Patents
Literature
194 results about "Path protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
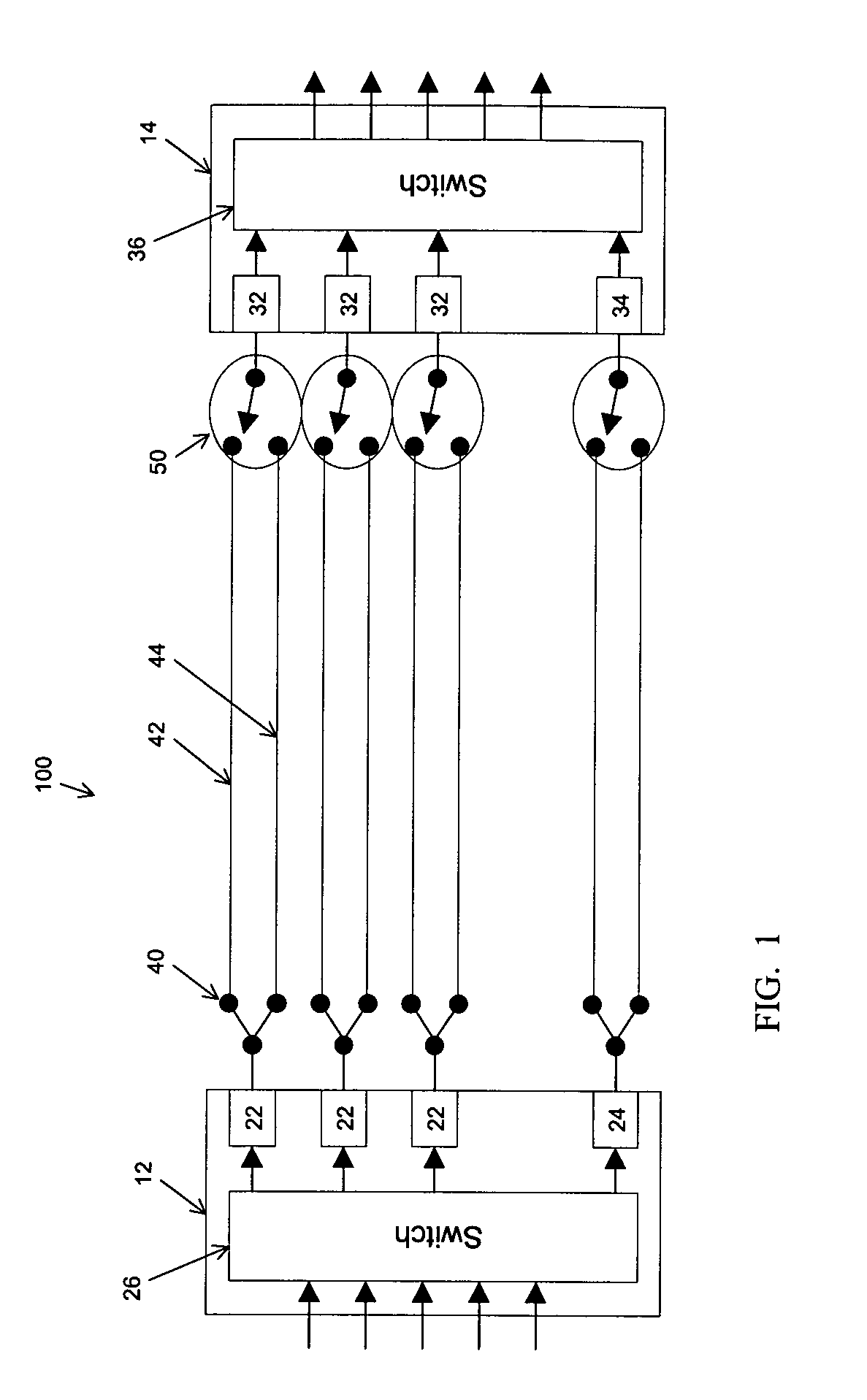
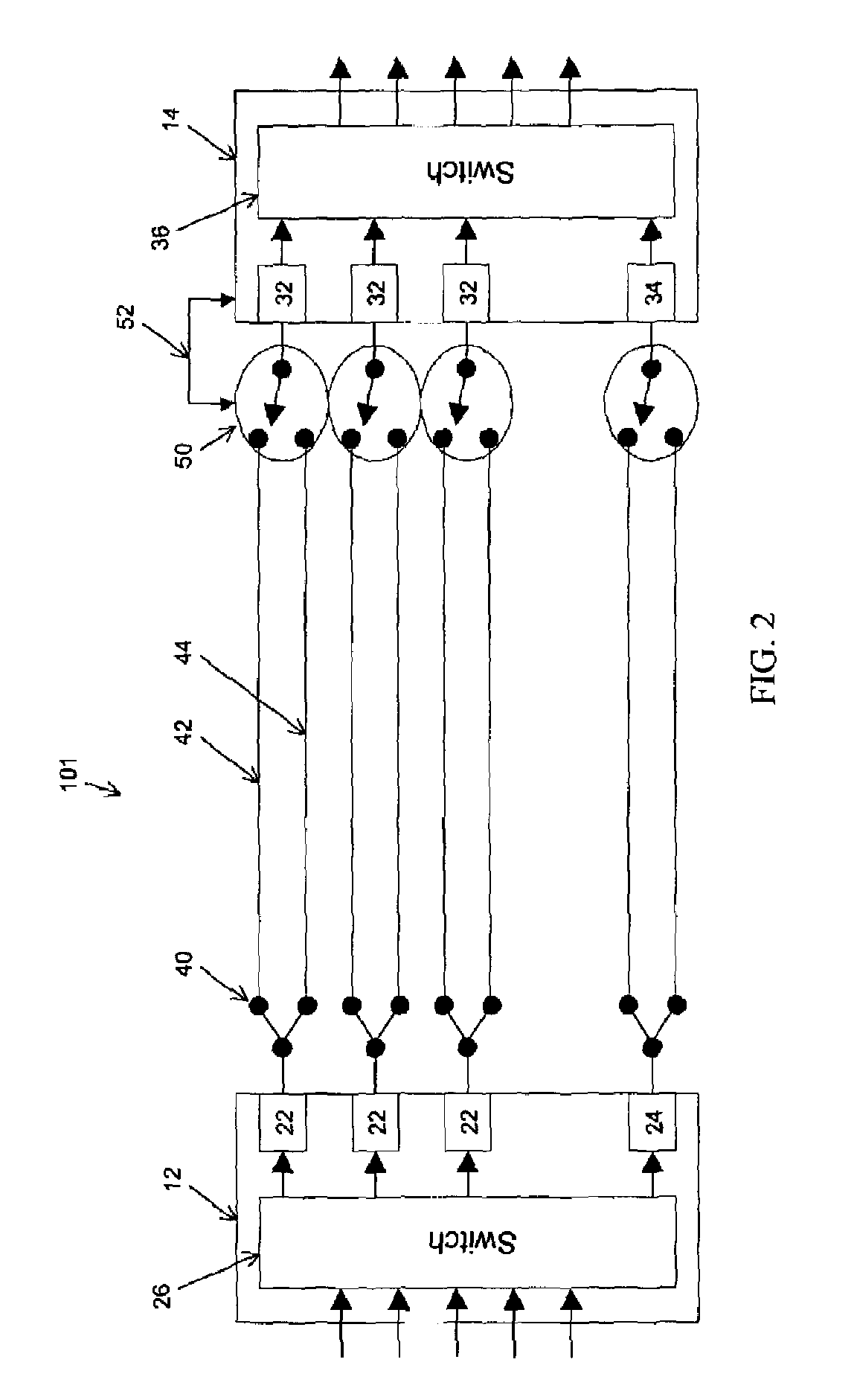
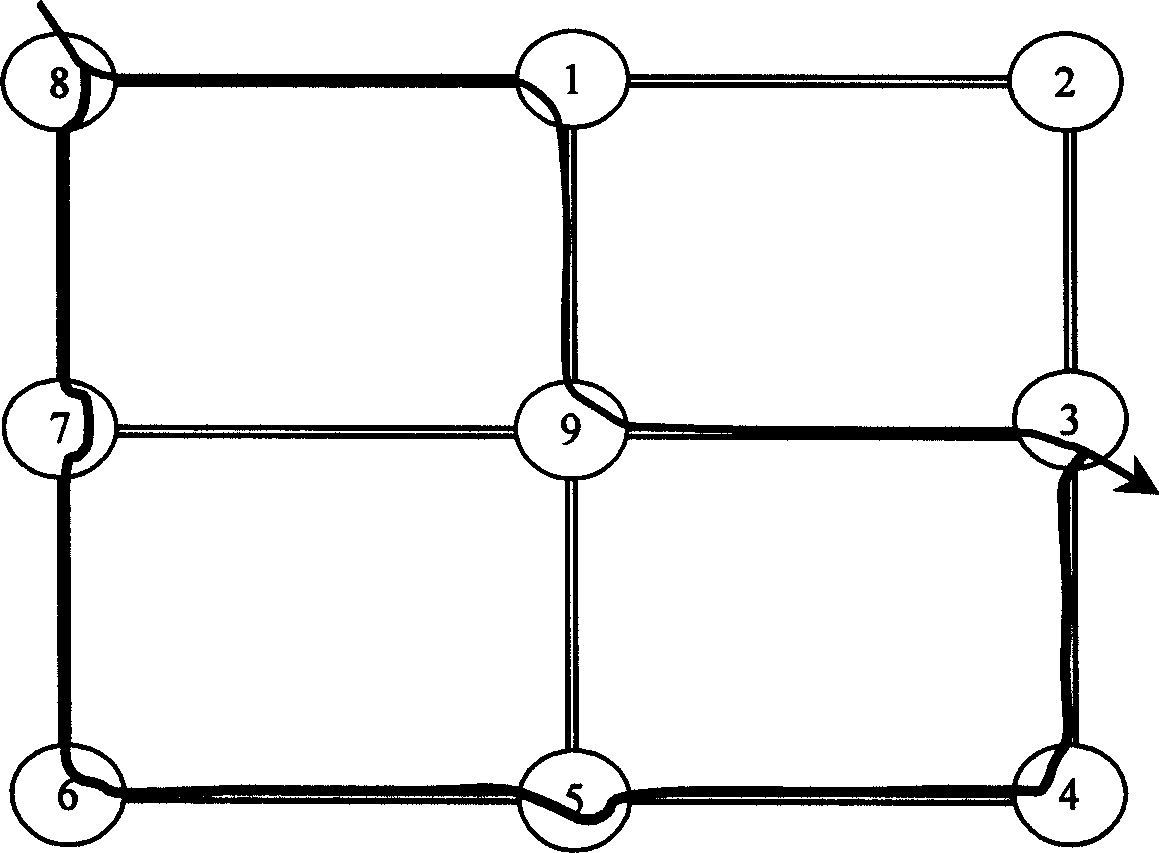
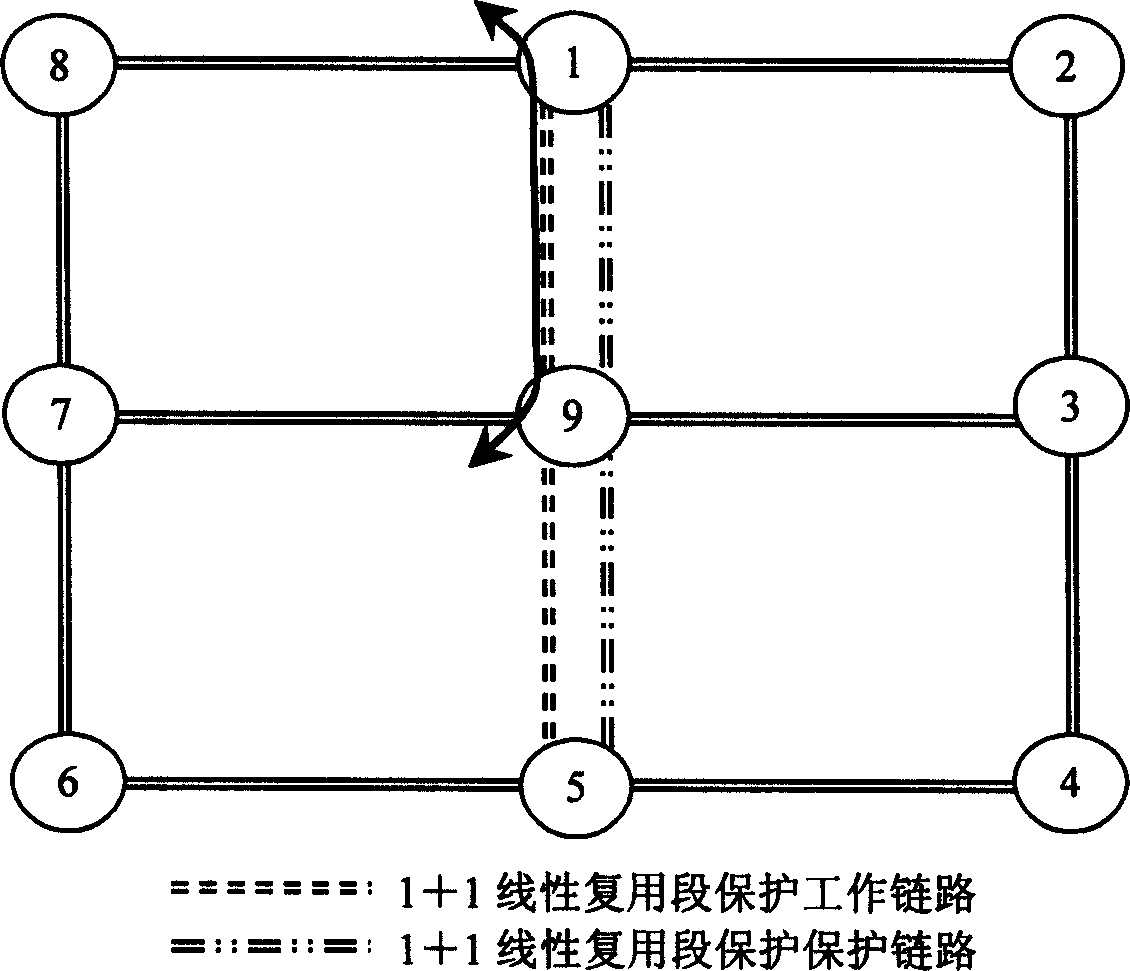
Path protection in telecommunications is an end-to-end protection scheme used in connection oriented circuits in different network architectures to protect against inevitable failures on service providers’ network that might affect the services offered to end customers. Any failure occurred at any point along the path of a circuit will cause the end nodes to move/pick the traffic to/from a new route. Finding paths with protection, especially in elastic optical networks, was considered a difficult problem, but an efficient and optimal algorithm was proposed .
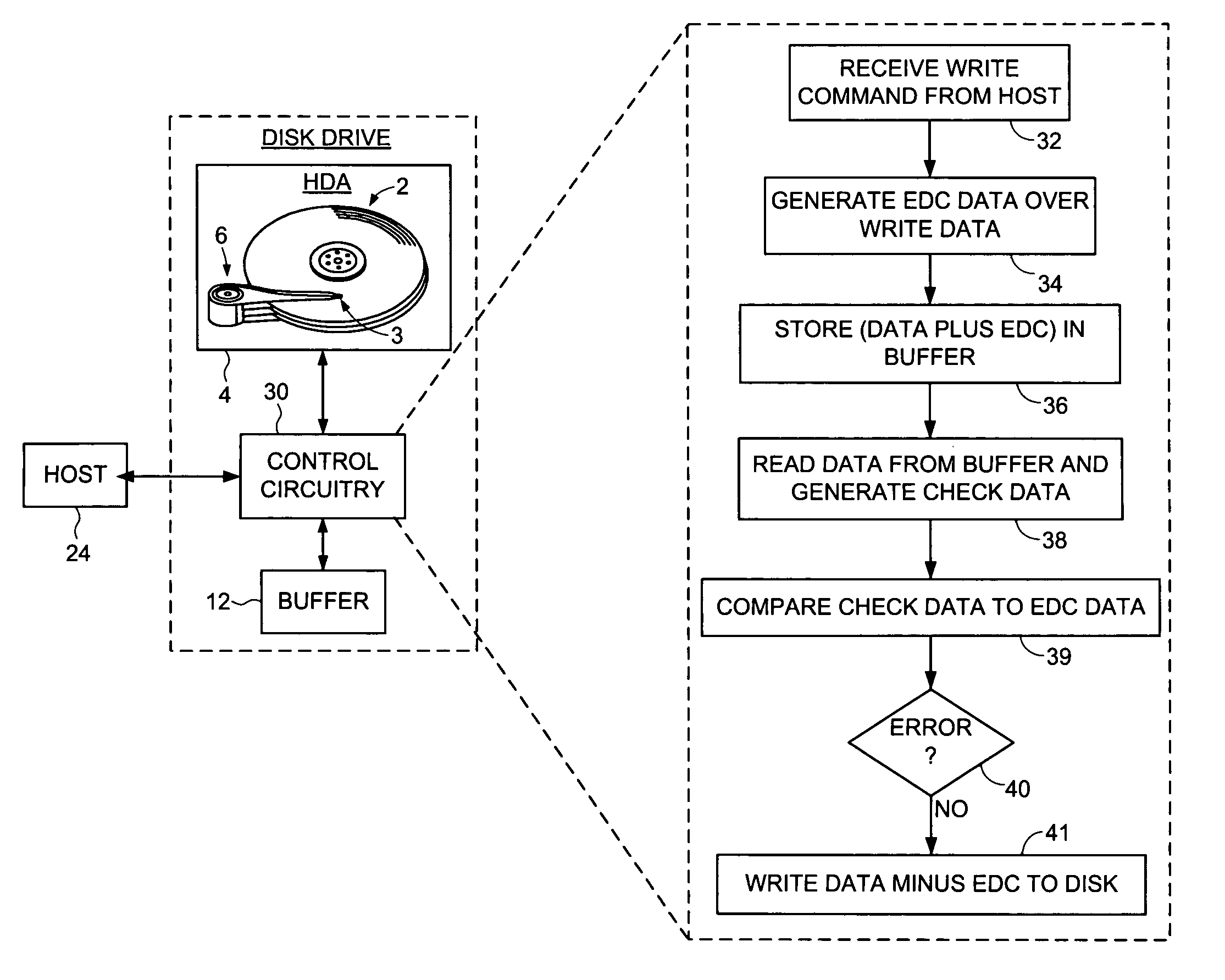
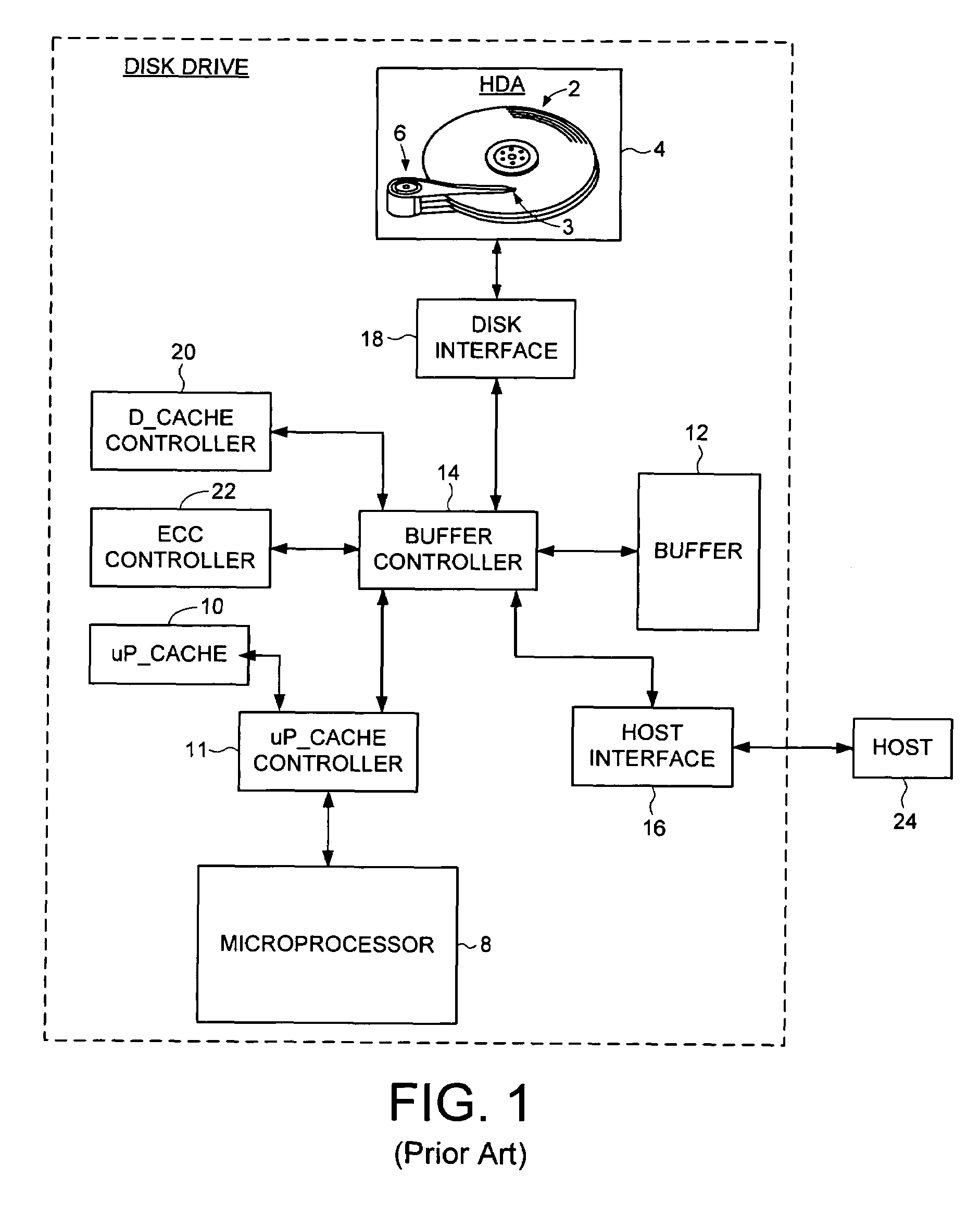
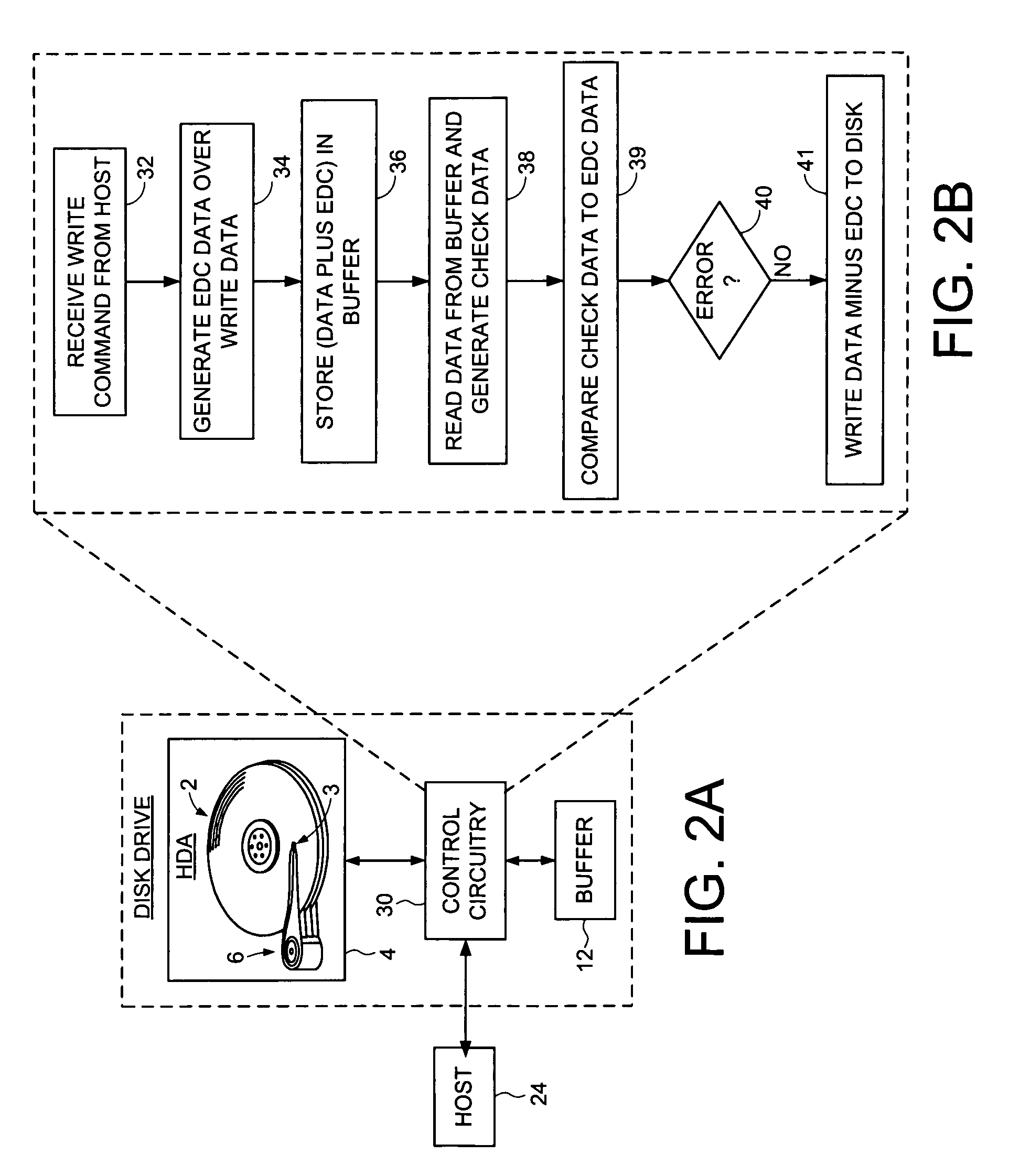
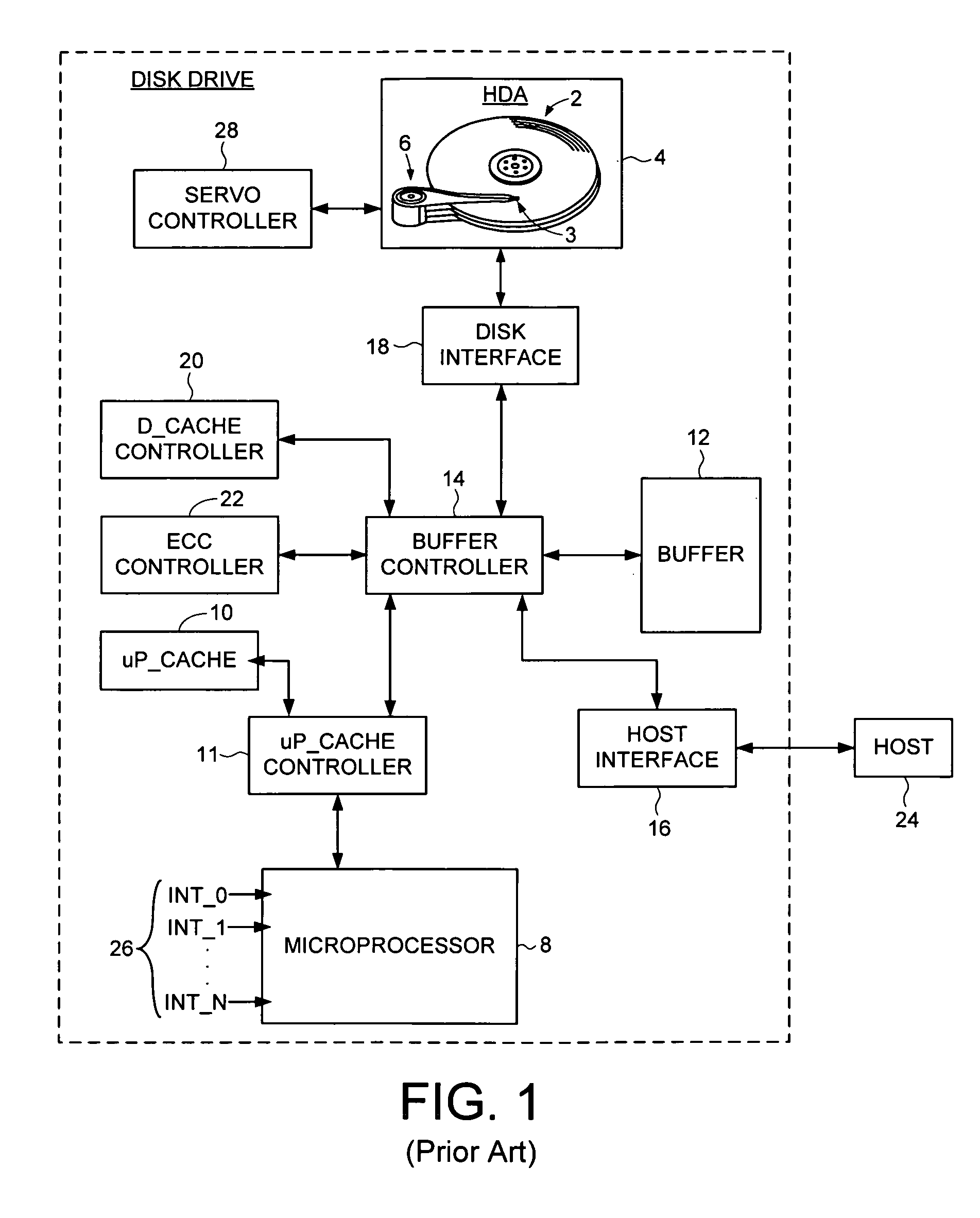
Disk drive implementing data path protection without writing the error detection code data to the disk
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
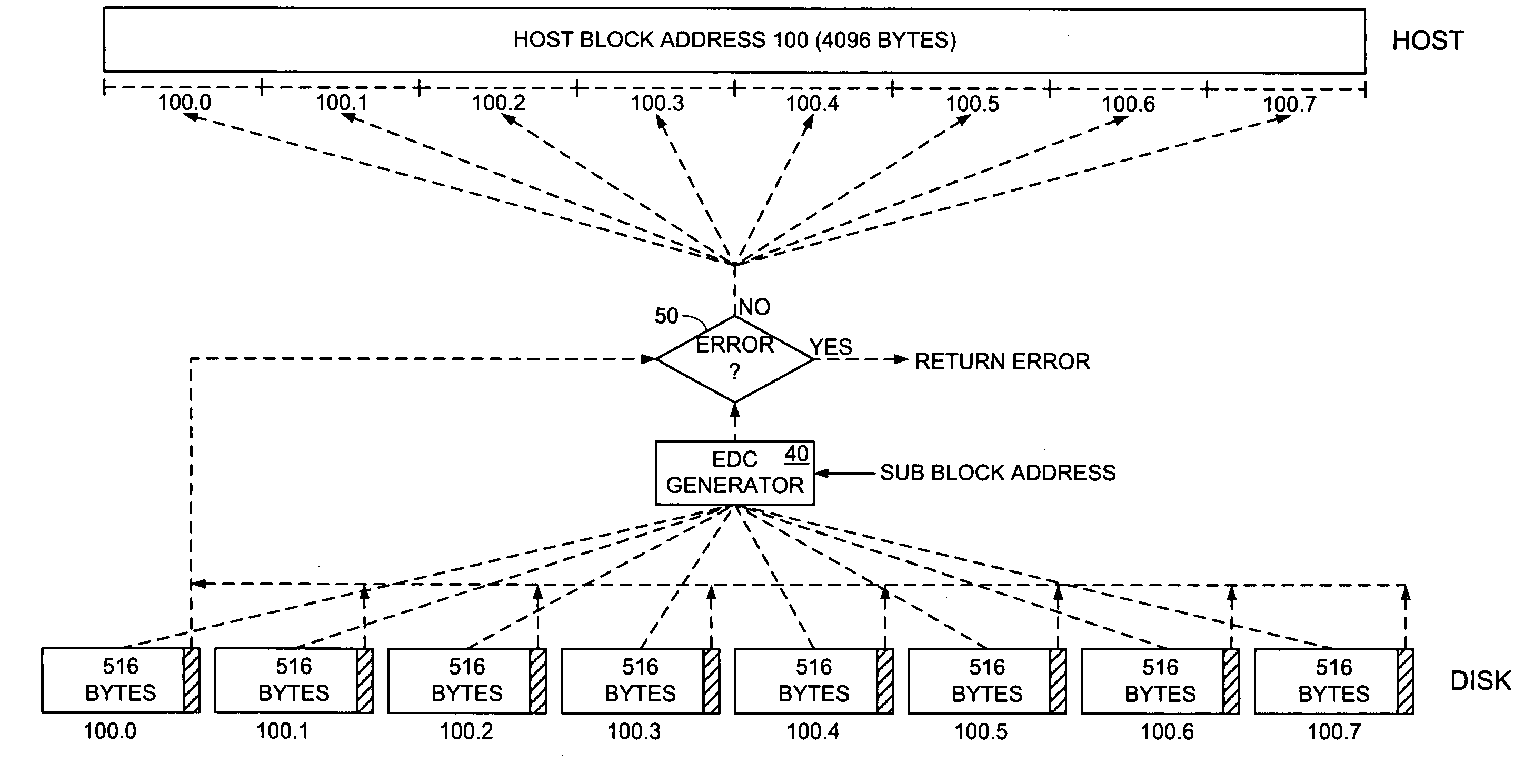
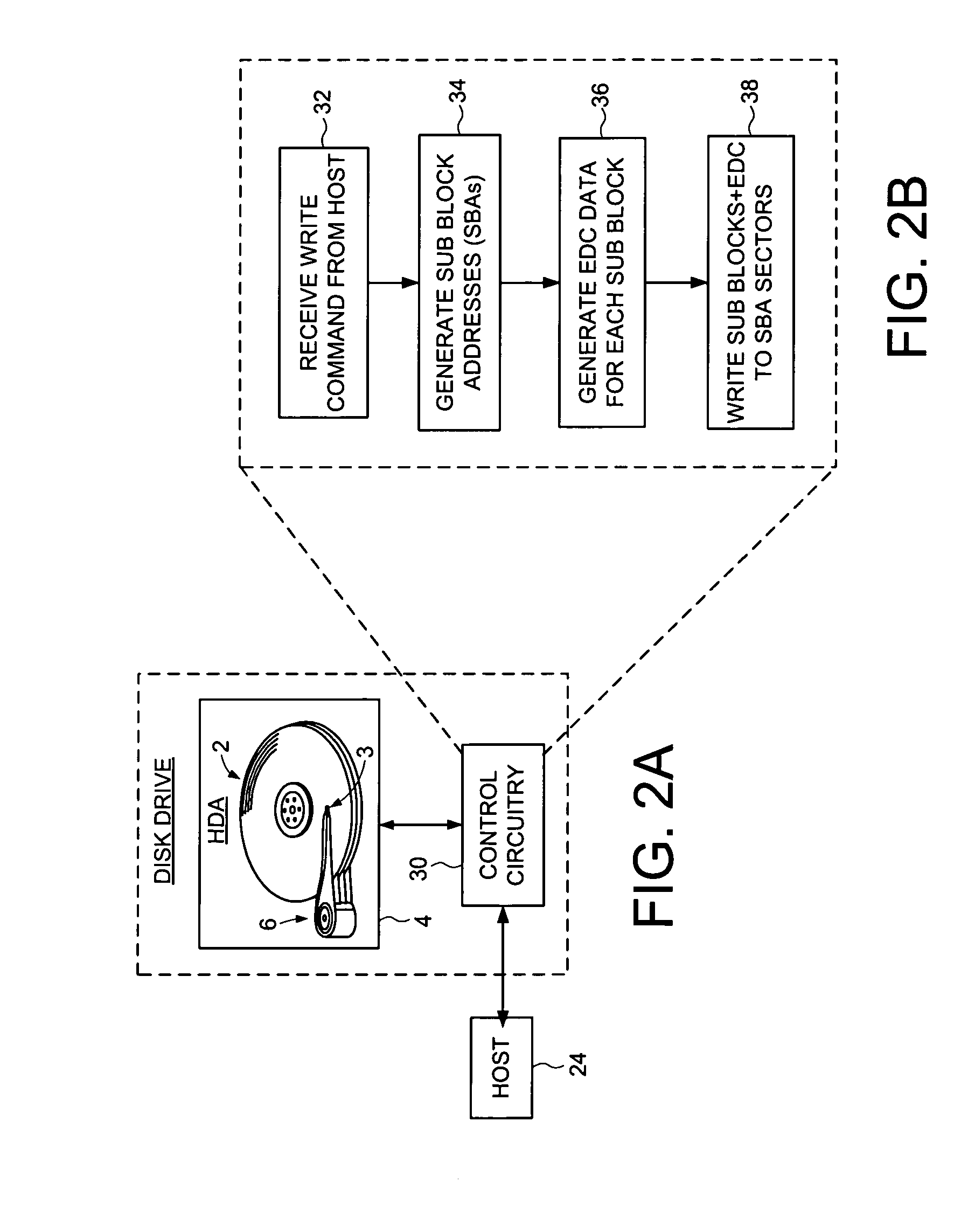
Disk drive implementing data path protection by encoding large host blocks into sub blocks
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk having a plurality of data tracks, wherein each data track includes a plurality of data sectors. A head is actuated over the disk for accessing the data sectors. A write command is received from a host, wherein the write command includes a host block and corresponding host block address. The host block is partitioned into a plurality of sub blocks, and a plurality of sub block addresses are generated in response to the host block address, wherein each sub block address corresponds to one of the sub blocks. Error detection code (EDC) data is generated for each sub block in response to the sub block and corresponding sub block address. Each sub block and corresponding EDC data are combined to generate a plurality of partial codewords that are written to the data sectors corresponding to the sub block addresses.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Optical network restoration
A method for protecting the flows of traffic against, and for restoring them from, a failure in a multifunctional, hybrid broadband access-and-transport network system includes the provisioning of at least two Virtual Flows (“VFs”) of traffic between each pair of ingress and egress (“I / E”) nodes in the system. The at least two VFs are provisioned such that each takes a different physical path from the other. The VFs taking the same physical path are then respectively grouped into two “Path Protection Groups” (“PPGs”). Each of the PPGs has a dedicated “Management Control Flow” (“MCF”) provisioned within it that is carried in the at least one VF contained therein. The detection of a fault in the traffic in an “active” PPG results in the generation of a protection switching signal (“PSS”) being generated and sent by the nodes detecting the fault along the MCF of the affected PPG to the relevant “protection switching entities” (“PSEs”), i.e., the affected I / E nodes, which responsively effect a protection switch of either the reception, or both the transmission and the reception, of the affected traffic from the affected “active” PPG to the associated “protect” PPG to thereby restore path and traffic continuity within the system. The method is independent of the transport layer and can thus be used to protect traffic in networks having transport systems other than SONET.
