Systems, devices, and methods for isotachophoresis
A technology of isotachophoresis and fluid equipment, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, laboratory containers, etc., can solve problems such as sample loss, labor, time and resource loss, and inability to perform downstream determinations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
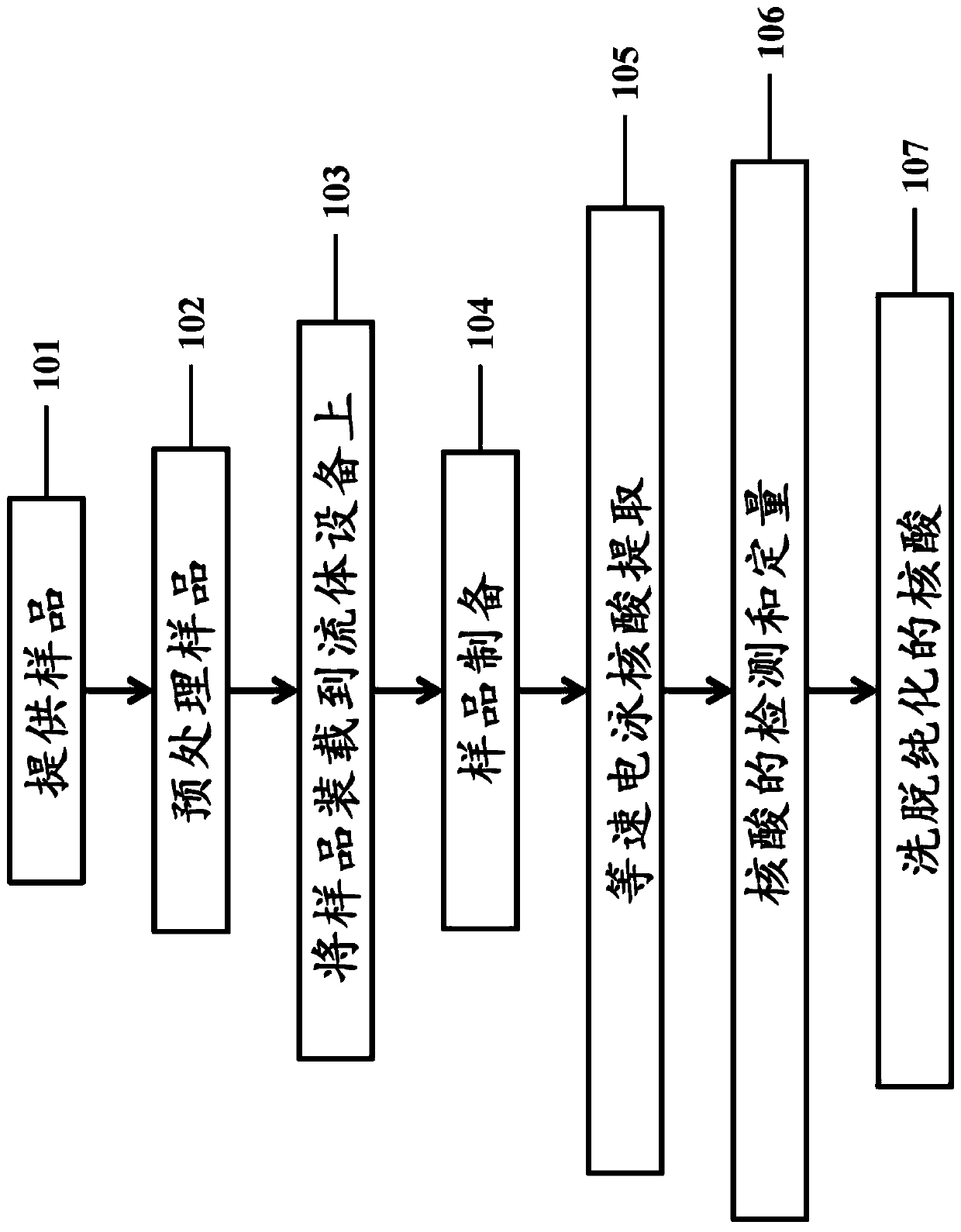
Embodiment 1
[0891] Example 1 - Extraction of DNA from FFPE samples
[0892] Obtain FFPE samples from human patients. Prepare a 1.1X alkaline aqueous buffer solution (solution A1) in nuclease-free distilled or deionized water with 80 mM NaOH, 11 mM DTT and 0.5% v / v Igepal CA-630. Prepare a 1OX quenching solution (Solution A2) with 776 mM HCl and 100 mM Tris base or Trizma base in nuclease-free distilled or deionized water. Commercially available proteinase K solutions and RNase are also provided. Alternatively, a neutral buffer (e.g., pH about 7.0 to about 8.0) with 0-80 mM NaCl, 5-10 mM DTT, and 0.1-0.5% v / v IGEPAL CA-630 can be prepared in nuclease-free distilled or deionized water 5-50mM Tris-HCl solution.
