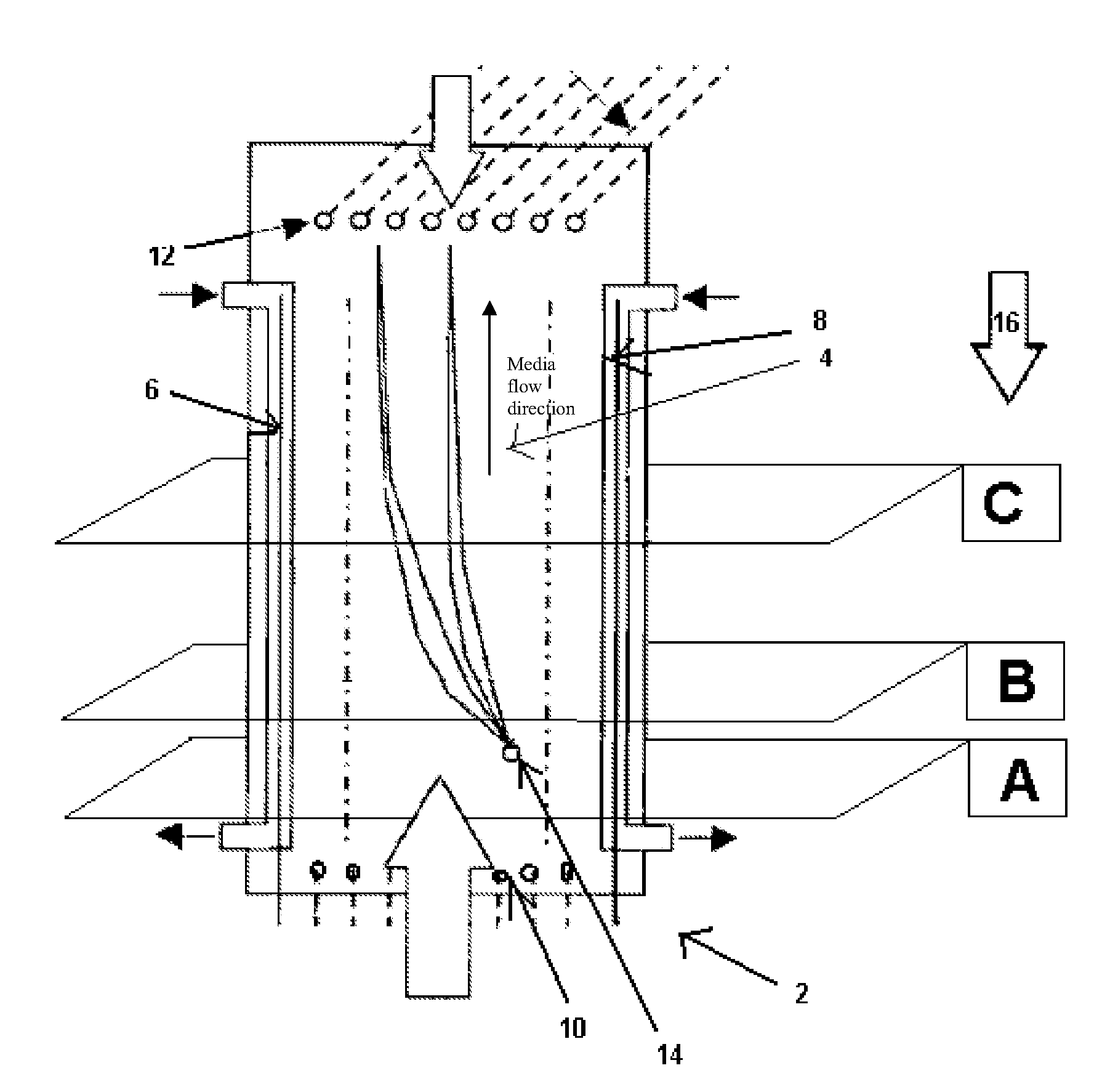
Methods and apparatus for carrier-free deflection electrophoresis
InactiveUS20080110758A1Exclude influenceImprove separation qualitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityIsotachophoresis
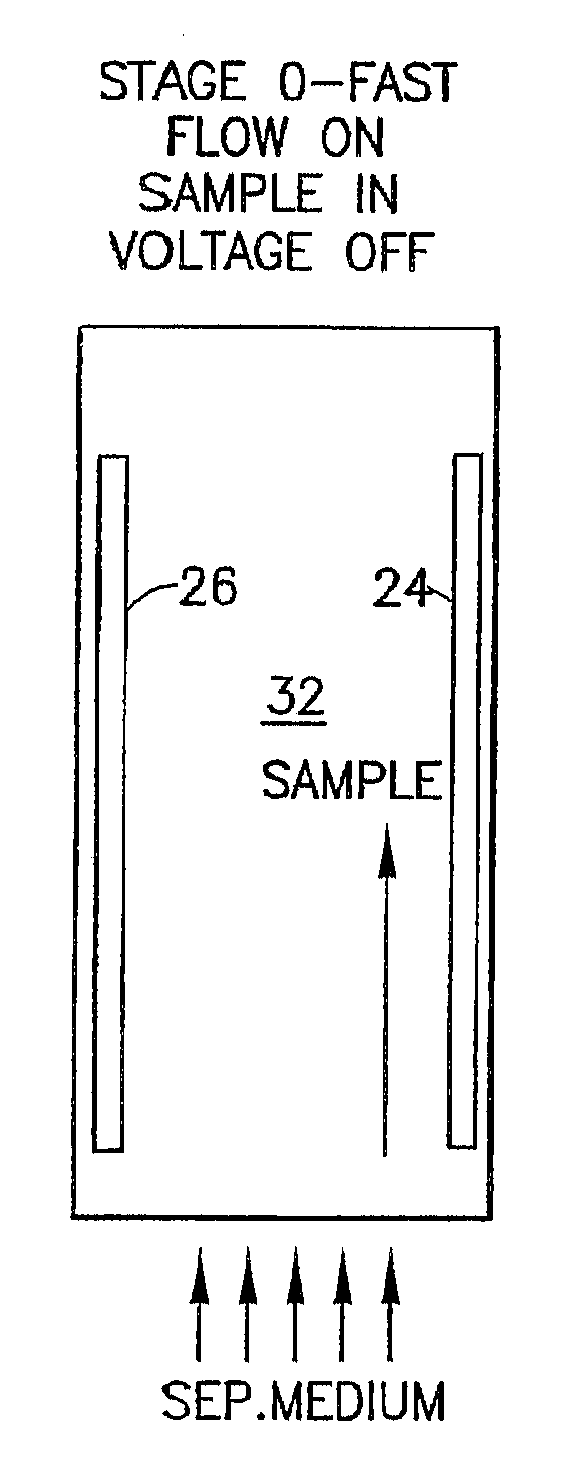
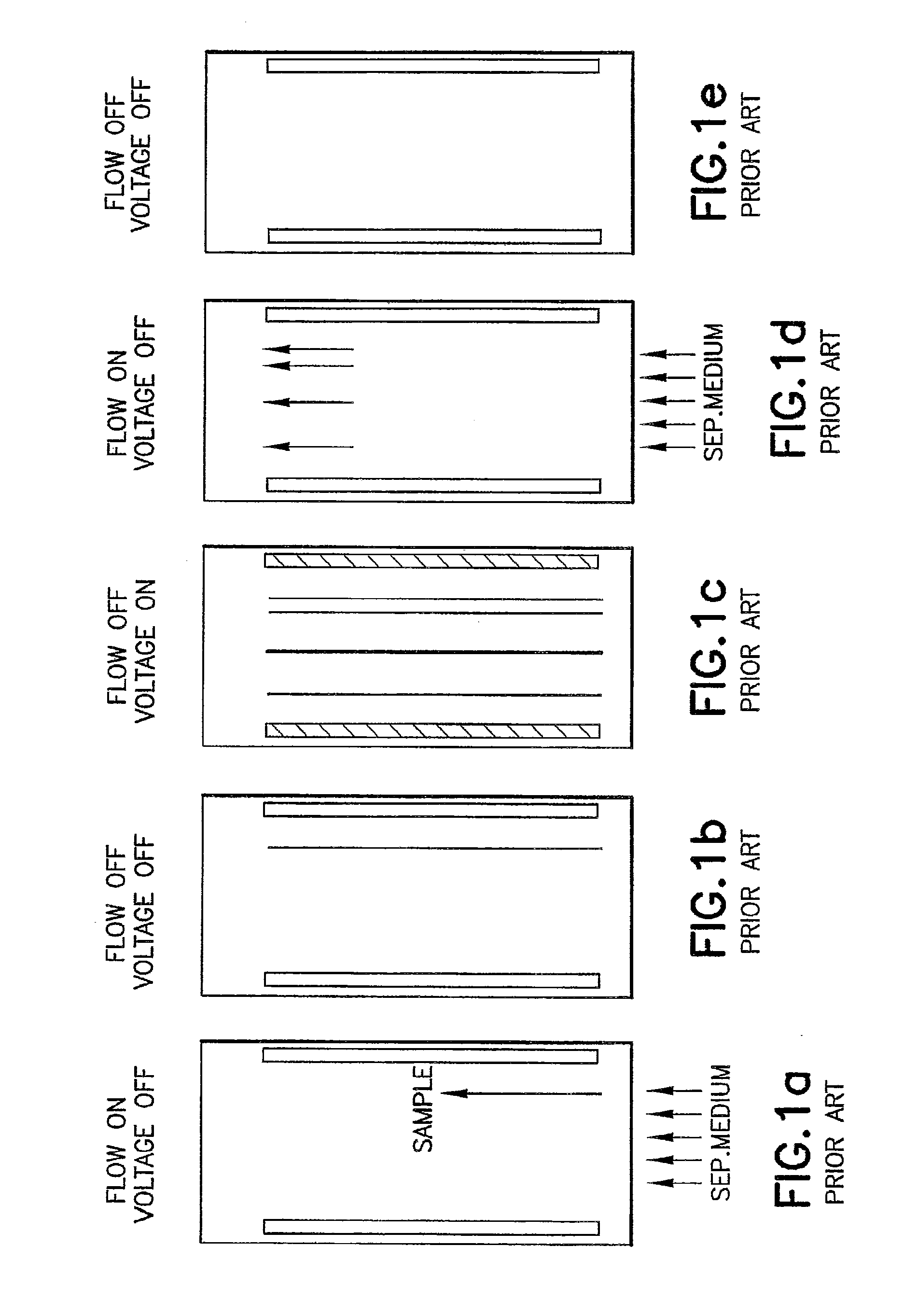
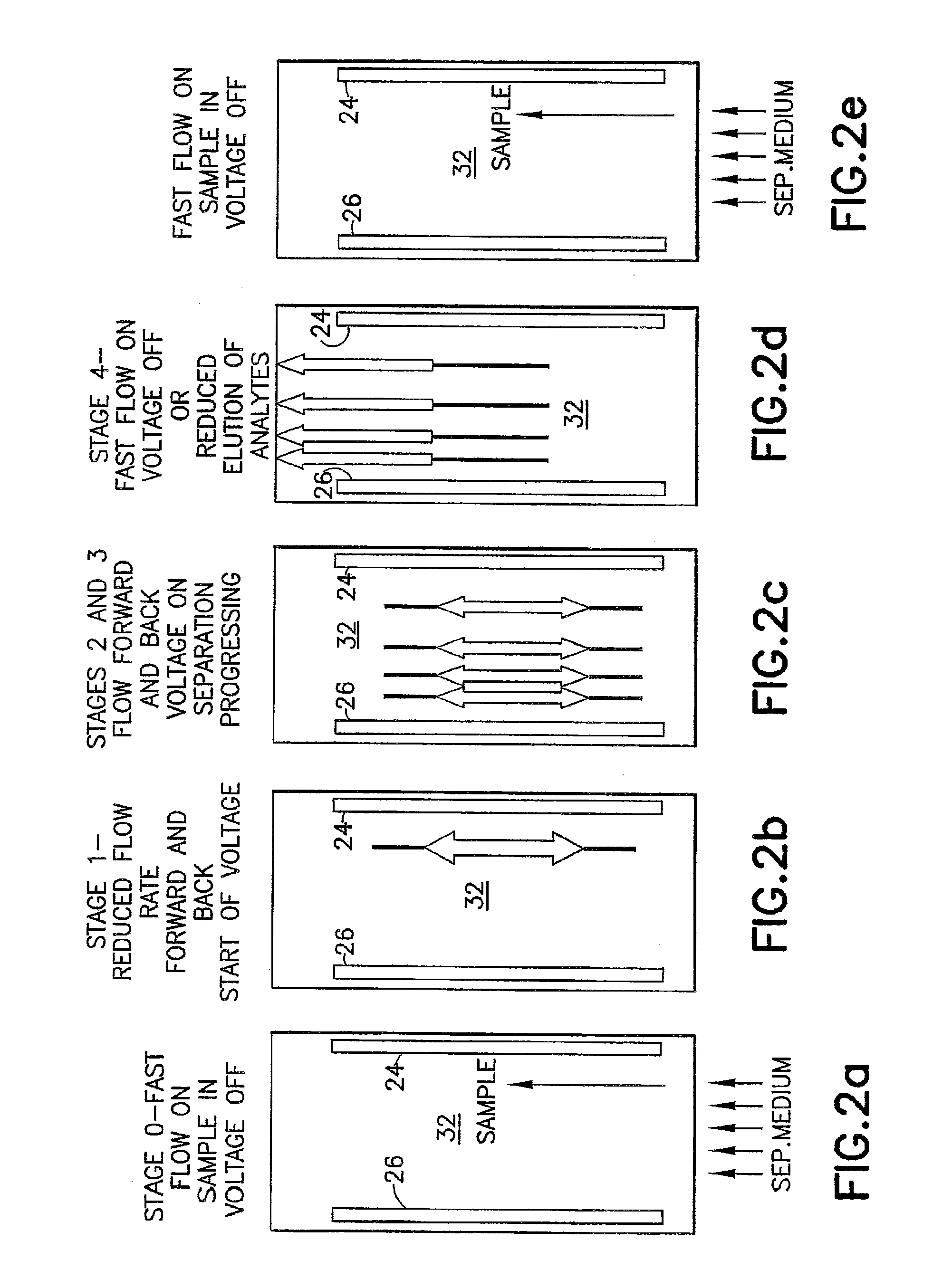
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for carrier-free deflection electrophoresis, in which a separating media and a sample to be examined flow through a separating chamber between a pair of electrodes in a series of reversing bulk fluid flow along the direction of the electrodes, thereby separating the sample into zones which are to be collected into fractions for analysis or further processing. Among other things, the apparatus and method enable high-resolution separation of particles that can be performed in miniaturized chambers in electrophoresis modes including isoelectric focusing, zone electrophoresis, and isotachophoresis.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Gradient elution isotachophoretic apparatus for separating, purifying, concentrating, quantifying, and/or extracting charged analytes and methods thereof
Gradient elution isotachophoretic apparatus, and systems for performing gradient elution isotachophoresis to separate, purify, concentrate, quantify, and / or extract charged analytes from a sample. The isotachophoretic apparatus include an electrophoretic assembly, a sampling assembly connected to the electrophoretic assembly, and / or a support structure connected to the electrophoretic assembly and / or to the sampling assembly. The system includes an isotachophoretic apparatus, and a controller communicatively coupled to the isotachophoretic apparatus. The controller includes a storage medium and a processor for executing computer readable and executable instructions.