Owner:WHITE OAK GLOBAL ADVISORS
Method and apparatus for discovering edge-disjoint shortest path pairs during shortest path tree computation
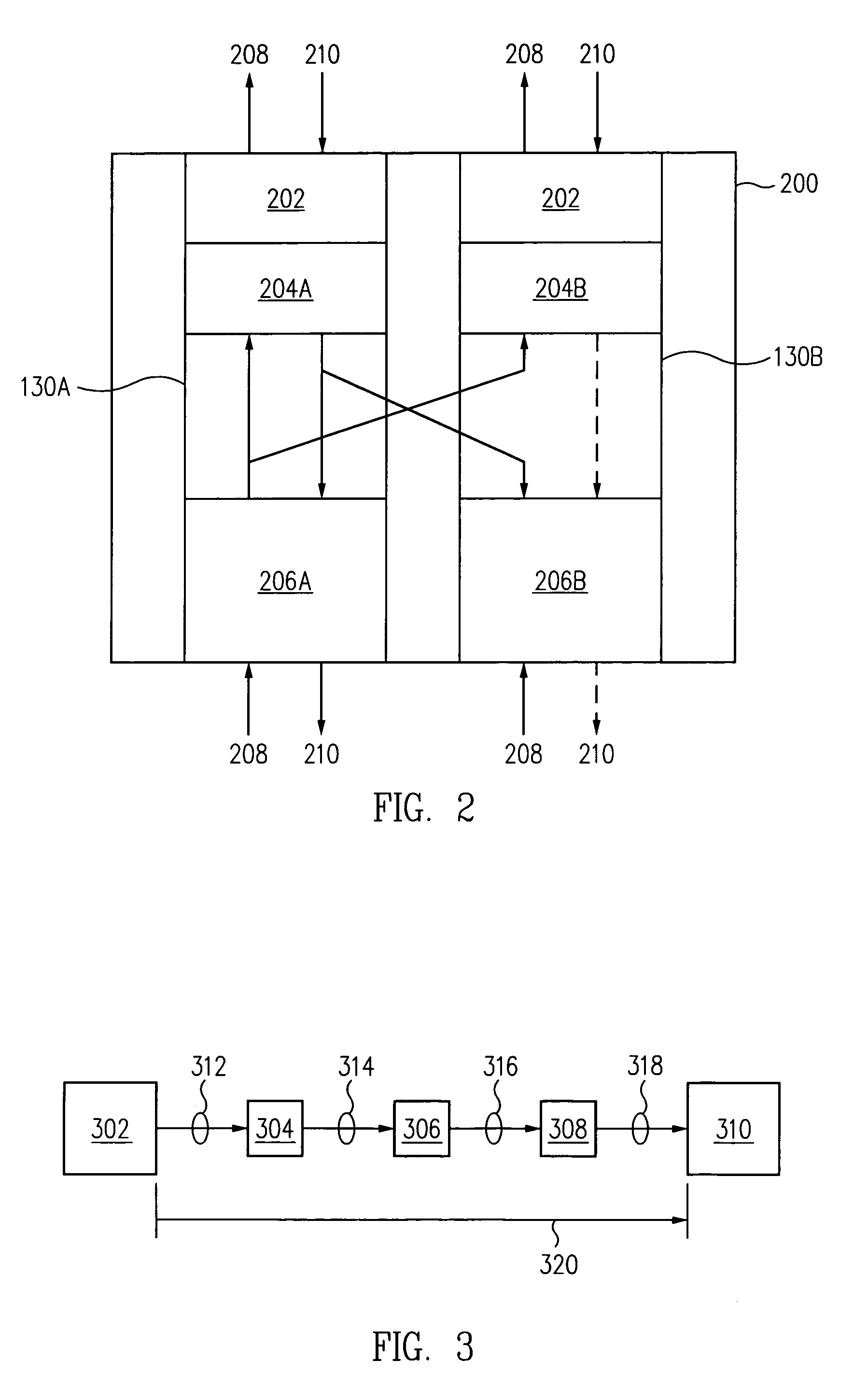
InactiveUS6928484B1Improve efficiencyReduced computing resourceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMethod selectionPath protection
A method for identifying and choosing a shortest path segment that has an alternate edge disjoint path segment. While routing Unidirectional Path Switched Ring (UPSR) path segments in a graph, there may be several equal distance paths to choose the shortest path from. Choosing a certain path as the shortest path may minimize or eliminate the chance of finding an alternative path segment. A method is provided such that if multiple shortest paths from the source node to a particular destination node exist, the method selects the shortest path which has an alternate edge disjoint path, and which can be used for path protection. The particular shortest path chosen by the method is not necessarily the first shortest path constructed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
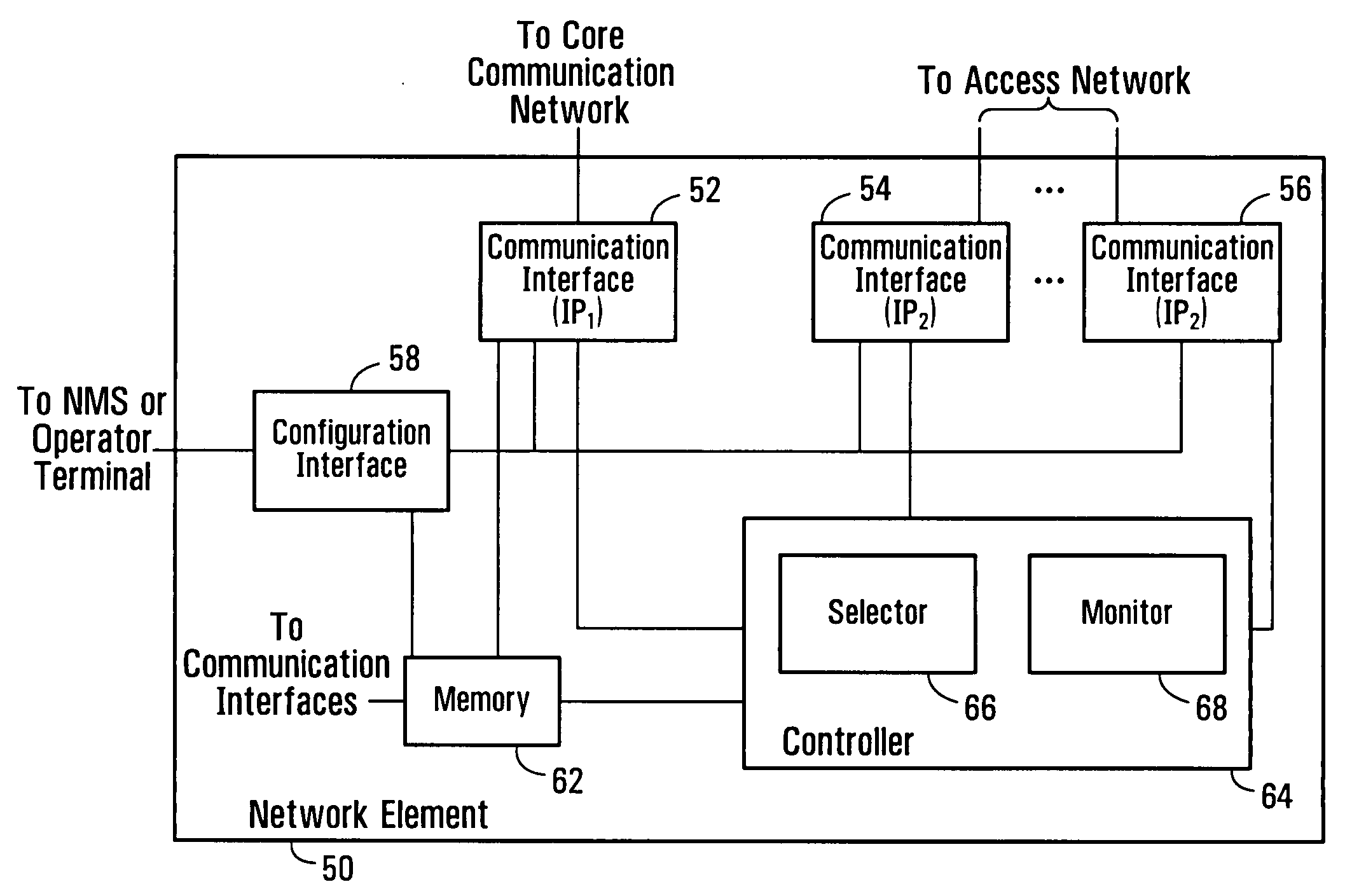
Communication path redundancy protection systems and methods
InactiveUS20060291378A1Improve usabilityError preventionTransmission systemsCommunication interfaceTraffic capacity
Communication path redundancy protection systems and methods are disclosed. Multiple communication interfaces having a common address support communications on respective communication paths. One of the interfaces or communication paths is selected as an active interface or path for transferring communication traffic. In the event of a fault associated with the active interface or path, another one of the interfaces or paths is selected to become active. The common address allows redundant interfaces to appear as a single interface to other communication equipment, whereas the multiple interfaces provide redundant path protection using a single piece of communication equipment. When embodiments of the invention are implemented in a gateway router of a core communication network, for example, activity switches between redundant access paths have no effect on routing in the core network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
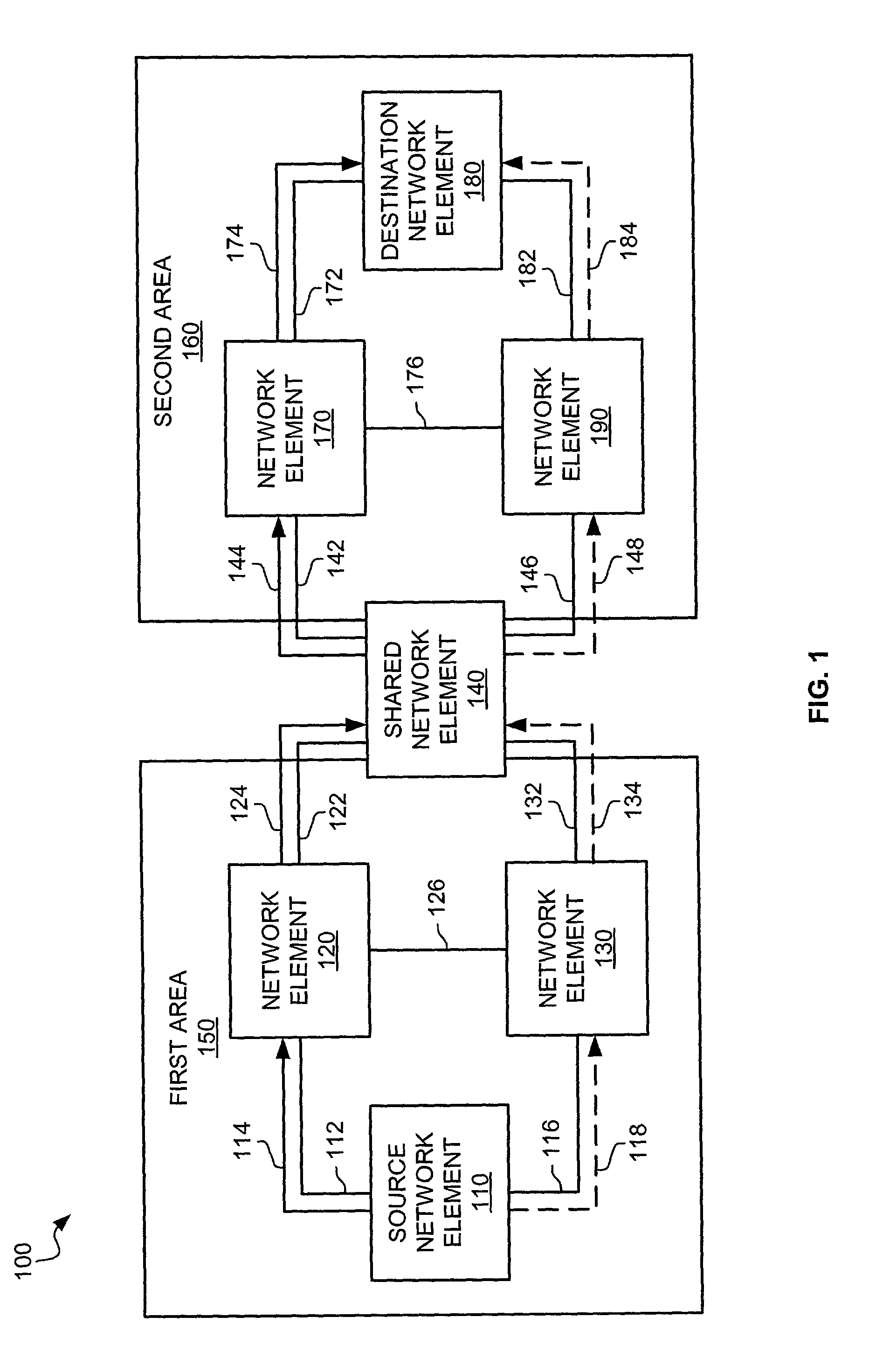
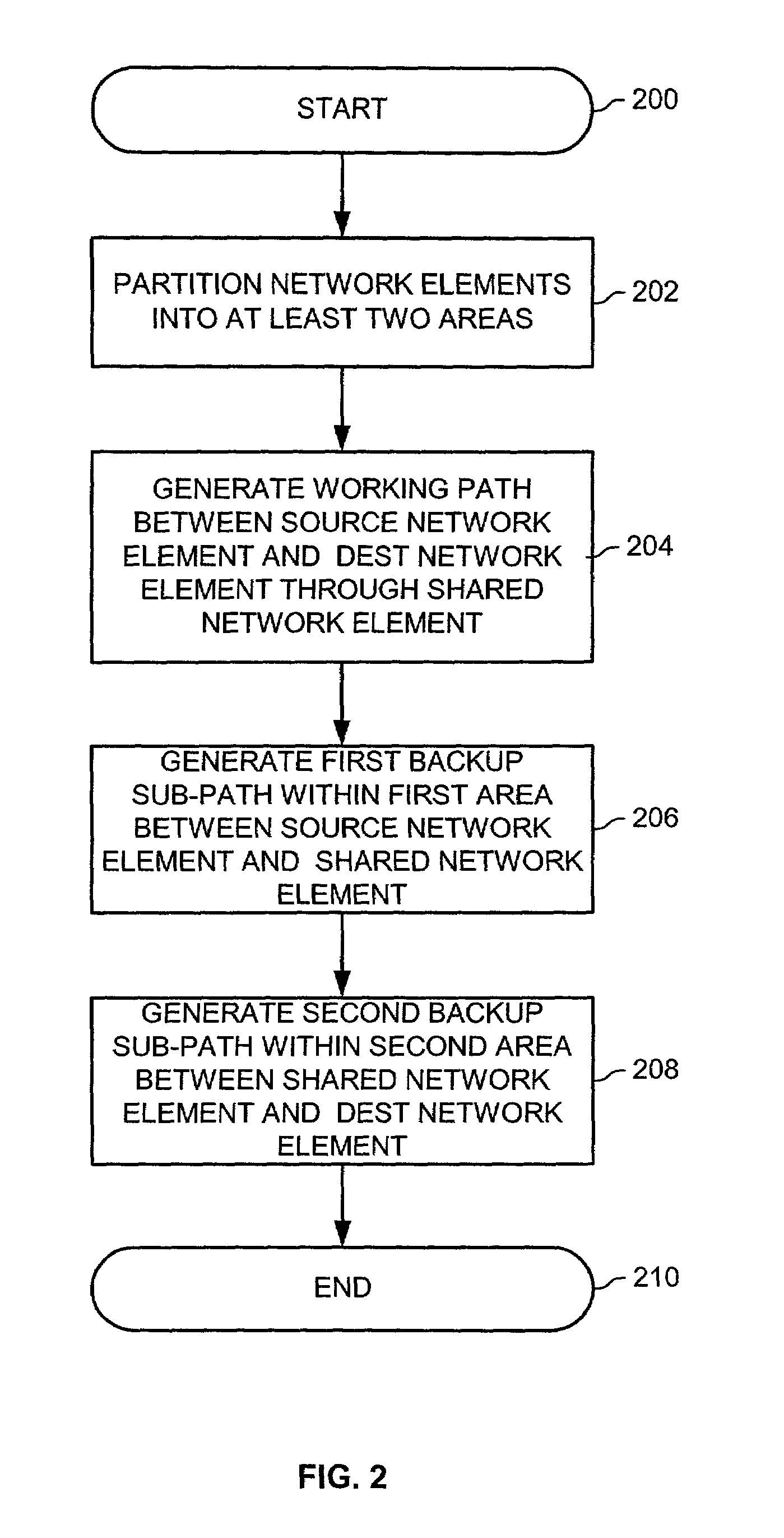
Area based sub-path protection for communication networks
ActiveUS7209975B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationPath protectionDistributed computing
Methods, software products, and systems establish a connection between a source network element and a destination network element in a communication network comprising a plurality of first network elements. The first network elements are partitioned into at least two areas wherein a shared network element is shared between the at least two areas. A working path is then generated between the source network element and the destination network element through the shared network element. A first backup sub-path is then generated within a first one of the at least two areas between the source network element and the shared network element. A second backup sub-path is generated within a second one of the at least two areas between the shared network element and the destination network element.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
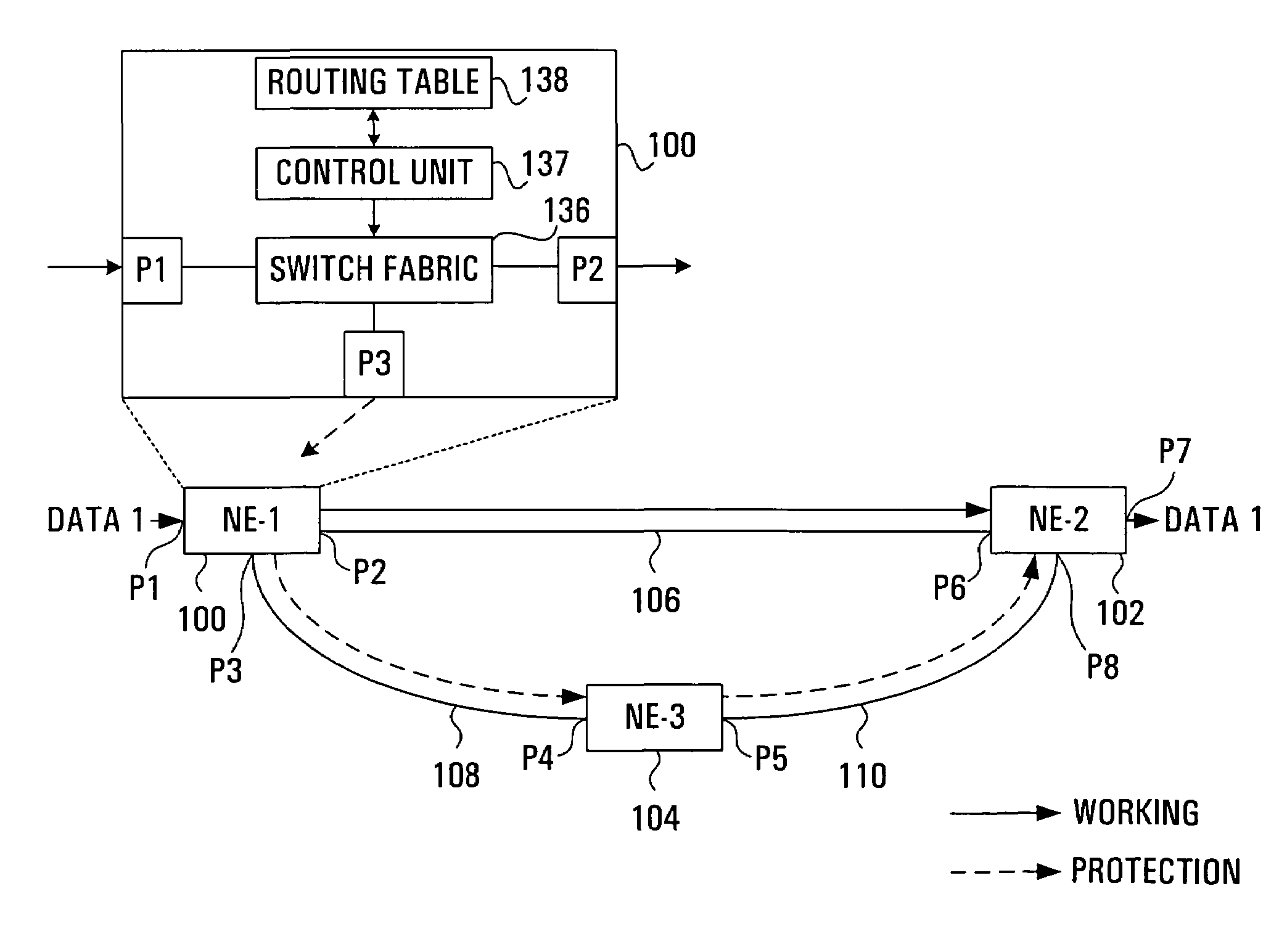
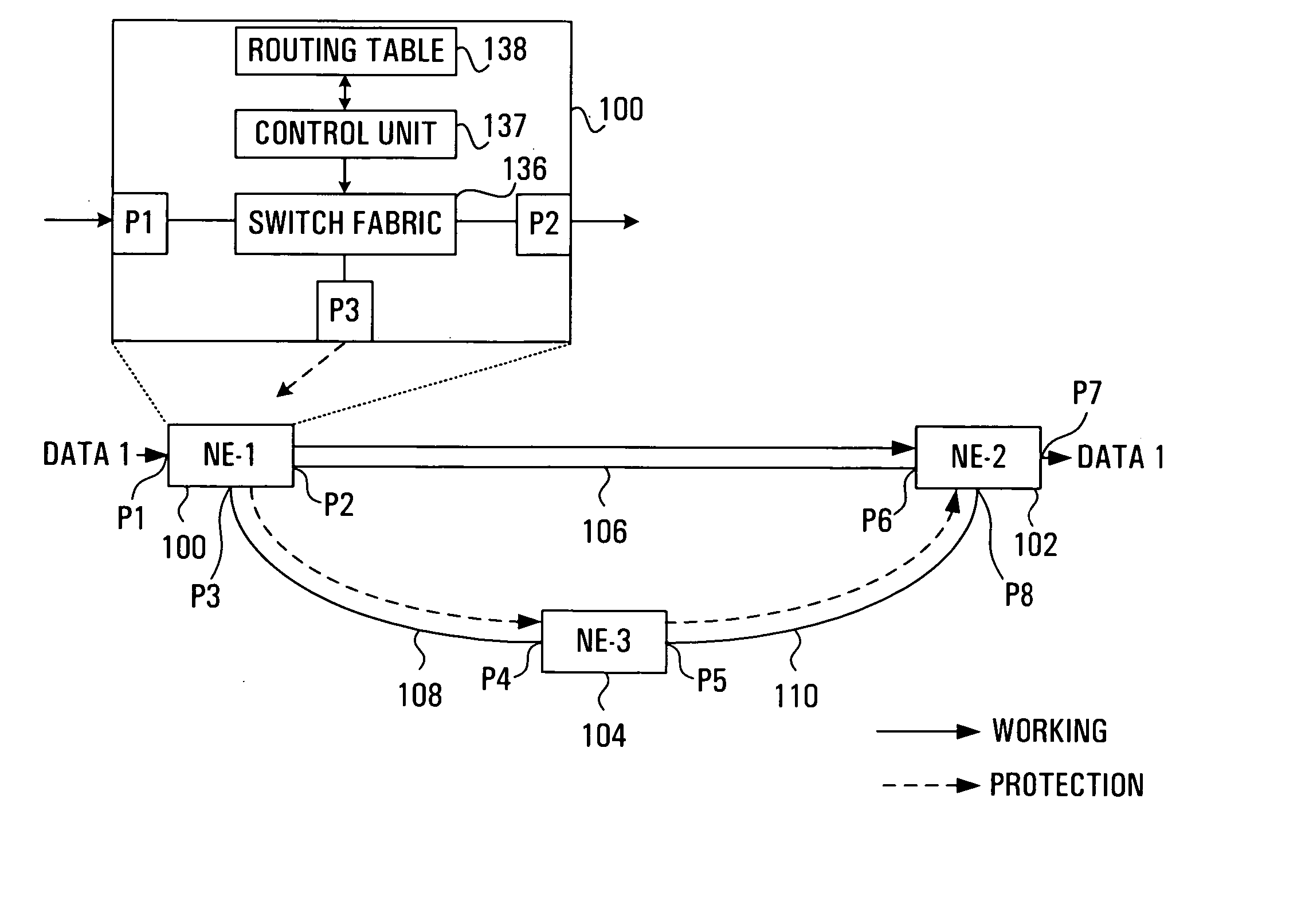
Apparatus and method for optical communication protection
InactiveUS6934248B1Improve efficiencyRing-type electromagnetic networksError preventionTraffic capacityRouting table
Protection techniques within optical communication networks are extremely important. An alternative to a line protection scheme, as most current optical communication networks use, is to utilize a path protection technique in which working and protection paths that are desired are assigned during network setup. During normal operations, only the working path is configured within the network elements' switch fabric with protection paths being left unconfigured. If a failure indication is detected in the working path by a network element, a protection entry within a routing table of the network element is looked up to determine protection switching data that is required to switch the data traffic to the pre-assigned protection path. This protection switching data is inserted within the path overhead for the data traffic so that it can be communicated to all of the network elements that require their switch fabrics reconfigured to establish the protection path of communications. This protection technique allows for similar switching speed to that of line switching protection such as BLSR designs, but with an increase in efficiency in terms of protection bandwidth.
