Patents
Literature
618 results about "Heartbeat message" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
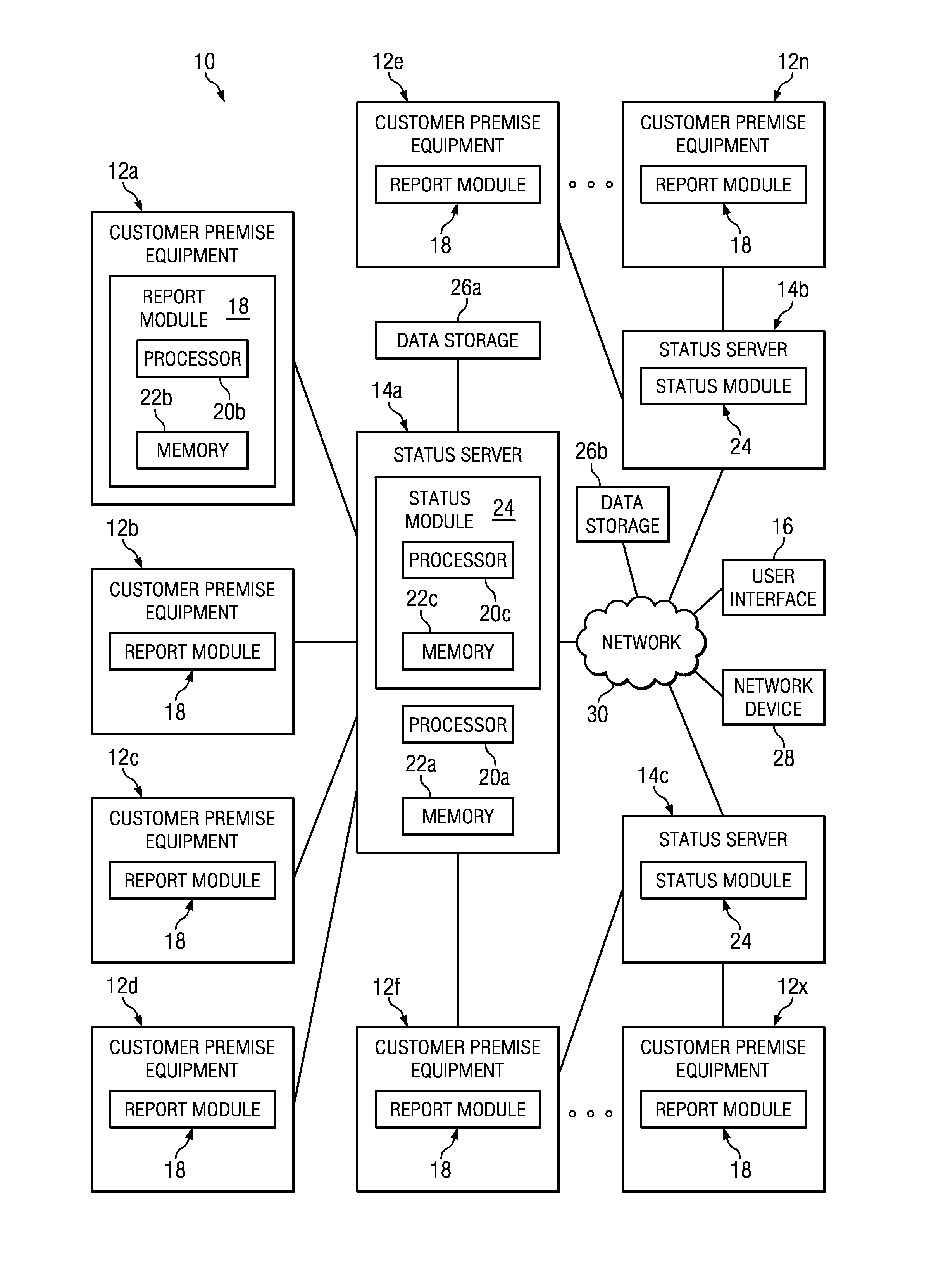
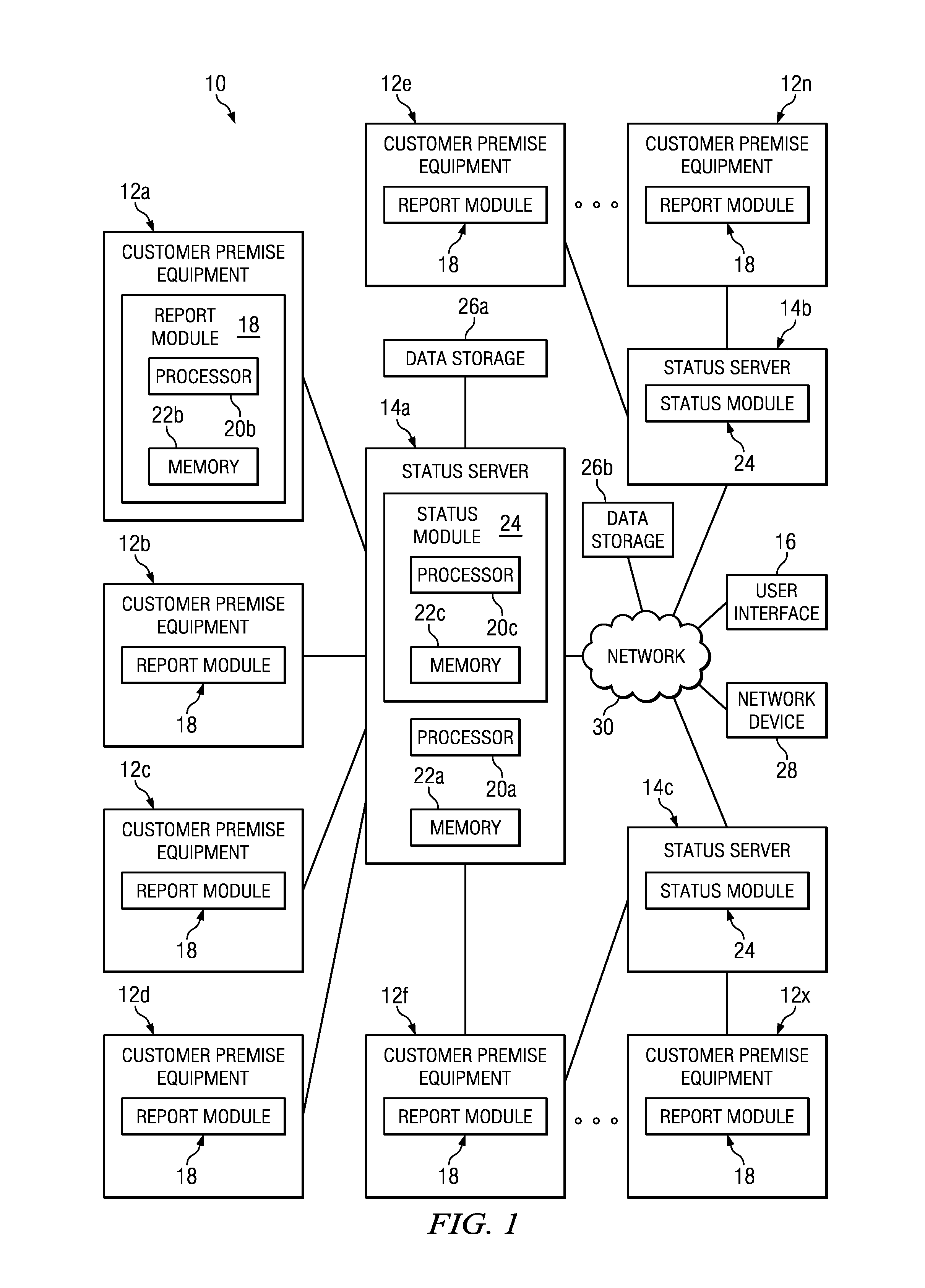
A heartbeat message in signal processing is a message sent from an originator to a destination that enables the destination to identify if and when the originator fails or is no longer available. Heartbeat messages are typically sent non-stop on a periodic or recurring basis from the originator's start-up until the originator's shutdown. When the destination identifies a lack of heartbeat messages during an anticipated arrival period, the destination may determine that the originator has failed, shutdown, or is generally no longer available. Heartbeat messages may be used for high-availability and fault tolerance purposes.
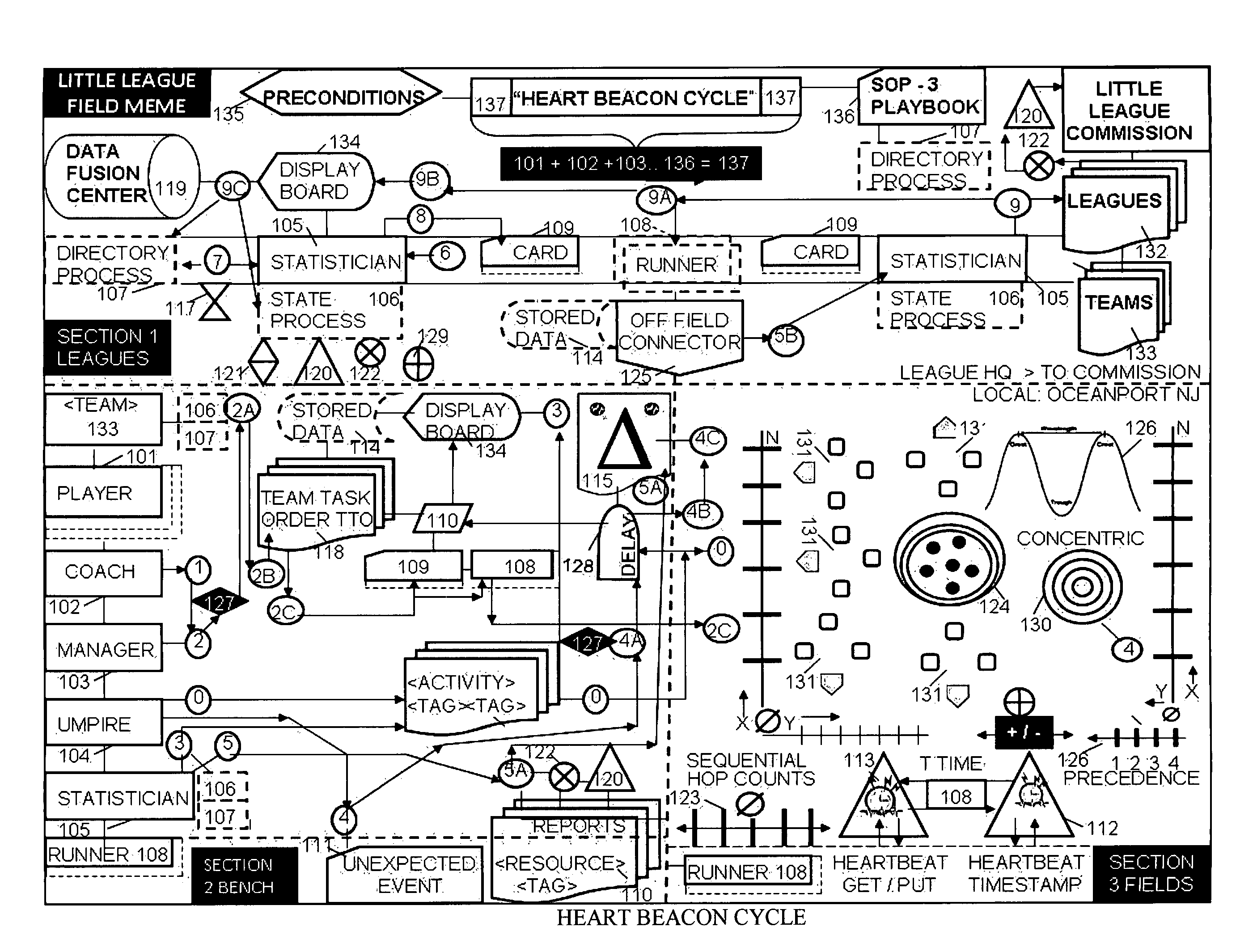
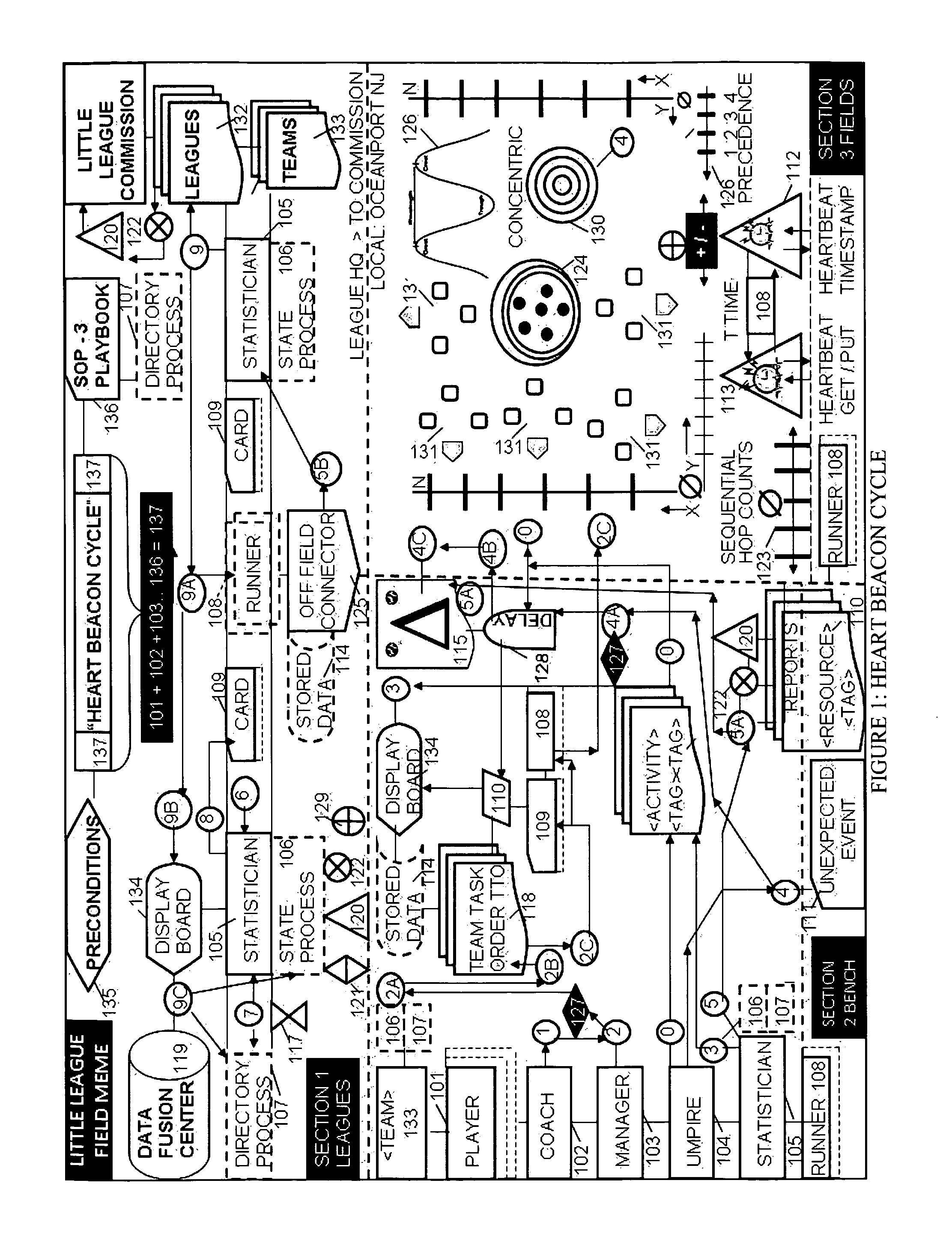
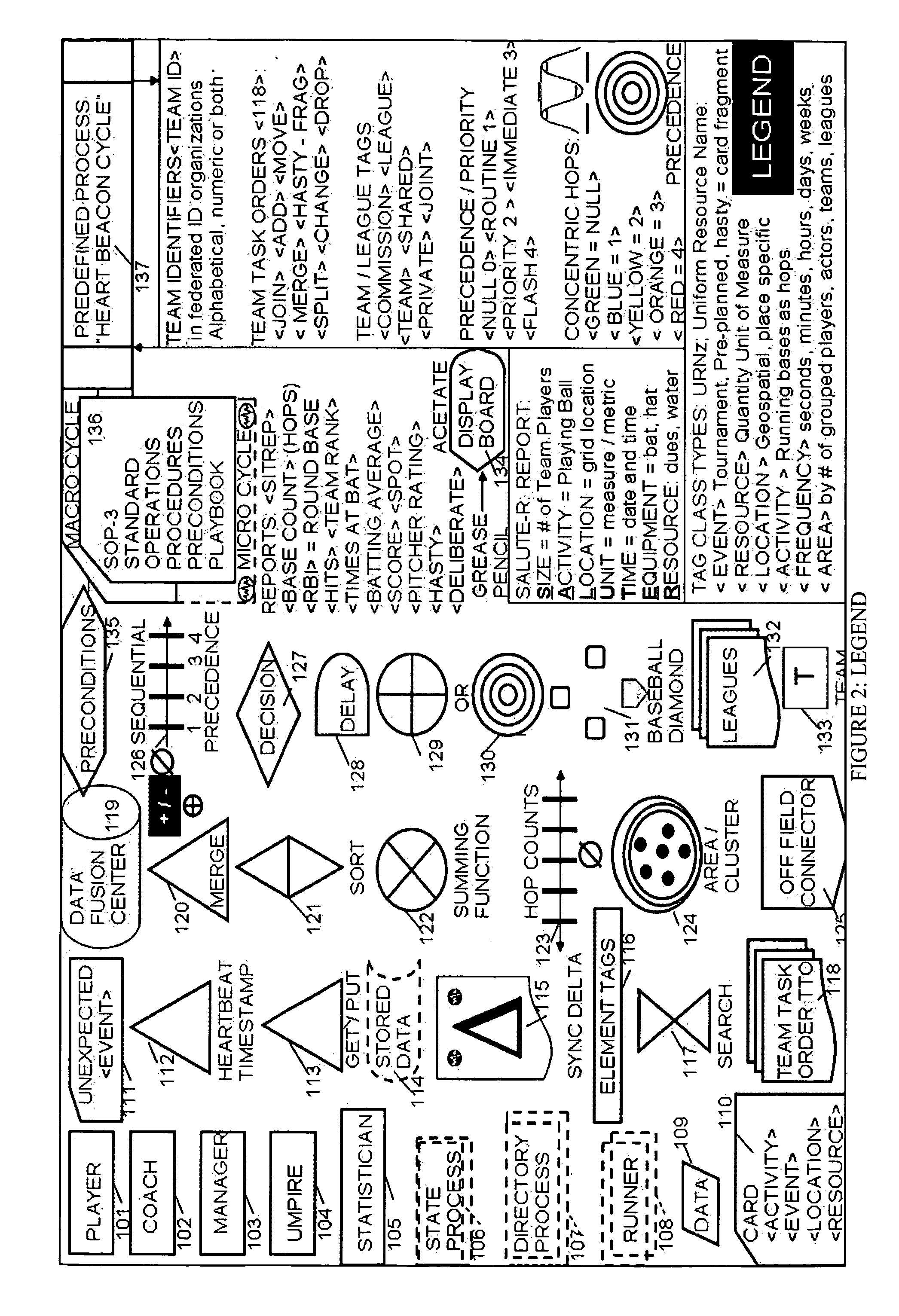
Heart beacon cycle
InactiveUS20140310243A1FinanceDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceGood practice
Systemic, adaptive procedural template comprised of common building blocks forming template frameworks i.e., self-organizing, mutually reinforcing service, system, process, procedure components derived situational understanding, state meta data signaling replication systems consisting of TCP / IP heartbeat, heartbeat messages signaling during micro-macro report cycles of state meta-data sync deltas <class> typed with <ORG_ID>, <URN> time stamped prior to data fusion-center insertion followed by reports aggregated, recalculated, relayed through synchronization, conversion gateways then merged into macro-cycle reports where metrics, metering are described by using Paul Revere meme linear, sequential hop count, water-drop in-pond meme geo-spatial temporal intensity measures, metrics recording sync deltas change across time / space viewed on appliqué displays using Russian Matryoshka doll techniques where each view adds to, changes the nature, meaning of composite views while retaining original appliqué views unique qualities as decision support aids in best effort, best practice by federated groups
Owner:MCGEE MR STEVEN JAMES
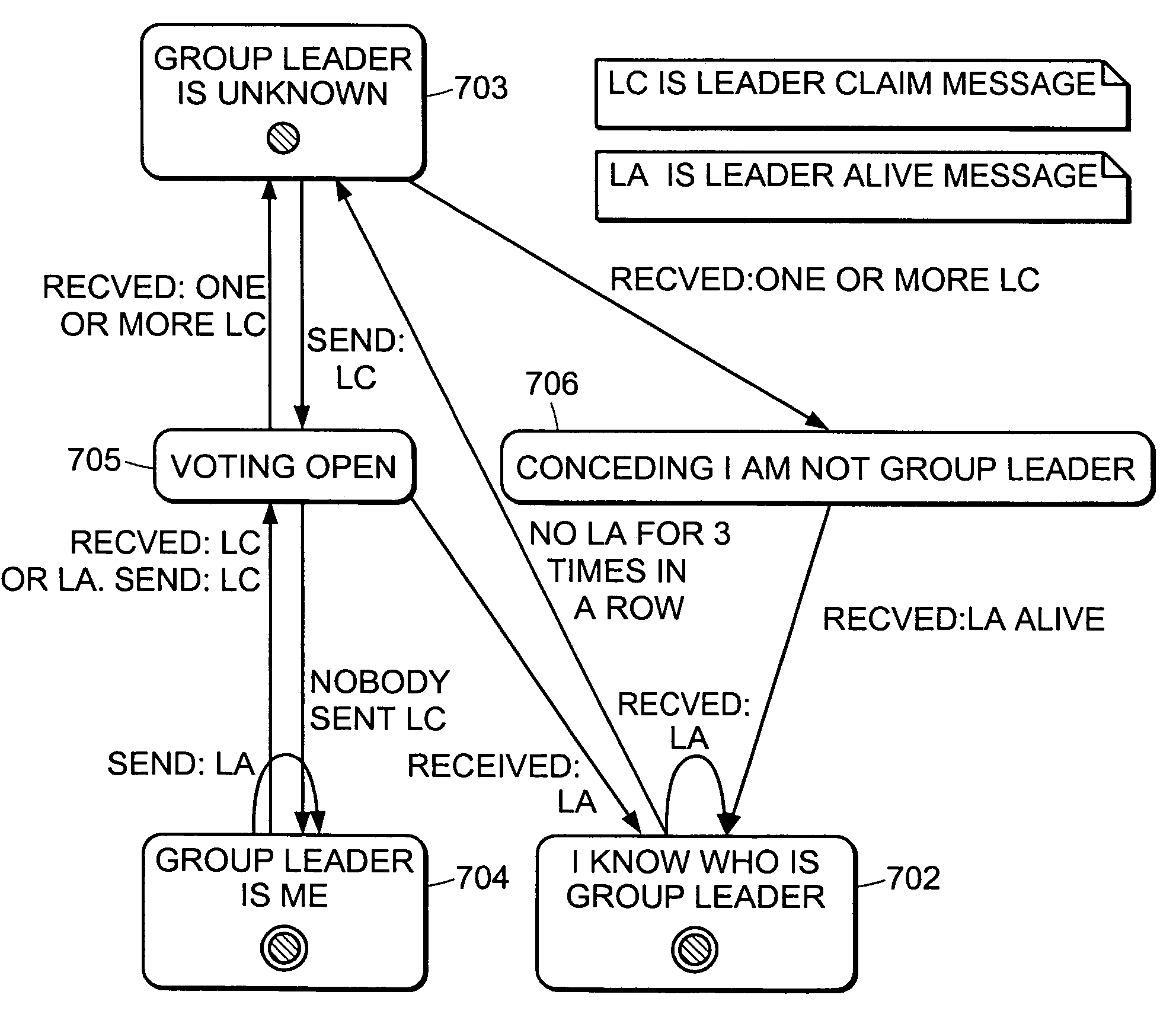
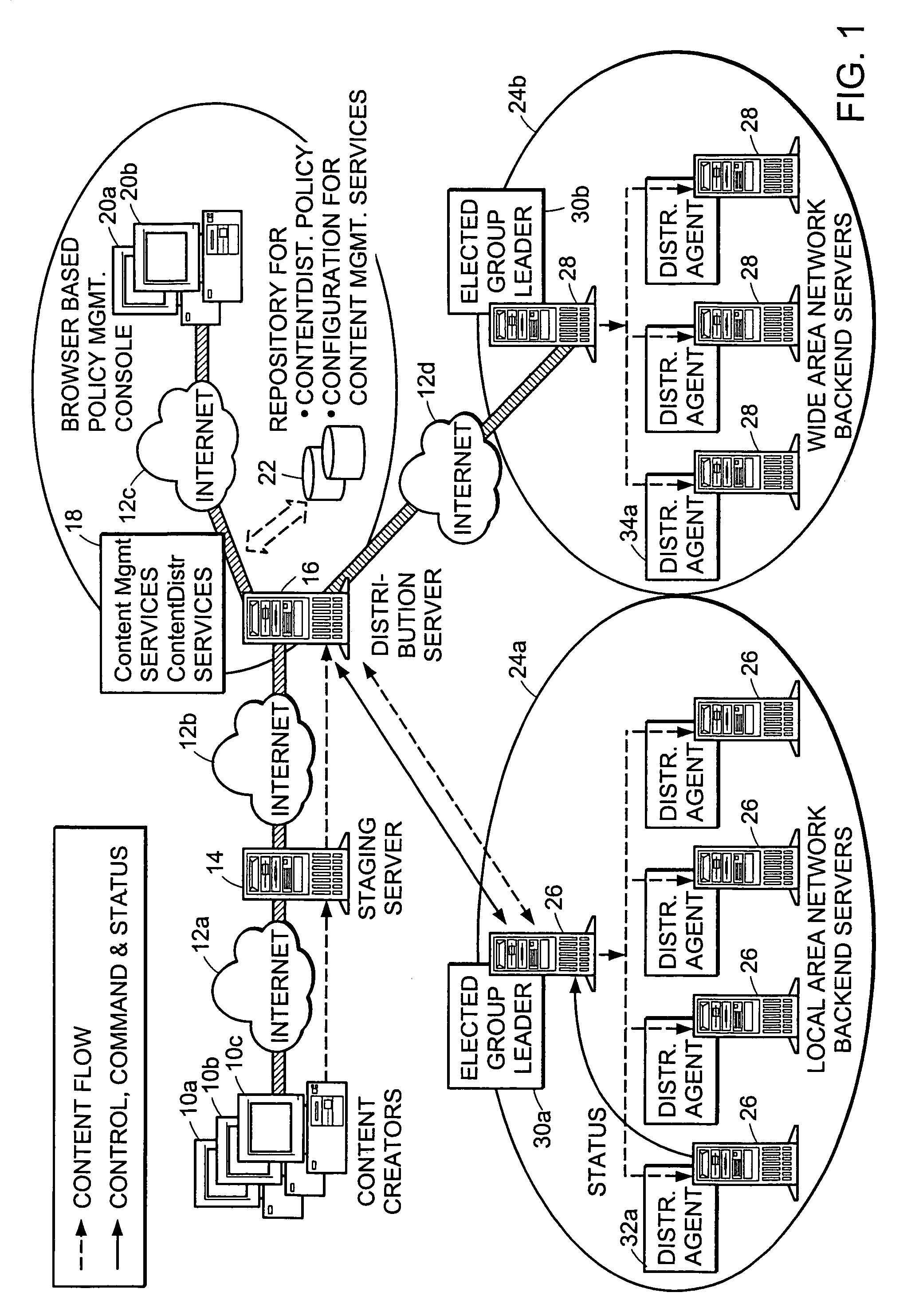
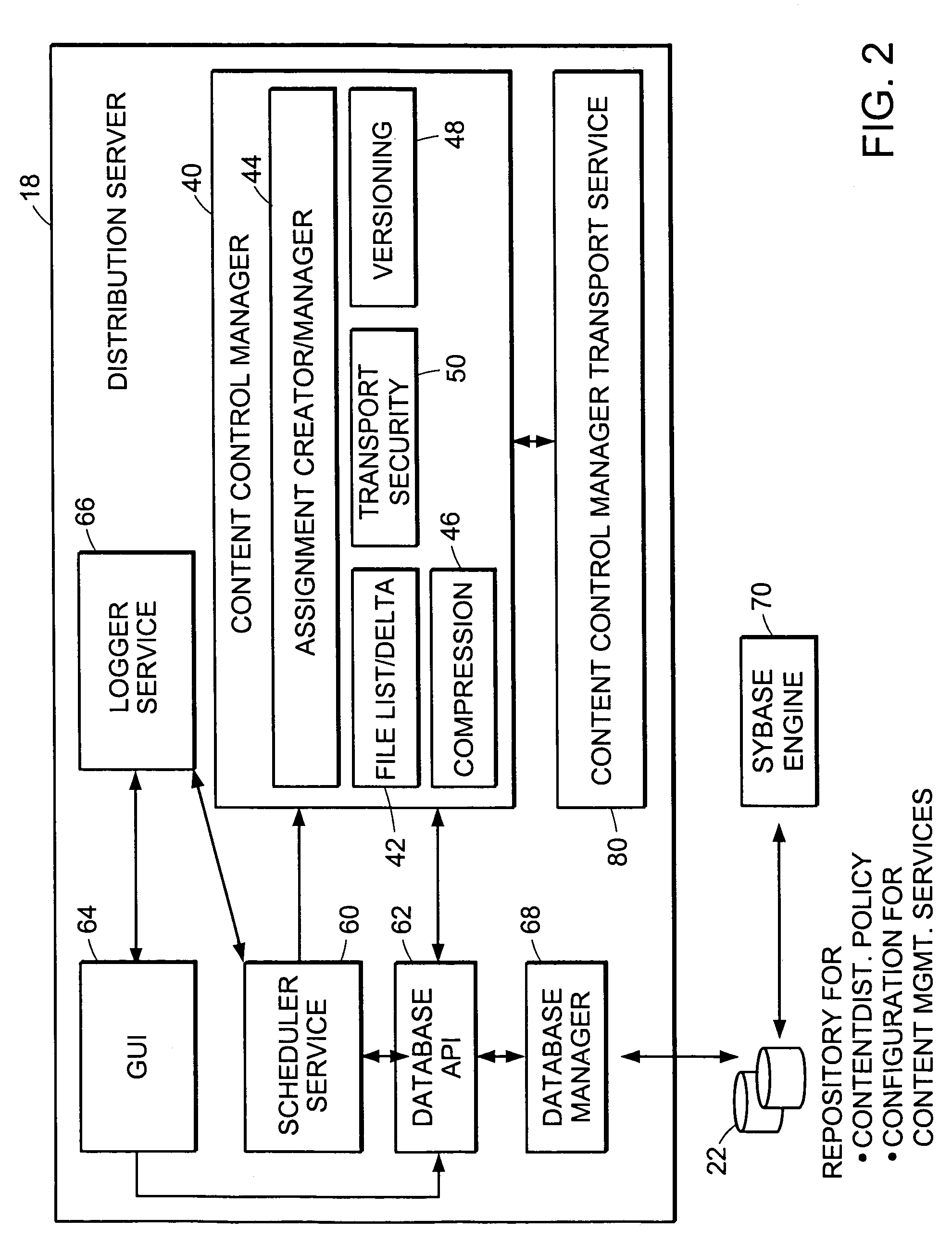
Method and apparatus for election of group leaders in a distributed network
InactiveUS6993587B1Effective controlEffective distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData fileMulticast network
The present invention provides a system and apparatus for efficient and reliable, control and distribution of data files in large-scale distributed networks. The members of a group of servers in a multicast network elect a group leader whenever a new group leader is required, as when the prior group leader become unavailable, as detected by absence of a periodic heartbeat message published by the leader. The election is carried out by a system of voting by each candidate whereby each candidate has a priority calculated from its configuration, and the server with the highest priority is configured to claim the leadership faster than the other candidates. As part of the claim, each candidate multicasts its priority. Each candidate that receives a multicast claim for leadership from another candidate compares its own priority against the claimant and only votes for itself if its own priority is higher. After a preconfigured period of hearing no other claimants with higher priority, the candidate with the highest priority becomes the new leader.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
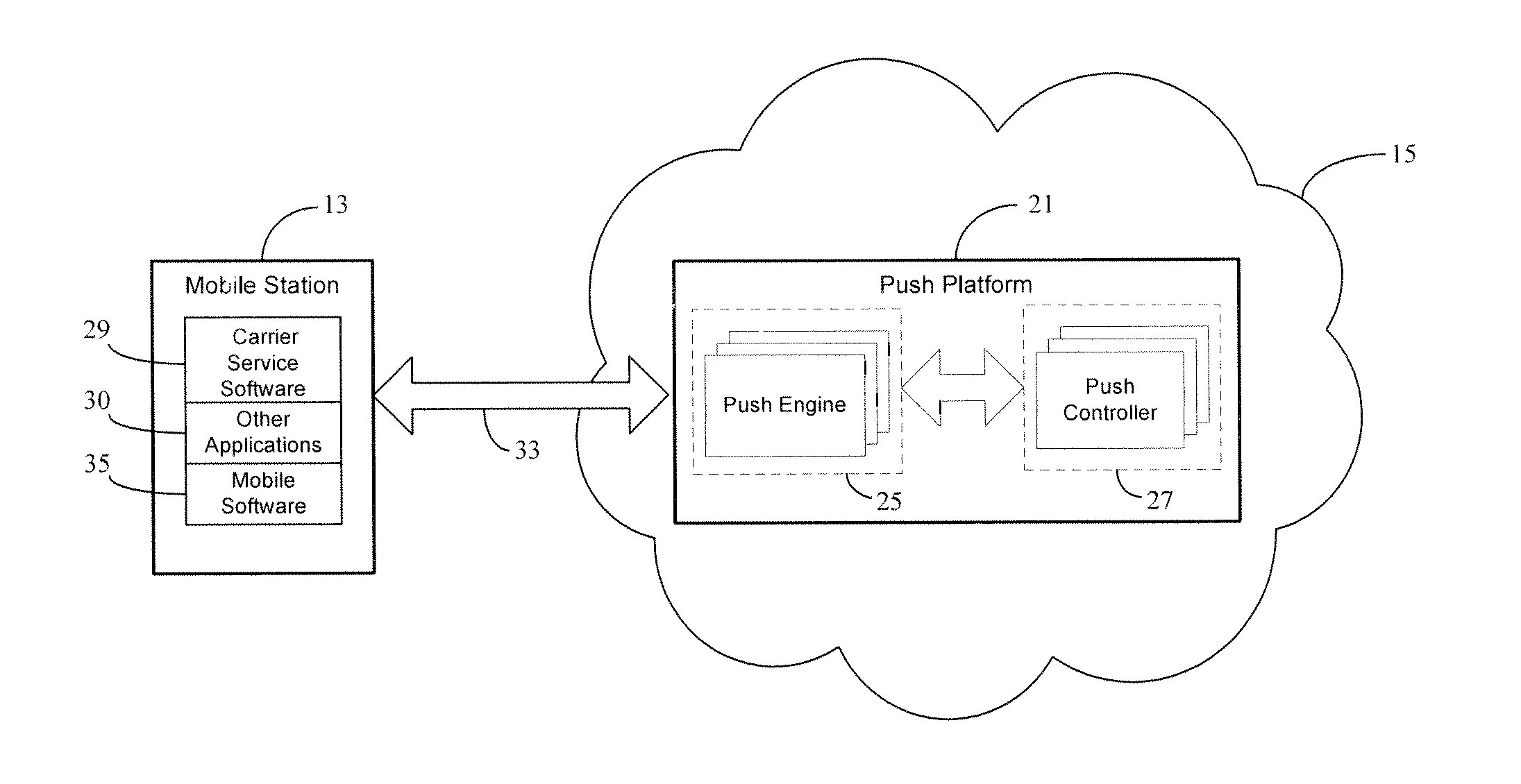
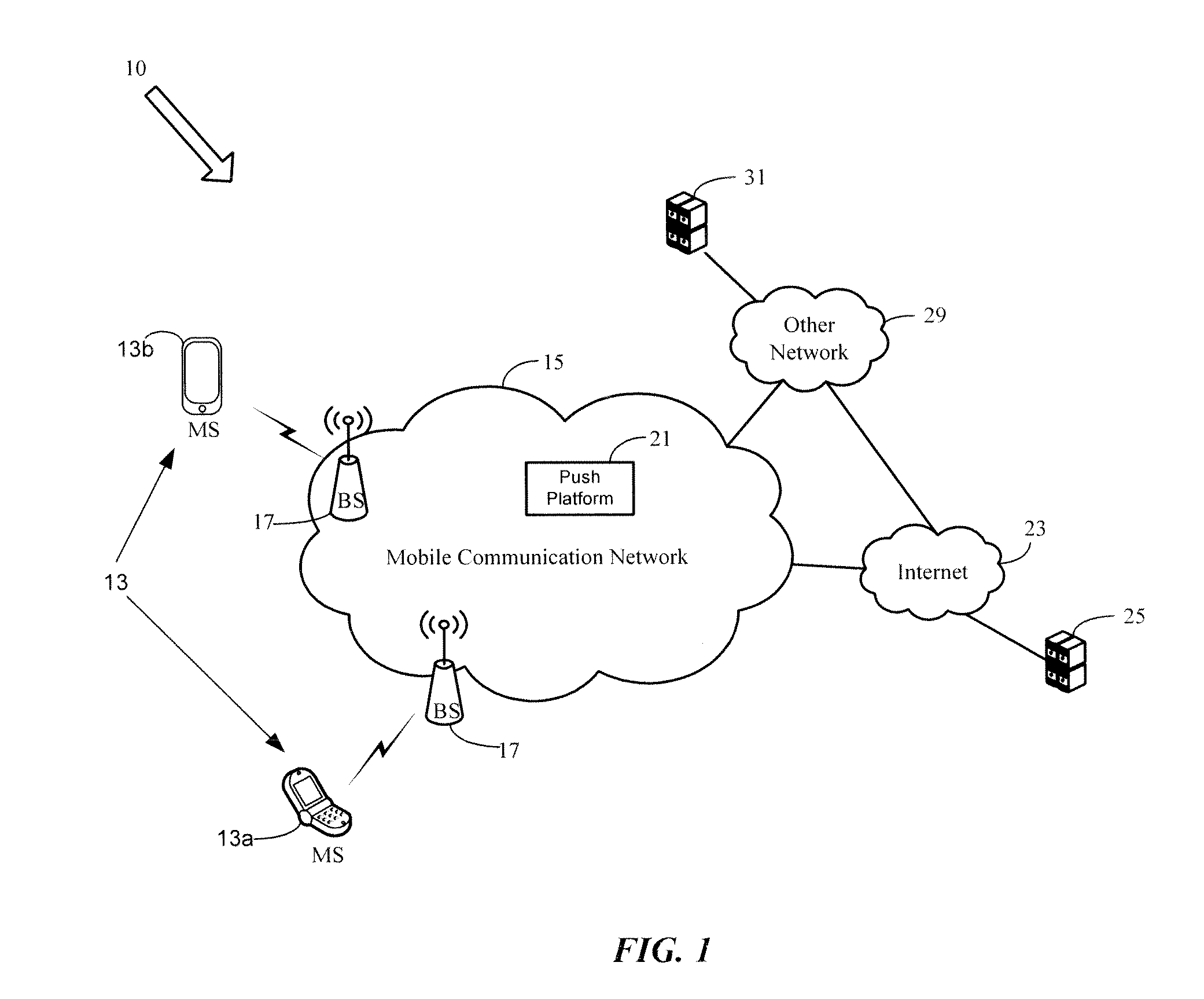
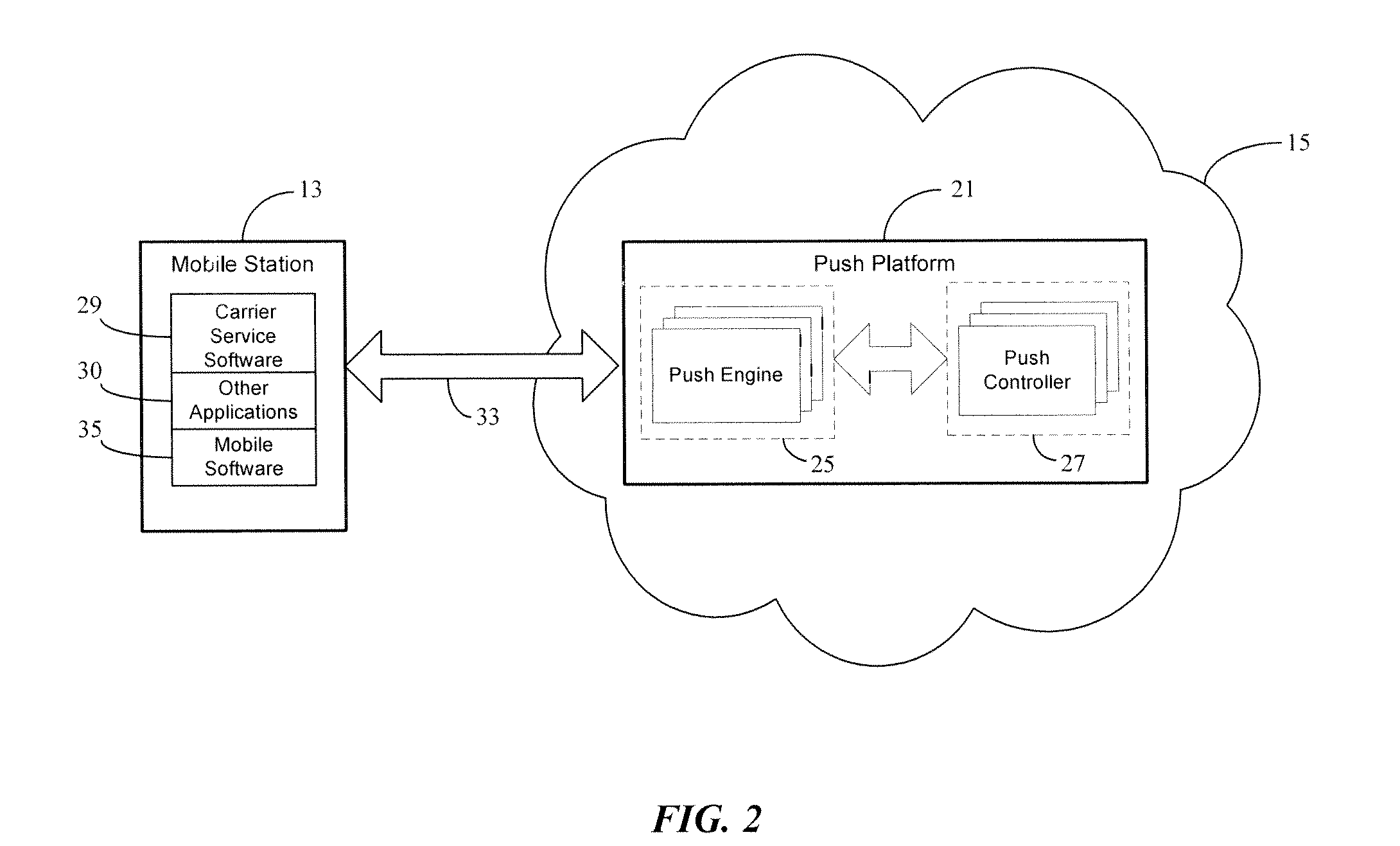
IP push platform and connection protocol in a push notification framework
ActiveUS20130111572A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationReal-time dataData source
A persistent connection is used for real-time or near real-time data transfer from a push platform on a network to a mobile station. To establish and maintain the persistent connection between the mobile station and push platform on the network, various protocols are defined over a packet connection between the mobile station and push platform. The real-time or near real-time data is pushed or sent by the push platform to the mobile station, as the data becomes available from a data source. In particular, heartbeat messages are used to determine whether or not the persistent connection is alive and available for real-time or near real-time data transfer. When the persistent connection is lost, the mobile station uses a retry connection scheme based on the number of connection attempts made by the mobile station for establishing a new persistent connection to the push platform.
