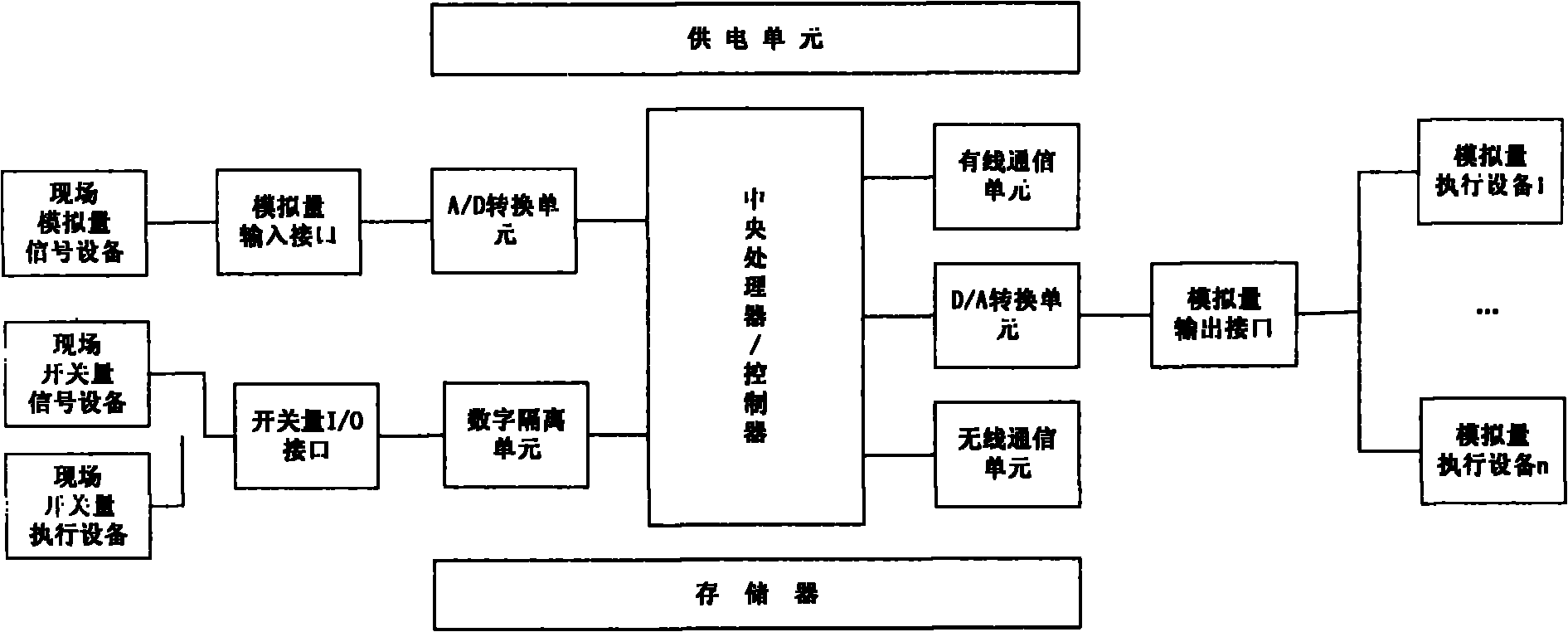
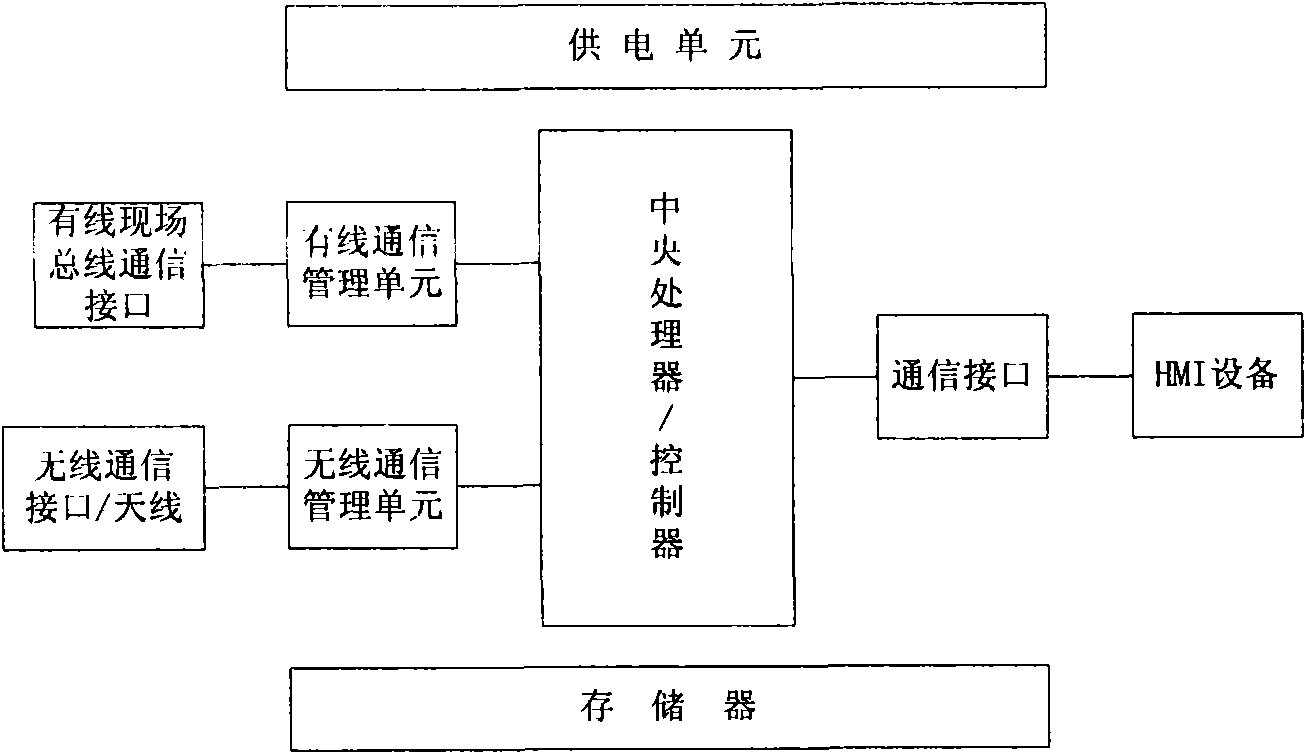
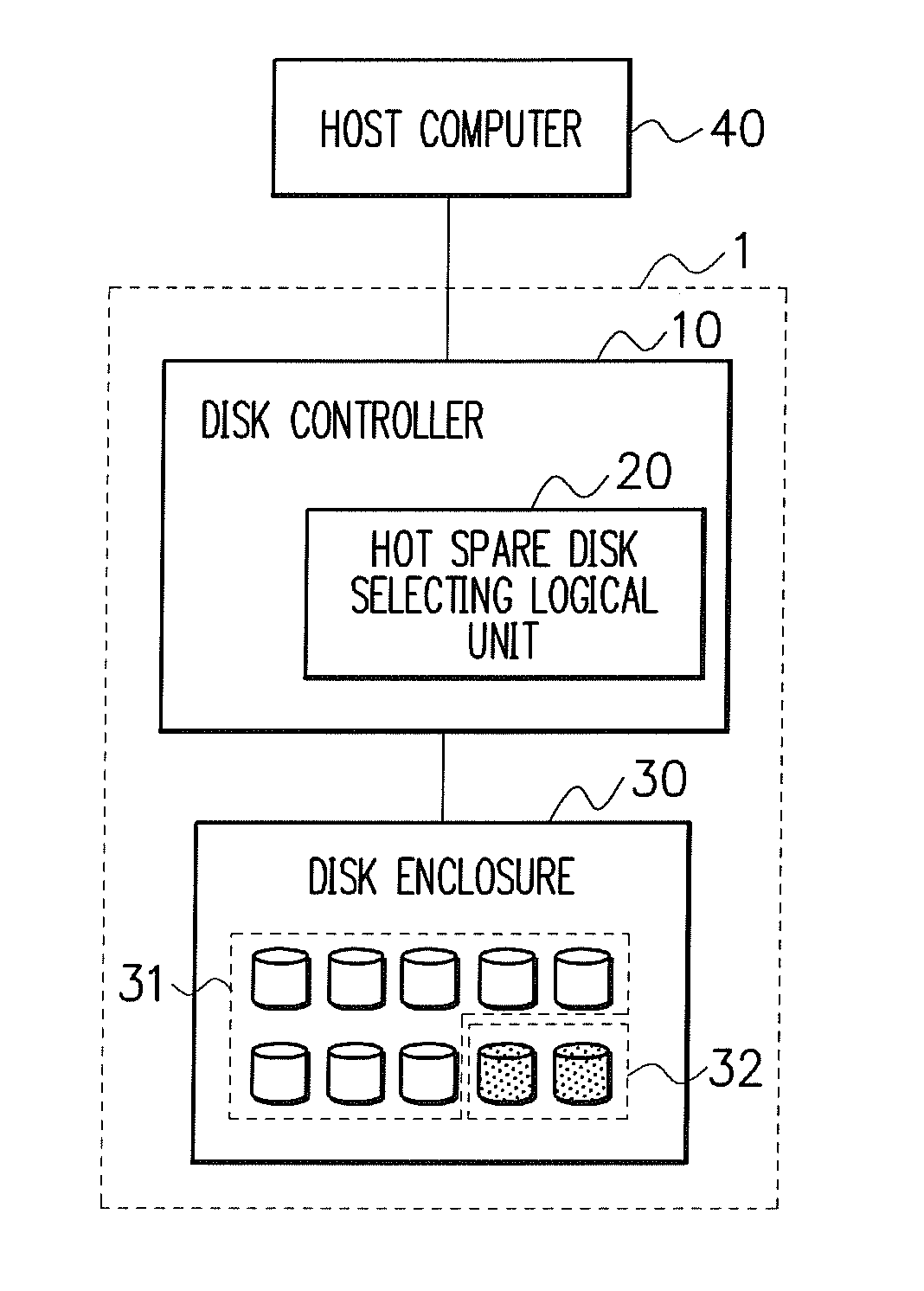
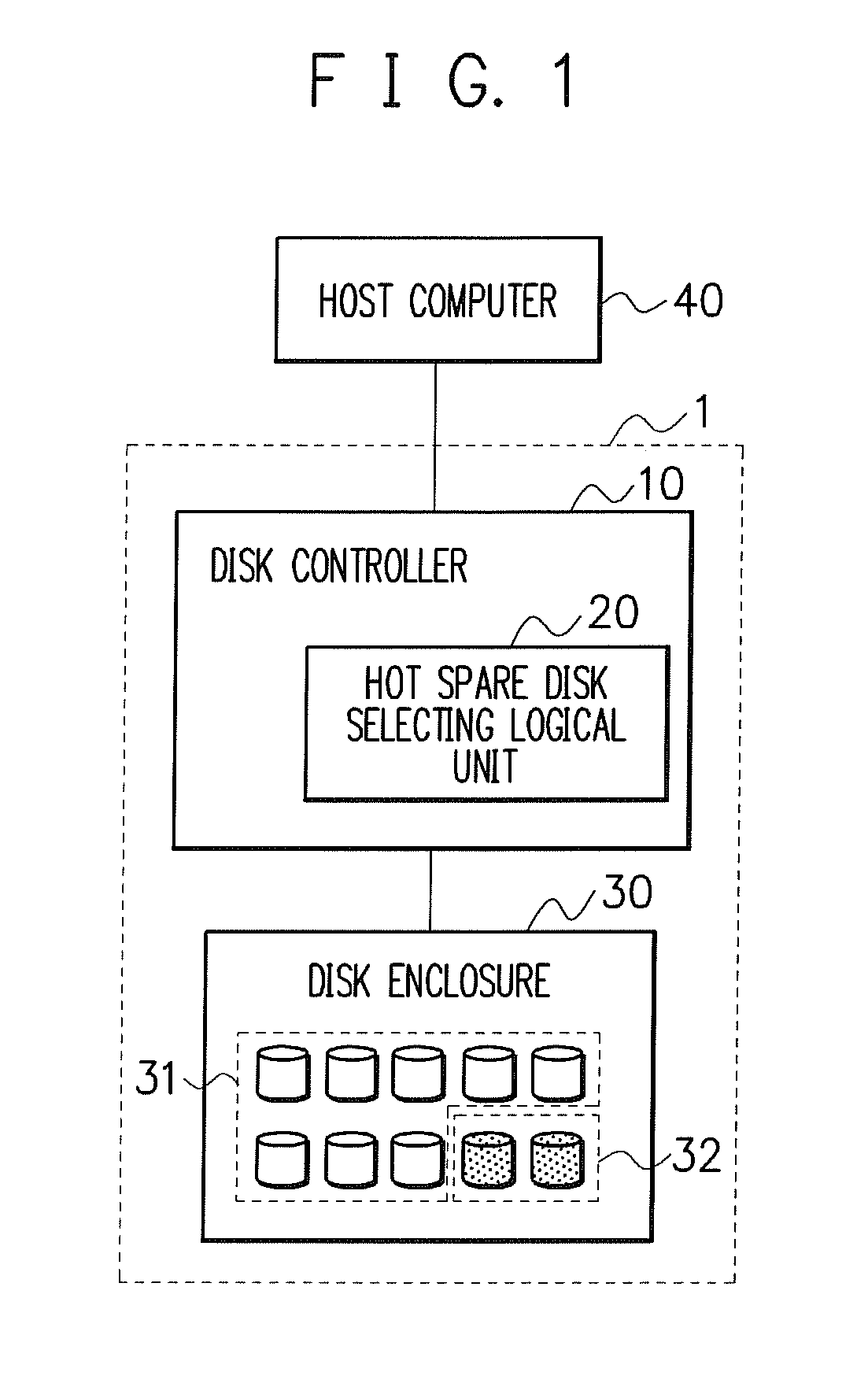
Patents
Literature
169 results about "Hot spare" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
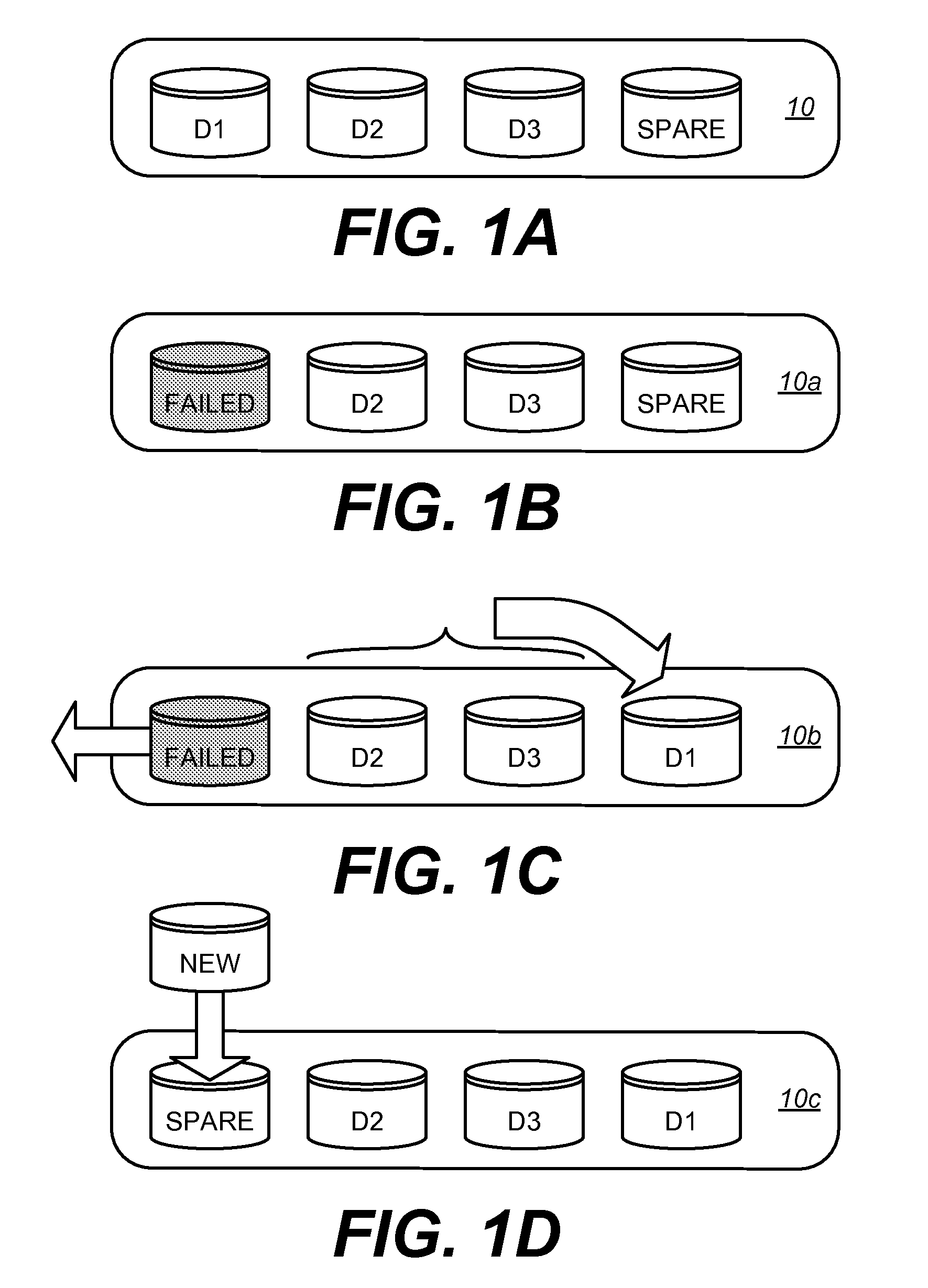
A hot spare or warm spare or hot standby is used as a failover mechanism to provide reliability in system configurations. The hot spare is active and connected as part of a working system. When a key component fails, the hot spare is switched into operation. More generally, a hot standby can be used to refer to any device or system that is held in readiness to overcome an otherwise significant start-up delay.
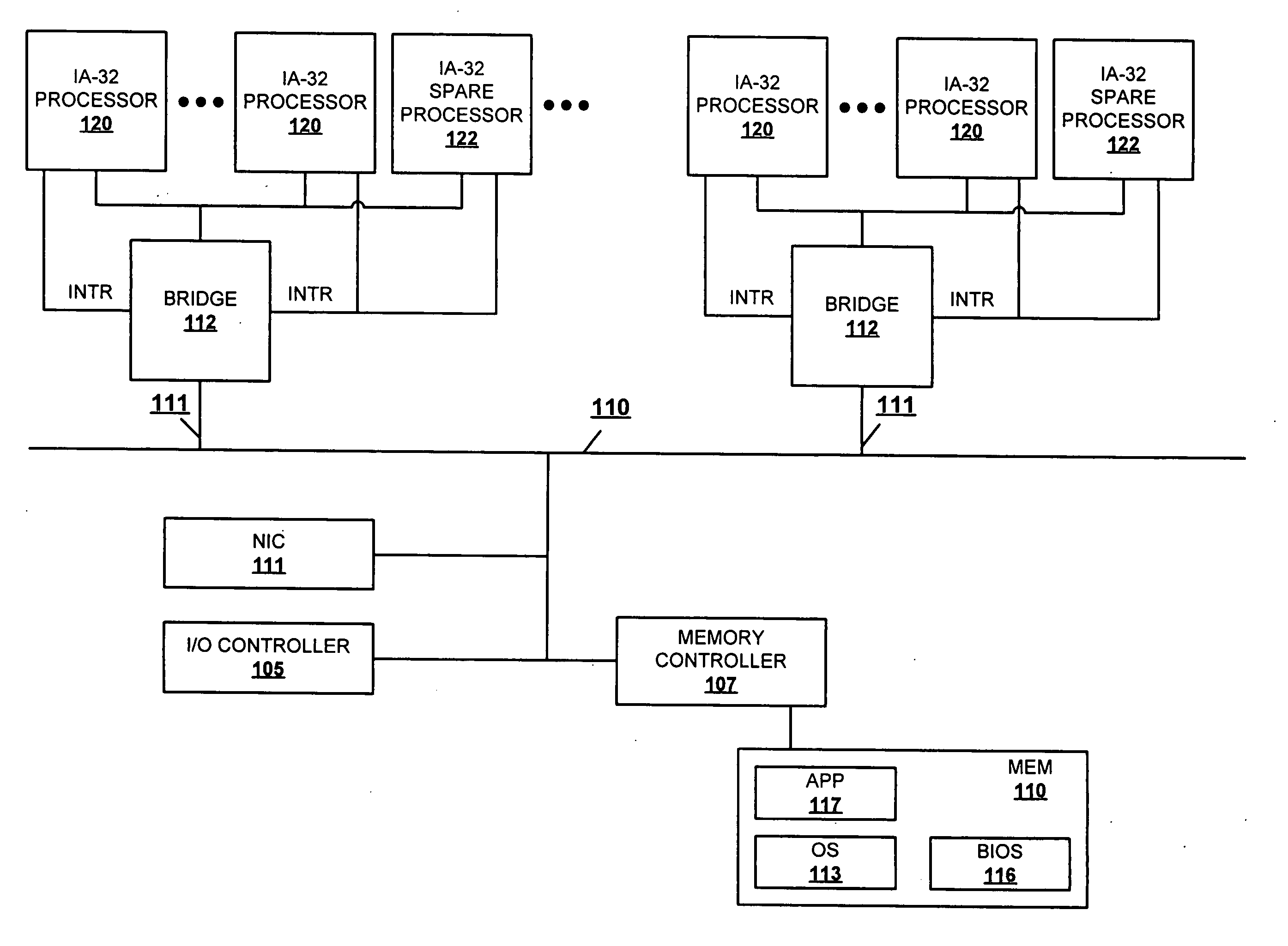
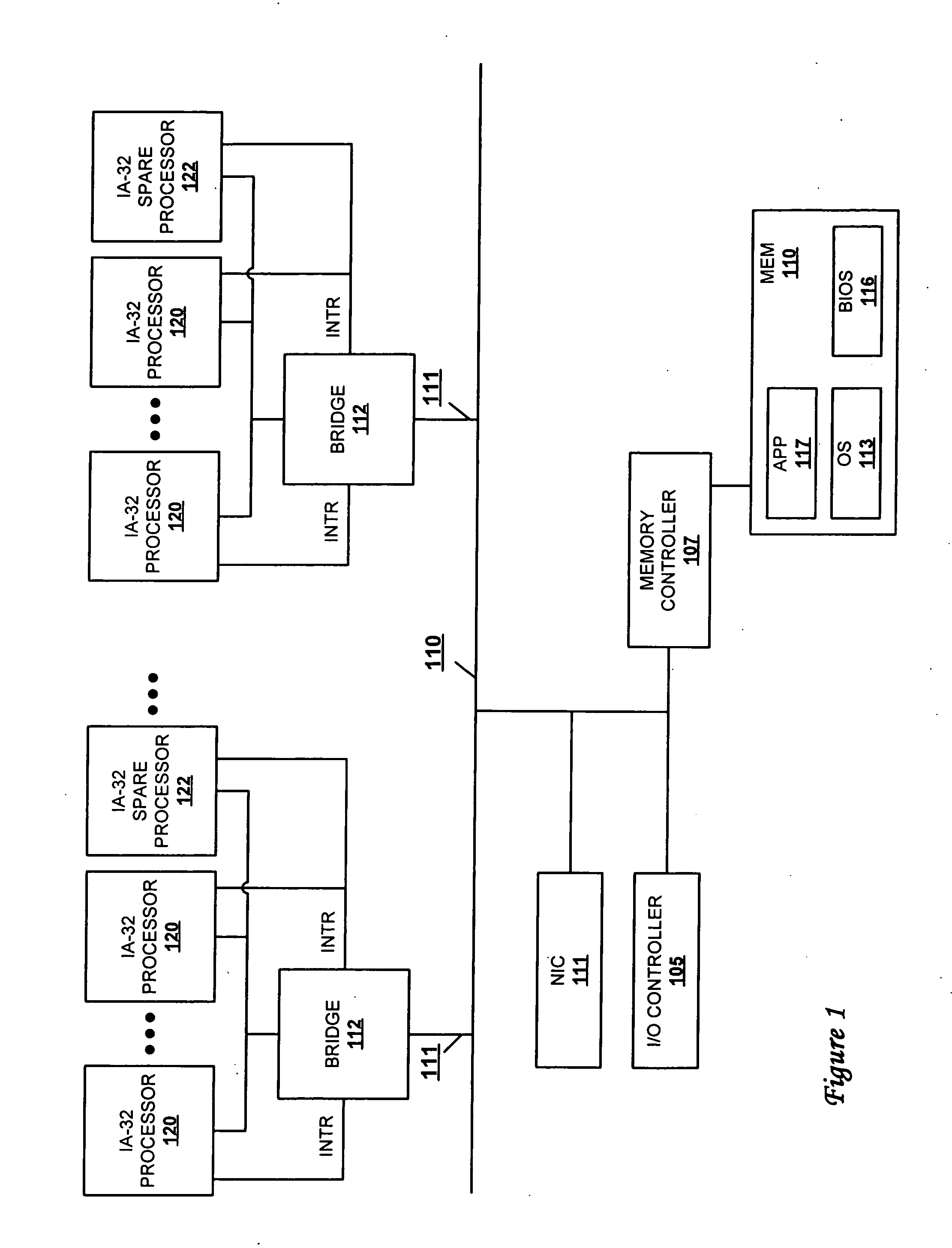
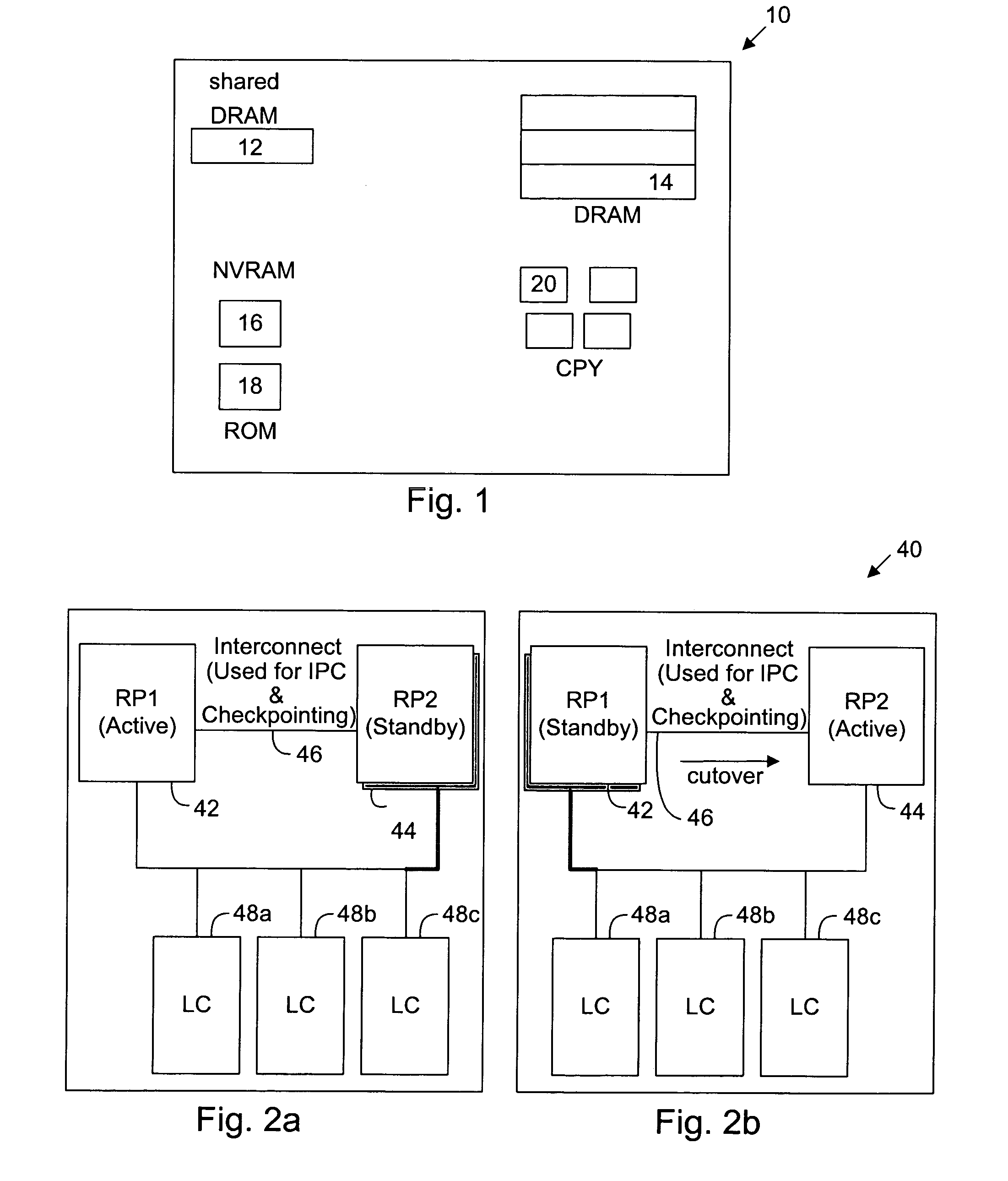
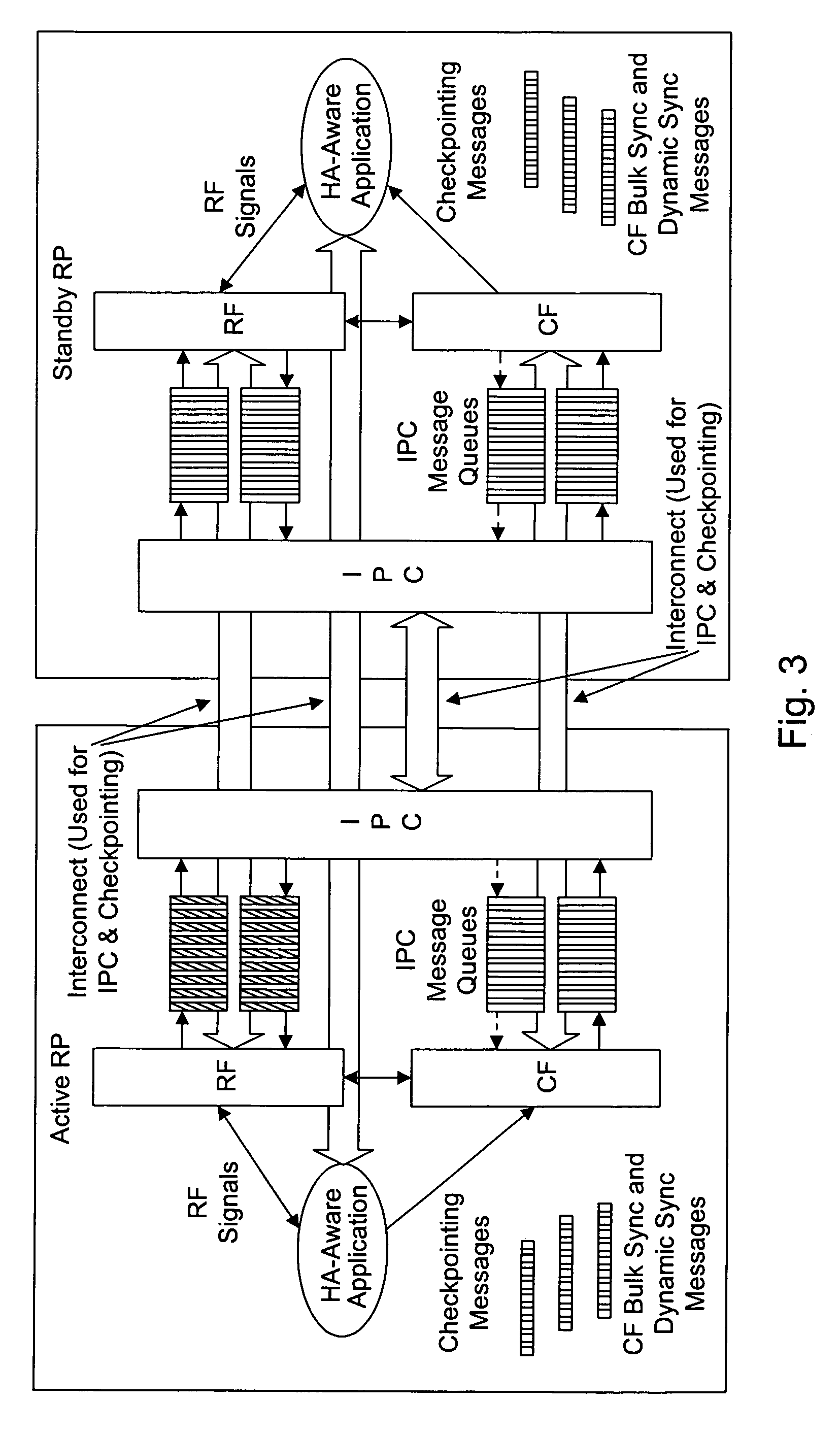
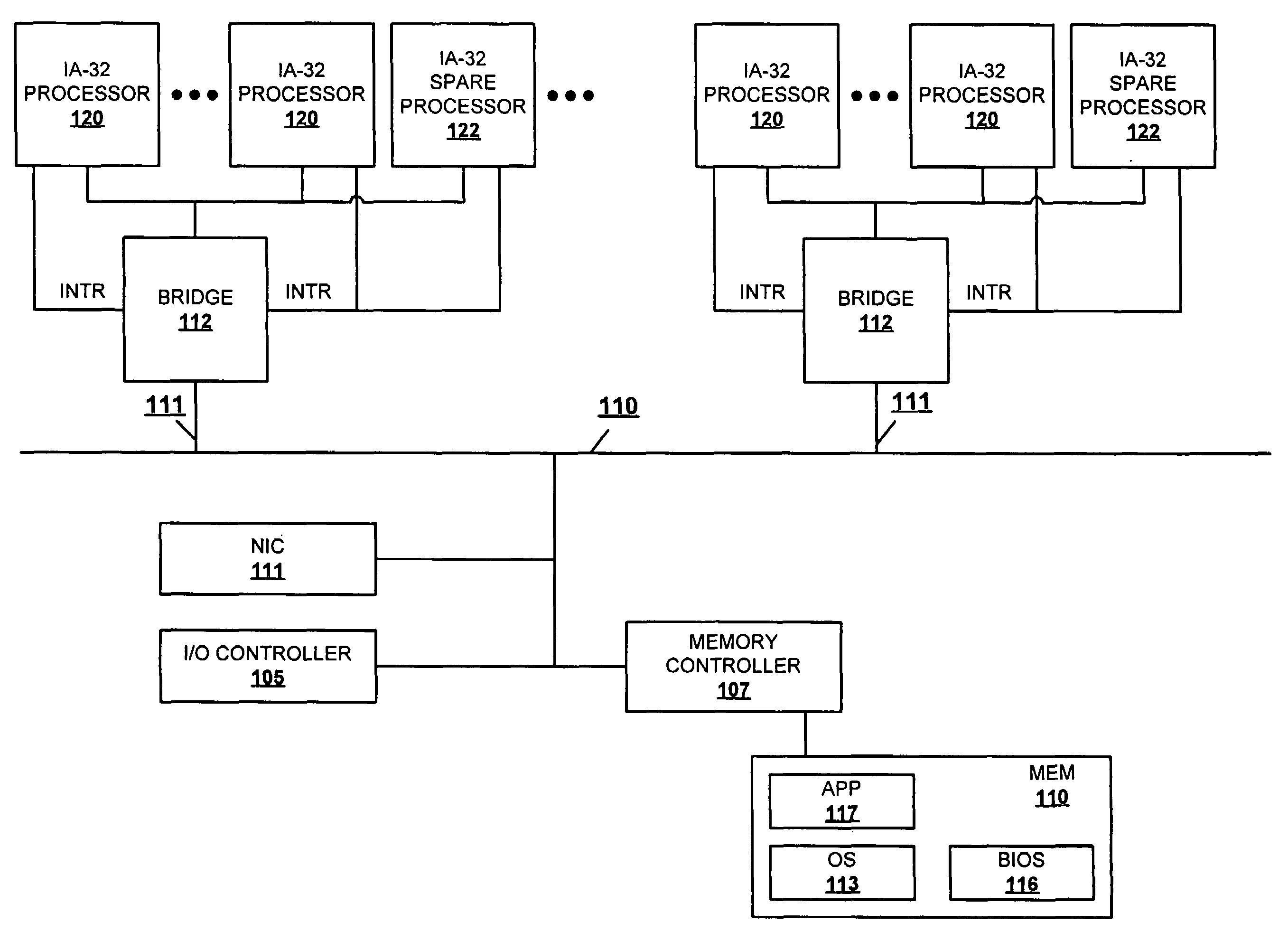
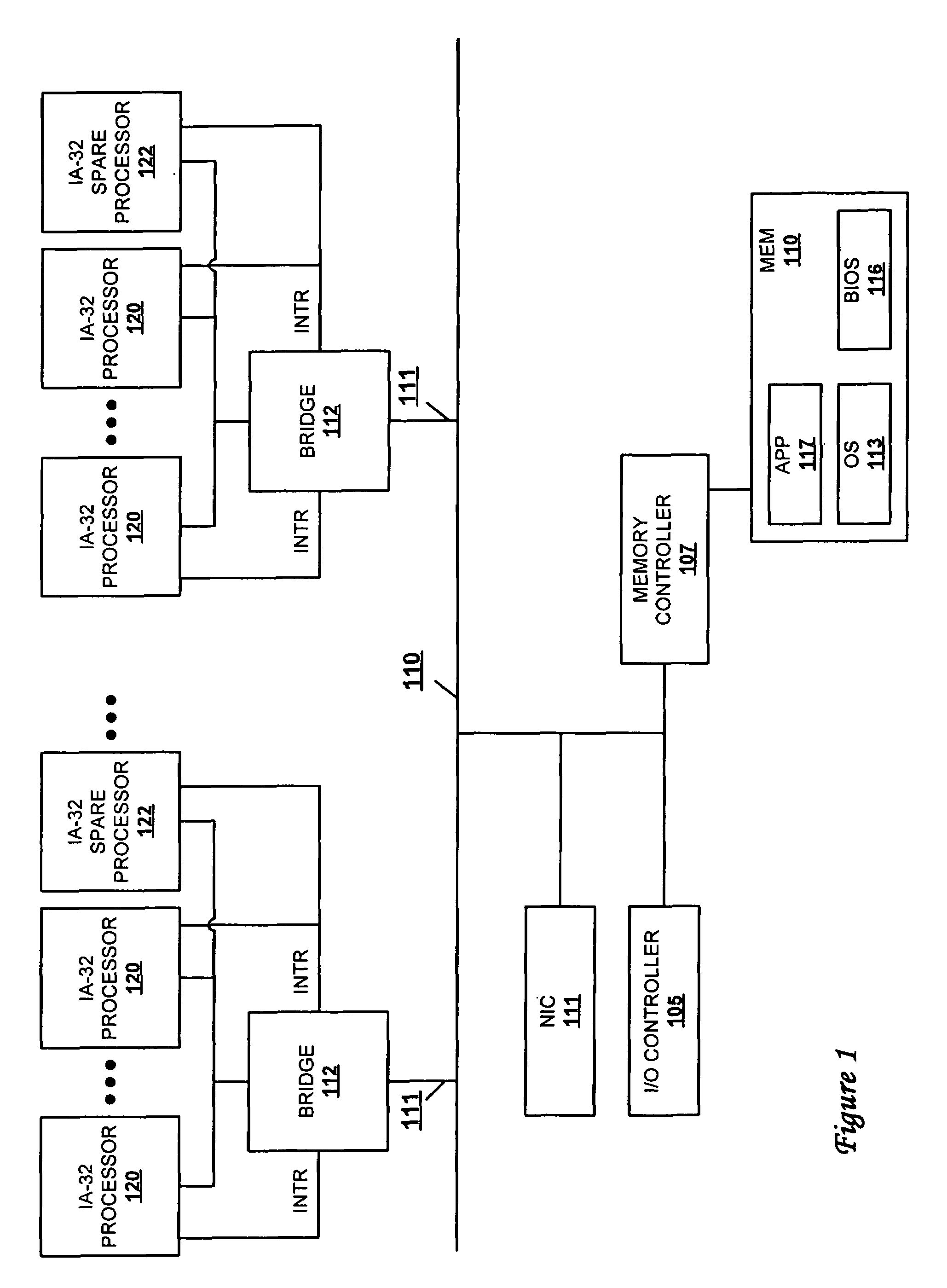
Autonomous fail-over to hot-spare processor using SMI
ActiveUS20050172164A1None of can remain in operationEliminate the problemRedundant hardware error correctionPower modeFailover
A method and system for dynamically replacing a failing processor in a server system configured with IA-32 architecture without requiring hardware changes to the IA-32 architecture or administrative effort. At least one processor of the multiprocessor system (MP) is initially provided as a reserve (or hot-spare) processor that remains in an idle, off, or low-power mode. While in that mode, the OS is prevented from initially utilizing the hot-spare processor. When a processor failure is detected, SMI code running on a good processor instructs the OS to hold off allocating processes to the failing processor. Contemporaneously, the SMI (and OS) activates and completes an initialization of the hot-spare processor to prepare it to begin receiving the held-off processes. Control is then returned to the OS, which updates the “active” processor list and allocates the threads that were running on the failing processor to the hot-spare processor.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
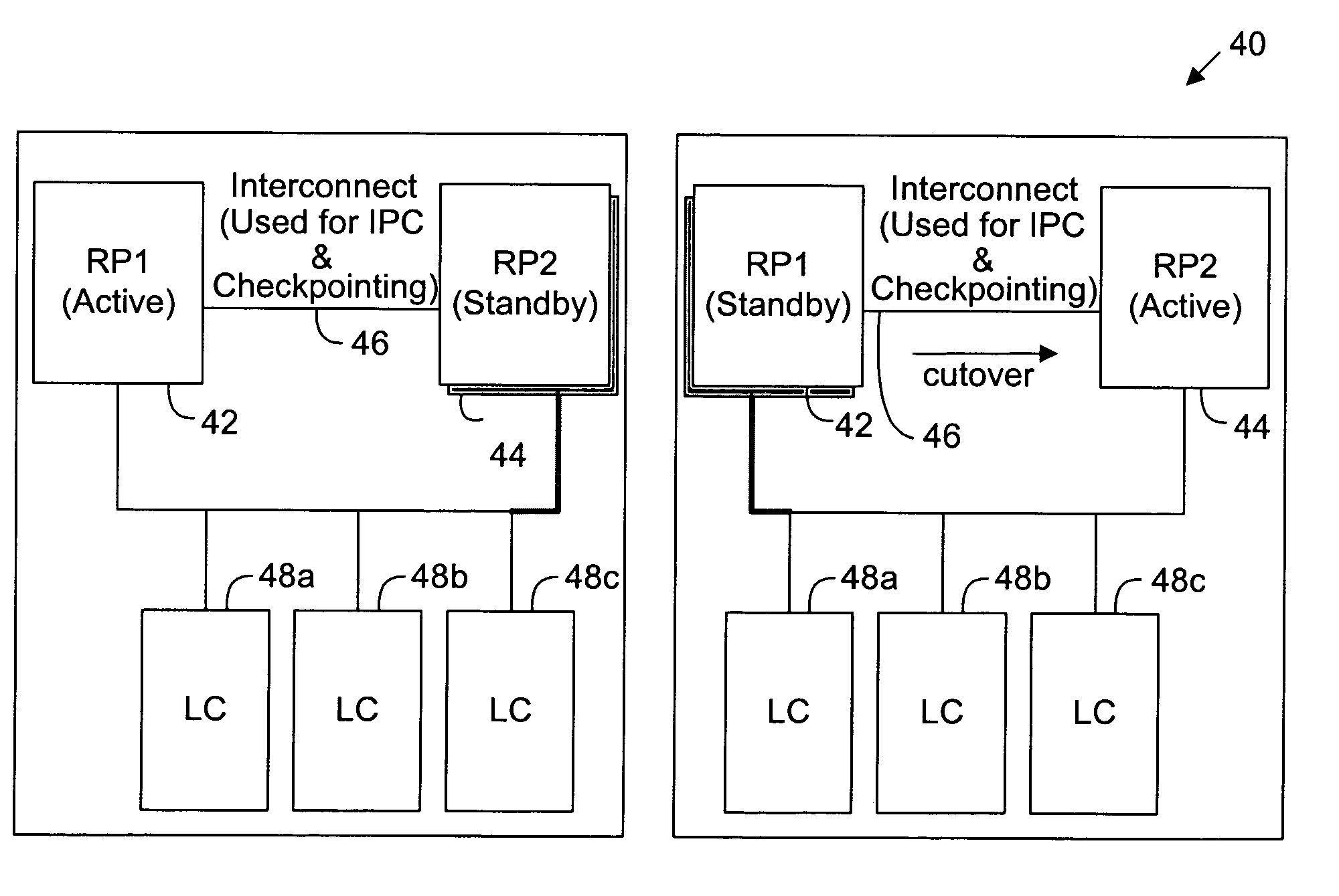
Dynamic configuration synchronization in support of a "hot" standby stateful switchover
A system and method for supporting a “hitless” switchover from an Active to a Standby processor utilizes several points of configuration synchronization. The startup and running configuration files are copied to the Standby processor and subsequent modifications to the Active configuration are synchronized to the Standby configuration.
Owner:CISCO SYSTEMS INC
Rebuilding redundant disk arrays using distributed hot spare space
InactiveUS6976187B2Addressing slow performanceError preventionRedundant data error correctionDisk arrayComputer science
