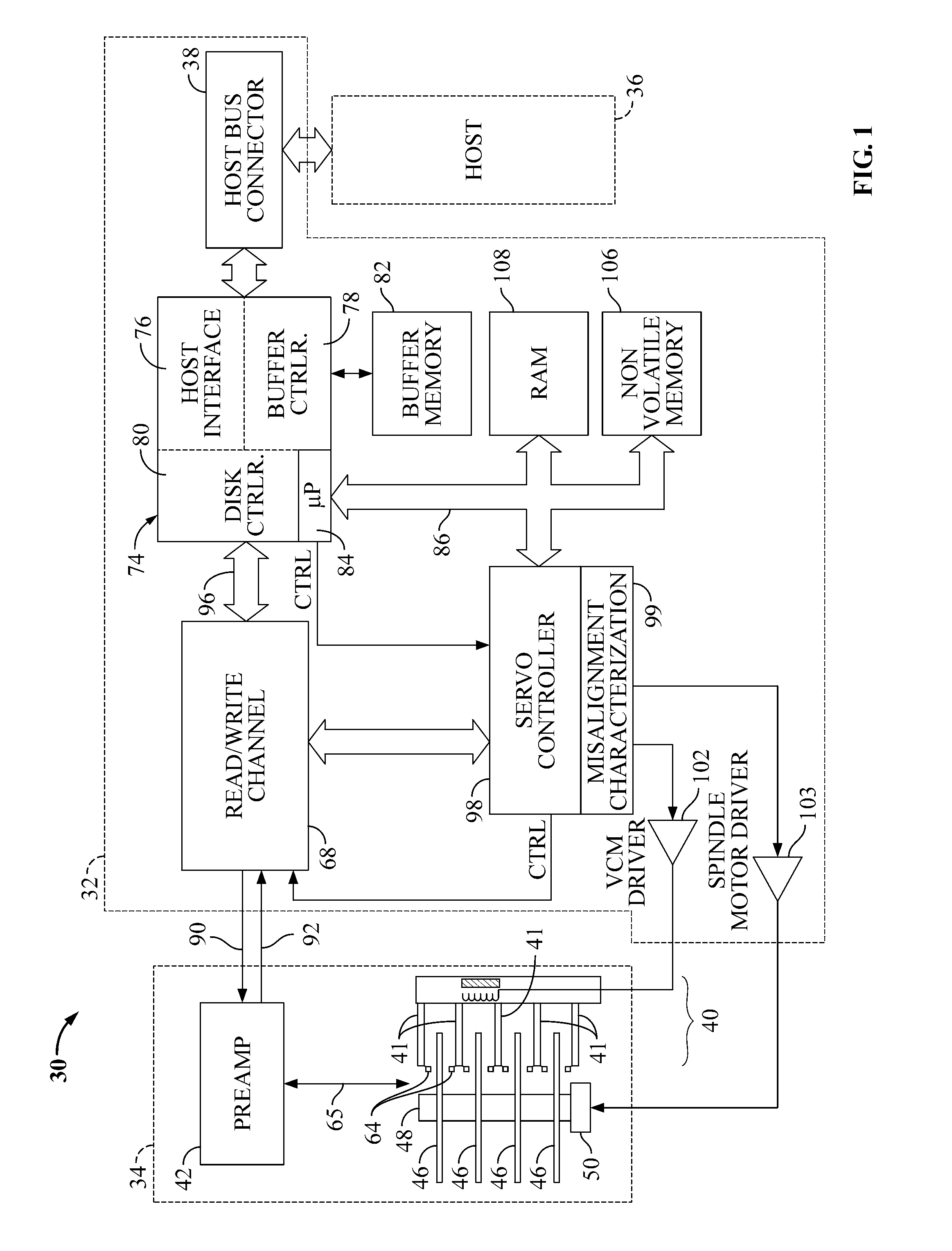
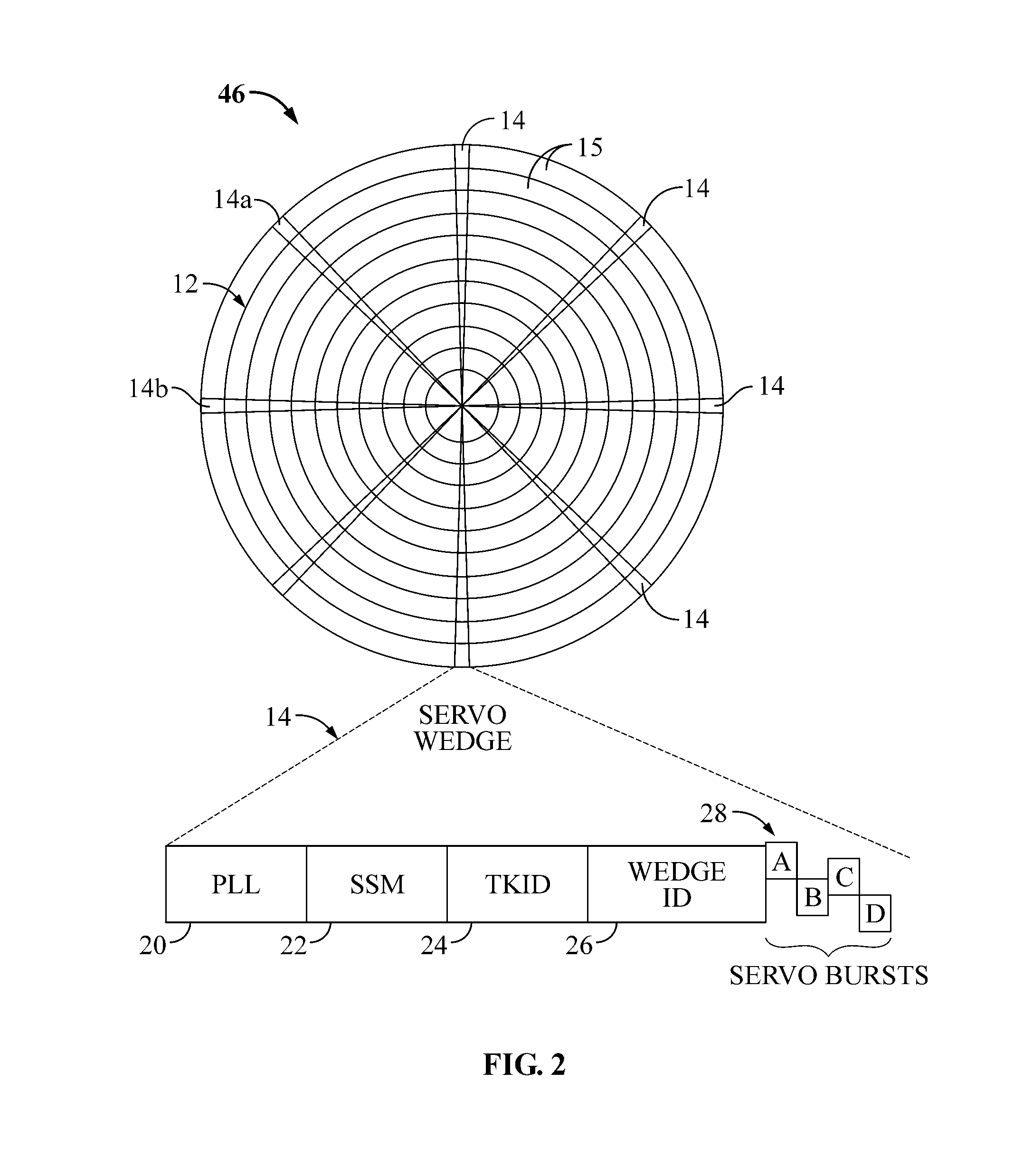
Patents
Literature
124 results about "Track (disk drive)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
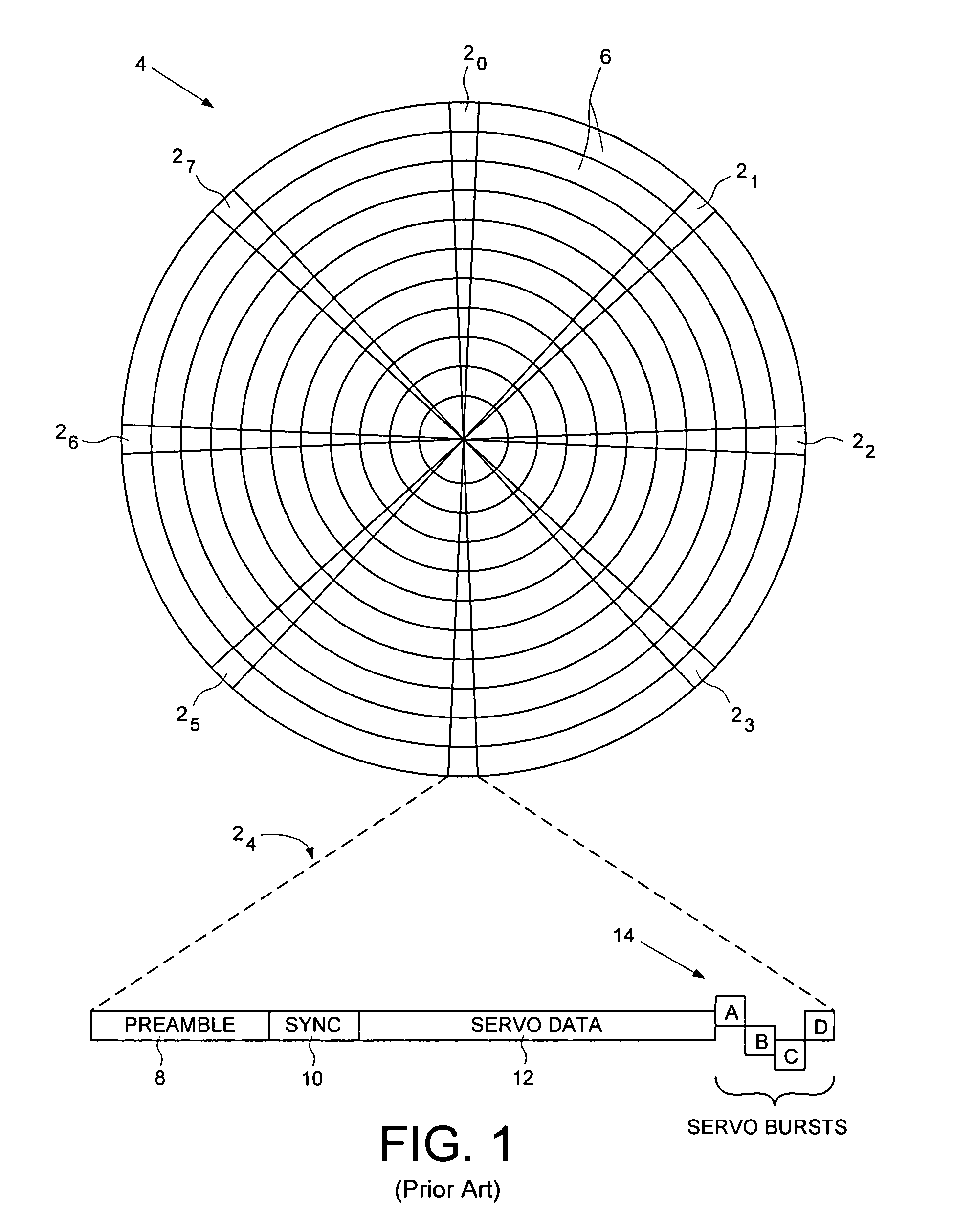
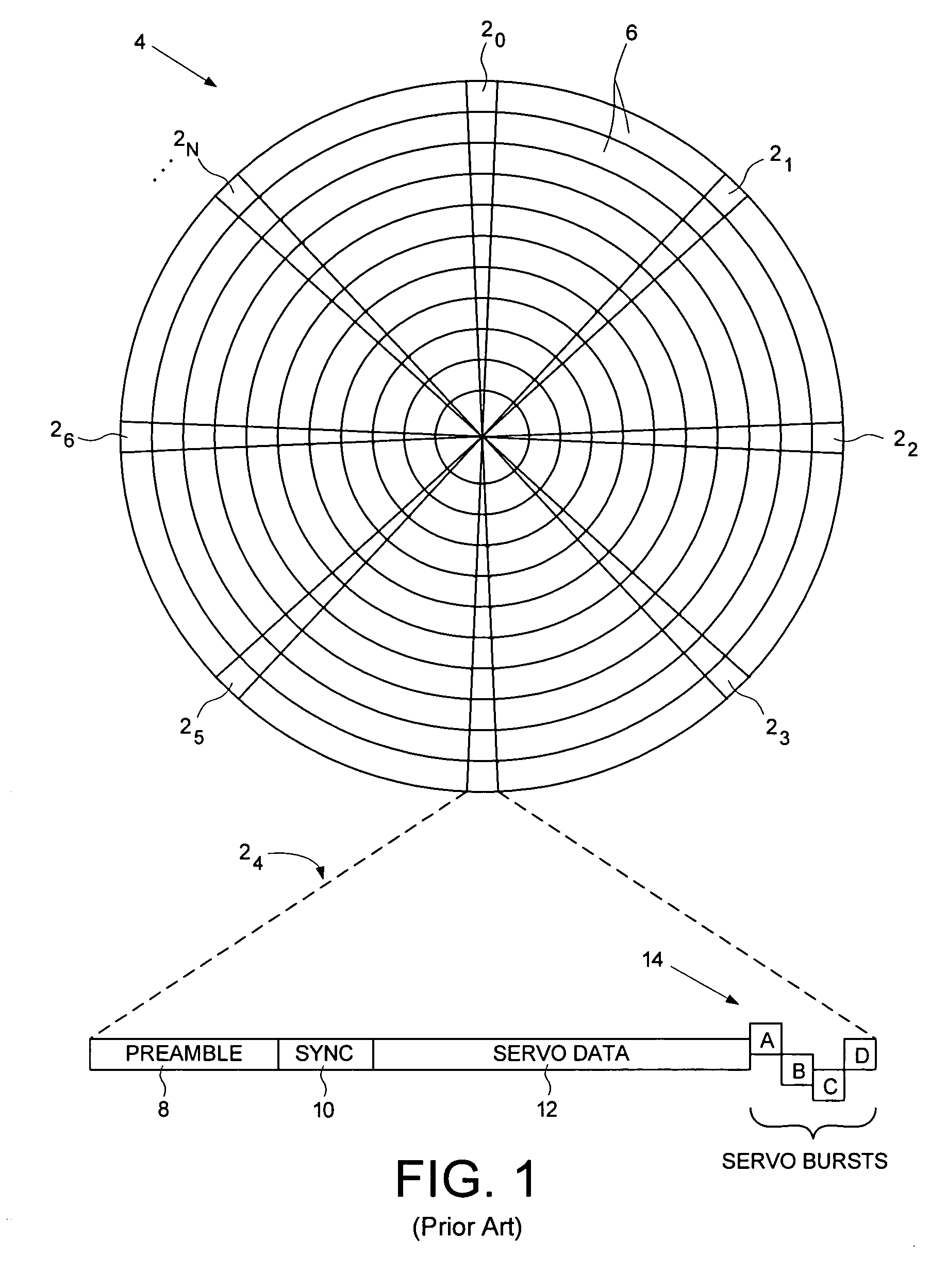
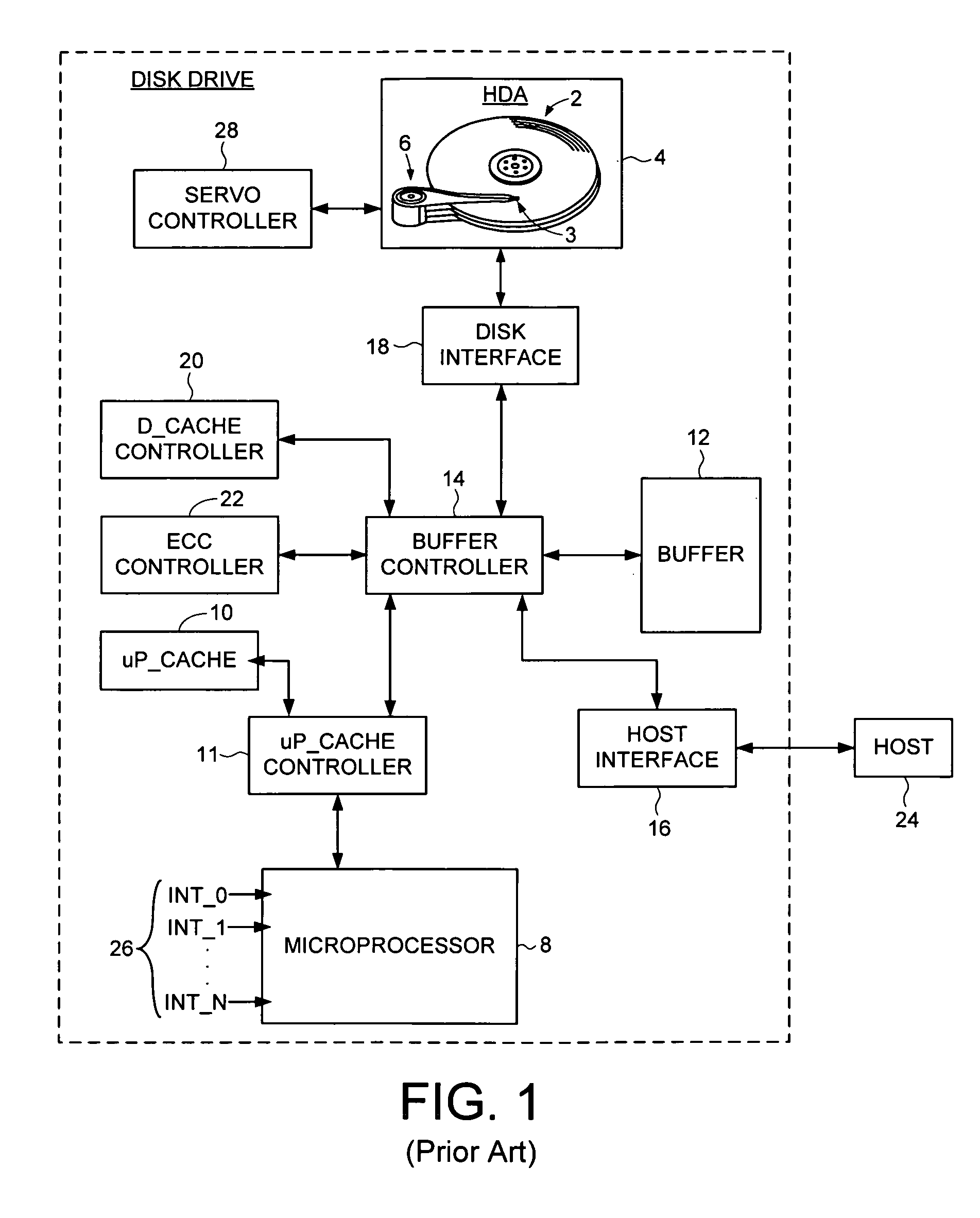
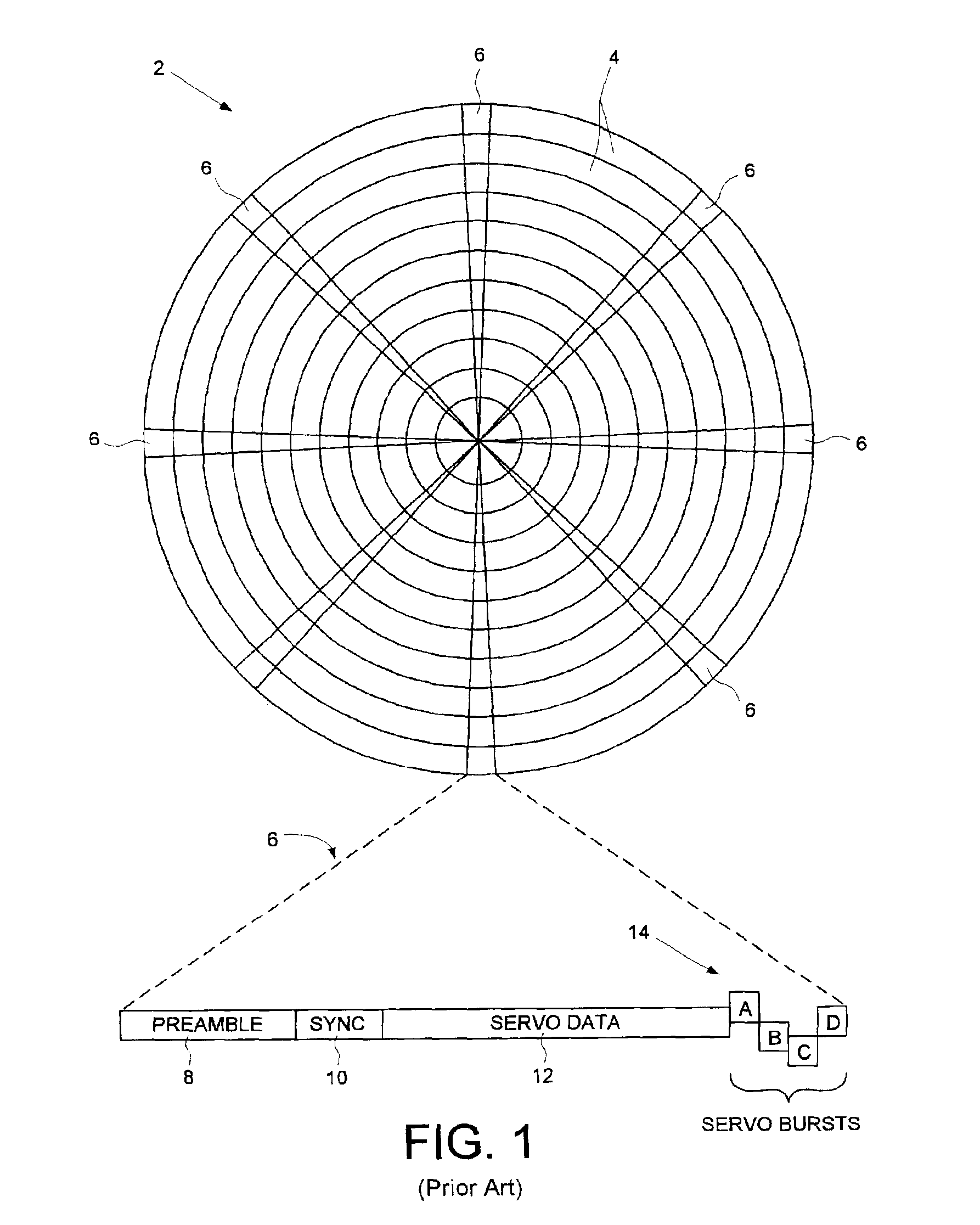
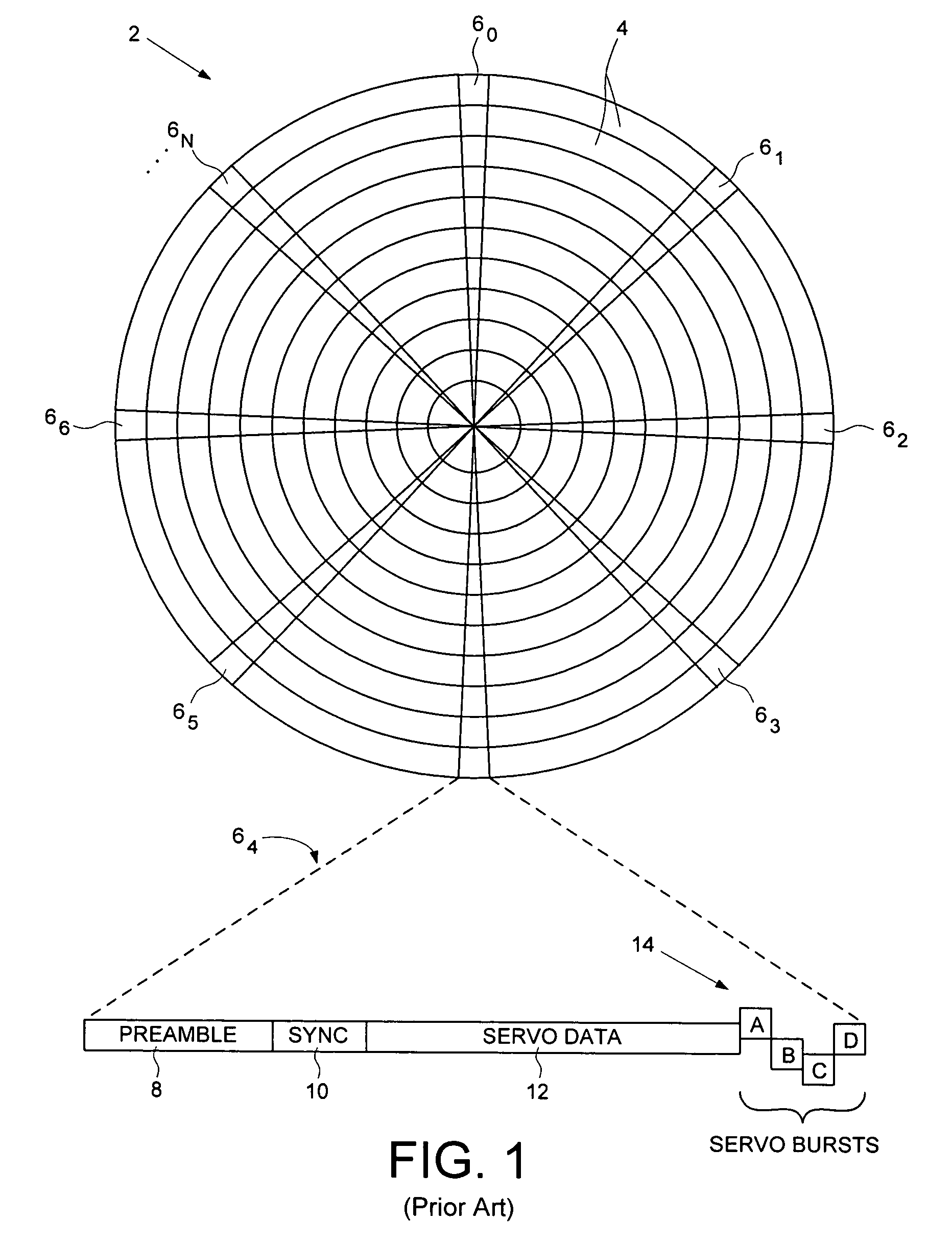
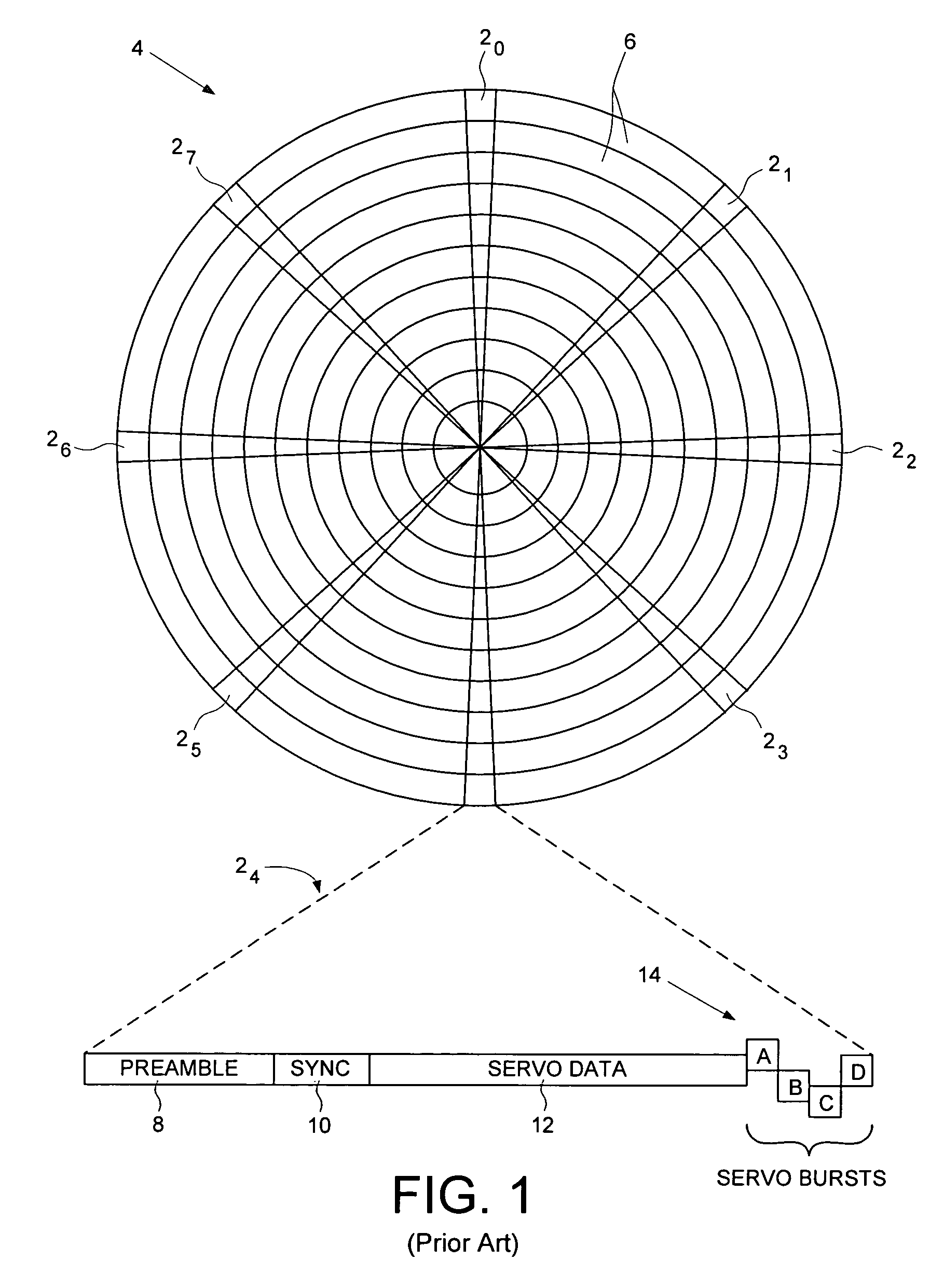
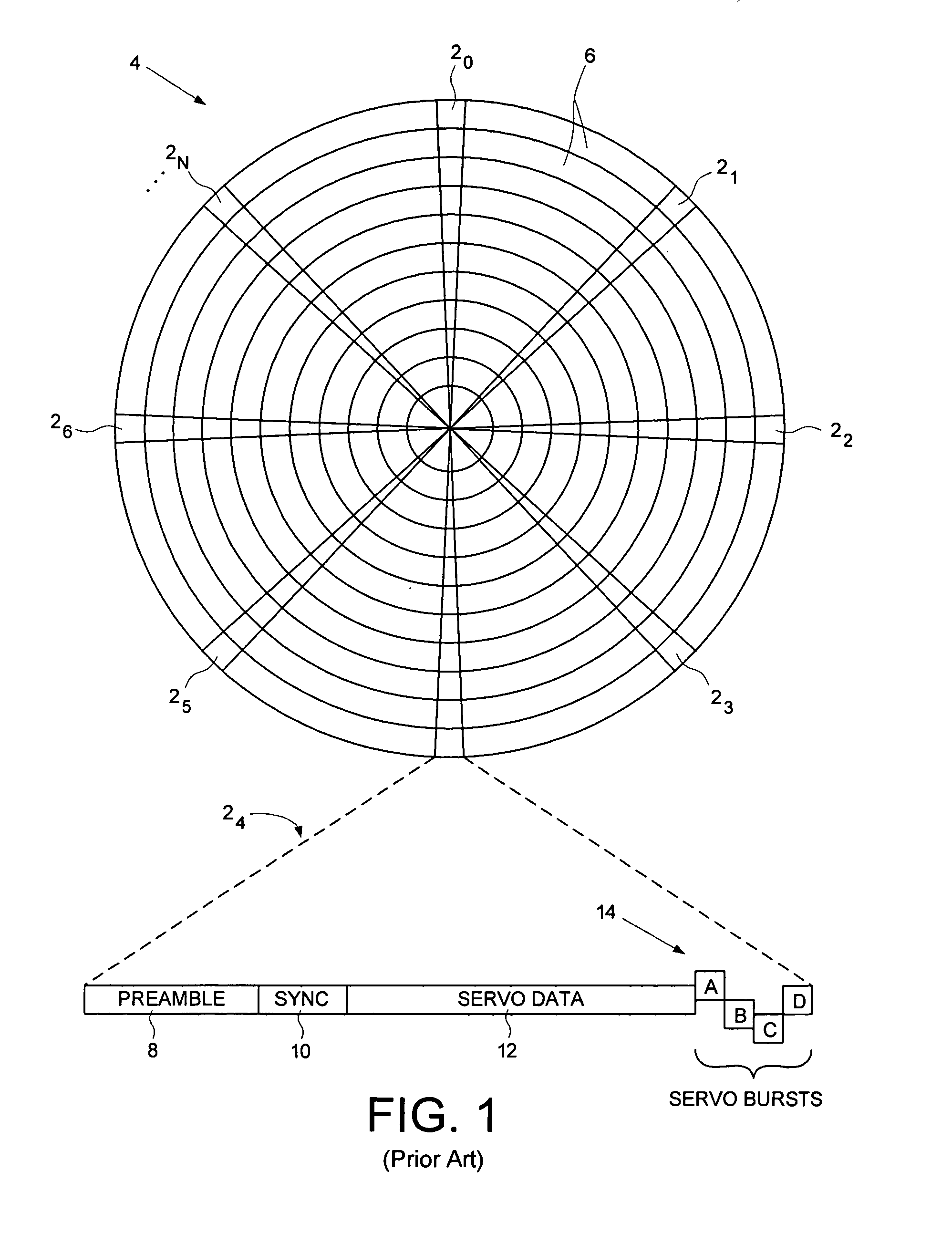
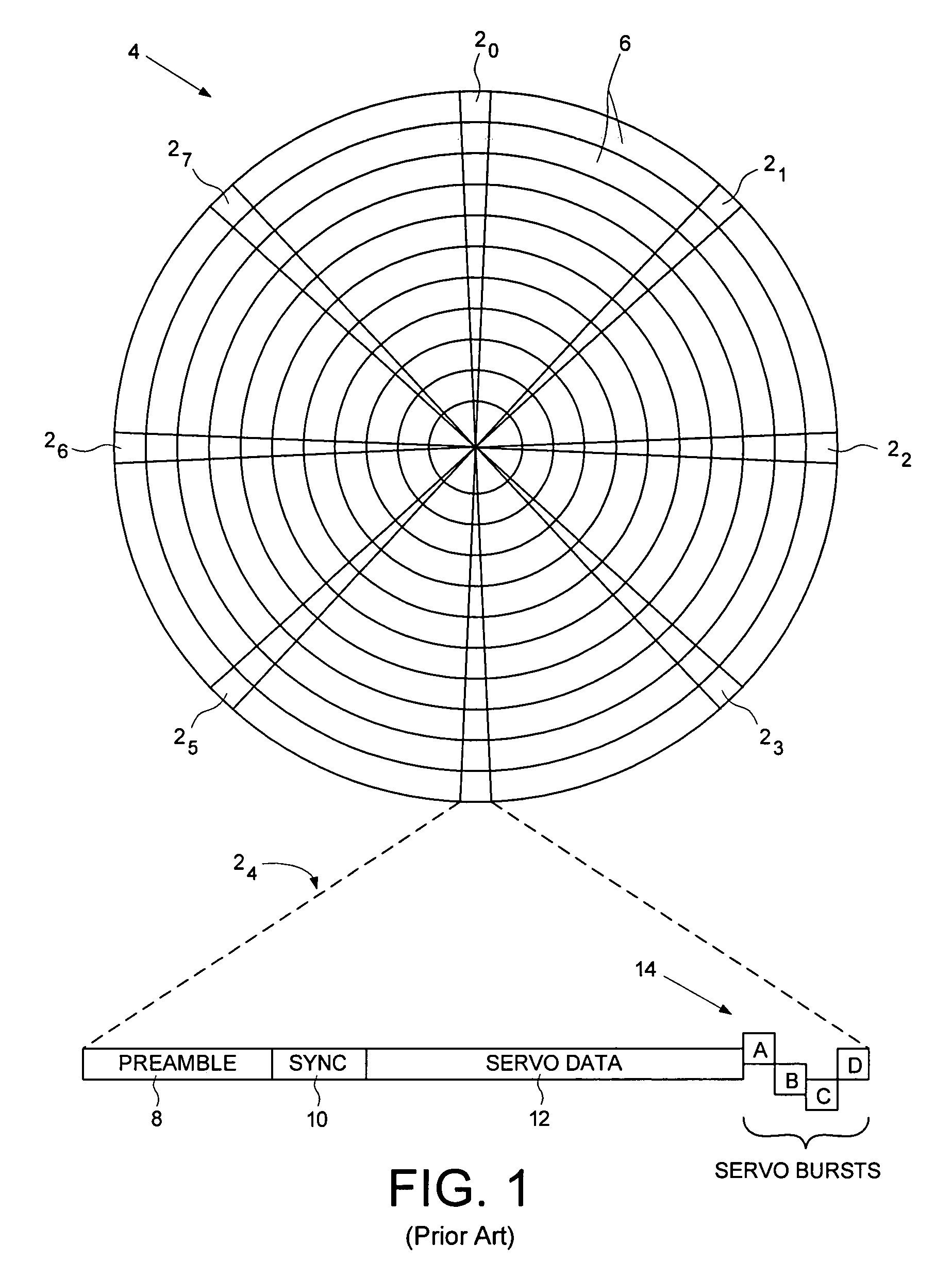
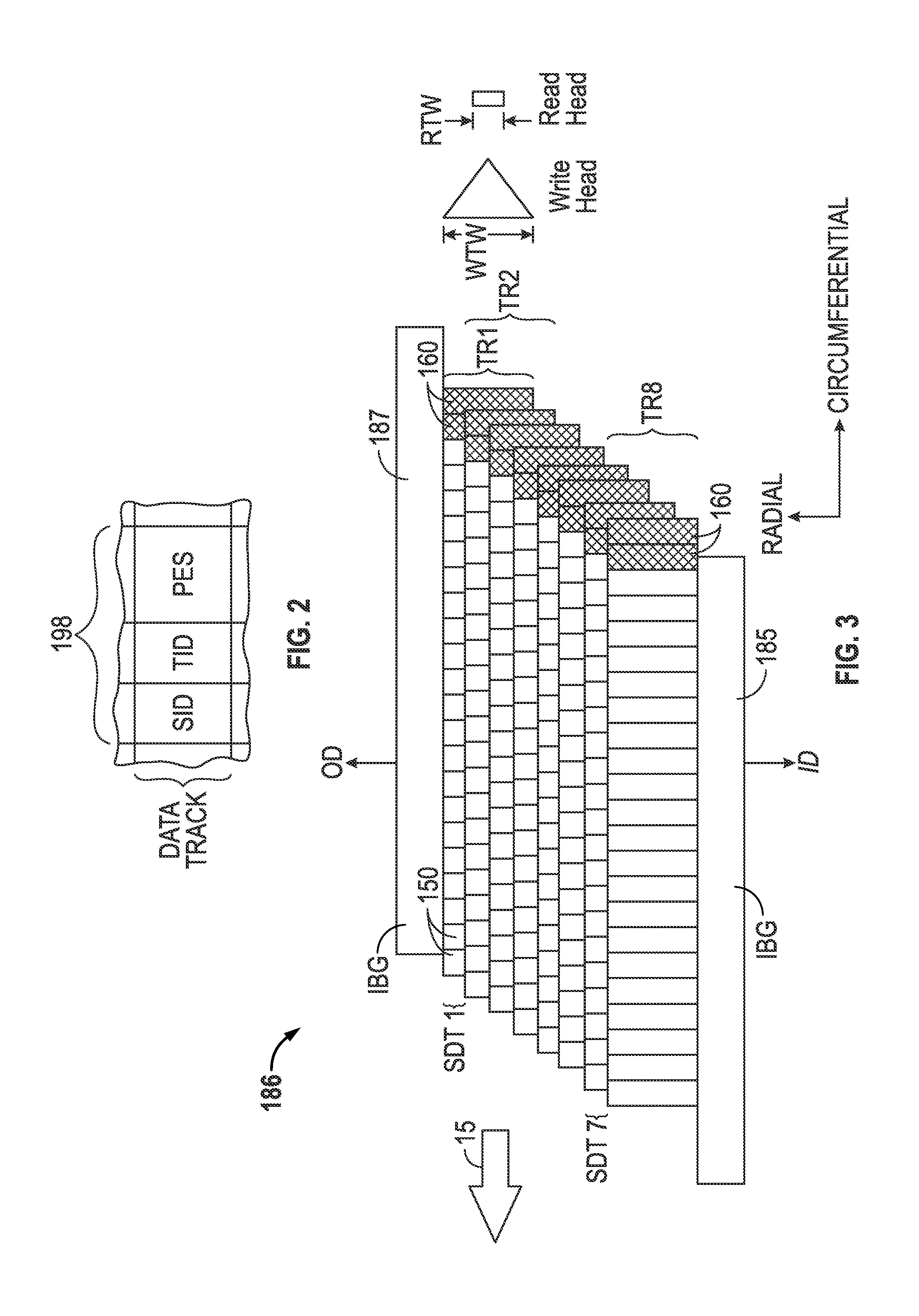
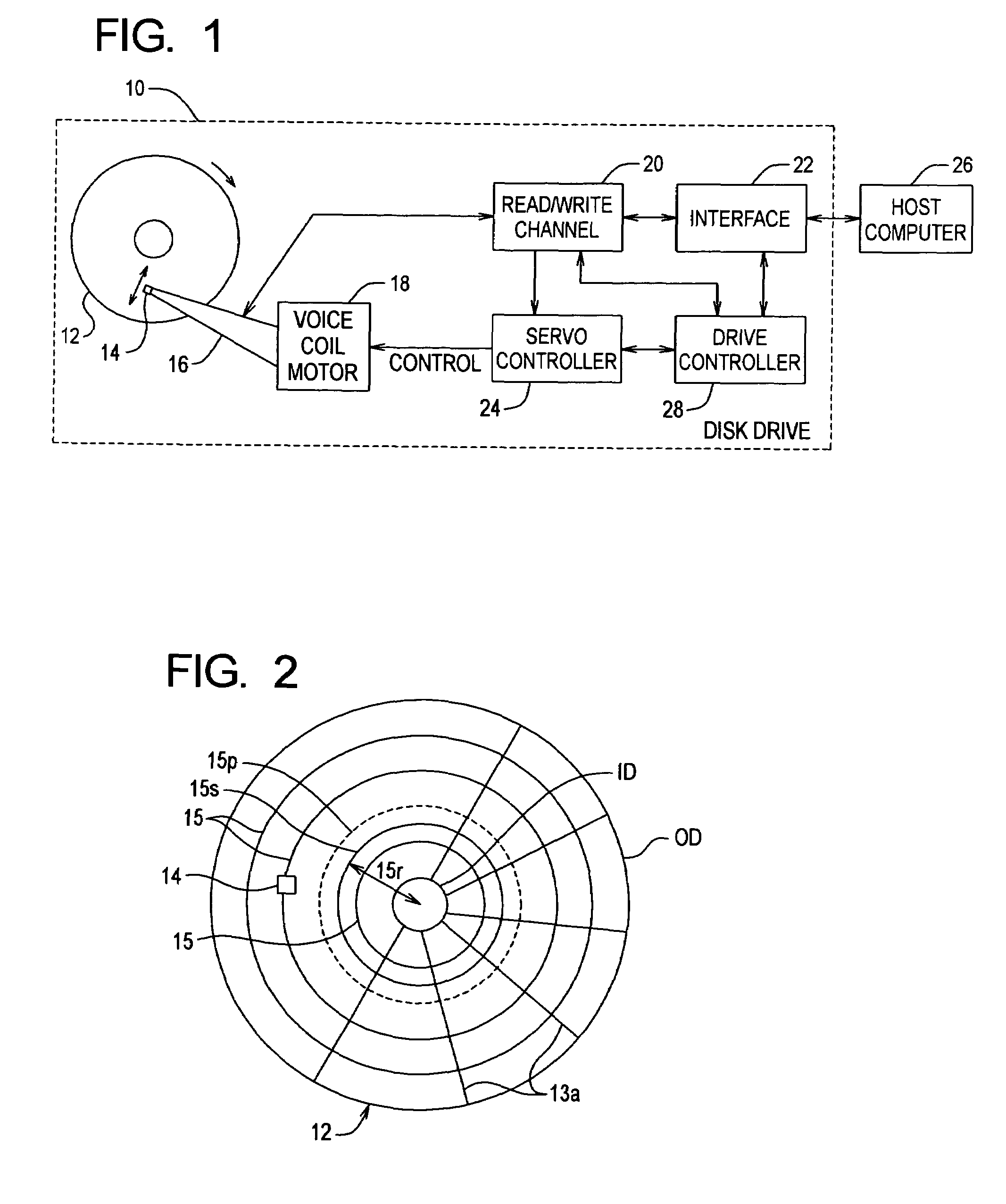
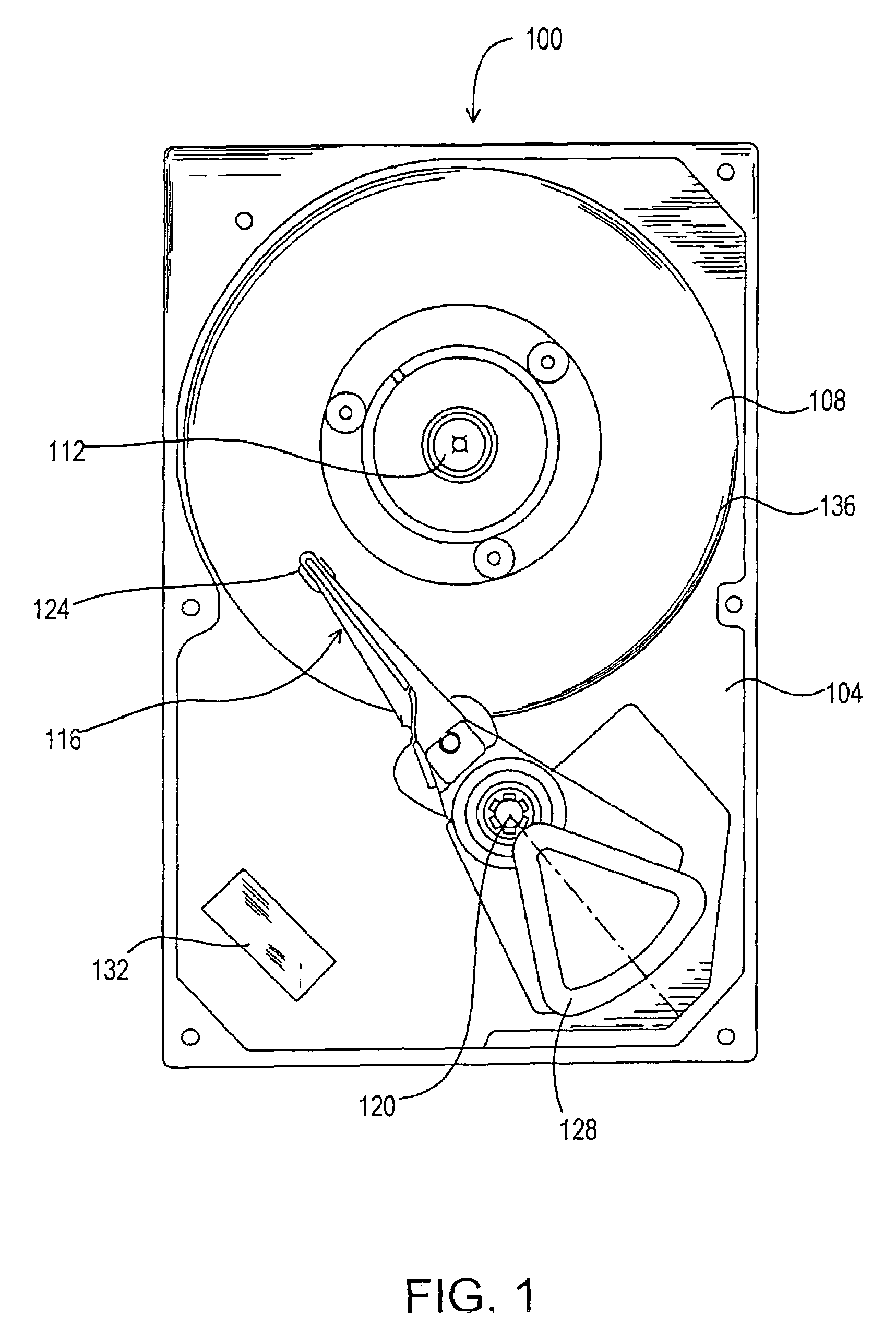
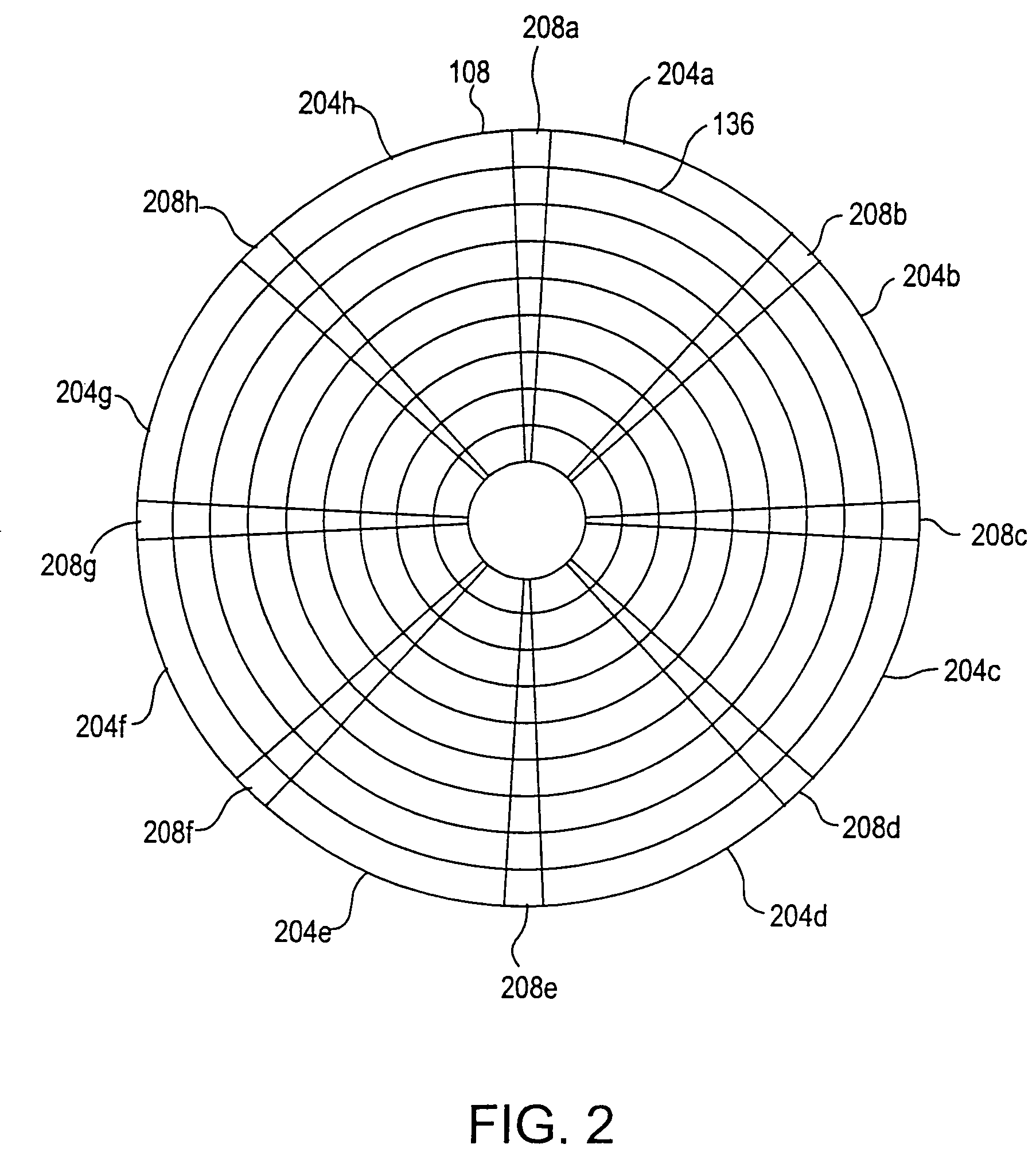
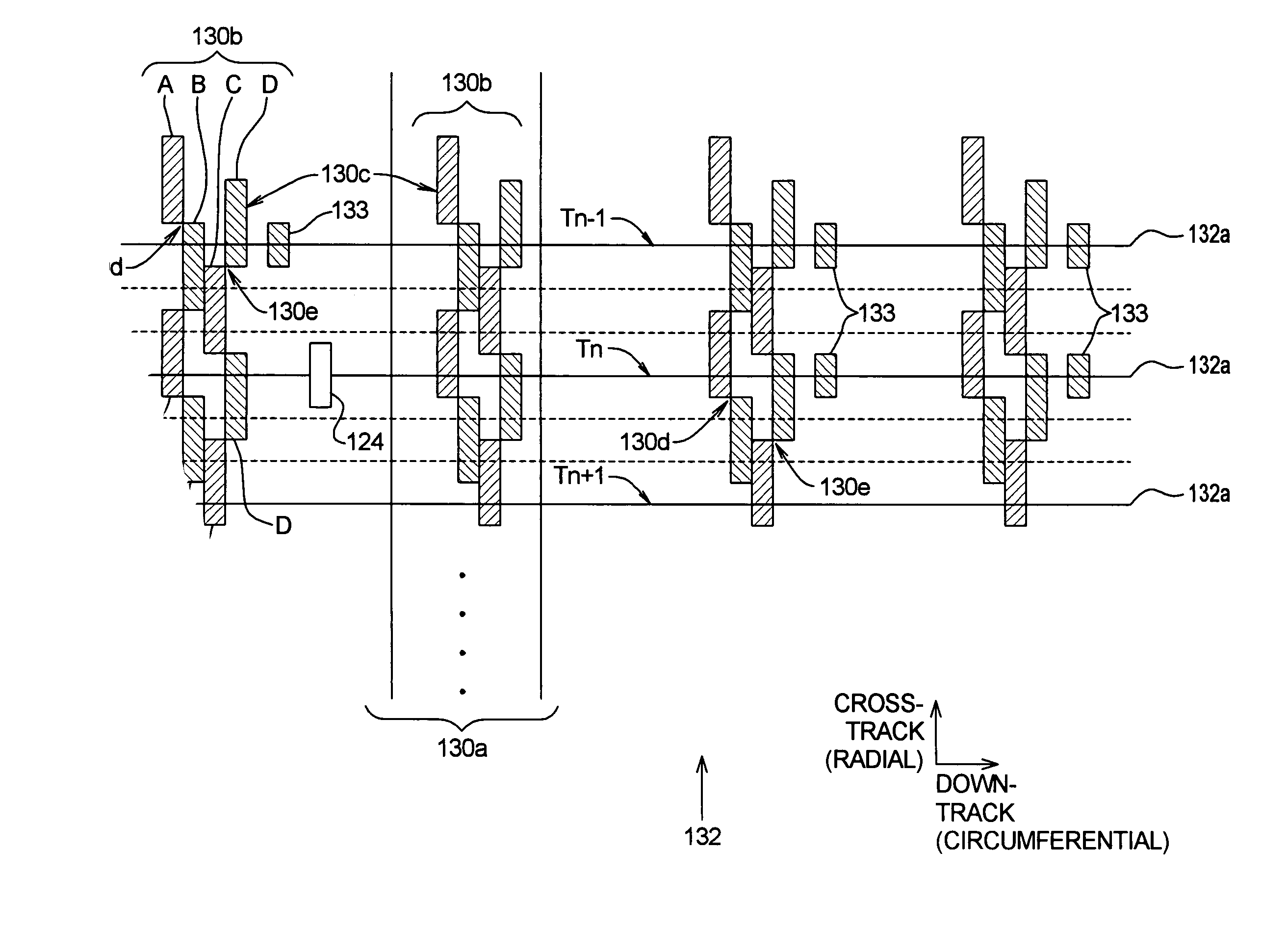
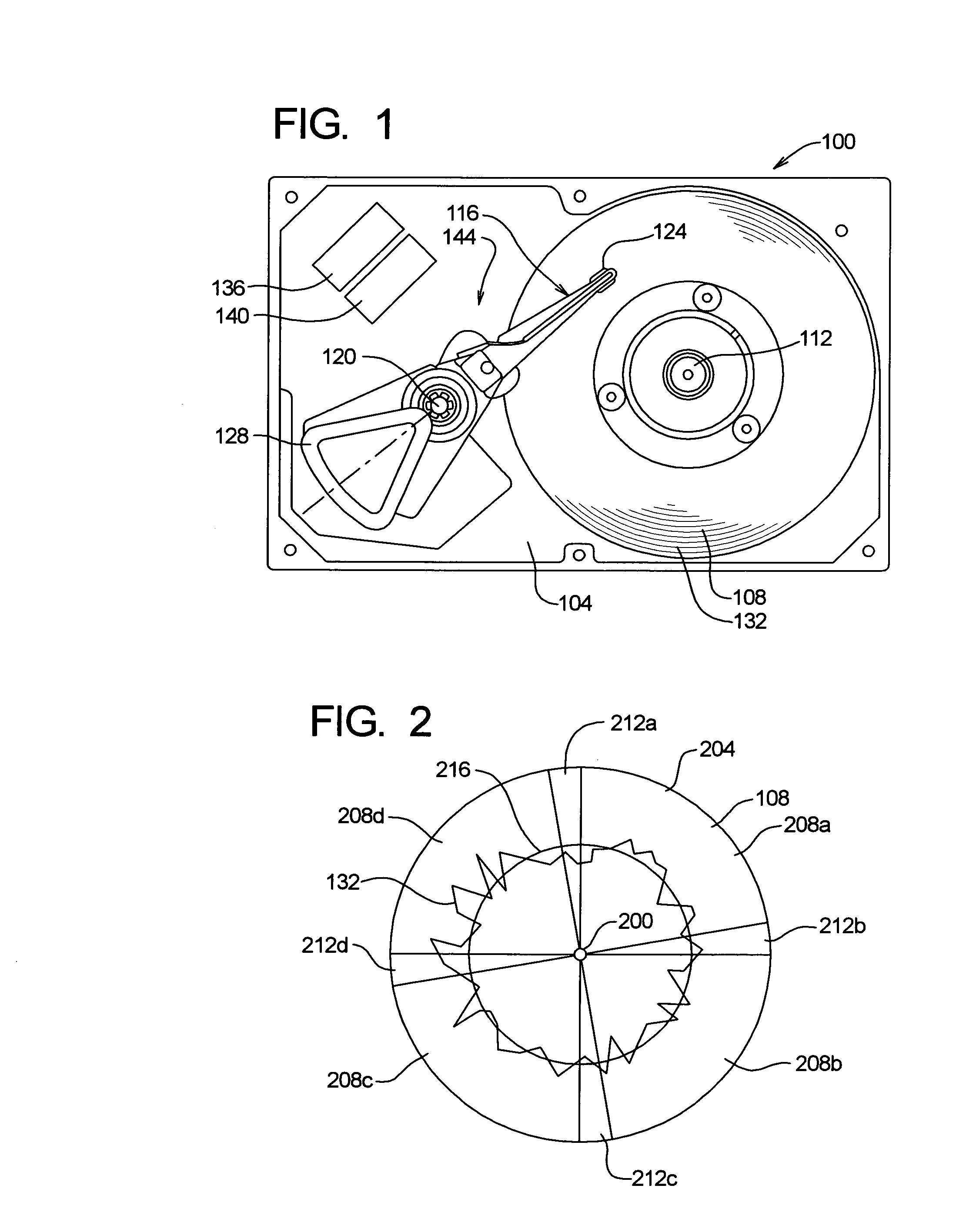
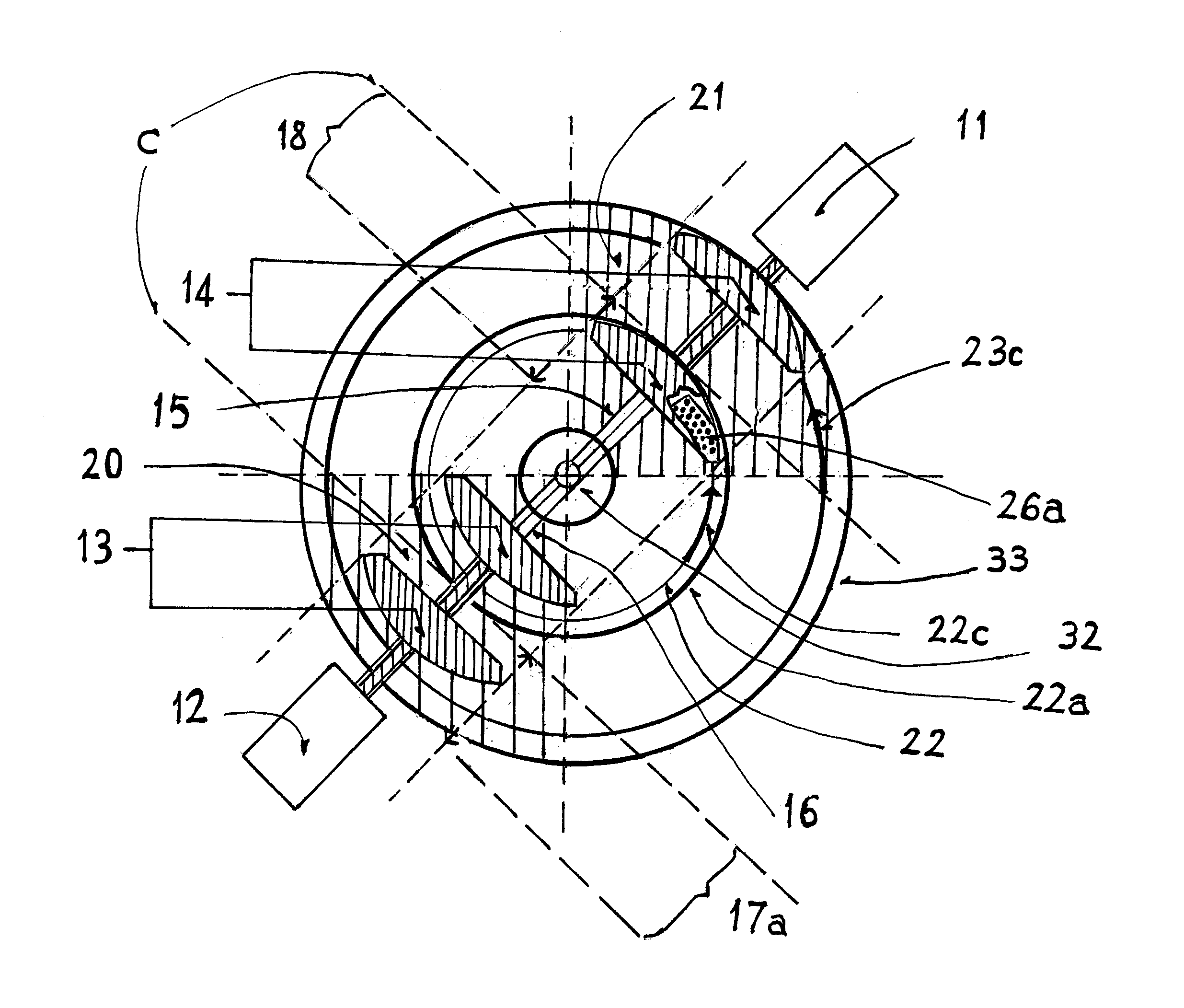
