Patents
Literature
99 results about "Frequency profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
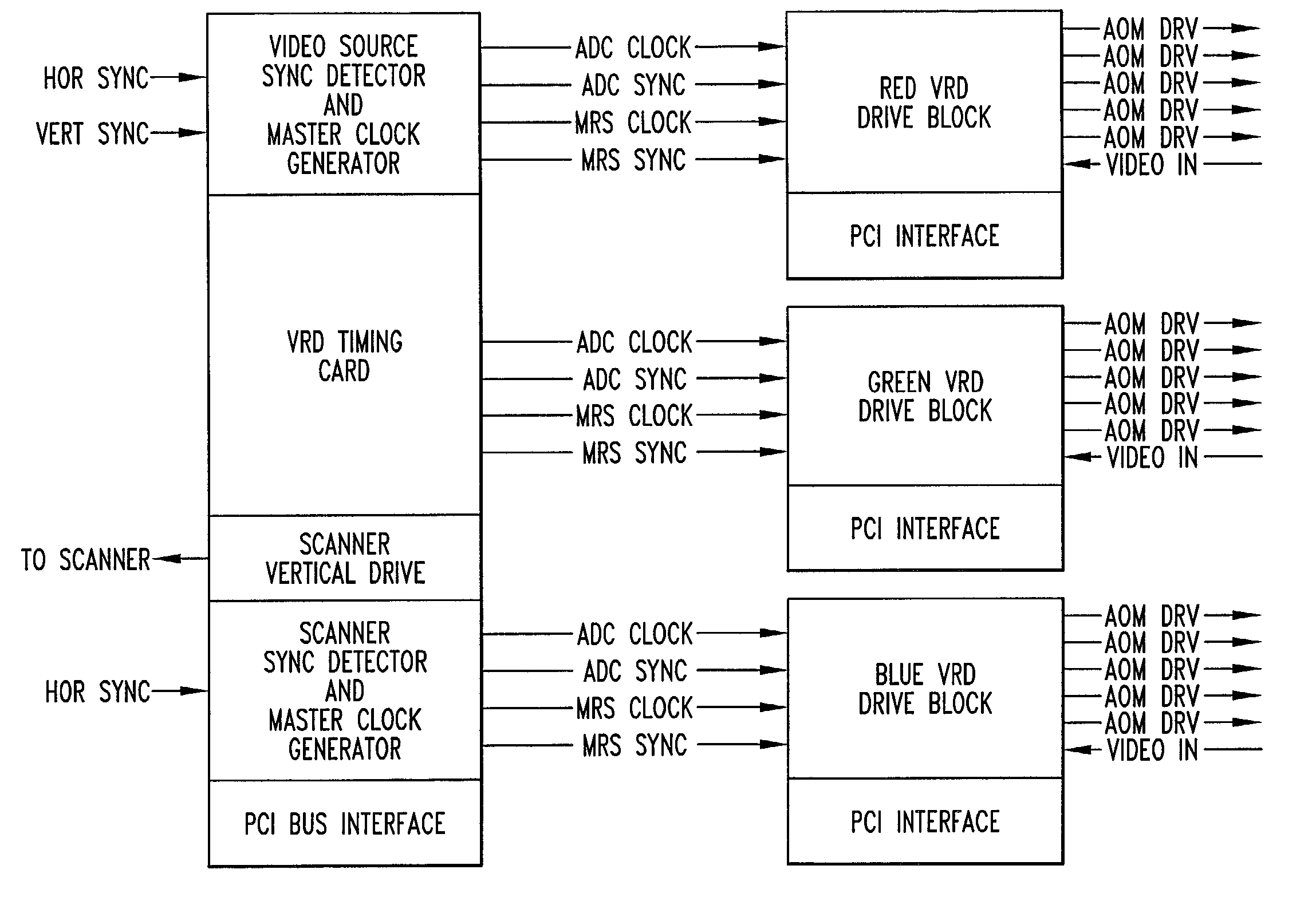
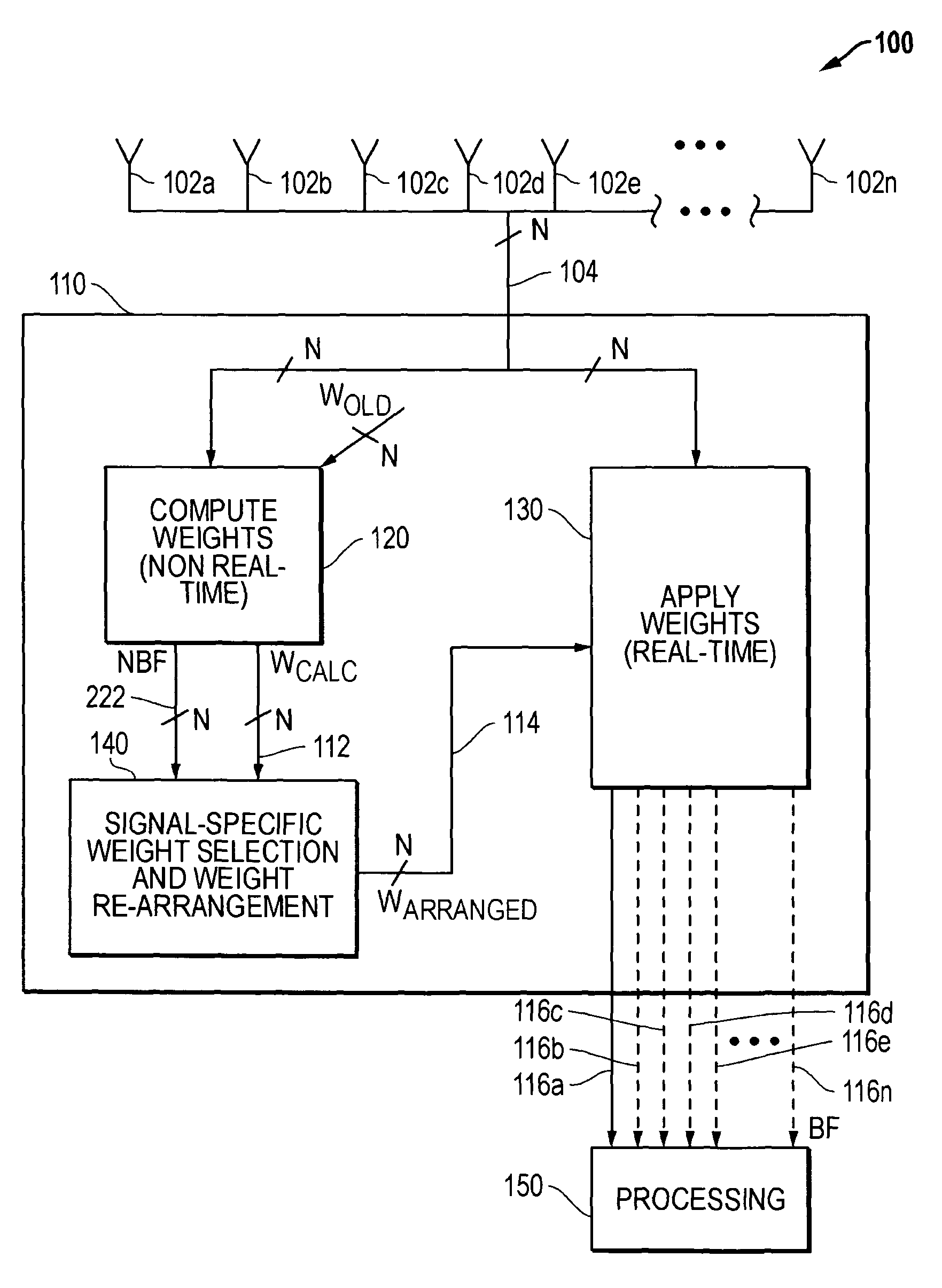
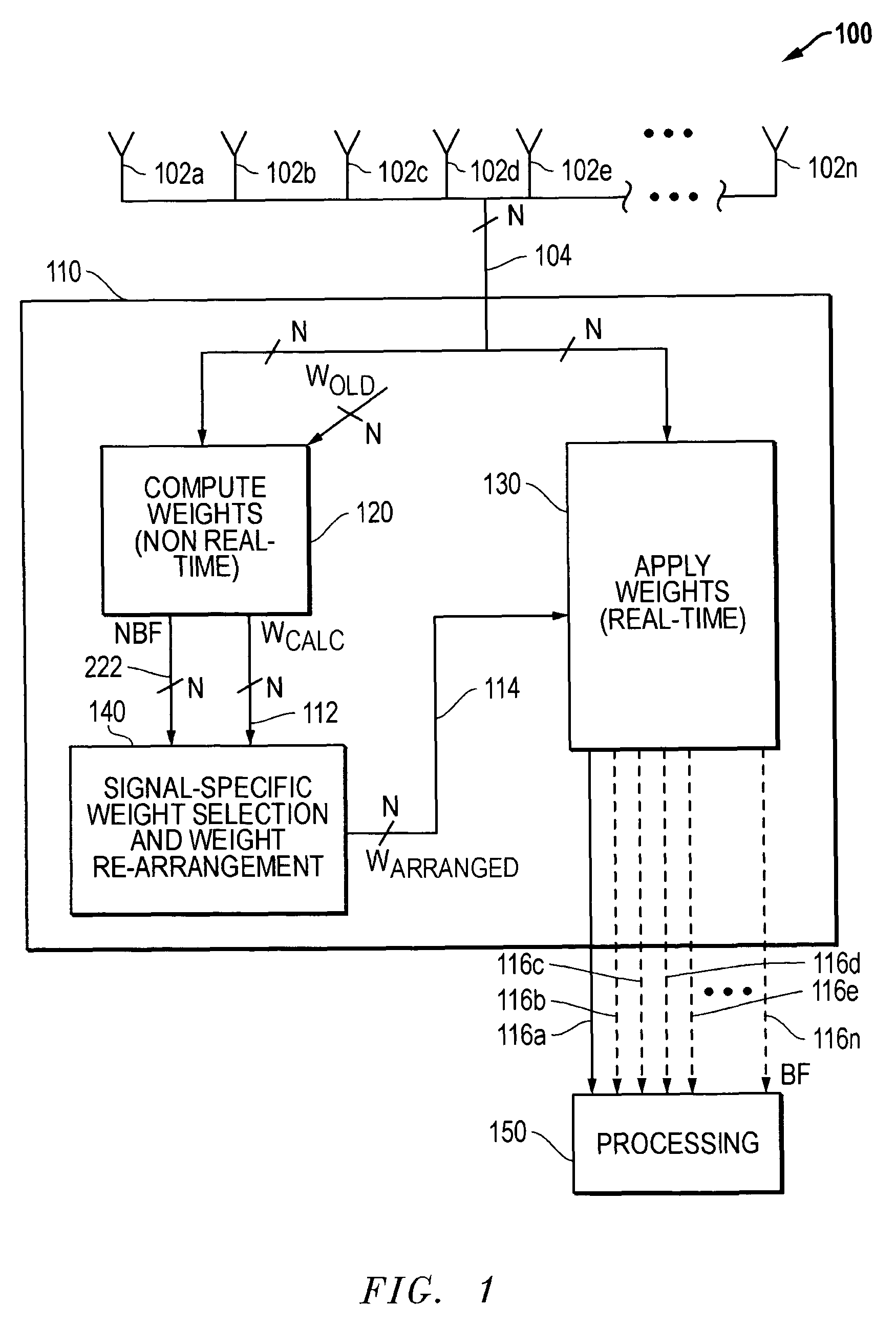
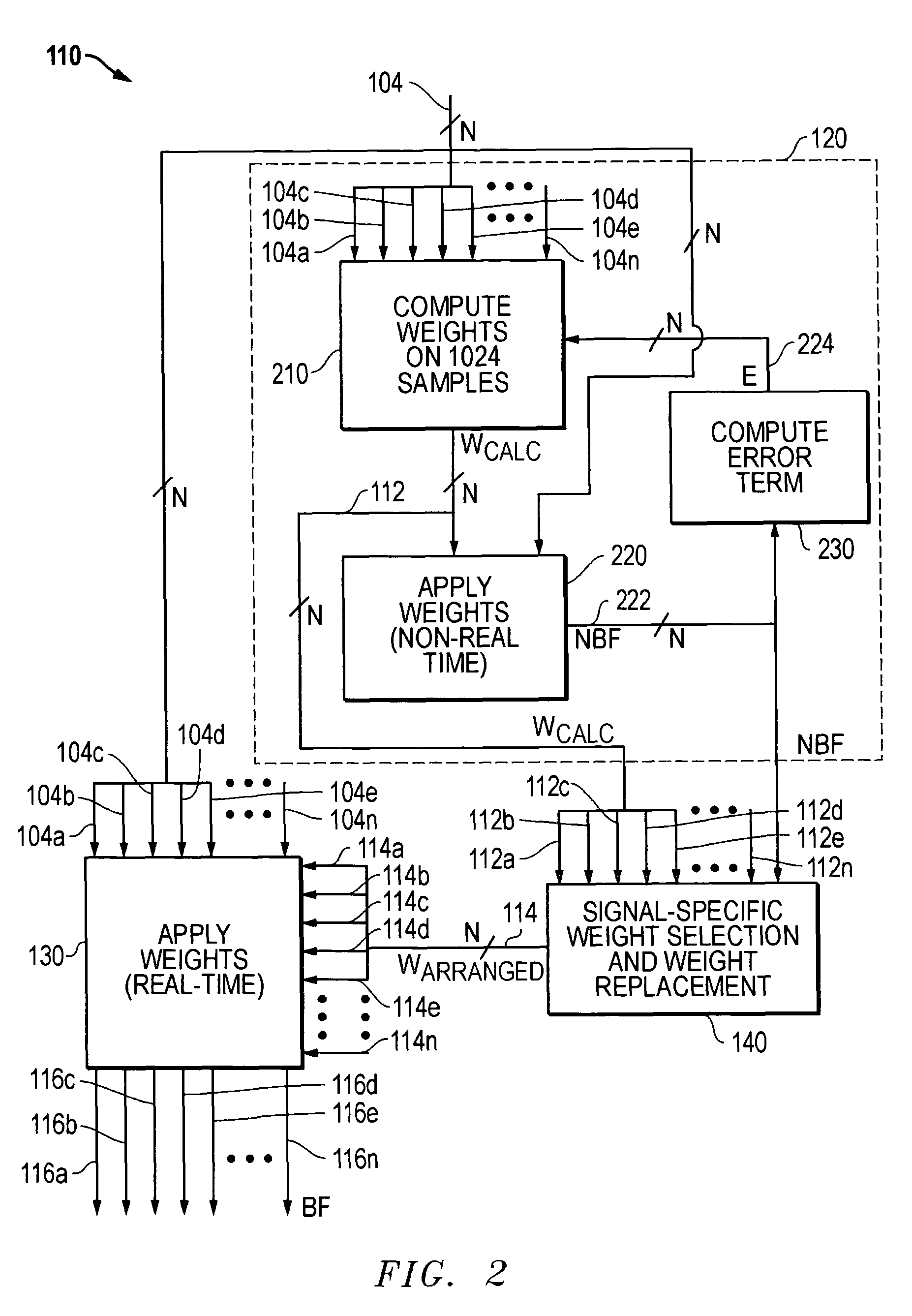
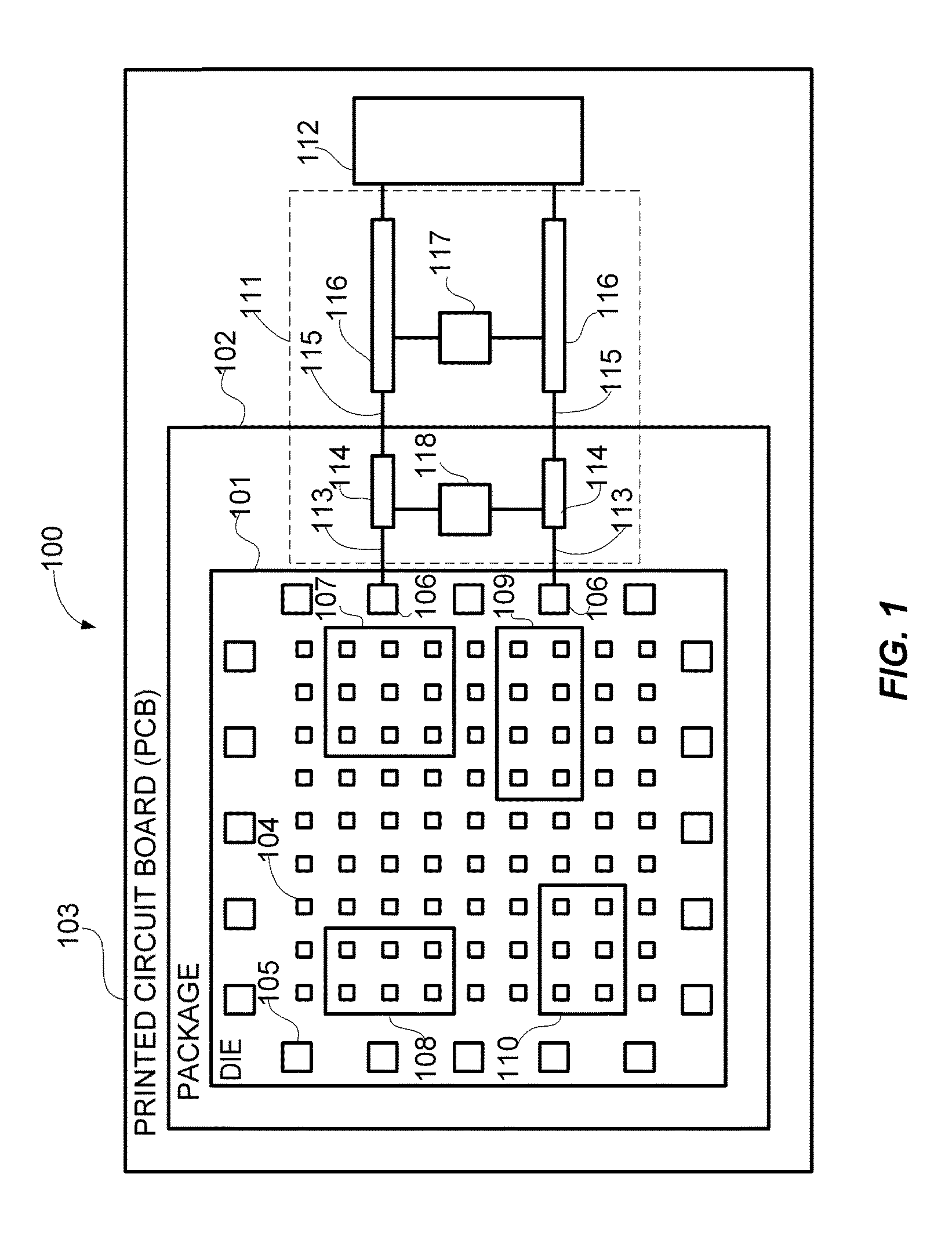
Electronically scanned beam display
InactiveUS7061450B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsRelative phaseLight beam
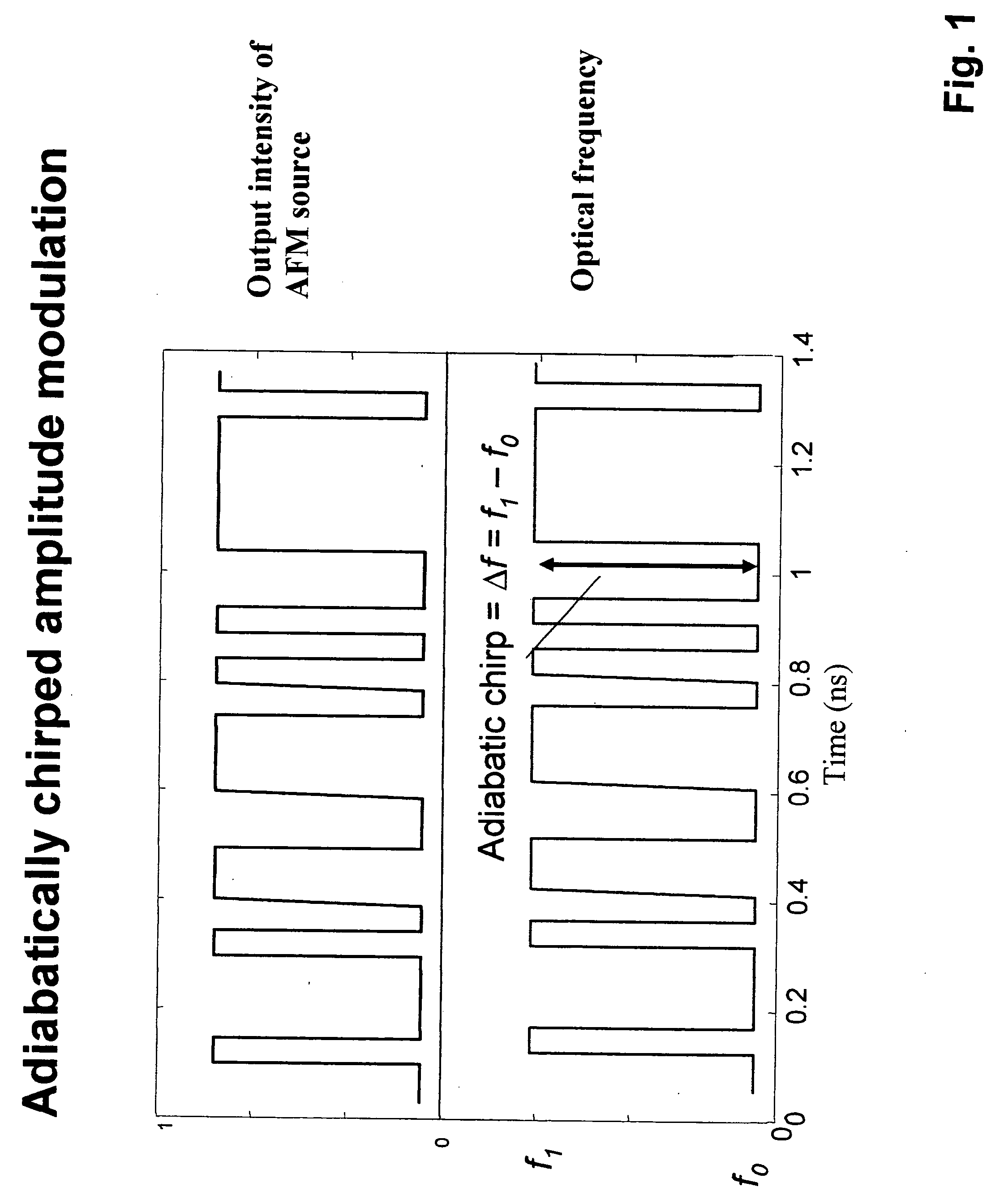
A scanning control circuit generates a clock signal corresponding to an expected scan timing of a resonant scanner. In one approach, the control circuit uses a pair of direct digital synthesis (DDS) integrated circuits. A first DDS chip provides a system clock that is synchronized to the monitored period of the scanner. A second DDS chip generates a frequency chirped signal that has a frequency profile corresponding to a desired pixel clock timing. To control phase precisely, four complementary clock signals are weighted and mixed at light source drivers to produce relative phase shifts for different light sources.
Owner:MICROVISION
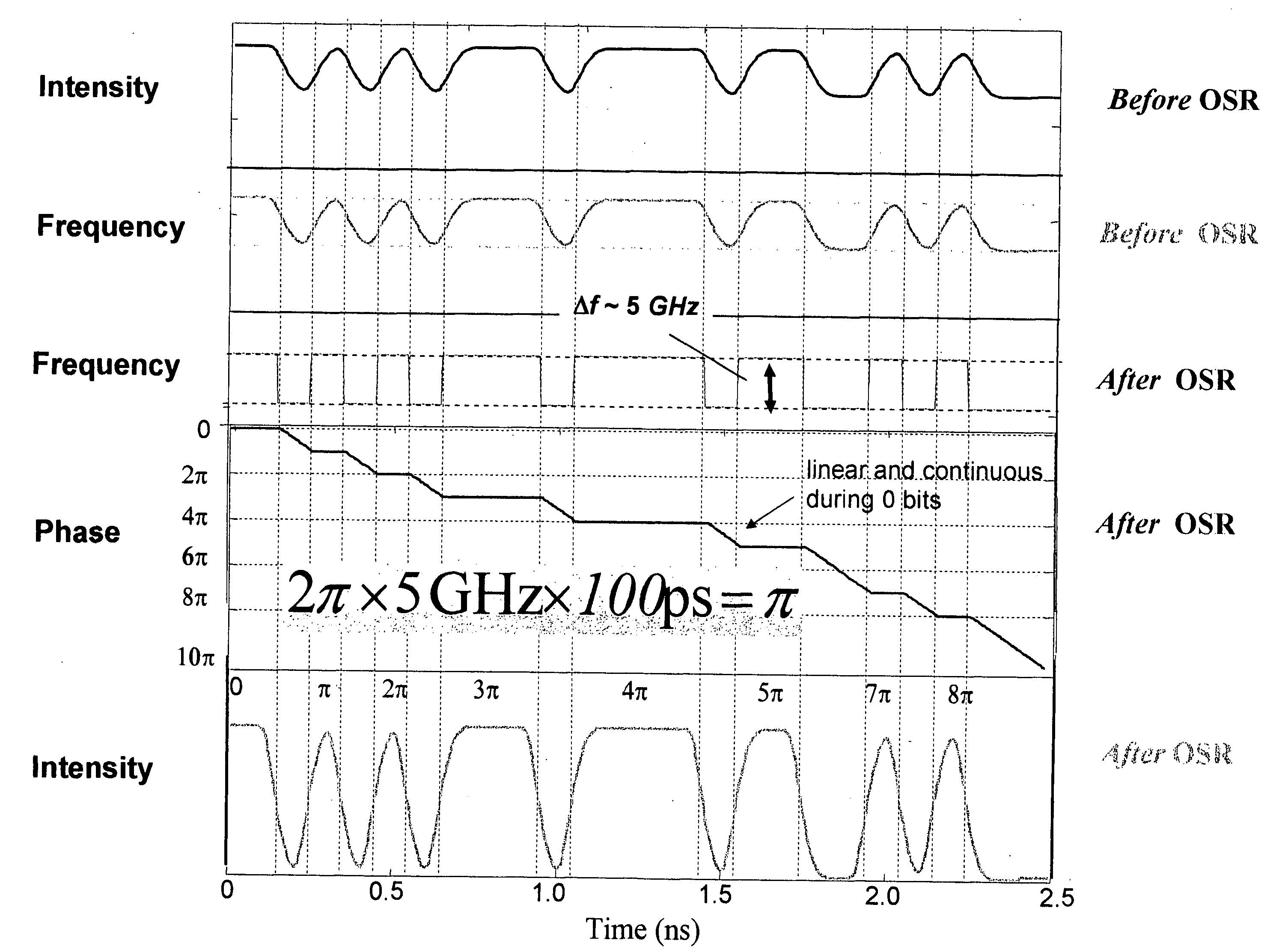
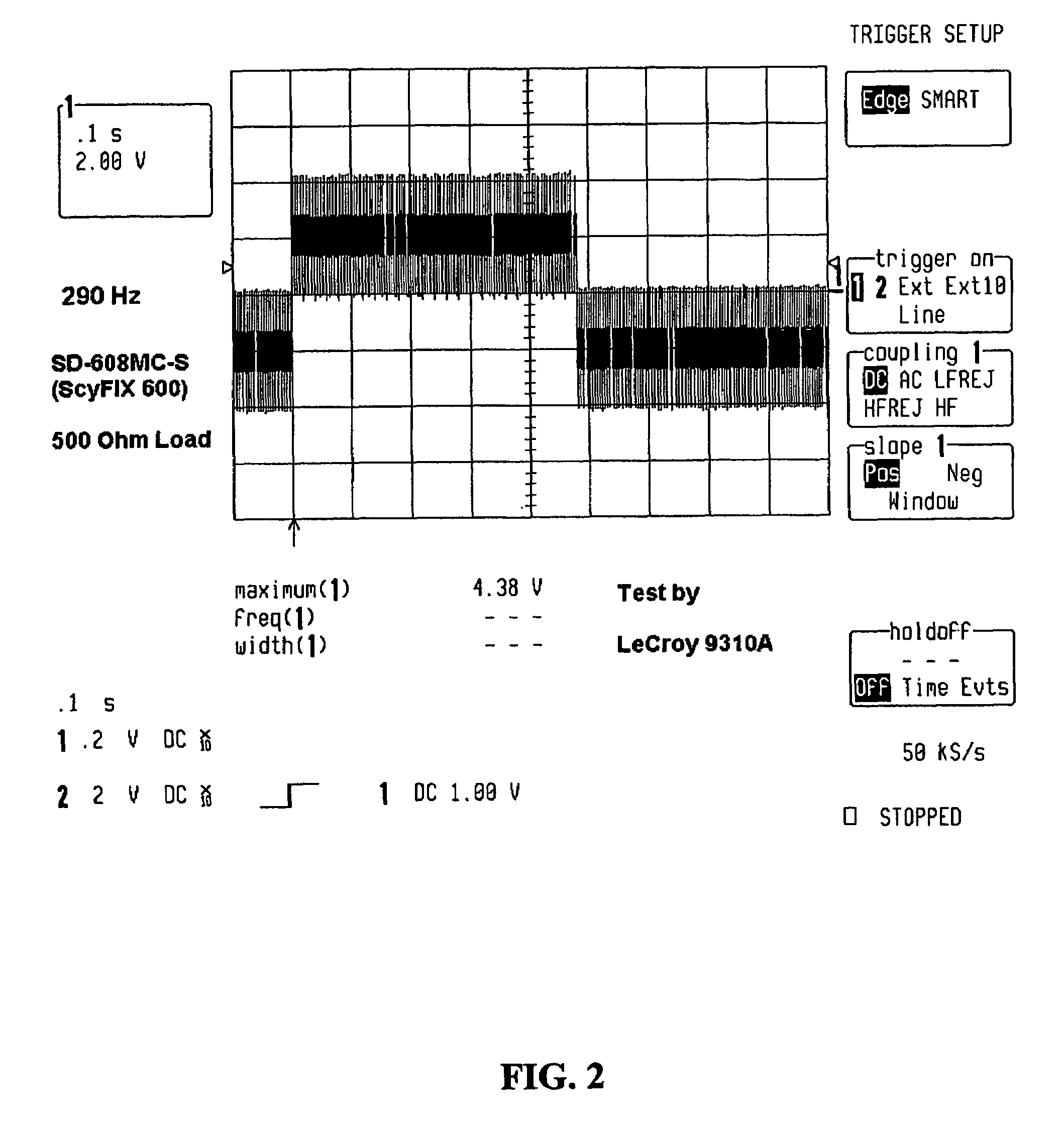
Method and apparatus for transmitting a signal using simultaneous FM and AM modulation
There is provided method for transmitting binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: independently adjusting the 0 bit mean amplitude relative to the 1 bit mean amplitude; independently adjusting the 0 bit frequency relative to the 1 bit frequency; and independently adjusting time duration of the frequency profile of the 1 bit relative to the time duration of the amplitude profile of the 1 bit, whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit. There is provided a method for transmitting Non-Return-To-Zero (NRZ) binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: the phase across each 1 bit data value is substantially constant, and the phase of the carrier changes across each and every 0 bit by an amount equal to the product of the frequency difference between the 1 bit and the 0 bit and the duration of the 0 bit; whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit. In accordance with one form of the present invention, there is provided a method for transmitting binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: the amplitude profile of the 1 bit is substantially bell-shaped, and the frequency profile of the 1 bit is substantially square-shaped, with steeper rise and fall time and a wider flat top region; whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit.