Owner:US REPRESENTED BY SEC OF COMMERCE +1
Control of chemical reactions using isotachophoresis
ActiveUS8821704B2Simple control timingEffectively increase rateSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementChemical reactionIsotachophoresis
Isotachophoresis (ITP) is exploited to control various aspects of chemical reactions. In a first aspect, at least one of the reactants of a chemical reaction is confined to an ITP zone, but the resulting product of the chemical reaction is separated from this ITP zone by the ITP process. In a second aspect, one or more reactants of a chemical reaction are confined to an ITP zone, and one or more other reactants of the chemical reaction are not confined to this ITP zone. In a third aspect, ITP is employed to confine at least one reactant of a chemical reaction to an ITP zone, and at least one reactant of the chemical reaction is delivered to the ITP zone in two or more discrete doses. These aspects are especially relevant to performing polymerase chain reactions using chemical denaturants as opposed to thermal cycling.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for electrophoretic separations using dynamically generated opposite mobilities
InactiveUS7052589B1Improve bindingElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementProduction rateIsotachophoresis
Method and materials to carry out preparative-scale electrophoretic separations based on the principle of dynamically created non-co-directional effective electrophoretic mobilities are disclosed. The primary application areas of the method are in the separation, purification, enrichment, concentration or conditioning of both small and large molecular weight, weak and strong electrolyte compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, oligo- and polypeptides, proteins, oligonucleotides, etc. These objectives can be achieved based on the use of a secondary chemical equilibrium, alone or in combination with multiple protic and other secondary chemical equilibria. Though such electrophoretic operations could be achieved by other means, such as by conventional zone electrophoresis or isotachophoresis, the method disclosed here can provide greater separation power, simplicity and higher production rates.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Microfluidic electrokinetic paper based devices
InactiveUS20170136457A1Short analysis timeComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotachophoresisPaper based
A paper-based micro fluidic device suitable for electrokinetics and particularly isotachophoresis (ITP) and a kit comprising same is provided. Further, a method for the preparation of said paper-based micro fluidic device and a method of use thereof for the detection and / or separation of molecules of interest are provided.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Kit for co-purification and concentration of DNA and proteins using isotachophoresis