[0893] Add FFPE slices or scrolls to 1.5-2.0 mL microcentrifuge tubes. Add 175 μL of solution A1 to the tube. The tube contents were incubated at 50-99.9°C for 1-20 minutes (in some cases, the tube contents were incubated at 95-99.9°C for 5-20 minutes) to deparaffinize the samp...
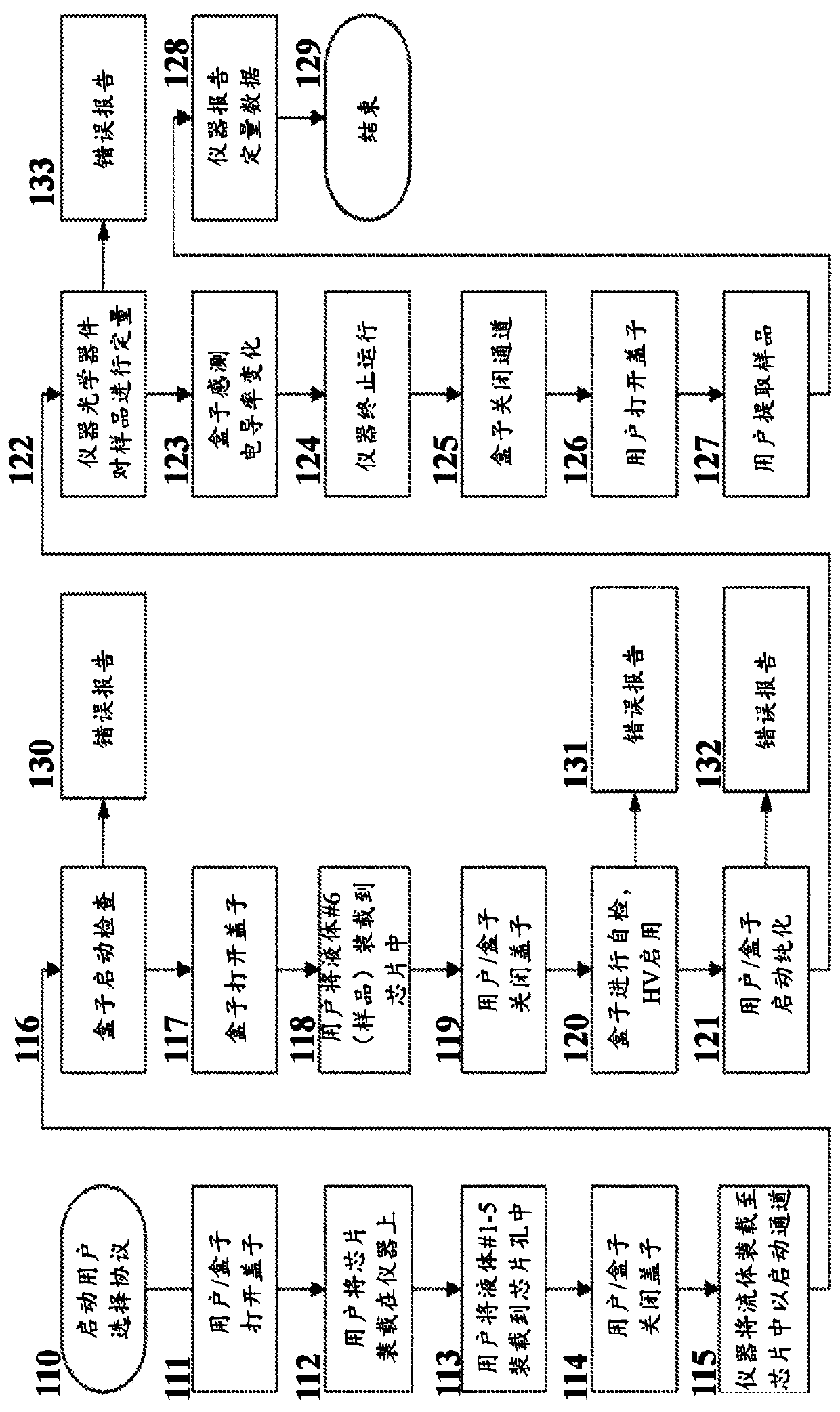
Embodiment 2
[0895] The comparison of embodiment 2-DNA extraction yield
[0896] DNA was extracted using a benchtop controller unit to automate isotachophoresis in a fluidic device from (i) qPCR buffer as a post-PCR cleanup ( image 3 , triangle data points) and (ii) cell culture lysate ( image 3 , square data points), where the yield was calculated using qPCR. Published DNA yield data using conventional solid-phase extraction columns (SPE; image 3 , diamond data points) for comparison. image 3 DNA yields are shown compared to input DNA quality. The leading electrolyte buffer for isotachophoresis contained 88 mM Tris with 44 mM HCl. A trailing electrolyte containing 1.2M Tris with 0.3M hexanoic acid and 0.6M MOPS was loaded into the trailing electrolyte reservoir. Cell lysate samples were prepared in a second leading electrolyte buffer (sample buffer) containing 10 mM Tris and 5.6 mM HCl. for about 10 -2 Nanogram (ng) to about 10 3 ng of input DNA mass, DNA was extracted from hu...