Owner:AZNA +1
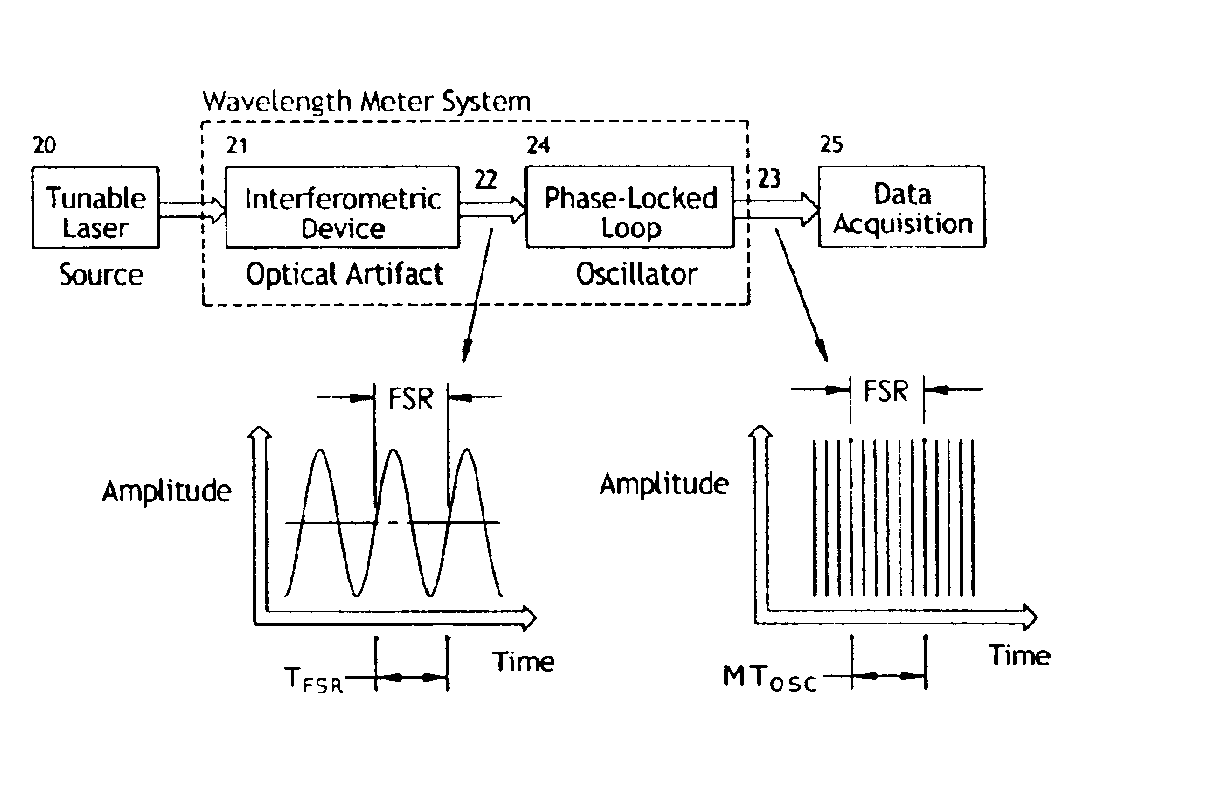
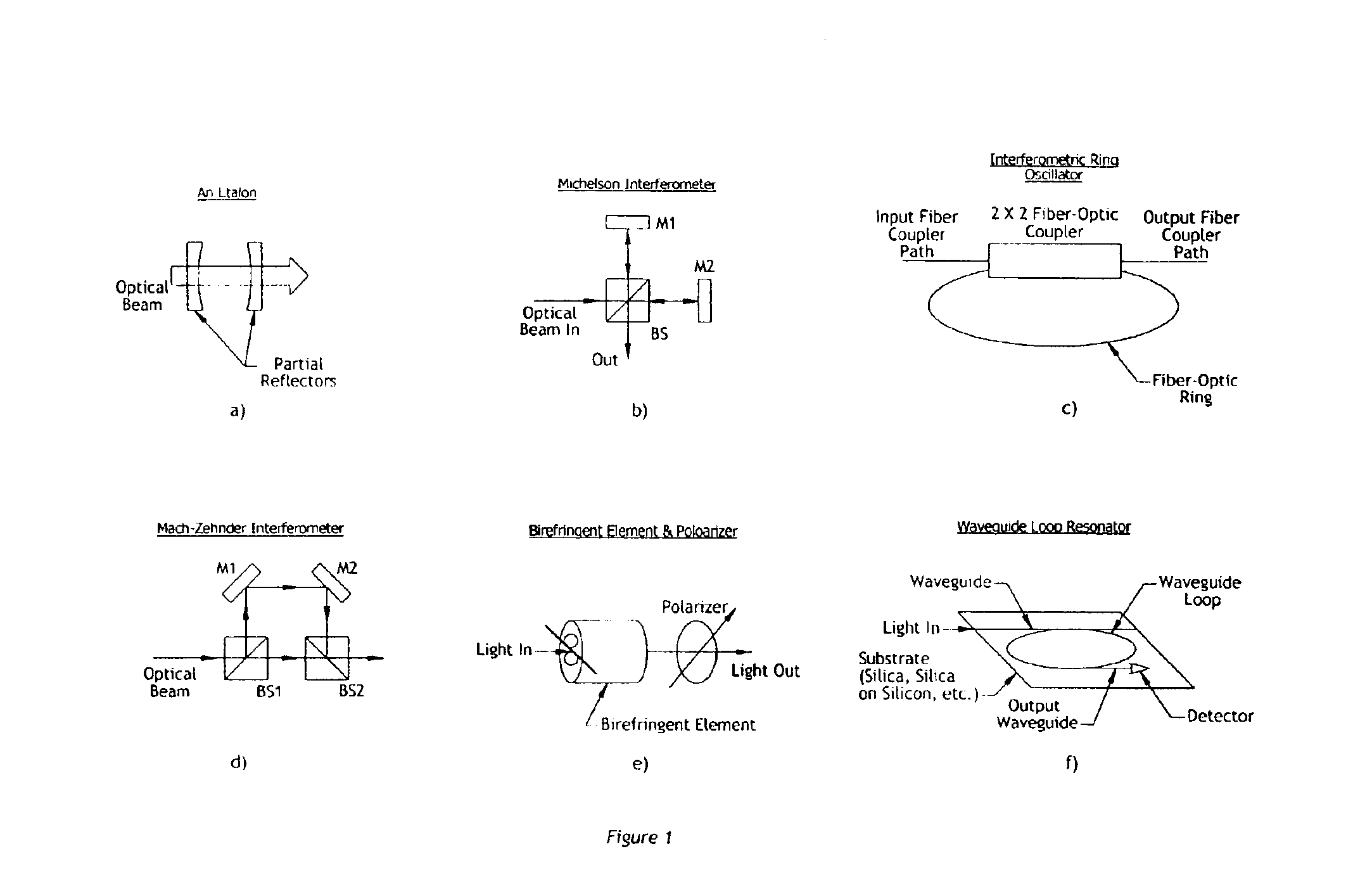
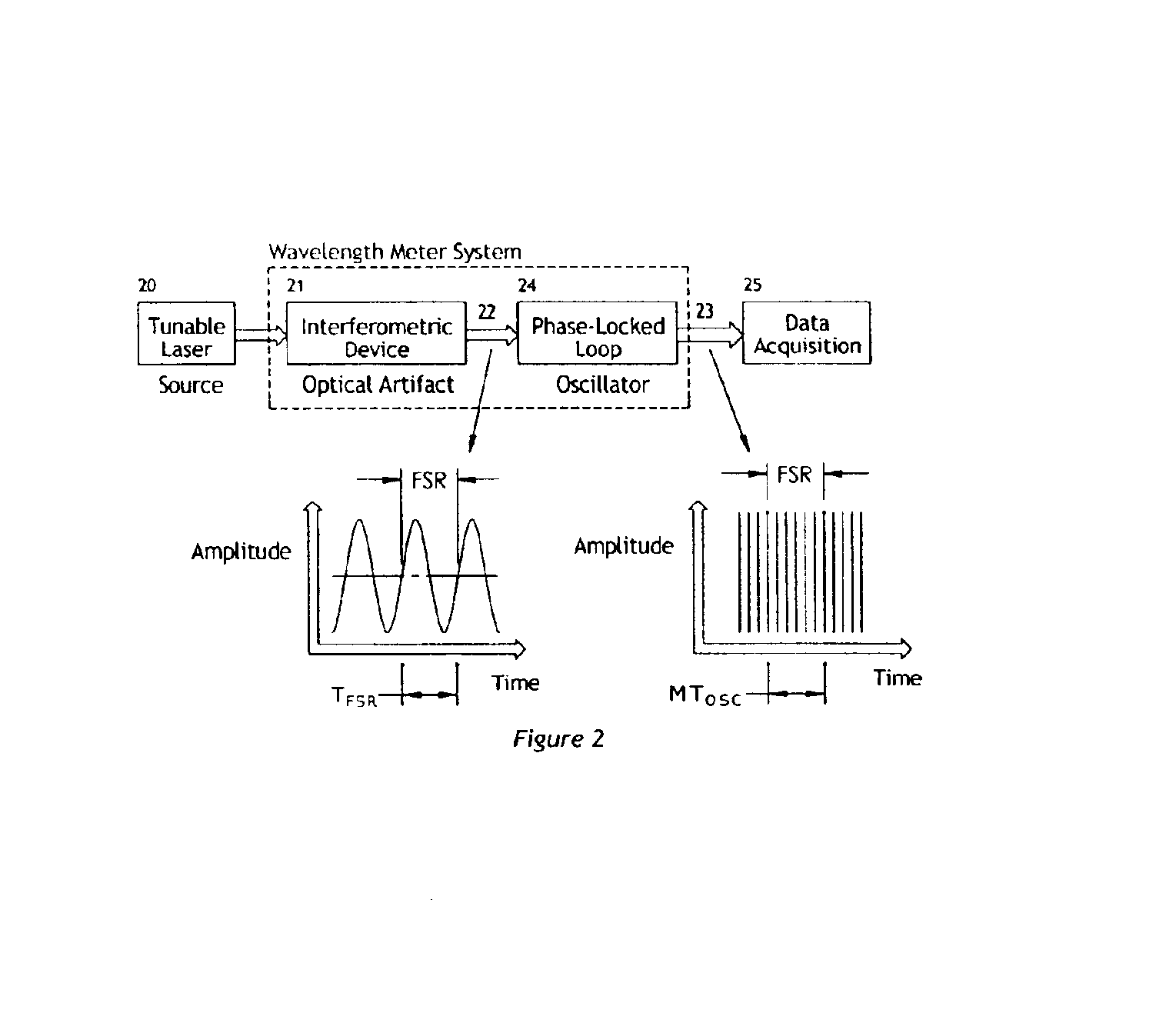
Optical frequency sweep control and readout by using a phase lock
InactiveUS6870629B1Reduce frequencyFrequency errorOptical measurementsLaser detailsOptical frequenciesControl signal
The invention allows for the accurate, real-time readout of the optical frequency of a swept-wavelength laser device by counting the number of fringes of a calibrated etalon that occur as the laser is swept. The distinguishing feature of the present invention is that the etalon fringe signal is phase-locked to a slave signal of a higher multiple frequency. The higher frequency of the slave signal divides the frequency interval of the etalon fringe spacing by the additional frequency multiple. The slave signal therefore generates a scale for optical frequency that is of higher resolution than possible with the etalon alone. The phase-lock also insures that the slave signal tracks monotonic scans of the optical frequency regardless of scan profile.The invention also allows for the precise, real-time control of the optical frequency of a laser during the sweep of the laser. By comparing a signal proportional to the transmission of light through a calibrated Fabry-Perot etalon to a reference control signal, the phase difference between etalon transmission signal and the reference signal may be fed back to the laser to drive the phase difference to zero (phase-lock). The phase-lock ensures that the optical frequency profile of the sweep follows exactly the frequency profile of the reference signal. Tailoring the input reference signal controls the velocity of the optical-frequency sweep.
Owner:PRECISION PHOTONICS CORP
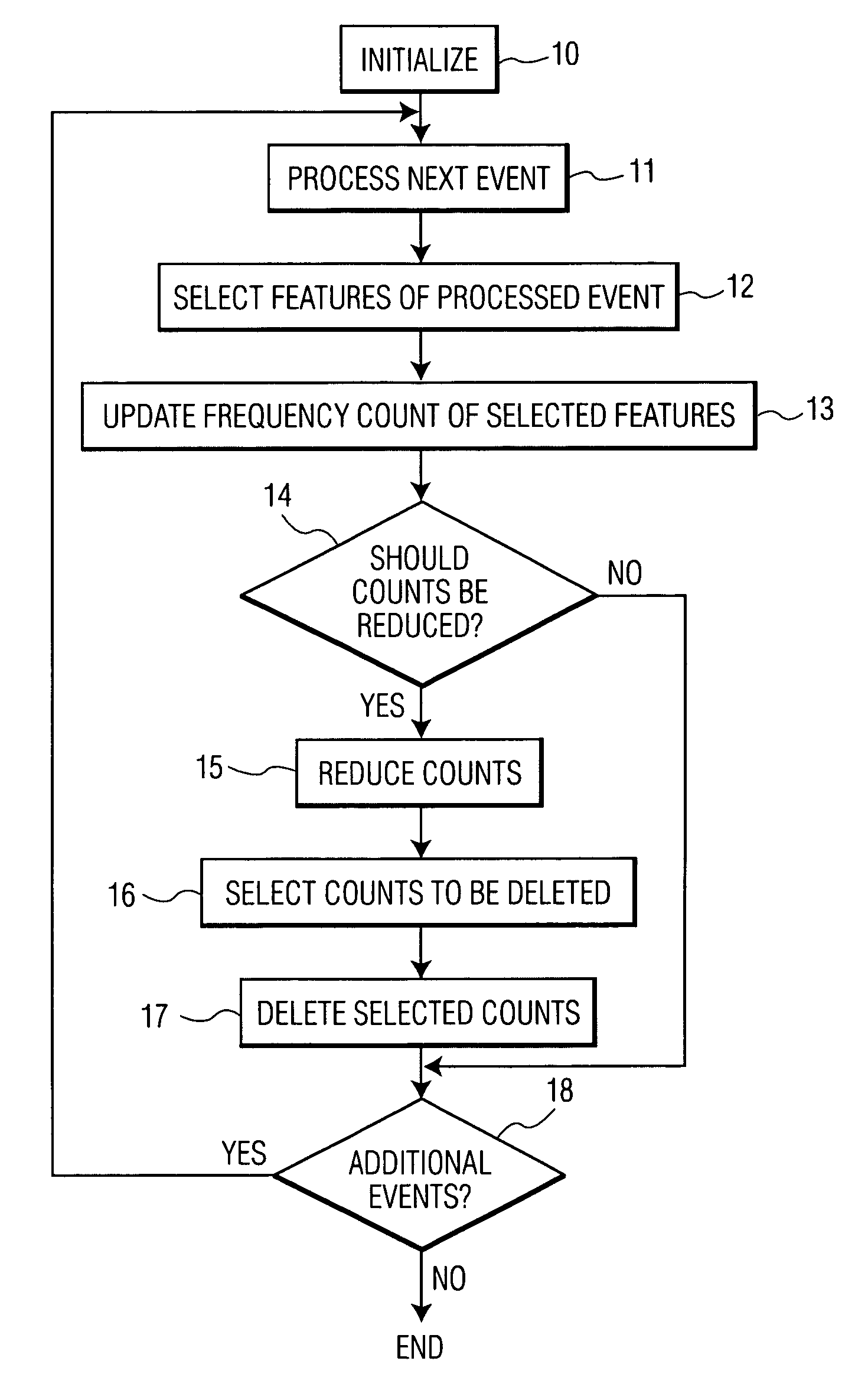
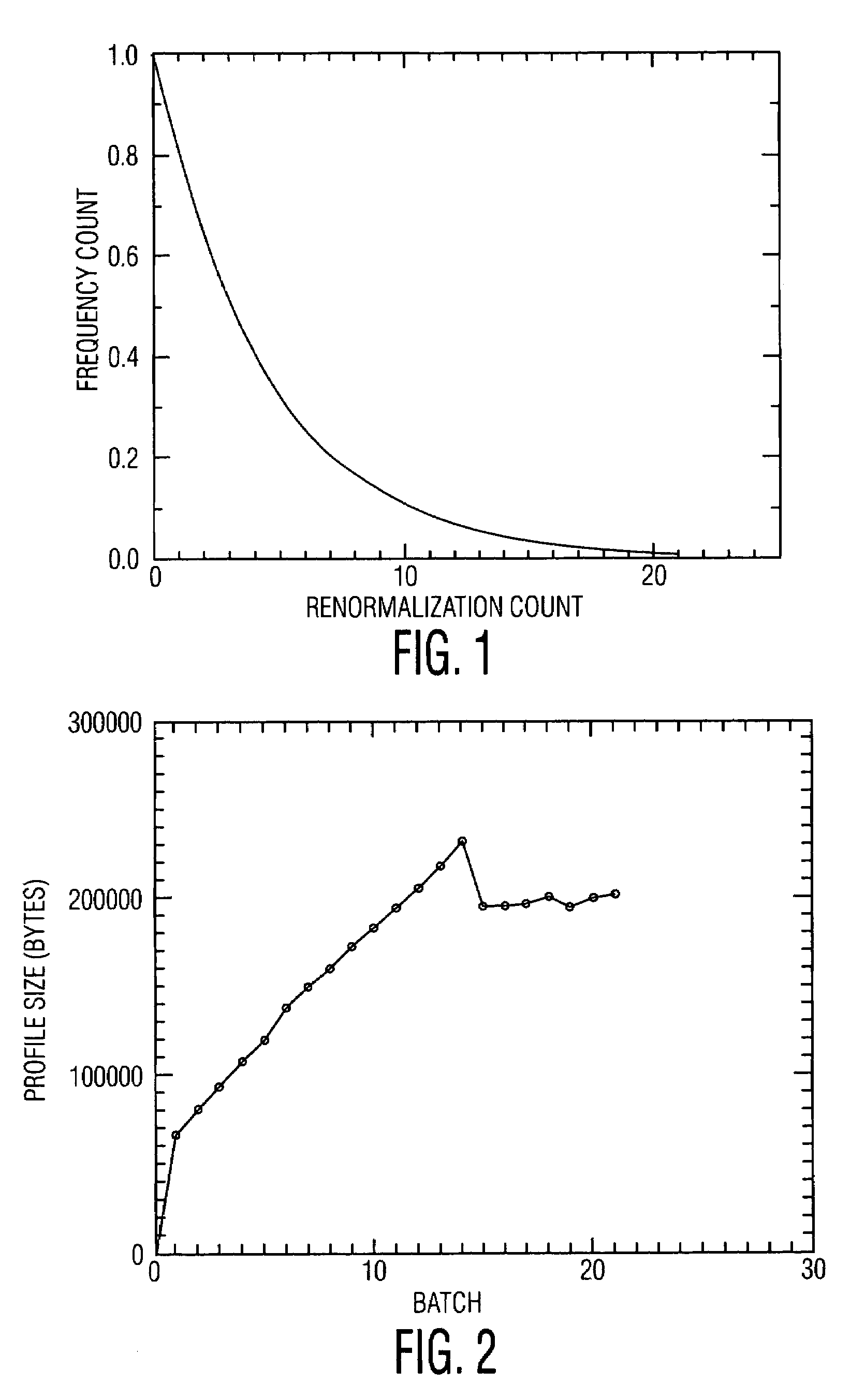
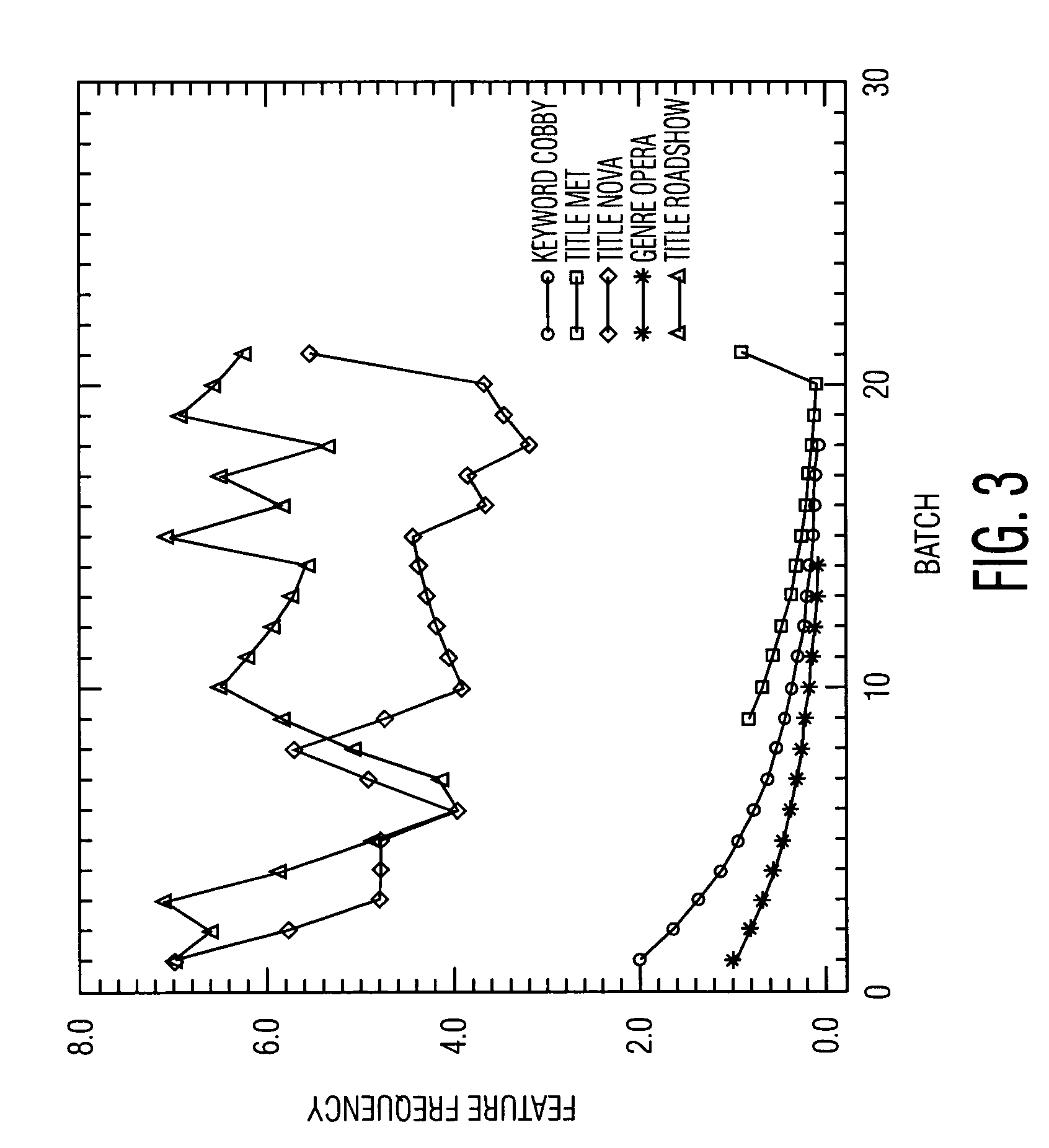
Controlling the growth of a feature frequency profile by deleting selected frequency counts of features of events
ActiveUS7130866B2Prevent data storedAvoid dataTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsReduction factorData mining
A method and system for controlling the growth of a features frequency profile of a time-ordered sequence of events, wherein each event has features specific to each event. The events are sequentially processed in an order of processing. The processing includes selecting for each event processed at least one feature comprised by the event. The processing updates a frequency count of each feature selected. The frequency counts are periodically reduced in magnitude by a reduction factor. Frequency counts are selected for deletion upon satisfaction of a condition that favors deletion of those frequency counts having a magnitude less than a threshold value. The selected frequency counts are then deleted. The present invention employs an economical use of memory to store data associated with the features frequency profile and uses a features preference profile that is more responsive to recent information than to older information.
Owner:S I SV EL SOC ITAL PER LO SVILUPPO DELLELETTRONICA SPA
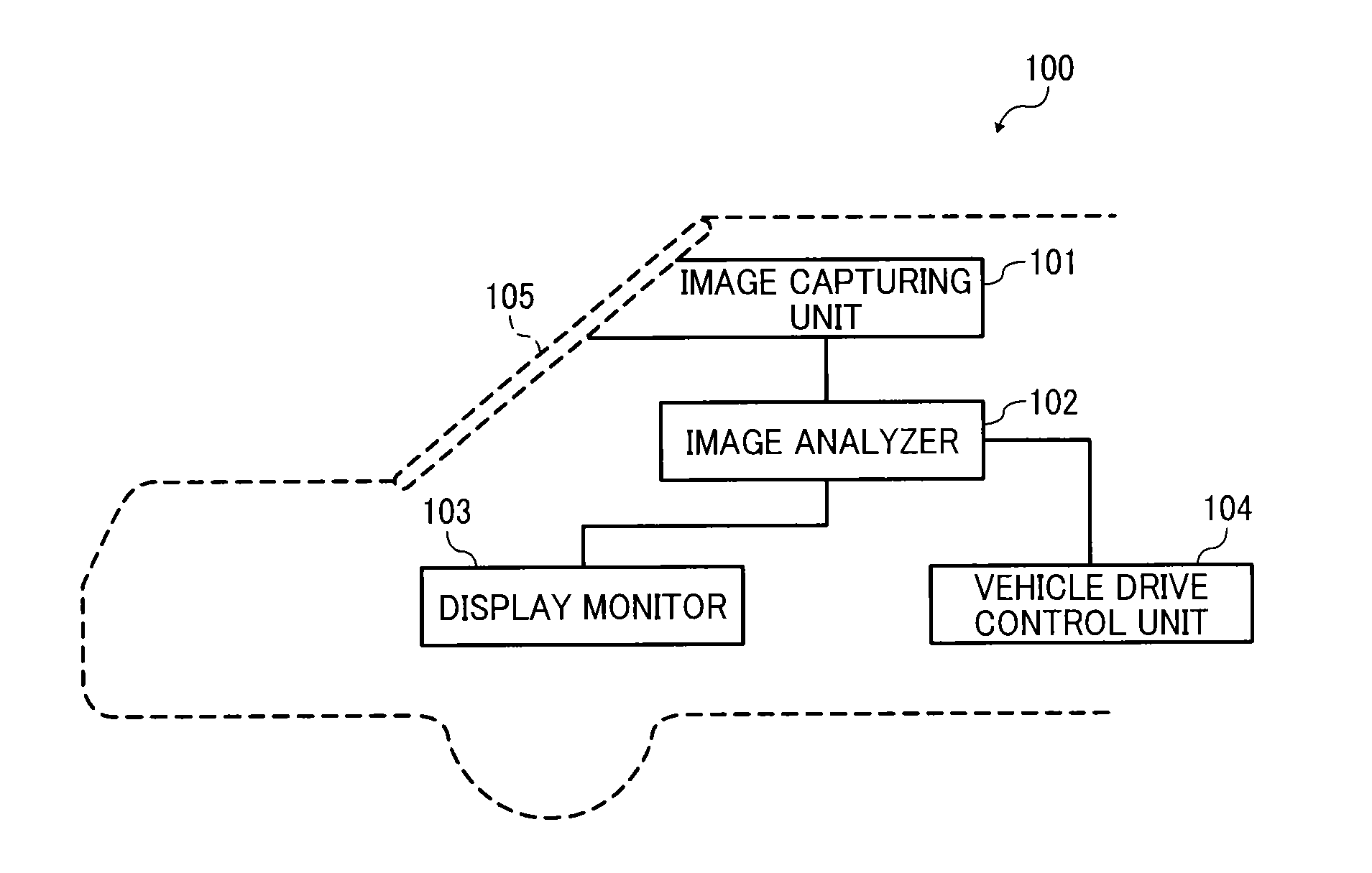
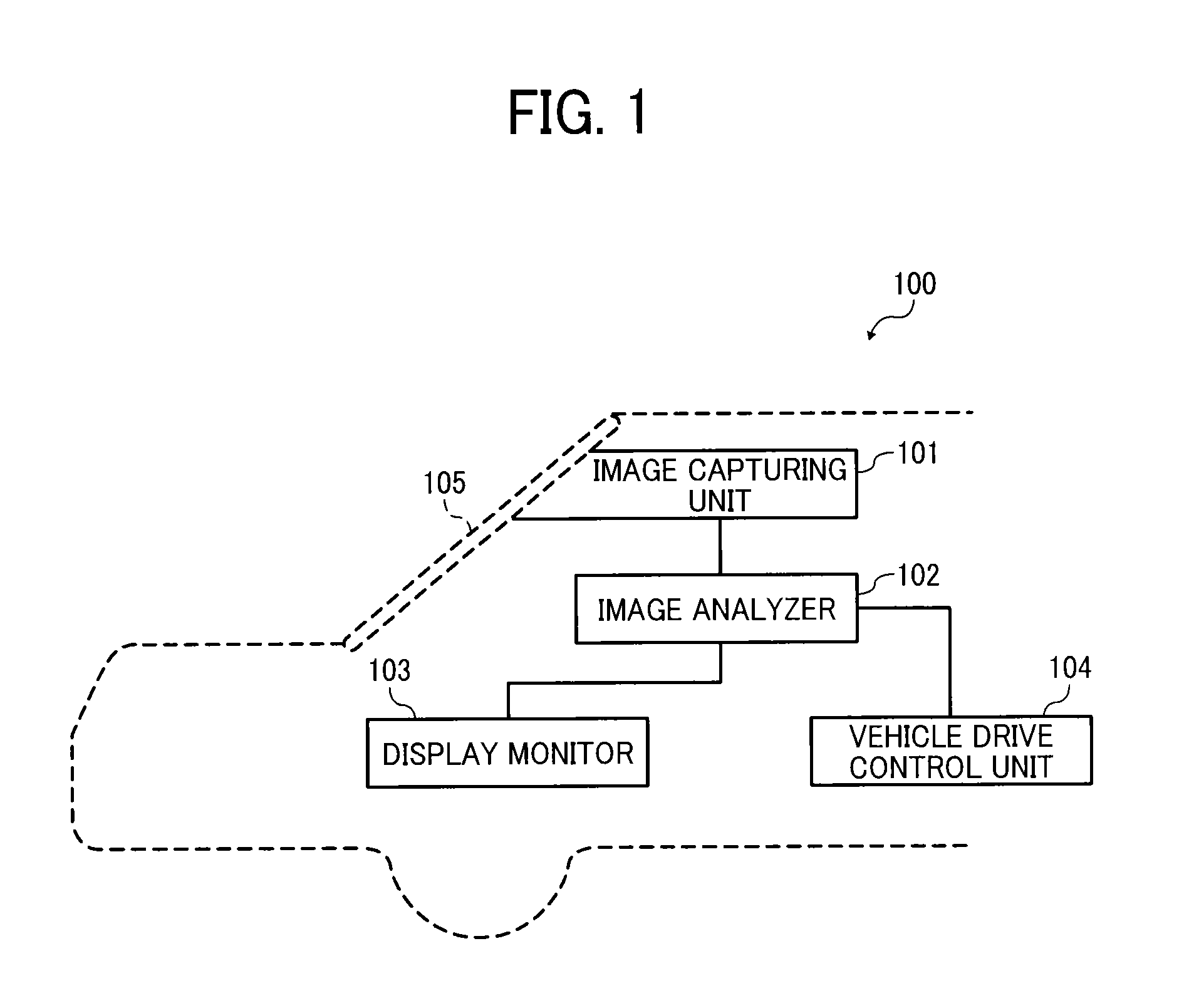
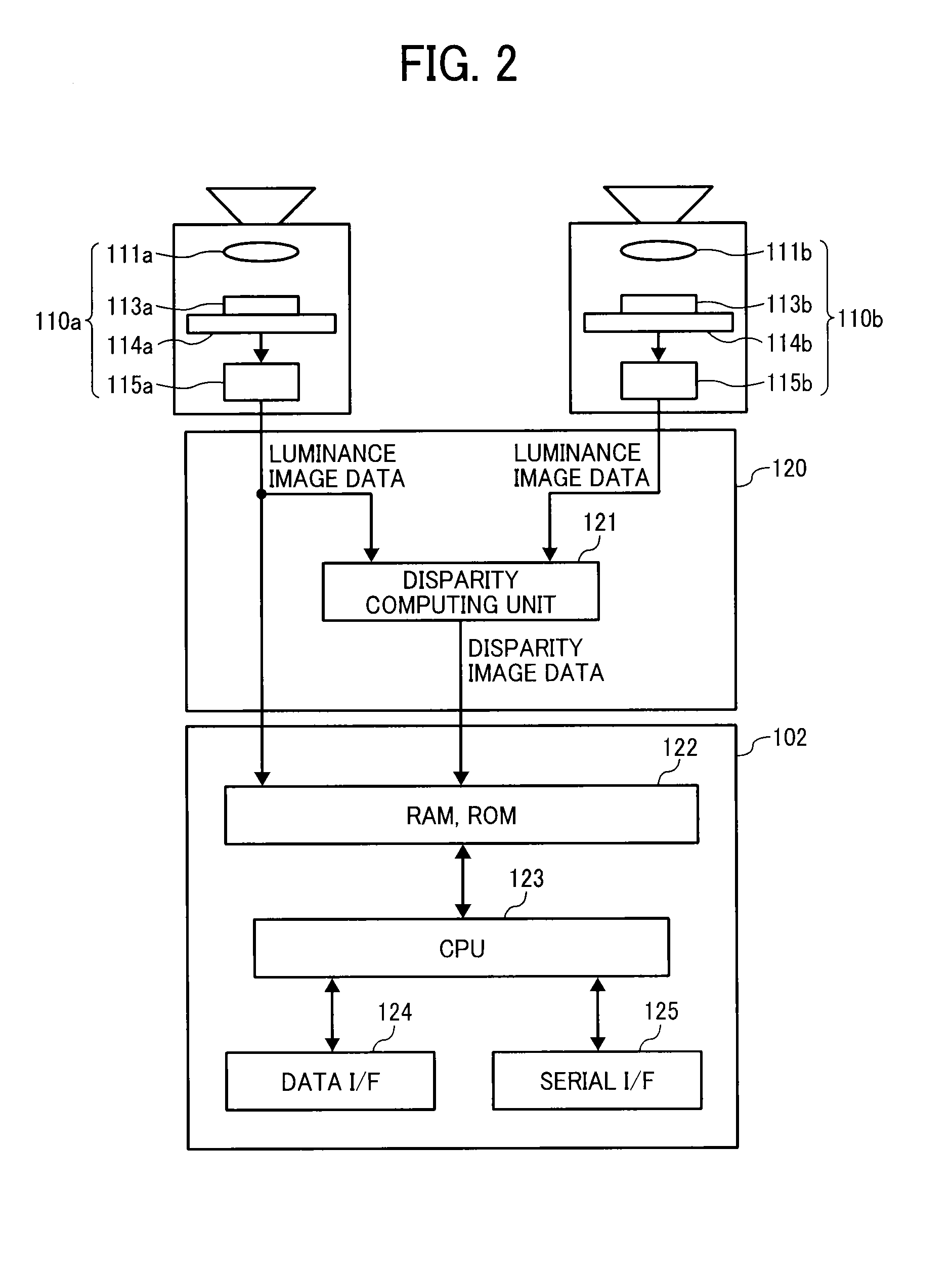
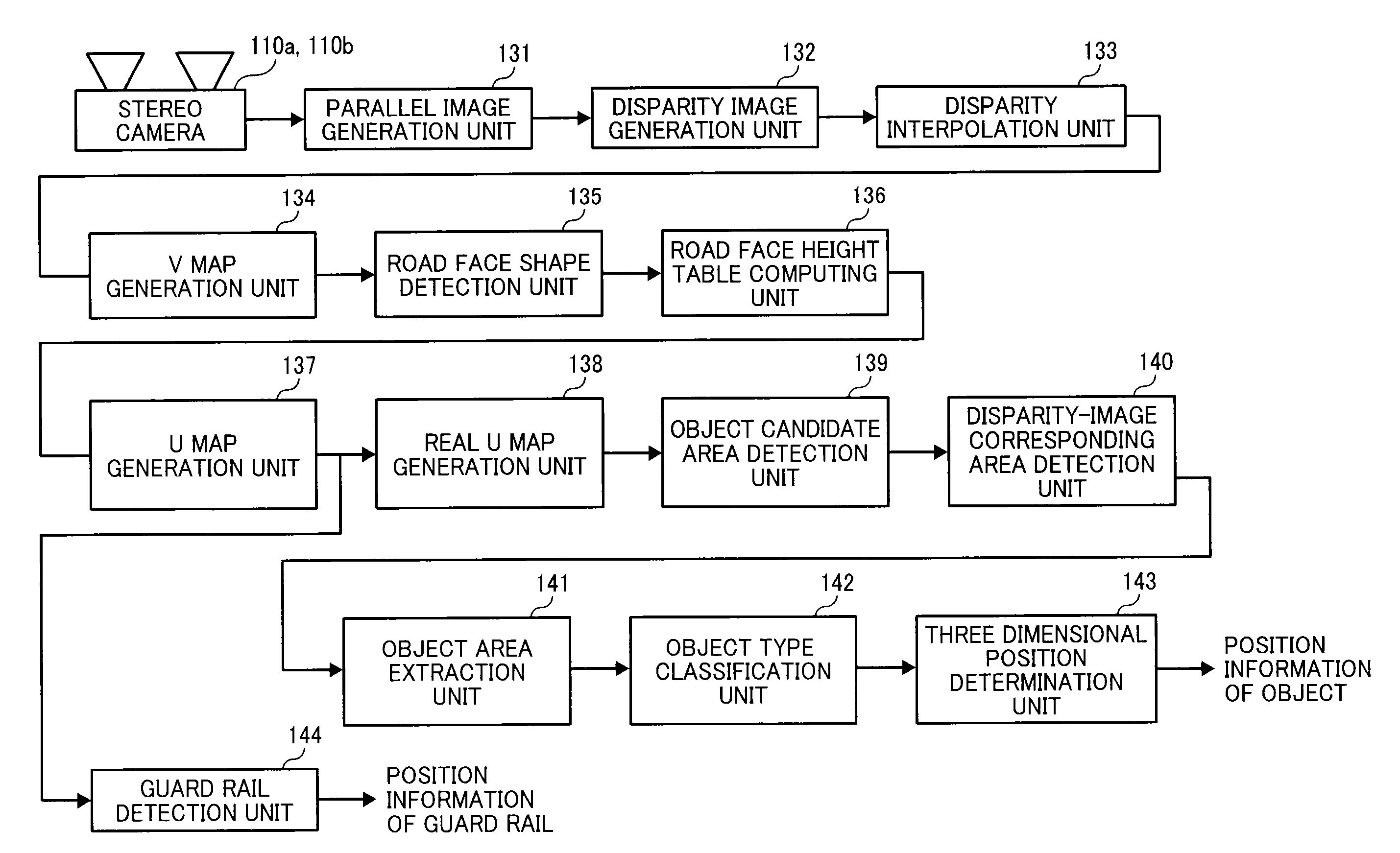
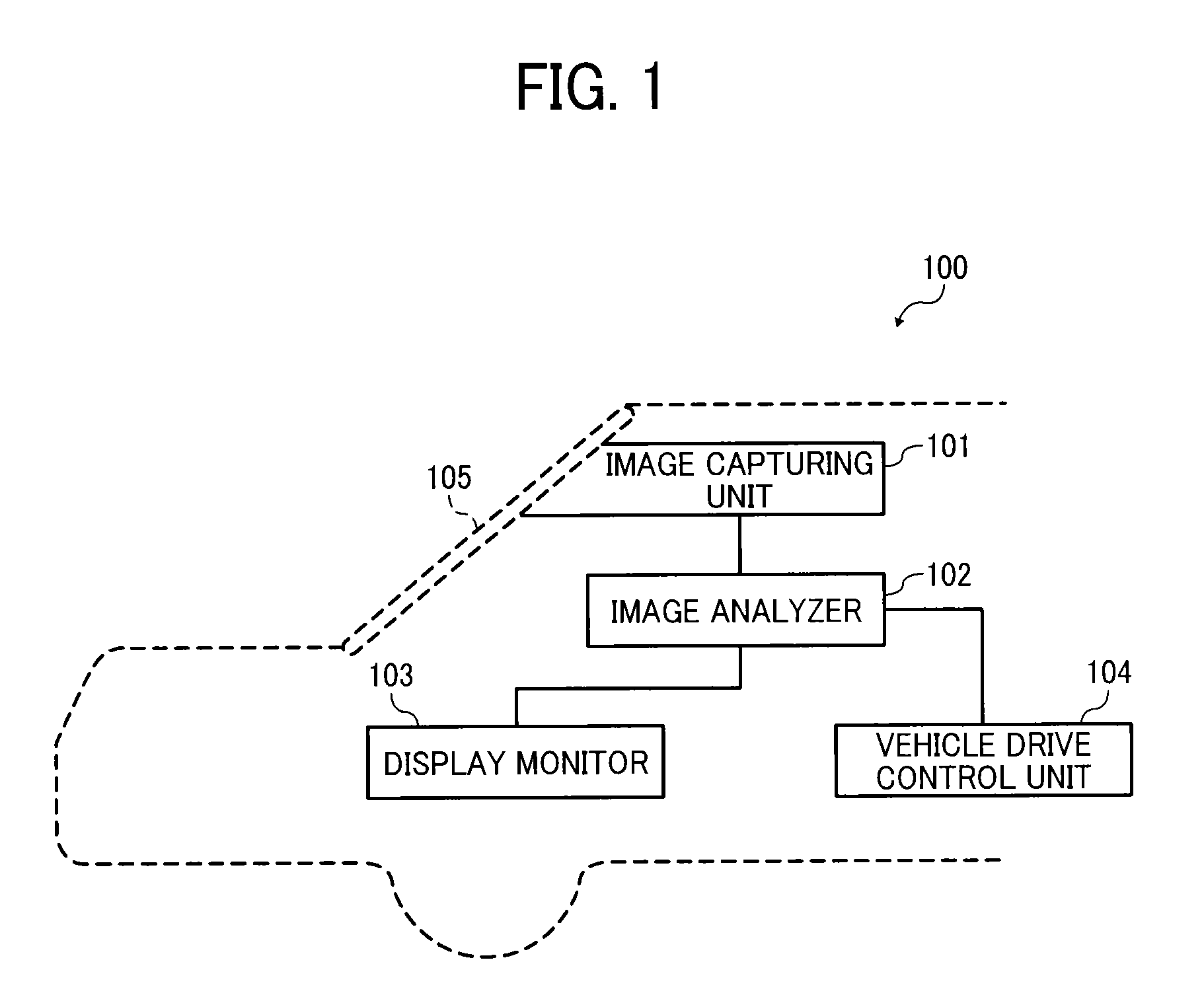
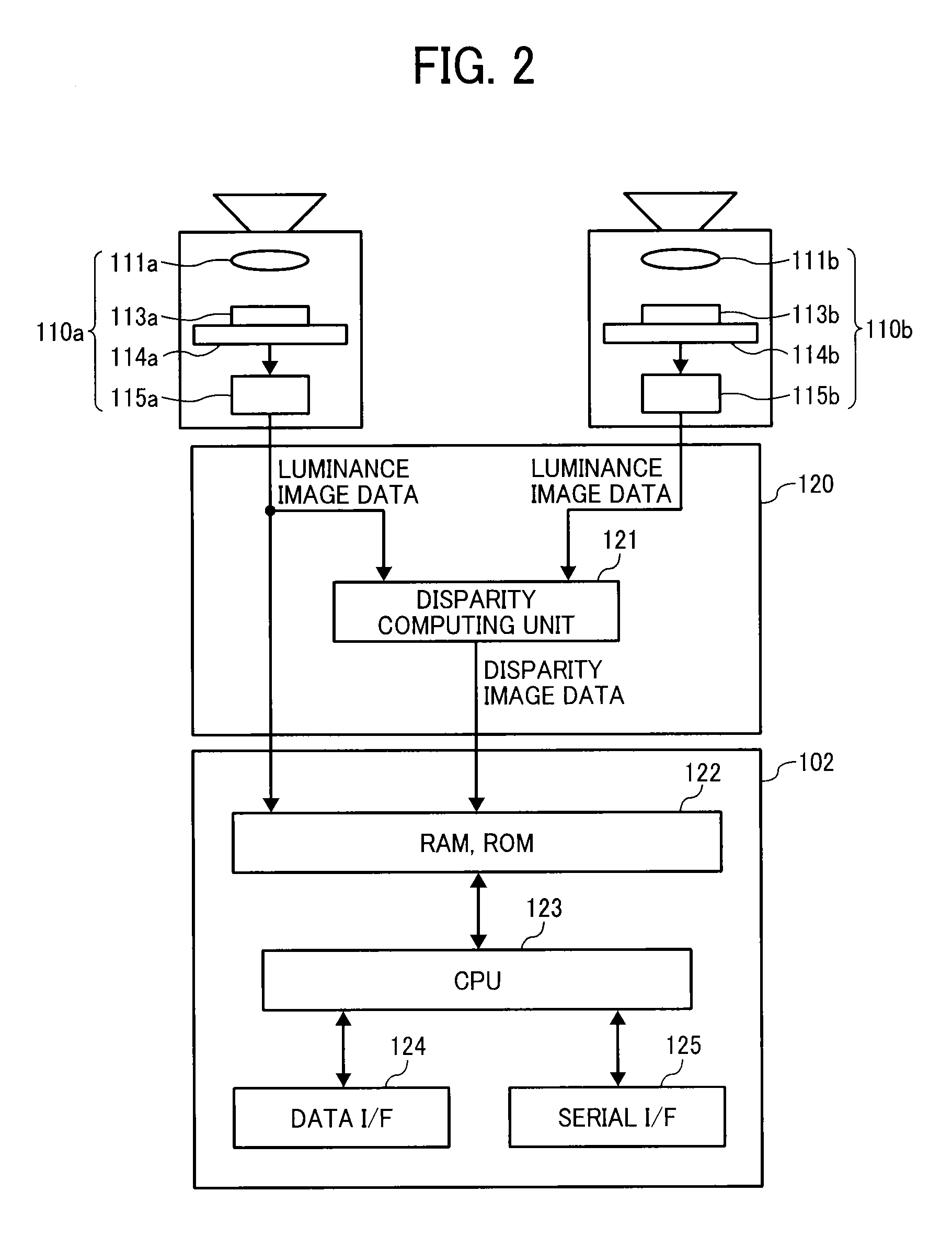
Object detection apparatus, object detection method, object detection program and device control system for moveable apparatus
An object detection apparatus mountable to a moveable apparatus for detecting an object existing outside the moveable apparatus by capturing a plurality of images using a plurality of imaging devices mounted to the moveable apparatus and generating a disparity image from the captured images includes a map generator to generate a map indicating a frequency profile of disparity values correlating a horizontal direction distance of the object with respect to a movement direction of the moveable apparatus, and a distance to the object in the movement direction of the moveable apparatus based on the disparity image, an isolated area detection unit to detect an isolated area based on the frequency profile, an isolated area divider to divide the isolated area into two or more isolated areas based on the frequency profile in the isolated area, and an object detector to detect an object based on the divided isolated area.