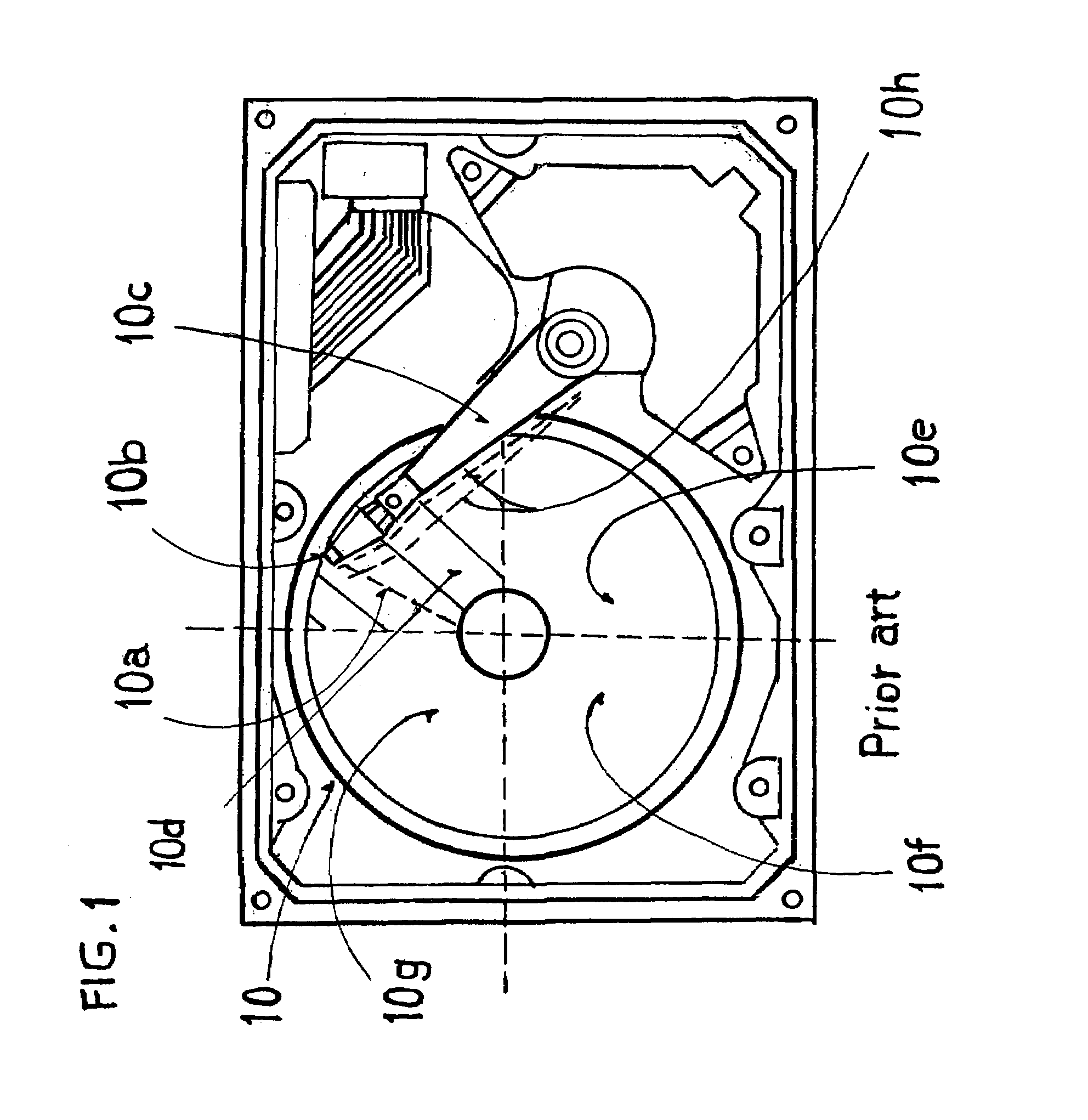
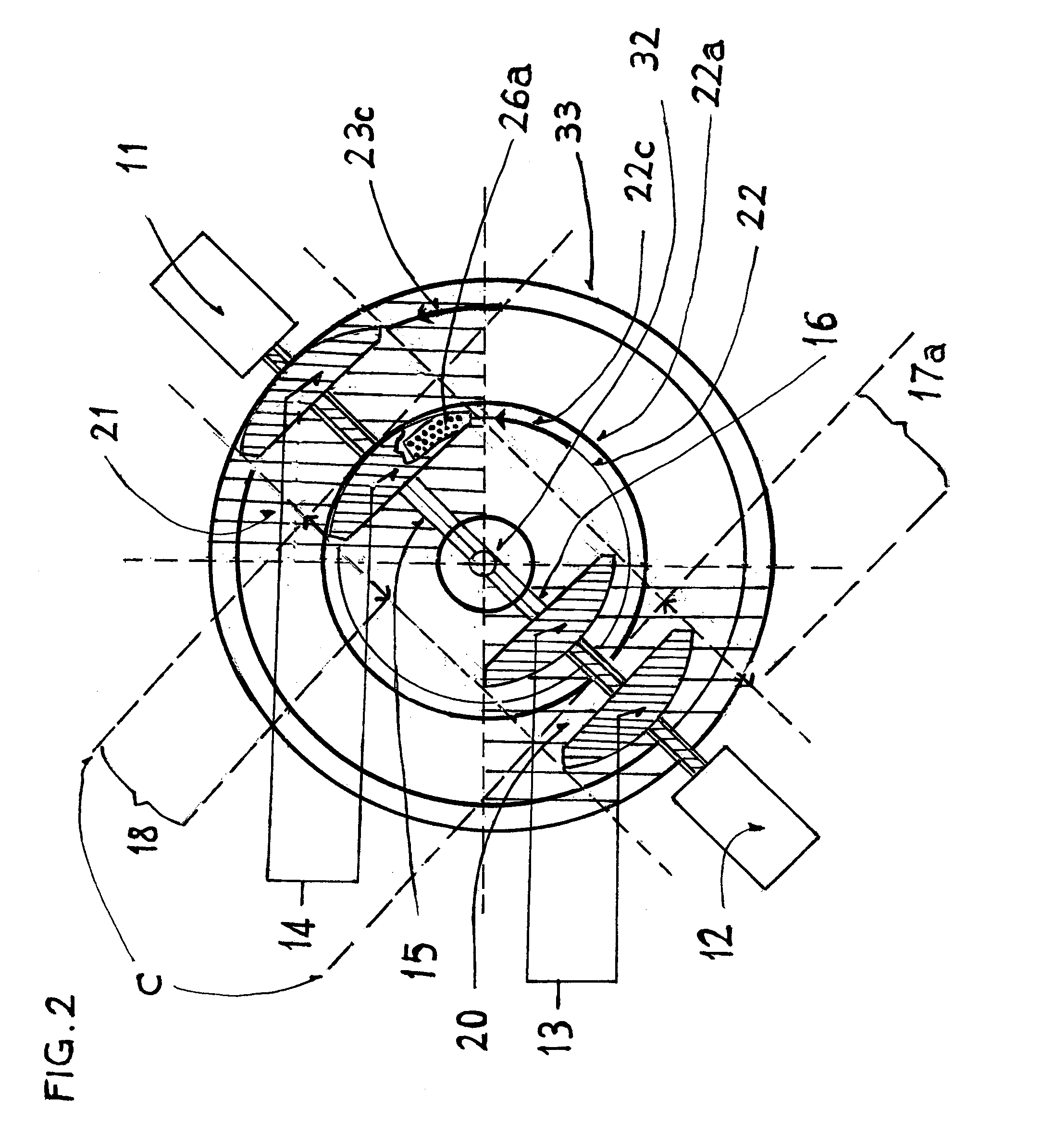
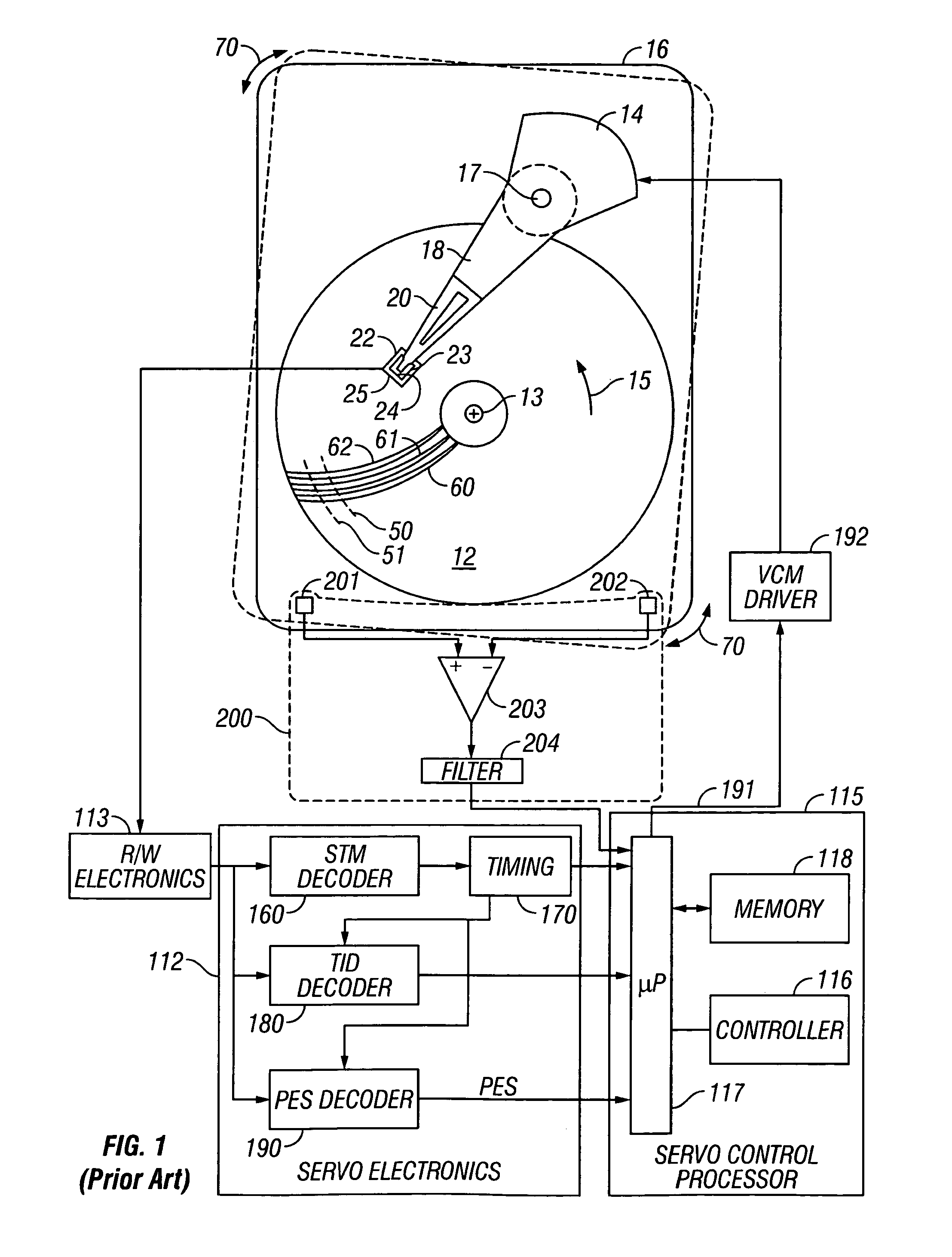
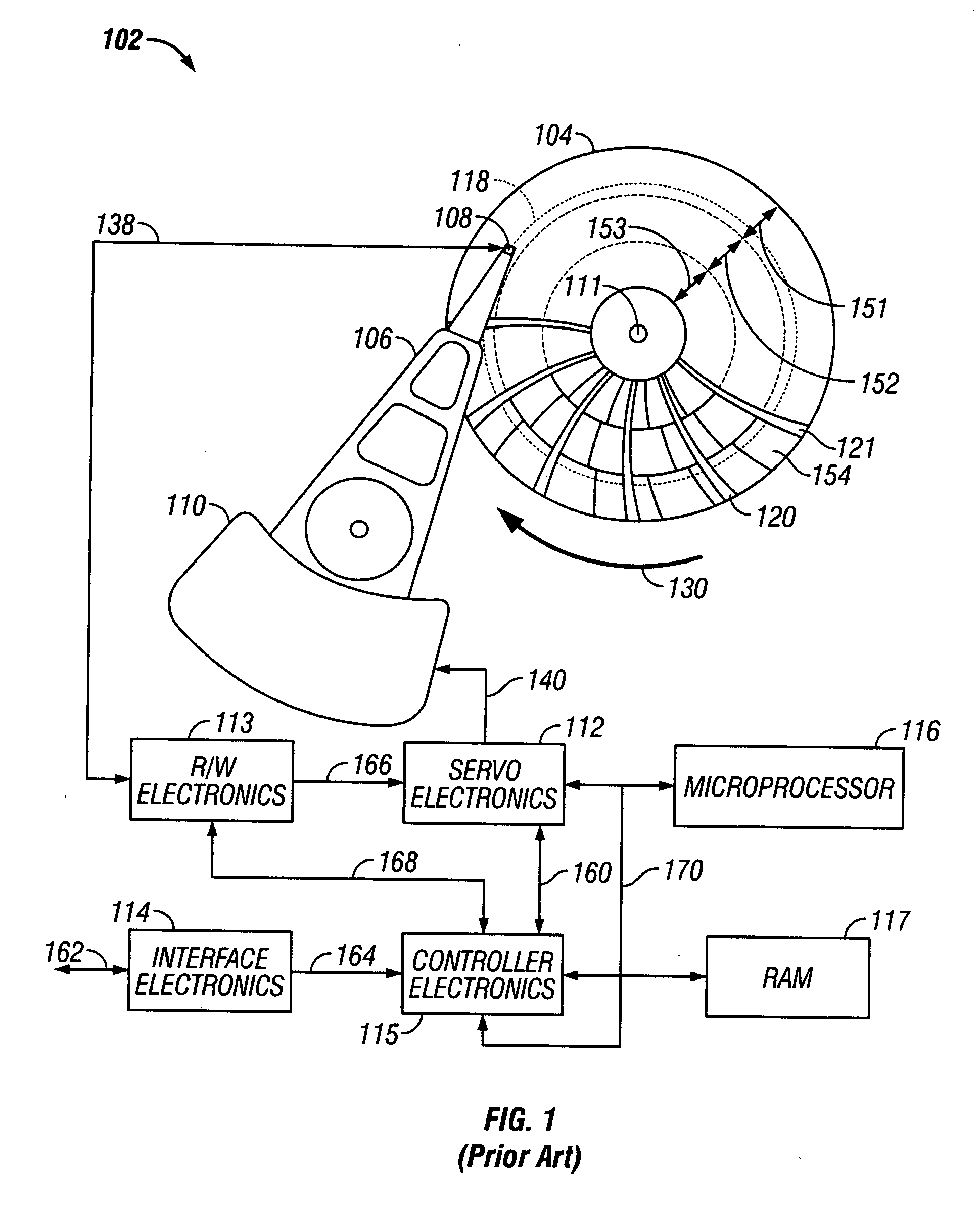
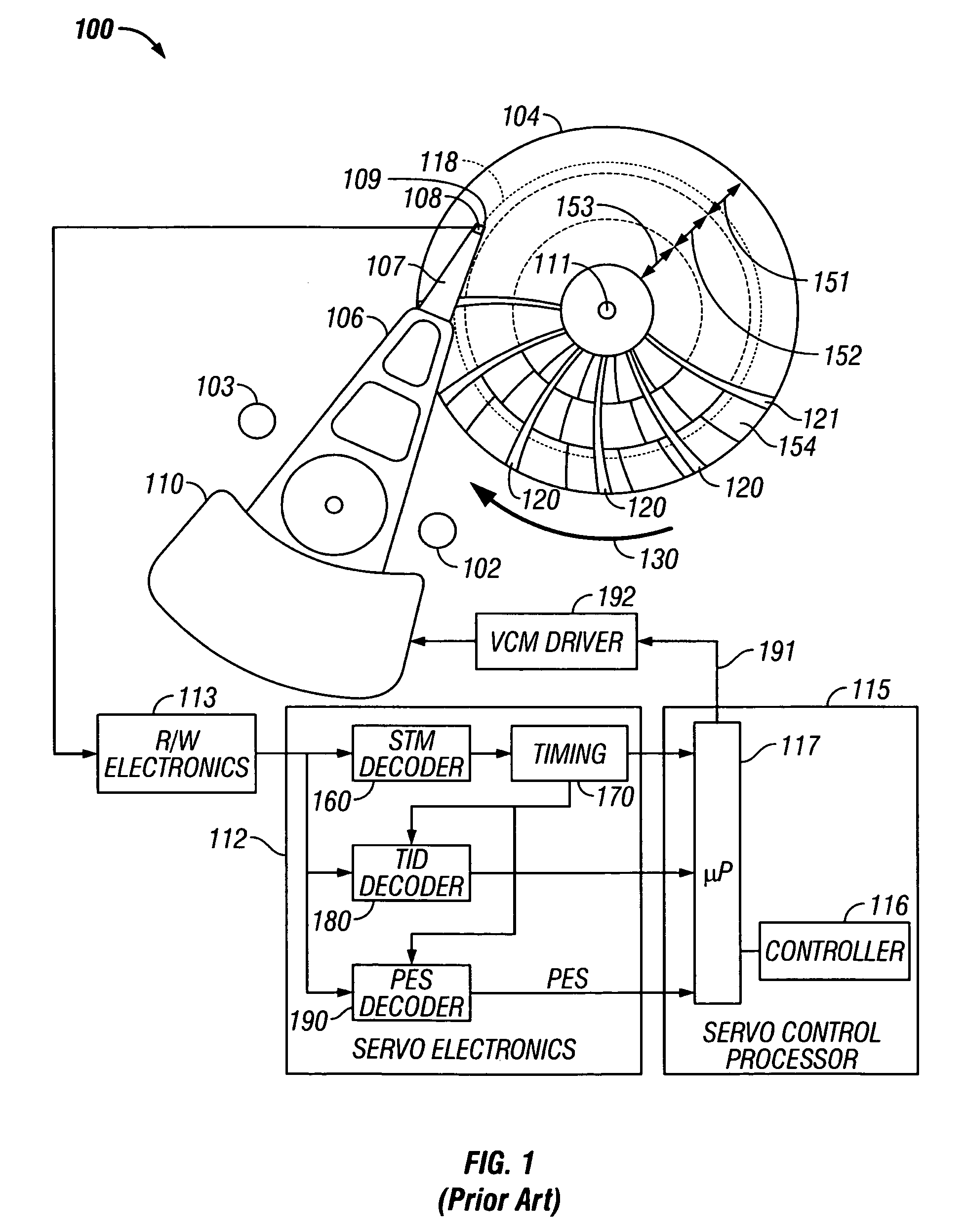
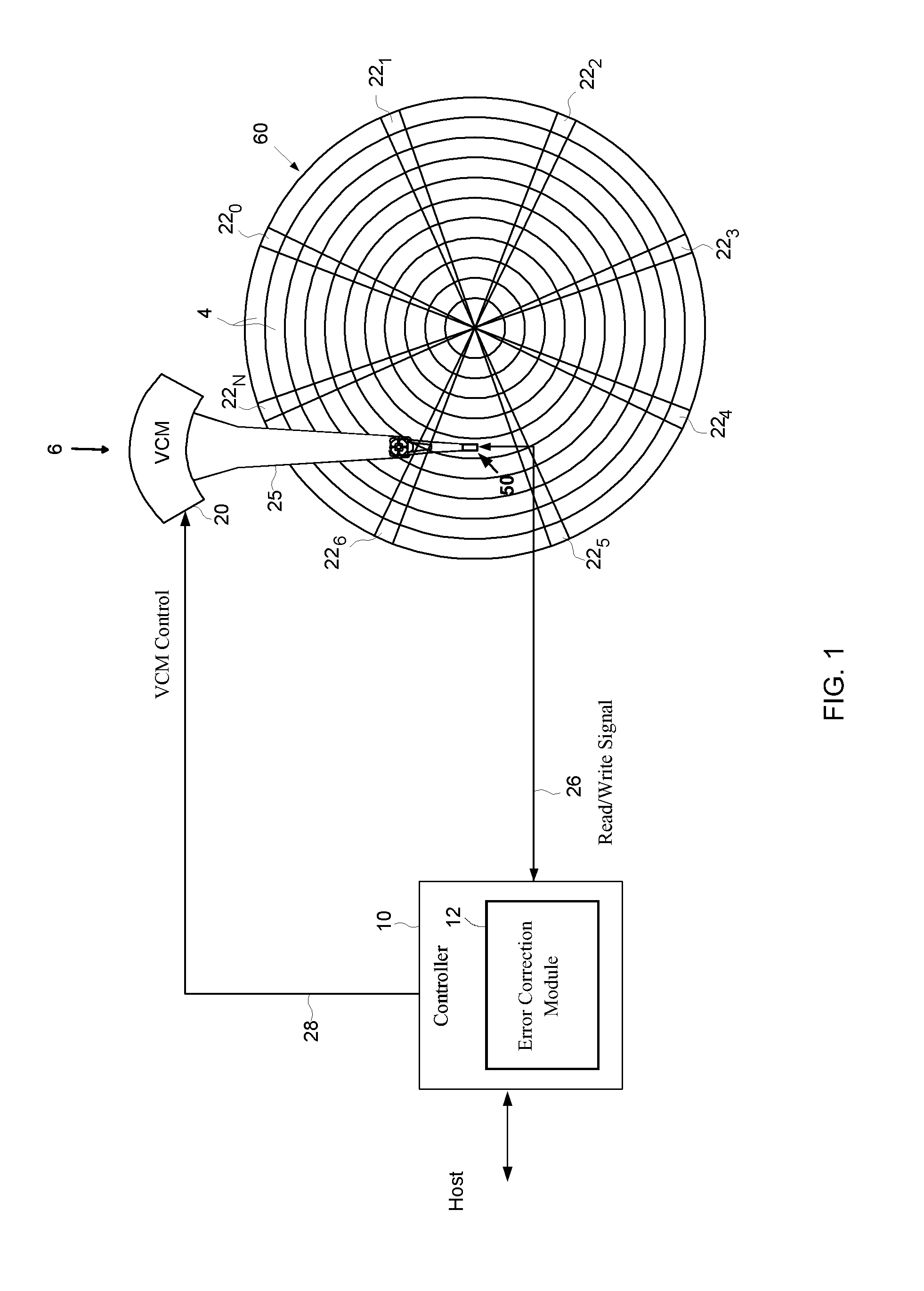
A disk drive track is a circular path on the surface of a disk or diskette on which information is magnetically recorded and from which recorded information is read. A track is a physical division of data in a disk drive, as used in the Cylinder-Head-Record (CCHHR) addressing mode of a CKD disk. The concept is concentric, through the physical platters, being a data circle per each cylinder of the whole disk drive. In other words, the number of tracks on a single surface in the drive exactly equals the number of cylinders of the drive.