ActiveUS20140332389A1Improve automationCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesProtein target3-aminopropanesulfonic acid
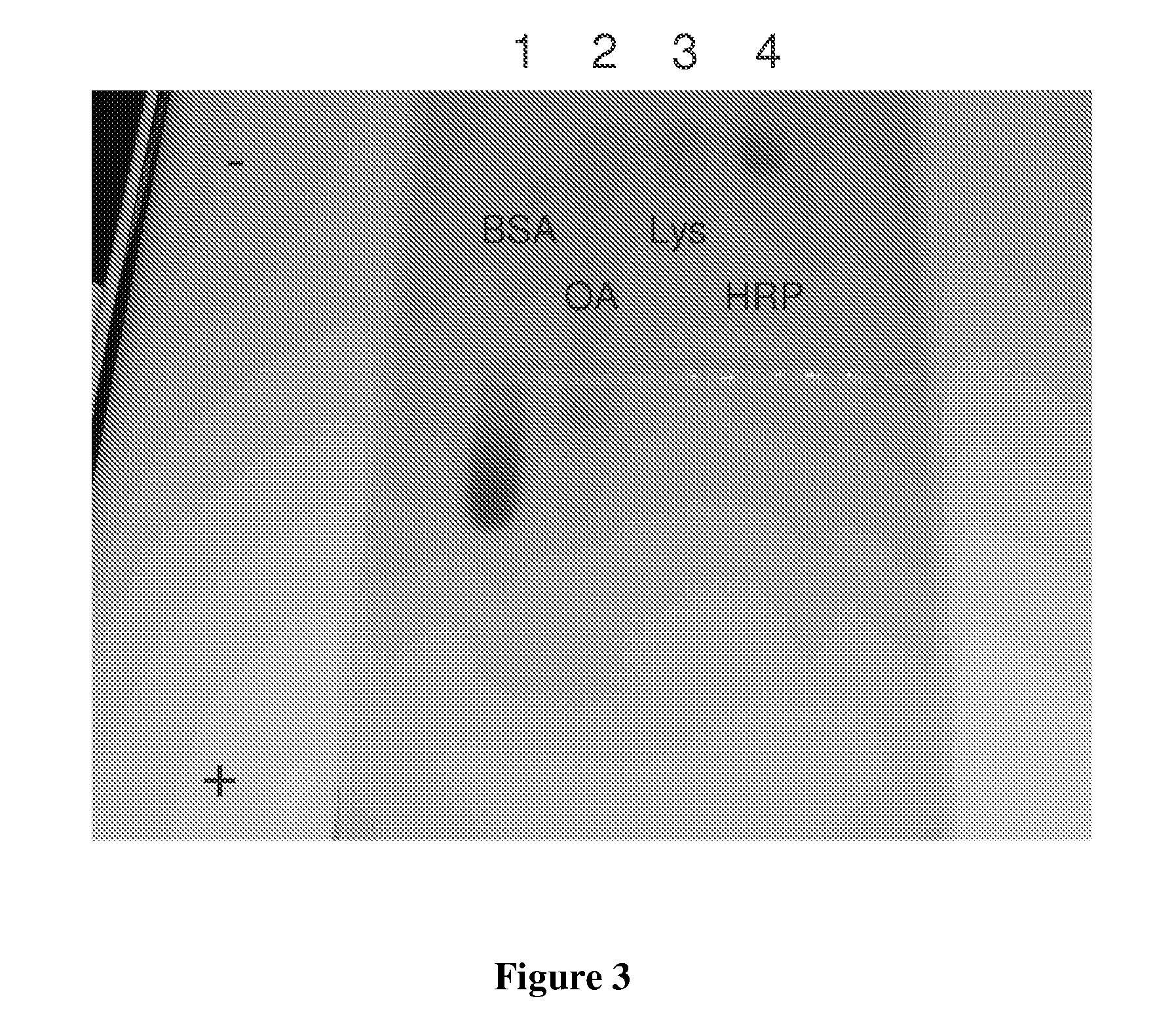
A kit for separating and concentrating nucleic acid and protein targets includes labeled reagents which affect simultaneous co-purification and concentration of a nucleic acid and a protein, a gel isotachophoresis separation unit to which a sample comprising the nucleic acid and the protein is added, a detection unit for the detection of the presence of the nucleic acid and the protein, and instructions for use. The gel electrophoresis includes a gel box having a negative electrode side and a positive electrode side, the negative electrode side being filled with a first buffer comprising 2-Hydroxy-N-(tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl)-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid buffer and the positive electrode side being filled with a second buffer being different than the first buffer. The gel isotachophoresis separation is configured to subject the sample to isotachophoresis using a voltage.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
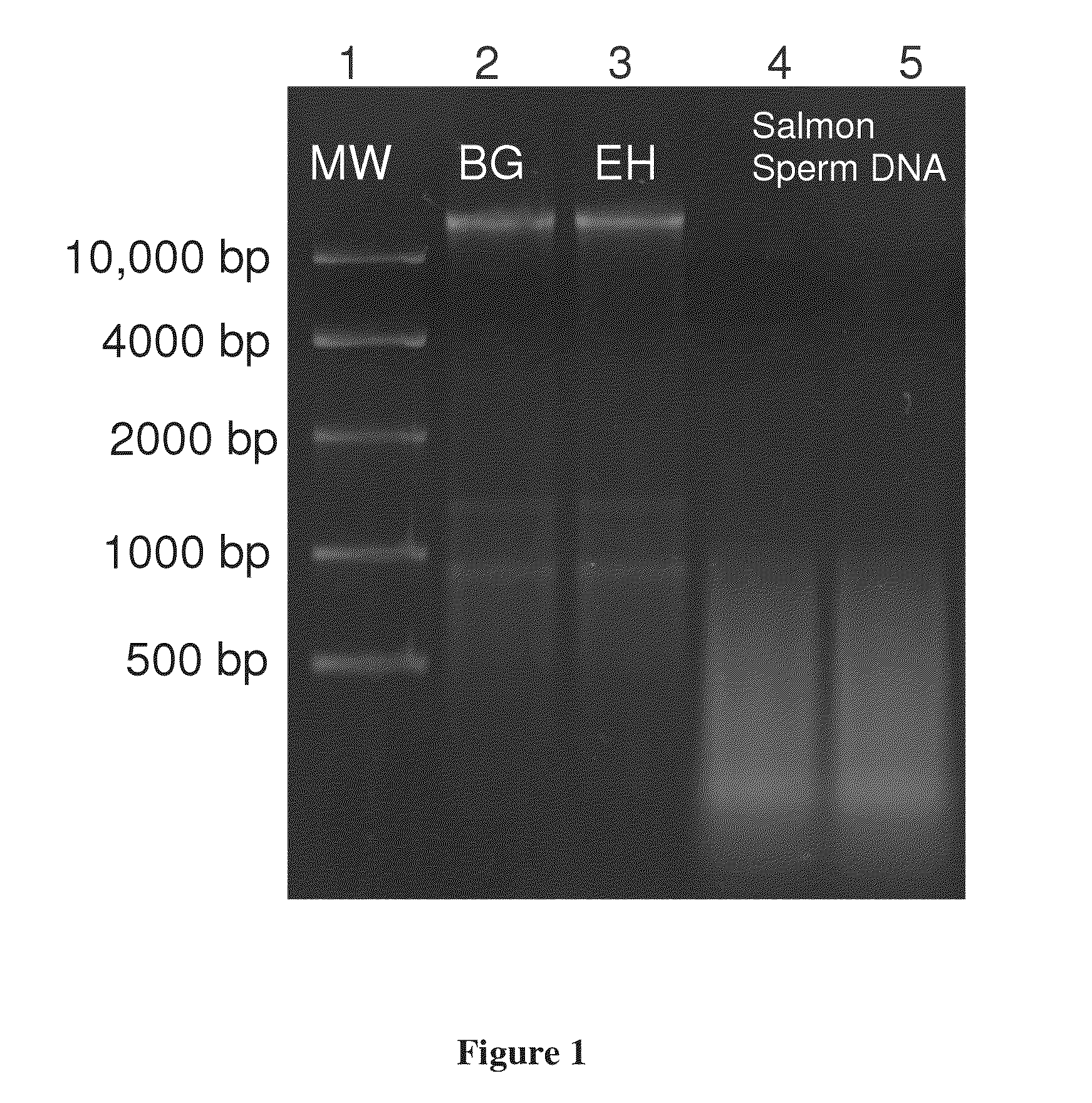
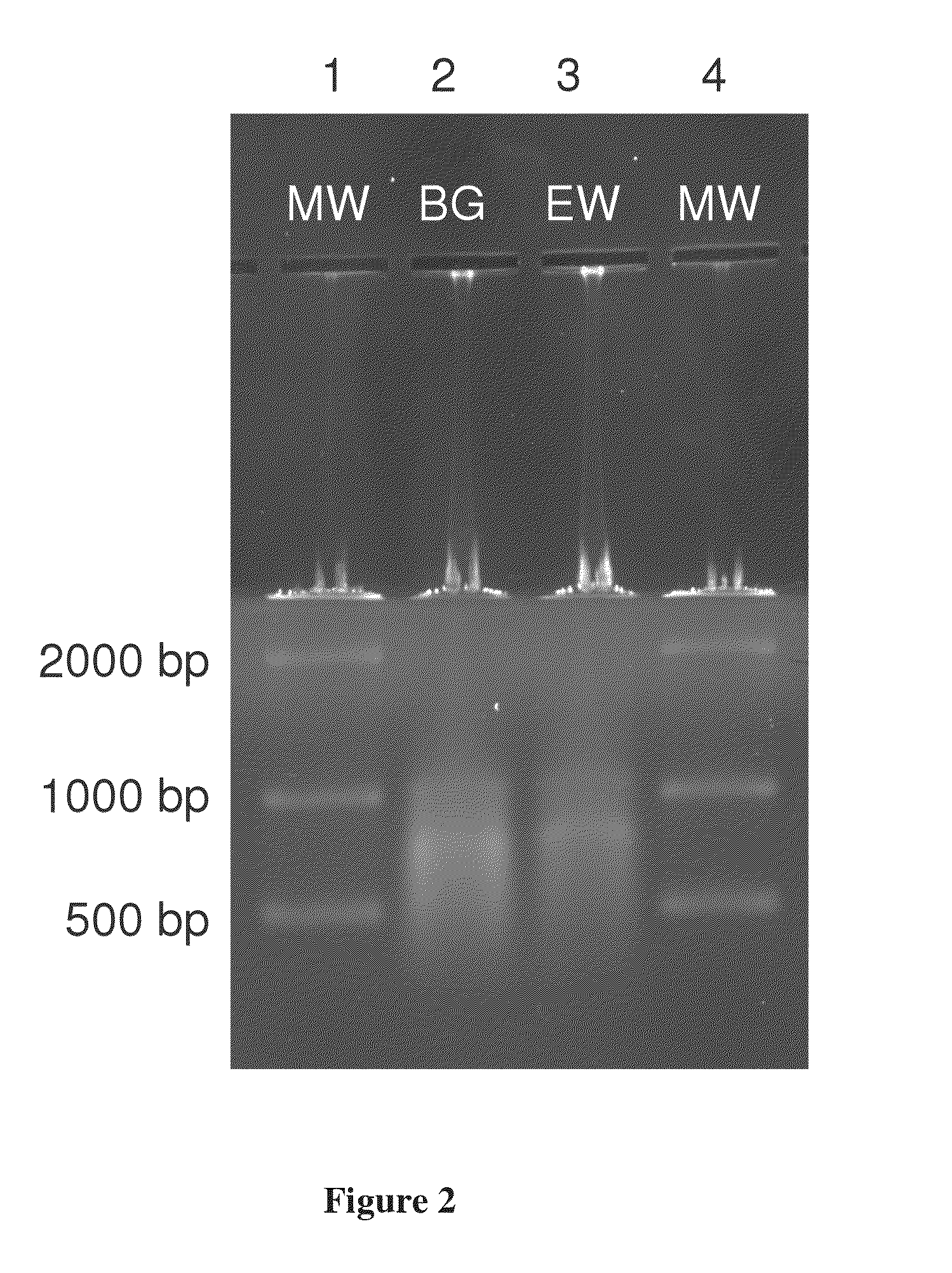
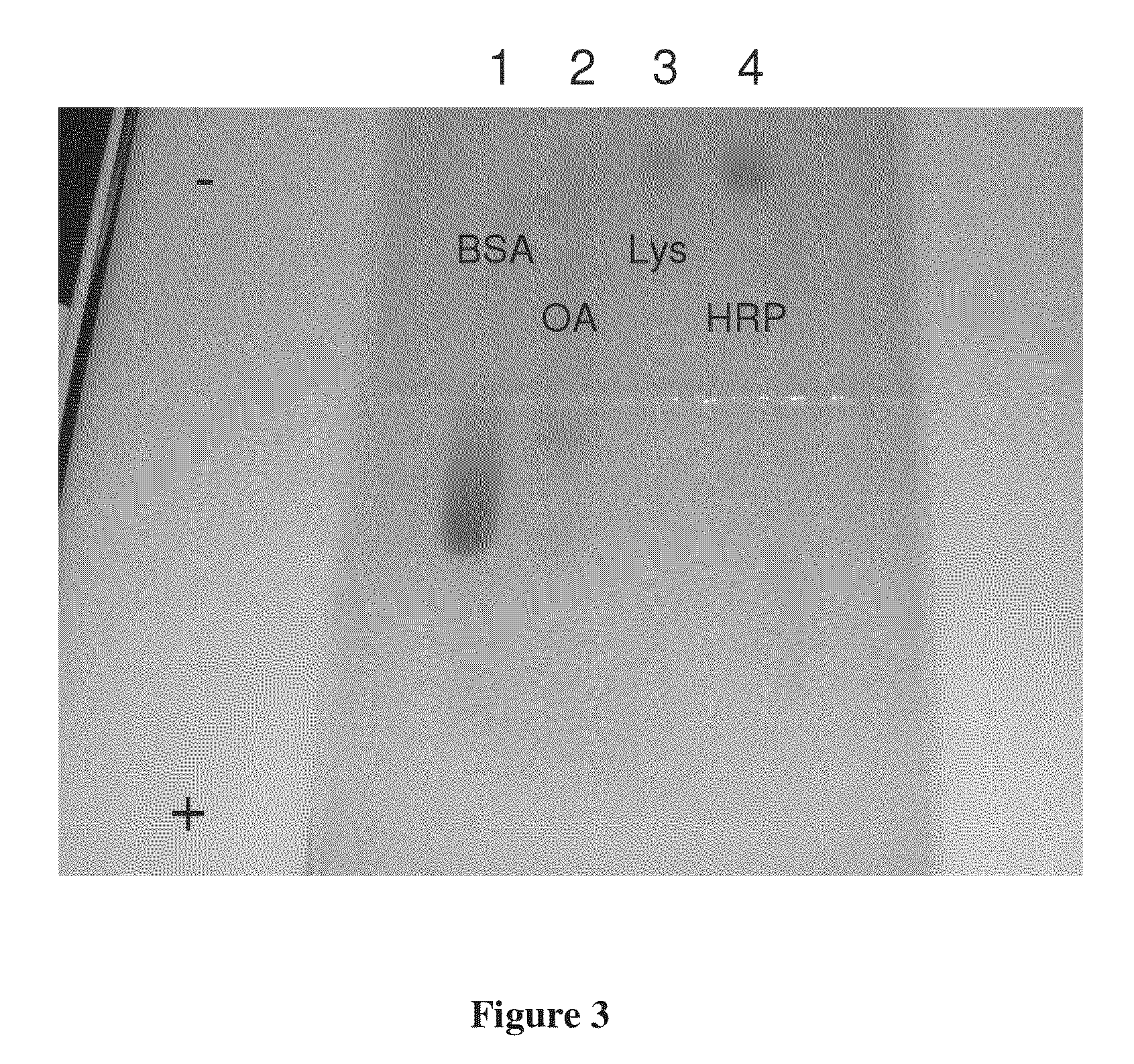
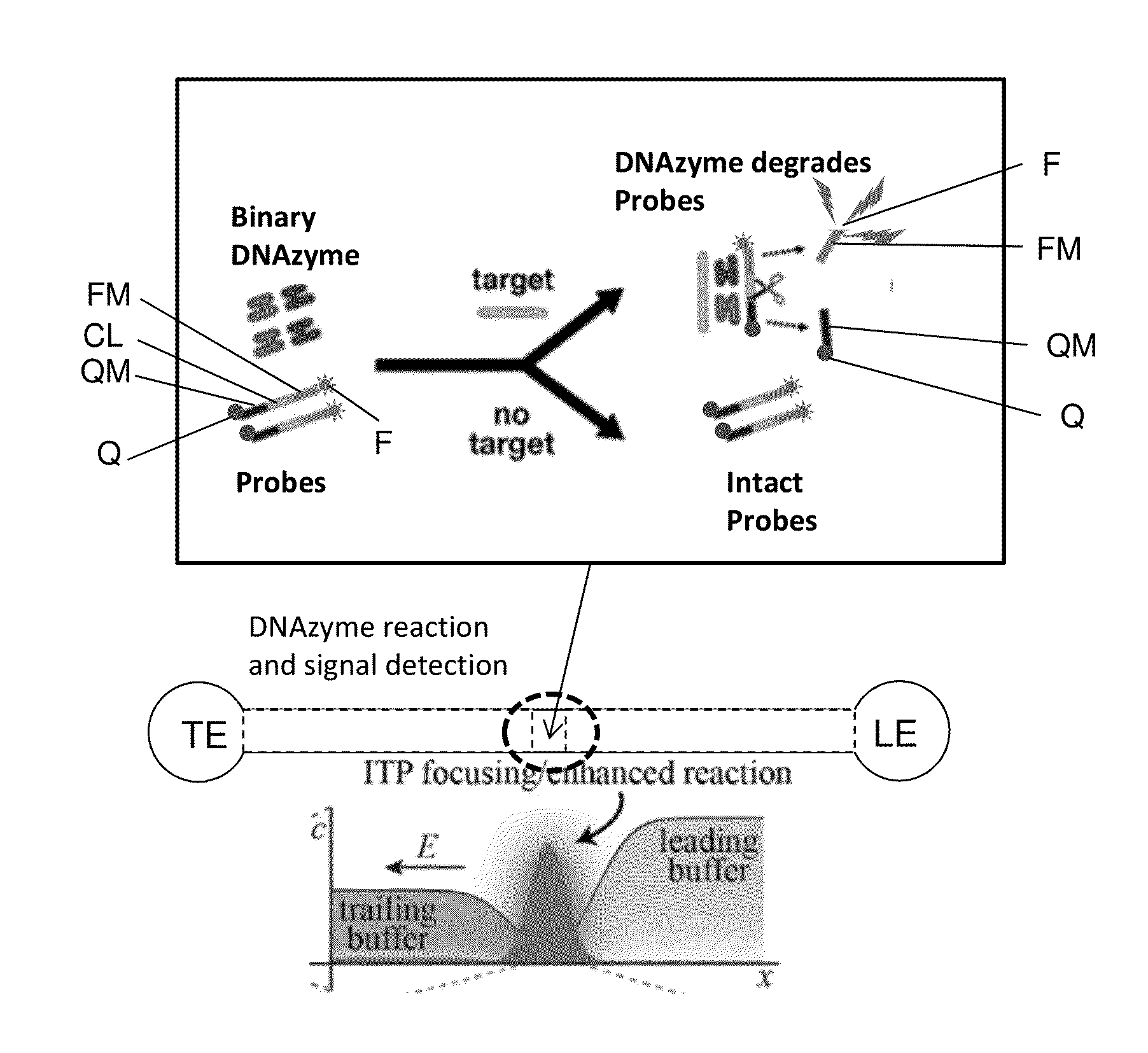
Ultra-rapid and sensitive DNA detection using dnazyme and on-chip isotachophoresis