Owner:CELLO PARTNERSHIP DBA VERIZON WIRELESS
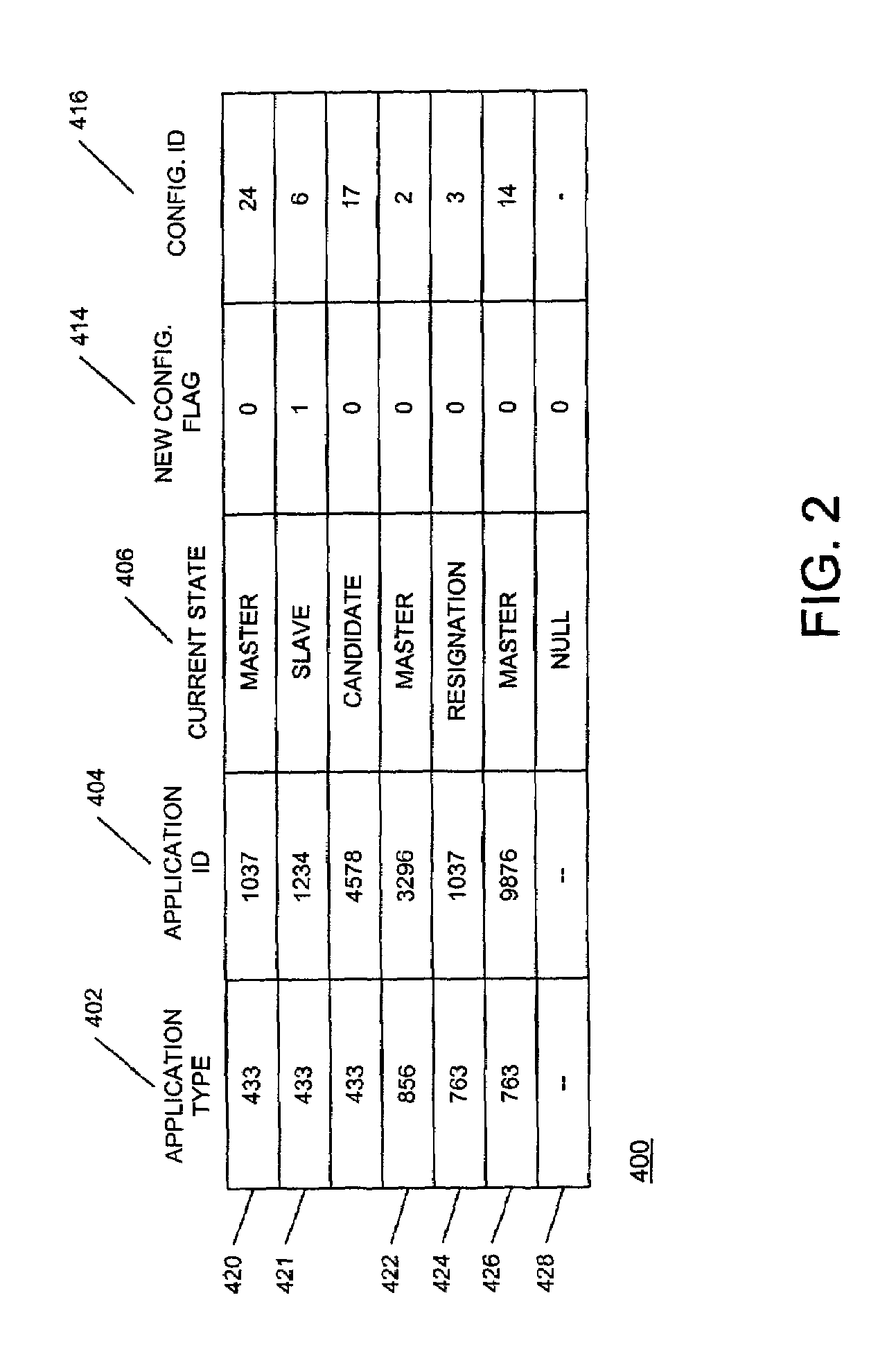
Method and apparatus for exchanging configuration information between nodes operating in a master-slave configuration
InactiveUS7353259B1Multiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingComputerized systemApplication software
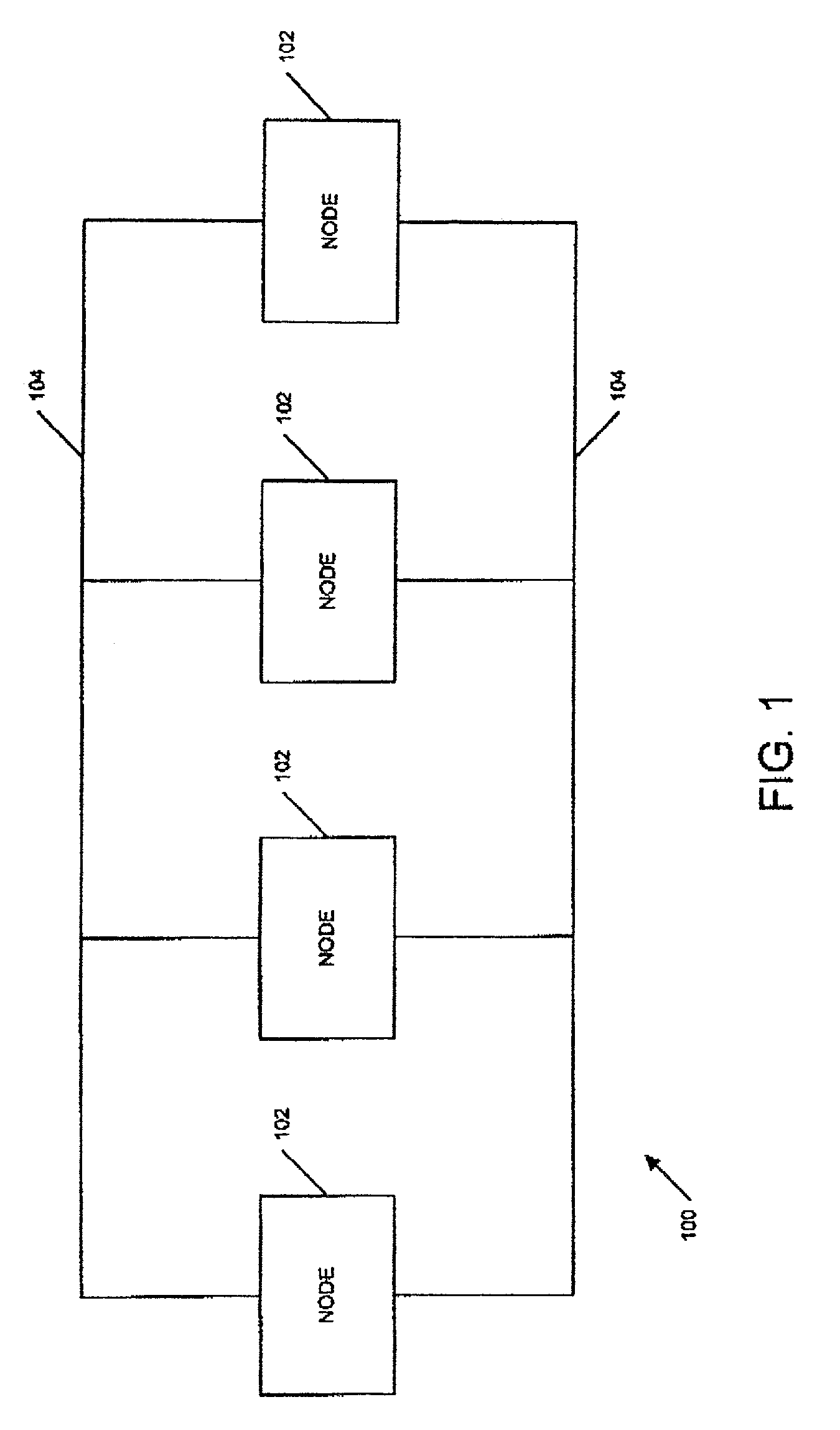
A node, within a networked computer system, is capable of supporting communications with other nodes relating to operating multiple application instances in a master-slave configuration. Each node periodically generates and sends a Heartbeat message that indicates the operational status and configuration information for one or more application instances being managed by the node. When a node receives a Heartbeat message from a remote node, it determines whether new configuration information should be obtained for each of the application instances the node is managing, and establishes a connection with a remote node that can access the new configuration information. The connection is an HTTP connection, in one embodiment. The node then requests and receives that new configuration information from the remote node. In one embodiment, the new configuration information is received in an XML format.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
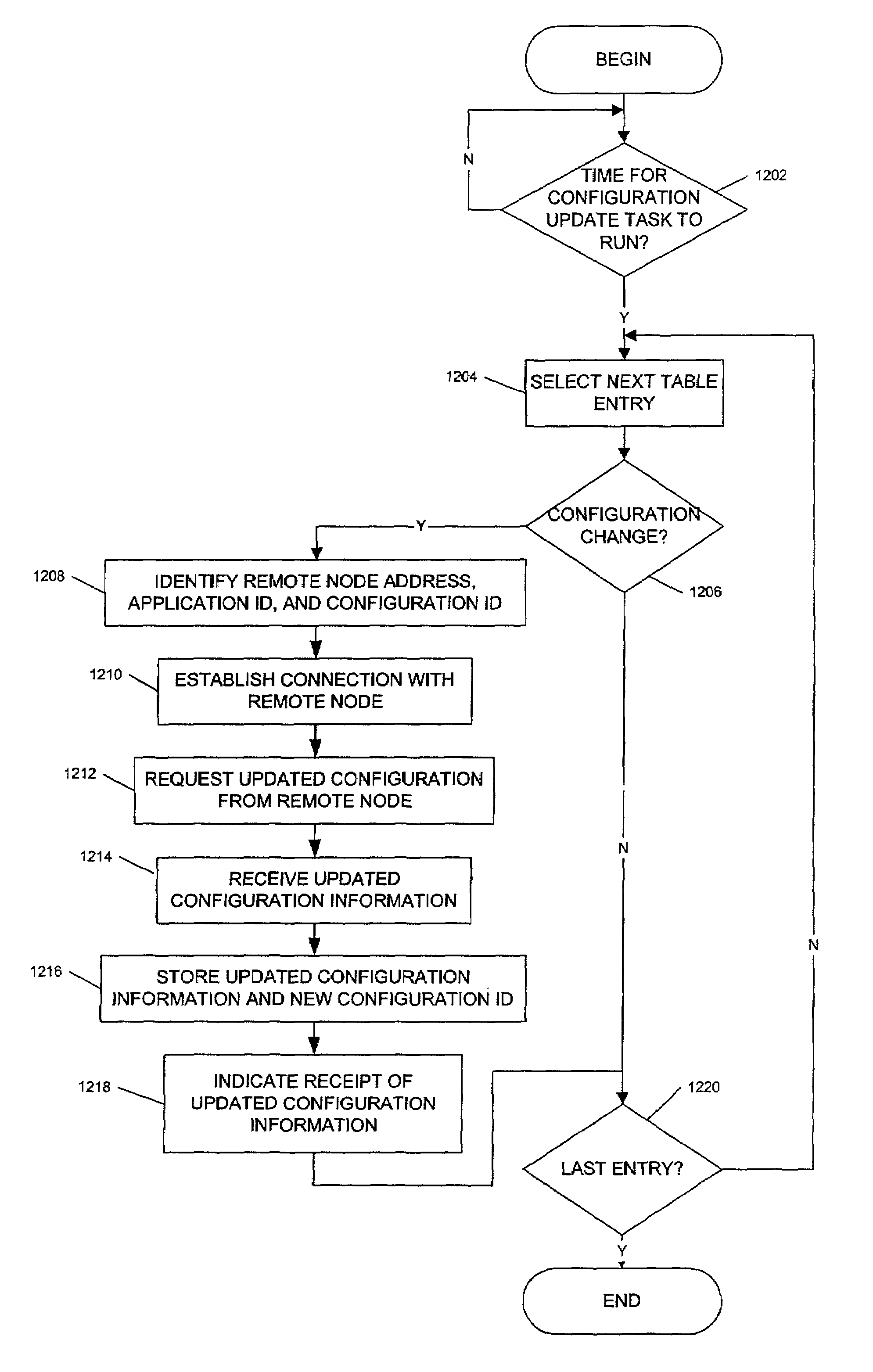
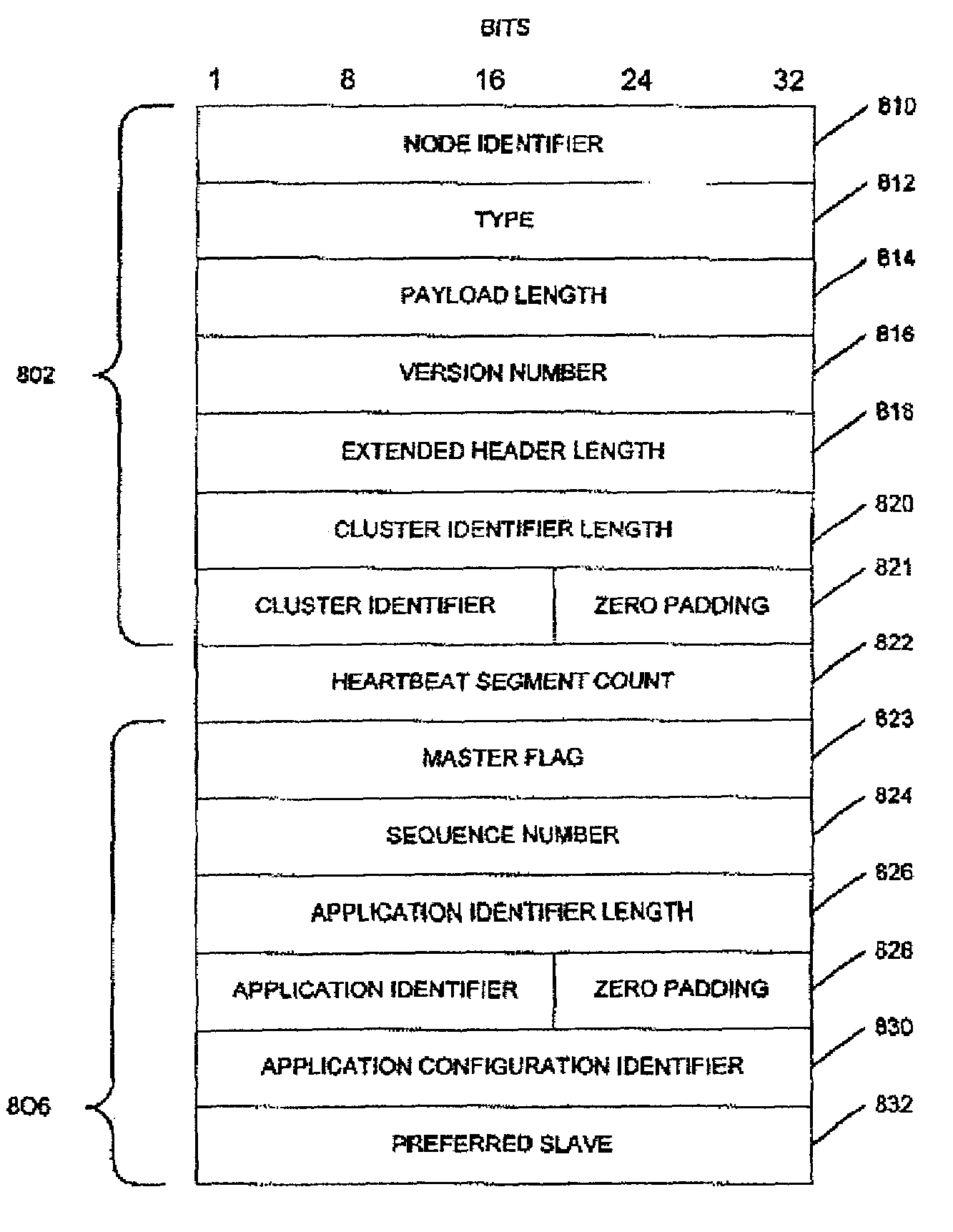
Method and apparatus for exchanging heartbeat messages and configuration information between nodes operating in a master-slave configuration
InactiveUS7421478B1Multiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingMultiple applicationsComputer science
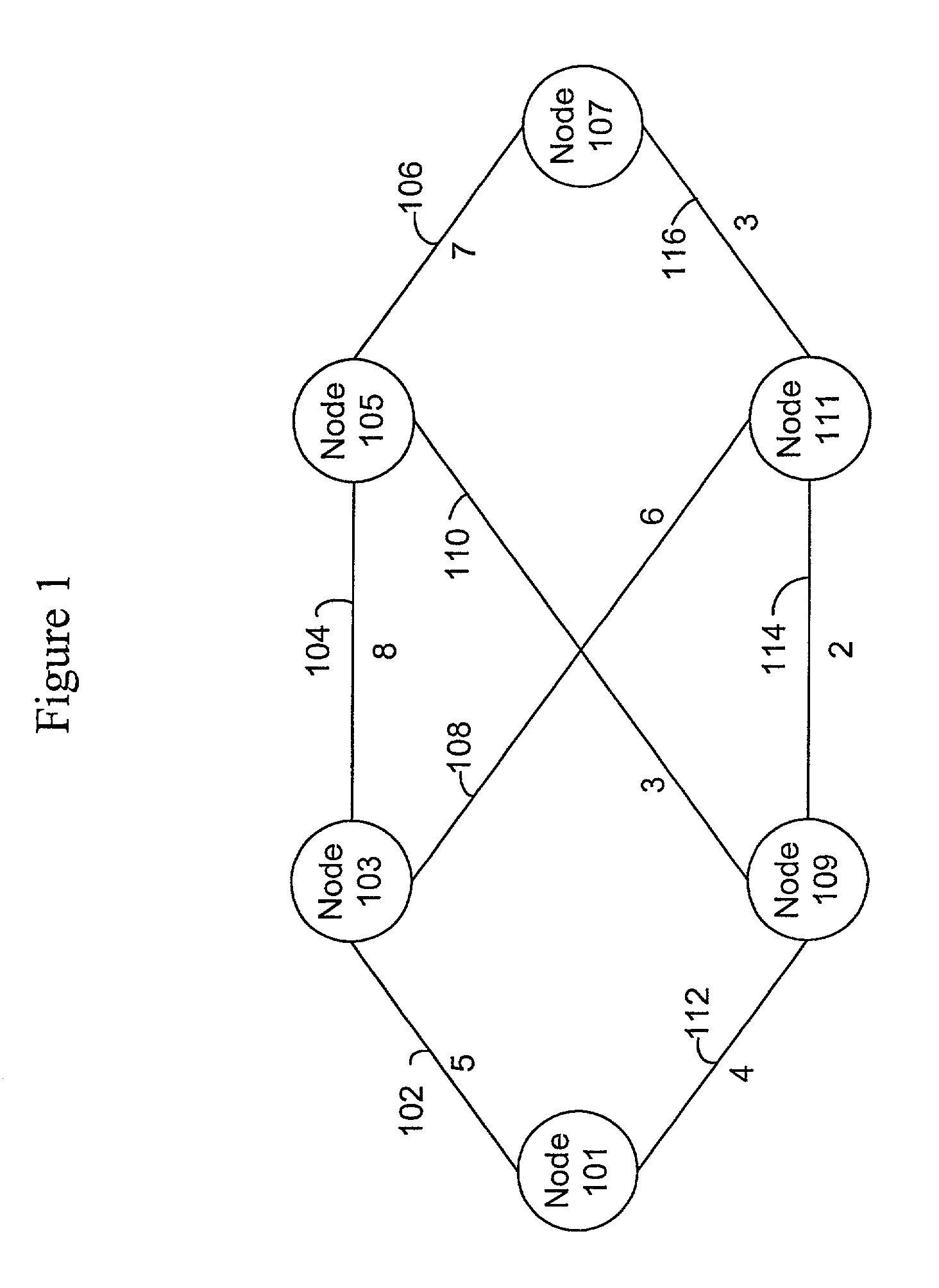
A node (101, FIG. 1), within a networked computer system (100), is capable of supporting communications with other nodes relating to operating multiple application instances in a master-slave configuration. Each node periodically generates and sends (520, 526, FIG. 5) a Heartbeat message (FIG. 8) that indicates the operational status for one or more application instances being managed by the node. When a node receives a Heartbeat message from a remote node, it evaluates (FIG. 10) the Heartbeat information for each application instance reported in the message, and takes any appropriate actions. The node also determines (1206, FIG. 12) whether new configuration information should be obtained for each of the application instances the node is managing, and requests (1210, FIG. 12) that new configuration information, when necessary.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for requesting link state information
InactiveUS7174387B1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkComplete sequence
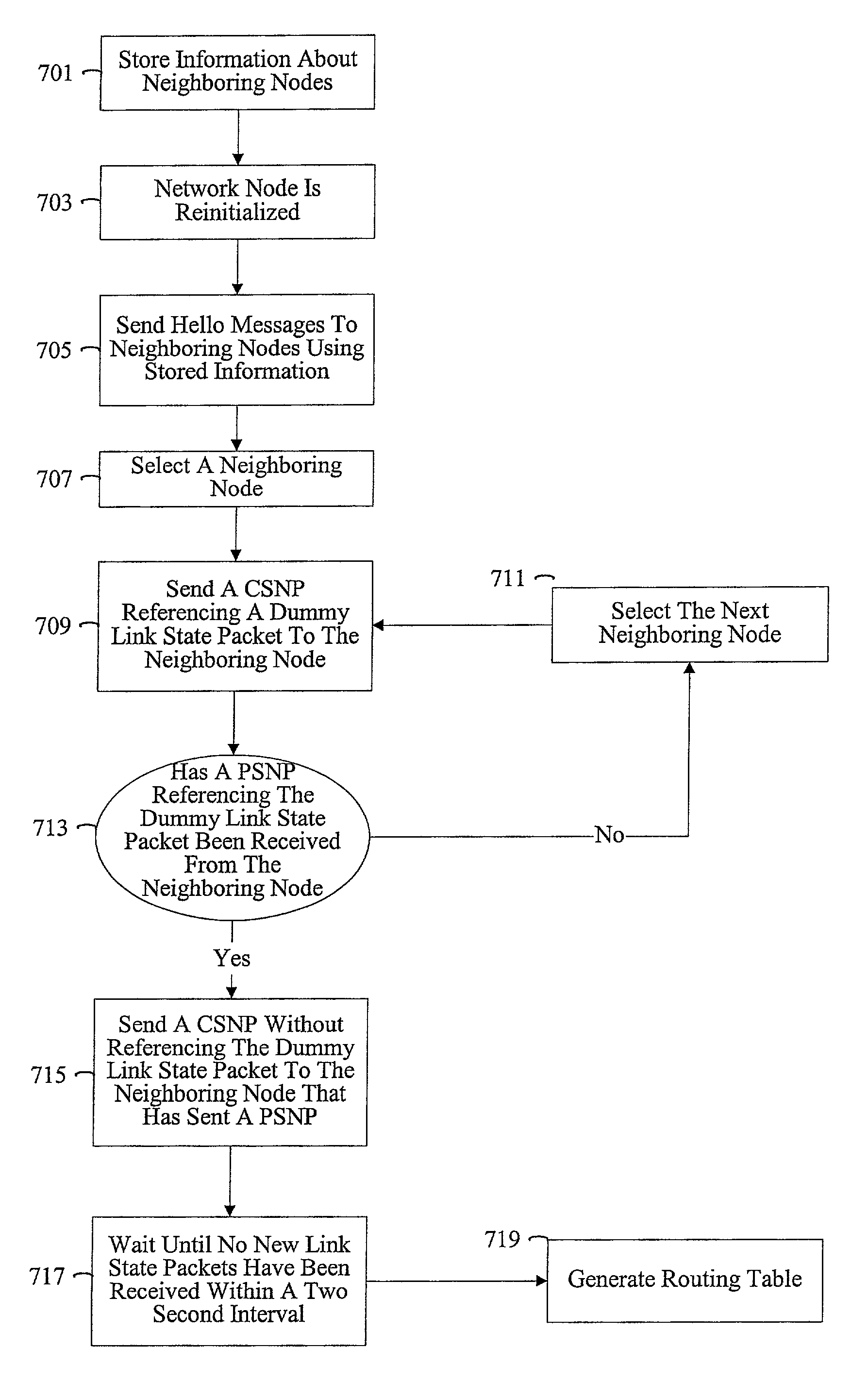
Methods and apparatus are provided for optimizing the reintroduction of a network node into a network. Information about neighboring nodes is stored in persistent memory. The network node can then be reinitialized and reintroduced into the network. Upon reintroduction, the network node can transmit heartbeat messages such as Hello messages to its neighboring nodes using information stored in persistent memory. A link state packet request message such as a Complete Sequence Numbers Packet referencing dummy link state information is transmitted to a neighboring node. A partial packet request message such as a Partial Sequence Numbers Packet referencing the dummy link state packet from the neighboring node can acknowledge that the Complete Sequence Numbers Packet has been received.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for providing availability and reliability for a telecommunication network entity
InactiveUS20070165516A1Error preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications networkNatural disaster
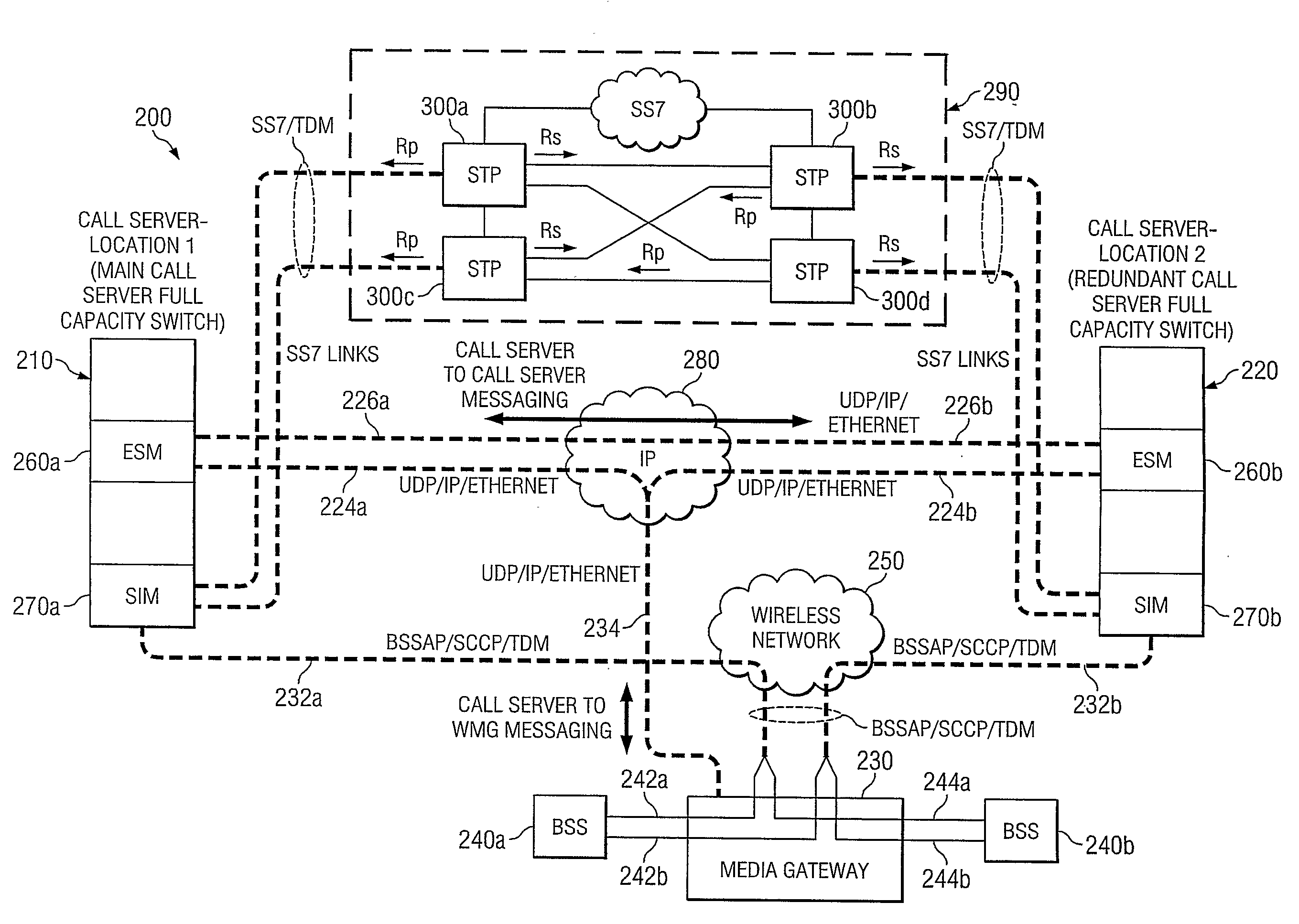
Geographical redundancy and an efficient switchover process to redundant equipment (210) is achieved by separating active main equipment (220) and standby redundant equipment in different geographical locations so that failures can be avoided in the event of a natural disaster or other event that affects an entire building or region. In addition, partial switchover can be performed for components or functions that become inoperative to corresponding redundant components in the standby equipment. To provide further redundancy and prevent unneeded switchovers, status or heartbeat messages are transmitted between the active main equipment and standby redundant equipment over two different networks.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Network security monitoring system employing bi-directional communication