A method and system that allows the distribution of hot spare space across multiple disk drives that also store the data and redundant data in a fully active array of redundant independent disks, so that an automatic rebuilding of the array to an array of the identical level of redundancy can be achieved with fewer disk drives. The method configures the array with D disk drives of B physical blocks each. N user data and redundant data blocks are allocated to each disk drive, and F free blocks are allocated as hot spare space to each disk drive, where N+F<=B, and ((D−M)×F)>=N. Thus, rebuilding of data and redundant blocks of a failed disk drive in the free blocks of the remaining disk drives is enabled after M disk drive failures.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
System and method for managing raid storage system having a hot spare drive
ActiveUS20160357649A1Achieve redundancySolve insufficient storage spaceRedundant hardware error correctionRAIDOriginal data
A method provides rebuilding data in a hot spare storage device when multiple storage devices fail in a storage system. The method includes a storage controller determining if a first storage device storing first data has failed within a first group of storage devices. In response to the first storage device failing, the first data is rebuilt in the hot spare storage device from a copy of the first data stored in a first mirrored storage device of the first group of storage devices. In response to a second storage device failing, third data is generated by performing a first exclusive or (XOR) operation with the first data stored on the hot spare storage device and a copy of the second data stored in a second mirrored storage device of the second group of storage devices. The third data is rebuilt in the hot spare storage device. The method recovers original data and prevents complete failure of a virtual disk.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Data storage system employing a hot spare to proactively store array data in absence of a failure or pre-failure event
ActiveUS20180165169A1Input/output to record carriersRedundant hardware error correctionComputer hardwareData store
A data storage system includes a controller, a hot spare storage device and a plurality of primary storage devices. The controller utilizes the hot spare storage device to mirror only a subset of each stripe of logical pages written across the data storage array, where the subset includes a logical page determined by a write input / output operation (IOP) policy. In response to receipt of a write IOP, the controller writes a stripe including a plurality of logical data pages and a logical data protection page across the plurality of primary storage devices and mirrors the logical page determined by the write IOP policy on the hot spare storage device. In response to a failure of a storage device among the plurality of primary storage devices, contents of the failed storage device not already mirrored on the hot spare storage device are rebuilt on the hot spare storage device.
