Patents
Literature
89 results about "Shingled magnetic recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
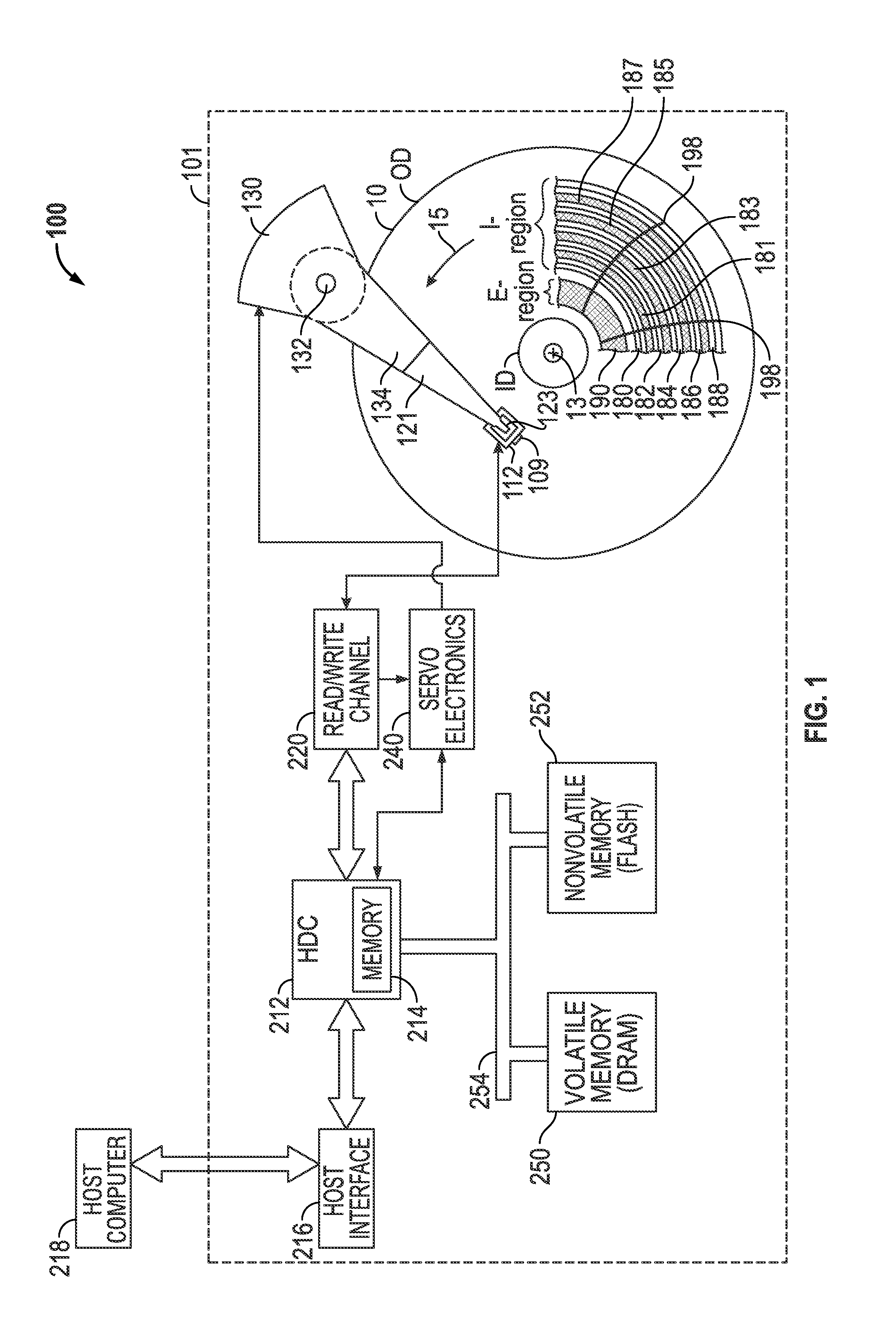
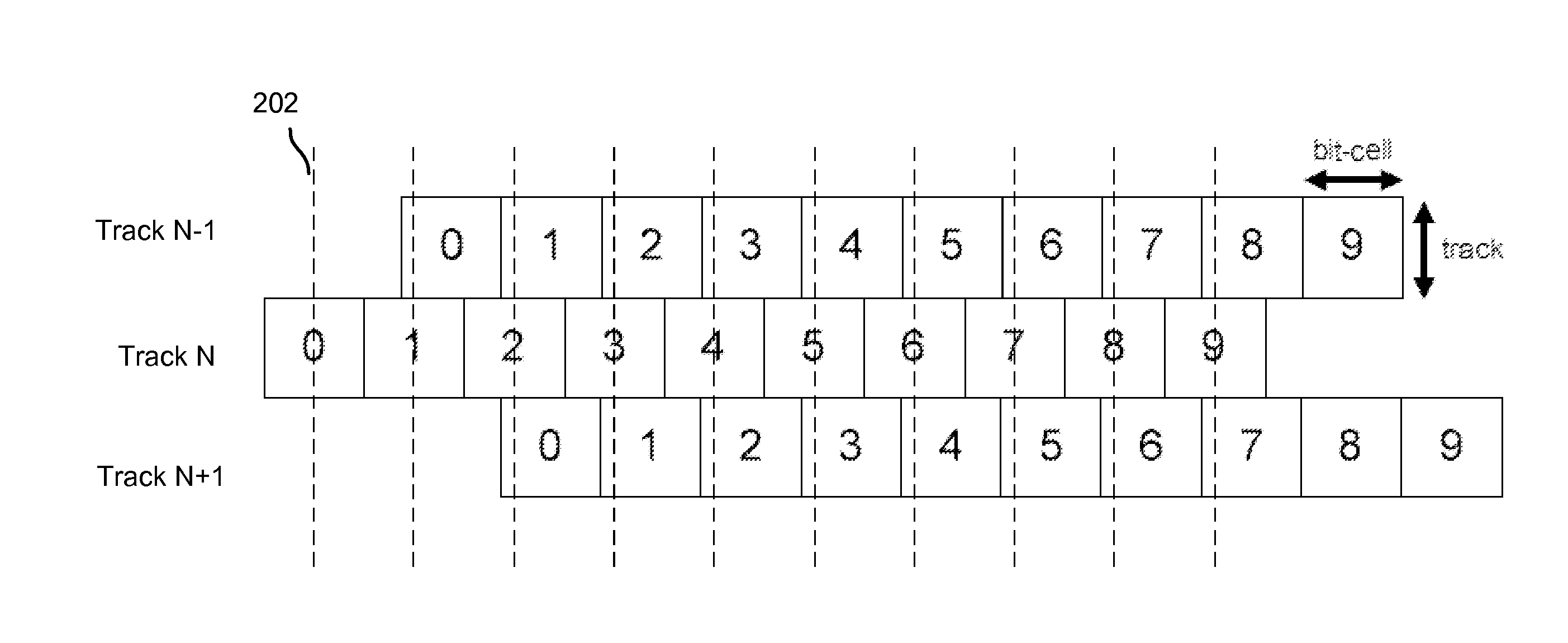
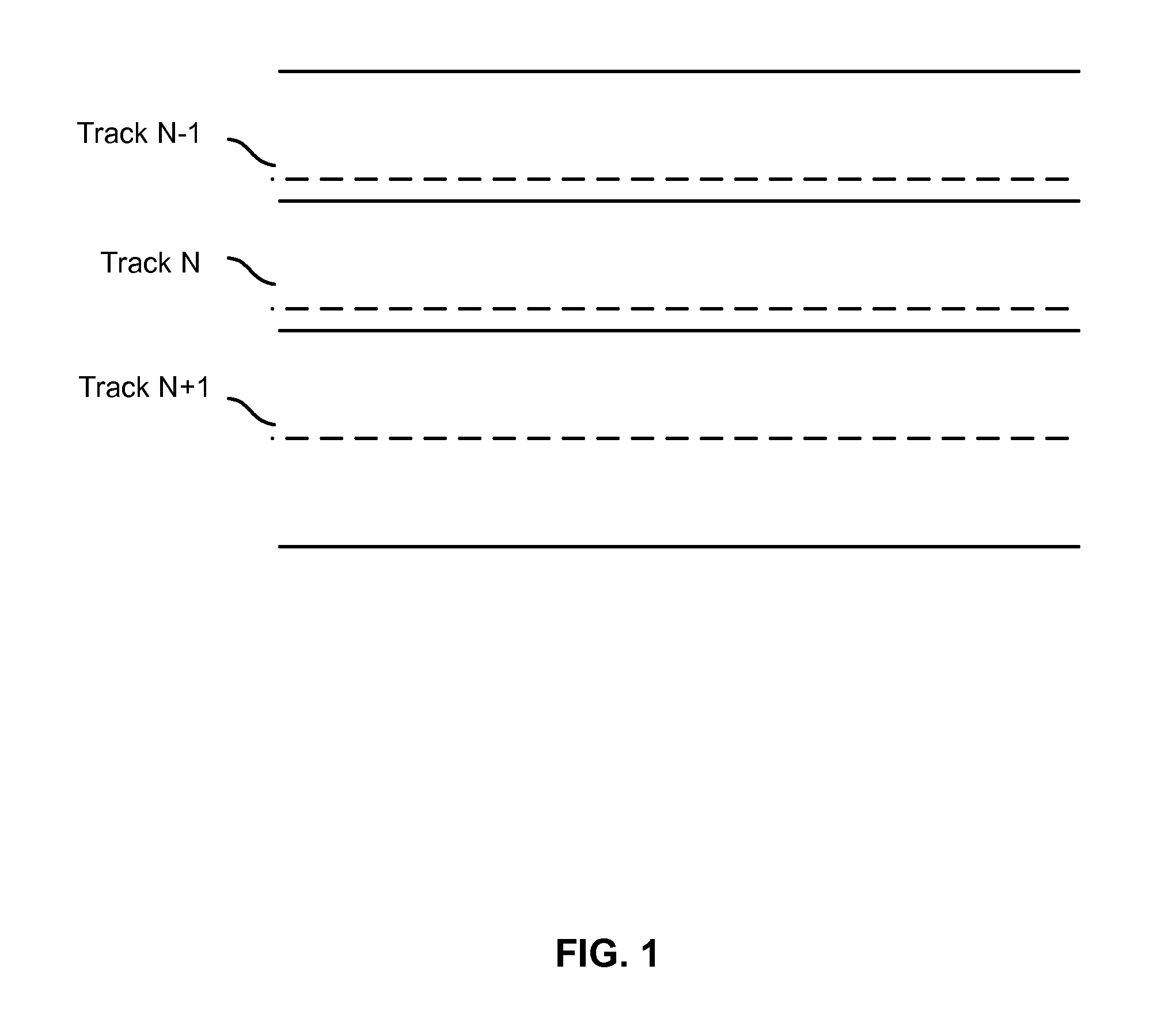
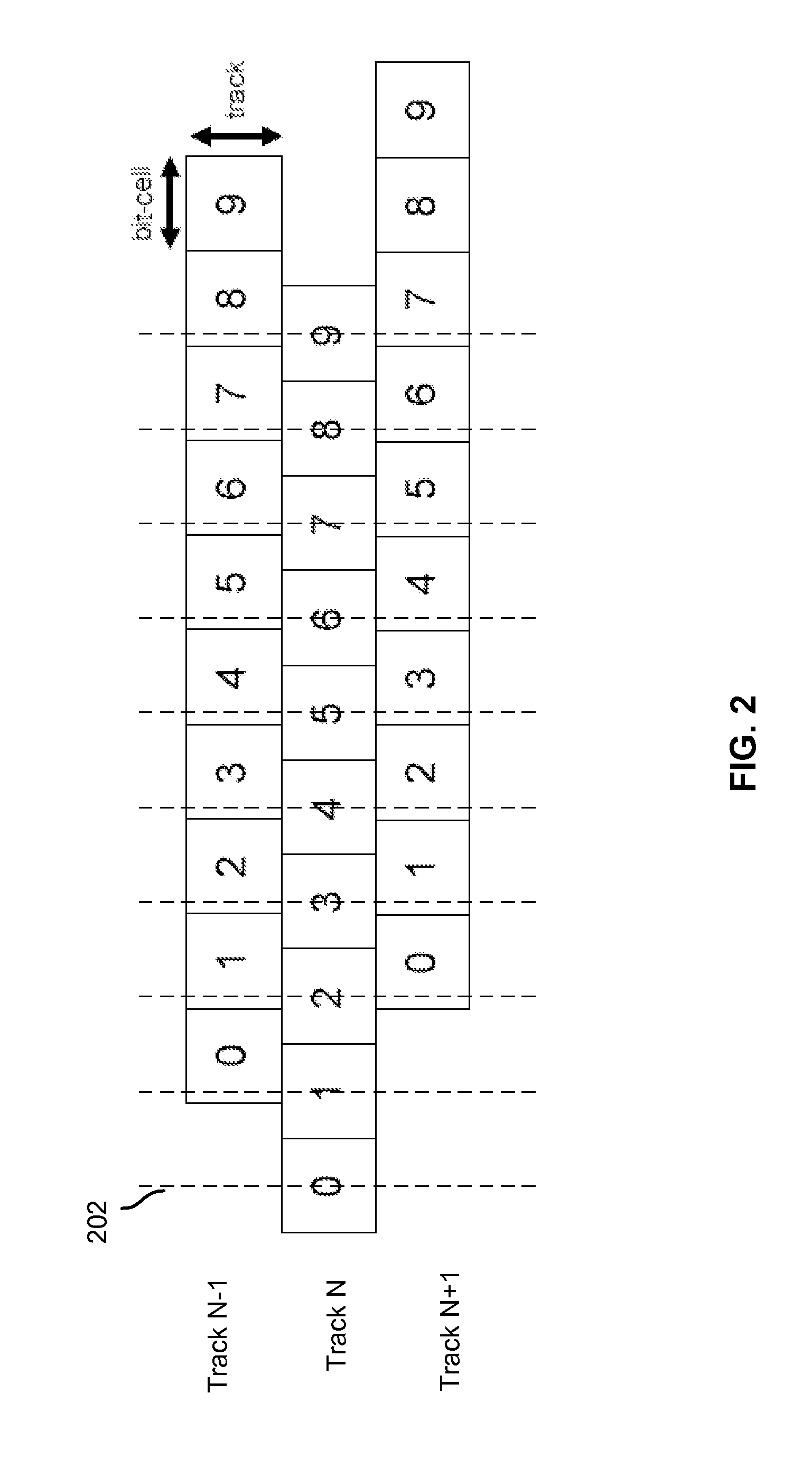
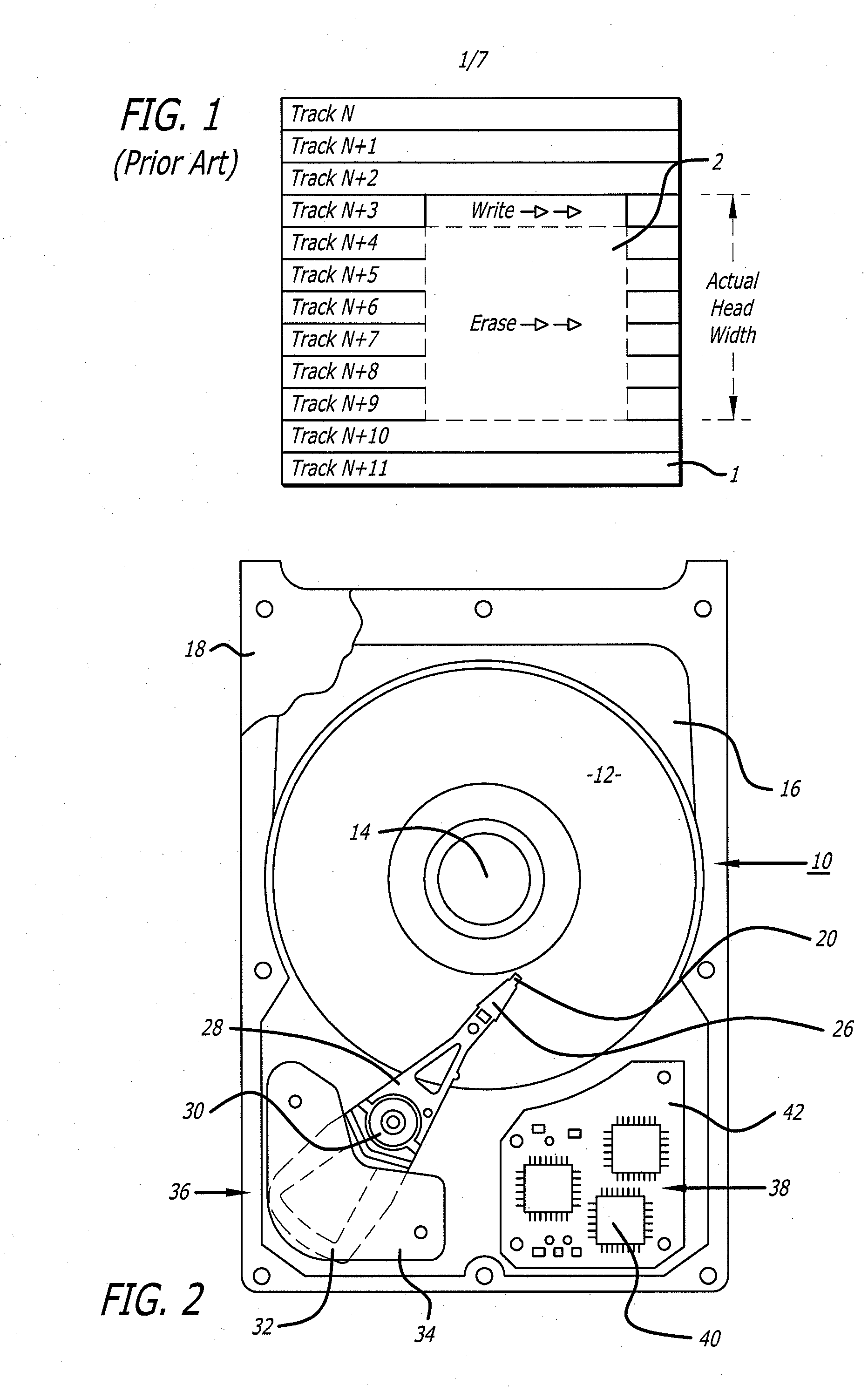
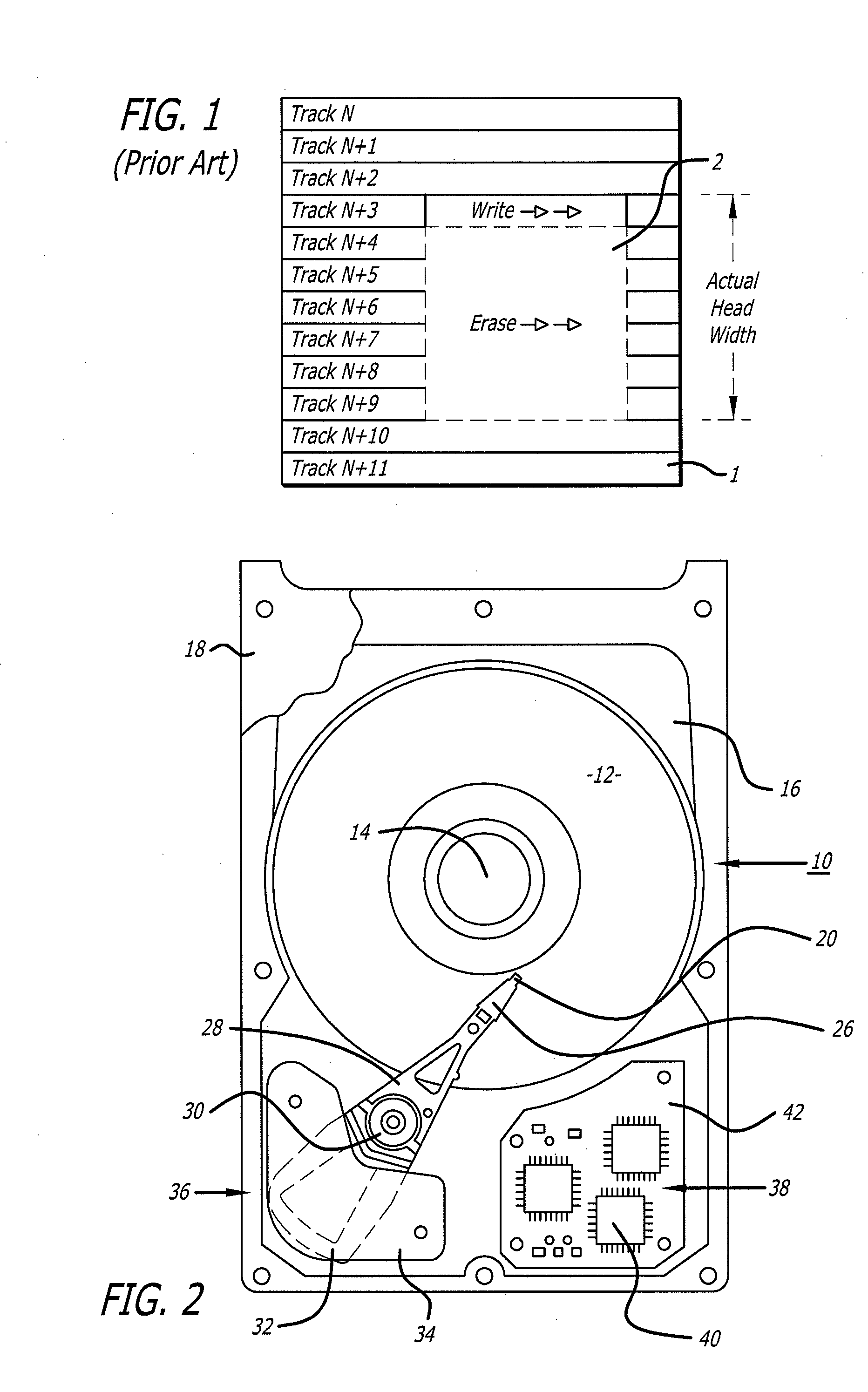
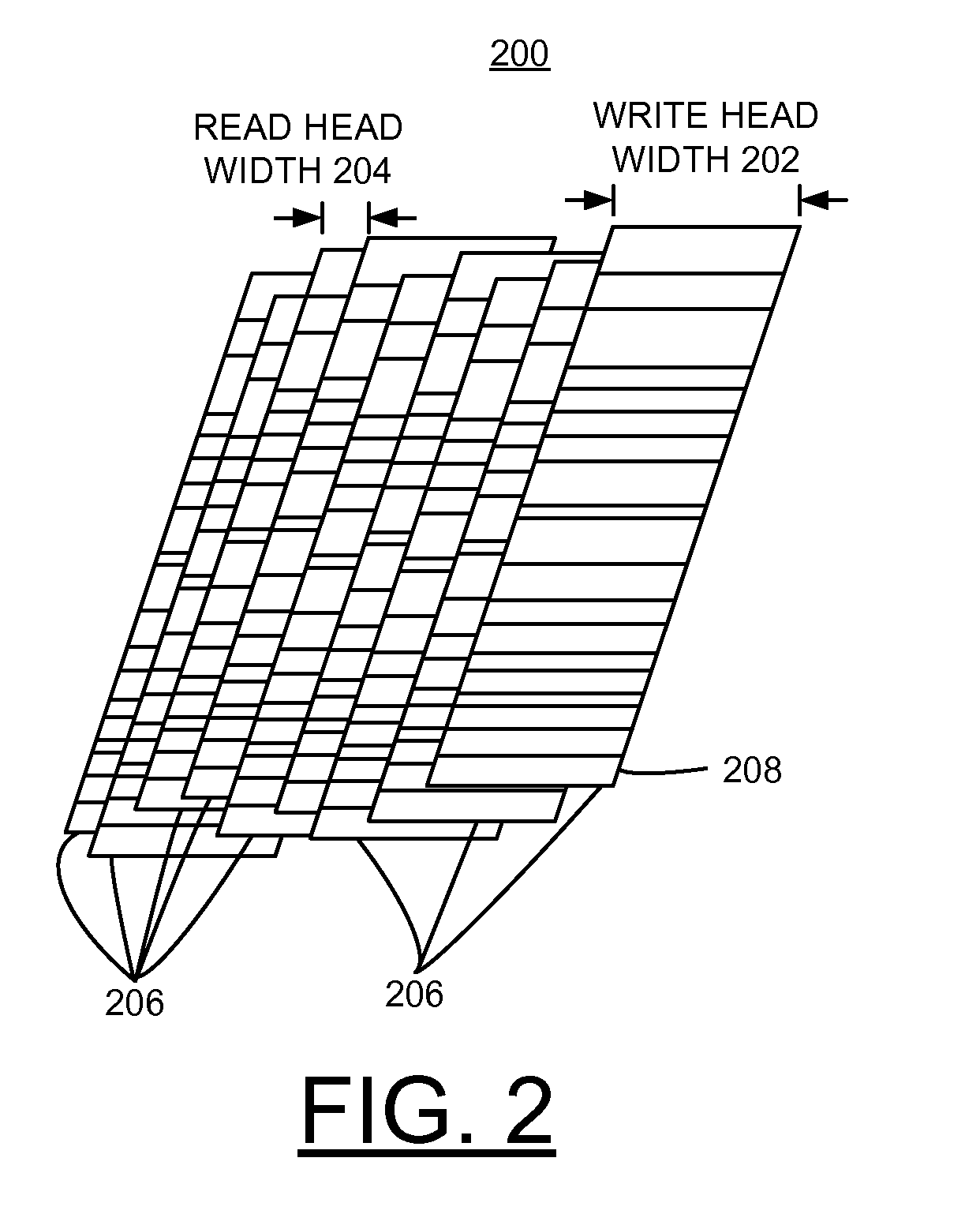
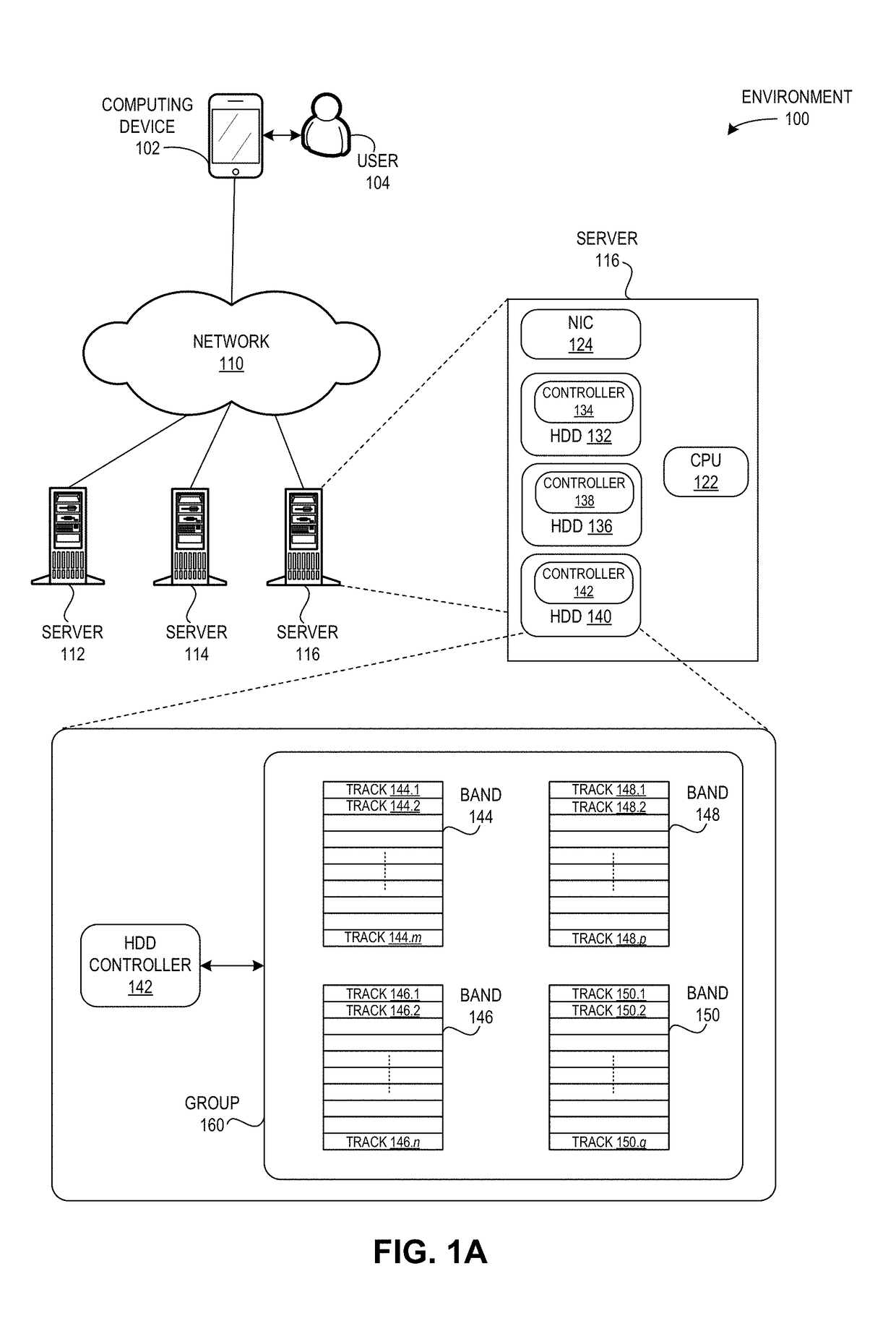
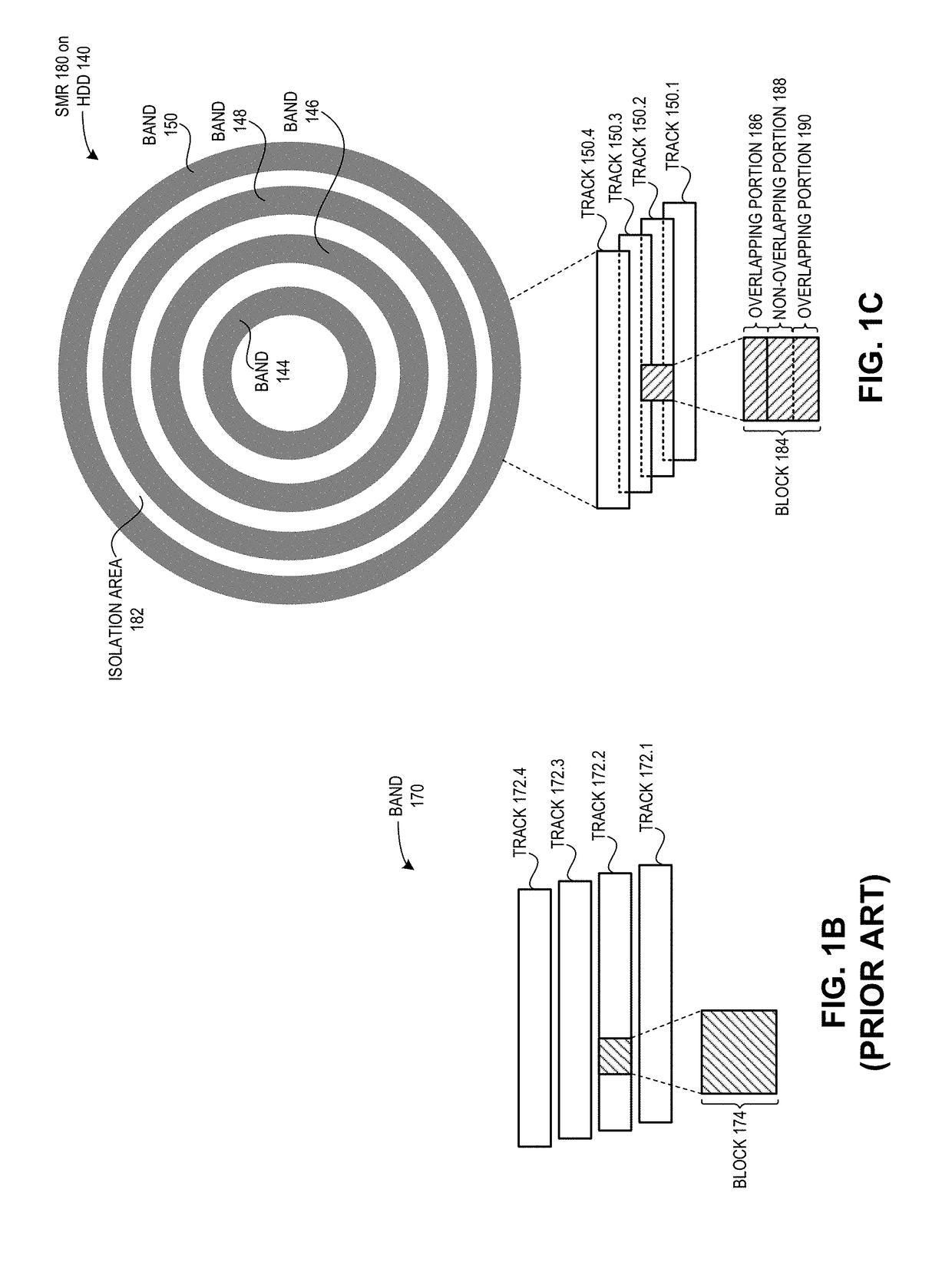
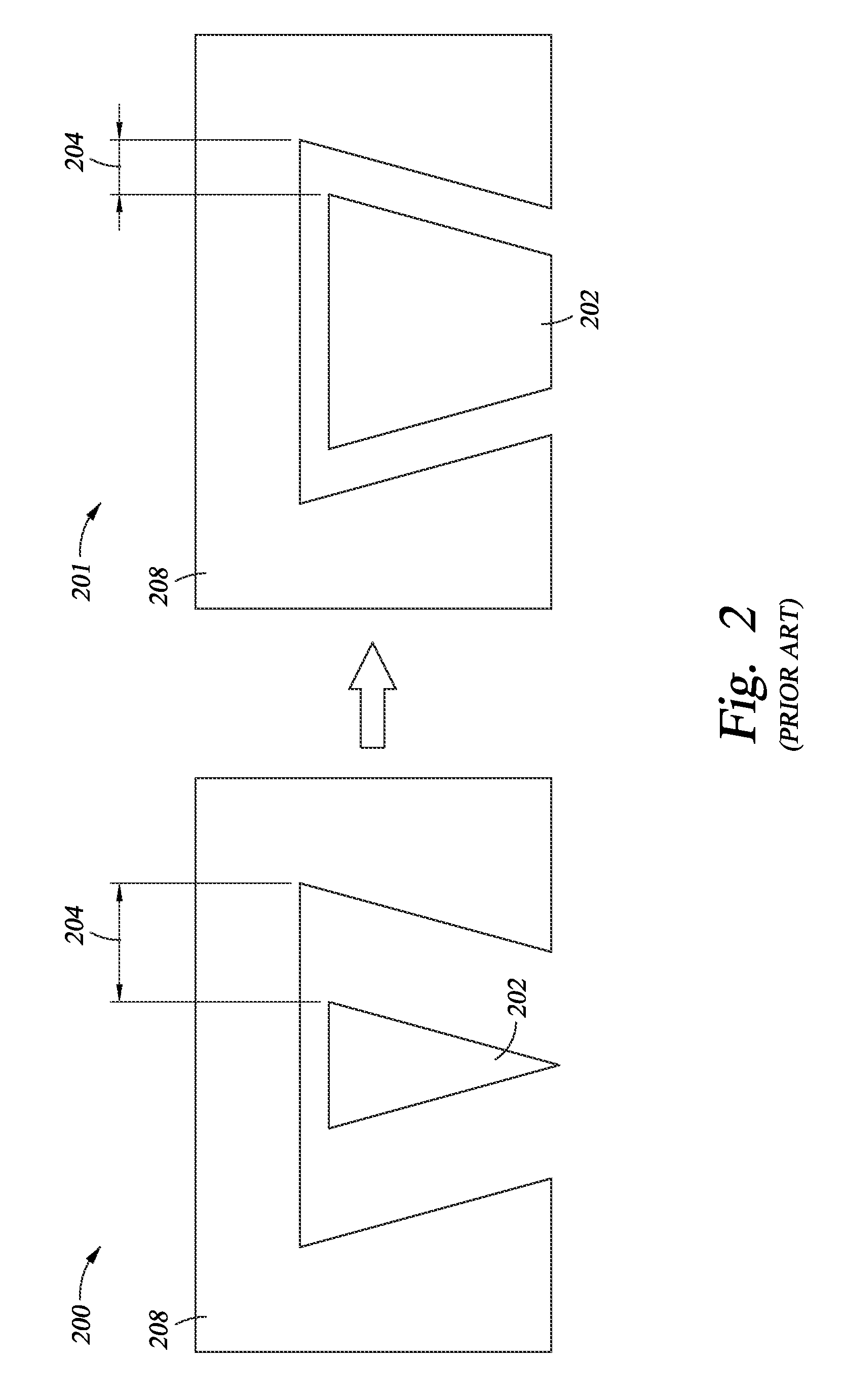
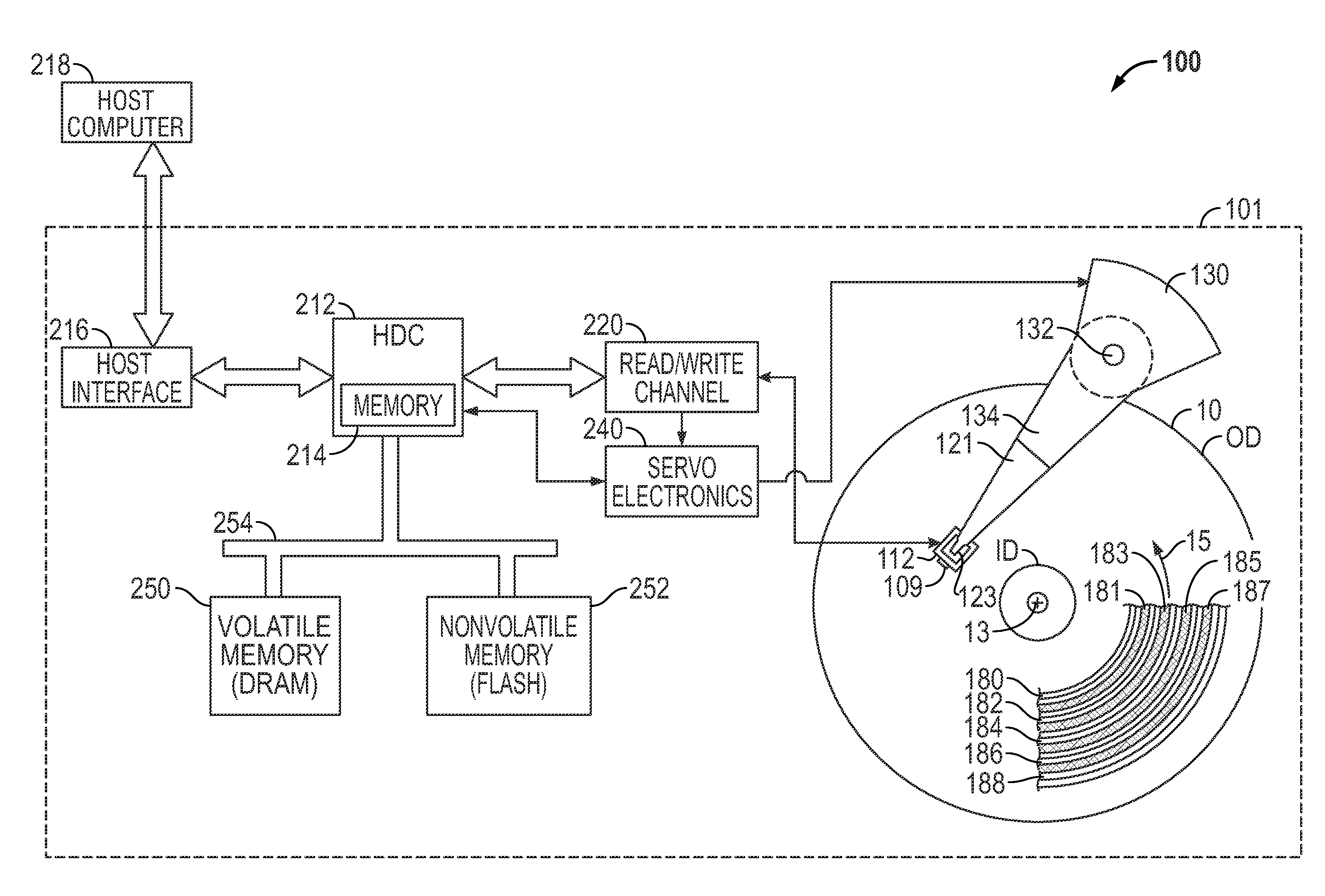
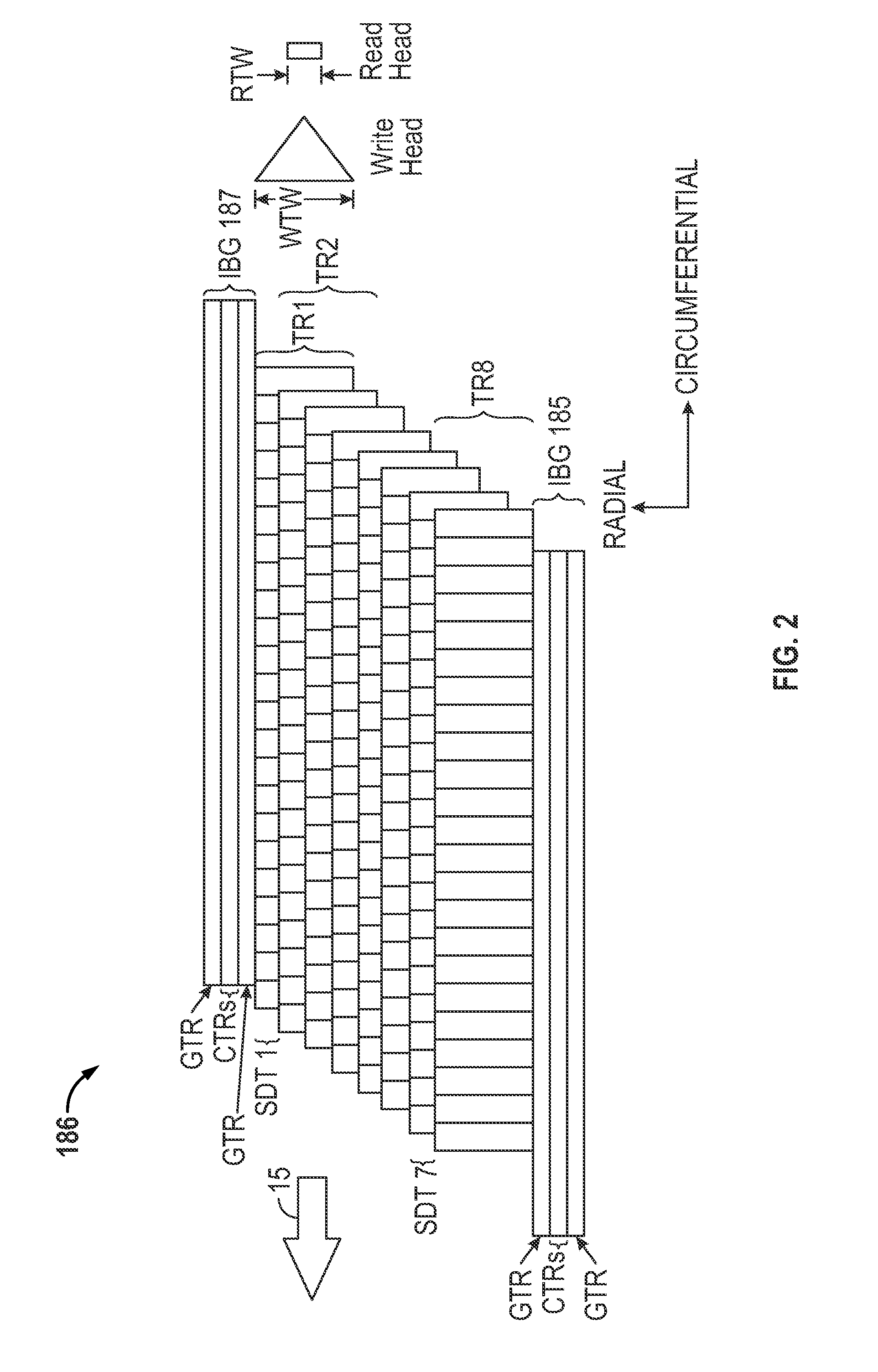
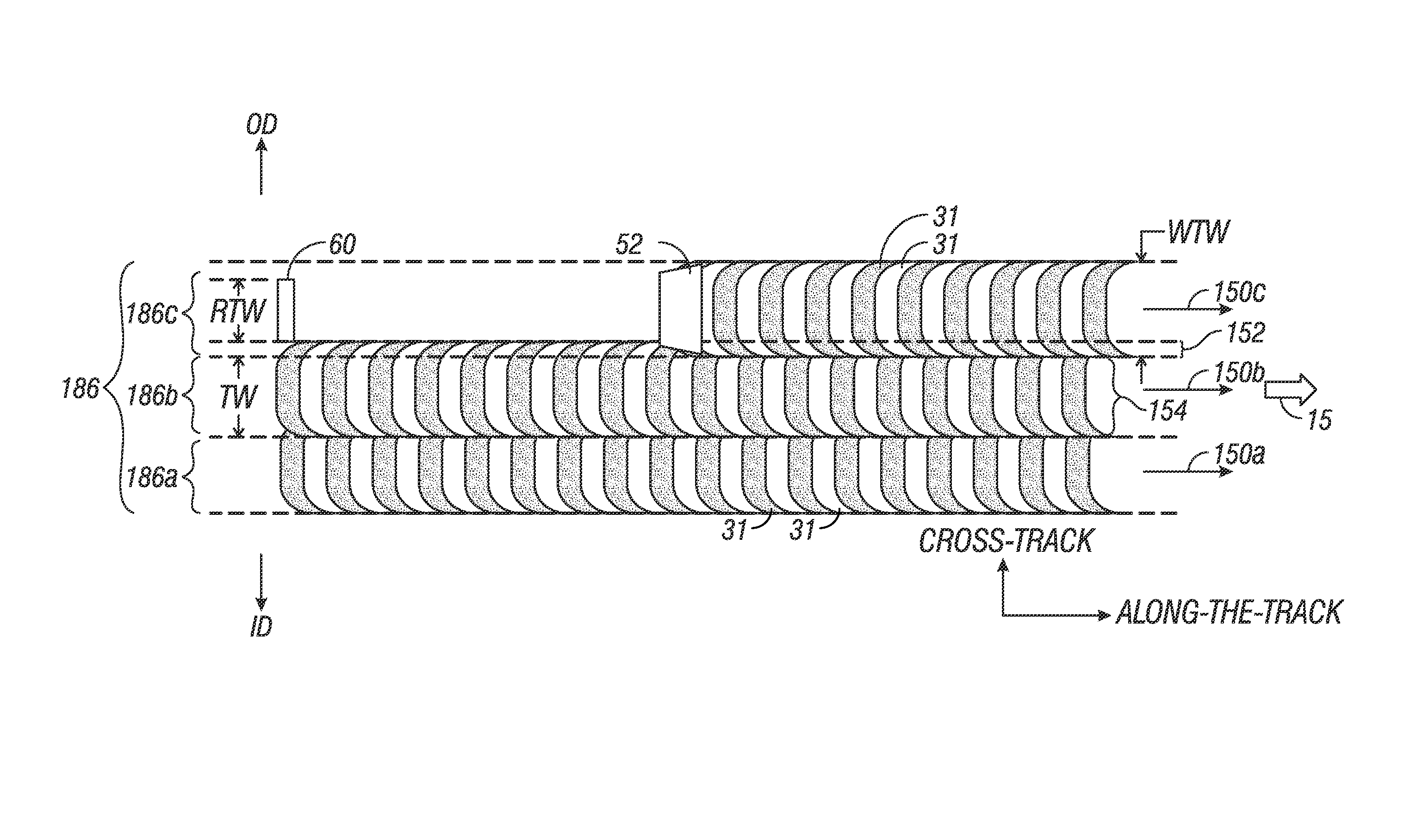
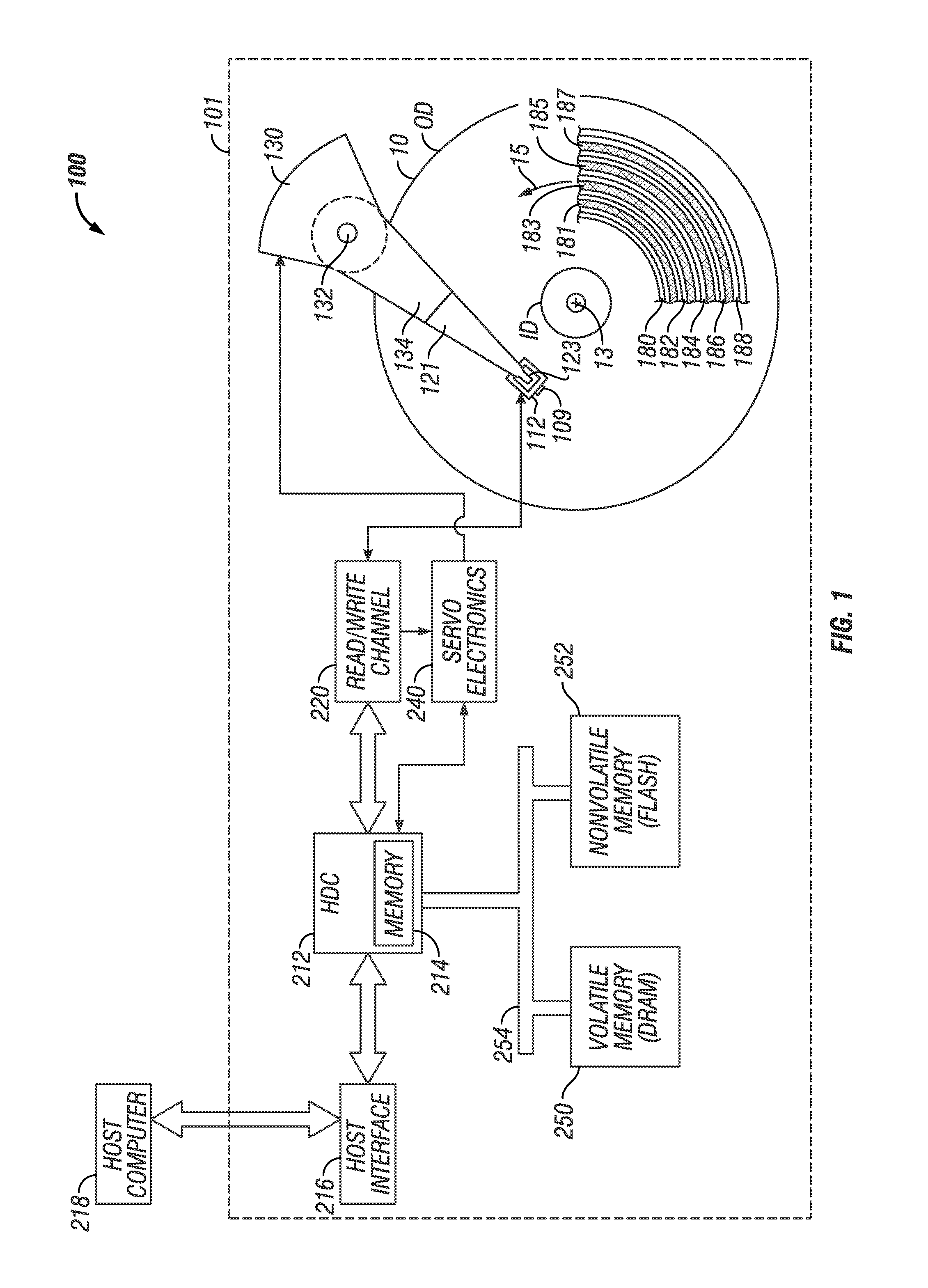
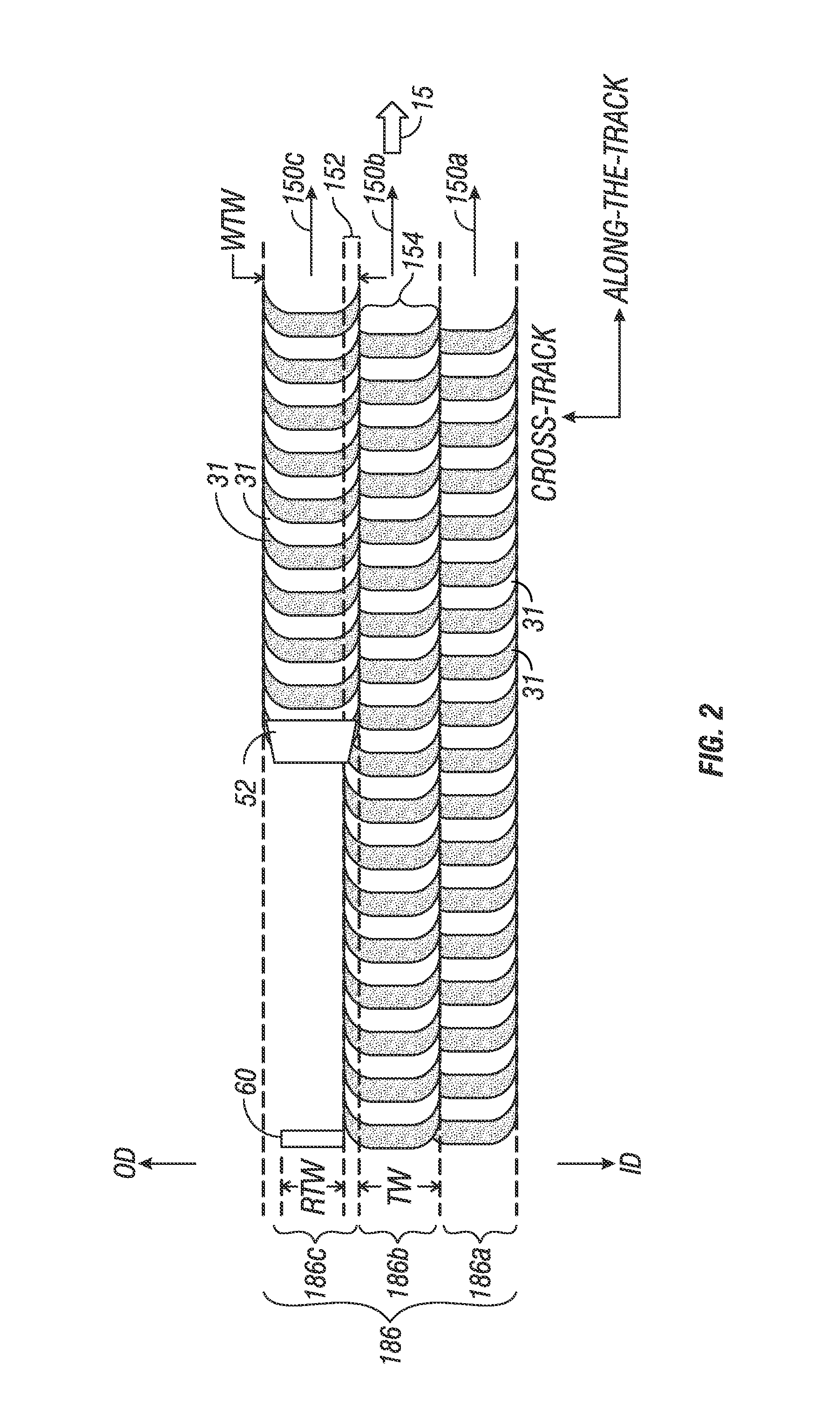