ActiveUS7650638B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionMonitoring systemCommunication link
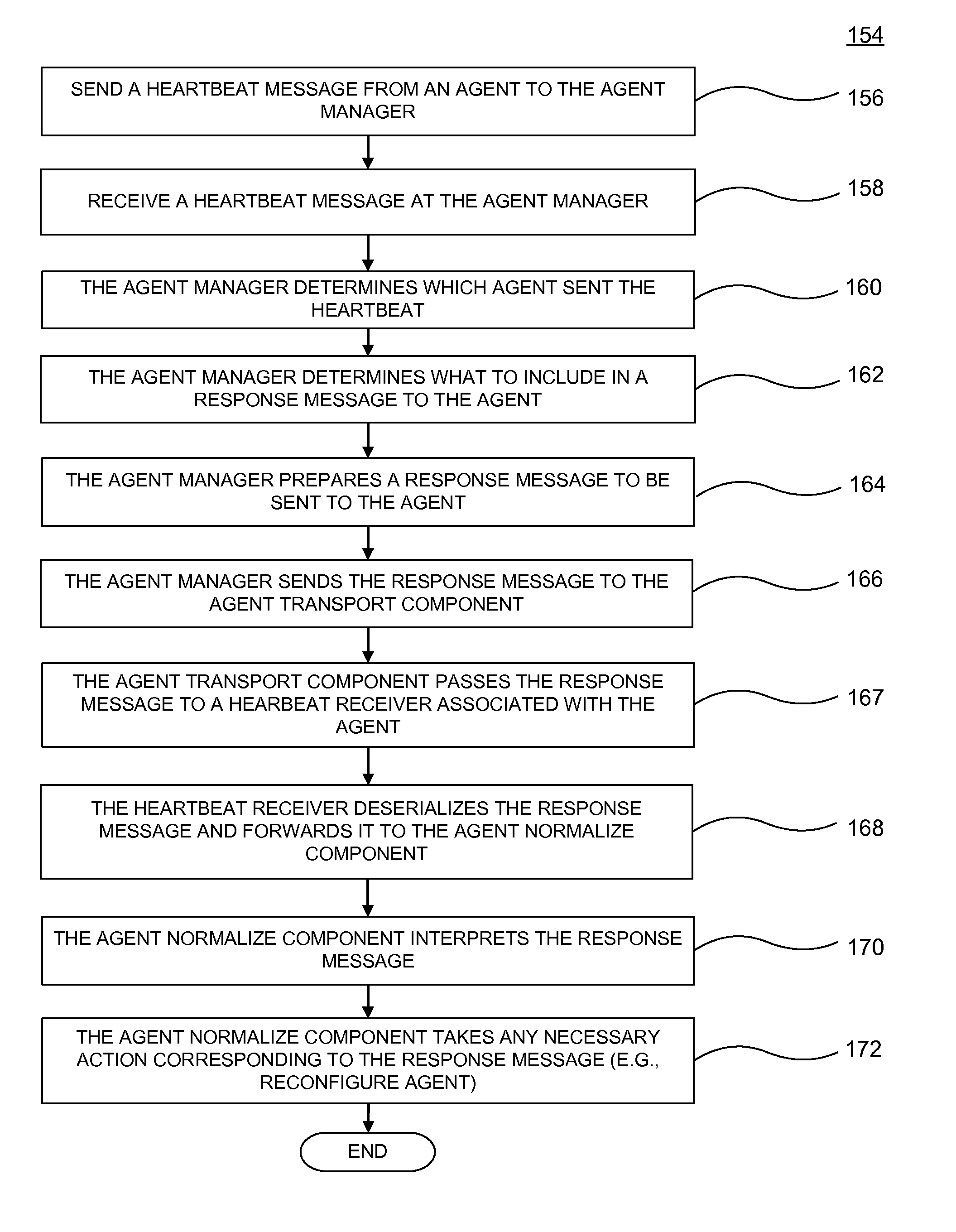
The present invention provides for the receipt of a heartbeat message transmitted from a software agent within a host machine to a server-based agent manager. The server-based agent manager analyzes the heartbeat message to determine the identity of the sending software agent. The server-based agent manager then determines what information is to be included in a response message to the software agent. The server-based agent manager prepares the response message to be sent to the software agent. The server-based agent manager transmits the response message to the software agent over a bi-directional communication link between the software agent and the server-based agent manager. The software agent receives the response message; deserializes the response message; reviews the instructions within the response message; and performs operations necessary to carry out the instructions delivered in the response message.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
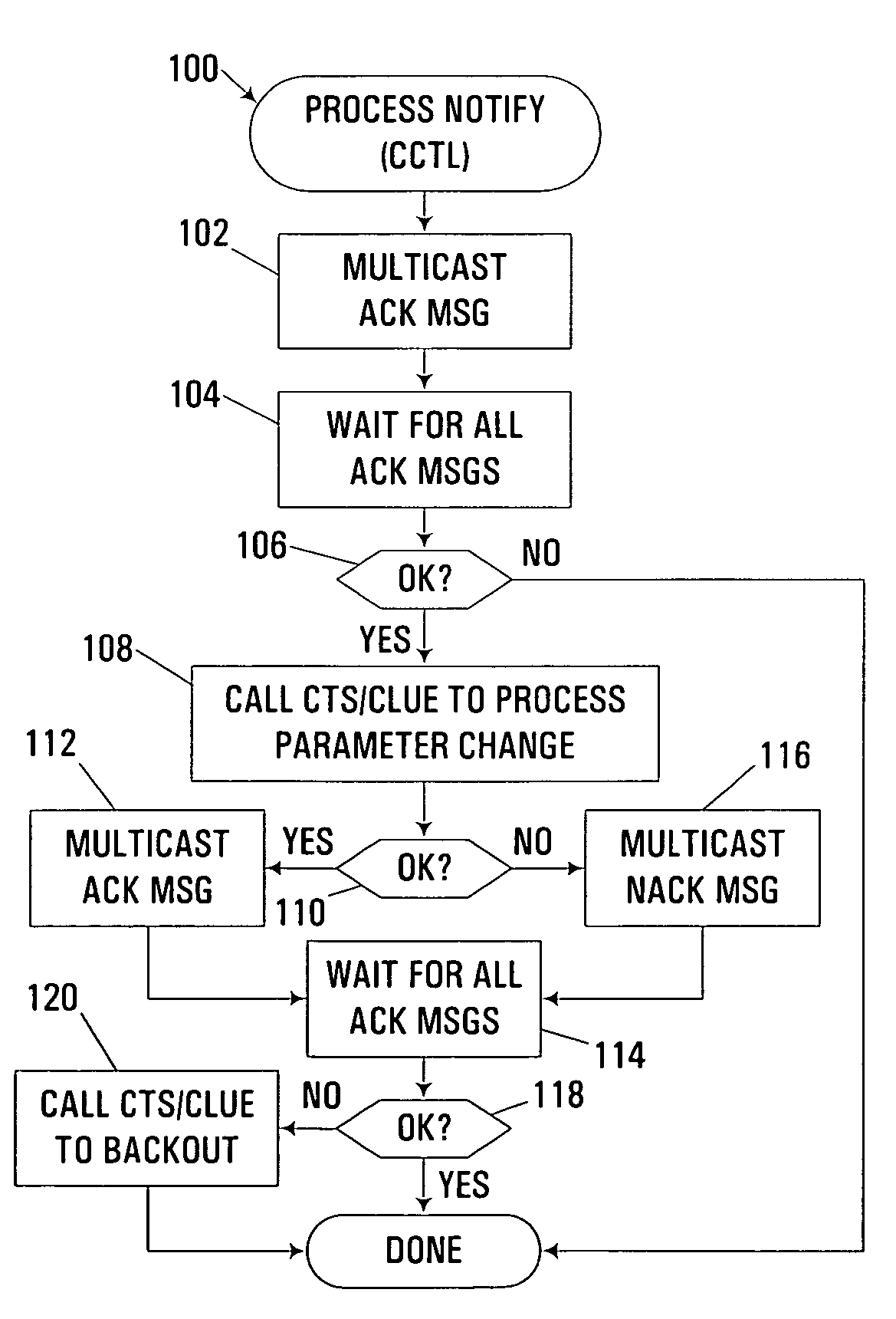
Dynamic modification of cluster communication parameters in clustered computer system
InactiveUS6983324B1Without any significant effect on availabilityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionReal-time computingHeartbeat message
An apparatus, program product and method support the dynamic modification of cluster communication parameters through a distributed protocol whereby individual nodes locally confirm initiation and status information for every node participating in a parameter modification operation. By doing so, individual nodes are also able to locally determine the need to undo locally-performed parameter modifications should any other node be incapable of performing a parameter modification. Moreover, specifically with respect to cluster communication parameters such as heartbeat parameters, such parameters may be dynamically modified by configuring a sending node to send a heartbeat message to a receiving node, with the heartbeat message indicating that a heartbeat parameter is to be modified. In response to the heartbeat message, the receiving node may then send an acknowledgment message to the sending node that indicates whether the heartbeat parameter has been modified in the receiving node. Further, modification of the heartbeat parameter in the sending node may be deferred until the acknowledgment message from the receiving node indicates that the heartbeat parameter has been modified in the receiving node.
Owner:IBM CORP
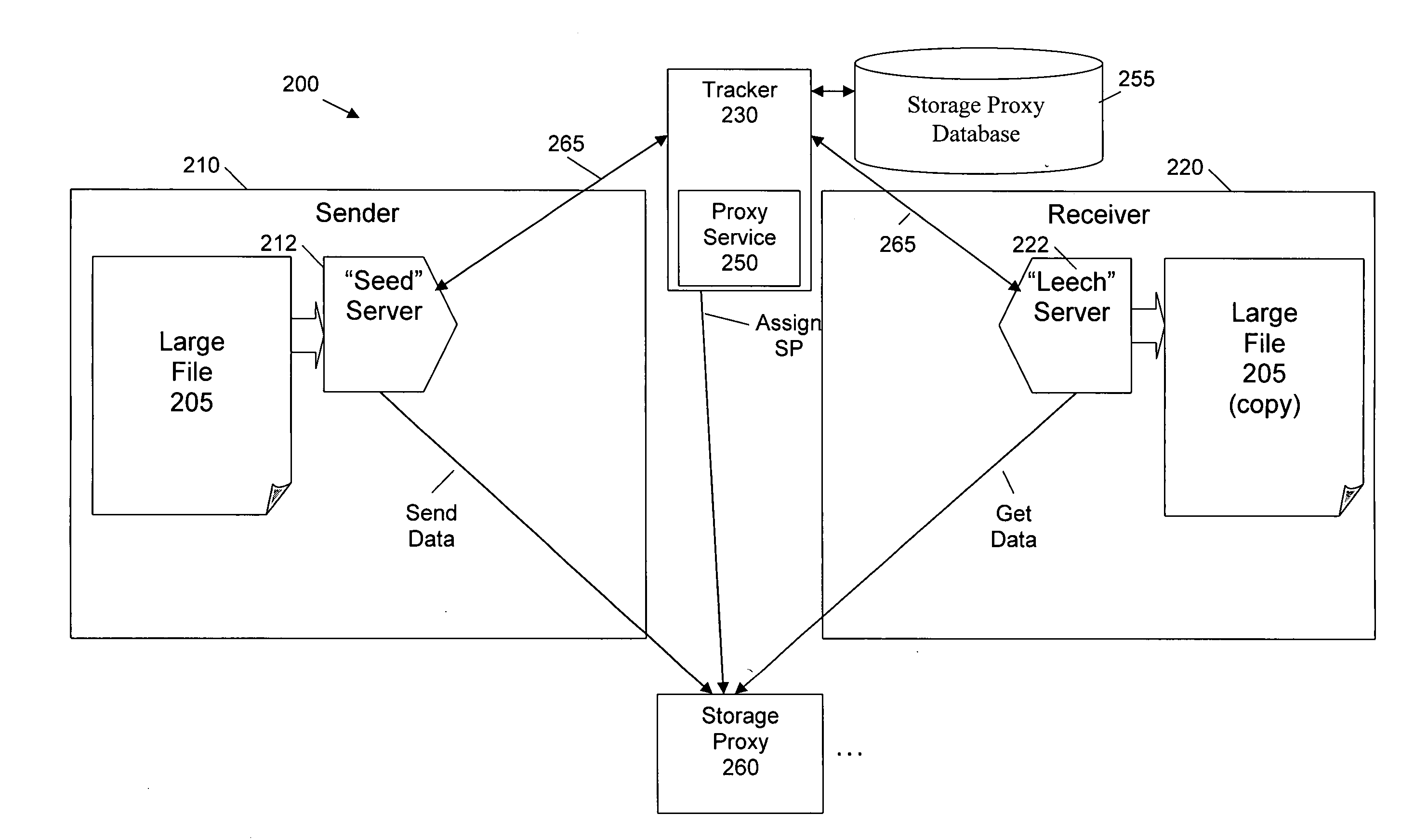
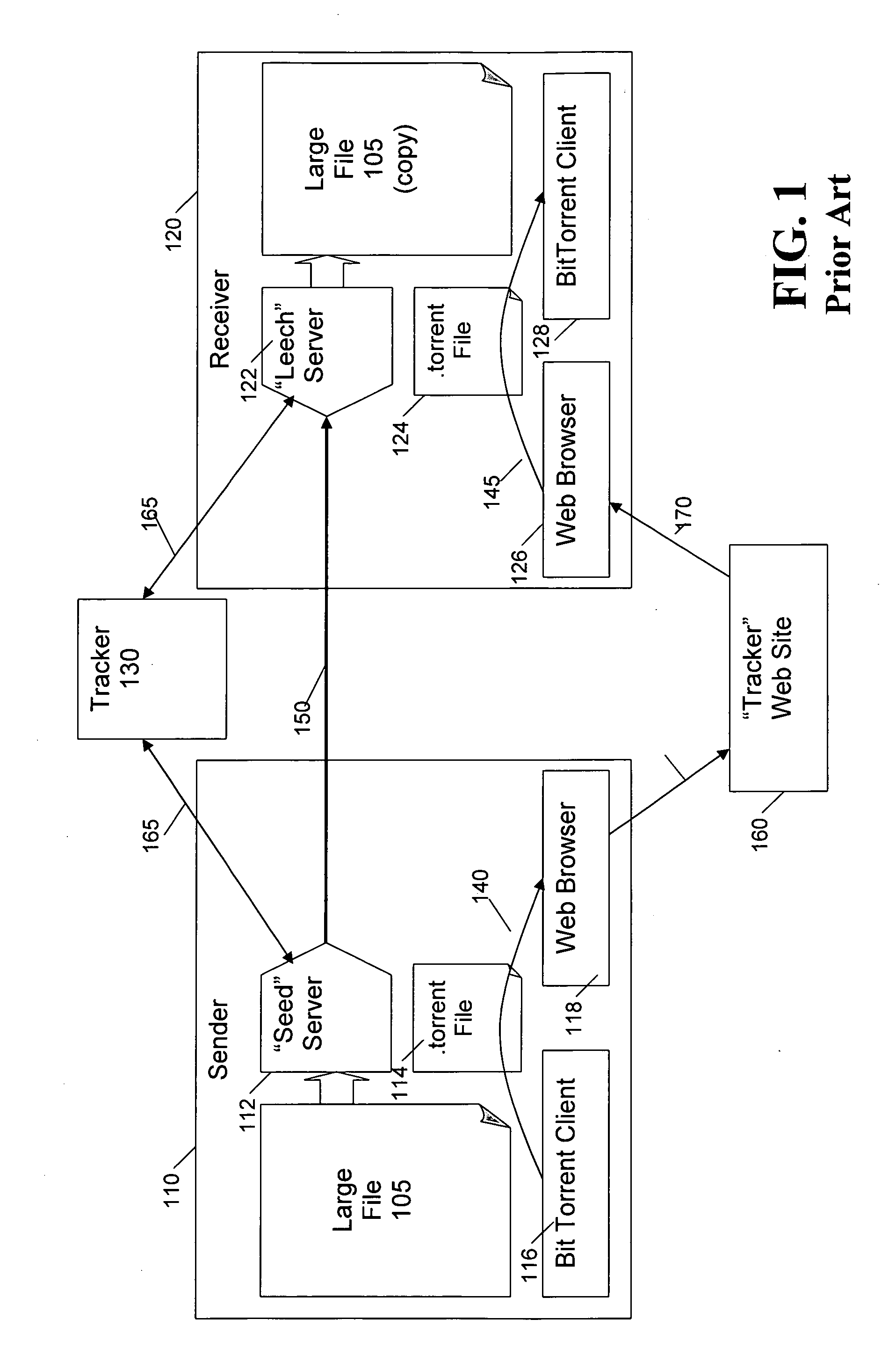
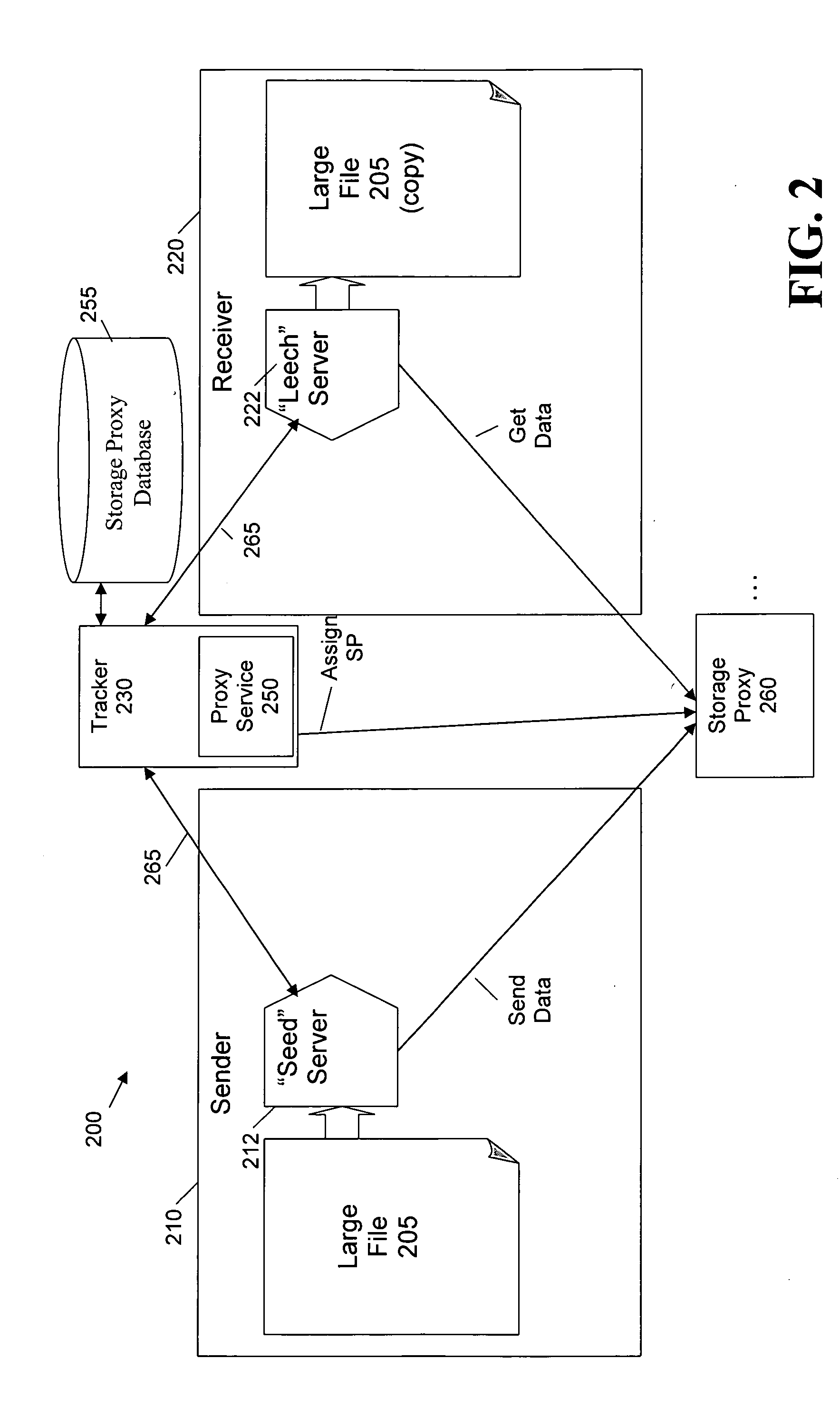
Security techniques for cooperative file distribution
InactiveUS20080066182A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDistribution systemEncryption
Security techniques are provided for cooperative file distribution. An encryption key or a nonce (or both) are generated for a package containing one or more files that are to be sent in a cooperative file distribution system. Random access encryption techniques can be employed to encrypt a package containing one or more files to be sent in a cooperative file distribution system. One or more storage proxies are allocated to a package to be transmitted in a cooperative file distribution system, based on load. Access to trackers in the cooperative file distribution system is controlled using security tokens. Content can automatically expire using a defined expiration period when the content is uploaded into the system. Variable announce intervals allow the tracker to control how often the tracker will receive a message, such as an announcement or a heartbeat message, from peers in the system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
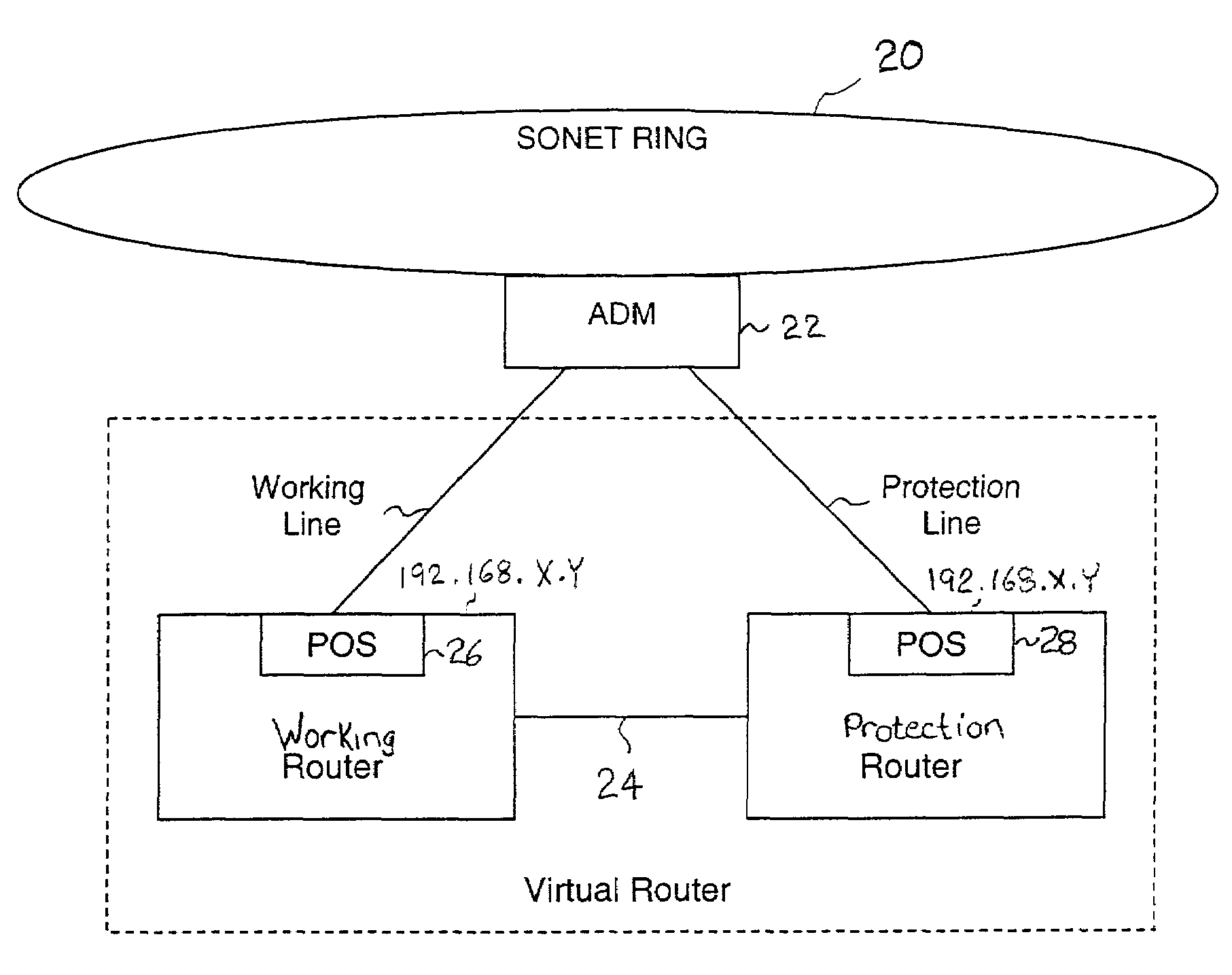
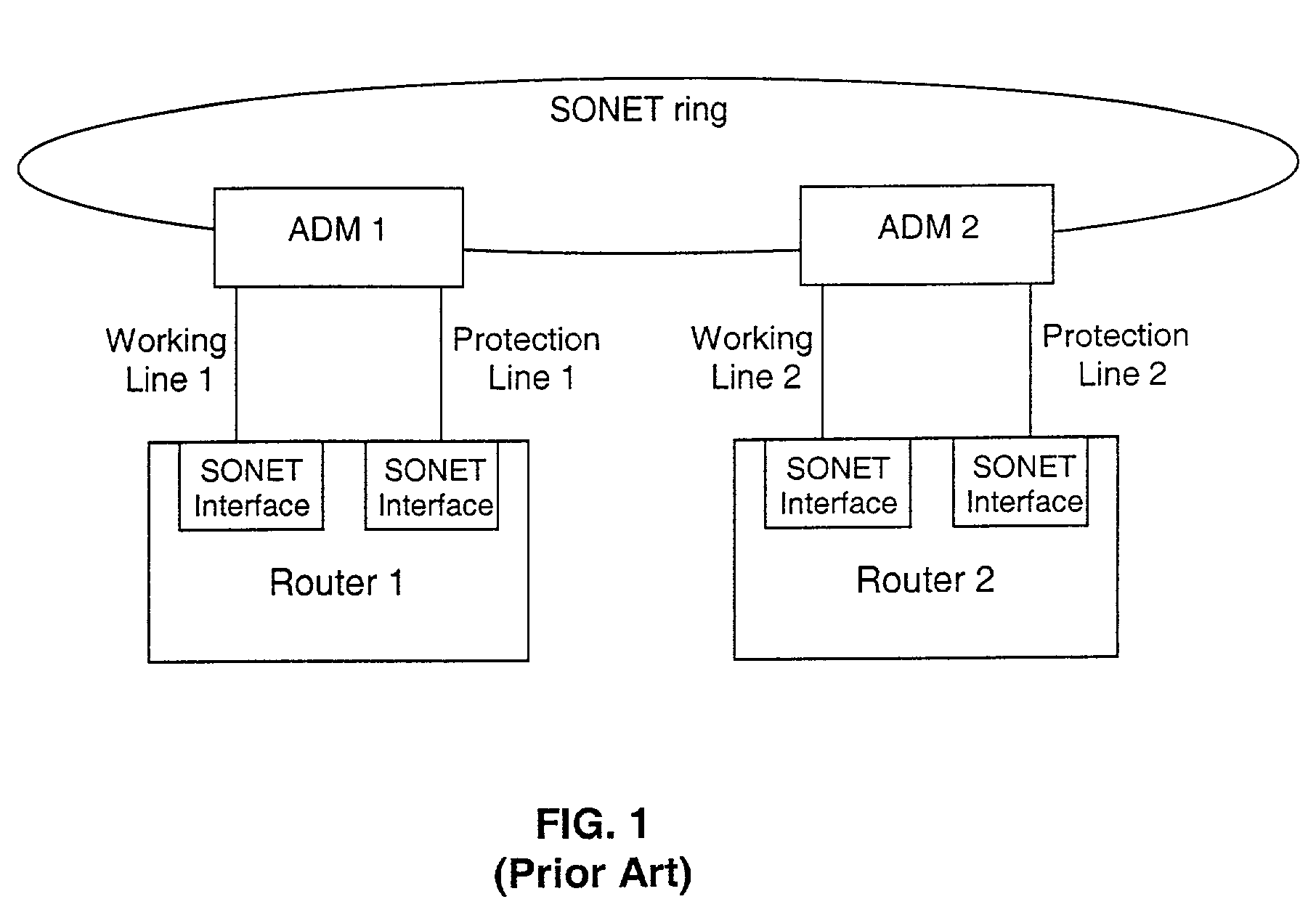
Fault tolerant automatic protection switching for distributed routers
InactiveUS6956816B1Providing fault toleranceError preventionTransmission systemsPoint-to-Point ProtocolAutomatic protection switching
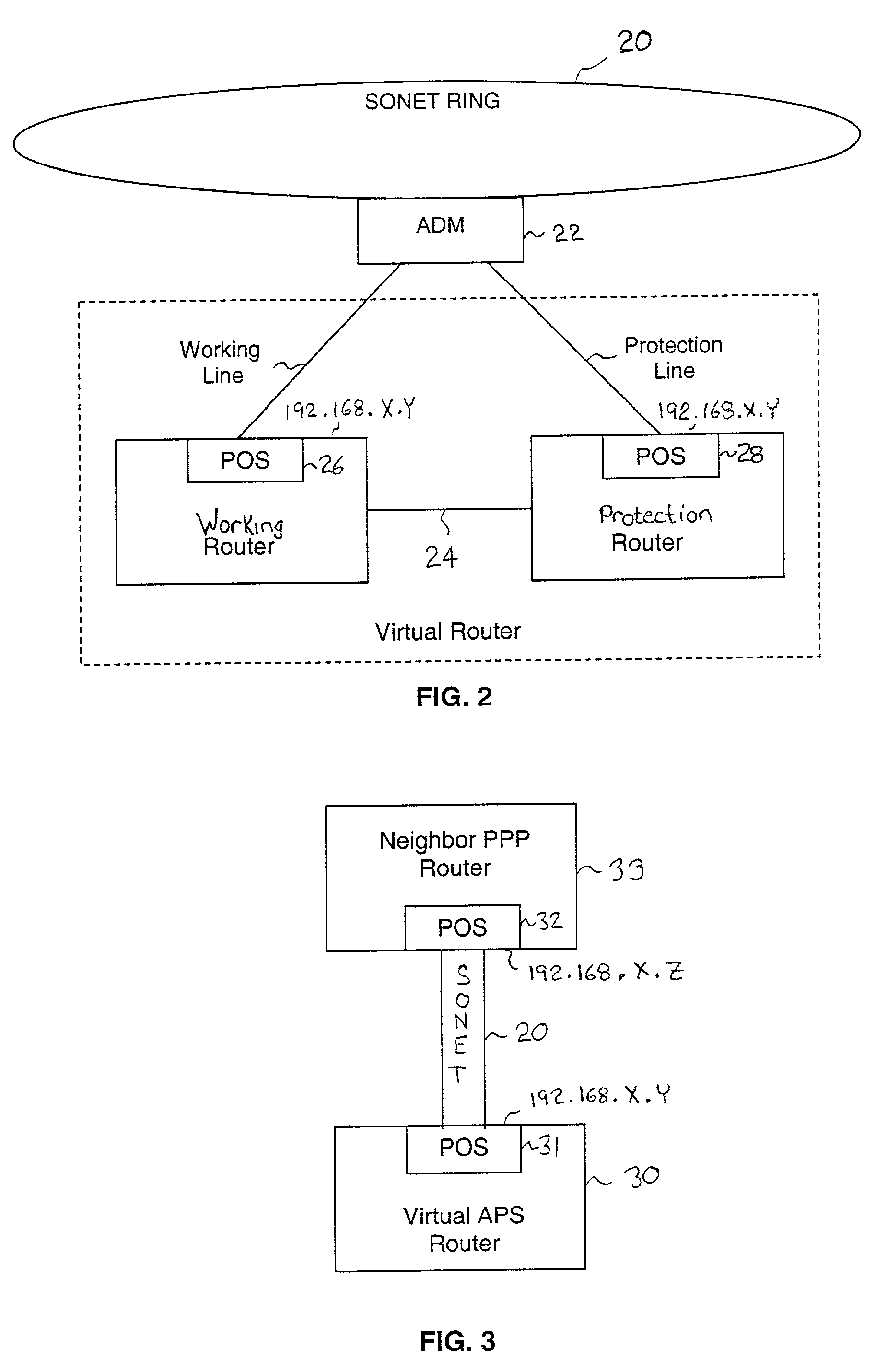