Owner:IBM CORP
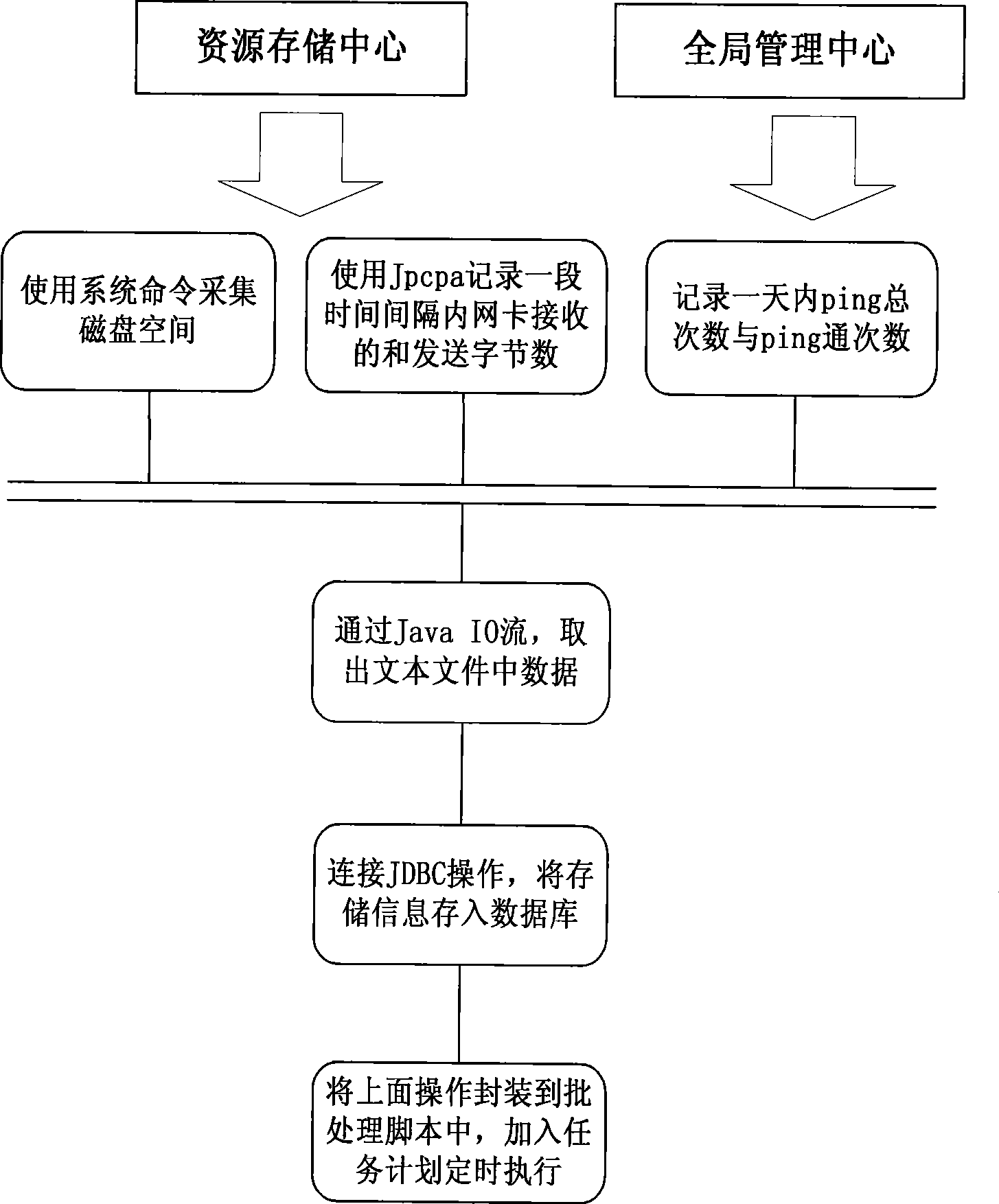
Resource load stabilization method based on contents duplication
InactiveCN101370030ALoad balancingFlexible Content ReplicationTransmissionAccess frequencyDistributed computing
A resource load balancing method concretely relates to content copy based resource load balancing method and an automatic distribution type resource monitoring structure. The method comprises: dynamically copying content of resource starting from every independent resource storage center node according to resource access condition of local node and information of resource storage center, selects a proper resource storage node for copied resource, at last accomplishes load balancing for resource. The resource storage center information such as bandwidth, magnetic disc space and credit needed by load balancing are collected and stored in monitoring information database of global hot spare management center by distribution type resource monitoring script program.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
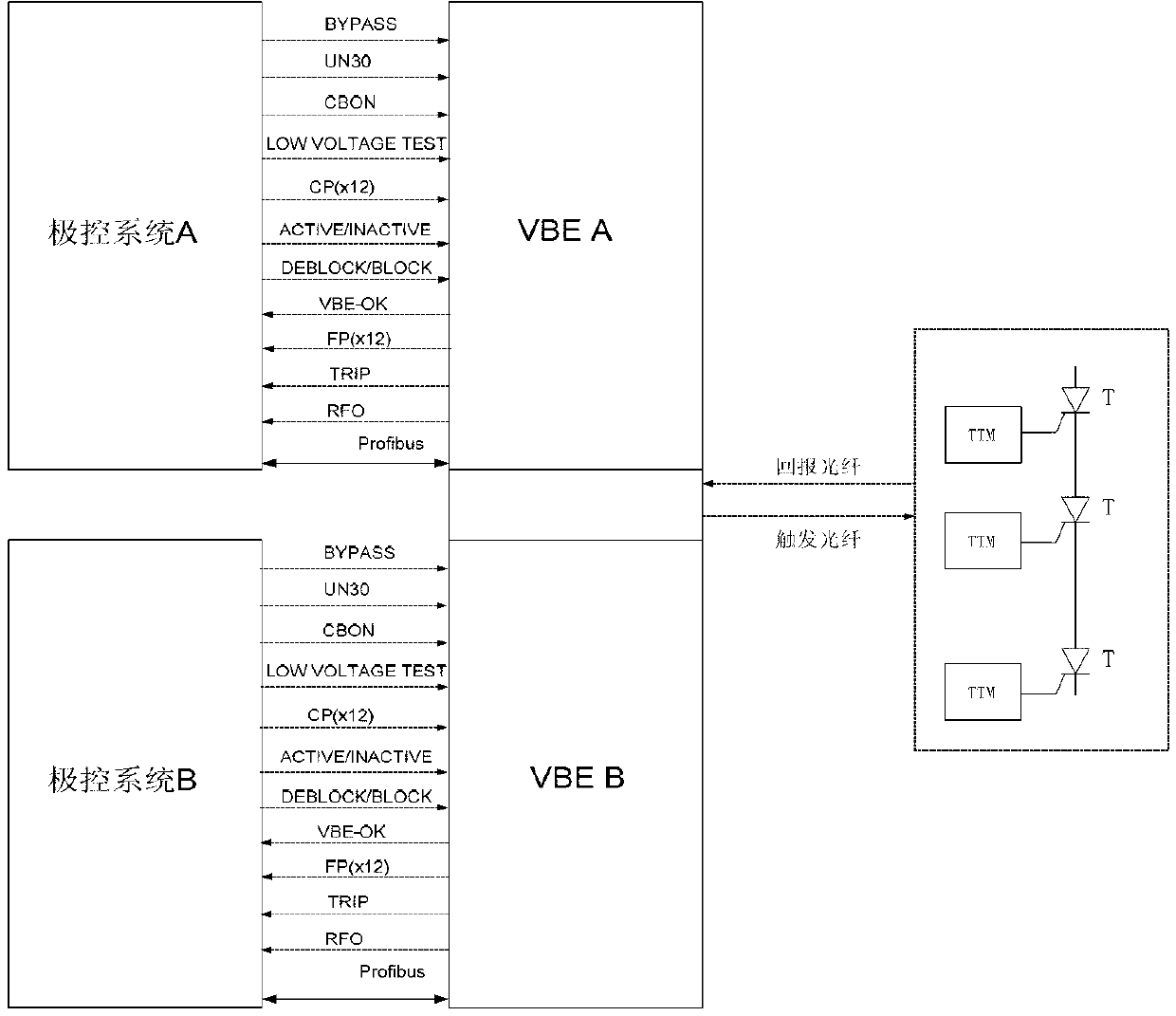
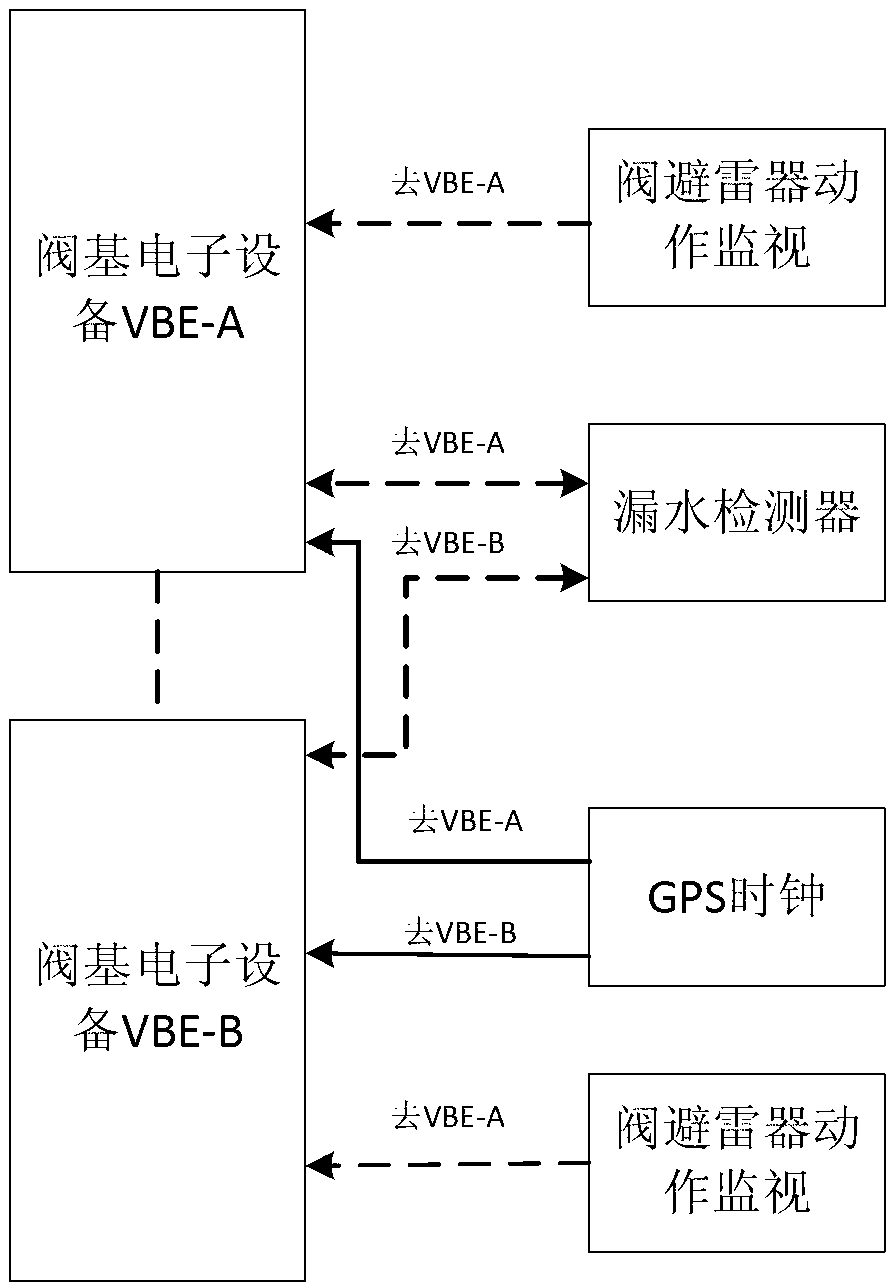
Direct-current transmission converter valve control protection system and control protection method thereof
ActiveCN103219798AImprove stabilityReduce downtimeDc network circuit arrangementsControl systemProtection system
The invention relates to the field of direct-current transmission, in particular to a direct-current transmission converter valve control protection system and a control protection method thereof. The control protection system is formed by an operation system and a hot spare system which are in redundancy. The operation system and the hot spare system comprise a pole control system and valve base electronic equipment communicated with the pole control system respectively, the operation system and the hot spare system are connected with a thyristor triggering monitoring subsystem through optical fibers, and the thyristor triggering monitoring subsystem comprises a thyristor and a thyrustor triggering monitoring unit matched with the thyristor. Protection objects of the protection method comprise a converter valve and the valve base electronic equipment. The action results of the protection method comprise alarm, request switch and request trip. The direct-current transmission converter valve control protection system greatly improves operation stability of the direct-current transmission system, greatly reduces shutdown time and overhaul time of the direct-current transmission system and enables economical benefit advantages of the direct-current transmission system to be fully played.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +2
Data storage system employing a hot spare to store and service accesses to data having lower associated wear
ActiveUS20160188424A1Reduce access latencyReduce wear rateRedundant hardware error correctionData setAccess frequency
A controller monitors access frequencies of address ranges mapped to a data storage array. Based on the monitoring, the controller identifies frequently accessed ones of the address ranges that have lower associated wear, for example, those that are read more often than written. In response to the identifying, the controller initiates copying of a dataset associated with the identified address ranges from the data storage array to a spare storage device while refraining from copying other data from the data storage array onto the spare storage device. The controller directs read input / output operations (IOPs) targeting the identified address ranges to be serviced by access to the spare storage device. In response to a failure of a failed storage device among the plurality of primary storage devices, the controller rebuilds contents of the failed storage device on the spare storage device in place of the dataset associated with the identified address ranges.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data reconstruction method for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) and appliance thereof
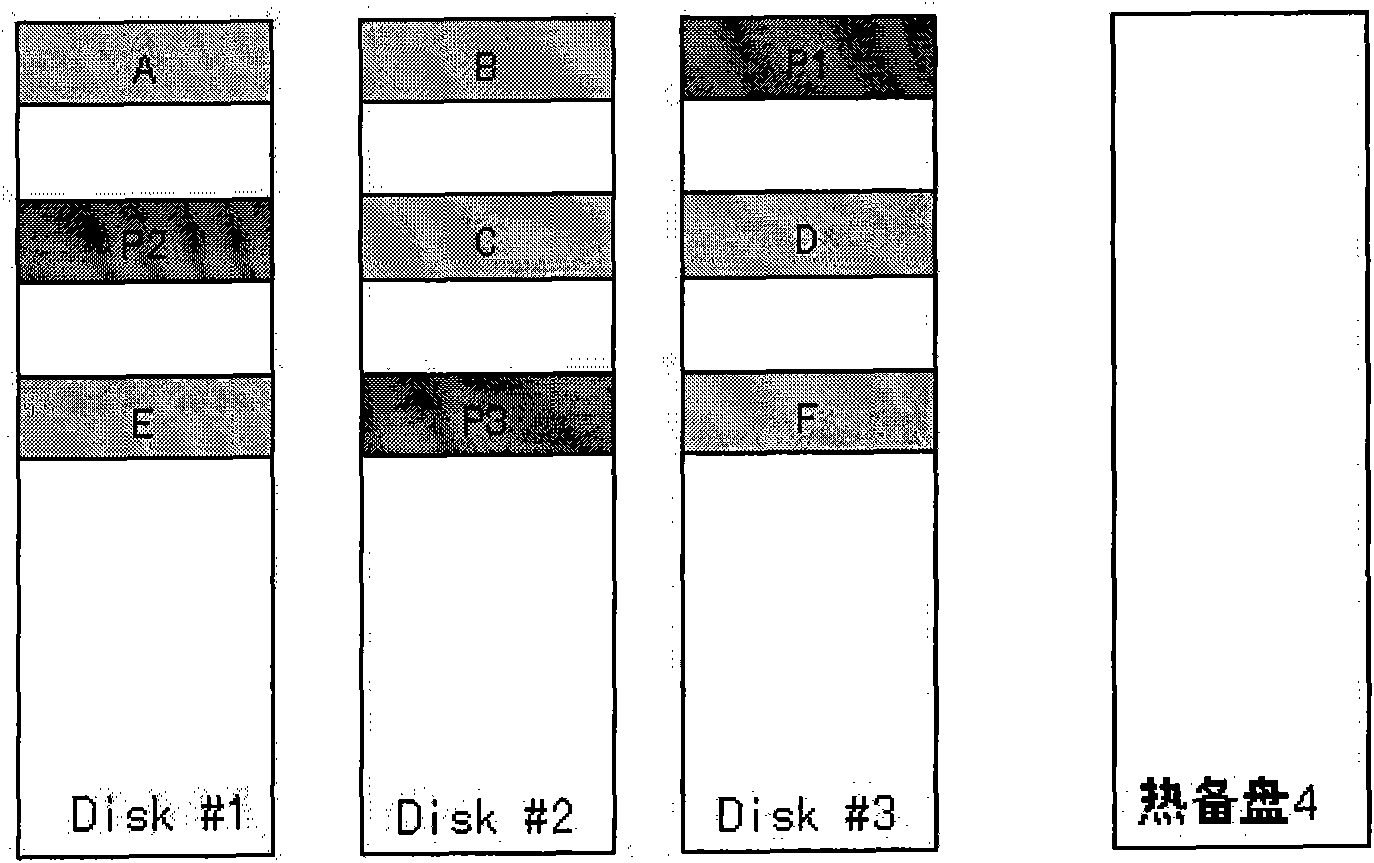
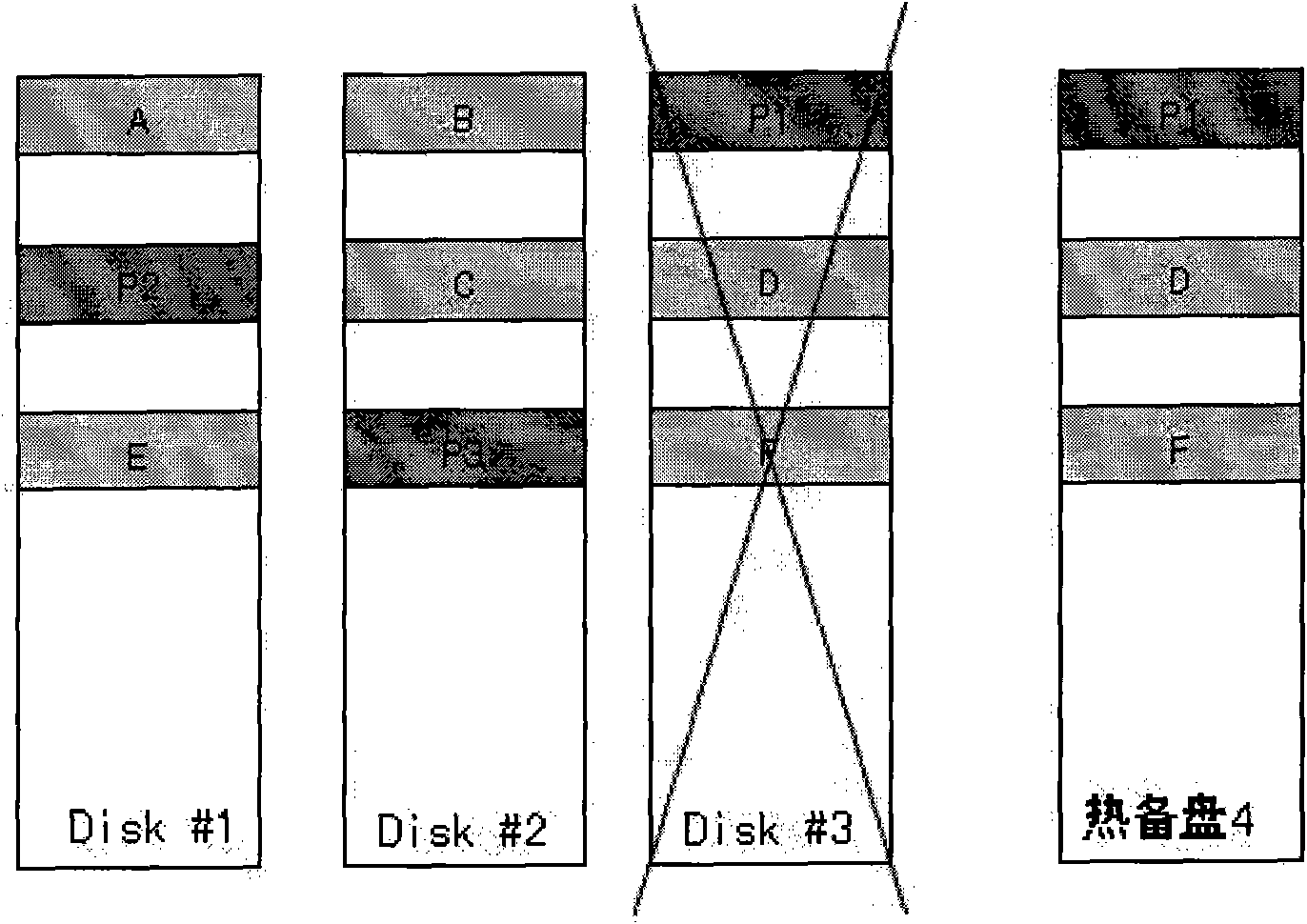
The invention discloses a data reconstruction method for Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID), which is used for data reconstruction of RAID. The RAID comprises a plurality of data disks and at least one hot spare disk; wherein, the amount of the hot spare disk is less than that of the data disk. The method comprises the following steps: when RAID is in normal operation, part of data in each data disk is copied into the hot spare disk; when a data disk breaks down, data reconstruction is carried out on RAID according to the stored data in the hot spare disk which are from the broken-down data disk and the data of other data disks. In the invention, when the data disk is in normal operation, data in the data disk is copied into the hot spare disk so as to reduce reconstructed data volume of RAID, shorten reconstructed time of RAID and lower the risk of data corruption. The invention also discloses a device which applies the method provided in the invention.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Substation automation system with increased availability
ActiveUS20080244044A1Improve usabilityError preventionCircuit arrangementsFailure rateMean time to repair
In automation systems, such as Substation Automation systems, the mean time to repair is reduced by remote reconfiguration and start-up of a replacement or spare Intelligent Electronic Device (IED), leaving some more hours for the maintenance personnel to repair an inactive or faulty IED. The time for the actual repair is irrelevant for the system availability as long as it is short enough compared to the IED failure rate. Exemplary embodiments can provide nearly the same availability as a hot-standby configuration, but without the need for doubling all the essential IEDs. Additionally, spare IEDs are supervised to be healthy, and a fault of the spare IED being detected before it is put in use. Only one spare online IED is needed for each set of IEDs of the same type connected to the same station bus and process bus. In a retrofit or extension case with limited downtime, a number of previous IEDs can be replaced by an equivalent set of new or real IEDs of a different type, but configured to perform the same functions as the previous IEDs.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Optimized reconstruction and copyback methodology for a failed drive in the presence of a global hot spare disc
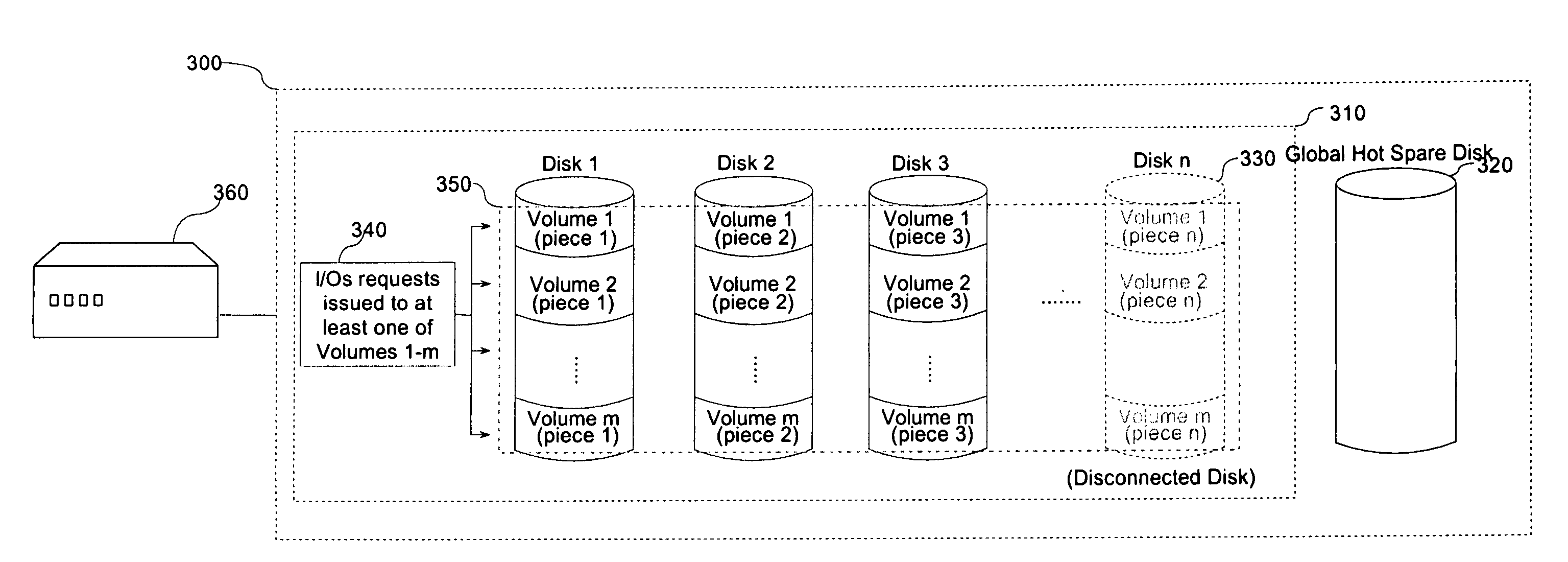
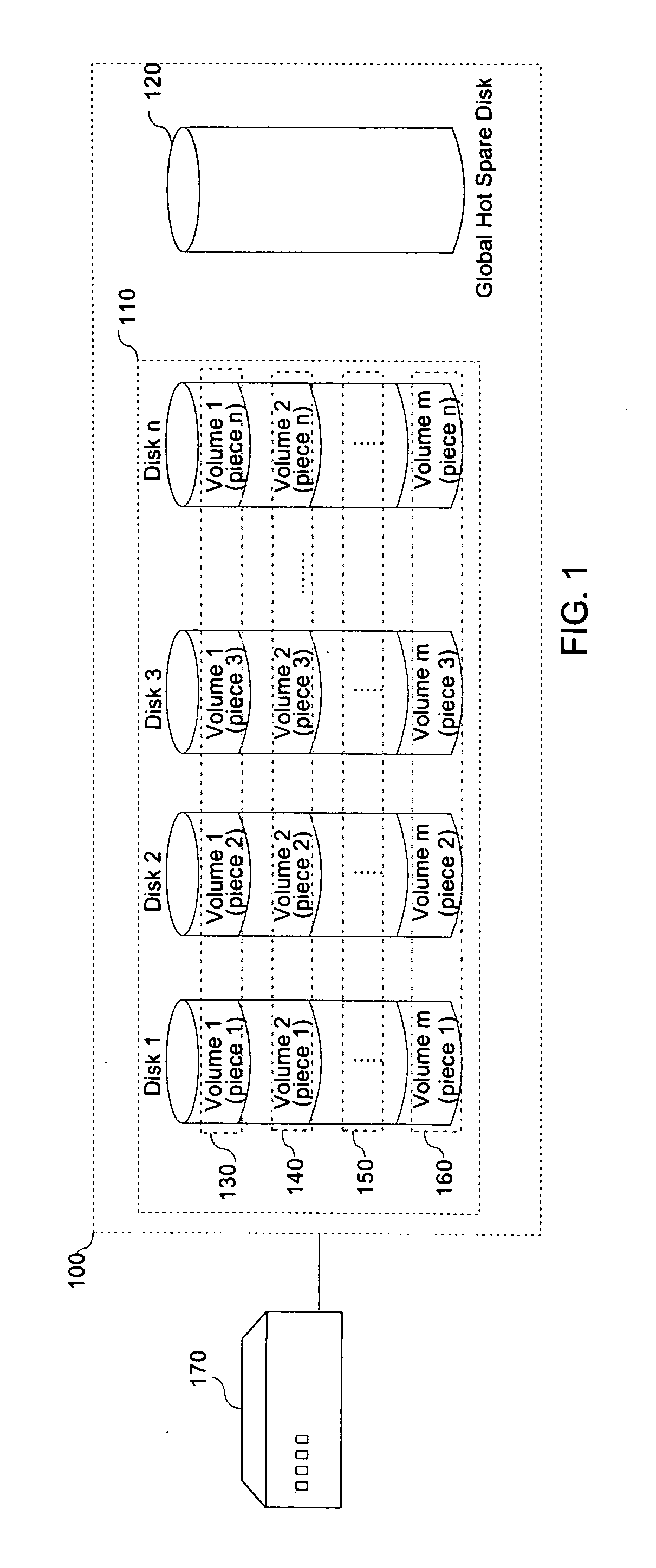
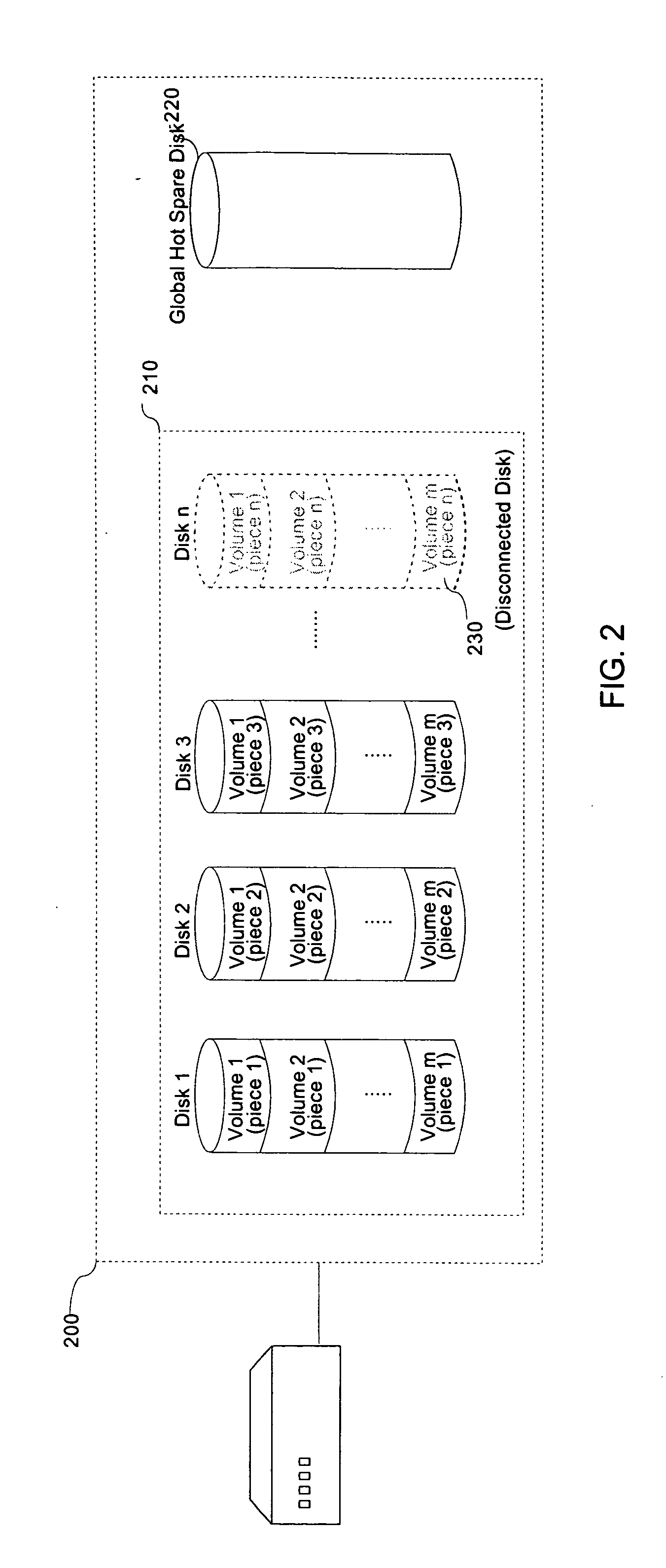
InactiveUS20080126839A1Sacrificing all of its material advantageMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDetecting faulty computer hardwareRAIDInterconnection
The present invention is a system for optimizing the reconstruction and copyback of data contained on a failed disk in a multi-disk mass storage system.A system in accordance with the present invention may comprise the following: a processing unit requiring mass-storage; one or more disks configured as a RAID system; an associated global hot spare disk; and interconnections linking the processing unit, the RAID and the global hot spare disk.In a further aspect of the present invention, a method for the reconstruction and copyback of a failed disk volume utilizing a global hot spare disk is disclosed. The method includes: detecting the failure of a RAID component disk; reconstructing a portion of the data contained on the failed RAID component disk to a global hot spare disk; replacing the failed RAID component disk; reconstructing any data on the failed RAID disk not already reconstructed to the global hot spare disk to the replacement disk; and copying any reconstructed data from the global hot spare disk back to the replacement RAID component disk.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
Realization method based on CPCI bus technology of dual module hot spare system switching
ActiveCN102001348AImprove scalabilityImprove operational efficiencyAutomatic systemsRedundant hardware error correctionSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
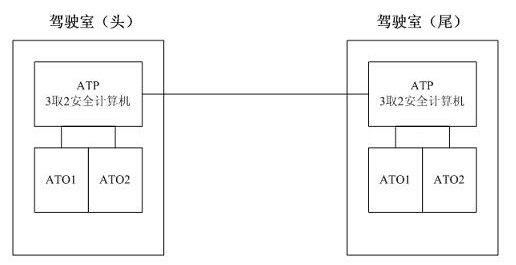
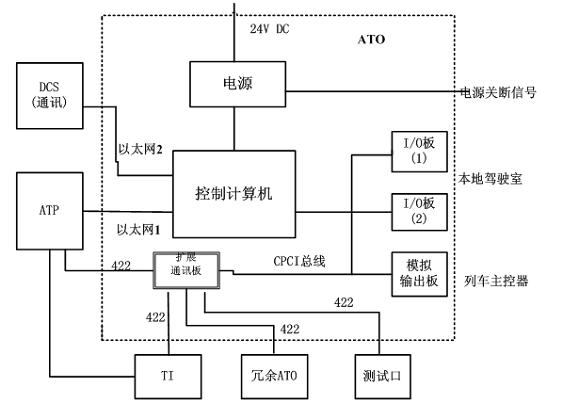
The invention relates to a realization method based on the CPCI bus technology of the dual module hot spare system switching. The realization method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) the cabs at the head and tail of a train are separately provided with an ATP and two ATOs, the ATP adopts 2-out-of-3 architecture, the same ATOs (ATO1, ATO2) are hot spares to each other; 2) when the train runs normally, only the ATPs and ATO of the front head cab in the advancing direction work, the tail cab is powered off; when the train enters a turning section, a driver in the head cab of the original advancing direction presses an AR button on the driving platform to power on the ATPs and ATO of the tail cab; the ATPs and ATO of the head cab and the ATPs and ATO of the tail cab exchange information, the driving privilege is exchanged according to the driving direction so that the original tail cab is reversed to become the head cab, the ATPs and ATO of the original head cab are powered off; and 3) the redundancy automatic switching of one ATO adopts the dual module hot spare mode. The system of the invention has simple hardware configuration, lower system cost and abundant interfaces and is convenient to test and debug.
