Patents
Literature
172 results about "Transport Layer Security" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
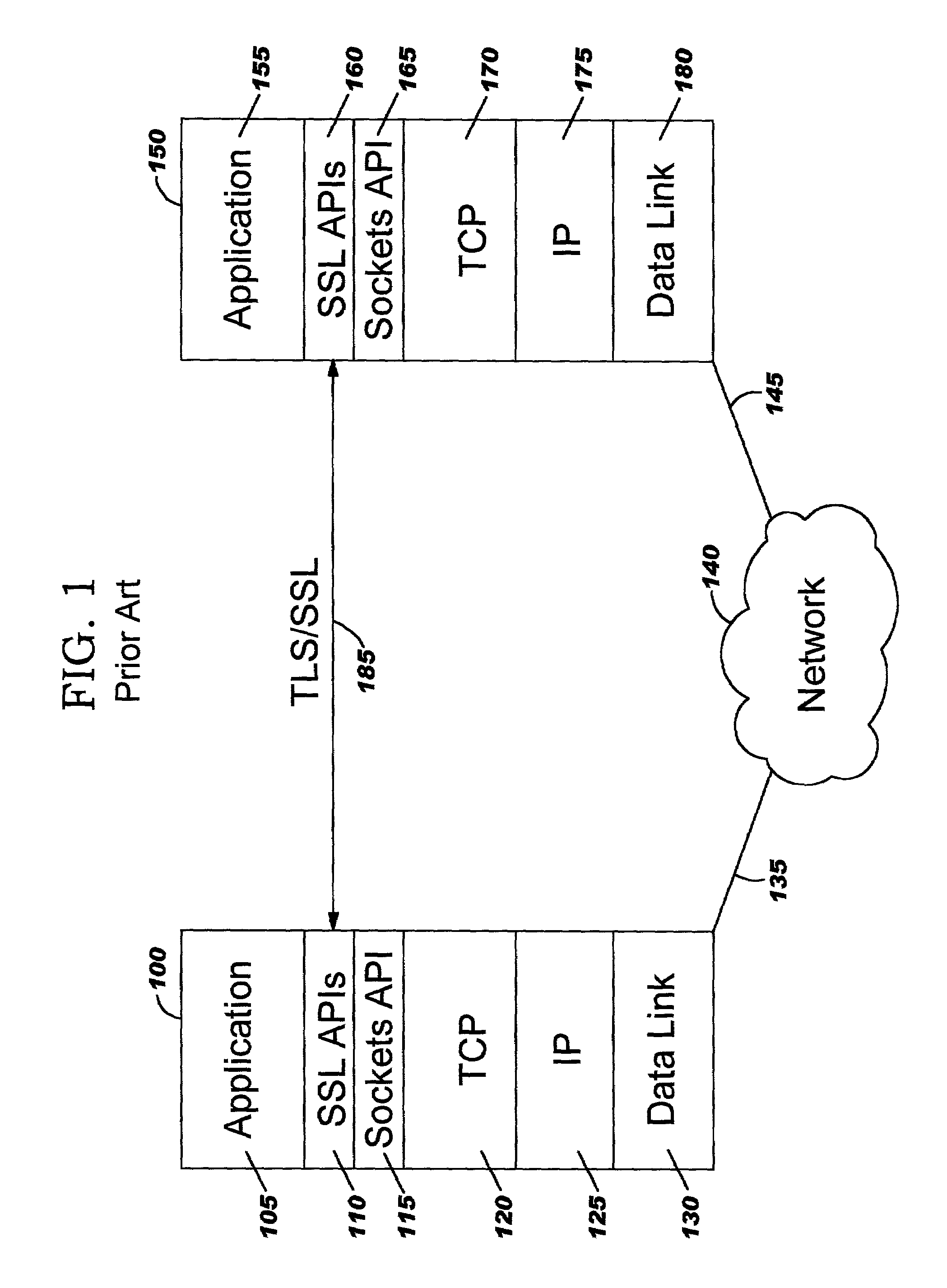
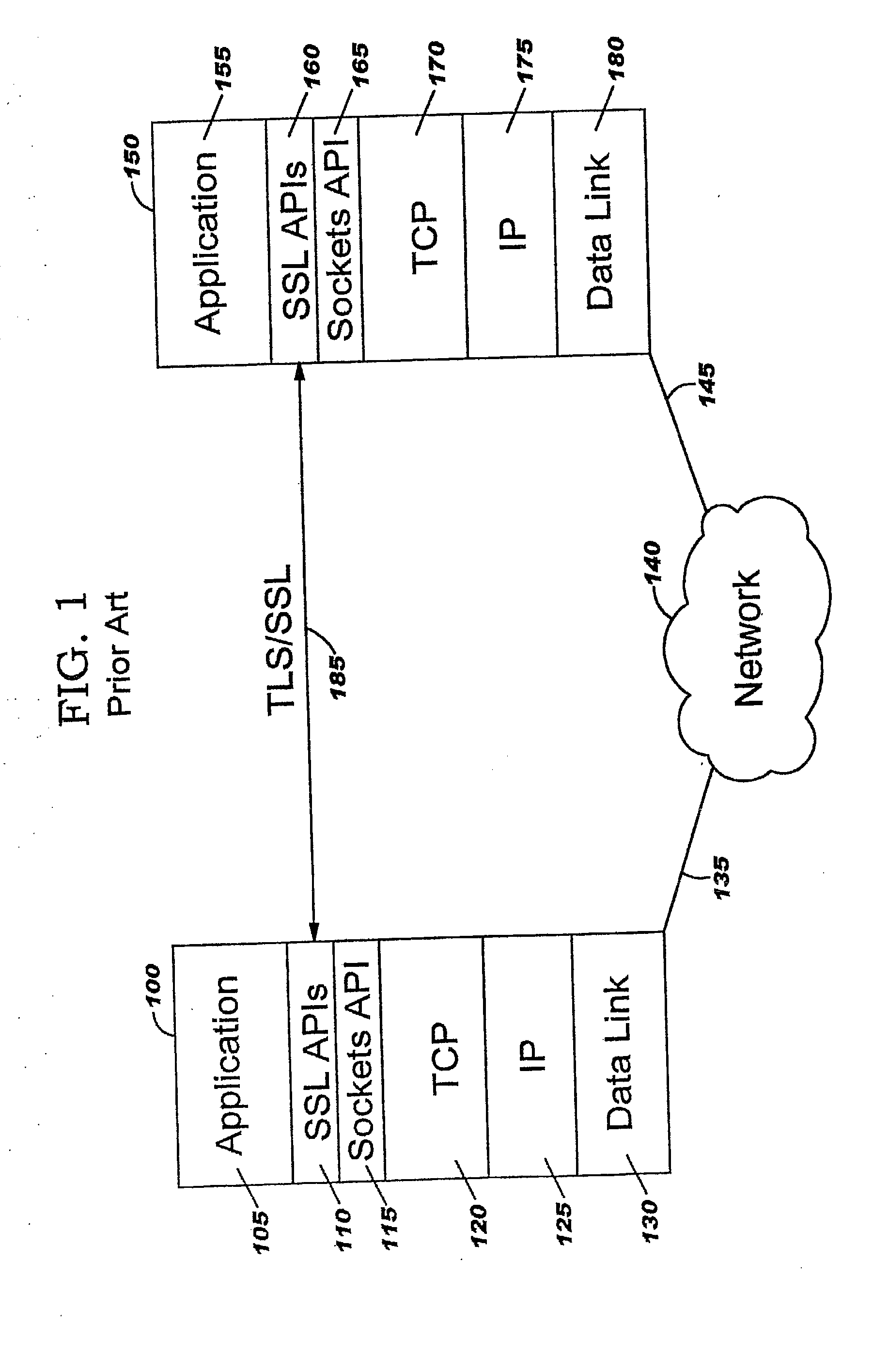
Transport Layer Security (TLS), and its now-deprecated predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols designed to provide communications security over a computer network. Several versions of the protocols find widespread use in applications such as web browsing, email, instant messaging, and voice over IP (VoIP). Websites can use TLS to secure all communications between their servers and web browsers.