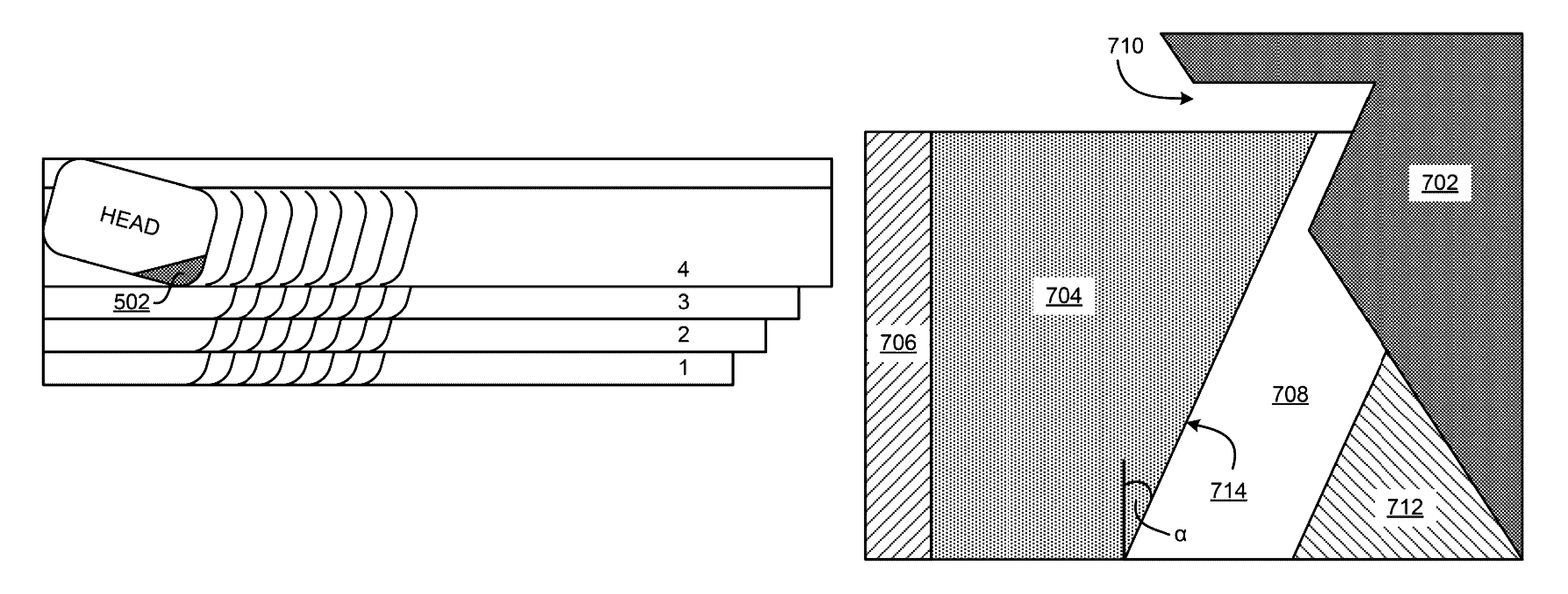
Shingled magnetic recording (SMR) is a magnetic storage data recording technology used in hard disk drives (HDDs) to increase storage density and overall per-drive storage capacity. Conventional hard disk drives record data by writing non-overlapping magnetic tracks parallel to each other (perpendicular recording), while shingled recording writes new tracks that overlap part of the previously written magnetic track, leaving the previous track narrower and allowing for higher track density. Thus, the tracks partially overlap similar to roof shingles. This approach was selected because physical limitations prevent recording magnetic heads from having the same width as reading heads, leaving recording heads wider.