Owner:NANJING NRIET IND CORP
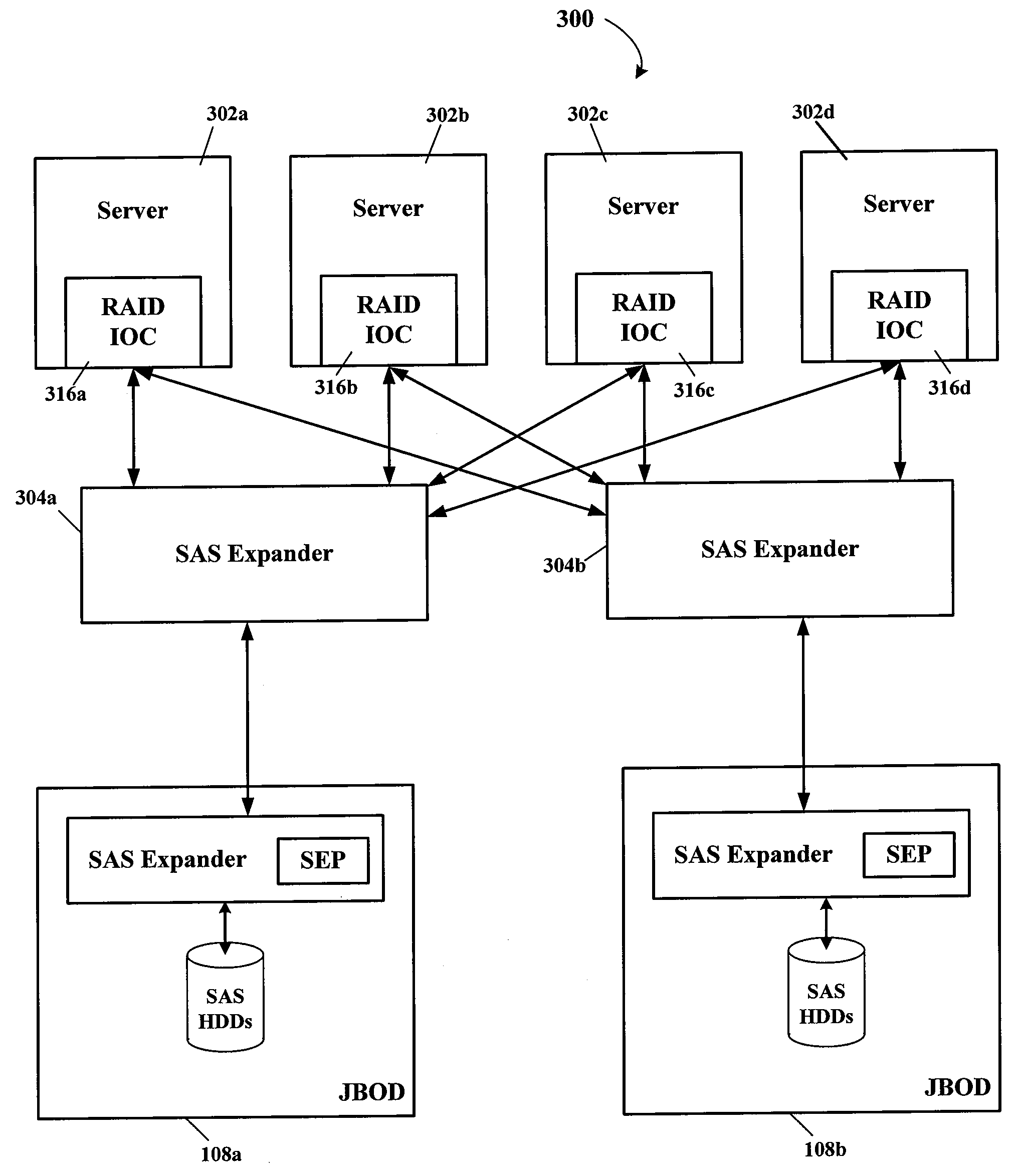
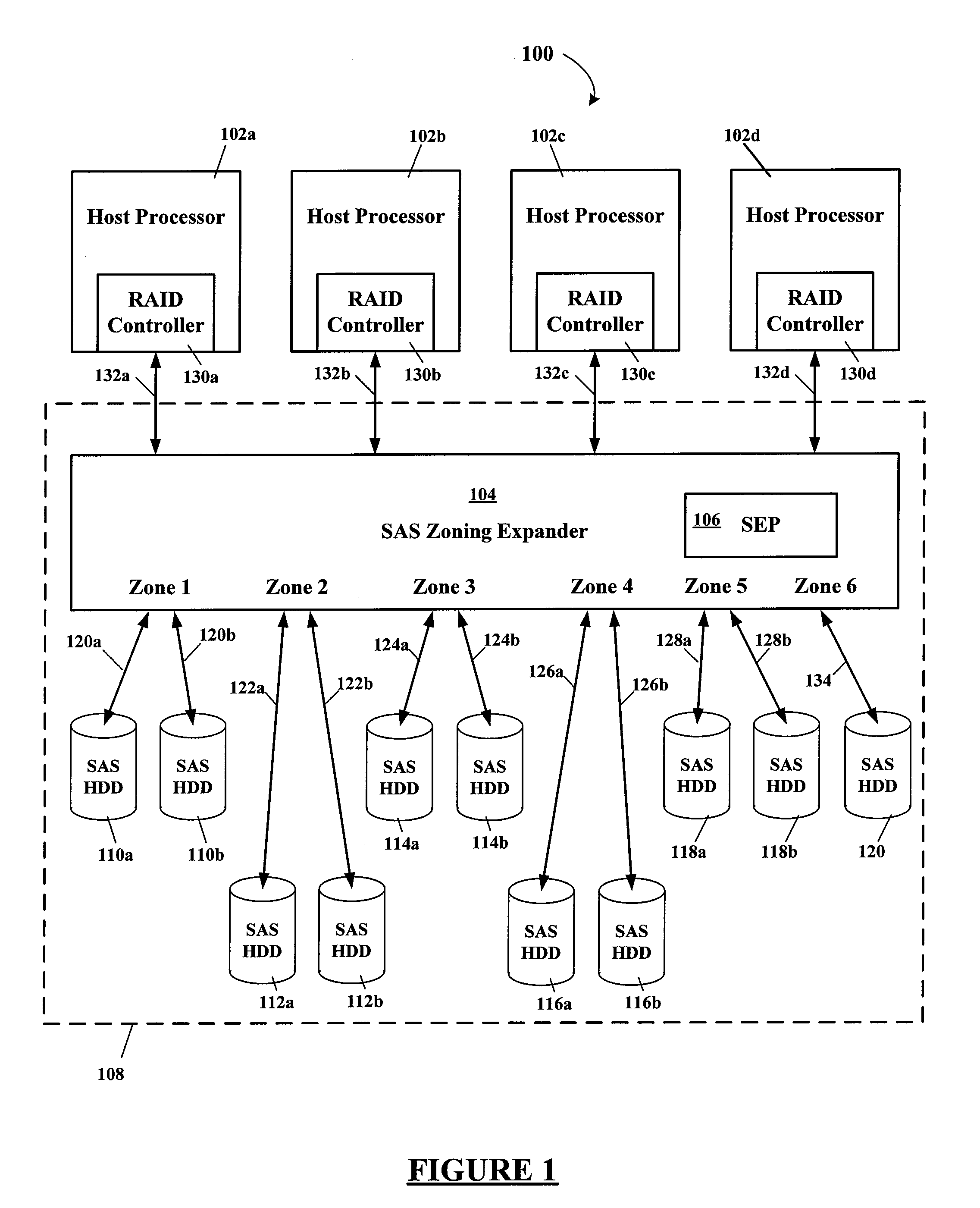
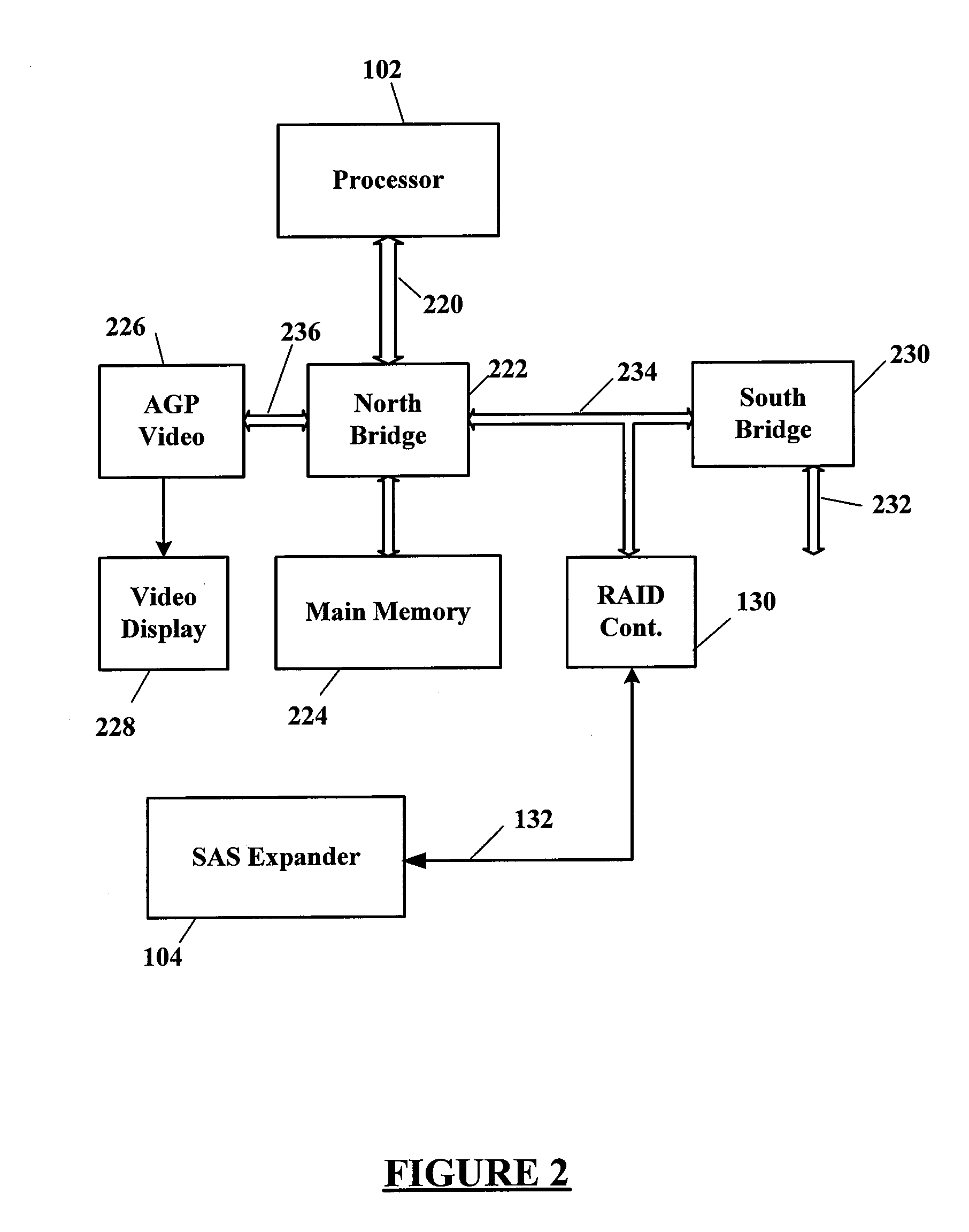
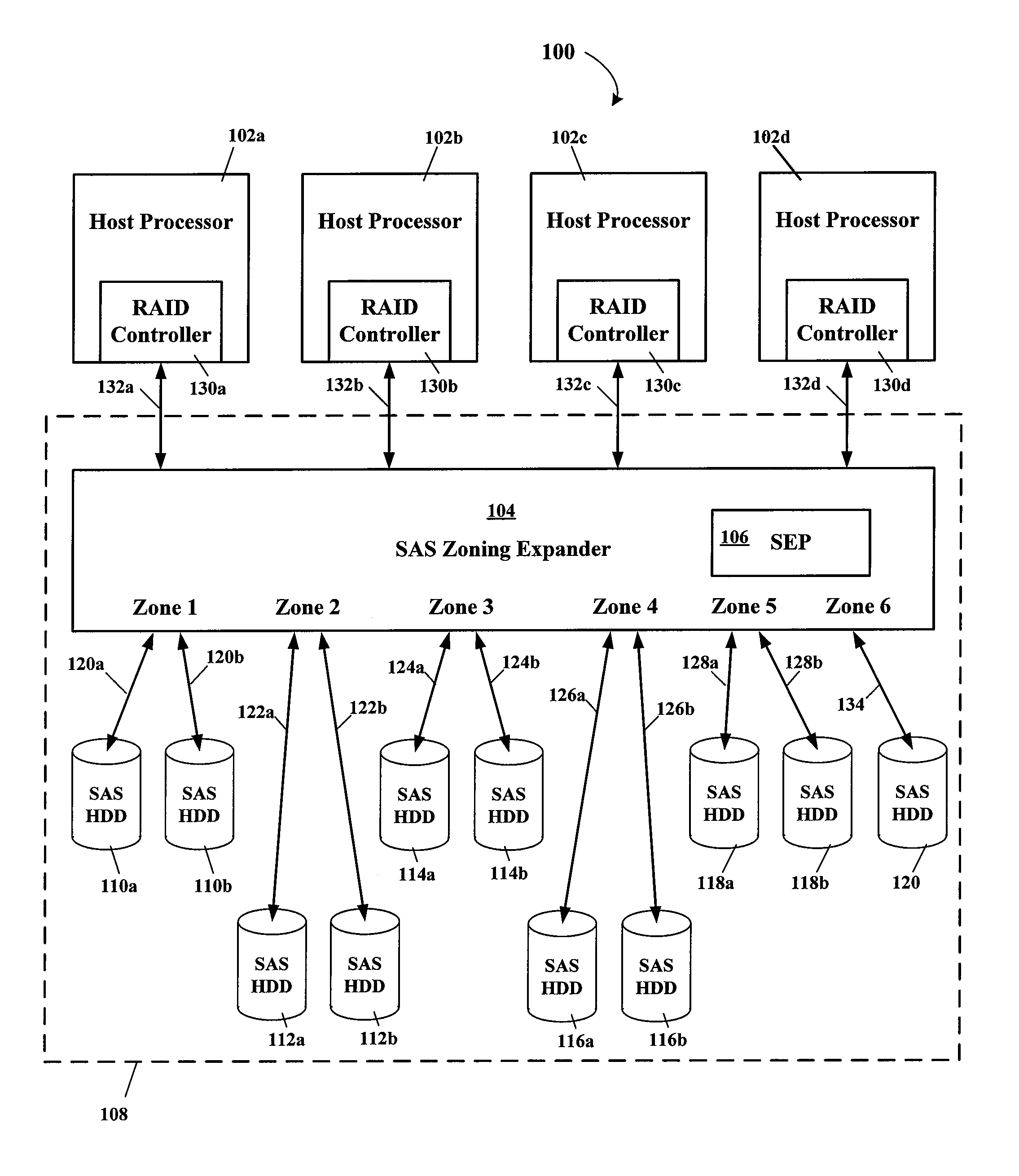
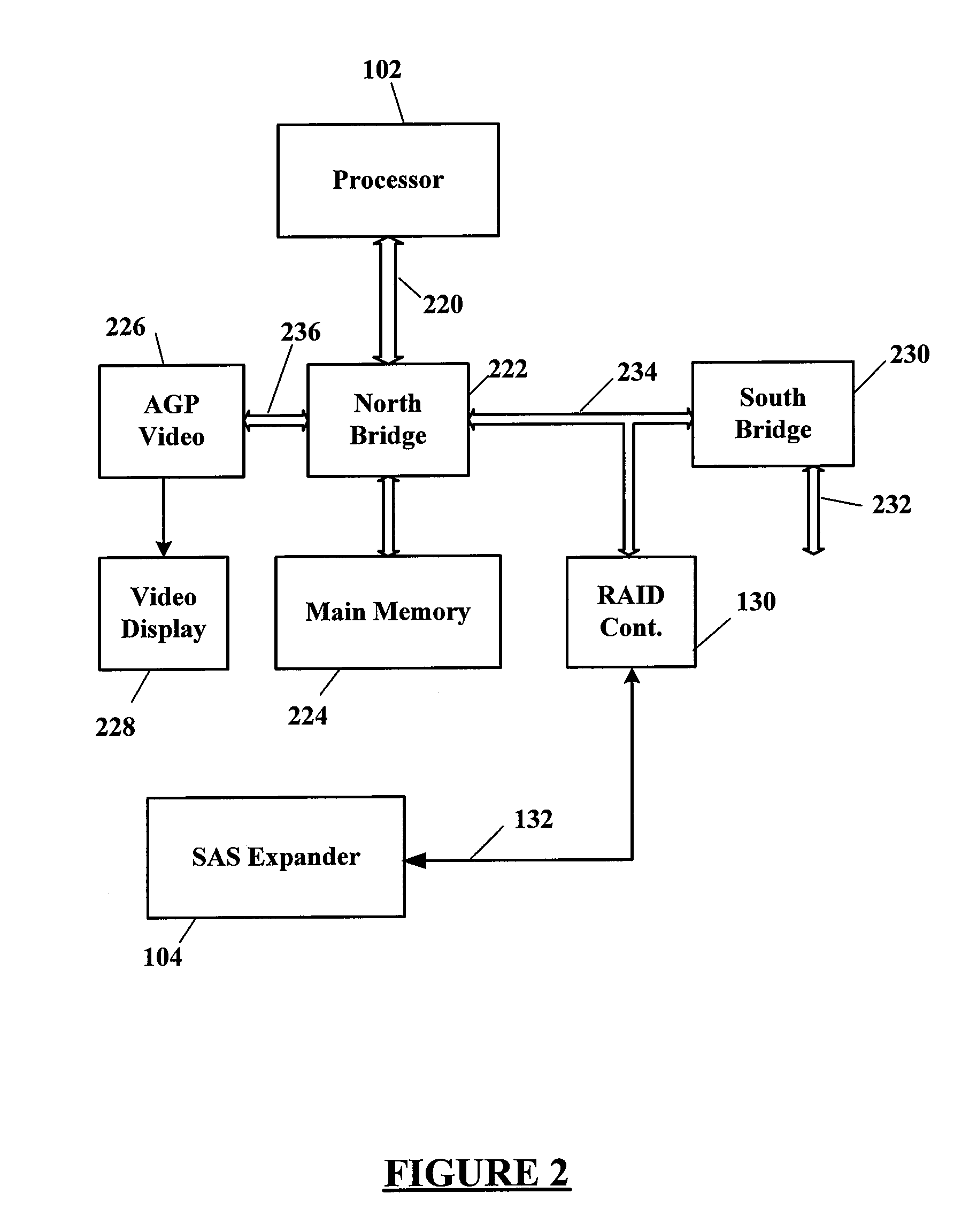
Using SAS address zoning to add/replace hot spares to RAID set
Certain ones of a plurality of SAS hard disk drives are assigned to different SAS zones using a SAS zoning expander(s). A processor and SAS RAID controller have access to only those SAS hard disk drives assigned to the same zone(s) as the processor and SAS RAID controller. Each SAS RAID controller determines when a RAID hard disk drive in its zone fails, and then notifies the RAID hard disk drive failure to a service enclosure processor (SEP) of the SAS zoning expander. The SEP re-allocates an available hot-spare hard disk drive to the zone of the failed RAID hard disk drive. When the SAS RAID controller detects that a functional hard disk drive is now available in its zone, the RAID image is rebuilt using the zone reassigned hot-spare hard disk drive that then becomes one of the RAID hard disk drives of that zone.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
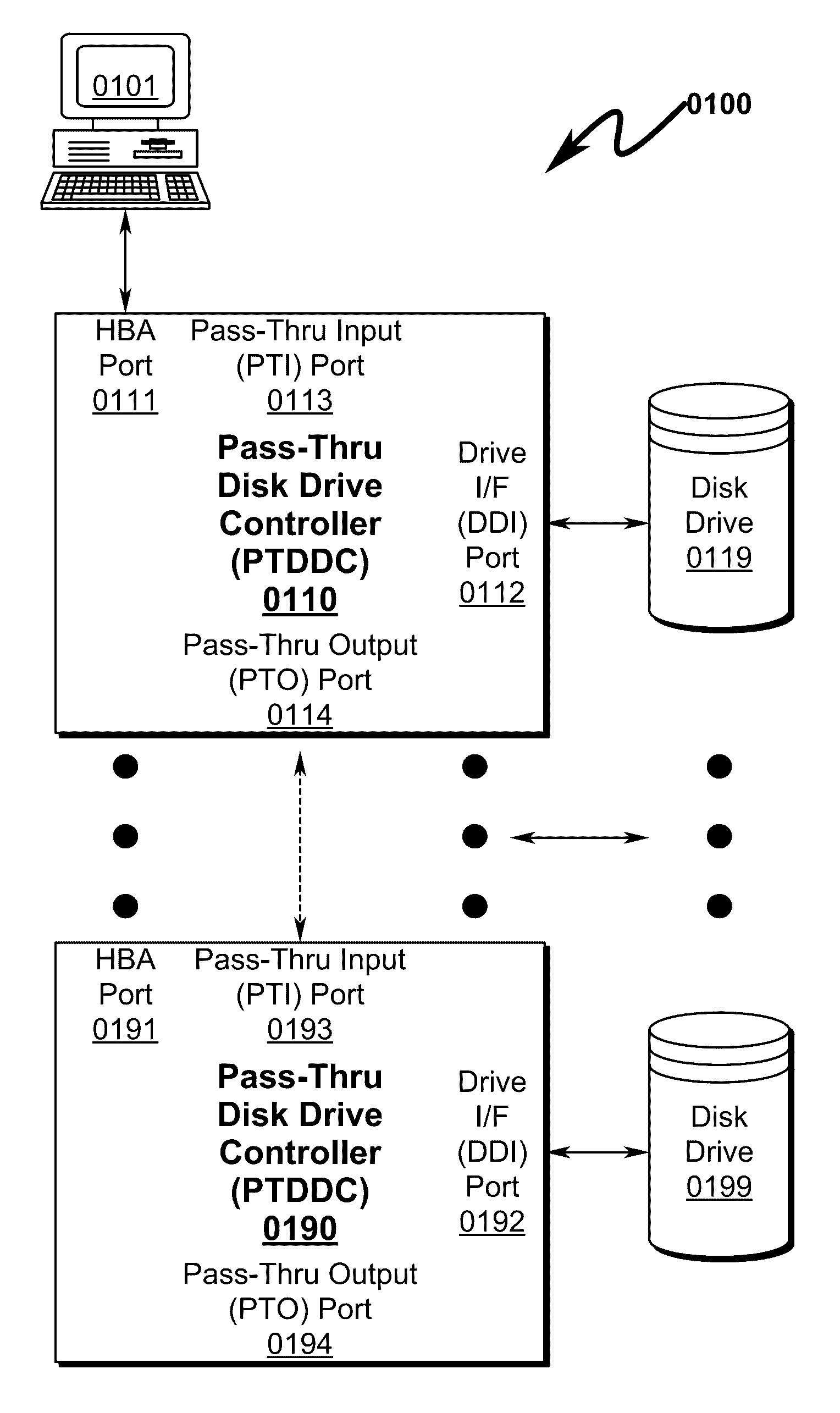
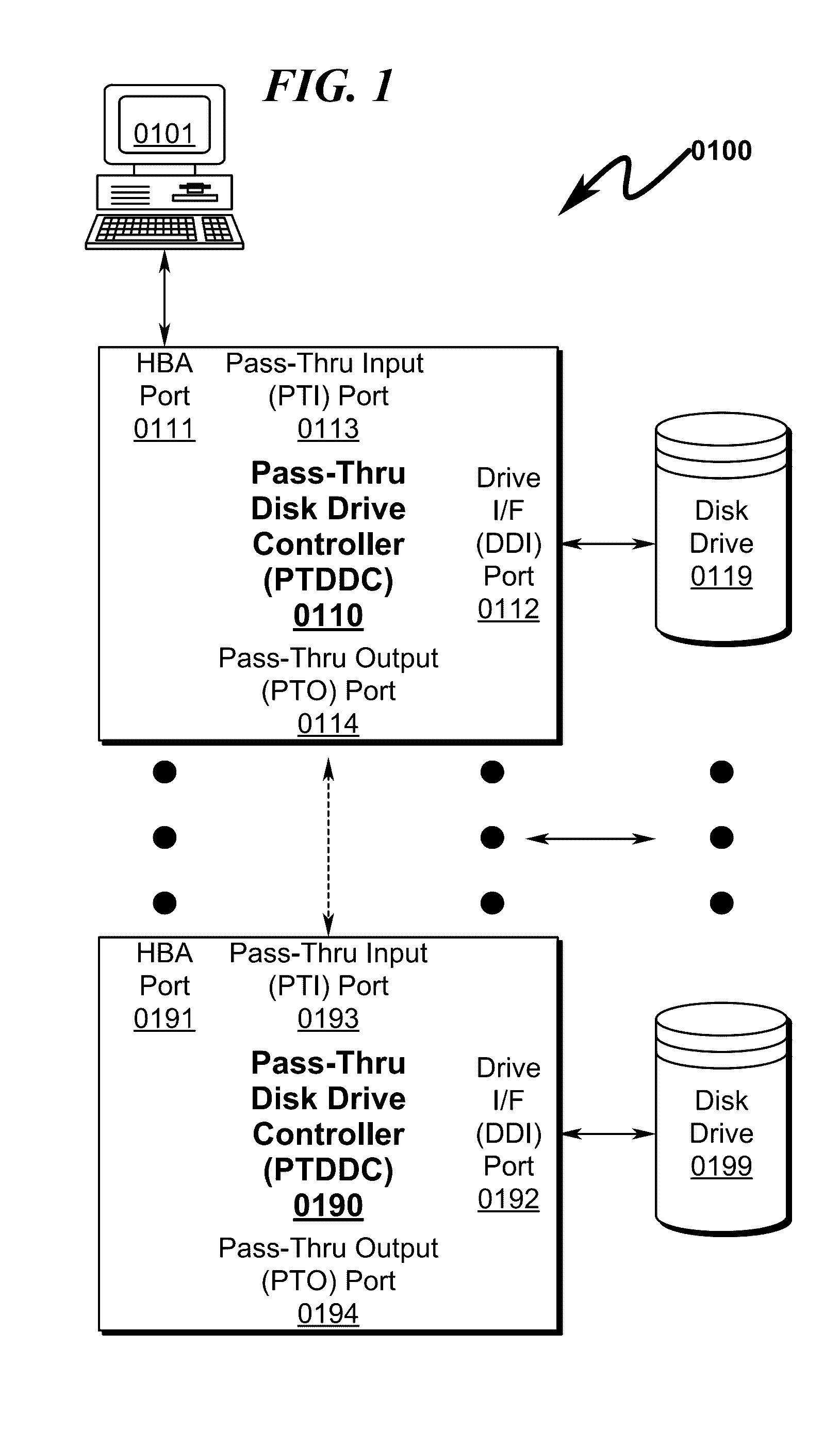
Raid hot spare system and method
ActiveUS20170024295A1Input/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsRAIDProcessor register
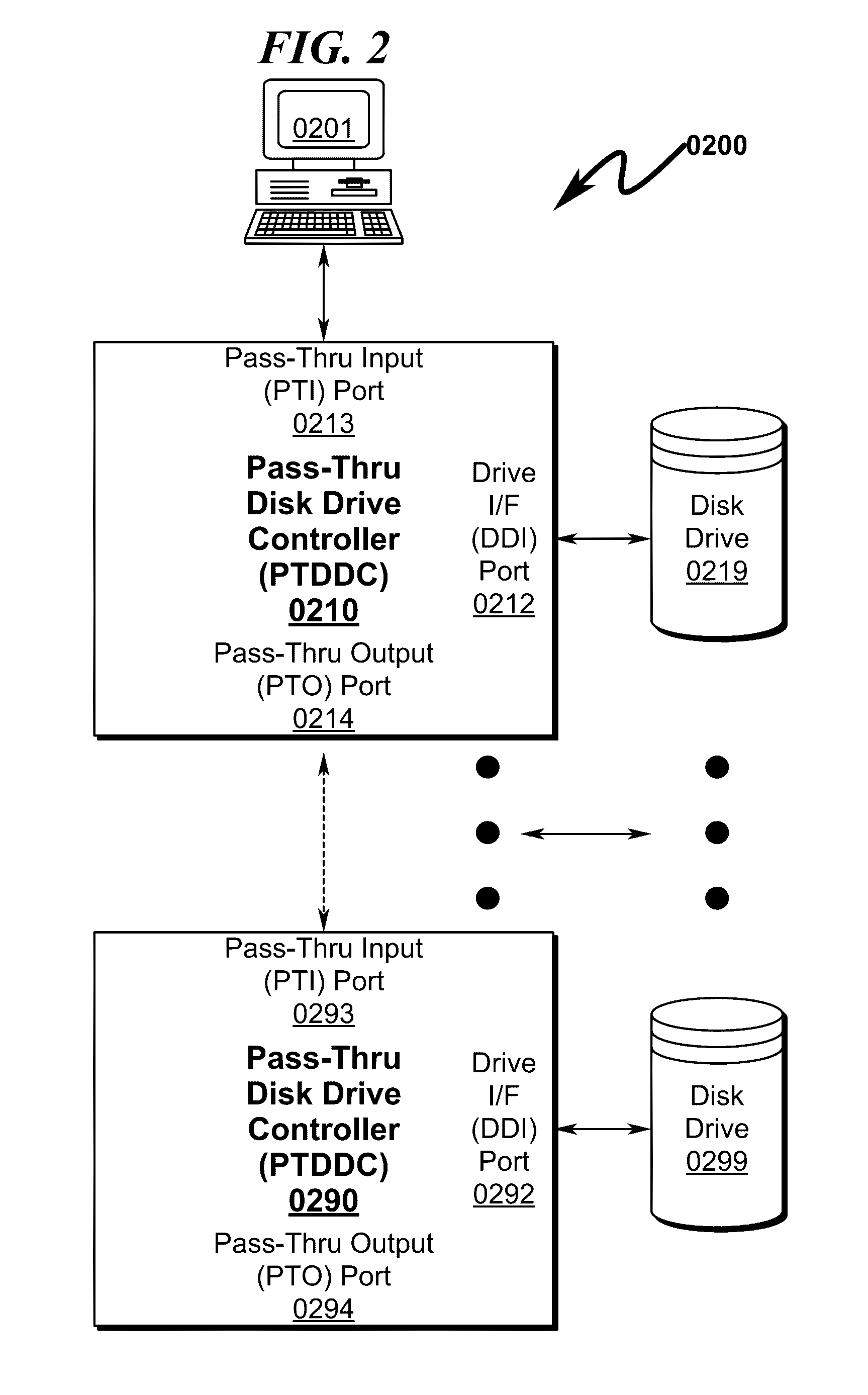
A RAID (redundant array of independent disks) hot spare (RHS) system and method that permits a daisy-chain of interconnected pass-thru disk drive controllers (PTDDCs) each connected to a SATA local disk drive (LDD) storage element (DSE) to support a hot spare disk (HSD) such that a failing disk drive (FDD) in the RAID array can be immediately replaced by a HSD within the PTDDC daisy-chain without operator intervention is disclosed. The PTDDCs within the daisy-chain are configured in RAID fashion to support mirroring of one or more drives in the PTDDC daisy-chain. The PTDDCs monitor functional status of LDDs attached to each PTDDC. FDD failure triggers activation of a HSD in the PTDDC daisy-chain and automatic mirror copying along the PTDDC daisy-chain of RAID data from a master disk drive (MDD) mirrored to the LDD. FDD-PTDDC and HSD-PTDDC LBA mapping registers are updated after mirror copying completes.
Owner:KLUGHART KEVIN MARK
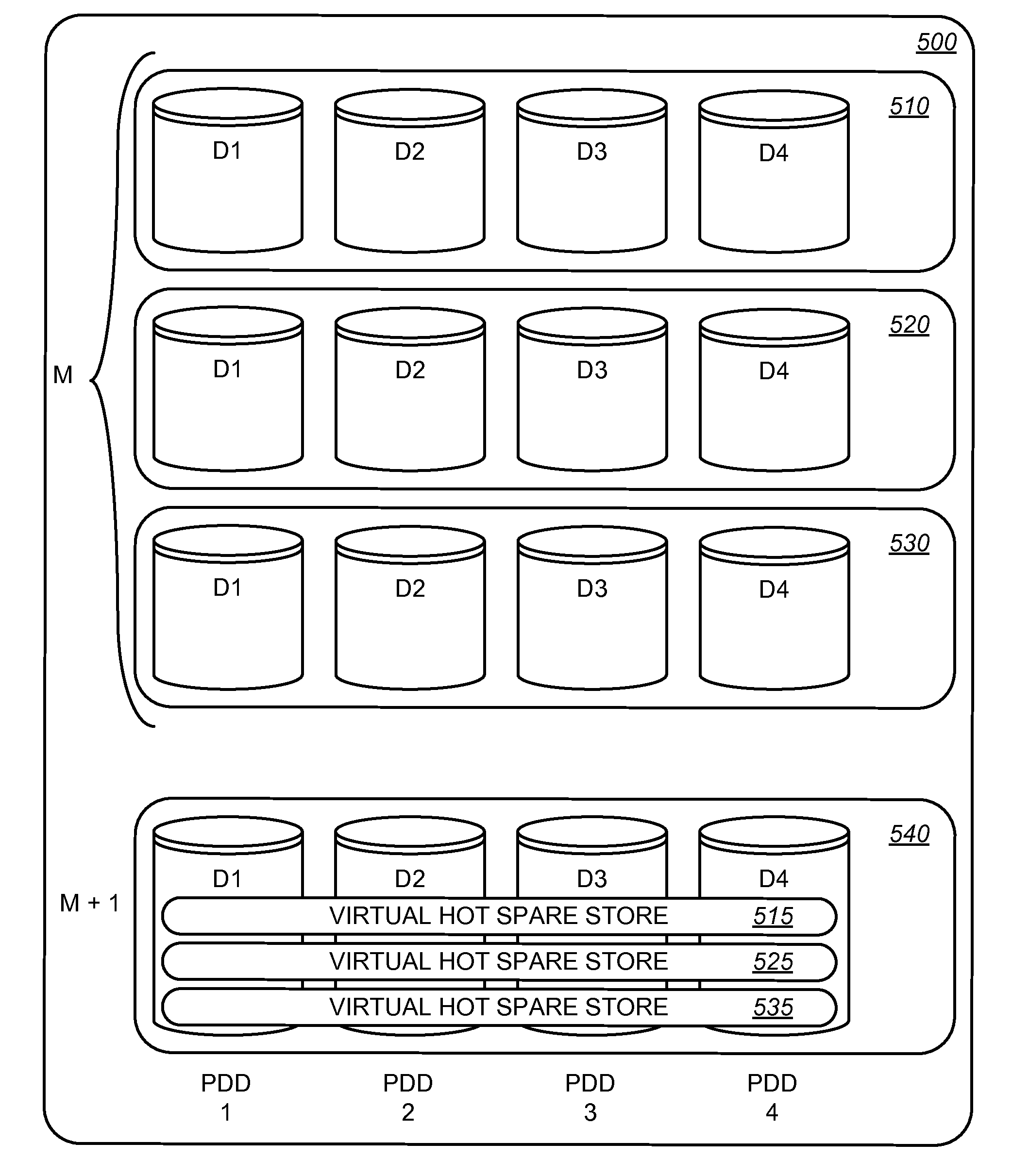
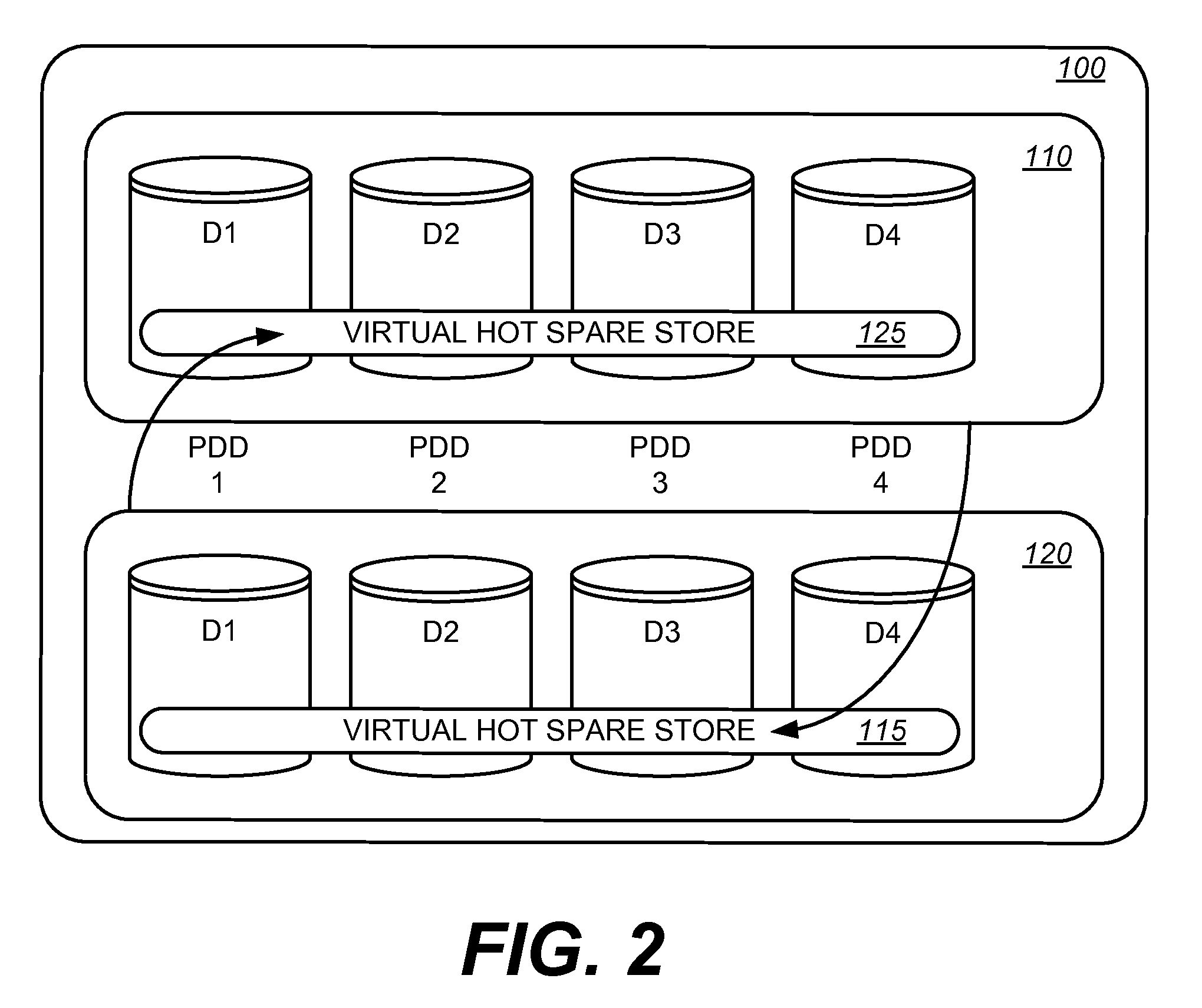
Method, apparatus and program storage device that provide virtual space to handle storage device failures in a storage system
A method, apparatus and program storage device that provides virtual hot spare space to handle storage device failures in a storage system is disclosed. Data is migrated from a failed storage device to a hot spare storage device, which may be a virtual hot spare device spanning multiple physical storage devices or even existing as a subset of a single physical storage device, until a replacement storage device is hot swapped for the failed storage device. Once the replacement storage device is installed, the recovered data on the hot spare is moved back to the replacement storage device.
Owner:XIOTECH CORP
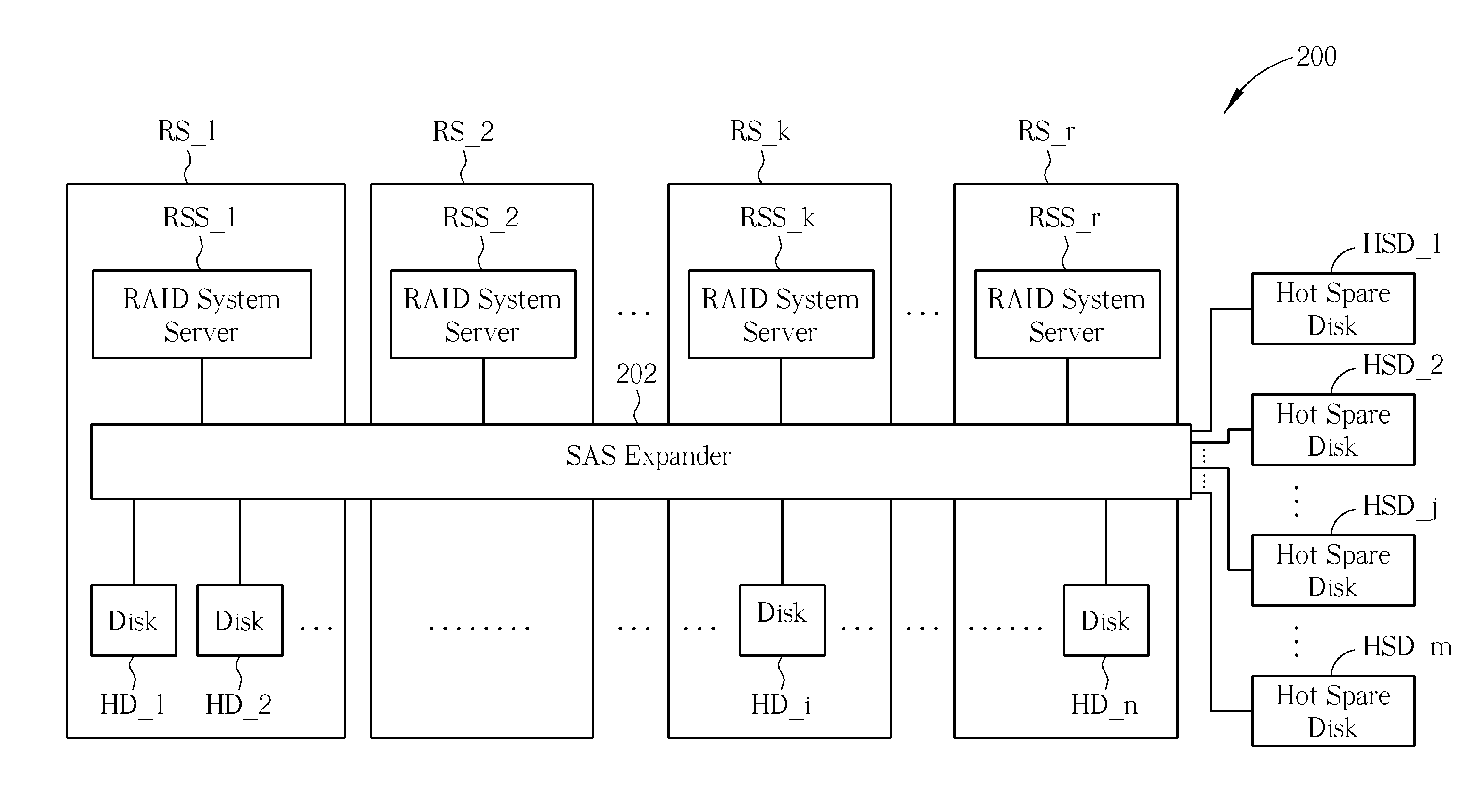
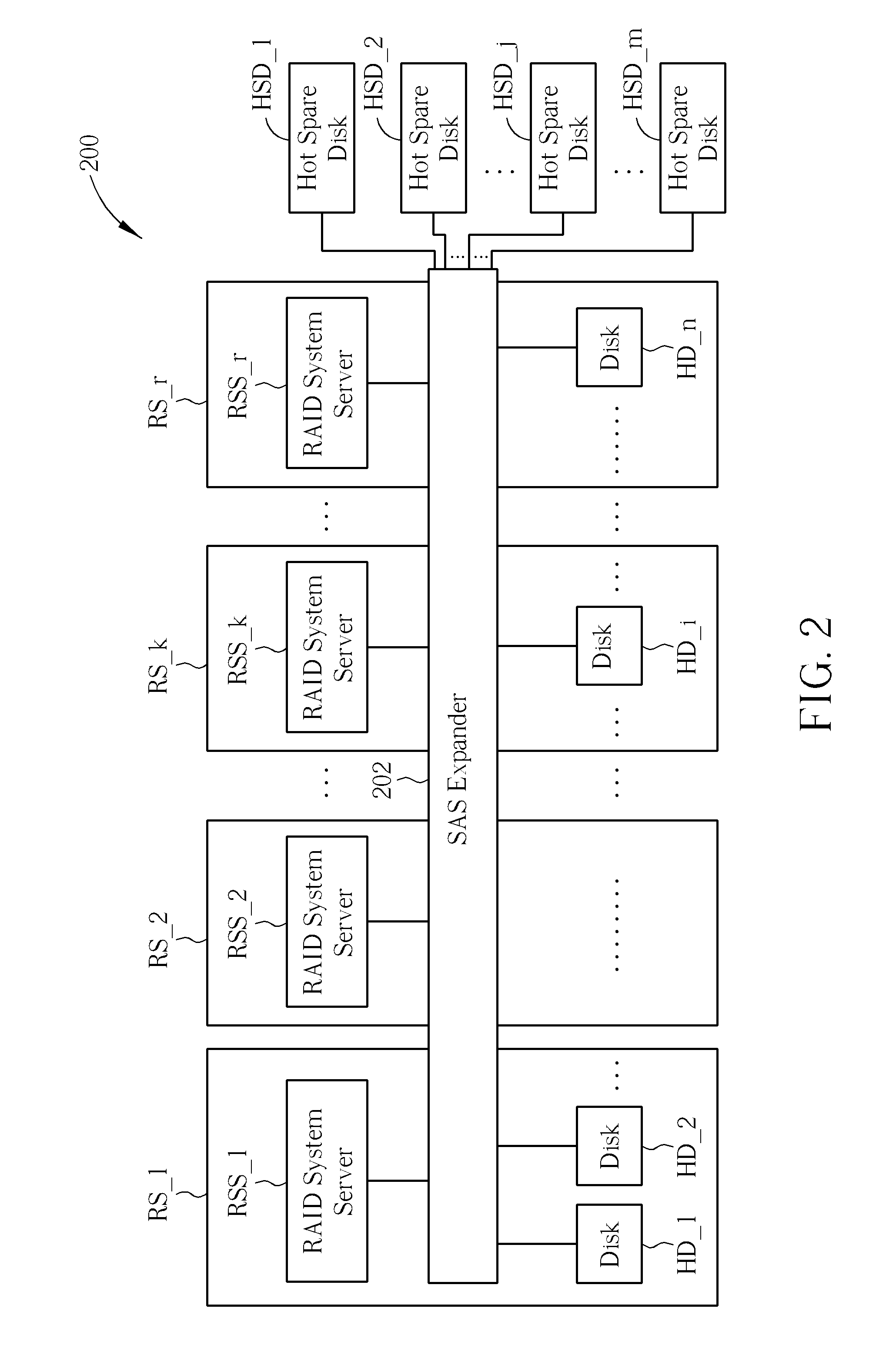
Method for a Plurality of RAID Systems and Data Storage System Thereof
A data storage method for a plurality of RAID systems includes an SAS expander recording information of failure of a disk of a plurality of RAID systems when failure of the disk is detected and reporting the information of failure of the disk to the RAID system server when the RAID system server sends a polling message to the SAS expander or tries accessing the failed disk. In response to the failure information of the failed disk from the SAS expander, the RAID system server sends a command to the SAS expander, to replace the disk with a hot spare disk.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Autonomous fail-over to hot-spare processor using SMI