Owner:CIENA
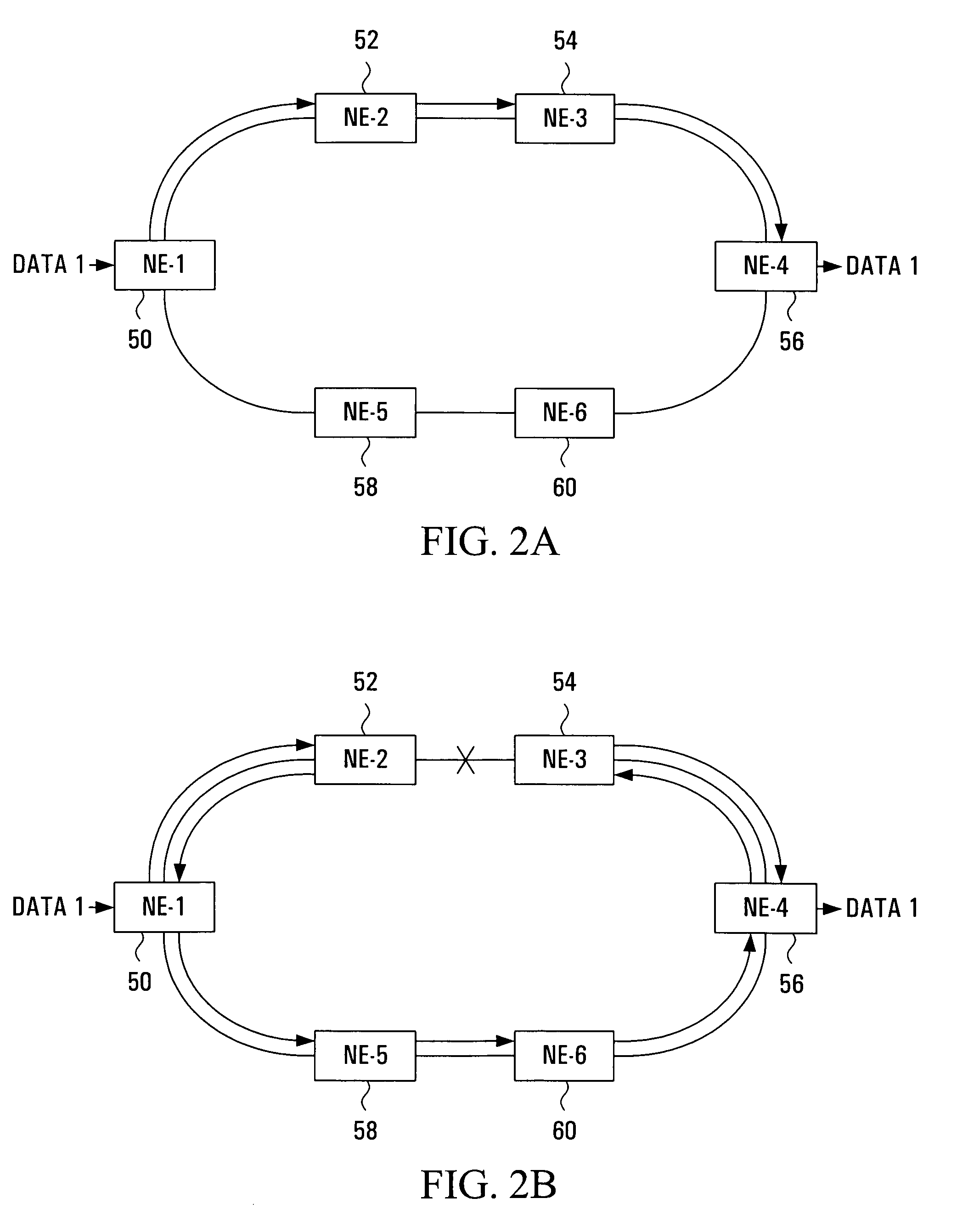
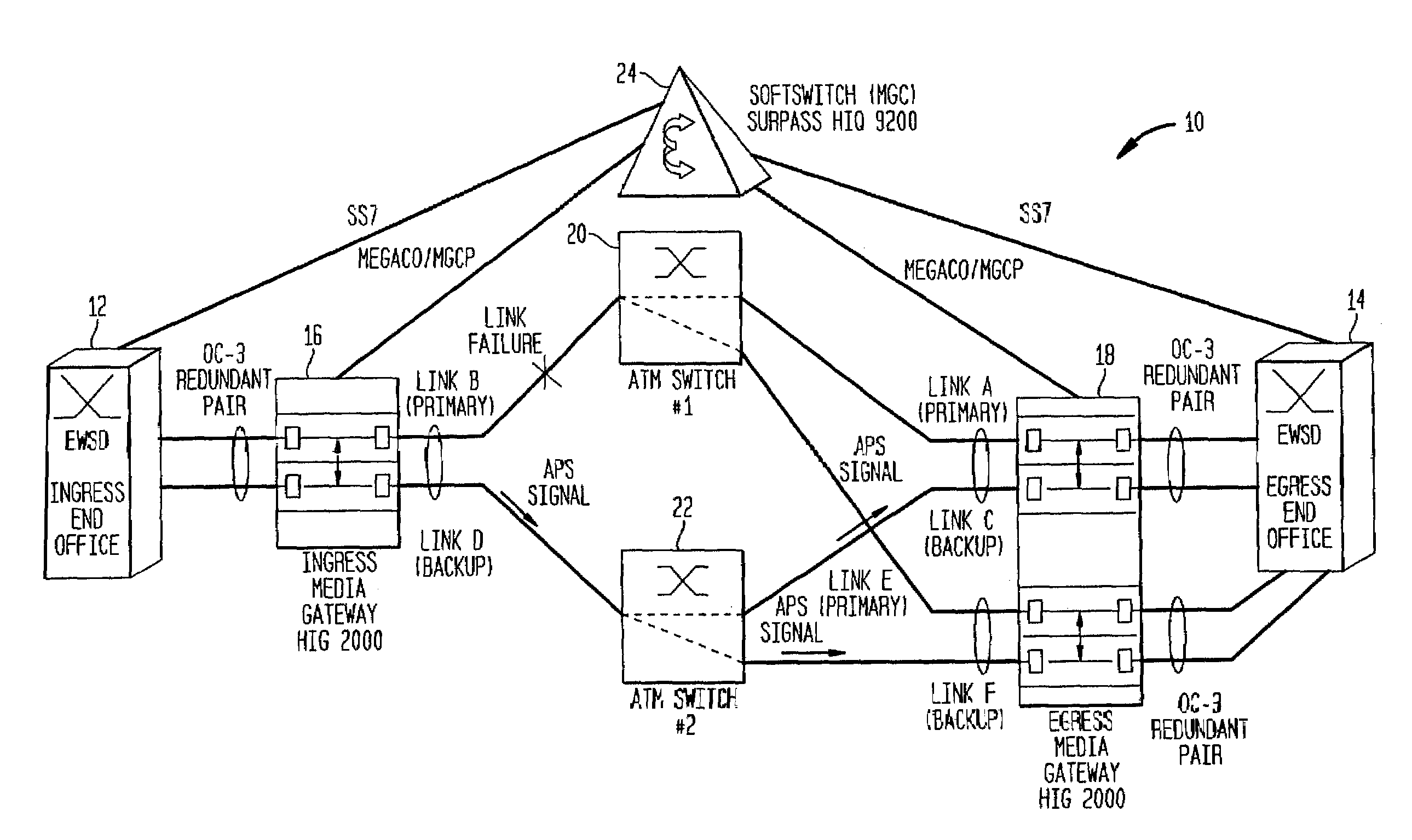
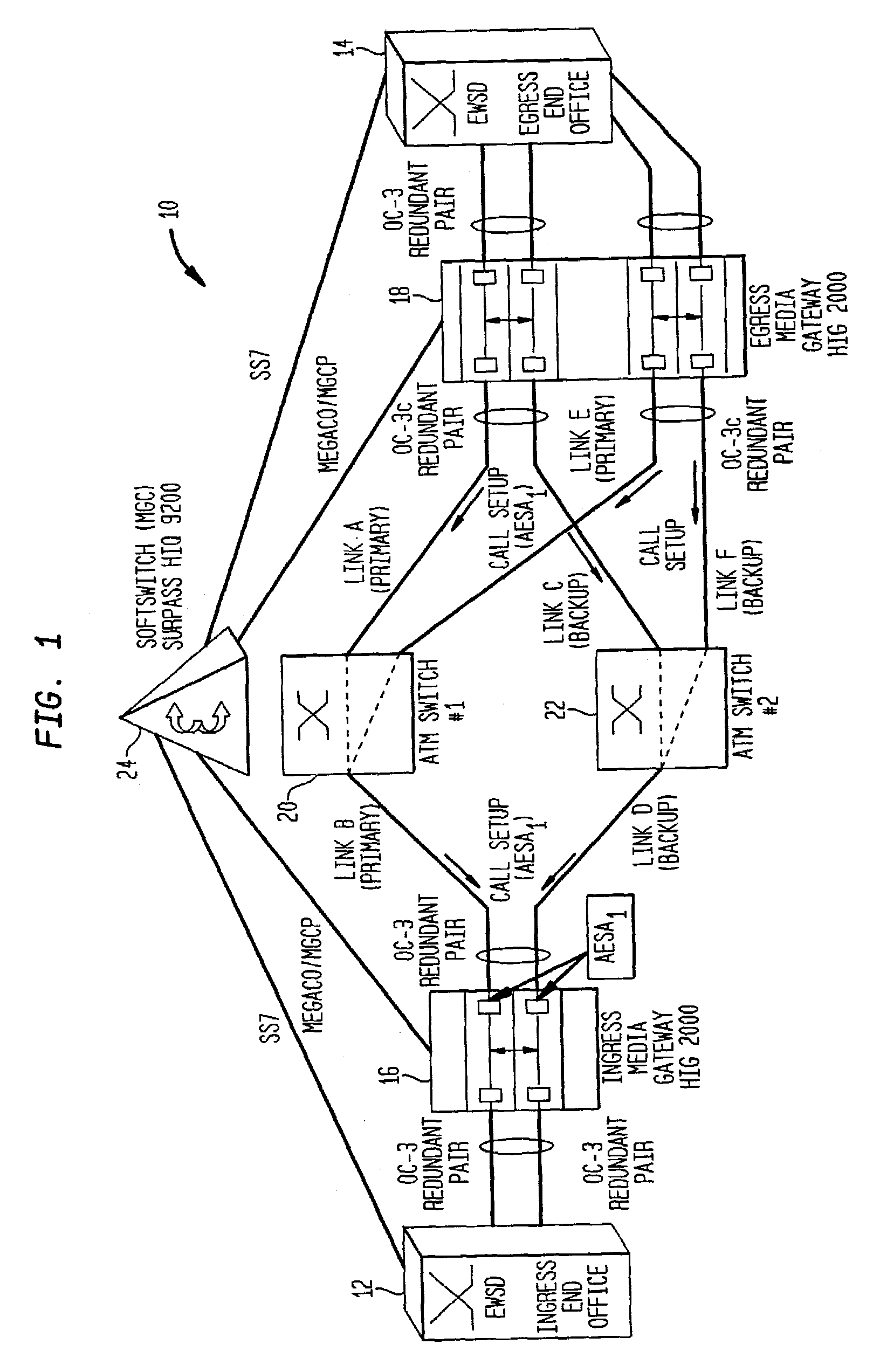
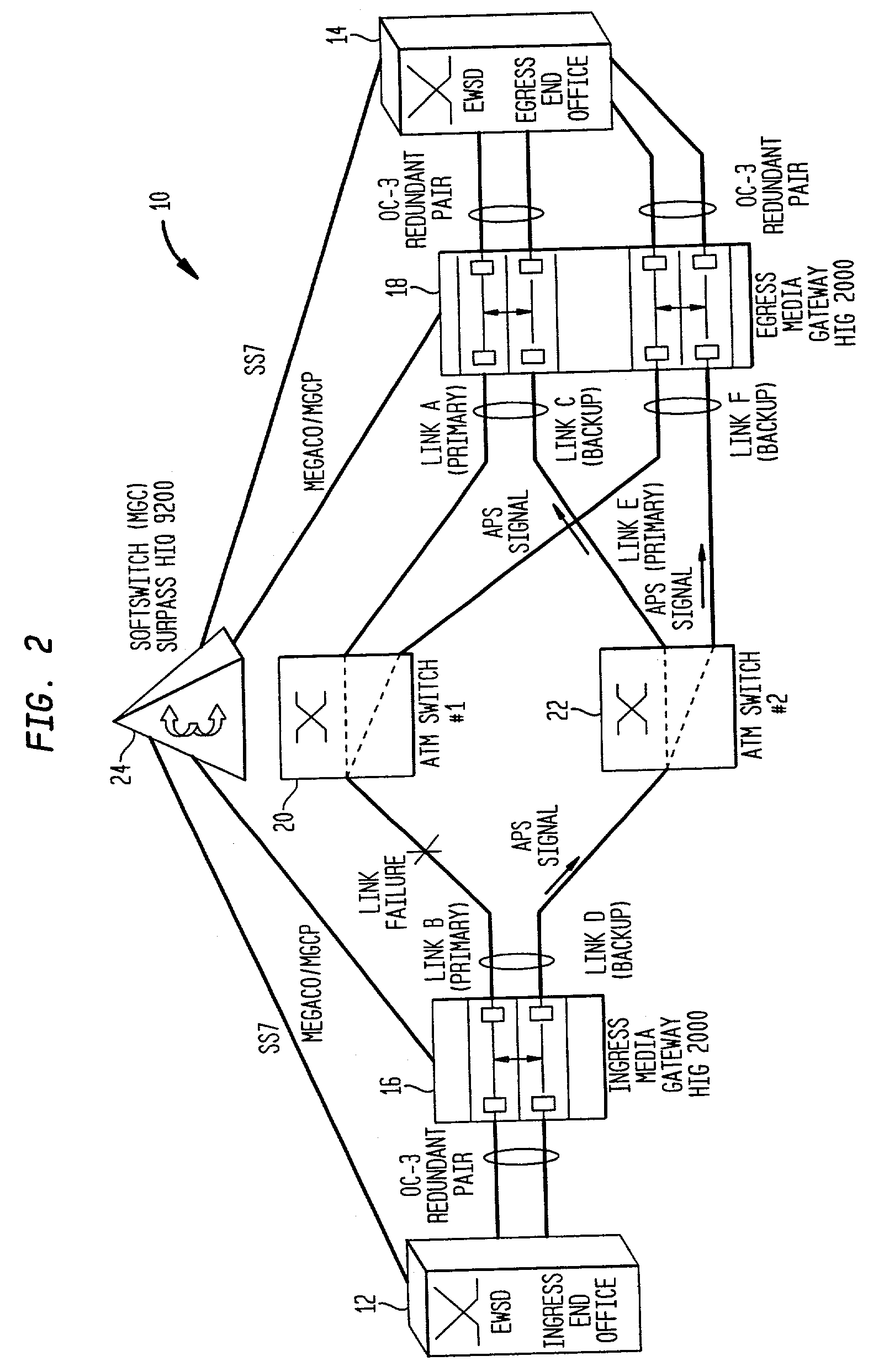
Method for resilient call setup through ATM networks for Softswitch applications
InactiveUS7065041B2Minimize effortEliminate needError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEnd systemSoftswitch
A method establishes two redundant Switched Virtual Channel (SVC) connections through ATM Networks using the same ATM End System Address (AESA) from a source ATM End Point to a destination ATM End Point. The method provides end-to-end path protection without relying on any underlying resiliency features of an ATM Network so that the set-up model is transparent to the underlying ATM Network.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Network restoration
ActiveUS20050013241A1No difference in the performance of the two mechanismsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransport networkPath protection
A method of restoring an active path between two nodes of a transport network upon occurrence of a failure includes the steps of determining an alternate path through the network and establishing a path protection involving the failed active path and the alternate path. If in layered networks, a failed path is restored at a lower layer and at a higher layer concurrently, the restoration actions in the higher network layer can thus be reverted easily.
Owner:RPX CORP
System, method and apparatus for dynamic path protection in networks
InactiveUS20050237950A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork modelPath protection
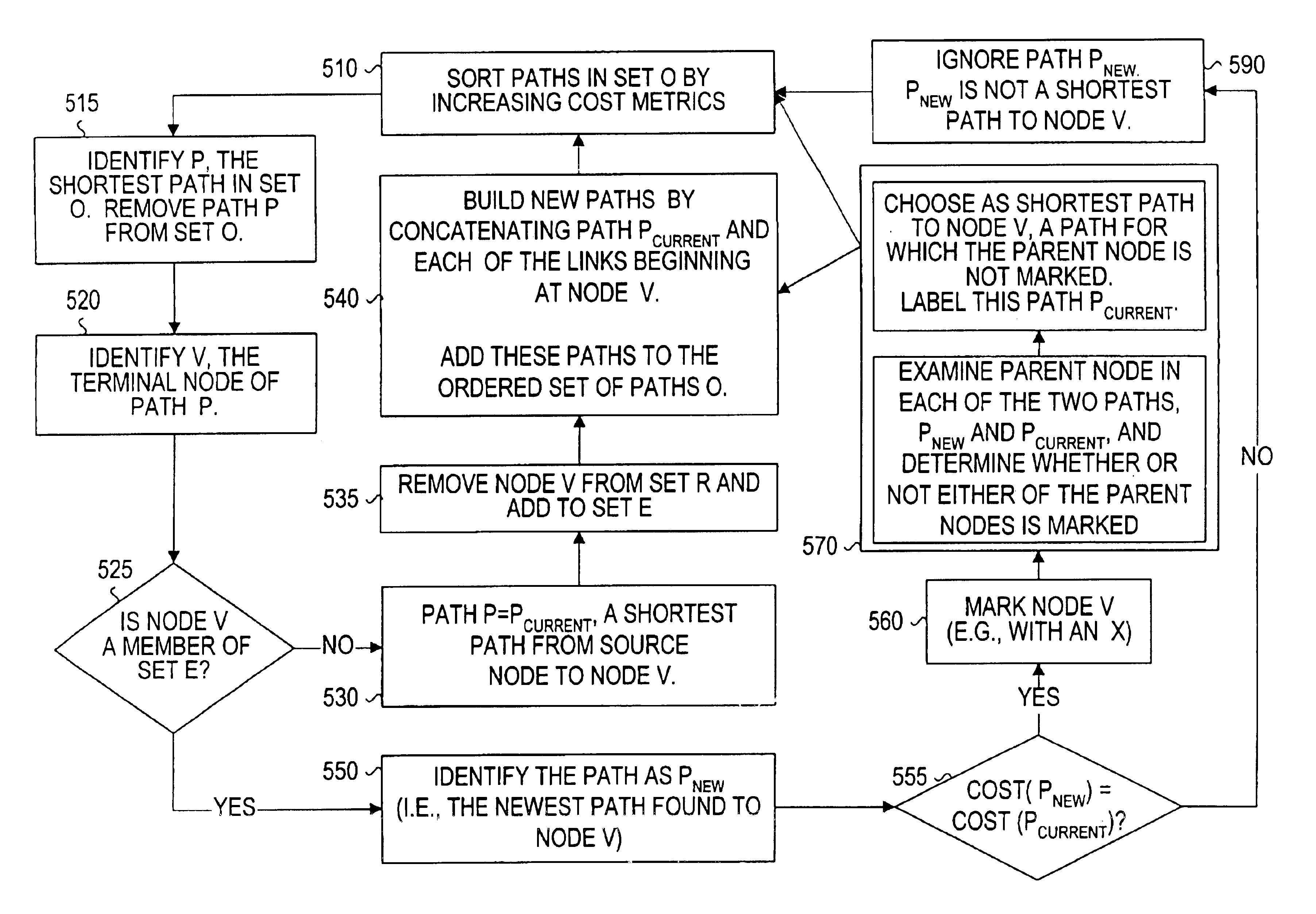
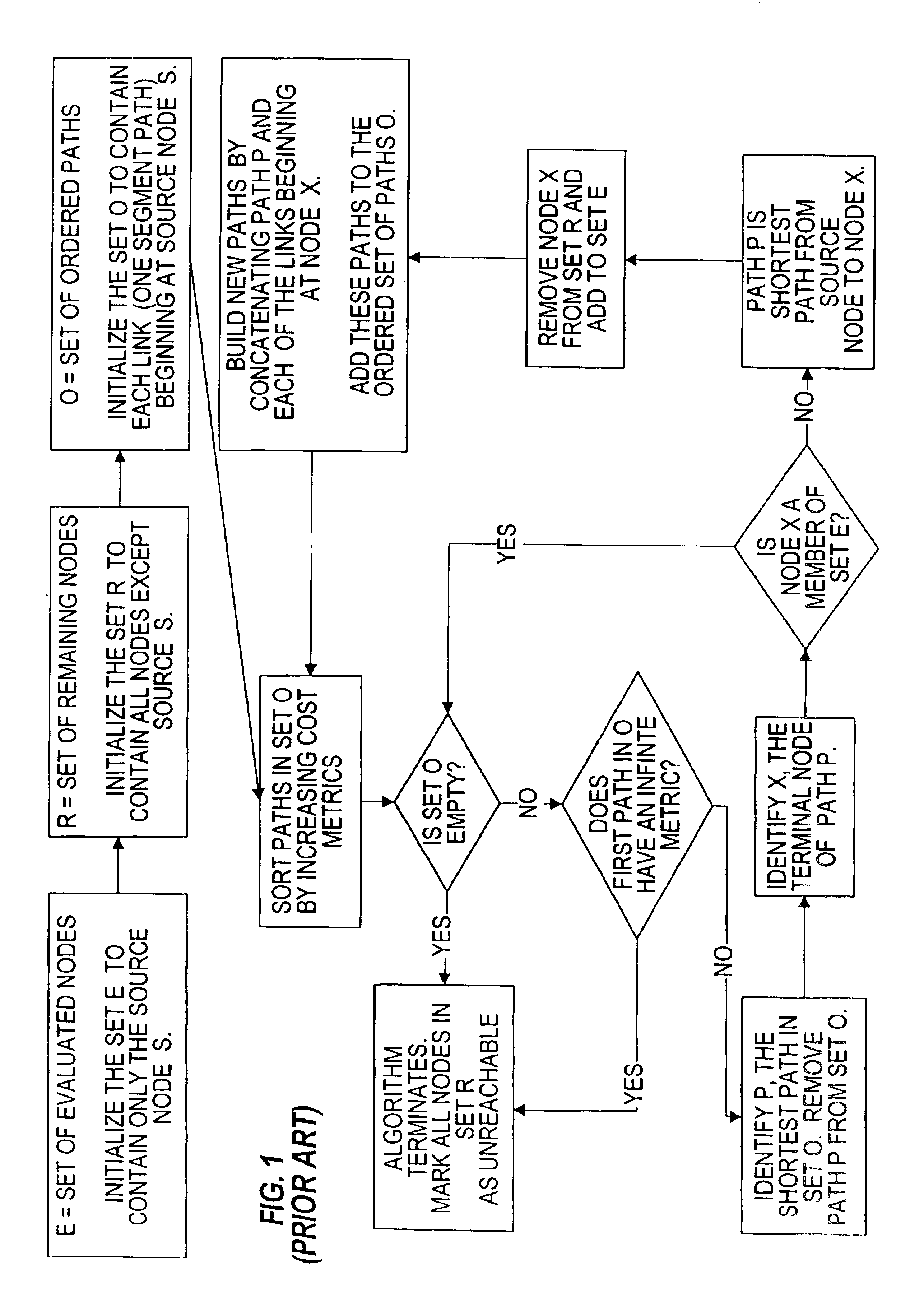
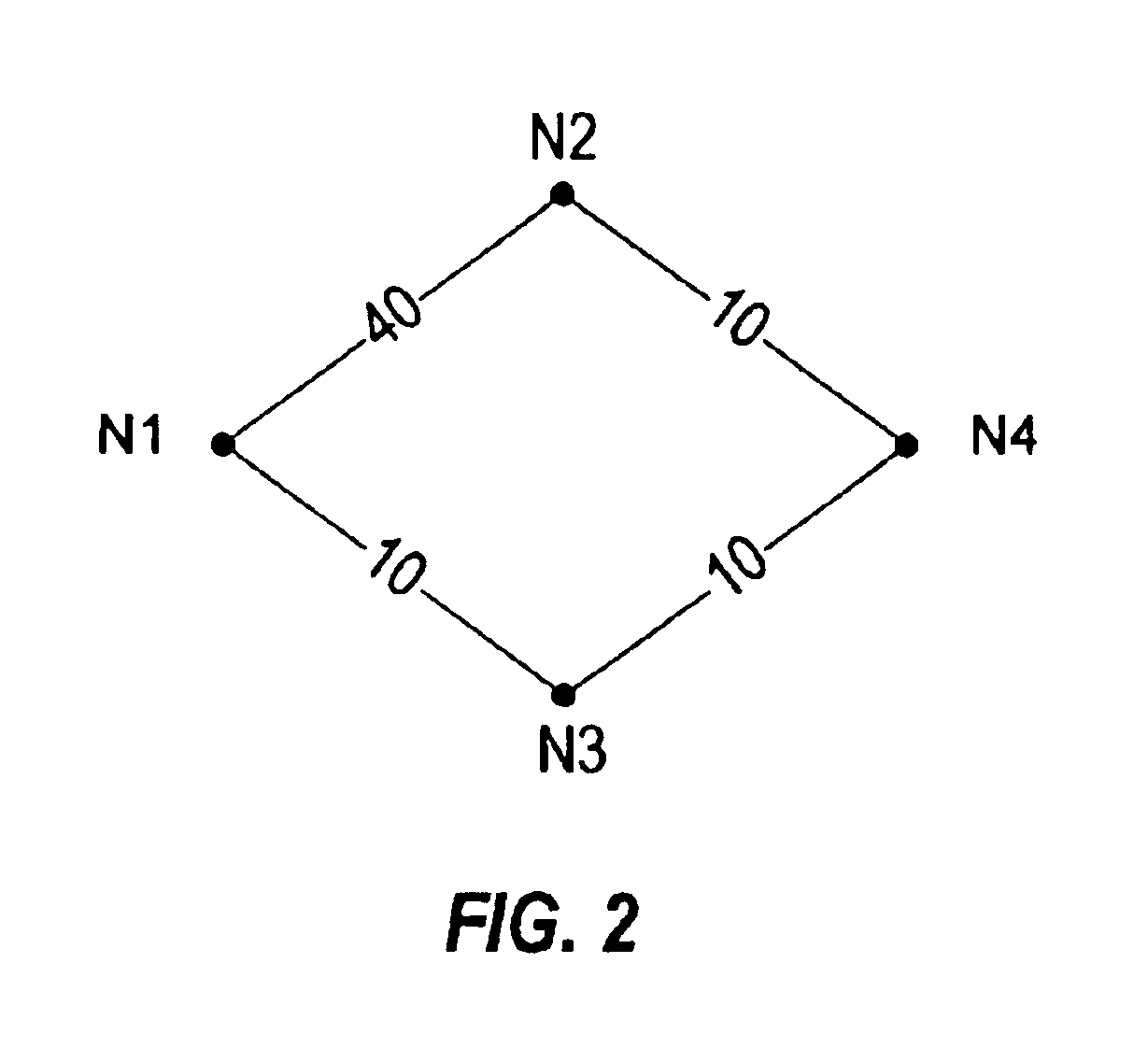
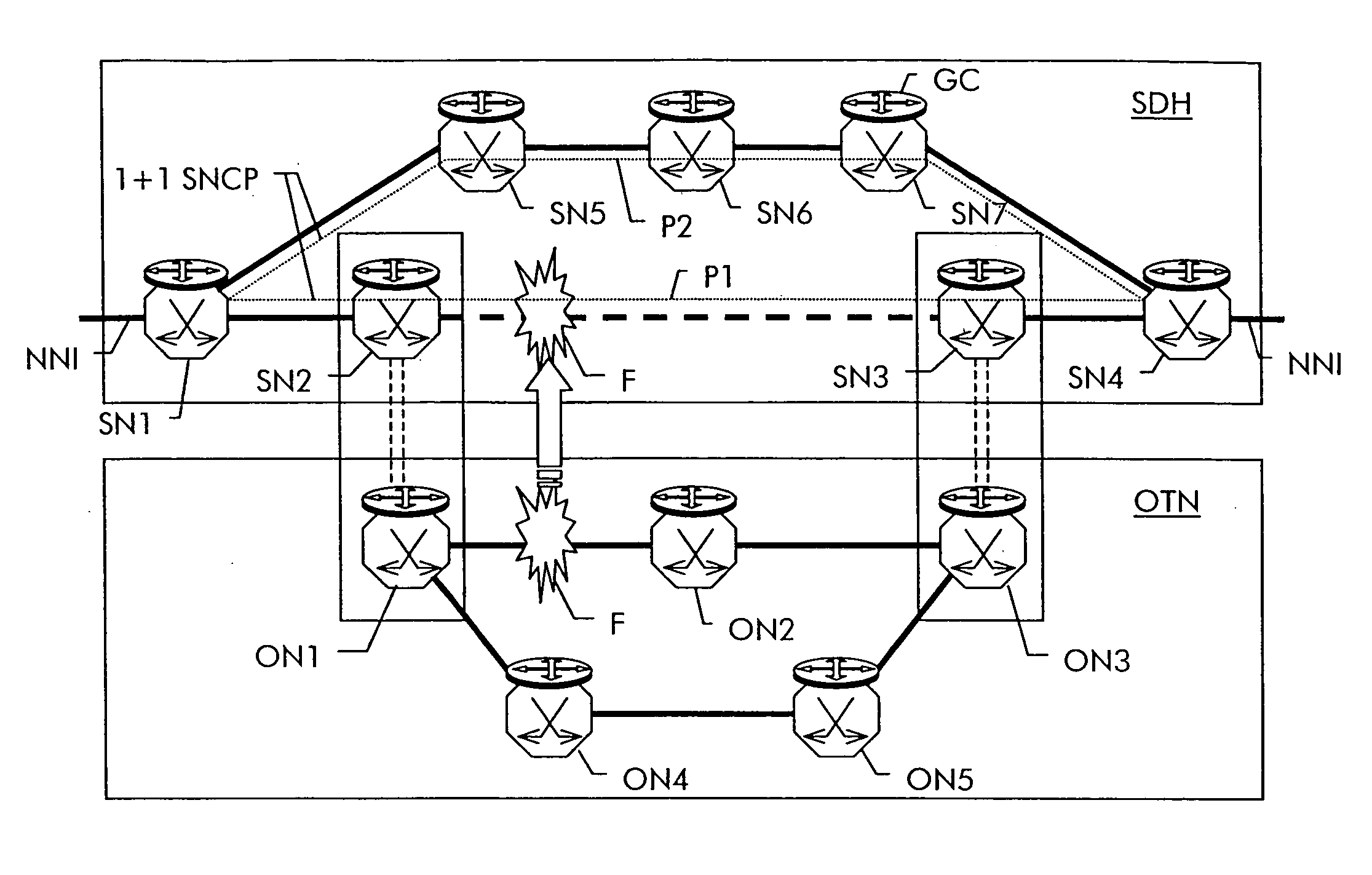
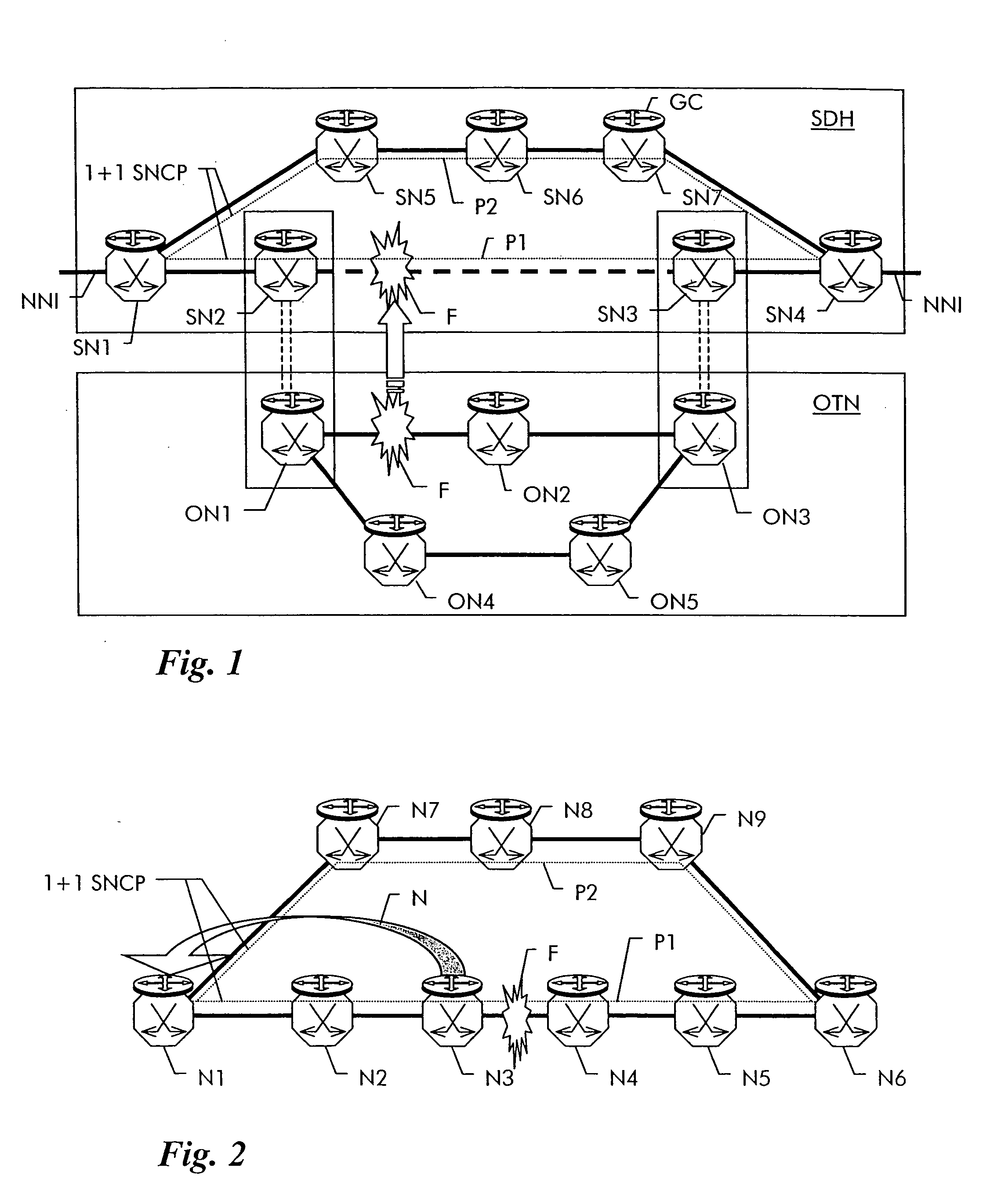
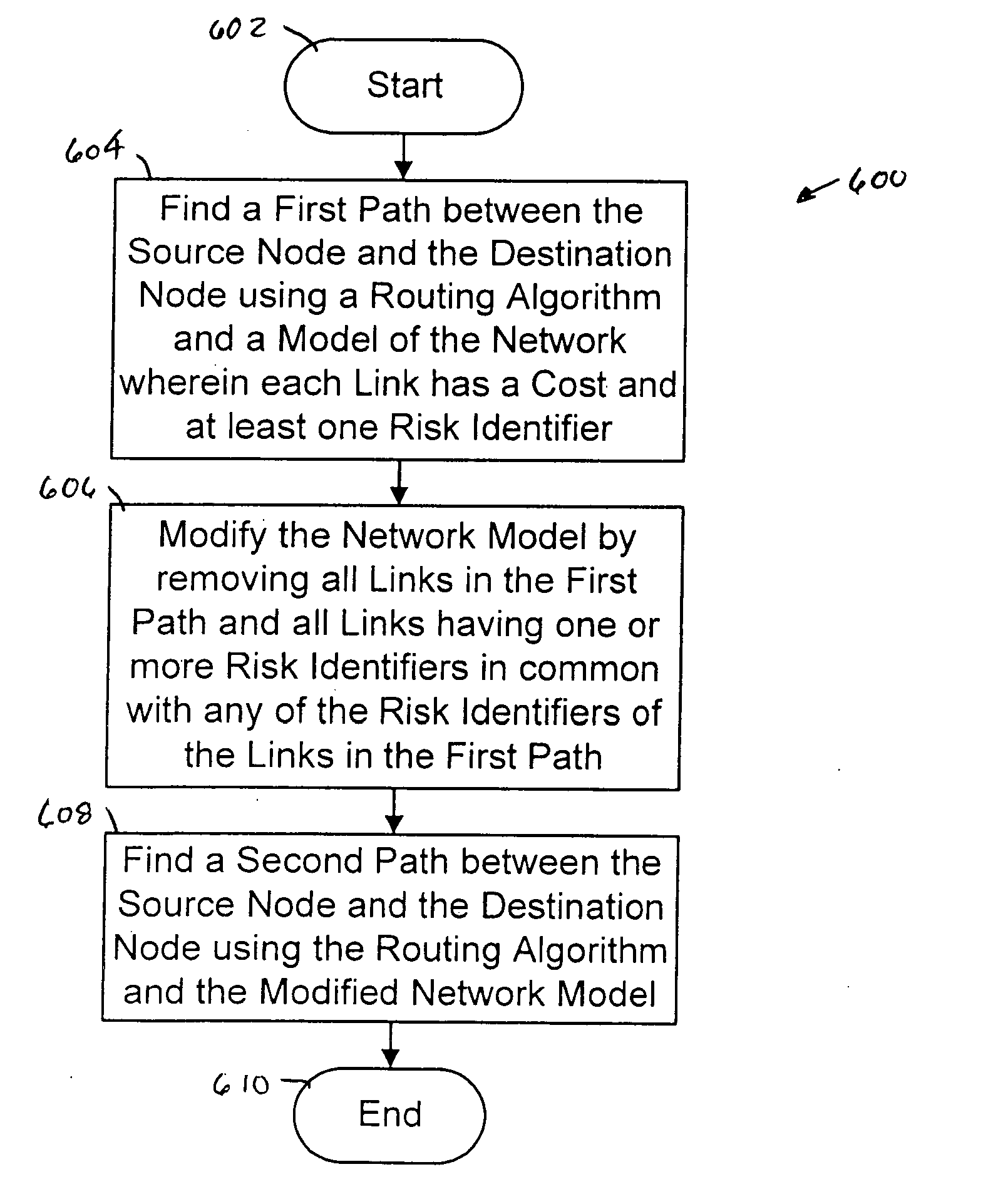
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for dynamic path protection in networks by finding two paths between a source node and a destination node in a network having multiple nodes and multiple links. A first path is found between the source node and the destination node using a routing algorithm and a model of the network. Each link has a cost and at least one risk identifier. The cost of the links having one or more risk identifiers that occur more than once in the network model are increased. The model is modified by removing all links in the first path and all links having one or more risk identifiers in common with any of the risk identifiers of the links in the first path. The second path is found between the source node and the destination node using the routing algorithm and the modified model.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Path protection method and layer-2 switch
ActiveUS20070086333A1Reduce investmentFunction increaseError preventionTransmission systemsPath protectionComputer science
A method of providing path protection includes setting a working path and a protection path by identifying, as a single path, a set of a control-purpose virtual network identifier and at least one virtual network identifier that are assigned to one or more users at a section defined as a point-to-point connection in a virtual network, and switching between the working path and the protection path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
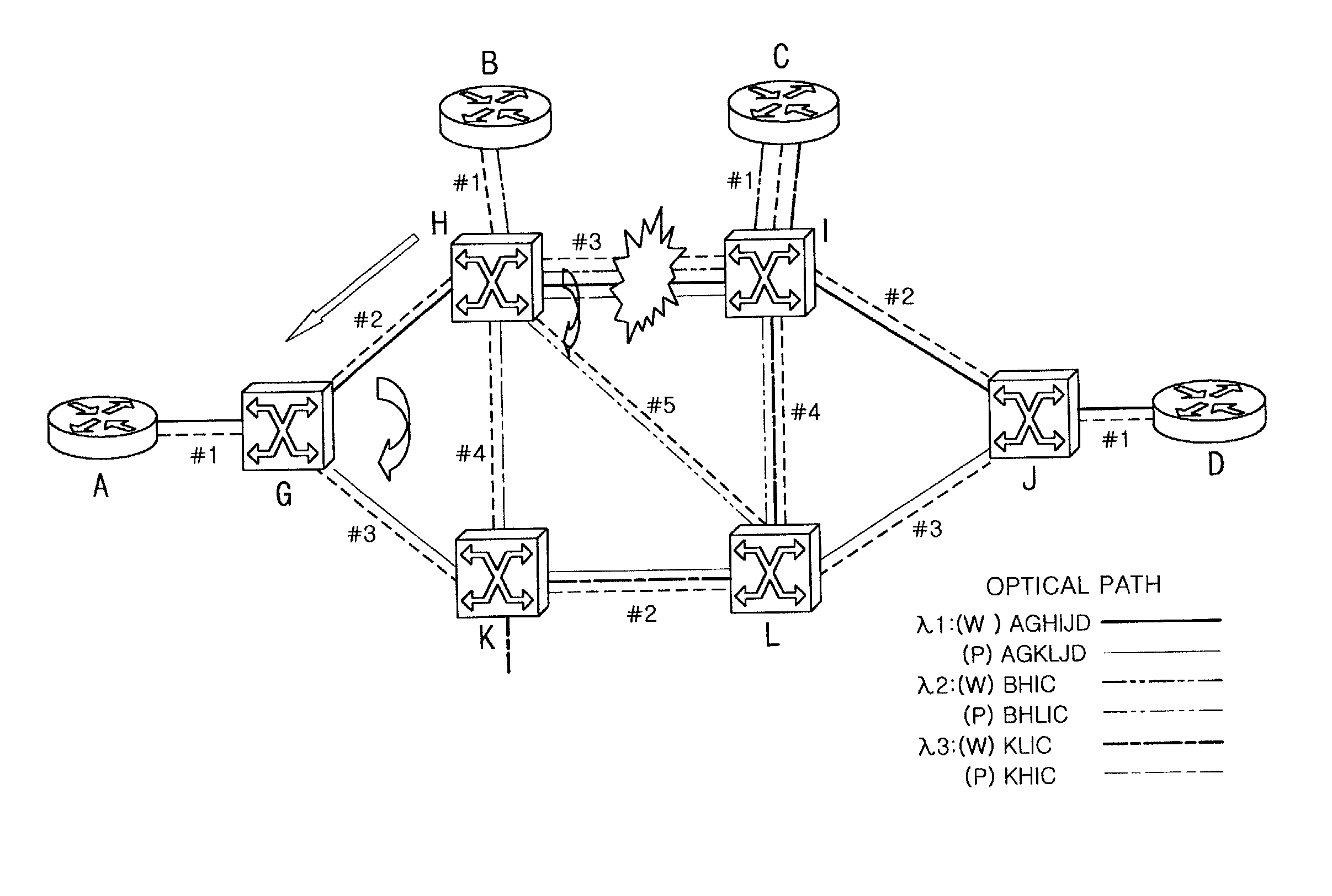
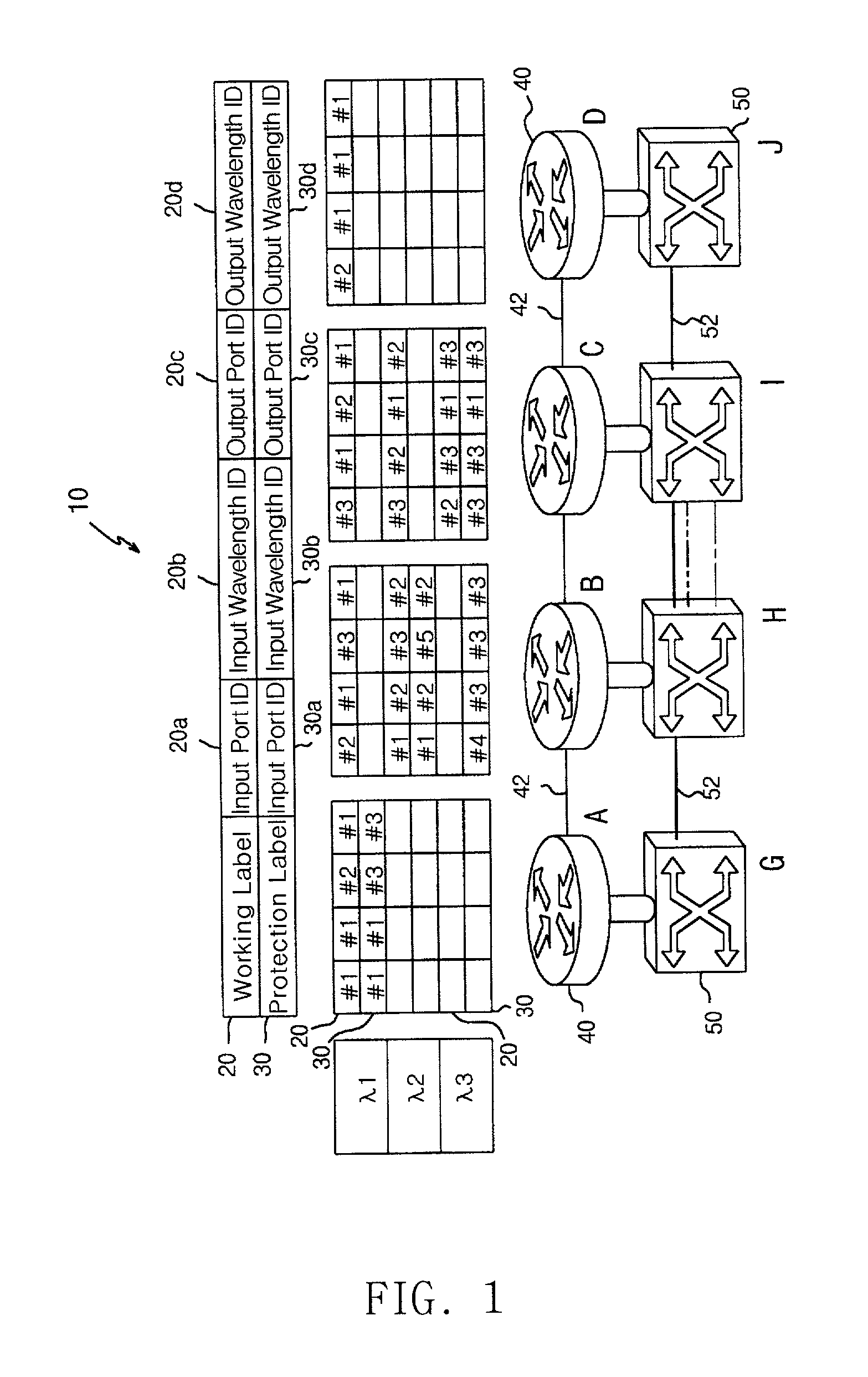
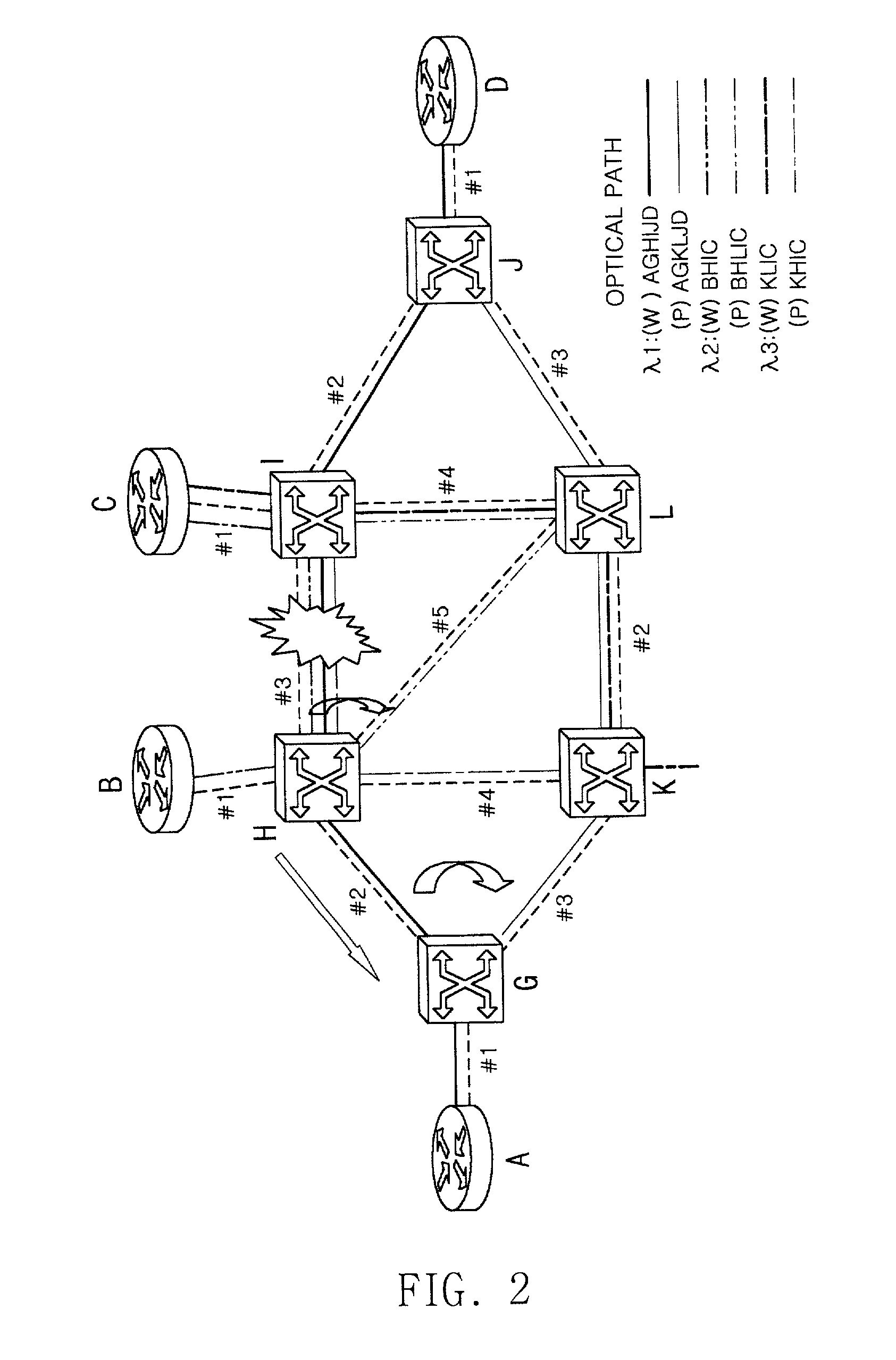