InactiveUS20150197791A1Rapid and inexpensiveMicrobiological testing/measurementIsotachophoresisFluorescence
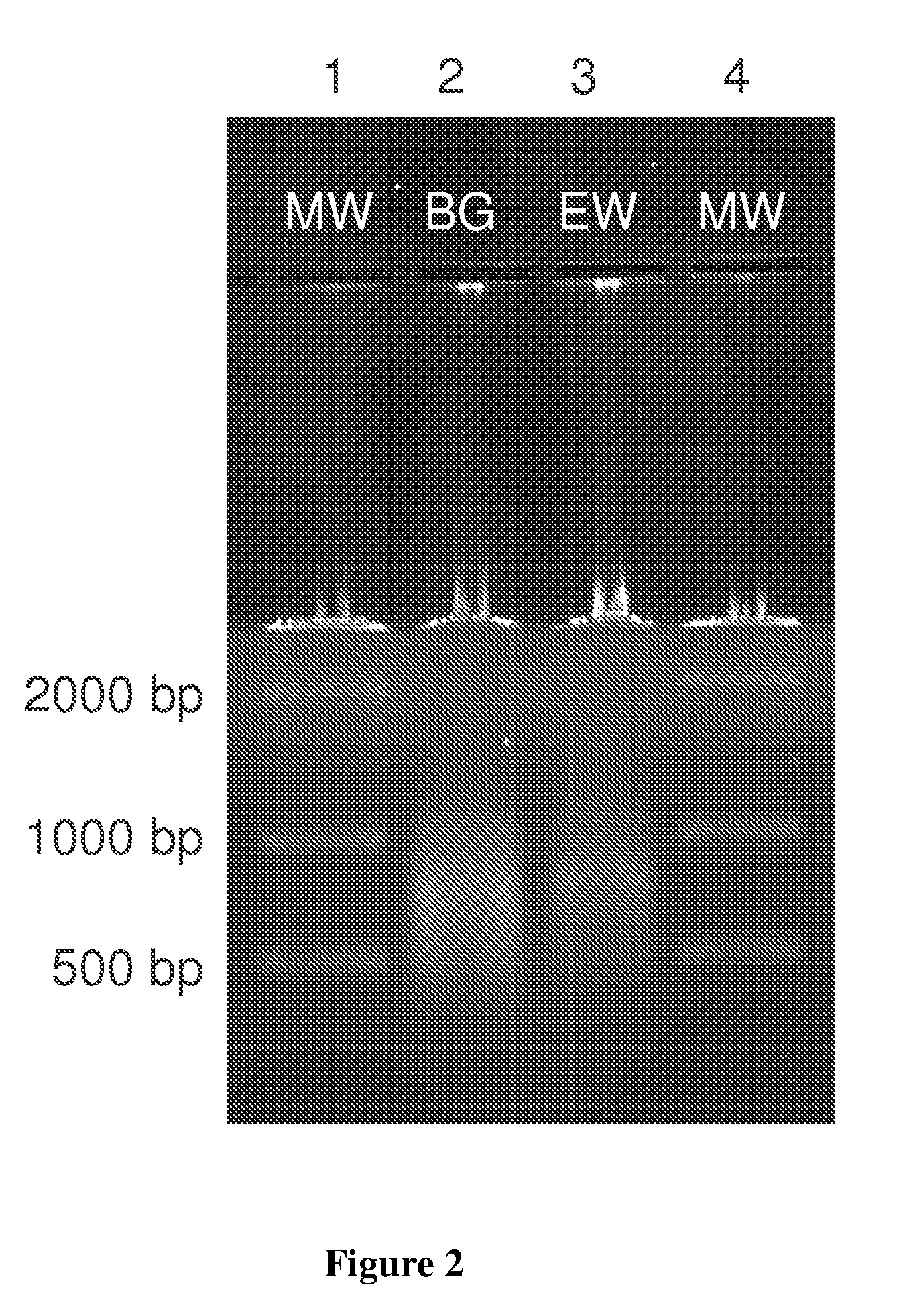
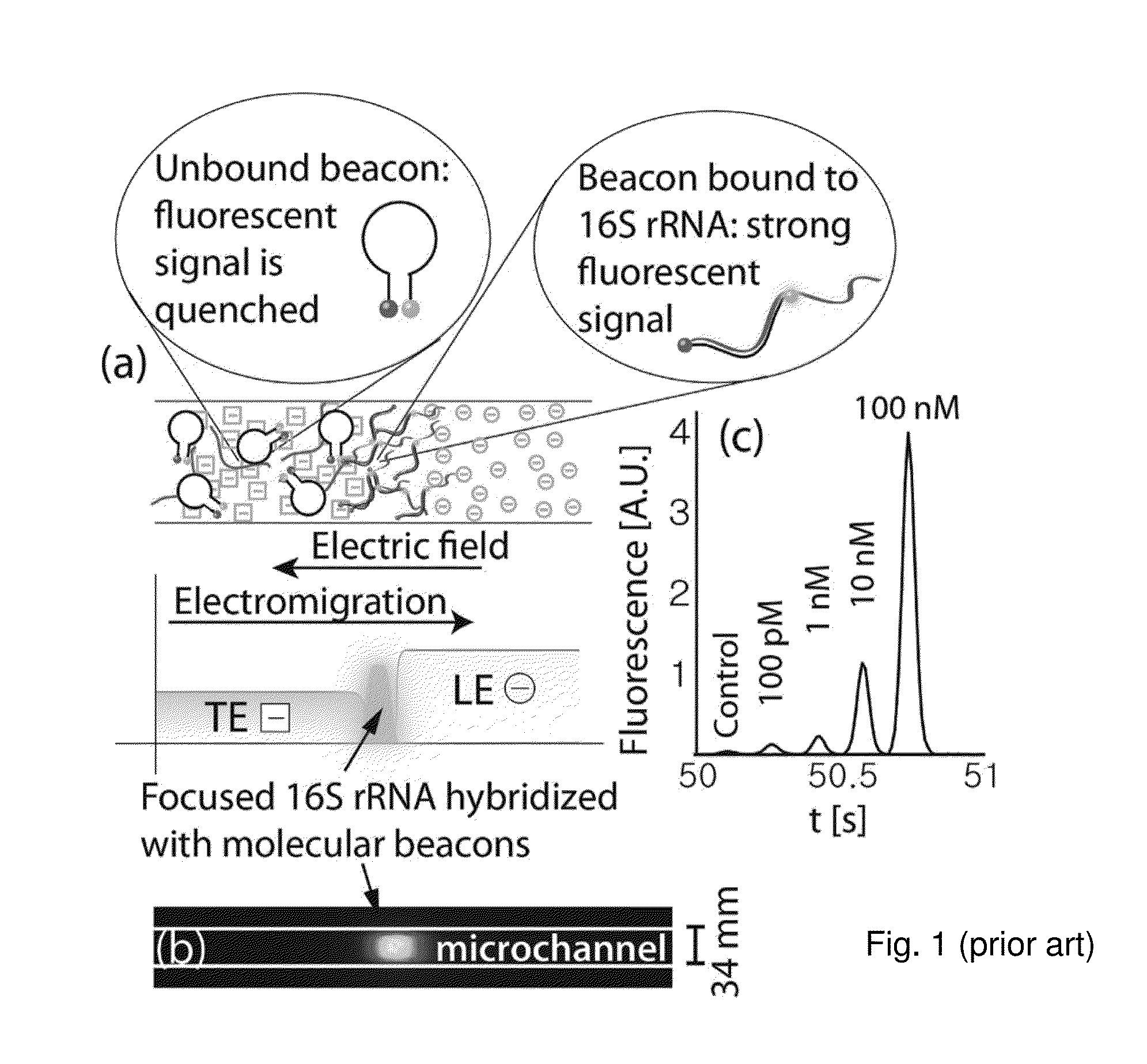
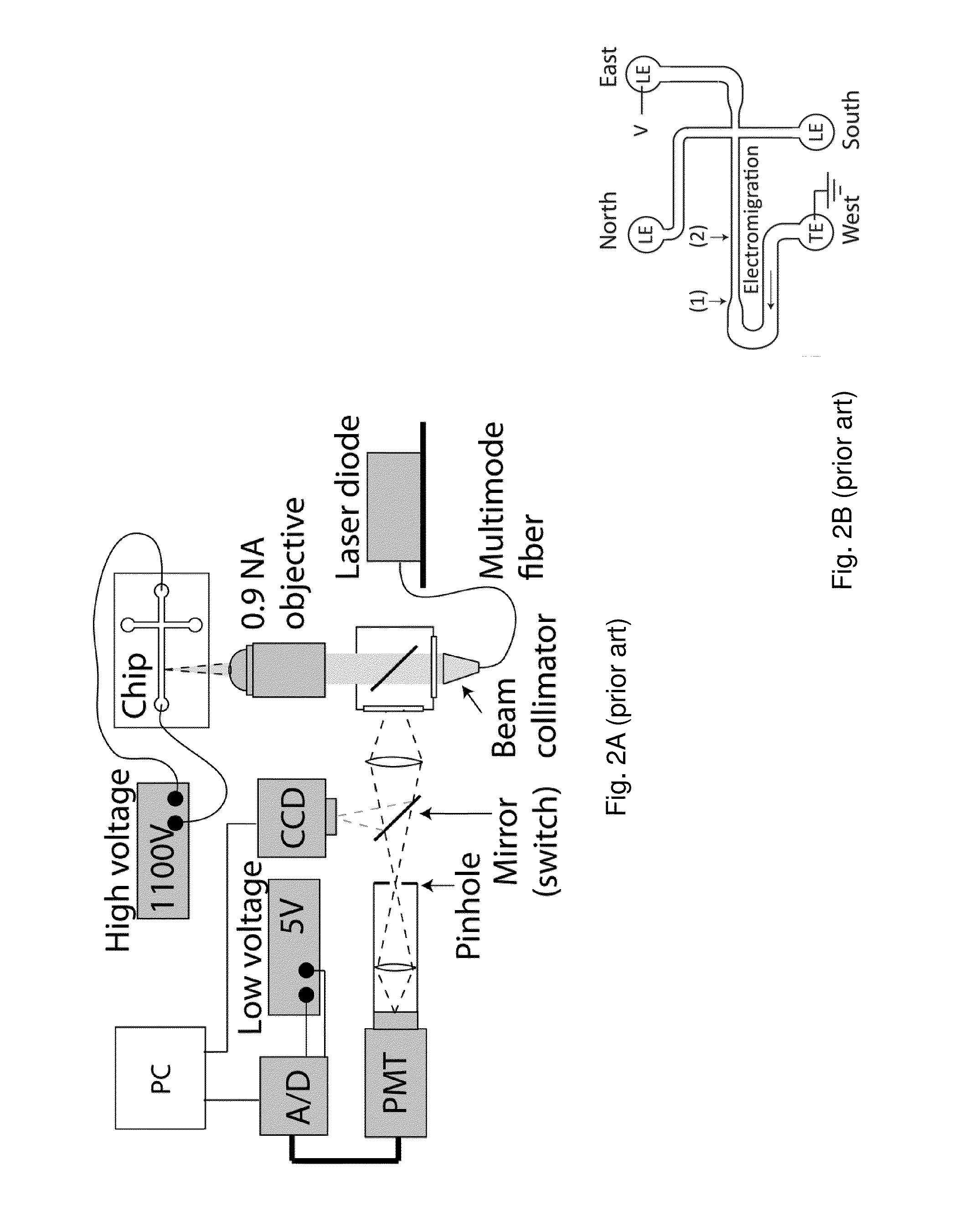
A DNA detection method combines DNAzyme reactions and on-chip isotachophoresis (ITP). A mixture of sample containing a target DNA and a DNAzyme sensor which is either (1) a catalytic molecular beacon or (2) a binary DNAzyme and a probe is loaded into a trailing electrolyte (TE) reservoir of a microfluidic chip. In the presence of the target DNA, the catalytic molecular beacon or the probe is cleaved to generate a fluorescent fragment. Enhanced DNAzyme reaction occurs at the TE-to-LE interface. Fluorescent signal from cleaved catalytic molecular beacon or probe is detected either at the location where DNAzyme reaction occurs or at a separate location. In the latter case, the microfluidic chip has a separation region containing a capture gel or a sieving matrix which allows the fluorescent fragment to pass through but captures or traps the uncleaved catalytic molecular beacon or probe.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
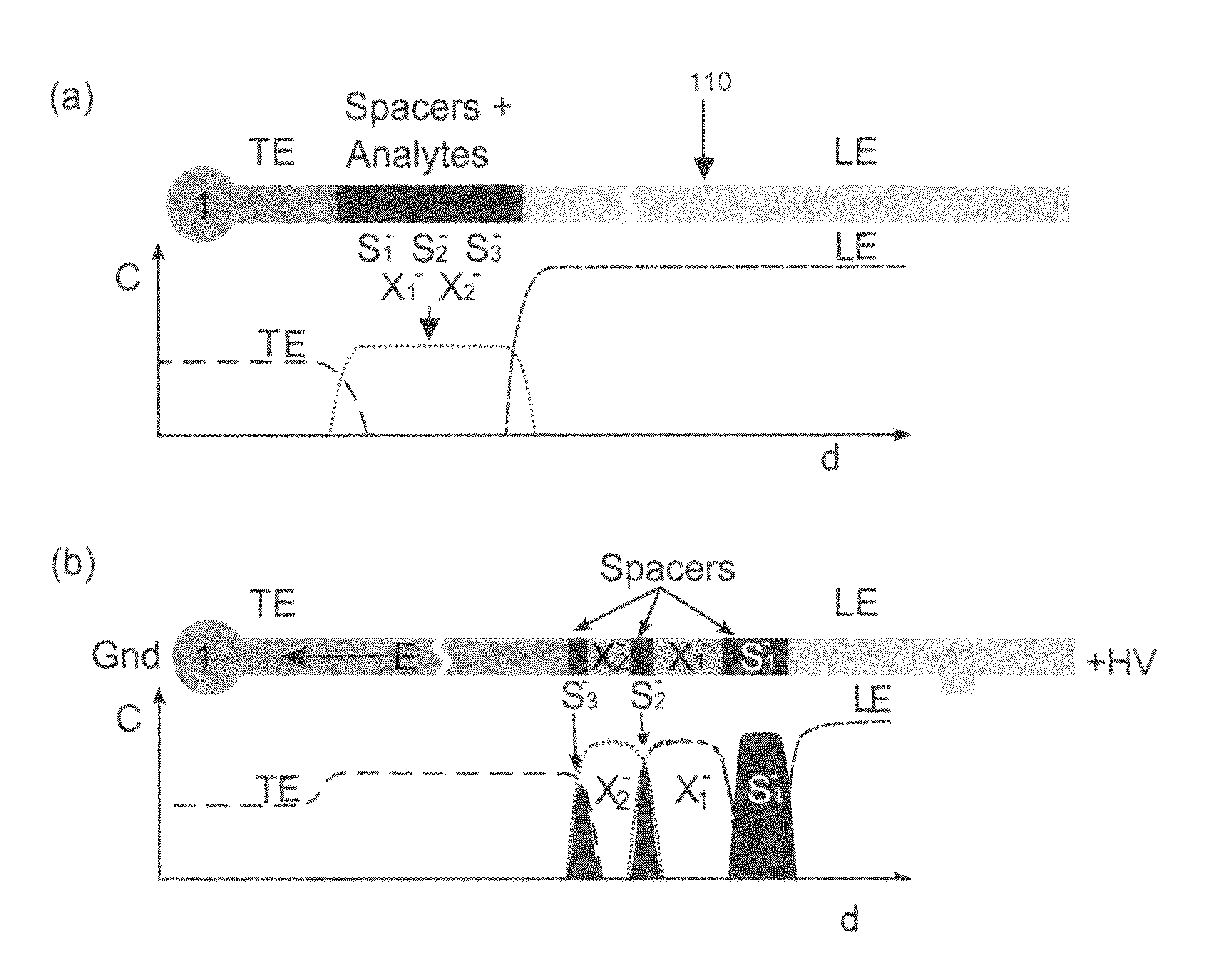
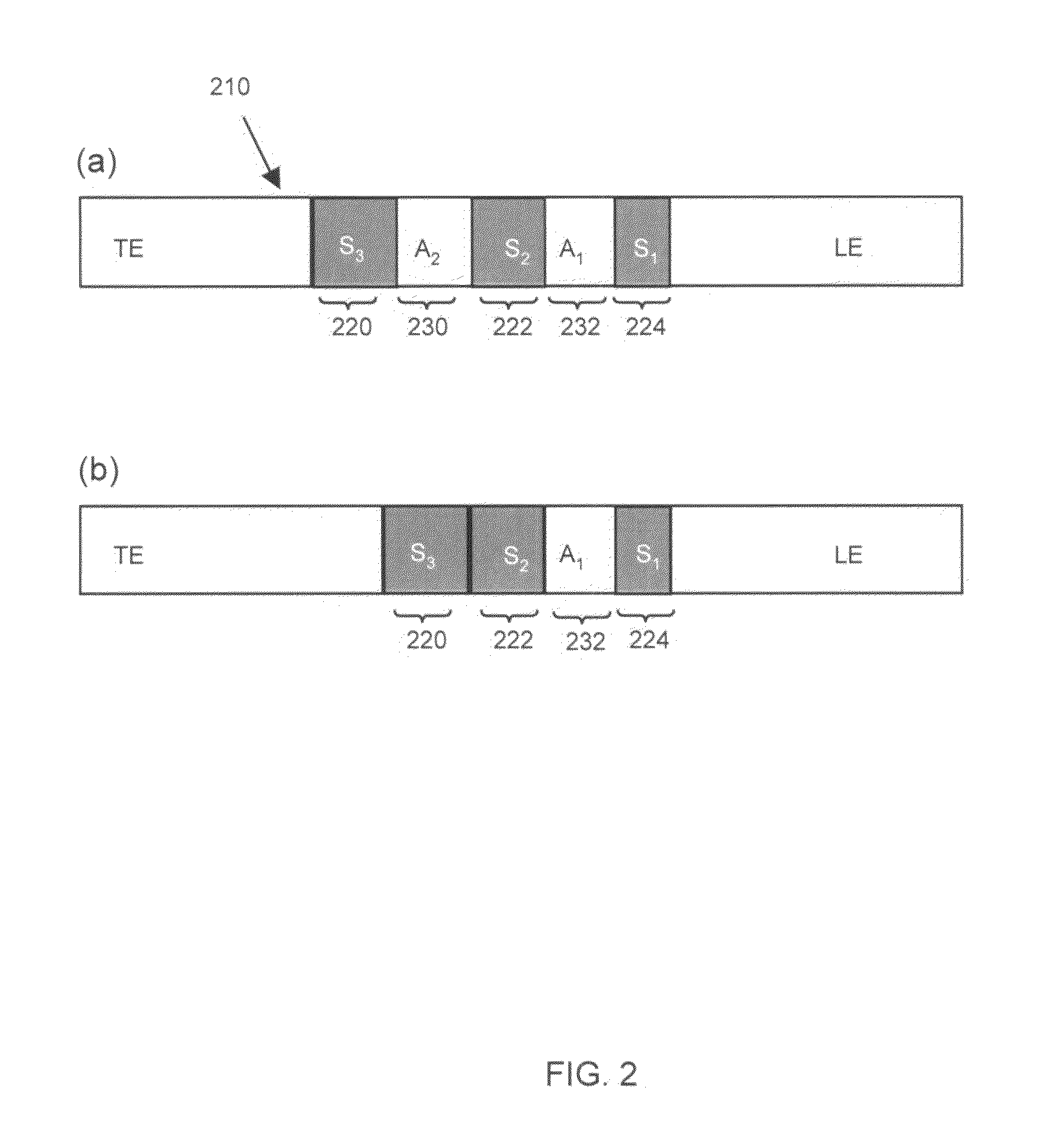
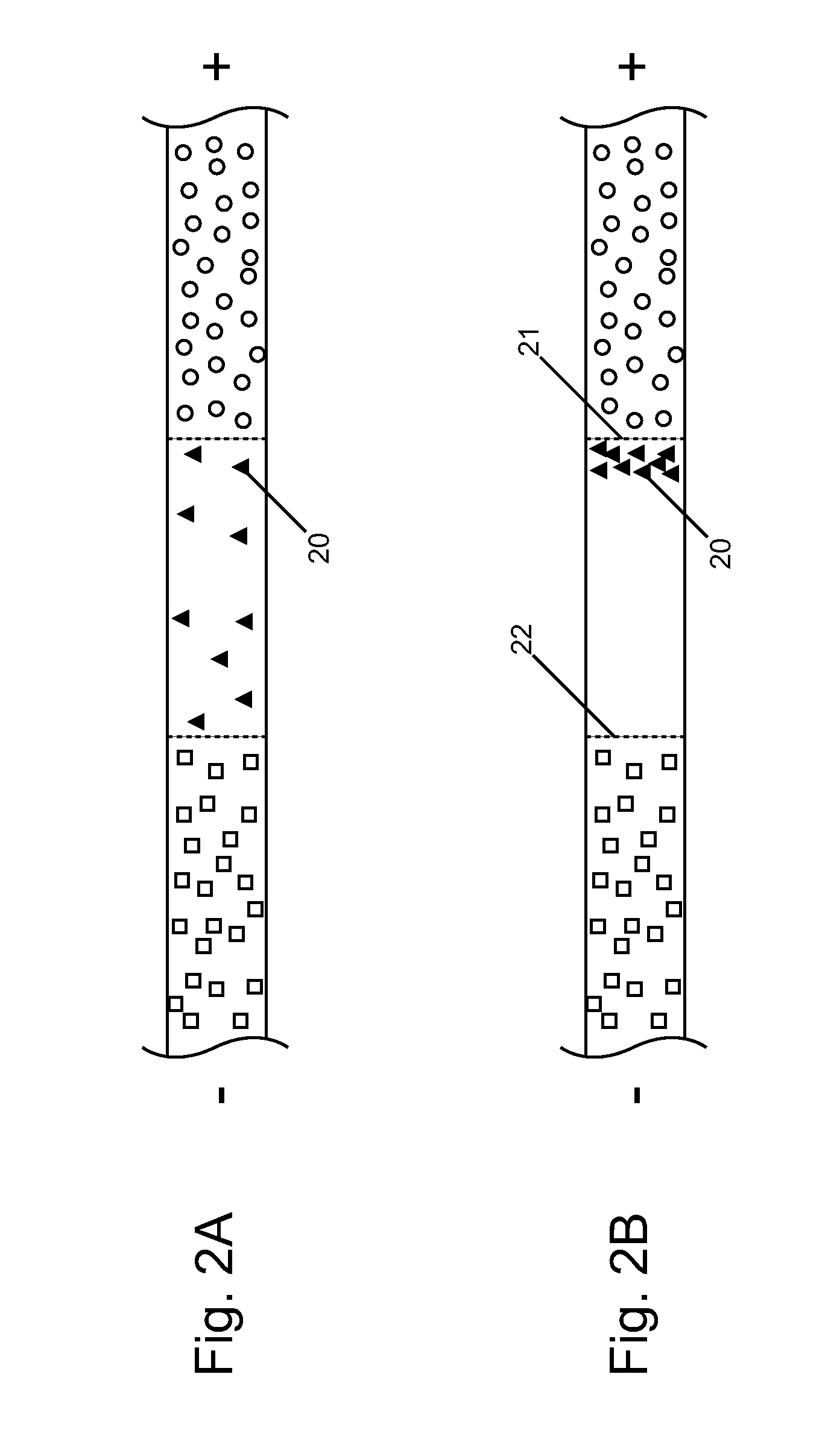
Isotachophoretic analyte extraction
InactiveUS8585883B2Easy to separateHigh puritySludge treatmentComponent separationIsotachophoresisAnalyte
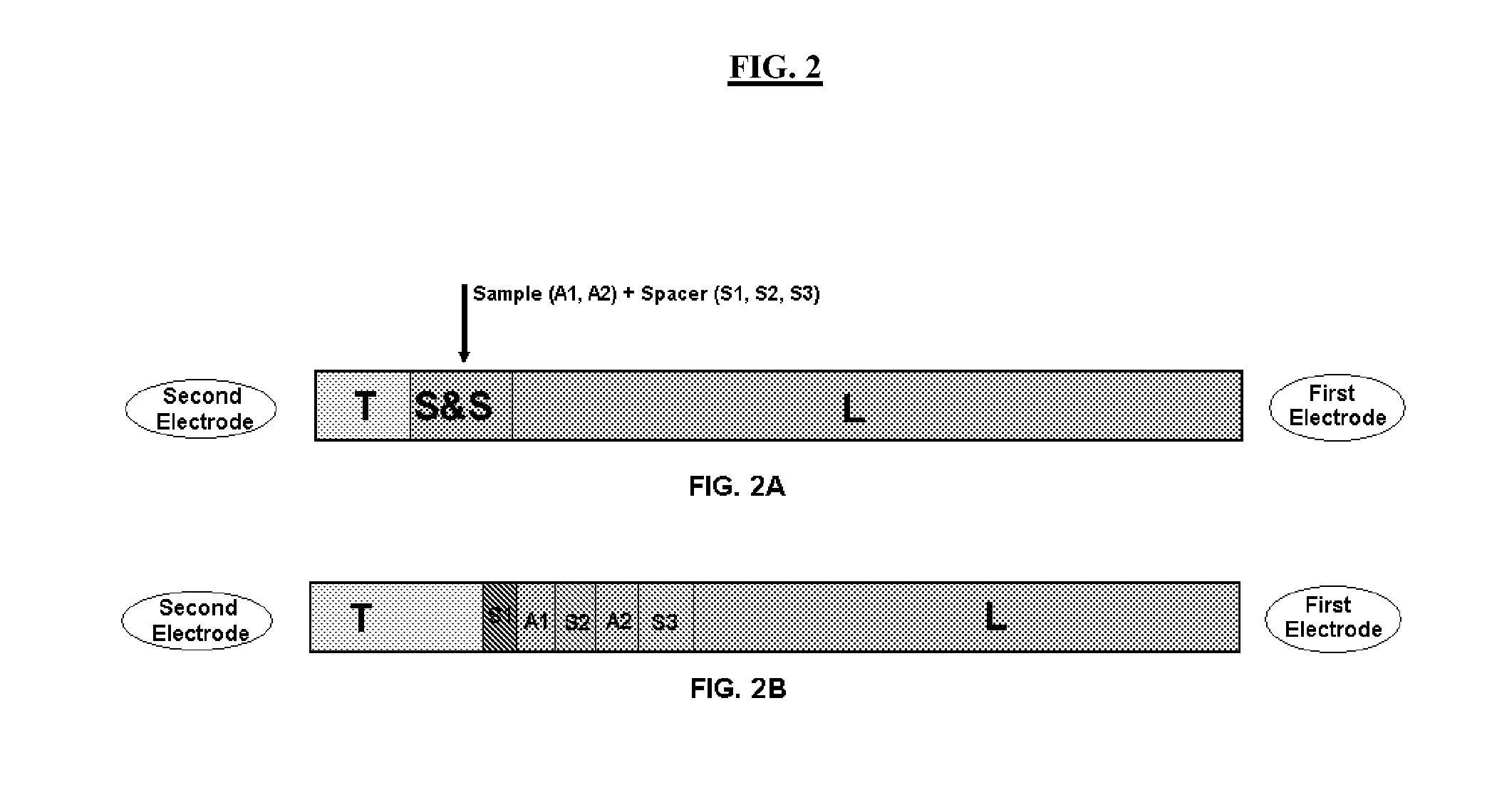