Owner:RICOH KK
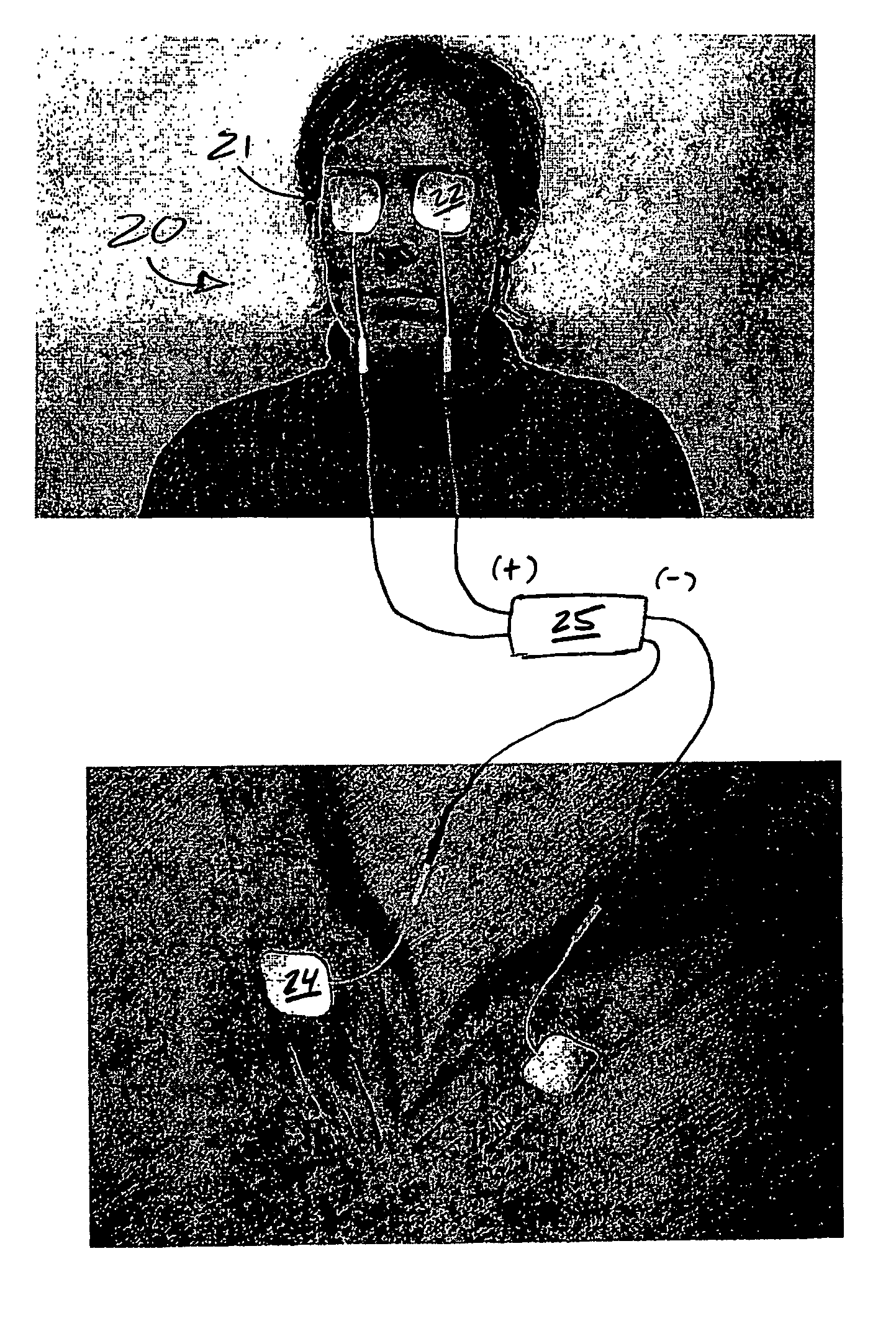
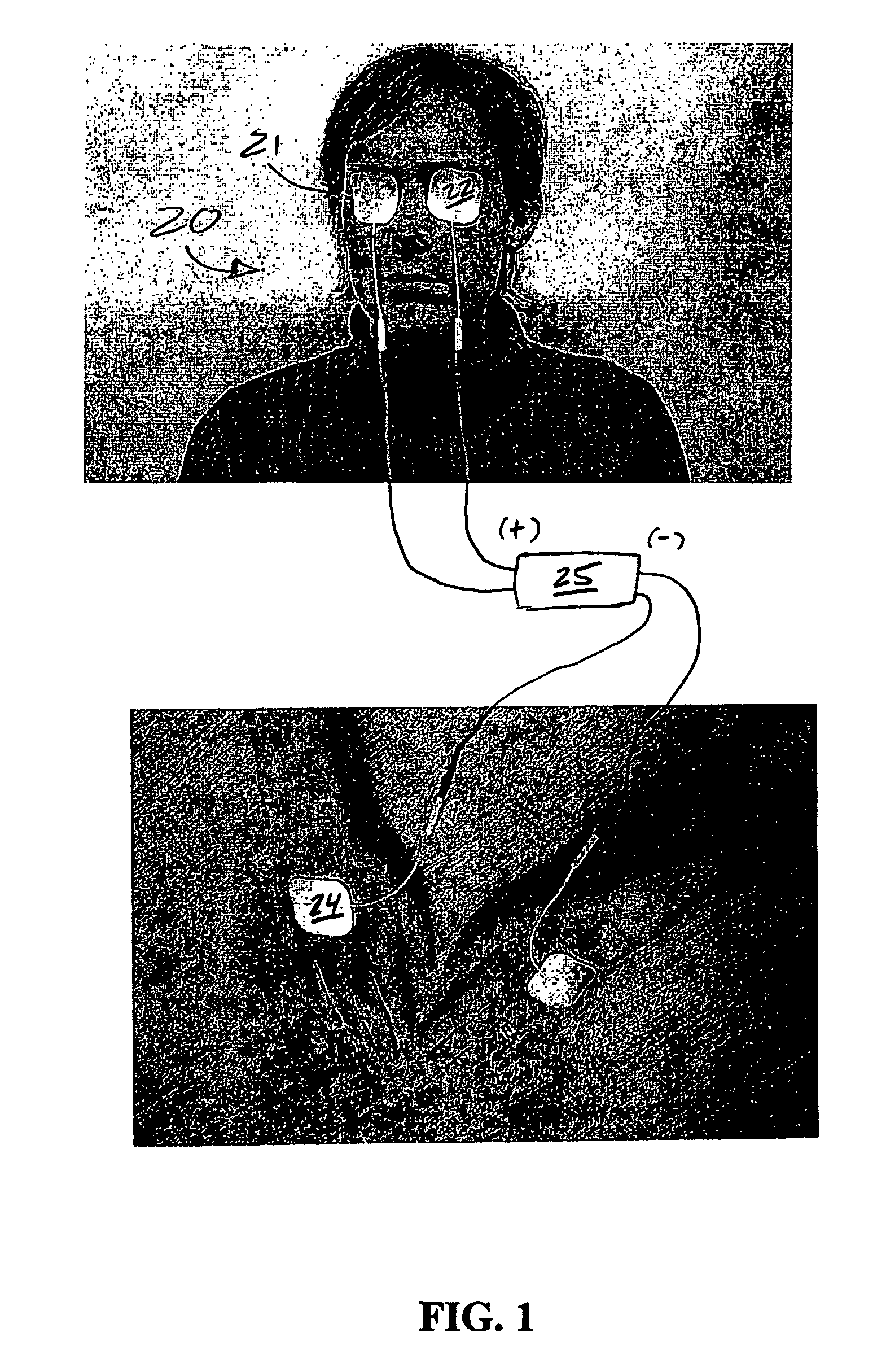
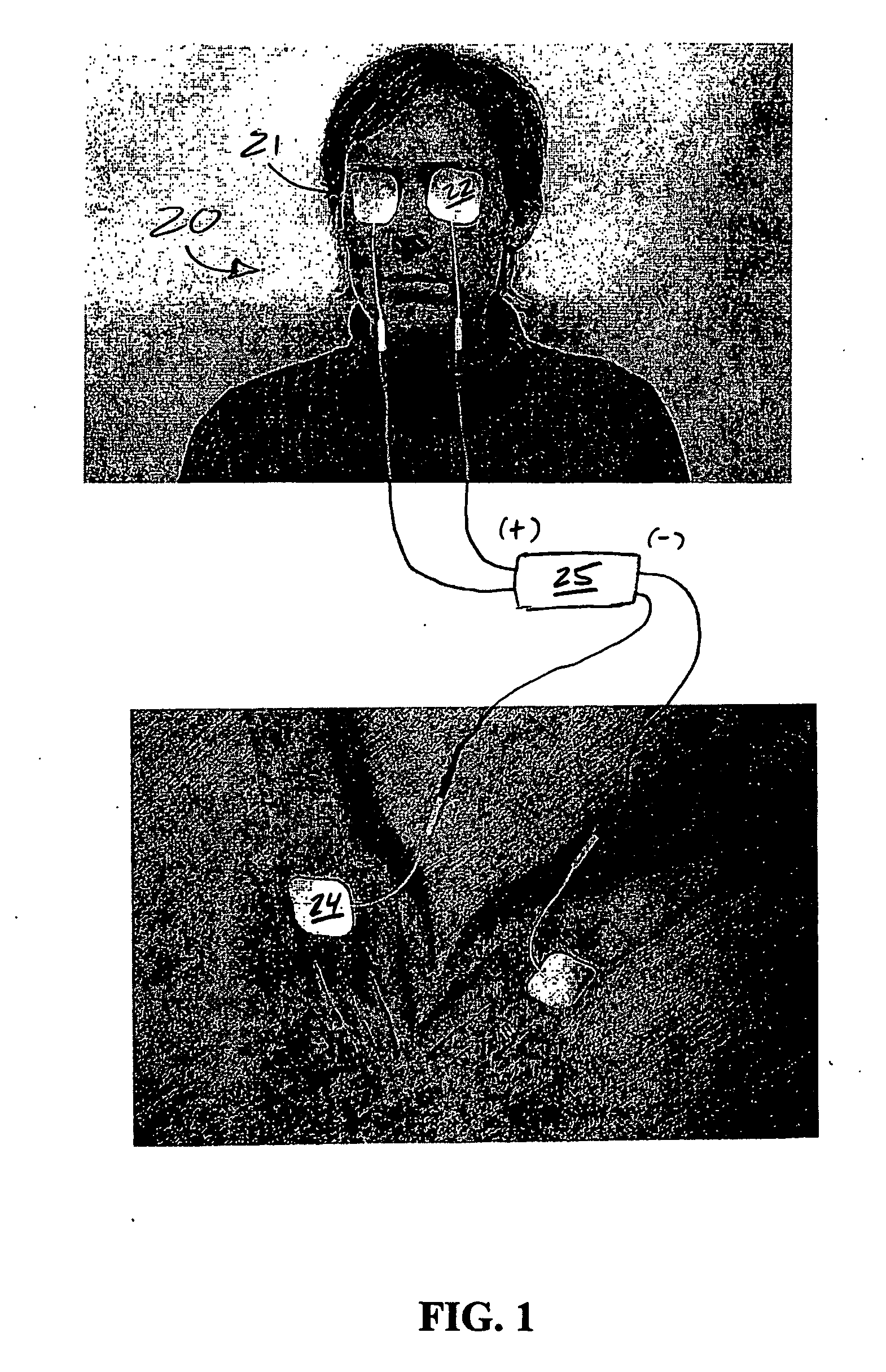
Treatment of vision disorders using electrical, light, and/or sound energy
ActiveUS7251528B2Restore visionSafe, improved, noninvasive method for the restoration of visionElectrotherapyLight therapySound energyLight energy
A non-invasive ocular therapy for vision disorders is provided. First and second electrodes of a direct current source are electrically contacted so as to deliver current to and / or about an area proximal one or more eyes of a subject. A direct electrical current of between about 1-800 microamps, at a resistance assumption of about 500 ohms, is generated between the electrodes for a preselected duration. Preferably, the direct electrical current is generated at a select frequency profile as a function of time, and with a carrier signal of about 10,000-12,000 hertz. Advantageously, the subject therapy is augmented via application of light energy to the eye(s), as well as by the application of infrasonic sound waves directly into eyes.
Owner:BIOVISICS MEDICAL INC
Computational Method for Comparing, Classifying, Indexing, and Cataloging of Electronically Stored Linear Information
InactiveUS20110196872A1Reduce complexityHigh frequencyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsMammalian genomeAnalysis data
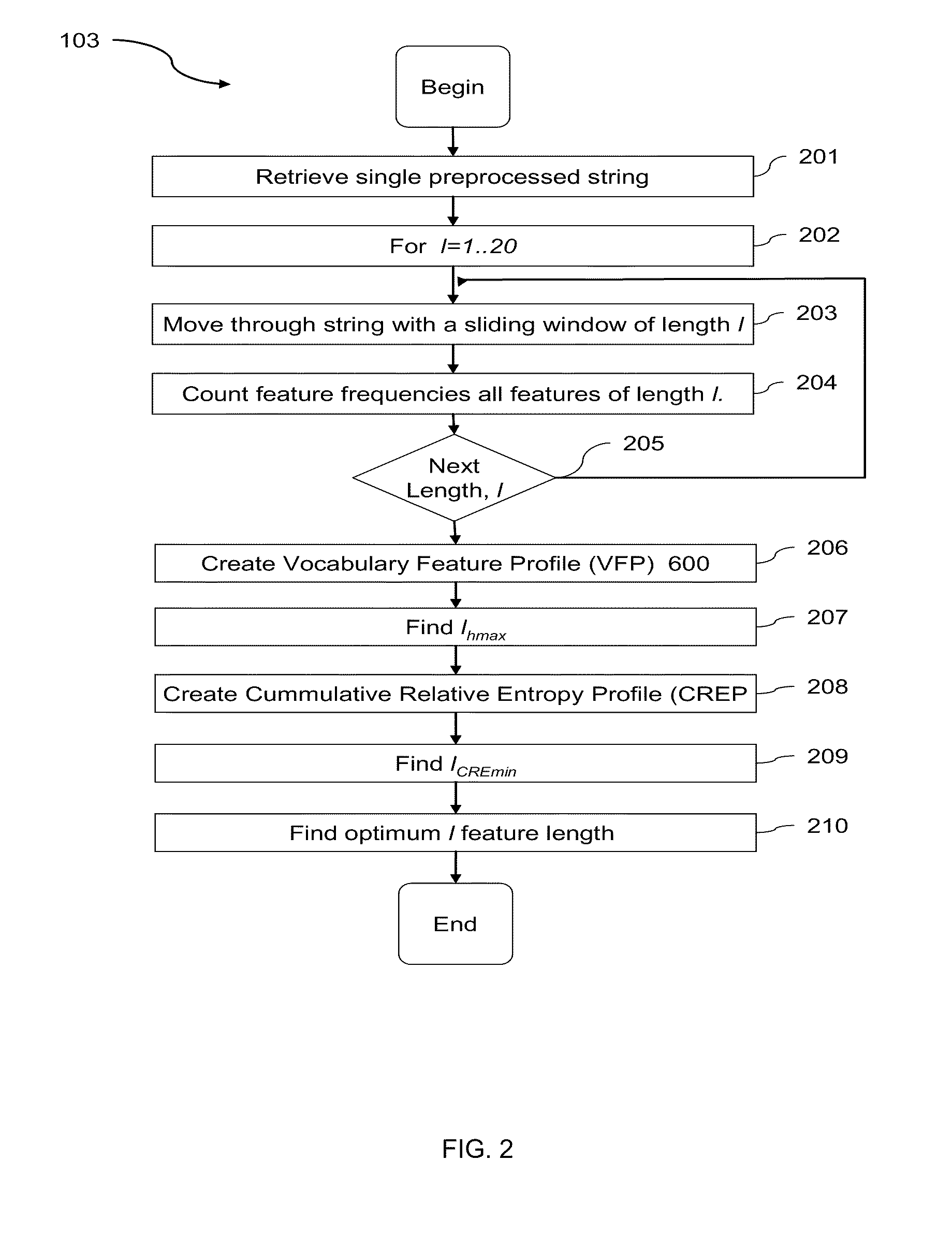
A computational method and system for the comparison and analysis of different objects of information within a database or collection. All objects are compared in a pair-wise fashion so the relative similarity between each object to every other object in the collection is known. A generalized alignment-free method is described for comparing whole genome (coding and non-coding) DNA sequences is used to investigate the relationship among placental mammalian genomes. Differences in word feature frequency profiles (FFP) are used to derive distance and infer evolutionary relationships.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Communication apparatus
InactiveUS8126495B2Limit transmission powerPower managementError preventionEvaluation resultEngineering
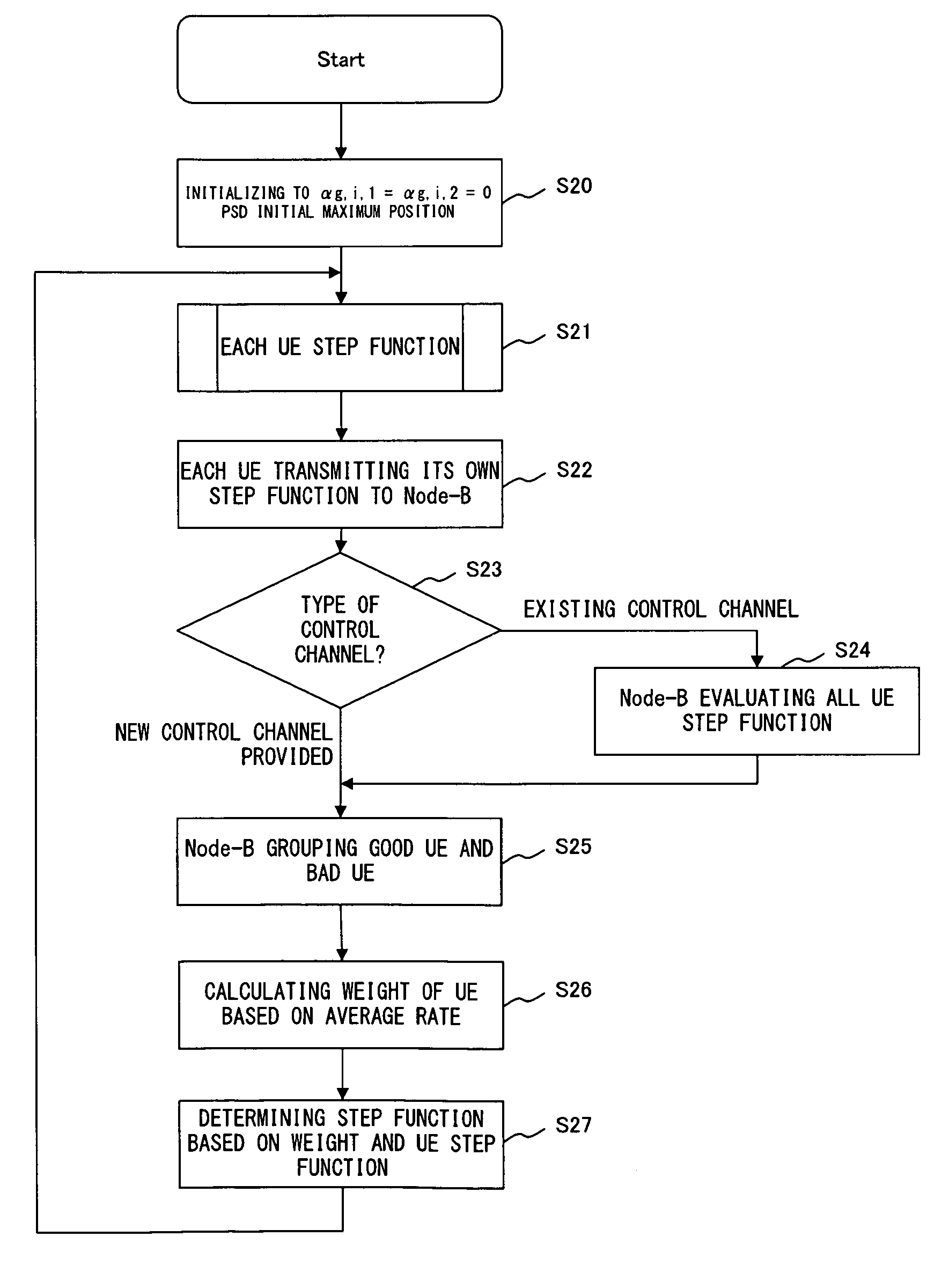
Node-B transmits a power profile of each frequency of transmission data as a step function to a UE. Each UE measures the amount of interference of a received signal, evaluates SINR over the entire frequency band with the power of the received signal, and transmits the evaluation result to Node-B. Node-B evaluates the interference profile in Node-B from the information about the SINR transmitted from the UE and the power of the transmission signal, and determines the frequency profile of the power of the signal transmitted to the UE.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
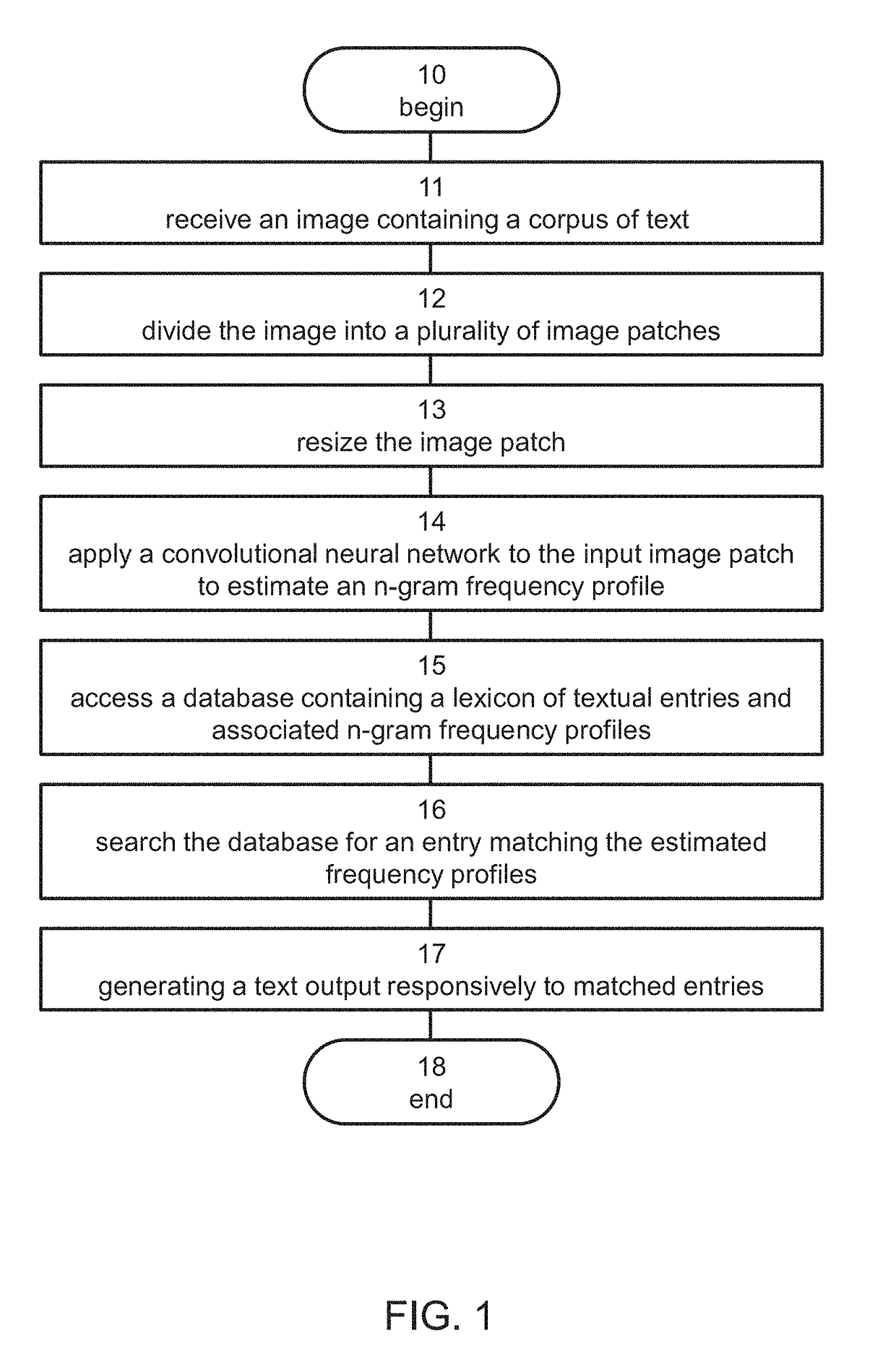
Method and system for converting an image to text
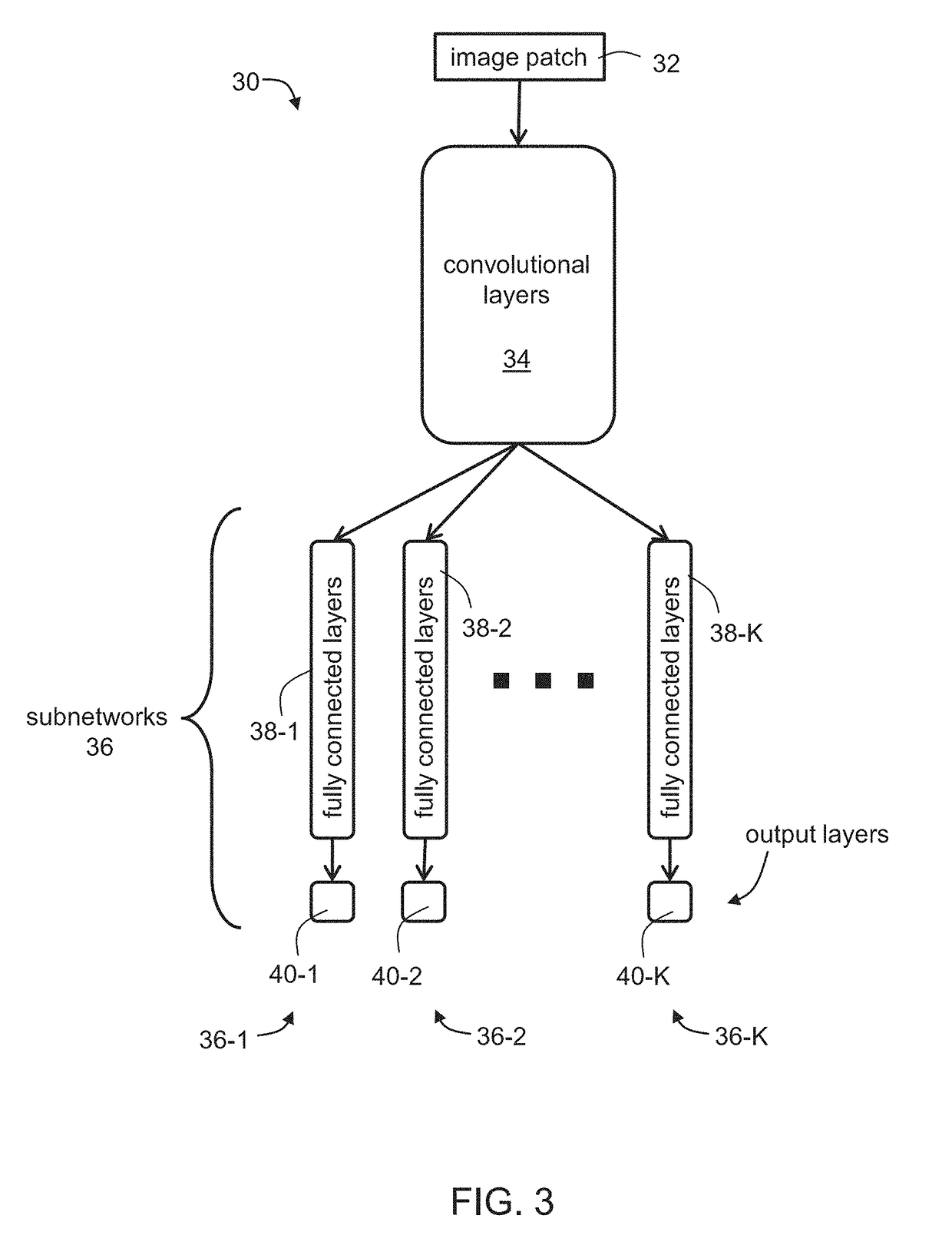
InactiveUS20190087677A1Neural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency profileImage transformation
In a method of converting an input image patch to a text output, a convolutional neural network (CNN) is applied to the input image patch to estimate an n-gram frequency profile of the input image patch. A computer-readable database containing a lexicon of textual entries and associated n-gram frequency profiles is accessed and searched for an entry matching the estimated frequency profile. A text output is generated responsively to the matched entries.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method and apparatus for microphone matching for wearable directional hearing device using wearer's own voice