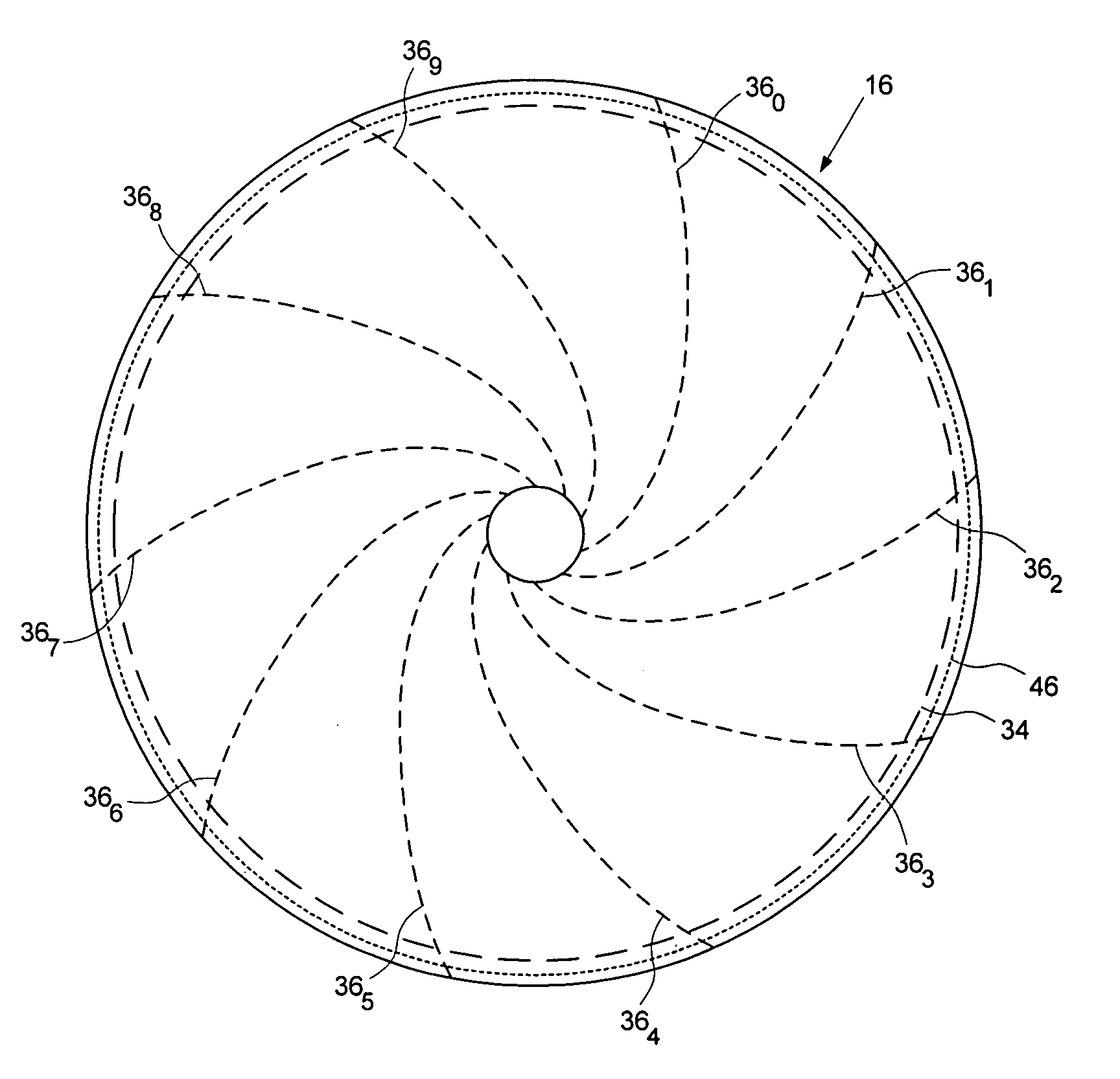
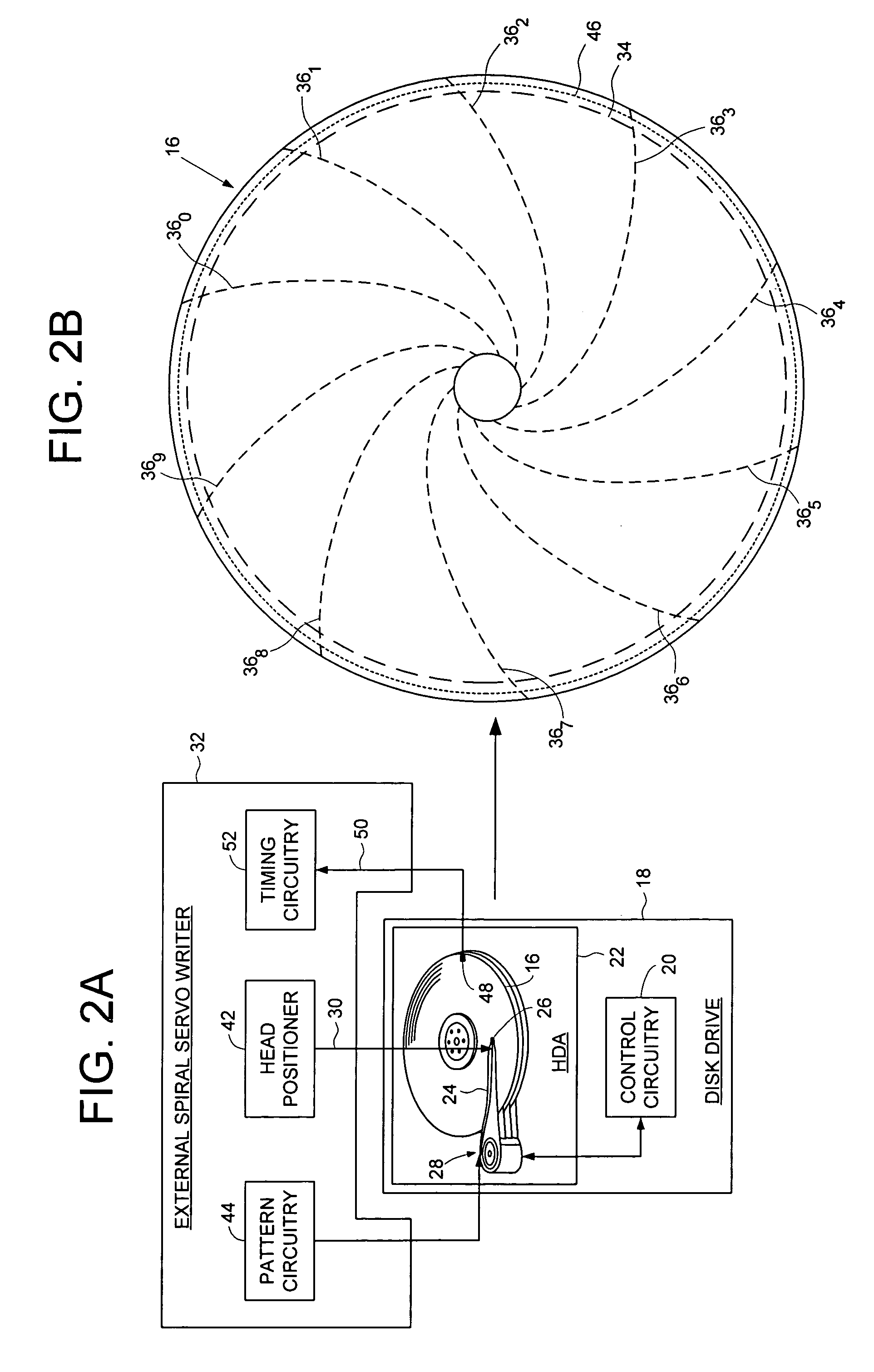
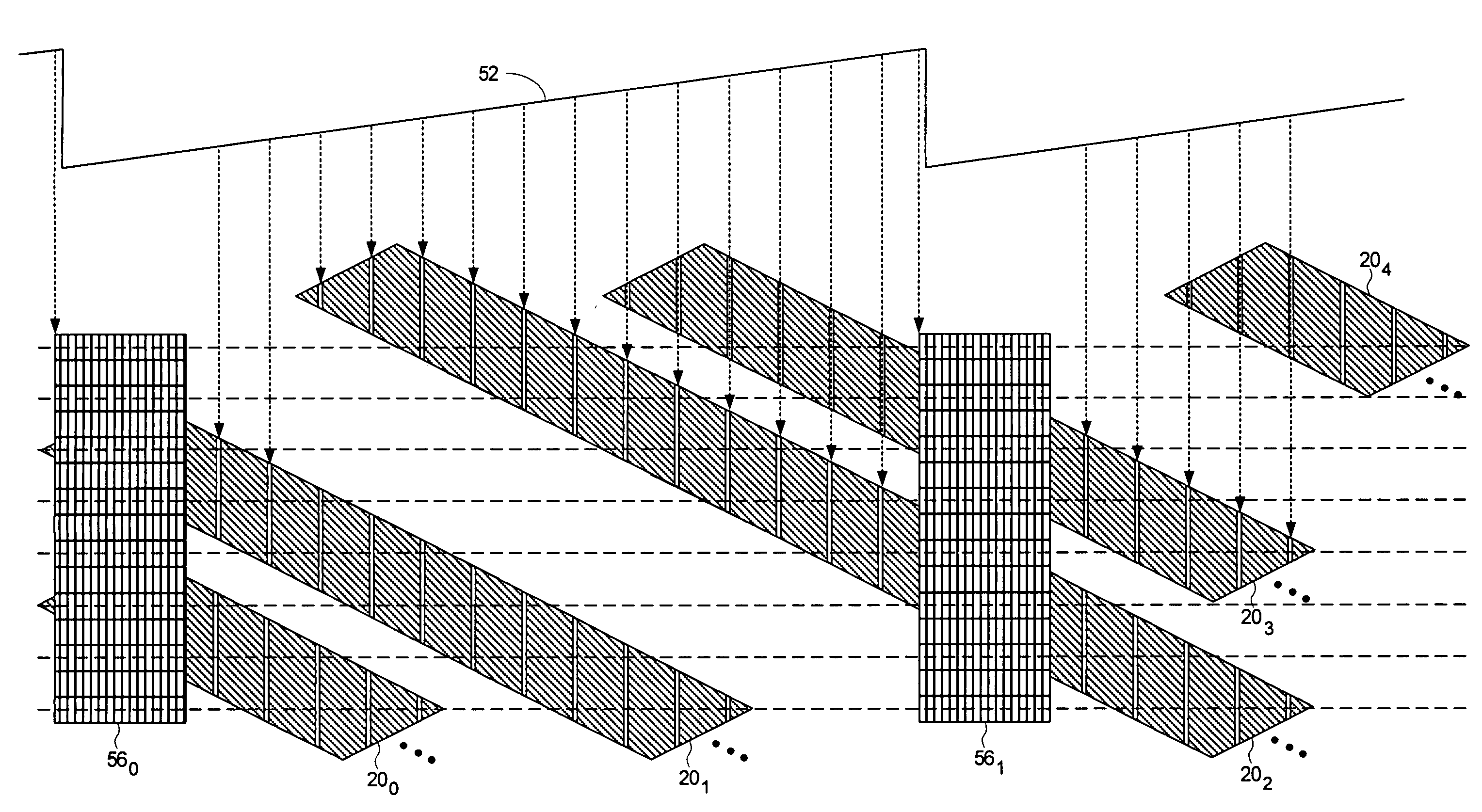
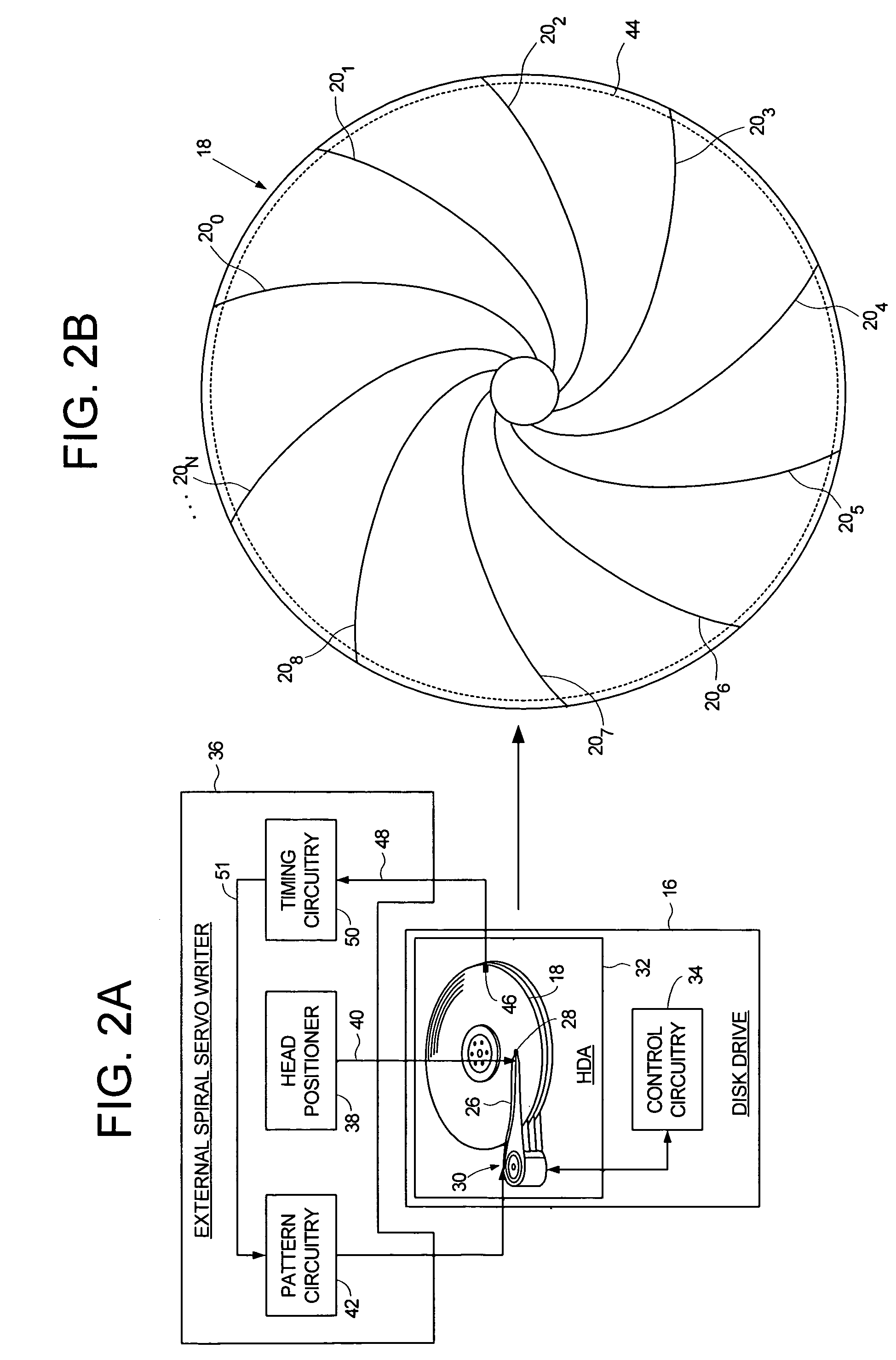
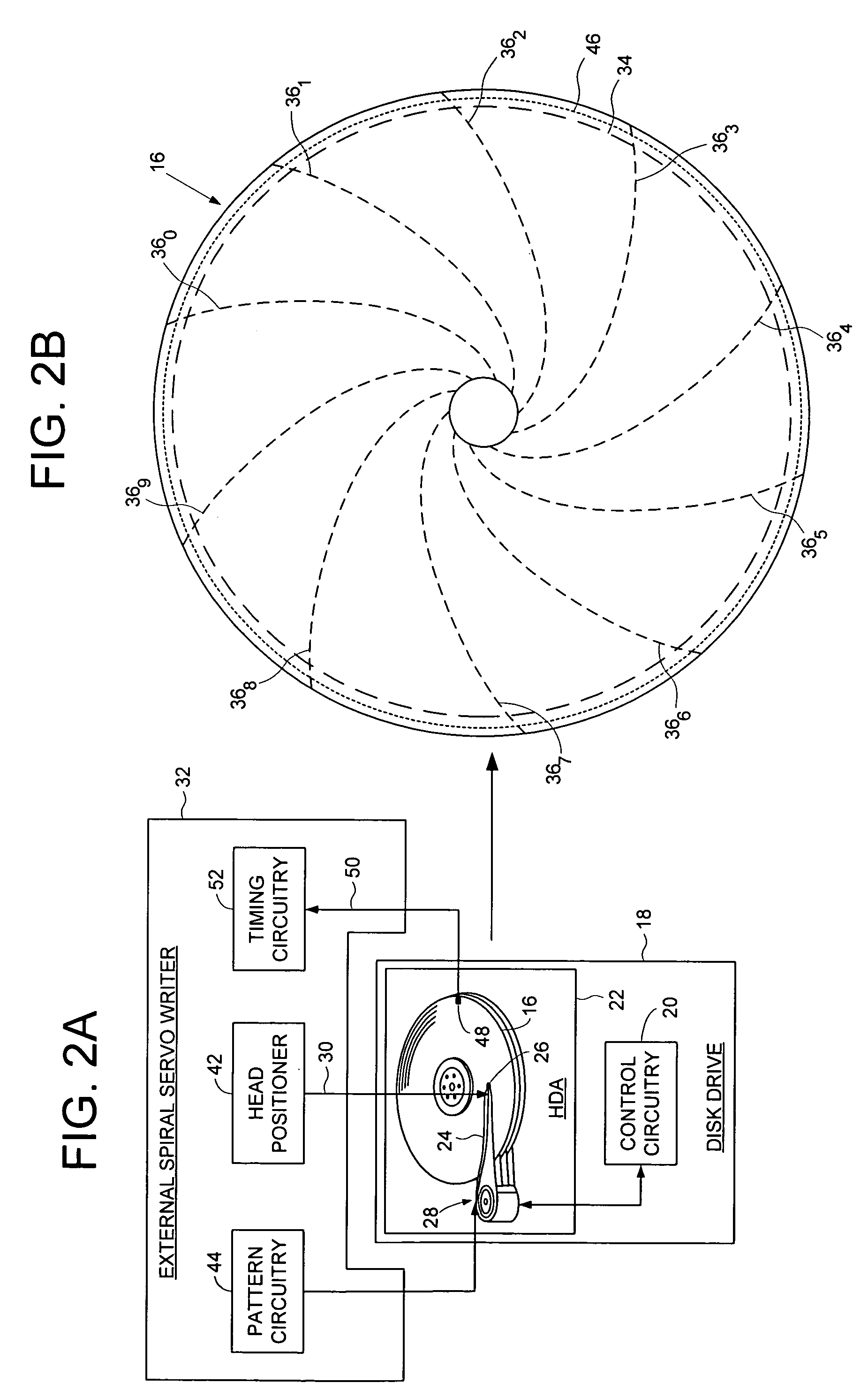
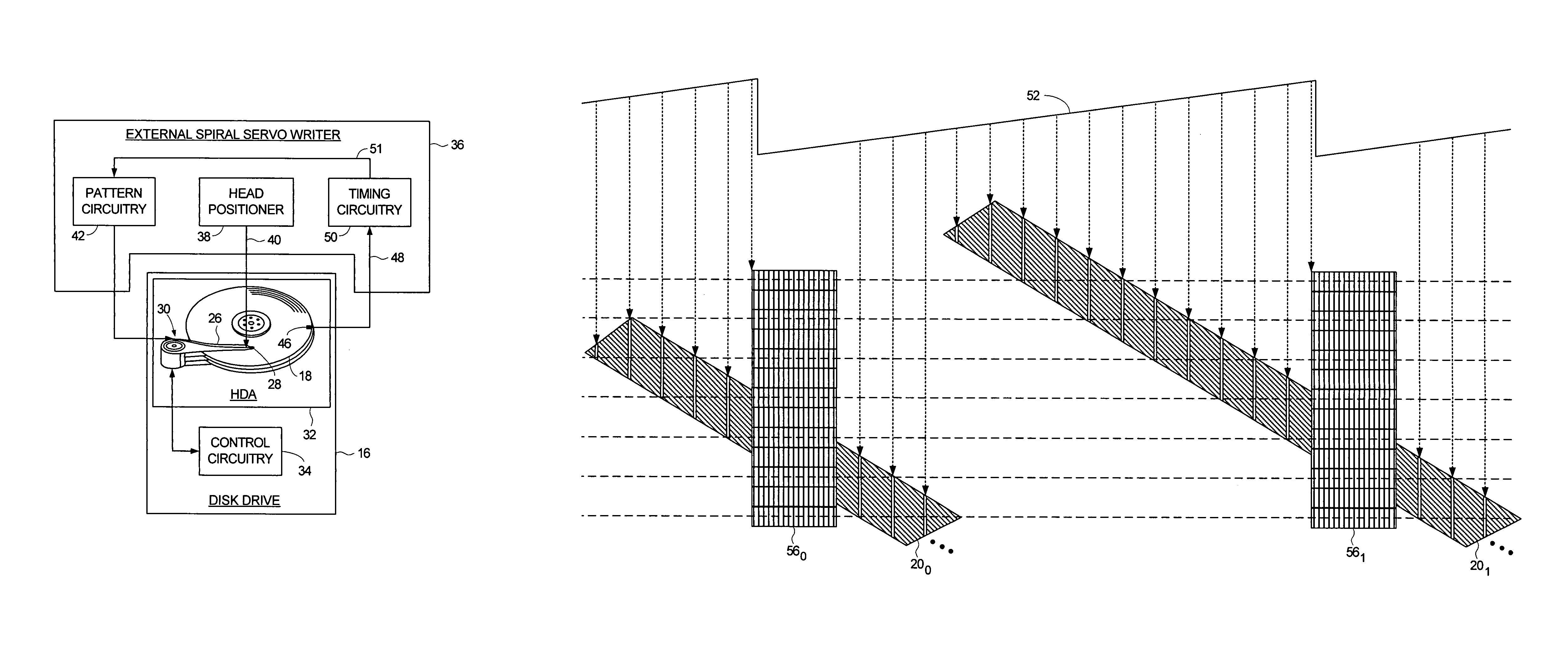
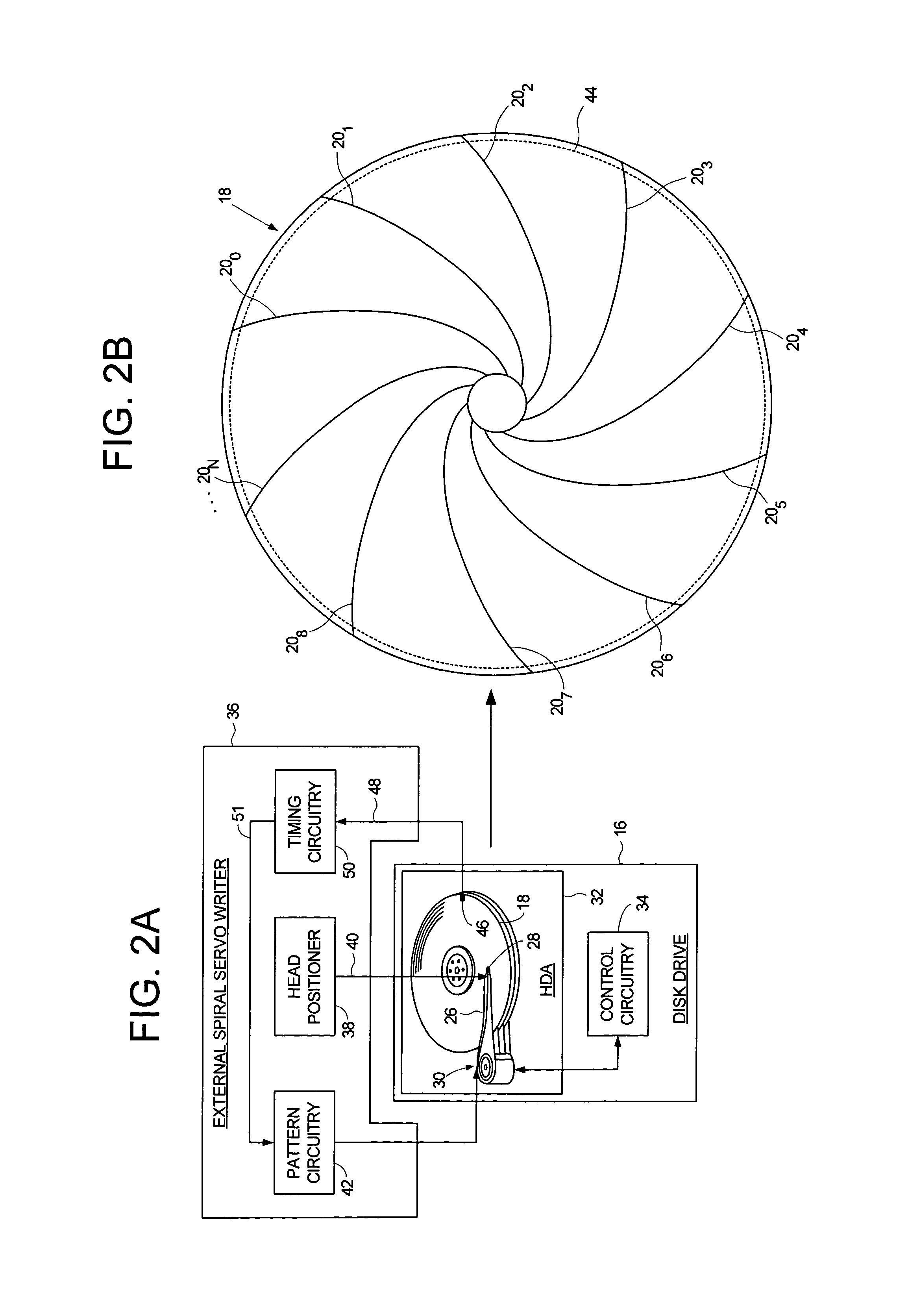
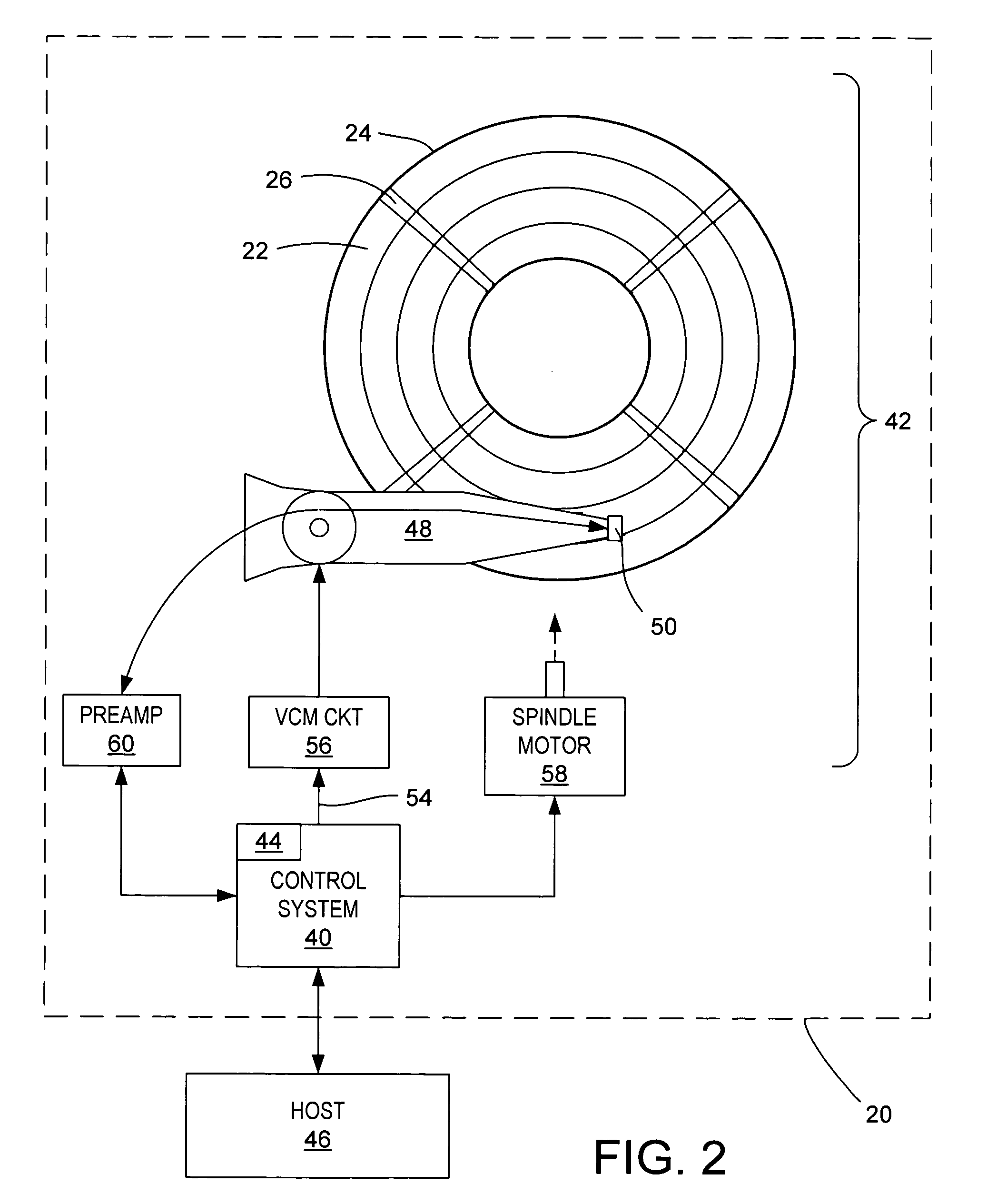
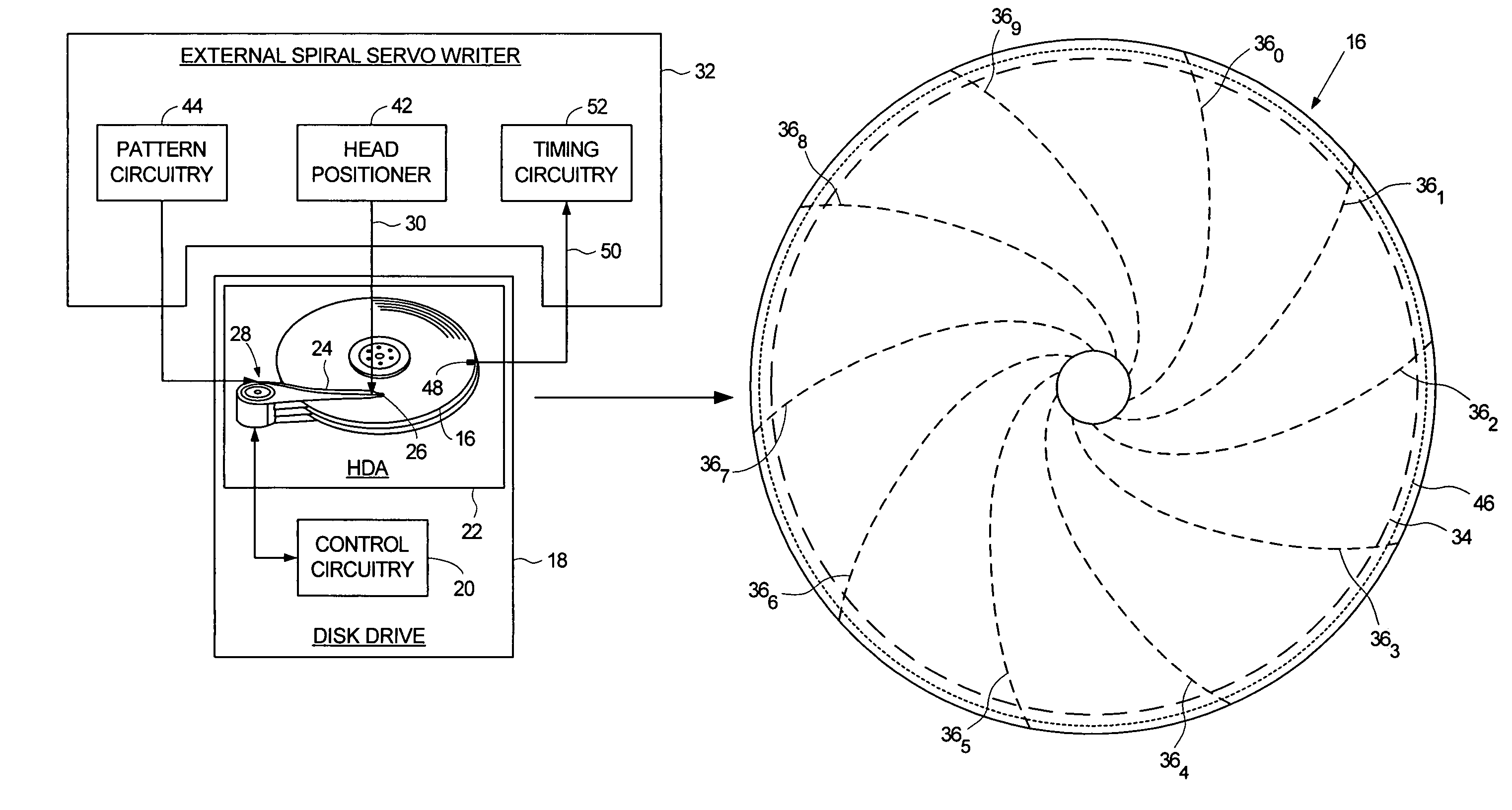
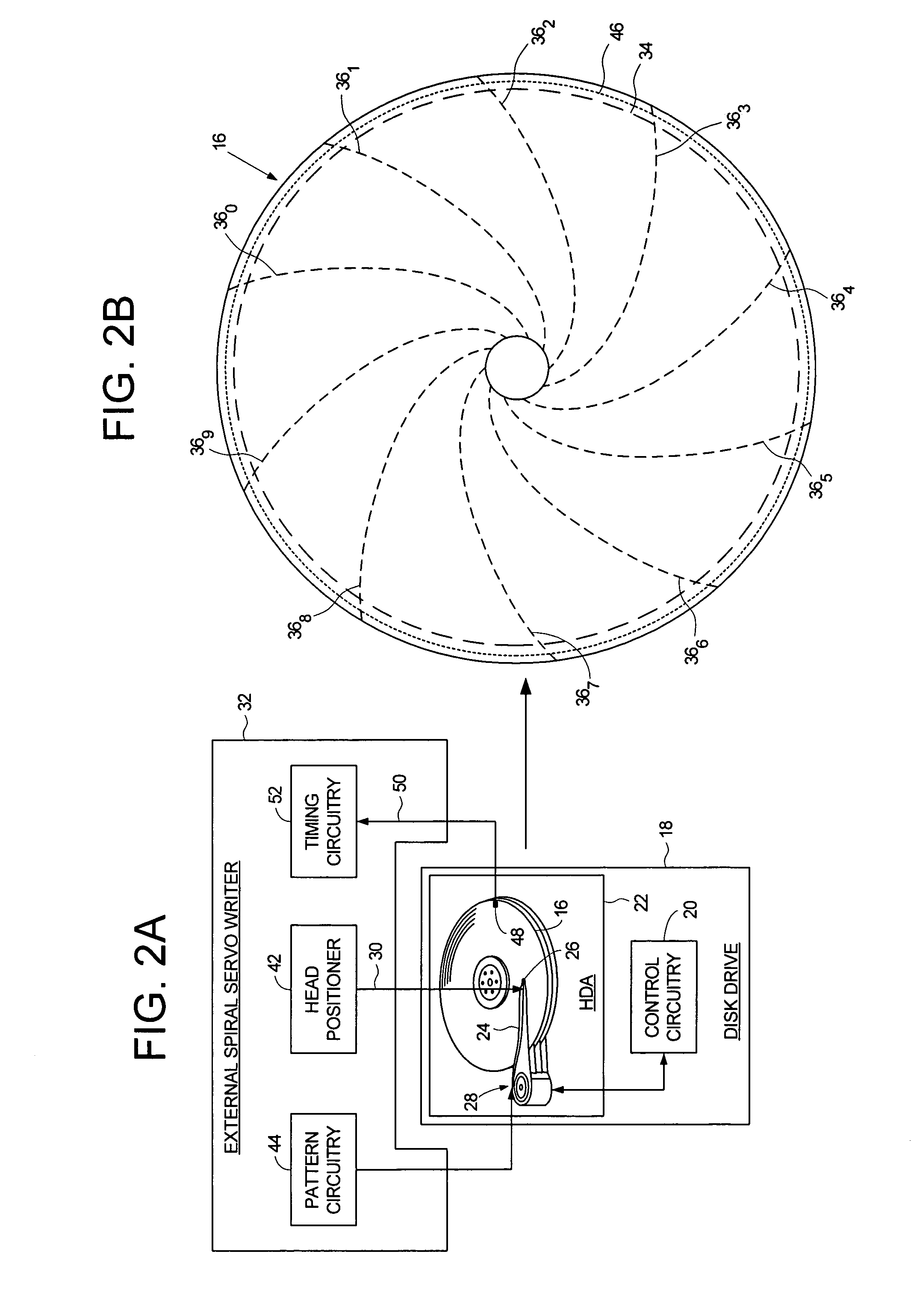
Using an external spiral servo writer to write reference servo sectors and spiral tracks to a disk to facilitate writing product servo sectors to the disk
A method of writing product servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive is disclosed. An external spiral servo writer writes a plurality of reference servo sectors at an outer diameter of the disk and a plurality of spiral tracks that spiral from an outer diameter to an inner diameter of the disk. At the beginning of the product servo writing process, the reference servo sectors are demodulated to initially synchronize a servo write clock. The spiral tracks are then demodulated to maintain synchronization of the servo write clock as well as maintain the head along a target circumferential path while writing product servo sectors to the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Adjusting track density over disk radius by changing slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive
InactiveUS6987636B1Steep slopeDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for adjusting the track density over the disk radius by changing the slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive. A plurality of spiral tracks are written to the disk wherein each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark. A slope of the spiral tracks over a first radial segment of the disk is substantially steeper than the slope of the spiral tracks over a second radial segment of the disk. The head internal to the disk drive is used to read the spiral tracks in order to write product servo sectors to the disk to define a plurality of data tracks. The steeper slope of the spiral tracks over the first radial segment causes a track density of the data tracks to be lower over the first radial segment compared to the track density of the data tracks over the second radial segment.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
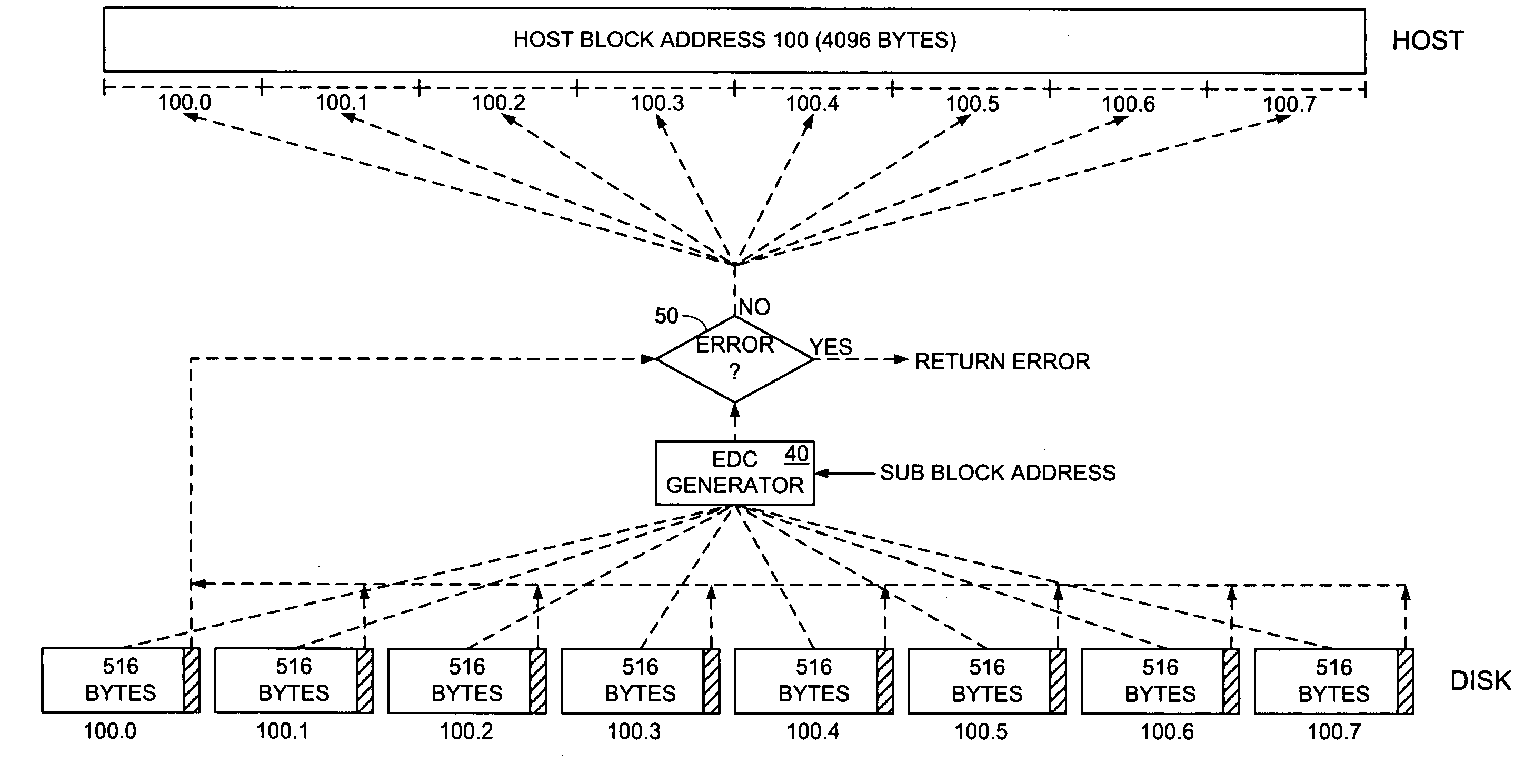
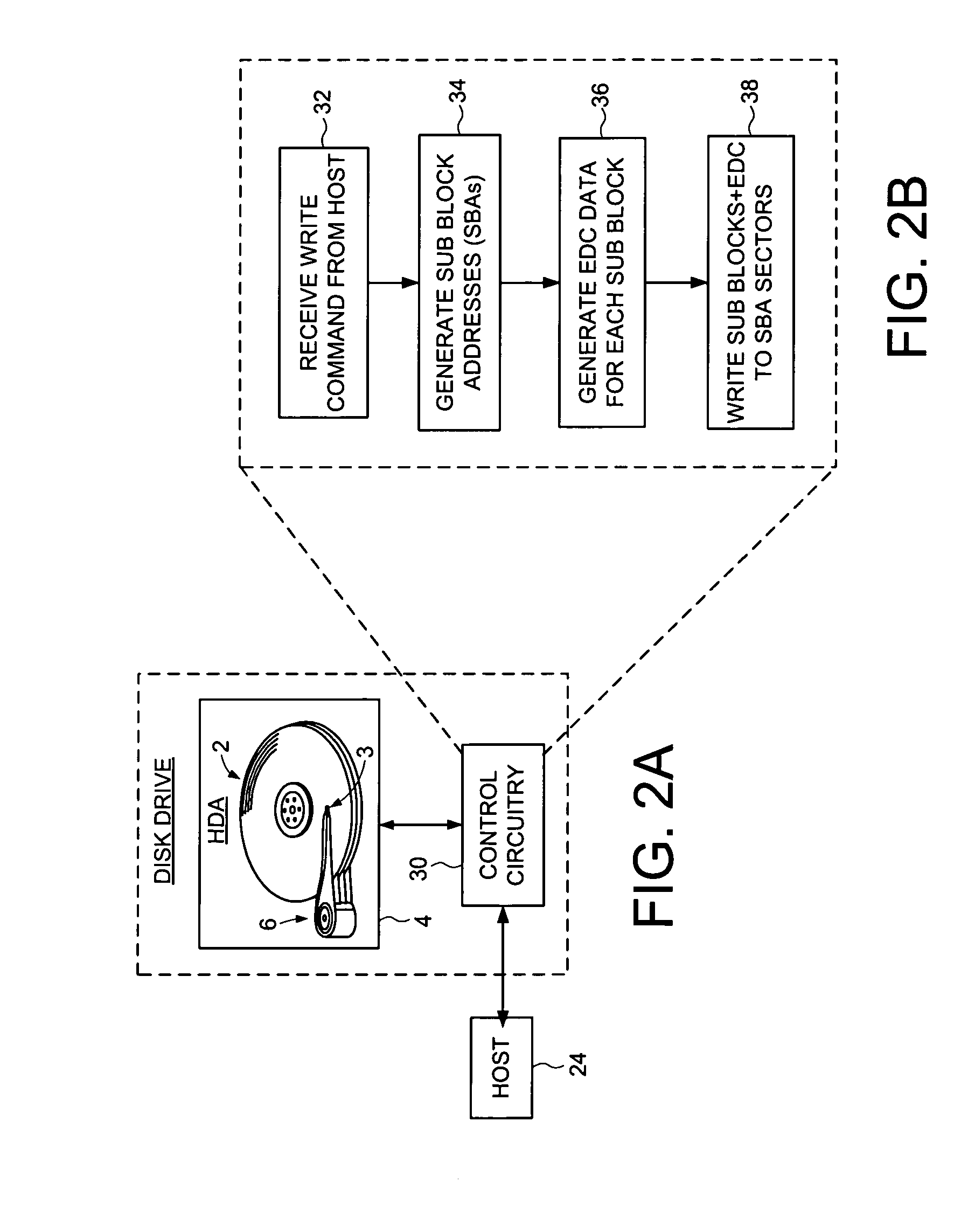
Disk drive implementing data path protection by encoding large host blocks into sub blocks
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk having a plurality of data tracks, wherein each data track includes a plurality of data sectors. A head is actuated over the disk for accessing the data sectors. A write command is received from a host, wherein the write command includes a host block and corresponding host block address. The host block is partitioned into a plurality of sub blocks, and a plurality of sub block addresses are generated in response to the host block address, wherein each sub block address corresponds to one of the sub blocks. Error detection code (EDC) data is generated for each sub block in response to the sub block and corresponding sub block address. Each sub block and corresponding EDC data are combined to generate a plurality of partial codewords that are written to the data sectors corresponding to the sub block addresses.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
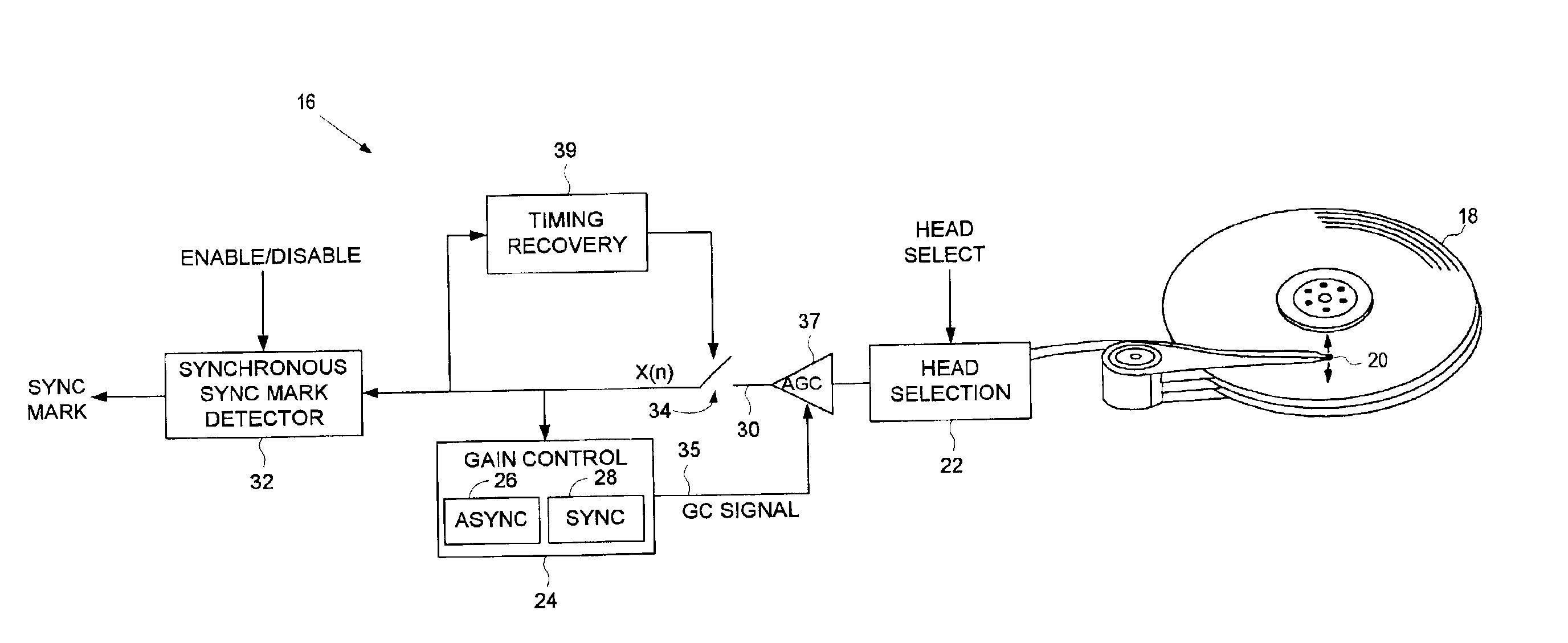
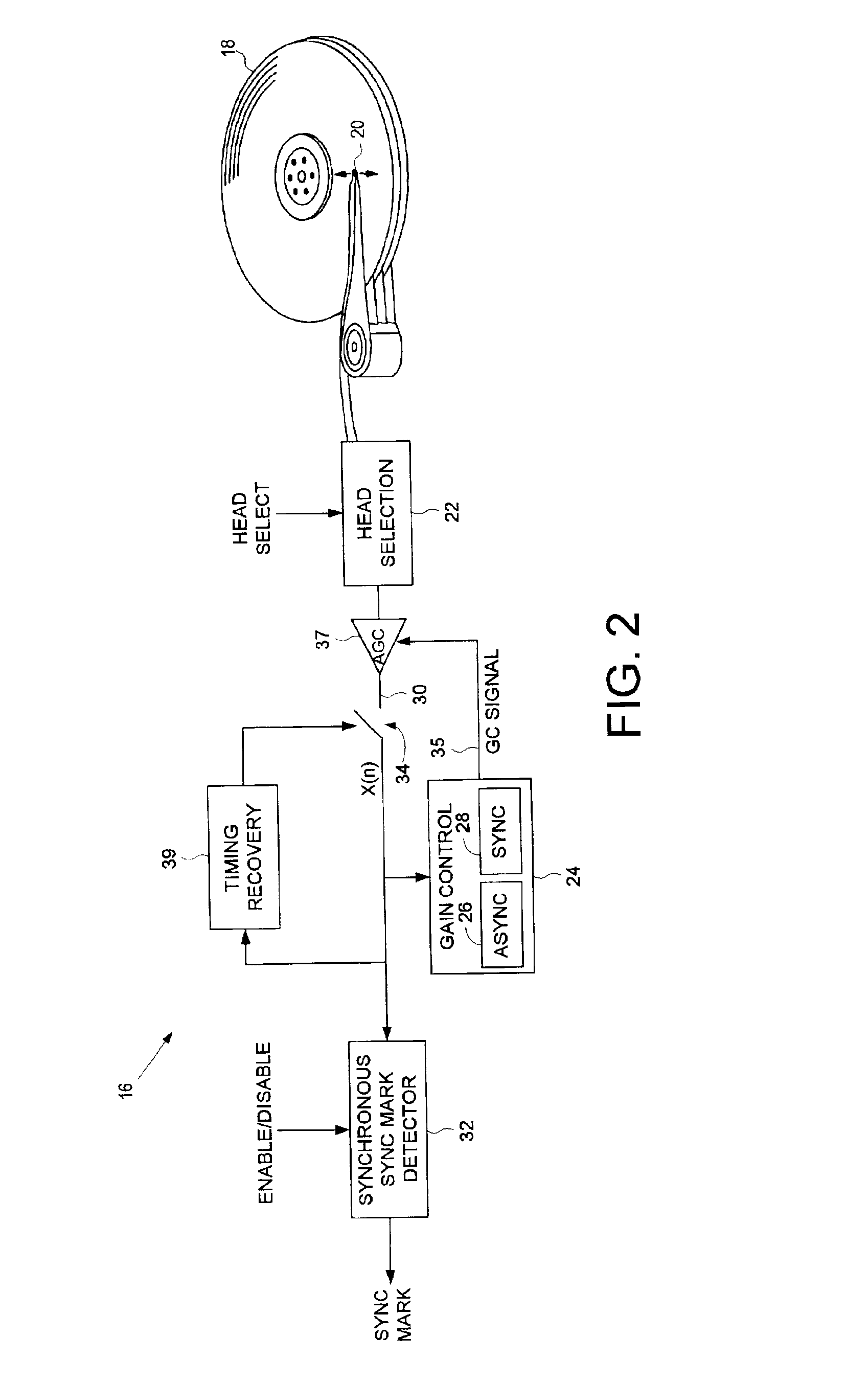
Disk drive comprising asynchronous/synchronous gain control for fault tolerant detection of servo sync mark after head switch
InactiveUS6882486B1Accurate gainModification of read/write signalsDisc-shaped record carriersControl systemControl algorithm