ActiveUS7251746B2None of can remain in operationEliminate the problemRedundant hardware error correctionPower modeFailover
A method and system for dynamically replacing a failing processor in a server system configured with IA-32 architecture without requiring hardware changes to the IA-32 architecture or administrative effort. At least one processor of the multiprocessor system (MP) is initially provided as a reserve (or hot-spare) processor that remains in an idle, off, or low-power mode. While in that mode, the OS is prevented from initially utilizing the hot-spare processor. When a processor failure is detected, SMI code running on a good processor instructs the OS to hold off allocating processes to the failing processor. Contemporaneously, the SMI (and OS) activates and completes an initialization of the hot-spare processor to prepare it to begin receiving the held-off processes. Control is then returned to the OS, which updates the “active” processor list and allocates the threads that were running on the failing processor to the hot-spare processor.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
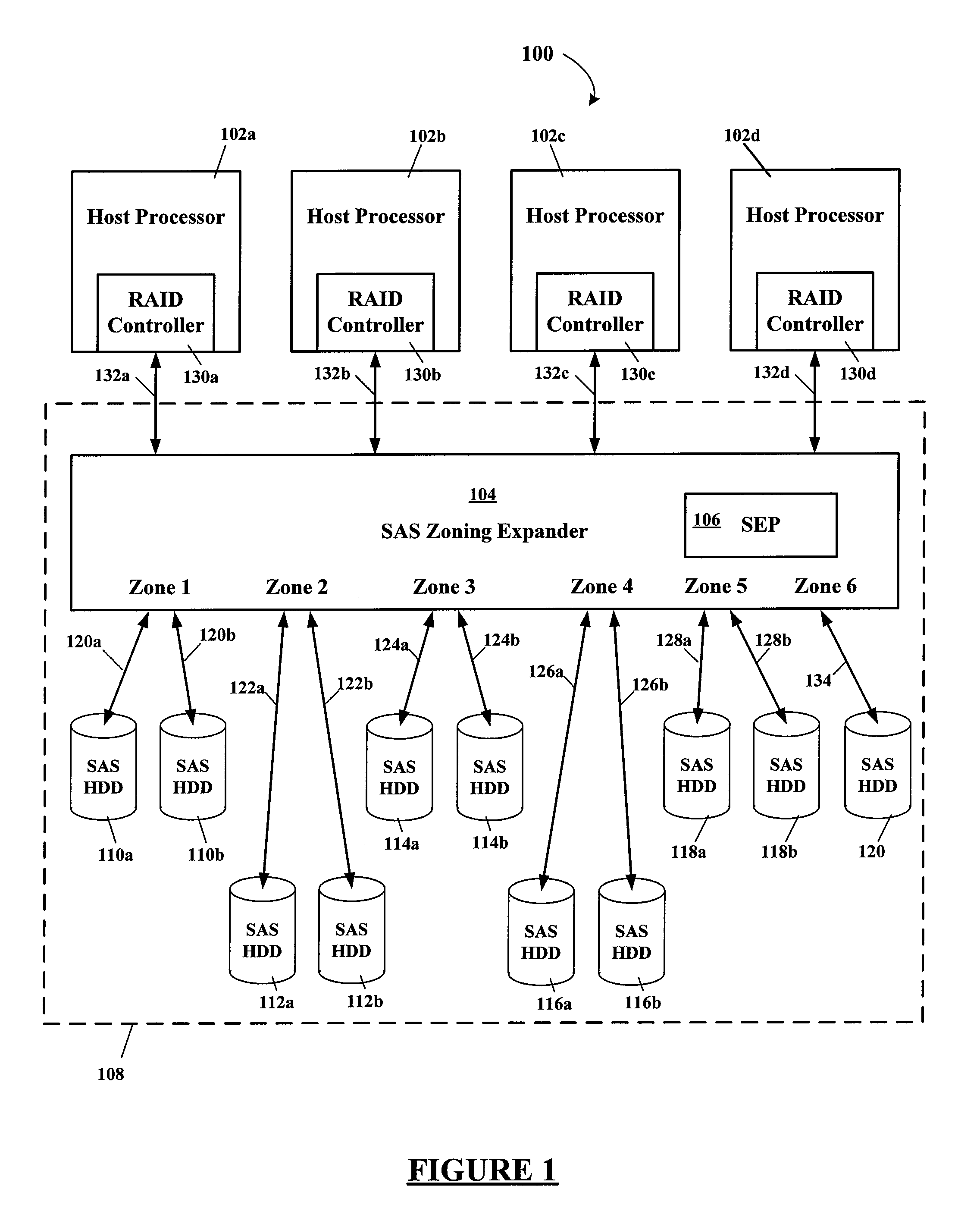
Using SAS address zoning to add/replace hot spares to RAID set
Certain ones of a plurality of SAS hard disk drives are assigned to different SAS zones using a SAS zoning expander(s). A processor and SAS RAID controller have access to only those SAS hard disk drives assigned to the same zone(s) as the processor and SAS RAID controller. Each SAS RAID controller determines when a RAID hard disk drive in its zone fails, and then notifies the RAID hard disk drive failure to a service enclosure processor (SEP) of the SAS zoning expander. The SEP re-allocates an available hot-spare hard disk drive to the zone of the failed RAID hard disk drive. When the SAS RAID controller detects that a functional hard disk drive is now available in its zone, the RAID image is rebuilt using the zone reassigned hot-spare hard disk drive that then becomes one of the RAID hard disk drives of that zone.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Improved disk array reconstruction method
ActiveCN102012847AReduce the risk of lossShorten the timeInput/output to record carriersRedundant data error correctionRAIDReconstruction method
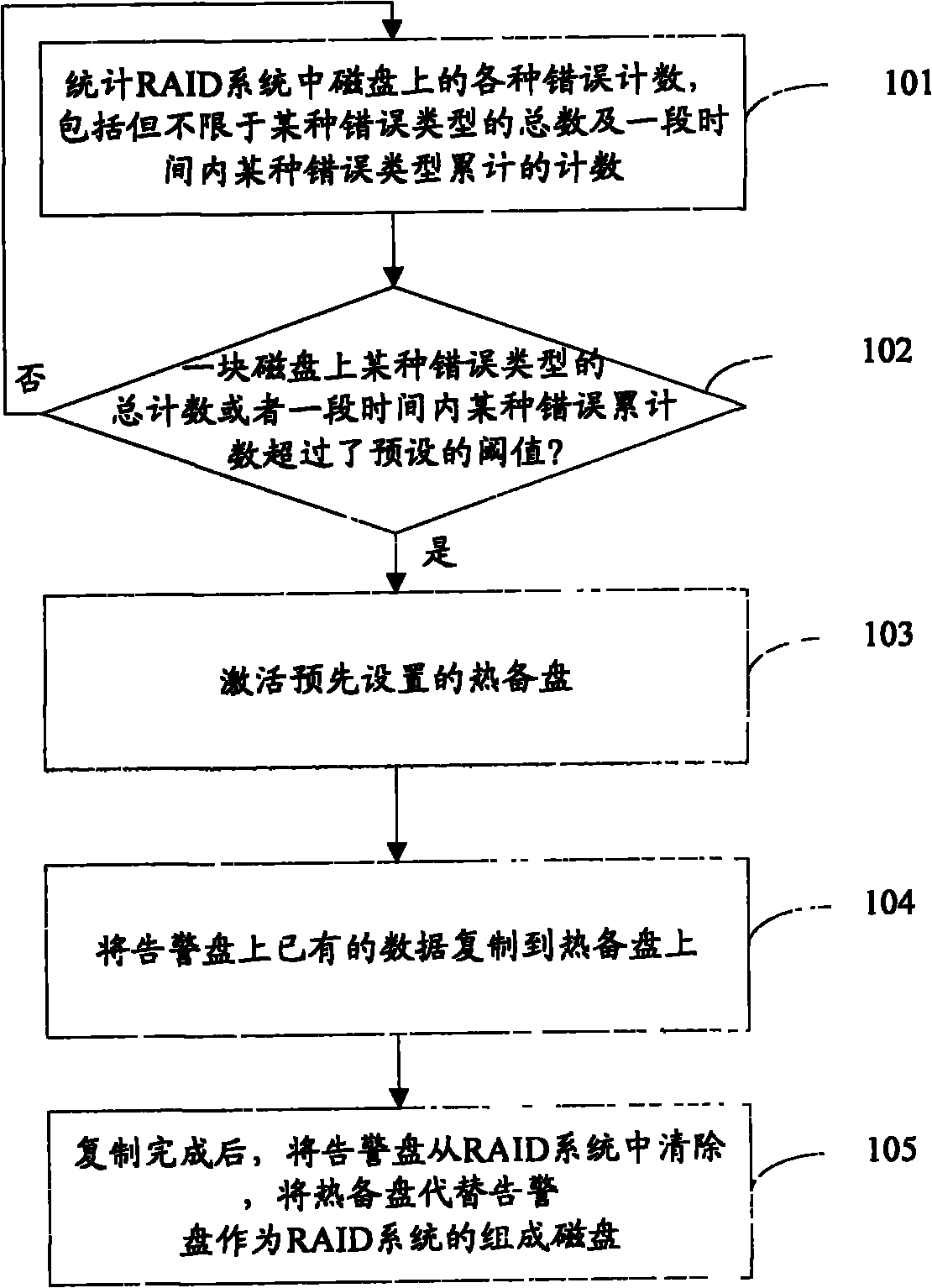
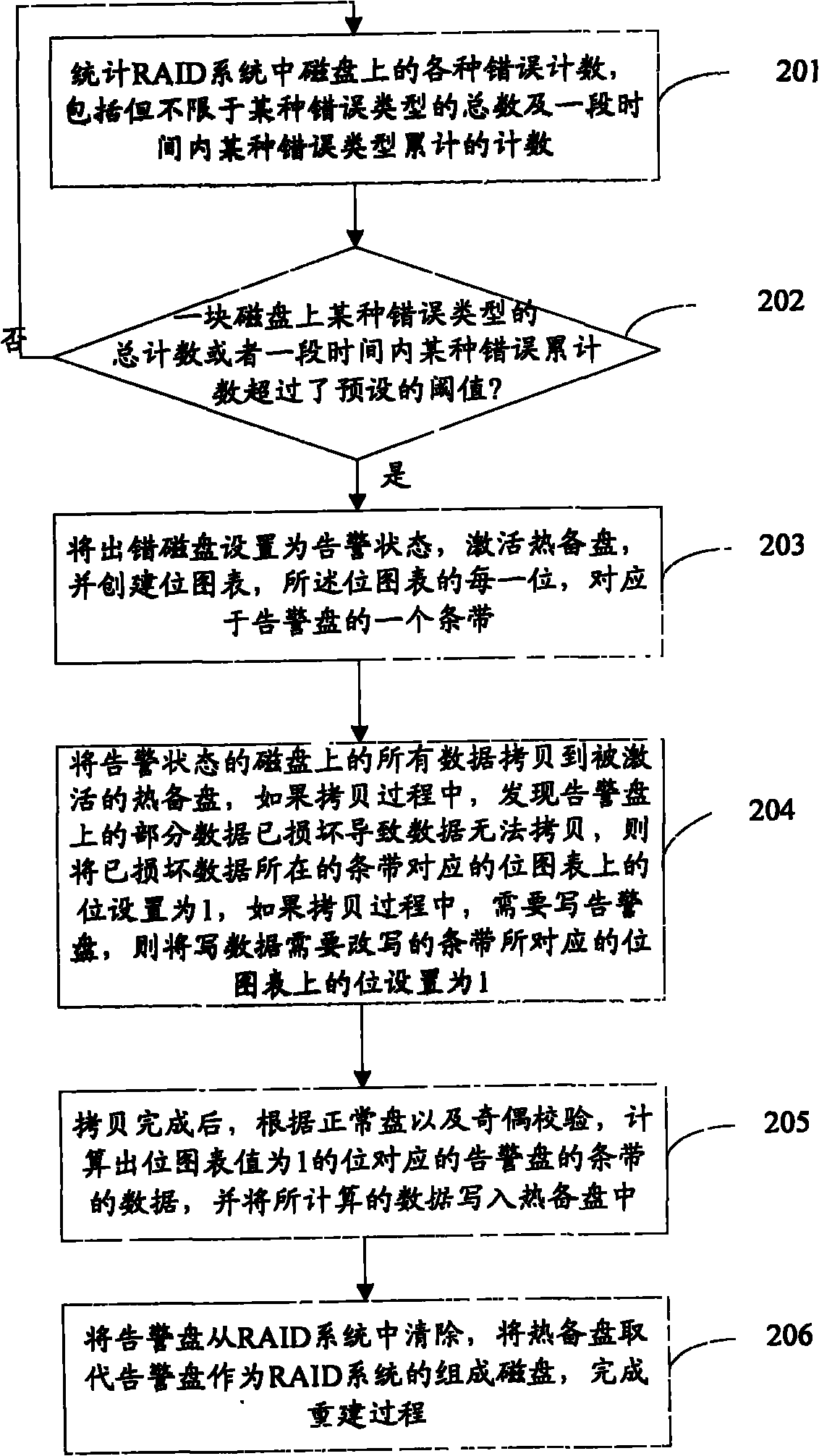
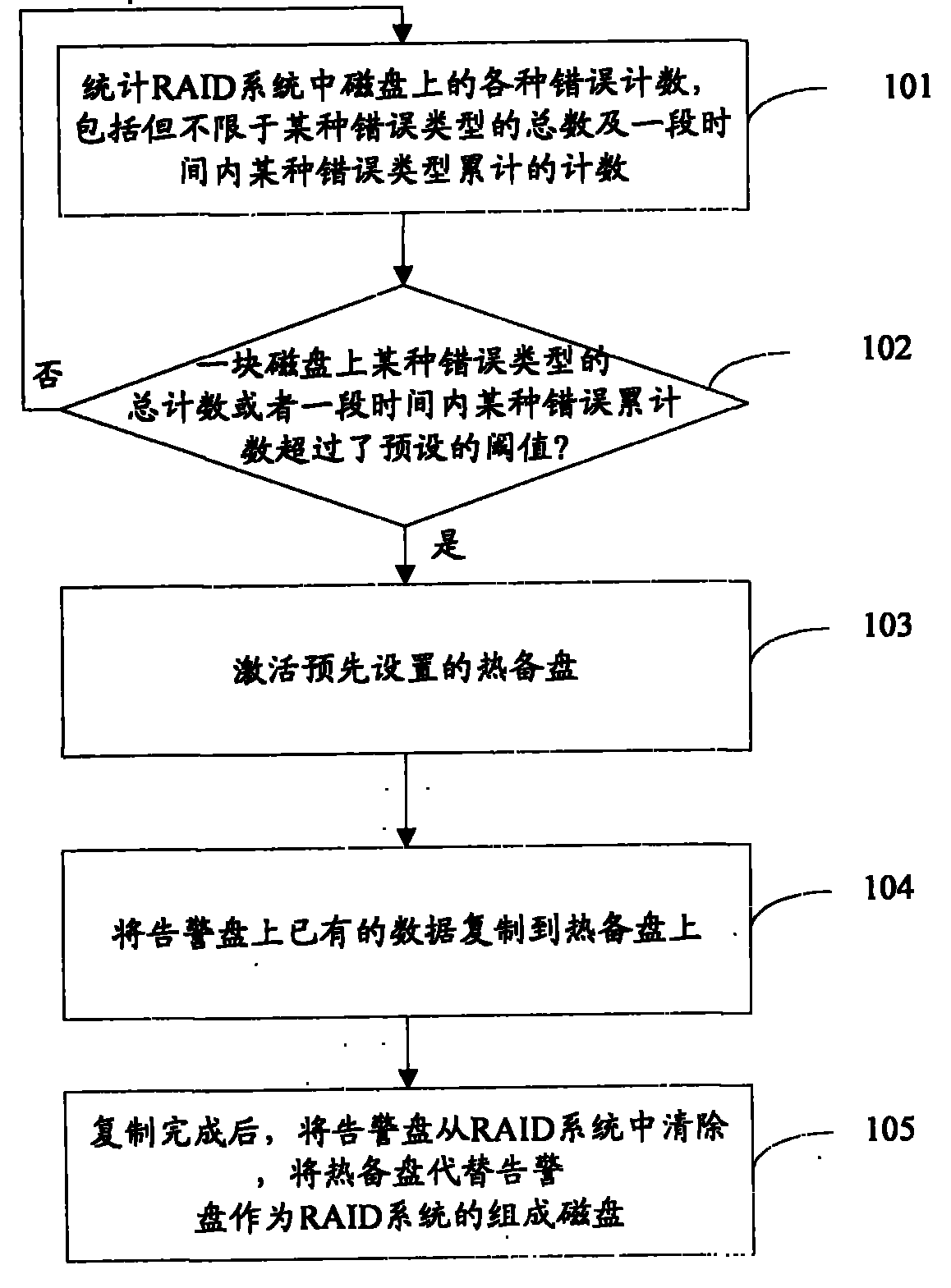
The invention provides a disk array reconstruction method. The improved disk array reconstruction method comprises the following steps of: A, counting error counts in disks in a redundant array of independent disks (RAID) system; B, judging whether the error count in one disk of the RAID system exceeds a preset threshold value or not, if so, executing a step C, otherwise returning to the step a; C, setting the disk as a warning disk, activating a preset hot spare disk and replicating existing data in the warning disk into the hot spare disk; and D, after the replication, deleting the warning disk from the RAID system and substituting the hot spare disk for the error disk as the component disk of the RAID system. In the scheme, the risk of data loss in the reconstruction process can be effectively reduced and the reconstruction process is accelerated.
Owner:UNITED INFORMATION TECH +1
Redundant array of independent disks (RAID) system backup management
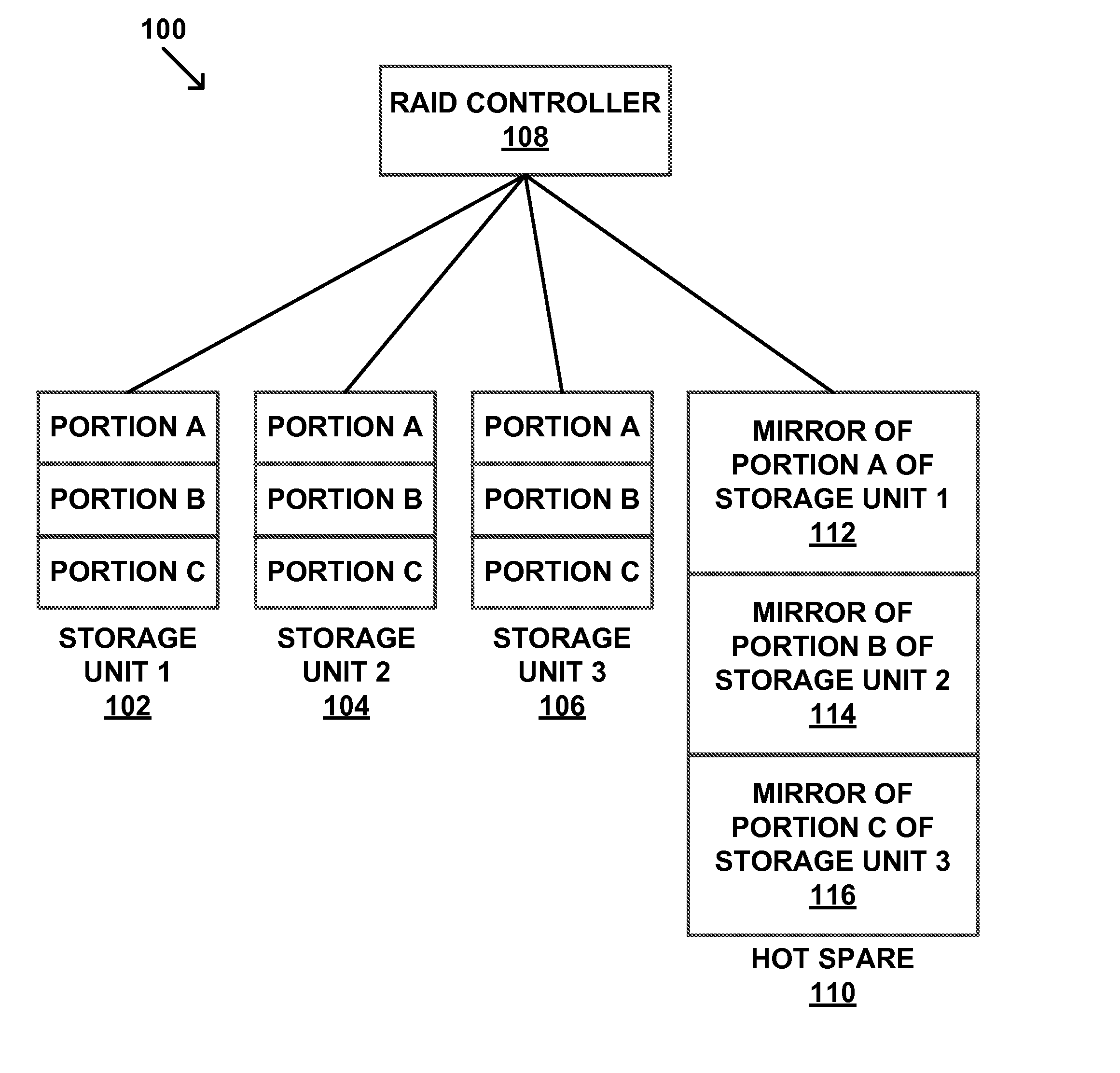
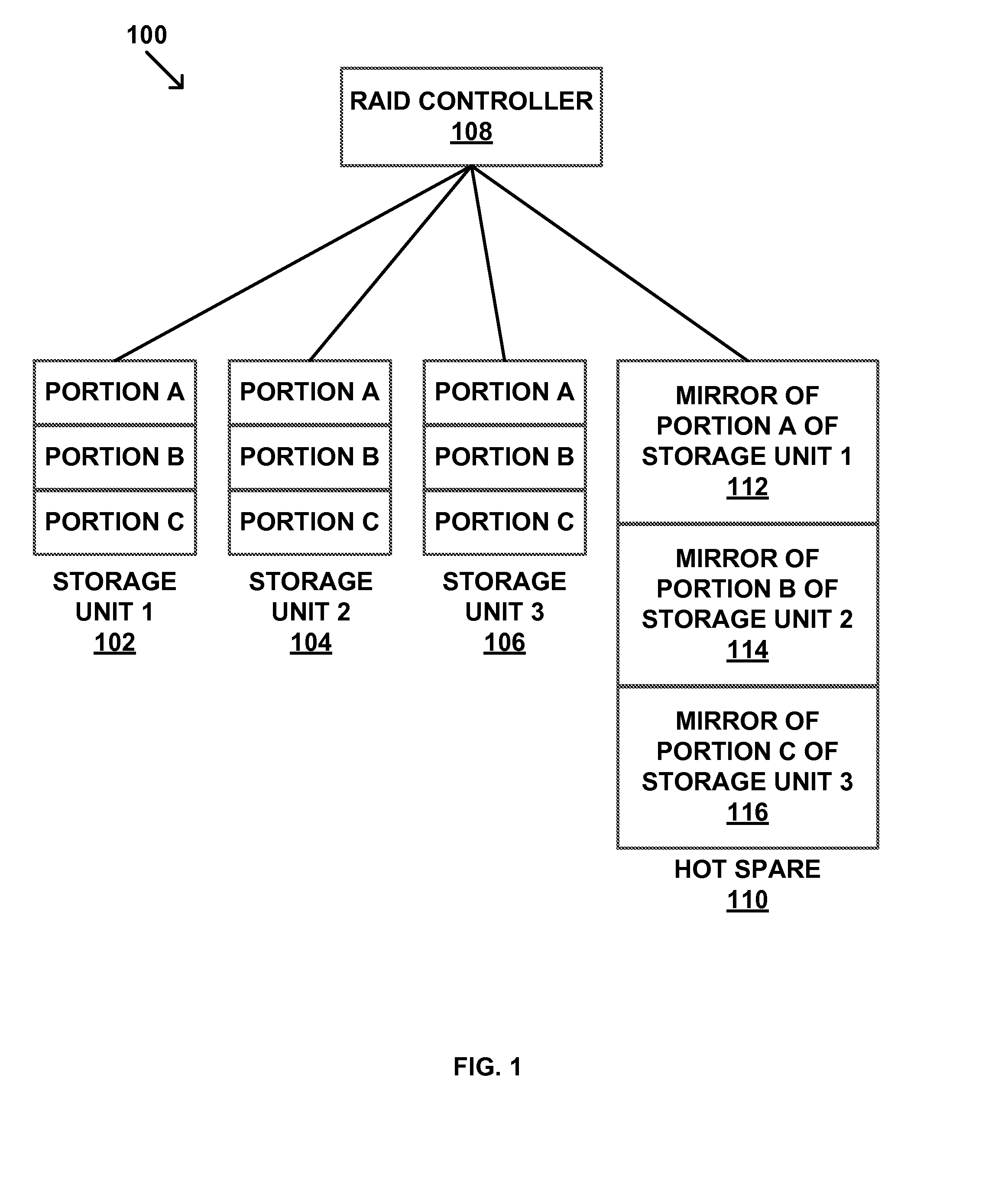
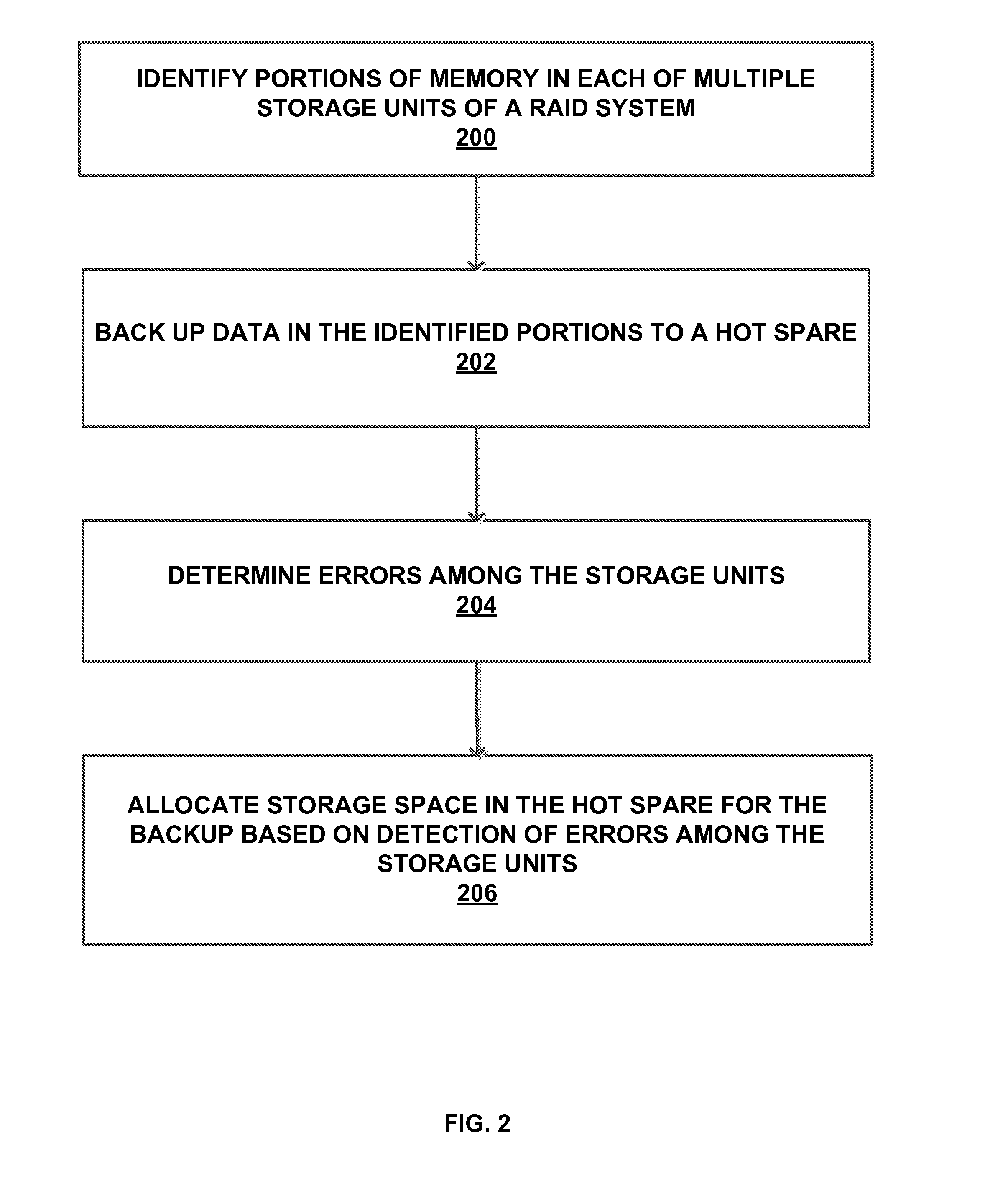
InactiveUS20150012775A1Reliability/availability analysisRedundant operation error correctionRAIDDisk array
Disclosed herein are RAID backup management systems and methods. According to an aspect, a method may include identifying portions of data in each of multiple storage units of a RAID system. The method may also include backing up data in the identified portions to a hot spare. Further, the method may include allocating storage space in the hot spare for the backup based on detection of errors among the storage units.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Data processing method and device for disk array