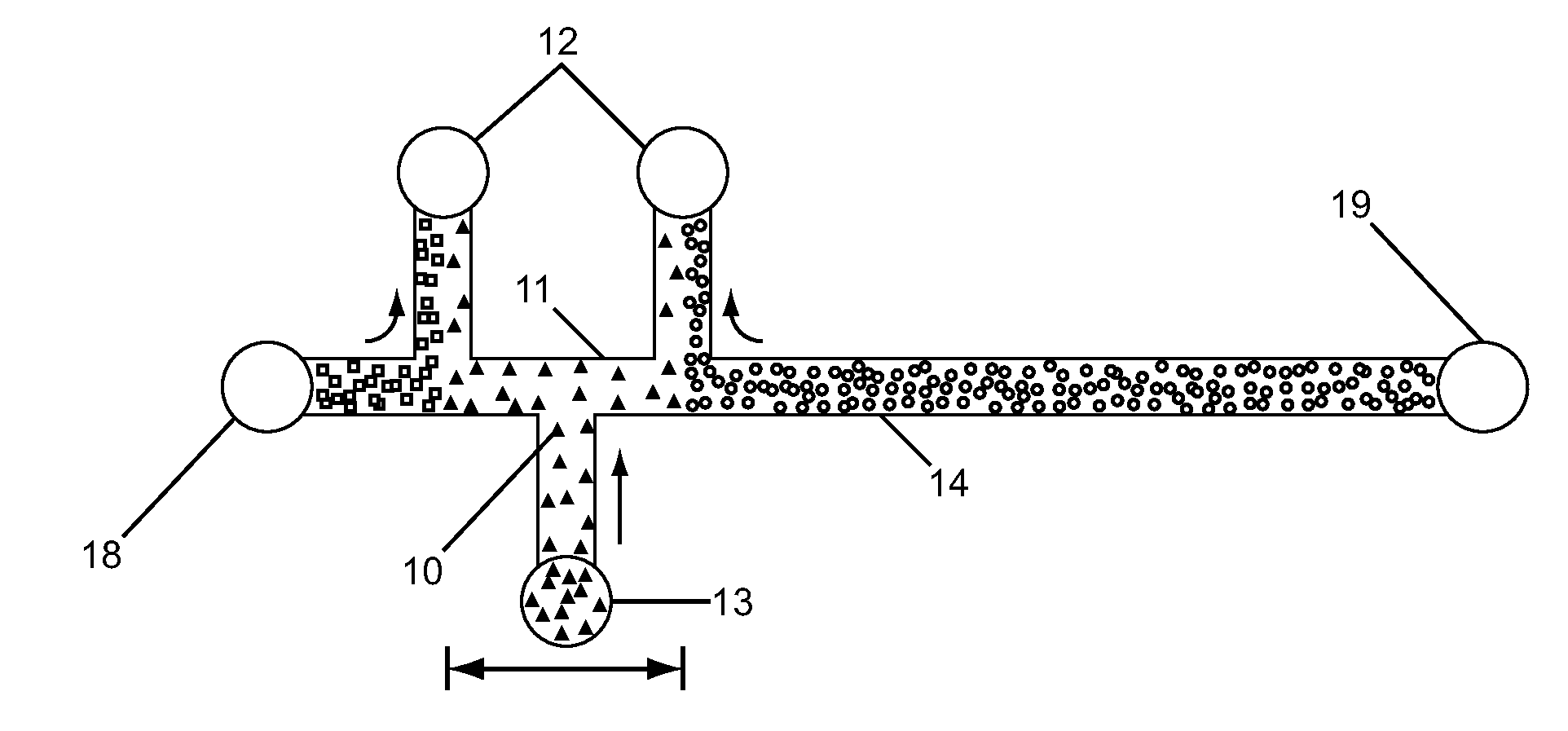
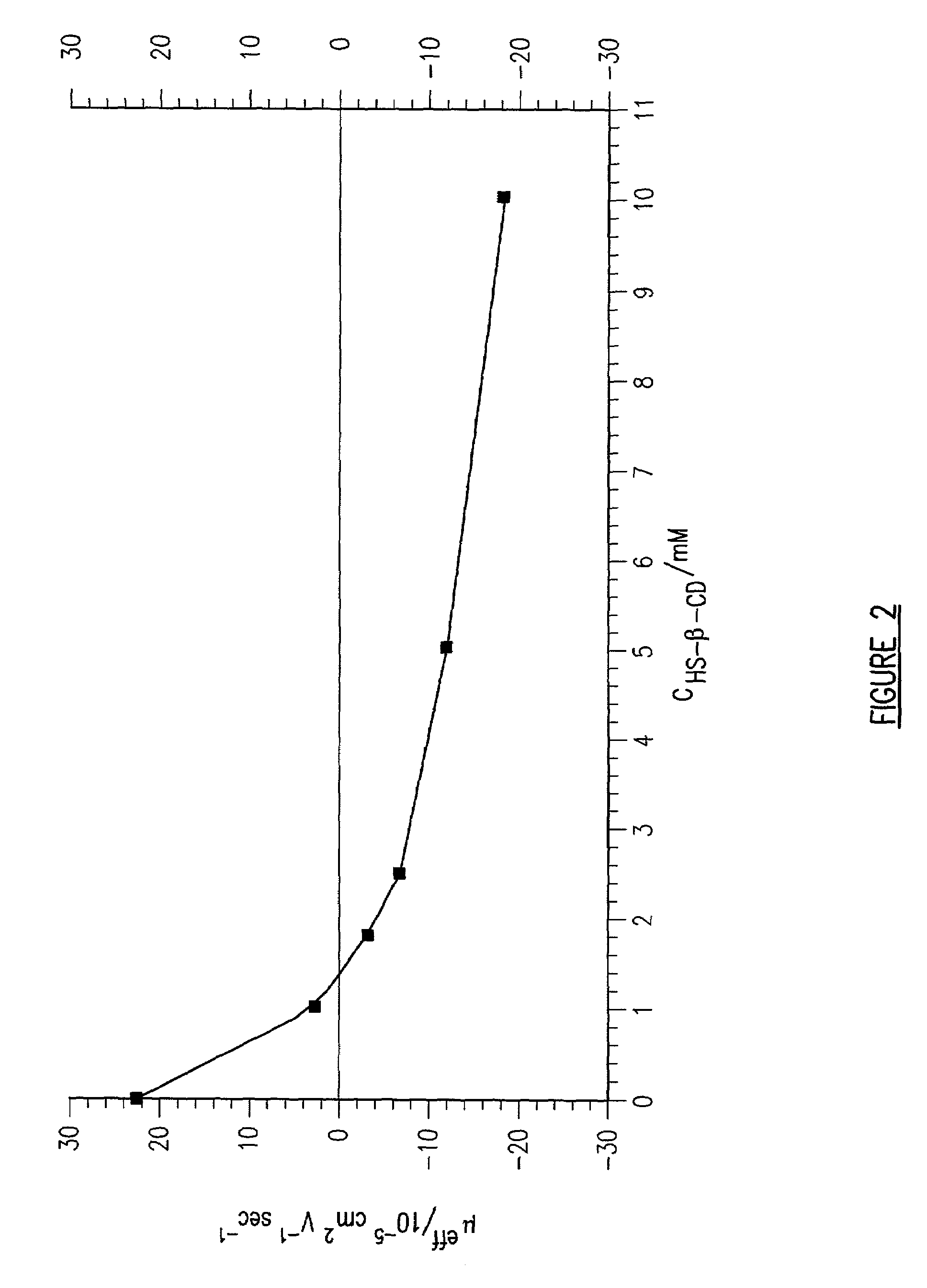
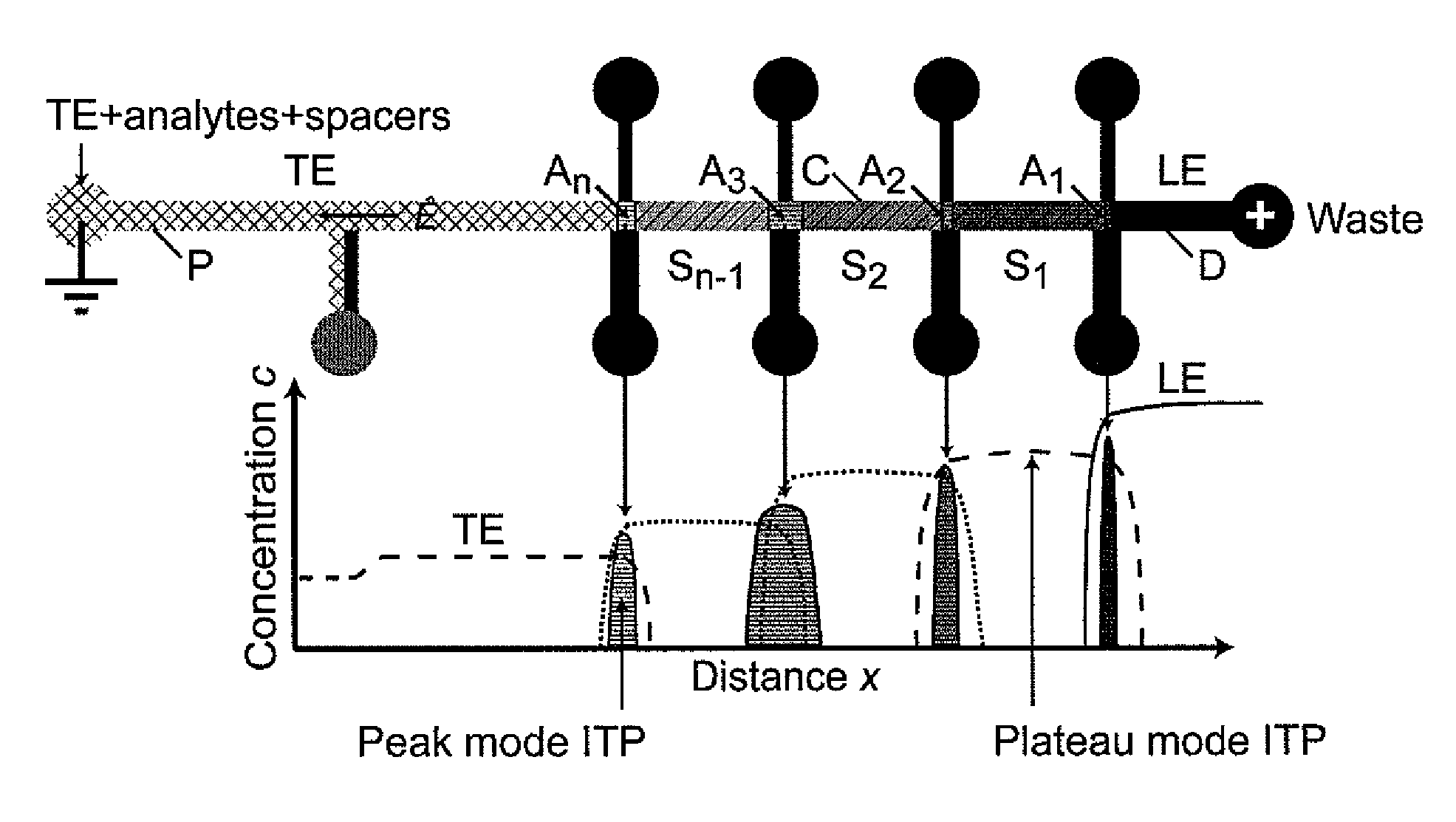
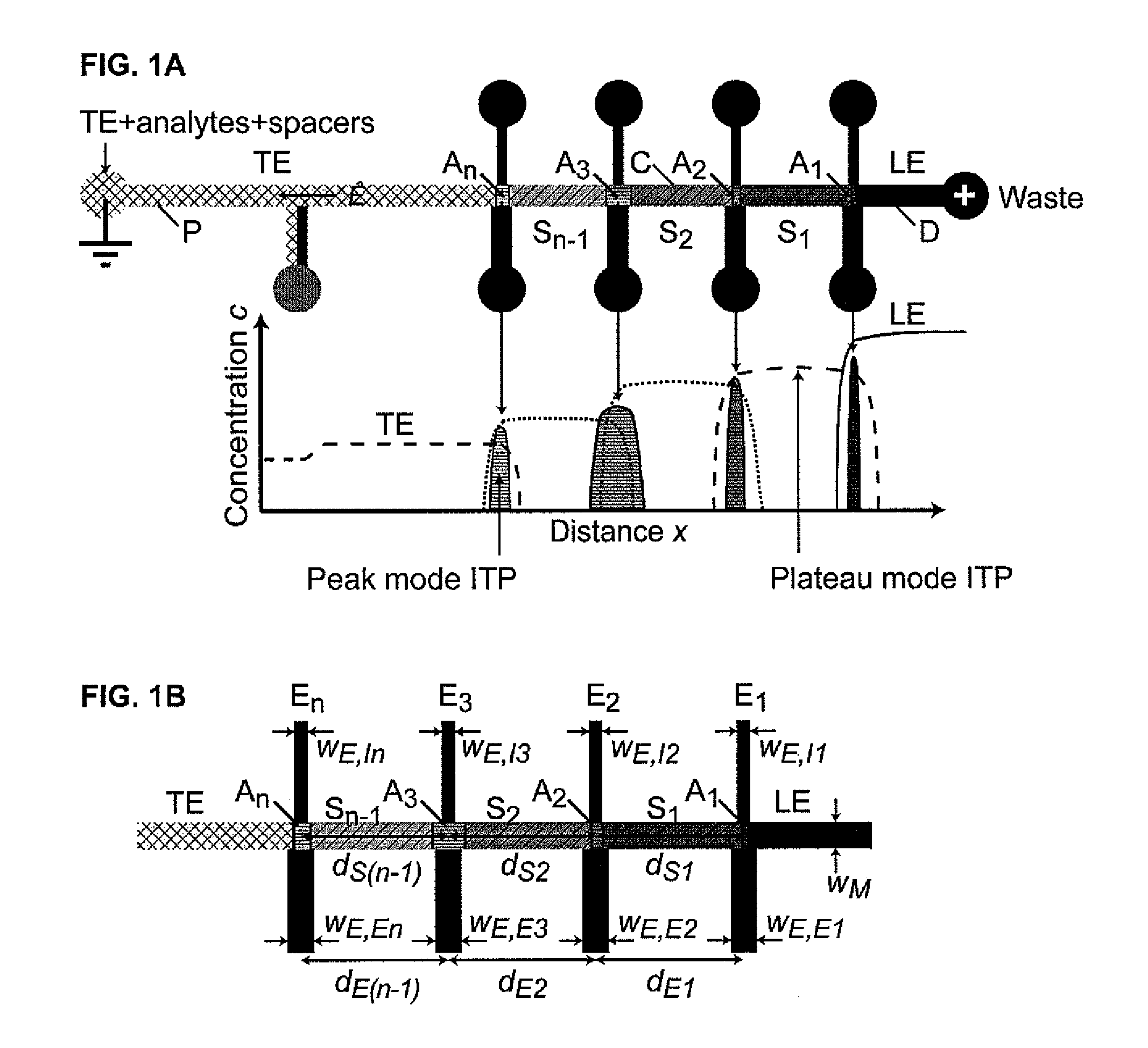
An isotachophoresis method for preconcentrating and isolating a plurality n of charged analytes (Ai, with i=1 to n) contained in a sample is disclosed, wherein each one of the analytes Ai has an effective electrophoretic mobility μAi obeying the fully ordered relationship μA1>μA2>etc.>μAn, comprising the step of preparing a mixture of said sample and a number n−1 of spacer compounds (Sk, with k=1 to n−1) wherein each one of said spacer compounds (Sk) has an effective electrophoretic mobility μSk obeying the fully ordered relationship μAk>μSk>μAk+1. An axial electric field is applied along the longitudinal axis of a separation channel, thereby causing a preconcentration and separation of the analytes and spacers forming respective focused spacer zones and focused analyte zones that flow along the longitudinal axis. Each one of the spacer compounds (Sk) has an initial concentration (c0,Sk) selected in such manner as to substantially correspond, at its preconcentrated concentration (cSk) in the respective focused spacer zone, to a volume of the main separation channel enclosed between an associated pair of adjacent extraction channels (Ek) and (Ek+1). Through this spatial displacement of analytes Ai by spacers Sk, the analytes can be selectively extracted into the extraction channels Ei.