Routing table configuration for MPlambdaS (multi-protocol lambda switching) protection and restoration in optical mesh networks
InactiveUS20020089712A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsOptical mesh networkRouting table
The present invention relates to protection and restoration method for MPXS in optical mesh networks, particularly to protection and restoration method which can find and restore fast failures by configuring routing table with working label and protection label when failures occur at links or nodes. According to the present invention, by configuring a routing table consisted of working label and protection label and by setting an optical path as working path and protection path, data is transferred through the working path, and when a failure occurs in a optical path, data is transferred through a protection path by using a preliminarily configured protection label and by switching to. According to the present invention, by configuring routing table with working label and protection label, failures can be restored fast when failures occur at links or nodes, and whole network resources can be applicable.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
Connection-oriented network node
InactiveUS20070036073A1Efficiently settingEfficiently setError preventionTransmission systemsNetworked systemPath protection
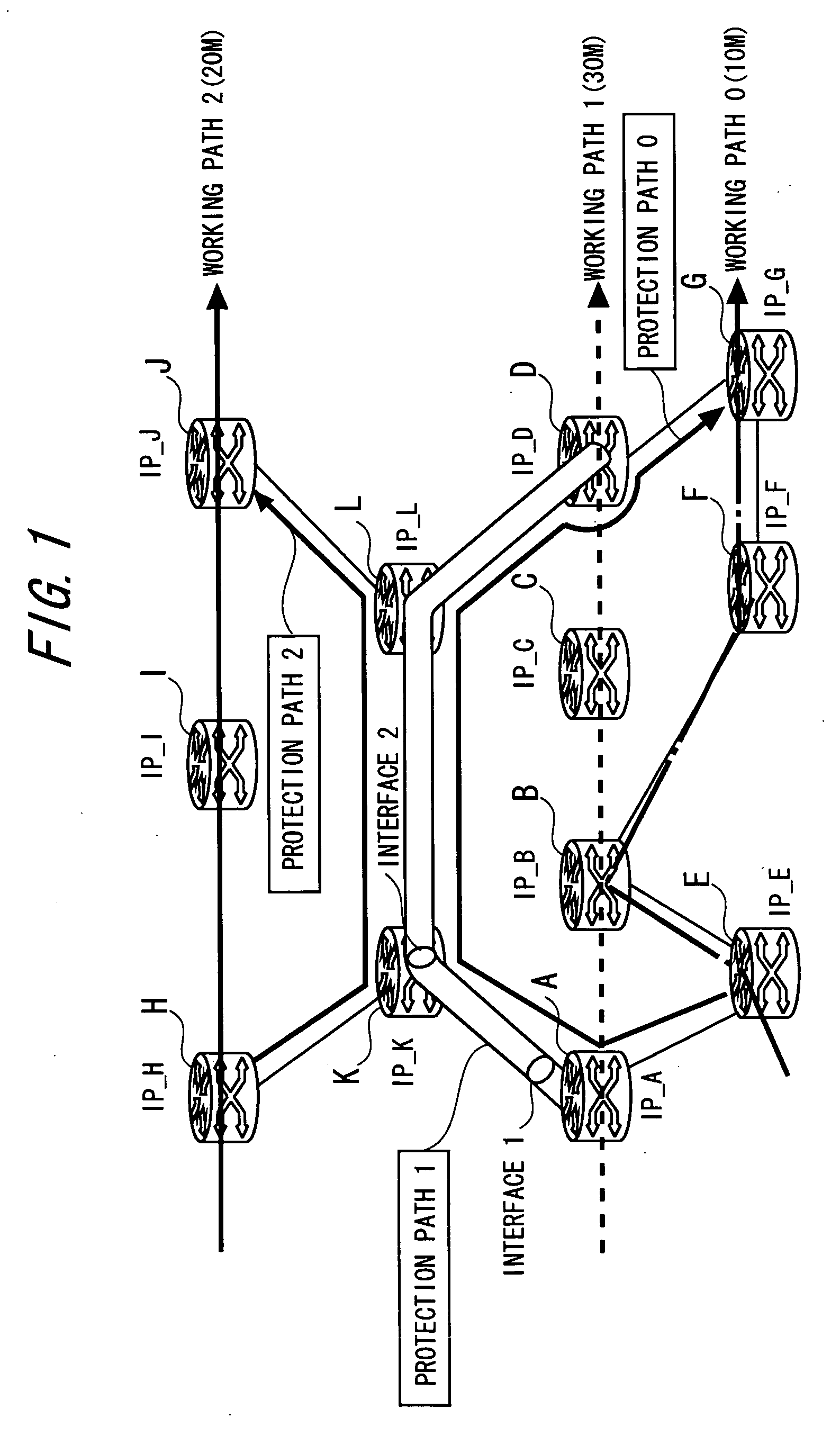
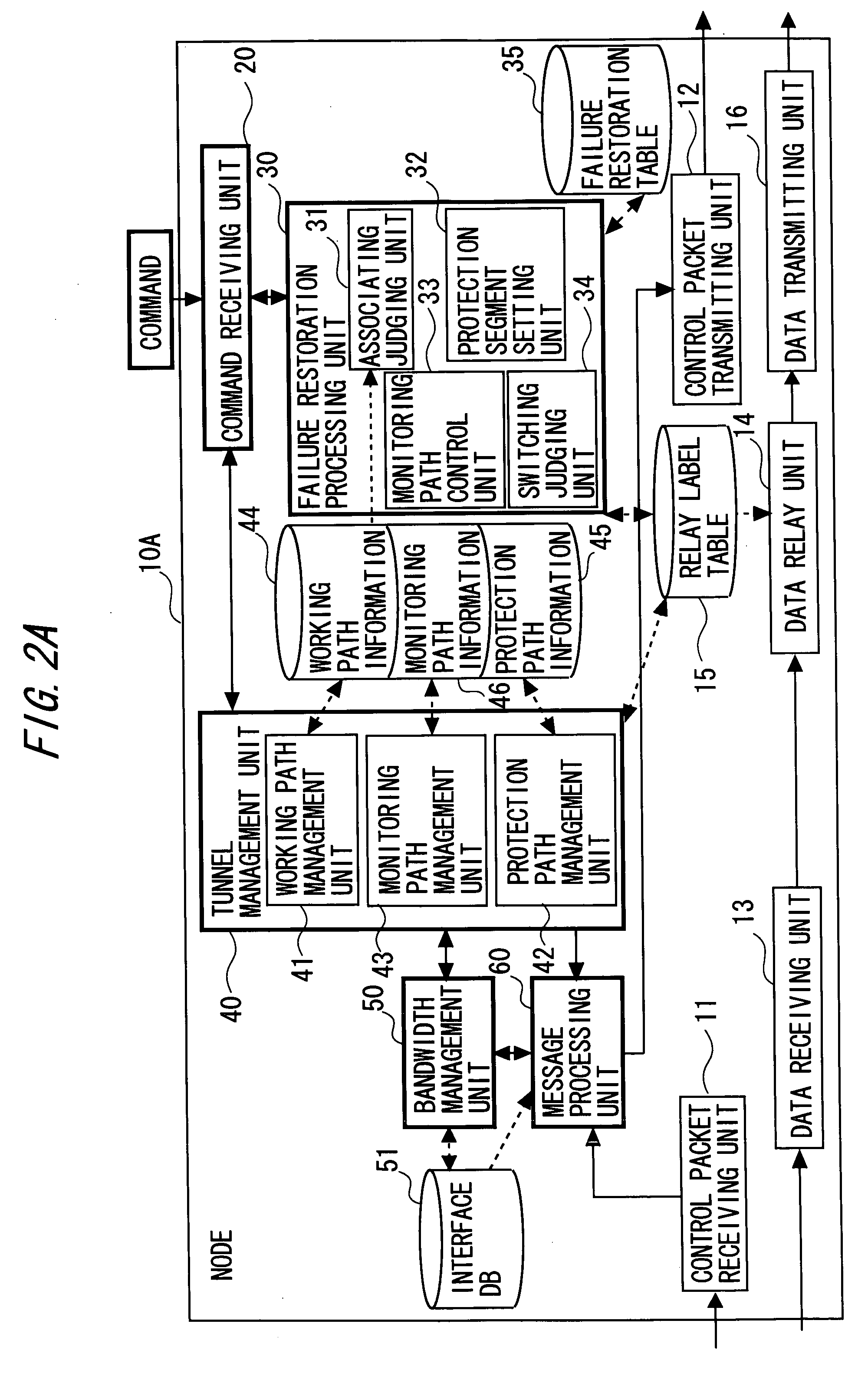
A connection-oriented network node capable of becoming an originating node of a protection path serving as a bypath of a protection segment included in a working path in a network system in which data is transferred via a path previously set up between nodes, comprises a usage bandwidth determining unit determining, when setting up the protection path, a usage bandwidth of the setup target protection path on the basis of a working path including the protection segment to be protected by the setup target protection path, and a generation unit generating, if a value obtained by adding the determined usage bandwidth to a current protection path usage bandwidth of an interface transmitting data that is forwarded on the setup target protection path, does not exceed a usable bandwidth for the protection path that is preset with respect to the interface, a signaling message for setting up the setup target protection path to send this message.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Segment protection scheme for a network
InactiveUS7398321B2Facilitates bandwidth sharingShorten recovery timeMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSurvivabilityHigh-speed link
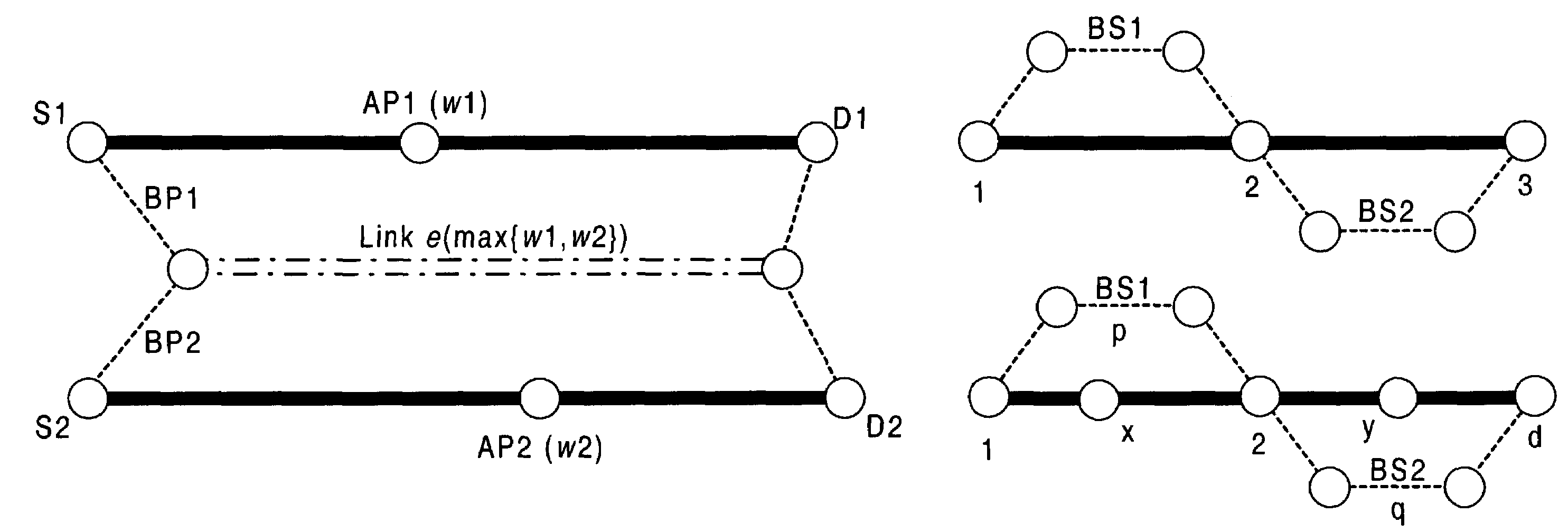
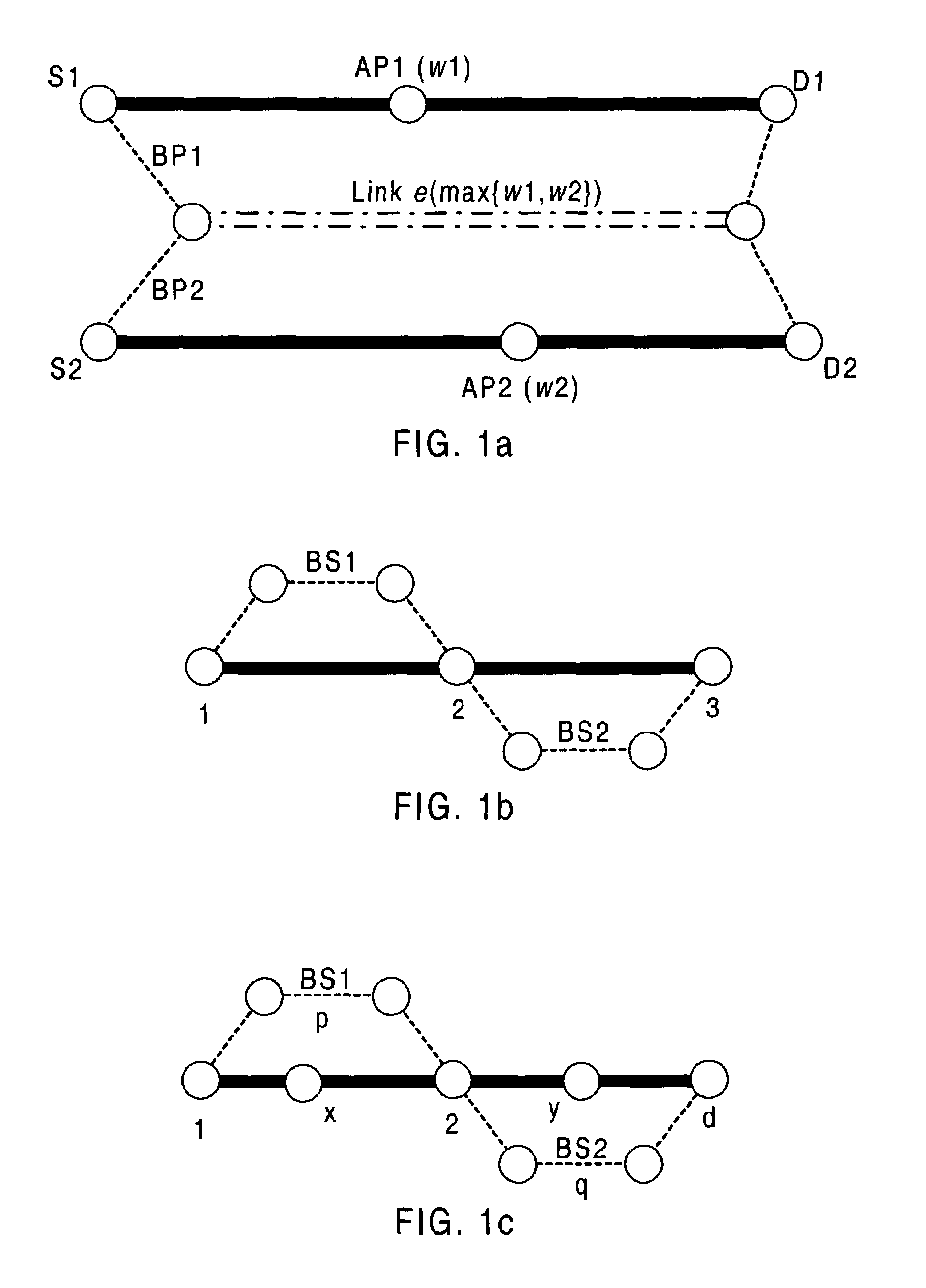
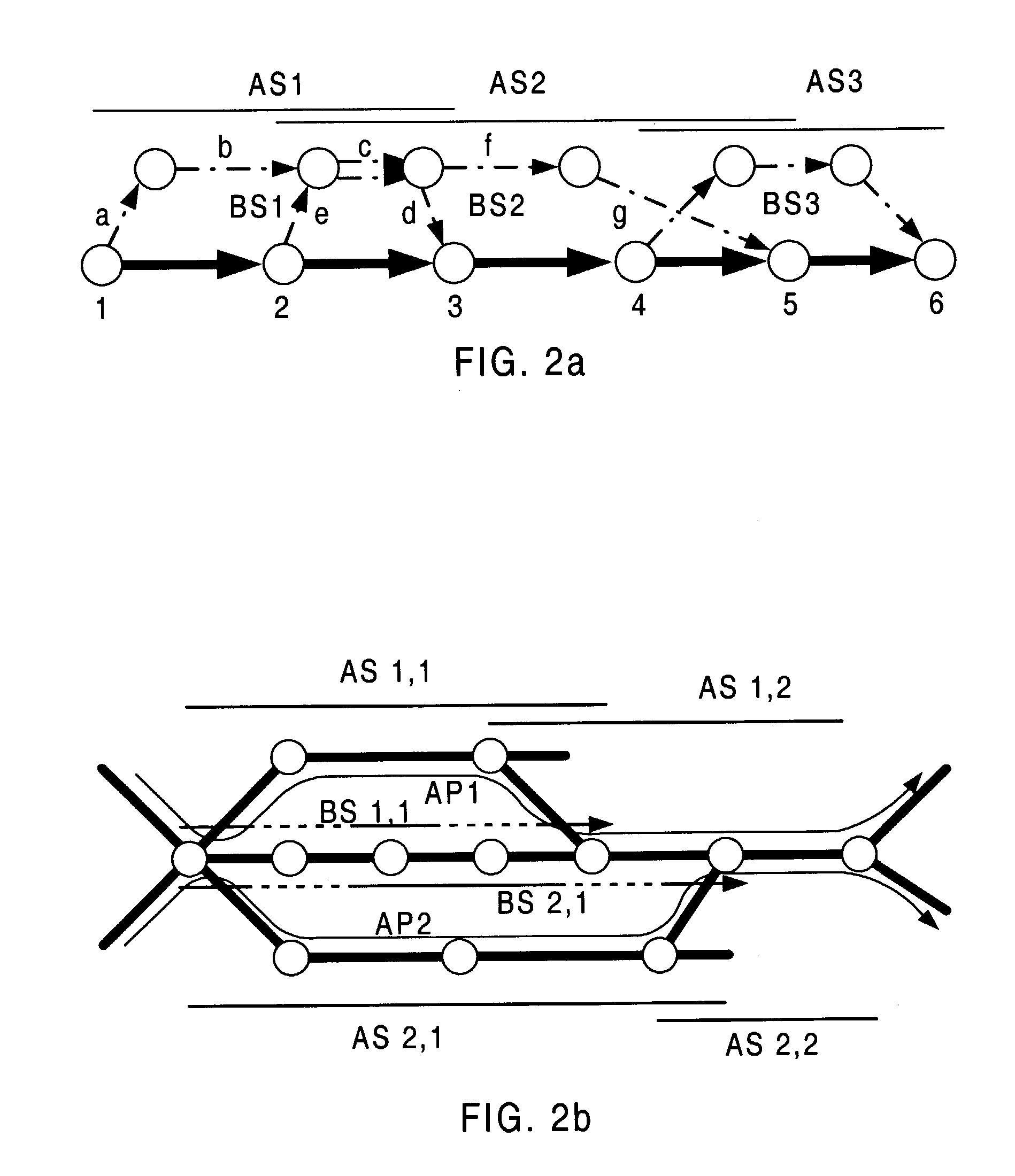
This invention broadly comprises a novel segment protection scheme (survivability framework) for a network, which we refer to as PROMISE (Protection using MultIple SEgments). It combines the best of existing link and path protection schemes (e.g., bandwidth efficiency and fast recovery). The PROMISE approach divides an active path or AP (along which a survivable connection is established) into several, possibly overlapping active segments or ASs, and then protects each AS with a detour called backup segment or BS (instead of protecting the AP as a whole as in path protection schemes). This facilitates the bandwidth sharing not only among the BSs for different APs, but also among those for the same AP. In addition, recovery time can be shortened due to the limited length of each AS and BS. This technology can be applied to MPLS, ATM, SONET, WDM and other high-speed link layers under the evolving G-MPLS framework.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and system for providing protection in an optical communication network