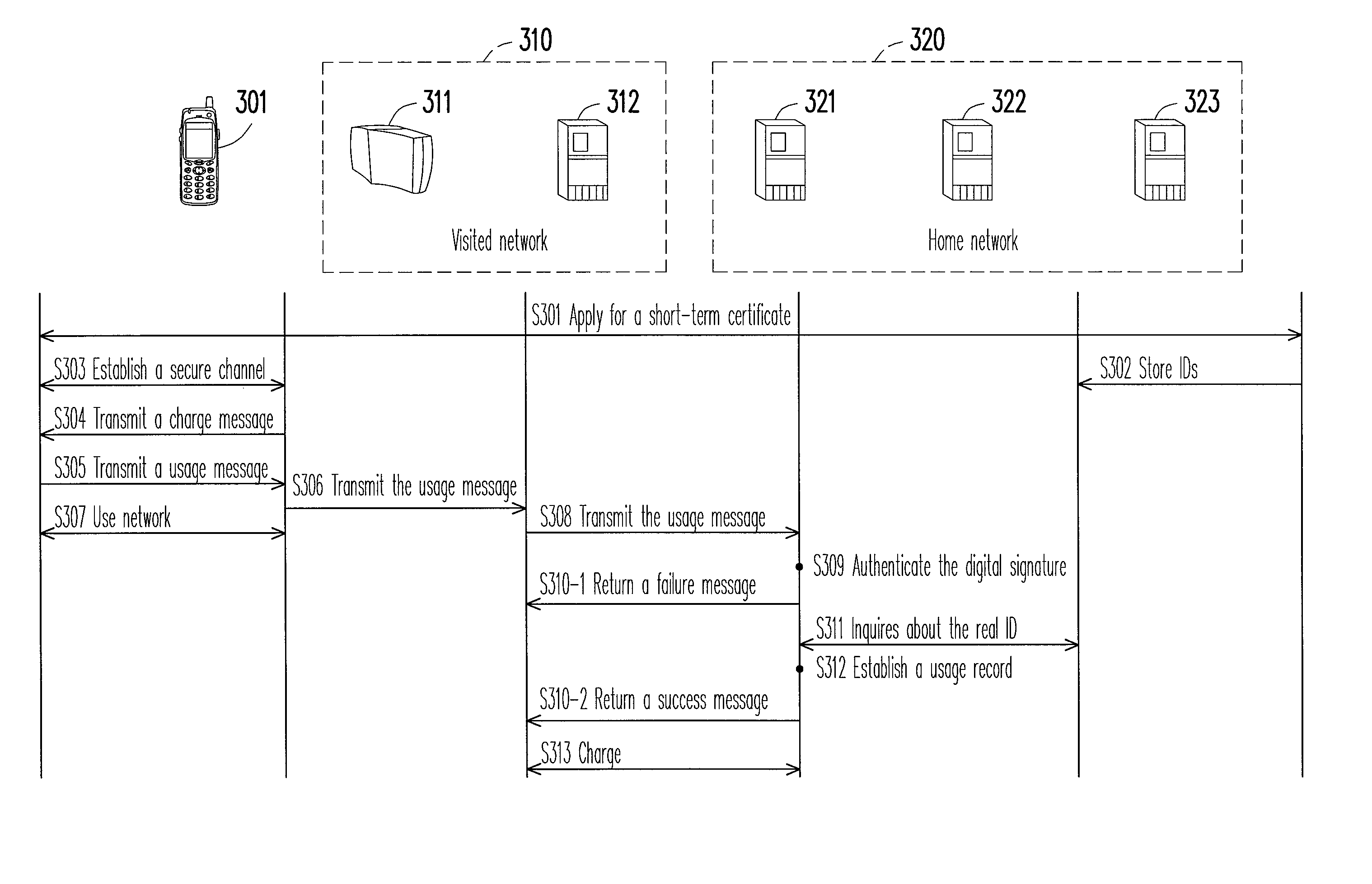
Method and system for managing network identity
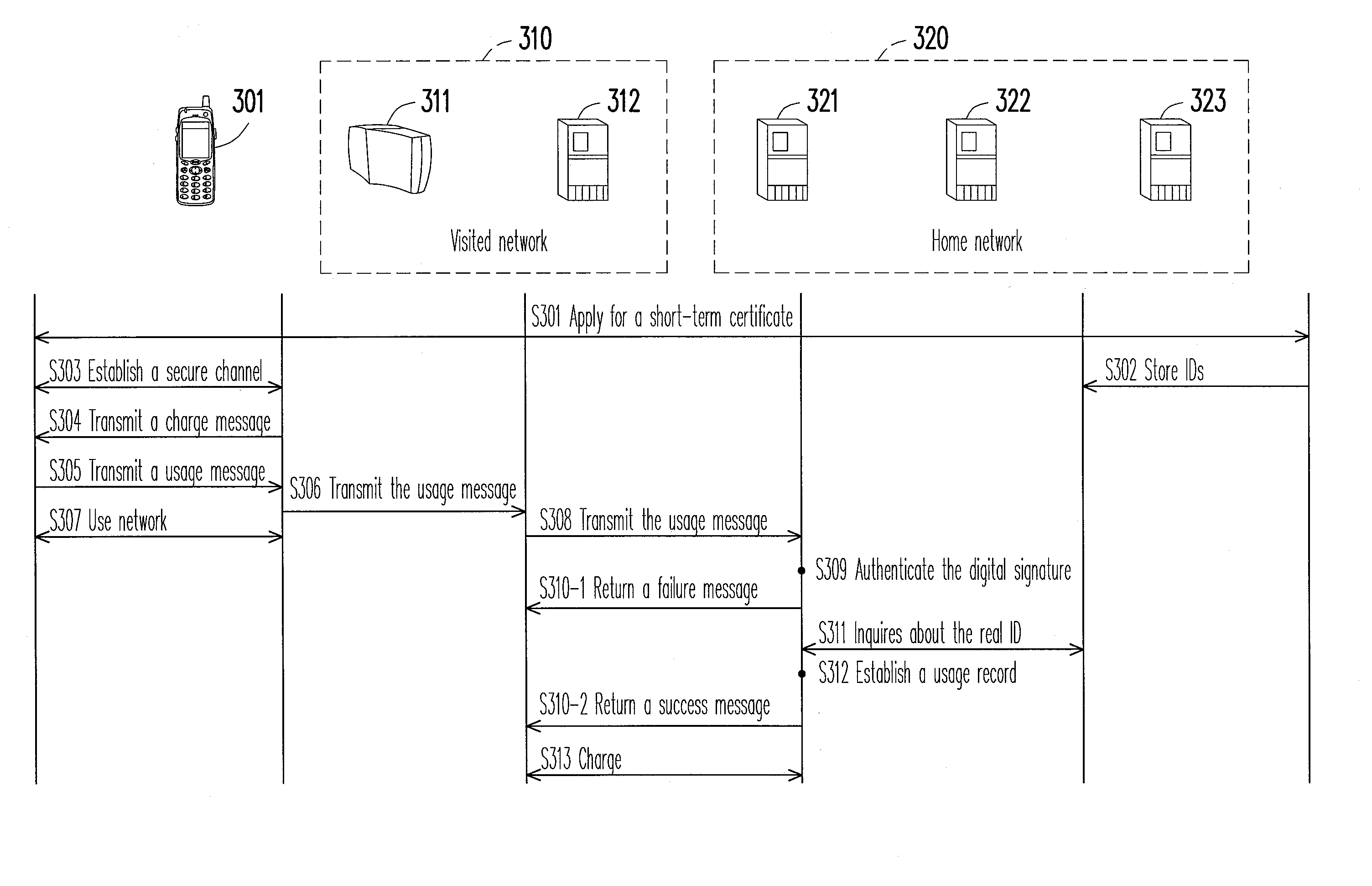
A method and a system for managing network identity are provided. The method and the system realize a management mechanism of temporary identification (ID) and real ID, which simultaneously achieves functionalities such as anonymity, accounting, and authorization. A short-term certificate and a corresponding public / private key pair are used to protect a temporary ID usable for accounting. This protection prevents the temporary ID from theft. The user generates a digital signature in the reply to a charge schedule statement from the visited network. This procedure is incorporated into an existing authentication framework based on Transport Layer Security (TLS) in order to provide an undeniable payment mechanism. The payment mechanism is applicable in an environment of multiple network operators and reduces the difficulty of integrating network operators. The method and the system do not have to consult a certificate revocation list (CRL) for authentication and thus are able to shorten authentication time.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