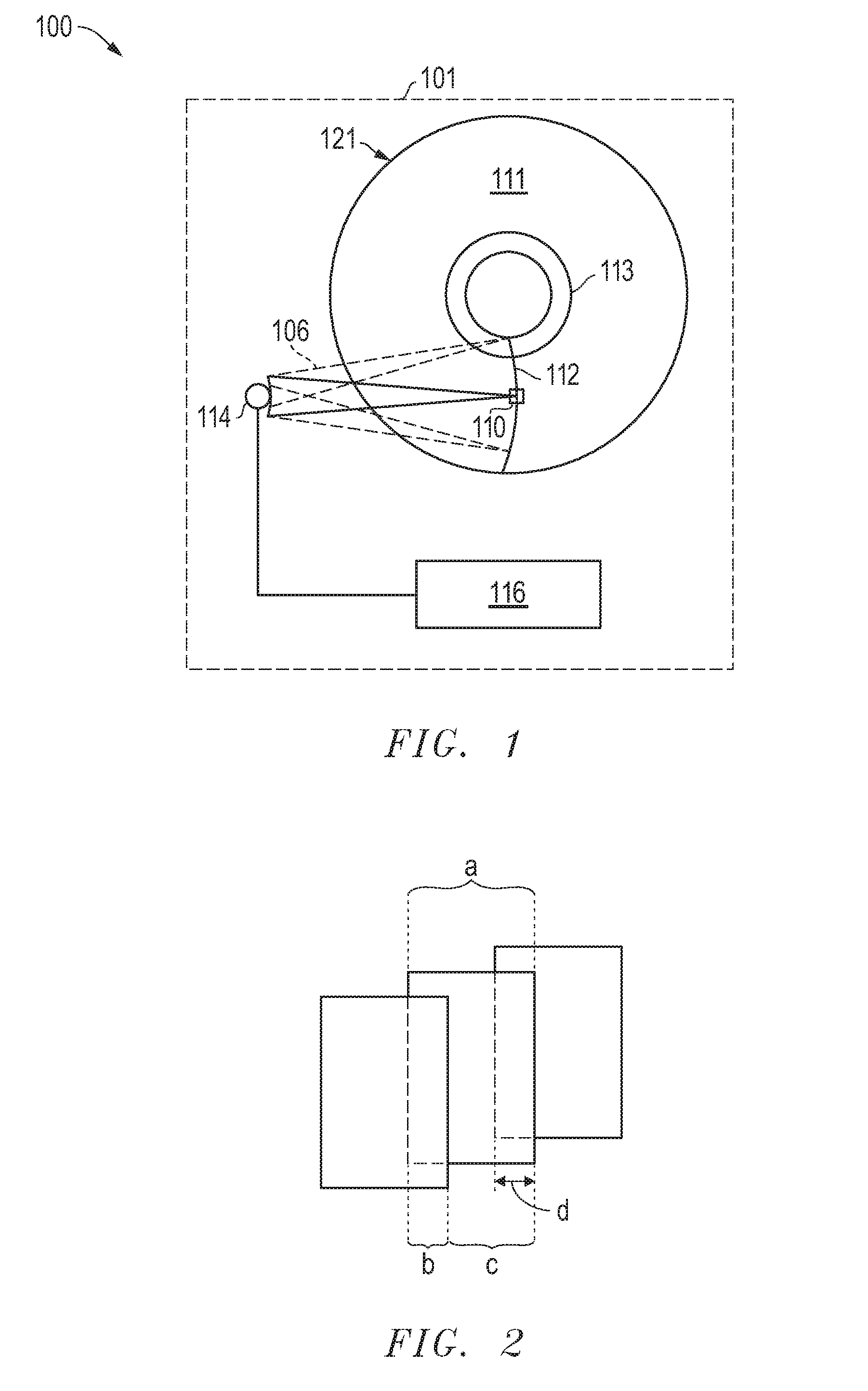
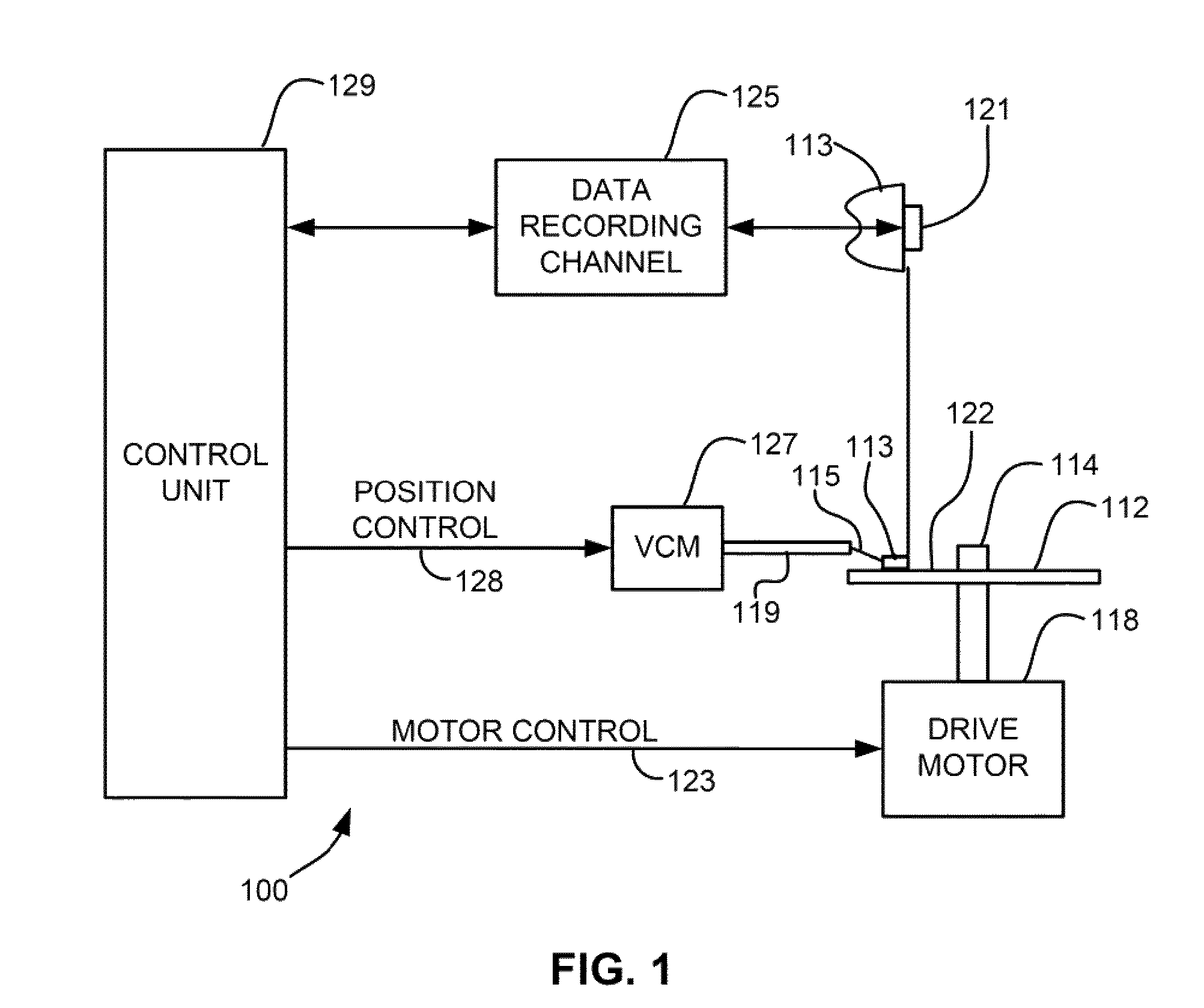
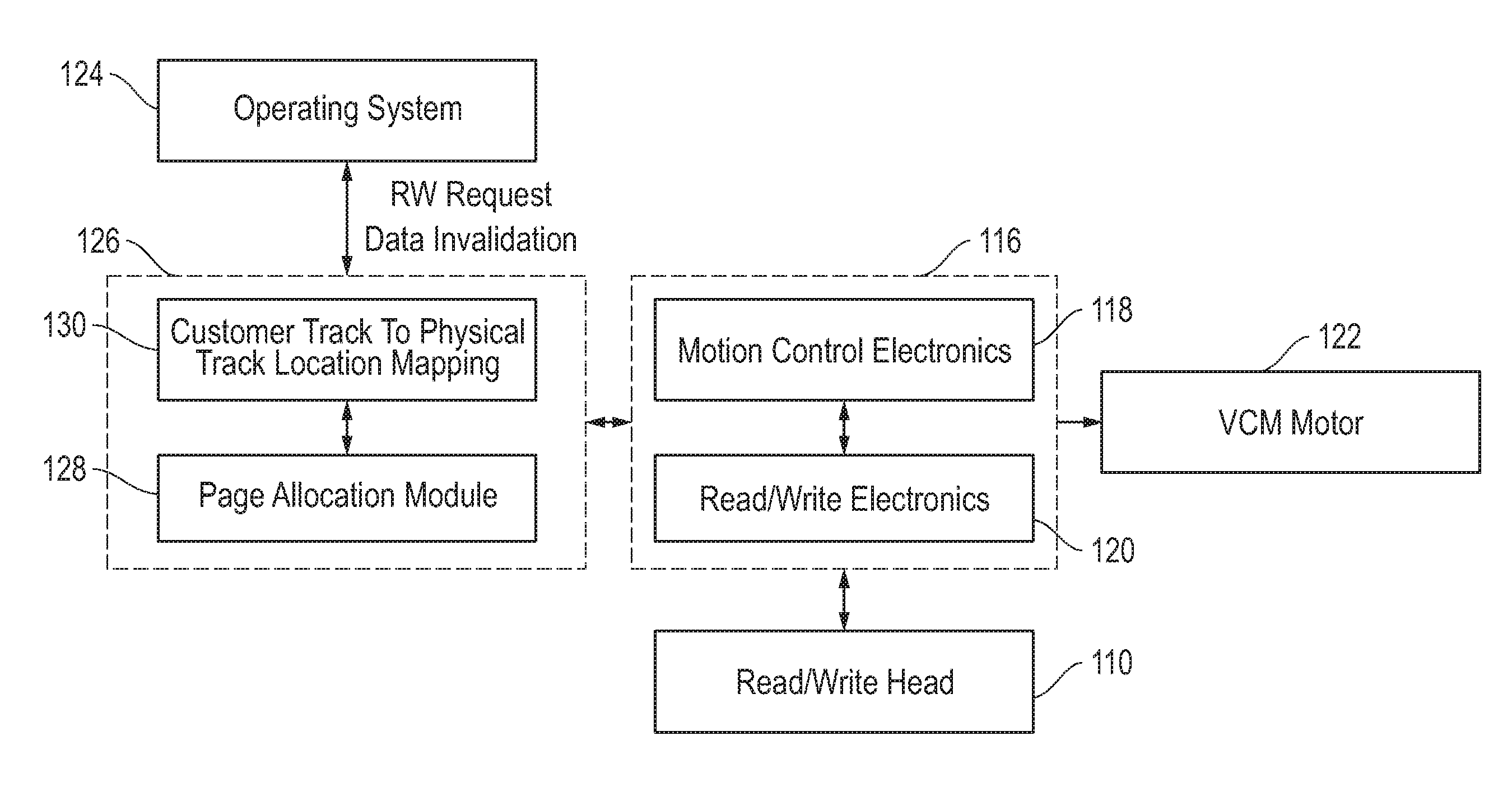
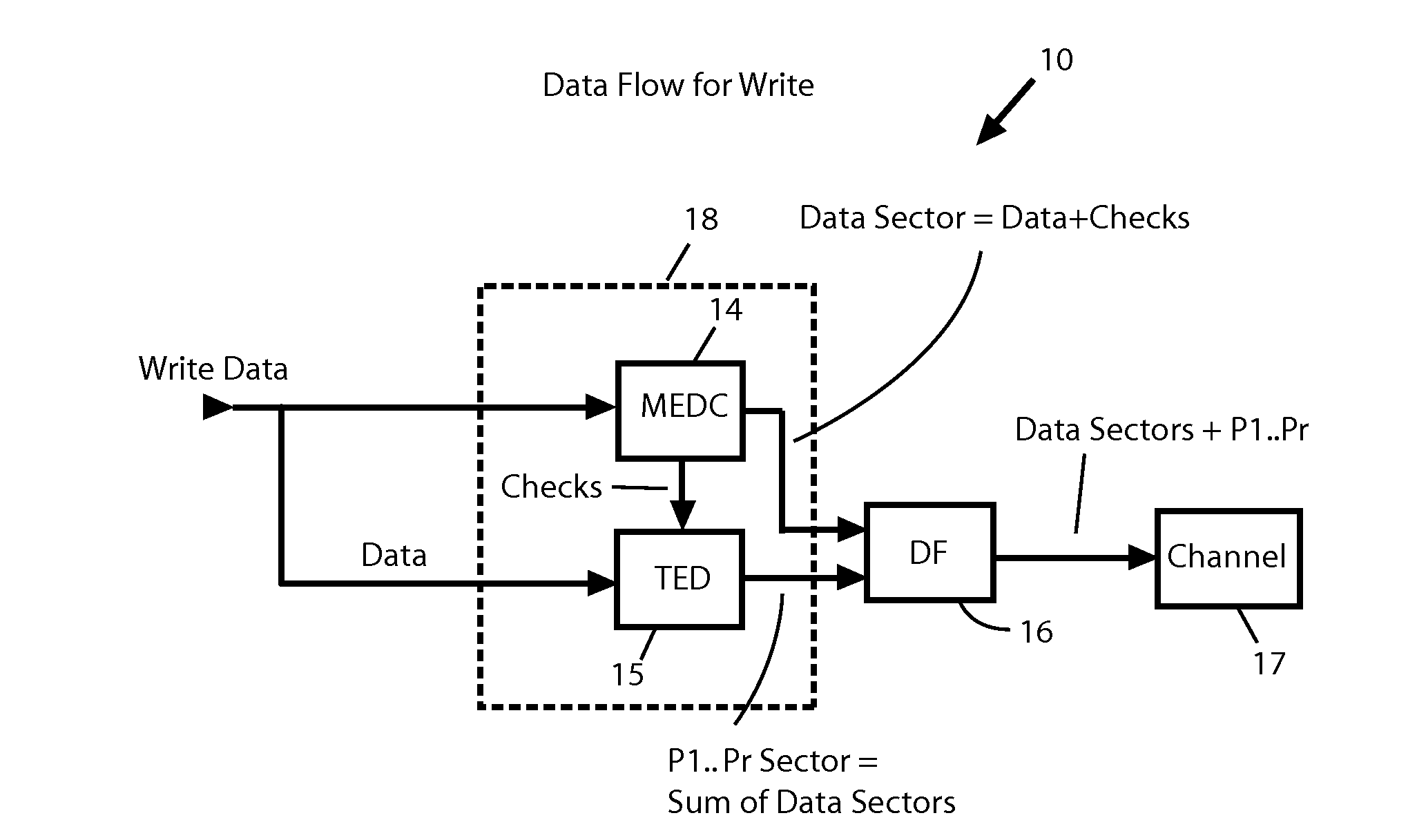
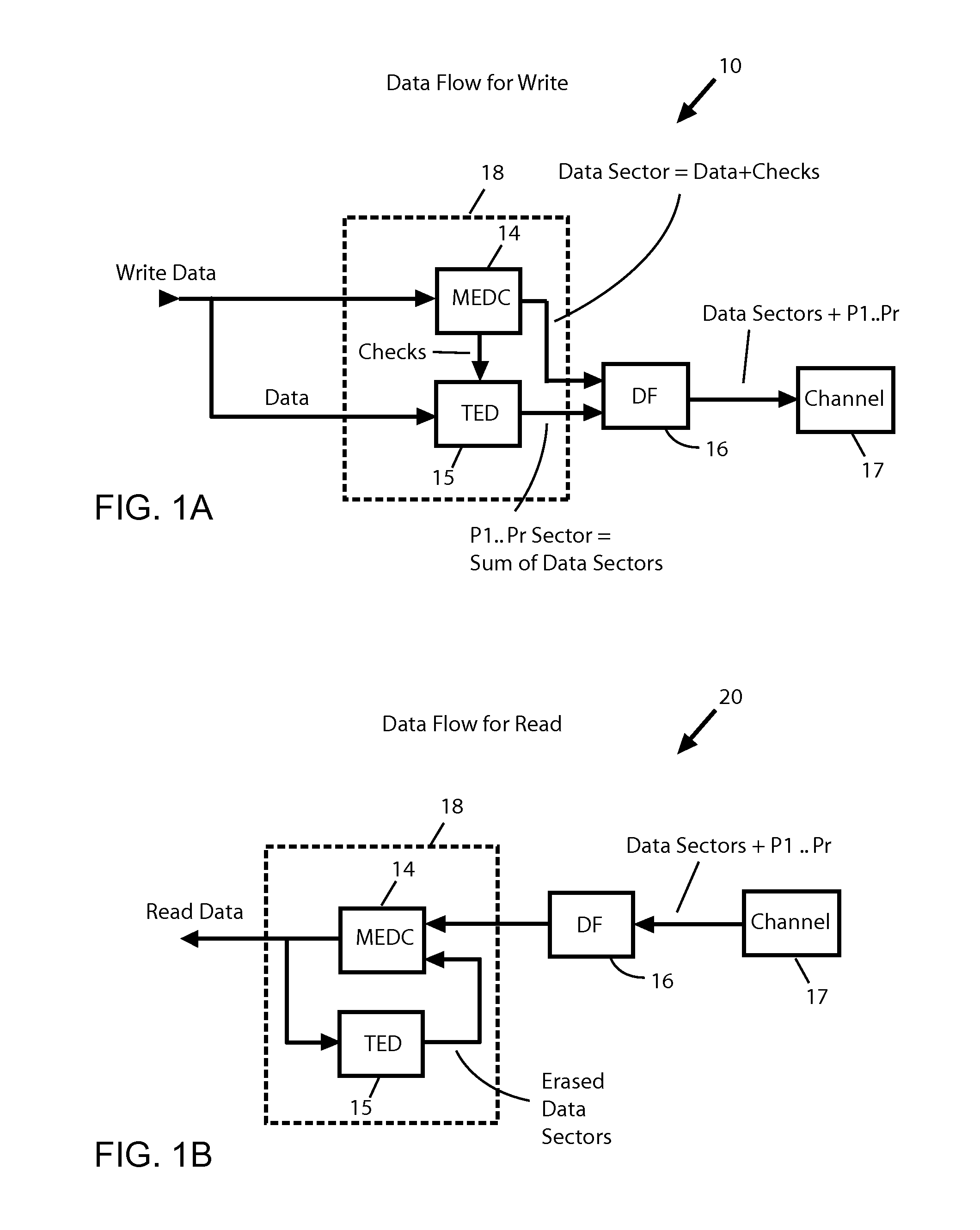
Shingled magnetic recording (SMR) disk drive with verification of written data
ActiveUS20130148225A1Improve writing efficiencyTrack density can not be increasedRecord information storageCarrier monitoringData validationShingled magnetic recording
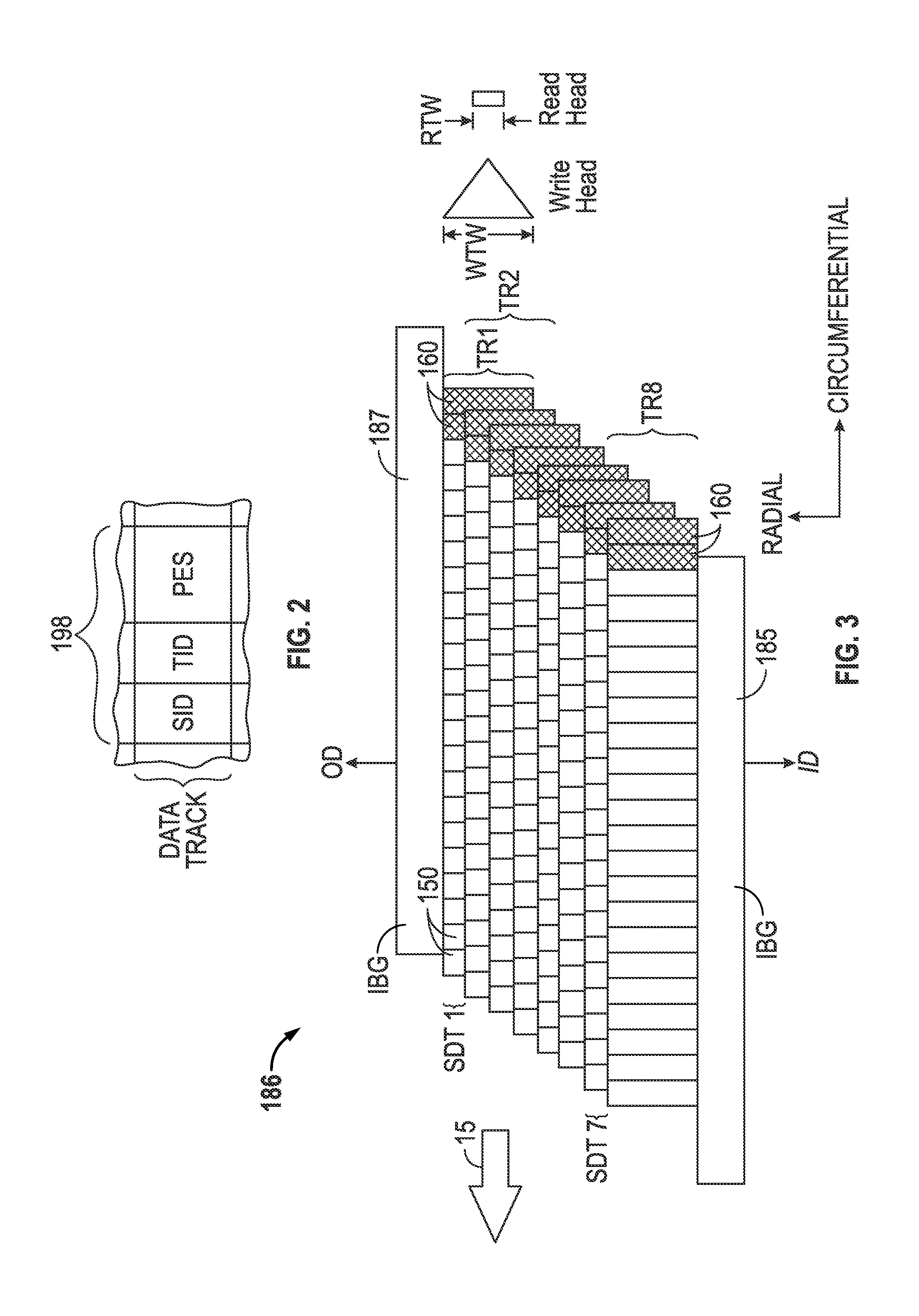
A “write-squeeze-verify” method is used for verification of the data that has been written in the annular bands of a shingled magnetic recording disk drive. The writing of data along a track overwrites a portion of the previously written track and thus “squeezes” the data of the previously written track to thereby form a “shingled data track” (SDT). The data in each SDT is read back and verified by performing an error correction check using error correction bits associated with the data written in the SDT, or by comparing the readback data with the data stored in memory. If the data read back is not verified, a write error counter is incremented and a write error frequency is calculated. One or more attempts to write the data can be performed. If the data in the SDT cannot be verified after the attempted rewrite(s), then a “re-try fail” is reported.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Shingled magnetic recording disk drive with multiple data zones containing different numbers of error-correction-code sectors
ActiveUS8699162B1Data errorDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingComputer science
A shingled magnetic recording disk drive with sector error correction code (ECC) has the disk recording surface divided into multiple zones. Each zone is assigned a sector-ECC strength, i.e., a unique number of ECC sectors associated with a block of data sectors. The zone in which data is to be written is determined from the time average of the position-error signal (PES), which is an indication of the track misregistration (TMR) and thus the current environmental condition to which the HDD is subjected.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Inter-track interference cancelation for shingled magnetic recording
ActiveUS20120105994A1Modification of read/write signalsManufacture head surfaceShingled magnetic recordingInterference cancelation
Inter-track interference cancelation is disclosed, including: receiving an input sequence of samples associated with a track on magnetic storage; using a processor to generate inter-track interference (ITI) data associated with a first side track including by performing a correlation between the input sequence of samples and a sequence of data associated with the first side track.
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
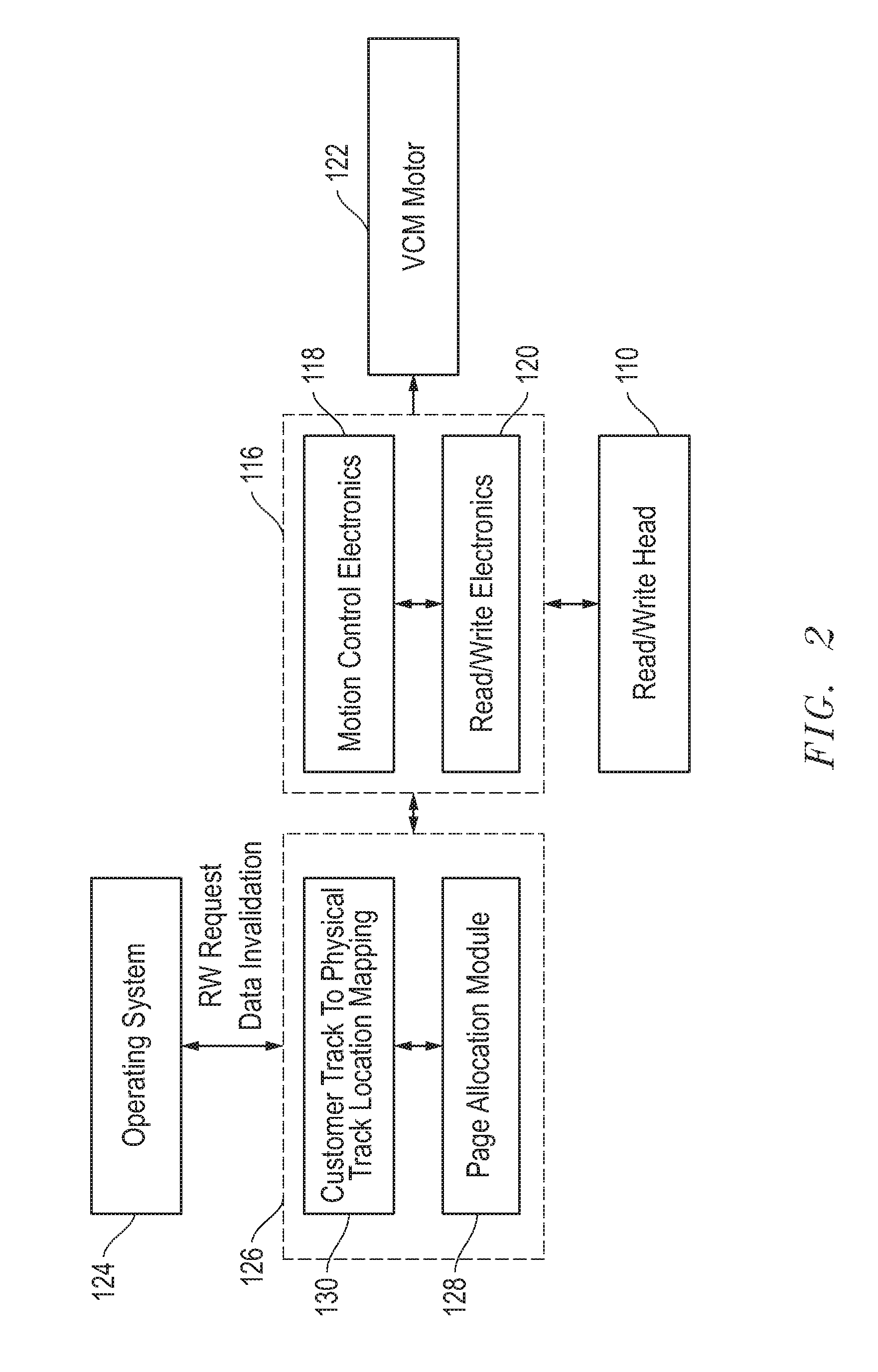
Method and system for data placement in a hard disk drive based on access frequency for improved iops and utilization efficiency
ActiveUS20190391748A1Facilitates data placementEnhanced data placementMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
One embodiment facilitates a write operation in a shingled magnetic recording device. During operation, the system receives, by the storage device, data to be written to the storage device and access-frequency information associated with the data, wherein the storage device includes a plurality of concentric tracks. The system distributes a plurality of spare sector pools among the plurality of concentric tracks. The system selects a track onto which to write the data based on the access-frequency information, wherein data with a highest access-frequency is written to an outer track. The system appends the data at a current write pointer location of the selected track, thereby facilitating an enhanced data placement for subsequent access in the storage device.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
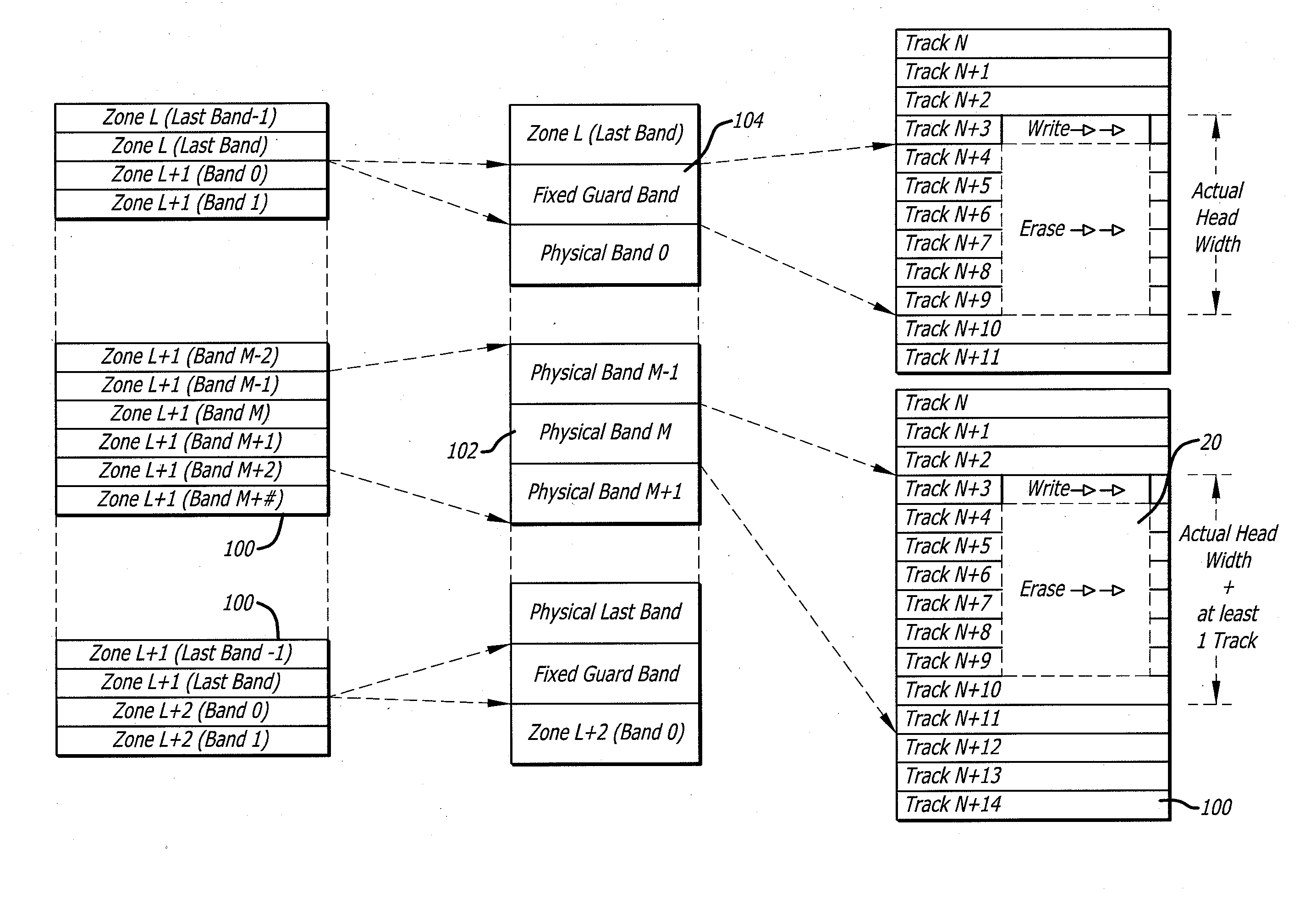
Floating guard band for shingle magnetic recording
ActiveUS20110304935A1Filamentary/web carriers operation controlRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
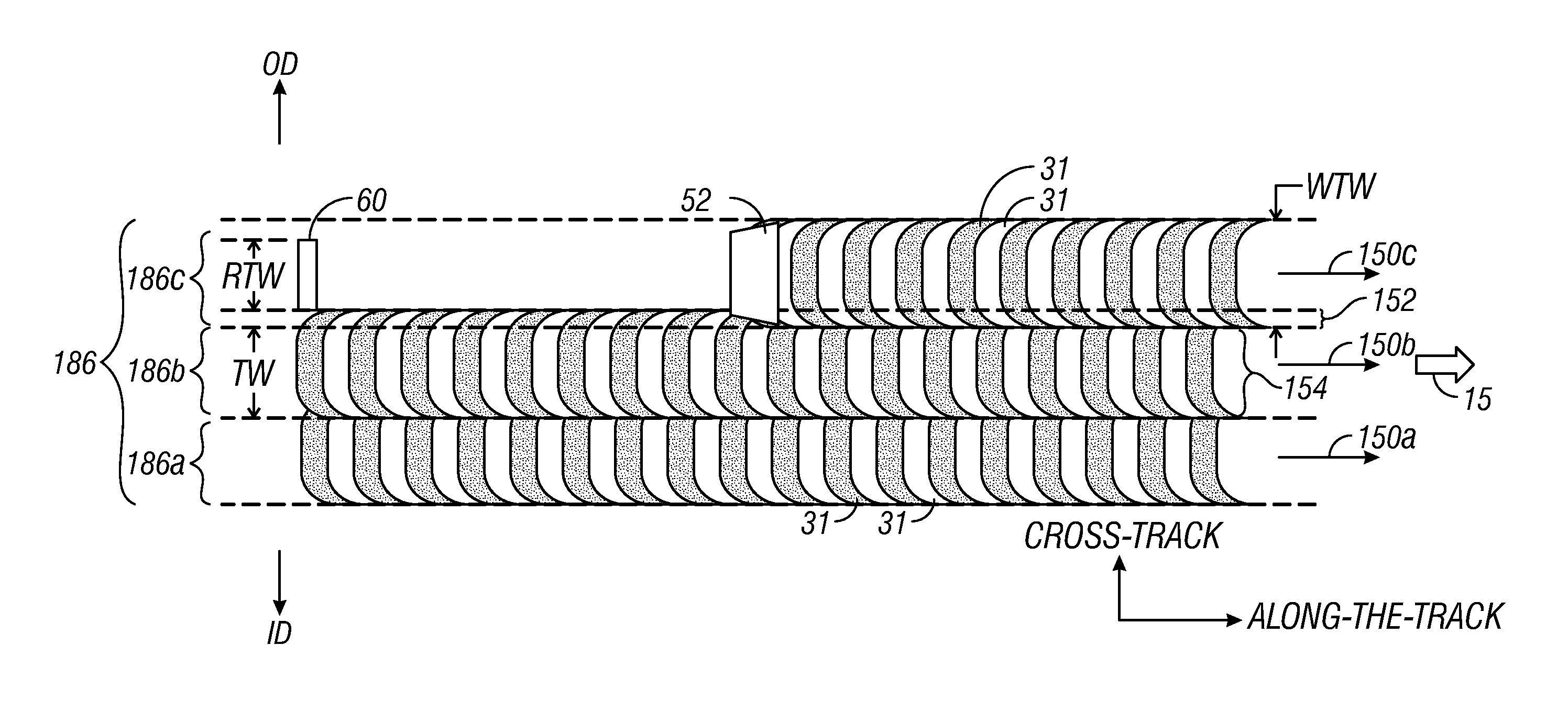
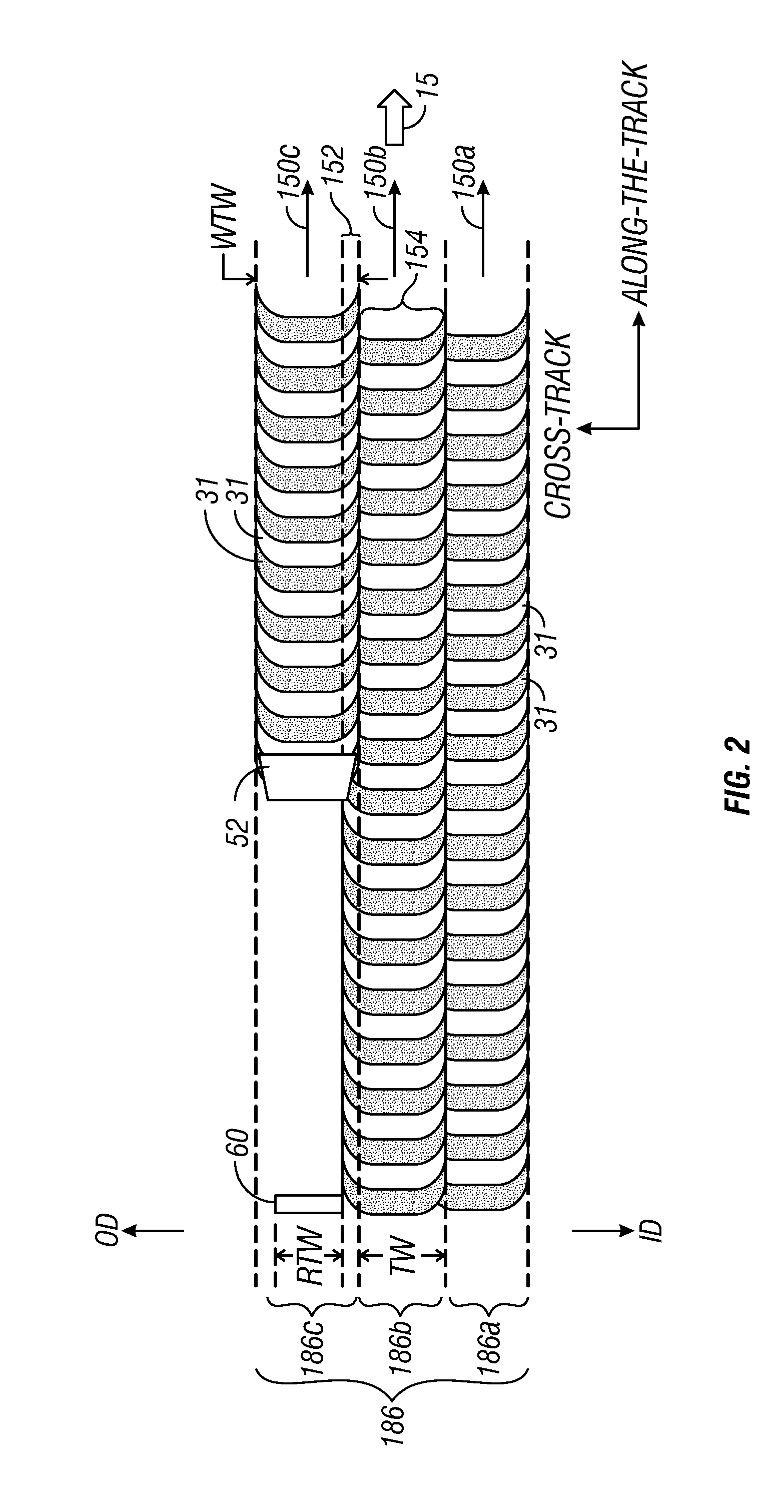
A hard disk drive that includes a disk with data written onto a plurality of tracks, a spindle motor that rotates the disk, and a head that is coupled to the disk. The disk drive also includes a circuit that writes data onto a first writable shingle band of tracks if the first writable shingle band is adjacent to a guard band of tracks. The first writable shingle band includes a number of tracks that is a function of a head width. The guard band of tracks is capable of becoming a writable shingle band. Changing the designation of a shingle band between guard and writable creates floating guard bands. The creation of floating guard bands allows for the writing of a single band without having to move and restore adjacent tracks until reaching a fixed guard band as required in the prior art.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Floating guard band for shingle magnetic recording
ActiveUS8179627B2Filamentary/web carriers operation controlRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