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a plurality of disk surfaces and a plurality of respective heads actuated radially over the disk surfaces. Each disk surface comprises a plurality of tracks, each track comprising a plurality of data sectors and a plurality of embedded servo sectors, each embedded servo sector comprising a servo sync mark for synchronizing to the embedded servo sector. When the disk drive switches heads, a detection window for detecting the servo sync mark is opened early. An asynchronous gain control algorithm prevents a gain control system from diverging while reading an area of the disk surface preceding the servo sync mark, and a synchronous gain control algorithm maintains a proper gain of the read signal while reading the servo sync mark.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
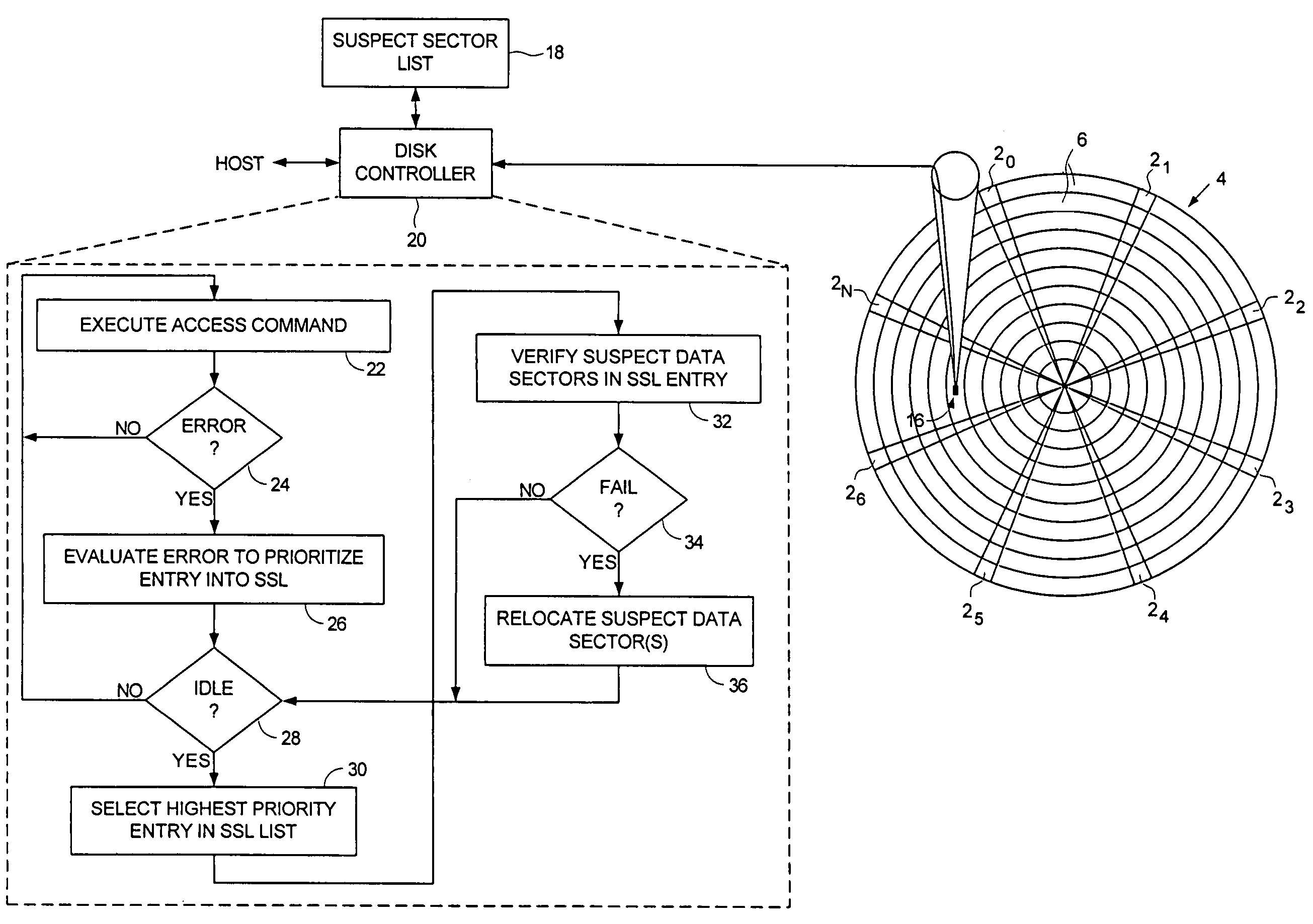
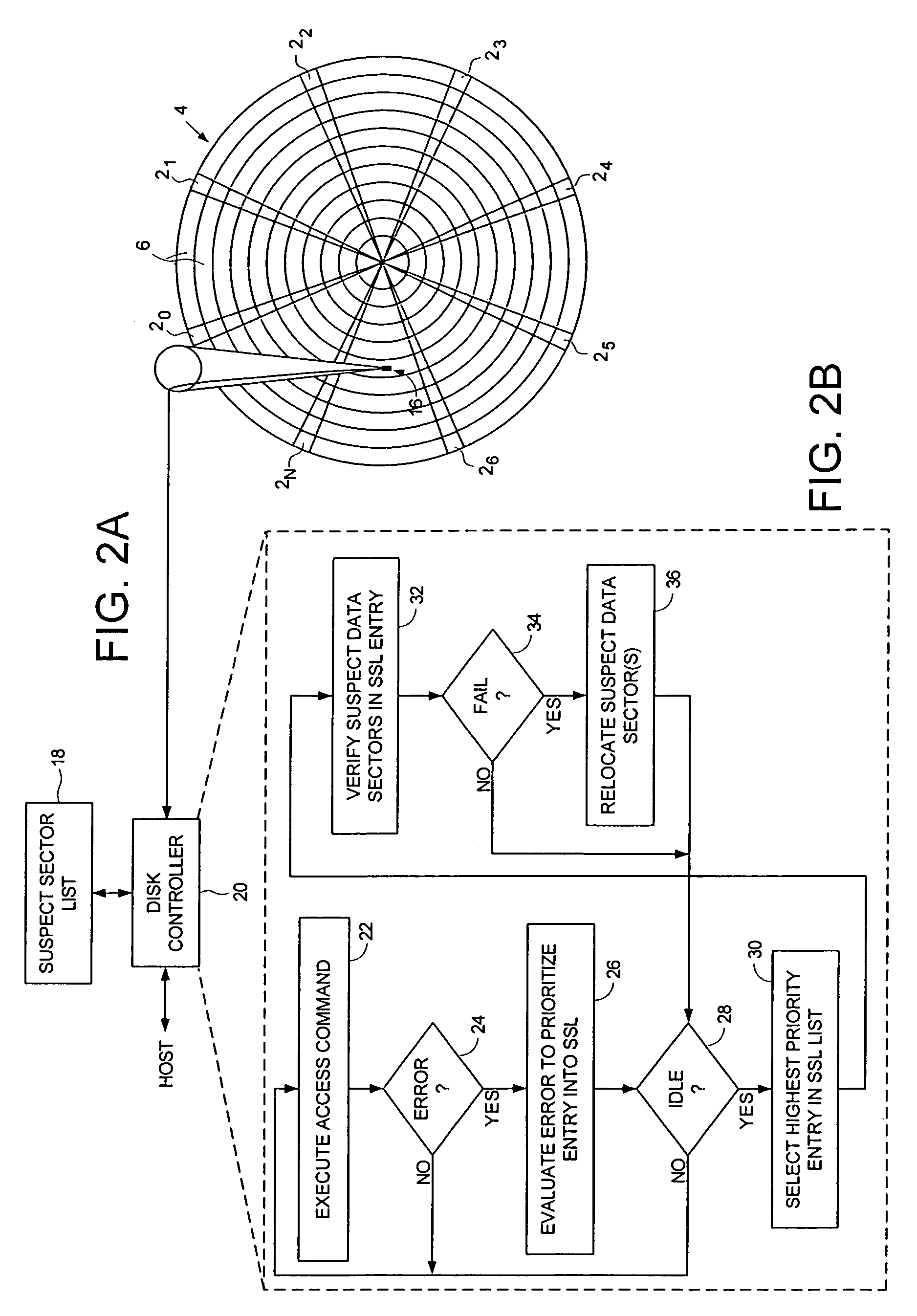
Disk drive performing multi-level prioritization of entries in a suspect sector list to identify and relocate defective data sectors
InactiveUS7274639B1Delay minimizationCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersDisk controllerOperating system
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk having a plurality of data tracks, wherein each data track comprises a plurality of data sectors, and a head is actuated over the disk. A suspect sector list (SSL) stores a plurality of SSL entries, wherein each SSL entry identifies at least one suspect data sector. The disk drive further comprises a disk controller for executing an access command received from a host computer to access at least one of the data sectors. If an error is detected while executing the access command, the disk controller generates an SSL entry having a priority level selected from at least three priority levels and adds the SSL entry to the SSL. A verification operation is executed for each suspect data sector identified by each SSL entry, wherein the SSL entries are processed relative to the priority level assigned to each SSL entry.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
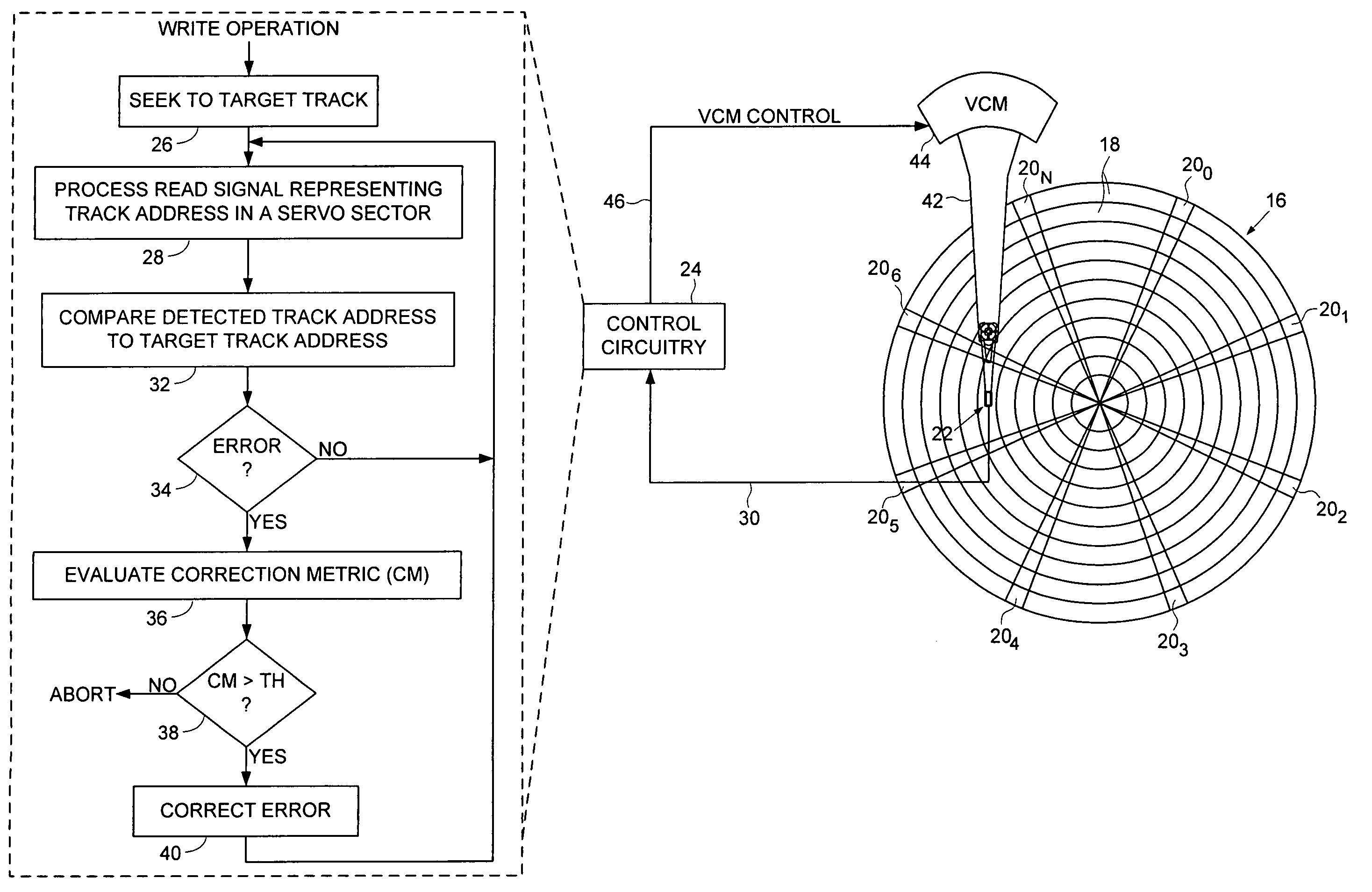
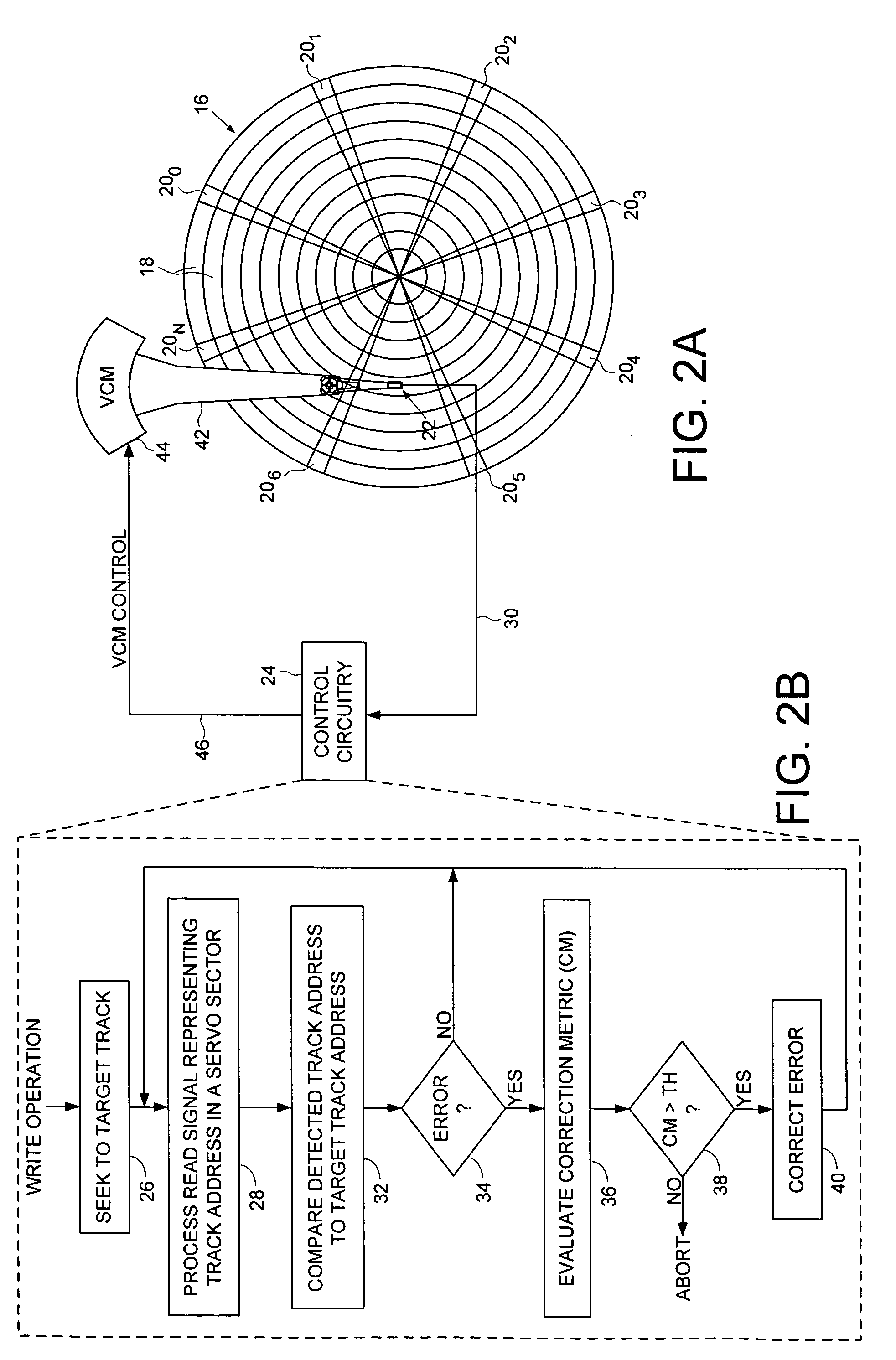
Disk drive correcting track address during a write operation
InactiveUS7369343B1Recording carrier detailsRecord information storageControl theoryComputer hardware
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a head actuated over a disk having a plurality of servo tracks, wherein each servo track comprises a plurality of servo sectors and each servo sector comprises a track address. A read signal from the head representing a first track address in one of the servo sectors is processed in order to generate a detected track address which is compared to a first target track address to obtain a first track address error. A correction metric is generated representing a likelihood that the first track address error was caused by a detection error, and if the correction metric exceeds a threshold, the detected track address is corrected in response to the first track address error, and the write operation is continued. If the correction metric does not exceed the threshold, the write operation is aborted.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Demodulating servo sectors and spiral tracks using common circuitry
InactiveUS6989954B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl theoryDemodulation
A method of manufacturing a disk drive by demodulating product servo sectors and spiral tracks written on a disk of the disk drive is disclosed. An external spiral servo writer writes a plurality of spiral tracks that spiral from an outer diameter to an inner diameter of the disk. Each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark. The spiral tracks are used to write product servo sectors to the disk during a fill operation. Common circuitry, such as burst demodulation circuitry, is used to demodulate the high frequency signal in the spiral tracks during the fill operation as well as demodulate the product servo sectors.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Adjusting track density by changing slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive