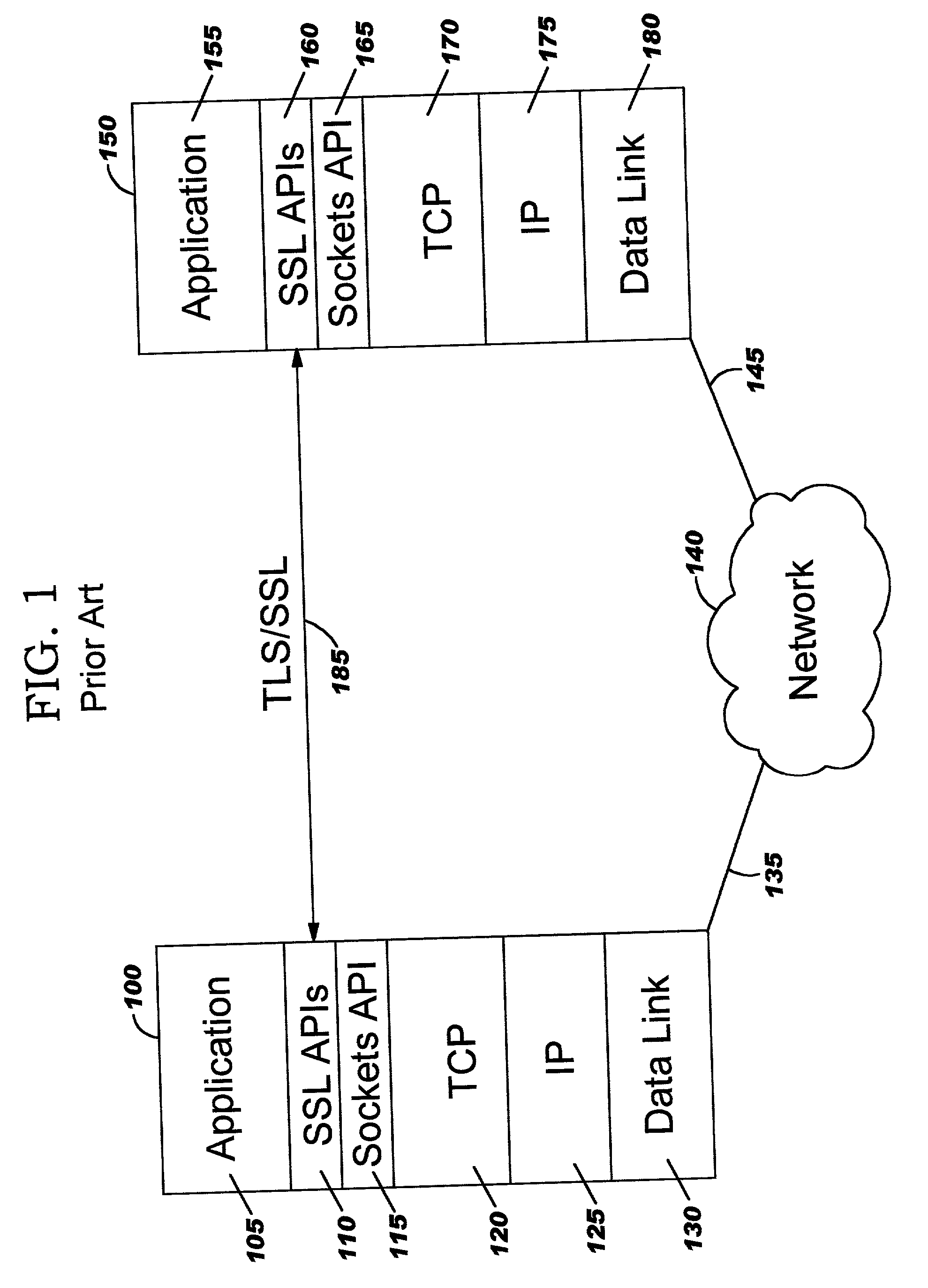
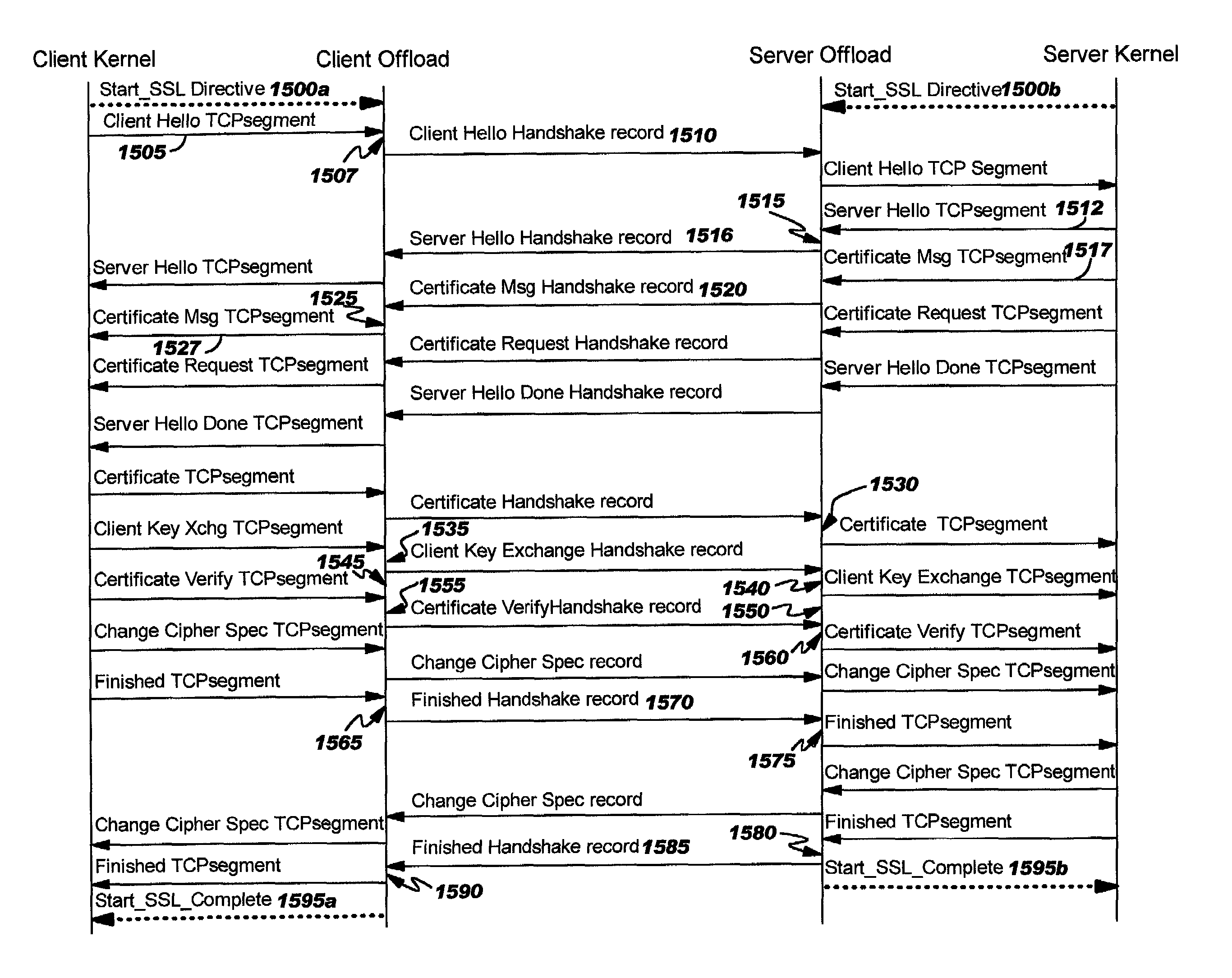
Offload processing for secure data transfer
InactiveUS20030105977A1Safe handlingMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlPlaintextSafe handling
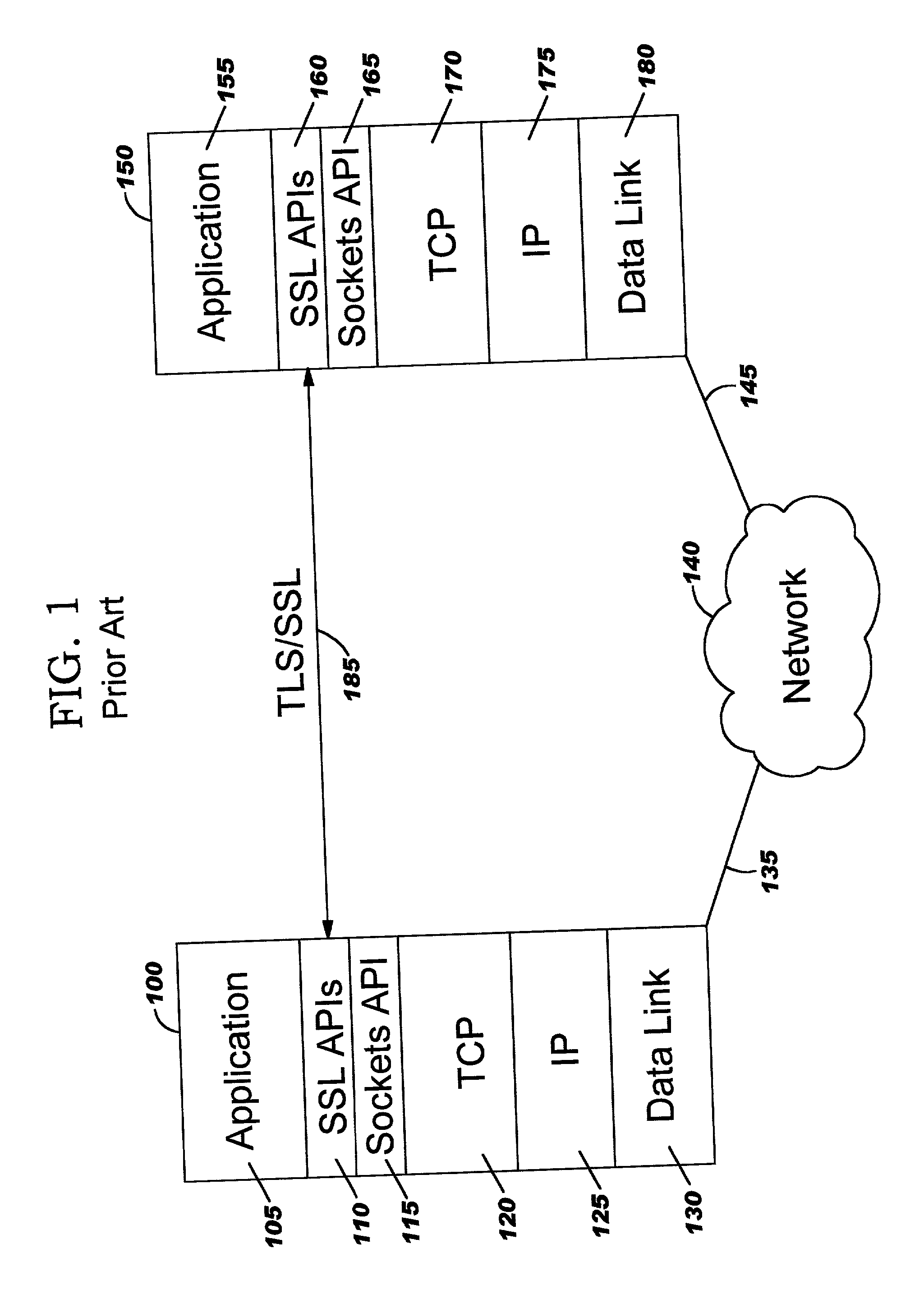
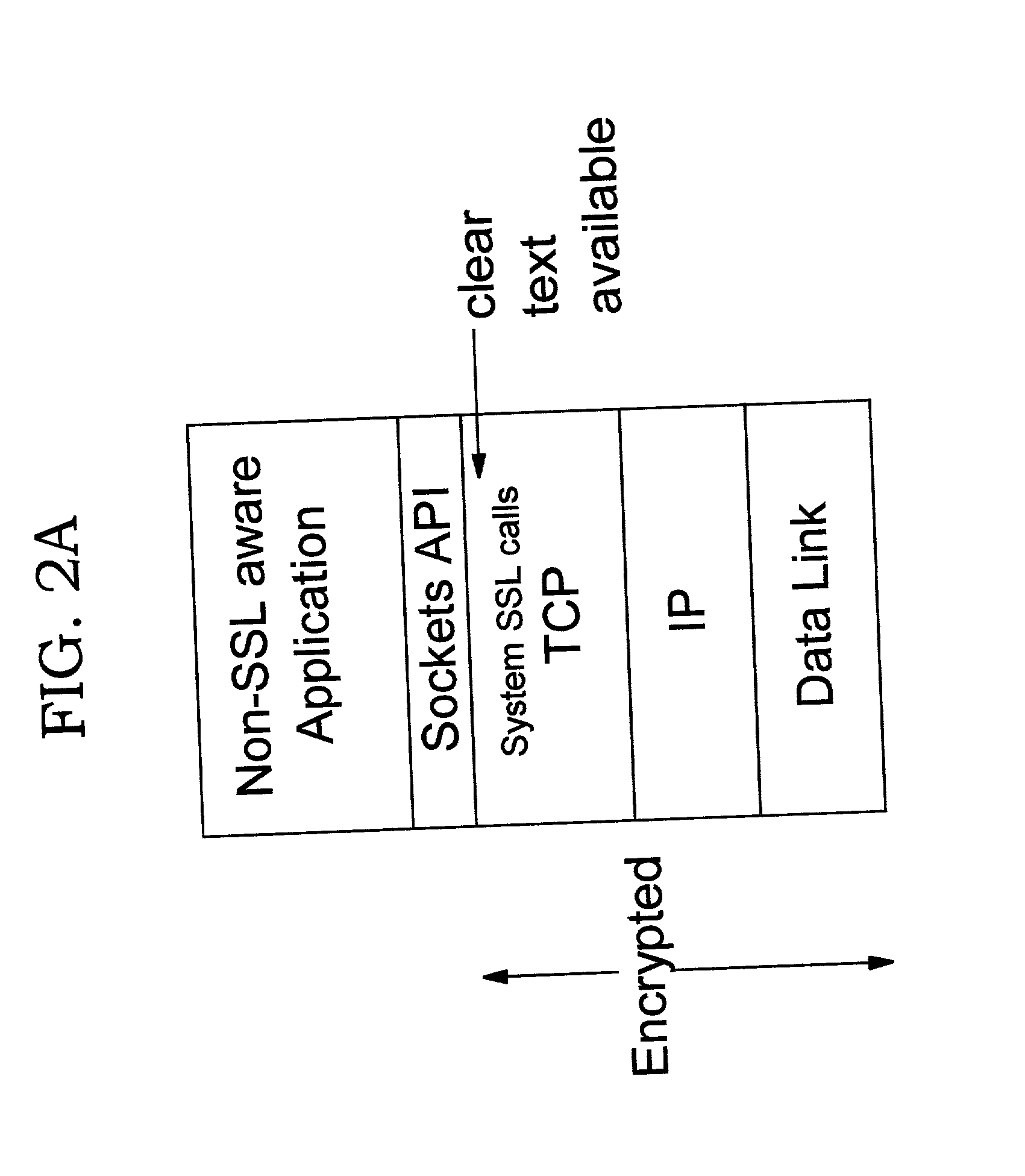
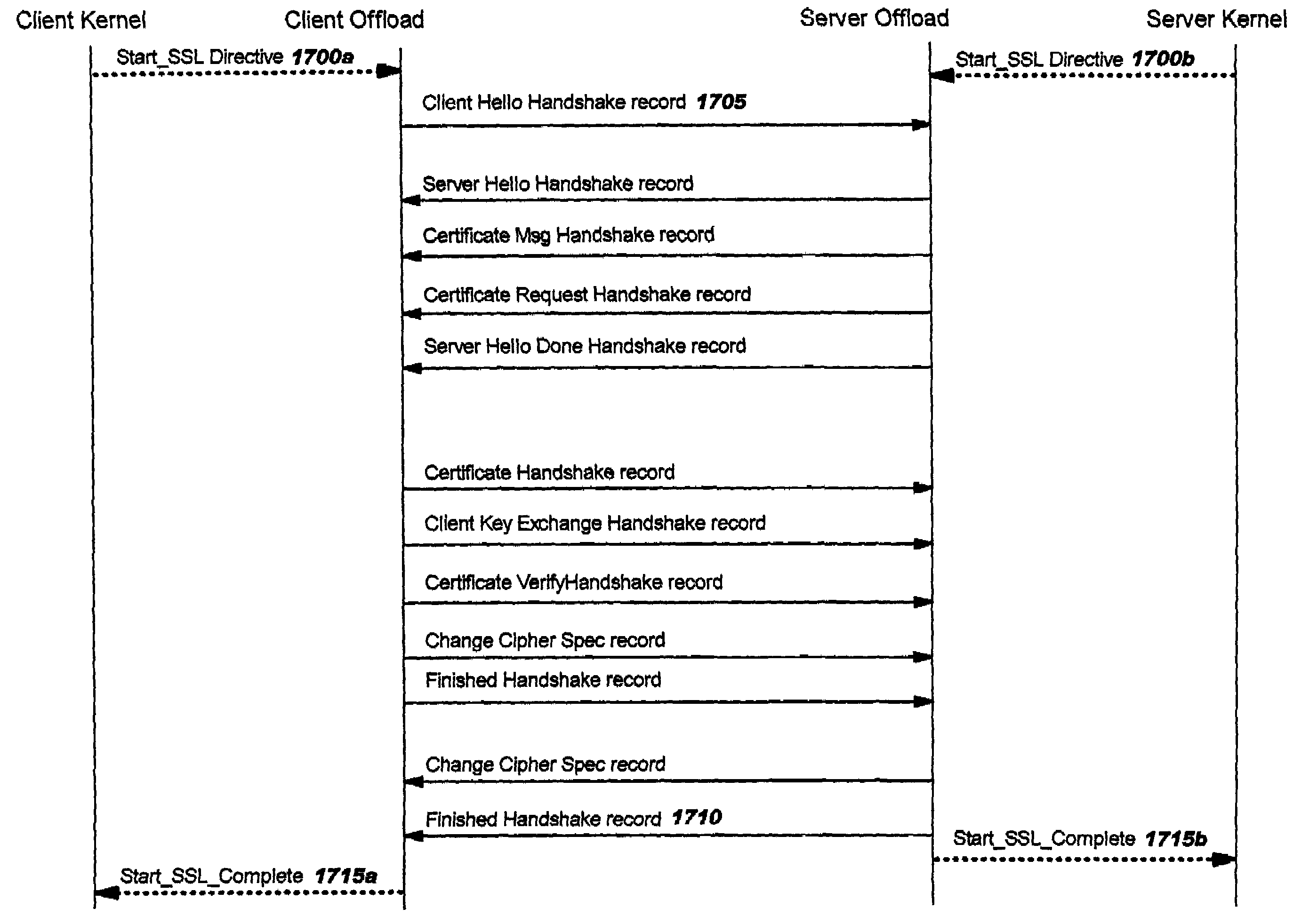
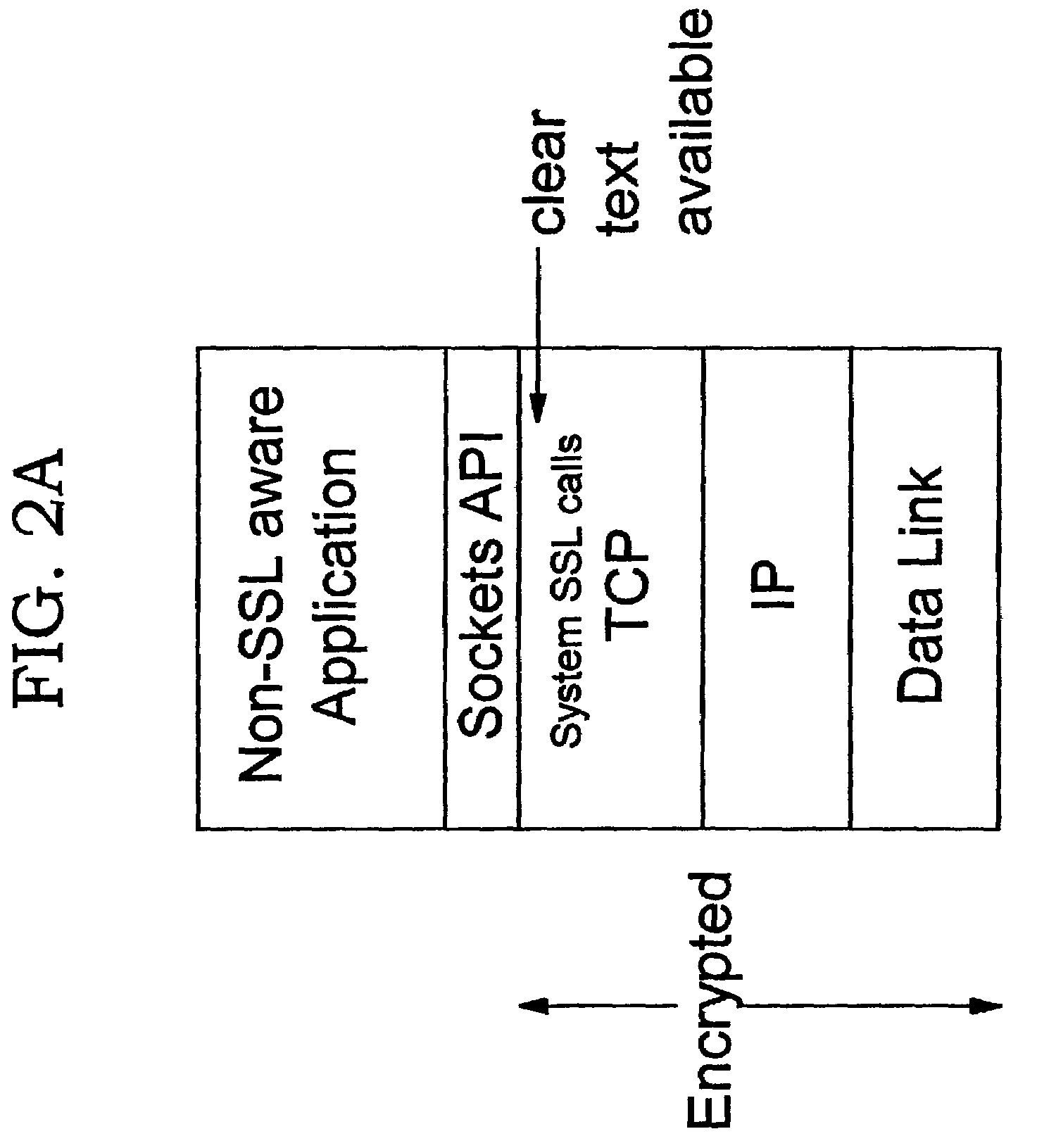
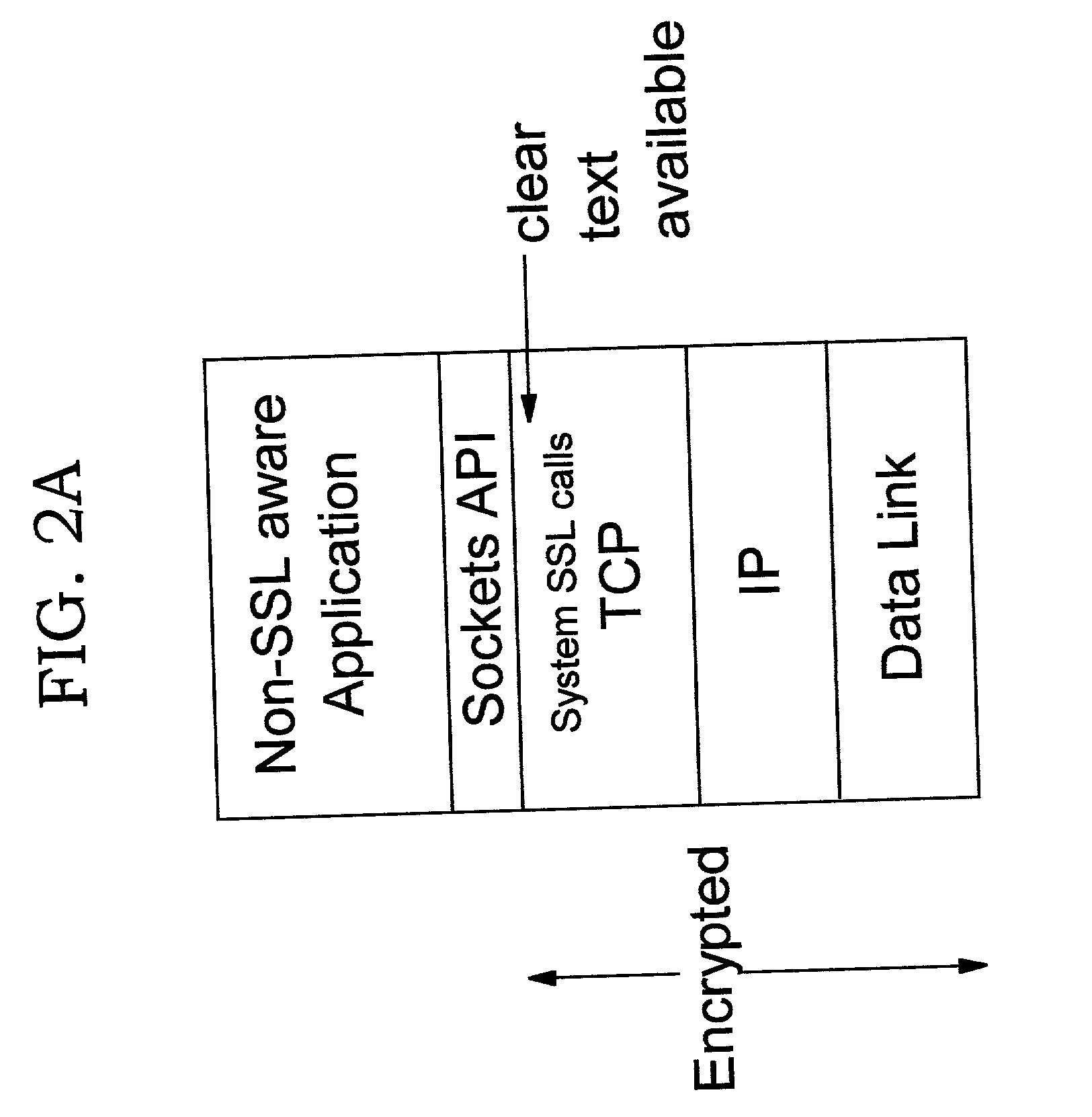
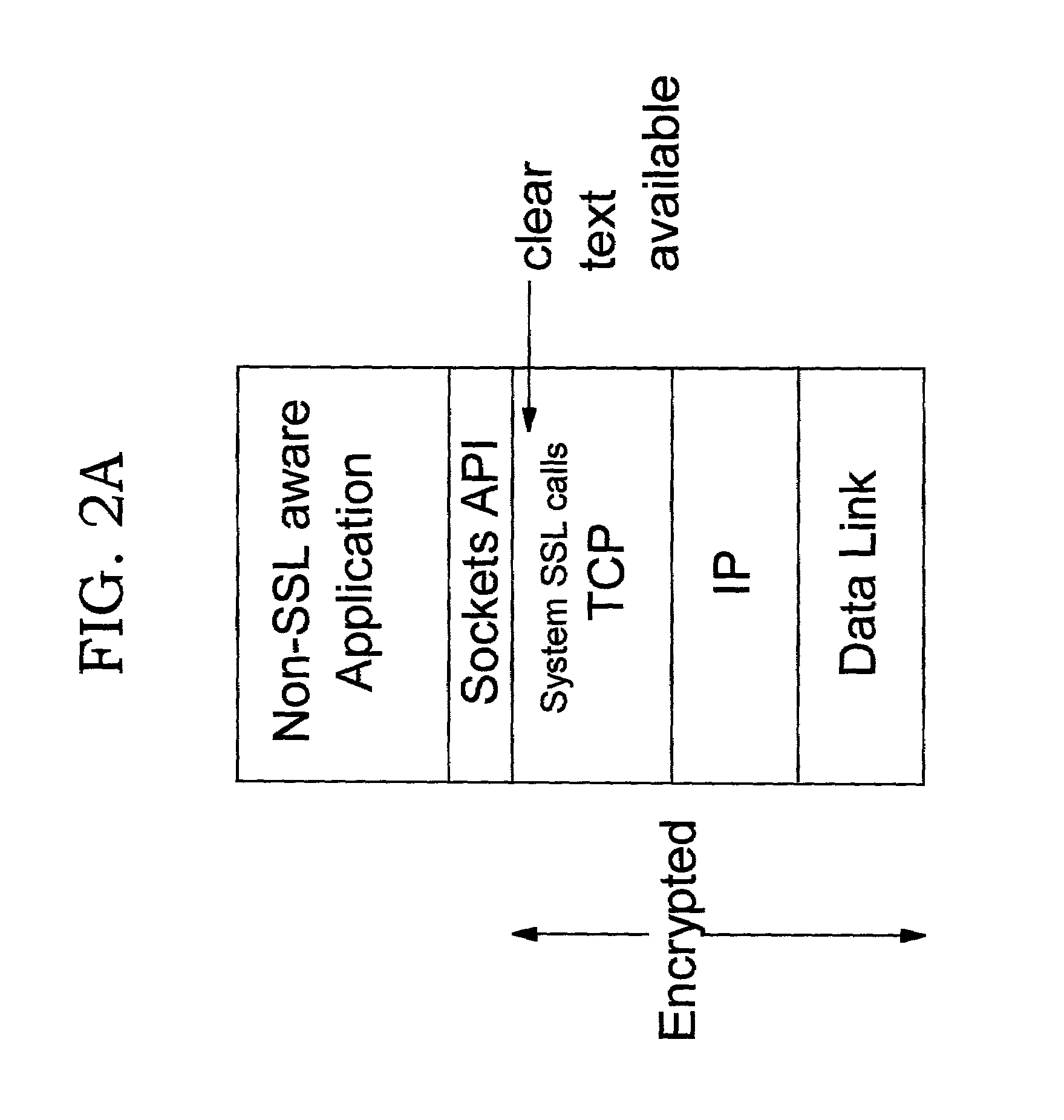
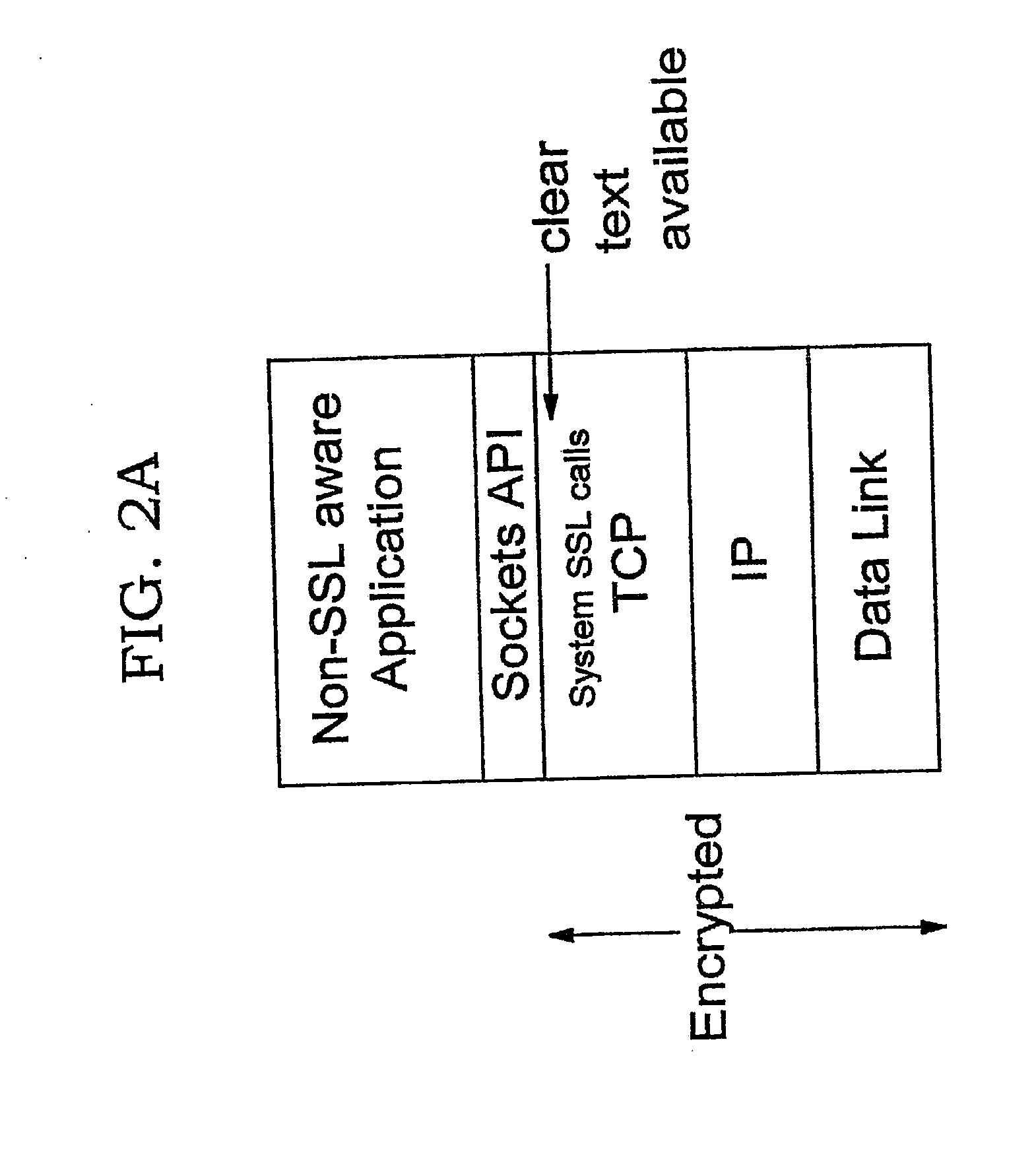
Improvements in security processing are disclosed which enable security processing to be transparent to the application. Security processing (such as Secure Sockets Layer, or "SSL", or Transport Layer Security, or "TLS") is performed in (or controlled by) the stack. A decision to enable security processing on a connection can be based on configuration data or security policy, and can also be controlled using explicit enablement directives. Directives may also be provided for allowing applications to communicate with the security processing in the stack for