A working router is coupled to a SONET add-drop multiplexor (ADM) through a working line and a protection router is coupled to the ADM through a protection line. The routers are coupled to each other by a separate side-band connection and comprise a virtual router from the perspective of the neighboring router, which communicates with the virtual router over the SONET network using the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). The protection router transmits a heartbeat message to the working router over the side-band connection. If the protection router does not receive a response thereto, it initiates a line switch within the add-drop multiplexor. Once the line switch is complete, the protection router exchanges datagrams with the neighboring router, via the ADM and SONET ring to which the ADM is coupled. The protection router establishes a PPP connection between itself and the neighboring router device coupled to the SONET ring, utilizing the Link Control Protocol (LCP). The protection router includes a predetermined identifier value that identifies the originator of the request, in the LCP Identifier field of LCP request datagrams. The neighboring router includes the Identifier value received in a request datagram in the corresponding response datagram transmitted over the SONET ring to the ADM. Because datagrams received by the ADM from the SONET link are transmitted over both the working and the protect lines, the working router receives the same response as the protection router. Thus, by examining the identifier field, and recognizing the identifier value as that assigned to the protection router, the working router determines that the line switch to the protection router has occurred.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Distributed database weighted voting method based on operating sequence number
InactiveCN104933132AImprove work efficiencyDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsAnomaly detectionDistributed database
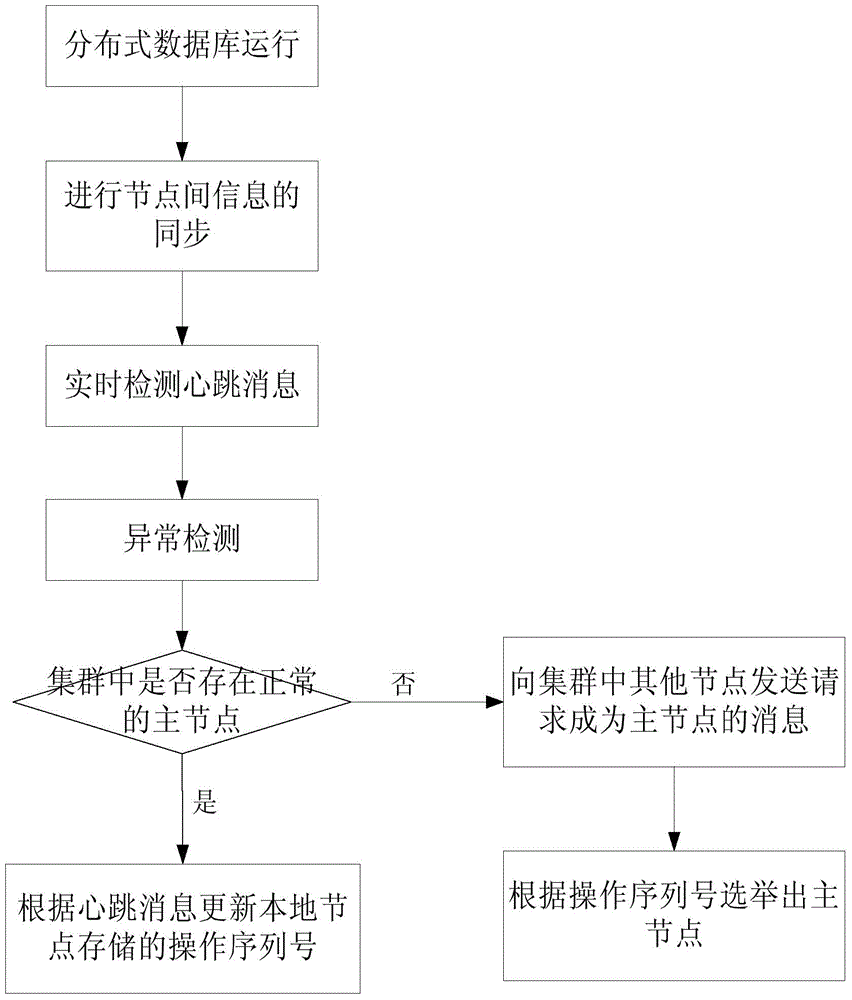
The invention discloses a distributed database weighted voting method based on an operating sequence number. The method comprises the steps as follows: S1, synchronizing information among nodes by transmitting a heartbeat message comprising the operating sequence number when a distributed database is operated; S2, judging whether there is a normal host node in a cluster via anomaly detection, and updating the operating sequence number stored by a local node according to the heartbeat message when there is the normal host node; otherwise, turning to a step S3; S3, transmitting a message for requesting to be the host node to other nodes in the cluster while detecting that there is no normal host node in the cluster from the node and voting the host node according to the operating sequence number. The distributed database weighted voting method of the invention could incorporate the operating sequence number for describing the newest operating state of the node so that the node comprising the newest operating sequence number could be voted as the host node to ensure maximum user operations to be remained, thereby improving work efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN SEQUOIADB DATABASE SOFTWARE CO
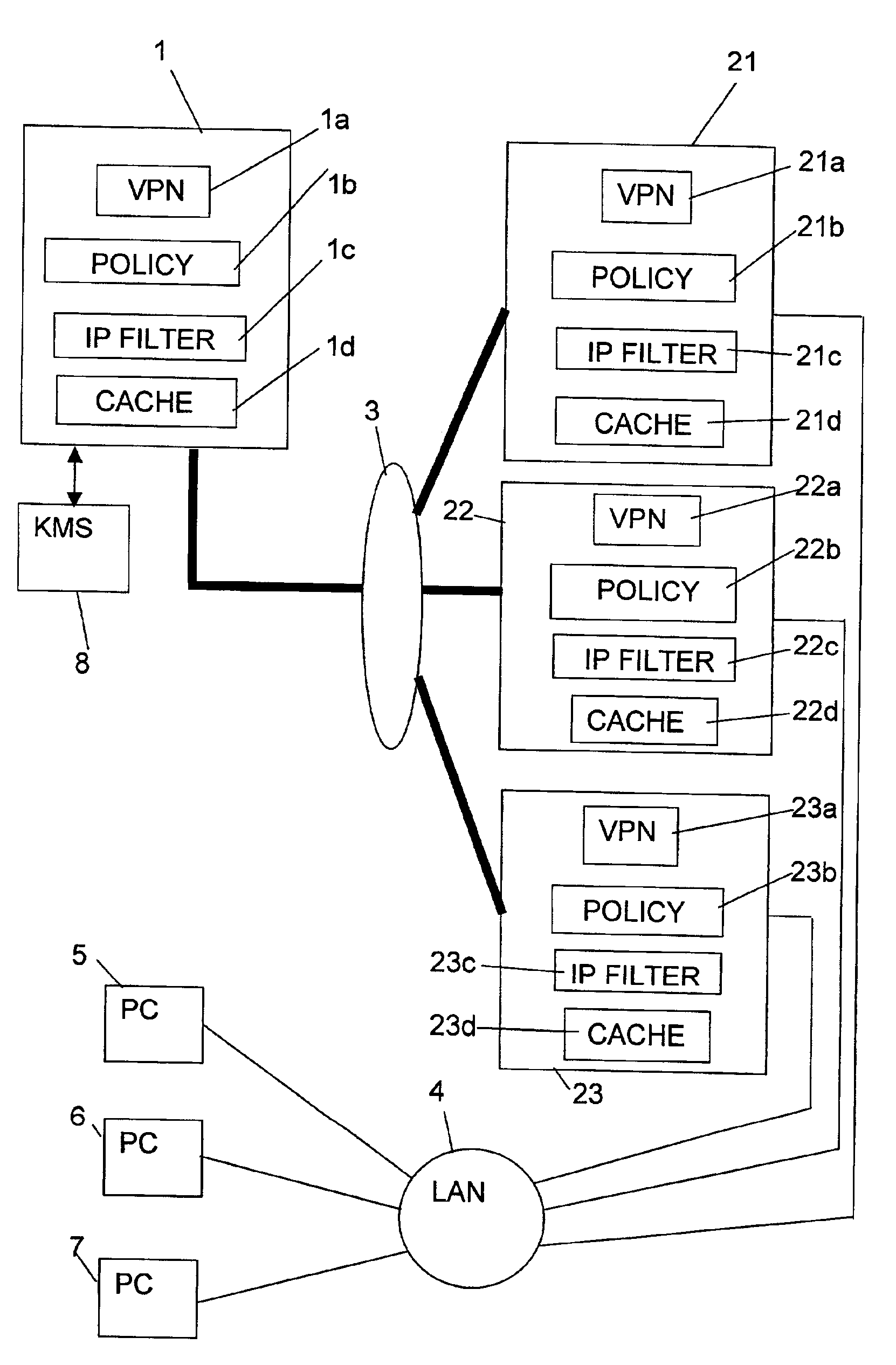
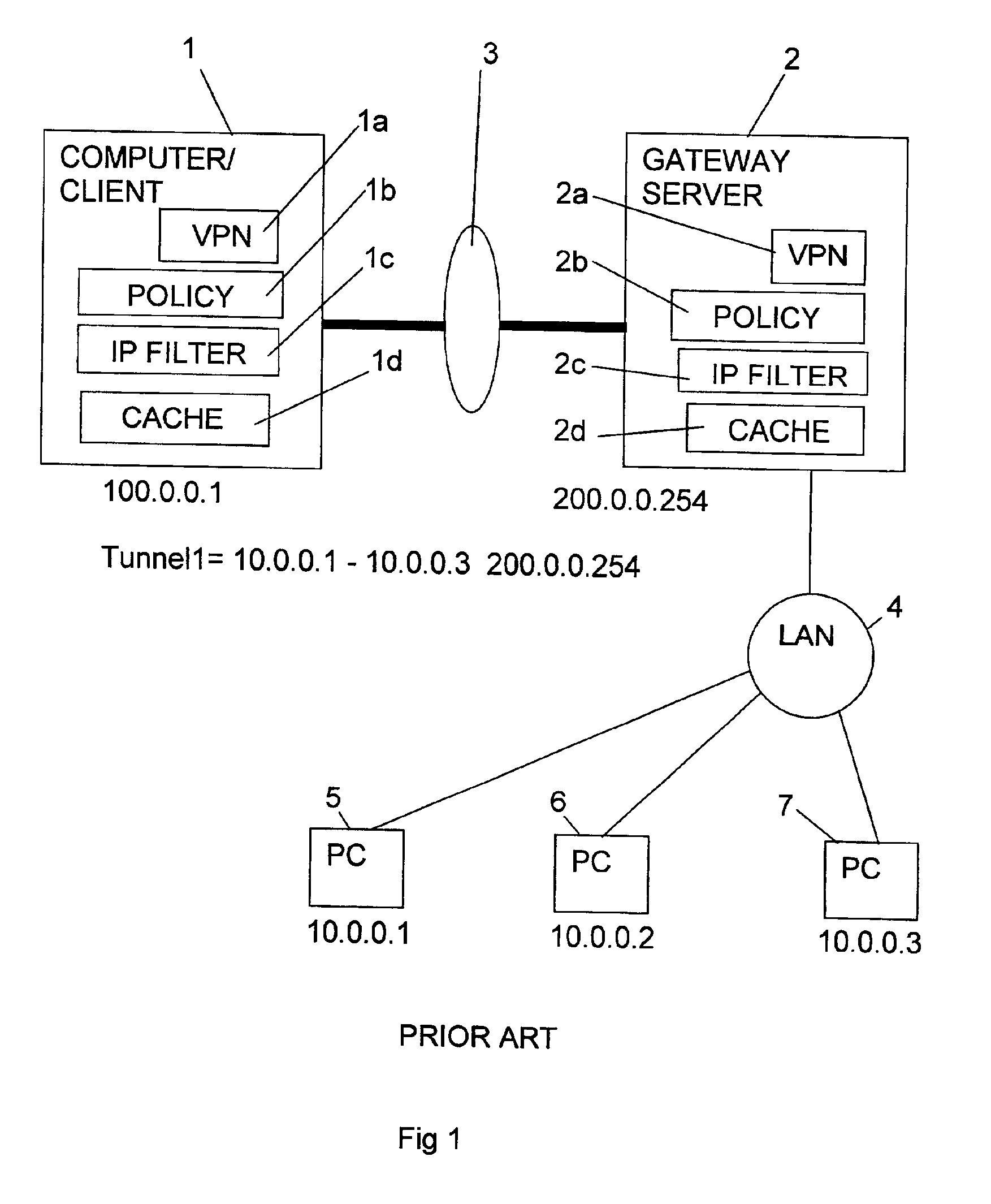
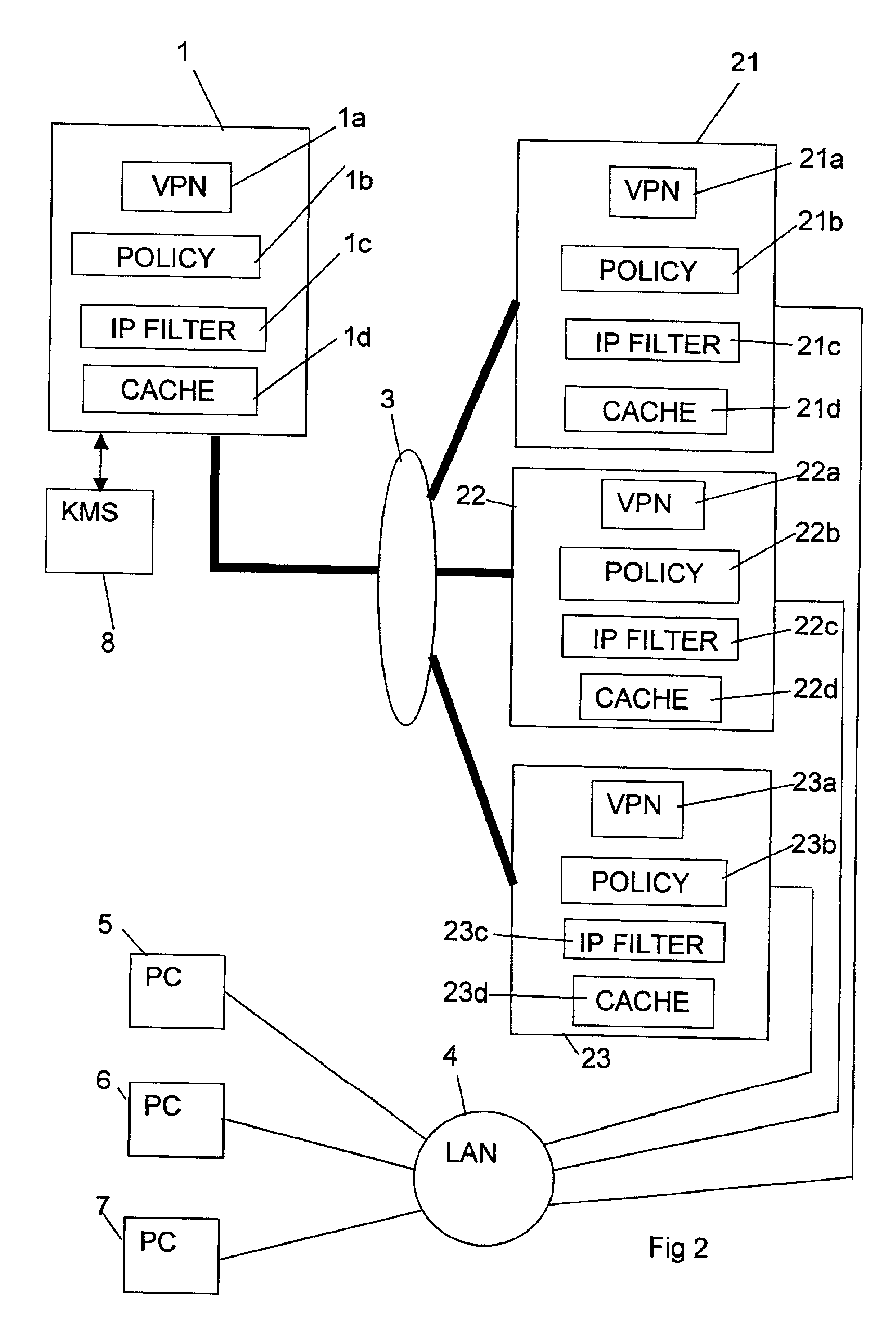
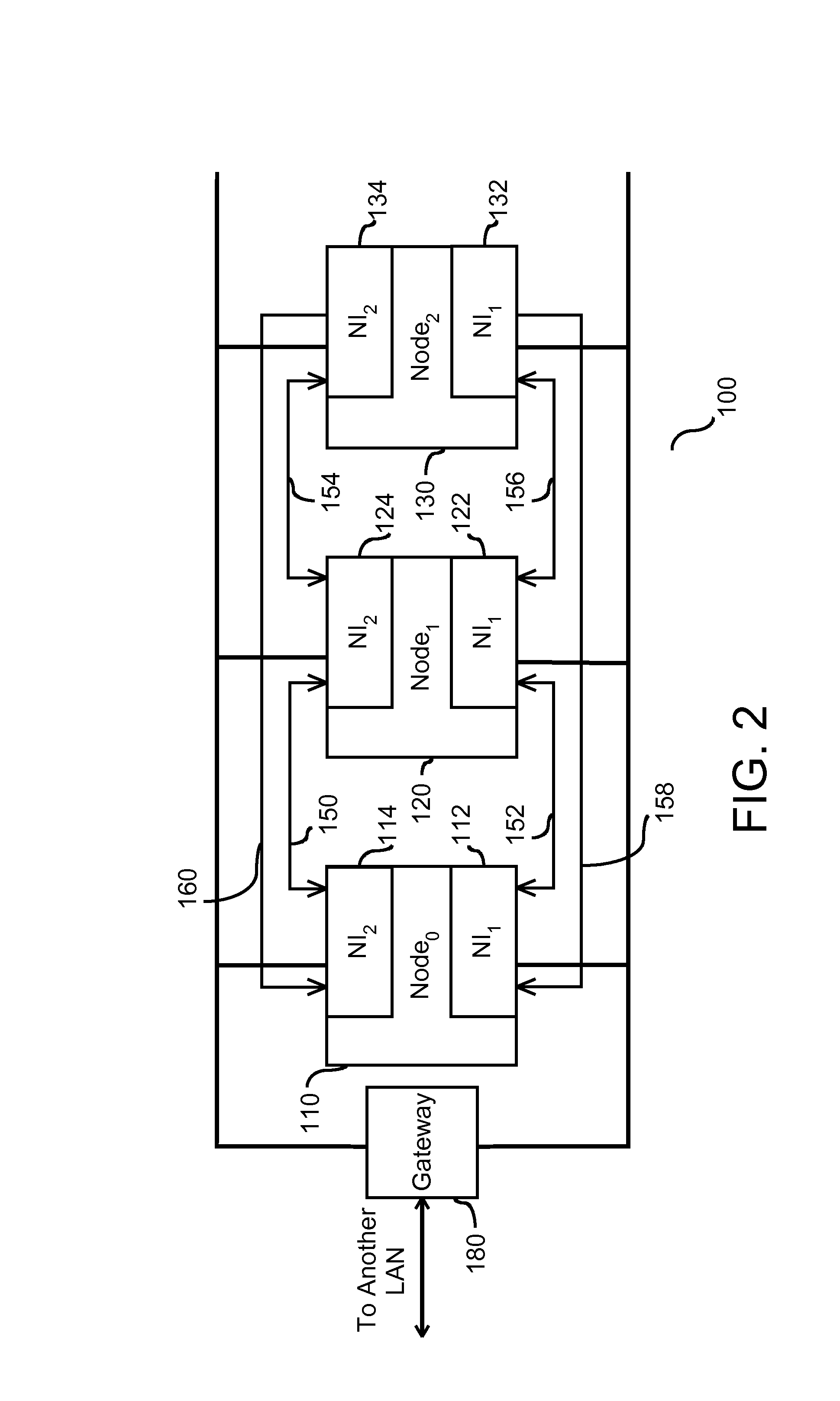
Computer systems, in particular virtual private networks
ActiveUS7000121B2User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkComputerized system
A first node (client) (1) is in communication with one of a plurality of second nodes (5, 6, 7) connected to a local area network (LAN) (4) via a virtual private network including a link (3), such as the Internet, and a selected one of a plurality of third nodes (gateway servers) (21, 22, 23). Communication between the first node (1) and the third nodes (21, 22, 23) is encrypted, whereas communication between the third nodes and the second nodes (5, 6, 7) is unencrypted. Communication from the first node (1) to one of the second nodes (5, 6, 7) is initially set up via a selected one of the third nodes after suitable authentication. If that third node should subsequently fail, an alternative third node can be used. To detect the failure of a third node, the first node (1) sends a “heartbeat” packet (failure detection signal) to it. An operational third node responds with an answer, indicating that all is well. If no answer is received within a predetermined time interval, the first node sends another “heartbeat” packet. If there is still no answer, another third node is selected for use. This other third node can be one that was previously authenticated, or alternatively one that must be authenticated at this time. In order to reduce workload heartbeat messages may only be sent at selected times.