InactiveUS7433143B1Steep slopeTrack density can not be increasedRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksTrack densityEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed for adjusting the track density by changing the slope of spiral tracks used to servo write a disk drive. A target track density is established for a disk surface, and a plurality of spiral tracks are written to the disk surface in response to the target track density. Each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark, and a slope of the spiral tracks is selected in response to the target track density. The head internal to the disk drive is used to read the spiral tracks in order to write product servo sectors to the disk to define a plurality of data tracks, wherein the slope of the spiral tracks determines the density of the data tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
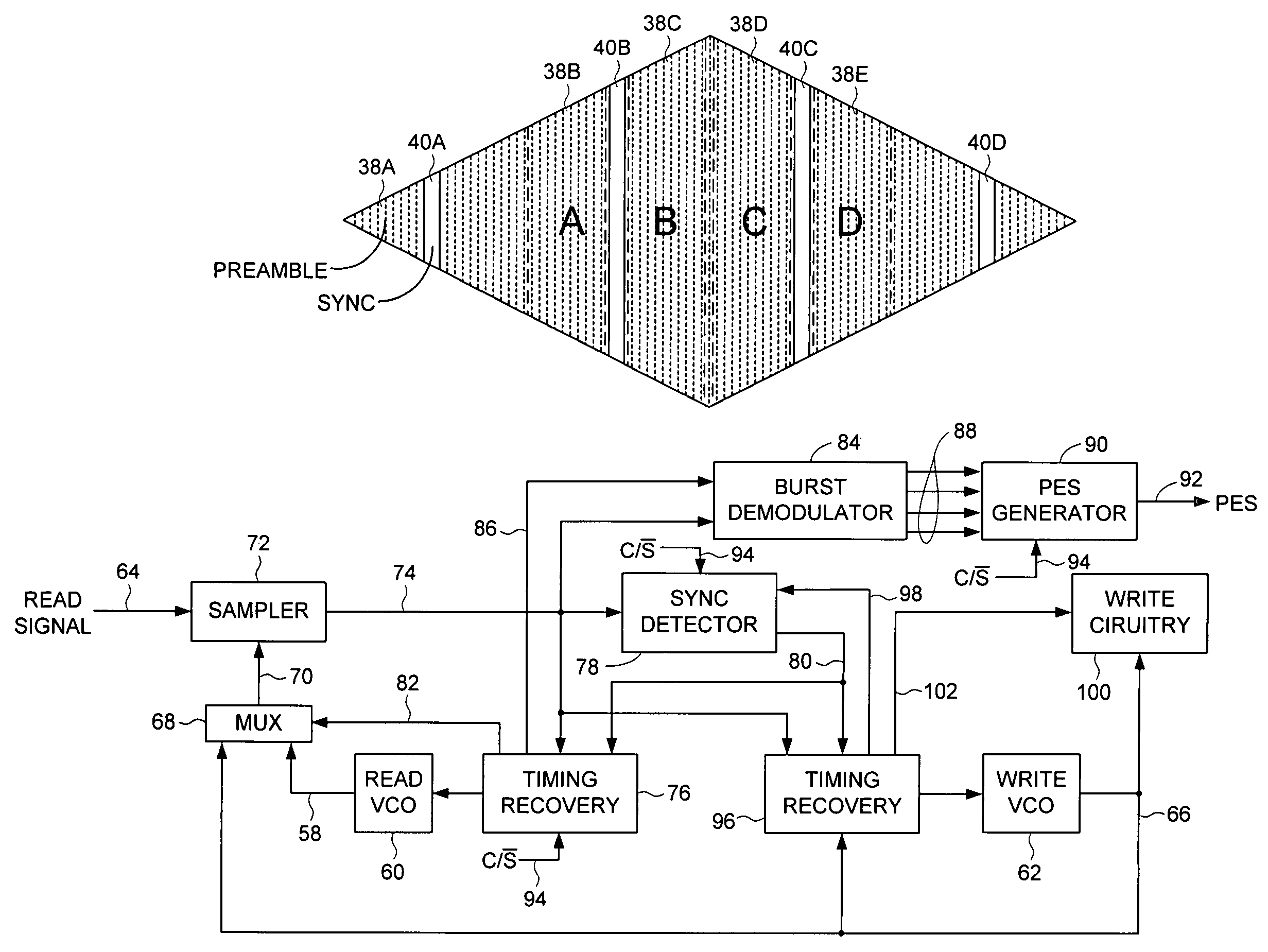
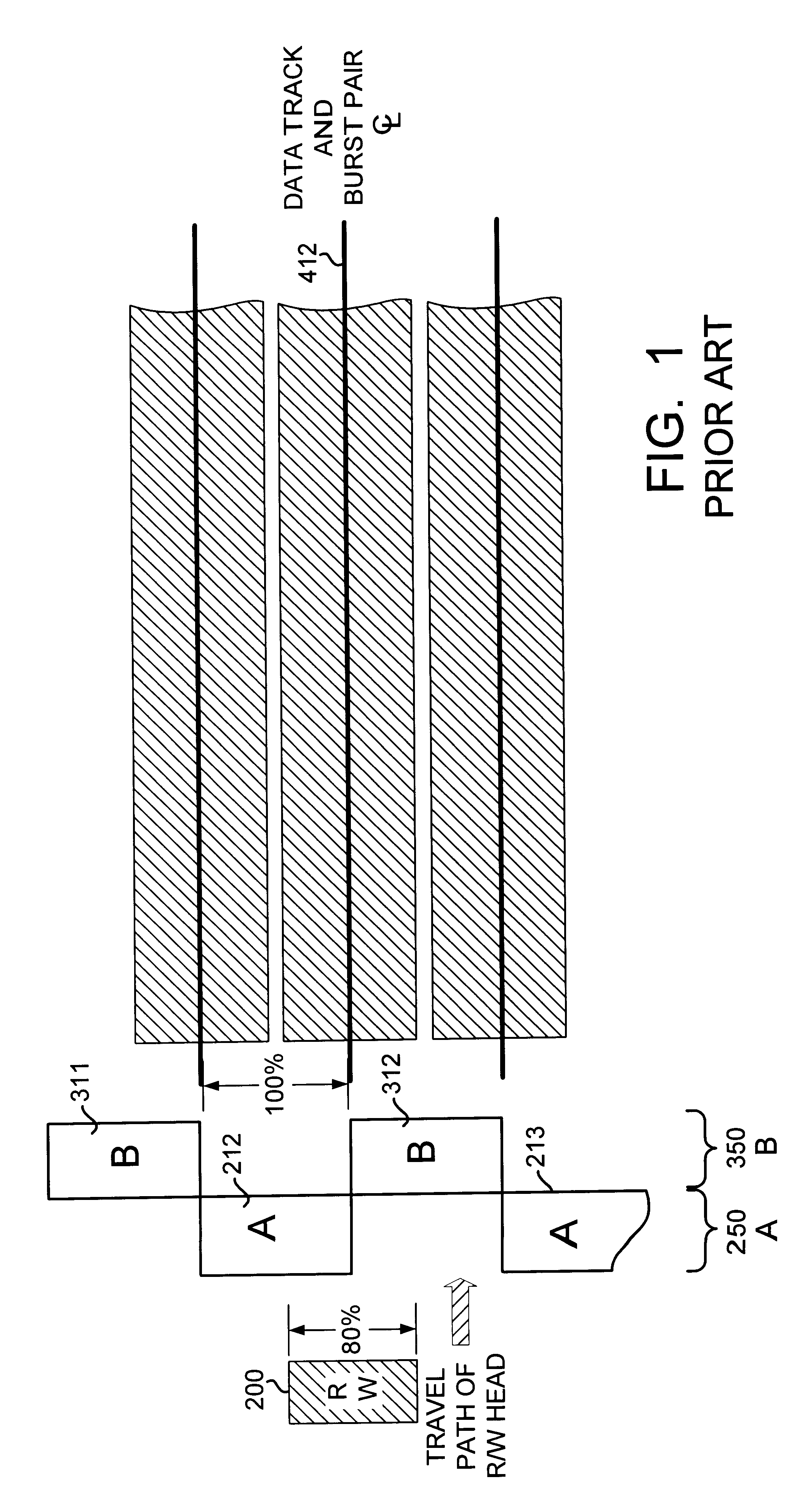
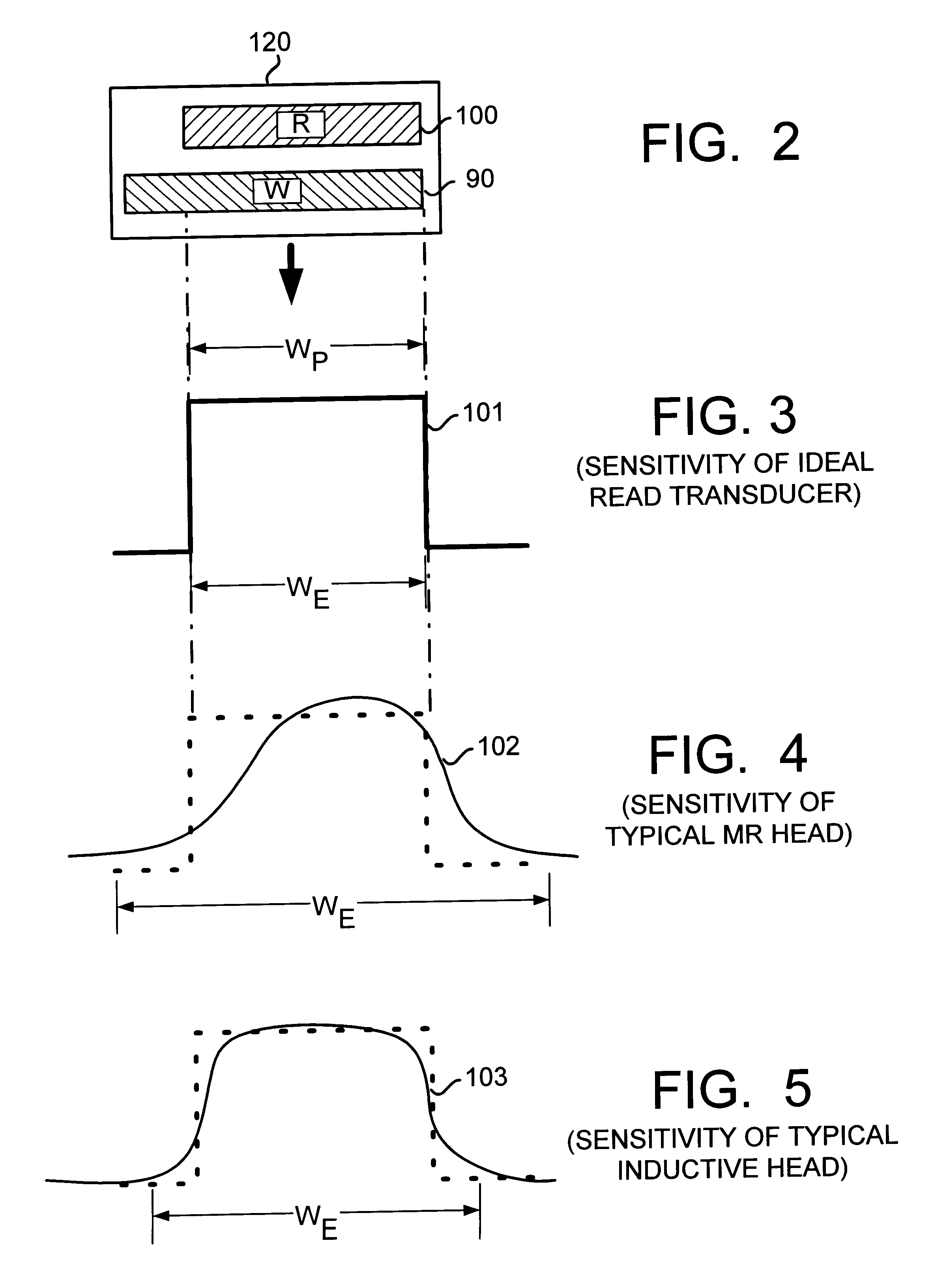
Disk drive with servo burst phasing for improved linearity and off-track performance with a wide reading transducer
InactiveUS6243223B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksTransducerTrack (disk drive)
A disk drive has a sampled servo system controller and a disk with a plurality of angularly spaced servo wedges. Each of the servo wedges contains angularly aligned servo burst fields that are radially adjacent to one another and spaced apart by an erase field. In order to eliminate or minimize servo position signal errors caused by a wide-reading transducer head encountering signals from both of a pair of angularly aligned servo burst fields, the servo burst fields are recorded in opposing phase.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
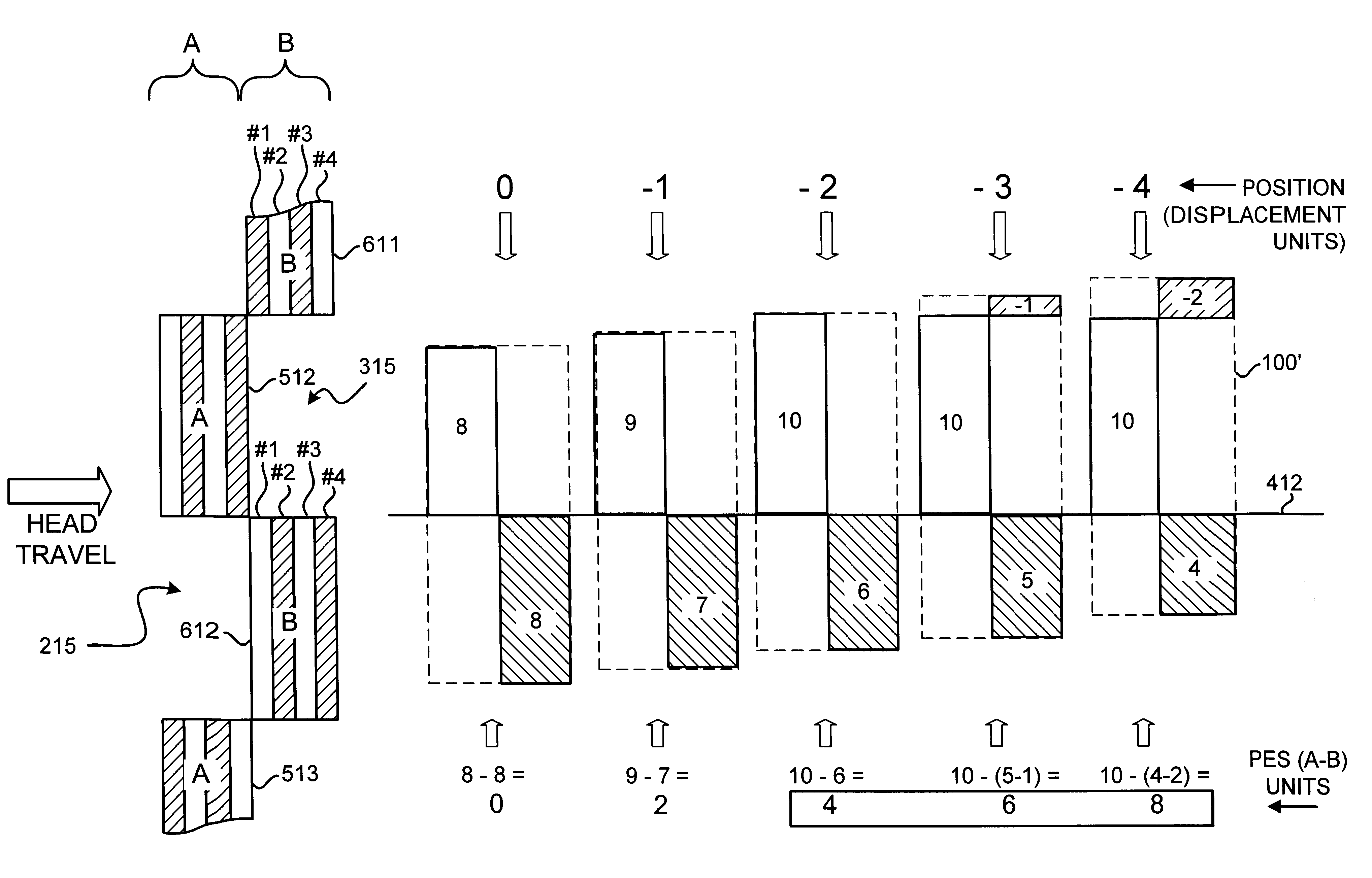
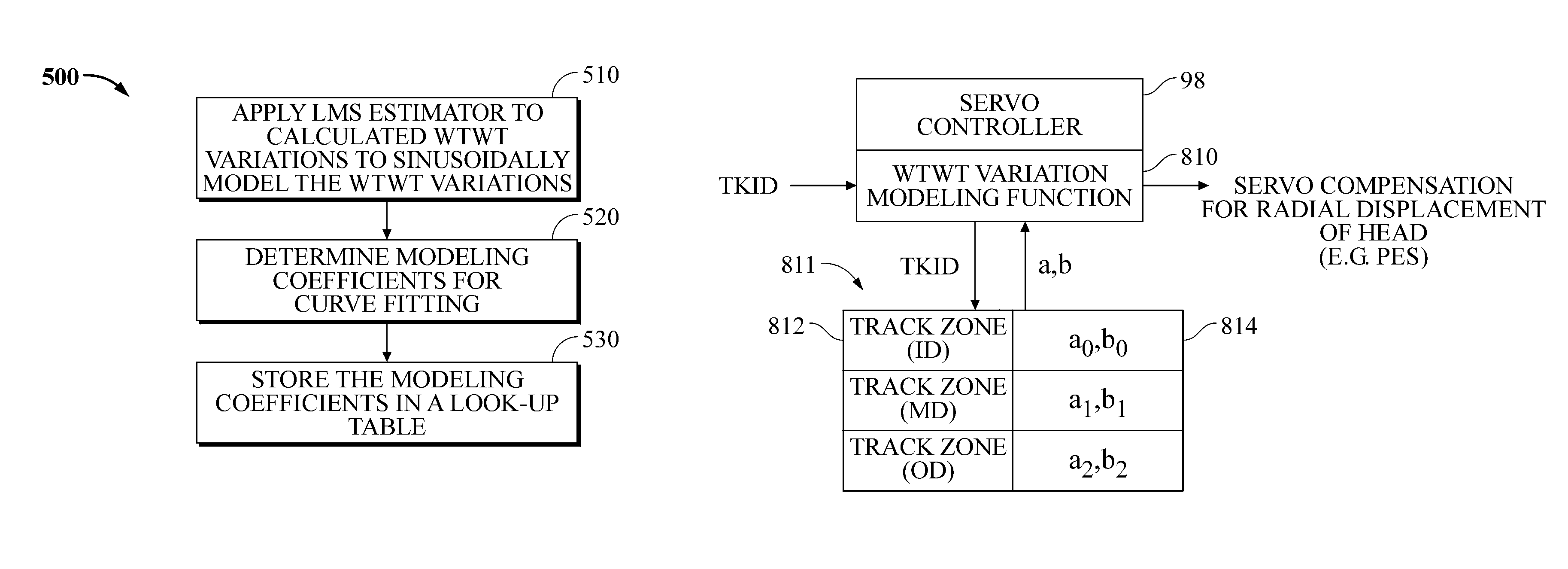
Disk drive to characterize misaligned servo wedges
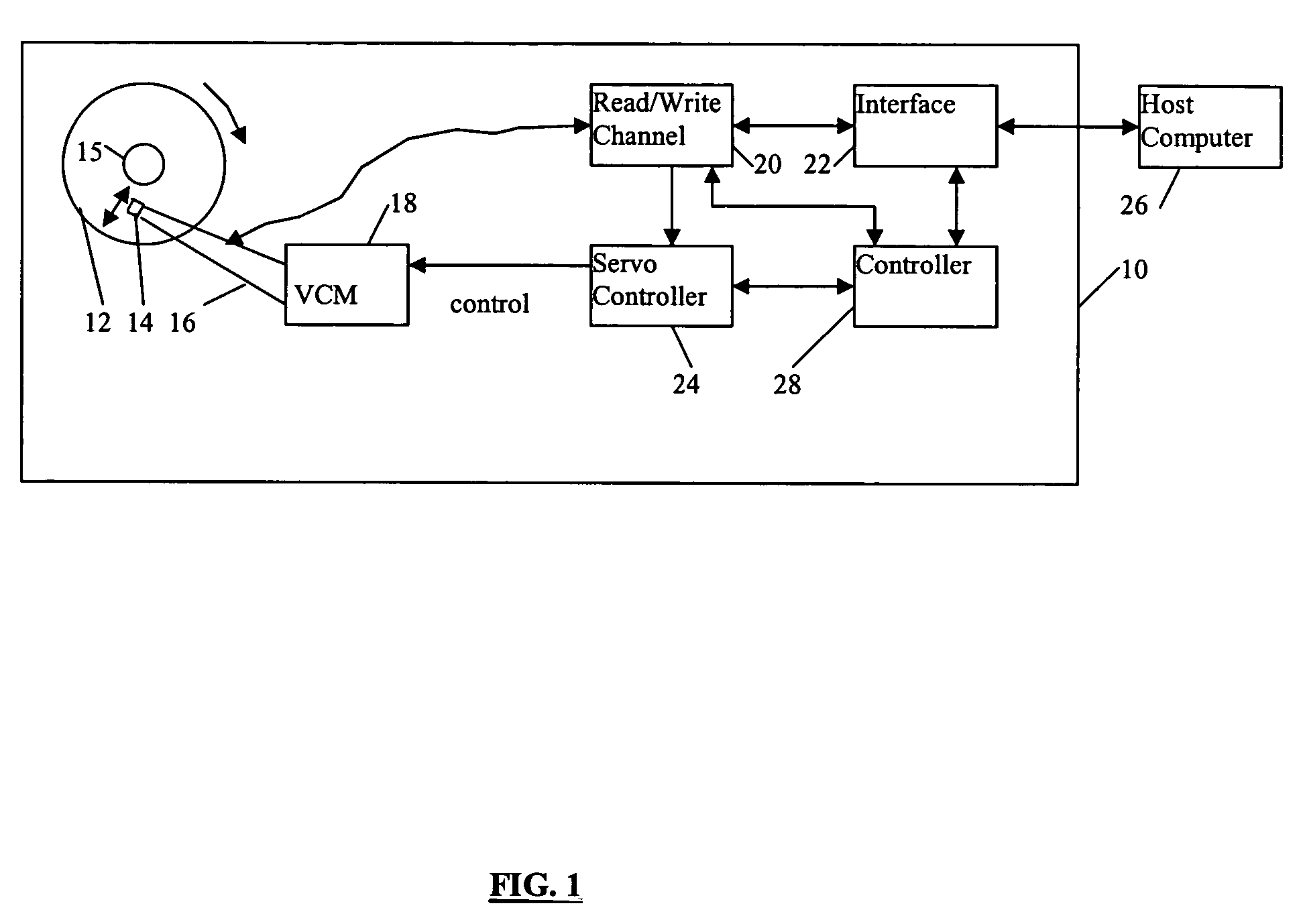
Disclosed is a disk drive and method to characterize misaligned servo wedges. The disk drive includes an actuator arm, a head, a disk, and a servo controller. The head is connected to a distal end of the actuator arm in which the actuator arm is rotatable about a pivot to move the head radially over the disk. The servo controller is used to characterize misaligned servo wedges by implementing operations including: commanding the head to track follow on a track; measuring wedge-to-wedge time (WTWT) values corresponding to time intervals between identified servo wedges; calculating wedge-to-wedge time (WTWT) variations for the measured WTWT values; and characterizing the calculated WTWT variations, wherein, characterizing the calculated WTWT variations for the track includes utilizing a WTWT variation modeling function to model the WTWT variations.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
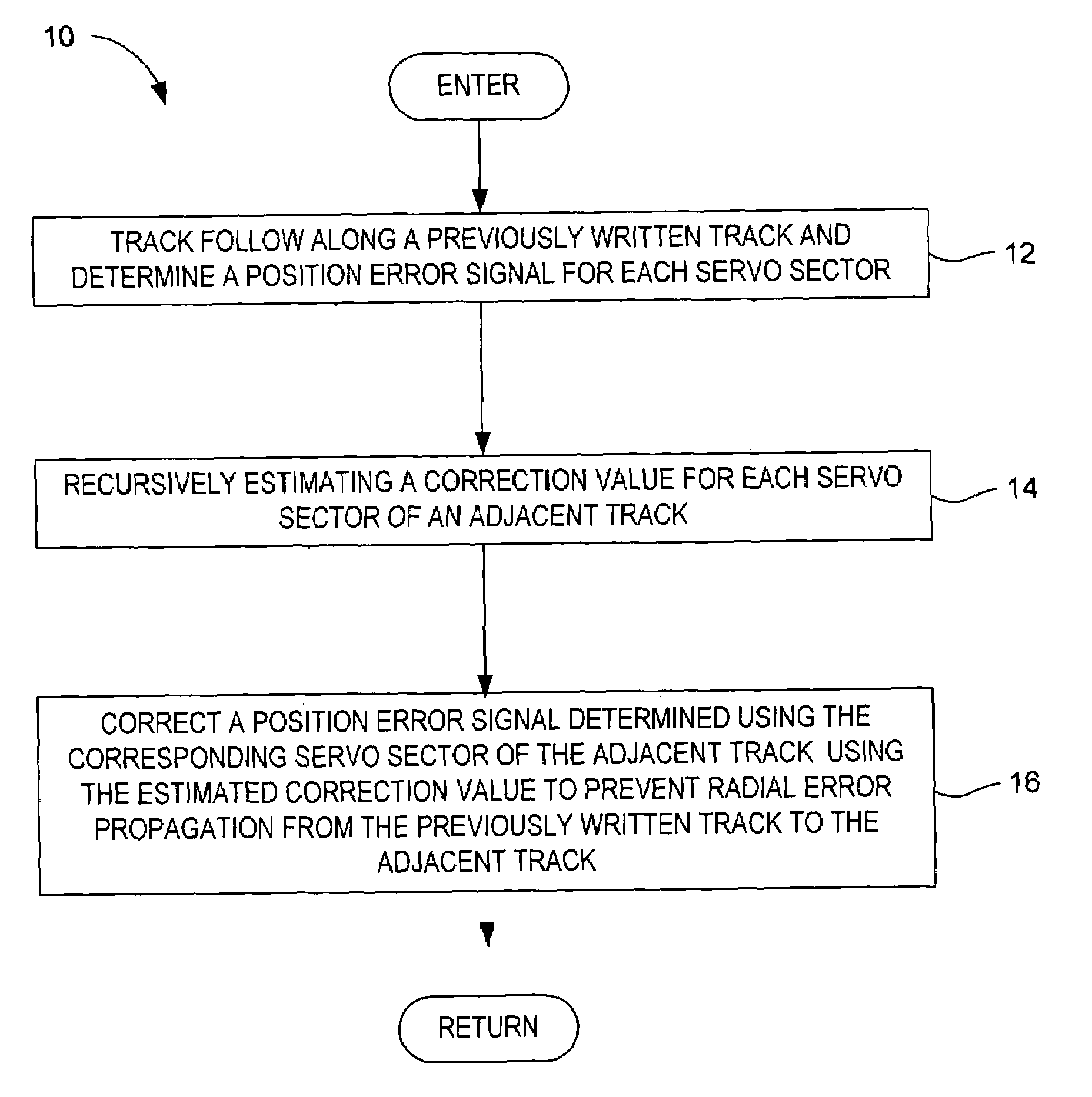
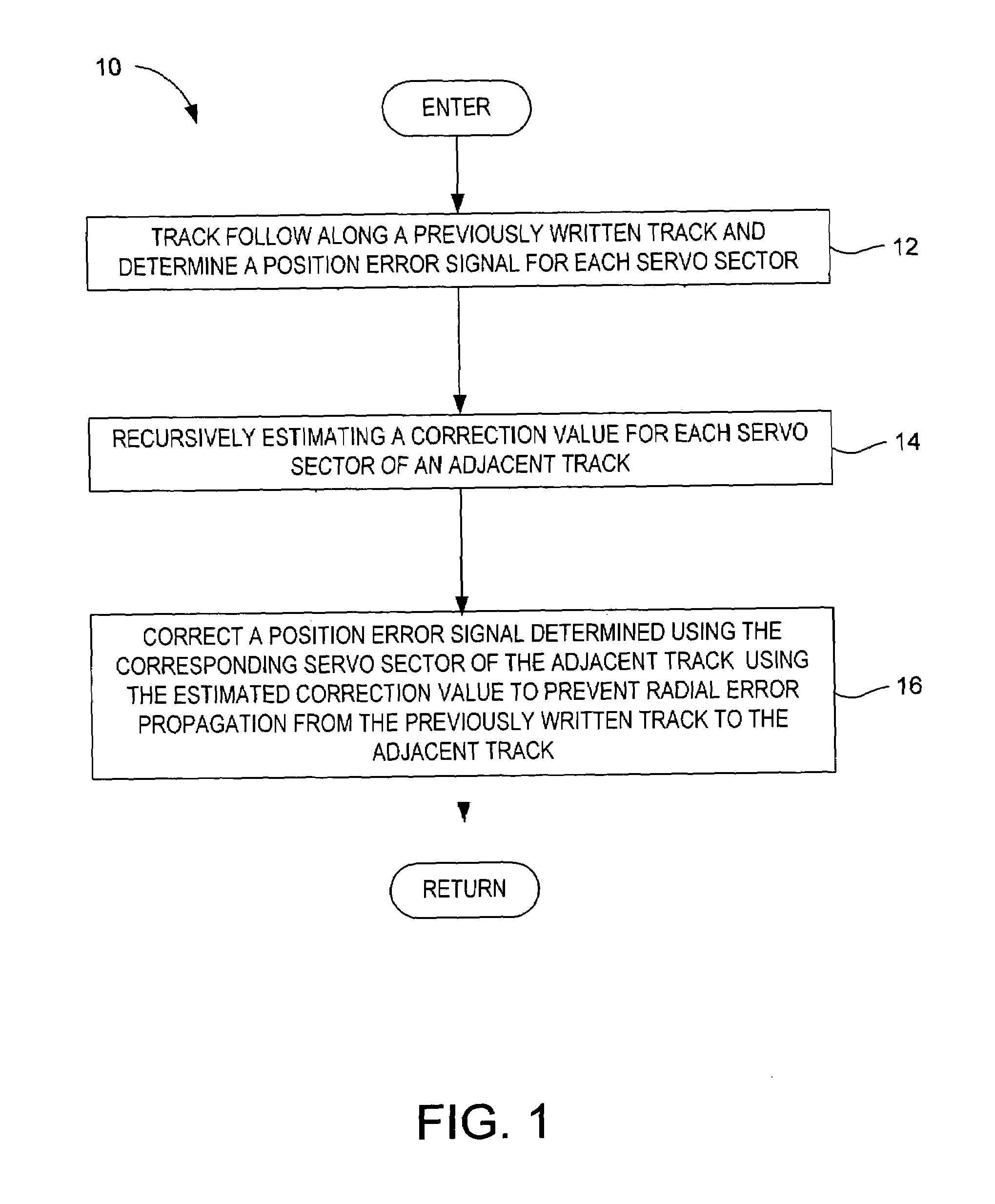
Method for preventing radial error propagation during self-servowriting of tracks in a magnetic disk drive
InactiveUS6963465B1Preventing radial error propagationPrevent radial error propagationDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageRadial errorControl theory
The present invention may be embodied in a method for preventing radial error propagation during self-servowriting of concentric tracks on a magnetic disk in a disk drive. Each written track comprises a plurality of embedded servo sectors that define a circumferential path and that eventually form corresponding servo wedges extending radially across the magnetic disk such that each servo sector t of a track corresponds to a particular servo wedge. In the method comprising, track following is performed along a previously written track and a position error signal is determined for each servo sector. A correction value is recursively estimated for each servo sector of an adjacent track. The correction value is for use in correcting a position error signal determined using the corresponding servo sector of the adjacent track to prevent radial error propagation from previously written track to the adjacent track.