InactiveUS20040114925A1Laser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemSignal quality
A method and system for providing tandem protection in a communication system. Path protection is provided using at least two redundant communication paths and selecting the communication path having a higher signal quality. Interface protection is provided through a protection transceiver. The interface protection may be delayed while the path protection attempts to restore communication.
Owner:CIENA
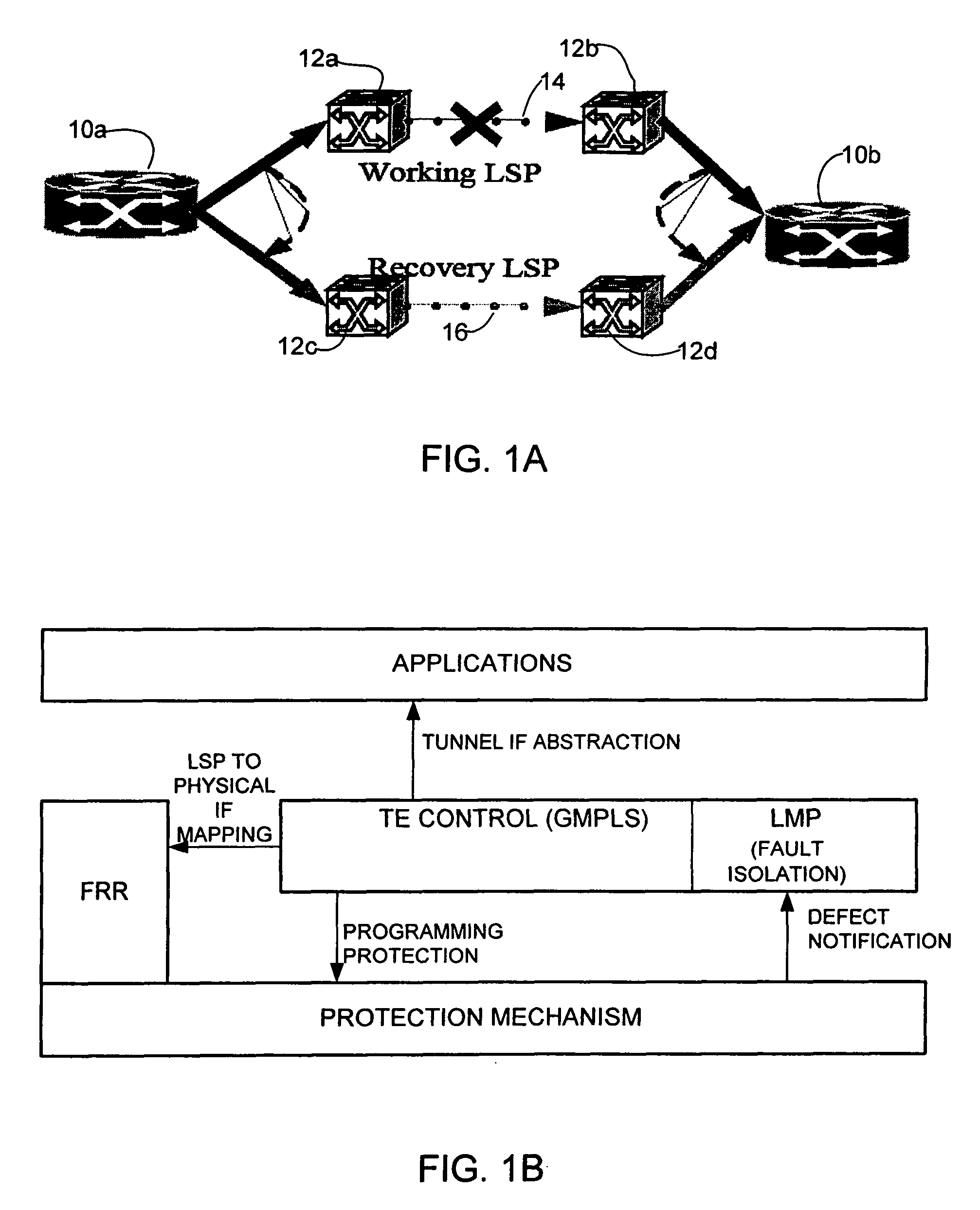
Fast rerouting method and label exchange router
InactiveCN101369958AAchieve protectionImprove reliabilityData switching networksType-length-valuePath protection
The invention relates to quick heavy-route method and label switching router. The method comprises: setting standby path for label switching path based on constrained routing and binding with the label switching path, first node of label switching path receiving notice information with path protection type-length-value TLV from insert knot of standby path when the label switching path is in failure, switching data of failure path to standby path for label transmission. The inventive example provides a label exchange tunnel based on constrained condition as prefabricated standby path to protect CR-LSP and avoid link and node failure.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
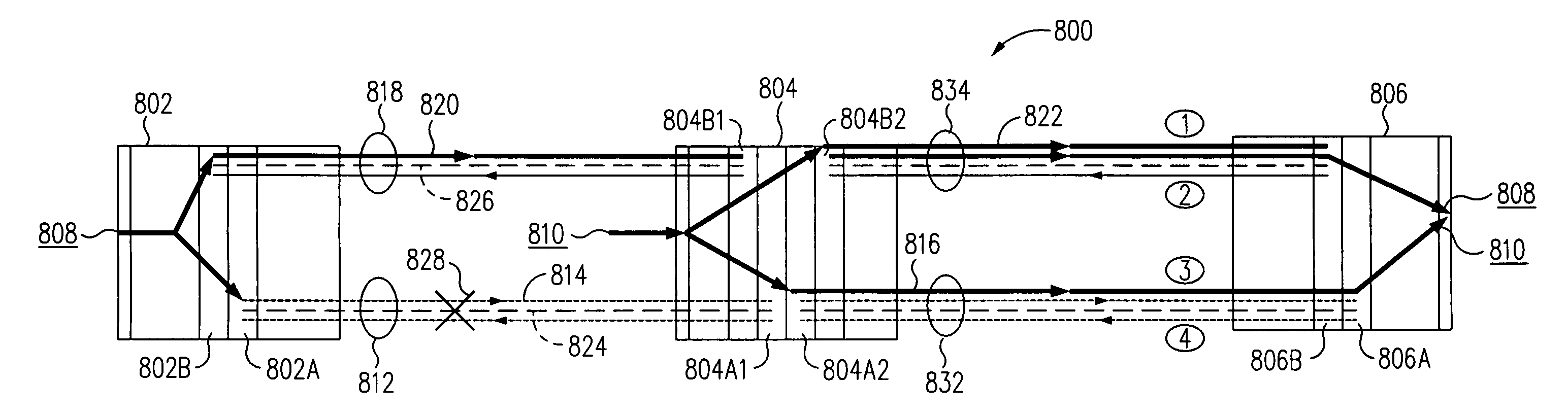
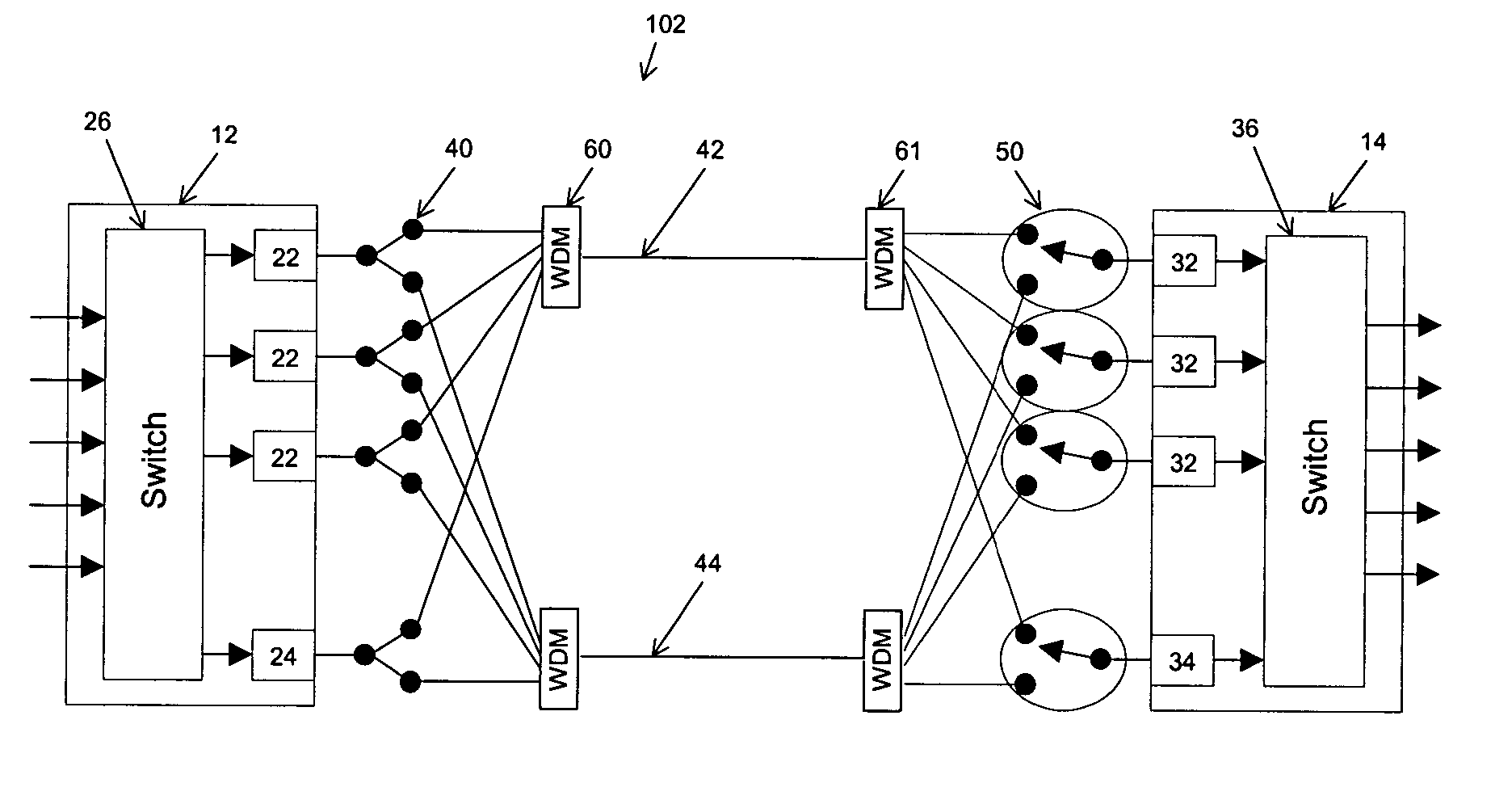
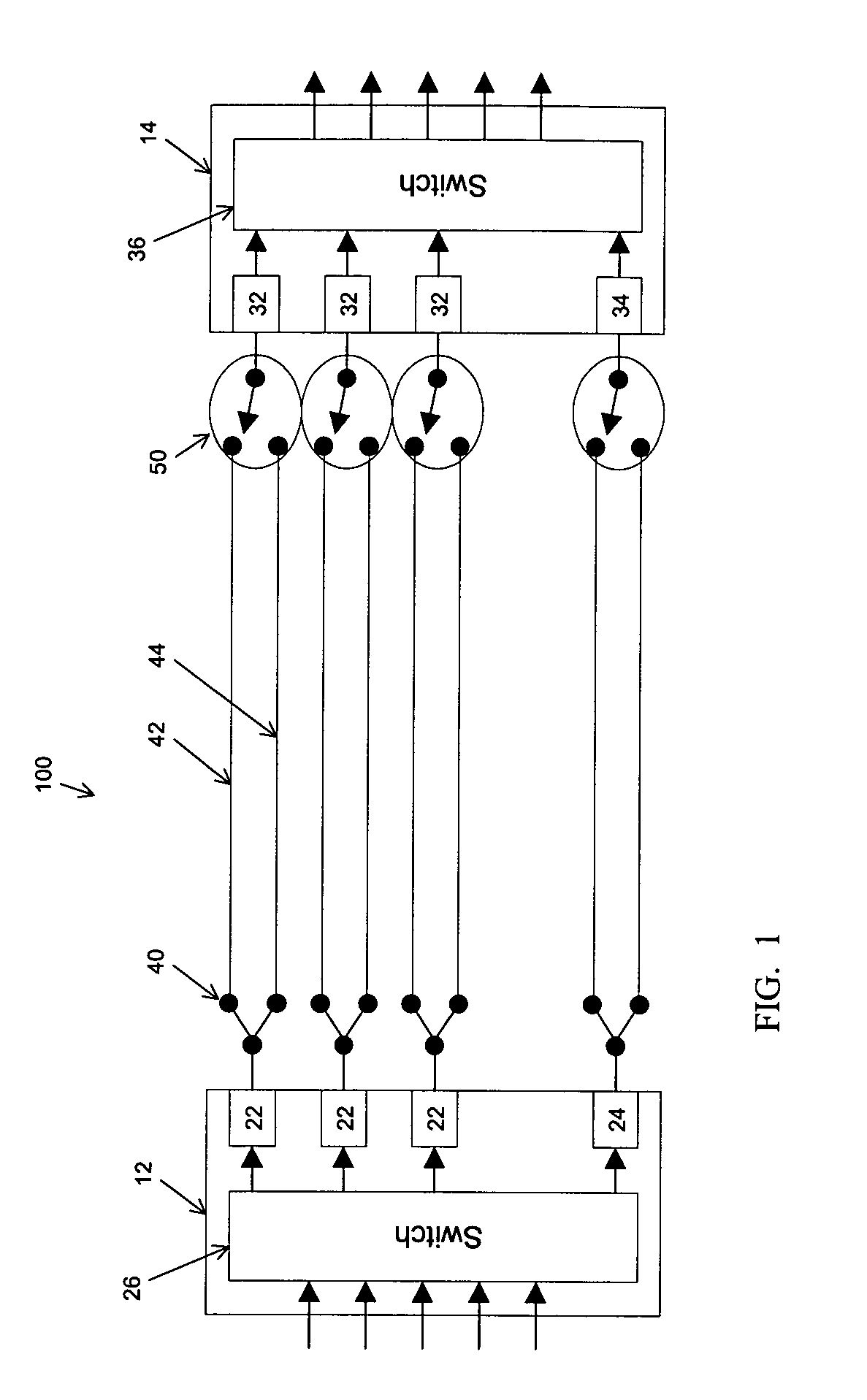
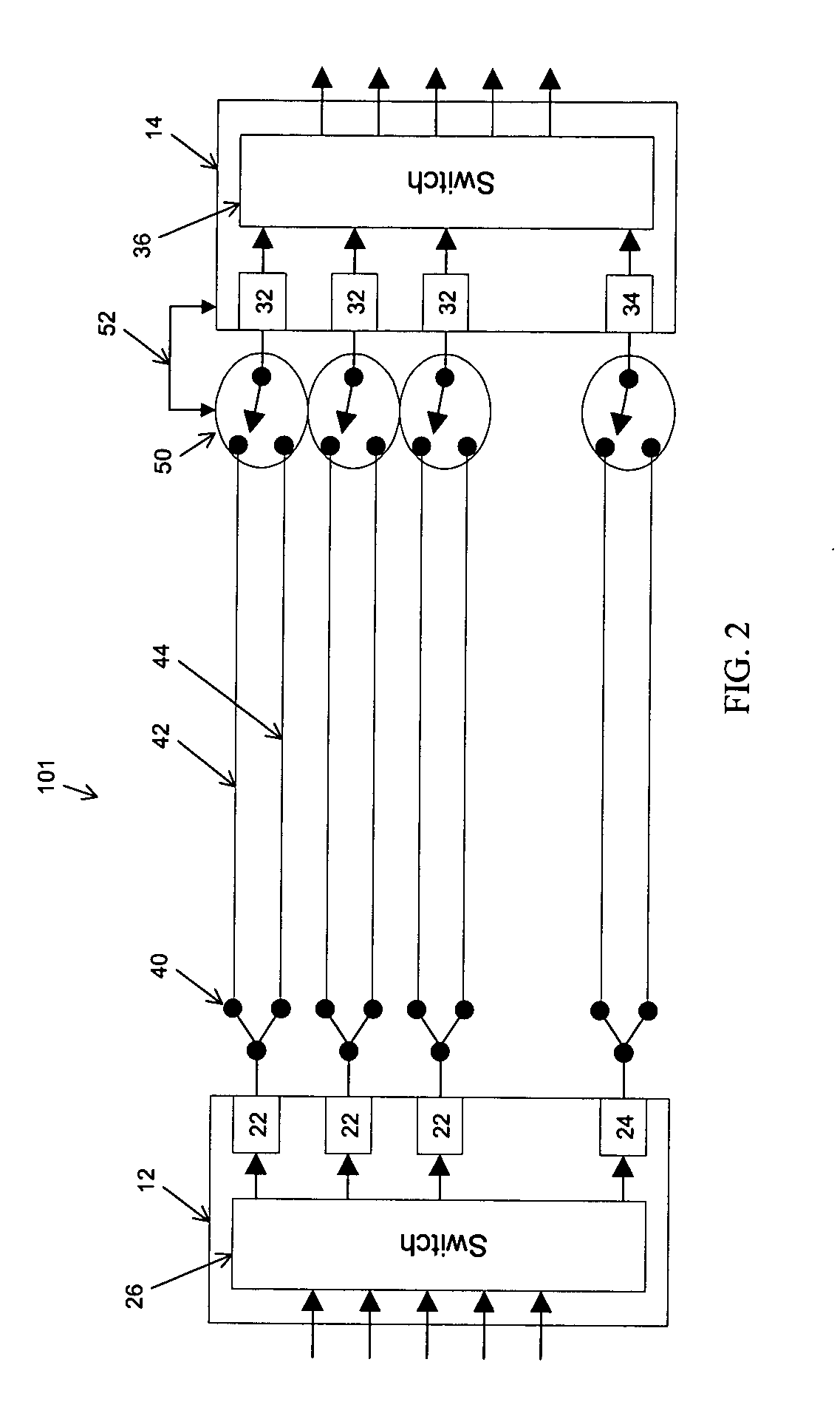
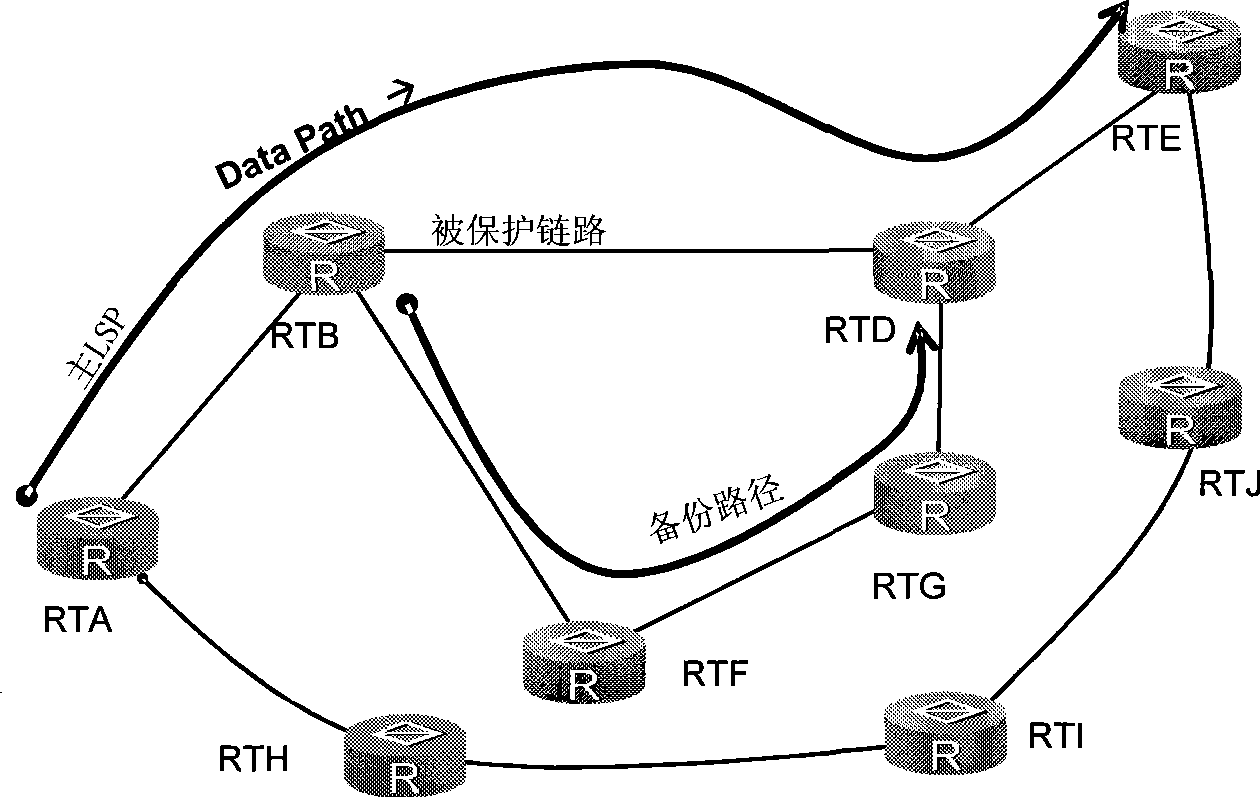
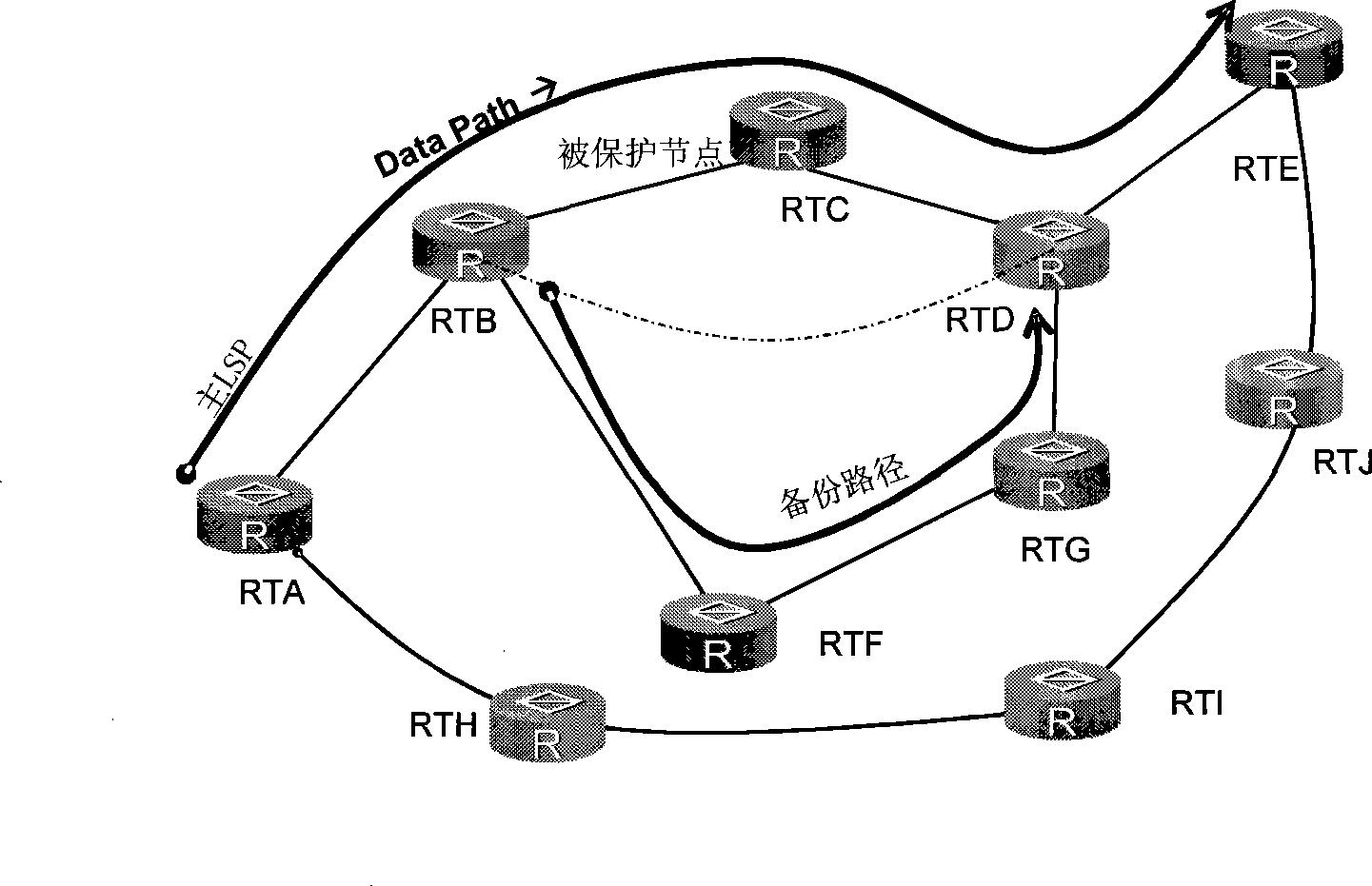
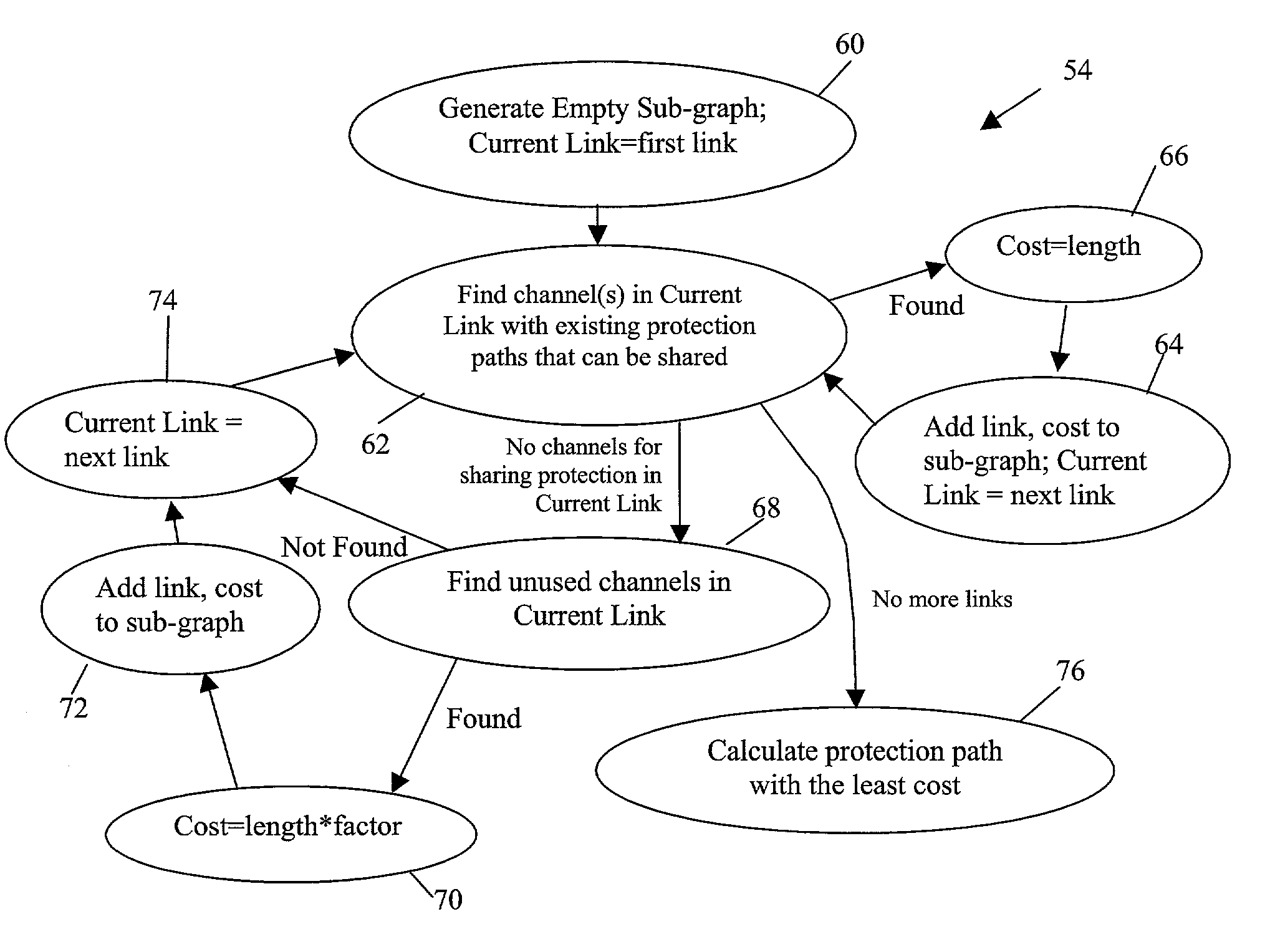
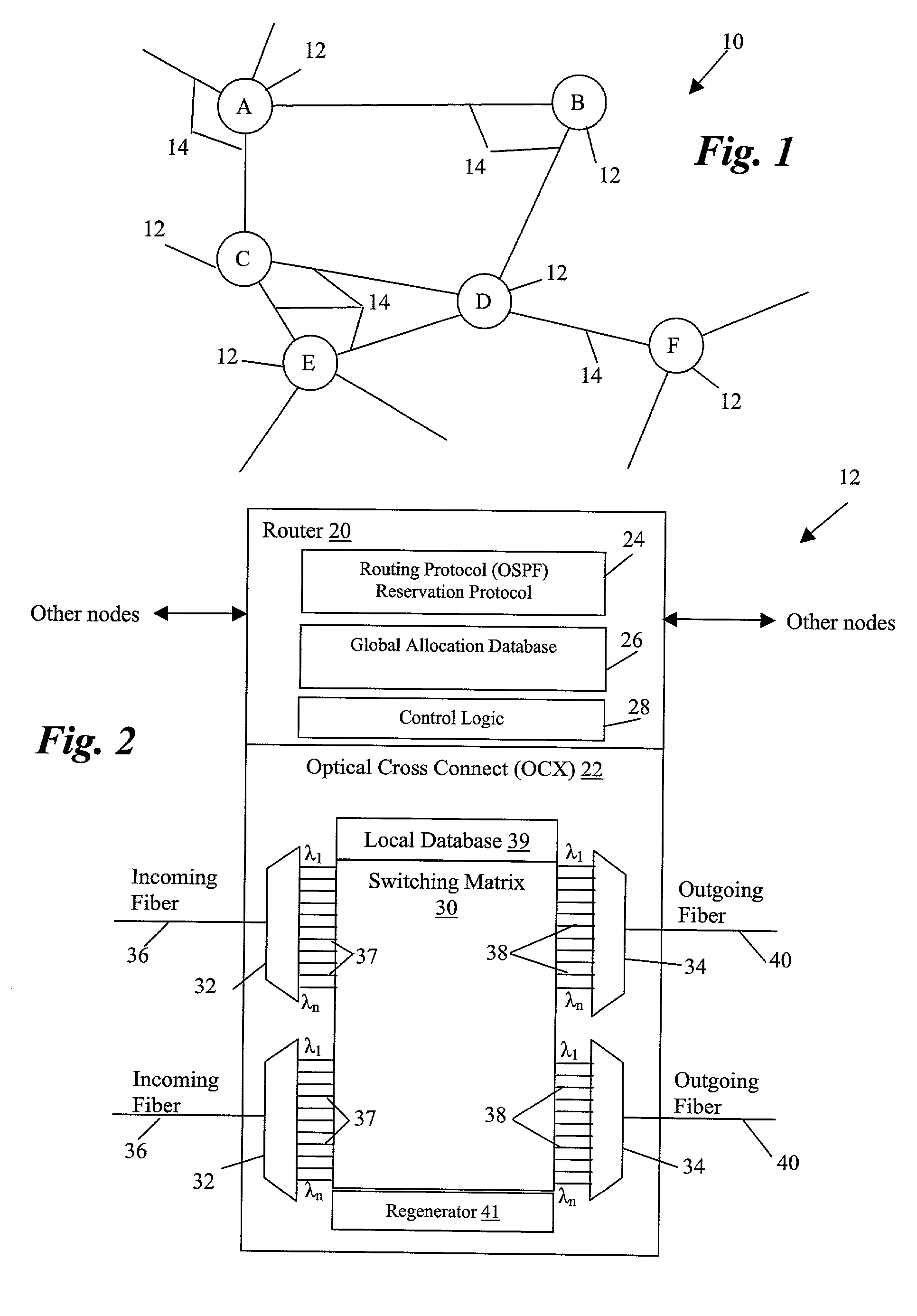
Informed dynamic path protection for optical networks
ActiveUS7113481B2Effective distributionPromote sharing protection channel resourcesError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Protection paths are dynamically allocated in a wavelength-division multiplexed network including a plurality of nodes (12) coupled by communication links (14). A database (26) stores information regarding the status of the network including information associating channels in each link of the node to one or more protection paths and information associating channels in each link to respective working paths. Upon receiving a request for a new protection path to protect a defined working path, links are identified that have at least one shareable channel which may be shared between the new protection path and one or more existing protection paths, as are links that do not have a shareable channel but do have an unused channel that may be used for the new protection path. Costs are assigned to identified links where links that have at least one shareable channel are weighted differently than links that do not have a shareable channel. A protection path is determined using the found links based on the costs.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
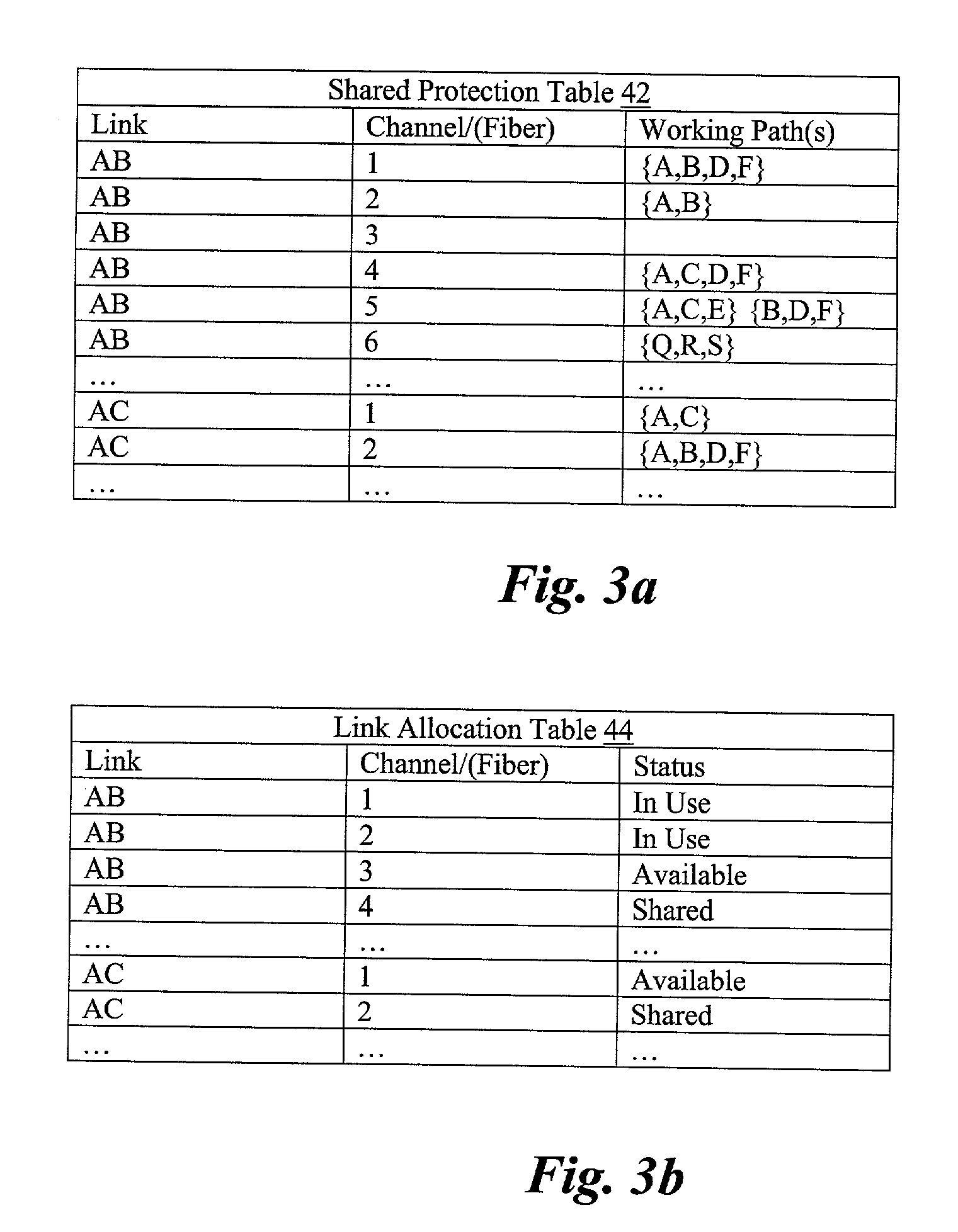
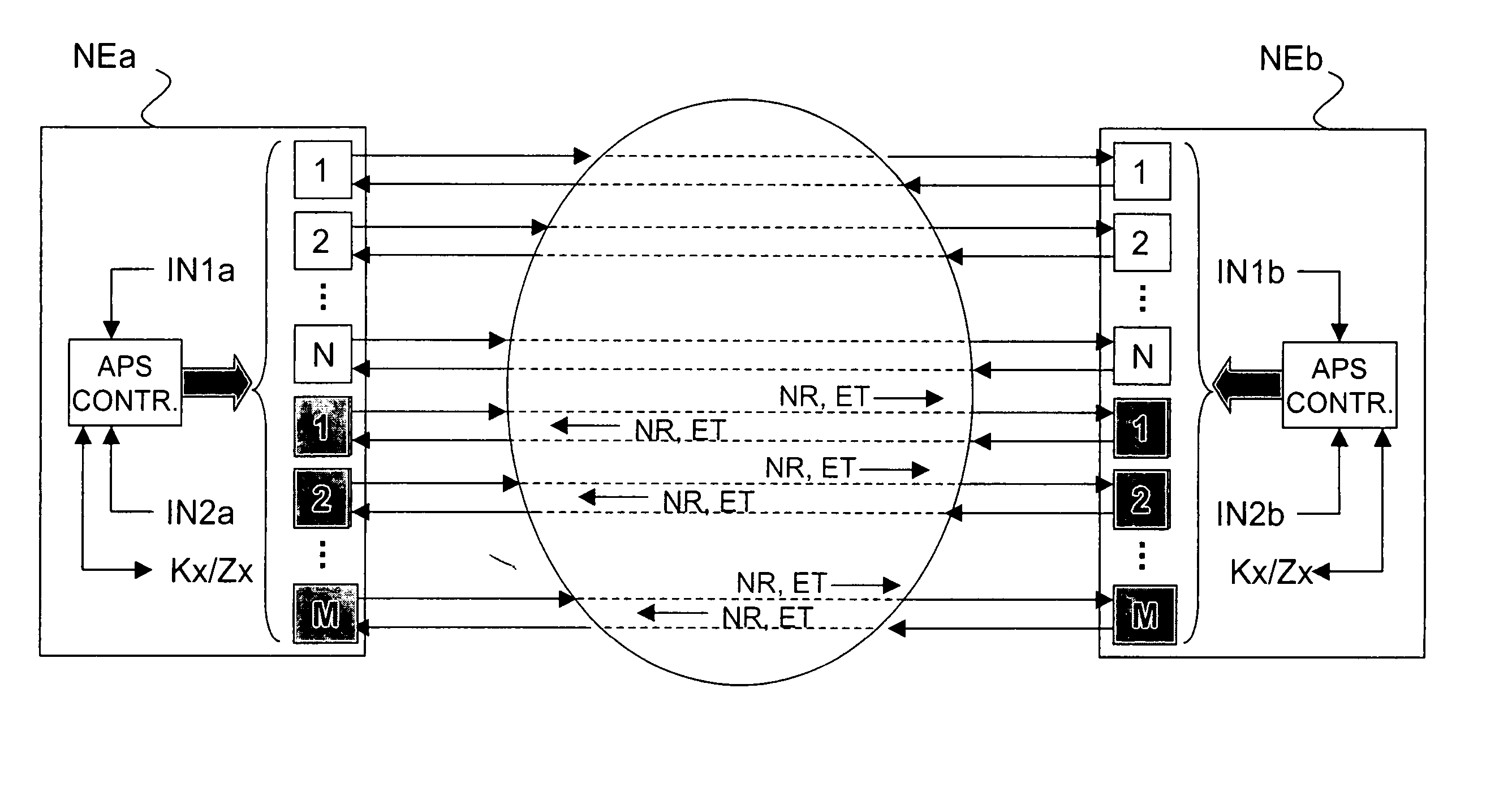
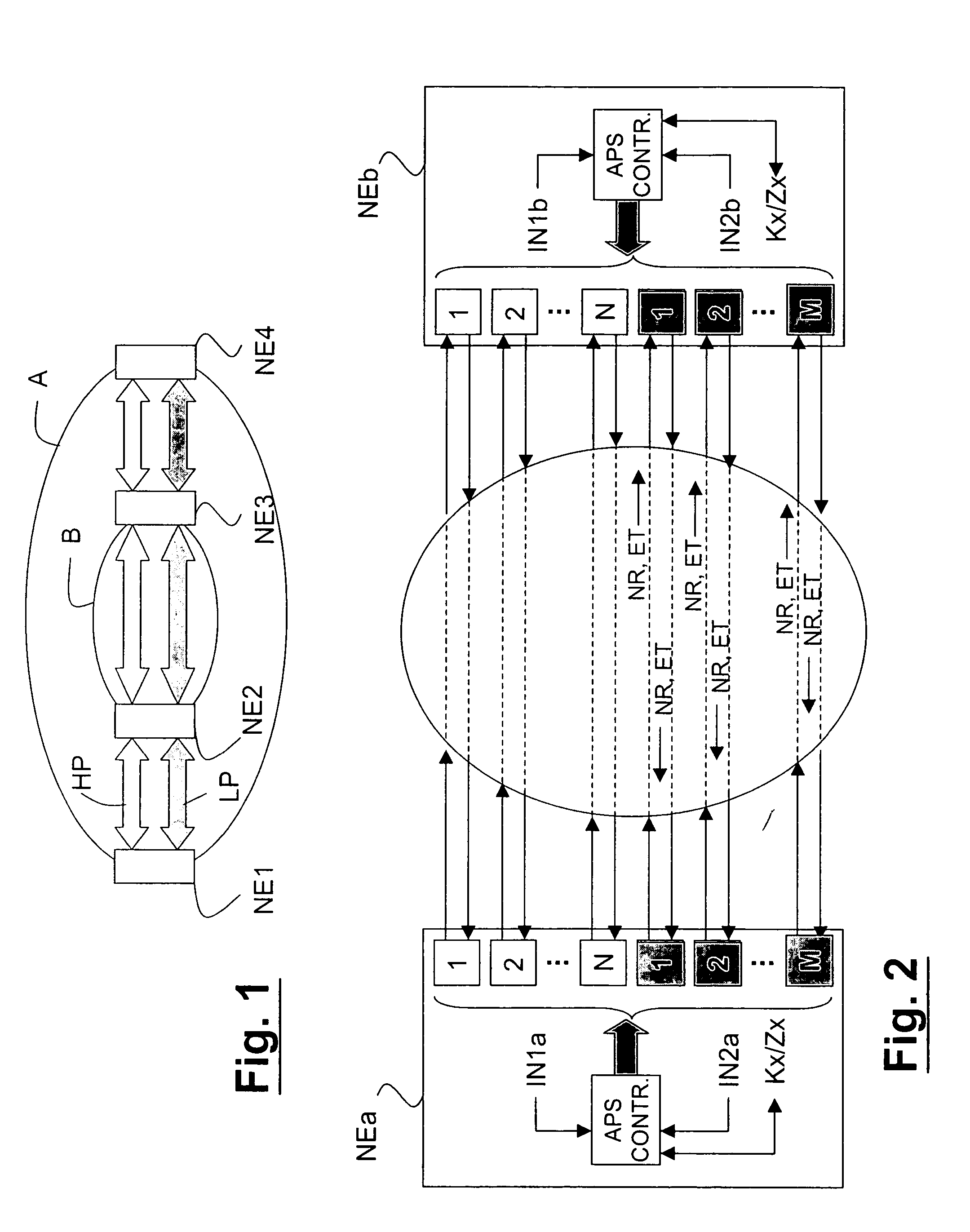
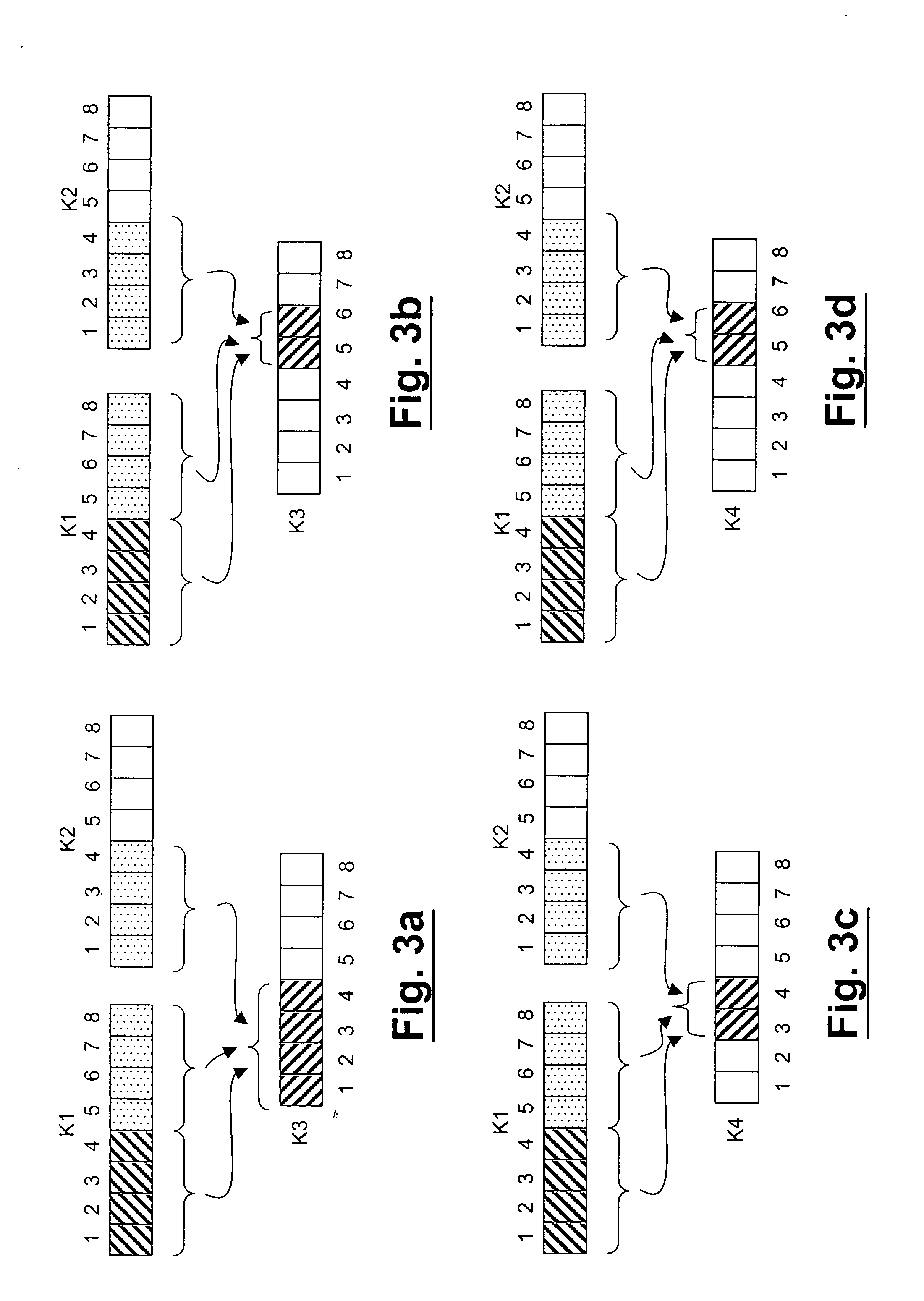
Trail/path protection for SDH/SONET networks