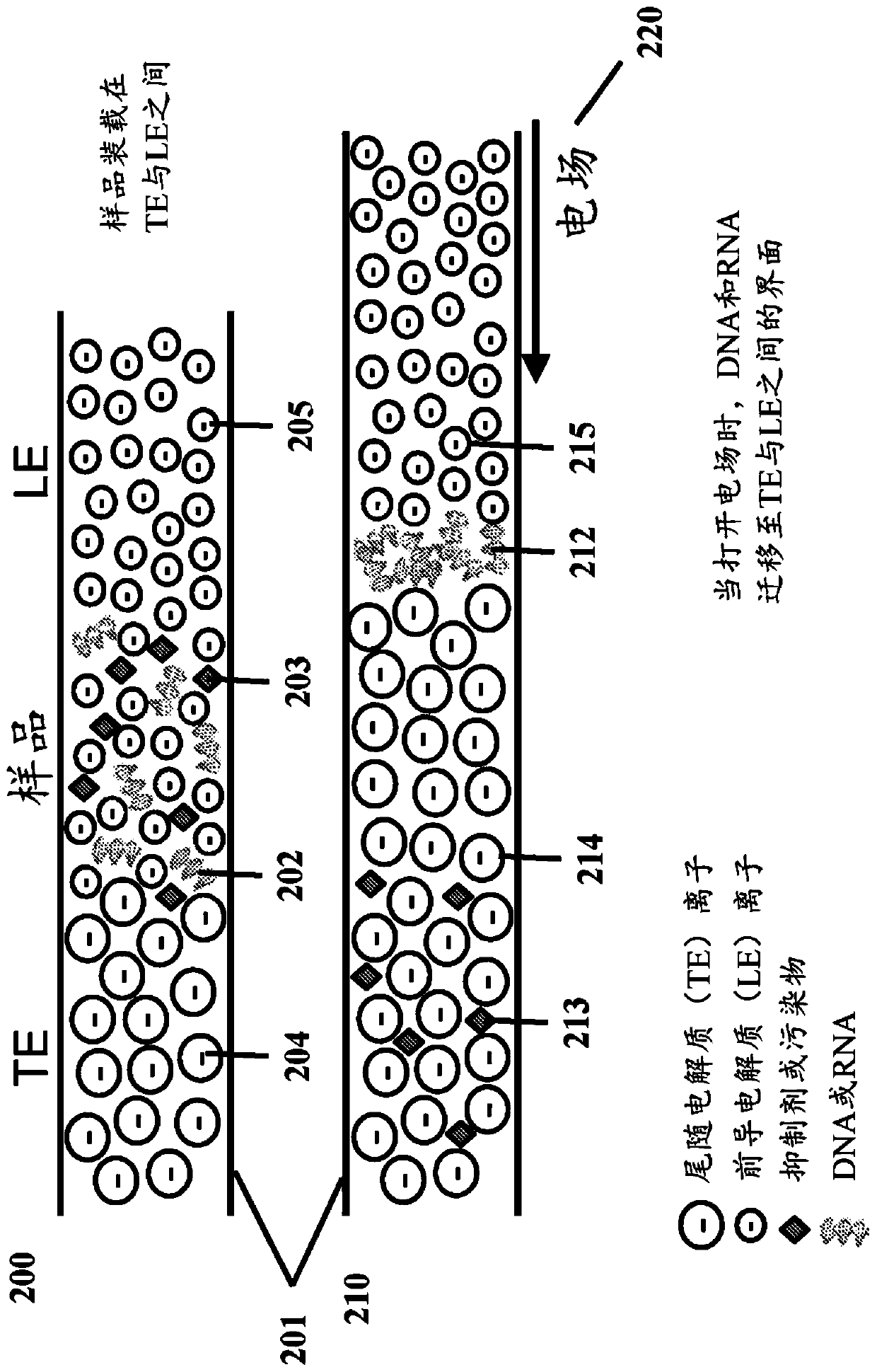
Embodiment 3
[0898] Example 3 - Separation of Crosslinked and Non-crosslinked Nucleic Acids
[0899] Deparaffinized and lysed mouse FFPE tissue samples (processed as described in Example 1) containing cross-linked and non-cross-linked nucleic acids were loaded onto the fluidic device for isotachophoresis with leading and trailing electrolytes. Samples were lysed as described in Example 1 and prepared to a final concentration of 10 mM Tris with 5.6 mM HCl in the lead electrolyte solution. The lead electrolyte contained 140 mM Tris with 70 mM HCl. The trailing electrolyte comprised a mixture of 2.1M Tris with 0.5M hexanoic acid as a spacer ion having a higher effective mobility magnitude than HEPES and 0.7M HEPES as an ion having a lower effective mobility magnitude. During isotachophoresis, non-crosslinked nucleic acids with higher effective mobility magnitudes focus before the caproic acid region and after the leading electrolyte region. Cross-linked nucleic acids and sample contaminants...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com