A hard disk drive that includes a disk with data written onto a plurality of tracks, a spindle motor that rotates the disk, and a head that is coupled to the disk. The disk drive also includes a circuit that writes data onto a first writable shingle band of tracks if the first writable shingle band is adjacent to a guard band of tracks. The first writable shingle band includes a number of tracks that is a function of a head width. The guard band of tracks is capable of becoming a writable shingle band. Changing the designation of a shingle band between guard and writable creates floating guard bands. The creation of floating guard bands allows for the writing of a single band without having to move and restore adjacent tracks until reaching a fixed guard band as required in the prior art.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Shingled magnetic recording disk drive with minimization of the effect of far track erasure on adjacent data bands
ActiveUS8537481B1Eliminate the effects ofRaise countRecord information storageCarrier monitoringShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
A shingled magnetic recording (SMR) hard disk drive (HDD) essentially eliminates the effect of far track erasure (FTE) in the boundary regions of annular data bands caused by writing in the boundary regions of adjacent annular data bands. The extent of the FTE effect is determined for each track within a range of tracks of the track being written. Based on the relative FTE effect for all the tracks in the range, a count increment (CI) table or a cumulative count increment (CCI) table is maintained for all the tracks in the range. For every writing to a track in a boundary region, a count for each track in an adjacent boundary region, or a cumulative count for the adjacent boundary region, is increased. When the count reaches a predetermined threshold the data is read from that band and rewritten to the same band.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
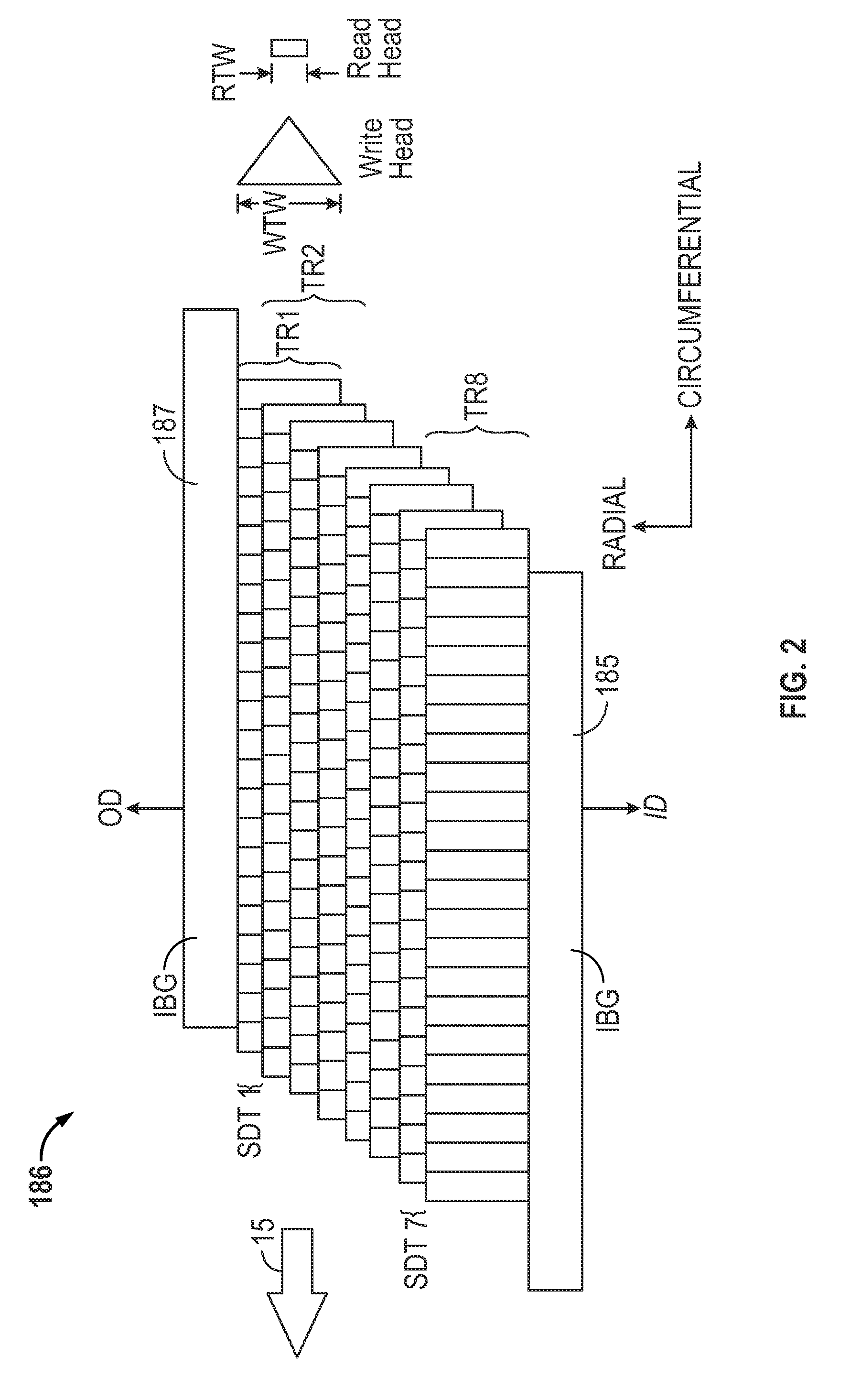
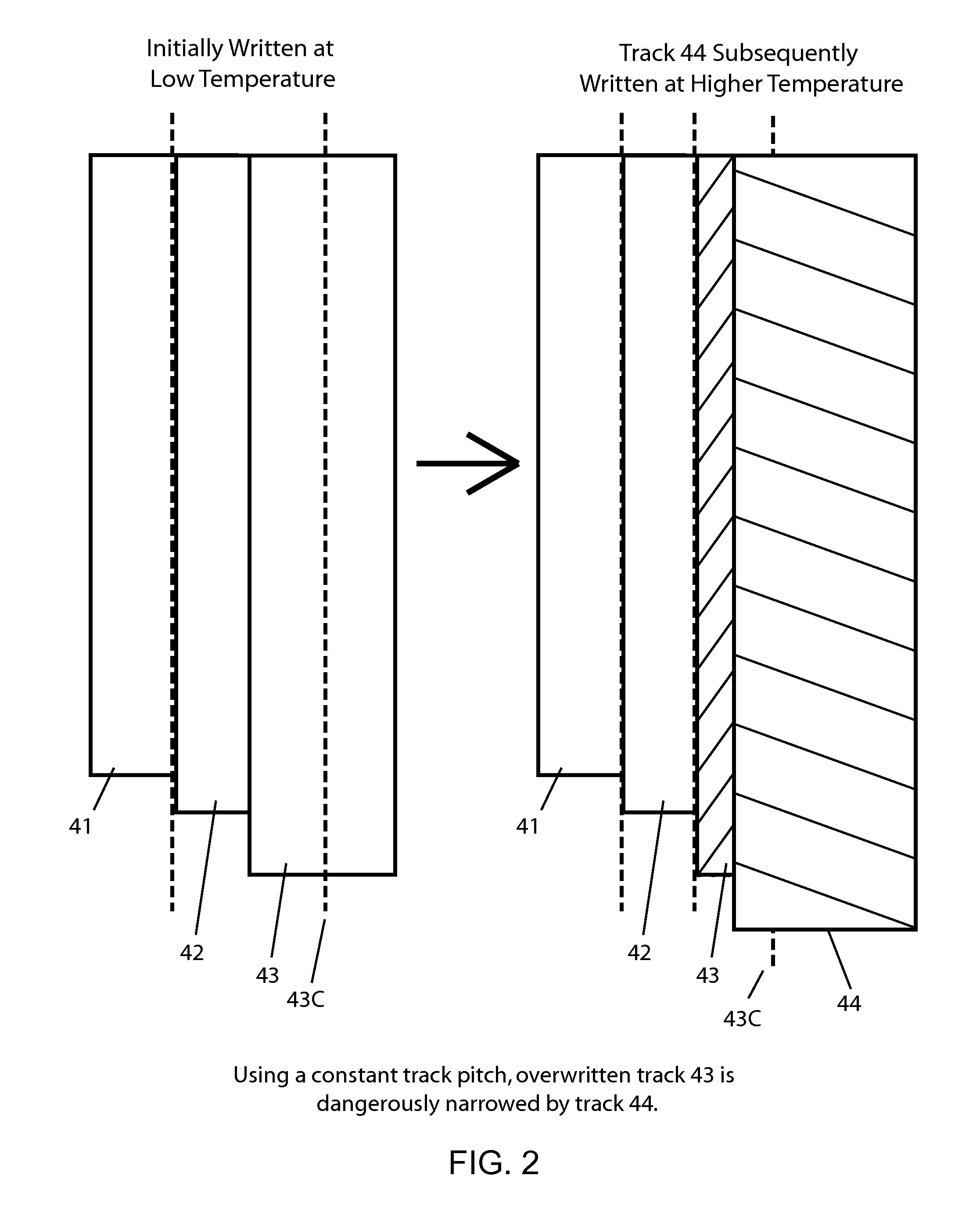
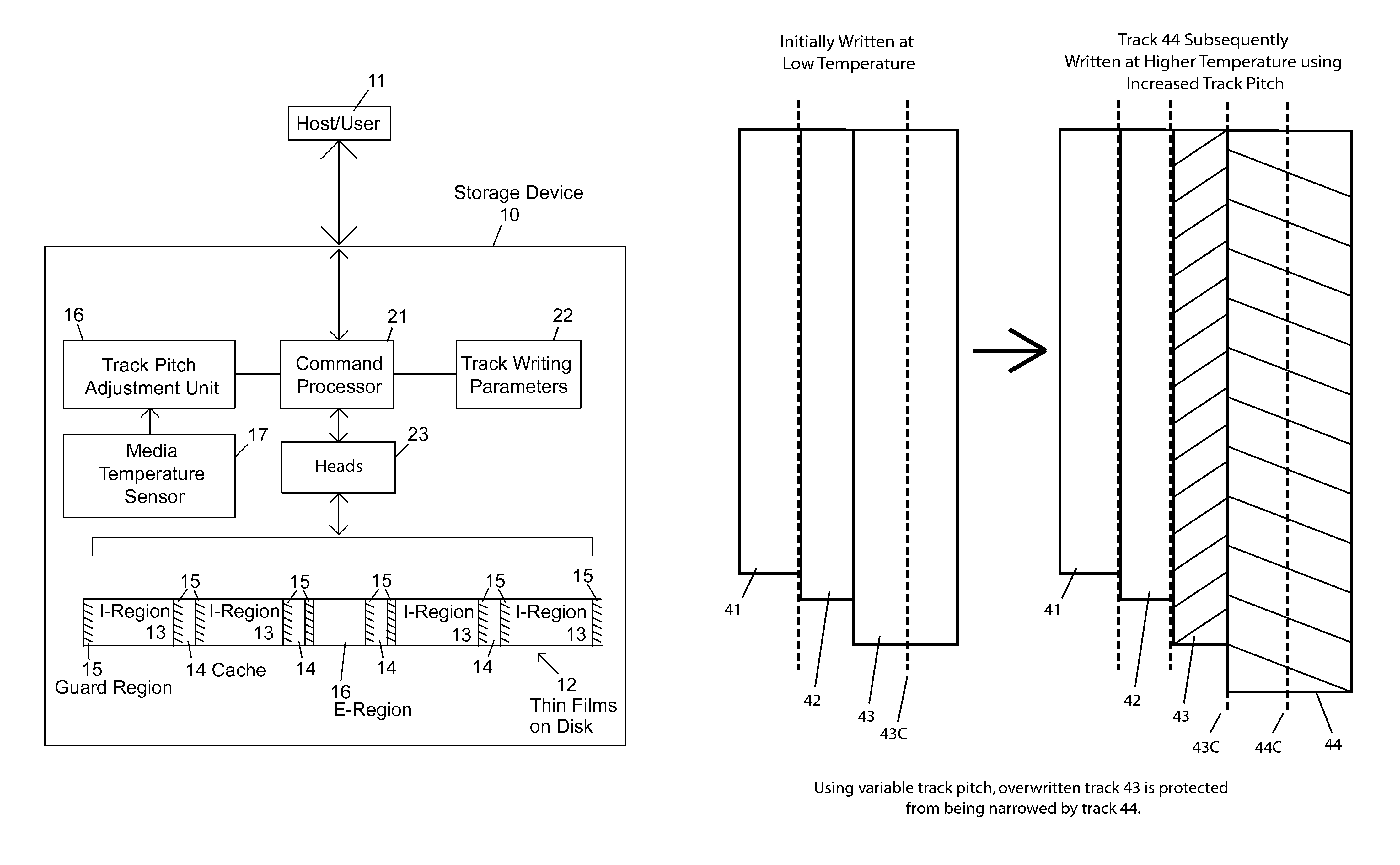
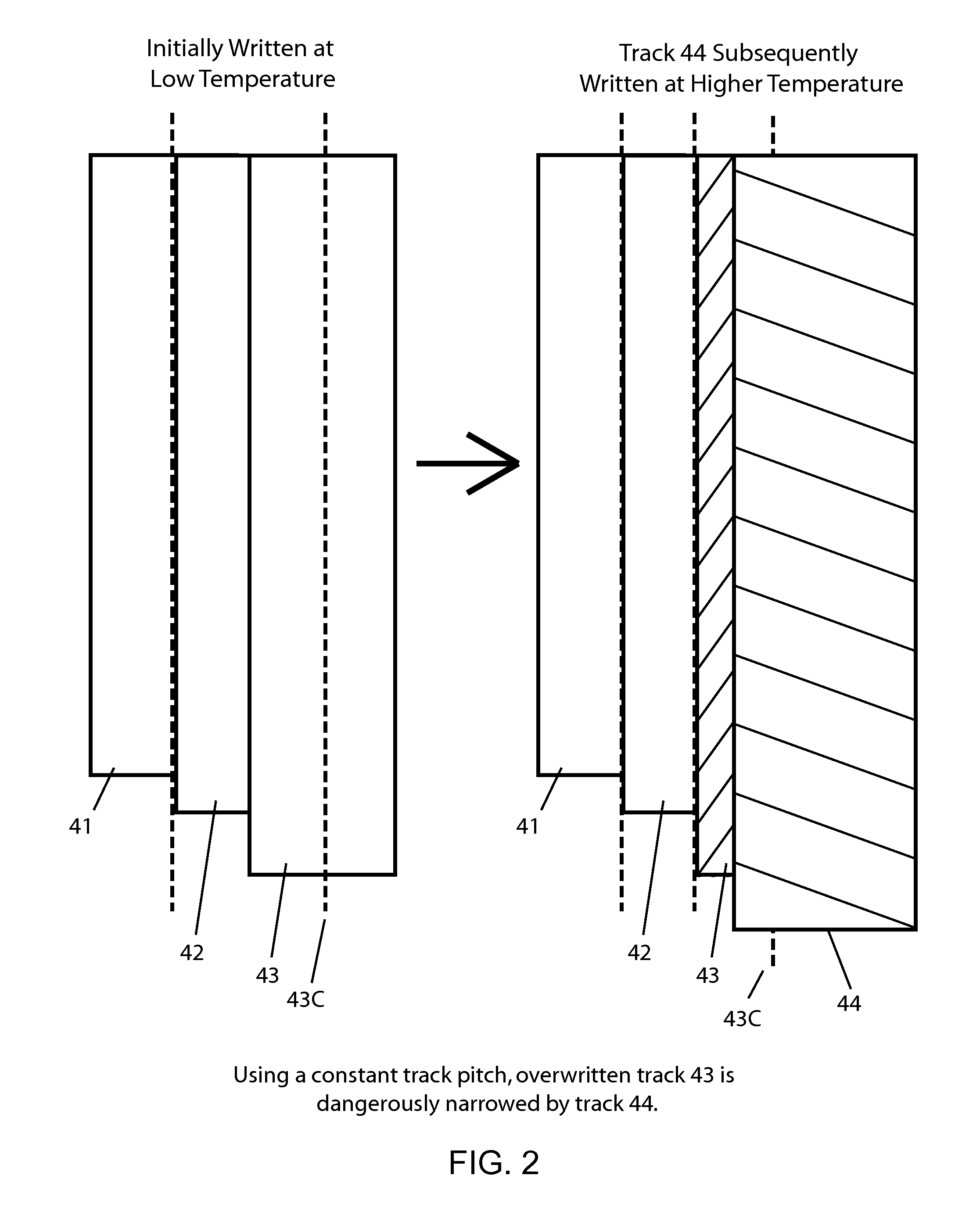
Dynamic Track Pitch Control for Shingled Magnetic Recording (SMR)
ActiveUS20130335856A1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingMagnetic media
SMR disk drives are described that adjust track pitch or magnetic write width to compensate for external temperature effects. In one embodiment track pitch is increased when the media temperature increases. The temperature of magnetic media during write operations can be determined from the drives' temperature sensor. In other embodiments track pitch is adjusted based on the magnetic write width (MWW) which is determined from read-back testing of previously written data tracks. In an alternative embodiment, the width of the MWW is adjusted instead of the track pitch. The various factors that affect the MWW that can be used to increase or decrease the MWW, including write current characteristics and when available thermal-assistance parameters.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
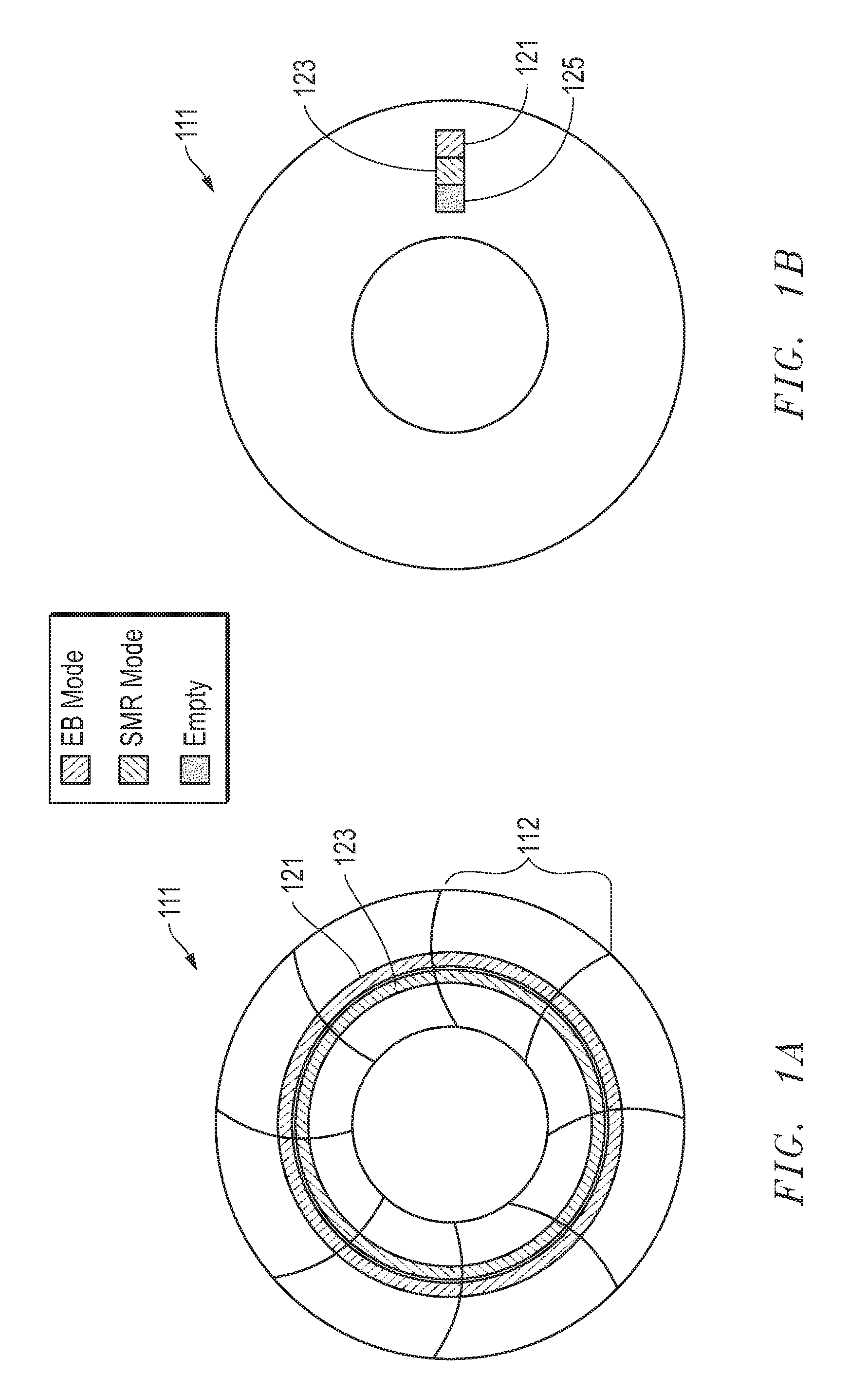
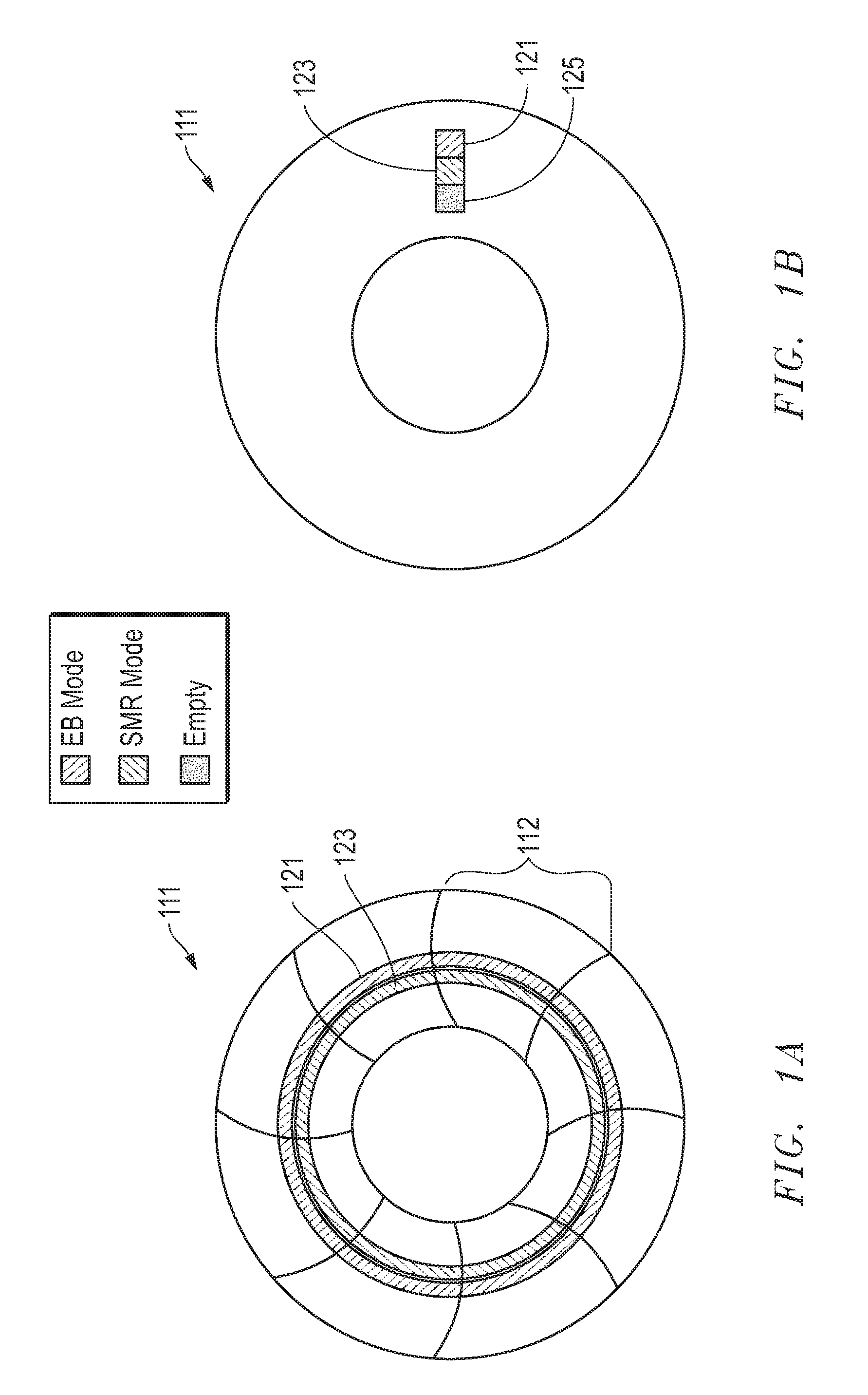
System, method and apparatus for storage architecture for bit patterned media using both erase band and shingled magnetic recording
ActiveUS20120099216A1Improve performanceFilamentary/web record carriersPatterned record carriersHard disc driveShingled magnetic recording
Storage architecture for bit patterned media uses both erase band and shingled magnetic recording. A hard disk drive may comprise a disk having bit patterned media with a plurality of data tracks arrayed in architecture pages having at least one of erase band mode (EBM), shingled mode (SM) and unallocated space. An actuator has a head for writing data to the data tracks of the bit patterned media. A control system monitors, reallocates and reconfigures the architecture pages from EBM, SM or unallocated space to a different one of EBM, SM or unallocated space to enhance performance of the hard disk drive.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
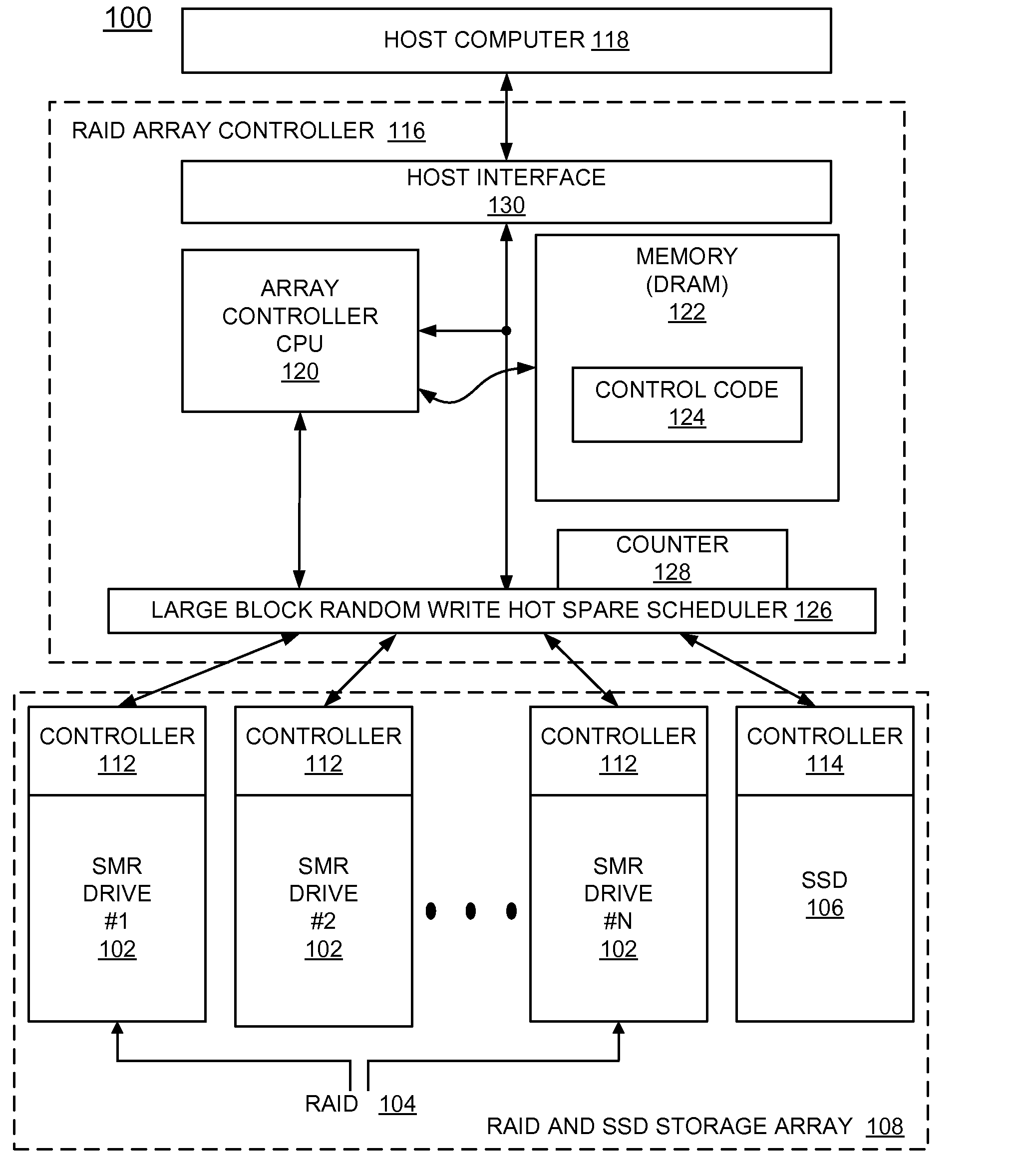
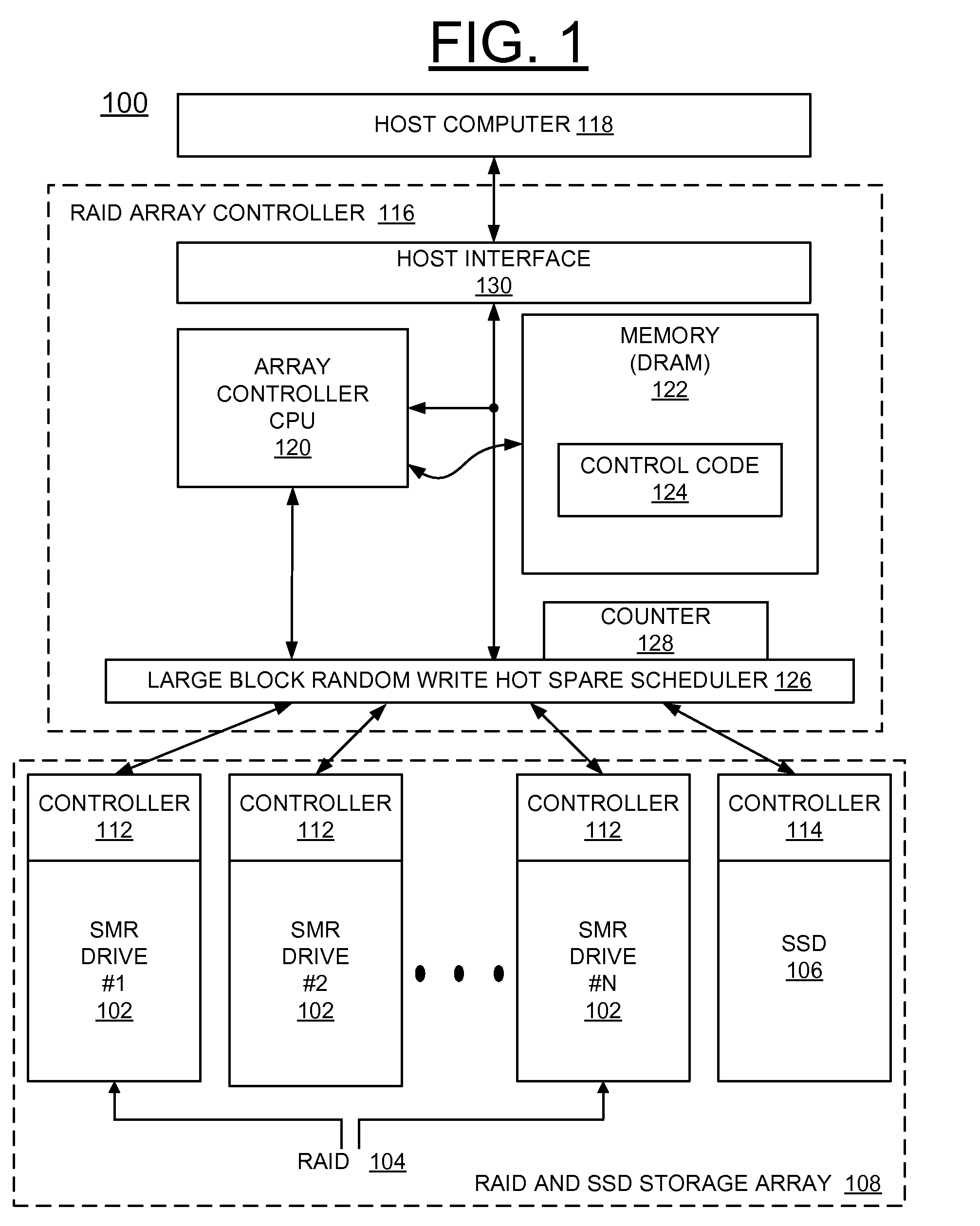
Implementing large block random write hot spare SSD for smr raid
ActiveUS20130232292A1Overcome disadvantagesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRecord information storageRAIDShingled magnetic recording
A method and a storage system are provided for implementing a sustained large block random write performance mechanism for shingled magnetic recording (SMR) drives in a redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID). A Solid State Drive (SSD) is provided with the SMR drives in the RAID. The SSD is used in a hot spare mode, which is activated when a large block random-write event is identified for a SMR drive in the RAID. In the hot spare mode, the SSD temporarily receives new incoming writes for the identified SMR drive. Then the identified SMR drive is updated from the SSD to restore the state of the identified SMR drive, and operations continue with normal writing only using the SMR drives in the RAID.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for rearranging a write operation in a shingled magnetic recording device