InactiveUS20050099941A1Improving traffic (path) reliabilityEasy to useError preventionTransmission systemsBytePath protection
A method is described for enhancing a trail / path protection function in a SDH / SONET network, the network comprising a number of working resources and a number of protection resources and transmitting signal frames having a section overhead in SDH technology, or a Line OverHead in SONET technology, and a POH, said protection function comprising linear MSP N:1 trail protection function based on transmission of protection information through K1 and K2 bytes of Section OverHead in SDH or Line OverHead in SONET, wherein the method further comprises the step of mapping the content of said K1 and K2 bytes by protocol exchange into POH bytes of the path overhead in SDH or SONET, at Low Order and / or High Order level, so as to allow the handling of more than one protecting resource shared among different working resources, both in end-to-end handling and in intermediate handling.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
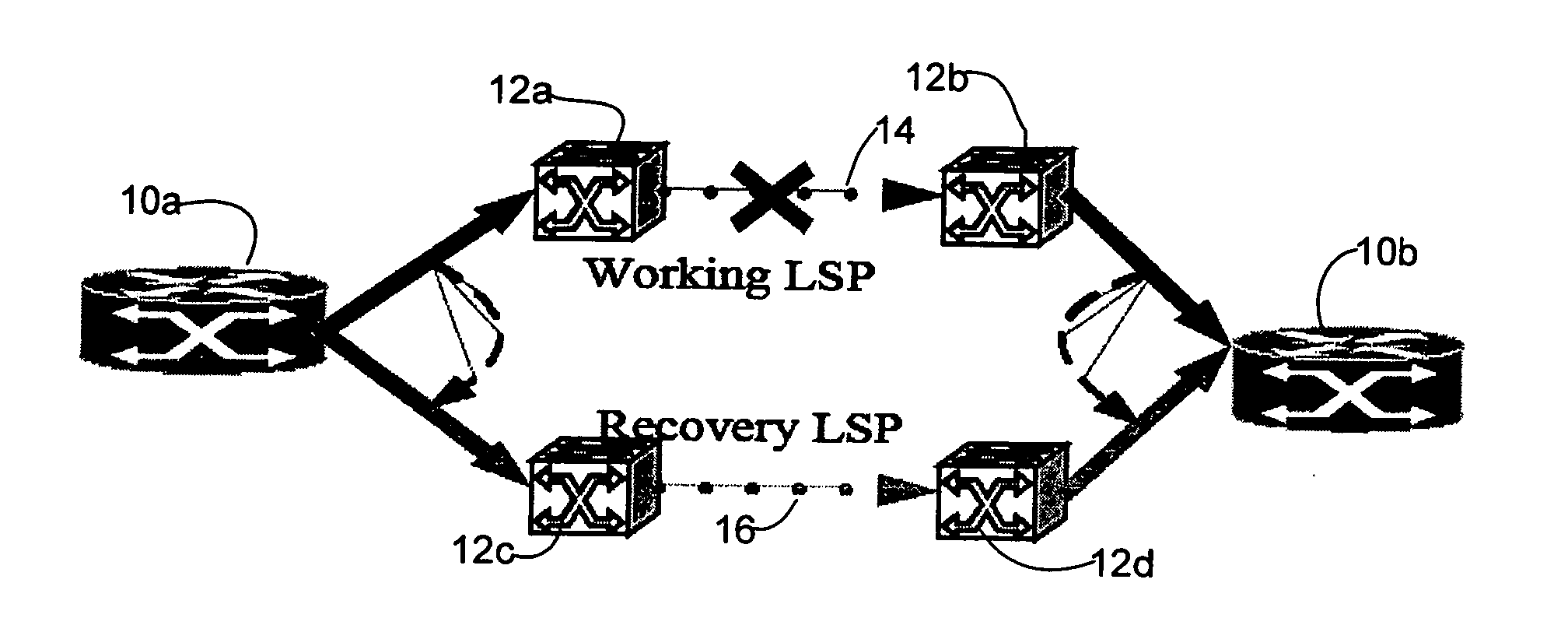
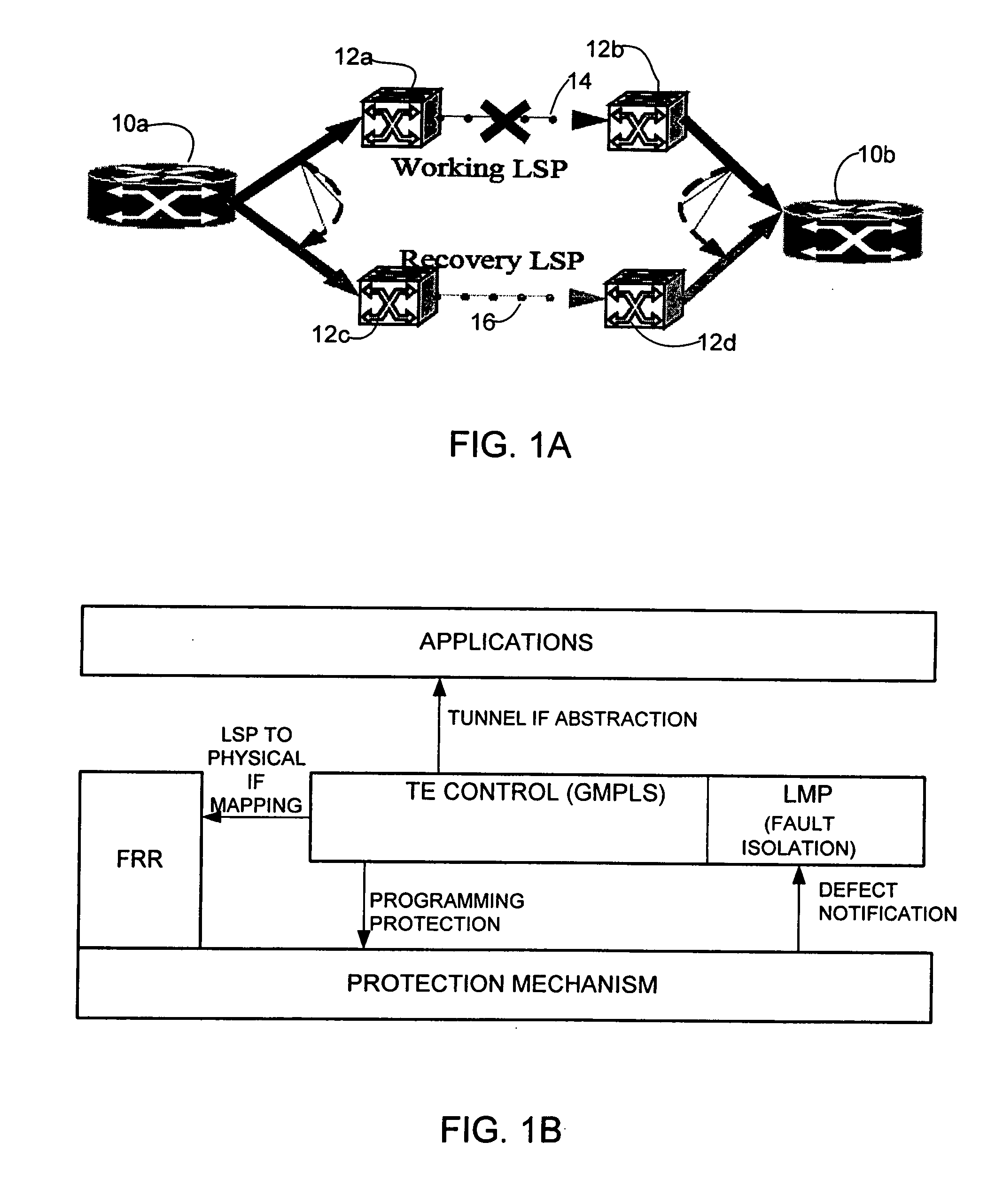
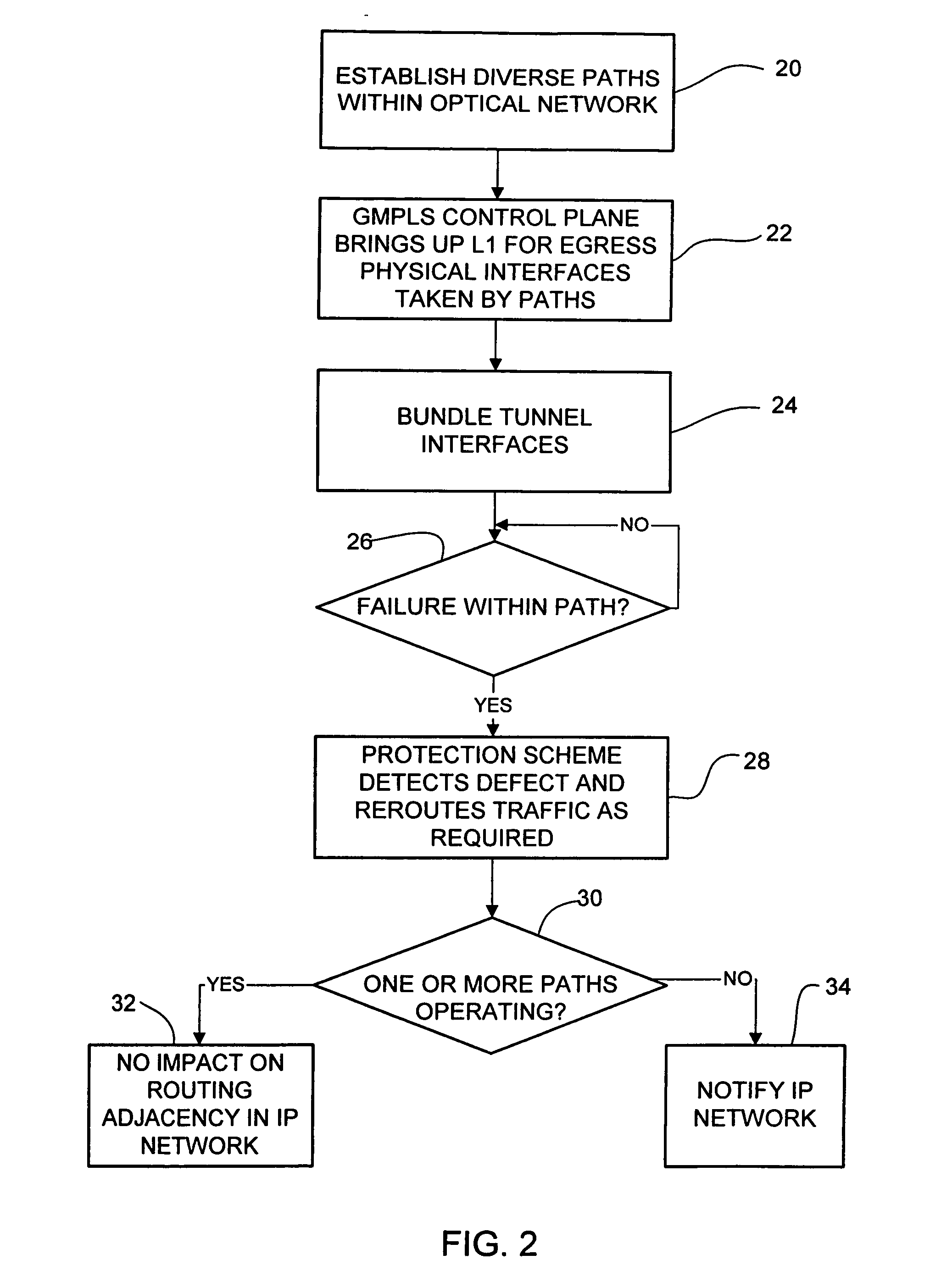
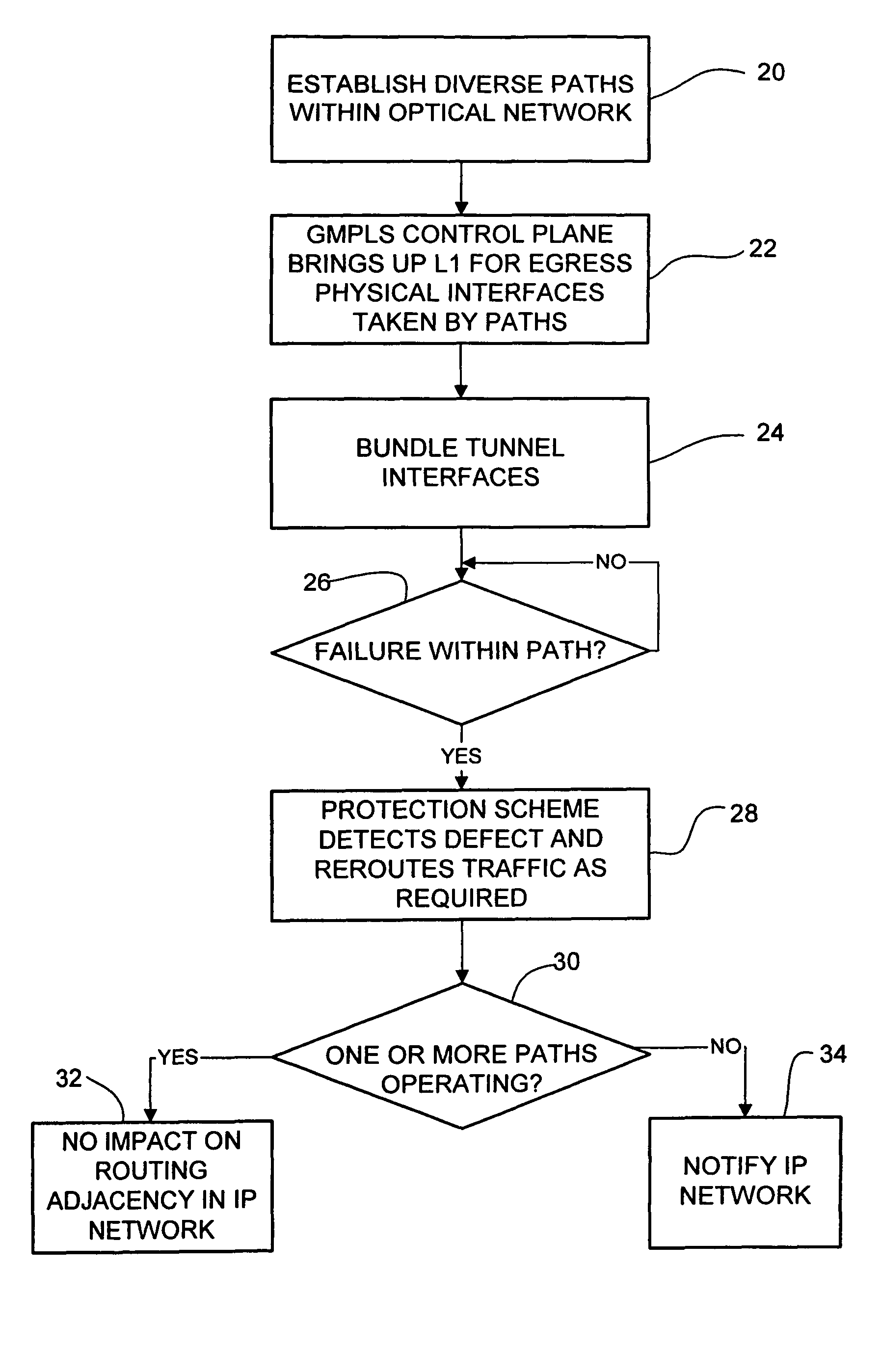
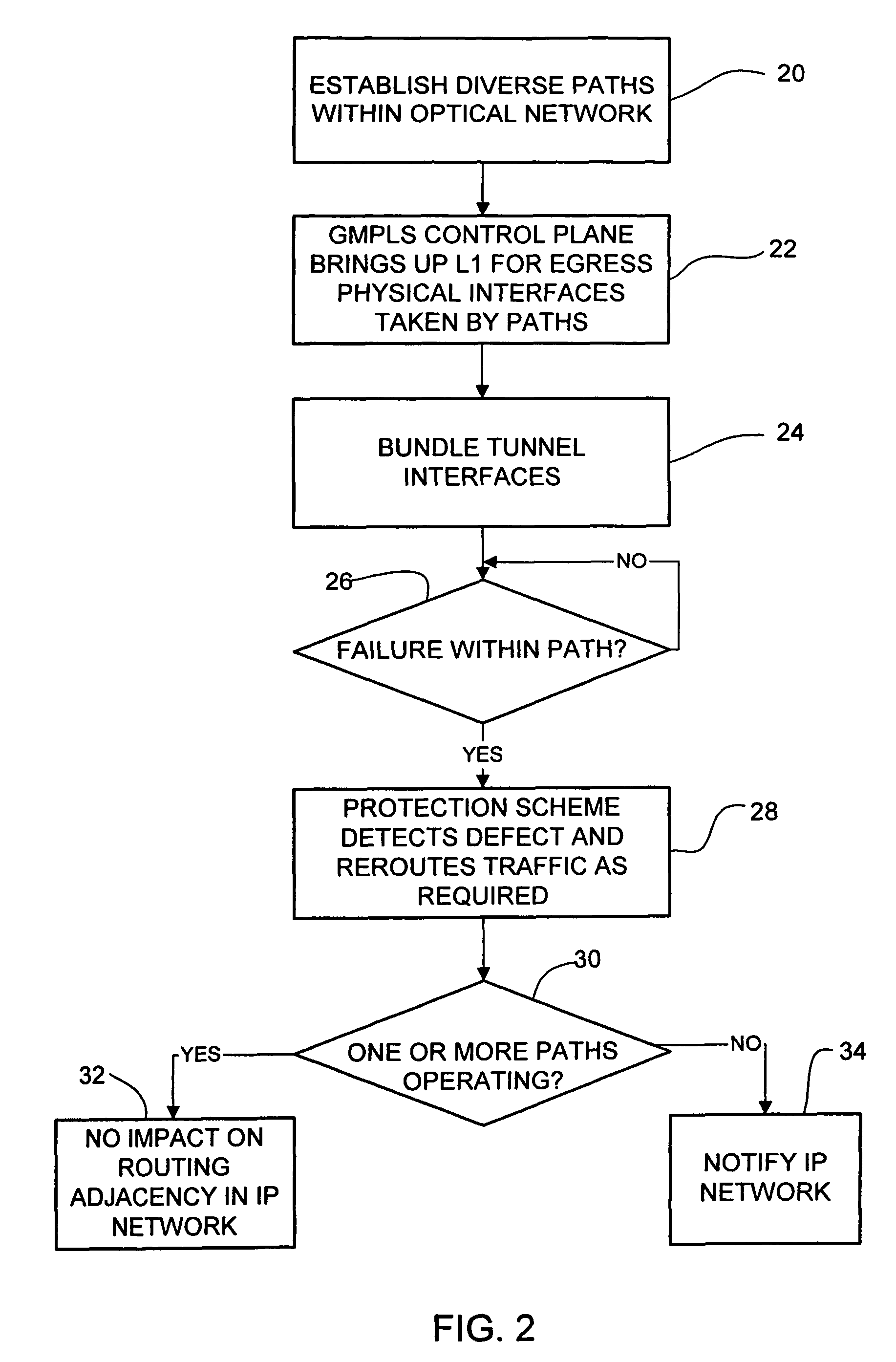
Dynamic path protection in an optical network
ActiveUS20060250948A1Not affectError preventionTransmission systemsPath protectionDistributed computing
A method and system for dynamic protection of virtual links for paths of an optical network in communication with an IP network are disclosed. The method includes establishing two or more paths within the optical network and grouping the paths in a dynamic bundle. The grouping is selected at a control plane level and the bundle of paths are recognized as a single routing adjacency in the IP network so that as long as one or more paths within the bundle is operating, the routing adjacency in the IP network is not affected by changes within the bundle.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for controlling plane participation protective rotation in ASON network
InactiveCN1588890AImprove survivabilityData switching networksAutomatically switched optical networkPath protection
This invention relates to a method for protecting inversions involved by a control plane in an automatic exchange light network which utilize the GMPLS technology to set up label switching paths (LSP) and takes the protected attribute of LSP as one of conditions to provide it to the control plane for route selection operation to realize the route protection and multiplex segment protection involved by the control plane on ASON nod and realize inversion protection by this invented method.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Line-level path protection in the optical layer
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Communication path redundancy protection systems and methods
Communication path redundancy protection systems and methods are disclosed. Multiple communication interfaces having a common address support communications on respective communication paths. One of the interfaces or communication paths is selected as an active interface or path for transferring communication traffic. In the event of a fault associated with the active interface or path, another one of the interfaces or paths is selected to become active. The common address allows redundant interfaces to appear as a single interface to other communication equipment, whereas the multiple interfaces provide redundant path protection using a single piece of communication equipment. When embodiments of the invention are implemented in a gateway router of a core communication network, for example, activity switches between redundant access paths have no effect on routing in the core network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