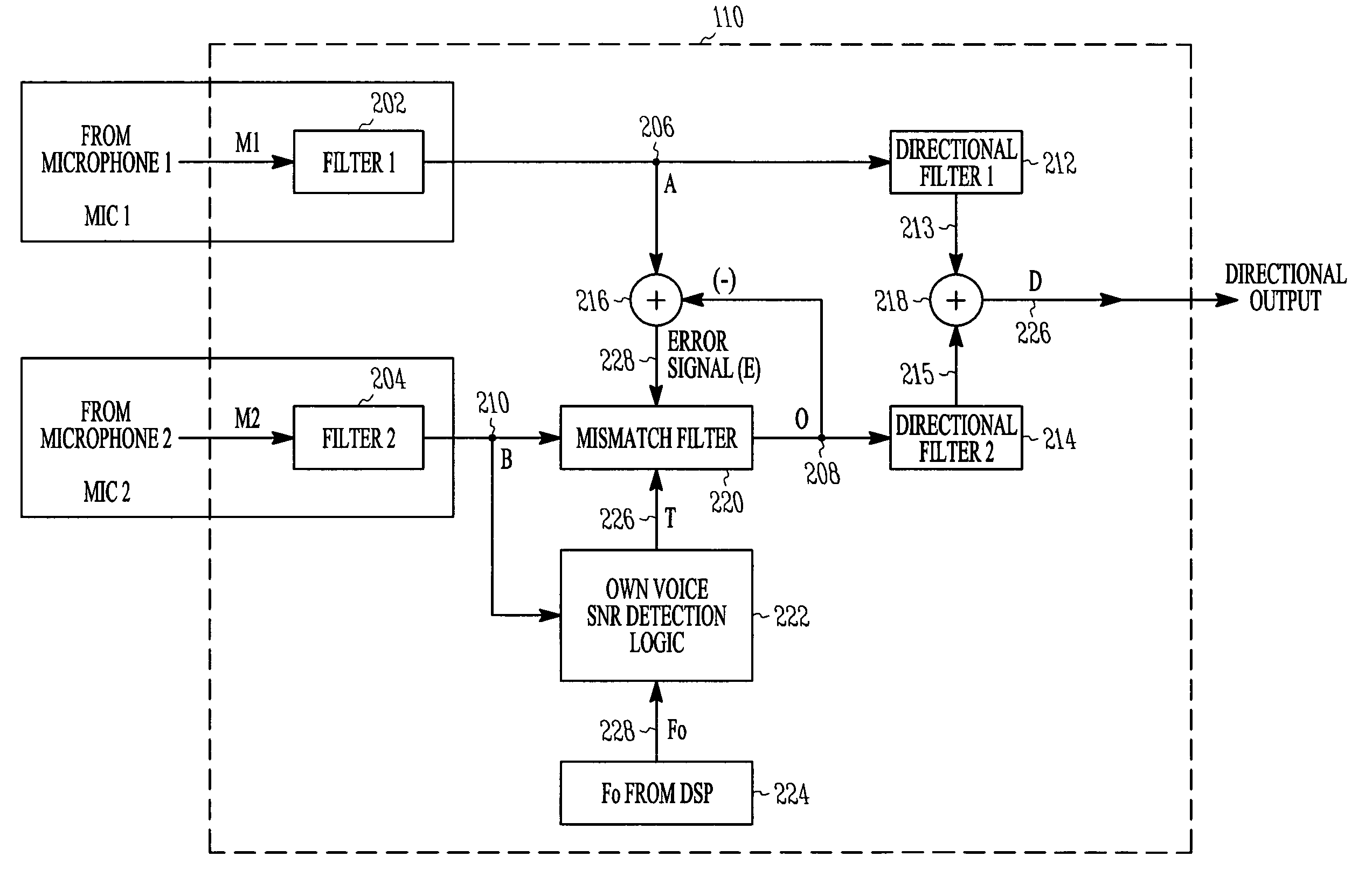
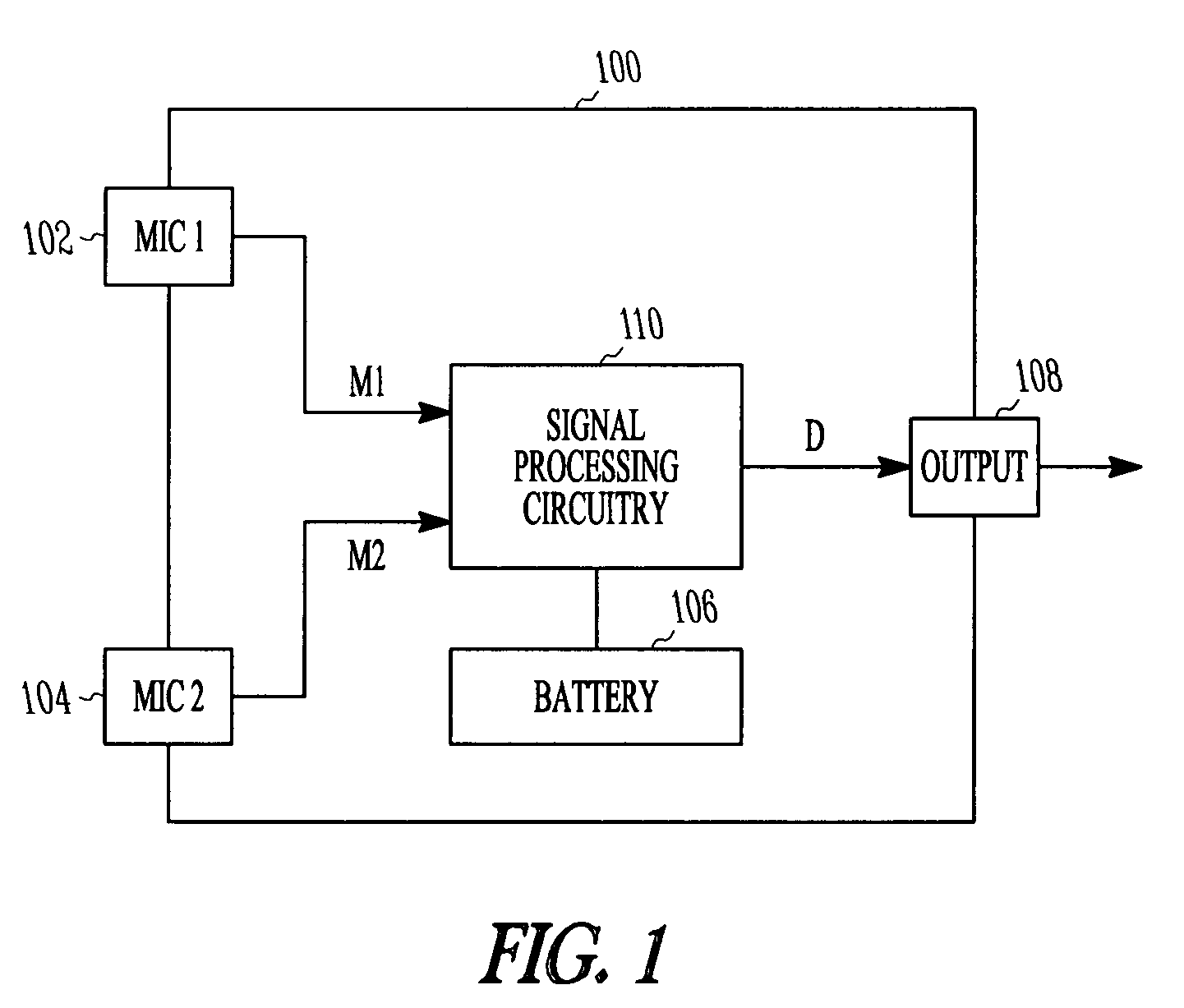
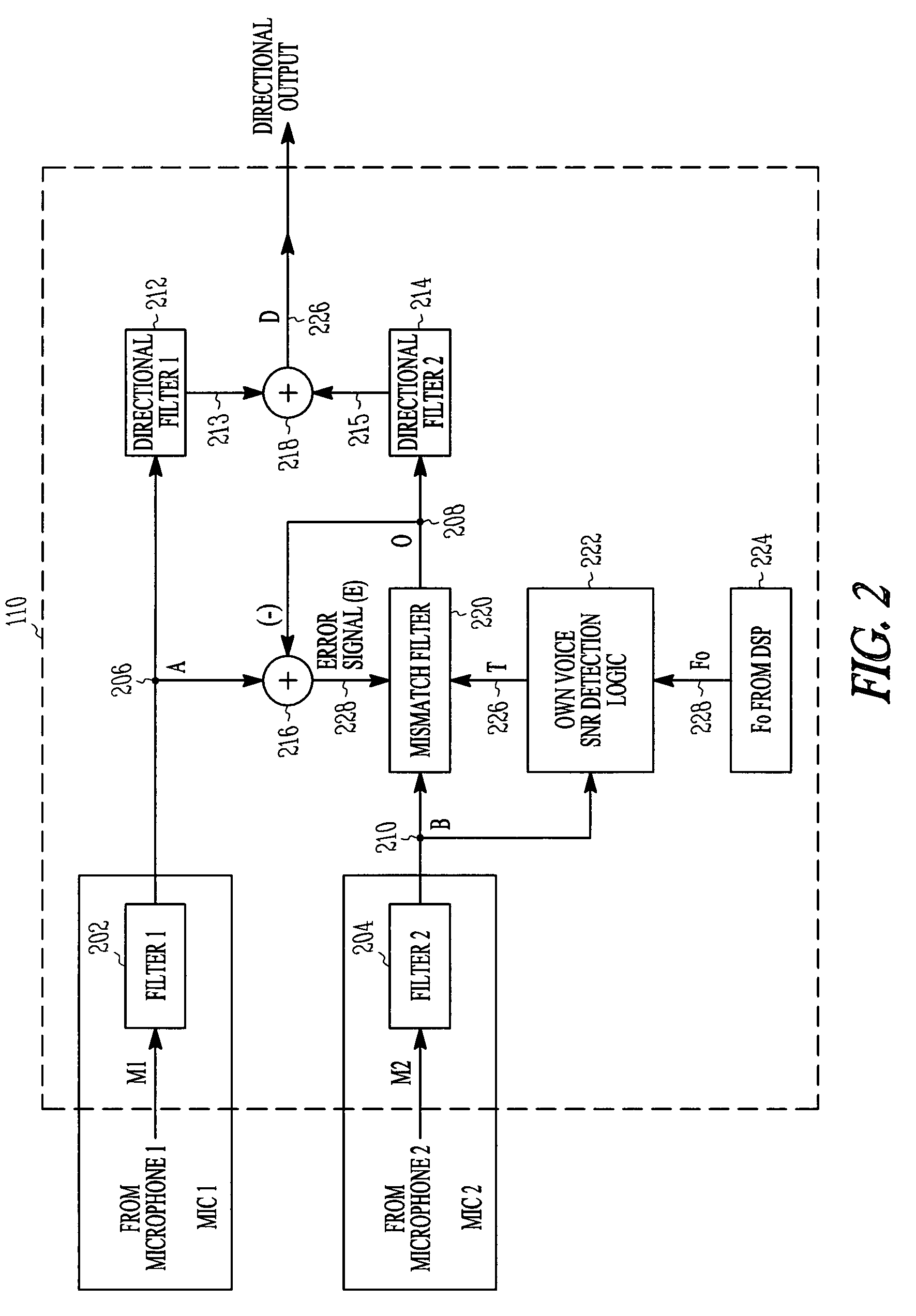
ActiveUS8031881B2Speech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionDirectional hearingComputer science
Method and apparatus for microphone matching for wearable directional hearing assistance devices are provided. An embodiment includes a method for matching at least a first microphone to a second microphone, using a user's voice from the user's mouth. The user's voice is processed as received by at least one microphone to determine a frequency profile associated with voice of the user. Intervals are detected where the user is speaking using the frequency profile. Variations in microphone reception between the first microphone and the second microphone are adaptively canceled during the intervals and when the first microphone and second microphone are in relatively constant spatial position with respect to the user's mouth.
Owner:STARKEY LAB INC
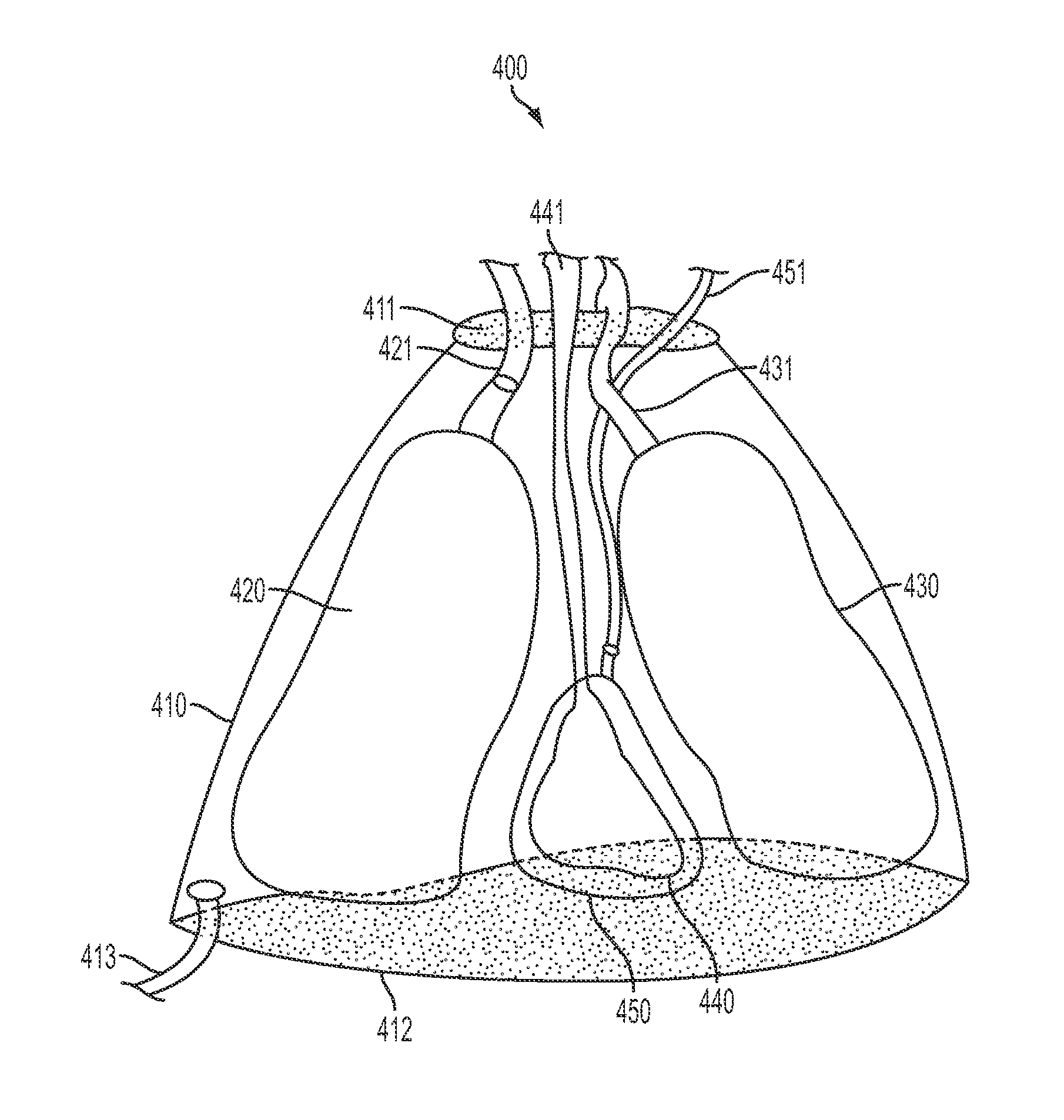
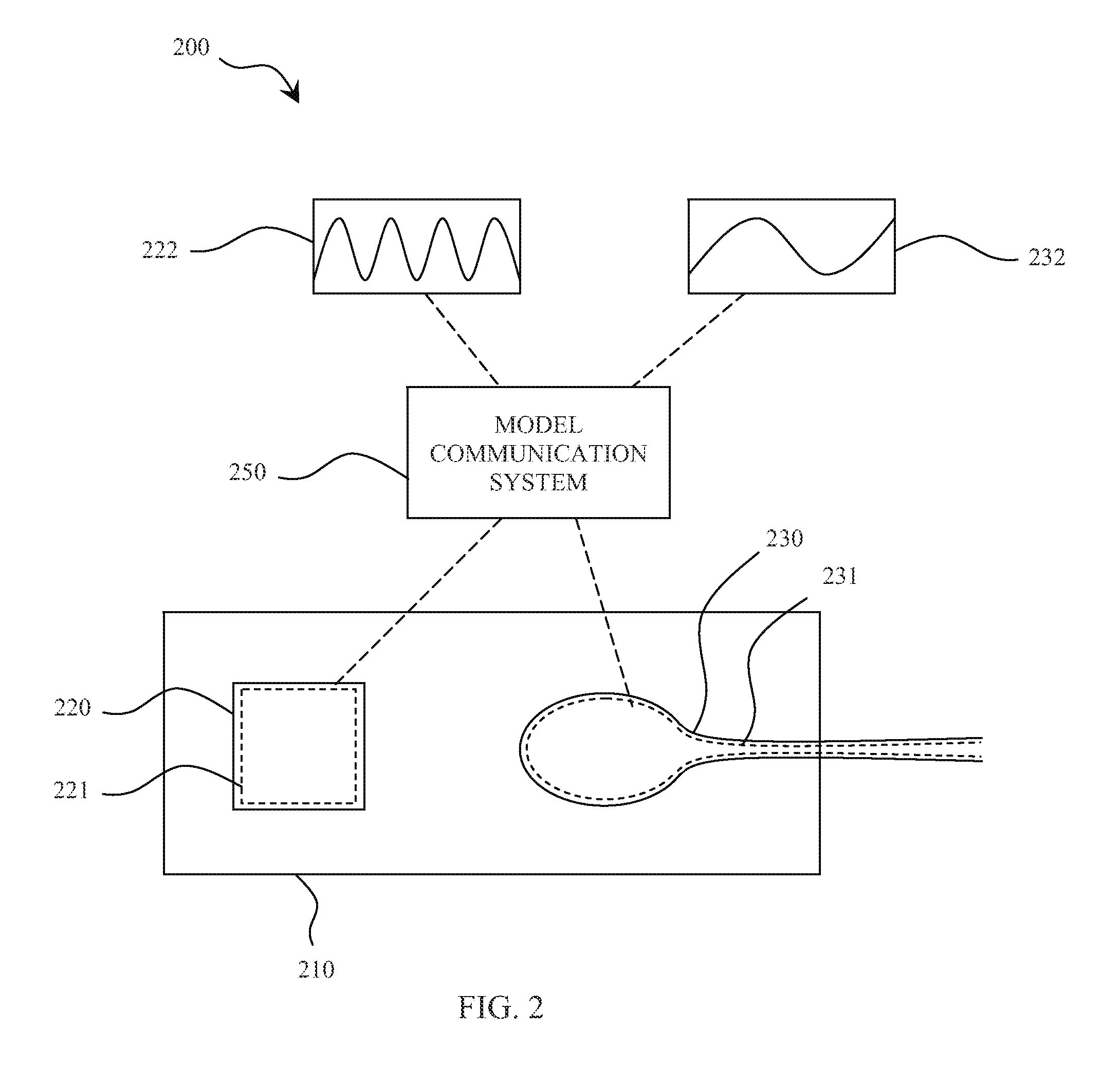
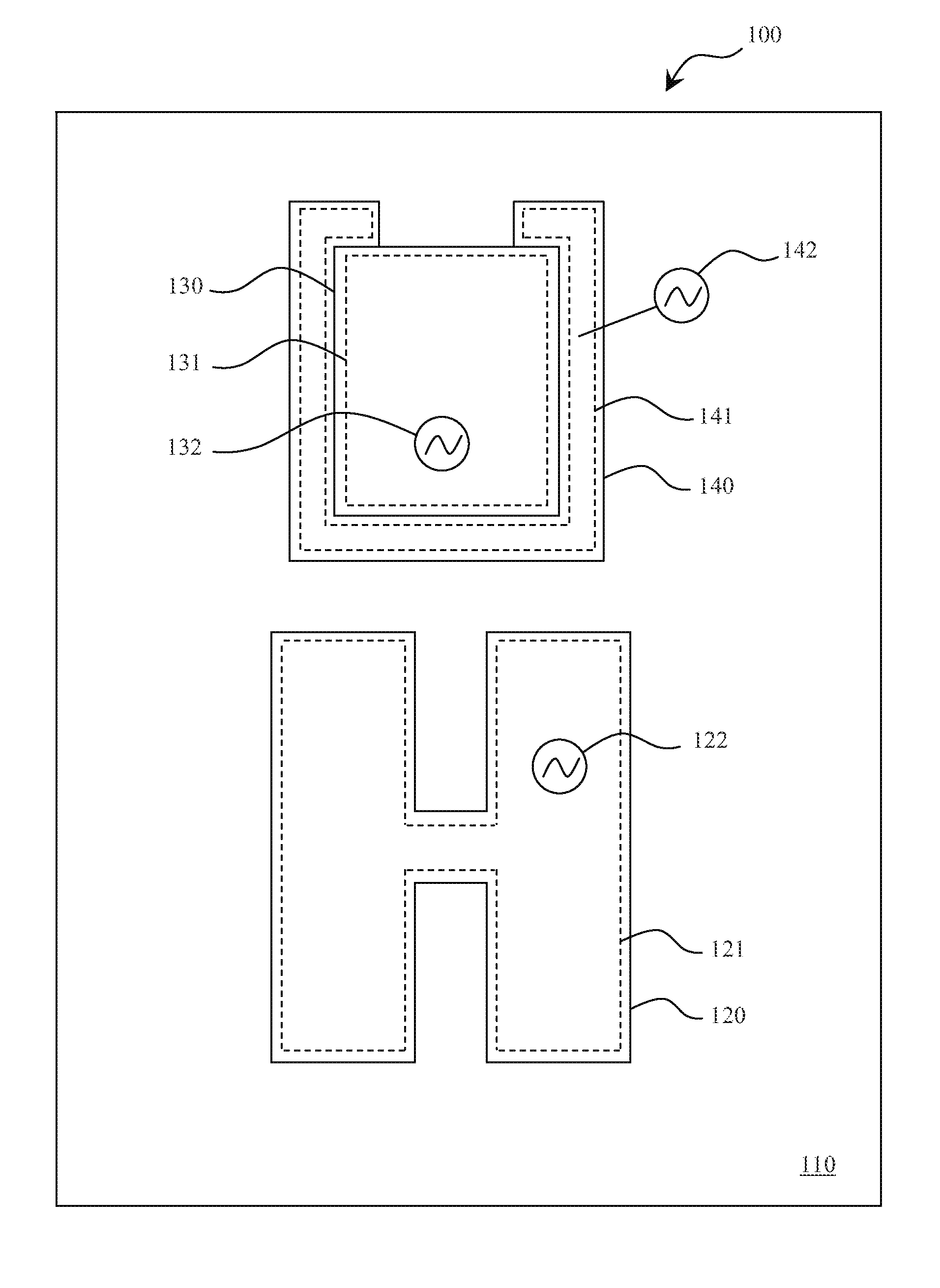
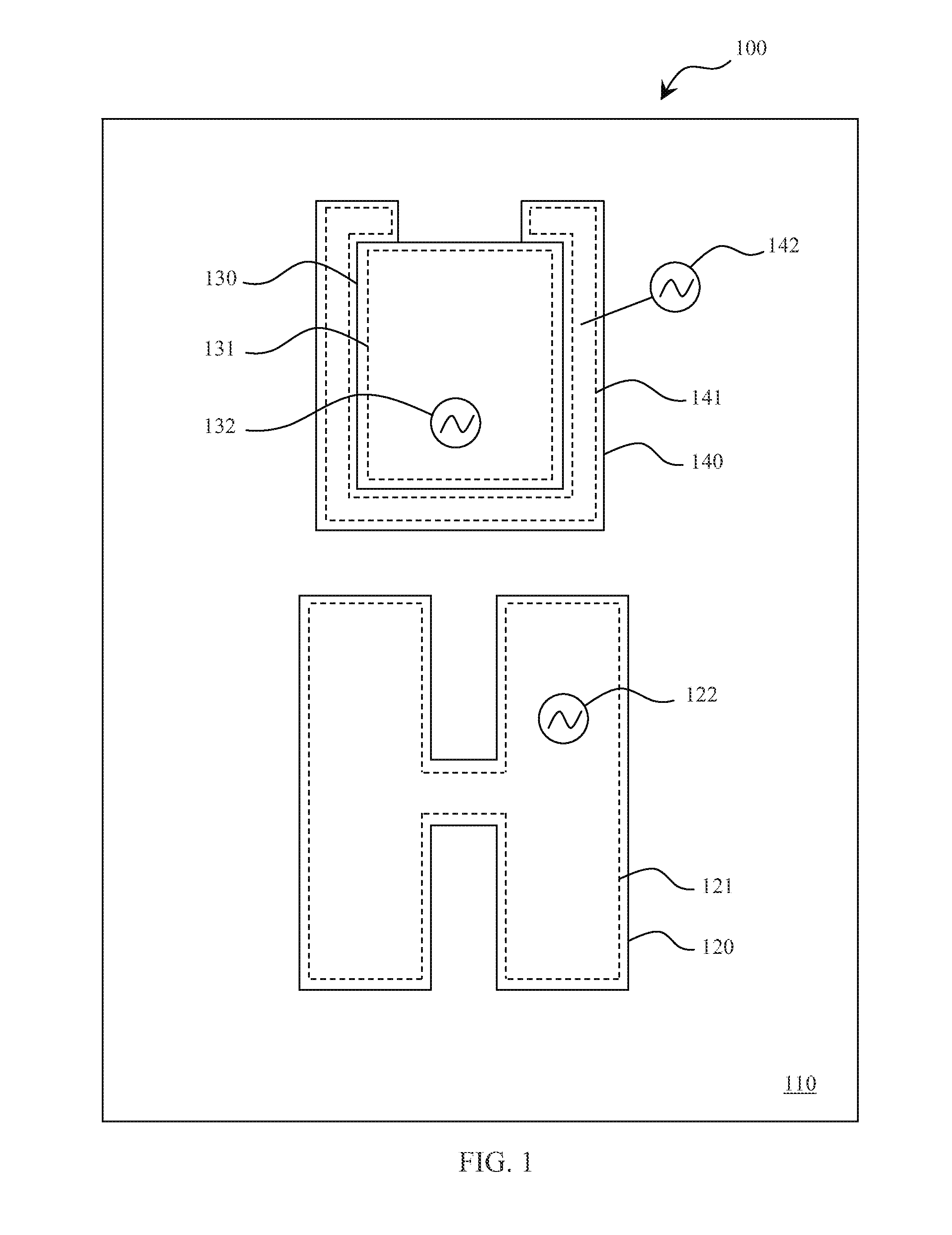
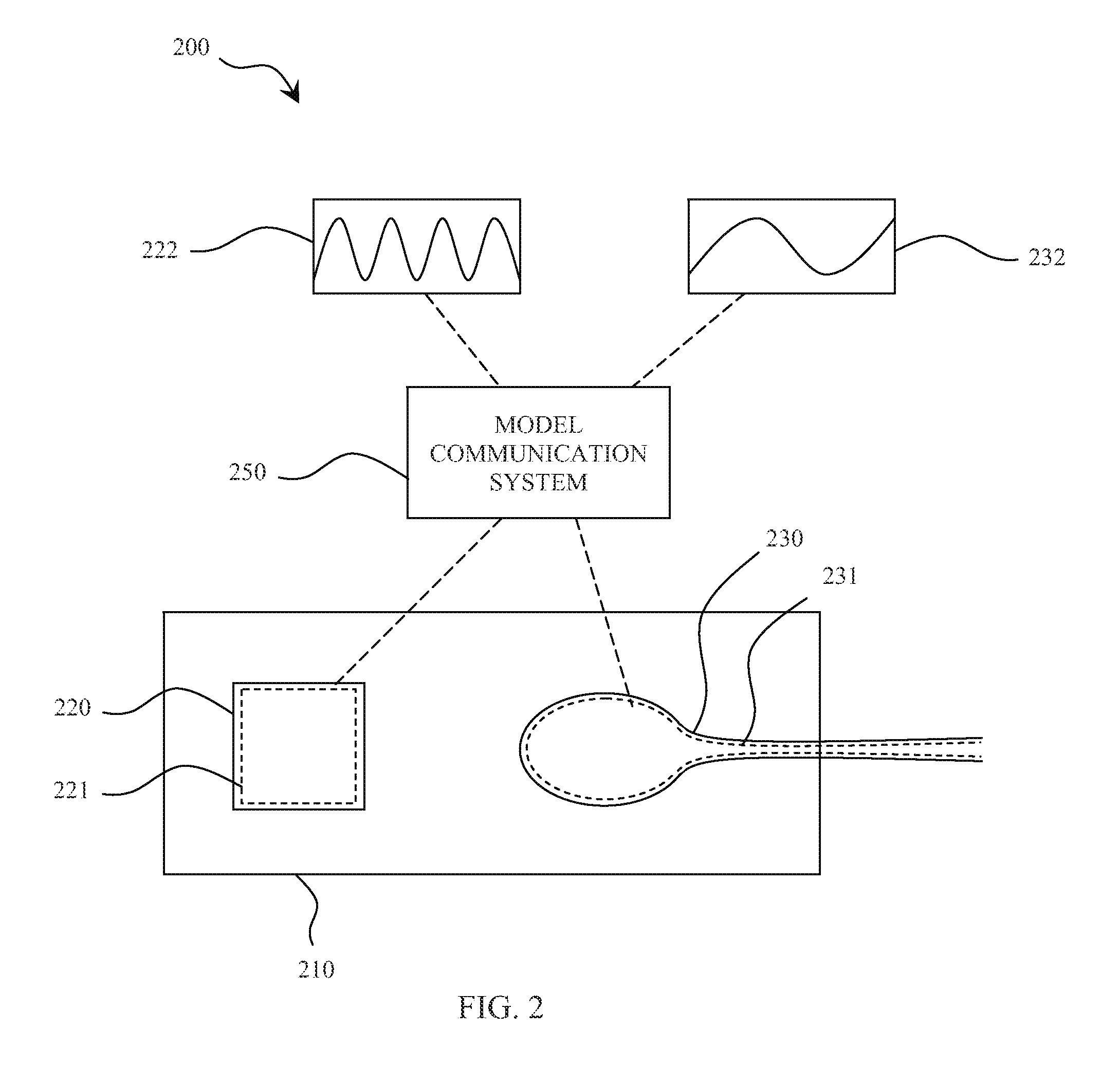
System, method, and computer program product for simulating epicardial electrophysiology procedures
ActiveUS20130108999A1Cost-effectiveOvercome limitationsSurgical instrument detailsEducational modelsPericardiumIn vivo
An aspect of various systems and methods provides, but not limited thereto, novel means for simulating physiological systems and processes in vitro in order to test surgical devices and train practitioners in the use of surgical devices. An aspect of various embodiments further provides in vitro anatomical components, such as a thorax, lungs, heart and pericardium, configured to contain at least one fluid having a pressure-frequency profile that may mimic typical pressure-frequency waveforms of in vivo anatomical fluids. A model communication system may be used to communicate the desired pressure-frequency profiles to the in vitro anatomical fluids. In a further aspect of various embodiments, an access device, e.g. a surgical instrument, configured to sense pressure, frequency, and / or a pressure-frequency profile may be inserted into one or more anatomical components of the in vitro model in order to test the instrument and / or train a practitioner in proper use of the instrument. An access device communication system may be used to communicate data to the practitioner. This data may include, for example, pressure-frequency data and / or the location of a portion of the access device with respect to the various in vitro anatomical components.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
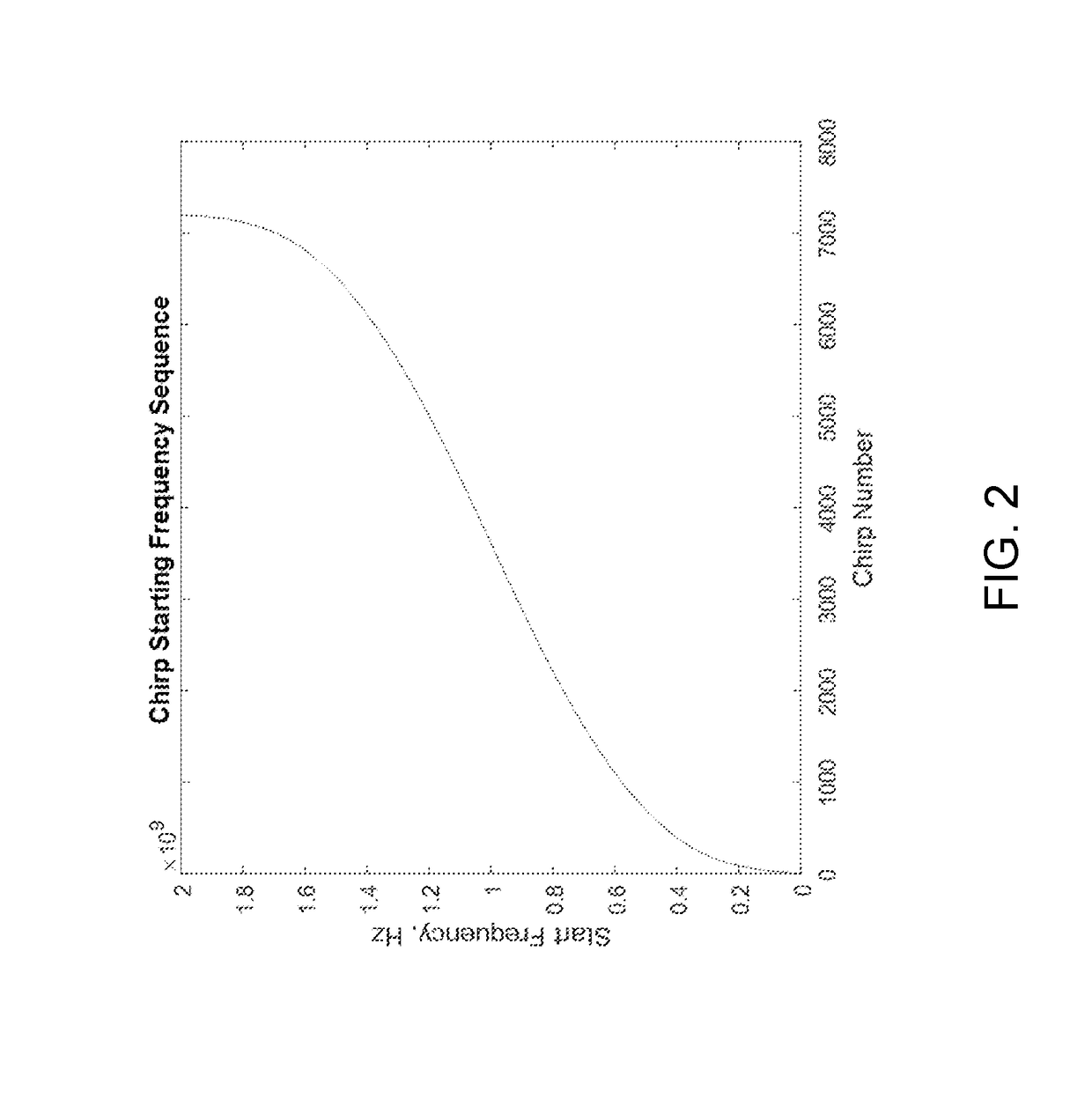
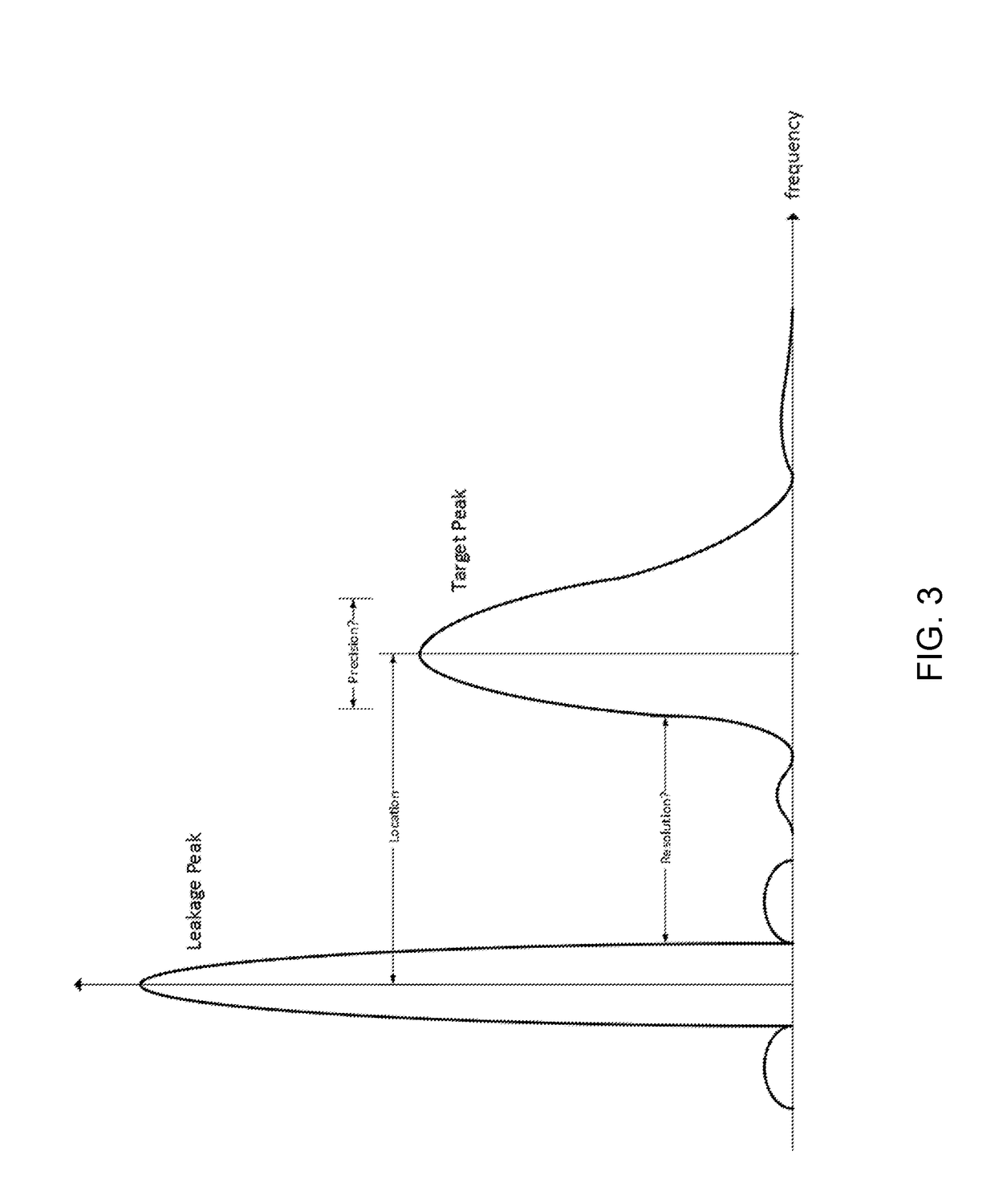
Frequency profiles for non-contact range measurement with multi-scale analysis
A method for constructing a frequency profile of an emitted signal suitable for use in a non-contact ranging system with multi-scale spectral analysis includes determining N stepped frequency chirps, wherein each frequency chirp of the N stepped frequency chirps has a linear FM modulation of predetermined bandwidth and slope, and wherein a starting frequency for each of the plurality of stepped frequency chirps is chosen so that a non-linear step profile is created which extends over a predetermined total bandwidth, sorting the plurality of N stepped frequency chirps into P sub-sequences, where P is equal to the product of decimation factors to be used in the multi-scale spectral analysis, and ordering the P sub-sequences end to end in time.