Owner:FUJITSU SERVICES
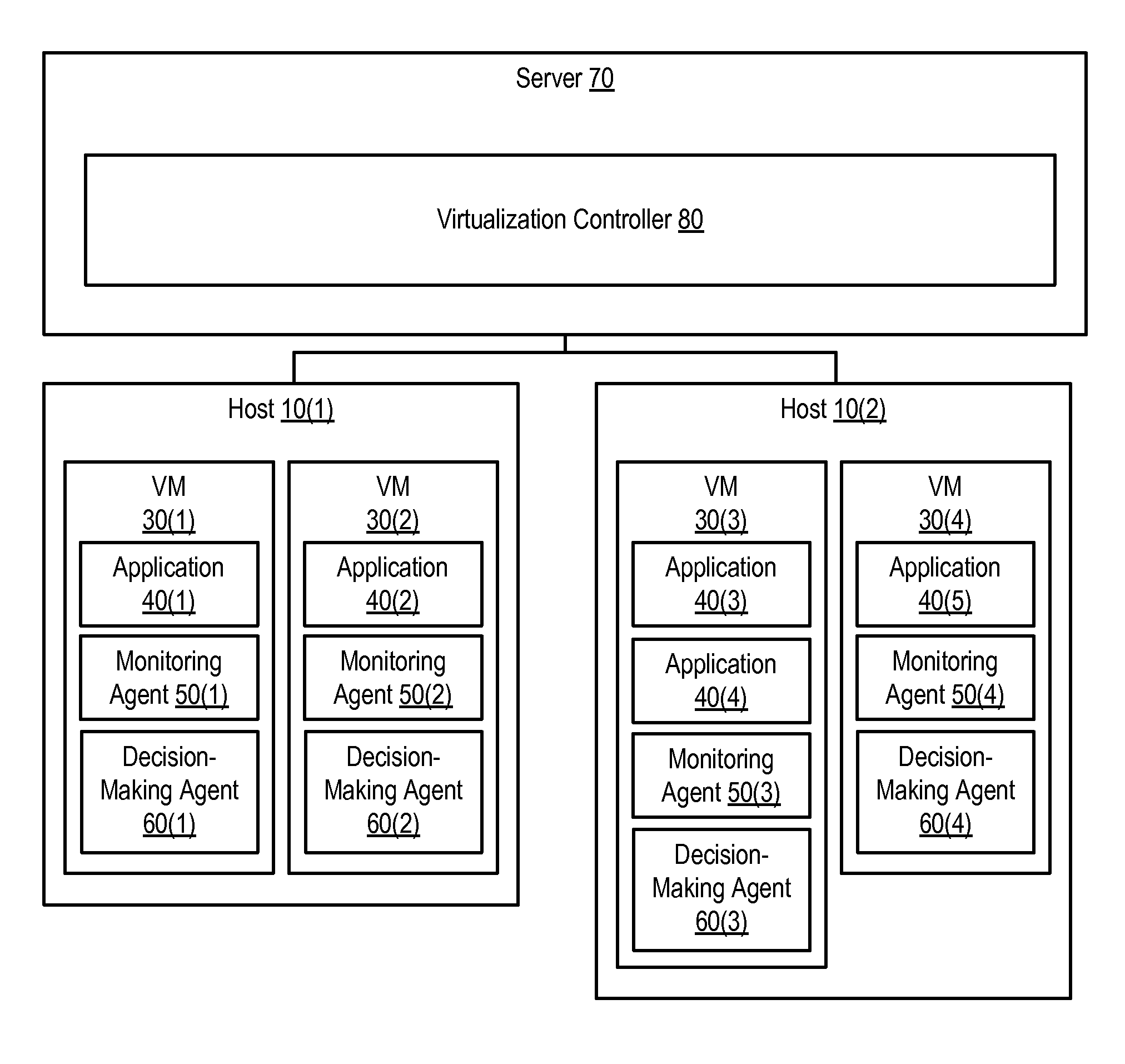
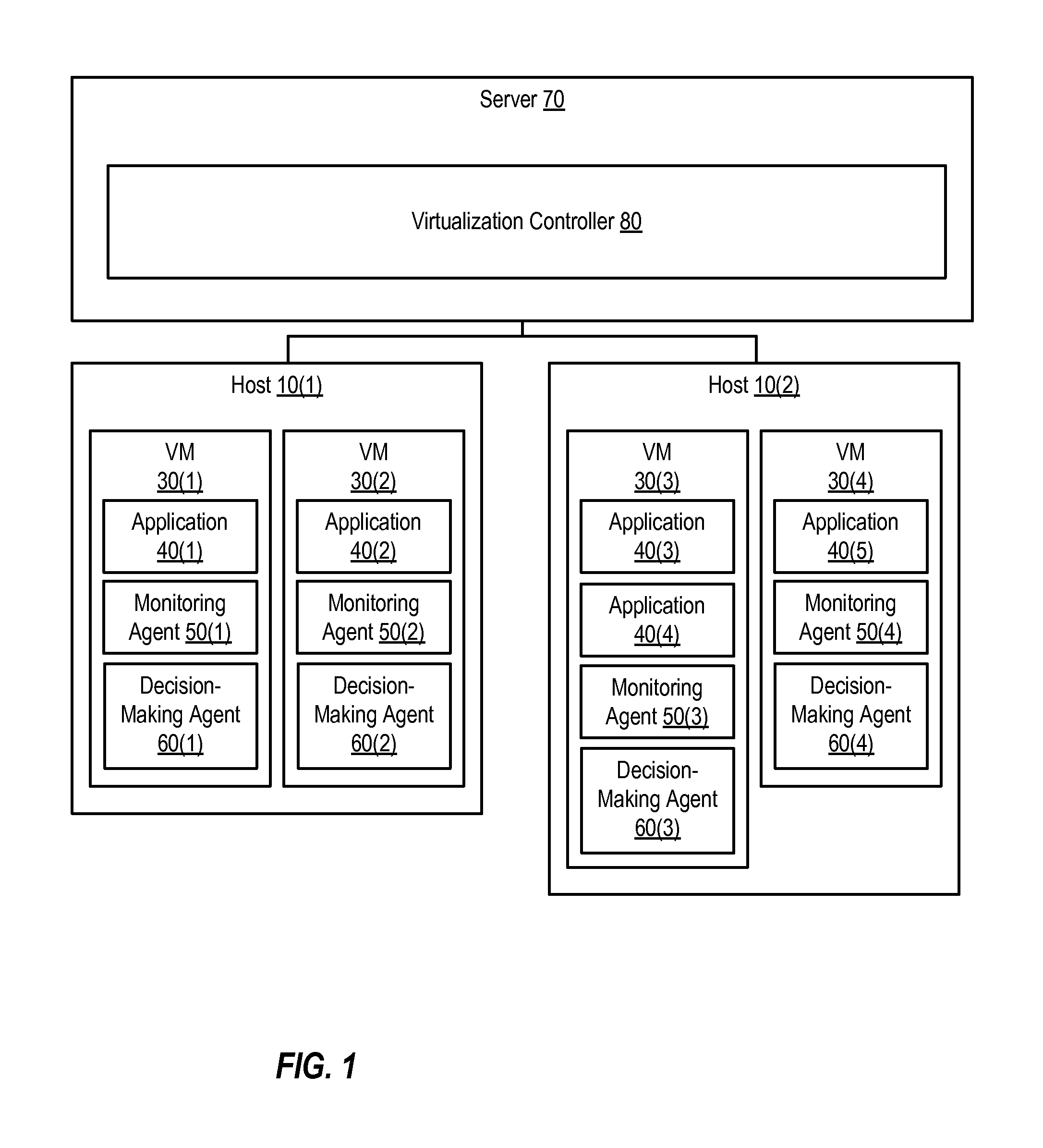
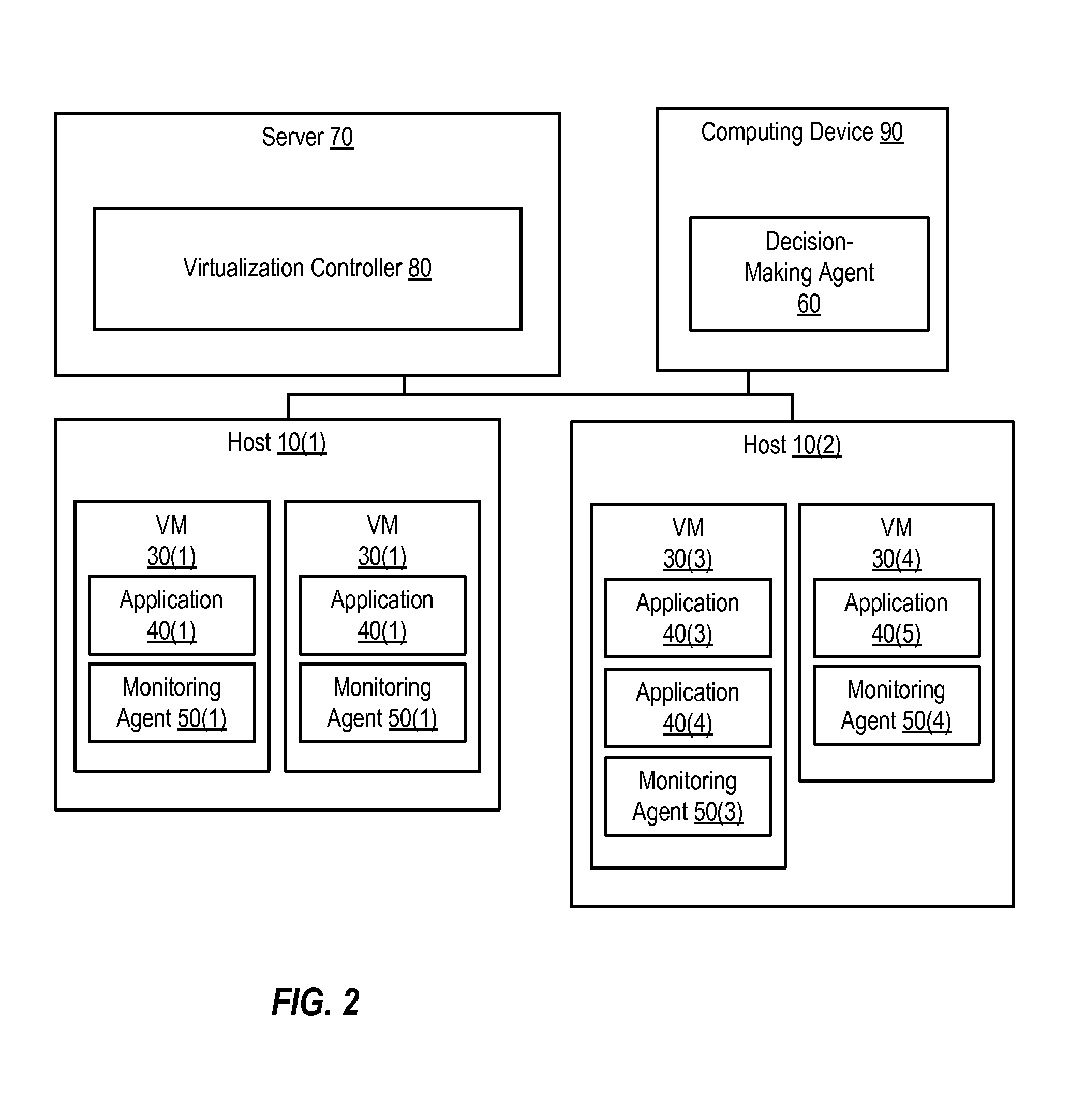
Providing Application High Availability in Highly-Available Virtual Machine Environments
ActiveUS20120030670A1Non-redundant fault processingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationHigh availability
Various systems and methods can provide high availability of an application executing in a highly-available virtual machine environment. One method involves receiving information indicating a state of an application executing in a virtual machine from a monitoring agent executing in the virtual machine. In response to receiving the information, the method involves determining whether the virtual machine should be restarted. Based upon that determination, the method then determines whether the monitoring agent should send a heartbeat message to a virtualization controller prior to expiration of a timeout interval. The virtualization controller is configured to restart the virtual machine if the virtual machine does not send the heartbeat message prior to expiration of the timeout interval.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
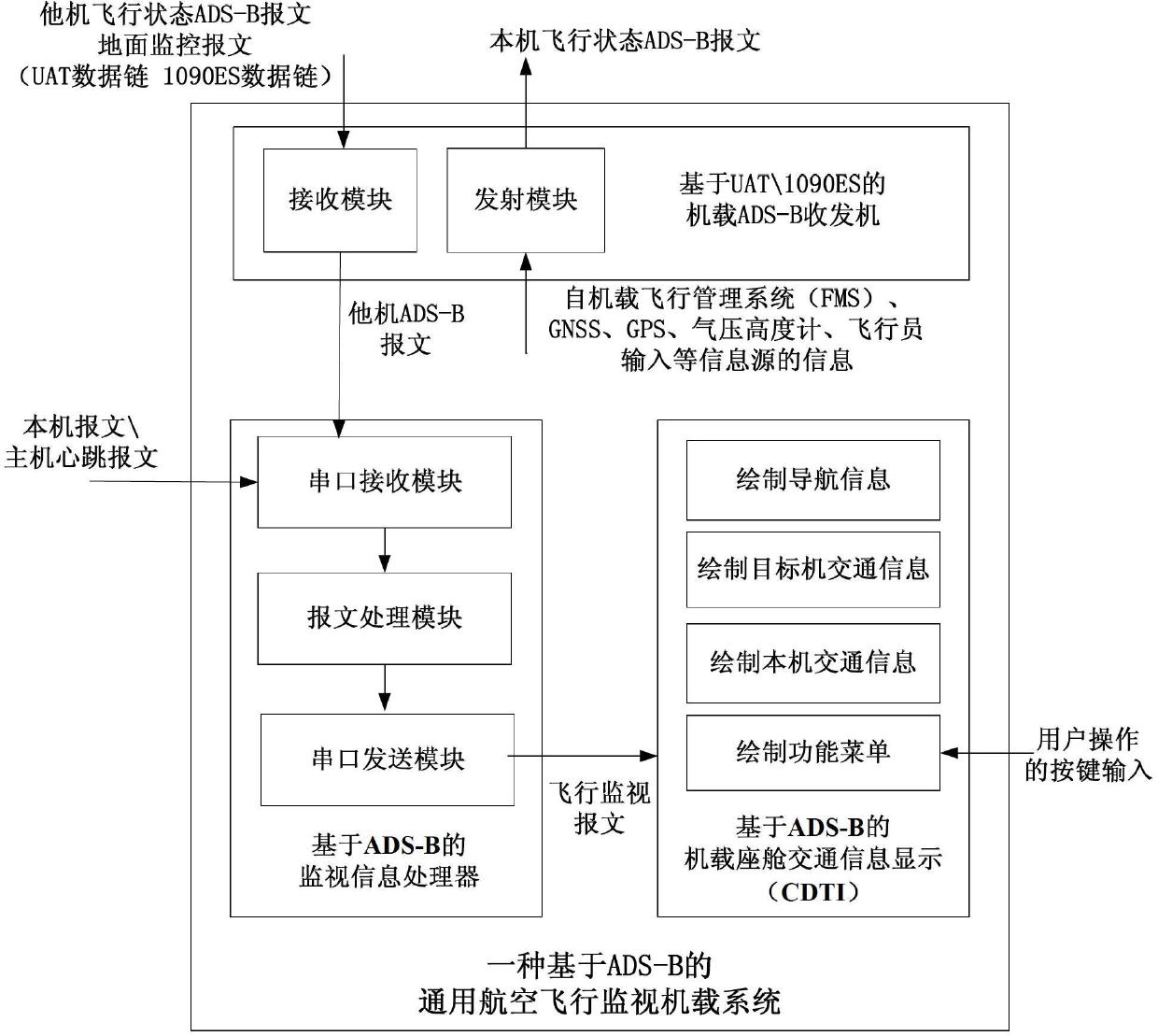
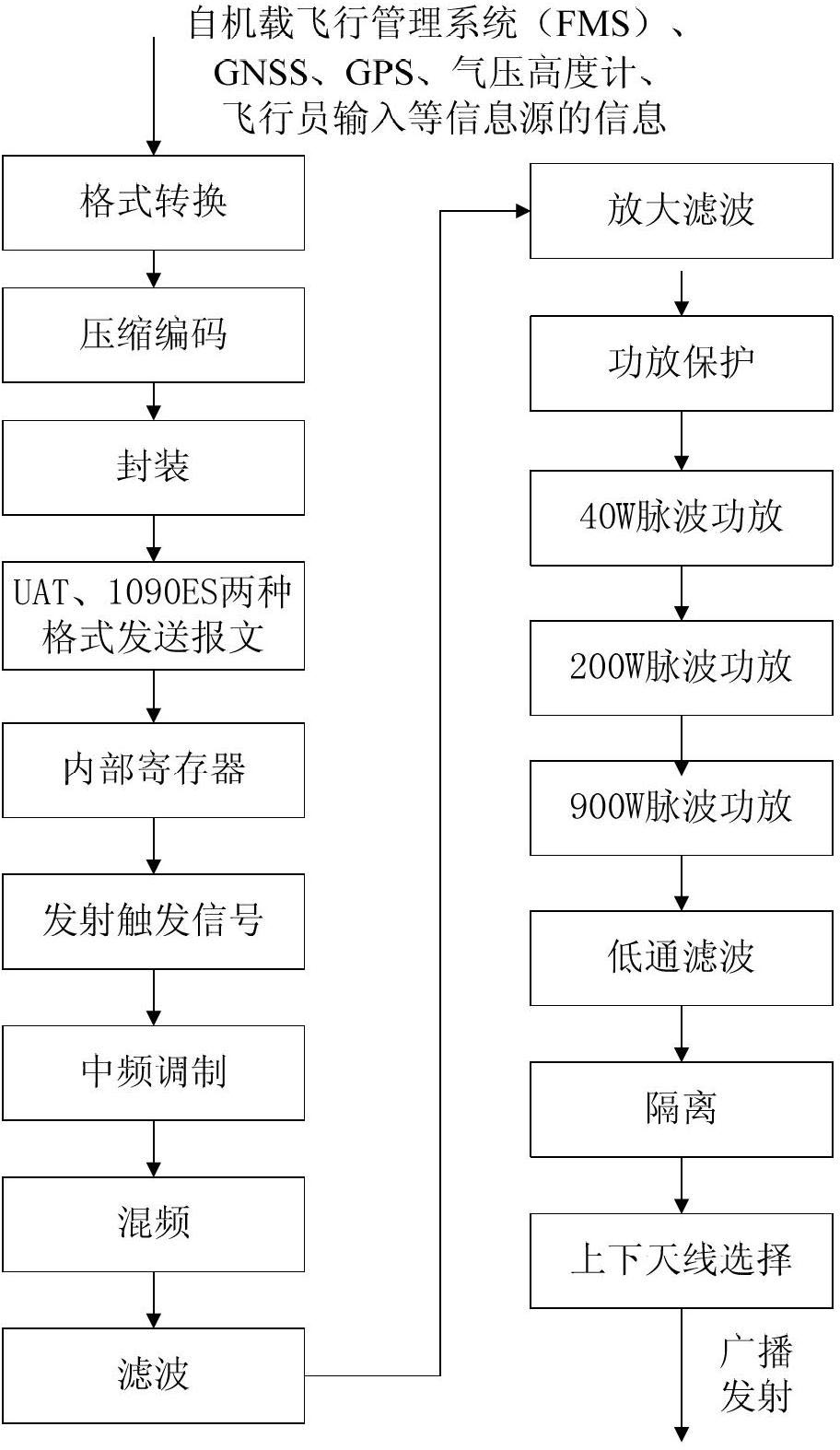
General aviation flight monitoring airborne system based on ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast)
ActiveCN102682627ARealize the monitoring functionReduce volumeAircraft traffic controlTransceiverFlight management system
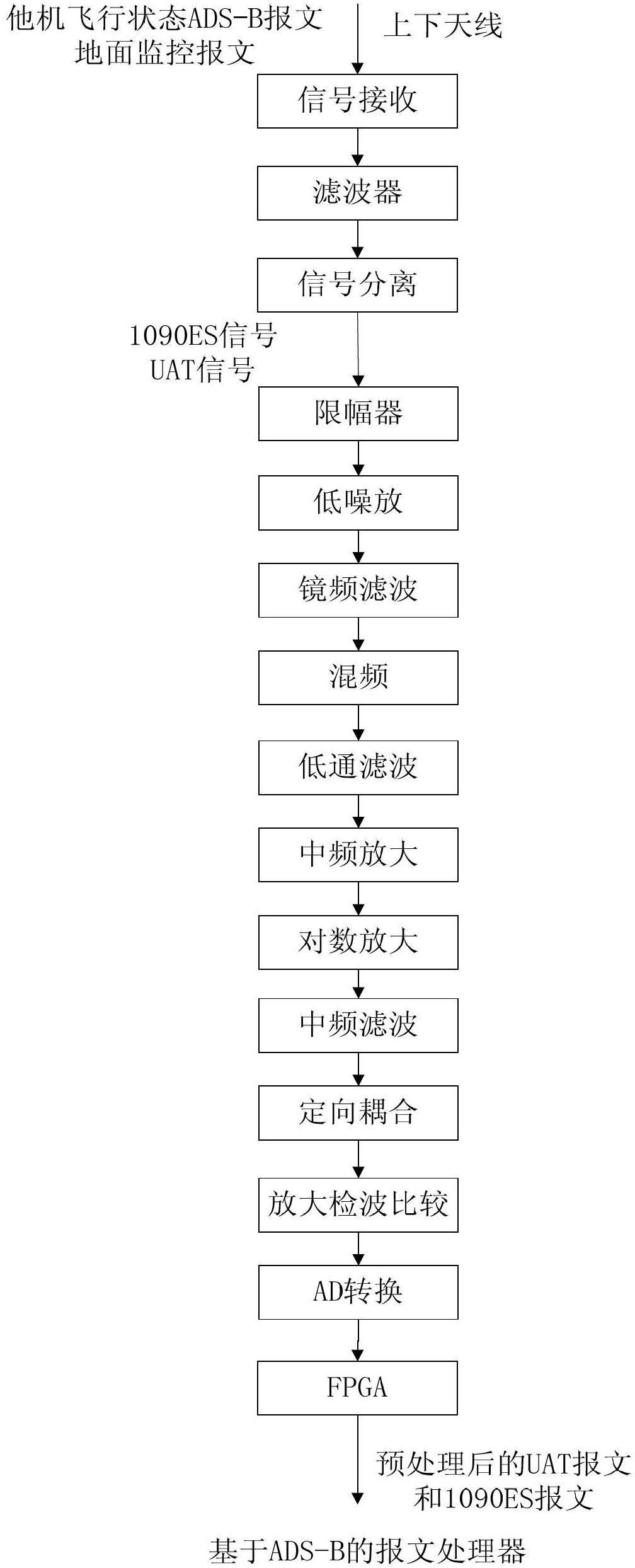
The invention provides a general aviation flight monitoring airborne system based on an ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast). The system comprises an airborne ADS-B transceiver based on UAT (Ultra Aperture Terminal)\1090ES (Echo Sounding), a message processor based on the ADS-B and an airborne CDTI (Cockpit Display of Traffic Information) based on the ADS-B. The system provided by the invention has an ADS-B OUT / IN function and can be used for coding information input by an airborne FMS (flight management system), a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System), a barometric altimeter and a pilot, generating a message and broadcasting the message; and the system can receive flight status ADS-B messages of other airplanes and ground monitoring messages and separate UAT signals from 1090ES signals by virtue of a UAT data chain and a 1090ES data chain. The system provided by the invention can be used for respectively verifying, storing and parsing the flight status of the other airplanes\ground monitoring messages, messages of a local airplane, heartbeat messages of a host, graphical display navigation information, traffic information of the local airplane and traffic information of the other airplanes within a certain range of the local airplane.
Owner:北京民航天宇科技发展股份有限公司
System and method for IP address discovery in rapidly changing network environment
InactiveUS20070214256A1Minimize network trafficTraffic minimizationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet trafficIp address
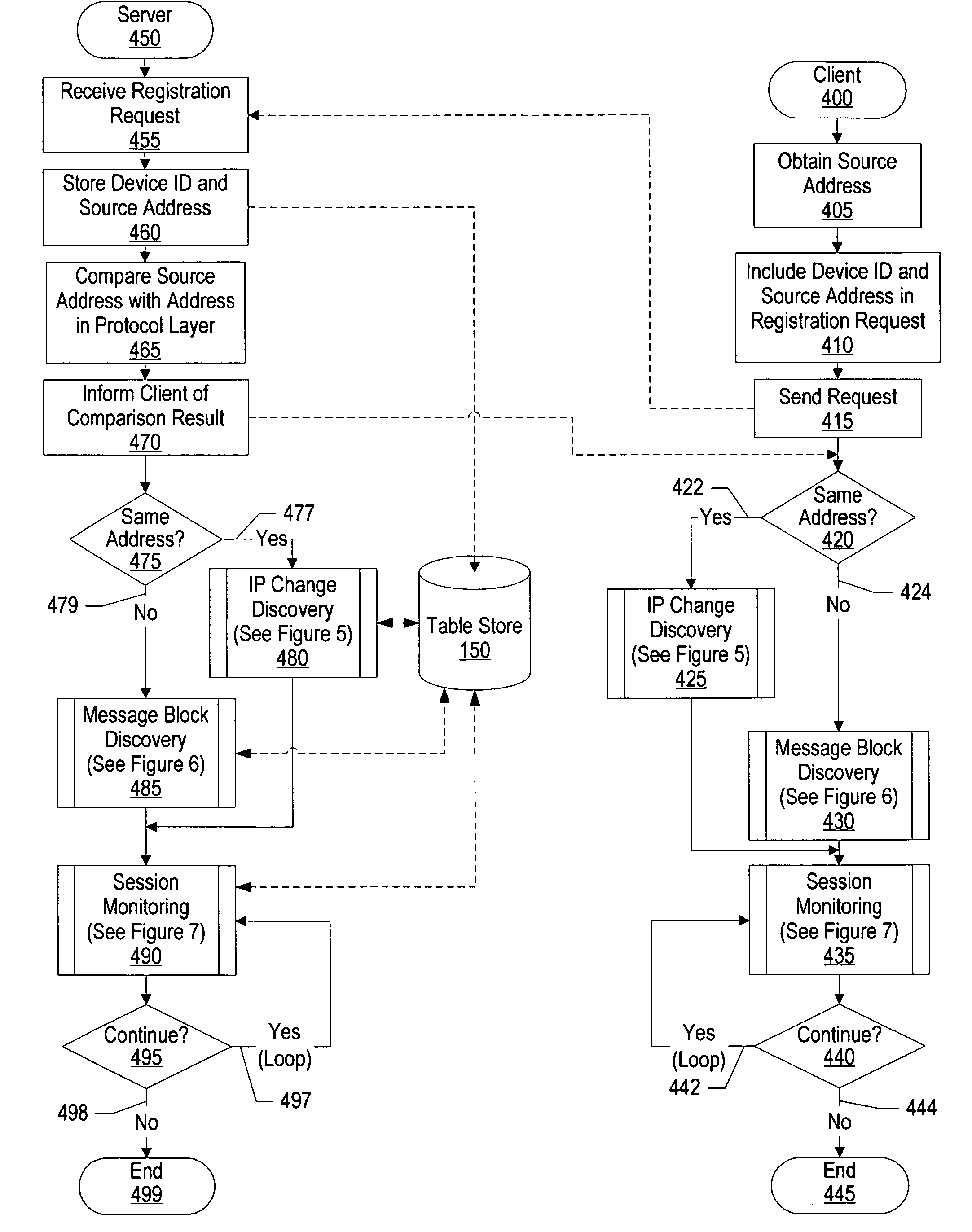
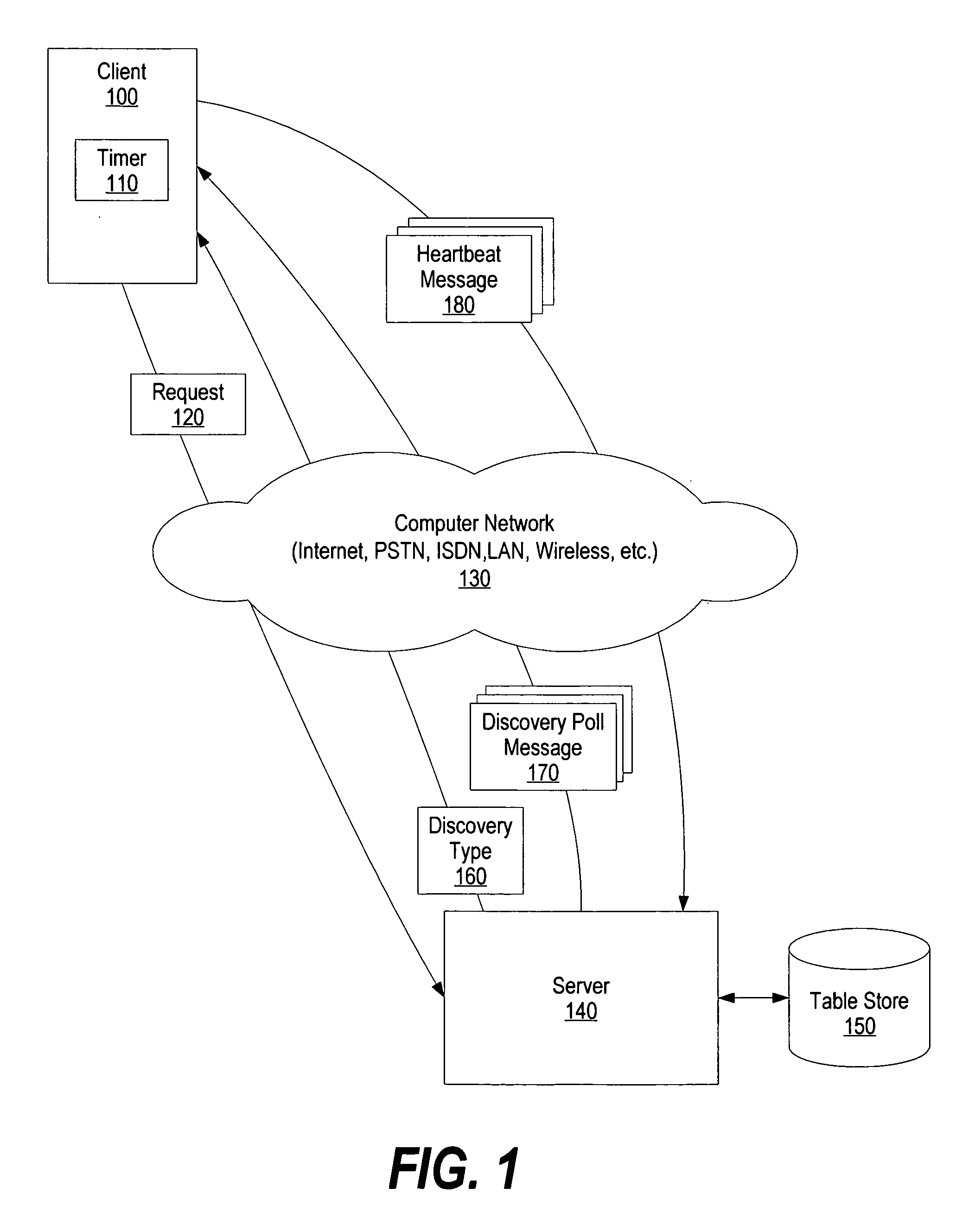
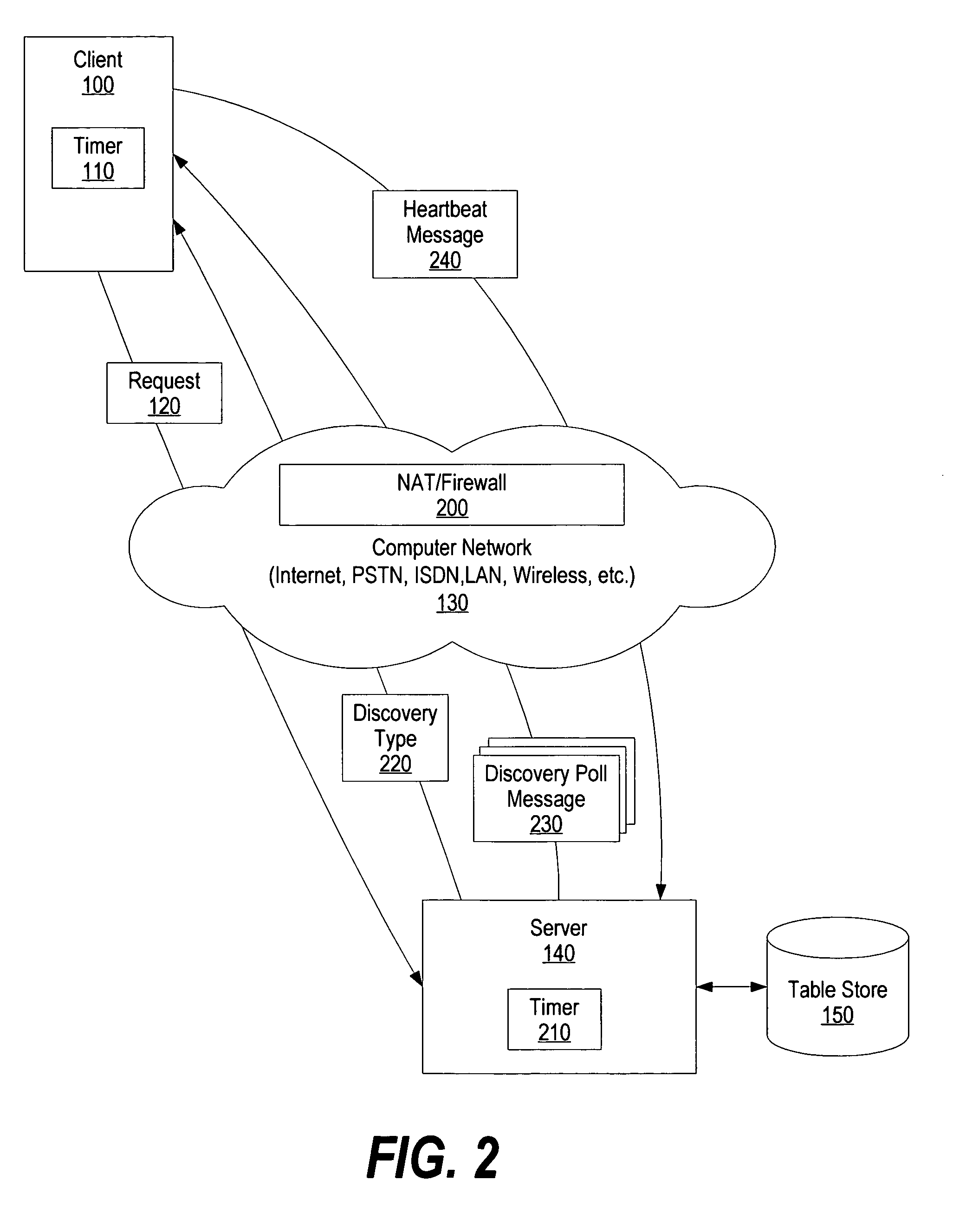
A system and method for Internet protocol (IP) address discovery in a rapidly changing network environment is presented. A server and a client use an adaptive discovery polling process to determine an optimum heartbeat interval that minimizes network traffic and allows the server to monitor the client's source address. The client and server exchange discovery poll messages and heartbeat messages at varying time intervals in order to identify a computer network's timeout period or a network address translator's message block timeout period. Once the timeout period is identified, the client sends heartbeat messages to the server at an “optimum heartbeat interval” that is less than the identified timeout period in order to maintain the network connection. As a result, the server is able to send messages to the client without delay.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method to contact and maintain status of managed devices
ActiveUS8843622B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDevice statusTransport Layer Security
A method is provided in one example and includes establishing a plurality of persistent connections with a plurality of devices at a server; receiving presence data associated with the plurality of devices; responding to heartbeat messages provided by the plurality of devices; receiving a status change notification from a particular one of the devices; and updating status data and heartbeat data for the particular one of the devices. In more particular embodiments, the method includes encoding messages communicated on the persistent connections using an extensible messaging and presence protocol (XMPP). The method may also include communicating script configuration data over a particular one of the persistent connections for execution by the particular device. The persistent connections may be secured using transport layer security (TLS).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for fault detection/isolation in metro Ethernet service
InactiveUS7644317B1Error detection/correctionMetropolitian area networksAccess networkMetro Ethernet
Apparatus and method of detecting a fault in a network service includes an Ethernet access network domain in which a heartbeat message is broadcast at a periodic interval by each of a plurality of edge devices associated with an instance of the network service. Each of the edge devices also receives the heartbeat messages broadcast at the periodic interval from other edge devices. A fault occurrence is identified when the edge device fails to receive an expected heartbeat message at the periodic interval from one of the other edge devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Path estimating method and device
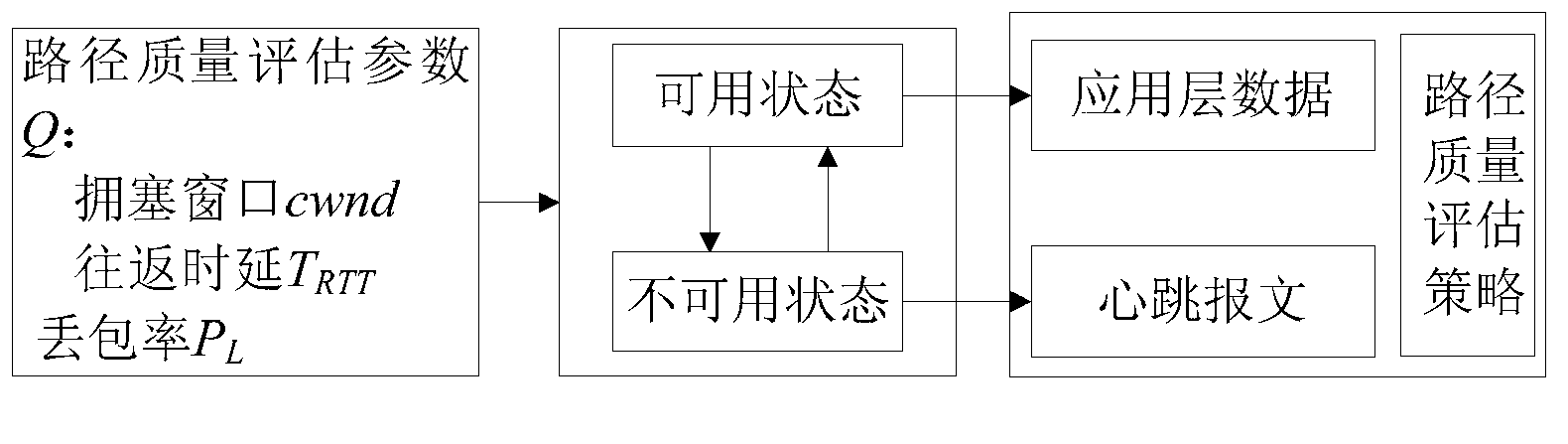
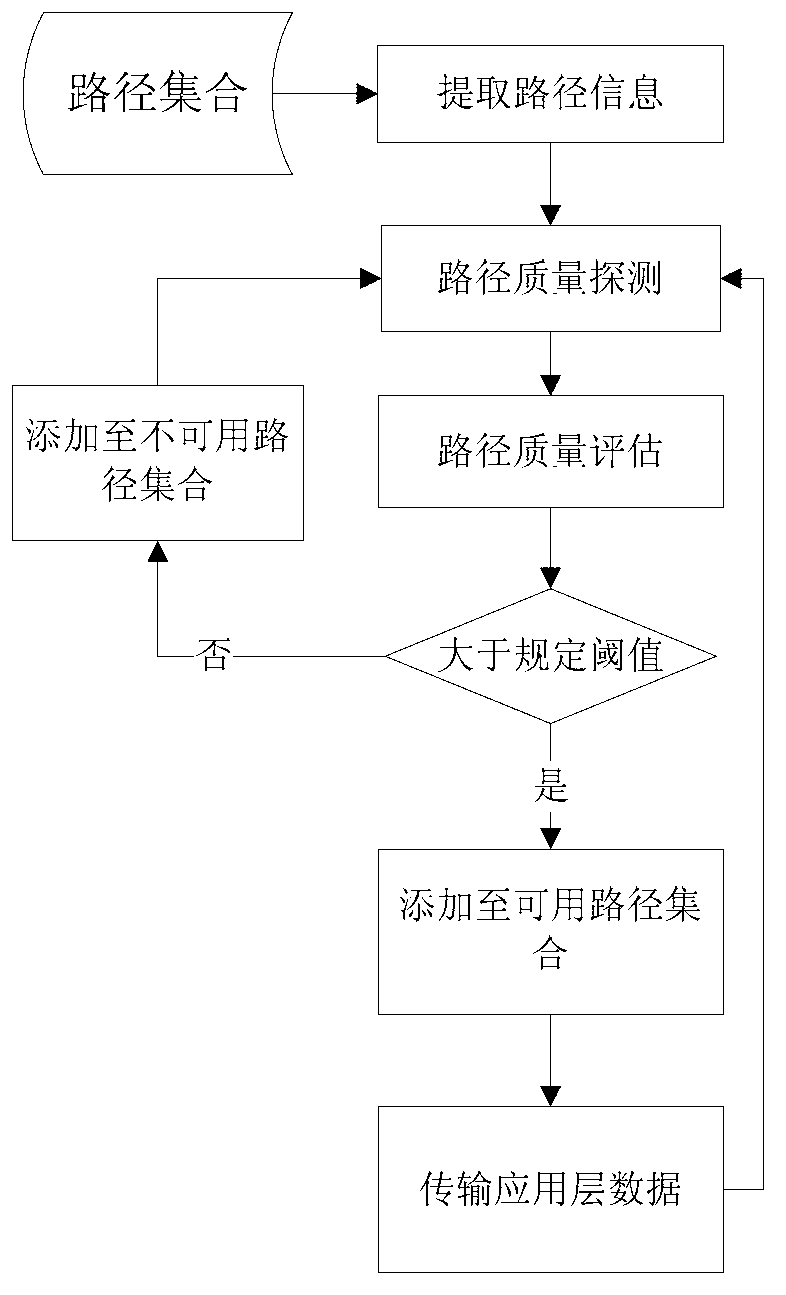
ActiveCN102843257AAccurate adjustment effectImprove data transmission qualityData switching networksCongestion windowPacket loss
The invention discloses a path estimating method which comprises the steps of: calculating a path quality estimating parameter according to a round-trip-delay, a packet loss probability and a congestion window of a path; dividing the path into an available path and an unavailable path according to the path quality estimating parameter; transmitting data on the available path and calculating the round-trip-delay, the packet loss probability and the congestion window of the path in a process of transmitting the data; and sending a heartbeat message in the unavailable path for calculating the round-trip-delay, the packet loss probability and the congestion window of the path. According to the invention, the path quality can be detected in real time, the path quality can be accurately calculated according to the simple parameter and the data transmission path is regulated and selected in real time, therefore the quality of the data transmission path is ensured, and the data is reliably transmitted. The path quality can be effectively estimated, and the transmission quality of streaming media data is improved.