other purposes. Functions within the protocol stack that need access to clear text can now be supported without loss of security processing capability. No modifications to application code, or in some cases only minor modifications (such as inclusion of code to invoke directives), are required to provide this security processing. Improved offloading of security processing is also disclosed, which provides processing efficiencies over prior art offloading techniques.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for secure messaging with network address translation firewall traversal
InactiveUS20060274899A1Key distribution for secure communicationSecure communicationApplication server
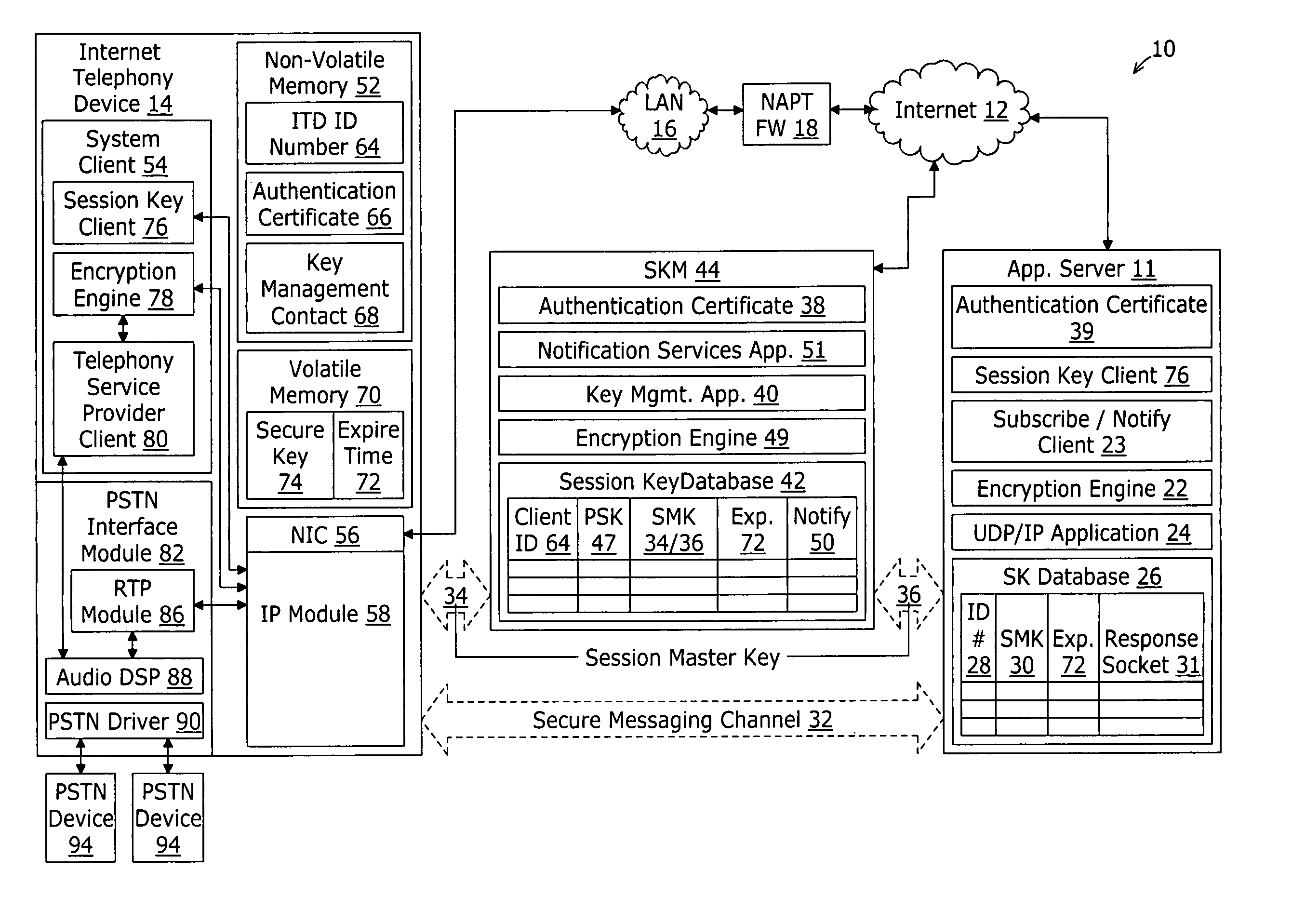
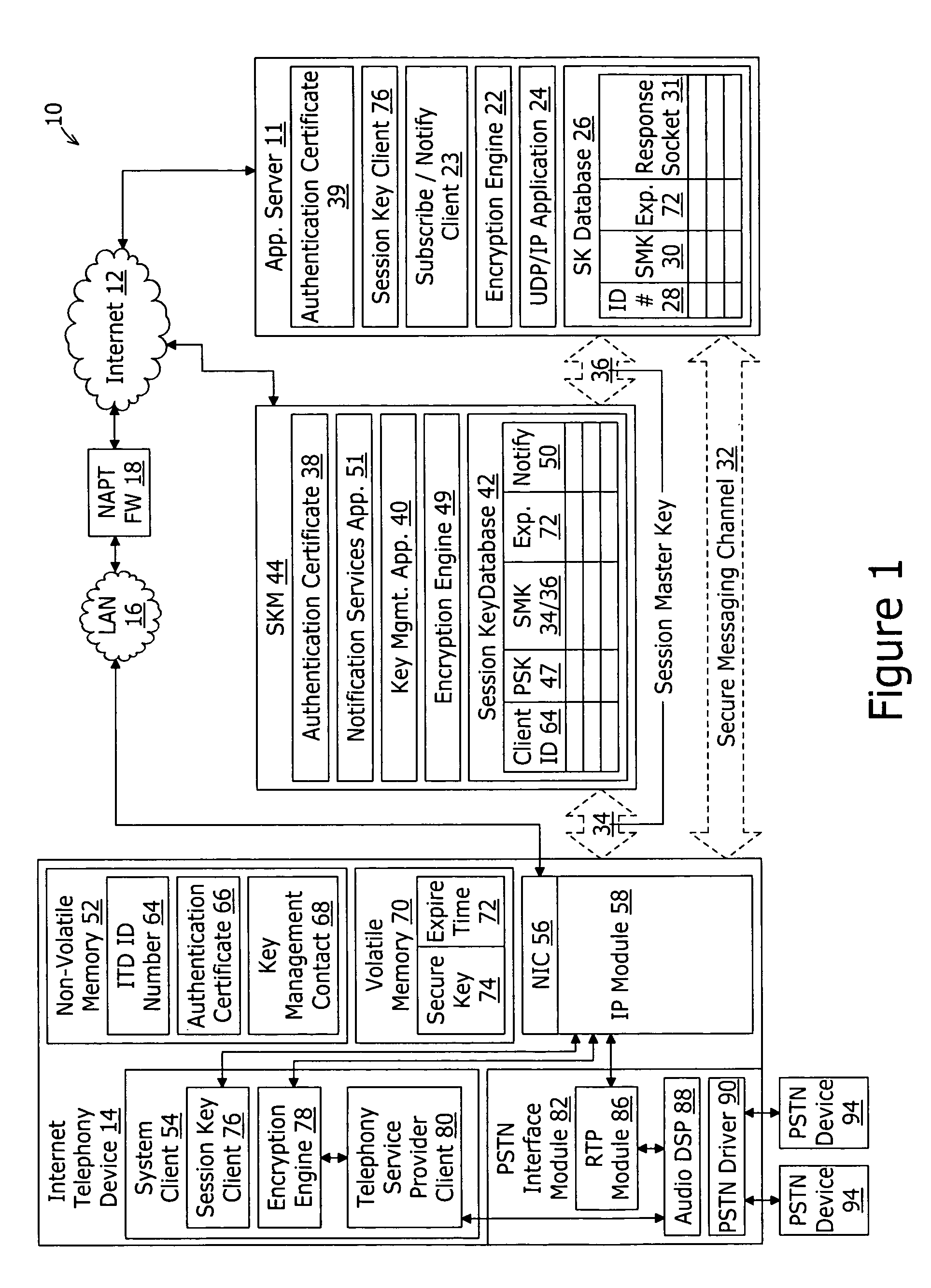
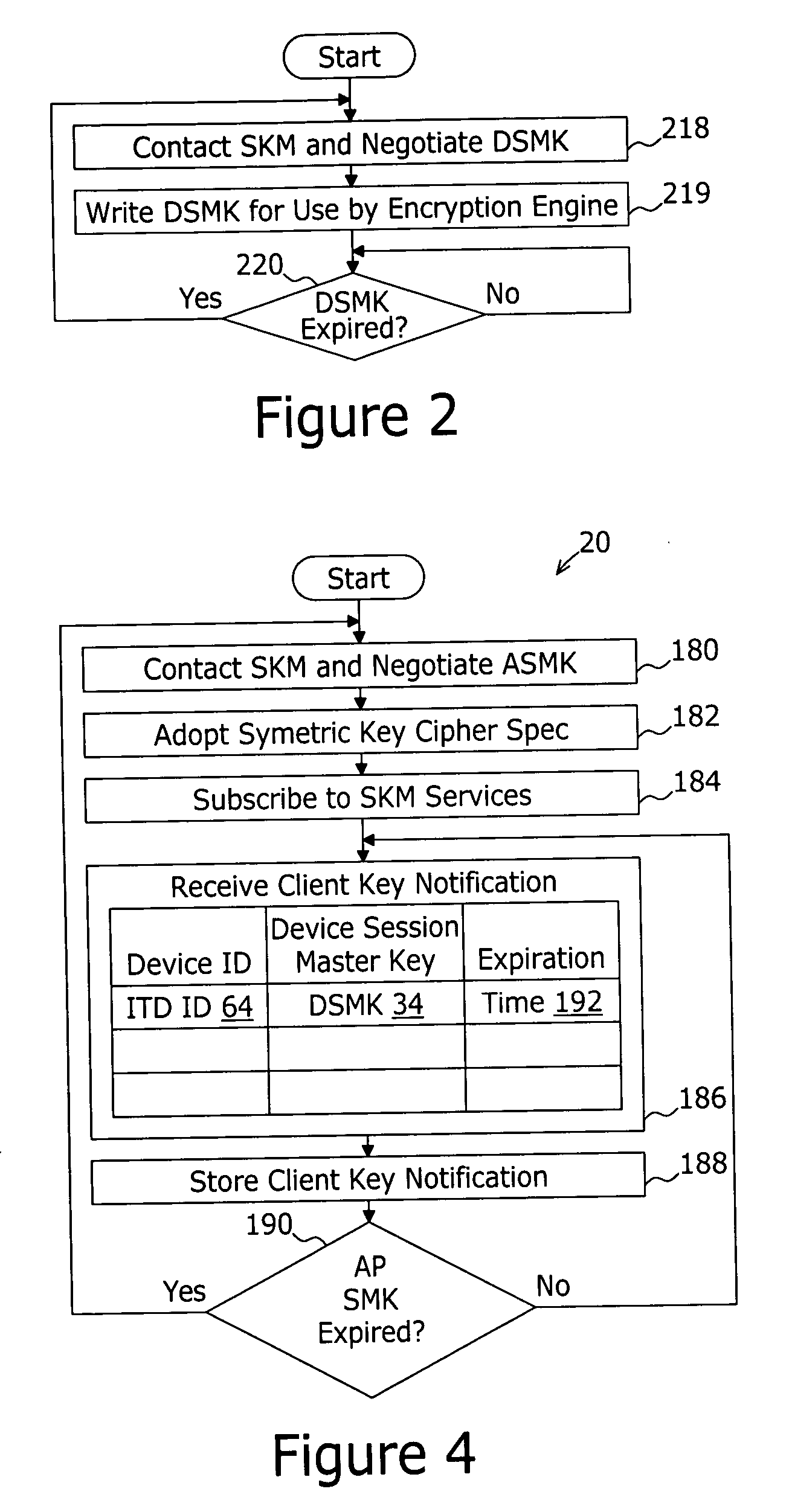
A system for securing communications between a client and an application server comprises a session key management server and the application server. The system enables network address translation firewall traversal. The session key management server comprises a key management application, a session key database, and a