Owner:HACH CO
Wireless multiple input hearing assist device
A wireless hearing assist device including a microphone unit and a receiver unit. The microphone unit includes a microphone that receives audio signals, a frequency profile adjustment control circuit that adjusts frequency profile of the received audio signals based on input by a user, and a transmitter that wirelessly transmits the adjusted audio signals. The receiver unit is adapted to be worn by the user and includes a receiver that wirelessly receives the adjusted audio signals transmitted by the transmitter, and a speaker that generates sound based on the adjusted audio signals. In at least one embodiment, the microphone unit includes a Bluetooth enabled RF communication link for wireless communication with an external device other than the receiver unit.
Owner:AMERICA HEARS
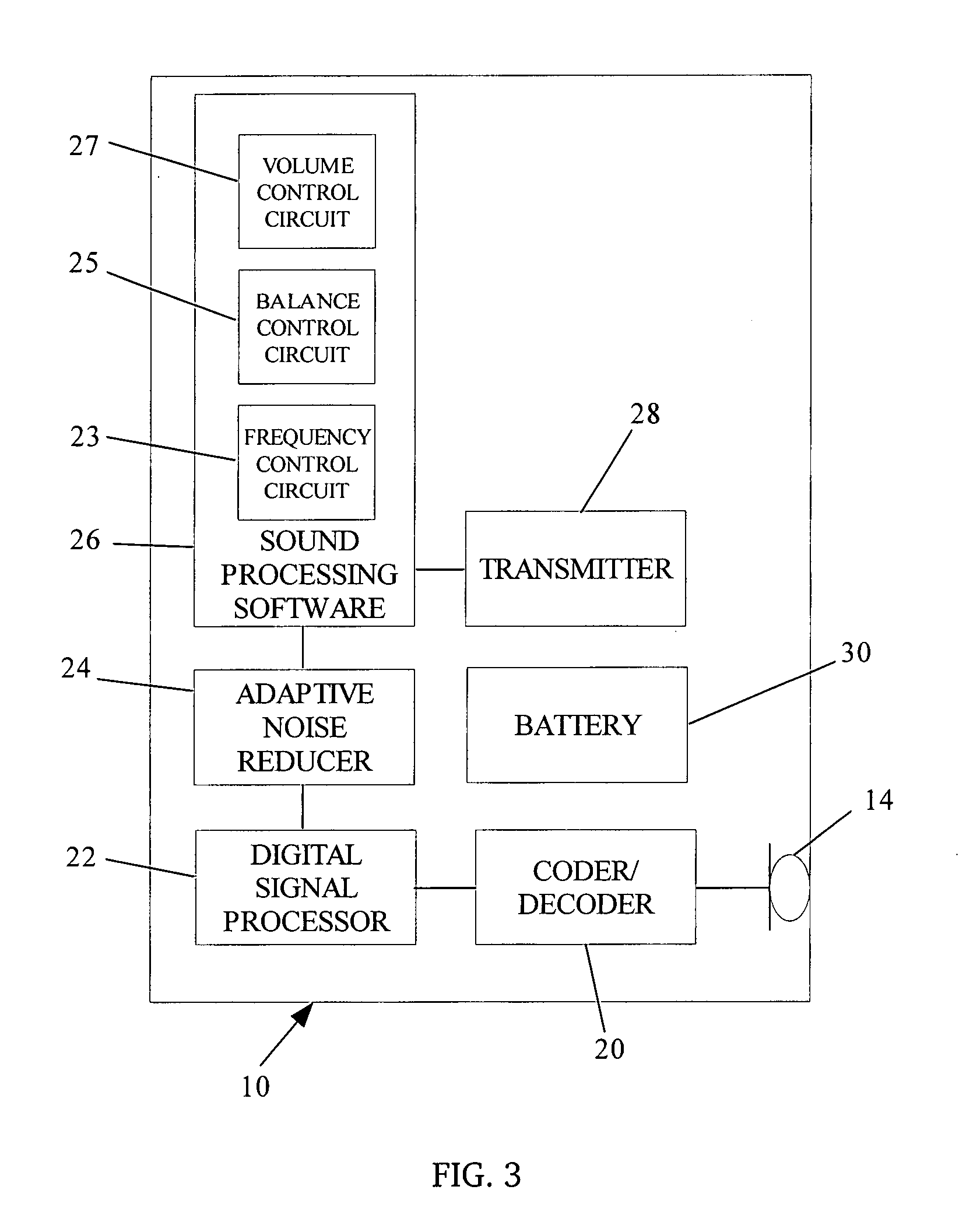
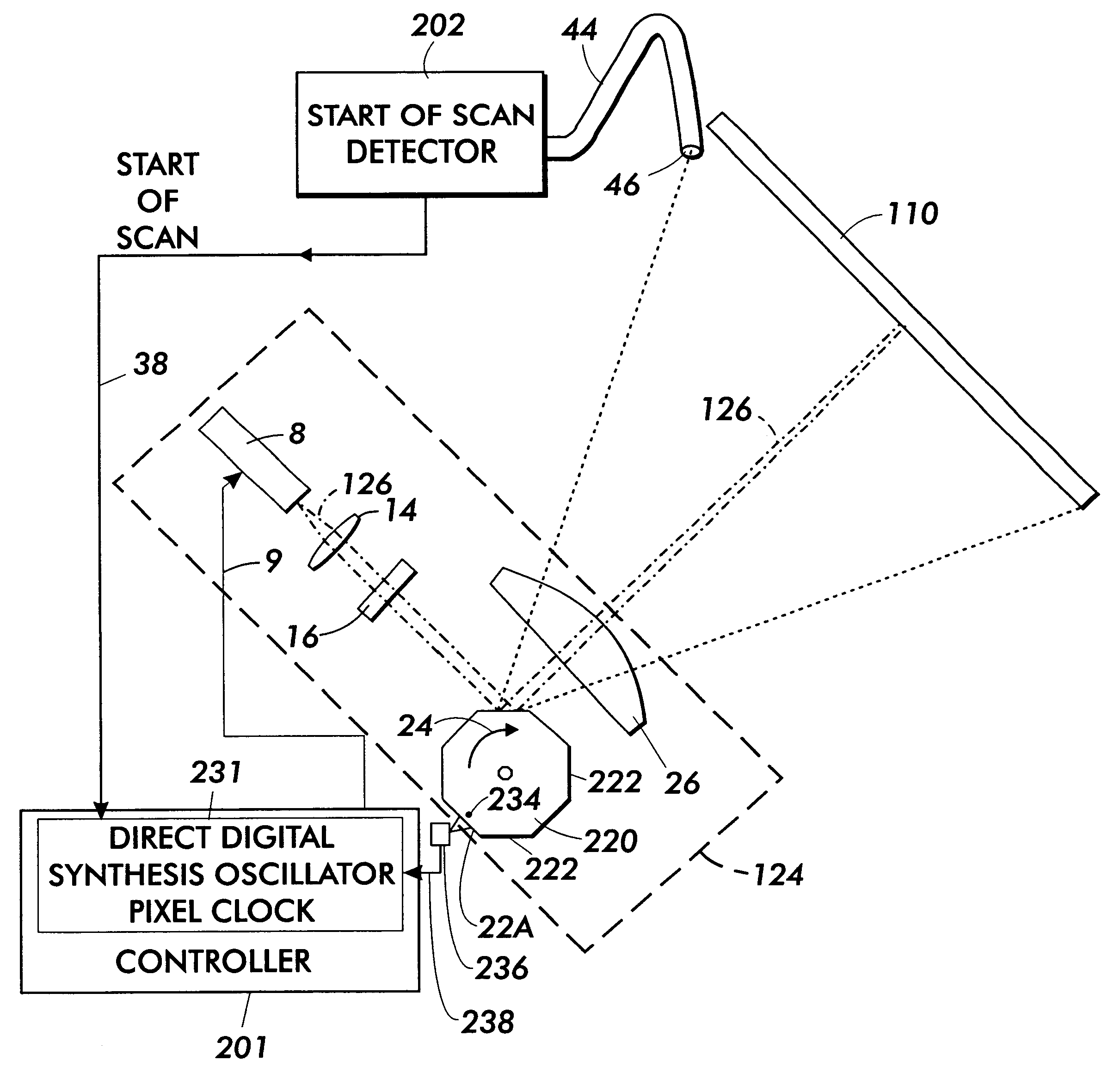
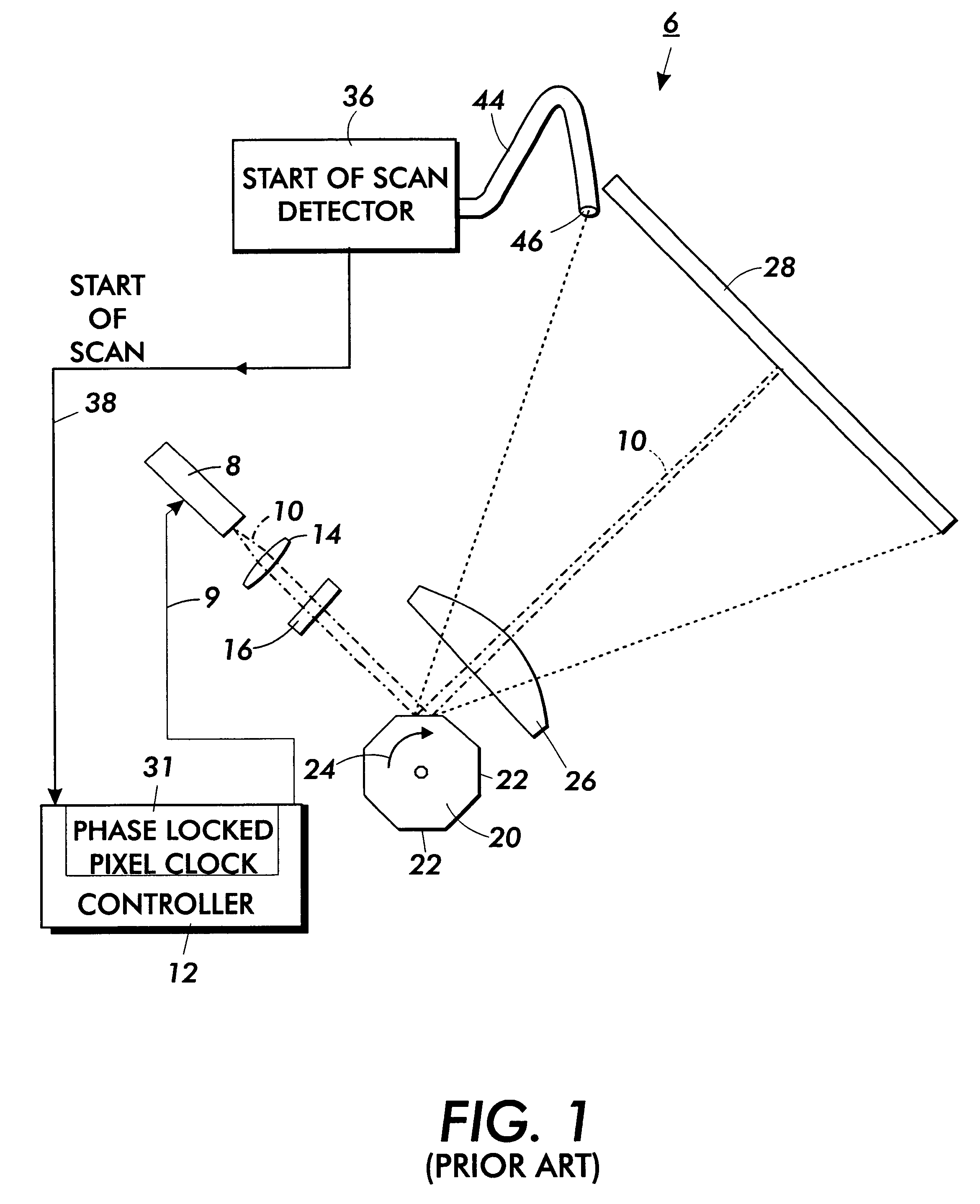
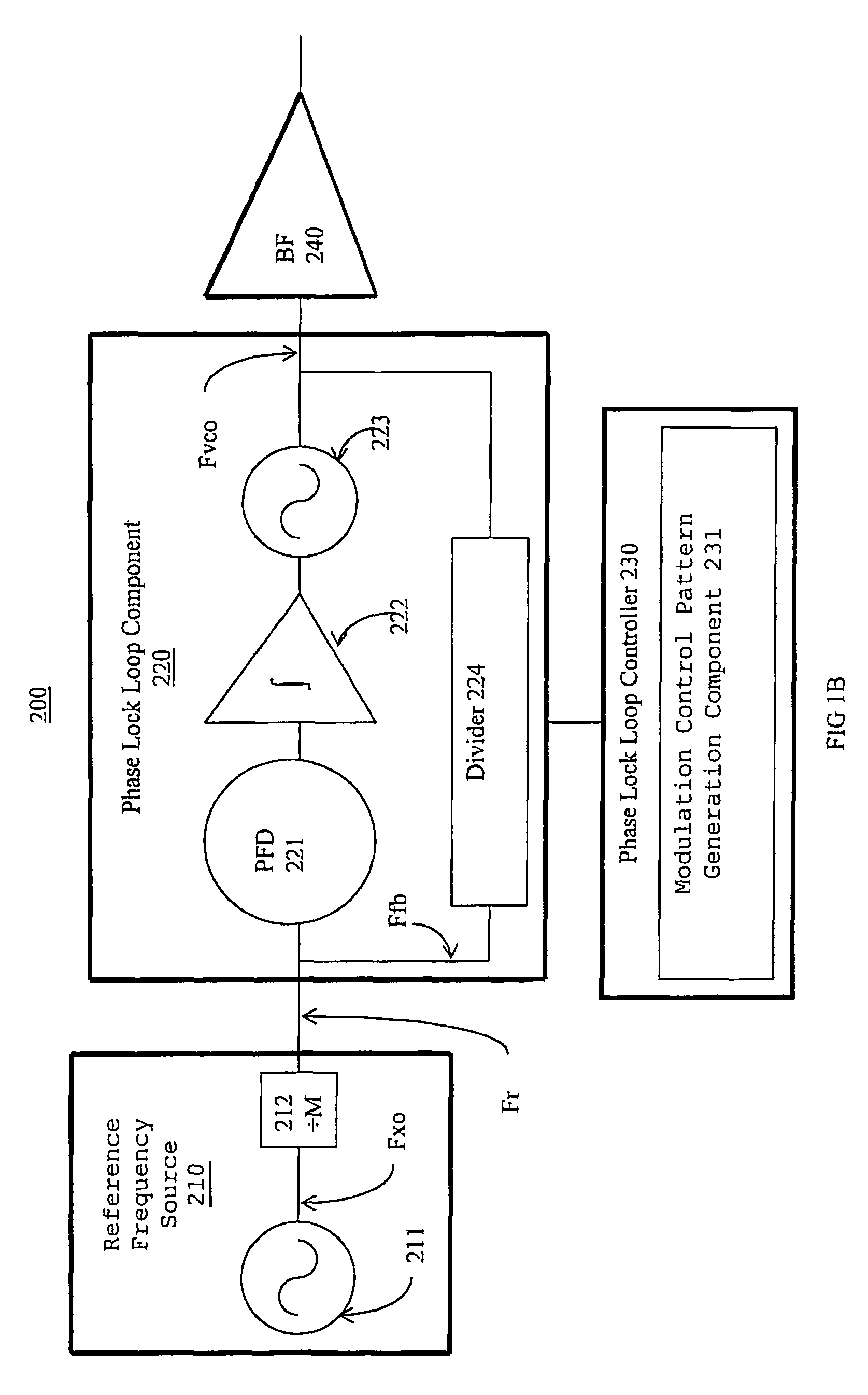
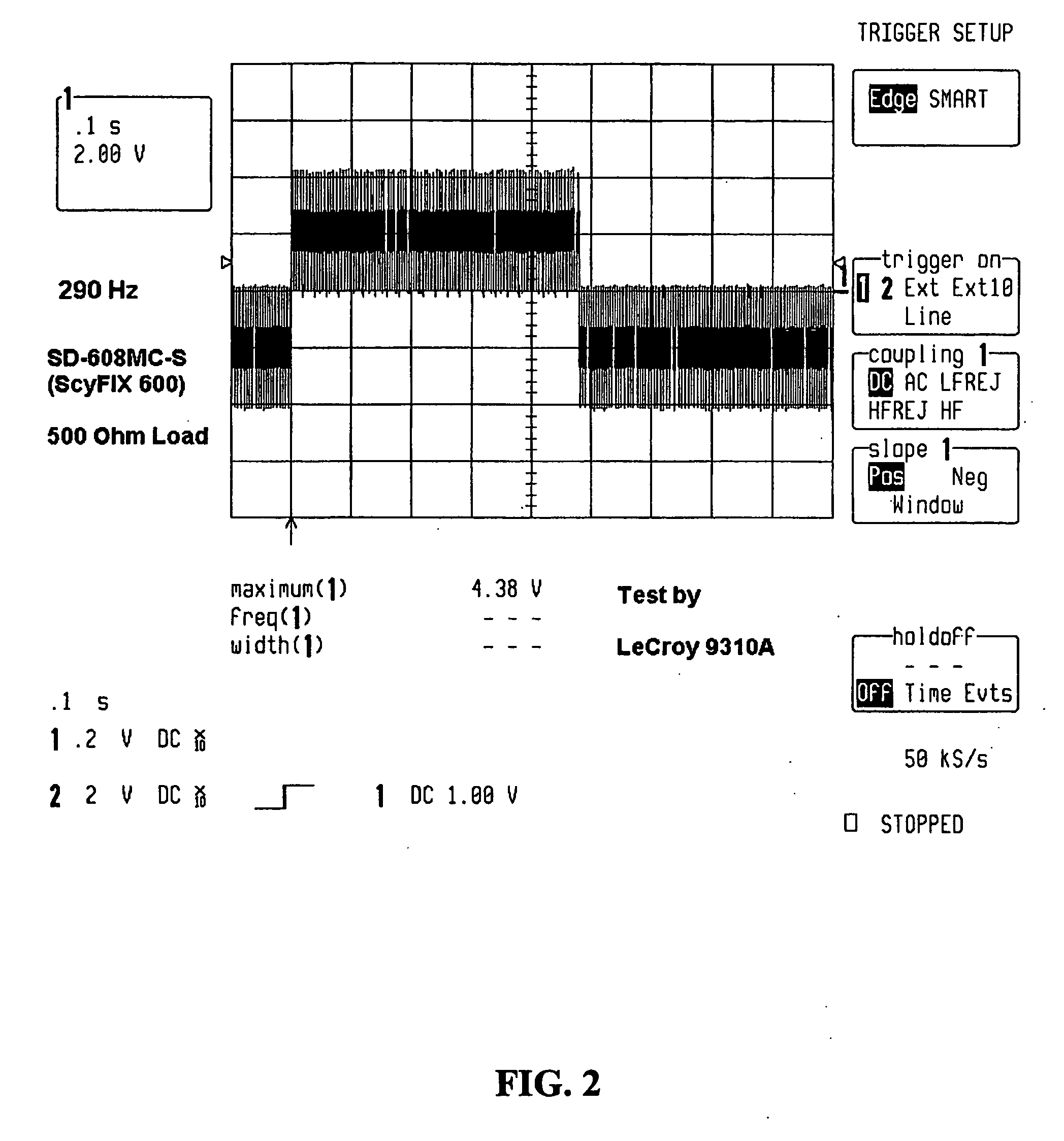
Direct digital synthesis pixel clock generator
InactiveUS6351277B1Visual representatino by photographic printingElectrographic process apparatusPhase shiftedPhase locked loop circuit
A Direct Digital Synthesis pixel clock generator for use in electrophotographic printers. A controller receives a start-of-scan signal and a facet 0 signal. In response, the controller sends a pre-stored frequency control word to a Direct Digital Synthesis Oscillator. The Direct Digital Synthesis Oscillator sends pulses at a frequency that depends on the frequency control word to a Digital Phase Shift Circuit. The controller also applies a sequence of delay profile words to the Digital Phase Shift Circuit. Each delay profile word causes the Digital Phase Shift Circuit to delay a contemporaneous pulse from the Direct Digital Synthesis Oscillator between 0° and 360° degrees, with the actual delay depending upon the delay profile word. The delay profile words are selected such that scan line pixels are "adjusted" in position. A phase-locked-loop circuit integrates and smoothes the frequency step changes. The output of the phase-locked loop circuit is applied to a synchronizer that synchronizes the pixel clocks with the start-of-scan. Alternatively, the controller applies a sequence of frequency profile words to a Direct Digital Synthesis Oscillator. The Direct Digital Synthesis Oscillator then generates pulses at a rate that depends upon the applied frequency profile word. The frequency profile words are selected such that the pixels are "adjusted" in position. A phase-locked-loop circuit then integrates and smoothes the output of the Direct Digital Synthesis Oscillator. The resulting pulse frequency is applied to a synchronizing circuit that synchronizes the pixel clocks with the start-of scan-signals.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Controller for processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050024927A1Less powerExtend battery lifePower managementEnergy efficient ICTSoftware define radioElectronic systems
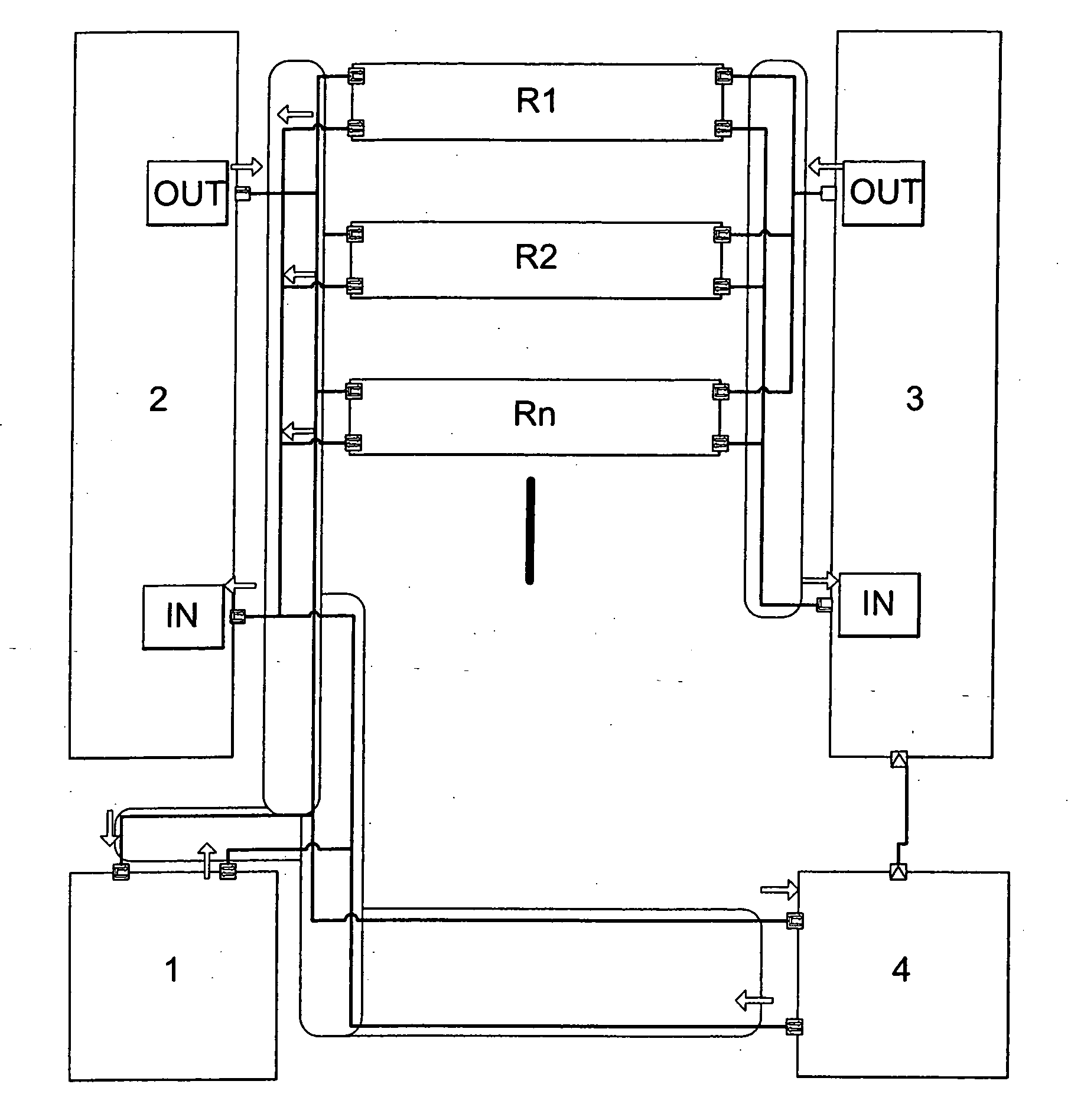
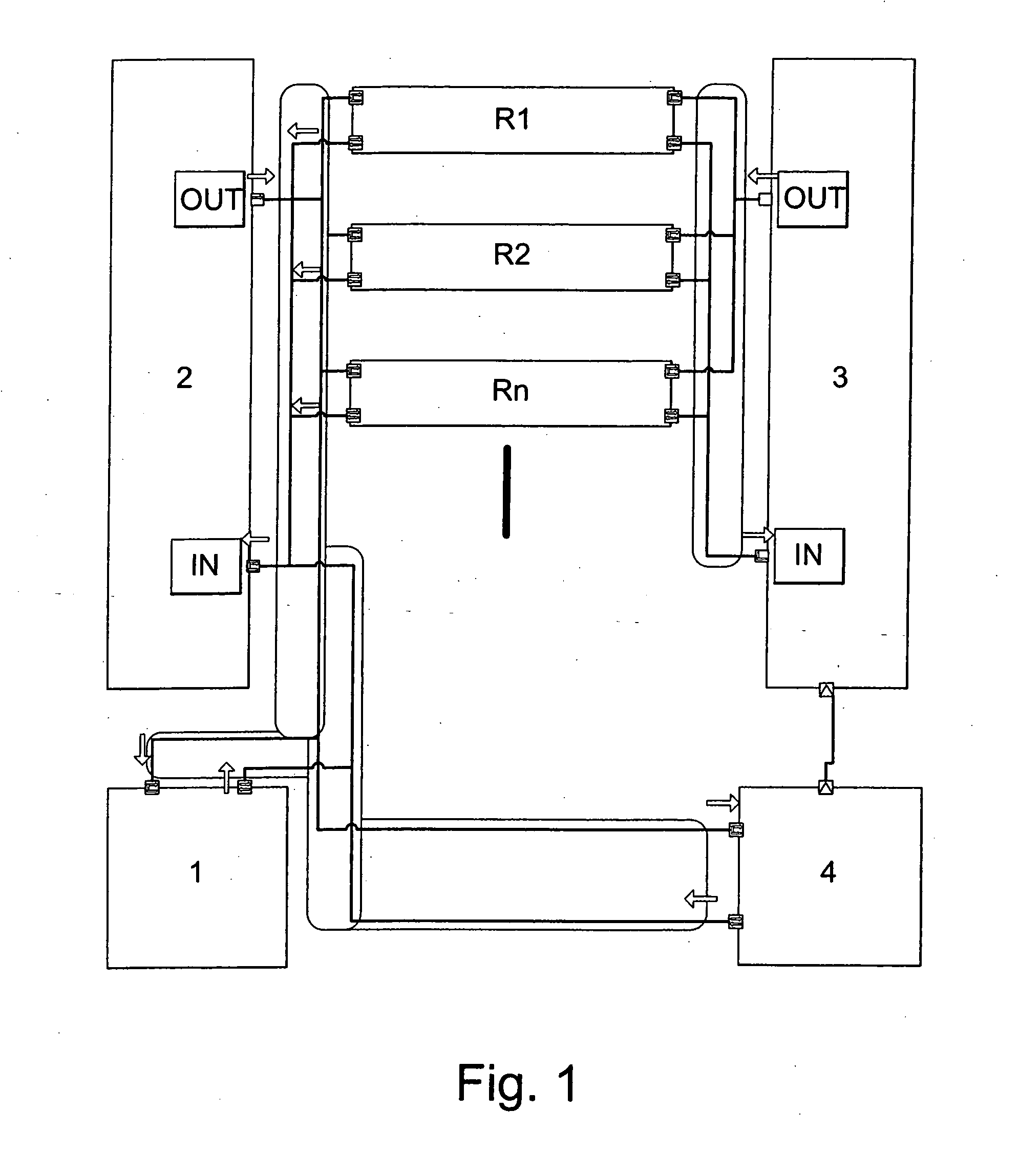
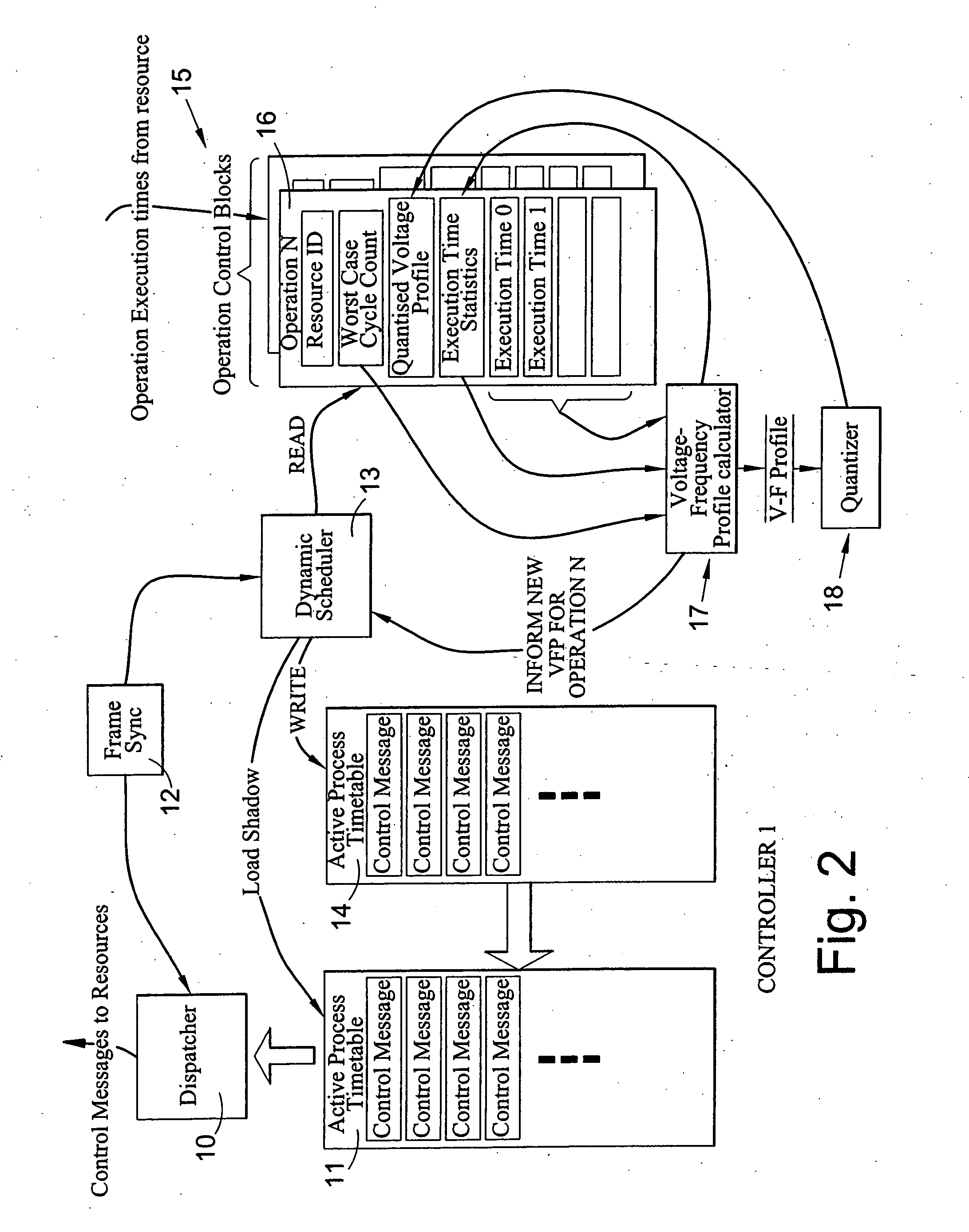
The present invention relates to processing apparatus utilising dynamic scaling of voltage (DVS), and in particular although not exclusively to a controller for such apparatus. The invention is especially applicable to software defined radio (SDR), but is not so limited and may be applied to other re-configurable electronic systems. The present invention provides a controller for a processing apparatus having a plurality of processing resources, at least some of said resources having controllable supply voltage and / or frequency; the controller comprising: means for scheduling operations on said resources, at least some of said operations having a predetermined deadline by which the operation must be performed; means for determining a voltage and / or frequency profile for a said operation having a said deadline; and means for instructing the resources to perform said operations according to said schedule and said profile.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
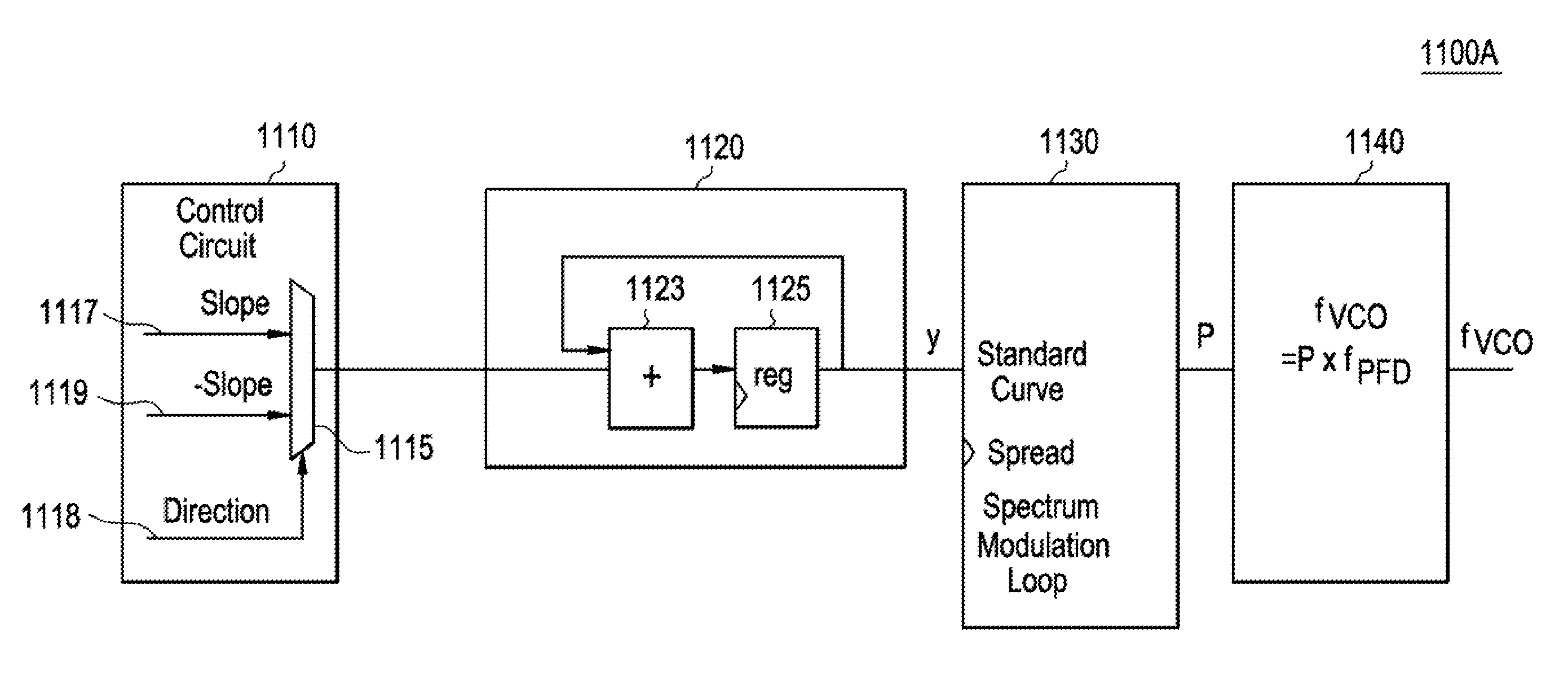
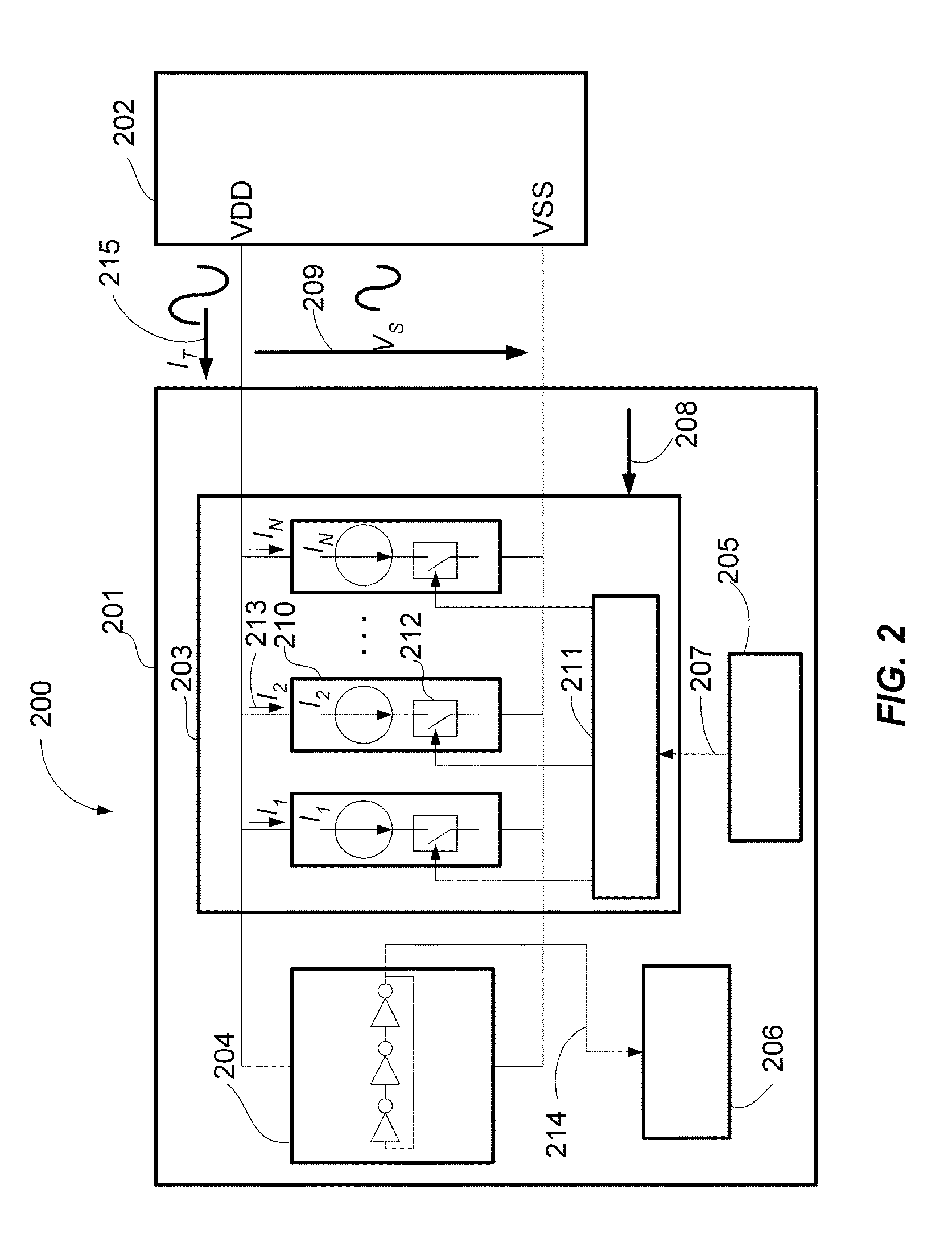
Spread spectrum frequency synthesizer with high order accumulation for frequency profile generation