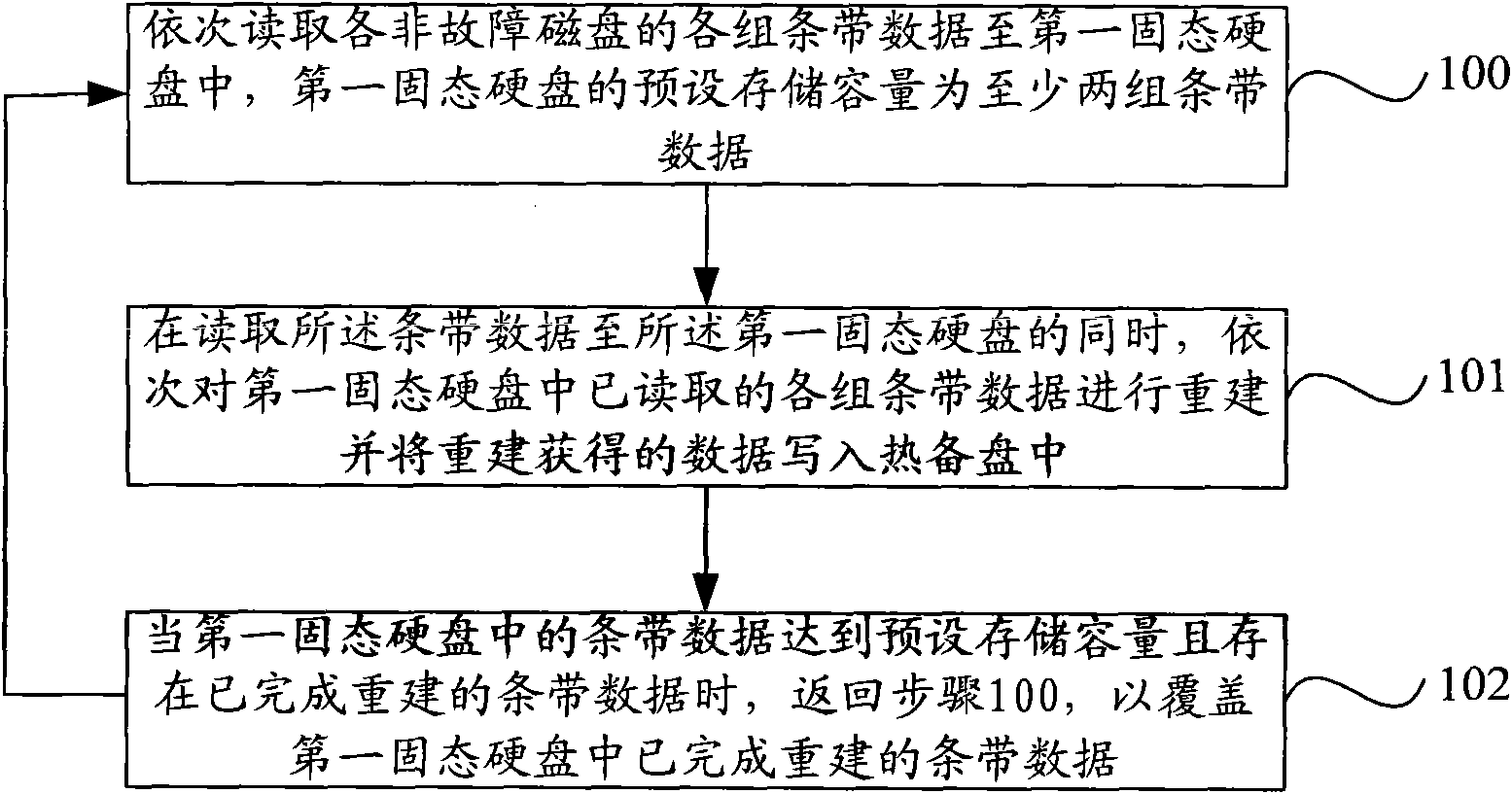
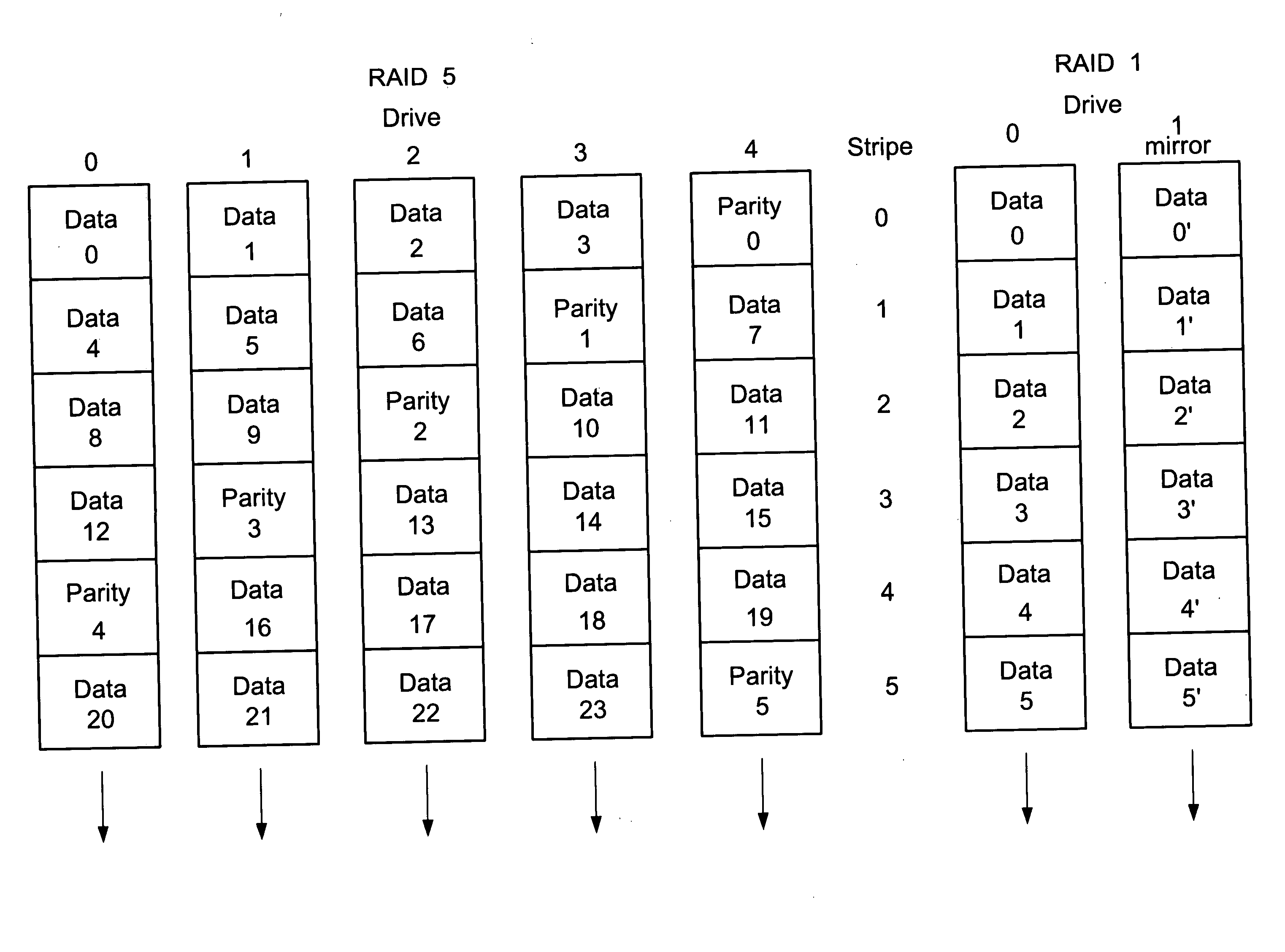
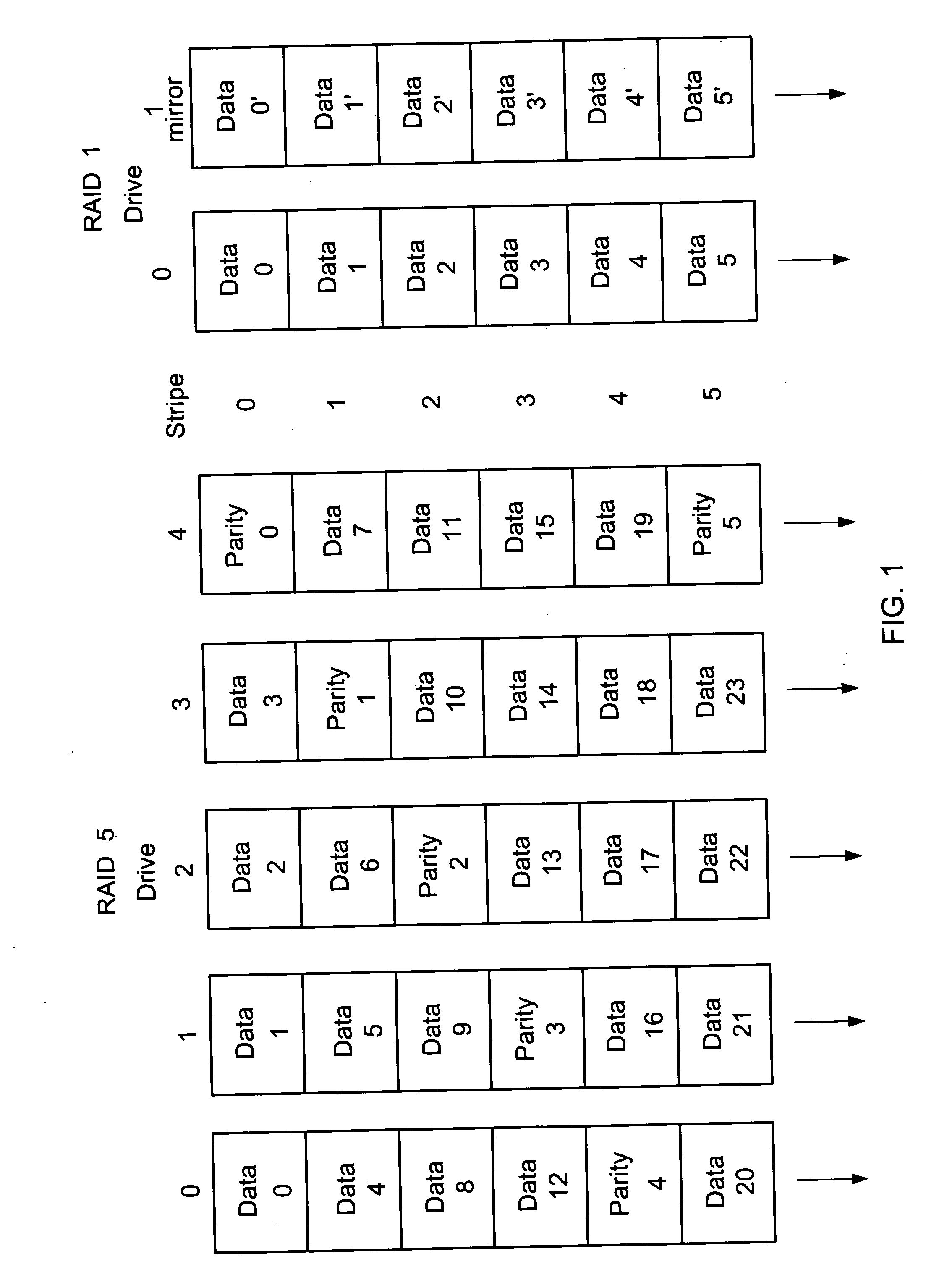
ActiveCN101833422AImprove rebuild speedReduce the risk of failureInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionSolid-state driveDisk array
The invention provides data processing method and device for a disk array. The method comprises the following steps of: orderly reading each set of strip data in each non-fault disk into a first solid hard disk of which the preset storage capacity is at least two sets of strip data; while reading the strip data to the first solid hard disk, orderly reconstructing the read strip data in each set in the first solid hard disk, and writing the data acquired by reconstruction into a hot spare disk; and when the strip data in the first solid hard disk reaches a preset storage capacity, orderly reading the strip data in each set in each non-fault disk into the first solid hard disk to cover the reconstructed strip data in the first solid hard disk. By introducing multiple sets of strip data into the RAID5 disk array, when the disk array is in the degrading mode, the SSD hard disk is used as a cache for prefetching the data in the non-fault disk, thereby enhancing the reconstruction speed of the disk array and reducing the risk of second disk failure in the degrading mode.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
Method for reducing rebuild time on a RAID device
InactiveUS20070168706A1Reduce rebuild timeError detection/correctionMemory systemsRAIDMethod selection
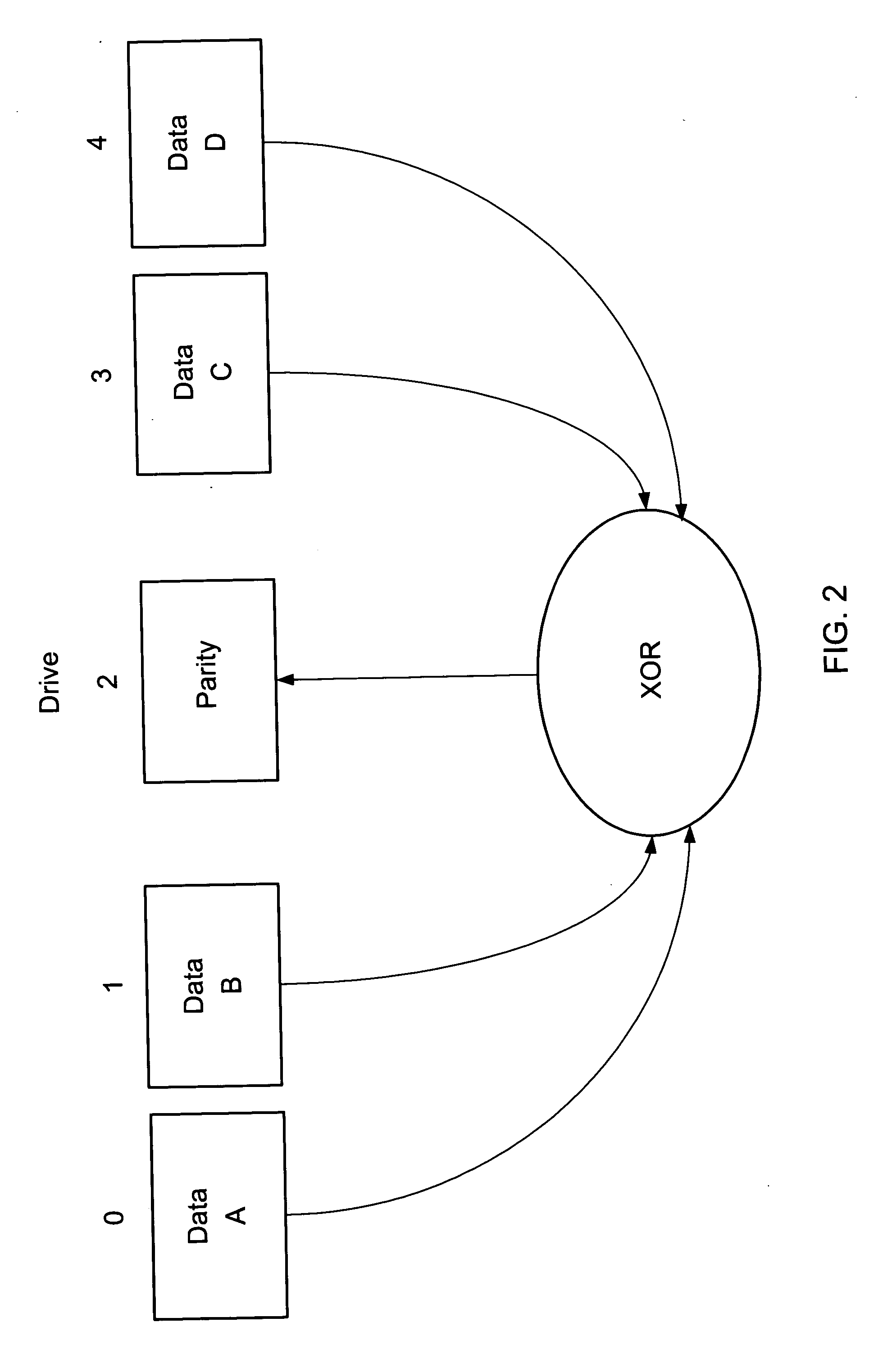
The present invention provides a method for reducing rebuild time on a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) device. A first stripe of the RAID device is selected. Write-back caching on a drive being built is enabled. Data and / or parity may be read from at least one other drive. The at least one other drive and the drive being built belong to a same stripe of the RAID device. When a RAID level of the RAID device is 5, the at least one of data or parity is XORed (exclusive ORed) to obtain a result. When the RAID level of the RAID device is 1, the at least one of data or parity is data and treated as the result. The result is written to a second drive, which is a repaired, replaced, or hot-spare drive for the drive being built.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Implementing large block random write hot spare SSD for smr raid
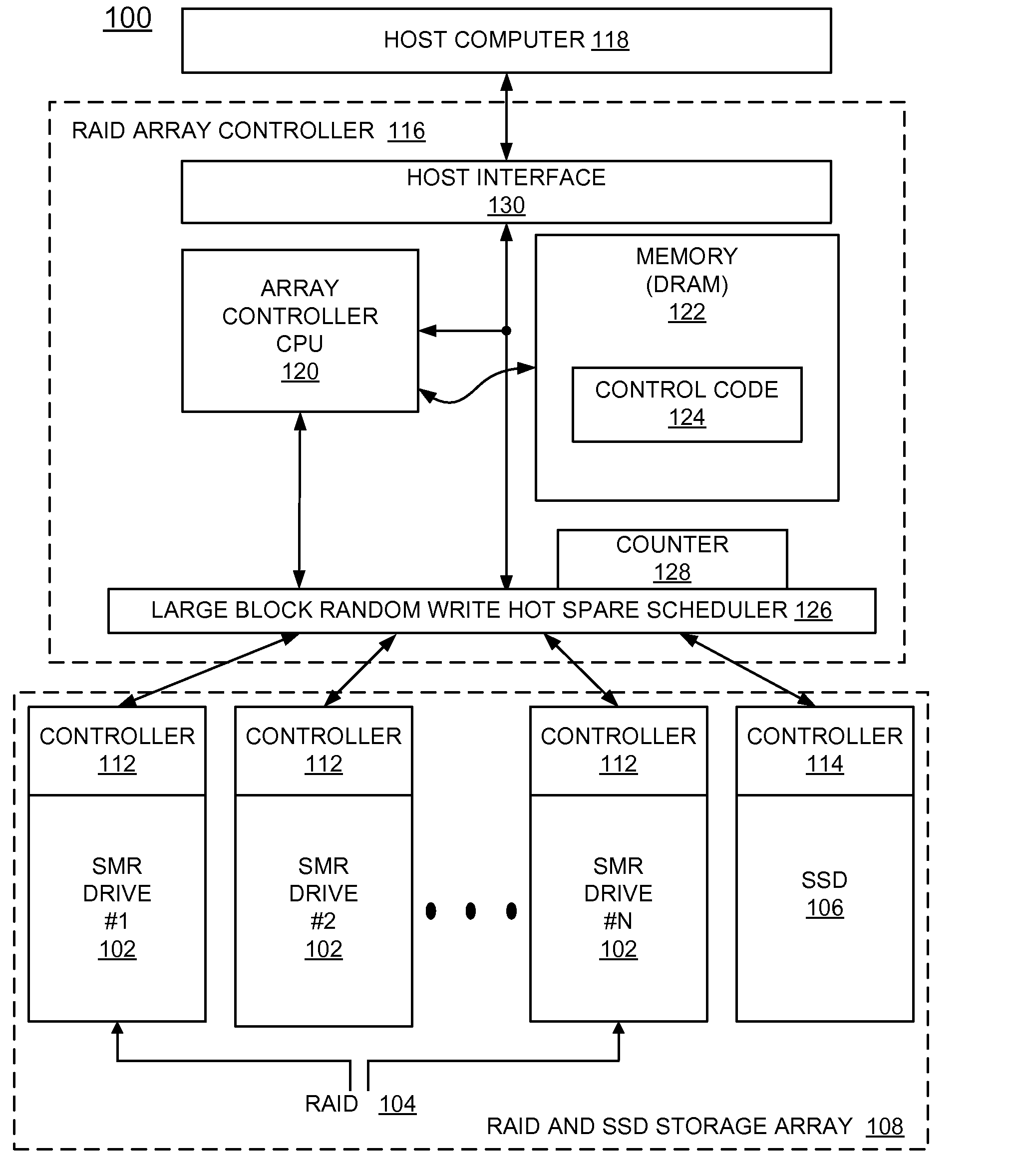
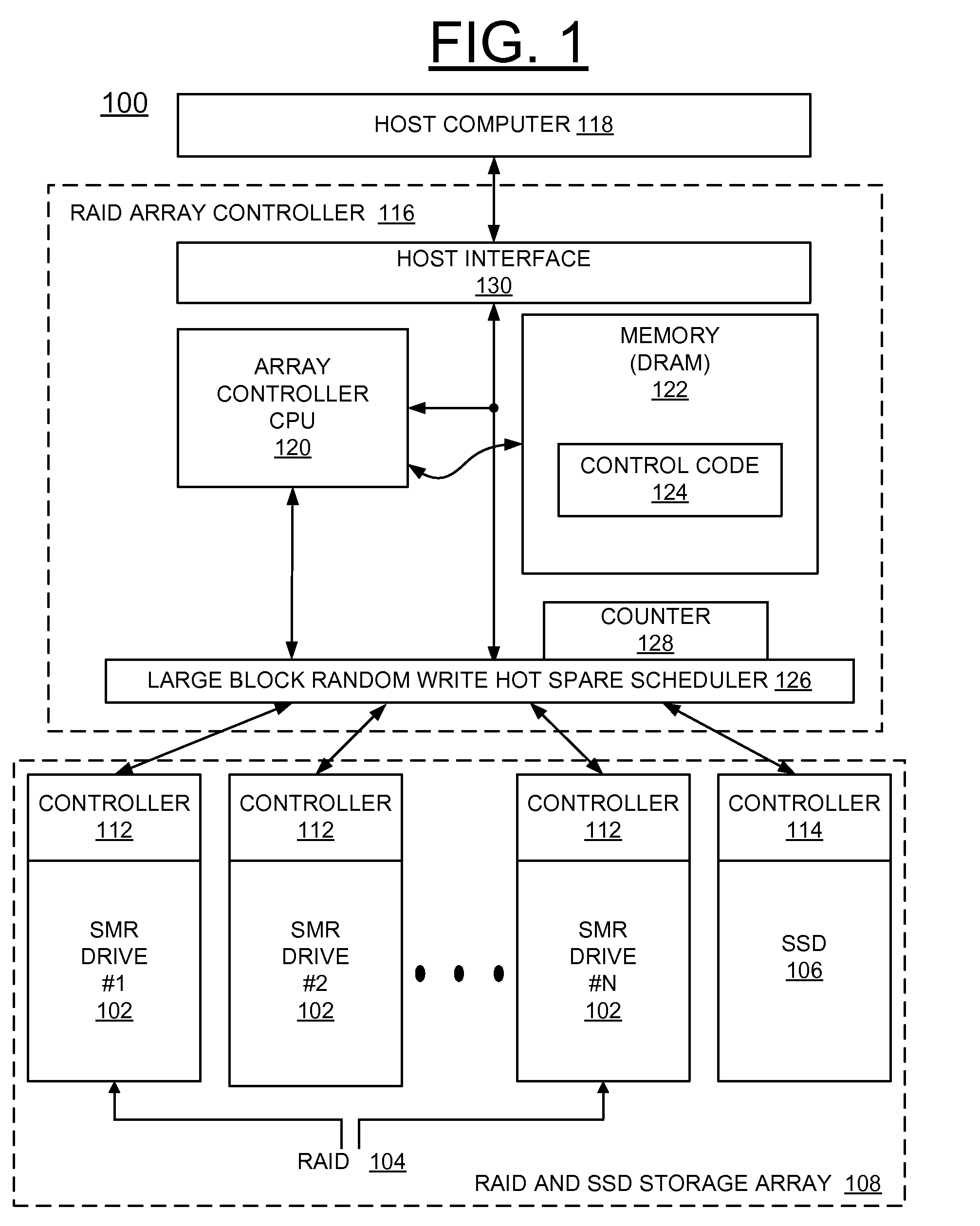
ActiveUS20130232292A1Overcome disadvantagesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRecord information storageRAIDShingled magnetic recording
A method and a storage system are provided for implementing a sustained large block random write performance mechanism for shingled magnetic recording (SMR) drives in a redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID). A Solid State Drive (SSD) is provided with the SMR drives in the RAID. The SSD is used in a hot spare mode, which is activated when a large block random-write event is identified for a SMR drive in the RAID. In the hot spare mode, the SSD temporarily receives new incoming writes for the identified SMR drive. Then the identified SMR drive is updated from the SSD to restore the state of the identified SMR drive, and operations continue with normal writing only using the SMR drives in the RAID.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
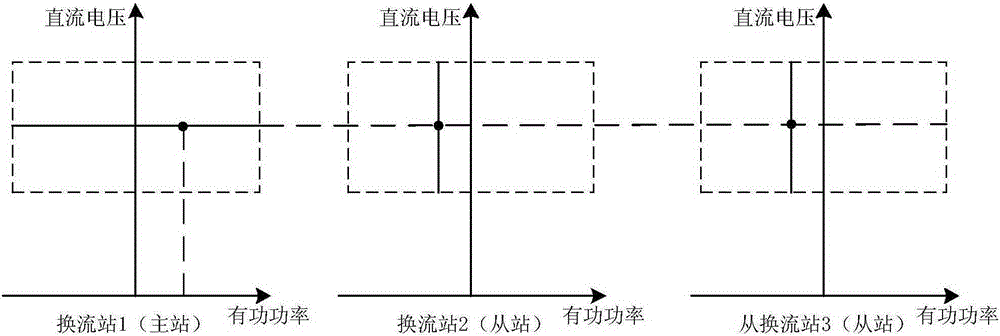
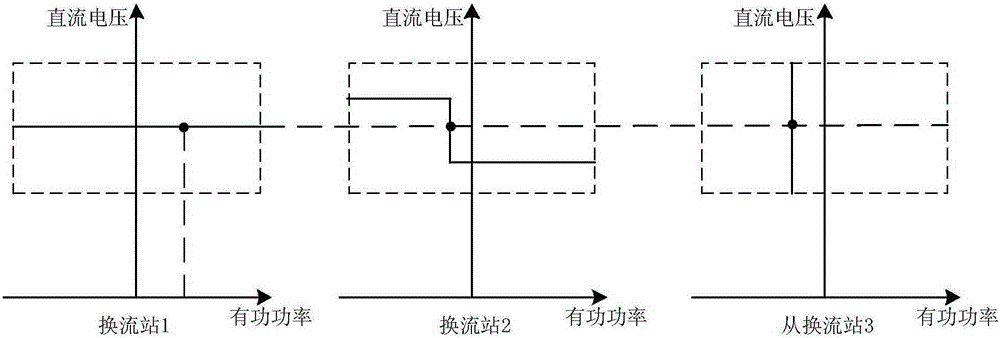
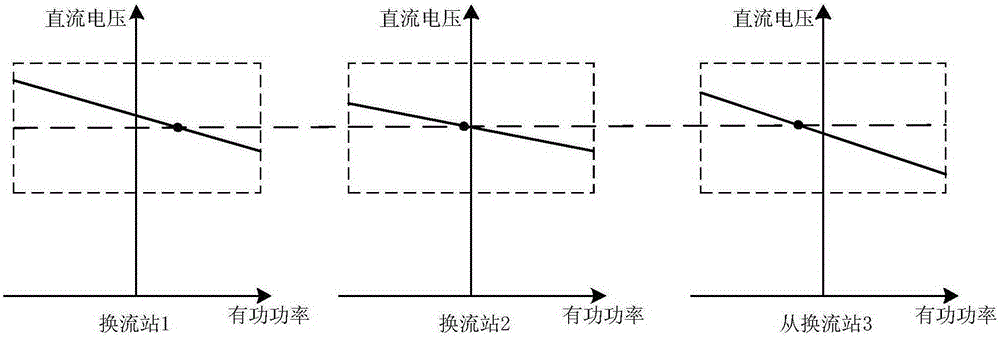
Coordination control method of multi-terminal flexible direct-current power transmission system
ActiveCN105281356AImprove operating economyImprove operational flexibilityElectric power transfer ac networkControl systemVoltage sag