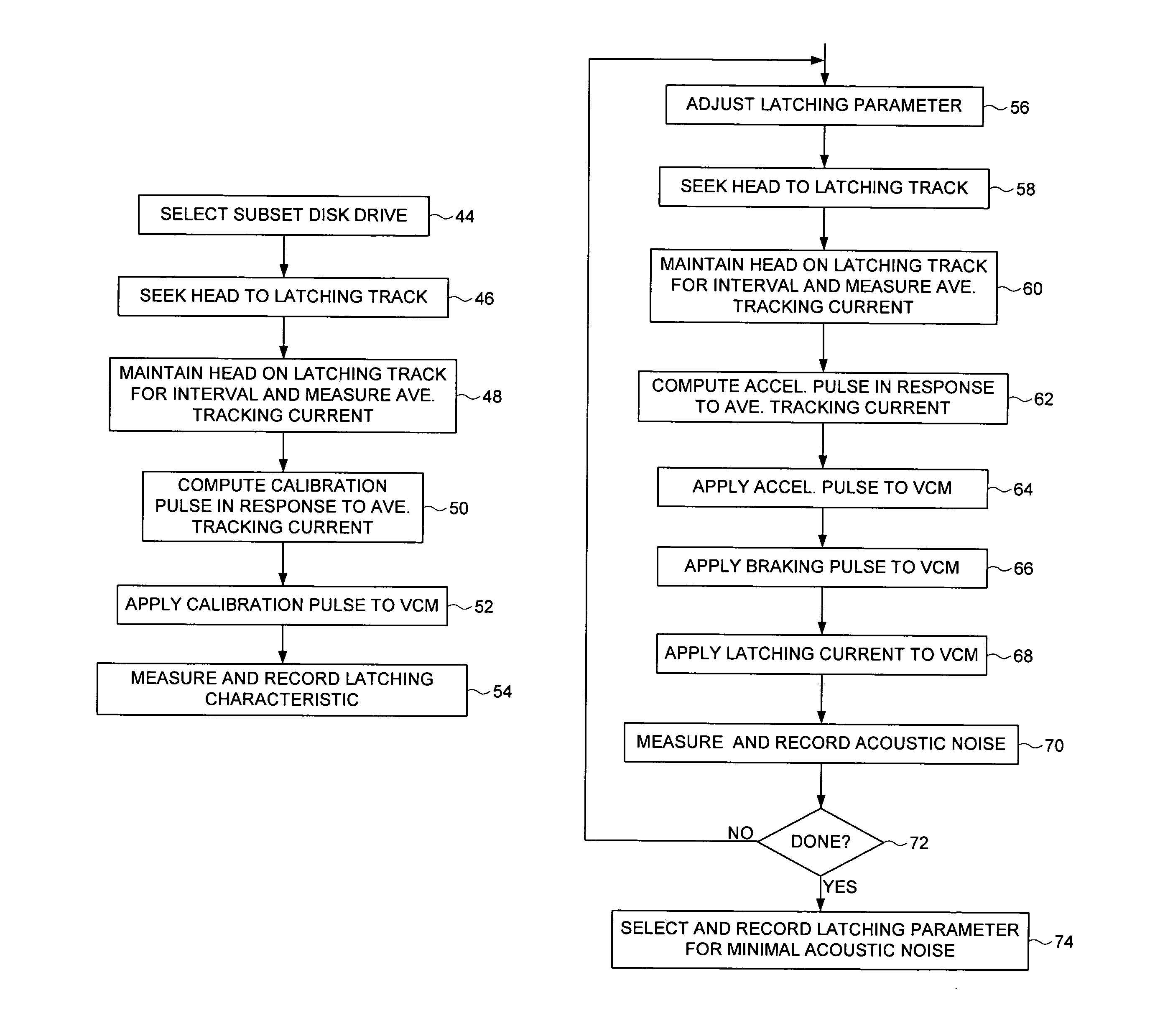
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Calibrating correlation between PES and off-track displacement by processing high frequency signal in spiral track
InactiveUS7499236B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringControl theory
A method is disclosed for writing product servo sectors to the disk of a disk drive by demodulating spiral tracks recorded on the disk. Each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted at a predetermined interval by a sync mark. The high frequency signal is demodulated into a plurality of servo burst signals, and a position error signal is generated from the servo burst signals. A correlation between the position error signal and an off-track displacement of a head is calibrated, for example, by moving the head radially over the disk until the servo burst signals attain a first predetermined relationship, and then calibrating the correlation in response to the corresponding position error signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
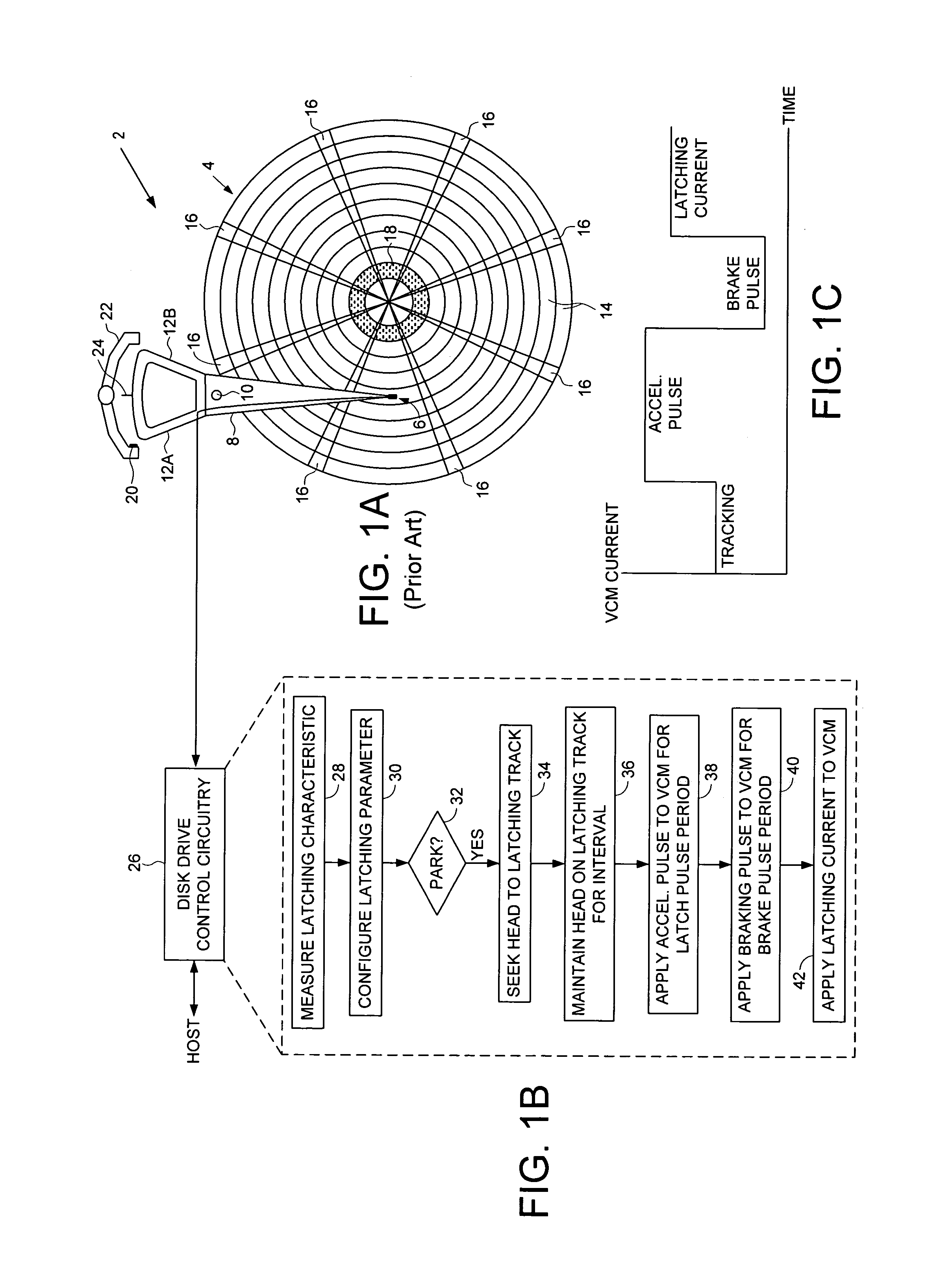
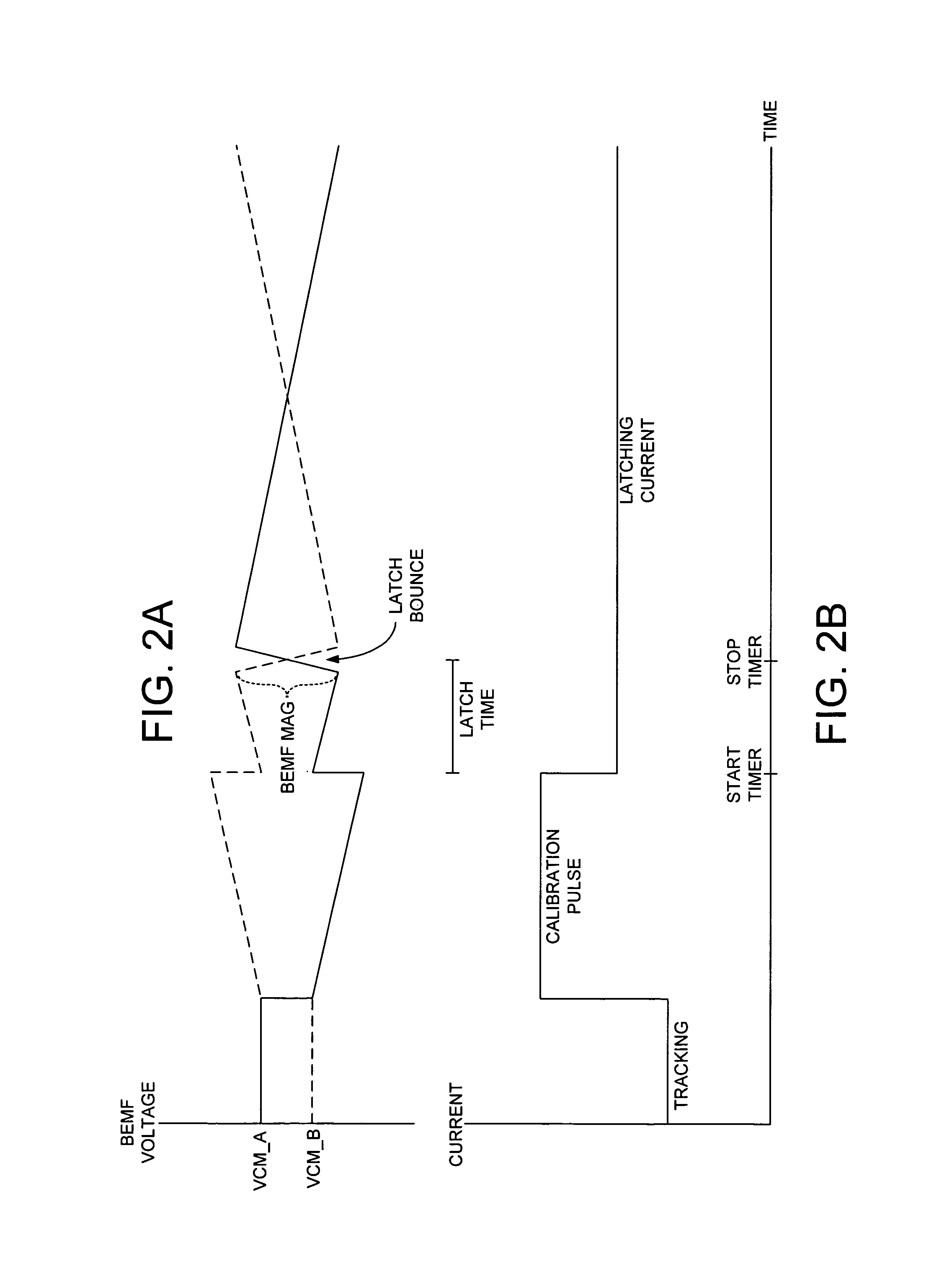
Disk drive employing a calibrated brake pulse to reduce acoustic noise when latching an actuator arm
InactiveUS7224546B1Reduce noiseMinimize acoustic noiseDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringControl theory
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a voice coil motor (VCM) for rotating an actuator arm about a pivot in order to actuate a head over the disk. During a park operation, a latching characteristic associated with latching the actuator arm is measured and used to configure a latching parameter that reduces acoustic noise. The latching parameter is used to latch the actuator arm by seeking the head to a latching track, maintaining the head over the latching track for a predetermined interval, applying an acceleration pulse to the VCM for an acceleration pulse period, applying a braking pulse to the VCM for a brake pulse period, and applying a latching current to the VCM.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
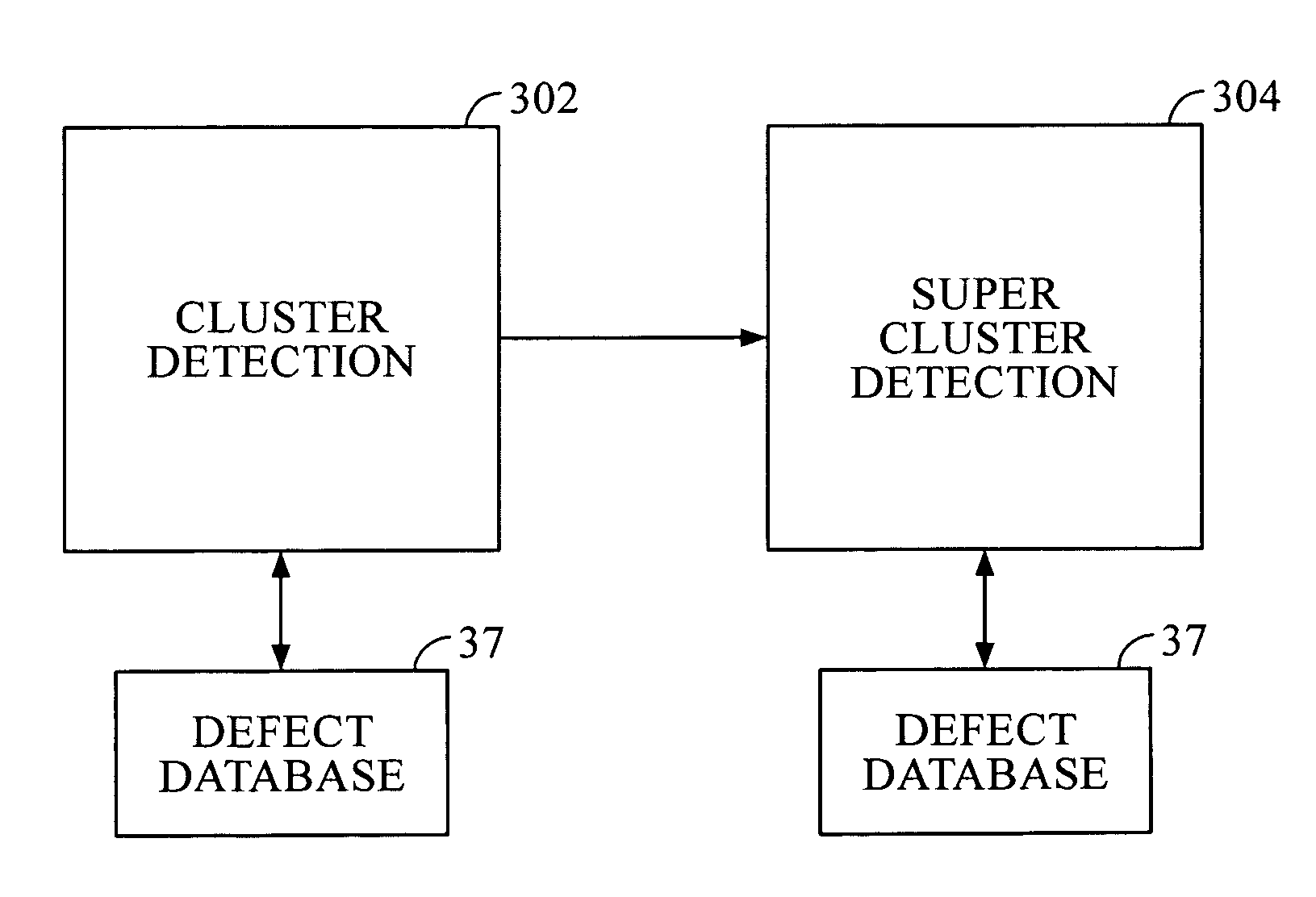
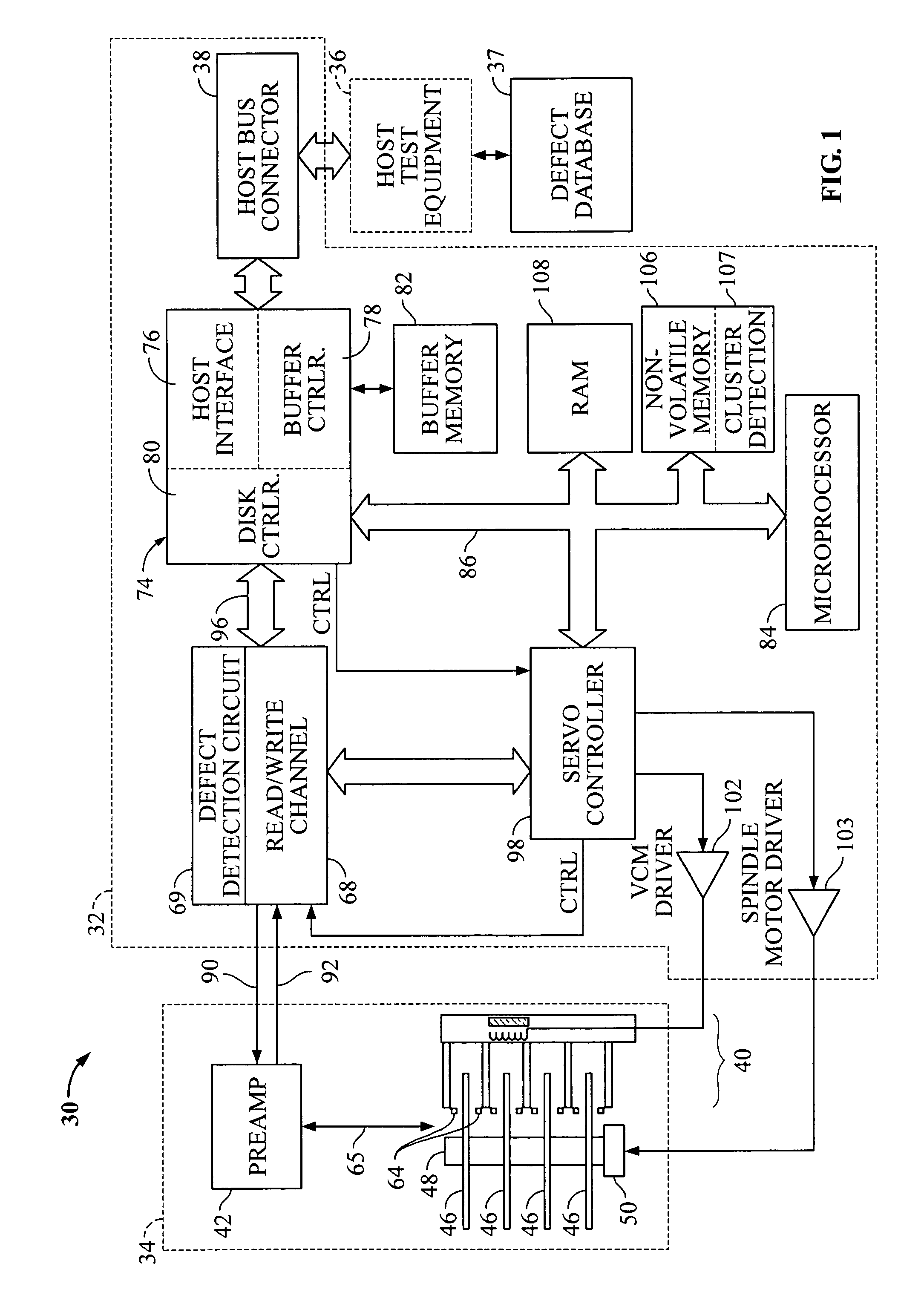
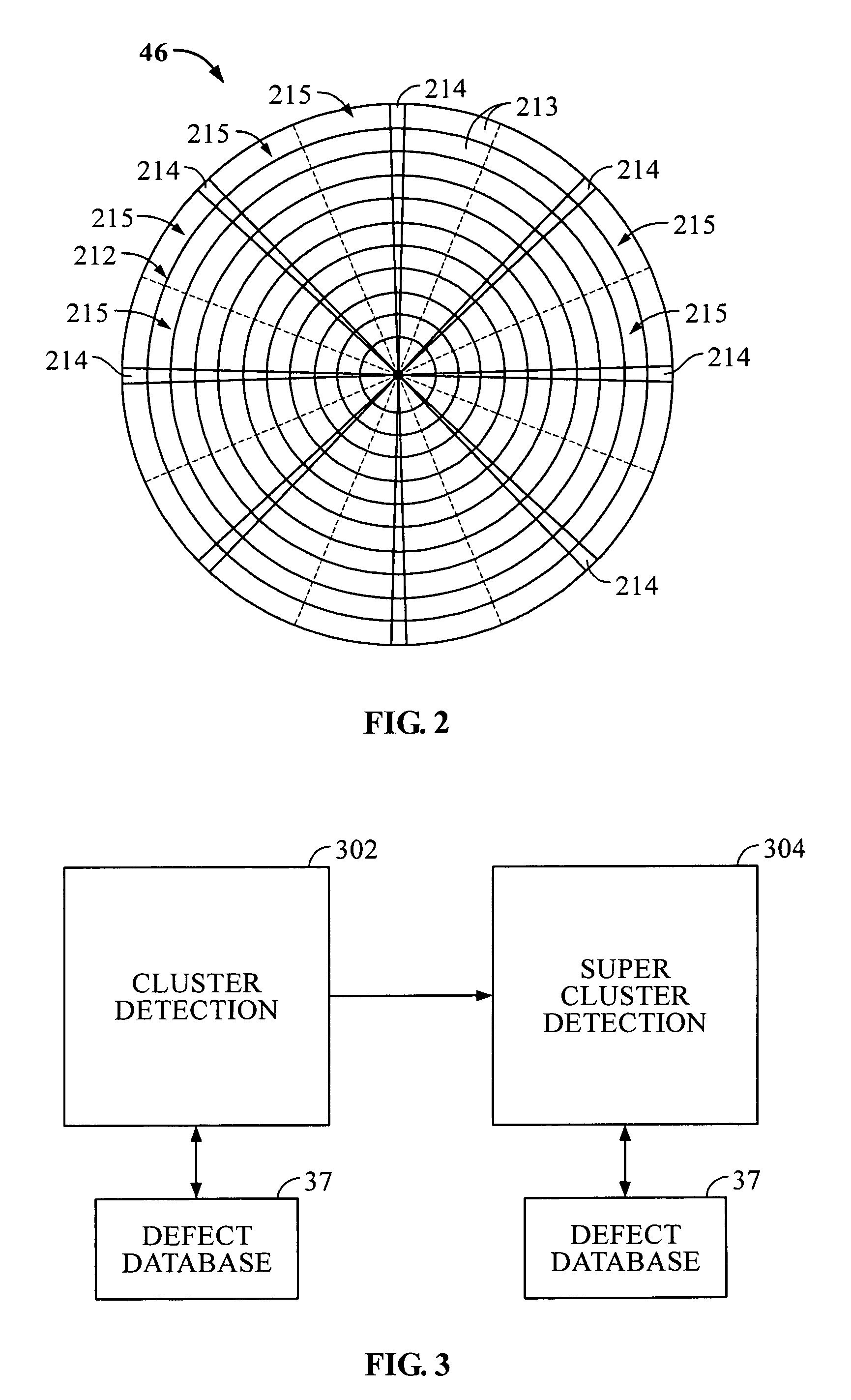
Cluster-based defect detection testing for disk drives
ActiveUS7139145B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksCluster basedMicroprocessor
Disclosed are techniques related to cluster-based defect detection testing for disk drives. A disk drive comprises a disk, a moveable head to scan the tracks of the disk, and a defect detection circuit to detect defects on the disk scanned by the moveable head. The disk drive includes a microprocessor for controlling operations in the disk drive including cluster-based defect detection. The microprocessor under the control of a cluster detection program defines a scan window. The scan window corresponds to an area of the disk scanned by the moveable head. The microprocessor under the control of the cluster detection program further defines a cluster threshold corresponding to a minimum number of defects required to occur within the scan window and identifies a defect cluster if a cluster threshold of defects occurs within the scan window. By identifying defect clusters on the disk these defect clusters can be margined.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Shingled magnetic recording disk drive with multiple data zones containing different numbers of error-correction-code sectors
ActiveUS8699162B1Data errorDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingComputer science
A shingled magnetic recording disk drive with sector error correction code (ECC) has the disk recording surface divided into multiple zones. Each zone is assigned a sector-ECC strength, i.e., a unique number of ECC sectors associated with a block of data sectors. The zone in which data is to be written is determined from the time average of the position-error signal (PES), which is an indication of the track misregistration (TMR) and thus the current environmental condition to which the HDD is subjected.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Optical data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary magneto-optical microhead array chips in place of flying-heads and rotary voice-coil actuators
InactiveUS6266712B1Input/output to record carriersHard disc driveVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
An optical data-storage hard disk drive, which uses stationary Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional Flying-Heads, Rotary Voice-Coil Actuators and other similar types of Servo-Tracking mechanisms to transcribe or retrieve digital information to or from at least one non-volatile memory medium's data-surface, using an optical magnetic process of recording and reading data. The Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip Hard Disk Drives will have at least one storage disk-platter with two disk-platter data-surfaces containing a multiplicity of concentric data-tracks that rotates at a substantially constant angular velocity. Every Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip will comprise a (VCSEL) "Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser" microhead array having a minimum of one thousand or a maximum of four billion individually addressable VCSELs. Each Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip is placed into a stationary position above each disk platter data-surface using a chip-positioning circuit board. While the number of cylinder / tracks available to each Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip is determined by the number of VCSEL microheads contained within a Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip's microhead array (e.g., "325,000" vertical cavity surface emitting laser microheads would therefore equal "325,000" corresponding cylinder / tracks).
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
Phase-change microhead array chip hard disk drive
InactiveUS20030161245A1Electron beam carrier recordingOptical beam sourcesStationary phaseEngineering
An optical data-storage hard disk drive that uses stationary Phase-Change Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional flying-heads, rotary voice-coil actuators, or other similar types of servo-tracking mechanisms to simultaneously record and / or reproduce data to and / or from a multitude of data-tracks located across the data-surfaces of a multitude of phase-change based disc media using a multitude of microheads.
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
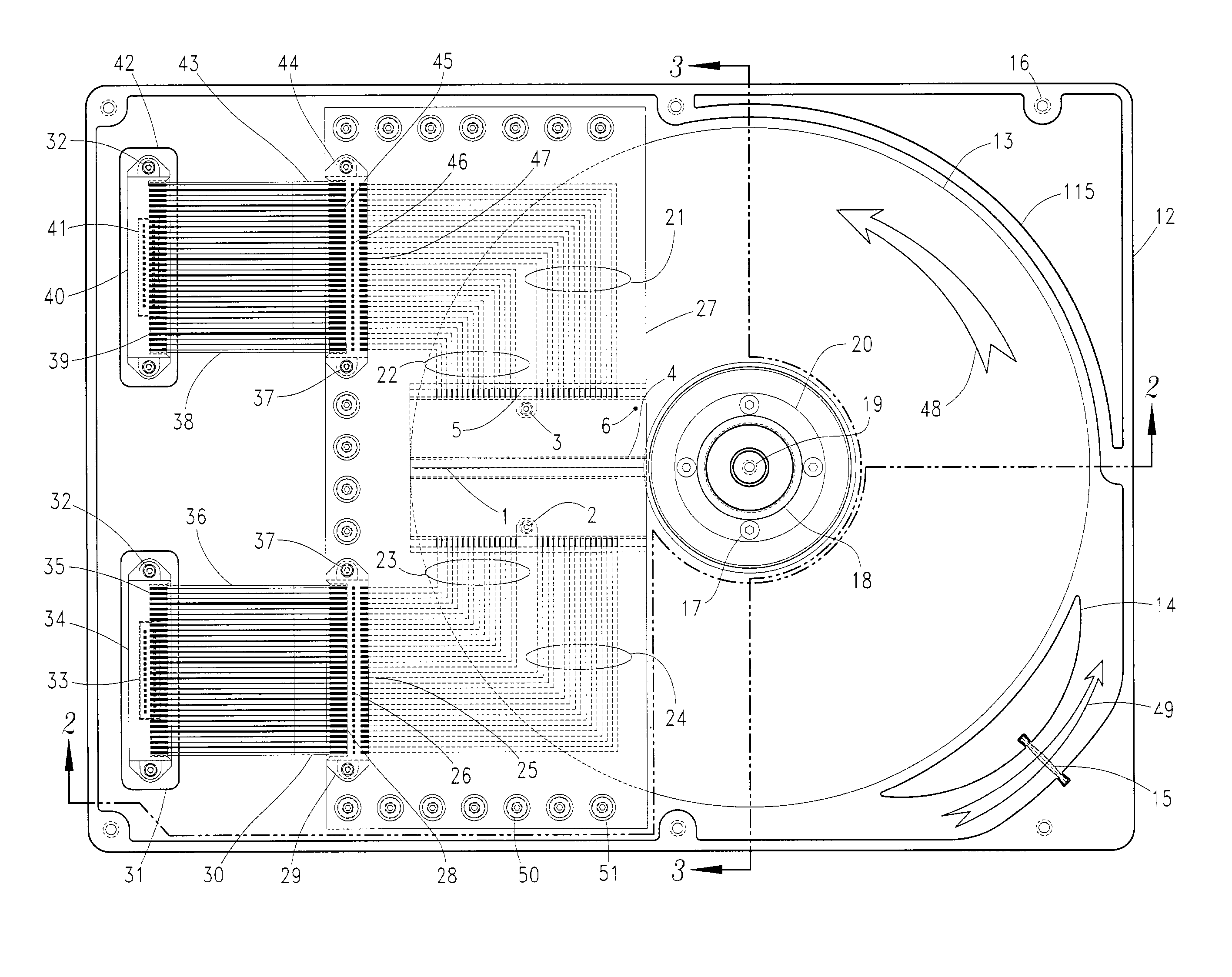
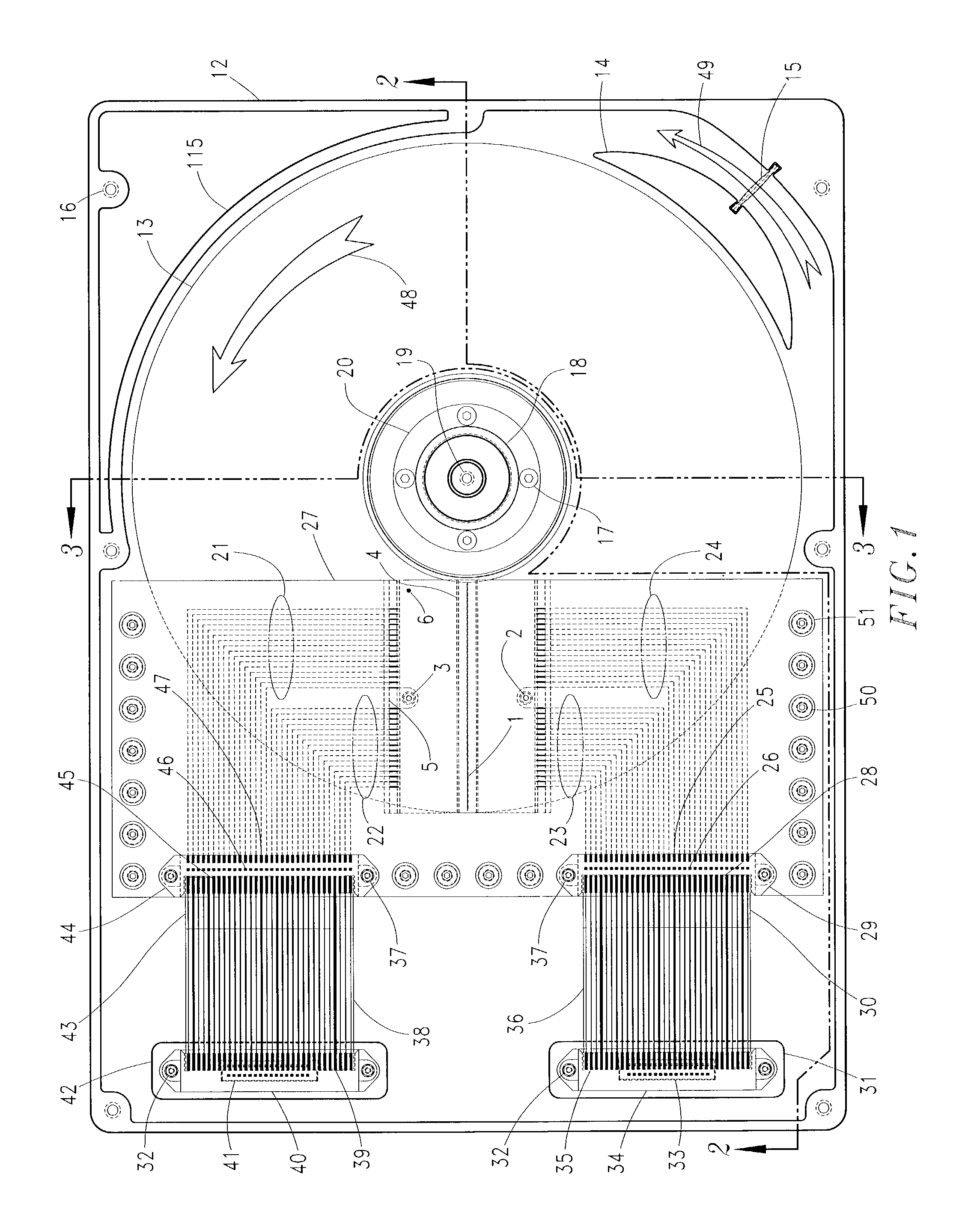
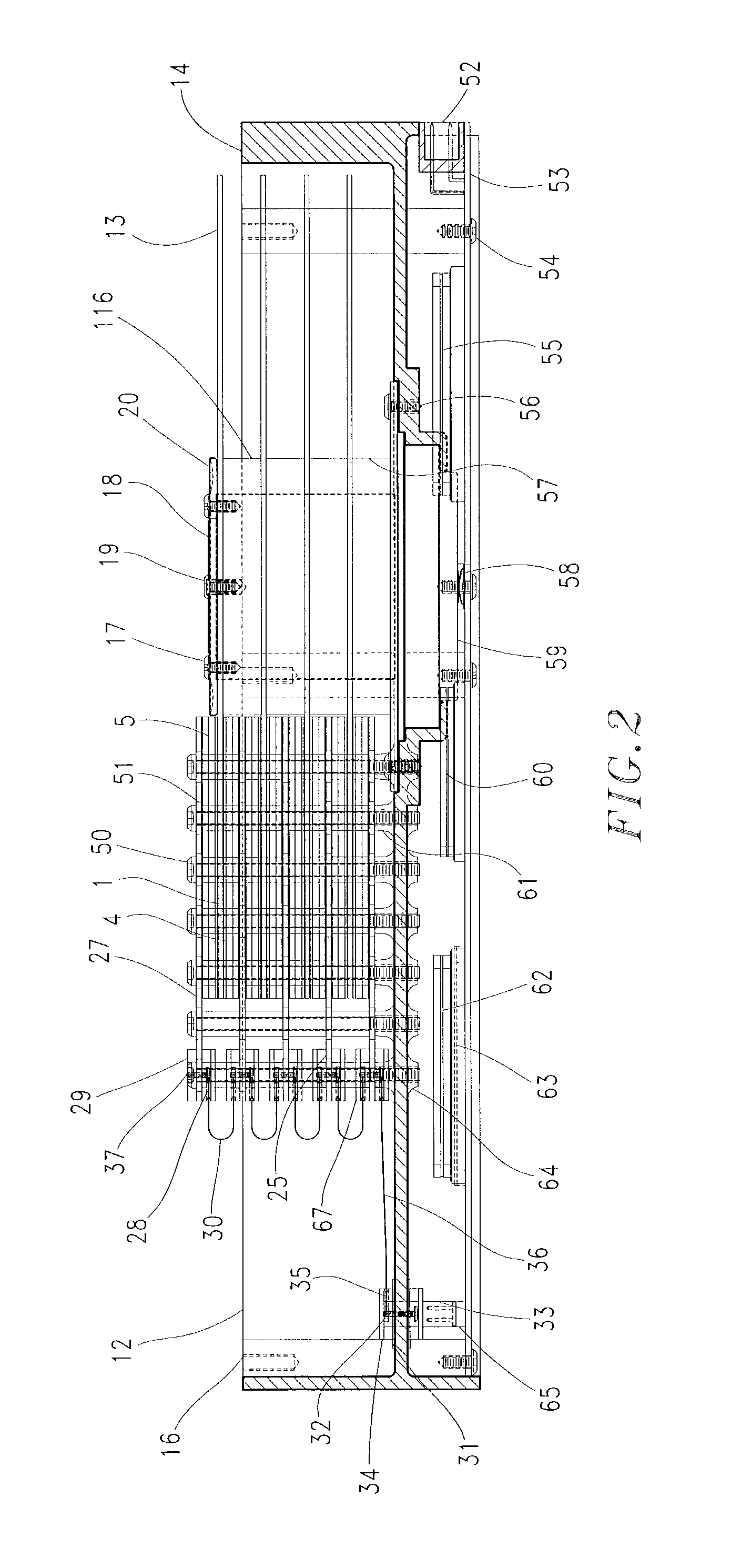
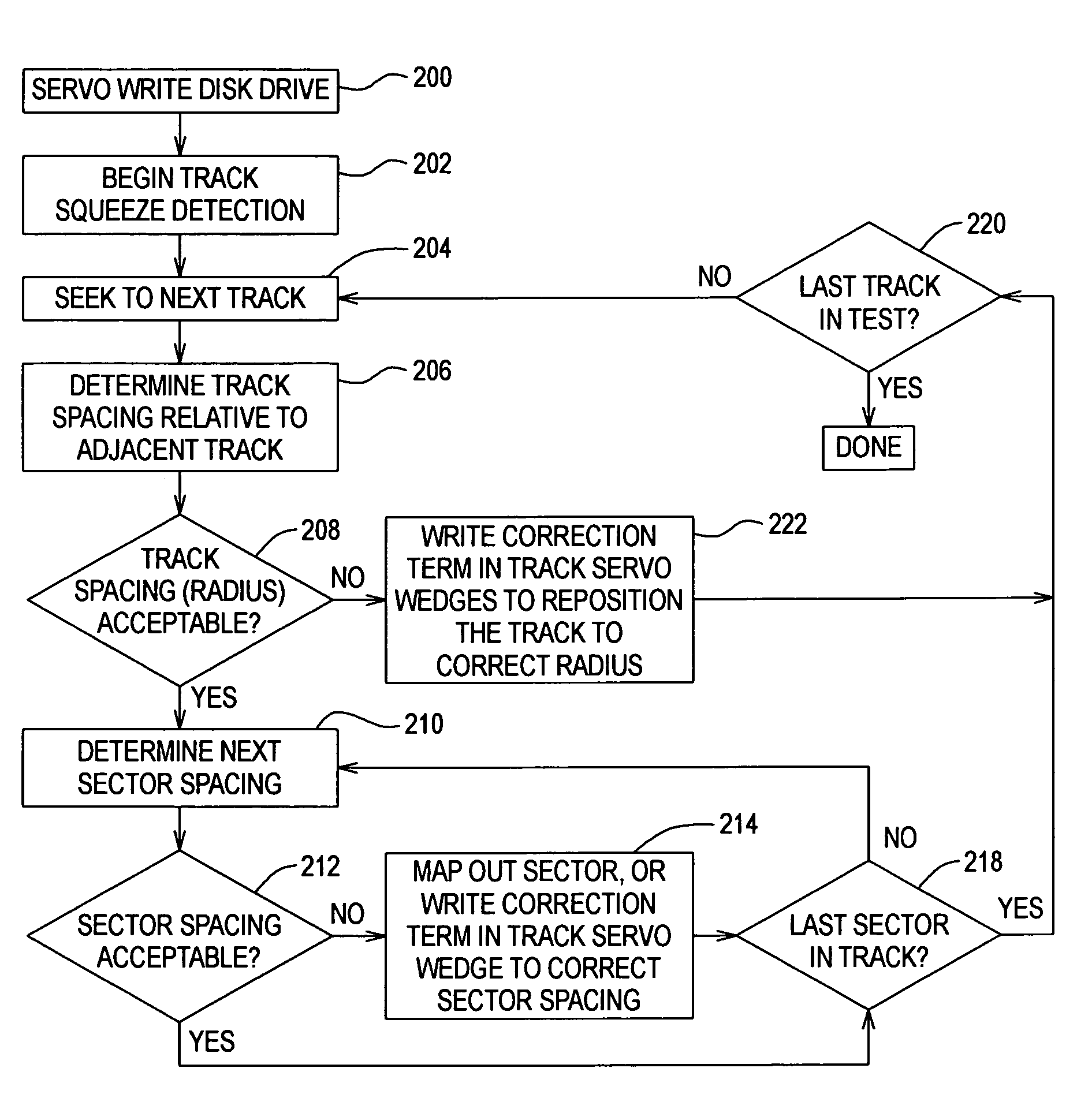
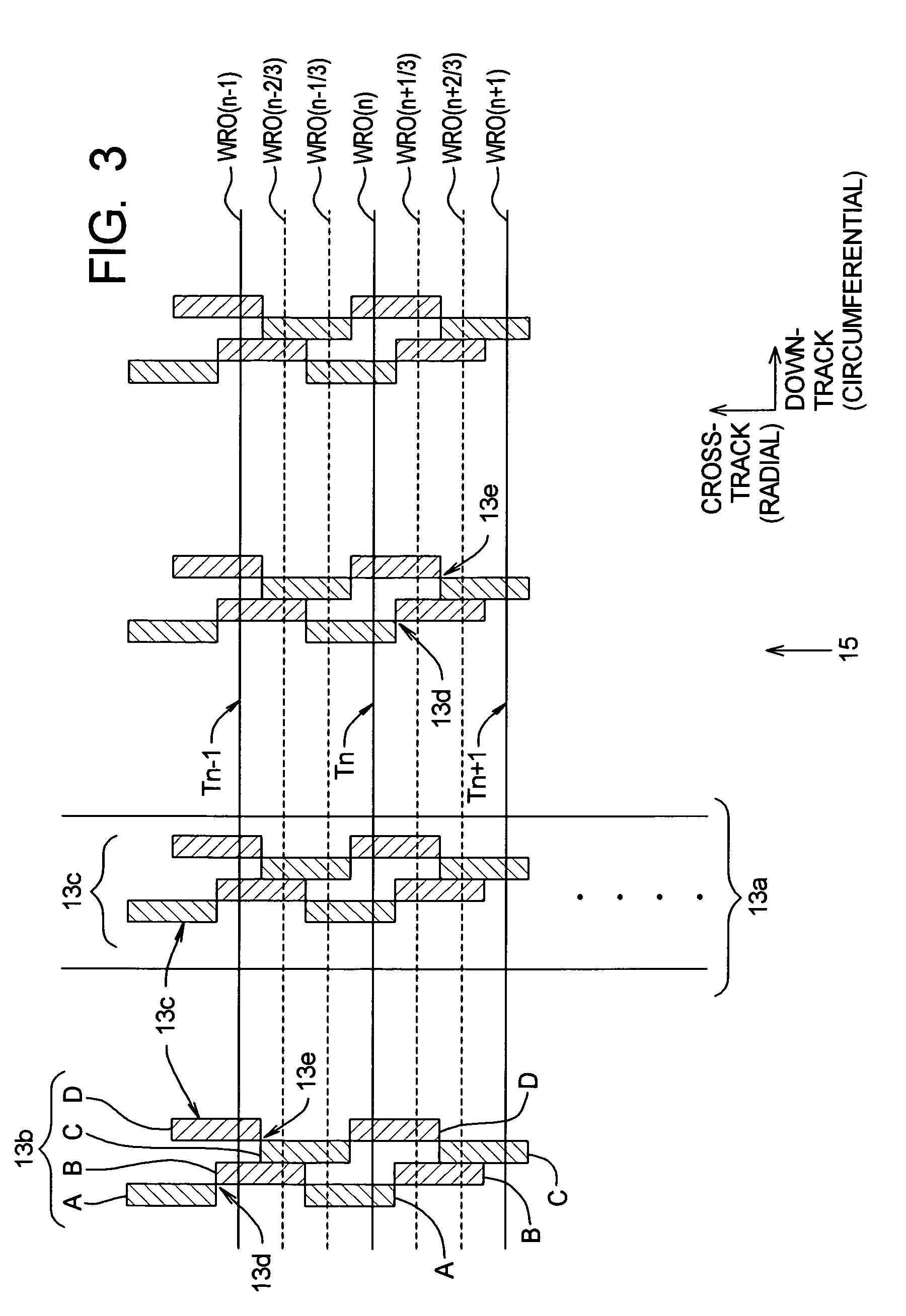
Method to correct radial misposition of data tracks
InactiveUS6965491B1Effectively repositionedAvoid violationsRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksControl theoryPosition error signal
A disk drive measures the radial misposition of tracks and repositions the tracks at regularly spaced intervals. Written in runout (WRO) in servo bursts is determined to calculate track spacing and squeeze among adjacent tracks. Tracks with improper spacing are repositioned by adding a squeeze correction term to the servo wedges. Thereafter, when the disk drive operates to store data, the servo bursts are used to calculate a position error signal (PES), and the squeeze correction term is combined with the PES to position the head at a proper track radius.