A frequency synthesizer is described illustrating a system and method for modulation. In particular, the frequency synthesizer includes a control circuit for producing a plurality of input signals that is scalable to a frequency profile. Each of the input signals includes a slope and a direction of the slope. A higher order accumulator block is coupled to the control circuit and receives the plurality of input signals. The higher order accumulator block includes at least two accumulators. The higher order accumulator block sums the plurality of input signals to generate a standard curve that is non-linear. A frequency spreading control pattern generation modulator is coupled to the higher order accumulator block and modulates the standard curve to generate the desired frequency profile.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
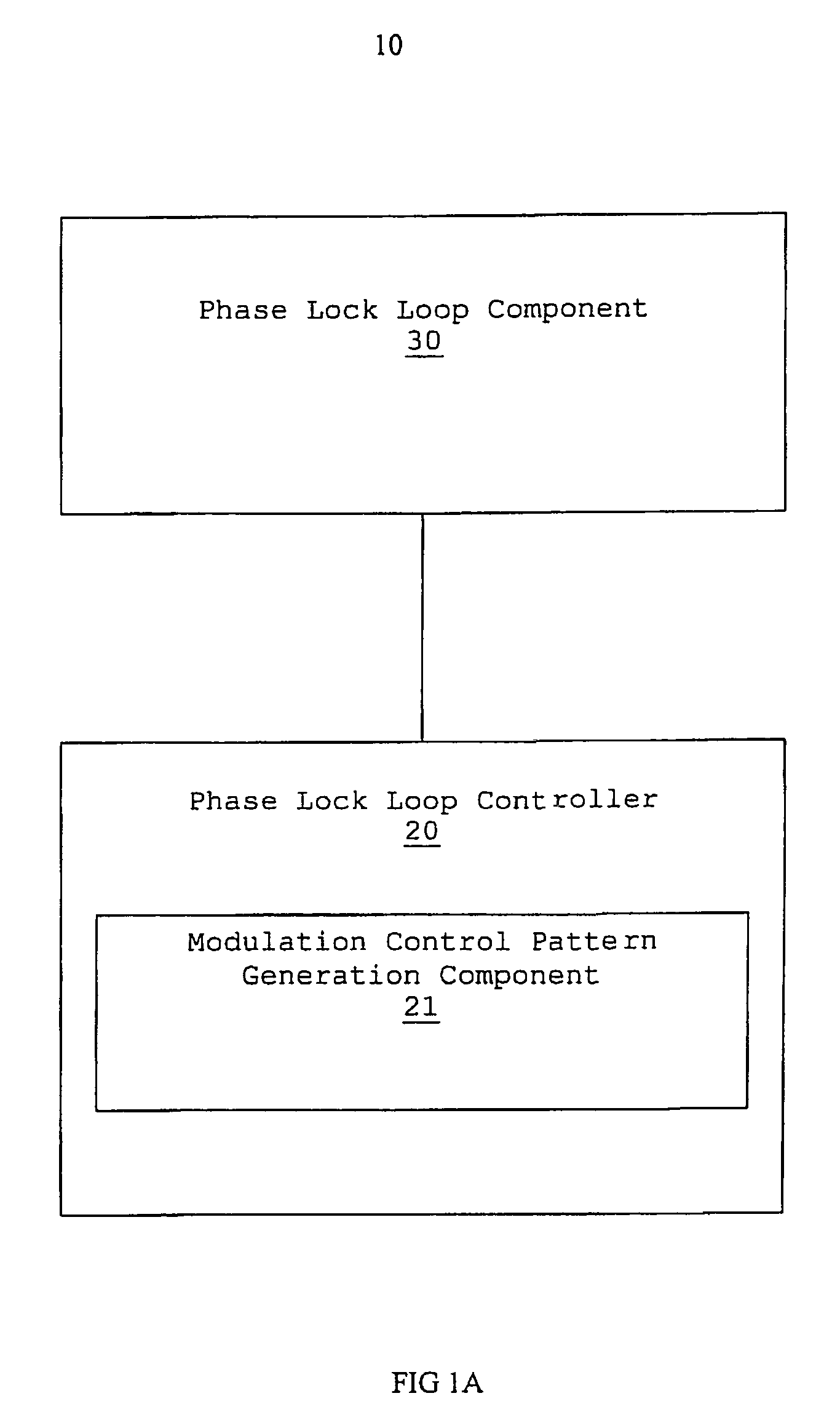
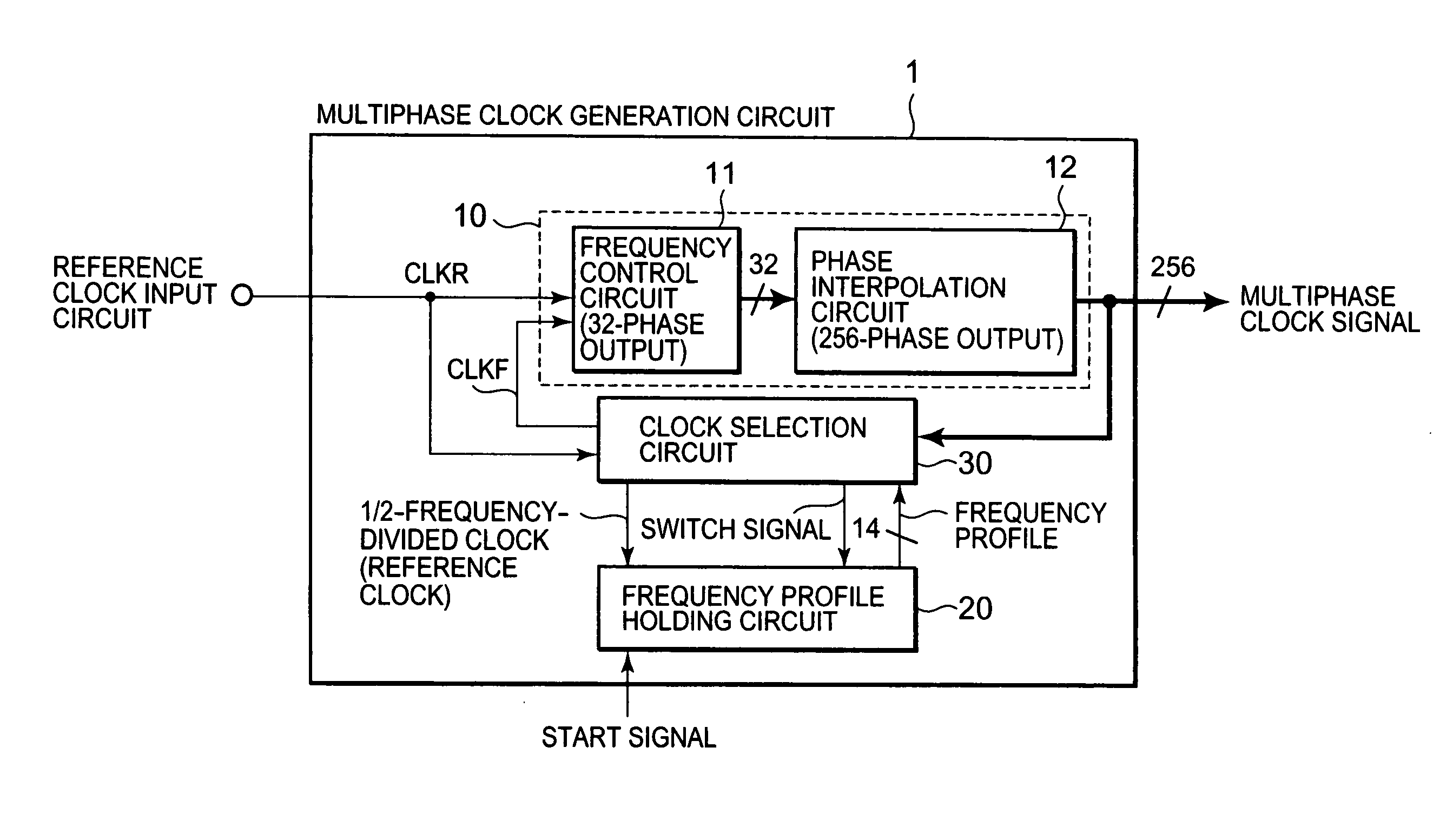
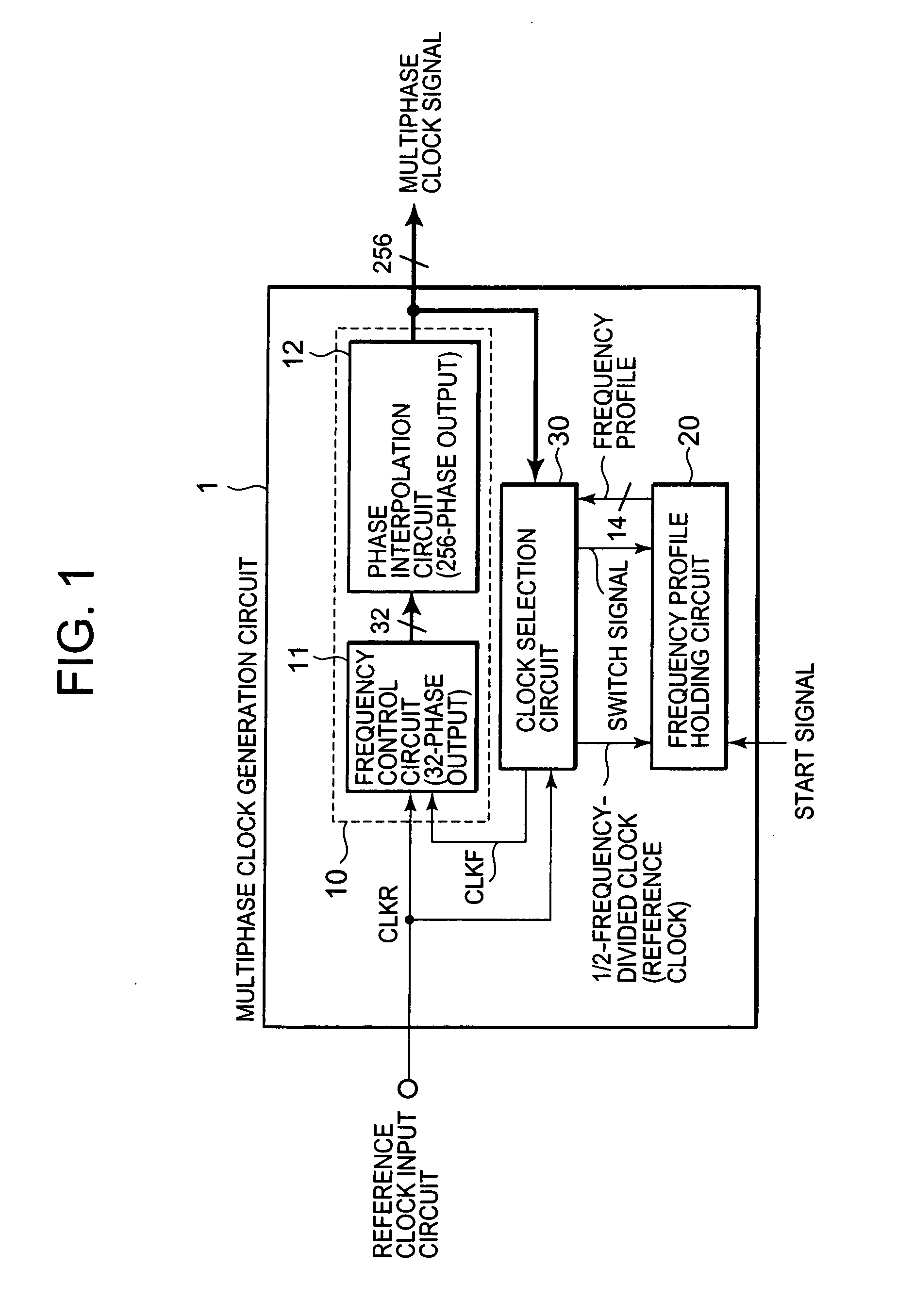
Multiphase clock generation circuit
ActiveUS20080100364A1Improve accuracyImprove precision controlPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase locked loop circuitEngineering
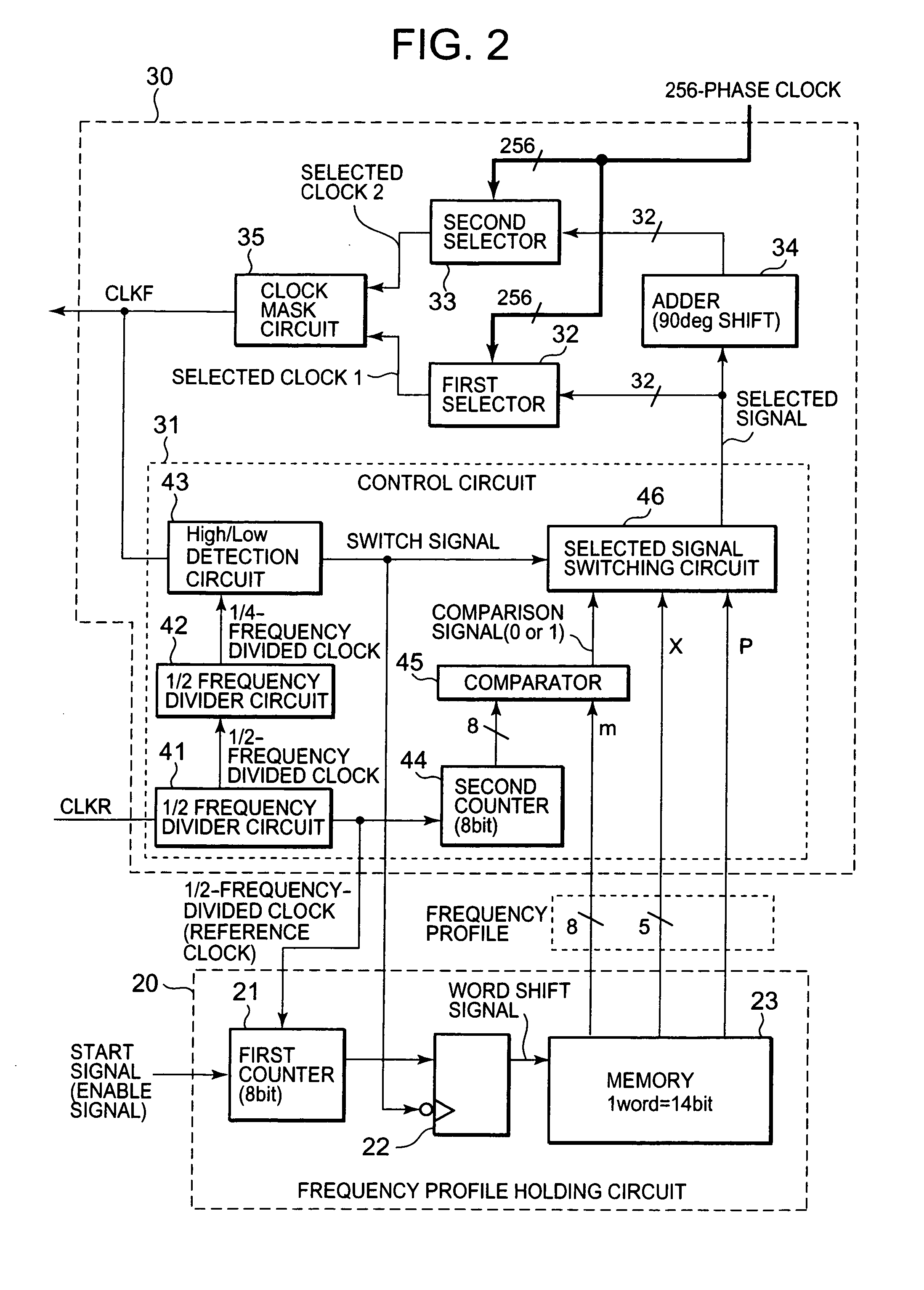
Provided is a multiphase clock generation circuit (1) including: a phase-locked loop circuit (10) for generating multiphase clock signals based on a reference clock signal; a frequency profile holding circuit (20) for holding a frequency profile of each of the multiphase clock signals, starting output of the frequency profile in response to a start signal, and for updating the frequency profile with a predetermined cycle based on the reference clock signal; and a clock selection circuit (30) for selecting a clock signal with an arbitrary phase from among the multiphase clock signals based on the frequency profile, and for feeding back the selected clock signal to the phase-locked loop circuit (10).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Earthquake stratum thickness variation analysis method
InactiveCN102508295ASmooth componentAccurate portionSeismic signal processingDamping factorContinuous wavelet transform
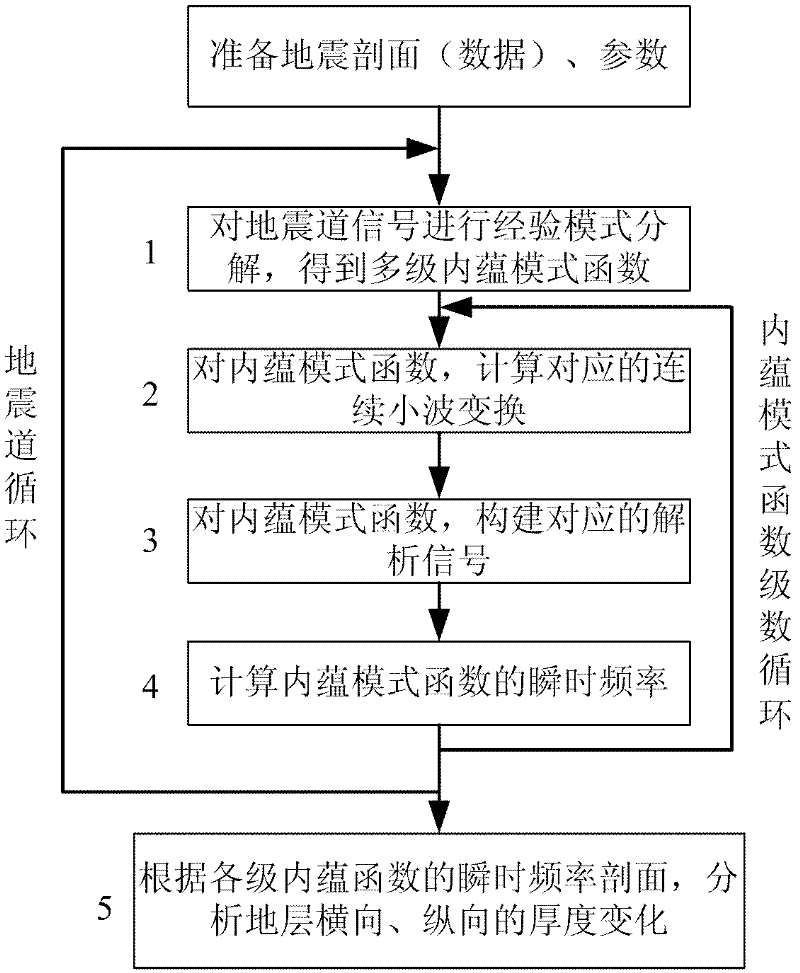
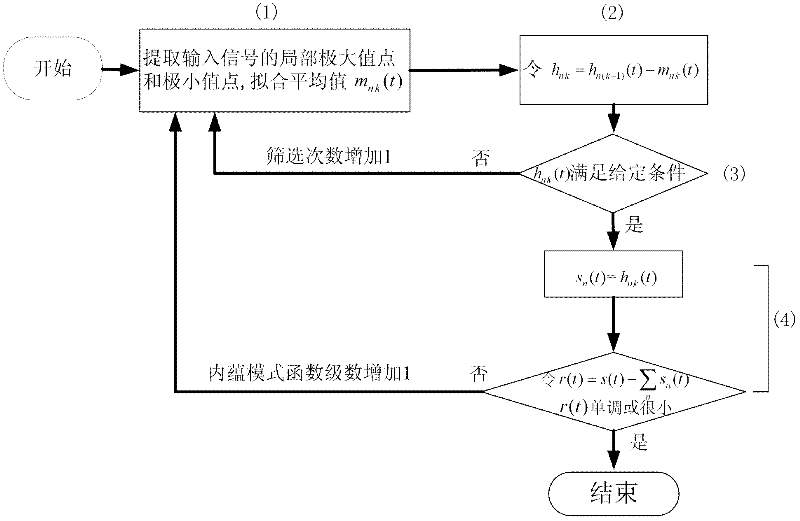
The invention discloses an earthquake stratum thickness variation analysis method in which a high-resolution instantaneous frequency decomposed on the basis of an empirical mode is used to analyze stratum thickness variation. Firstly, an earthquake signal is subjected to an empirical mode decomposing process to obtain a multilevel intrinsic mode function; then, the instantaneous frequency of the intrinsic mode function is calculated; and according to the variation of the instantaneous frequency, the stratum thickness variation is analyzed. According to the earthquake stratum thickness variation analysis method, a triple B spline is adopted as an interpolating function in the empirical mode decomposing process; the instantaneous frequency is calculated by using an instantaneous frequency calculation method with a damping factor on the basis of continuous wavelet transform; the obtained intrinsic mode function and instantaneous frequency profile have good lateral continuity and few false appearances, accord with the reality and also have good noise immunity. The earthquake stratum thickness variation analysis method is favorable for improvement of the reliability and the effectiveness of the earthquake stratum thickness variation analysis, is suitable for processing and explaining practical earthquake data, provides a powerful basis for predicting a reservoir stratum, and improves the precision of oil-gas field exploration and development.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
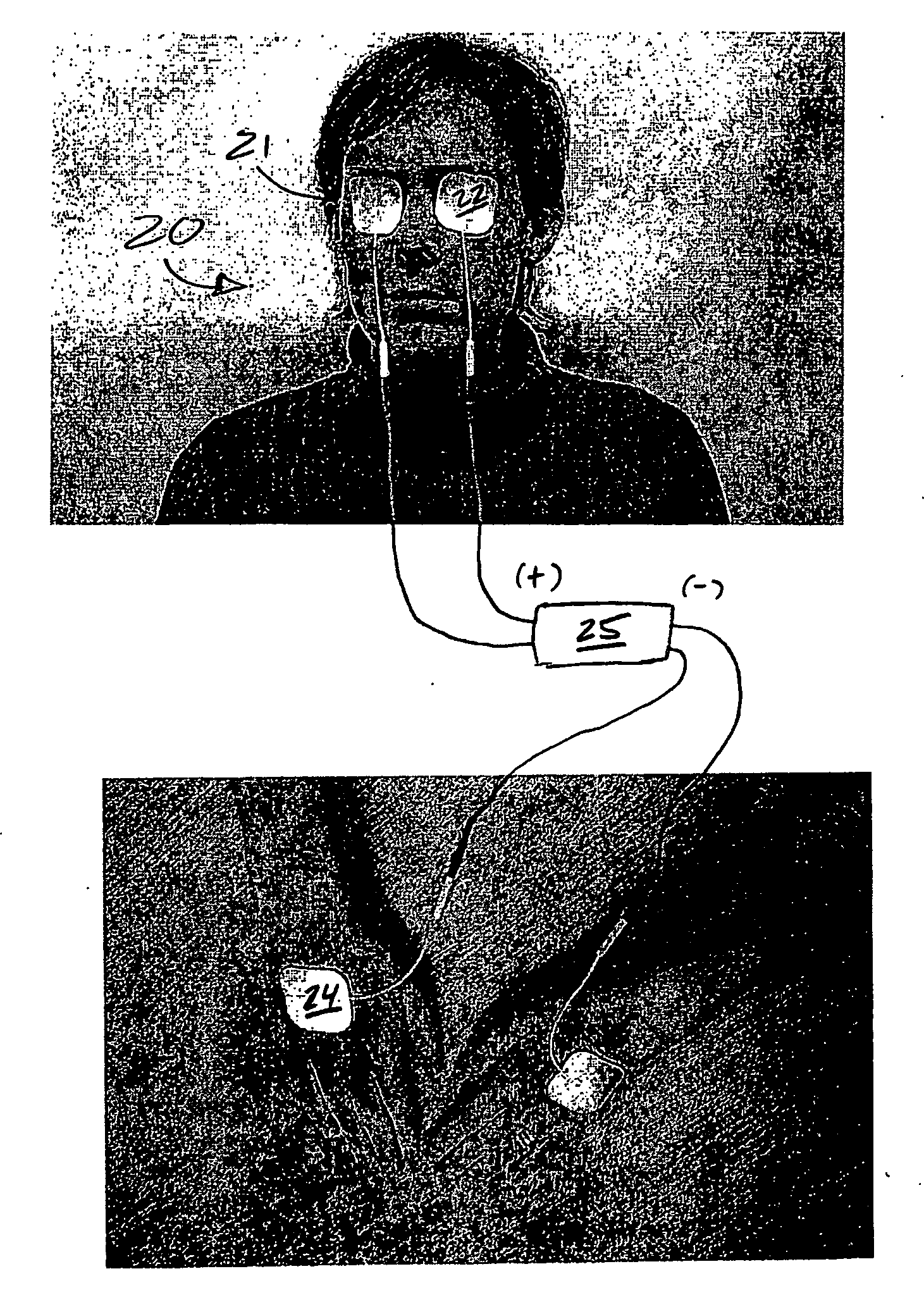
Treatment of vision disorders using electrical, light, and/or sound energy
ActiveUS20060217783A1Restore visionSafe, improved, noninvasive method for the restoration of visionElectrotherapyLight therapySound energyLight energy
A non-invasive ocular therapy for vision disorders is provided. First and second electrodes of a direct current source are electrically contacted so as to deliver current to and / or about an area proximal one or more eyes of a subject. A direct electrical current of between about 1-800 microamps, at a resistance assumption of about 500 ohms, is generated between the electrodes for a preselected duration. Preferably, the direct electrical current is generated at a select frequency profile as a function of time, and with a carrier signal of about 10,000-12,000 hertz. Advantageously, the subject therapy is augmented via application of light energy to the eye(s), as well as by the application of infrasonic sound waves directly into eyes.