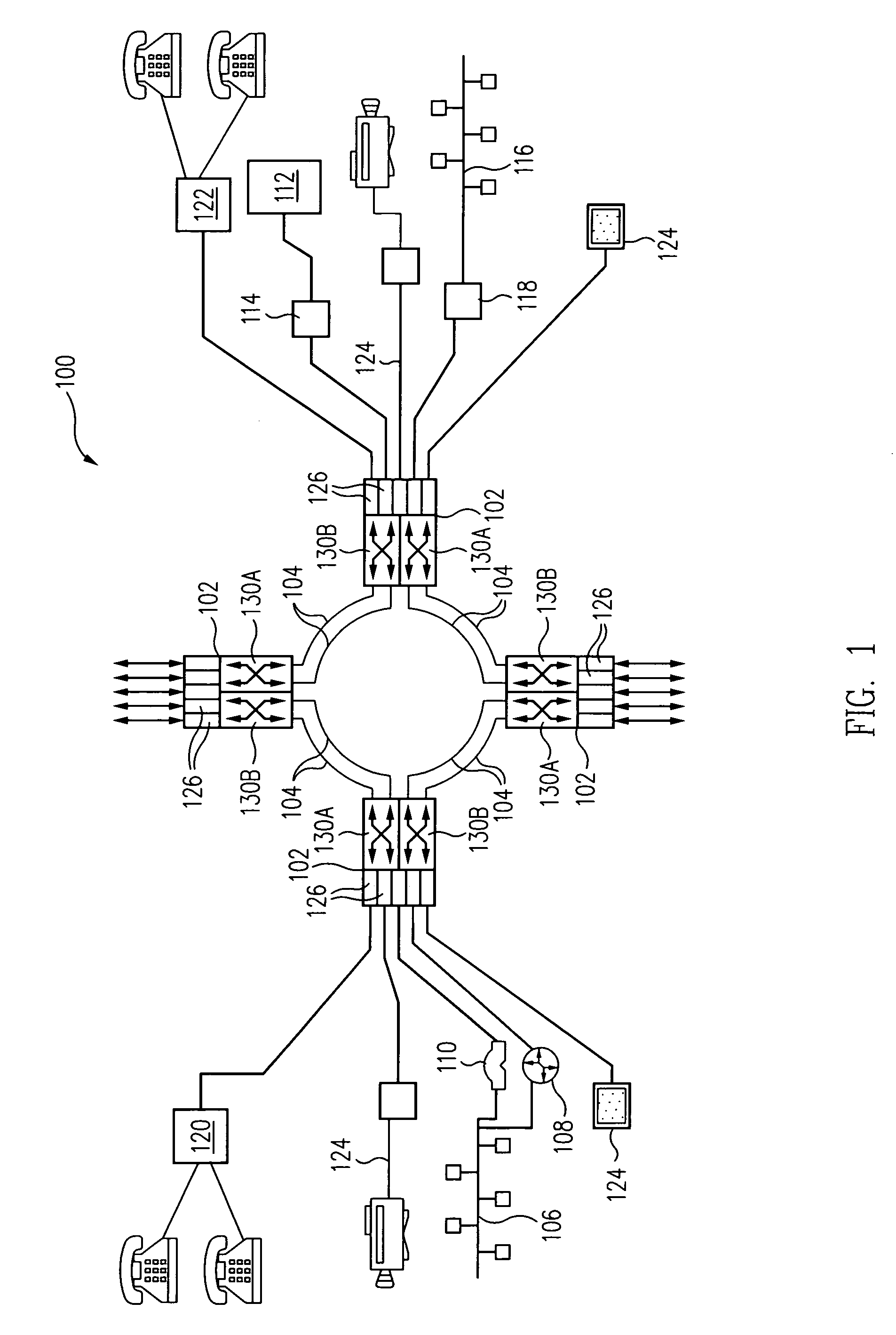
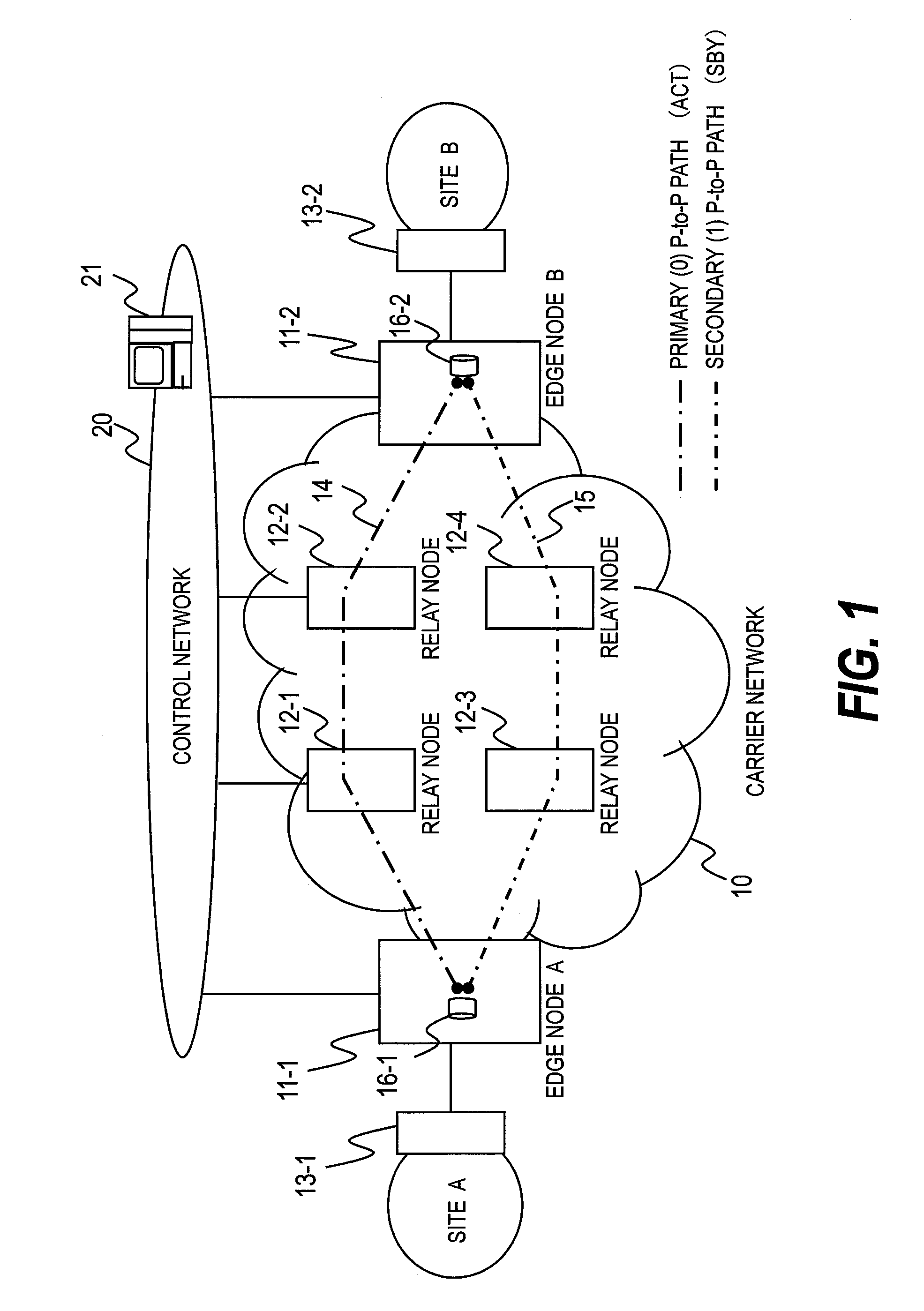
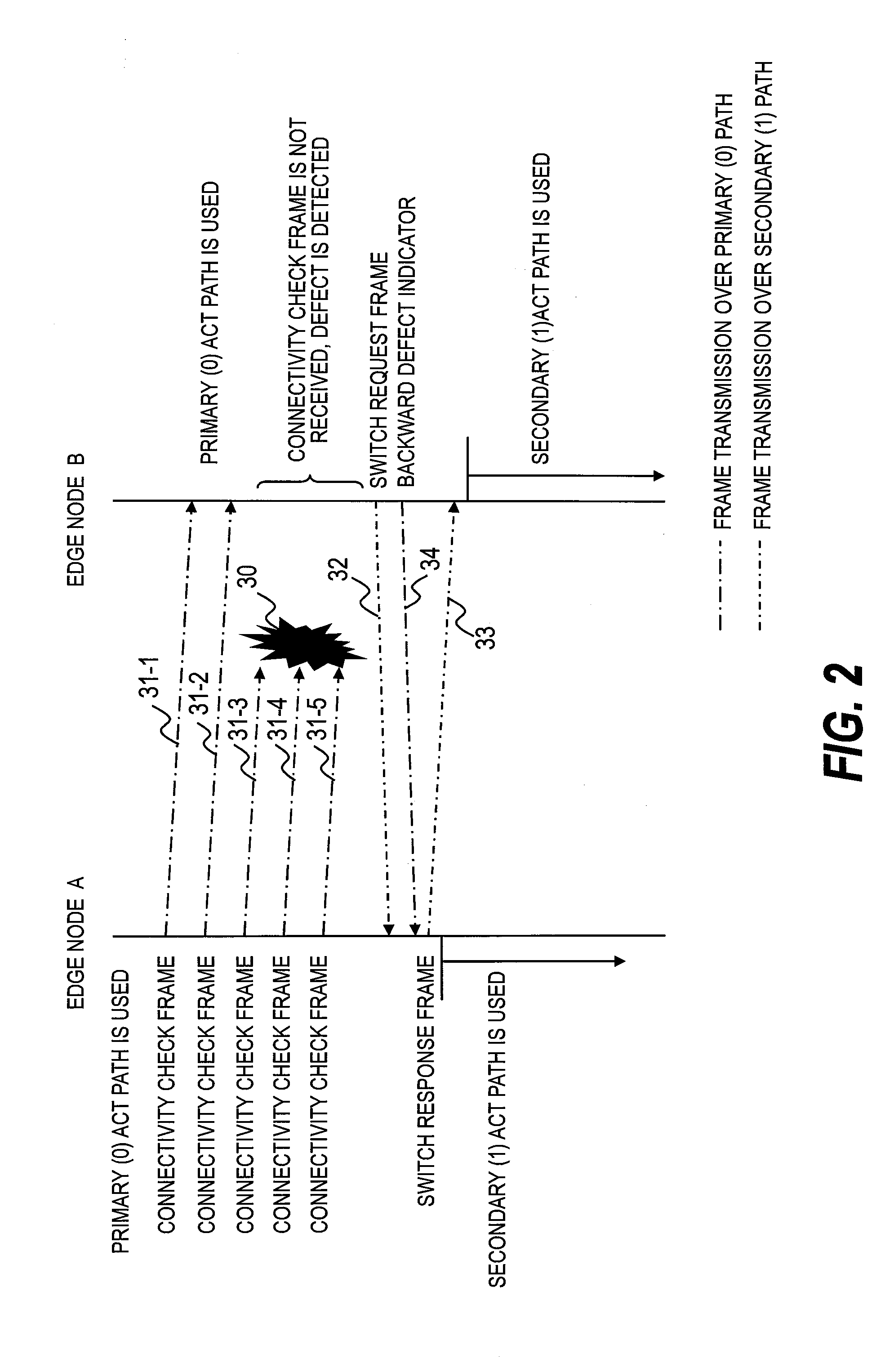
Communication device with a path protection function, and network system using the communication device
Provided is a network system including a start device and multiple end devices. A point-to-point (P-to-P) logical path is set to be used for unicast communication between the start device and each of the end devices. A first point-to-multipoint (P-to-M) logical path and a second P-to-M logical path are set to be used for multicast communication from the start device to the multiple end devices. The start device transmits data over the first P-to-M logical path. When one of the end devices detects a defect along the first P-to-M logical path, the end device that has detected the defect transmits a switch request over the P-to-P logical path set between this end device and the start device. The start device receives the switch request and transmits data over the second P-to-M logical path.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dynamic path protection in an optical network
ActiveUS7835267B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath protectionOptical network unit
A method and system for dynamic protection of virtual links for paths of an optical network in communication with an IP network are disclosed. The method includes establishing two or more paths within the optical network and grouping the paths in a dynamic bundle. The grouping is selected at a control plane level and the bundle of paths are recognized as a single routing adjacency in the IP network so that as long as one or more paths within the bundle is operating, the routing adjacency in the IP network is not affected by changes within the bundle.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for optical communication protection
InactiveUS20050122899A1Improve efficiencyRing-type electromagnetic networksError preventionTraffic capacityRouting table
Protection techniques within optical communication networks are extremely important. An alternative to a line protection scheme, as most current optical communication networks use, is to utilize a path protection technique in which working and protection paths that are desired are assigned during network setup. During normal operations, only the working path is configured within the network elements' switch fabric with protection paths being left unconfigured. If a failure indication is detected in the working path by a network element, a protection entry within a routing table of the network element is looked up to determine protection switching data that is required to switch the data traffic to the pre-assigned protection path. This protection switching data is inserted within the path overhead for the data traffic so that it can be communicated to all of the network elements that require their switch fabrics reconfigured to establish the protection path of communications. This protection technique allows for similar switching speed to that of line switching protection such as BLSR designs, but with an increase in efficiency in terms of protection bandwidth.