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY +1
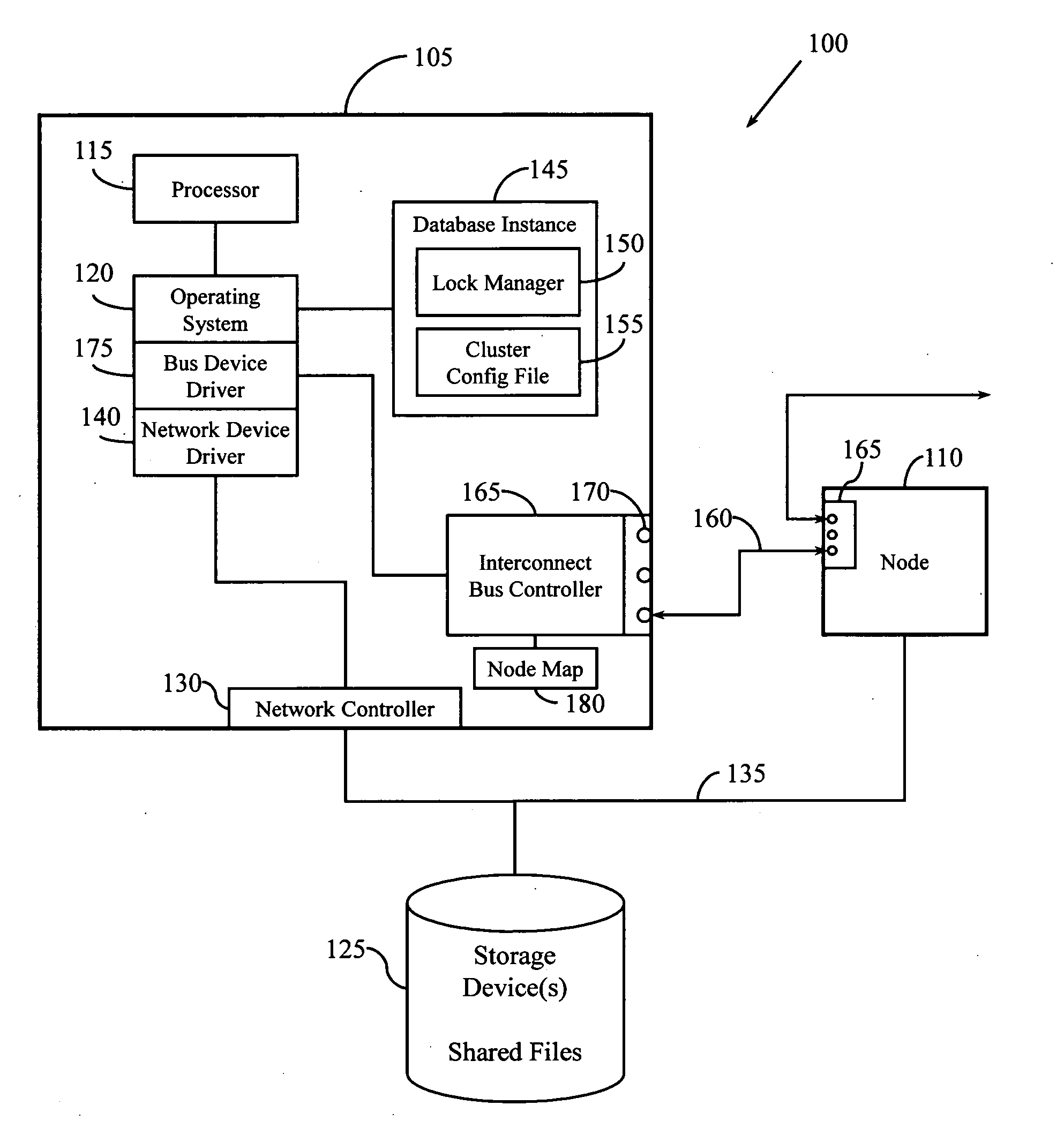
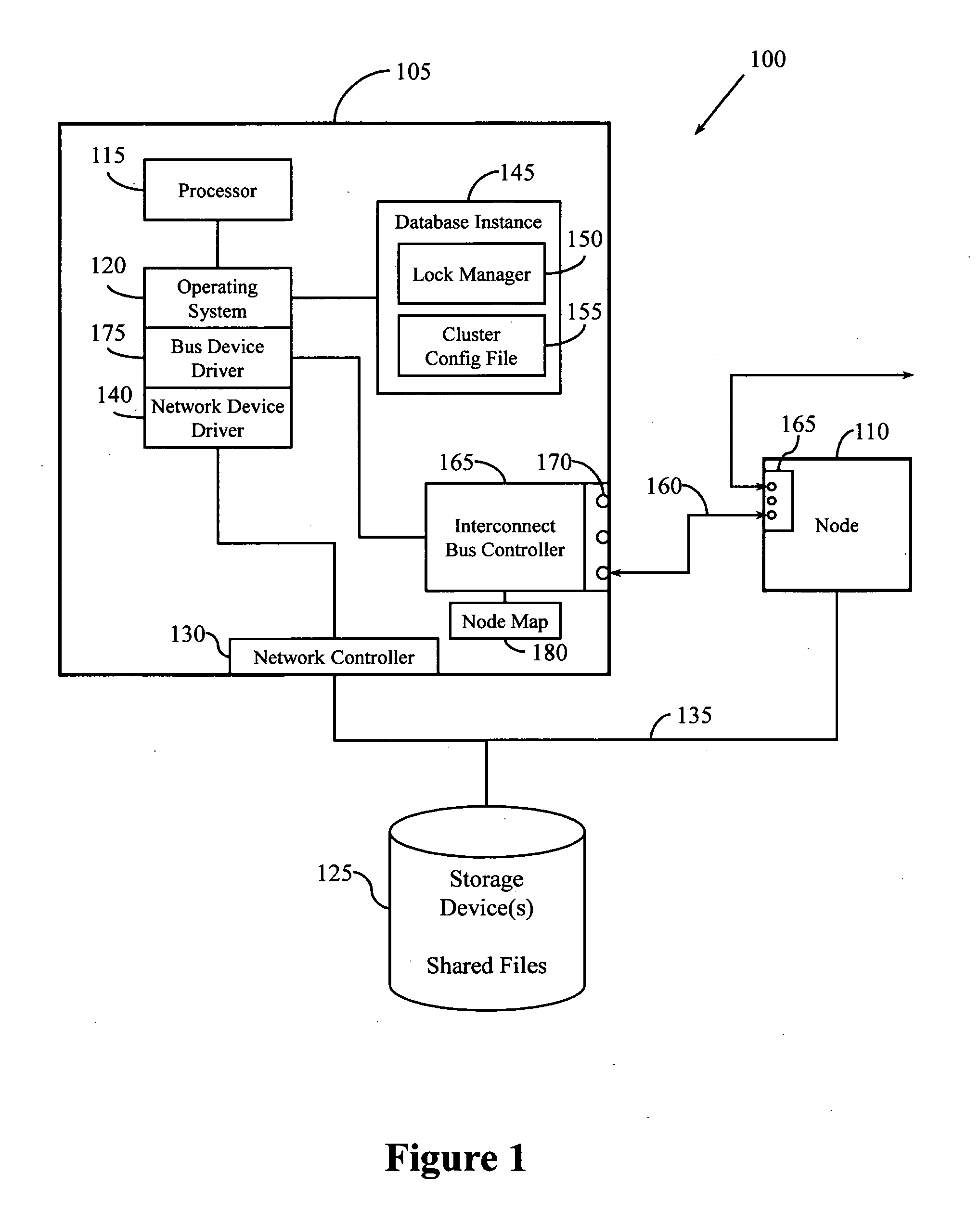
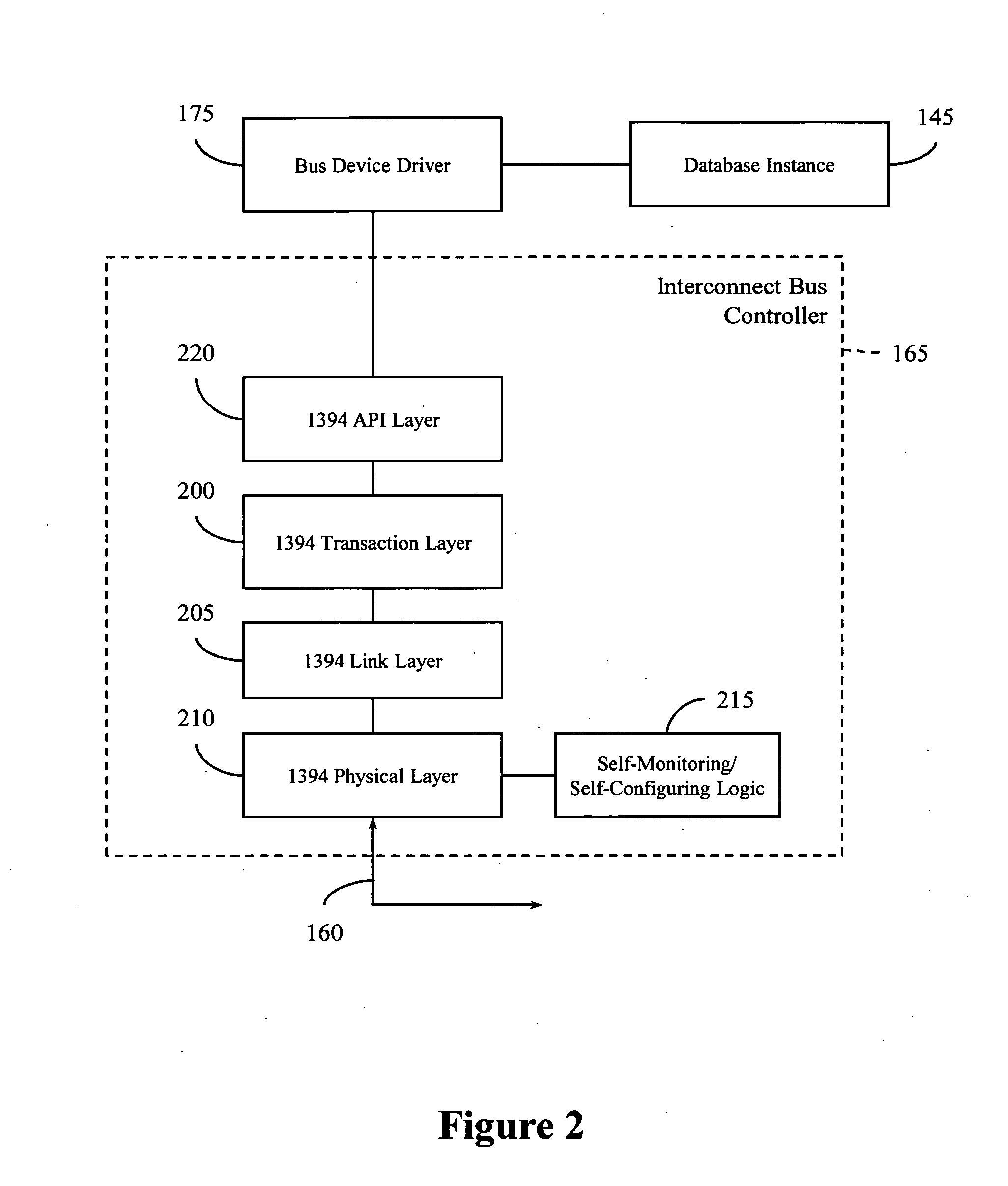
Heartbeat mechanism for cluster systems
InactiveUS20090043887A1Hardware monitoringMultiple digital computer combinationsCluster systemsNetwork control
A heartbeat system and method is provided for a cluster system. In one embodiment, a heartbeat mechanism includes a quorum file for receiving heartbeat messages from the plurality of nodes. A network controller connects the quorum file to the plurality of nodes with a serial bus that establishes peer-to-peer and point-to-point device communication. A node map maintained by the network controller identifies active nodes based on signals from the serial bus. A status logic for determining a status of a node from the plurality of nodes by comparing heartbeat messages in the quorum file written by the node and the node map.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
Adaptive method and adaptive device of heartbeat cycle
ActiveCN102843250ADynamically adjust the sending cycleAvoid wastingData switching networksNetwork conditionsNetwork management
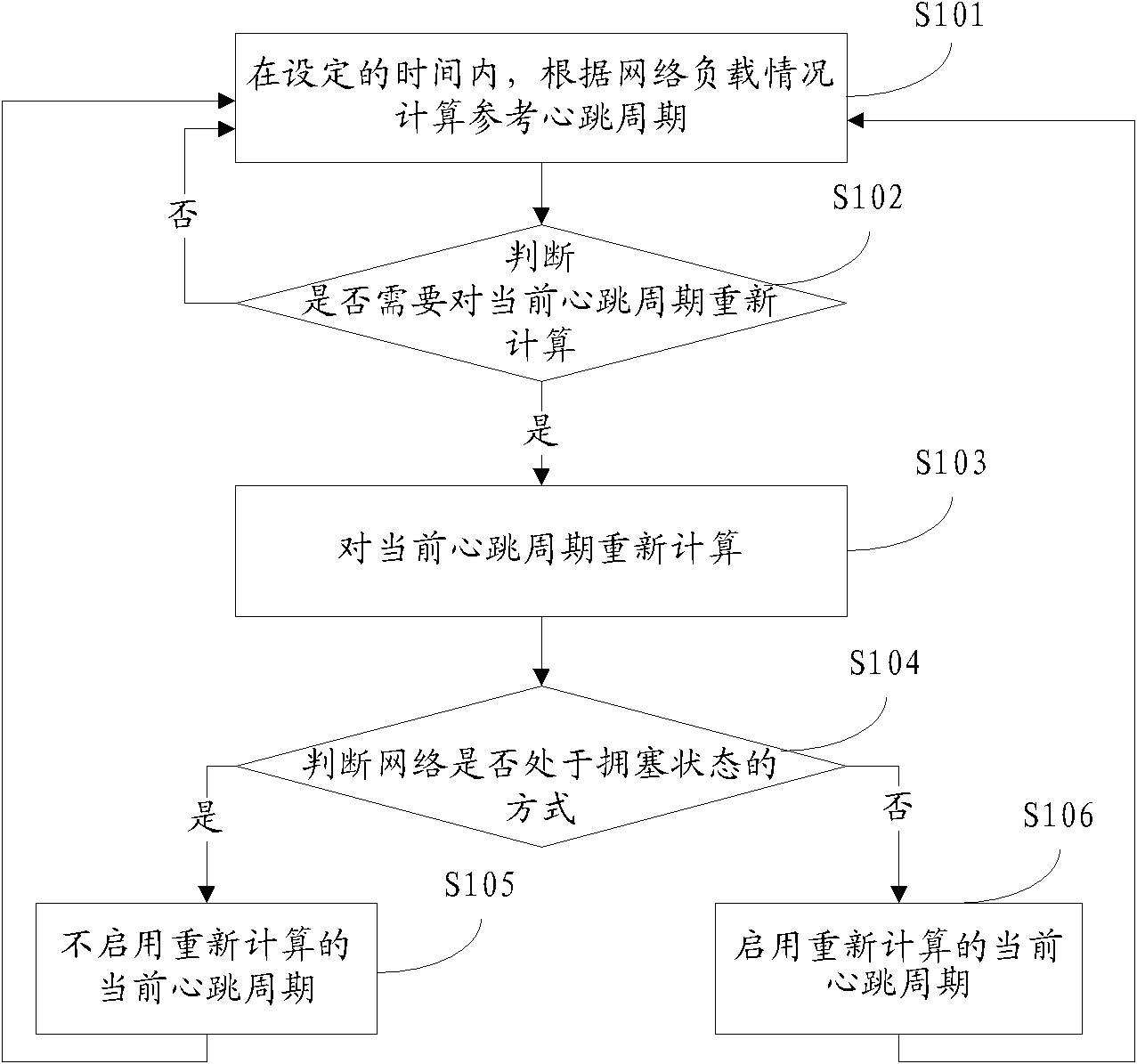
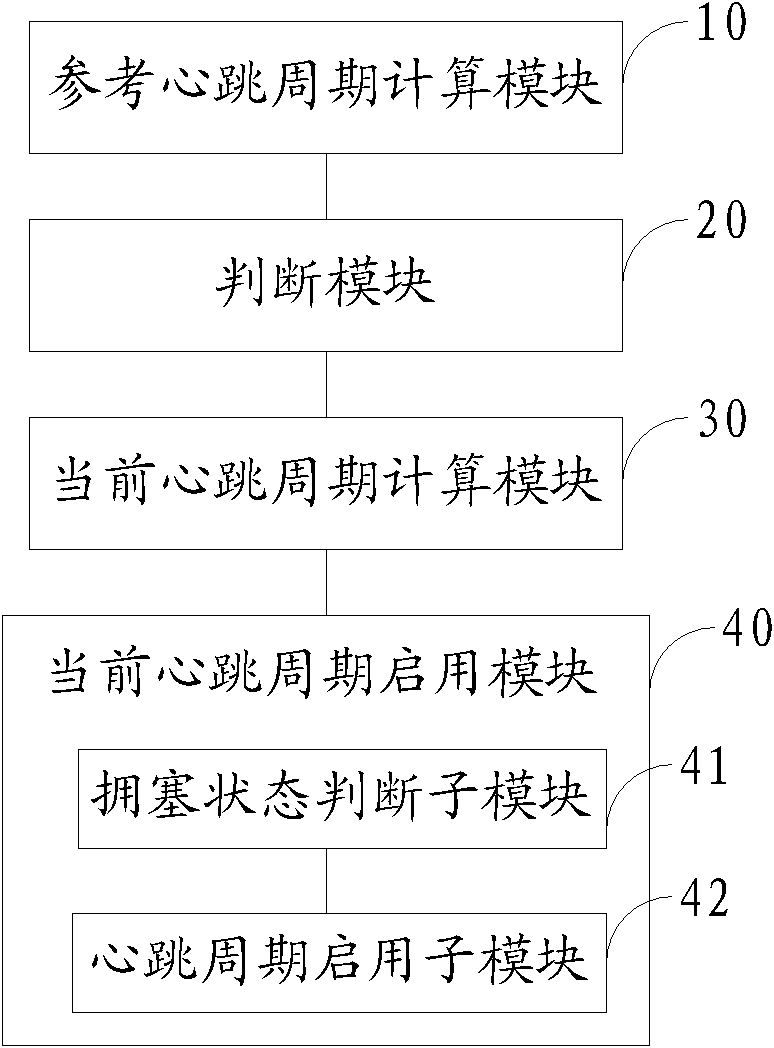
Disclosed is an adaptive method and device for a heartbeat period. Within a set time, a reference heartbeat period is calculated according to a network load condition; based on an offset condition of the reference heartbeat period and an offset condition between the reference heartbeat period and the current heartbeat period, it is determined whether the current heartbeat period requires to be recalculated; and after the current heartbeat period is recalculated, when the network is no longer in a congested state, the recalculated current heartbeat period is activated. The present invention implements dynamic adjustment of the period of sending a heartbeat message, so as to prevent important services from being affected due to inappropriate setting of the period of sending a heartbeat message in the case of excessively high network load for a network management or network element. Meanwhile, the waste of bandwidth and system resources and impacts on the network management performance as the heartbeat period fails to adapt to the network condition are avoided.