ActiveUS20190050327A1Facilitates write operationEasy to operateInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationShingled magnetic recordingOriginal data
One embodiment facilitates a write operation in a shingled magnetic recording device. During operation, the system receives, by a controller module of the device, a request to write first data, wherein the device has a plurality of bands with overlapping tracks for storing data. In response to determining that the first data is updated data corresponding to original data stored in a first band, the system appends the updated data to a second band with available storage space. The system merges the updated data with the original data.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
System, method and apparatus for shingled magnetic recording in disk drives
ActiveUS20130170061A1Effectively overwrite magnetic materialCarrier editingErasing methodShingled magnetic recordingData science
A method of targeted corruption of user data in a shingled magnetic recording disk includes identifying user data on a Track_N targeted for corruption; identifying a readback centerline of the Track_N; identifying a readback centerline of an adjacent track to Track_N; acquiring user data of the adjacent track; and rewriting the user data of the adjacent track with an offset write centerline to overwrite magnetic material at the readback centerlines of both Track_N and the adjacent track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
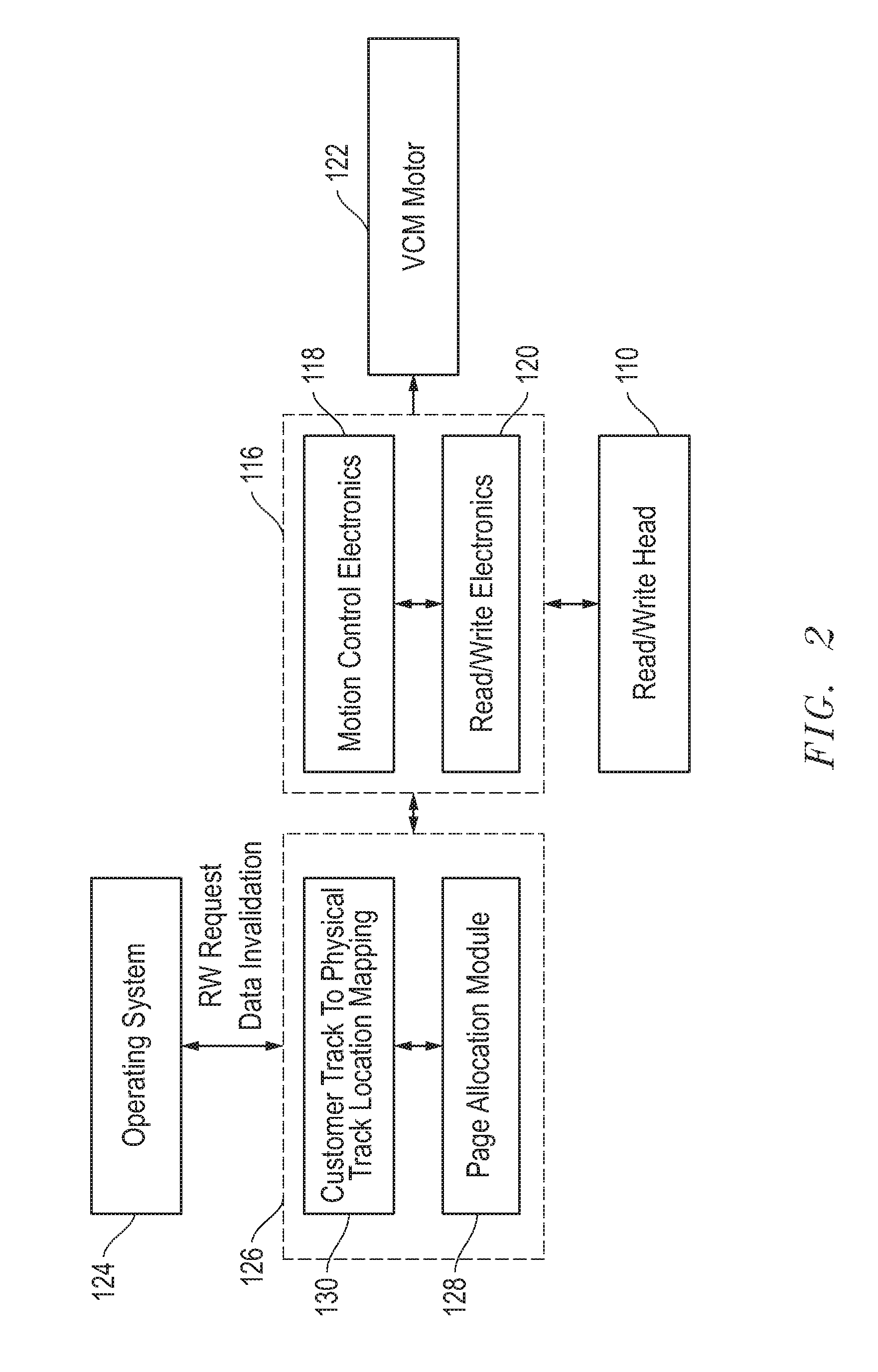
Indirection memory architecture with reduced memory requirements for shingled magnetic recording devices
ActiveUS20120303930A1Small sizeEfficient algorithmMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRecording on magnetic disksShingled magnetic recordingTheoretical computer science
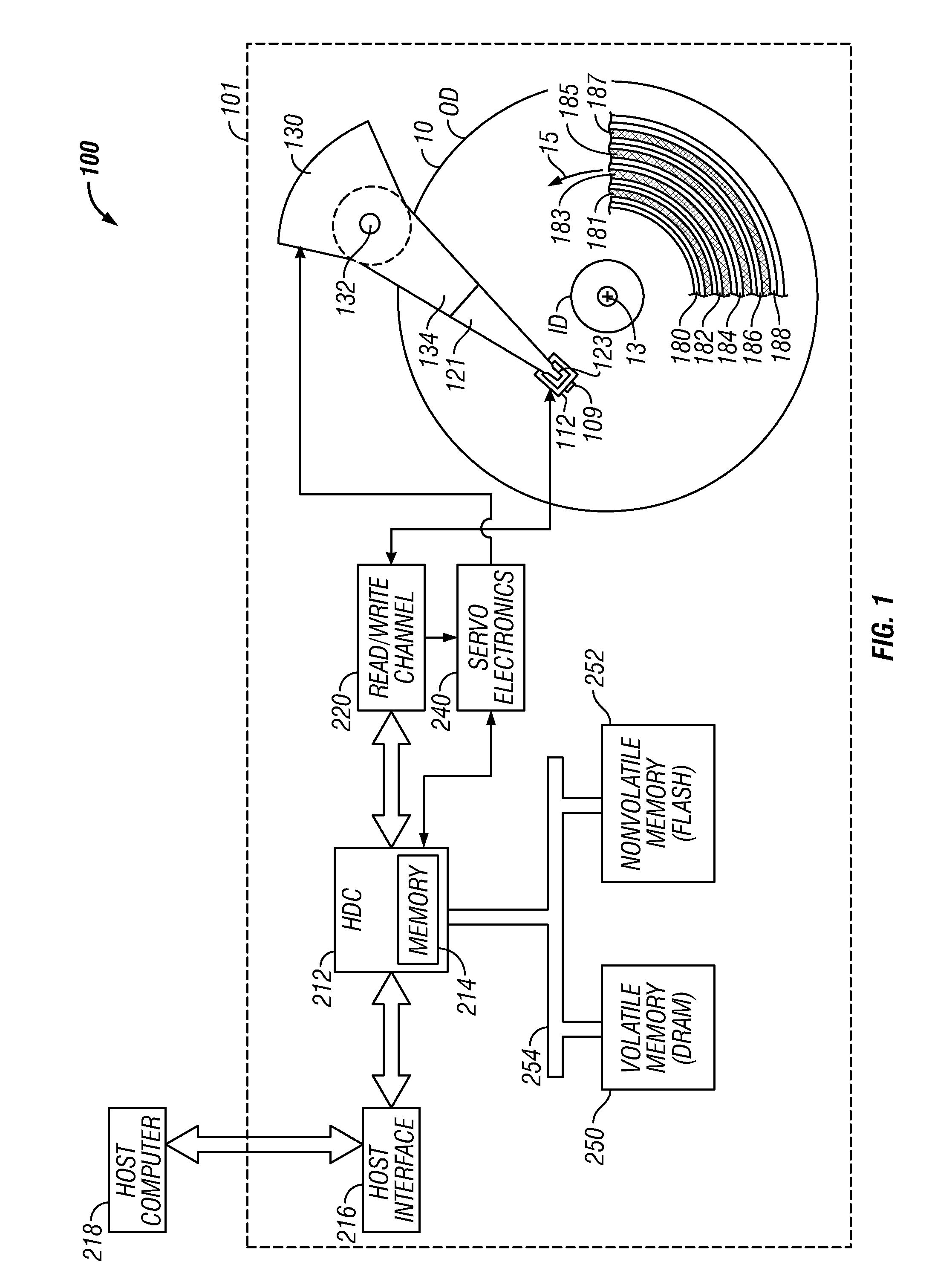
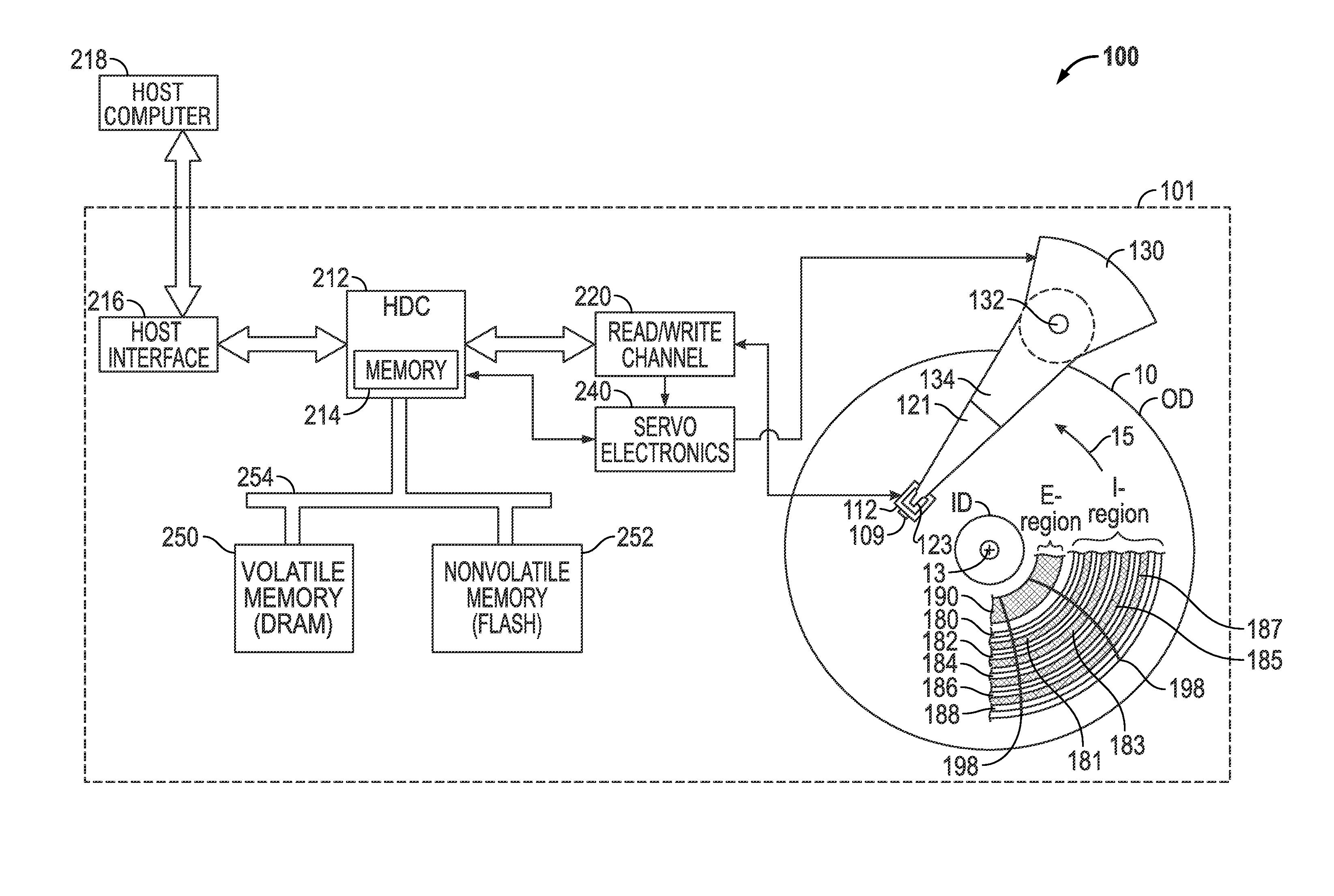
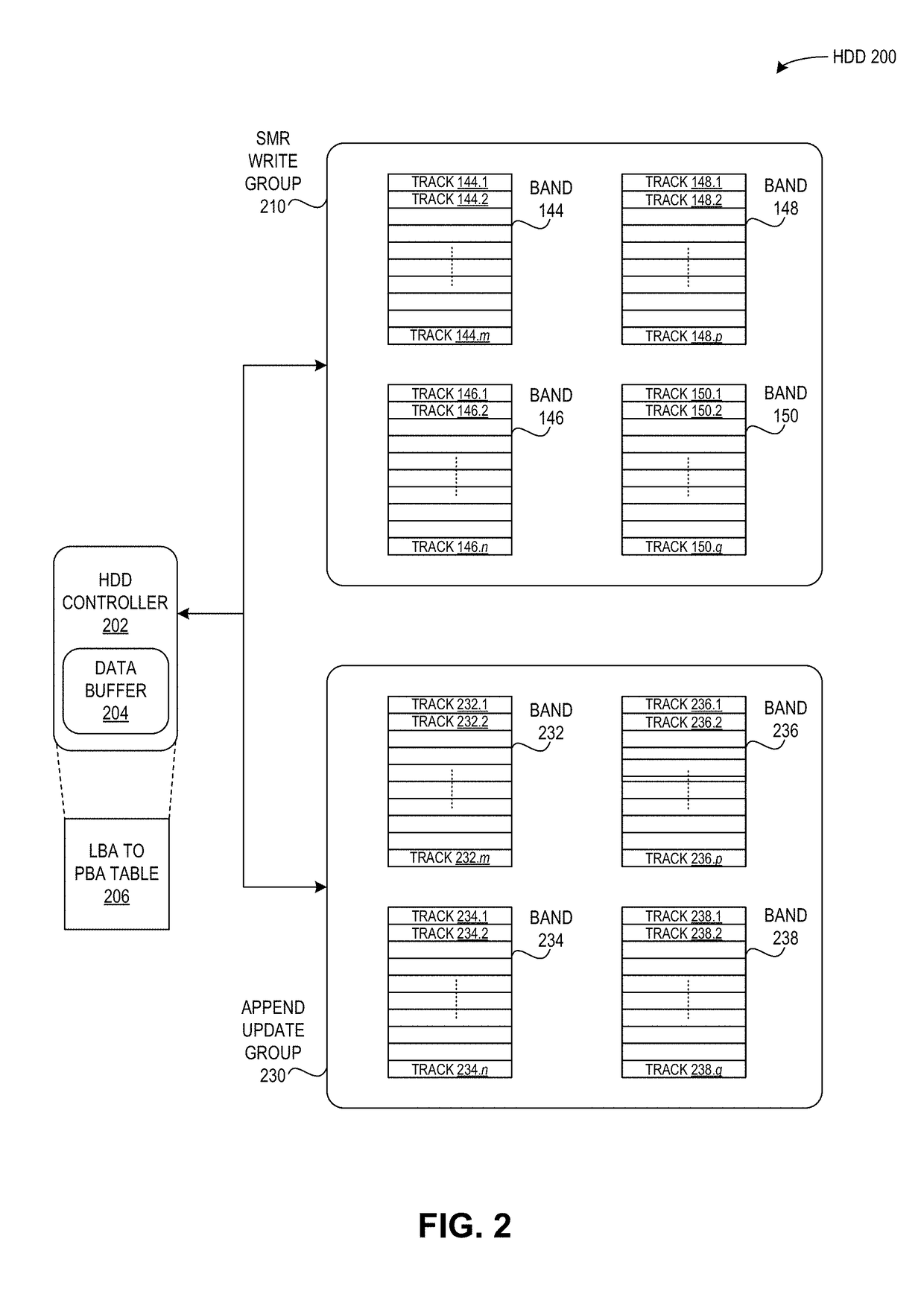
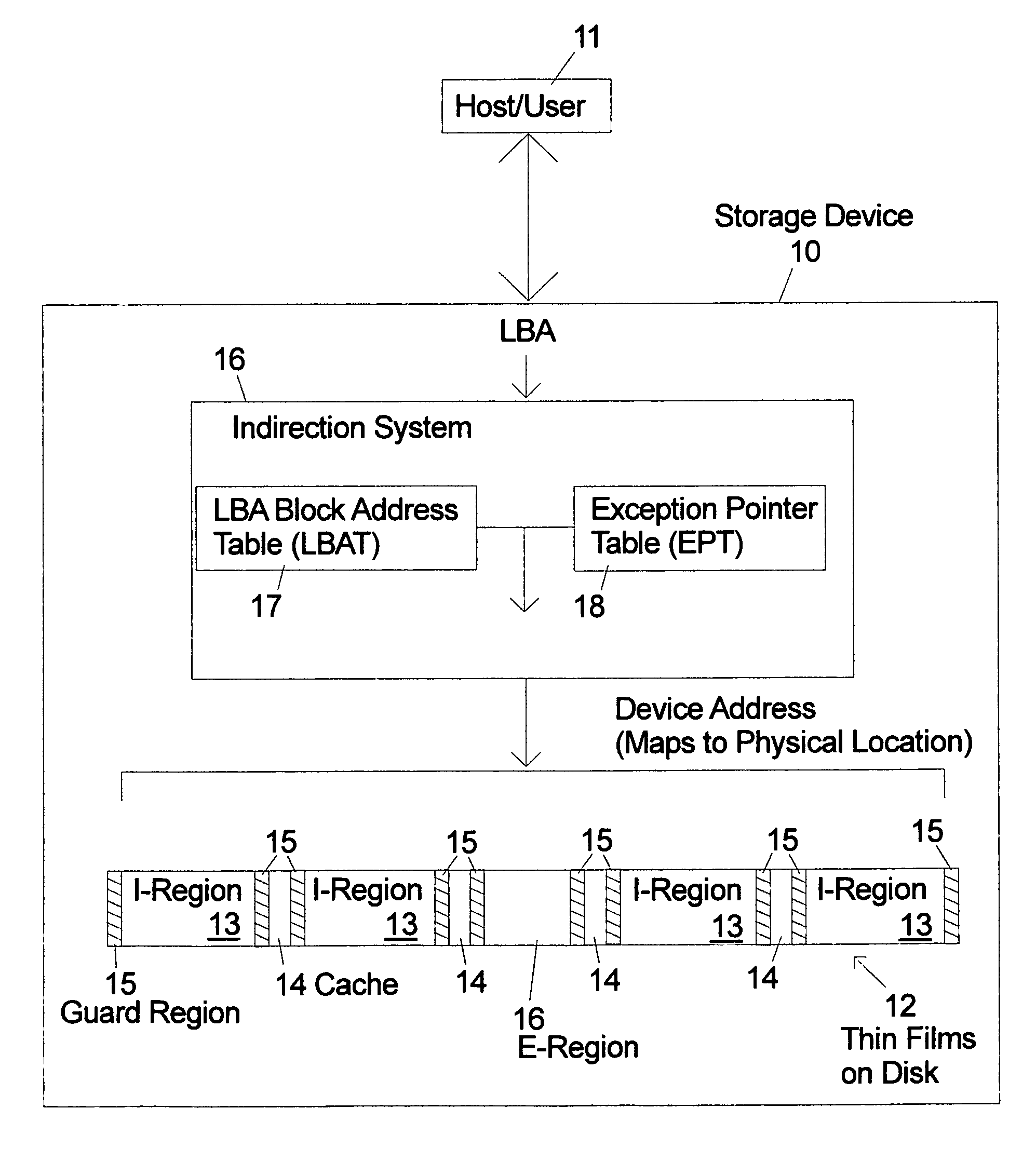
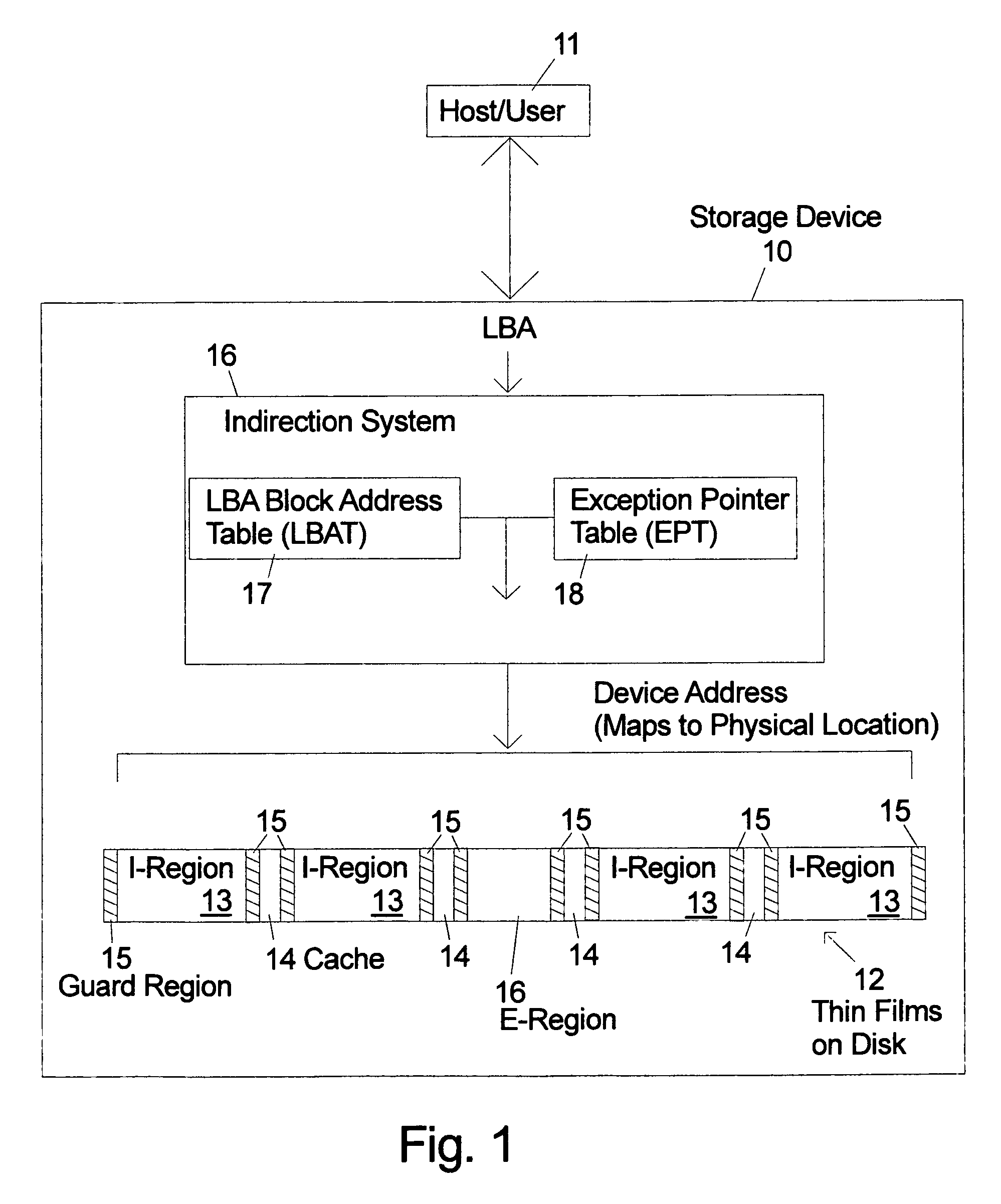
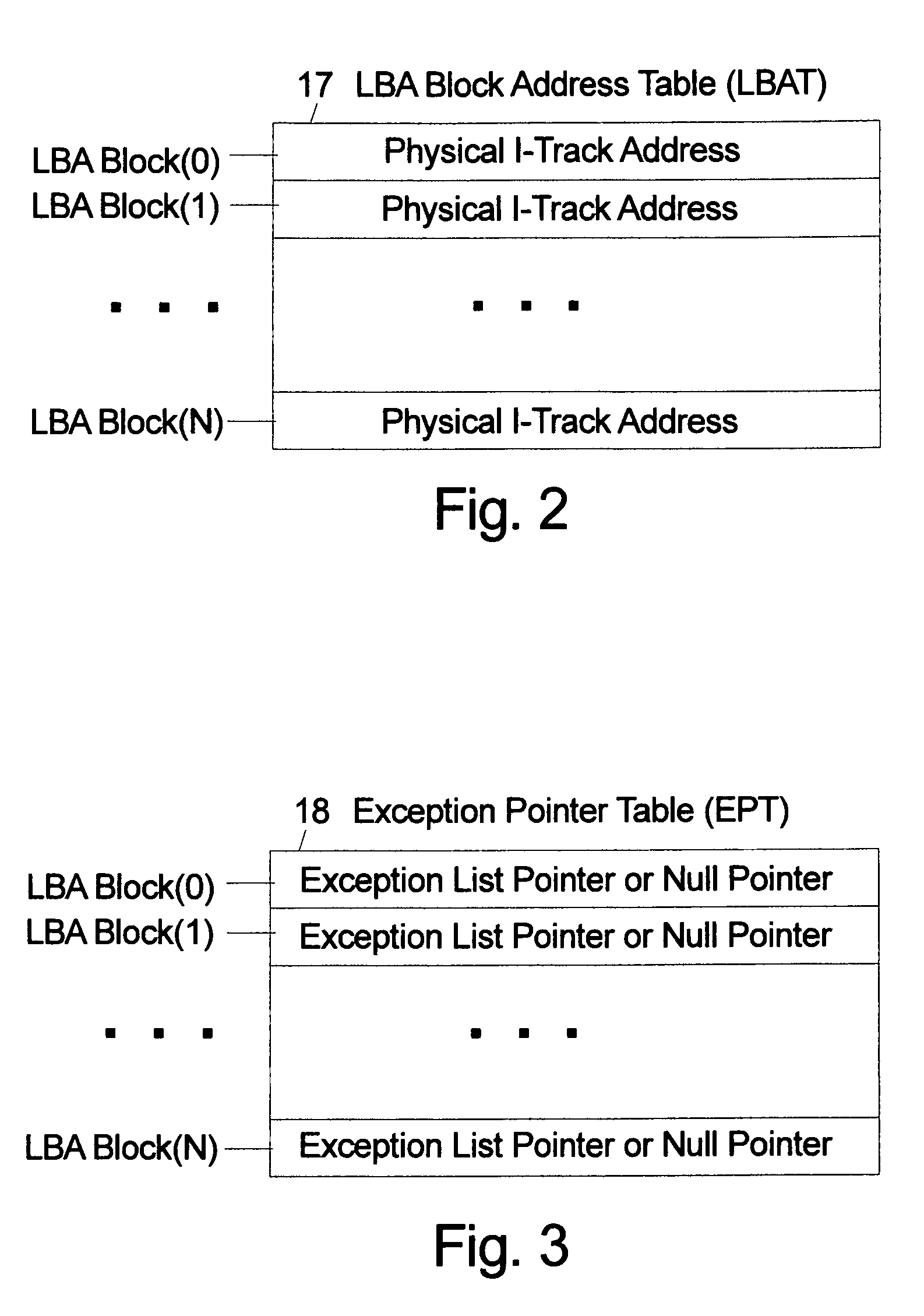
An indirection system in a shingled storage device is described that uses an efficient algorithm to map LBAs to DBAs based on a predetermined rule or assumption and then handles as exceptions LBAs that are not mapped according to the rule. The assumed rule is that a fixed-length set of sequential host LBAs are located at the start of an I-track. Embodiments of the invention use two tables to provide the mapping of LBAs to DBAs. The mapping assumed by the rule is embodied in the LBA Block Address Table (LBAT) which gives the corresponding I-track address for each LBA Block. The LBA exceptions are recorded using an Exception Pointer Table (EPT), which gives the pointer to the corresponding variable length Exception List for each LBA Block. The indexing into the LBAT and the EPT is made efficient by deriving the index from the LBA by a simple arithmetic operation.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Dynamic track pitch control for shingled magnetic recording (SMR)
ActiveUS8797672B2Driving/moving recording headsFilamentary/web record carriersShingled magnetic recordingPower flow
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Asymmetric MAMR head with self-aligned spin torque oscillator along flare edge for shingled magnetic recording
ActiveUS9406316B2Manufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsShingled magnetic recordingSpin torque oscillators
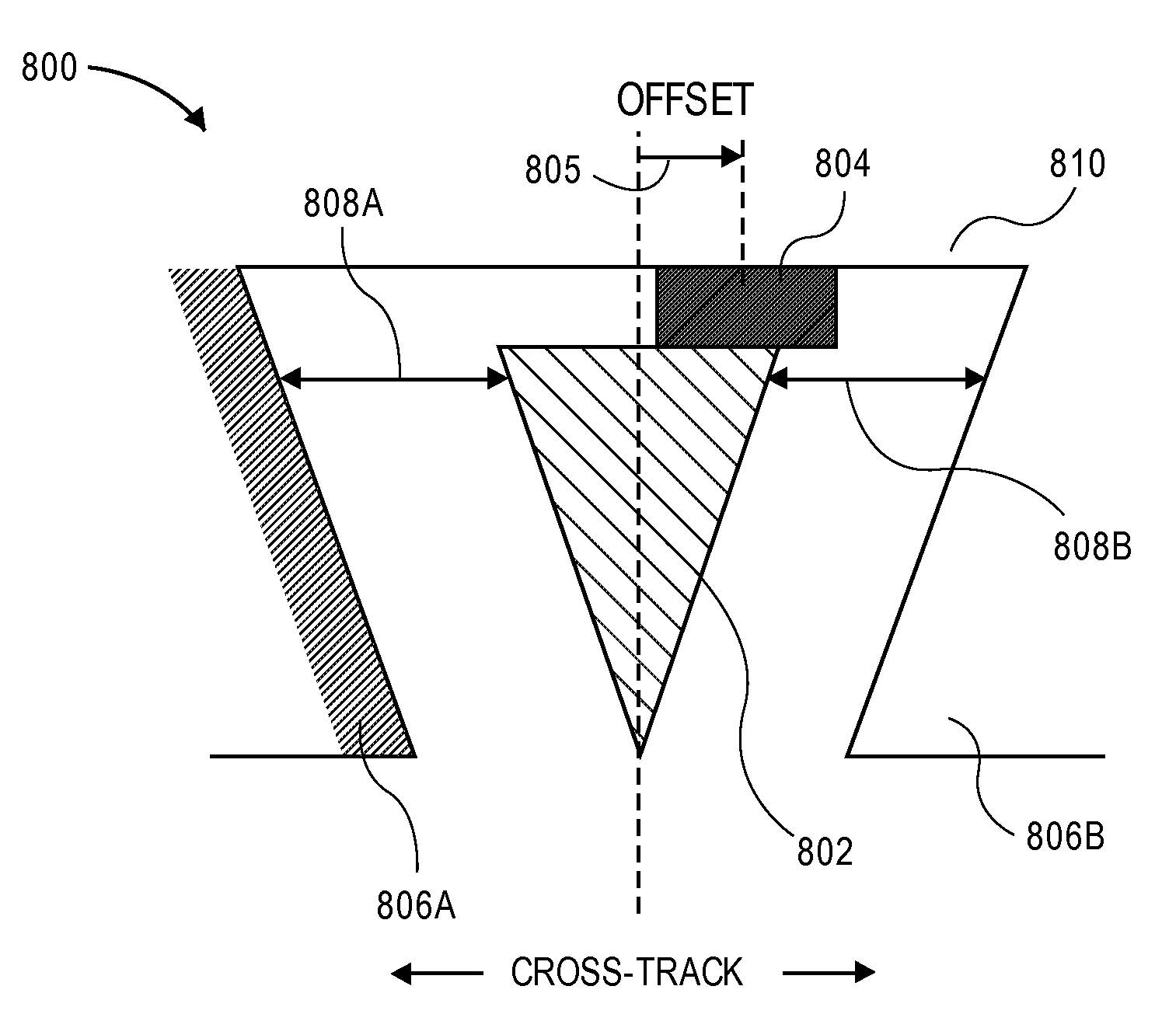
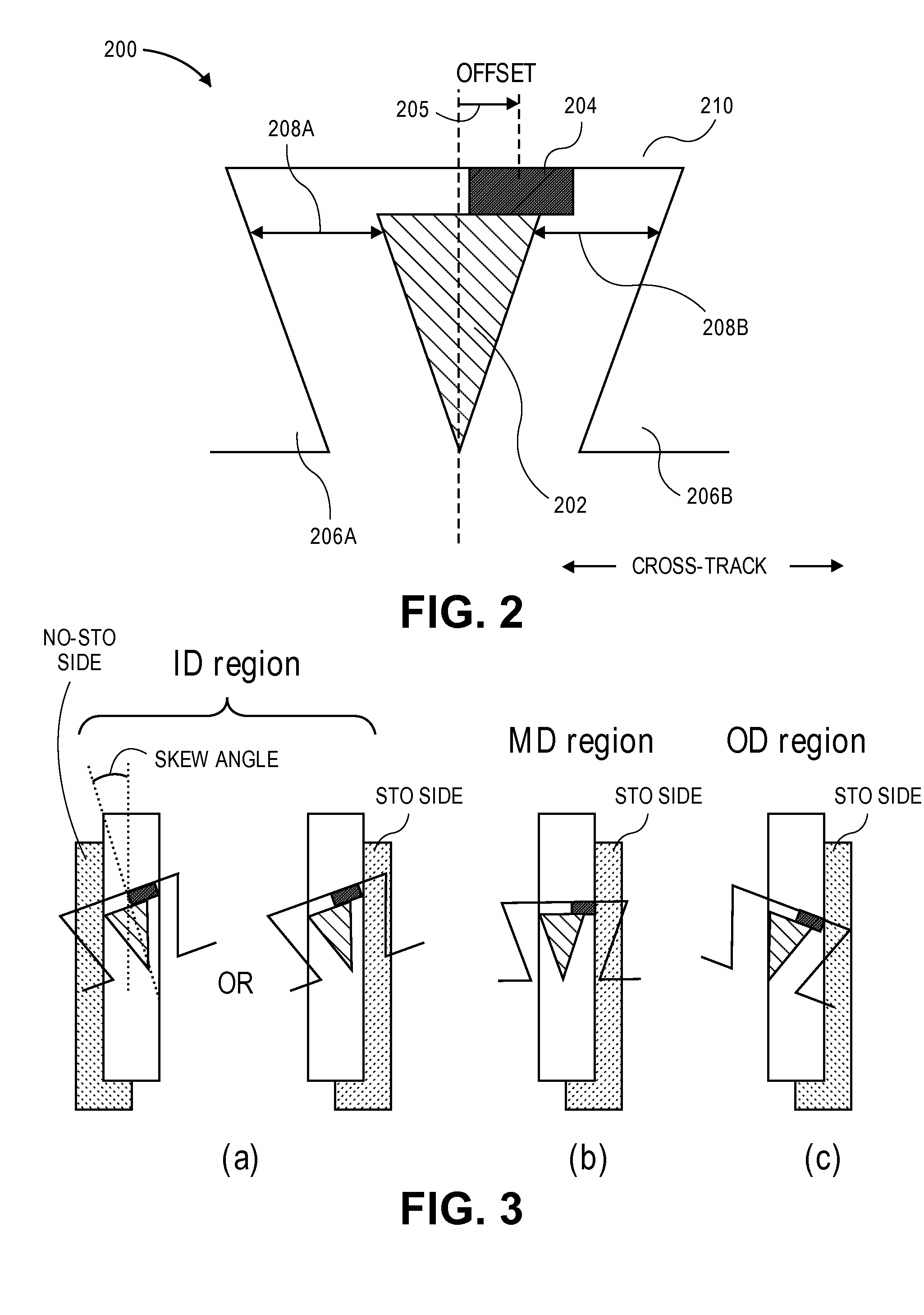
The present disclosure generally relates to the structure of a perpendicular magnetic write head for use in a magnetic disk drive. A shingled-microwave-assisted magnetic recording head for use in a high-areal-density hard disk drive comprises a trailing shield, a flare-shaped main pole, one or more side shields, a spin torque oscillator, and two asymmetric side gaps, where one side gap has a smaller width than the other side gap. The spin torque oscillator shares a first continuous edge with the main pole on a side adjacent the side gap having the smaller width and shares a second continuous edge adjacent a media facing surface. The angle of the spin torque oscillator and the main pole formed by the media facing surface and the narrow side gap is greater than about 90°.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and device for processing data and storage system
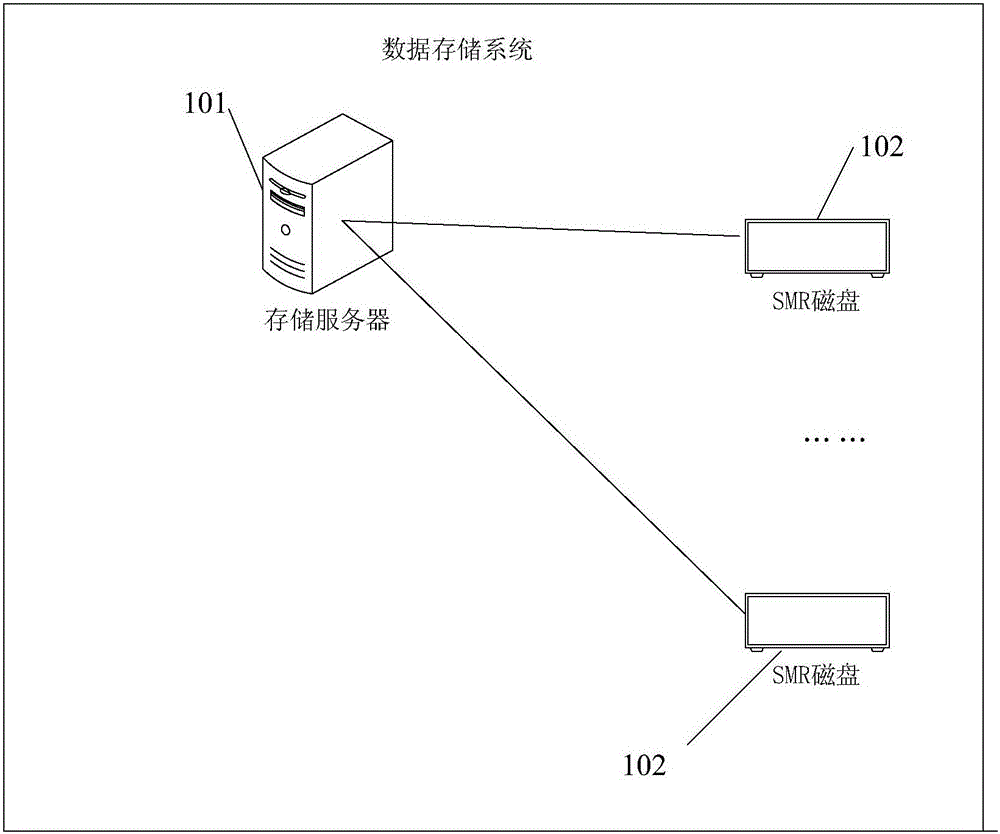
ActiveCN106201355AImplement parallel processingInput/output to record carriersShingled magnetic recordingData storage system
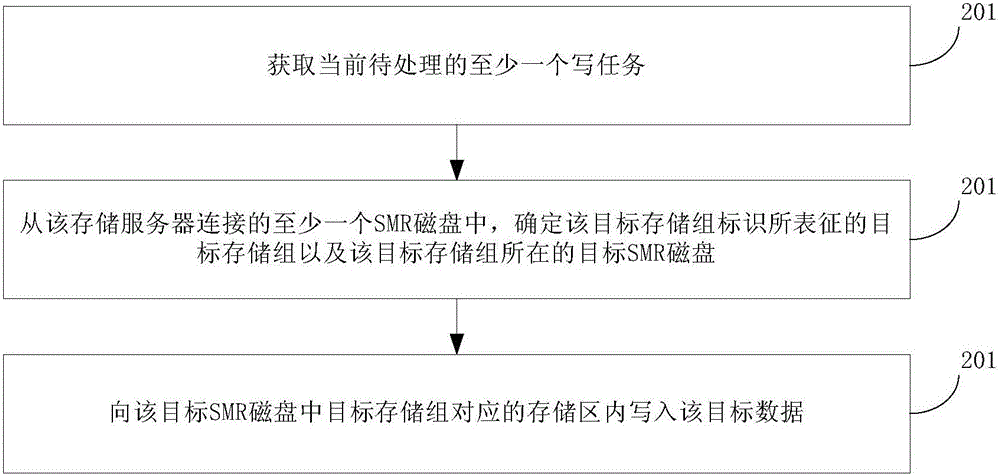
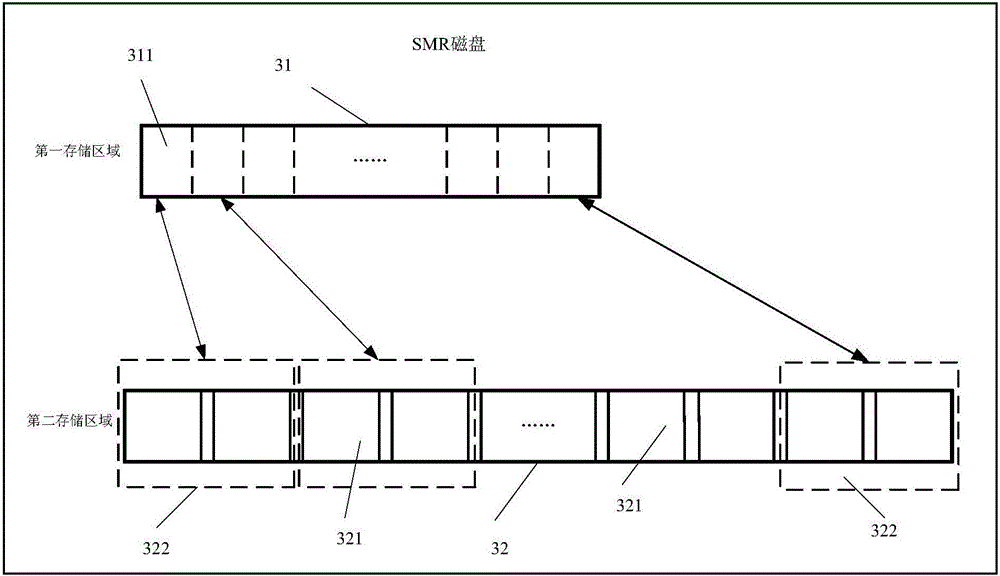