Owner:BIOVISICS MEDICAL INC
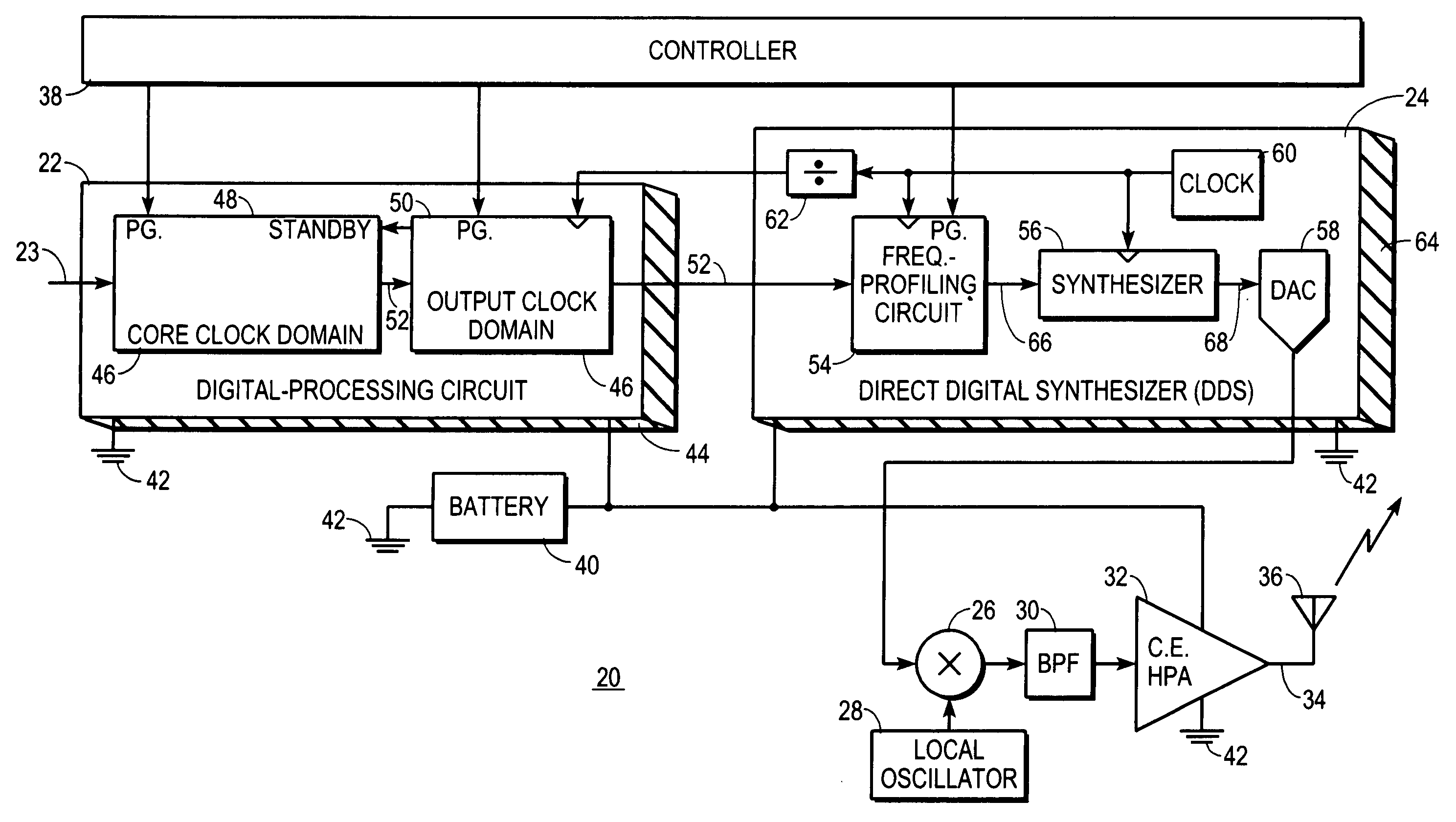
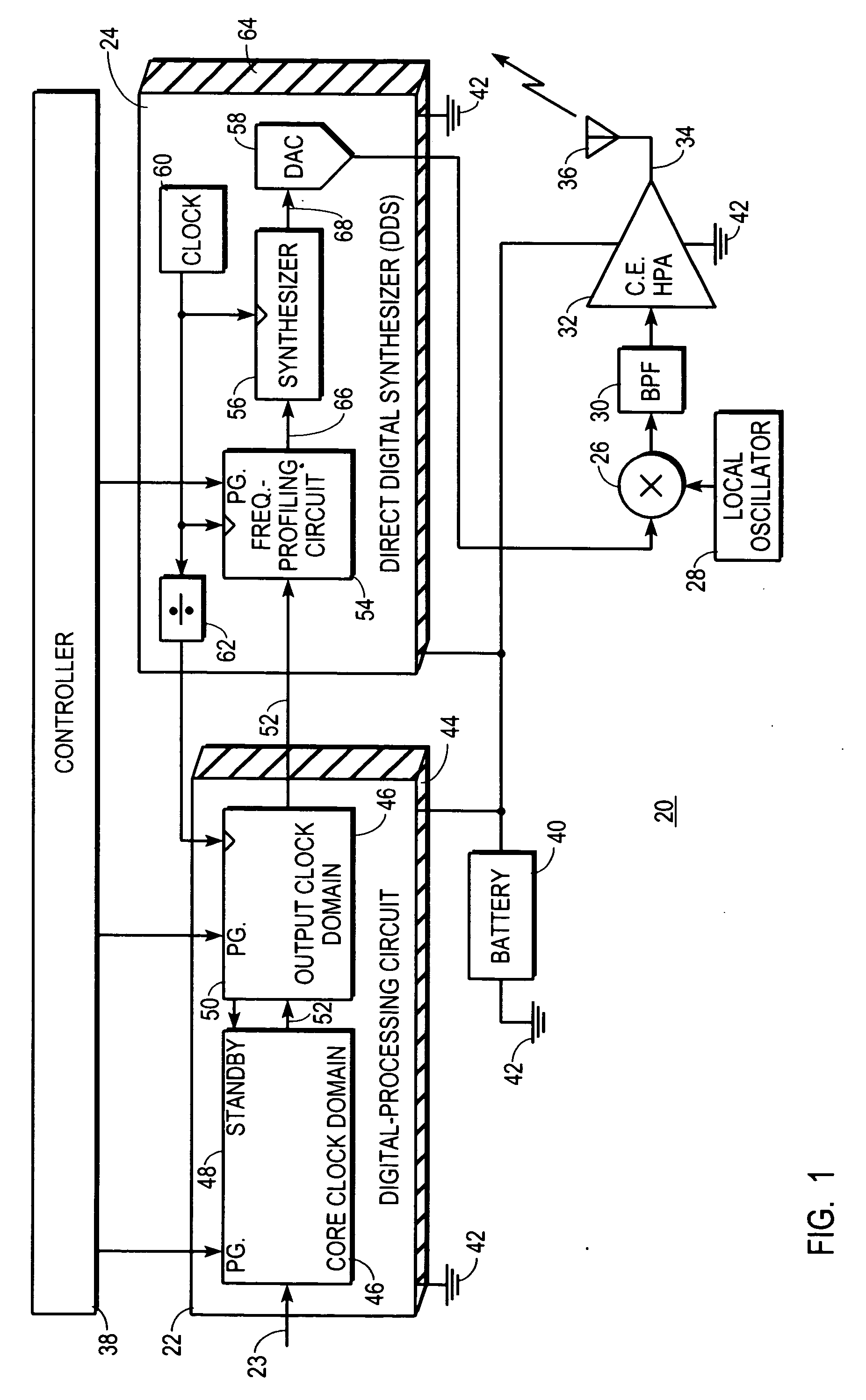
Digital communications transmitter with synthesizer-controlled modulation and method therefor
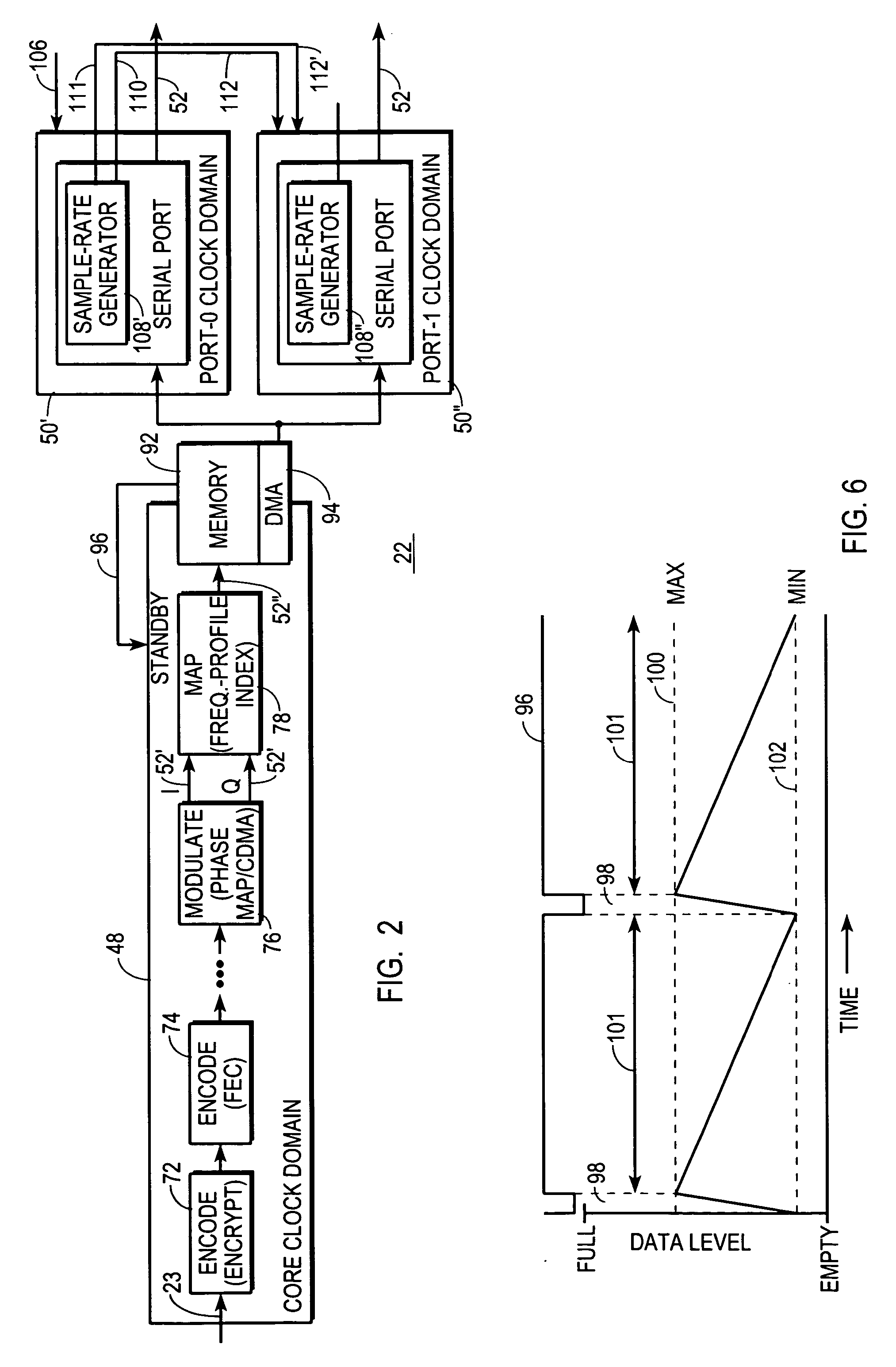
A low-power digital communications transmitter (20) includes a programmable digital-processing circuit (22), which may be provided by a digital signal processor (DSP), a programmable direct digital synthesizer (DDS), and a constant-envelope, high power amplifier (32). The DDS (24) is programmed to provide pulse-shaping and IF / RF signal modulation functions. The digital-processing circuit (22) produces only one sample per unit interval (134) and is programmed so that the one sample per unit interval (134) is a frequency-profile index symbol (52″) produced from a I,Q baseband symbol (52′). The DDS (24) converts each frequency-profile index symbol (52″) into a frequency profile (130) that controls the frequency of a synthesizer (56) to induce modulation into a periodic output (68) of the synthesizer. Moreover, the frequency profile (130) is configured to confine spectral emissions within a spectral mask (140).
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS C4 SYSTEMS
Methods and systems for signal selection
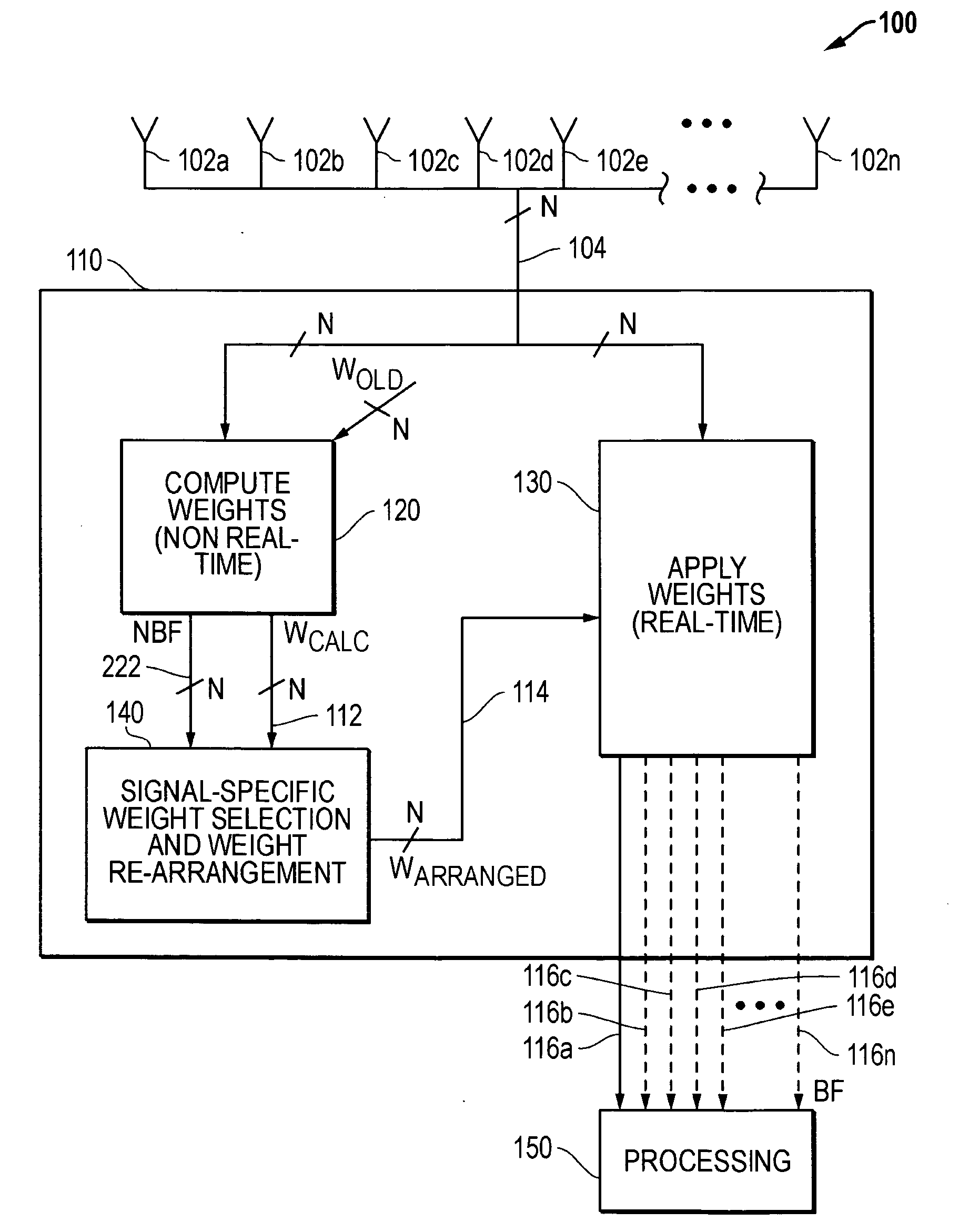
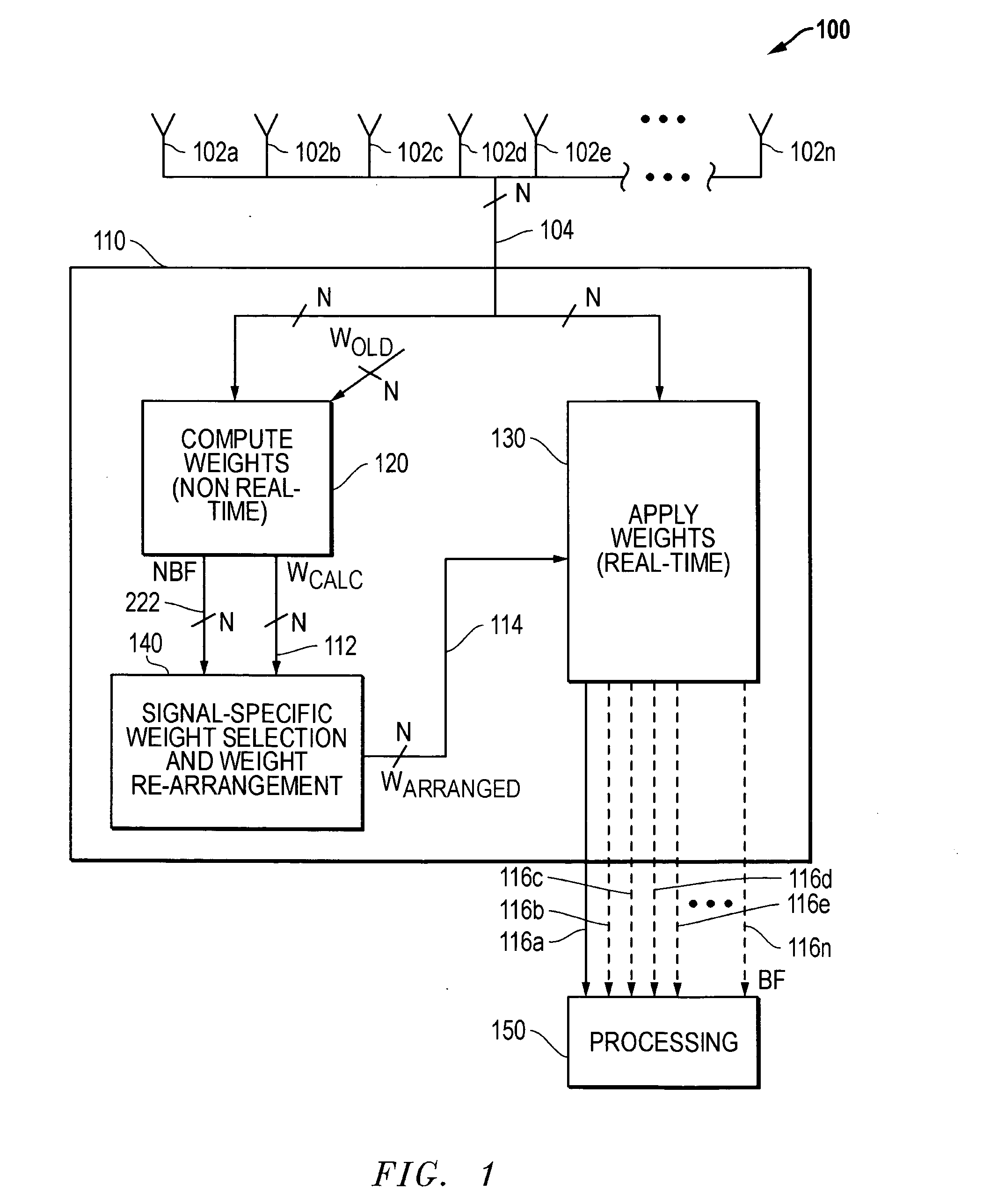
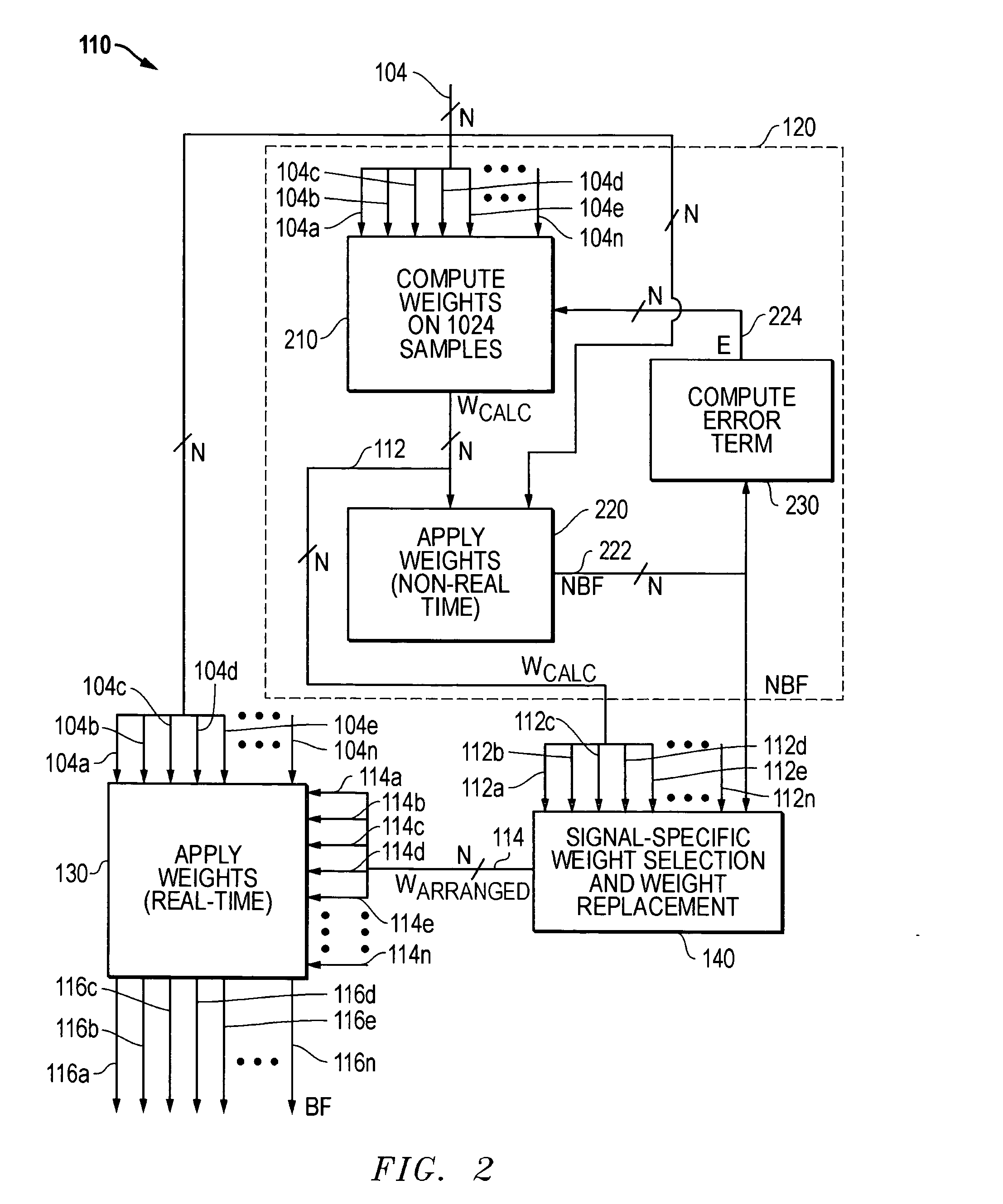
ActiveUS20080102764A1Reduces operational impactBig ratioDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSubstation equipmentTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A signal of interest (SOI) may be selected from among a plurality of cochannel signals based on one or more internal or external structural feature / s of the SOI, e.g., automatically selected based on any one or more internal or external structural features of the SOI that is known a priori. Examples of such internal structural features include, but are not limited to, number, frequency and / or absolute or relative signal strength (signal to noise ratio) of one or more transmitted signal components (e.g., pilot tones, squelch tones, etc.) present in the SOI; absence of a signal component at a given frequency in the SOI (i.e., present as a “dead spot” at a given frequency within the SOI); signal strength versus frequency profile of the SOI, signal strength versus time domain profile of the SOI, transient characteristics, time versus frequency profile, etc.
Owner:L3HARRIS TECH INTEGRATED SYST LP +1
Methods and systems for signal selection
ActiveUS7885688B2Reduces operational impactBig ratioDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSubstation equipmentTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:L3HARRIS TECH INTEGRATED SYST LP +1
Fault detection for bearings
ActiveUS20160327452A1Machine bearings testingConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEngineeringFrequency profile
A fault detection system is disclosed for predicting bearing failure in a system with a bearing-supported shaft. A position sensor may sense a position of the shaft as the shaft rotates. A controller may receive, from the position sensor, position data indicating a plurality of sensed positions of the shaft. The controller may determine a position or velocity profile for the shaft based upon the received position data and may determine a frequency profile based upon the position or velocity profile. The controller may identify a characteristic of the frequency profile, and identify an expected bearing failure based upon the identified characteristic.
Owner:DEERE & CO
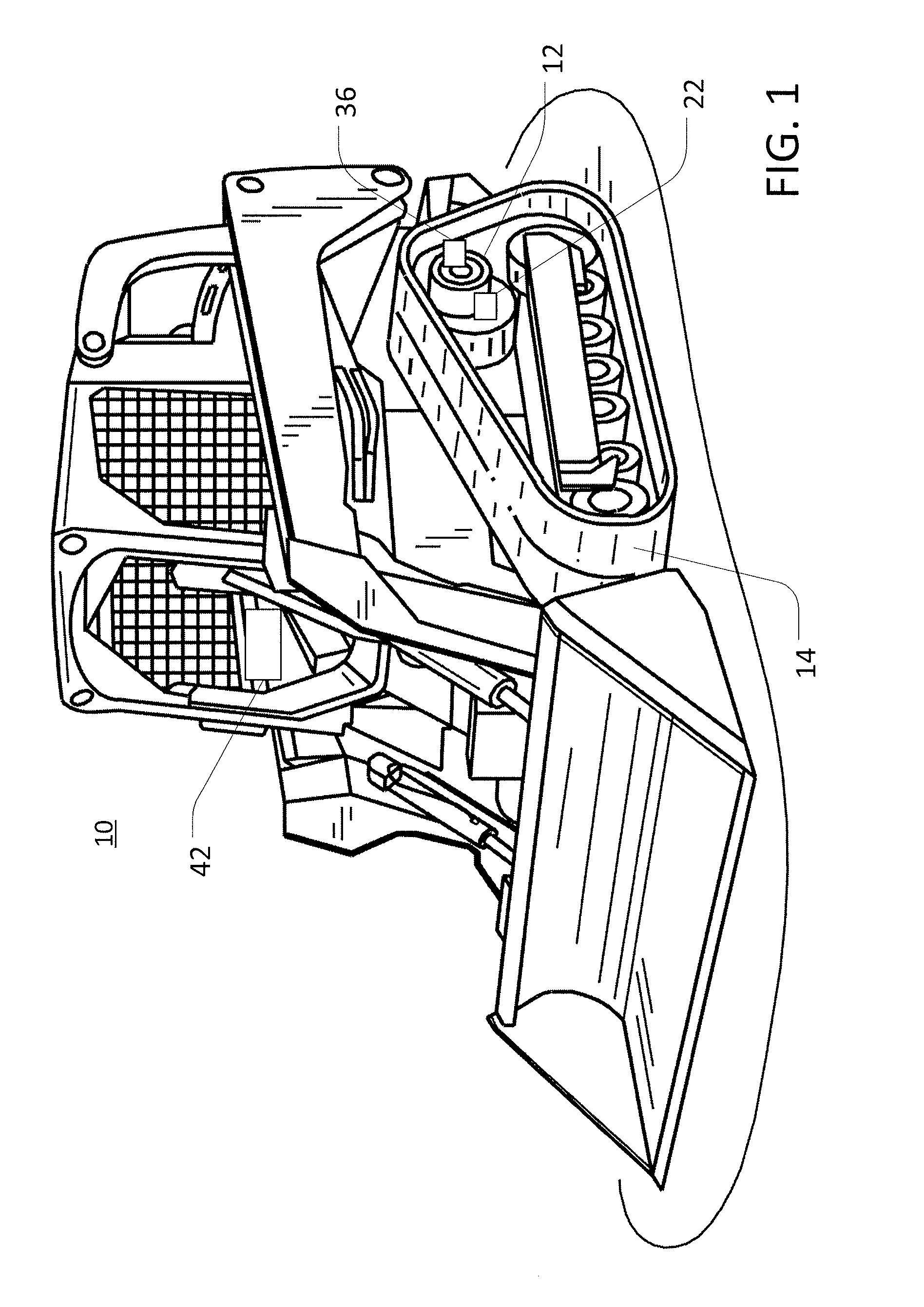
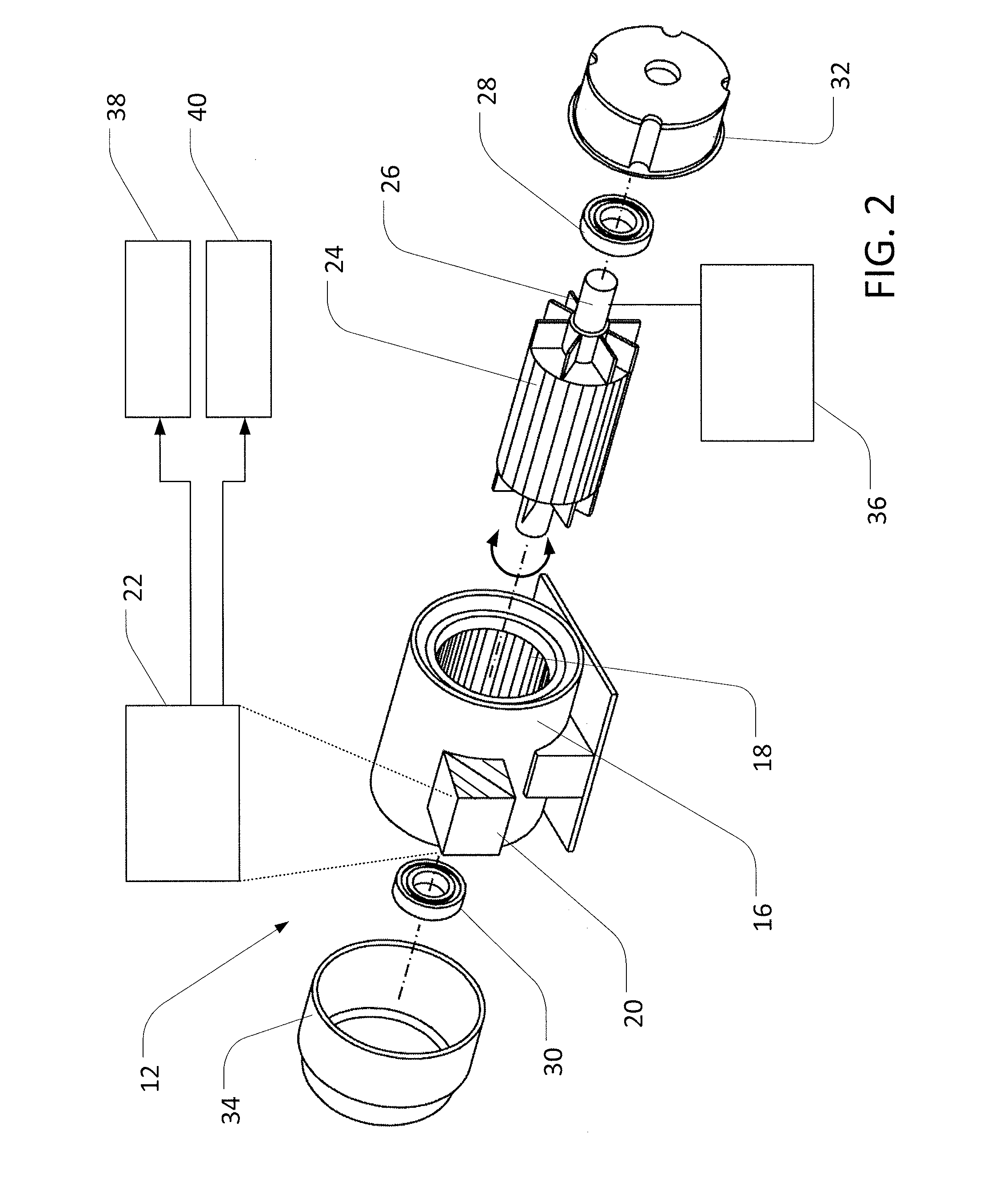
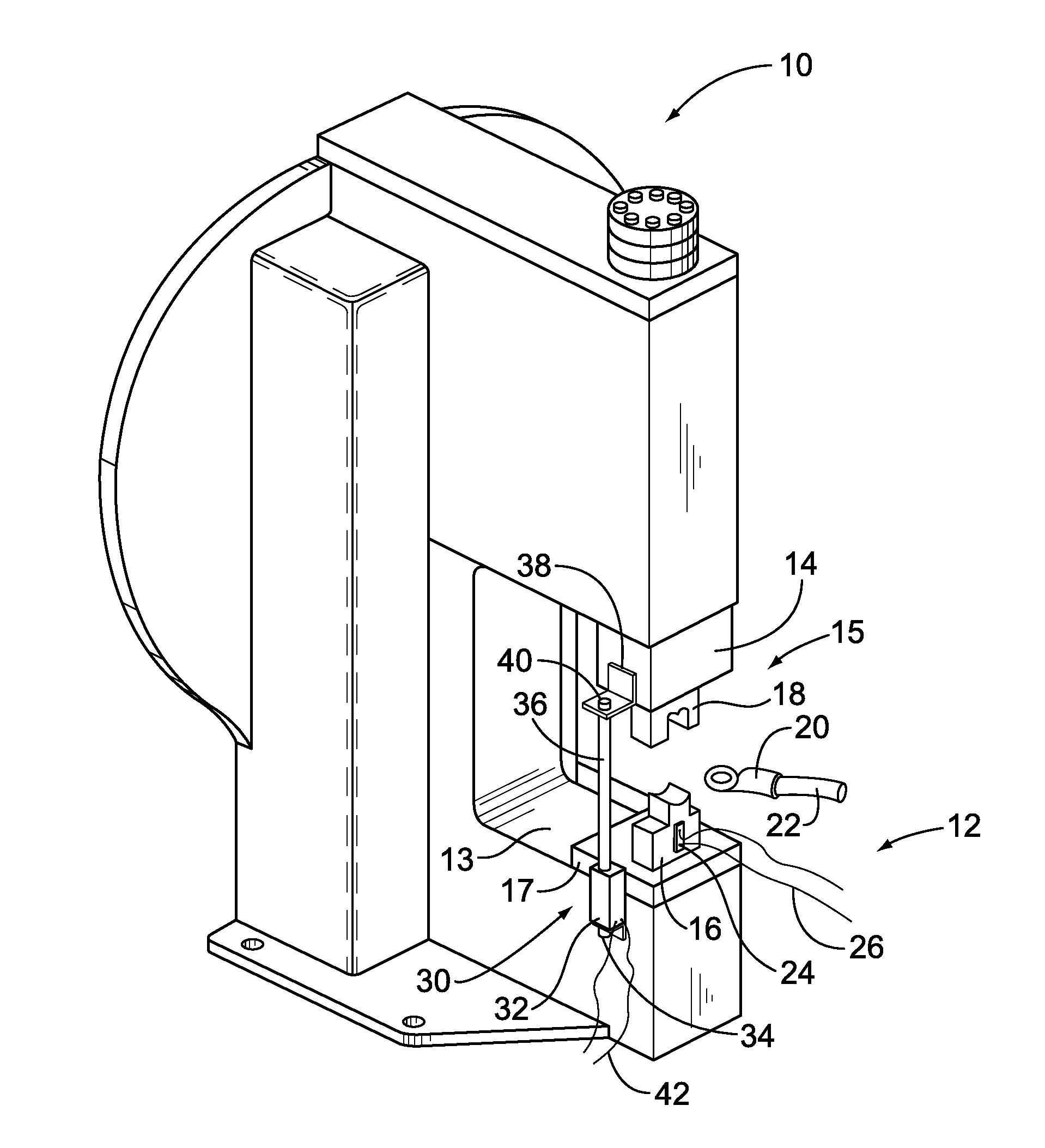
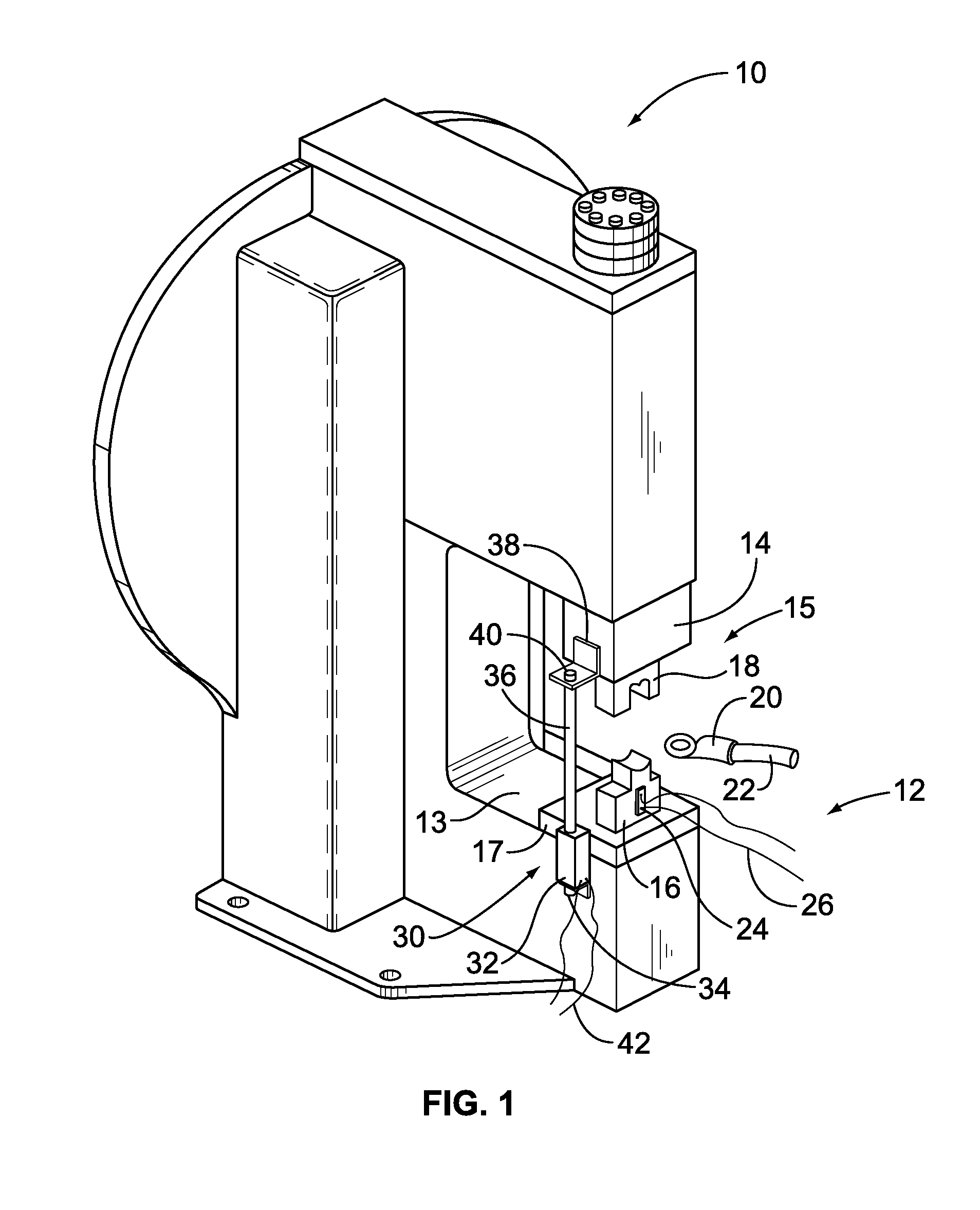
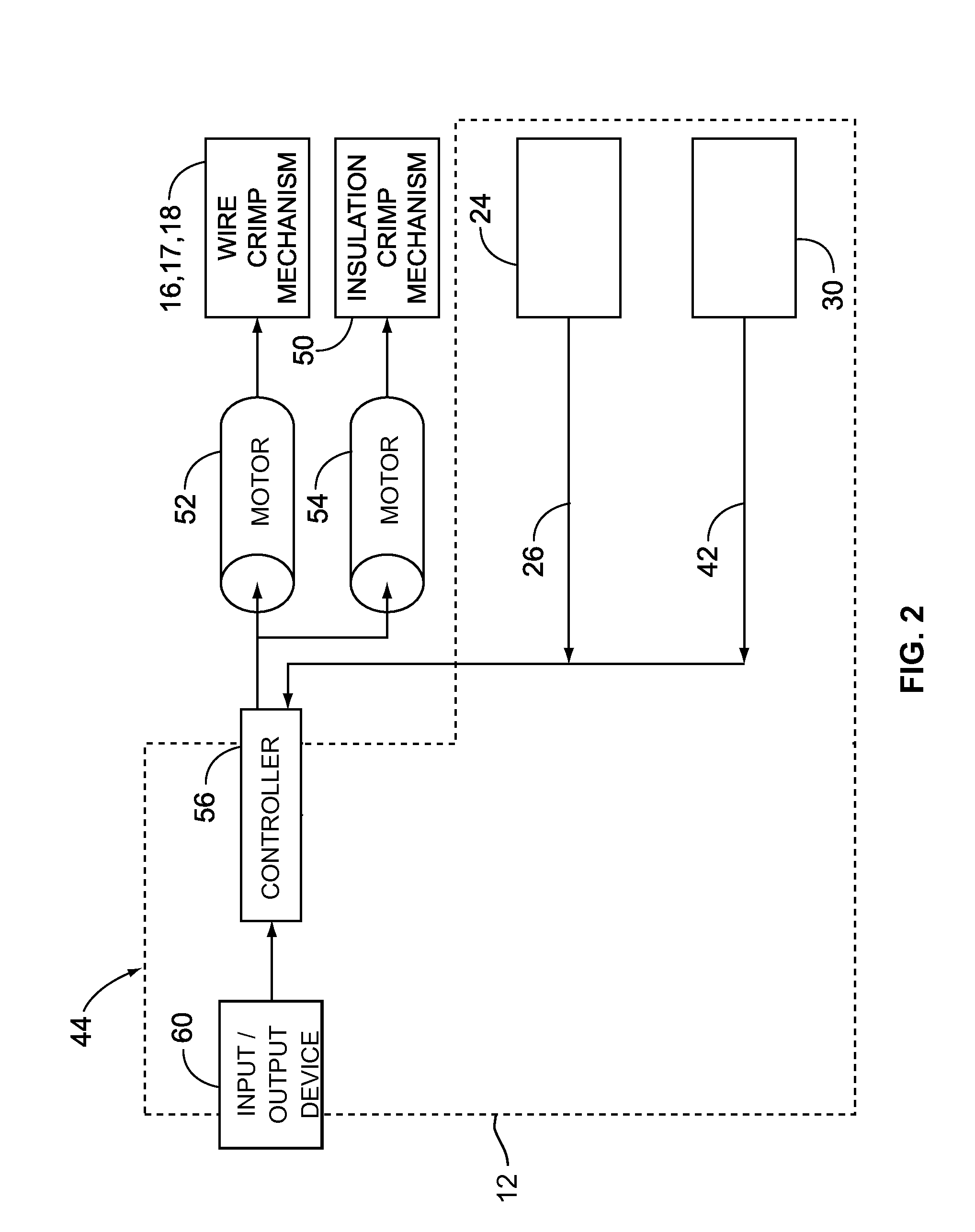
Crimping apparatus having a crimp quality monitoring system
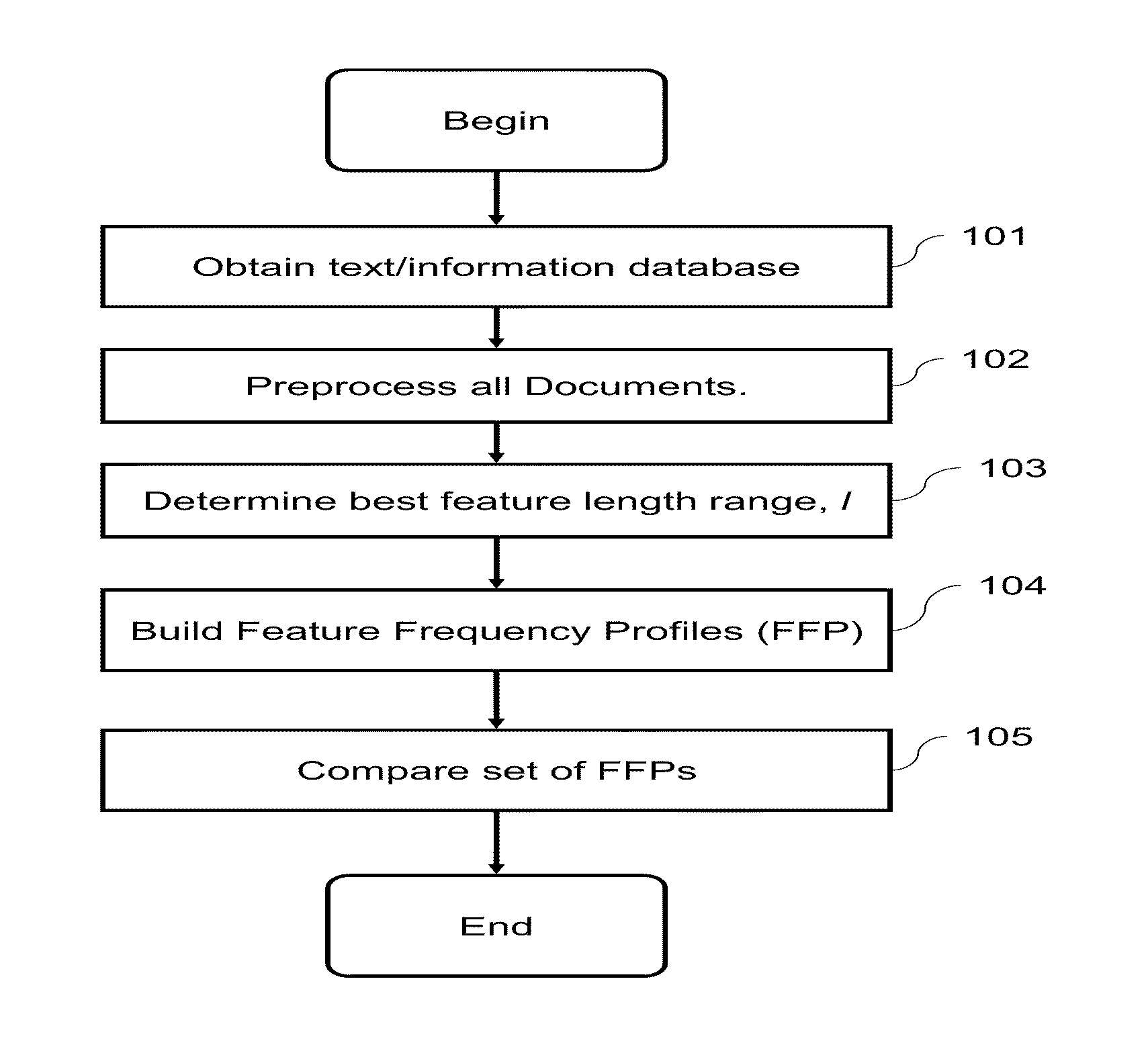
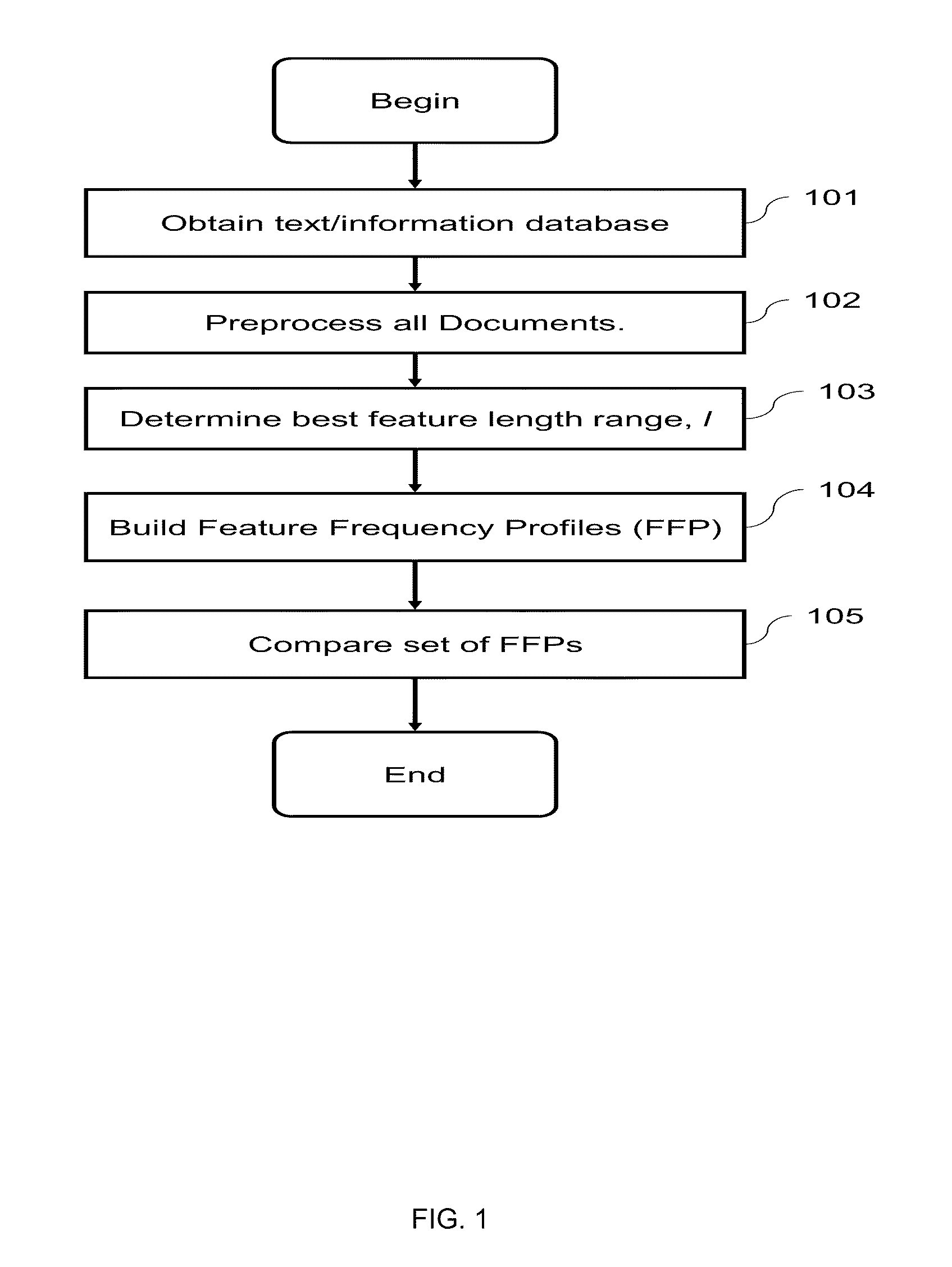
ActiveUS20120137486A1Line/current collector detailsAutomatic control devicesFast Fourier transformEngineering
A crimping apparatus includes a ram having crimp tooling for crimping a terminal to a wire during a crimp stroke and a force sensor detecting a crimp force during the crimp stroke. The crimping apparatus also includes a controller that monitors the crimp quality of a crimp based on a frequency profile of the crimp. Optionally, the controller may create the frequency profile based on a force profile using a frequency transform algorithm. The frequency transform algorithm may be a Fast Fourier Transform algorithm.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Identifying layout pattern candidates
A method, system or computer usable program product for automatically identifying layout pattern candidates in selected regions for use in analyzing semiconductor device performance issues including identifying a set of target regions and a set of reference regions from a design layout; utilizing a processor to generate a reference baseline of layout patterns from the set of reference regions; utilizing the processor to compare a frequency profile of layout patterns in the set of target regions to a frequency profile of layout patterns in the reference baseline; and based on the comparison, utilizing the processor to identify candidate layout patterns from the set of target regions for further analysis.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Object detection apparatus, object detection method, object detection program and device control system for moveable apparatus