notification services application. The key management application receives a first transport layer security connection request from the client and negotiates a device session master key with the client as part of the transport layer security exchange. The session key database is coupled to the key management application for storing the device session master key in conjunction with an identification of the client. The notification services application coupled to the session key database and provides a notification message to subscribing application servers. The notification message comprises the device session master key in conjunction with an identification of the client.
Owner:INNOMEDIA PTE
Multiparty conference authentication
InactiveUS6851053B1Increase reachMasquerading particularly easySpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsProtocol ApplicationTransport Layer Security
A method and system for controlling admission of new nodes to a secured conference combines transport layer security mechanism and application layer certificate exchange. A new node that is not directly connected to the top provider of the conference sends a request to join the conference and a certification identifying itself to a first conference node connected to the top provider. The first node performs transport level authentication of the new node, and then forwards the request and certificate of the new node on an application level to the top provider. The top provider verifies the identity of the new node based on the certificate. If the new node is allowed to join the conference, the top provider updates a list of conference participants and makes the certificate of the new node available to other conference nodes so that they can also verify the identity of the new node.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Offload processing for secure data transfer
InactiveUS7441119B2Safe handlingSpecial data processing applicationsSecuring communicationPlaintextData transmission
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
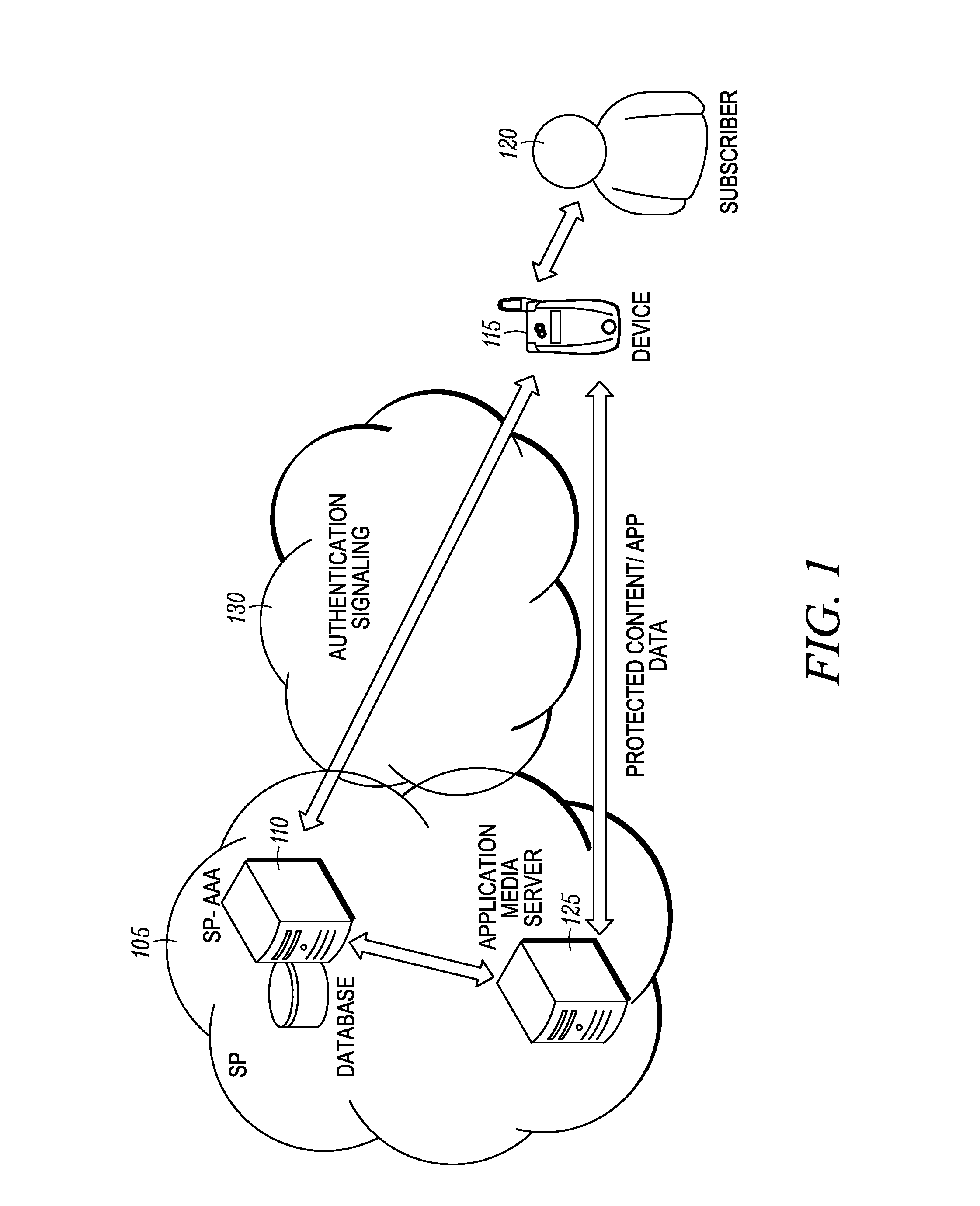
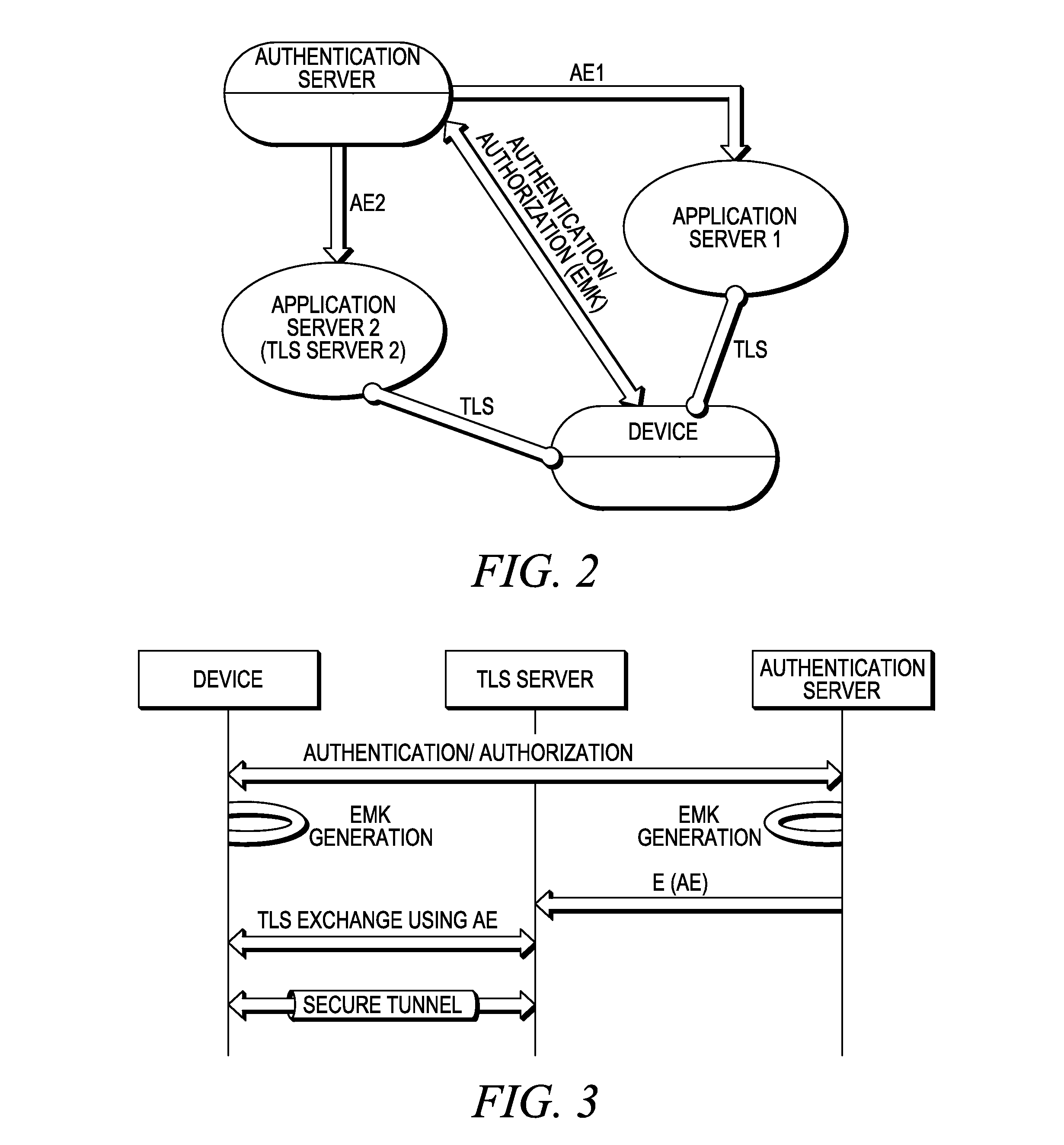
System and method for cognizant transport layer security (CTLS)
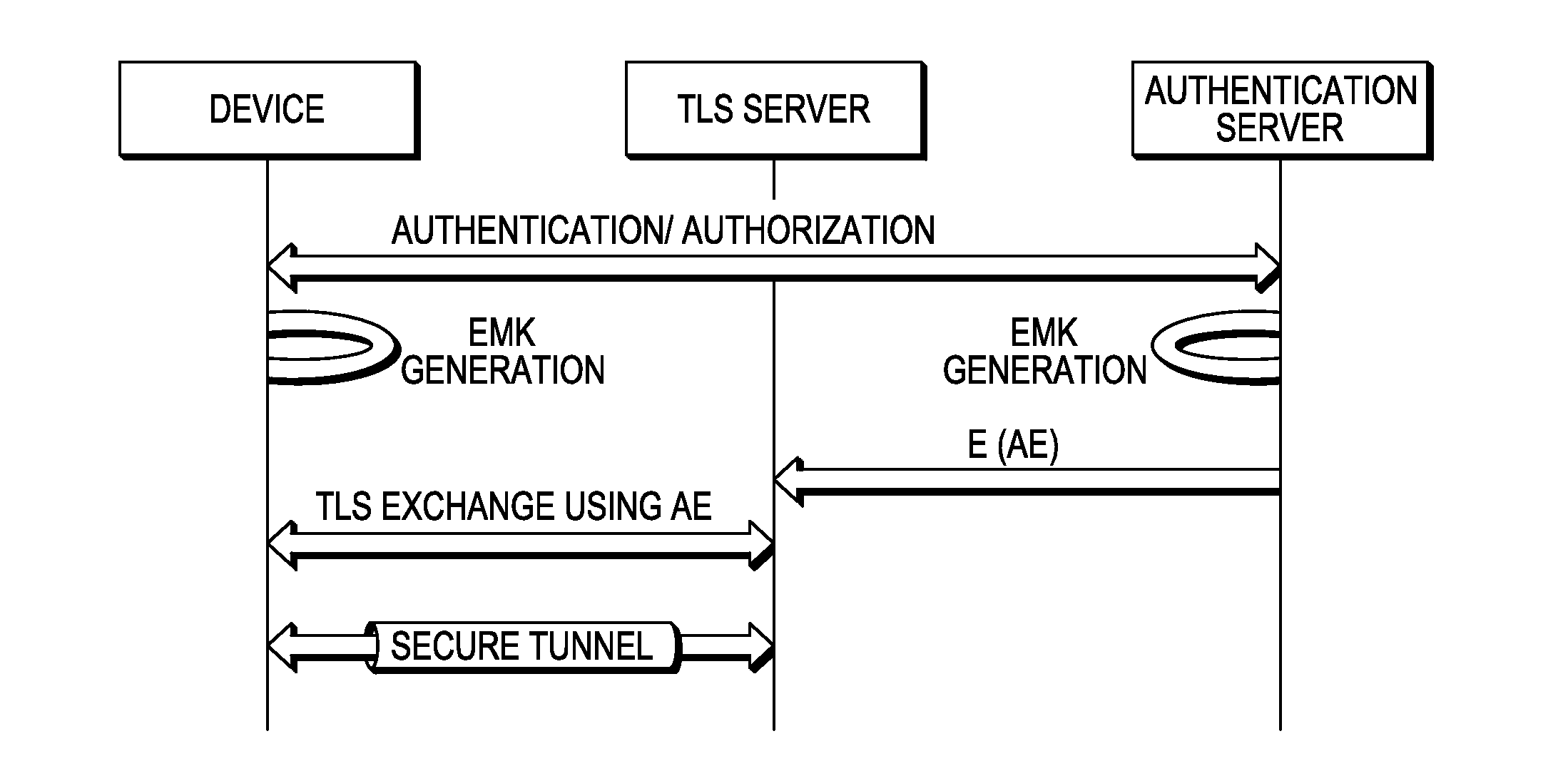