The invention provides a method and a device for processing data and a storage system. The data storage system comprises at least one storage server and at least one SMR (shingled magnetic recording) disk. The SMR disks are connected with the storage servers; a plurality of storage zones in second storage regions of the SMR disks are classified as a plurality of storage groups, each storage group comprises at least one storage zones, and each optional storage zone only belongs to the single corresponding storage group; at least one write task currently to be processed can be acquired by each storage server and comprises to-be-written target data and identification of the corresponding target storage groups, the different write tasks comprise the identification of the different target storage groups, and the target storage groups and the target SMR disks where the target storage groups are located can be determined by the storage servers; the target data can be written into the storage zones corresponding to the target storage groups in the target SMR disks. According to the scheme, the method, the device and the storage system have the advantages that the write performance of the SMR disks can be improved, and accordingly the write performance of the storage system on the basis of the SMR disks can be improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
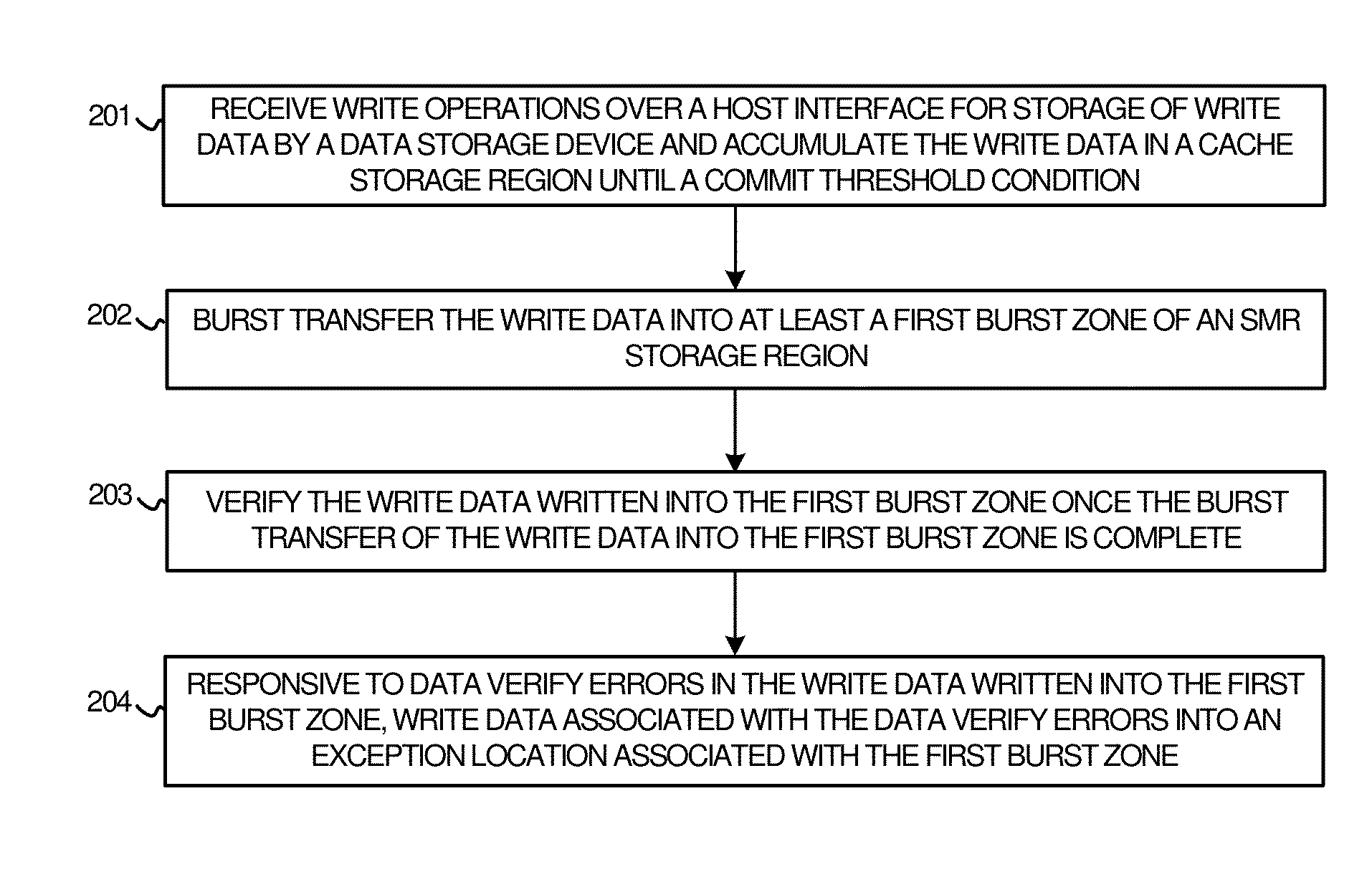
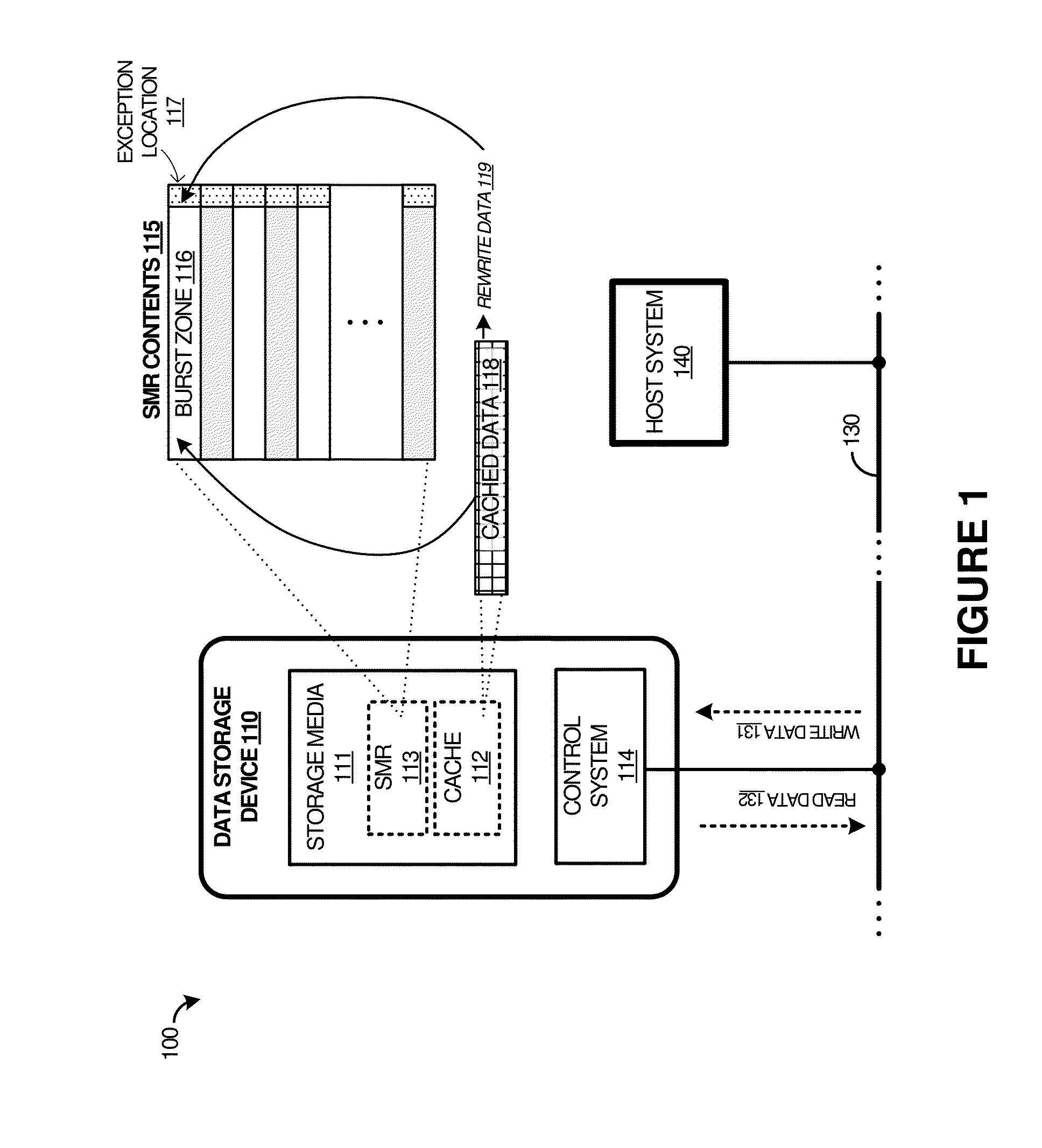
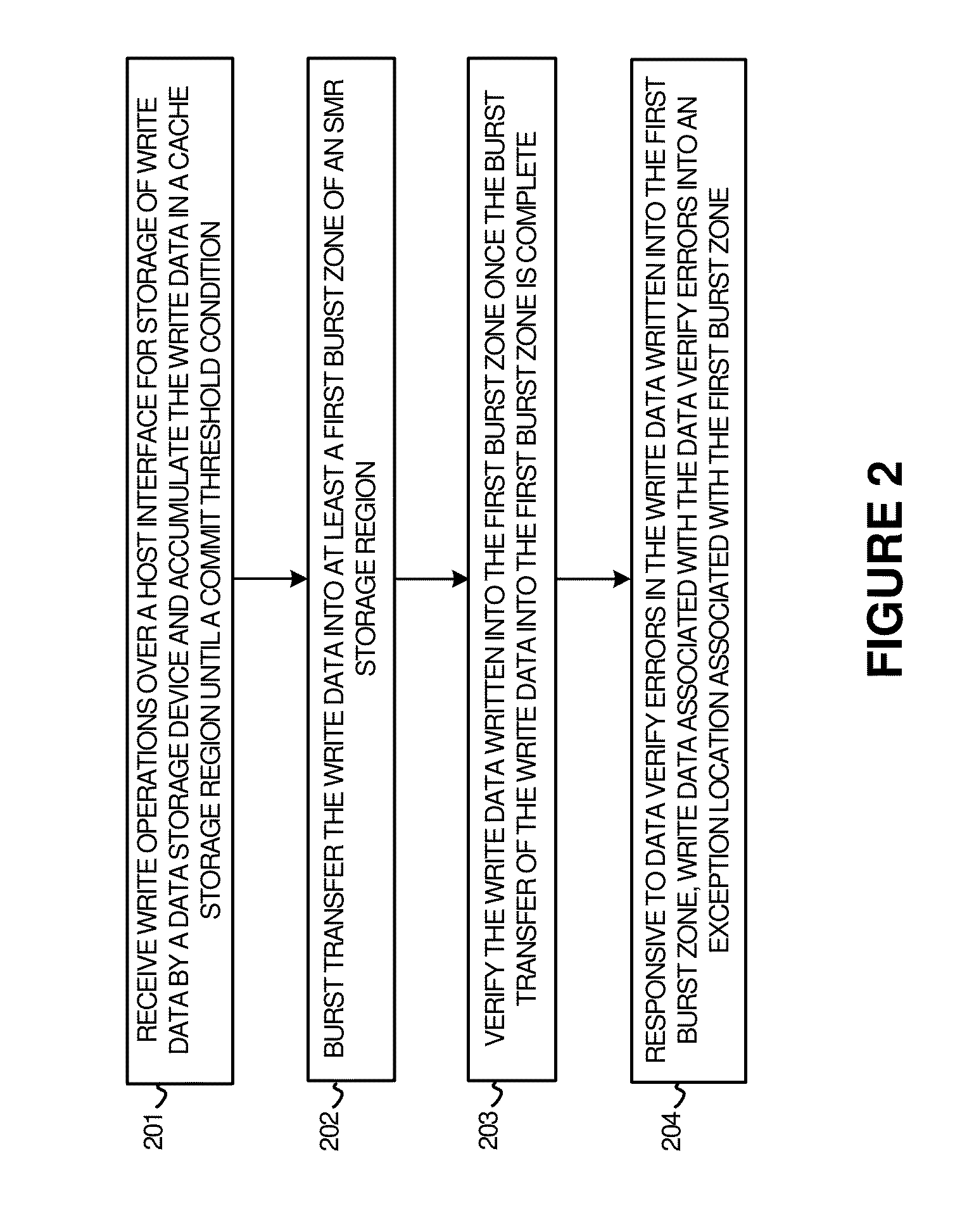
Efficient burst data verify in shingled data storage drives
ActiveUS9269376B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingData validation
To provide enhanced operation of data storage devices and systems, various systems, apparatuses, methods, and software are provided herein. In a first example, a data storage device is presented with storage media comprising a cache storage region and a shingled magnetic recording (SMR) storage region that is divided into burst zones. A storage control system receives write operations and accumulates write data in the cache storage region until a commit threshold condition. Responsively, the storage control system transfers the write data into a burst zone of the SMR storage region, and verifies the write data written into the burst zone once the burst transfer is complete. Responsive to data verify errors in the write data written into the burst zone, the storage control system writes data associated with the data verify errors into an exception location associated with the burst zone.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Shingled magnetic recording disk drive with compensation for the effect of far track erasure (FTE) on adjacent data bands
ActiveUS20130321948A1Eliminate the effects ofDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingBoundary region
A shingled magnetic recording (SMR) disk drive has concentric shingled data tracks having data sectors with physical block addresses (PBAs), with the tracks being arranged in annular bands separated by annular inter-band gaps. The disk drive also has an on-disk extended cache region and may have writable inter-band cache (IBC) tracks in the inter-band gaps. A count is maintained in memory for each band and each IBC, and the count is incremented for each writing to a band or an IBC. When a count for a band or IBC reaches a predetermined threshold, the data is read from the tracks in the boundary region of the adjacent band that are within the range of the FTE and that data is then written to the extended cache. The FTE-affected tracks are then invalidated, meaning that PBAs can no longer be assigned to the data sectors in those tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
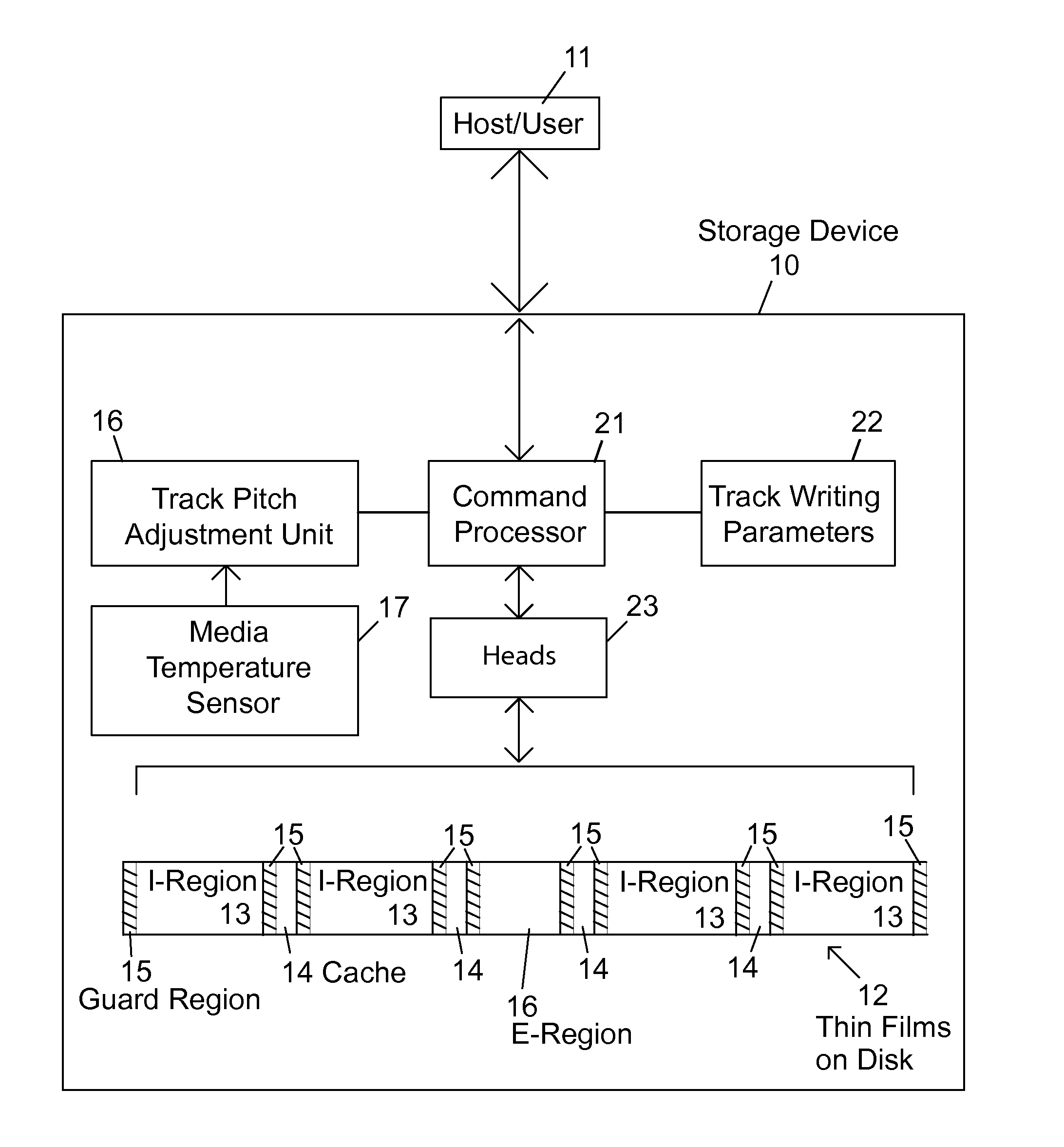
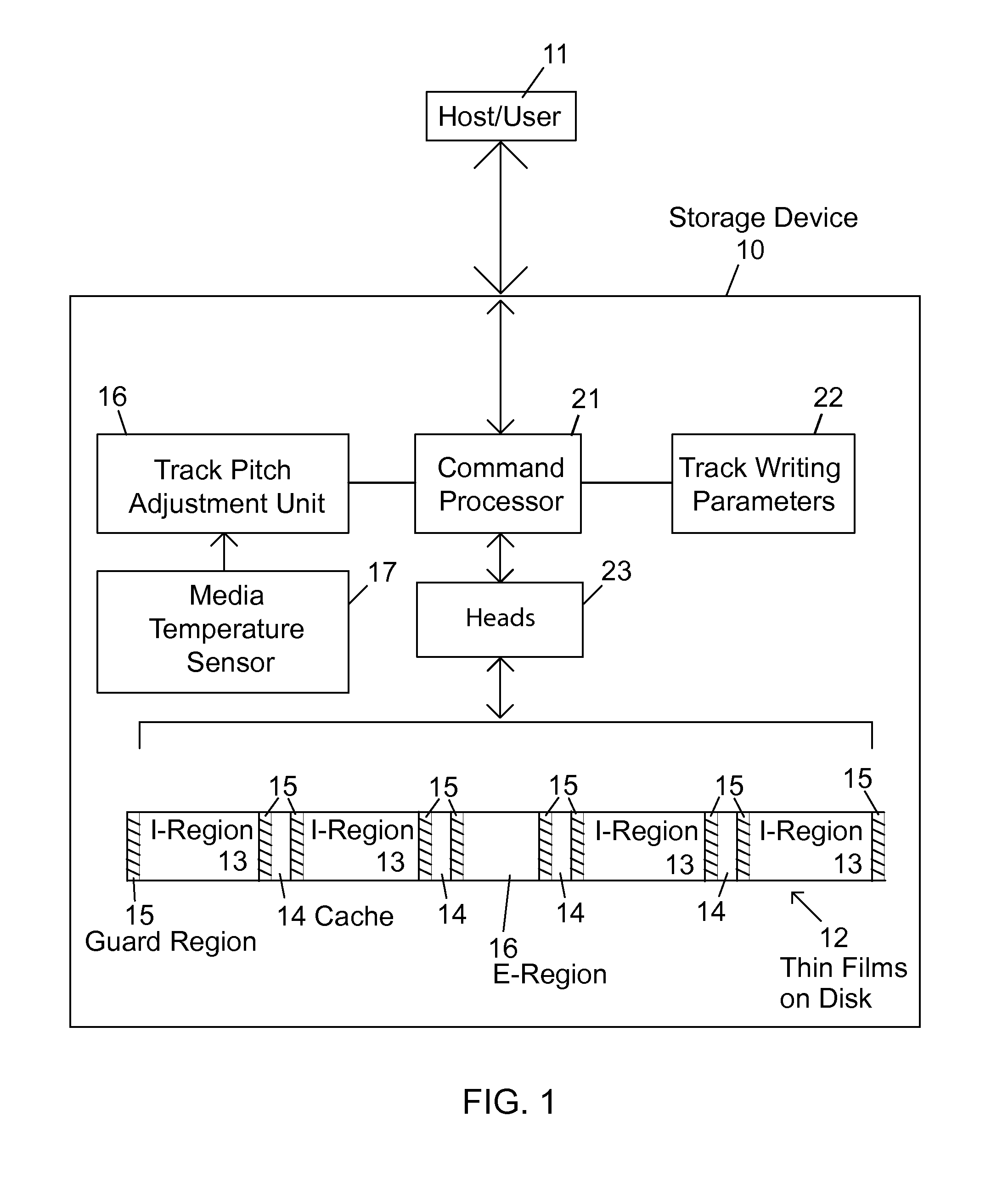
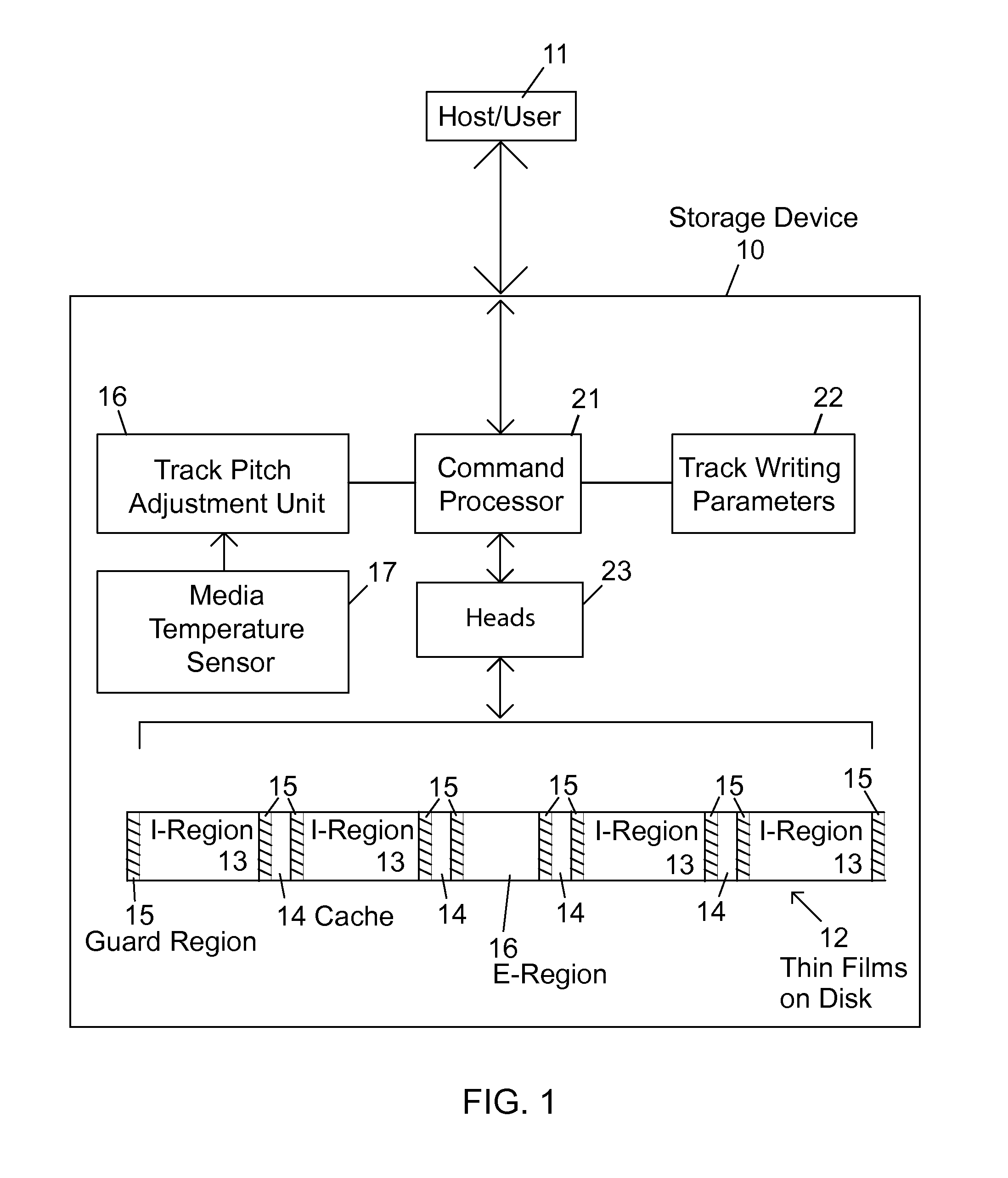
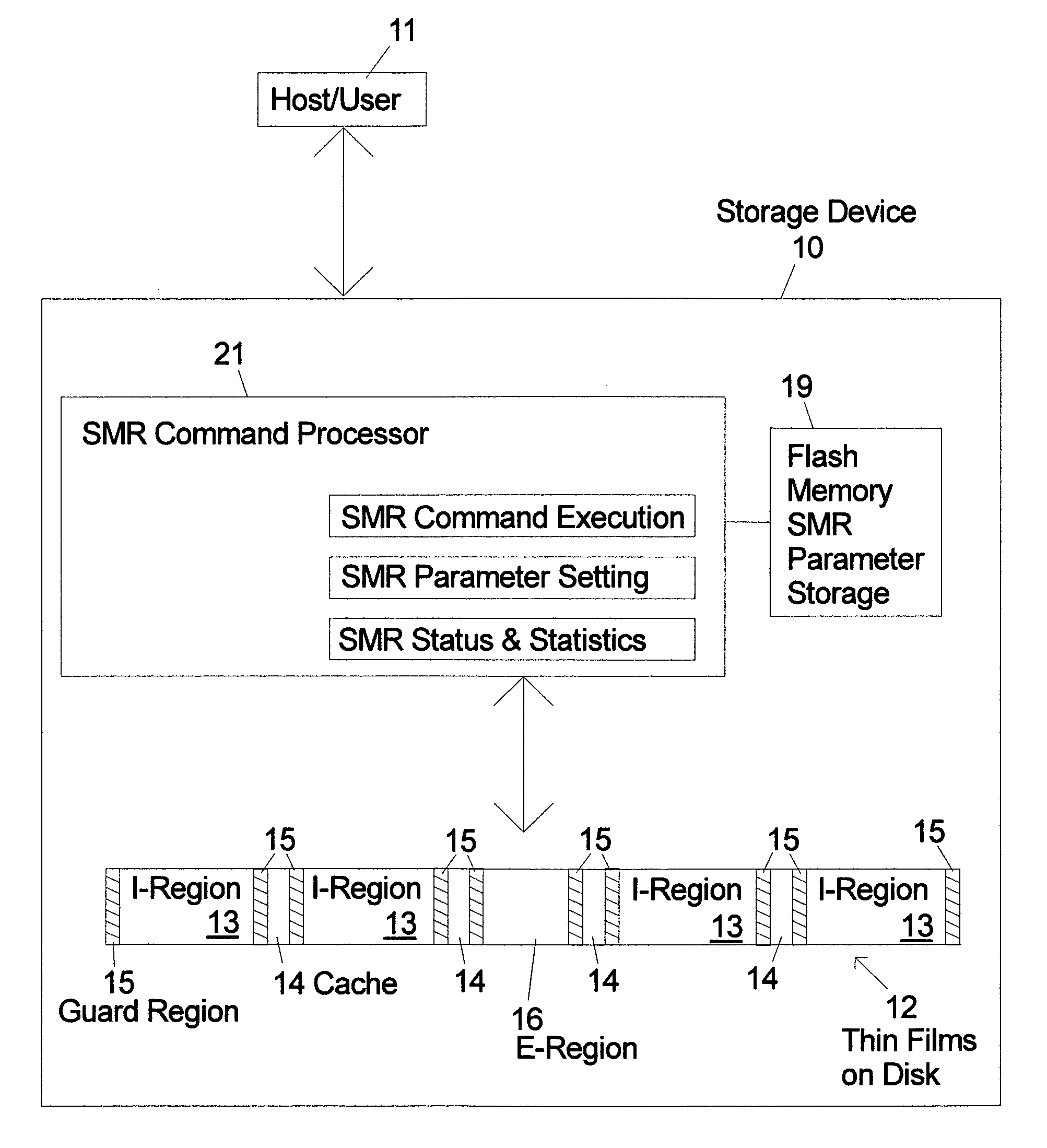
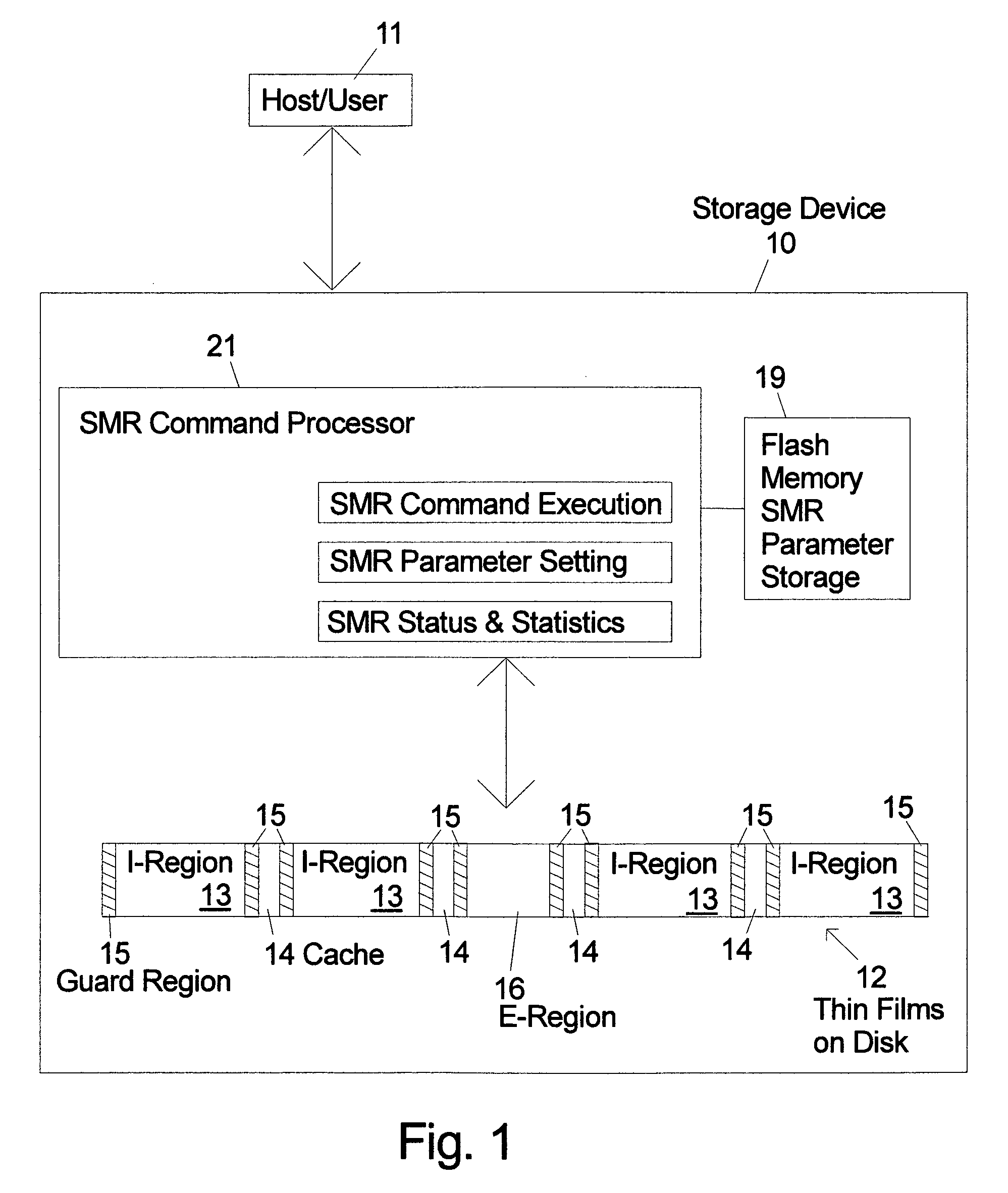
SMR storage device with user controls and access to status information and parameter settings
ActiveUS20120303889A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationRecording on magnetic disksShingled magnetic recordingComputer science
Shingled magnetic recording (SMR) devices are described that include a command processor for accepting commands from the host / user for executing selected SMR related operations, setting selected SMR parameters and reading selected SMR related statistics and status indicators. The commands allow a host / user to control defragmentation and destaging operations. Embodiments include some or all of the set of features allowing selection of formatting settings, selection of optimization settings; command to immediately run defragmentation operation; command to change waiting time before starting defragmentation operation; and command to temporarily suspend defragmentation operation until certain usage threshold is met (e.g., E-region(s) near full).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
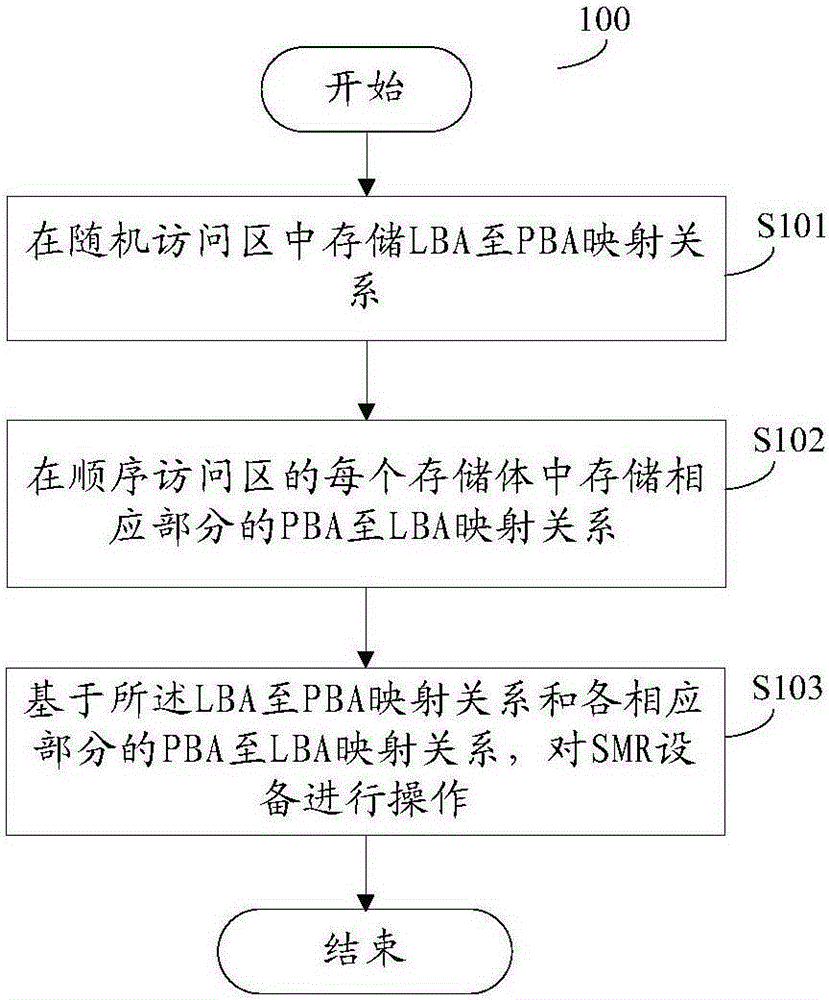
Method and device for operating shingled magnetic recording equipment
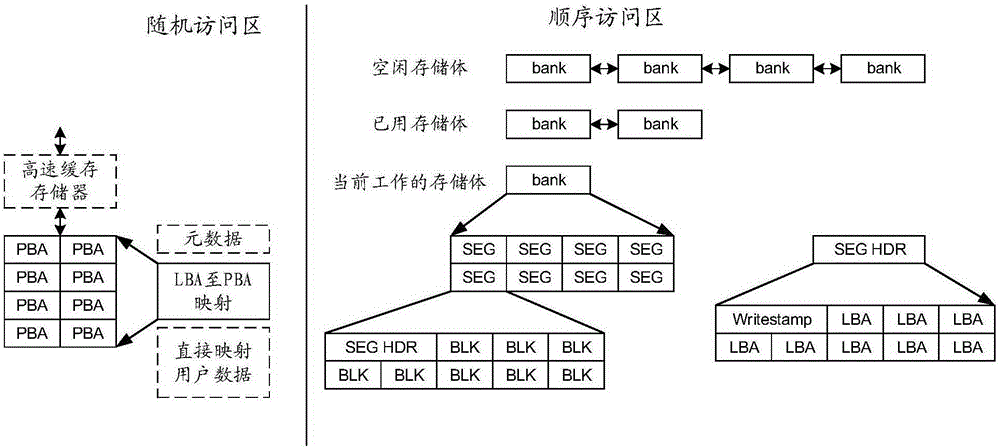
ActiveCN106548789AEasy to useMemory architecture accessing/allocationHeads using thin filmsShingled magnetic recordingOperational system
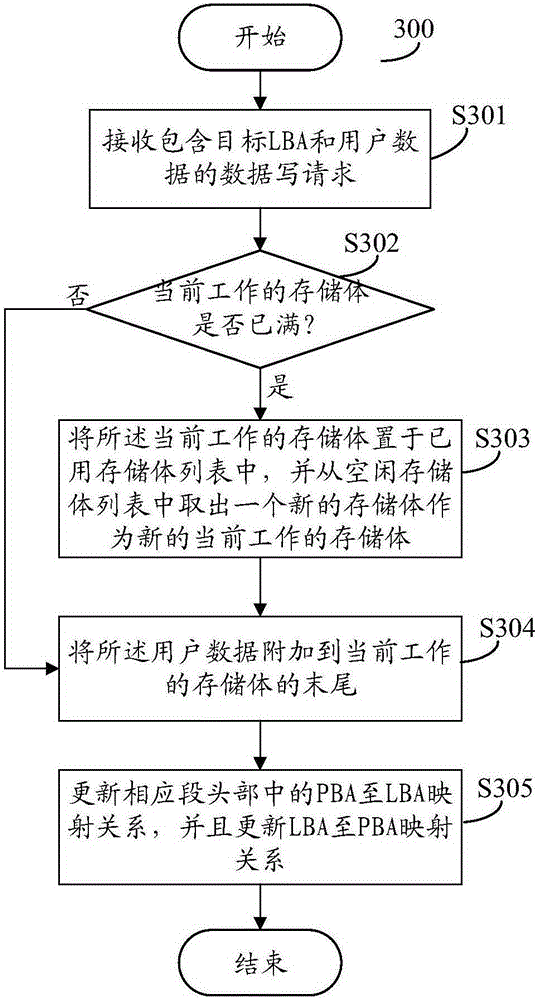