The invention relates to a coordination control method of a multi-terminal flexible direct-current power transmission system. The multi-terminal flexible direct-current power transmission system comprises a coordination control convertor station, a hot spare control convertor station, and a power input convertor station. The coordination control convertor station employs an active power-direct-current voltage sag control way; the power input convertor station employs a fixed active power control way; and the hot spare control convertor station serves as a standby convertor station of the coordination control convertor station. An upper-level control system selects parts of or all hot spare control convertor stations to participate in coordination control according to the transmission power of the direct-current power transmission system and a sag coefficient is corrected in real time. According to the invention, flexibility and economy of the system operation can be improved on the premise that reliability of the multi-terminal flexible direct-current power transmission system is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
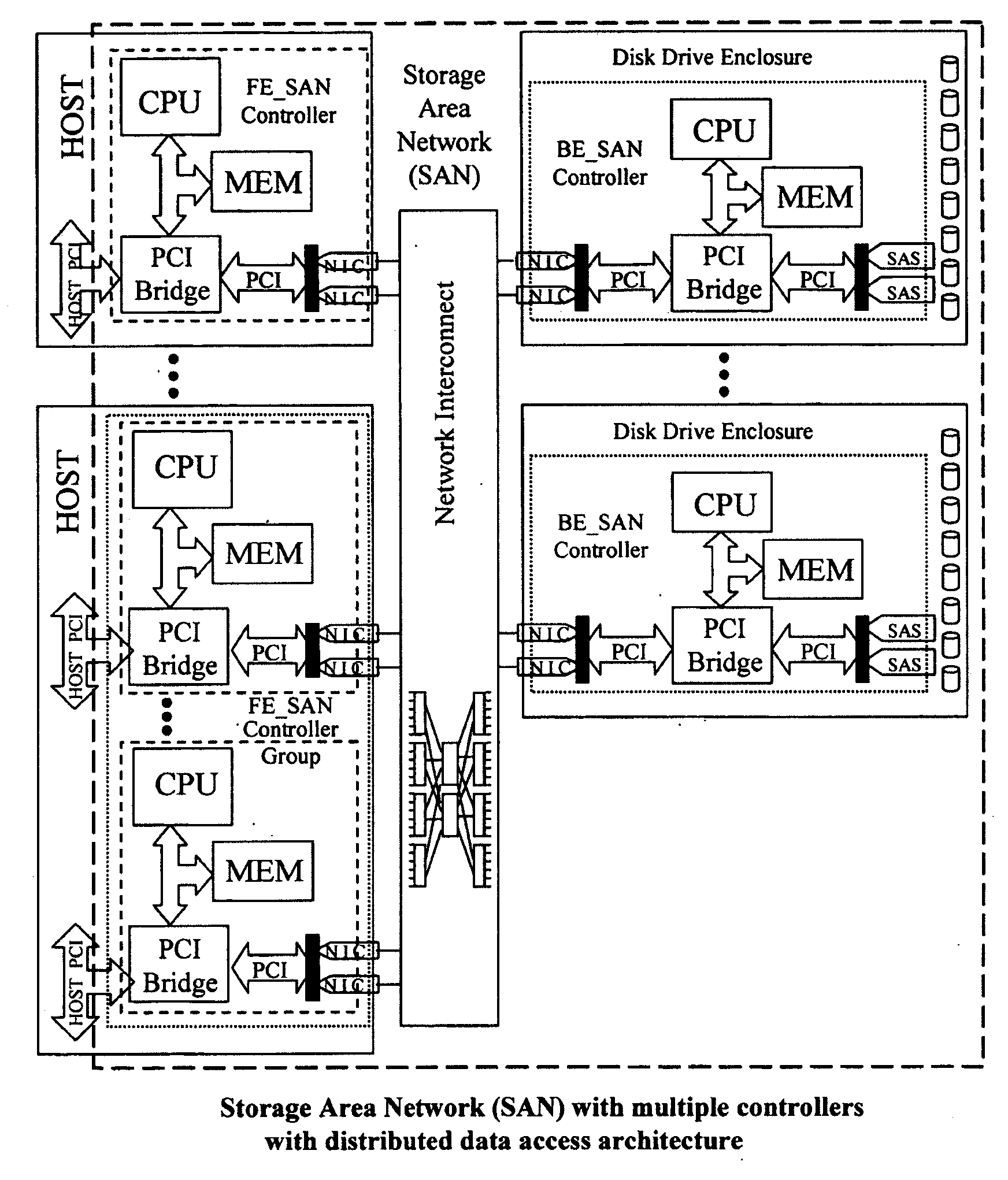
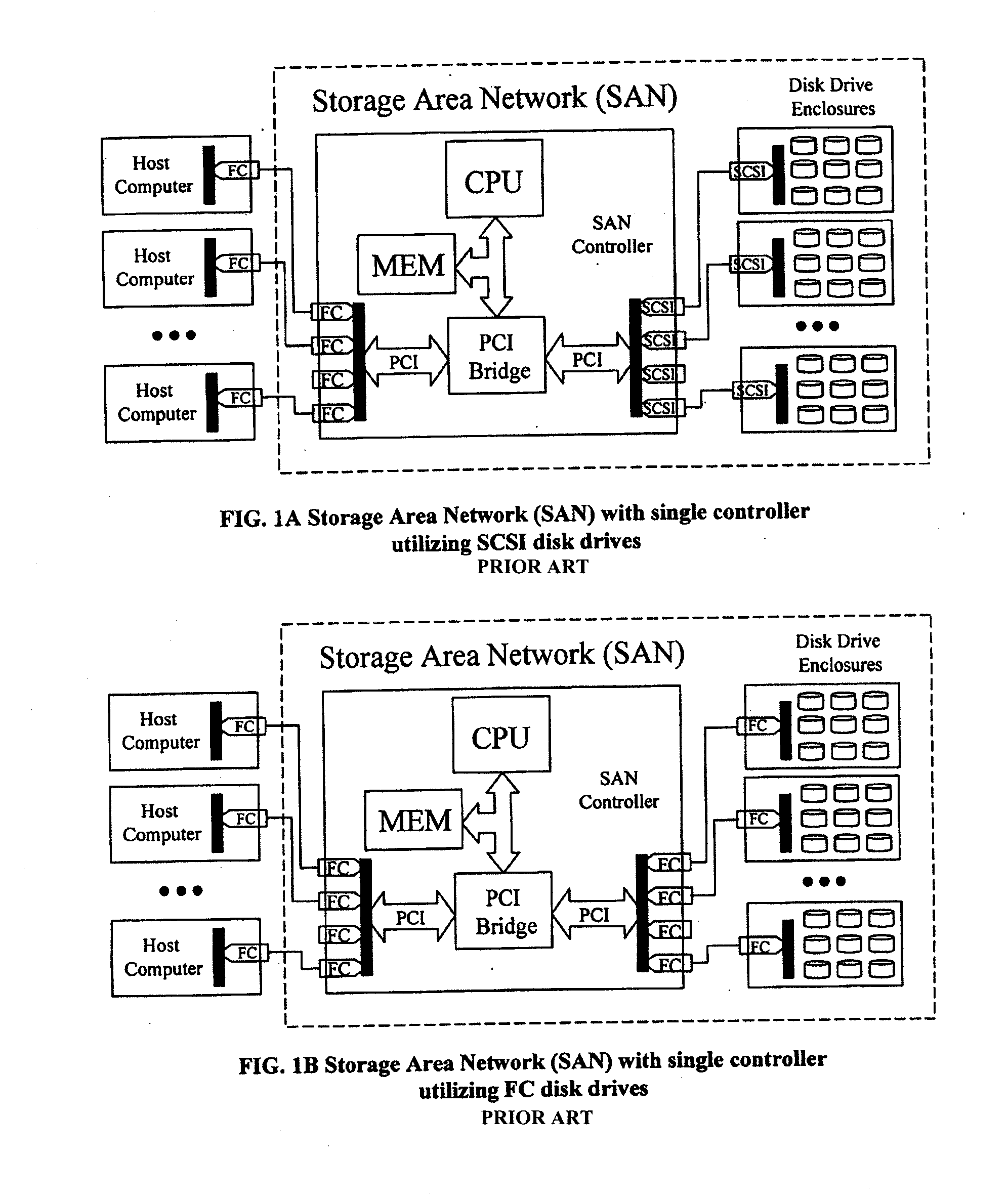
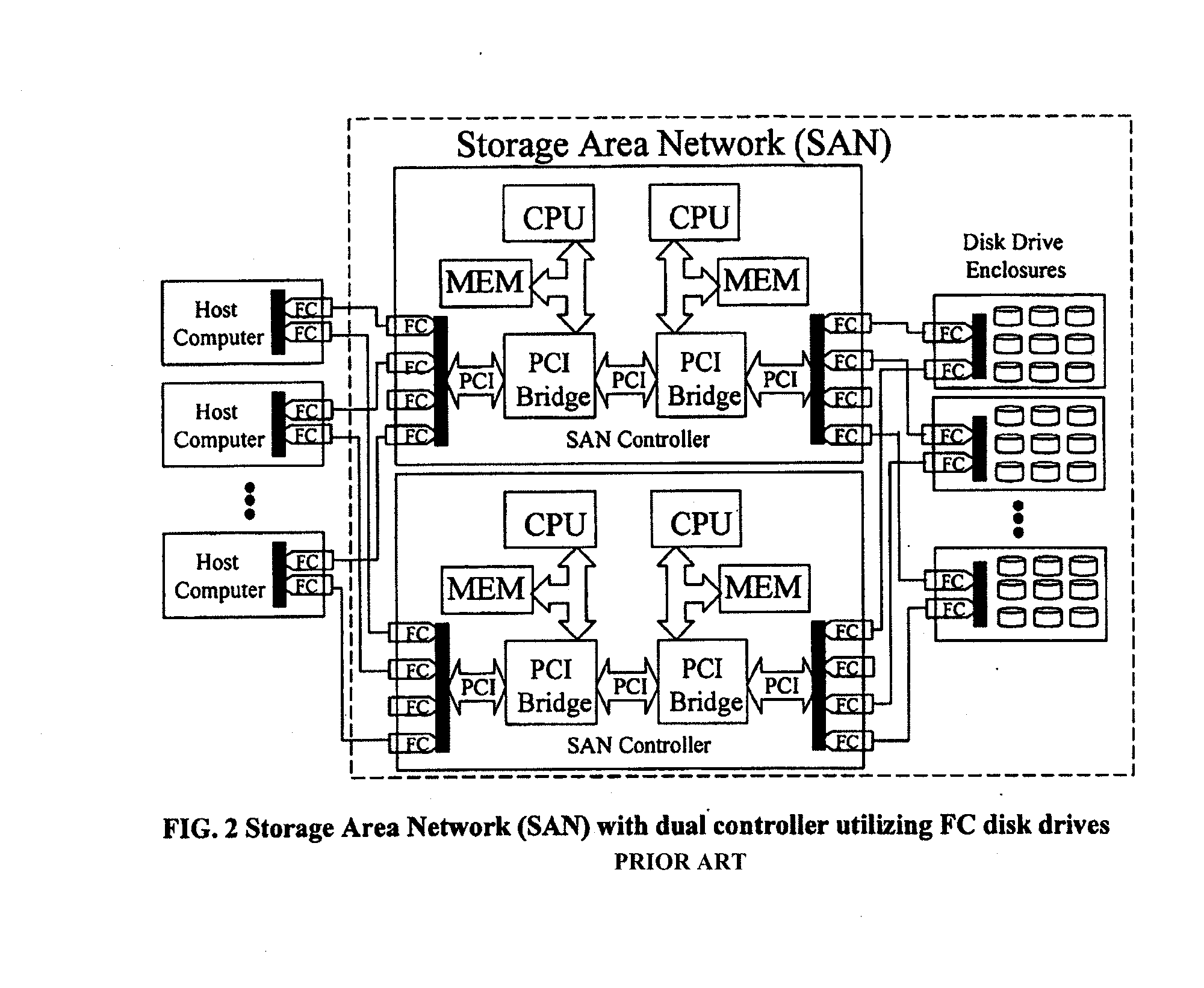
Scalable Data Storage Architecture And Methods Of Eliminating I/O Traffic Bottlenecks
ActiveUS20130145064A1Storage subsystems more affordableIncrease storage capacityInput/output processes for data processingRAIDExtensibility
A Storage Area Network (SAN) system has host computers, front-end SAN controllers (FE_SAN) connected via a bus or network interconnect to back-end SAN controllers (BE_SAN), and physical disk drives connected via network interconnect to the BE_SANs to provide distributed high performance centrally managed storage. Described are hardware and software architectural solutions designed to eliminate I / O traffic bottlenecks, improve scalability, and reduce the overall cost of SAN systems. In an embodiment, the BE_SAN has firmware to recognize when, in order to support a multidisc volume, such as a RAID volume, it is configured to support, it requires access to a physical disk attached to a second BE_SAN; when such a reference is recognized it passes assess commands to the second BE_SAN. Further, the BE_SAN has firmware to make use of the physical disk attached to the second BE_SAN as a hot-spare for RAID operations.
Owner:RADOVANOVIC BRANISLAV
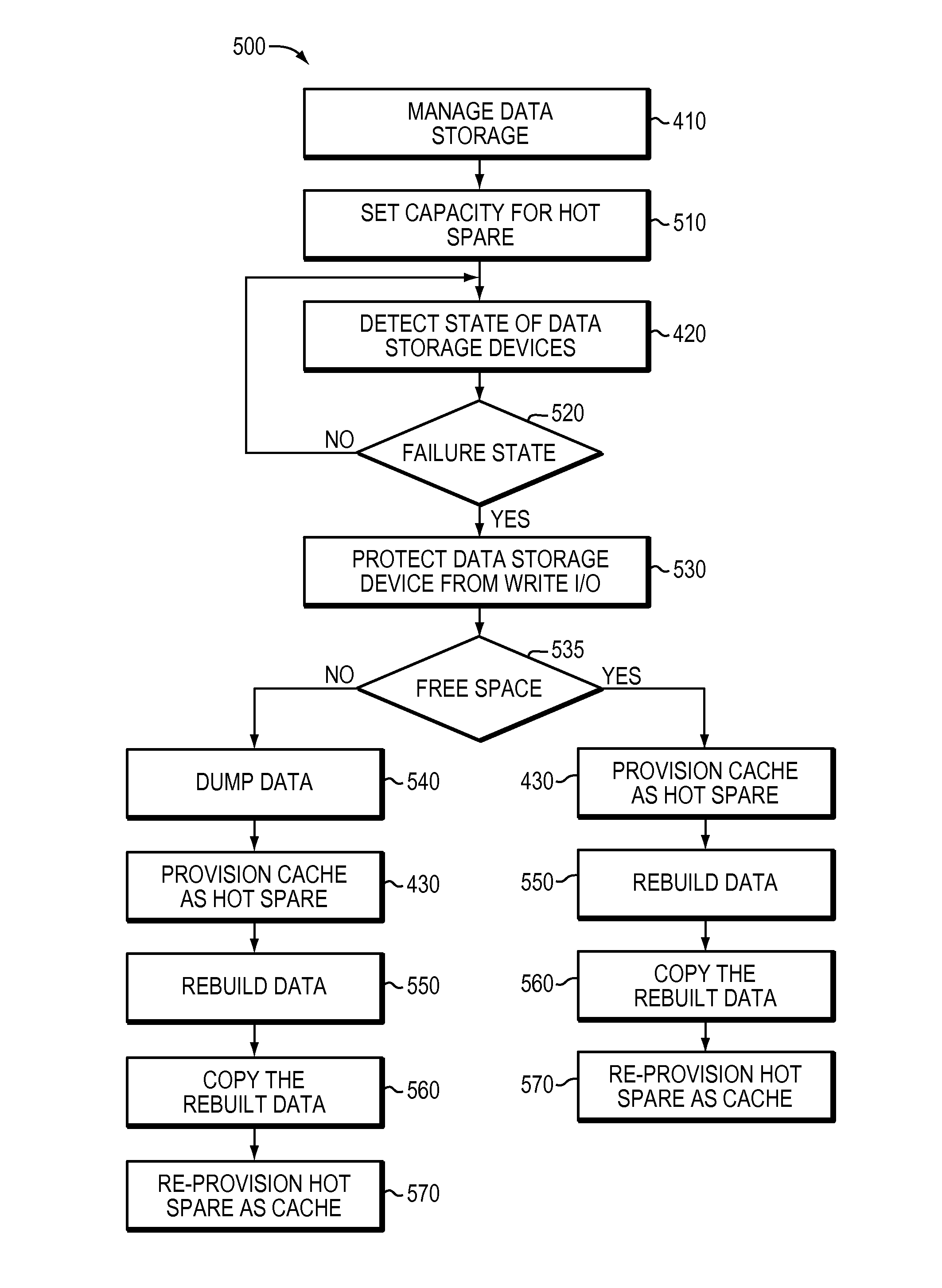
Managing data storage by provisioning cache as a virtual device
There is disclosed a technique for use in managing data storage. In one embodiment, the technique comprises managing data storage in a data storage system comprising a cache and data storage devices arranged in a RAID configuration. The technique also comprises detecting the state of the data storage devices and provisioning at least a portion of the cache as a virtual hot spare device in response to detecting a failure state in connection with a data storage device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
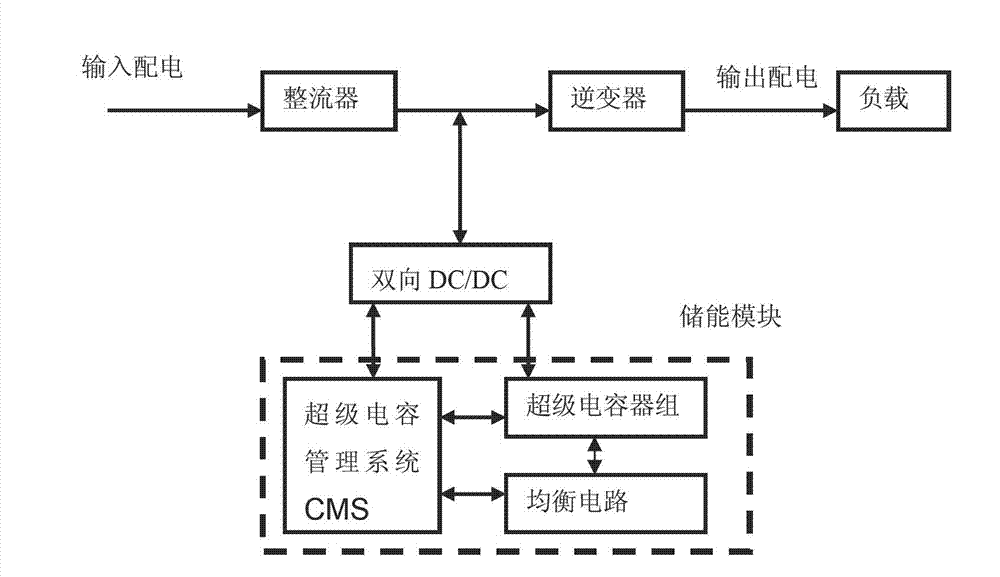
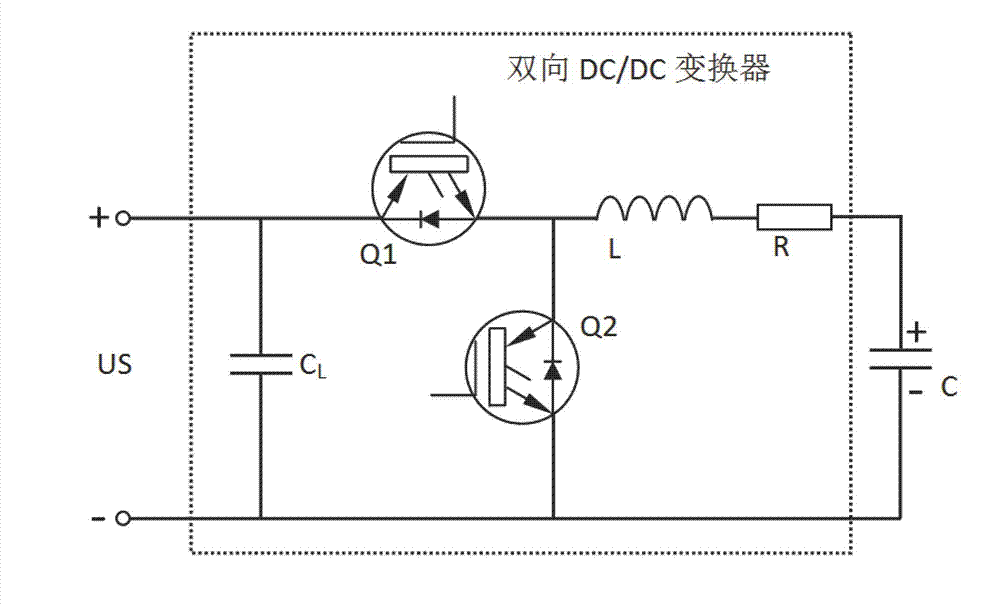
Power uninterruptible power supply (UPS) system based on super-capacitor and energy storage method thereof
InactiveCN102931721AMeet instantaneous power supply requirementsNo maintenanceElectrical storage systemEmission reduction for energy storageCapacitanceHigh-voltage direct current
The invention discloses a power UPS system based on a super-capacitor. The power UPS system comprises a rectifier, an inverter, a bidirectional direct current (DC) / DC converter and an energy storage system. The energy storage system is composed of a super-capacitor group, a super-capacitor equalization circuit and a super-capacitor management system (CMS). The rectifier is used for converting input distribution alternating voltages into high-voltage direct voltages and provides a power supply for the inverter; the inverter is used for converting the high-voltage direct voltages at the front end into alternating voltages meeting load use requirements; and the rectifier performs charge or floating charge on the energy storage system