Owner:CIENA
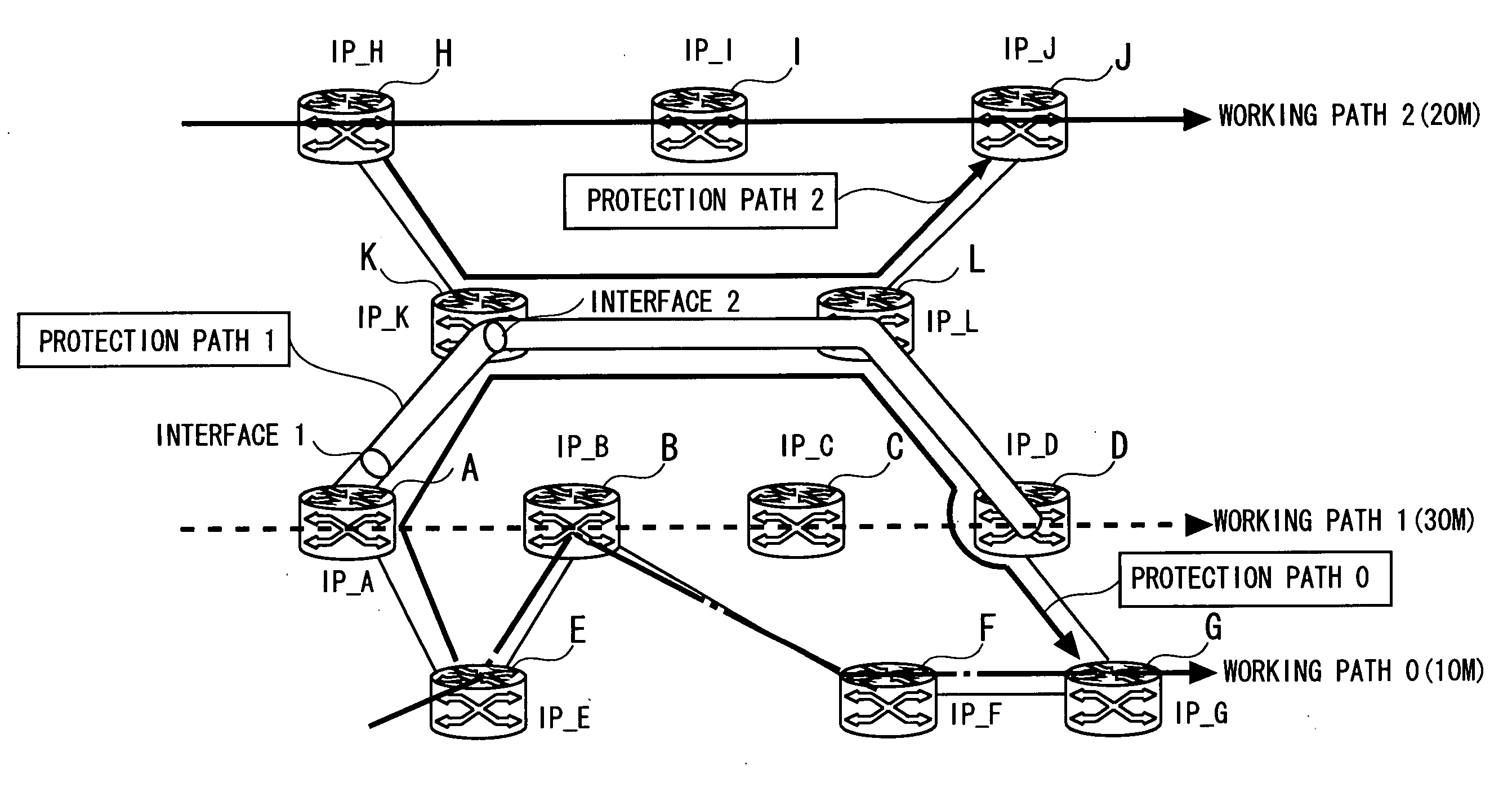
Route protection in a communication network
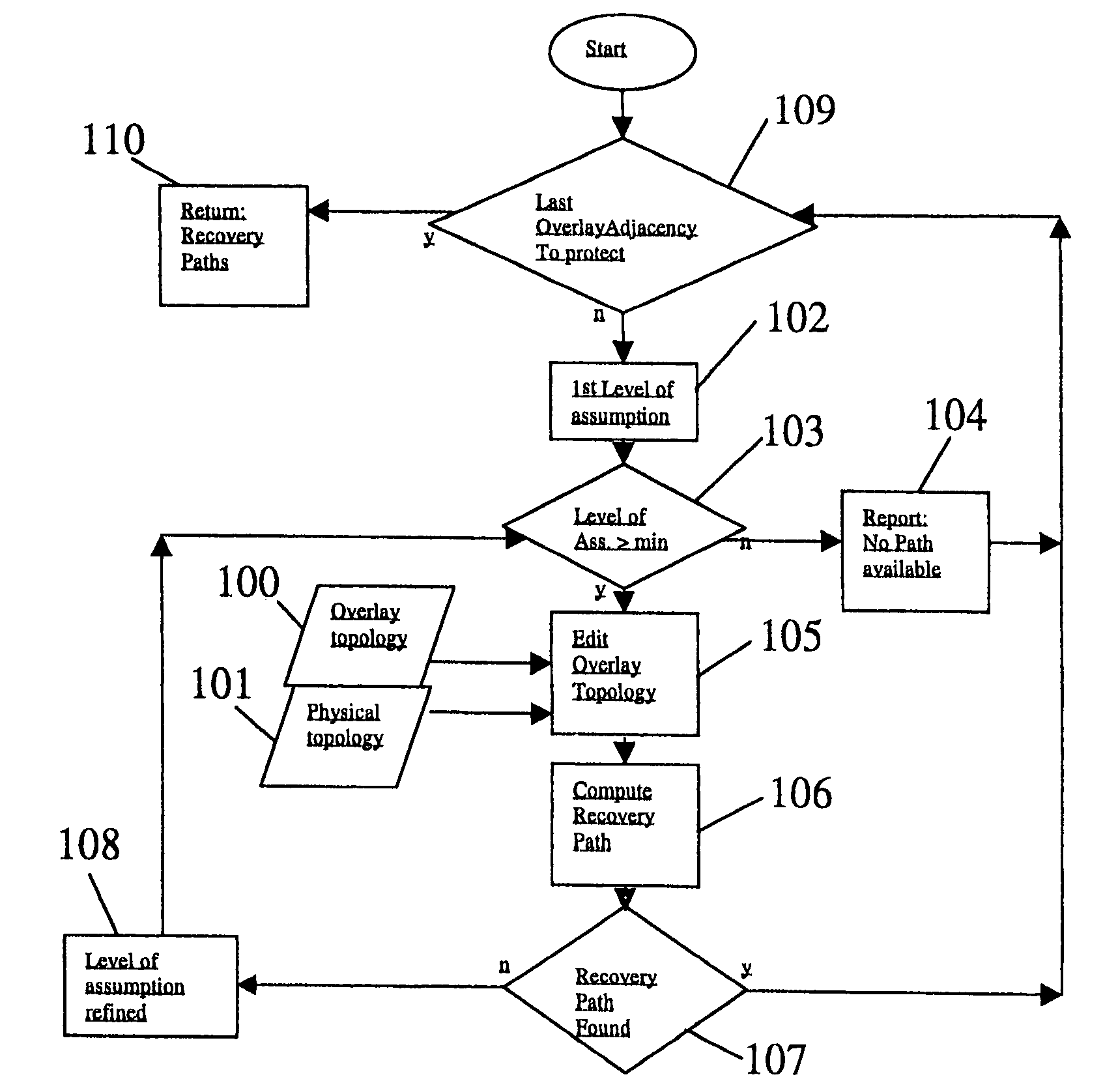
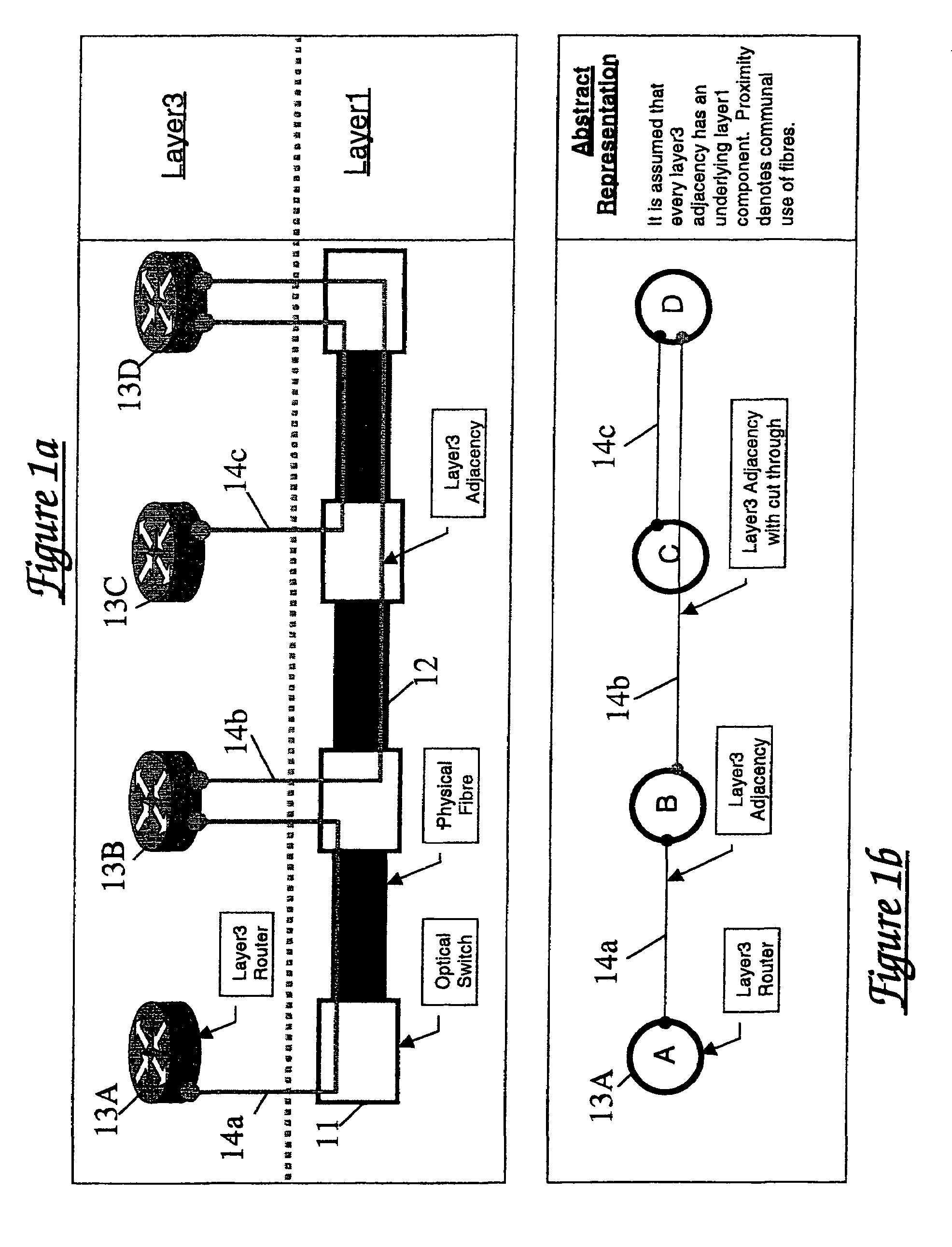
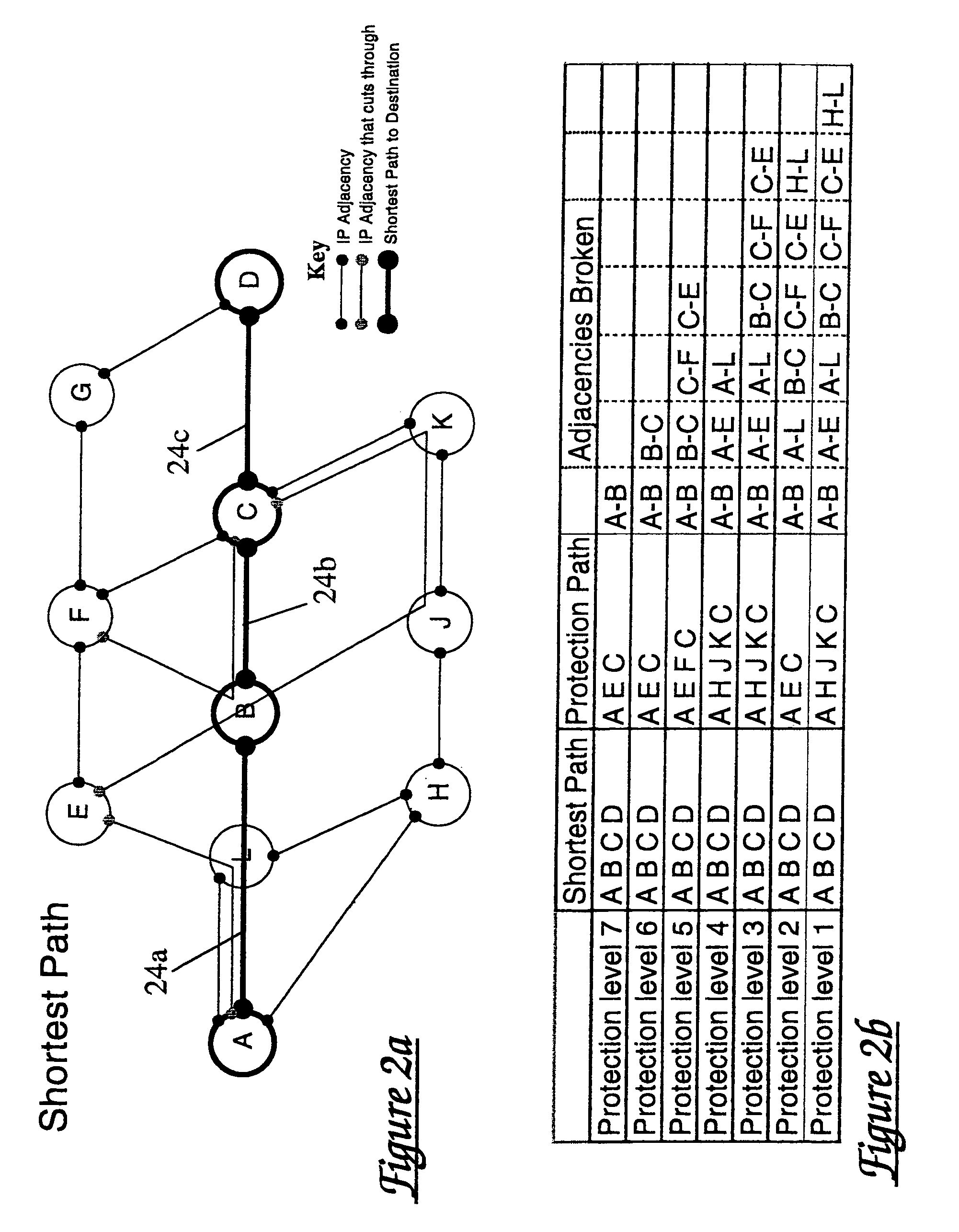
A communications network comprises a lower transport layer and an upper overlay incorporating a plurality of routers. Adjacencies are defined between respective pairs of routers. Path protection is provided by defining a software model of the overlay of the network and defining in the model a hierarchy of protection levels for the main path. Each protection level is characterised by a respective set of one or more broken adjacencies in the model, the adjacencies to be broken being determined from a knowledge of the underlying topology. A protection level is selected and a protection path avoiding the broken adjacencies associated with that protection level is calculated. If this calculated path is not available in the real network, a lower protection level in the hierarchy is selected and the protection path calculation repeated. The process continues until a suitable protection path is identified.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
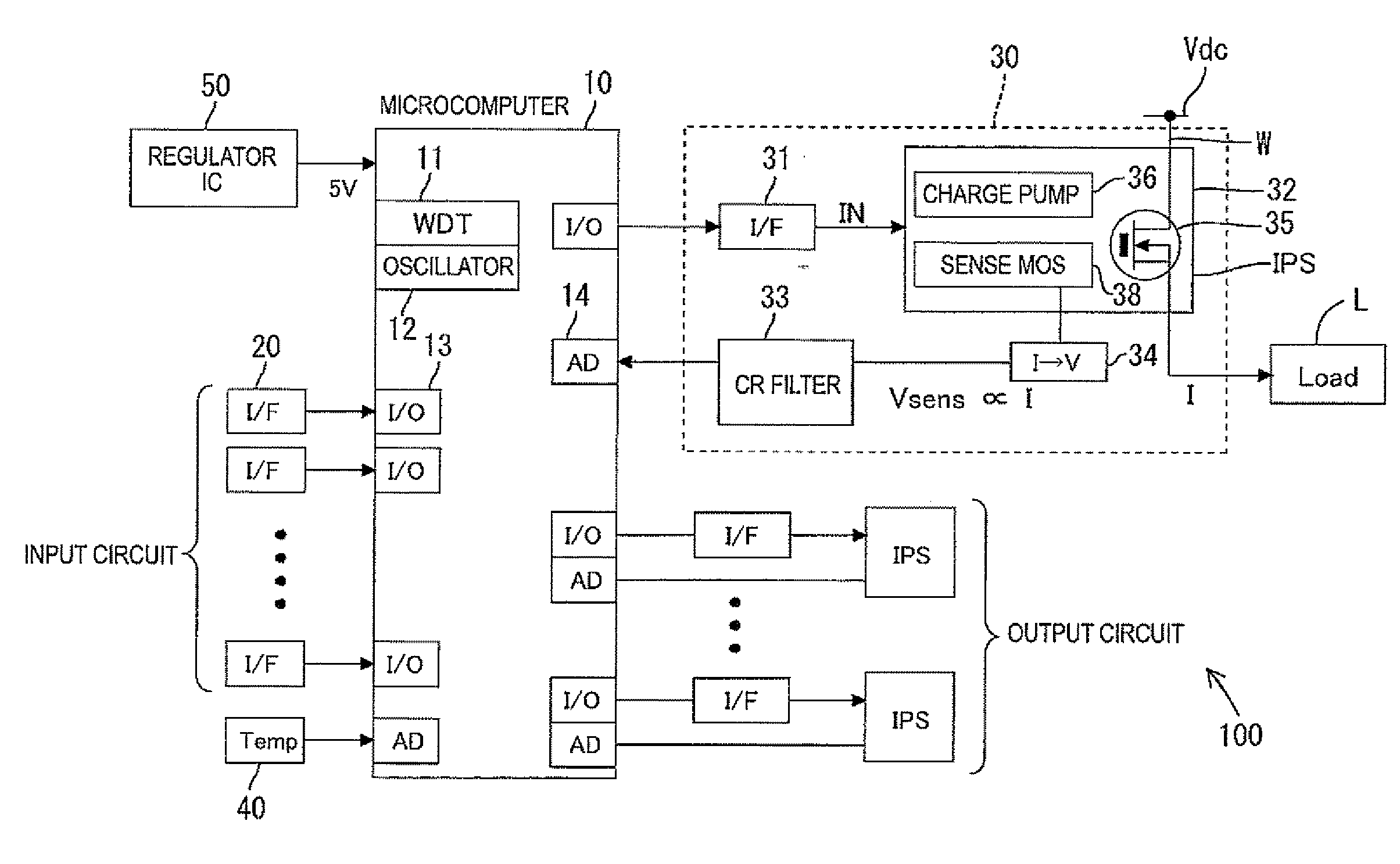
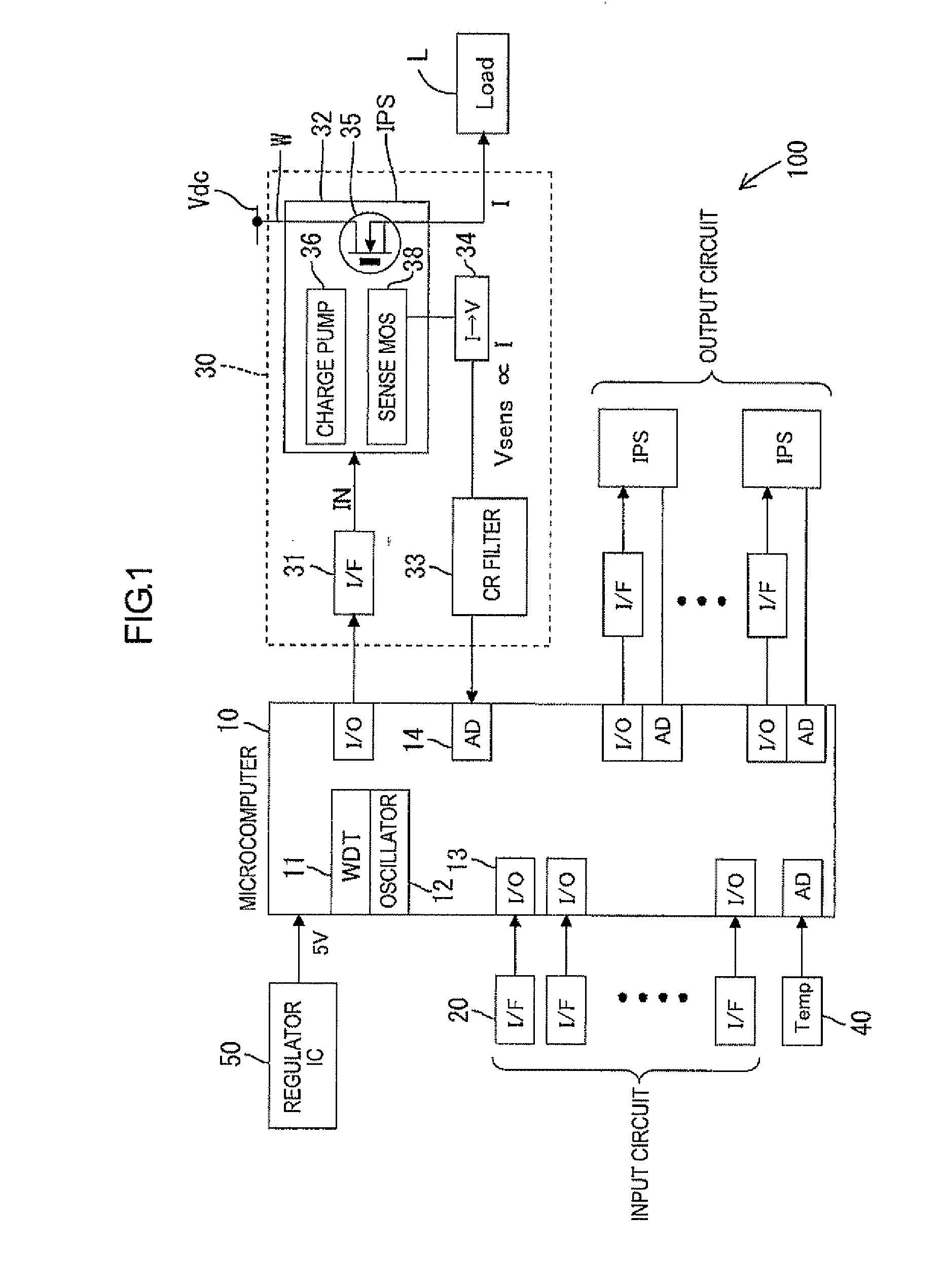
Power supply controller
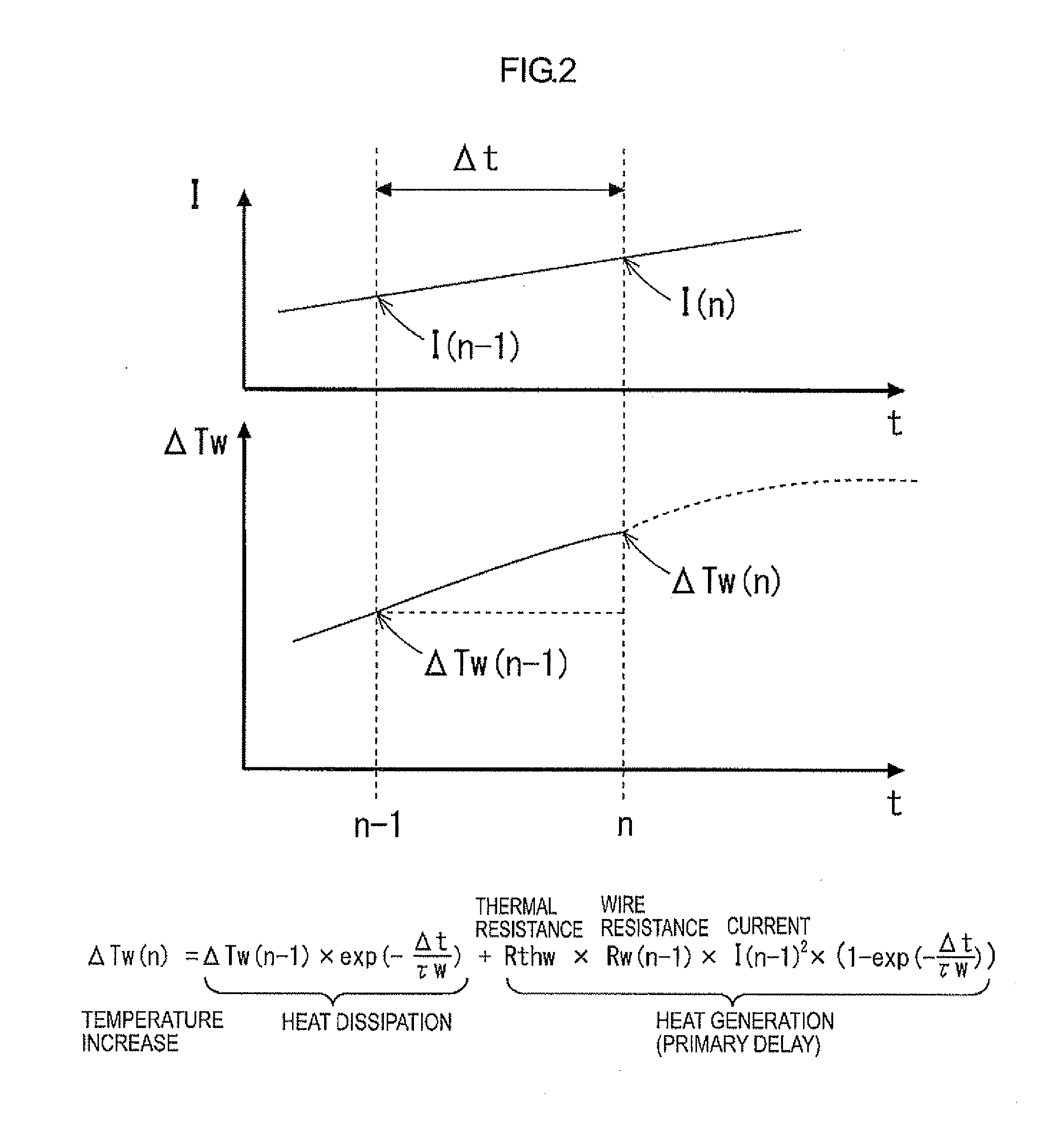
ActiveUS20120176115A1Reduce in quantityElectronic switchingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPower controllerCurrent threshold
The power supply controller performs the power-supply-path protection operation to restrict power supply through the switch element if a value of temperature increase of the power supply path W with respect to the reference temperature To exceeds the temperature threshold value and remove the restriction if the temperature decreases to the temperature threshold value or lower. And the controller performs the switch protection operation to restrict the power supply through the switch element if the value of the flowing current exceeds the current threshold value and remove the restriction after the reference time H elapses. And also the controller adds the additional value F to the value of temperature increase on condition that the value of the flowing current exceeds the current threshold value in the power supply protection operation and compares a post-addition temperature to the temperature threshold value.
Owner:AUTONETWORKS TECH LTD +2
Rapid rerouting method for protecting local path
ActiveCN101562536AReduce the numberFlexible configurationData switching networksPath protectionMessage passing
The invention discloses a rapid rerouting method for protecting a local path, which comprises the following step that: a bypass LSP is established among nodes of the local path of a main LSP needed to deploy rapid rerouting; an outgoing interface of a local restoration point and an incoming interface of a confluent point which a main tunnel passes through are deployed with fault detection; after the local restoration point detects a fault, service traffic is switched to the protective LSP for transmitting; simultaneously, a fault indication signal message is sent to a head node of the main tunnel; and the head node of the main tunnel receives the fault indication signal message and tries to establish a new main LSP. The method avoids the problems that in the prior path protection, the time for transferring a fault informing message is too long and the range of paths needing to be protected in the local protection is limited, and can implement fault protection among random nodes of the main tunnel.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
Welding method for circumferential weld of thick-wall nickel-based alloy header
ActiveCN105750708AGuaranteed performancePrevent oxidationArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsThick wallAlloy
The invention relates to the technical field of welding of nickel-based alloys, and discloses a welding method for a circumferential weld of a thick-wall nickel-based alloy header. The welding method mainly comprises the following steps: welding material selection, welding mode selection, preparation before welding and construction of welding. The welding mode adopts hot wire TIG welding; a welding head has a double-path protection gas function; preparation before welding comprises preparation of a groove, and the welding process comprises spot welding, backing welding, transitional welding, filling welding and cosmetic welding. Aiming at the problem of the conventional nickel-based alloy welding, the invention provides a welding method suitable for circumferential welds of the Ni-25Cr-20Co thick-wall nickel-based alloy header.
Owner:DONGFANG BOILER GROUP OF DONGFANG ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com