The invention provides a method and a device for operating shingled magnetic recording equipment. The shingled magnetic recording equipment comprises a random access area and a sequential access area. Data can be randomly read and written in the random access area. Data can be sequentially read and written in the sequential access area, and the sequential access area is logically divided into multiple memory banks independent of one another in operation. The method comprises the following steps: storing the LBA-to-PBA mapping relation in the random access area; respectively storing the PBA-to-LBA mapping relation of a corresponding part in each of the multiple memory banks in the sequential access area; and operating the shingled magnetic recording equipment based on the LBA-to-PBA mapping relation and the PBA-to-LBA mapping relation. According to the technical scheme of the invention, random access operation which cannot be supported directly by shingled magnetic recording equipment can be supported, so that the equipment has backward compatibility with an operating system or a file system, and convenience is brought to users.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Shingled magnetic recording disk drive with inter-band disk cache and minimization of the effect of far track erasure on adjacent data bands
ActiveUS20130246703A1Minimize impactRaise countMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
A shingled magnetic recording hard disk drive that uses writeable cache tracks in the inter-band gaps between the annular data bands minimizes the effect of far track erasure (FTE) in the boundary regions of annular data bands caused by writing to the cache tracks. Based on the relative FTE effect for all the tracks in a range of tracks of the cache track being written, a count increment (CI) table or a cumulative count increment (CCI) table is maintained. For every writing to a cache track, a count for each track in an adjacent boundary region, or a cumulative count for each adjacent boundary region, is increased. When the count value for a track, or the cumulative count for a boundary region, reaches a predetermined threshold the data is read from that band and rewritten to the same band.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Shingled magnetic recording (SMR) disk drive with verification of written data
ActiveUS8665545B2Improve writing efficiencyLow densityRecord information storageCarrier monitoringData validationShingled magnetic recording
A “write-squeeze-verify” method is used for verification of the data that has been written in the annular bands of a shingled magnetic recording disk drive. The writing of data along a track overwrites a portion of the previously written track and thus “squeezes” the data of the previously written track to thereby form a “shingled data track” (SDT). The data in each SDT is read back and verified by an error correction check using error correction bits associated with the data written in the SDT, or by comparing the readback data with the data stored in memory. If the data read back is not verified, a write error counter is incremented and a write error frequency is calculated. One or more attempts to write the data can be performed. If the data in the SDT cannot be verified after the attempted rewrite(s), then a “re-try fail” is reported.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for shingled magnetic recording in disk drives
ActiveUS8559121B2Effectively overwrite magnetic materialCarrier editingErasing methodShingled magnetic recordingData science
A method of targeted corruption of user data in a shingled magnetic recording disk includes identifying user data on a Track_N targeted for corruption; identifying a readback centerline of the Track_N; identifying a readback centerline of an adjacent track to Track_N; acquiring user data of the adjacent track; and rewriting the user data of the adjacent track with an offset write centerline to overwrite magnetic material at the readback centerlines of both Track_N and the adjacent track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
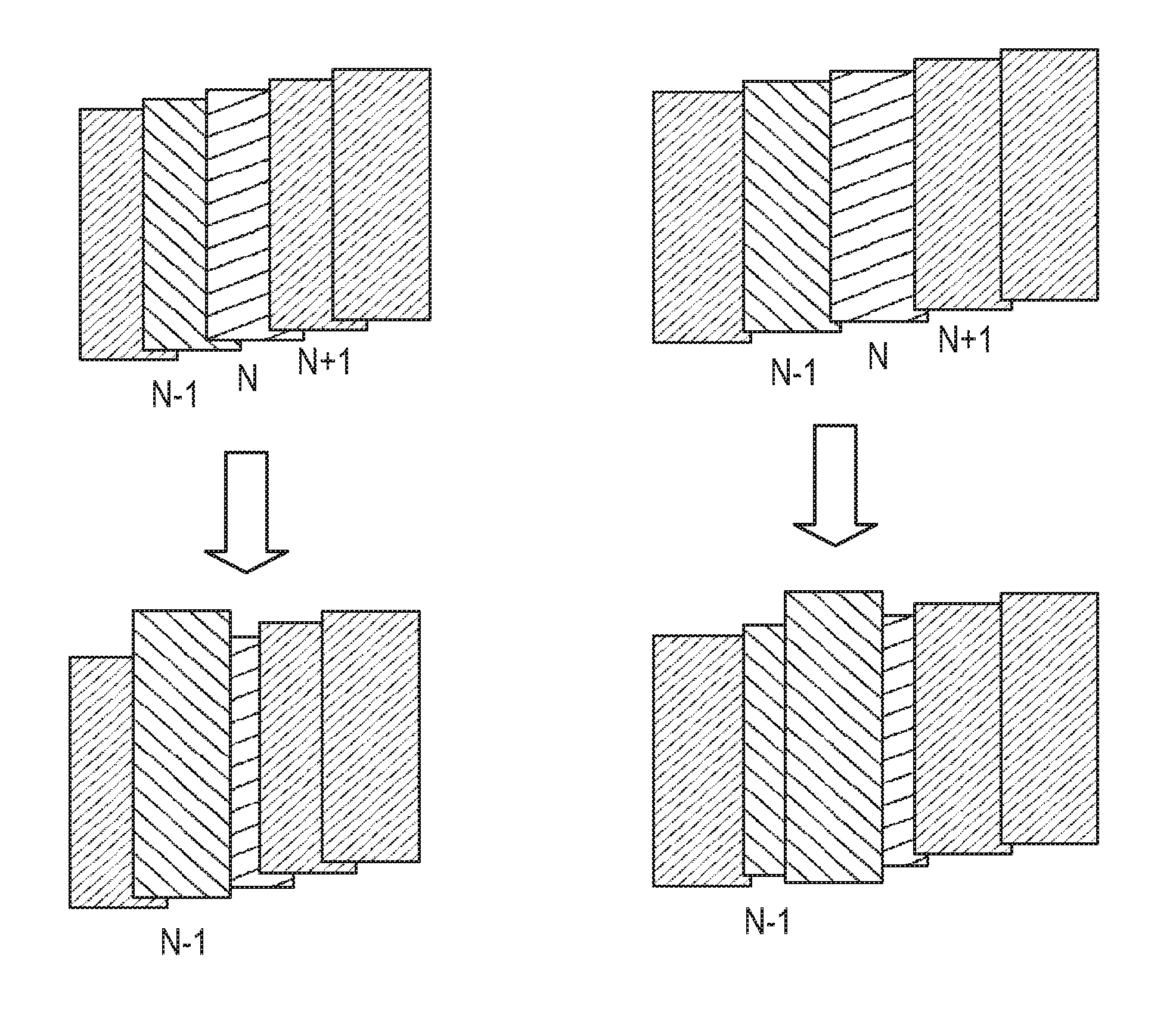
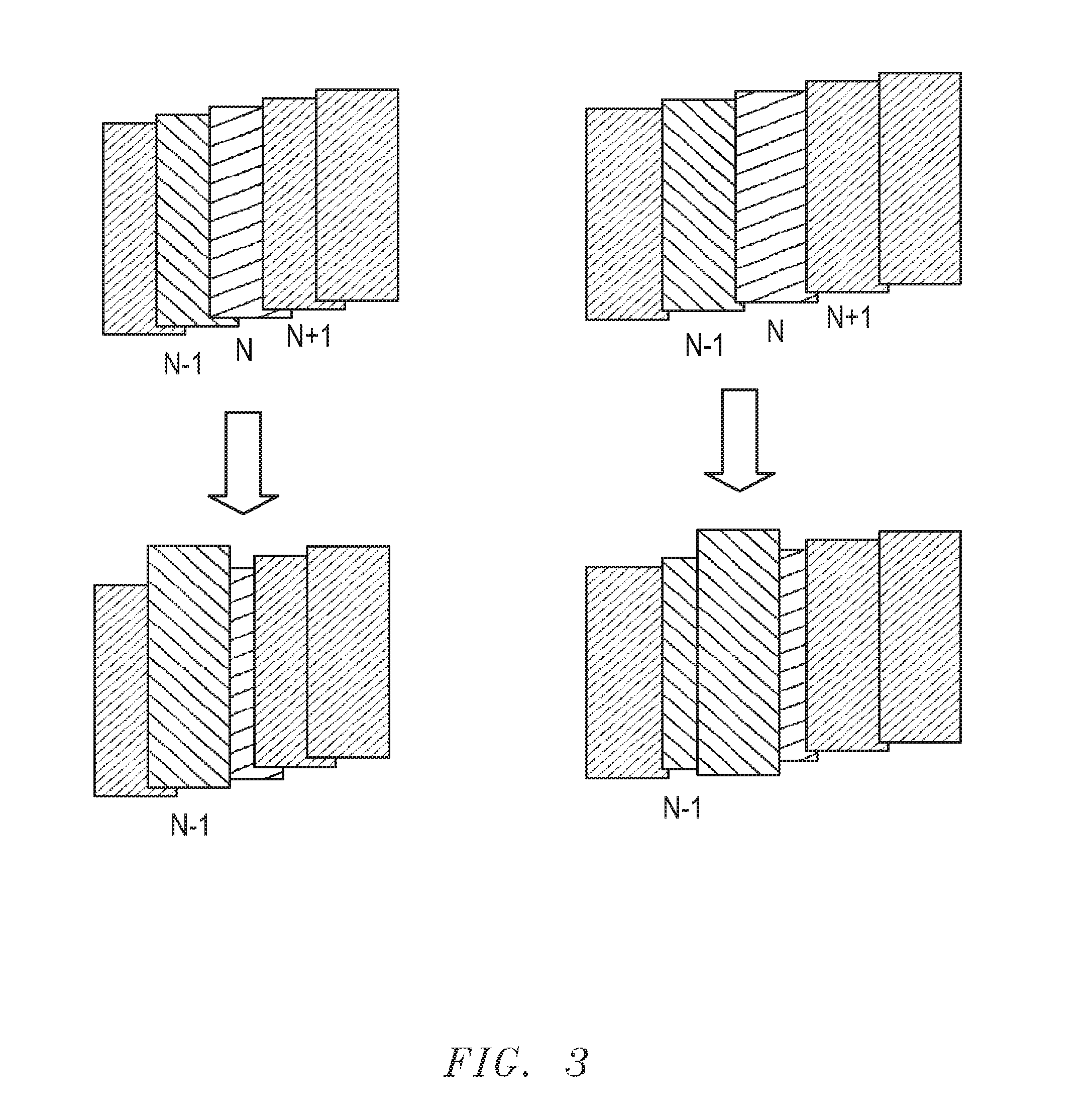
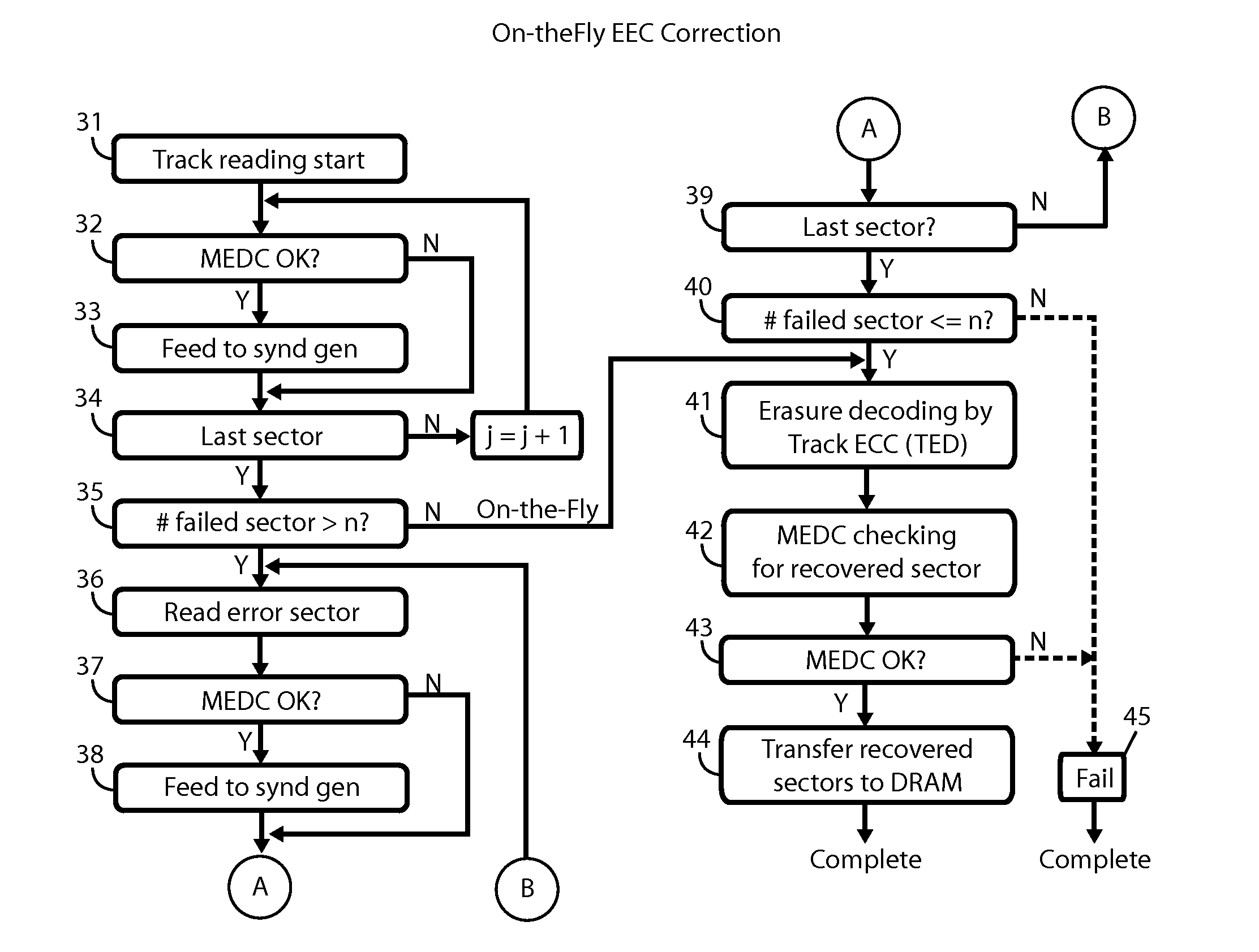
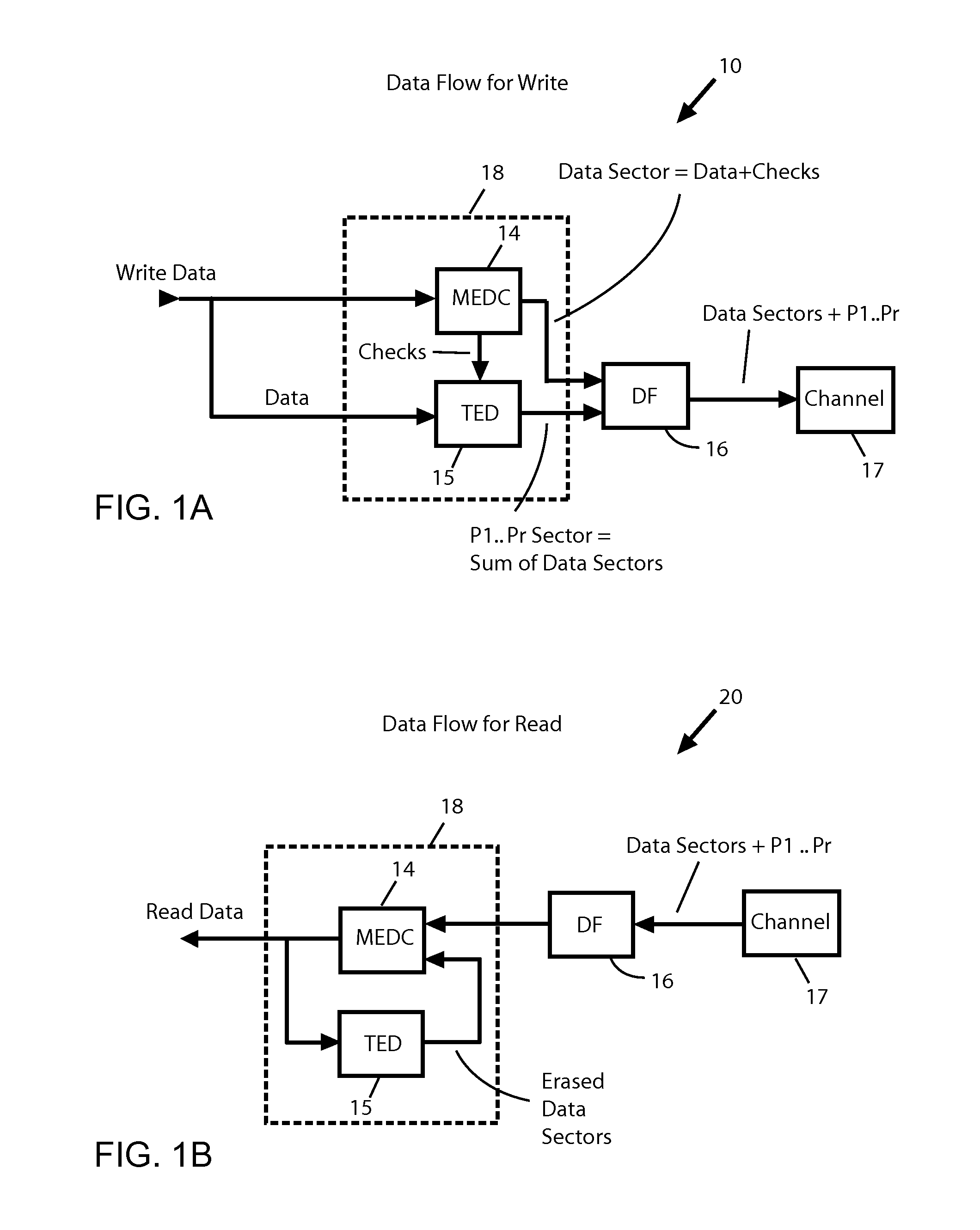
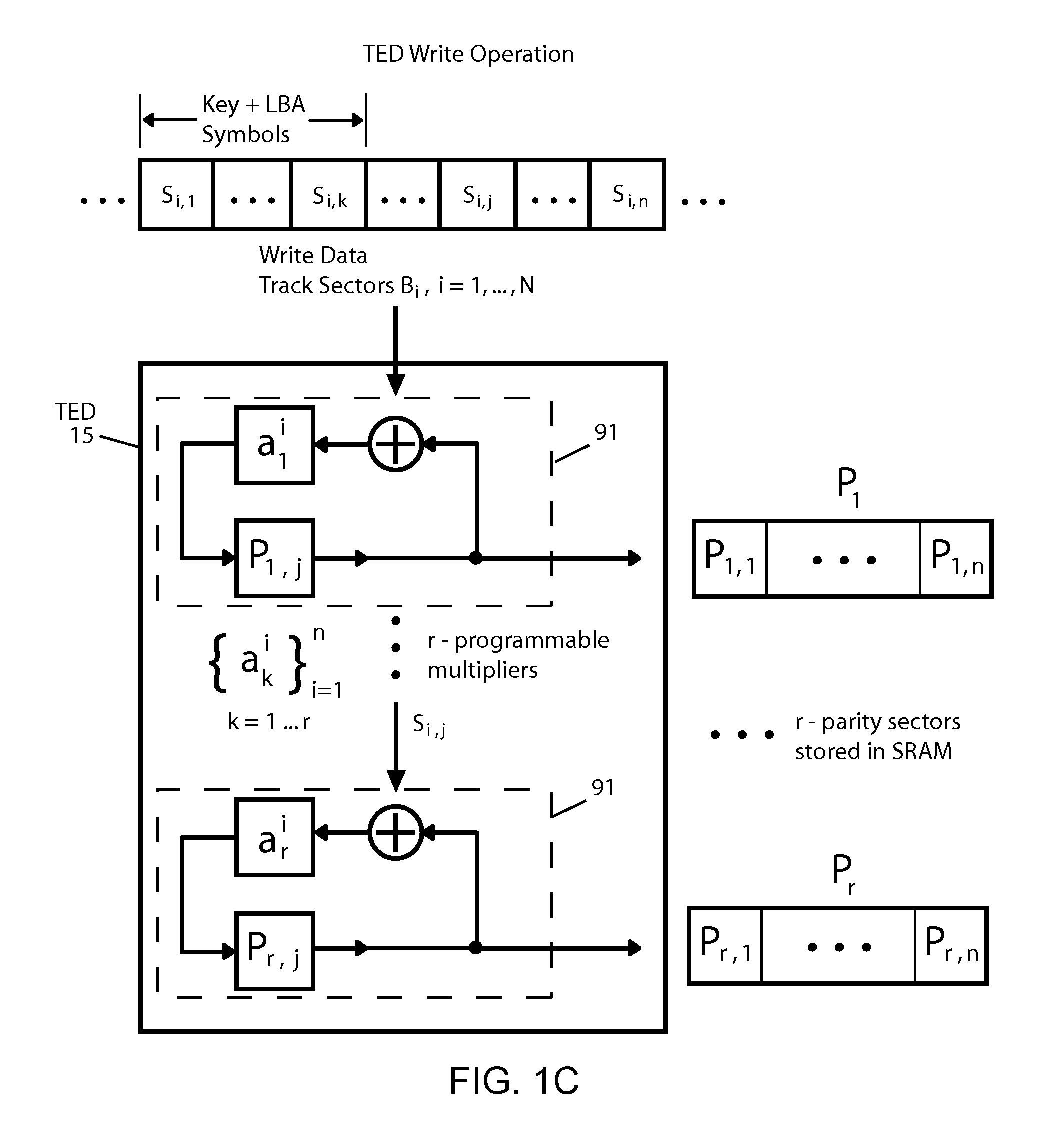
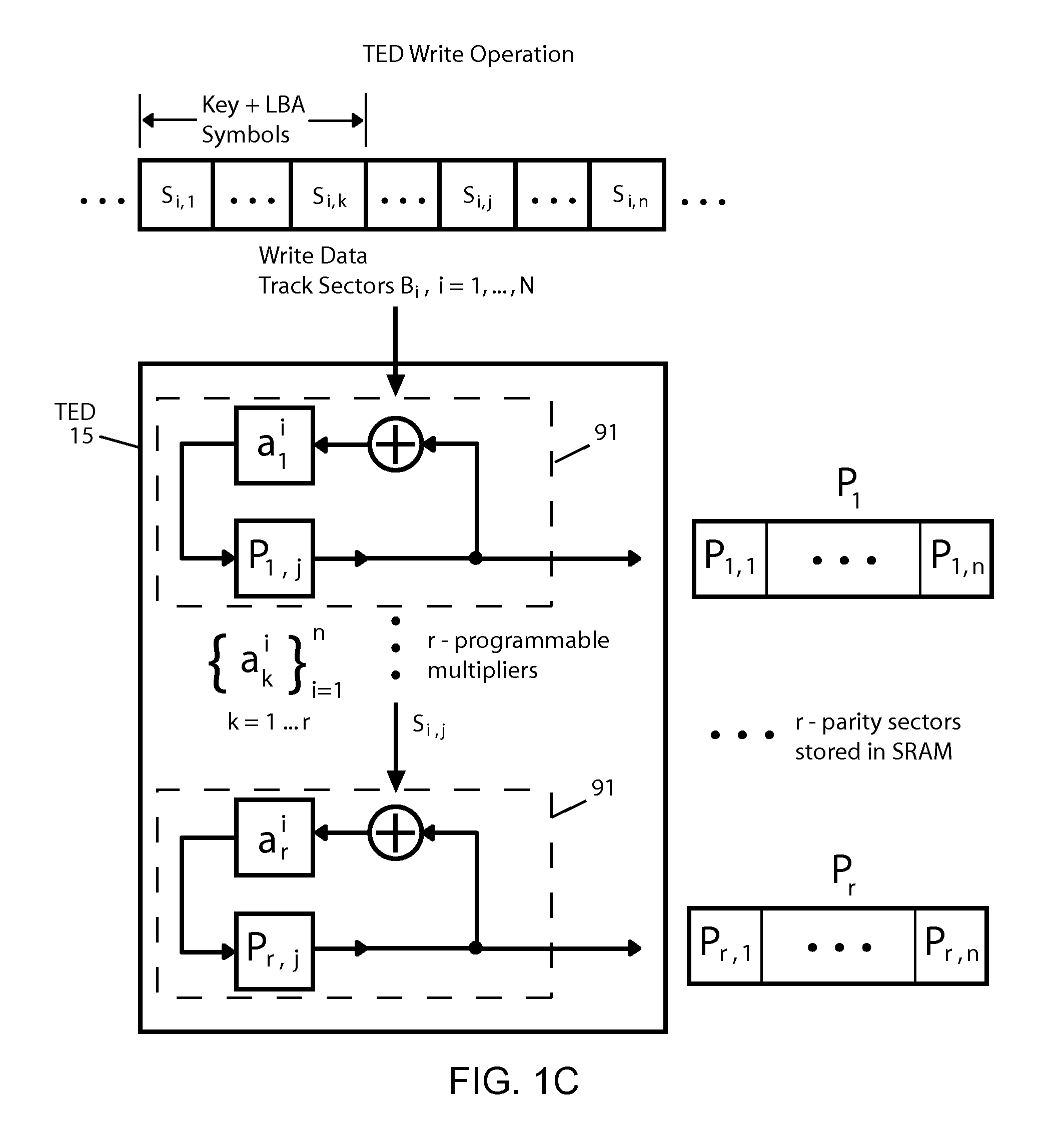
Scalable repair block error correction for sequential multiple data blocks in a magnetic data storage device
ActiveUS20140101515A1No performance lossIntegrity guaranteedRecord information storageError correction/detection using block codesShingled magnetic recordingOrbit
A technique for recovering of “squeezed” sectors in a set of sequential sectors such as are used in Shingled Magnetic Recording (SMR) is described. Embodiments of the invention use a programmable erased sector recovery scheme, which is a concatenation of a “Cauchy-type” track erasure correction code, together with a media-error correction code that generates N-weighted parity-sectors per track and is capable of replacing up to N-erased sectors per track in any possible combination.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
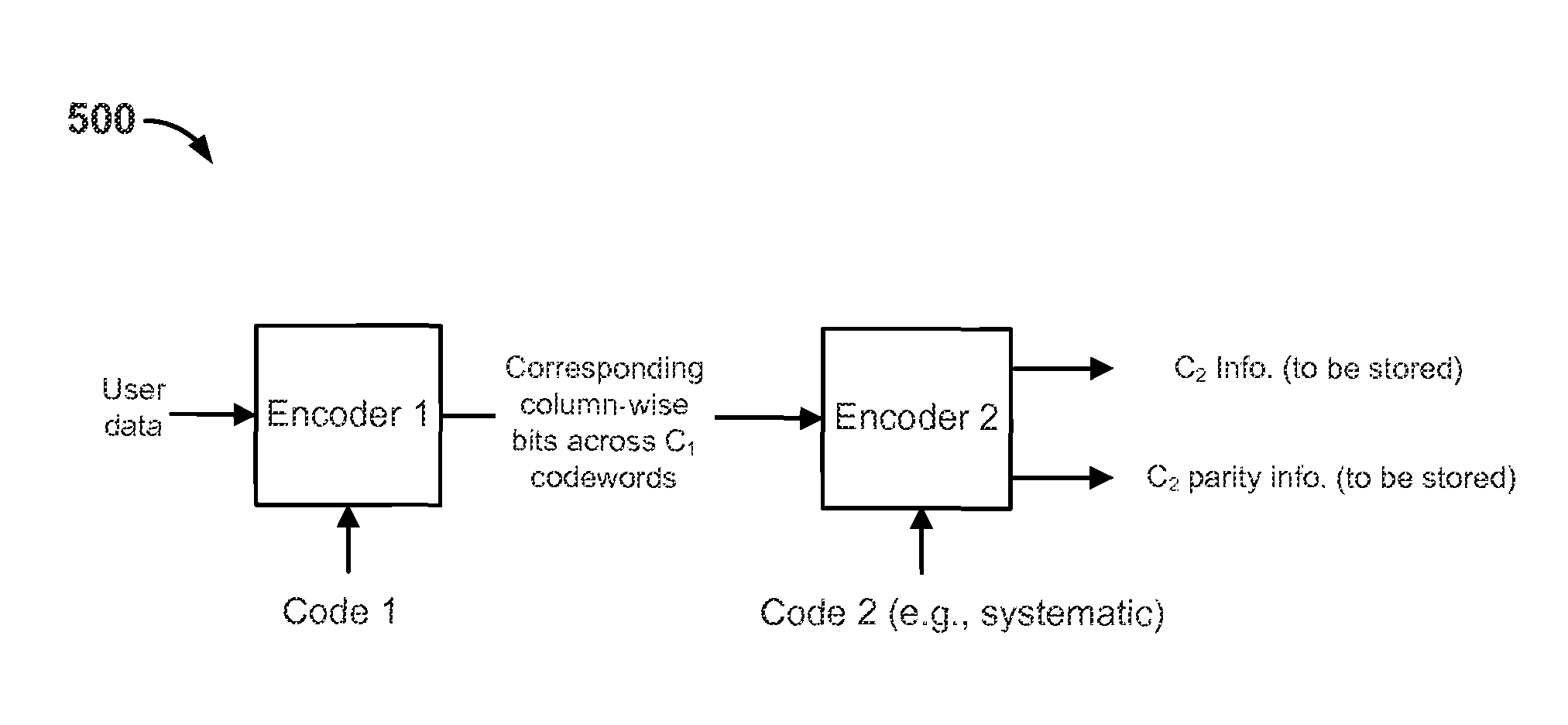
Concatenated codes for recovering stored data
A method of encoding user data into a first set of codewords using a first code, generating a first set of parity information based at least in part on the first set of codewords and at least a second code, and writing at least parity information associated with the first set of parity information to shingled magnetic recording storage. A method of performing decoding on a first set of read-back signal data read back from shingled magnetic recording storage and associated with a first set of codewords, and if decoding of at least one read-back signal in the first set of read-back signal data fails, performing decoding on at least some of a second set of read-back signal data associated with a set of parity information.