through the bidirectional DC / DC converter. The power UPS system based on the super-capacitor uses the super-capacitor as an energy storage unit, and compensates for electrical energy gaps caused by power equipment during the power shaking of power grids through an online parallel hot spare mode. The power UPS system based on the super-capacitor can work normally at a low temperature (an ultimate temperature minus 40 DEG C), has the advantages of being small in size, free of maintain, long in service life, high in power and reliability and the like and can meet instantaneous power supply requirements of large power.
Owner:MAISIBOER ENERGY TECH TIANJIN
Data volume rebuilder and methods for arranging data volumes for improved RAID reconstruction performance
A data volume rebuilder reduces the time required to reconstruct lost data in a RAID protected data volume operating with a failed physical disk drive. A data volume rebuilder uses the remaining functioning physical disk drives in the RAID protected data volume operating with the failed disk to regenerate the lost data and populate a virtual hot spare store allocated in a separate RAID protected data volume. The recovered data is distributed across the physical disk drives supporting the virtual hot spare store. Once the virtual hot spare store is populated, the data volume can recover from a subsequent failure of a second physical disk drive in either RAID group. After replacement of the failed physical disk drive, the data volume rebuilder moves the recovered data from the virtual hot spare store to the new physical disk drive.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Onsite-level low-cost redundancy measuring and controlling network based on wired and wireless hot spare redundancy communication
ActiveCN102692912AImprove reliabilitySimple structureTransmissionTotal factory controlWired communicationNetwork structure
The invention discloses an onsite-level low-cost redundancy measuring and controlling network based on wired and wireless hot spare redundancy communication, which comprises a host computer and a slave computer, wherein the slave computer is polled / controlled by the host computer; the states of the slave computer and a monitored object of the slave computer are obtained or a corresponding controlled object is controlled by the slave computer; the wired communication and wireless communication of the host computer and the slave computer are both on-line during a working process; one of the communication modes is selected by the host computer, so as to communicate the host computer with the slave computer; preferably, the wired mode is selected for communication; and the network is a reliable onsite measuring and controlling network with zero-cost communication operation. No additional redundancy management equipment is required; the cost is saved; a redundancy communication network structure is simplified; and the installment of the system is especially simple and quick, so that the installing cost is low and the period is short.
Owner:CHENGDU RUITE DIGITAL TECH
Disk array device, operating method thereof and program-storing medium
InactiveUS20080244309A1Reduce the probability of failureIncrease the probability of failureReliability/availability analysisRAIDDisk array
Even if failure probabilities are different for hard disks due to the individual specificity such as a hard disk manufacturer, model number or the like, a disk with high failure probability is reliably determined and removed from the operating RAID to be kept in a standby state as a hot spare disk, thereby keeping a low failure probability of the disk array device. In order to realize this, the disk array device includes a disk controlling unit for, based on S.M.A.R.T. information of each of the hard disks read by a S.M.A.R.T. information reading unit, assigning a predetermined number of hard disks to the hot spare disk in descending order of failure probability of the hard disks.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com