Owner:MOLECULAR CONTROL AG
Device and method for separation and analysis of trace and ultra-trace ionogenic compounds by isotachophoresis and zone electrophoresis on chip
Disclosed herein is a device for separation and analysis of trace and ultra-trace ionogenic compounds by isotachophoresis-zone electrophoresis on a chip with online detection and method of its use, concentrating trace and ultra-trace analytes by isotachophoretic migration in a wide separation channel when a manifold of auxiliary electrodes is employed. Then the isotachophoretic zones of trace and ultra-trace analytes are transferred by isotachophoretic migration through a tapered channel, while corresponding auxiliary electrodes are progressively disconnected from the power supply. When the isotachophoretic zones enter the analytical capillary channel, the mode switches to zone electrophoresis and an online detector detects analytes for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Owner:DOLNIK VLADISLAV
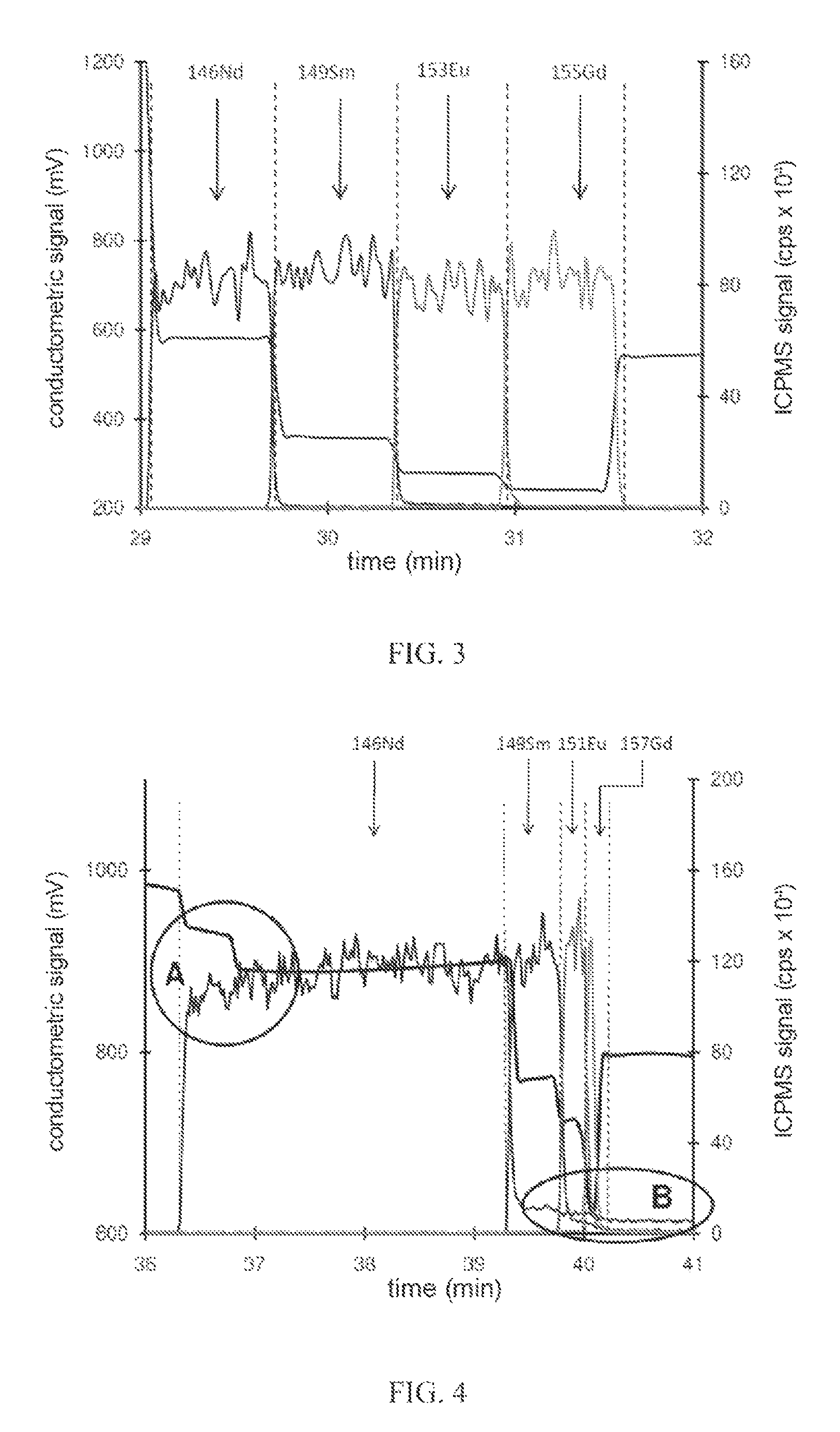
Multi-element isotopic measurement by direct coupling of a multi-cycle isotachophoresis technique and a mass spectrometry technique
ActiveUS20160181081A1Without diminishing efficiency of purificationReduce purification efficiencyElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementIsotachophoresisMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method for separating electrically charged species contained in a solution by an isotachophoresis method applied in an electrophoresis device, the isotachophoresis method being coupled to isotopic measurement using a mass spectrometer. The method notably comprises a step of stopping the voltage applied to the terminal of the electrophoresis capillary and transient application of a counter-pressure making it possible to utilize the length of the capillary several times and extend the separation distance artificially.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
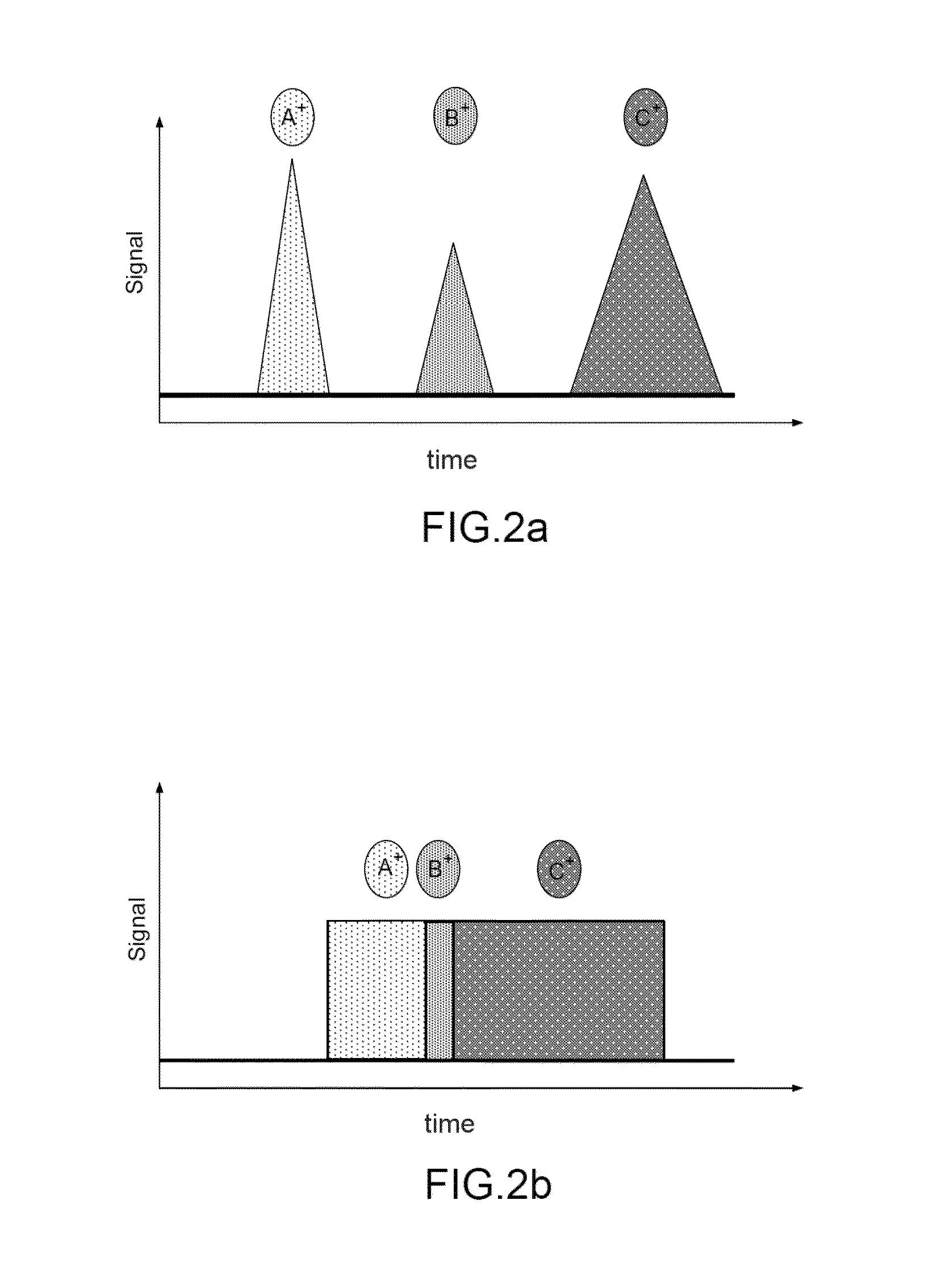
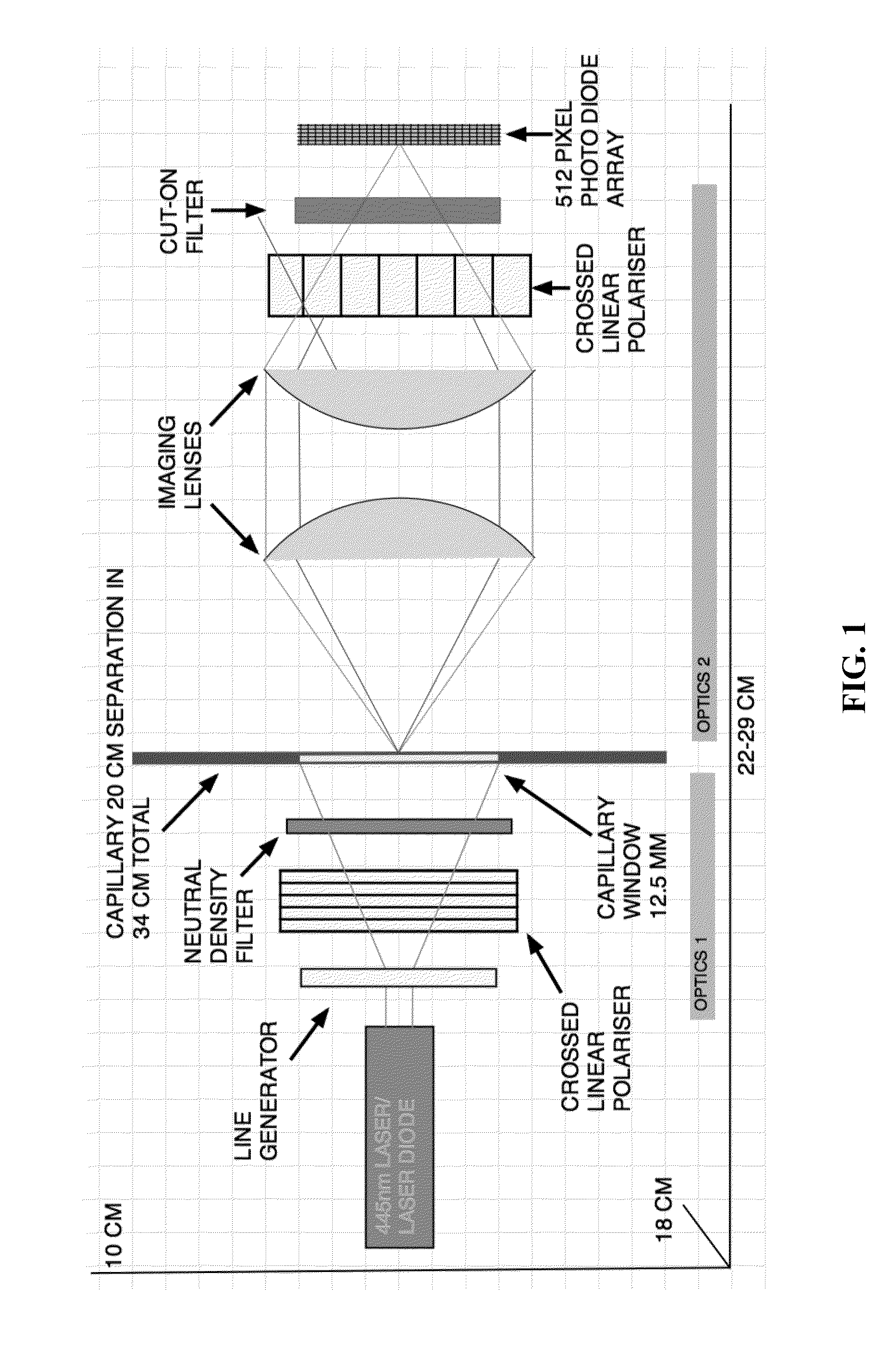
Quantitative molar concentration detection of specific apolipoprotein-containing particles present in bodily fluids by using capillary electrophoresis
InactiveUS20160109472A1Fast and accurate and detailed resolutionBiocideComponent separationDiseaseLipid particle
A method for determining the molar concentration of specific lipoprotein particles present in a bodily fluid is presented. Multipixel Capillary Isotachophoresis Laser Induced Fluorescence is applied to fluorescently-labeled lipoproteins or immunologically-labeled apolipoproteins, facilitating quantification of lipoproteins and / or lipid particles and / or their associated apolipoproteins in a sample. The measurements are used to predict the risks of developing, progressing in severity of diseases related to lipoprotein particles, including cardiovascular and metabolic disorders.