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
Microwave-assisted magnetic recording head with high saturation magnetization material side shield
ActiveUS9099102B2High gradientHigh magnetizationDisposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveShingled magnetic recording
Approaches to improving the signal-to-noise ratio in a microwave-assisted magnetic recording hard disk drive over the entire region from the inner diameter to the outer diameter of the disk, especially in the context of shingled magnetic recording, include a narrower side gap on the side opposing a spin torque oscillator offset direction than the side gap in the offset direction, thereby increasing the gradient of the recording magnetic field in the cross-track direction and reducing the track edge noise of the recording pattern. Embodiments include use of a side shield on the side opposing the offset direction that has a higher saturation magnetization than the side shield on the side in the offset direction, thereby further increasing the gradient of the recording magnetic field in the cross-track direction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
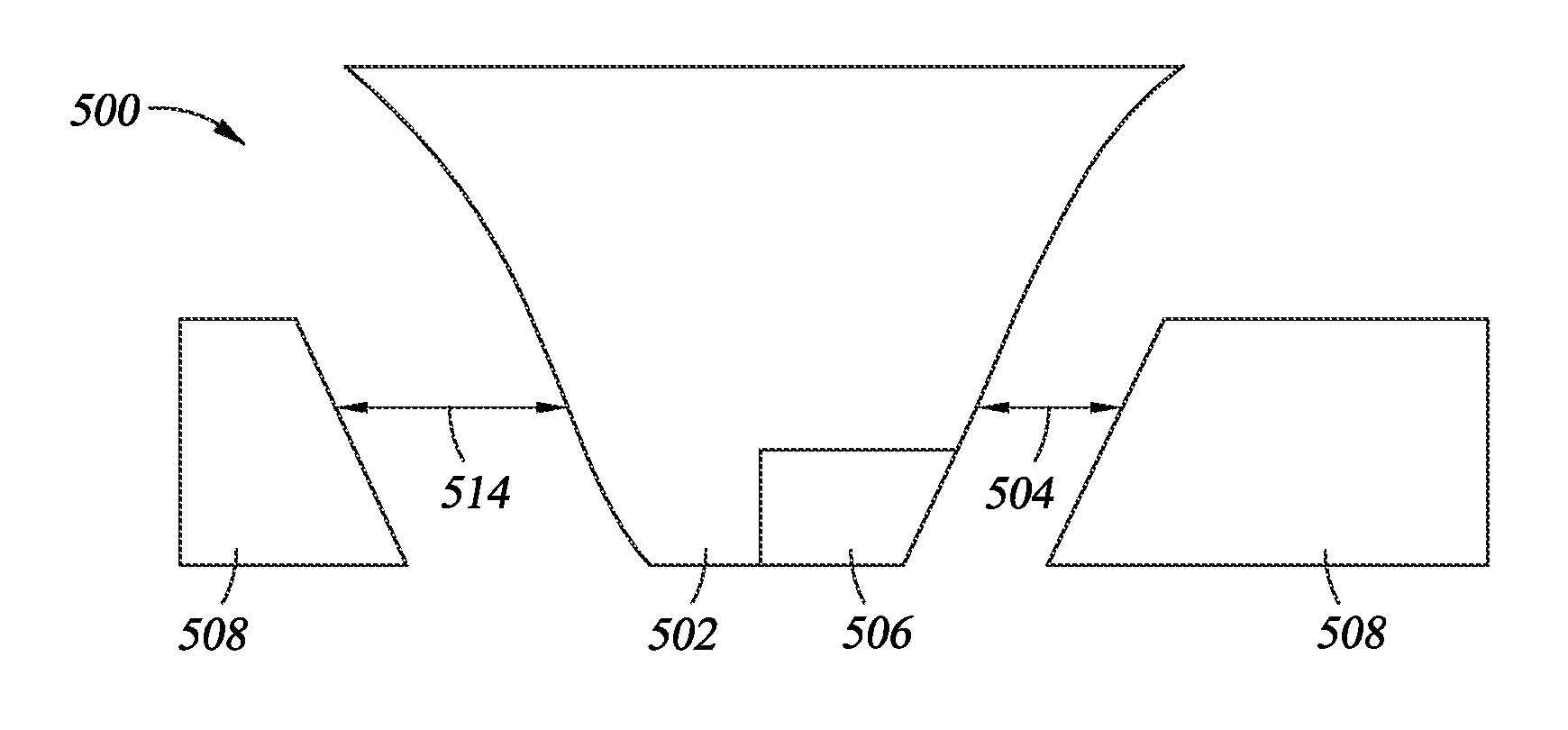
Asymmetric writer for shingled magnetic recording
ActiveUS8310786B2Manufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsShingled magnetic recordingTrailing edge
In one embodiment, a system includes a writer for shingled recording which includes a write pole having a trailing edge and first and second side edges extending from the trailing edge. The writer further includes a shield extending along and about parallel to only a portion of the trailing edge or only a portion of the first side edge, and the shield does not extend along the second side edge. In addition, an angle formed between the first side edge and the trailing edge along an air bearing surface side of the writer is different than an angle formed between the second side edge and the trailing edge along the air bearing surface side of the writer. Other systems are also presented which include advanced shingled writing head designs.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for storage architecture for bit patterned media using both erase band and shingled magnetic recording
ActiveUS8432633B2Improve performanceFilamentary/web record carriersPatterned record carriersShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
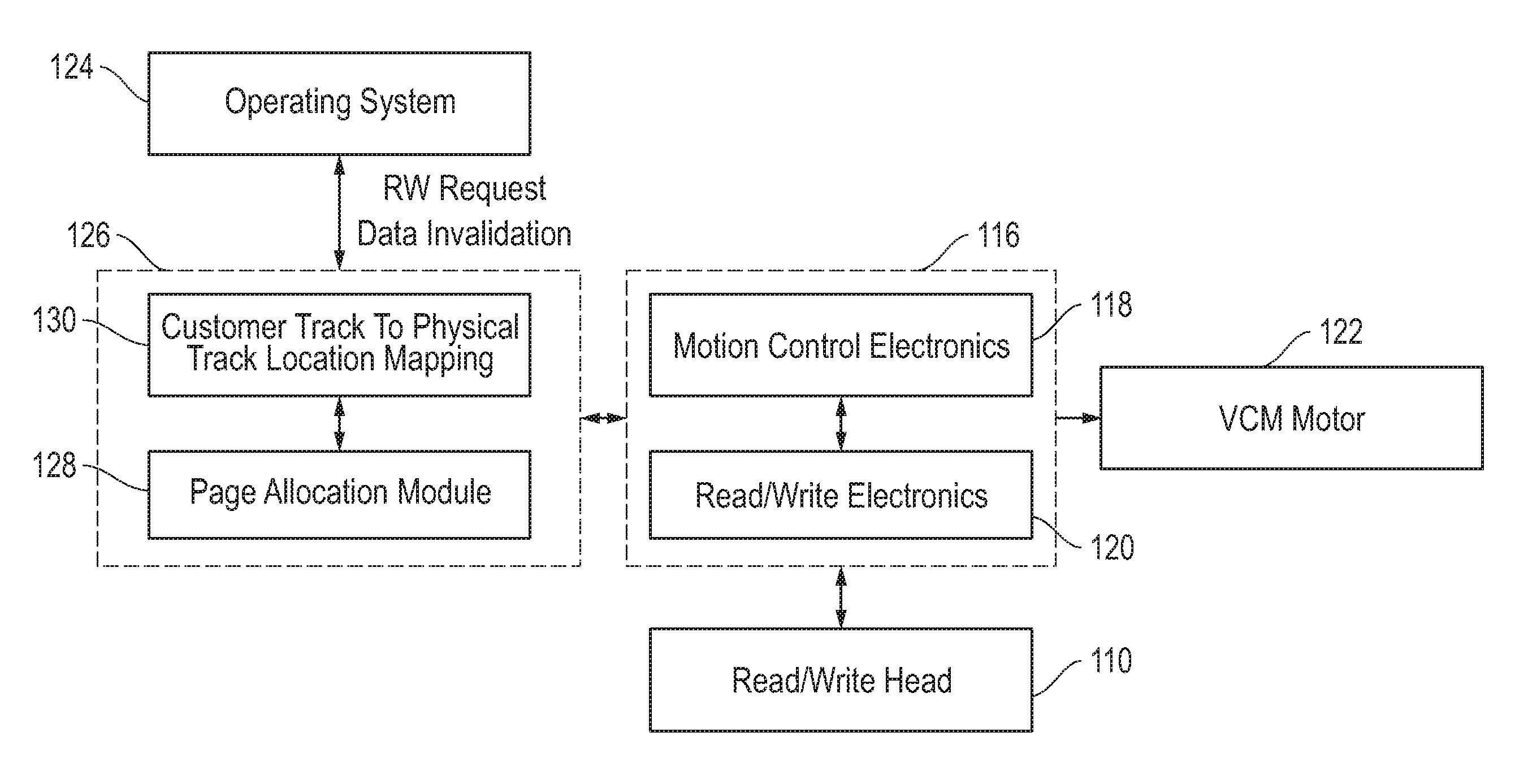
Storage architecture for bit patterned media uses both erase band and shingled magnetic recording. A hard disk drive may comprise a disk having bit patterned media with a plurality of data tracks arrayed in architecture pages having at least one of erase band mode (EBM), shingled mode (SM) and unallocated space. An actuator has a head for writing data to the data tracks of the bit patterned media. A control system monitors, reallocates and reconfigures the architecture pages from EBM, SM or unallocated space to a different one of EBM, SM or unallocated space to enhance performance of the hard disk drive.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
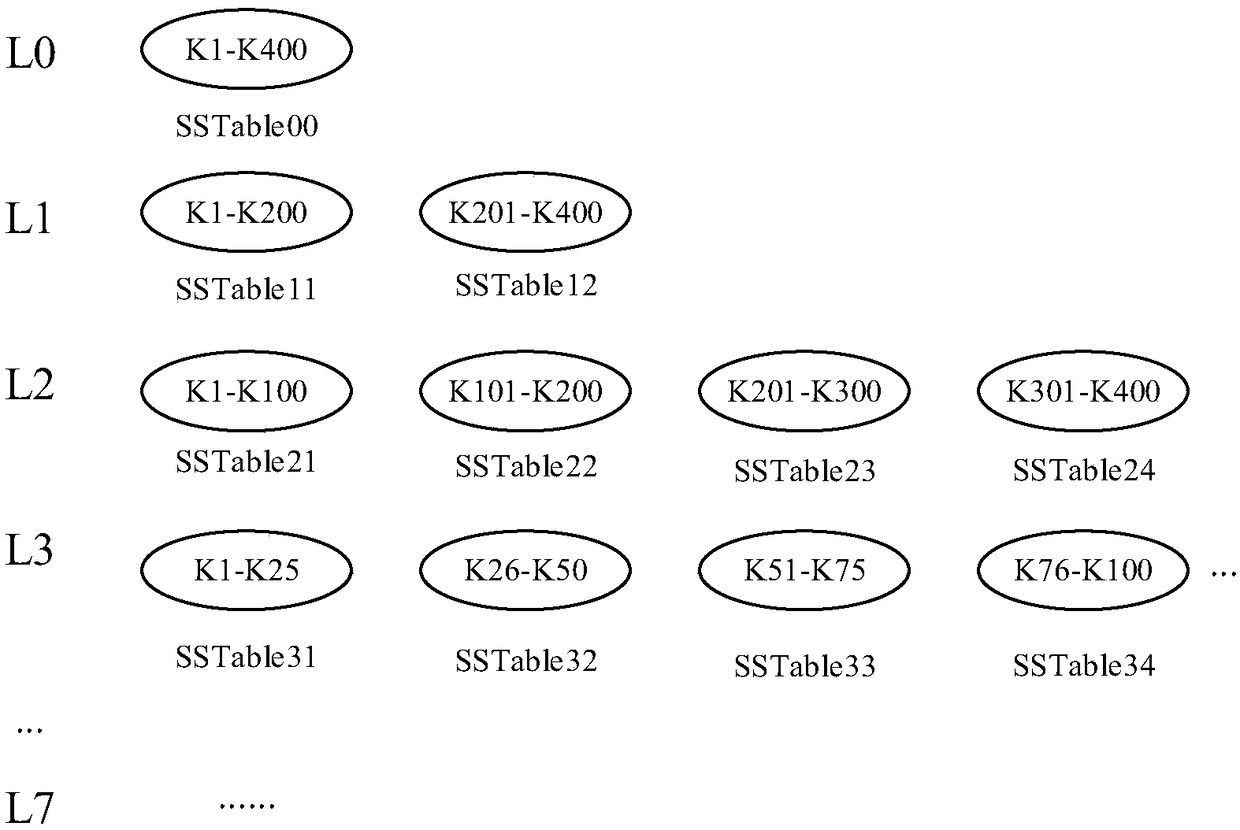
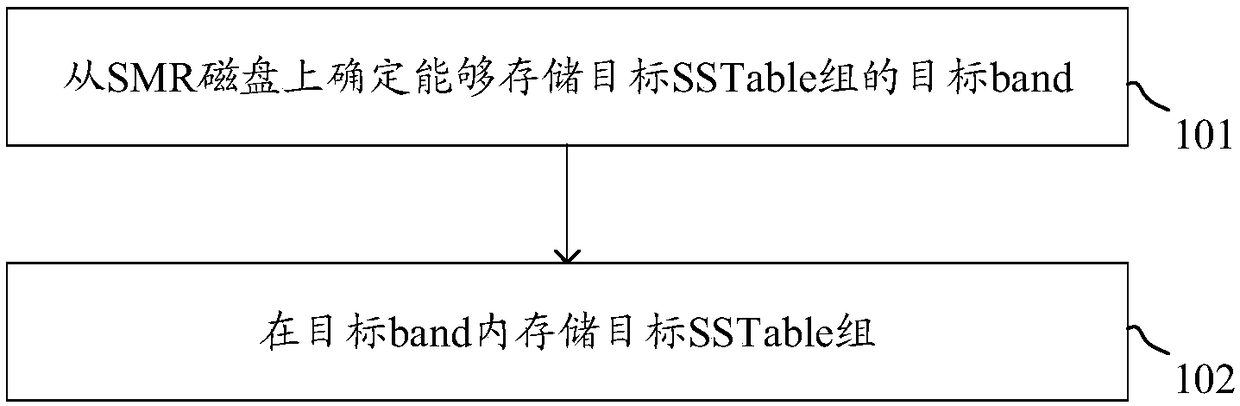
Data storage method and device
The invention relates to a data storage method and device, which are used for solving the problem of multiple read-write amplification and performance reduction of a storage system when the shingled recording technology is combined with the LSM tree technology. The data storage method comprises the following steps: determining a target band capable of storing a target sorted string table SSTable group from a shingled magnetic recording SMR disk, wherein the target SSTable group is stored in a log structured LSM tree, the LSM tree comprises at least two layers, each layer comprising at least one SSTable, and at least two SSTables in each layer of which the key value range is within the key value range of one SSTable in the upper layer are taken as one SSTable group; and storing the target SSTable group in the target band.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Scalable repair block error correction for sequential multiple data blocks in a magnetic data storage device
ActiveUS8856618B2No performance lossIntegrity guaranteedCode conversionRecord information storageShingled magnetic recordingConcatenation
A technique for recovering of “squeezed” sectors in a set of sequential sectors such as are used in Shingled Magnetic Recording (SMR) is described. Embodiments of the invention use a programmable erased sector recovery scheme, which is a concatenation of a “Cauchy-type” track erasure correction code, together with a media-error correction code that generates N-weighted parity-sectors per track and is capable of replacing up to N-erased sectors per track in any possible combination.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com