An object detection apparatus mountable to a moveable apparatus for detecting an object existing outside the moveable apparatus by capturing a plurality of images using a plurality of imaging devices mounted to the moveable apparatus and generating a disparity image from the captured images includes a map generator to generate a map indicating a frequency profile of disparity values correlating a horizontal direction distance of the object with respect to a movement direction of the moveable apparatus, and a distance to the object in the movement direction of the moveable apparatus based on the disparity image, an isolated area detection unit to detect an isolated area based on the frequency profile, an isolated area divider to divide the isolated area into two or more isolated areas based on the frequency profile in the isolated area, and an object detector to detect an object based on the divided isolated area.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and system for measuring the impedance of the power distribution network in programmable logic device applications
ActiveUS20130030741A1Low costReduce power consumptionResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingField programmable logic devicesProgrammable logic device
On-die measurement of power distribution impedance frequency profile of a programmable logic device (PLD), such as field programmable gate array (FPGA) or complex programmable logic device (CPLD), is performed by configuring and using only logic blocks resources commonly available in any existing programmable logic device, without the need of built-in dedicated circuits. All measurements are done inside the programmable logic device without the need of external instruments. The measurement method can be used during characterization to select decoupling capacitors or for troubleshooting existing systems, after which the programmable logic device may be reconfigured to perform any other user-defined function.
Owner:NOISECOUPLING LLC
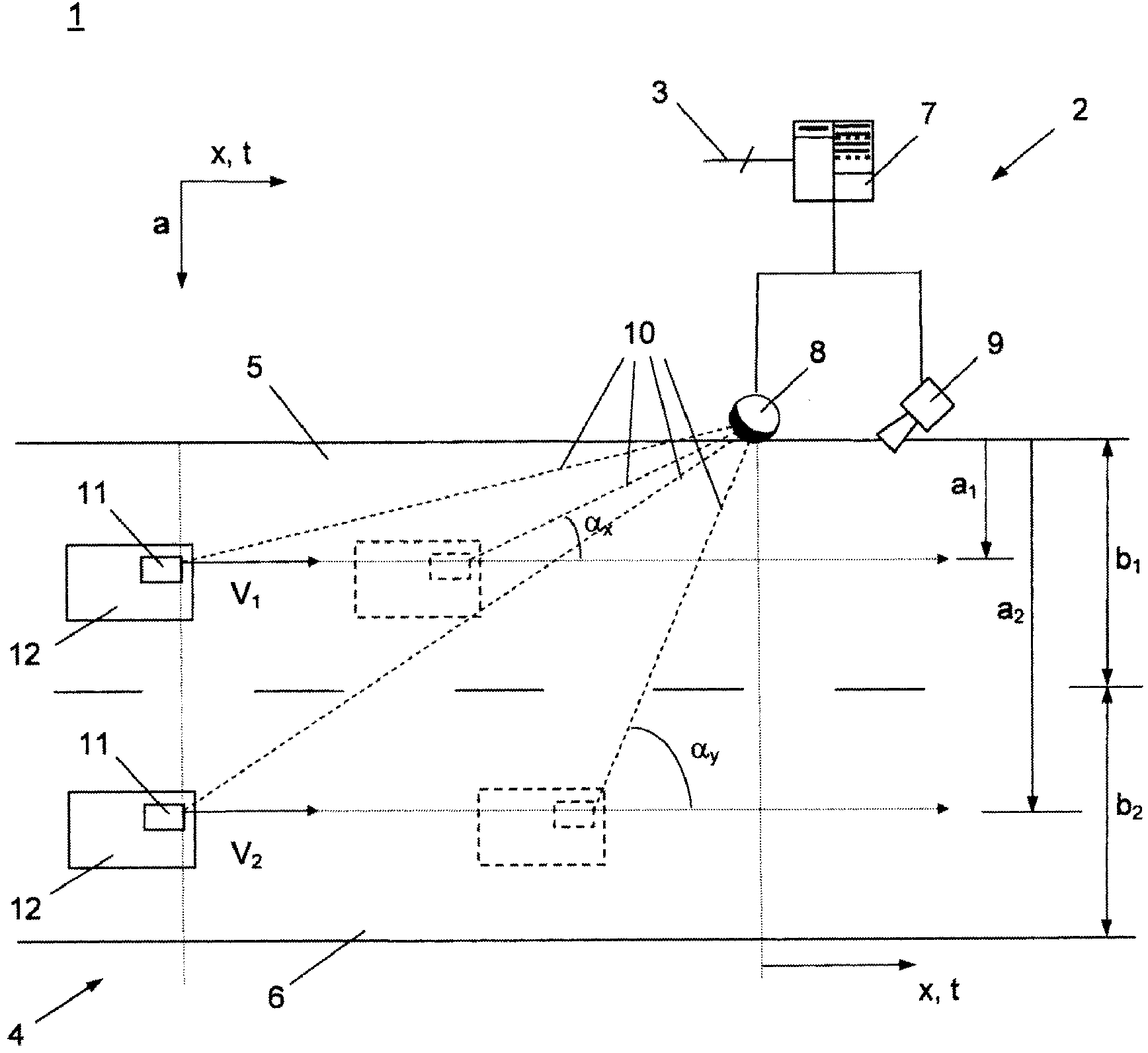
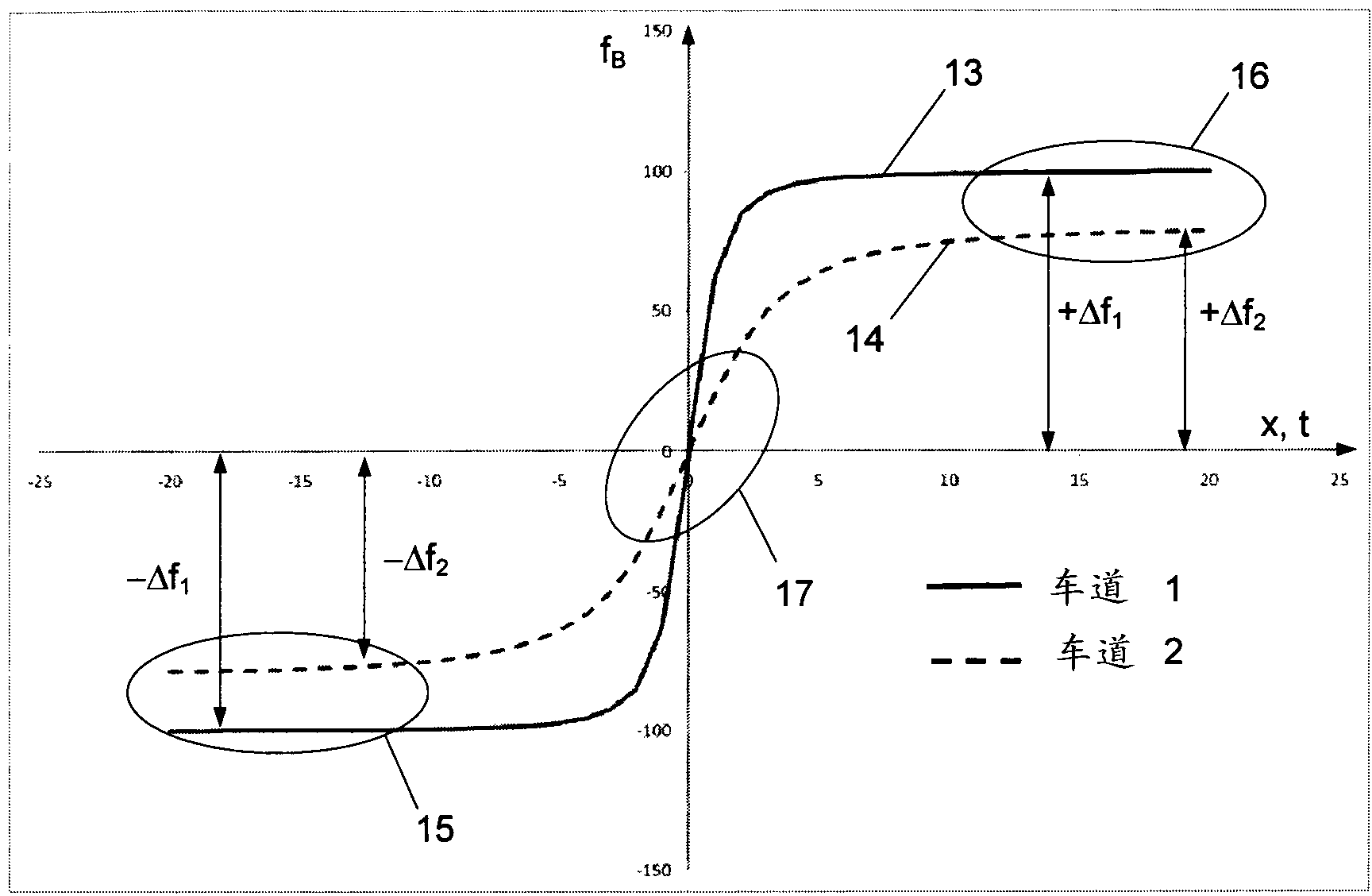
Method for determining the distance of a vehicle to a wireless beacon and apparatus for same
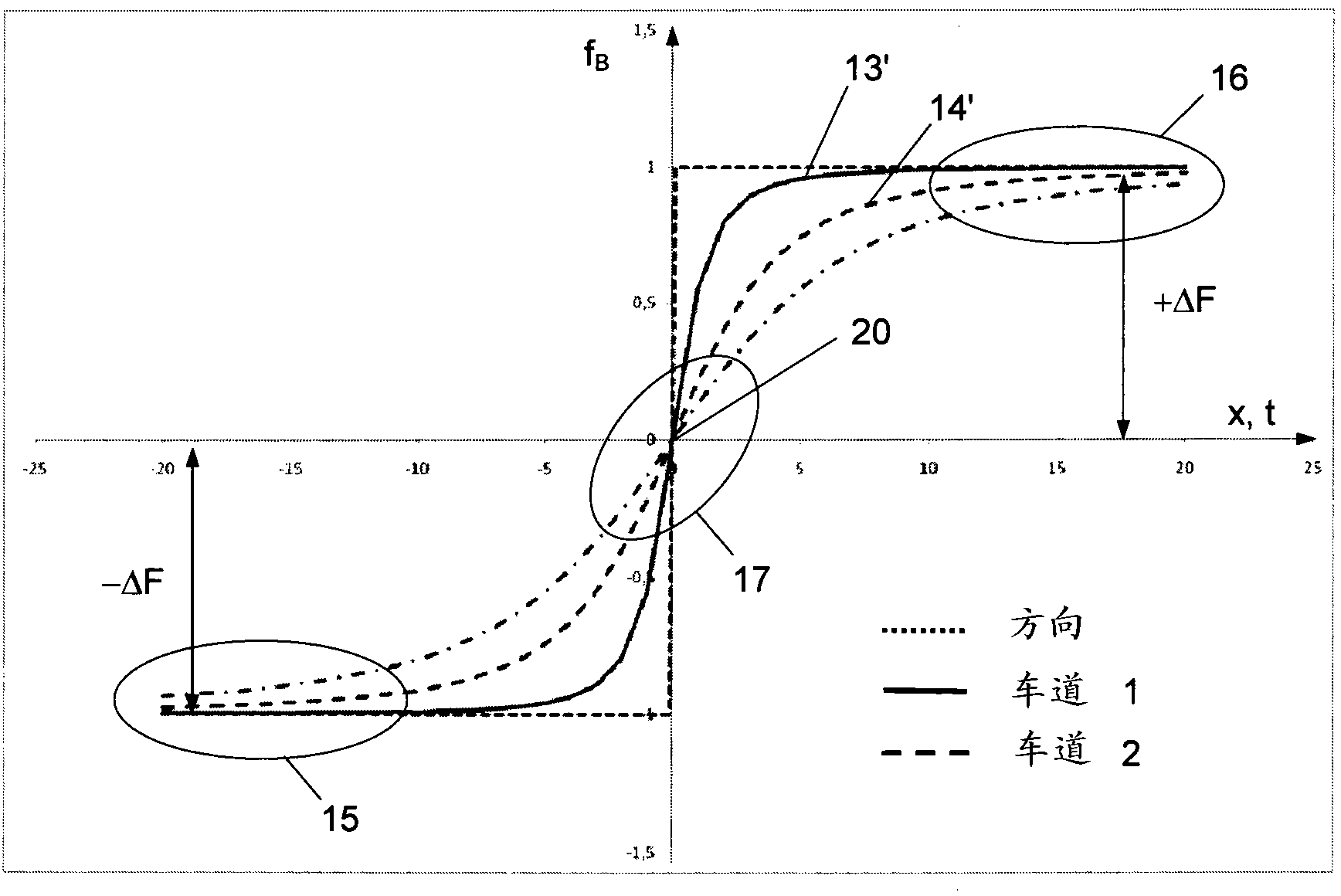
InactiveCN102933979AOmit differentialTicket-issuing apparatusDetection of traffic movementTelecommunicationsFrequency profile
The invention relates to a method for determining the distance (a) between a radio beacon (2) and a vehicle device (11) passing in front of said radio beacon, in a road toll system (1). A signal (10) of a frequency having a known temporal profile is emitted. Said method consists of the following steps: the signal is captured in the other component (2, 11) when passing and the temporal profile of the frequency is recorded in relation to the known temporal profile; a modification in the recorded frequency profile (13; 14) exceeding a first threshold value is detected; two distant wave zones in the frequency profile, lying temporally in front of and behind the detected modification, which displays a frequency modification below a second threshold value, are searched for; the recorded frequency profile is scaled in such a manner that the distance wave zones take the predetermined values; and said distance (a) from the scaled frequency path is determined. The invention also relates to radio beacons (2), installations and vehicle devices (11) for implementing the method.
Owner:KAPSCH TRAFFICCOM AG
System, method, and computer program product for simulating epicardial electrophysiology procedures
ActiveUS9218752B2Cost-effectiveOvercome limitationsSurgical instruments for heatingEducational modelsThoracic cavityIn vivo
An aspect of various systems and methods provides, but not limited thereto, novel means for simulating physiological systems and processes in vitro in order to test surgical devices and train practitioners in the use of surgical devices. An aspect of various embodiments further provides in vitro anatomical components, such as a thorax, lungs, heart and pericardium, configured to contain at least one fluid having a pressure-frequency profile that may mimic typical pressure-frequency waveforms of in vivo anatomical fluids. A model communication system may be used to communicate the desired pressure-frequency profiles to the in vitro anatomical fluids. In a further aspect of various embodiments, an access device, e.g. a surgical instrument, configured to sense pressure, frequency, and / or a pressure-frequency profile may be inserted into one or more anatomical components of the in vitro model in order to test the instrument and / or train a practitioner in proper use of the instrument. An access device communication system may be used to communicate data to the practitioner. This data may include, for example, pressure-frequency data and / or the location of a portion of the access device with respect to the various in vitro anatomical components.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
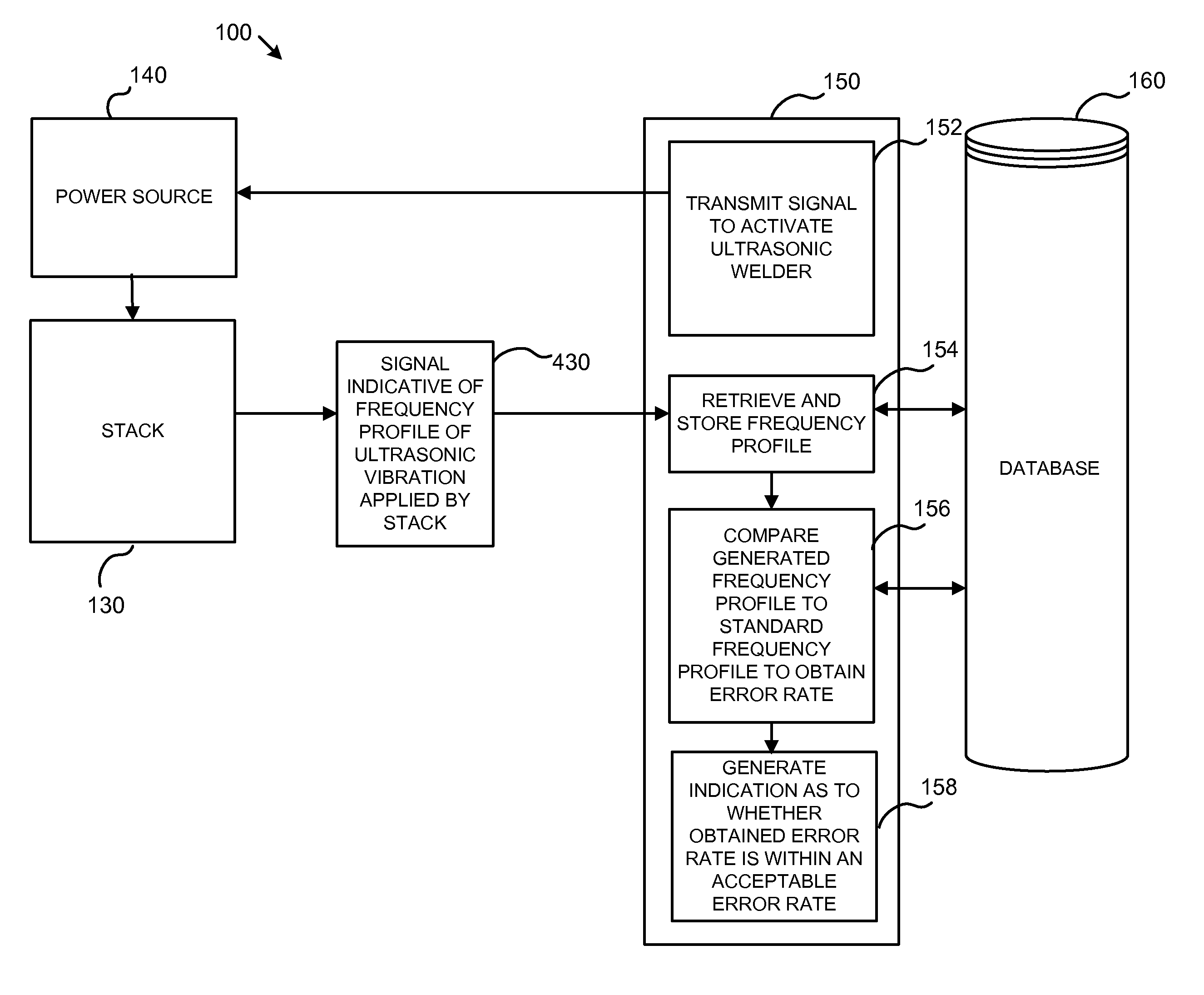
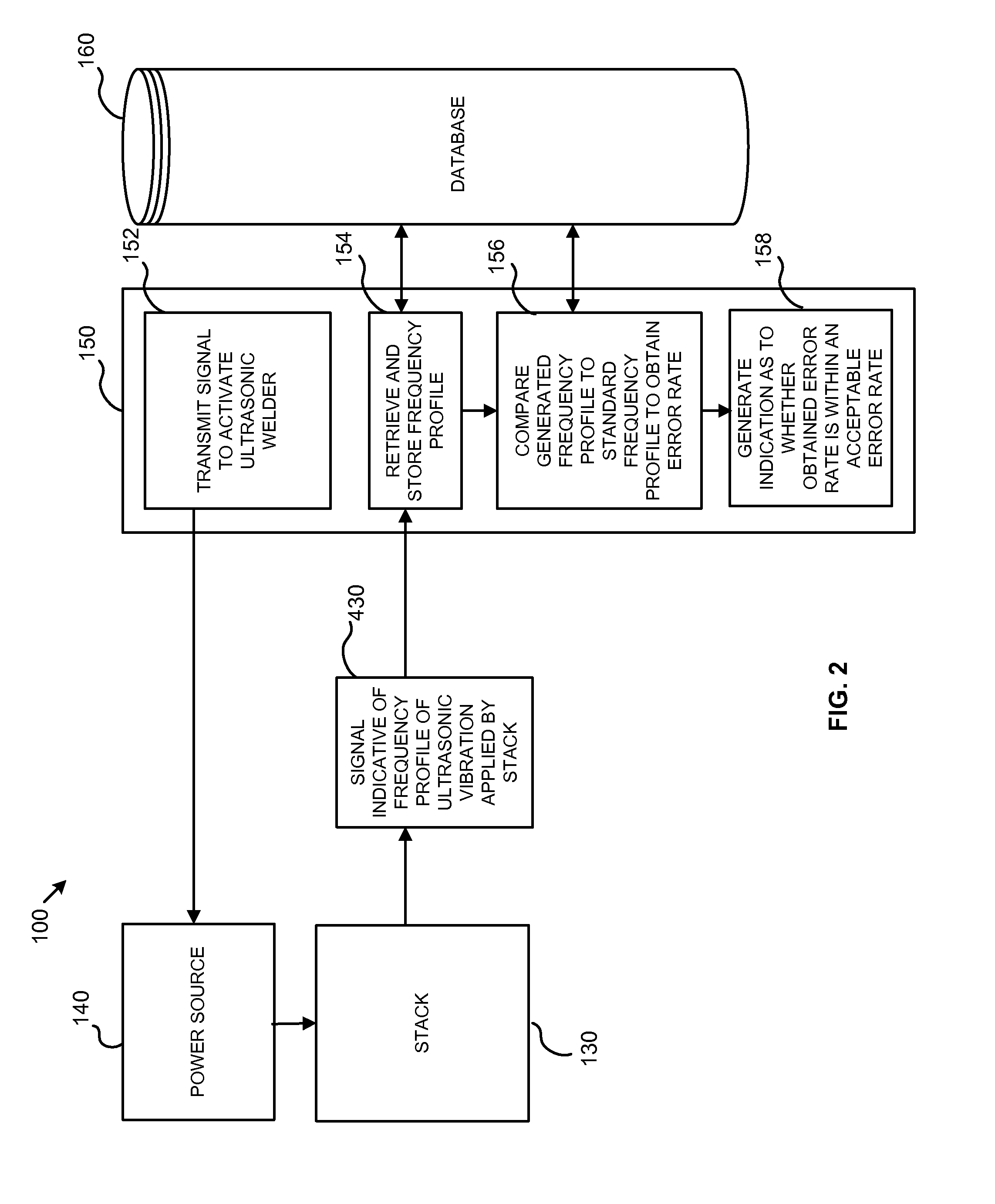
Diagnostic System and Method for Testing Integrity of Stack During Ultrasonic Welding
ActiveUS20150330952A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationUltrasonic weldingDiagnostic system
A method for testing the integrity of a stack during ultrasonic welding, includes the steps of: (i) ultrasonically welding two or more work pieces with a stack, the stack including a convertor and a horn; (ii) measuring a frequency profile based on a vibration of the horn during the welding step; and (iii) comparing the measured frequency profile to a standard frequency profile to obtain an error rate, the error rate being indicative of a difference between the measured frequency profile and the standard frequency profile. A system employing the aforementioned method is also provided.
Owner:SONICS & MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com