Owner:HELENA LAB
Method for isotopic measurement by ICPMS
ActiveUS9110016B2Less timeGood reproducibilityElectrolysis componentsComponent separationCapillary electrophoresisIsotachophoresis
A method for isotope measurement of charged species contained in a solution to be analyzed, particularly charged species having an isobaric interference, has the following consecutive steps:a) in the capillary of a capillary electrophoresis device, the solution to be analyzed is inserted contiguously between a terminating electrolyte and a leading electrolyte that, respectively, are placed after the inlet and before the outlet of the capillary and contain ions of the same charge but with mobility inferior and superior to those of said species;b) separating the species by using the capillary electrophoresis device according to the isotachophoresis mode; thenc) in the continuity of the preceding step, performing an isotope measurement of the species detected in the form of a substantially constant amplitude signal by using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICPMS) connected by direct coupling with the capillary electrophoresis device.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for trapping organic compound in aqueous solution
InactiveCN101823782ASimple and fast operationReduce usageWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsIsotachophoresisOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a method for trapping an organic compound in aqueous solution, which comprises the following steps of: taking inert metal materials as electrodes; adding precursor electrolyte aqueous solution, aqueous solution containing an organic matter to be trapped, ionic surfactant aqueous solution and following electrolyte aqueous solution into an electrolytic bath in turn, wherein the mobility of the ionic surfactant aggregate is less than that of the precursor ions in the precursor electrolyte and more than that of the following ions in the following electrolyte aqueous solution and the isotachophoresis condition is met as required; applying the DC voltage of 10V to 30kV; and when the ionic surfactant aggregate migrates to pass through the aqueous solution containing the organic matter to be trapped under the driving of an electric field, rapidly taking the surfactant-enriched solution out, namely trapping the organic compound in the aqueous solution. The method for trapping the organic compound in the aqueous solution has the application characteristics of avoiding combustible and toxic organic solvent, along with simple and convenient operation and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Systems, devices, and methods for isotachophoresis
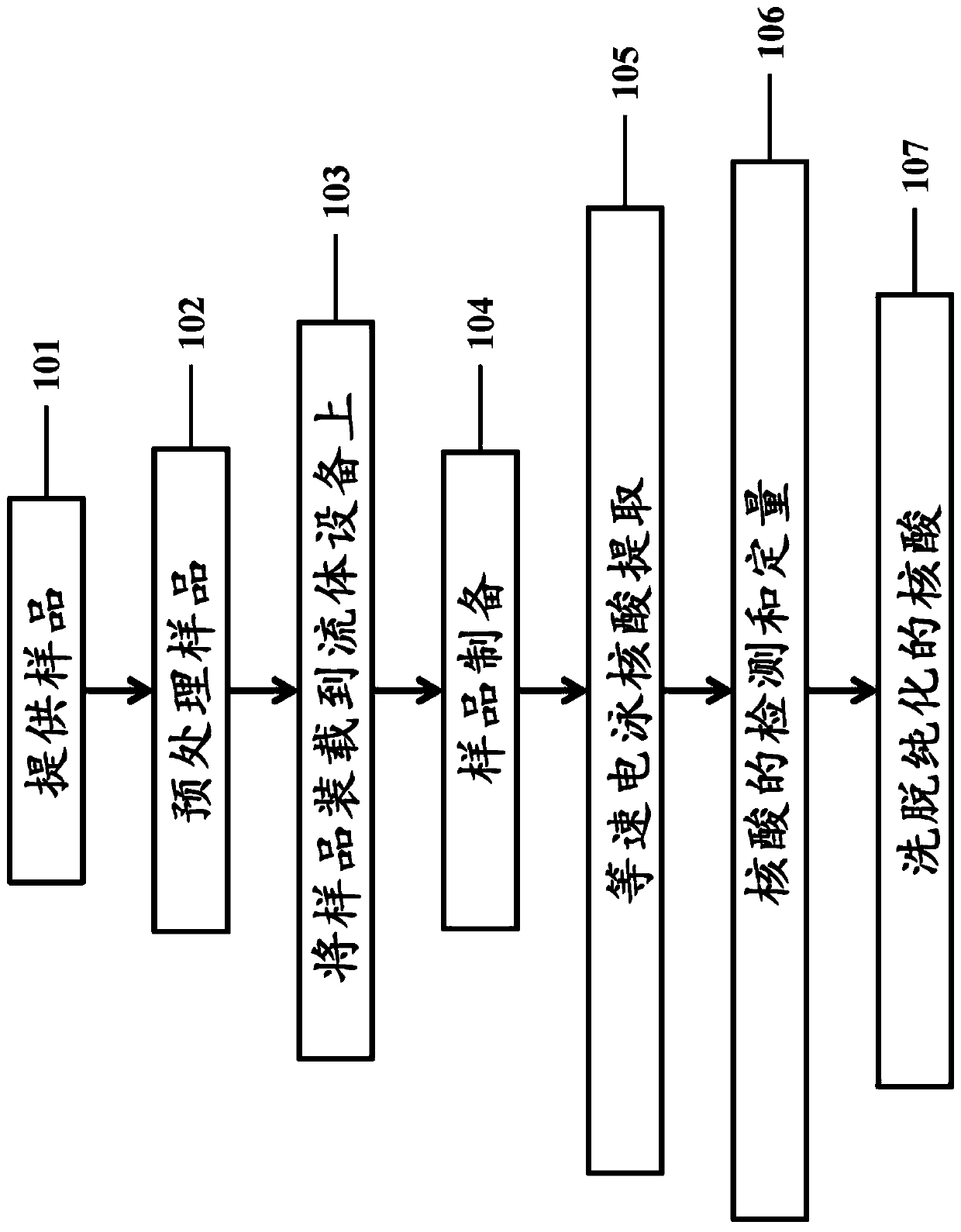
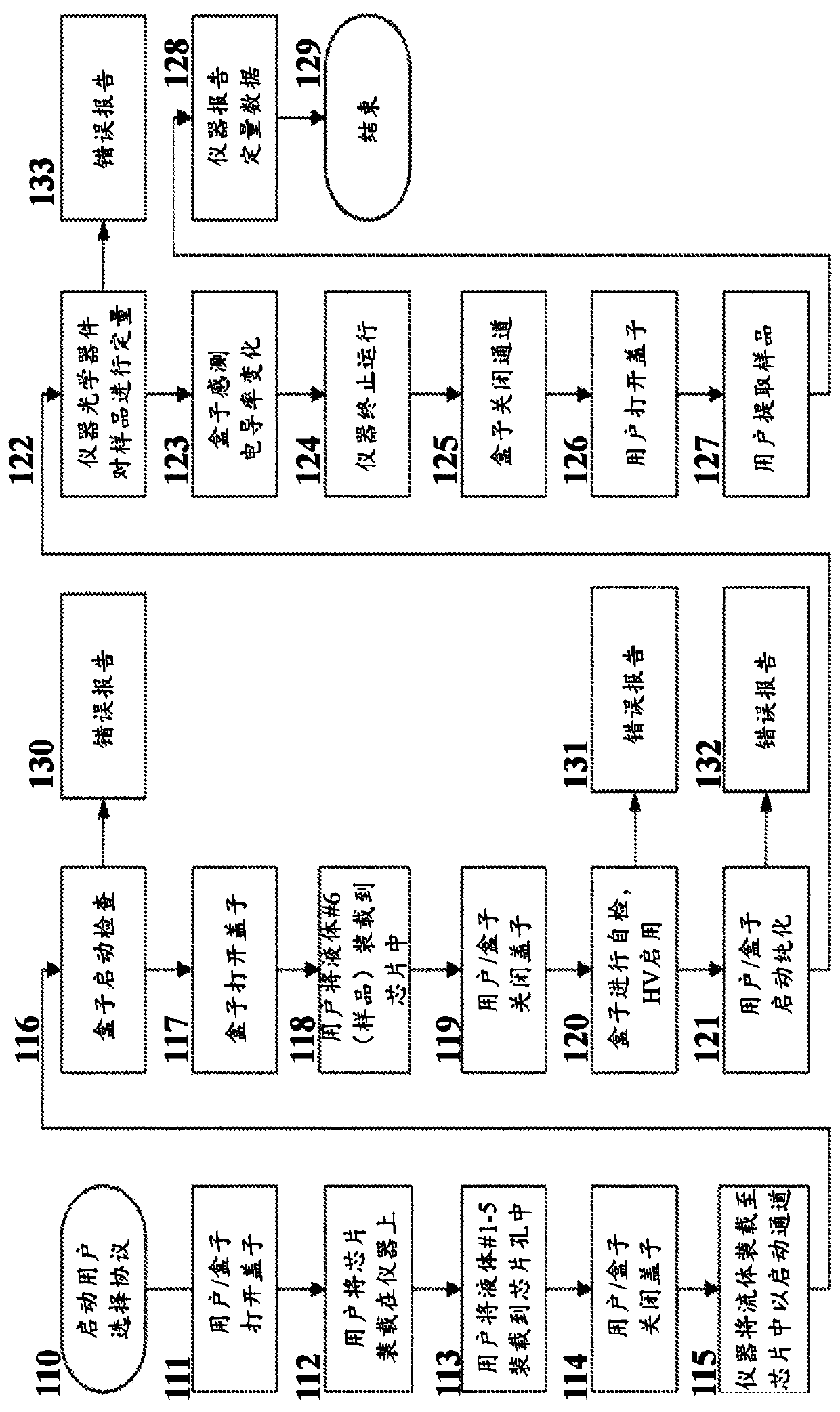
The present disclosure relates to fluidic systems and devices for processing, extracting, or purifying one or more analytes. These systems and devices can be used for processing samples and extractingnucleic acids, for example by isotachophoresis. In particular, the systems and related methods can allow for extraction of nucleic acids, including non-crosslinked nucleic acids, from samples such astissue or cells. The systems and devices can also be used for multiplex parallel sample processing.
Owner:PURIGEN BIOSYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com