Owner:ZTE CORP
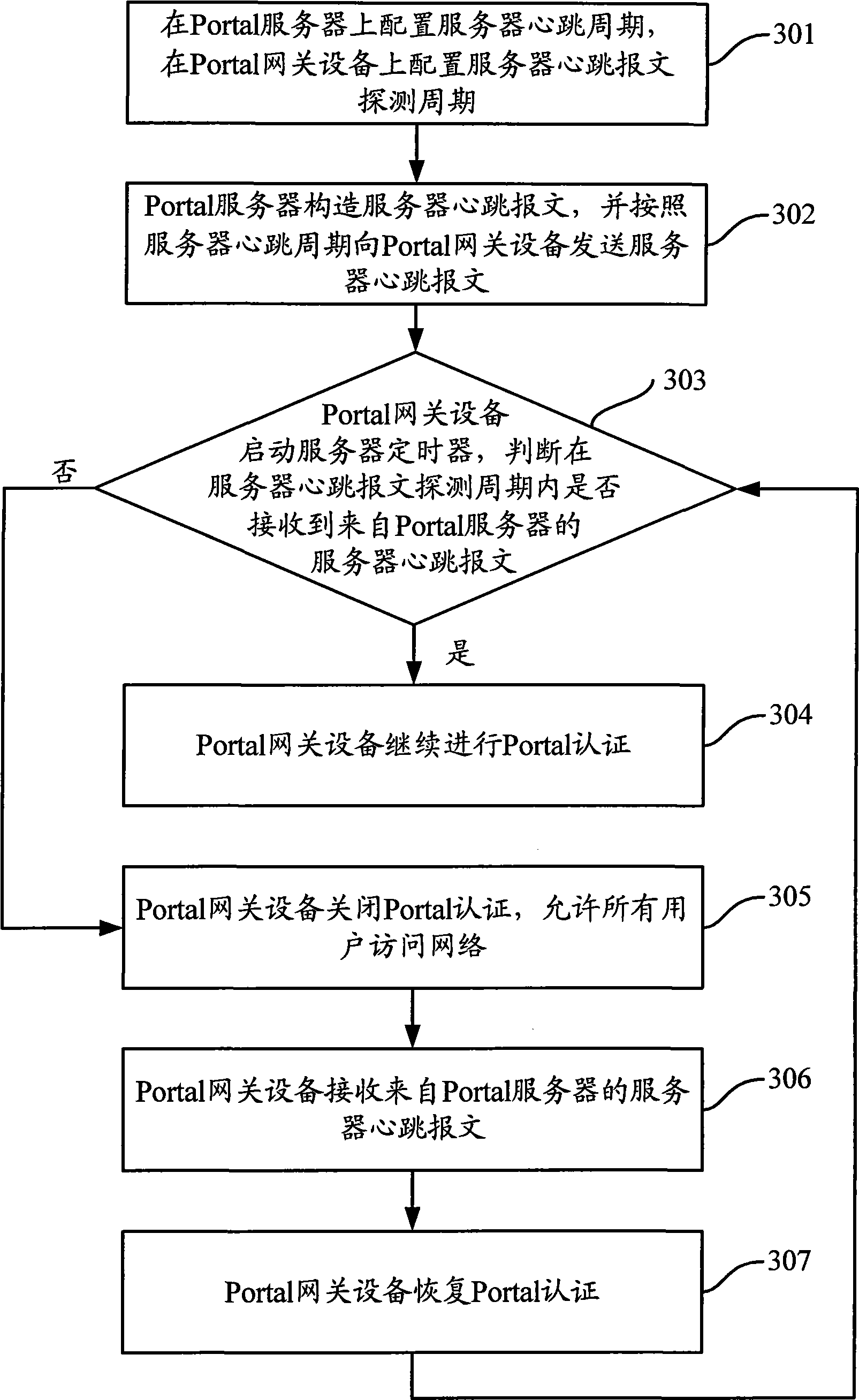
Portal authentication method and corresponding gateway equipment and server thereof
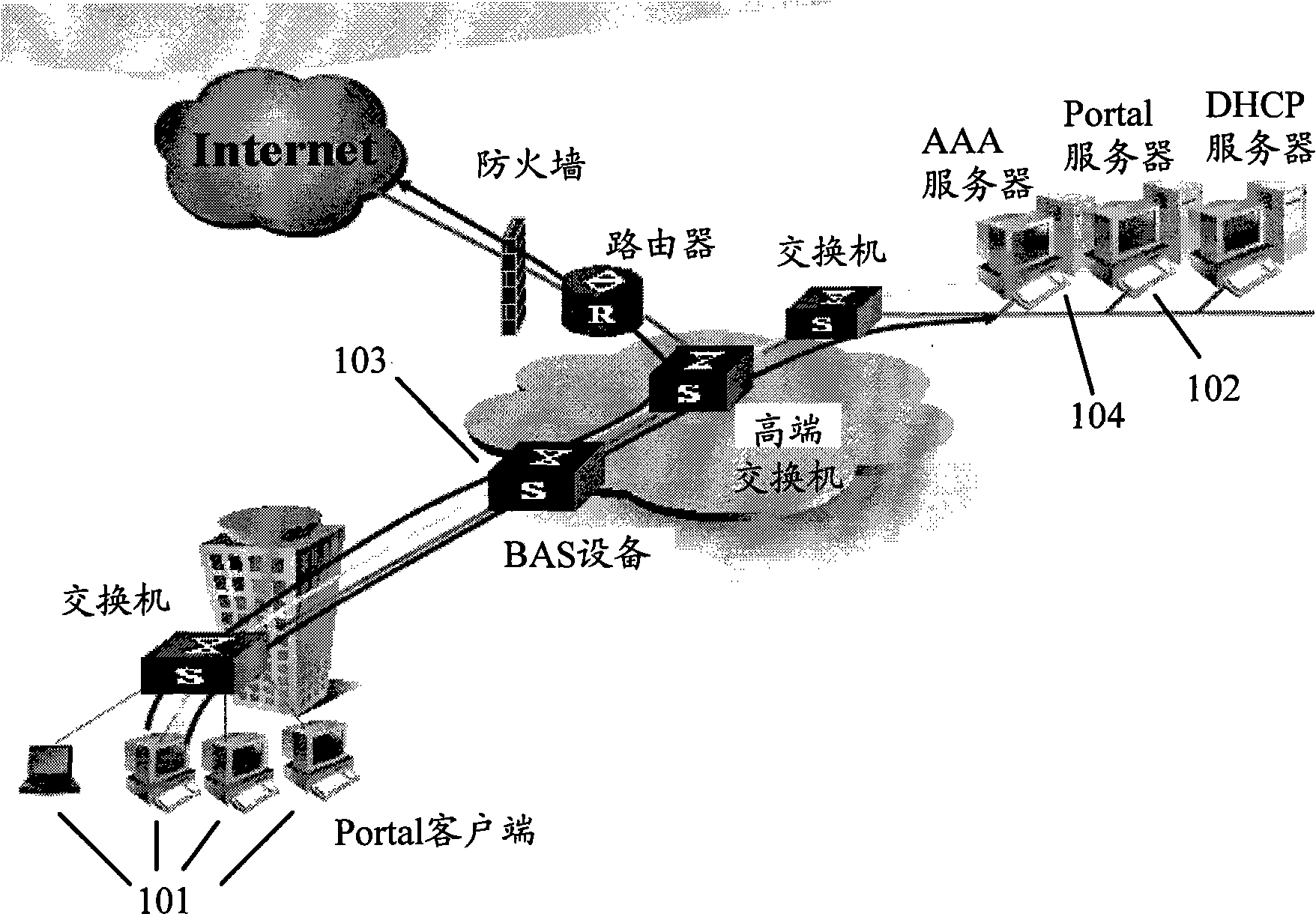
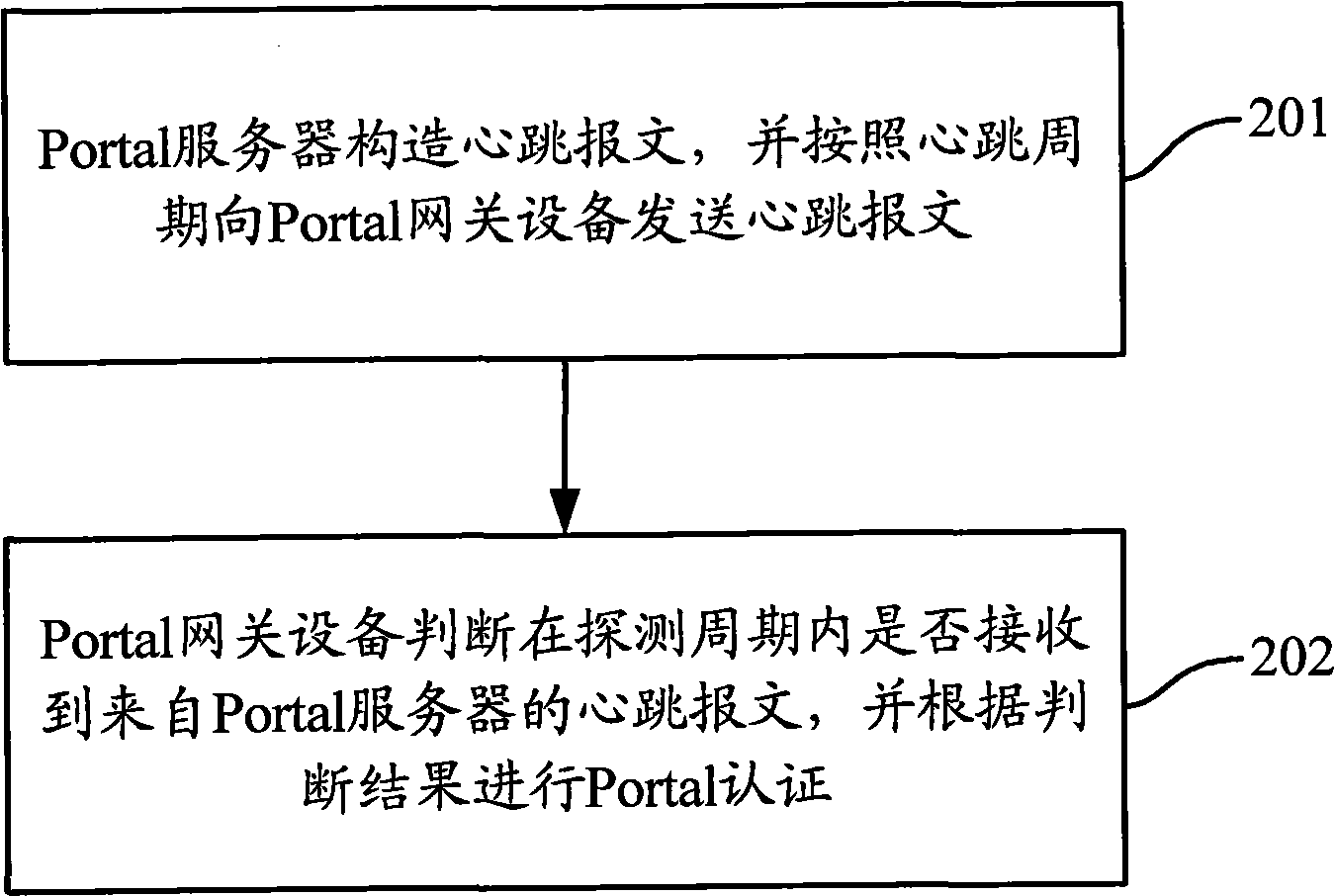
ActiveCN101557405AImprove usabilityImprove deployabilityNetwork connectionsNetworked systemUsability
The invention discloses a portal authentication method which is applied to a network system comprising portal gateway equipment and a portal server. The method comprises the following steps: the portal server generates a heartbeat message and sends the heartbeat message to the portal gateway equipment according to a heartbeat period; the portal gateway equipment judges whether the heartbeat message sent by the portal server is received within a detection period, wherein the detection period is not shorter than the heartbeat period; and the portal gateway equipment conducts portal authentication according to a judgment result. The method allows a network to continue to be used by a user under the condition that the portal server fails to work normally, thereby enhancing the usability and deployment performance of the network. The invention also discloses corresponding gateway equipment and a server thereof.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
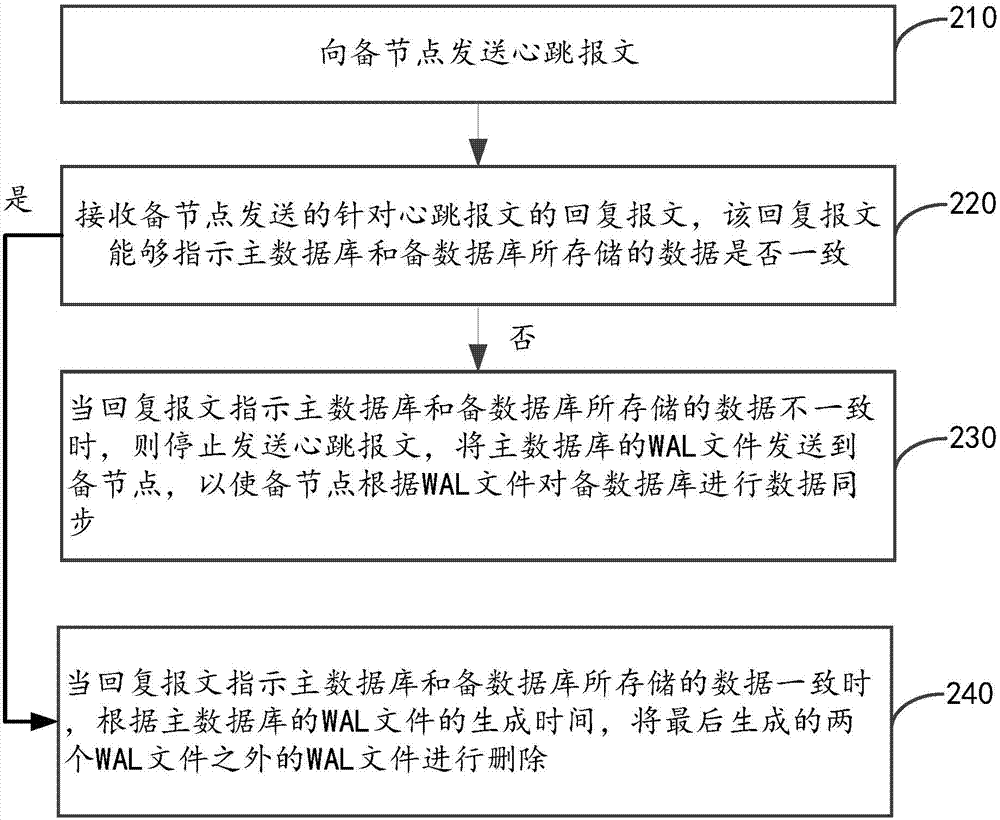
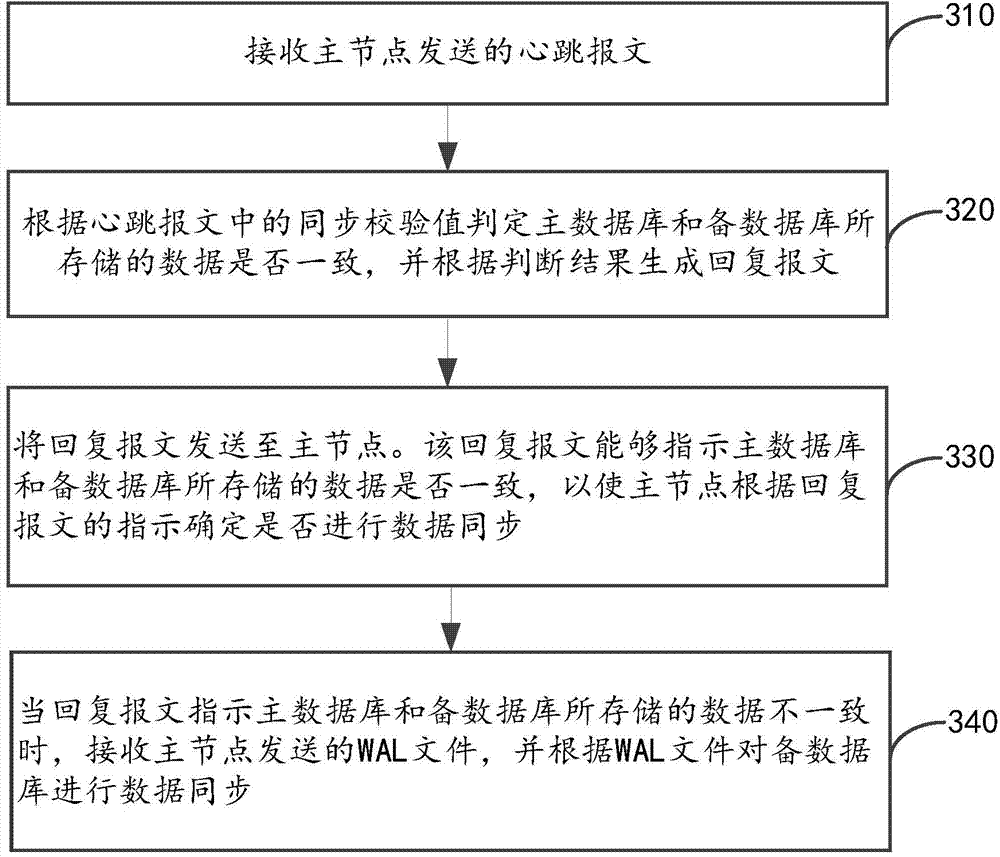
Data synchronization method and device of primary and standby databases
ActiveCN104504062AReduce the impactShorten the timeDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationHigh availability
The invention provides a data synchronization method and device of primary and standby databases. The data synchronization method is applied to main nodes of an HA (high availability) storage system, and includes: sending a heartbeat message to standby nodes, wherein the heartbeat message carries preset values or synchronous check values so that the standby nodes can judge whether data stored in the primary database and the standby database are consistent according to the synchronous check values; receiving a reply message sent by the standby nodes, wherein the reply message can indicate whether the data stored in the primary database and the standby database are consistent; stopping sending the heartbeat message and sending a WAL (write-ahead logging) file of the primary database to the standby nodes when the reply message indicates that the data stored in the primary database and the standby database are inconsistent, so the standby nodes can conduct data synchronization for the standby database according to the WAL file. The data synchronization method and device can reduce the data synchronization time and efficiency of the primary and standby databases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVIEW TECH CO LTD
System and method of operation for verifying and validating public switch telephone networks (PSTN) to (IP) network services
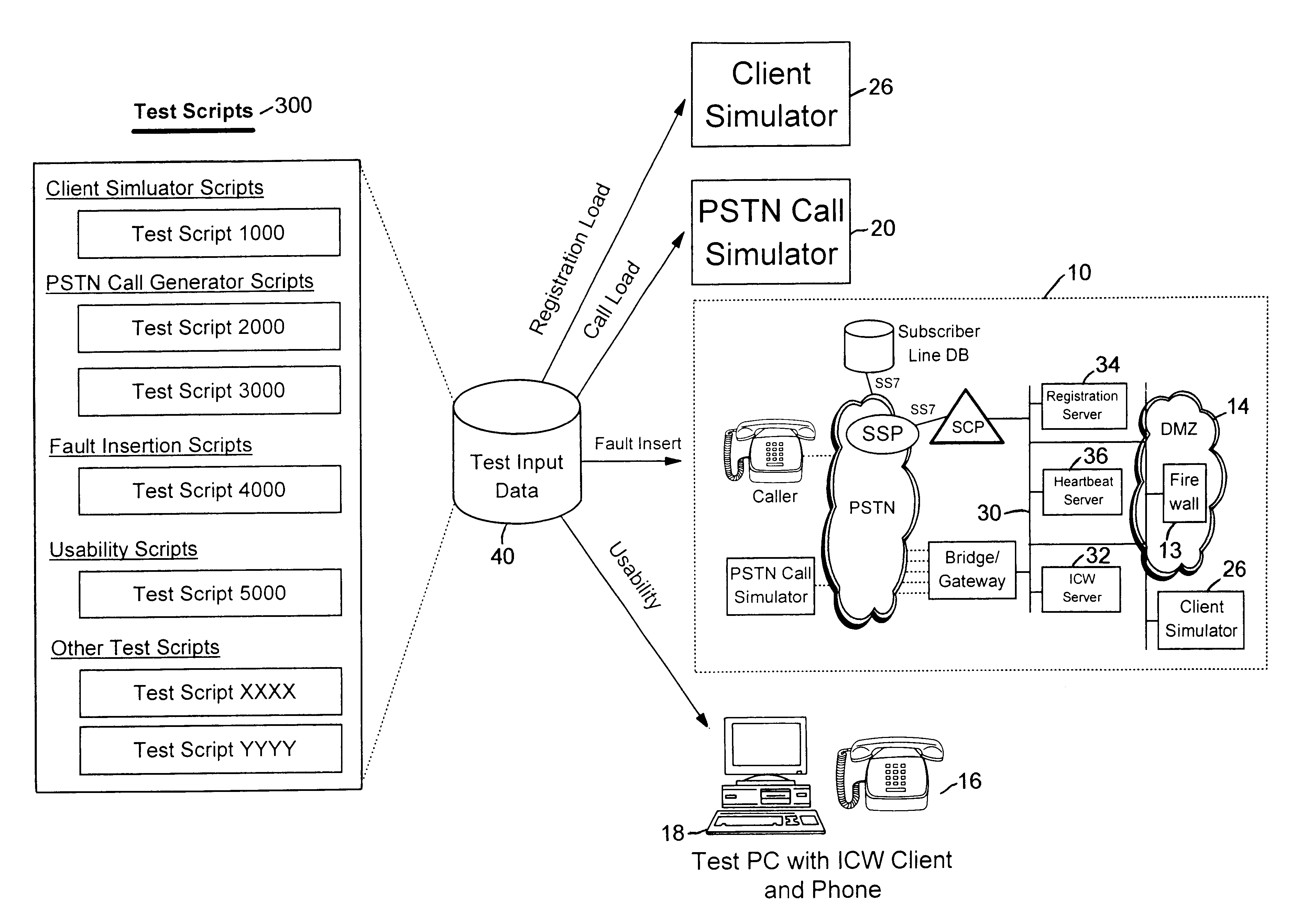
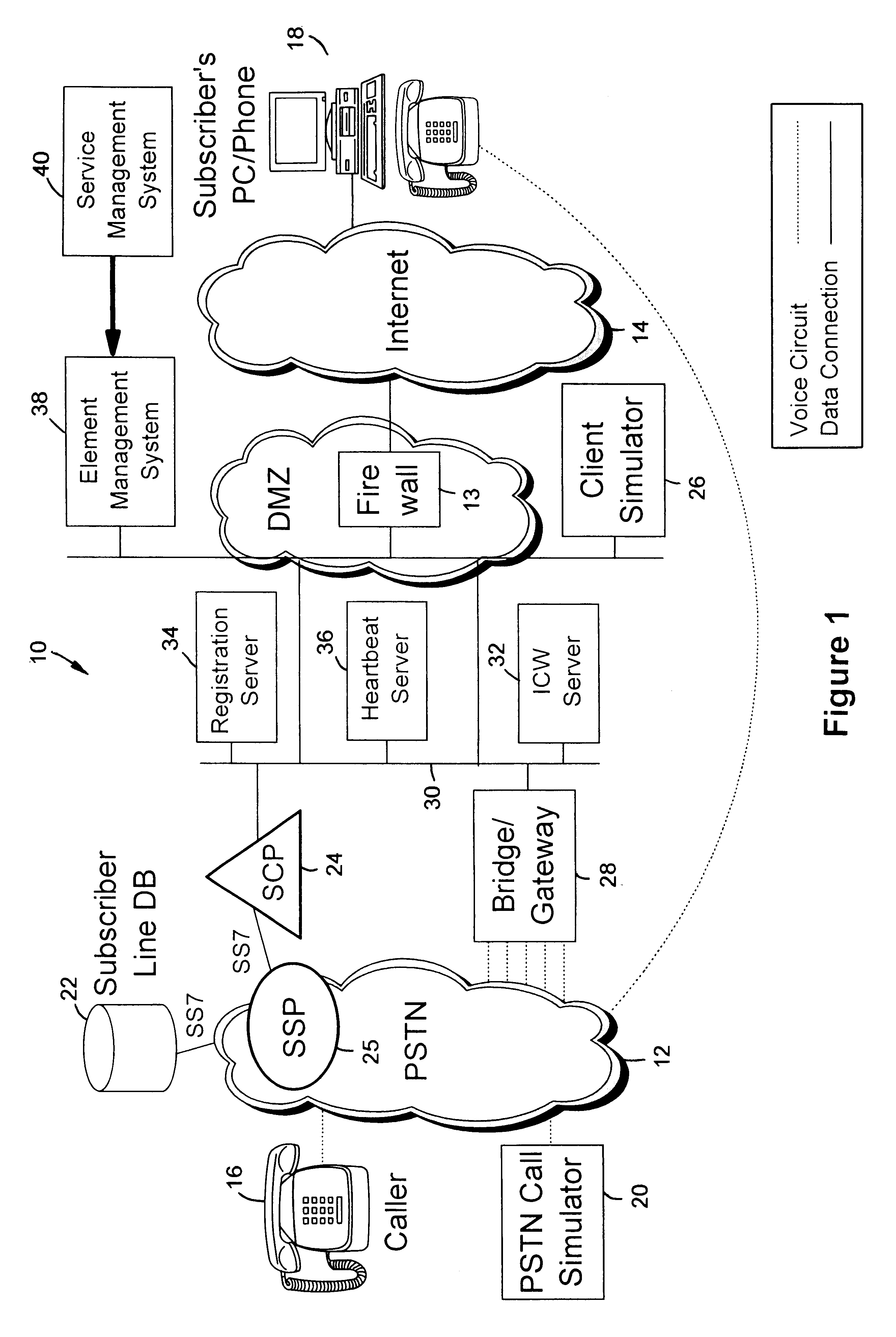
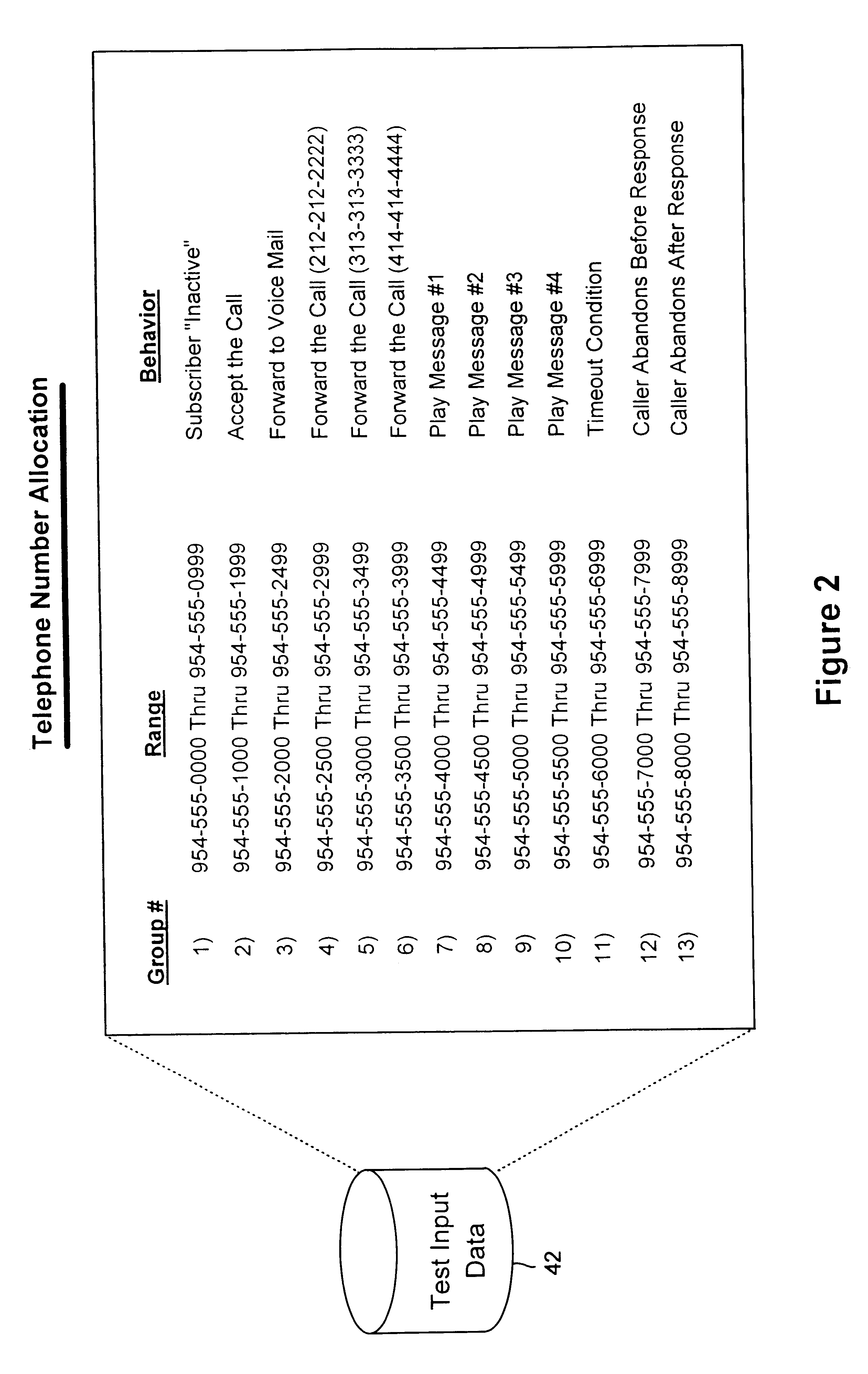
A system verifies and validates PSTN to IP Network services prior to the availability of the services to a plurality of subscribers. A PSTN call generator services a plurality of callers coupled to the PSTN and to a test database. An IP client simulator is coupled to the test database and to an IP Network. A data bus couples the PSTN and the IP Network to a registration server for registering the client and a heartbeat server for tracking the system for heartbeat message. An application server processes test service calls from the PSTN call generator whereby PSTN-IP Network services can be executed for all clients or individual clients as represented by the IP Client simulator for verification and validation of PSTN services to IP Network clients prior to the availability of the services to the clients.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-availability router redundancy method and apparatus
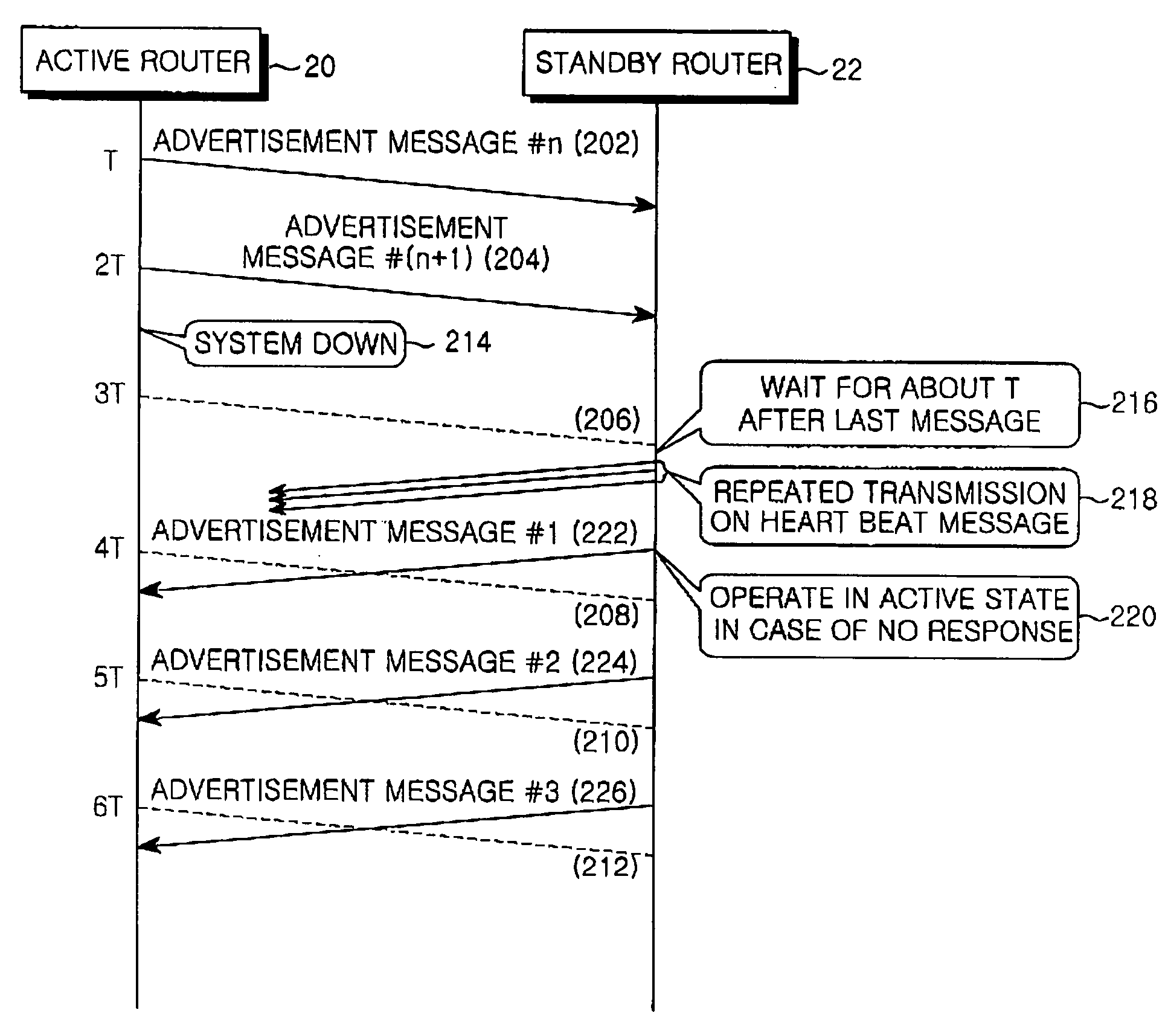
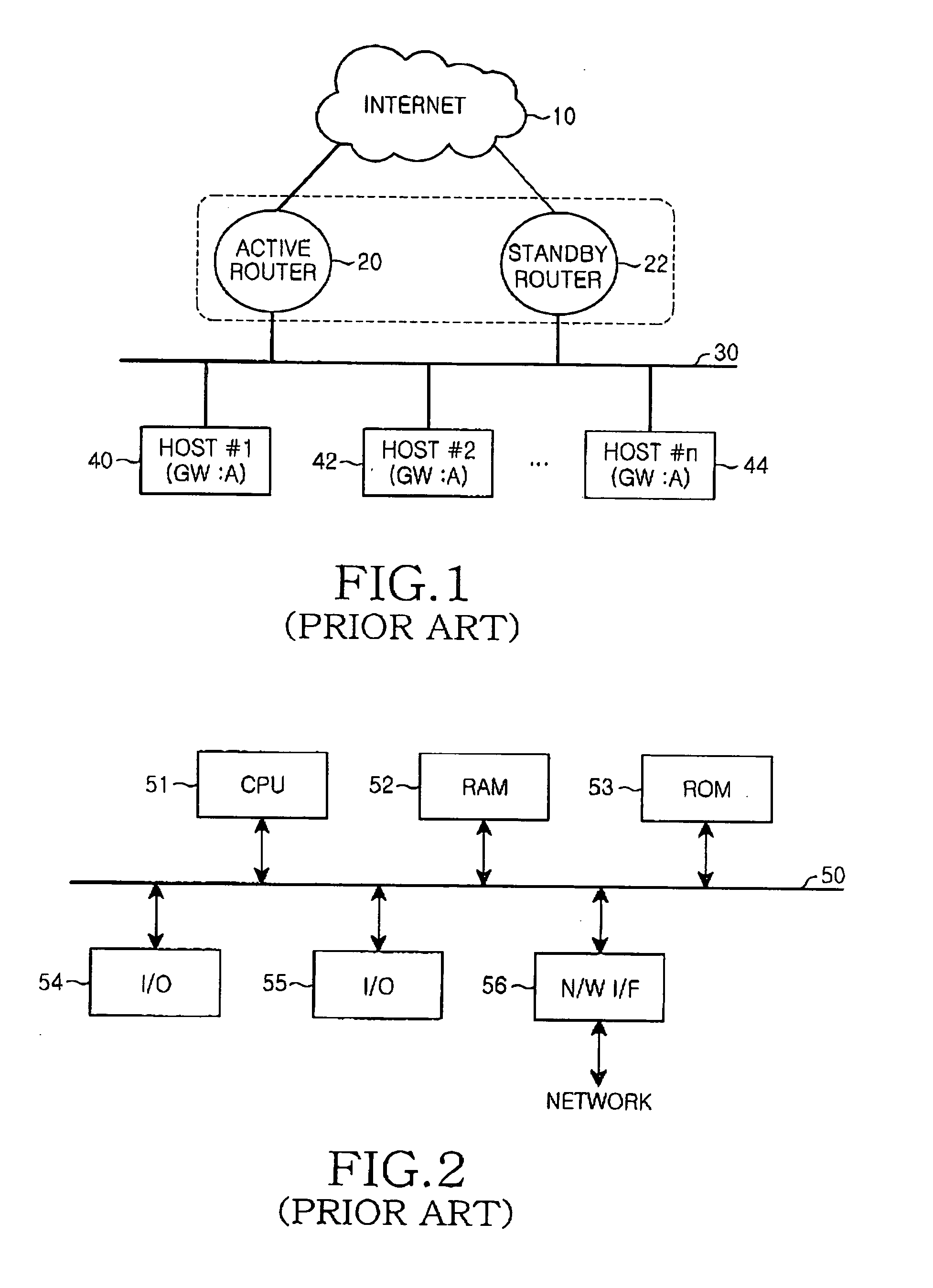
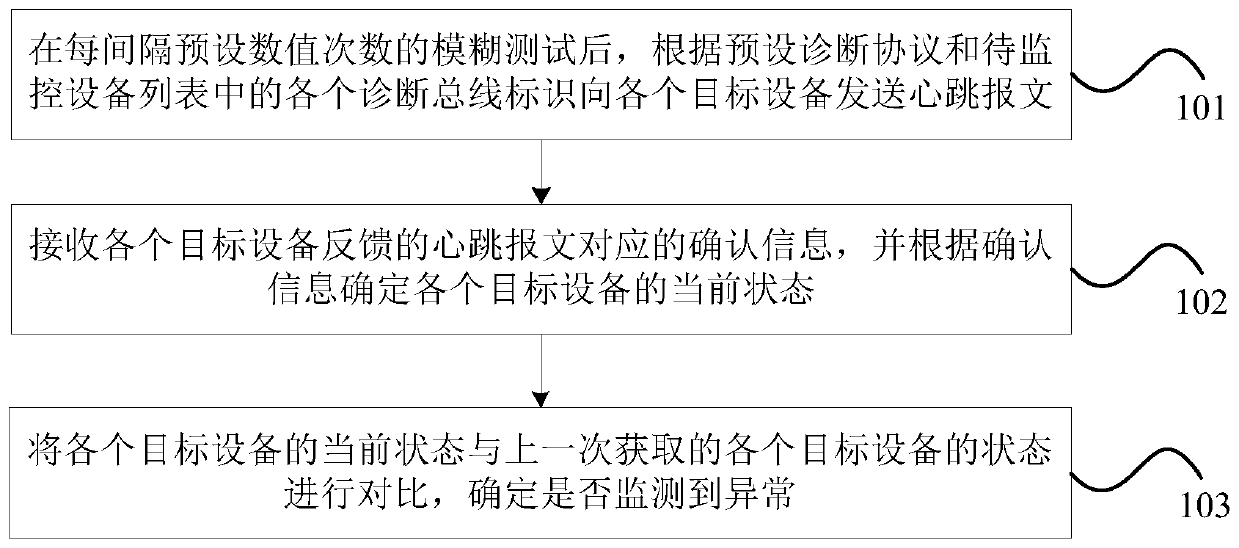
InactiveUS20050147028A1Minimizing recovery timeShorten the timeError preventionTransmission systemsHigh availabilityActive state
A redundancy method and apparatus for a default router of hosts in a local area network (LAN). The router redundancy system includes an active router and at least one standby router. The active router transmits a periodic advertisement message. The standby router determines whether a periodic advertisement message is received from the active router within a predetermined timeout period, and repeatedly transmits a heart beat message to the active router a predetermined number of times if the advertisement message is not received. After repeated transmission of the heart beat message, the standby router transitions to an active state if a response to the heart beat message is not received within a predetermined waiting time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Abnormity monitoring method and device for vehicle CAN bus and computer equipment
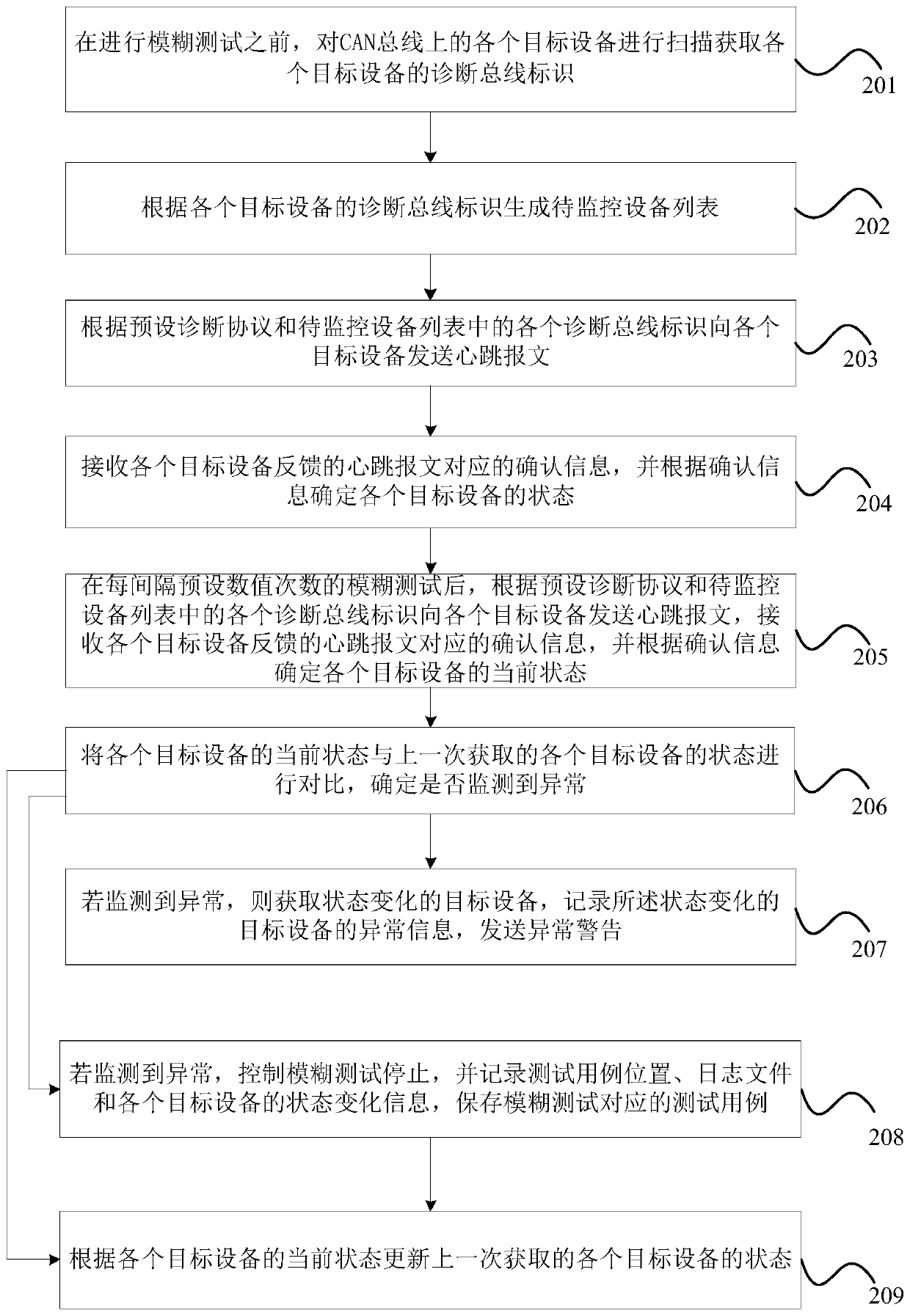
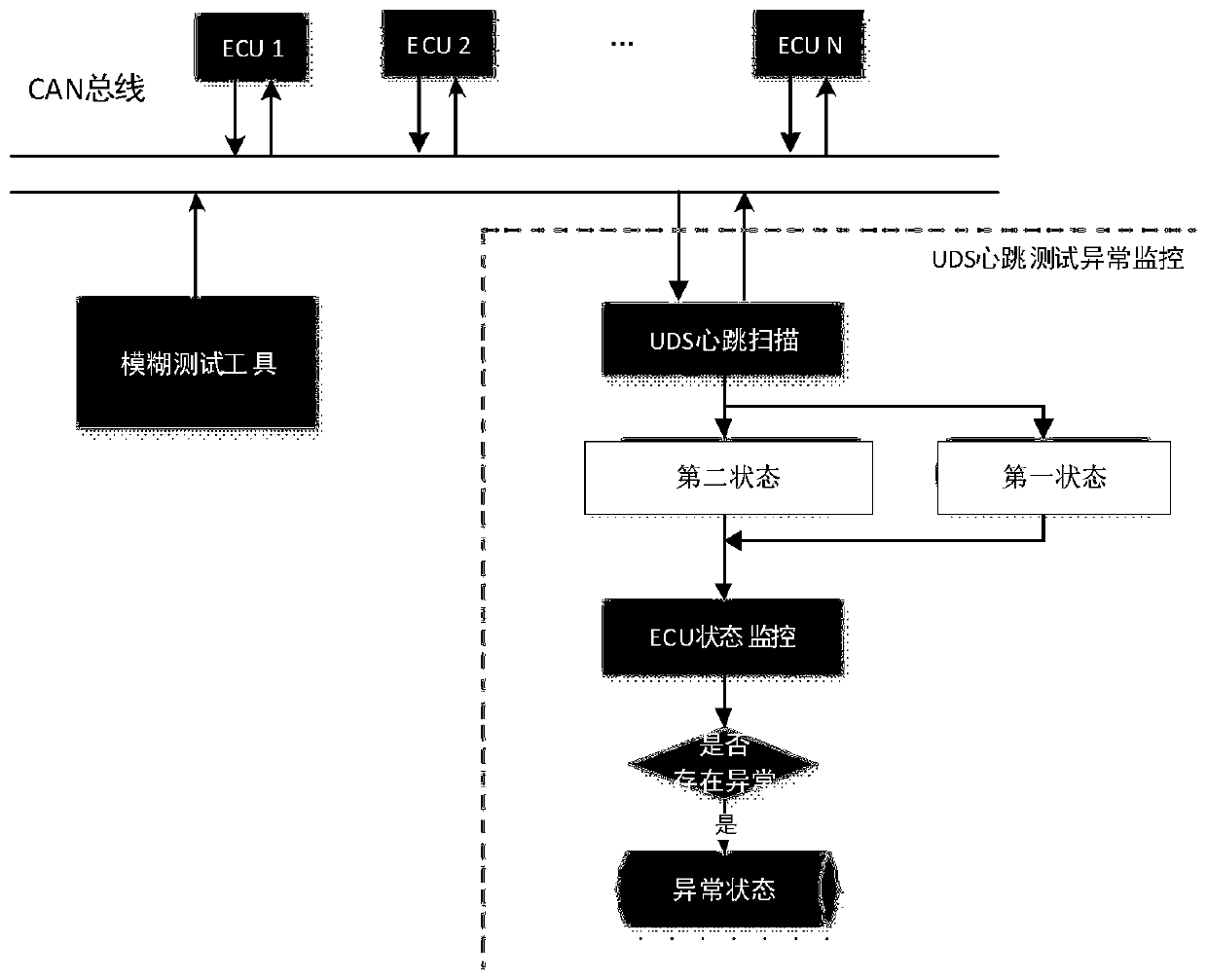
ActiveCN110191018AAutomate exception monitoringImprove anomaly monitoring efficiencyData switching networksTotal factory controlBusiness efficiencyMonitor equipment
The invention provides a abnormity monitoring method and device of a vehicle CAN bus, and a computer device, and the method comprises the steps: sending heartbeat messages to each target device according to a preset diagnosis protocol and each diagnosis bus identifier in a to-be-monitored device list after a fuzzy test is carried out at an interval of a preset number of times; receiving confirmation information corresponding to the heartbeat message fed back by each target device, and determining the current state of each target device according to the confirmation information; and comparing the current state of each target device with the state of each target device acquired last time, and determining whether the abnormity is monitored or not. The problem that whether the vehicle bus is abnormal or not is mainly judged manually, the cost is high, and the efficiency ratio is low, and abnormal monitoring cannot be automatically carried out in the prior art can be solved. Through comparing the current state of each target device with the state of each target device obtained last time after every other group of test cases in the fuzzy test process, whether the abnormity is monitored or not is determined, automatic abnormity monitoring of the bus is realized, and the bus abnormity monitoring efficiency is improved.