Owner:MAXTOR
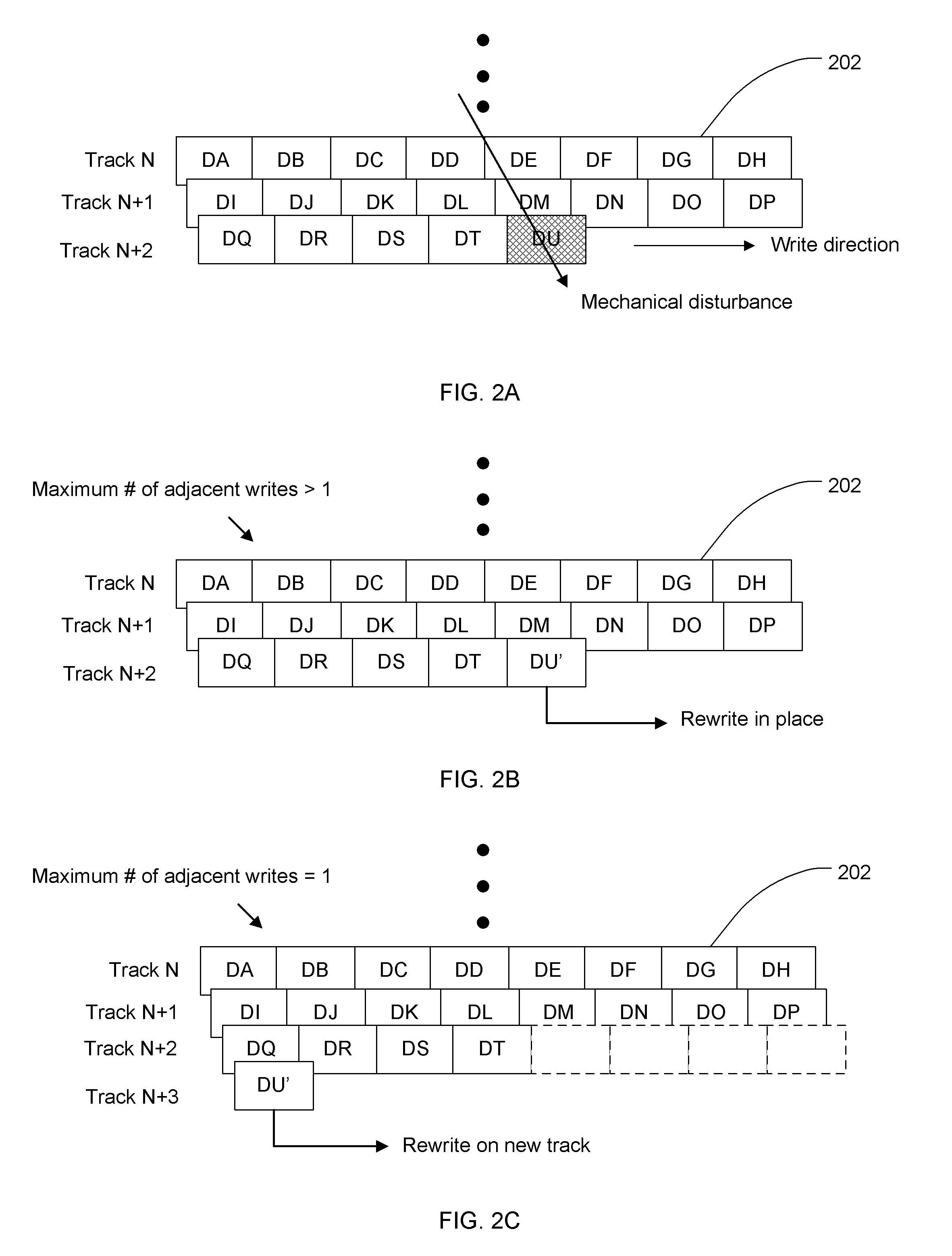
Method and system for mitigating adjacent track erasure in hard disk drives
InactiveUS20120089774A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationRecord information storageHard disc driveTrack (disk drive)
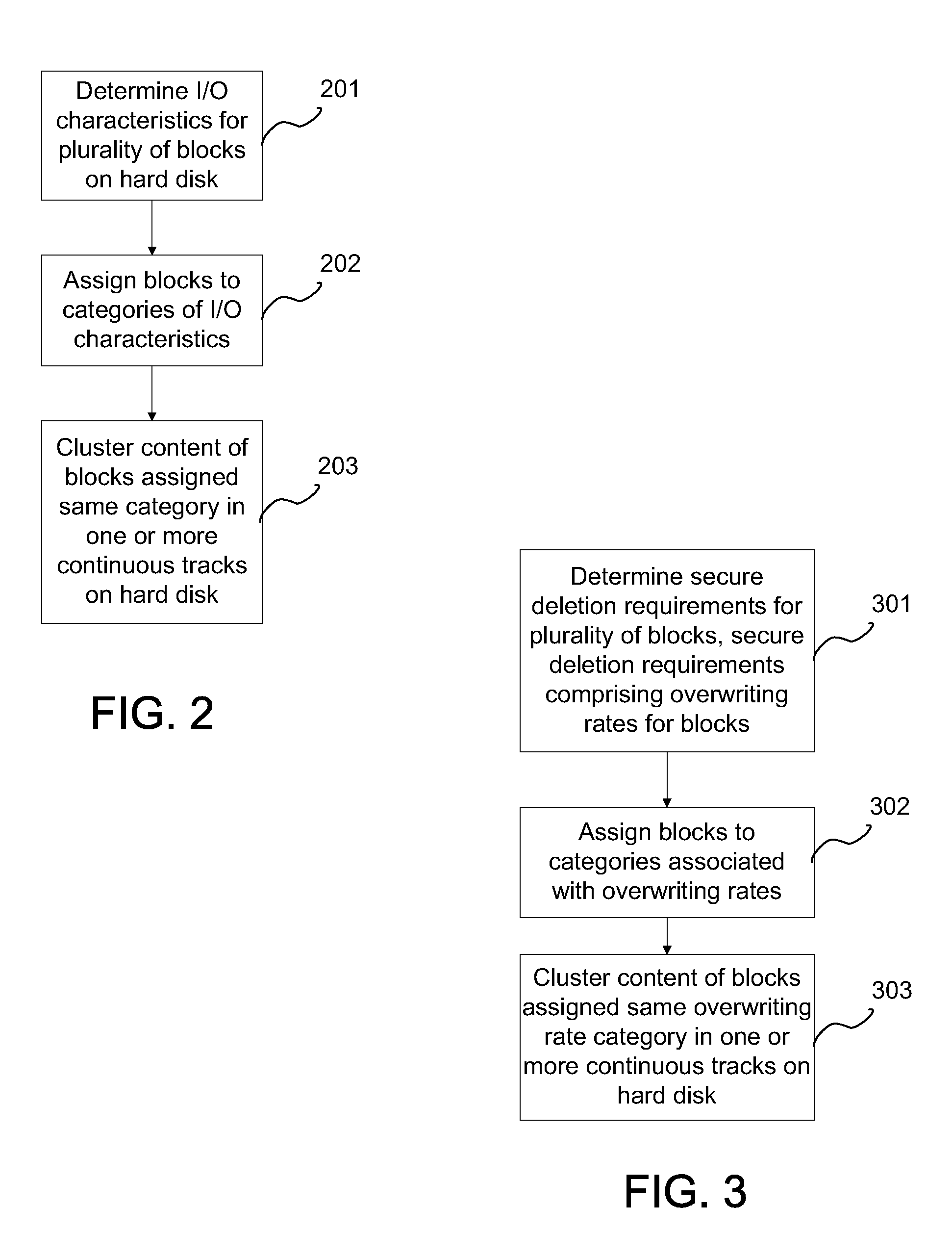
A method, system, and computer program product for mitigating adjacent track erasures in hard disks, includes: determining input / output (I / O) characteristics for a plurality of blocks on a hard disk; assigning the plurality of blocks to a plurality of categories of I / O characteristics by the processor; and clustering content of the blocks assigned to the same category in one or more continuous tracks on the hard disk. Each block is assigned to one category. Blocks with similar I / O characteristics are clustered on one or more continuous tracks. By performing this clustering, blocks with a high number of I / O operations are grouped and stored on fewer tracks than if they were scattered across numerous tracks. This reduces the number of tracks experiencing a high number of I / O operations, and in turn, the amount of refreshing of adjacent tracks is reduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
Light intensity modulated direct overwrite magneto-optical microhead array chip hard disk drive
InactiveUS20030007442A1Mechanical record carriersRecord information storageHard disc driveImage resolution
A magneto-optical data storage hard disk drive that uses stationary "Light Intensity Modulated Direct Over-Writey" (LIMDOW) or "Magnetically induced Super Resolution" (MSR) "Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chips' in place of conventional flying-heads, rotary voice-coil actuators, or other similar types of "servo-tracking' mechanisms to simultaneously record and / or reproduce data to and / or from a multitude of data-tracks located across the data-surfaces of a multitude of LIMDOW or MSR disc media that comprise two or more different coercive force regions at room temperature, using a multitude of microheads.
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
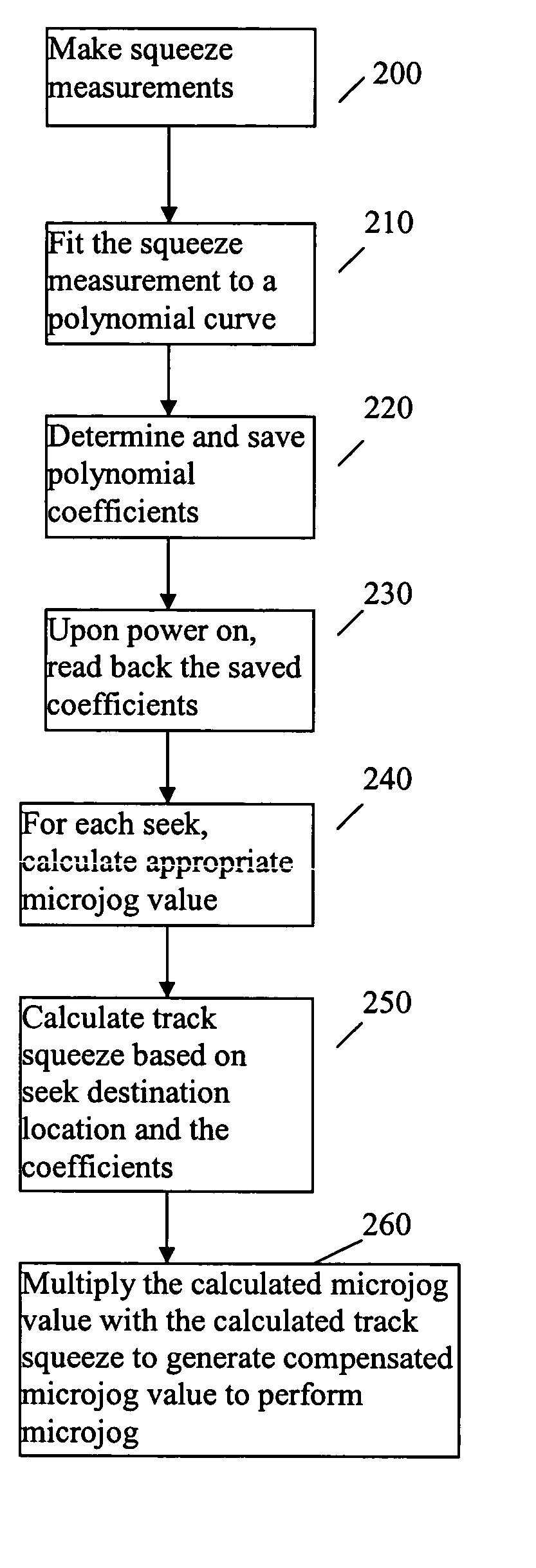
Method to compensate for microjog error induced by localized track squeeze
InactiveUS7271977B1Reducing microjog errorReduce microjog errorRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksTransducerControl theory
A method of reducing microjog errors in a disk drive having a data recording disk with data tracks and a transducer head positionable on the tracks. The head includes a writer element offset from a reader element. To reduce microjog errors, track squeeze is measured at a number of locations across the surface, wherein the squeeze is due to mis-positioning of the track relative to neighboring tracks. A microjog distance for the destination track is provided, and a microjog correction value based on the measured track squeeze is calculated. The correction value is applied to the microjog distance to obtain a corrected microjog distance that reduces microjog errors due to track squeeze.
Owner:FOURSTICKS +1
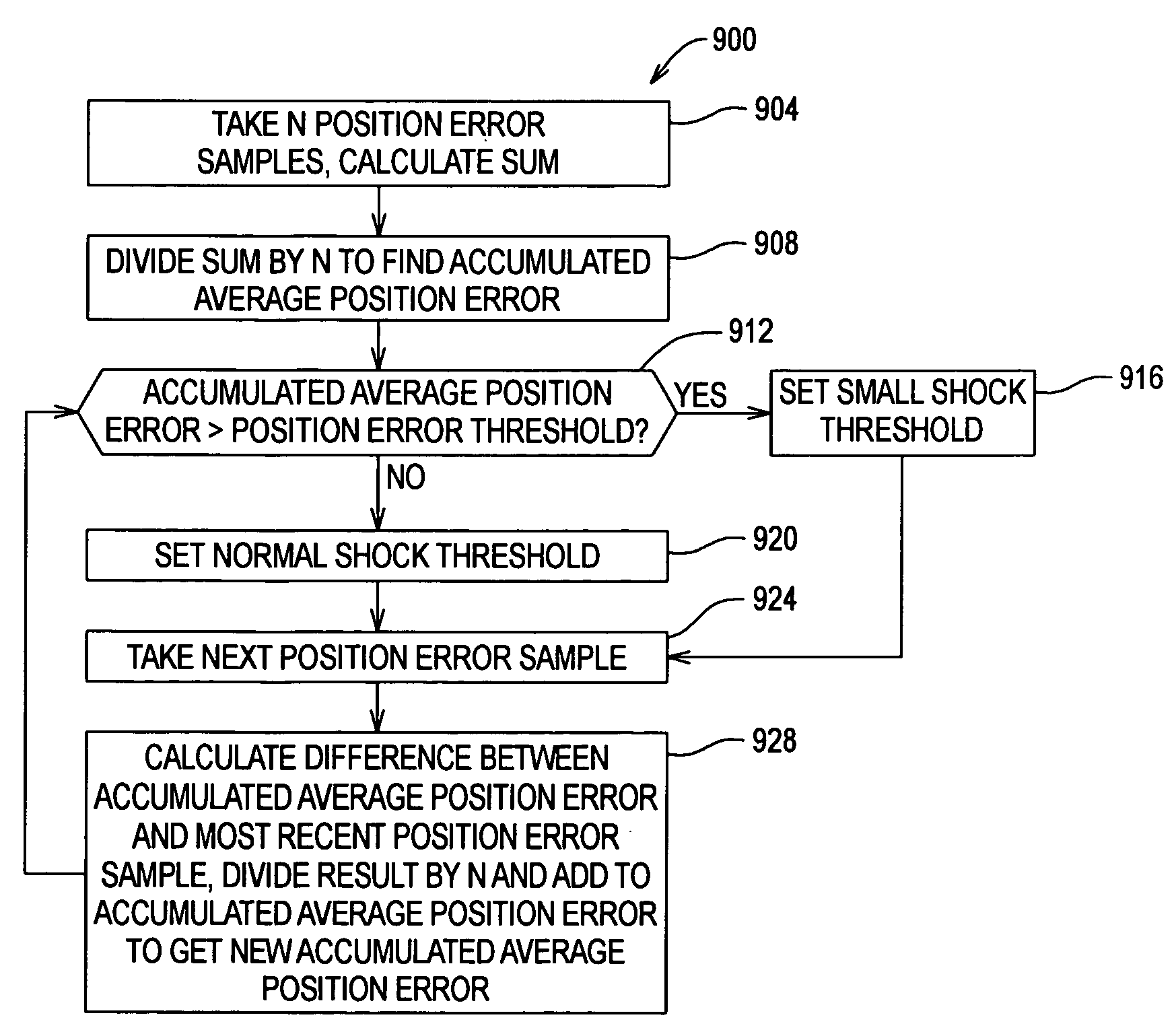
Dynamic shock detection in disk drive using accumulated average position error
InactiveUS7154690B1Keep for a long timeImprove protectionDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTransducerEngineering
Dynamically detecting off-track errors in a disk drive by adjusting transducer head position control parameters in response to shock events. In an embodiment, shock events with large magnitude trigger a severe shock timer which lengthens the write fault before write operations resume. In another embodiment, a lower shock threshold is used following an initial shock event. In yet another embodiment, a lower shock threshold is used if an accumulated average position error of the transducer head is large.
Owner:MAXTOR
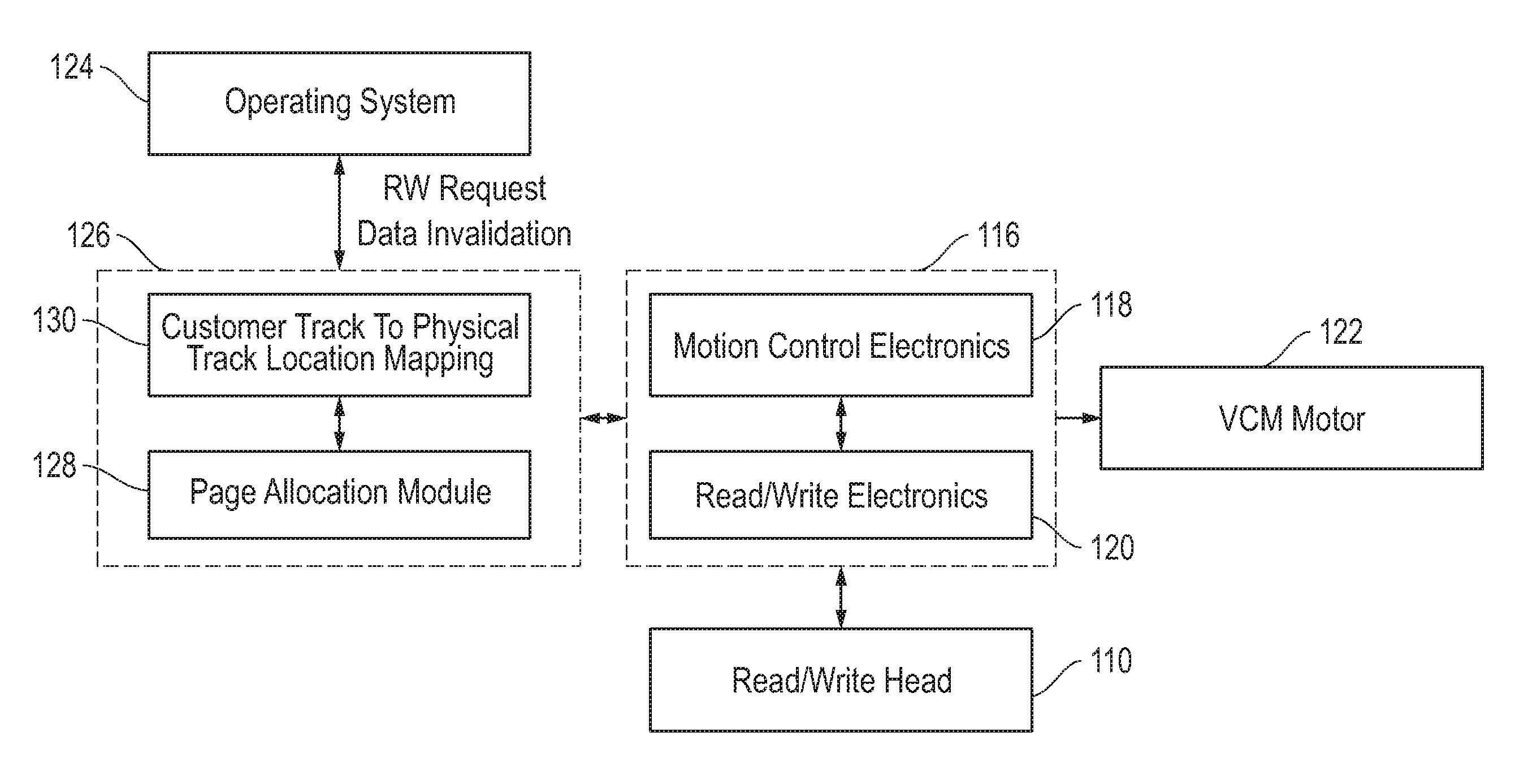
Method and apparatus for runout correction during self-servo writing
InactiveUS7123433B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTransducerReference patterns
A disk drive self-servo writes on a storage disk. Servo bursts are self-written along a track using a transducer, a position error signal (PES) indicating repeatable runout due (RRO) for the servo bursts is determined using a reference pattern, an embedded runout correction (ERC) value is calculated based on the PES and stored in a corresponding servo sector, and then the disk drive self-writes other servo bursts.
Owner:MAXTOR
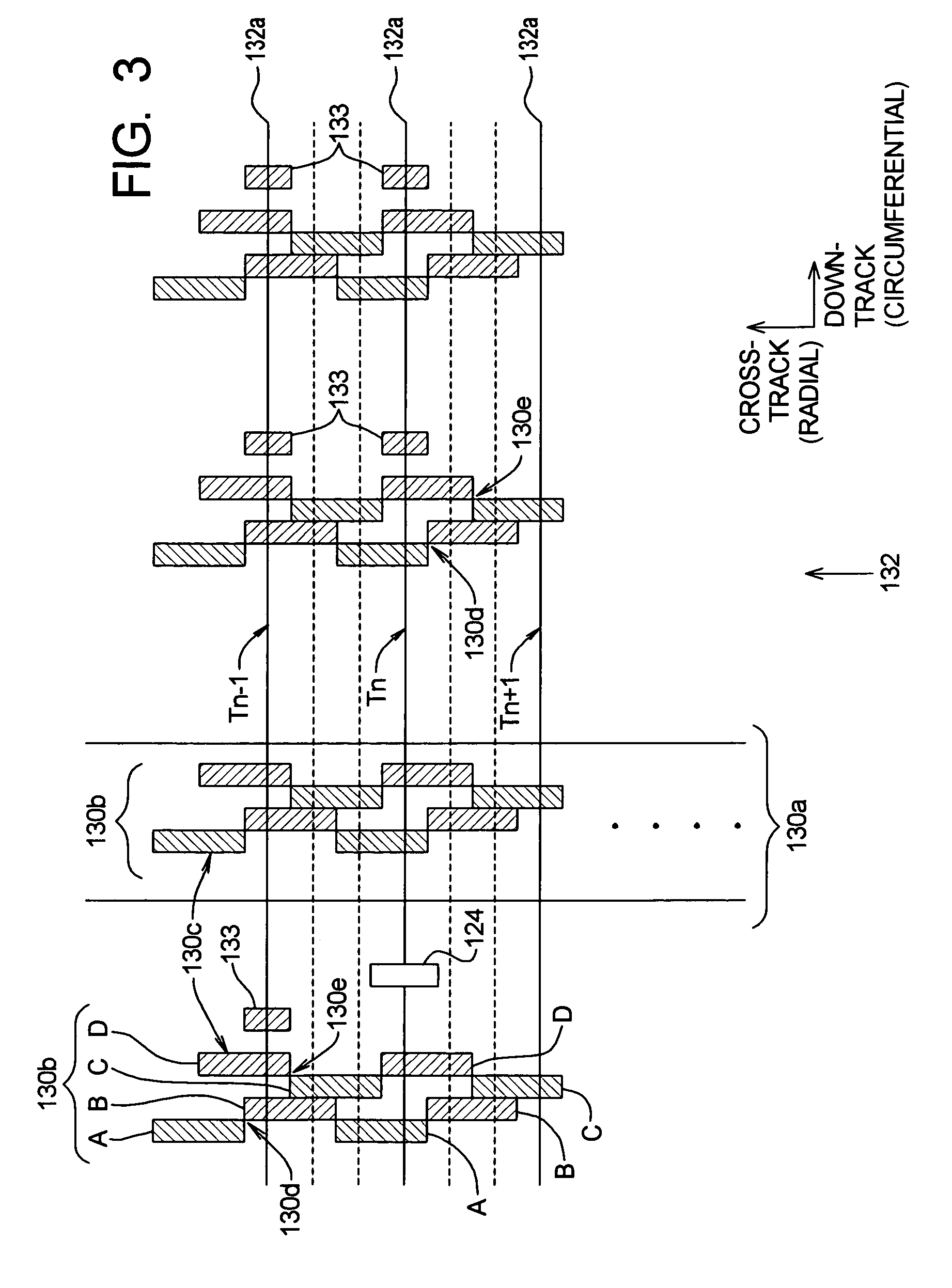
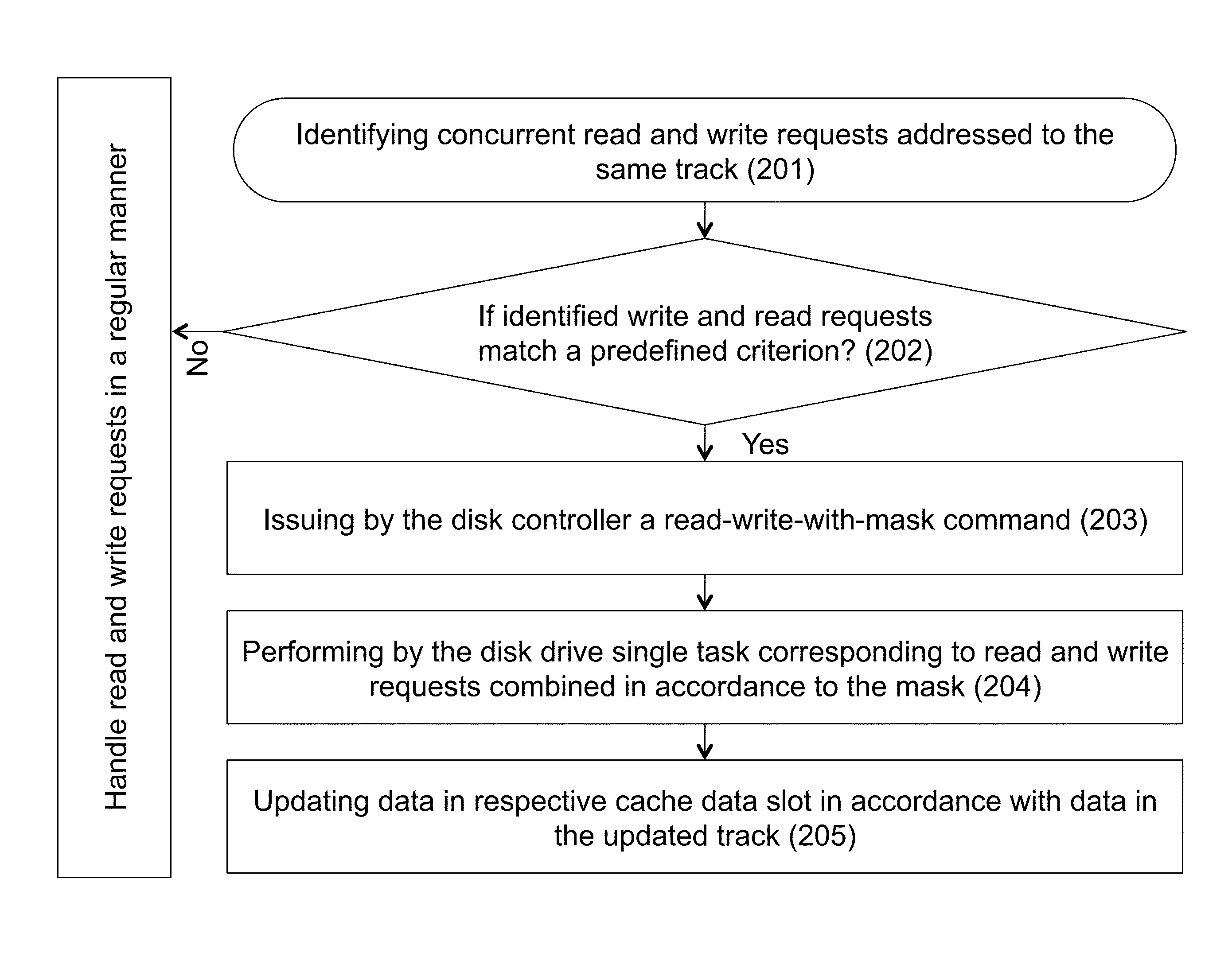
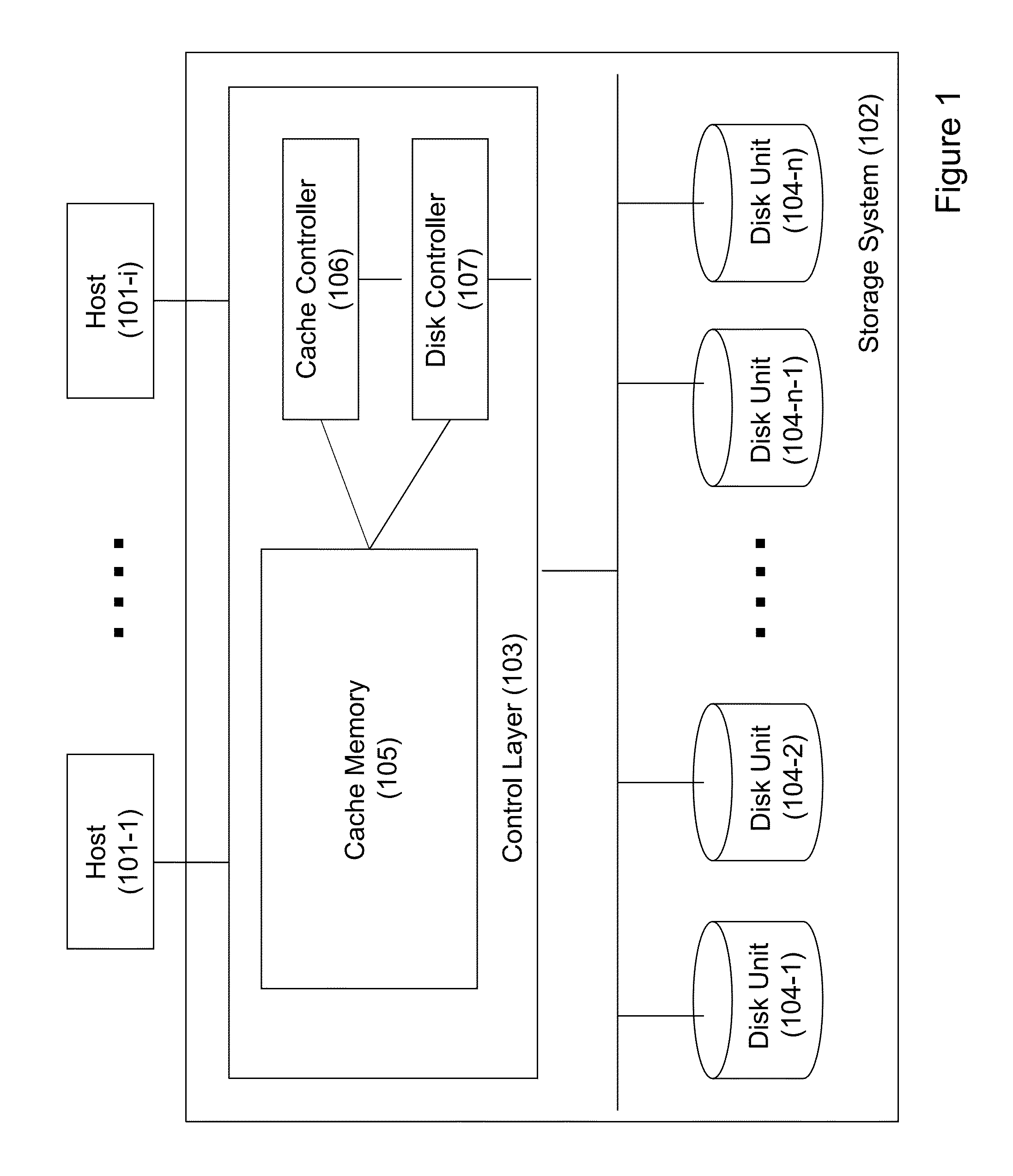
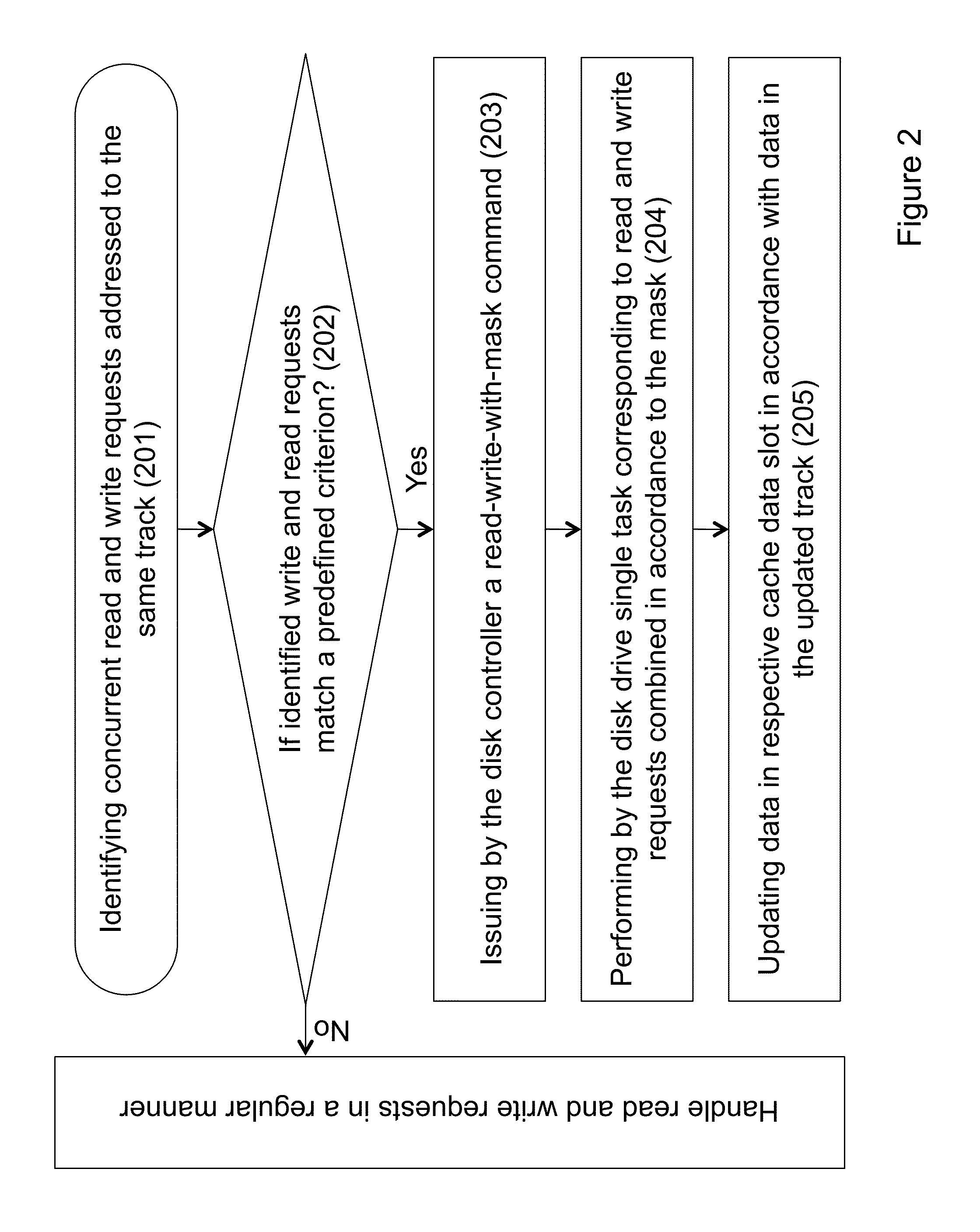
Concurrent access to a single disk track by combining reads and writes to a disk with a mask
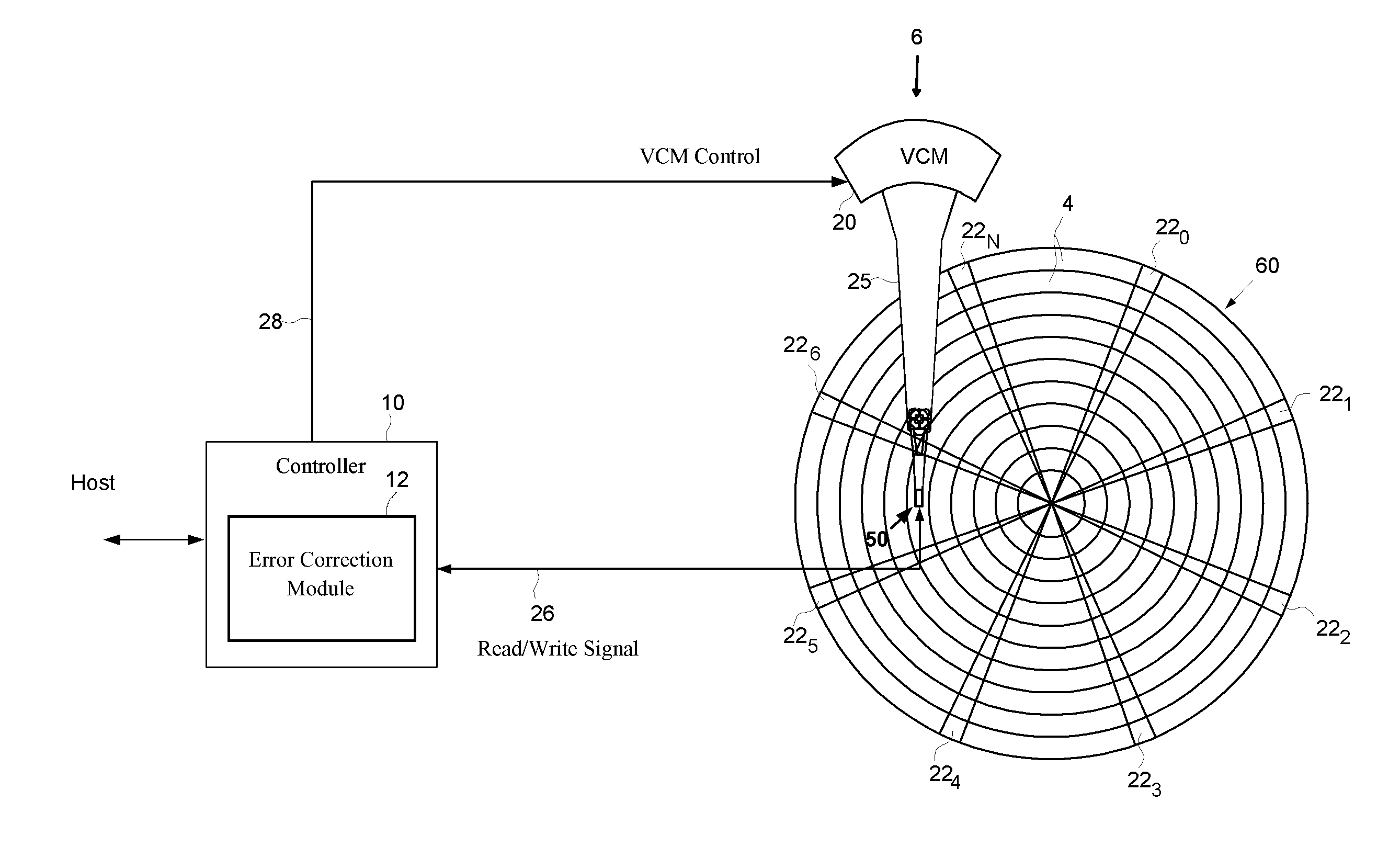
ActiveUS8468319B1Enhance performance of diskReduce in quantityInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsControl layerDisk controller
A storage system, a disk controller, a disk drive and a method of operating thereof. The method includes: configuring a disk drive in a manner enabling executing one or more read requests concurrently with executing one or more write requests addressed to the same data track of the disk drive; responsive to a received write request addressed to a certain track of the disk drive, identifying with the help of the control layer one or more read requests concurrent to received write request and addressed to the same track; if the received write request and the identified one or more read requests match a predefined criterion, generating and issuing, with the help of the control layer, a command to the disk drive for executing a single task corresponding to the concurrent read and write requests combined in accordance with a certain mask.