Owner:APOLLO INTELLIGENT CONNECTIVITY (BEIJING) TECH CO LTD
Method for dual-computer hot-standby of vehicle information management system on basis of VRRP
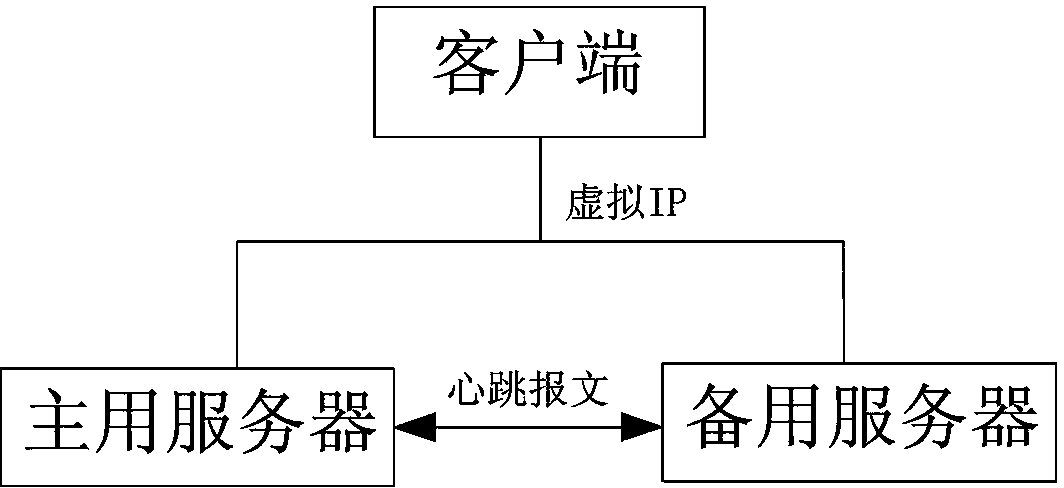
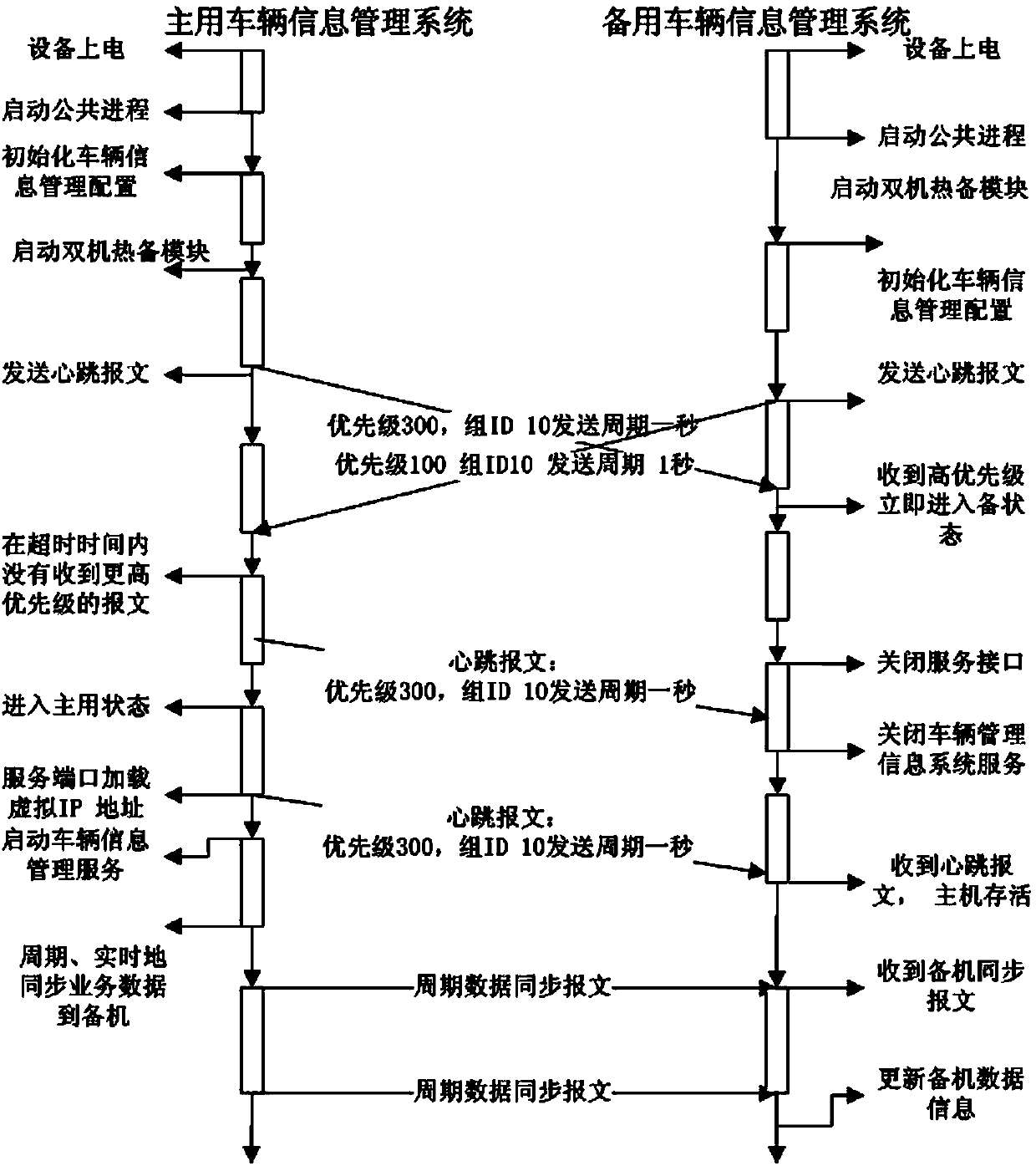
ActiveCN103744809AGuaranteed Hot Standby RelationshipImprove usabilityElectric digital data processingData synchronizationIn vehicle
The invention provides a method for dual-computer hot-standby of a vehicle information management system on the basis of a VRRP and relates to a dual-computer hot-standby method. The method is suitable for a system having important data storage. The method comprises a first step of configuring dual-computer hot-standby parameters; a second step of enabling a main server and a standby server to establish hot-standby relations; a third step of enabling a server high in priority to enter a main use state, and periodically sending heartbeat messages; a fourth step of enabling the main server to synchronize service data to the standby server in real time or periodically through an FTP file transfer protocol in a data synchronization message mode; a fifth step of enabling the standby server to receive data synchronization messages and FTP data, and instantly updating database information; a sixth step of enabling the standby server to enter a main use state when the main server is restarted or faults occur in vehicle information management services provided by the main server; a seventh step of enabling the main server to actively obtain service data on the standby server when the main server recovers, and starting to provide the vehicle information management services again.
Owner:TIANZE INFORMATION IND
Processing method of heartbeat message, acquisition method of heartbeat period and access network equipment
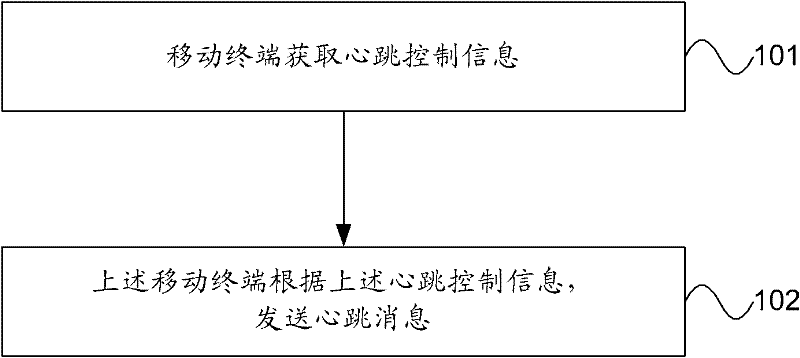
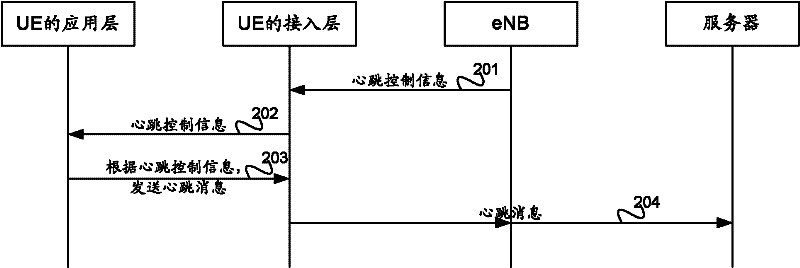
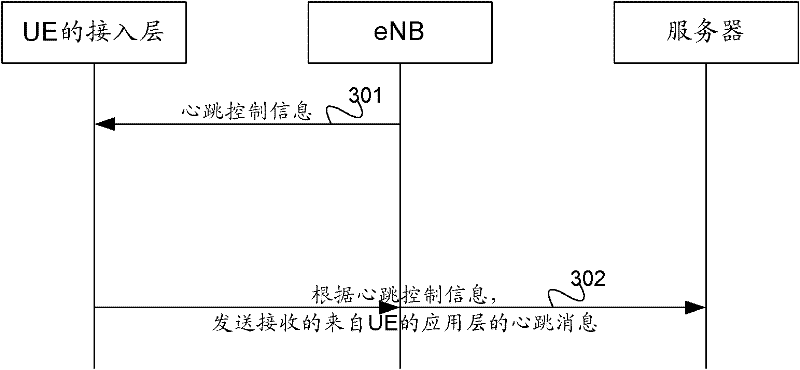
ActiveCN102685768AGuaranteed to proceed normallyGet heartbeat cycleSynchronisation arrangementConnection managementInformation processingAccess network
The invention provides a processing method of heartbeat message, an acquisition method of heartbeat period and access network equipment. The processing method of heartbeat message comprises acquiring heartbeat control information by a terminal; and sending heartbeat message by the terminal according to the heartbeat control information. The embodiment of the processing method of heartbeat message, acquisition method of heartbeat period and access network equipment provided by the invention can reduce information processing load of network-side equipment and electric power consumption of the terminal, to thereby ensure normal operation of terminal communication service.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Reliable fault resolution in a cluster
ActiveUS7284147B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationSoftware faultApplication software
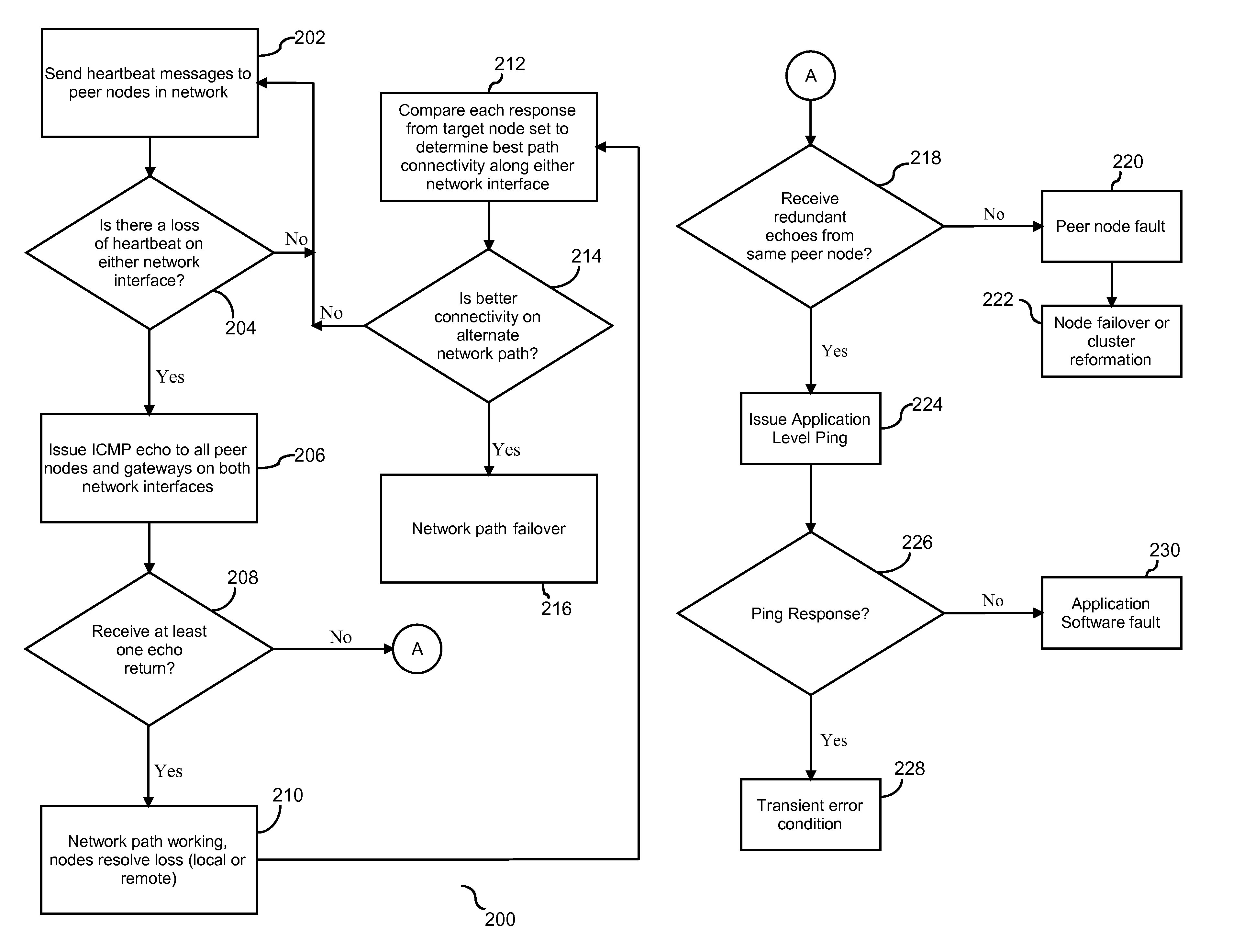
A method and system for localizing and resolving a fault in a cluster environment. The cluster is configured with at least one multi-homed node, and at least one gateway for each network interface. Heartbeat messages are sent between peer nodes and the gateway in predefined periodic intervals. In the event of loss of a heartbeat message by any node or gateway, an ICMP echo is issued to each node and gateway in the cluster for each network interface. If neither a node loss nor a network loss is validated in response to the ICMP echo, an application level ping is issued to determine if the fault associated with the absence of the heartbeat message is a transient error condition or an application software fault.
Owner:IBM CORP
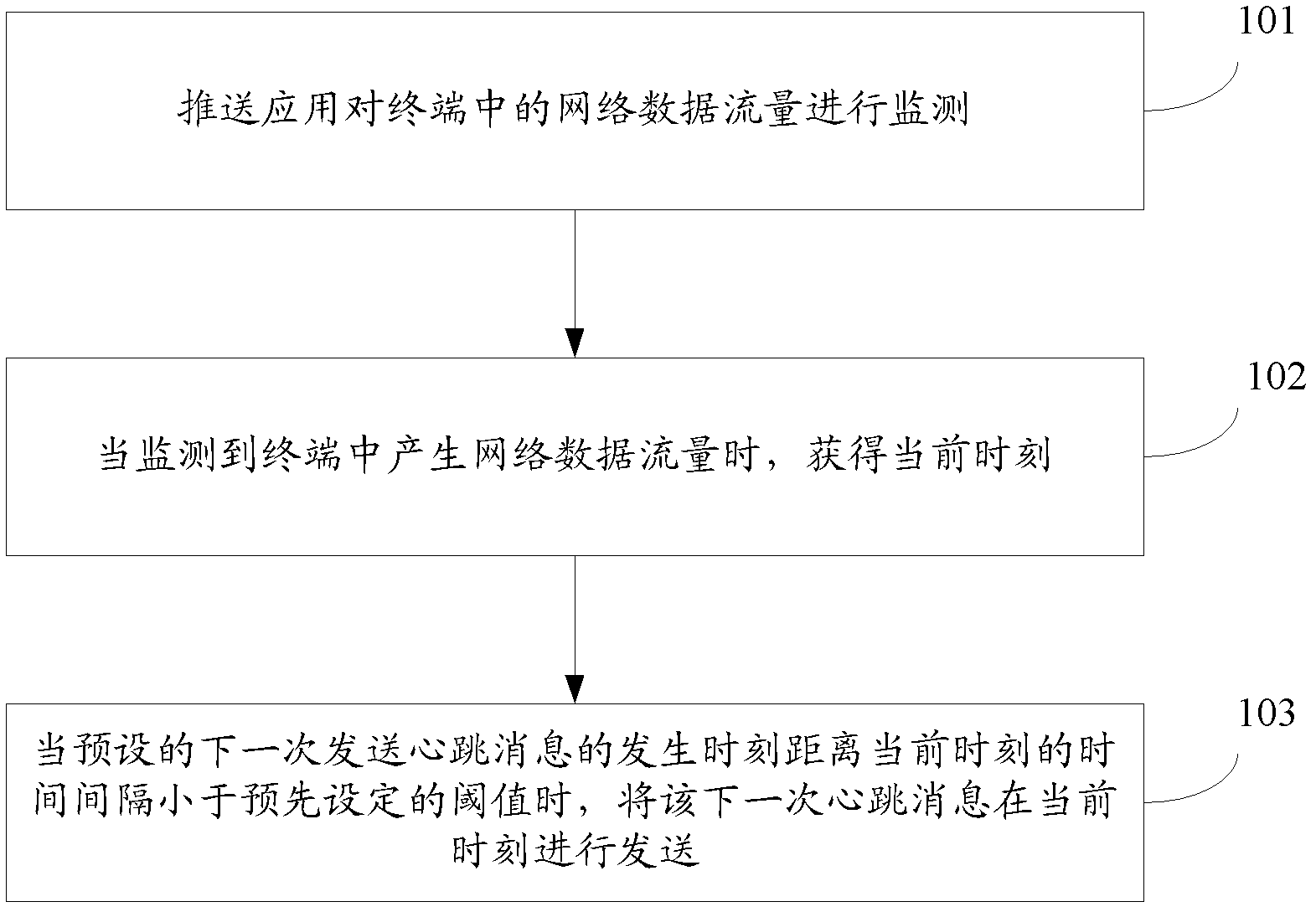
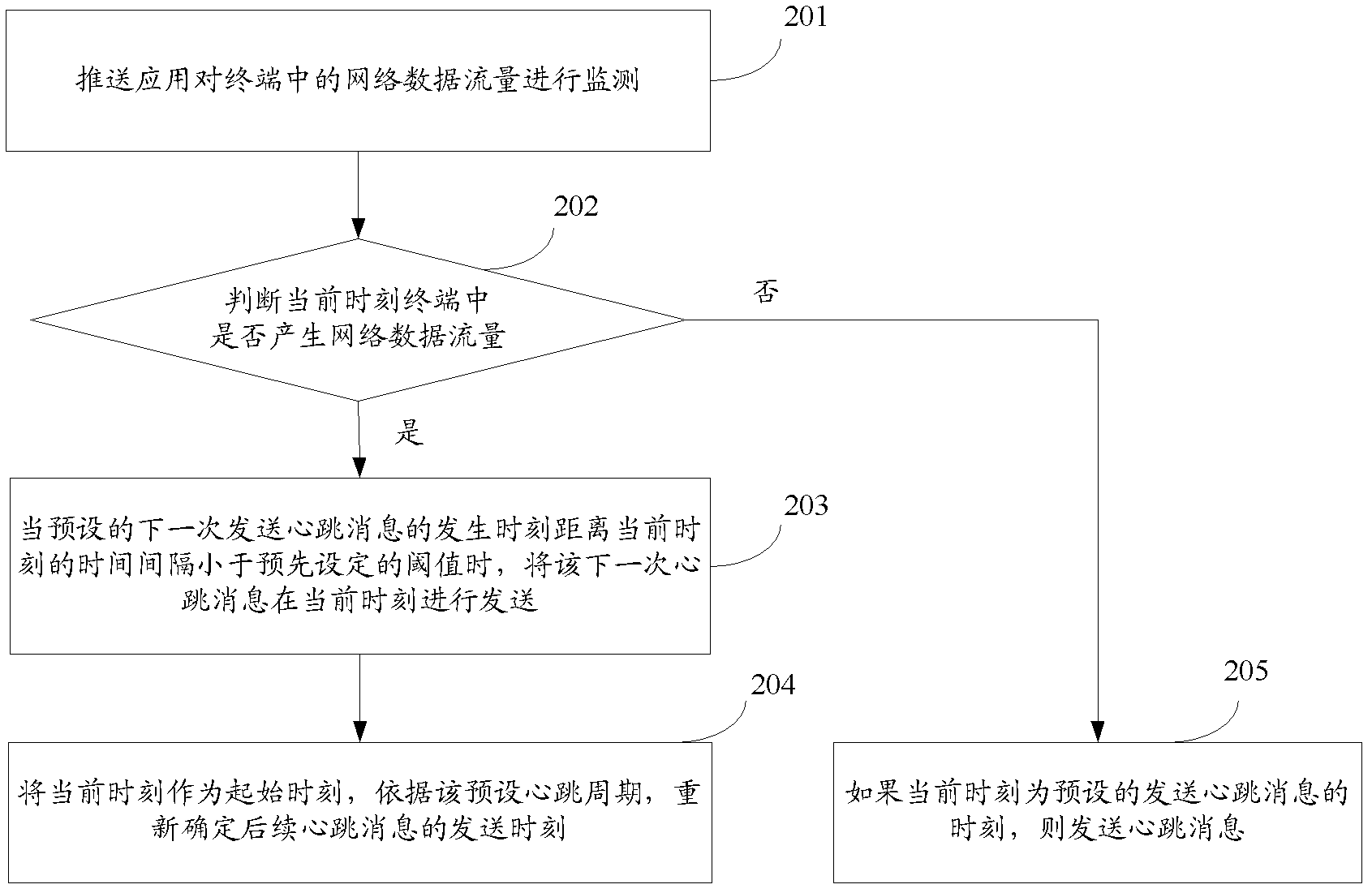
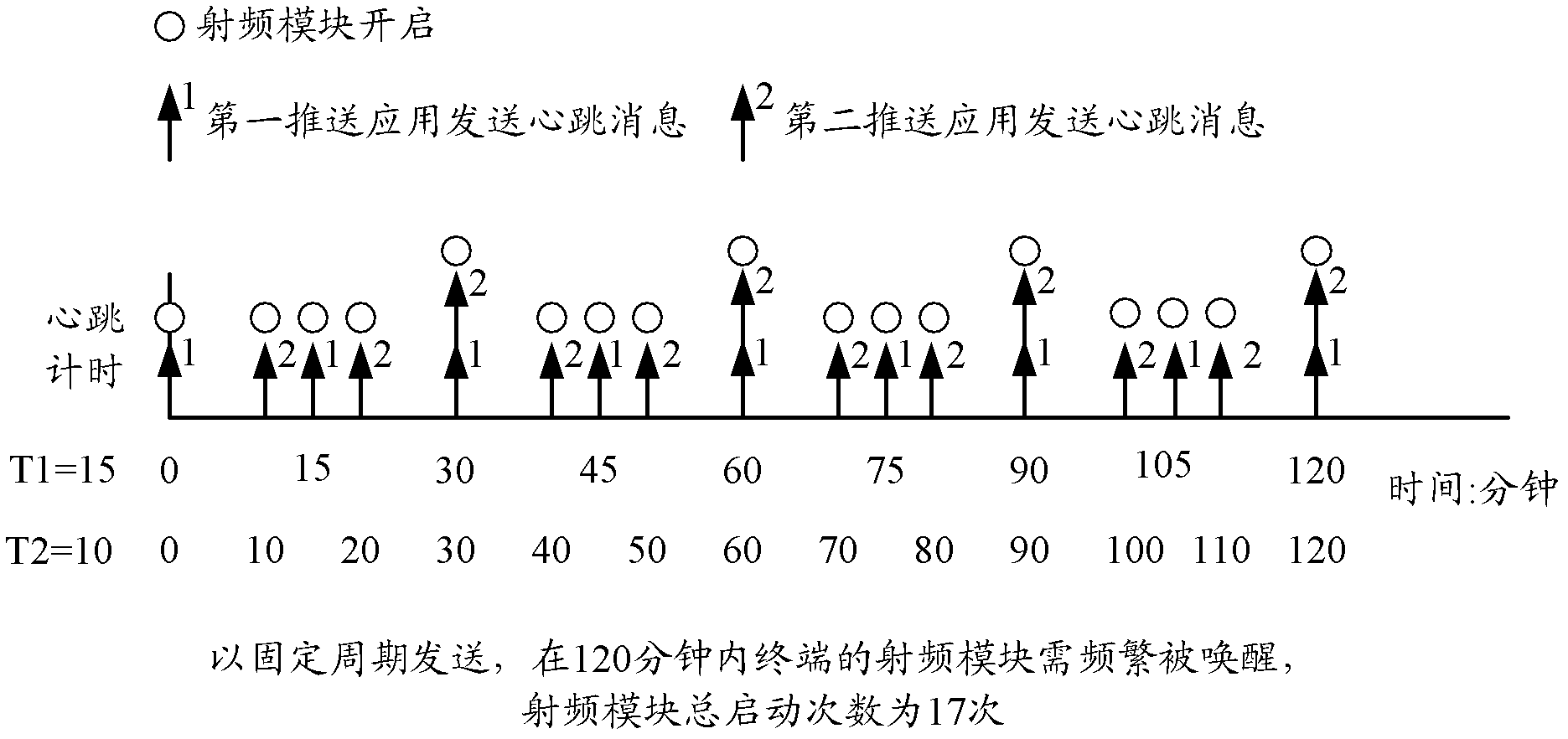
Push-based heartbeat message sending method and terminal
ActiveCN102523178AReduce the number of openingsExtended service lifeData switching networksTraffic capacityNetwork data
The invention discloses a push-based heartbeat message sending method and a terminal. The method comprises: push application monitors a network data flow in a terminal; when the push application monitors that a network data flow is generated in the terminal, a current time is obtained; and a time when the application push sends a heartbeat message the last time is used as an initial time and it is determined whether a time interval between the current time and an occurrence time when a heartbeat message should be sent at the next time after a preset heartbeat period of the push application has passed is less than a preset threshold; if so, the heartbeat message of the next time is sent at the current time; and the current time is used as an initial time and a time for sending a follow-up heartbeat message is redetermined according to the preset heartbeat period. According to the method provided in the invention, electric quantity loss caused by heartbeat message sending by push application can be reduced; and service life of a radio frequency module can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com