Owner:INFINIDAT
High reliability-parallel data transfer hard disk drive
InactiveUS7199981B2Avoid constraintsOvercomes shortcomingHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageData streamAccess time
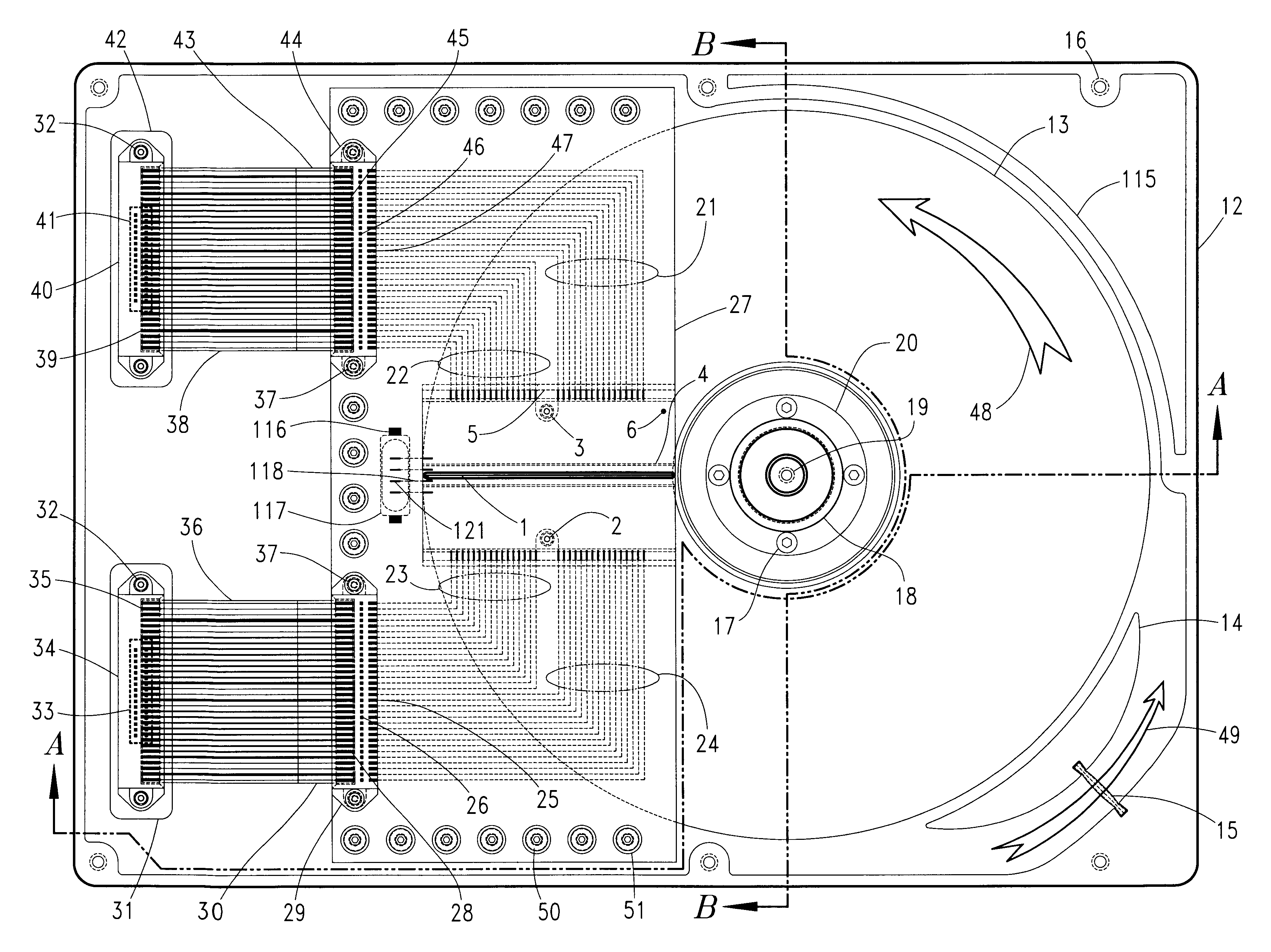
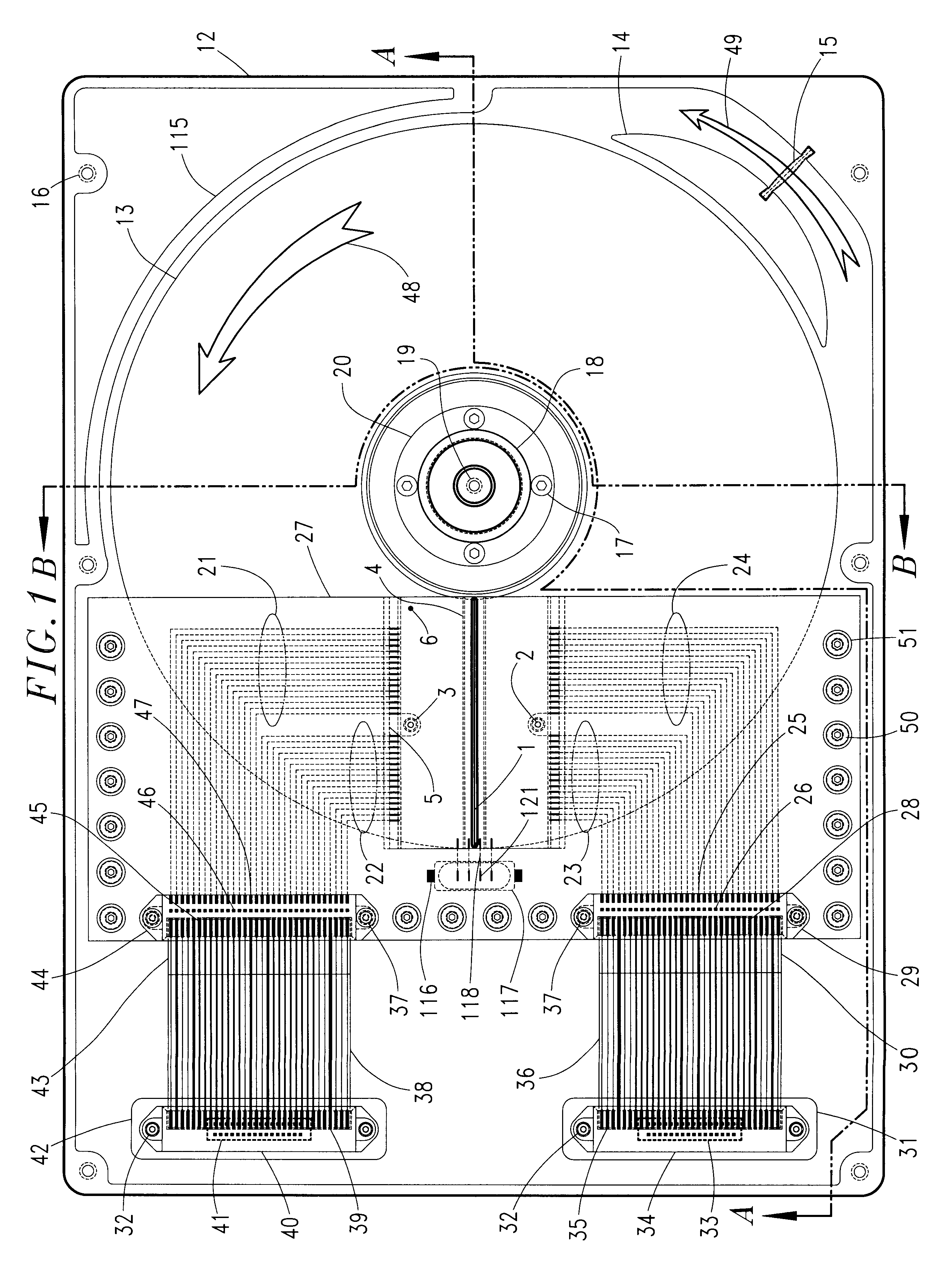
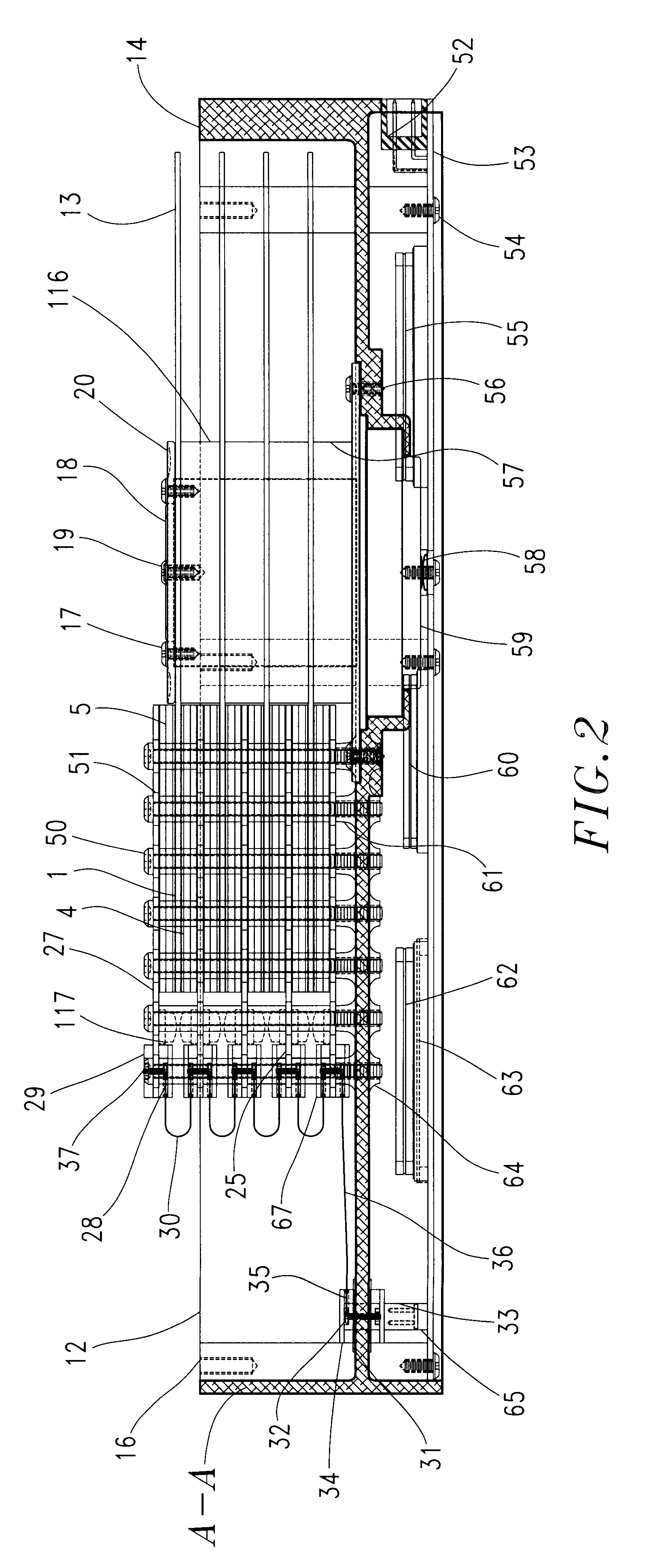
A dual actuator arm assembly system that uses two pairs of actuator-carriage arms that linearly move over a stationary micro-rail independently. The geometric shape of the two pairs of actuator carriage arms conform to the arcs of the data tracks at an acute angle. System enables micro-actuation that is integrated to actuator arm and is a function of its geometry. Uninterrupted data stream and sector coverage and thus parallel data transfer scheme is made possible. Each actuator move only within a limited range of disk area, thus precision is increased, vibration is minimized and external transfer rate is speeded up and overall access time is shortened. Instant access to two quarters of the disk with two pairs of actuators and to park these without landing the heads—by positioning and constant fly height during idle mode, or when system is turned off, are introduced as what are new in the art.
Owner:ZABTCIOGLU FIKRET M
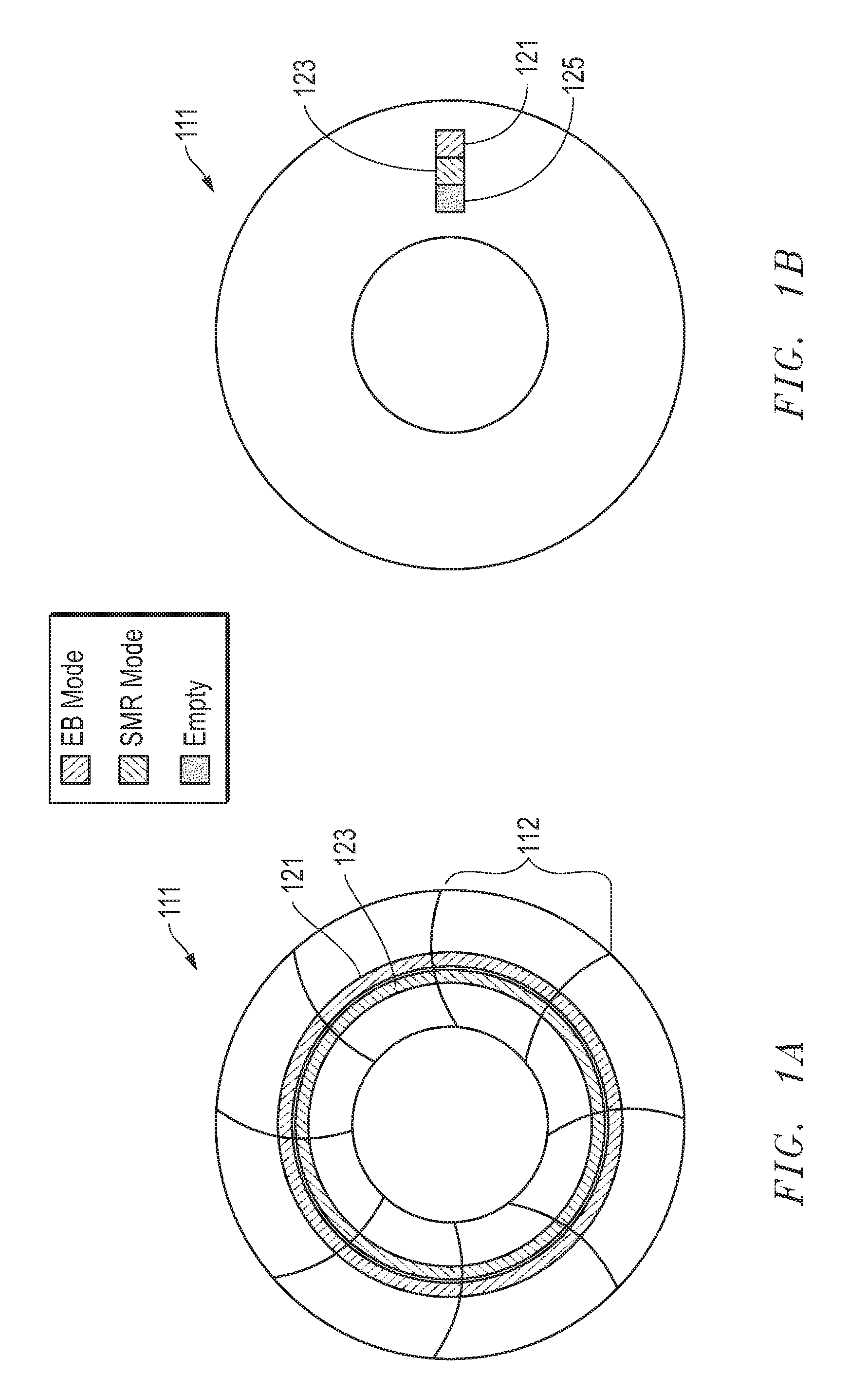
System, method and apparatus for storage architecture for bit patterned media using both erase band and shingled magnetic recording
ActiveUS20120099216A1Improve performanceFilamentary/web record carriersPatterned record carriersHard disc driveShingled magnetic recording
Storage architecture for bit patterned media uses both erase band and shingled magnetic recording. A hard disk drive may comprise a disk having bit patterned media with a plurality of data tracks arrayed in architecture pages having at least one of erase band mode (EBM), shingled mode (SM) and unallocated space. An actuator has a head for writing data to the data tracks of the bit patterned media. A control system monitors, reallocates and reconfigures the architecture pages from EBM, SM or unallocated space to a different one of EBM, SM or unallocated space to enhance performance of the hard disk drive.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
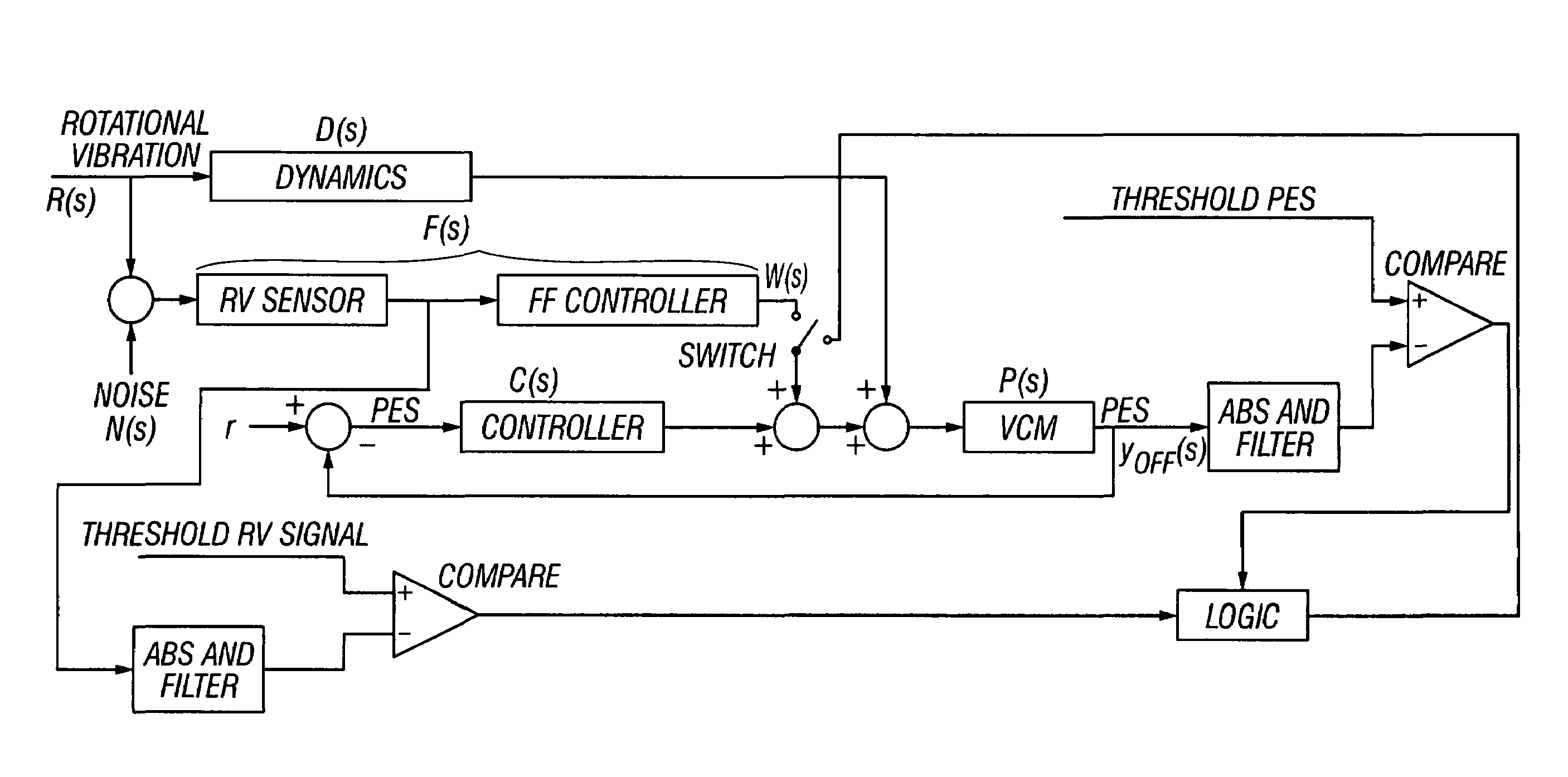
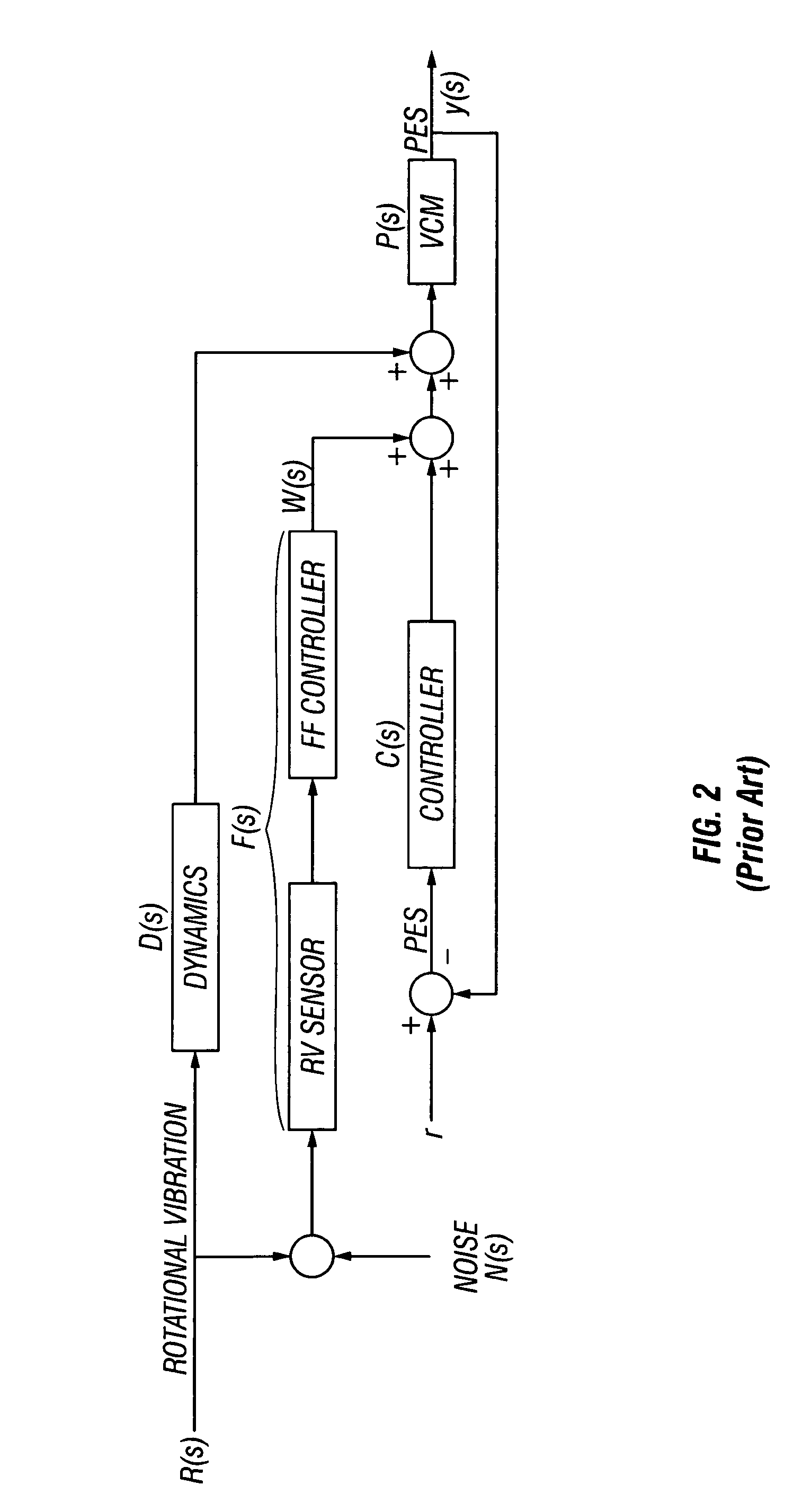
Magnetic recording disk drive with switchable rotational vibration cancellation
InactiveUS7177113B1Track finding/aligningRecord information storageControl signalRotational vibration
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
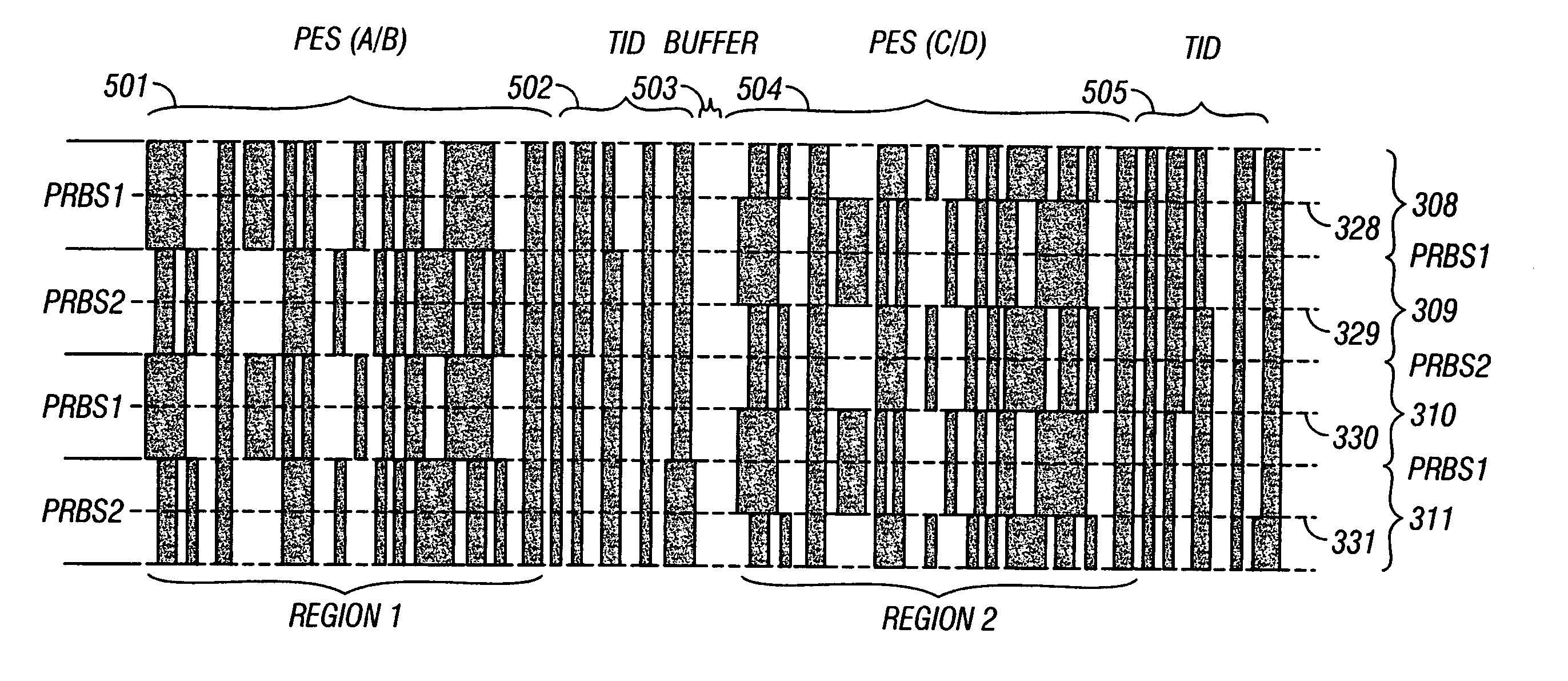
Data recording system with servo pattern having pseudo-random binary sequences
InactiveUS20050254160A1Large amplitudeTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveAudio power amplifier
A data recording system, such as a magnetic recording hard disk drive, has a recording medium in which the data tracks have pseudo-random binary sequences for the servo information used to control the position of the recording head. A first pseudo-random binary sequence (PRBS) and a second PRBS identical to the first PRBS but shifted by a portion of the period of the first PRBS are located between the track boundaries in alternating tracks in a first region of the servo pattern and between the track centers in alternating tracks in a second region spaced along the track from said first region. A servo decoder has two correlators, one for each PRBS. Each correlator outputs a dipulse when its PRBS repeats. The difference in amplitude of the dipulses represents the head position signal. The dipulses also control the amplifier for the signal read back by the head and the timing of the track identification (TID) detector.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
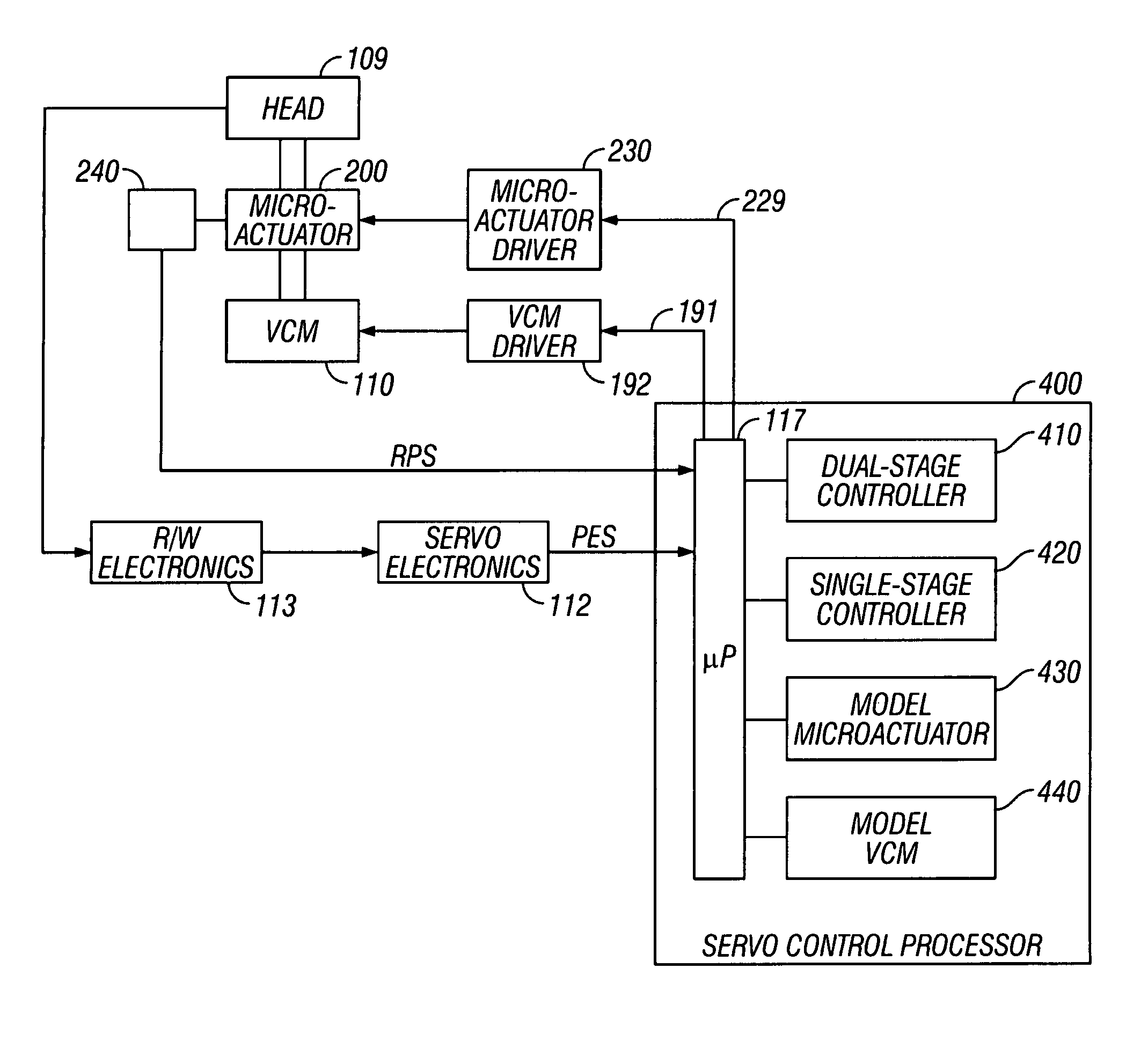
Disk drive with a dual-stage actuator and failure detection and recovery system for the secondary actuator
InactiveUS7075748B2Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksControl engineeringActuator fault detection
A dual-stage actuator disk drive has calibration tracks located in a nondata band, and uses a secondary-actuator failure detection and calibration test run by the servo control processor. The calibration tracks contain a pattern of pre-written magnetized test blocks. The test is run with the primary actuator biased against a crash stop, which enables the read head to access the calibration tracks. The servo control processor generates a test signal to the secondary actuator and receives a calibration signal from the read head as the read head detects the test blocks in the calibration tracks. The test comprises two measurements: a measurement of the secondary actuator static characteristics, and a measurement of the secondary actuator dynamic characteristics.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Directional write retry for shingled disk drive application
ActiveUS20120162806A1Record information storageCarrier monitoringComputer hardwareSoftware engineering
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com