ActiveUS20120042160A1Not availableDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemAuthentication server
A method of authentication and authorization over a communications system is provided. Disclosed herein are systems and methods for creating a cryptographic evidence, called authentication / authorization evidence, AE, when a successful authentication / authorization between a client and an authentication server is complete. There are a variety of methods for generating AE. For instance, the AE can be data that is exchanged during the authentication signaling or data that results from it. A distinctive point being that AE results from the authentication process and is used as prior state for the following TLS exchange. An example for creation of AE, is as follows: EAP authentications typically result in an Extended Master Session Key (EMSK). The EMSK can be used to create an Evidence Master Key (EMK) that can then be used to create AE for a variety of servers.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Kernel-based security implementation
InactiveUS20030105957A1Safe handlingSpecial data processing applicationsSecuring communicationSafe handlingSecurity policy
Improvements in security processing are disclosed which enable security processing to be transparent to the application. Security processing (such as Secure Sockets Layer, or "SSL", or Transport Layer Security, or "TLS") is performed in (or controlled by) the stack. A decision to enable security processing on a connection can be based on configuration data or security policy, and can also be controlled using explicit enablement directives. Directives may also be provided for allowing applications to communicate with the security processing in the stack for other purposes. Functions within the protocol stack that need access to clear text can now be supported without loss of security processing capability. No modifications to application code, or in some cases only minor modifications (such as inclusion of code to invoke directives), are required to provide this security processing. Improved offloading of security processing is also disclosed, which provides processing efficiencies over prior art offloading techniques.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method to contact and maintain status of managed devices
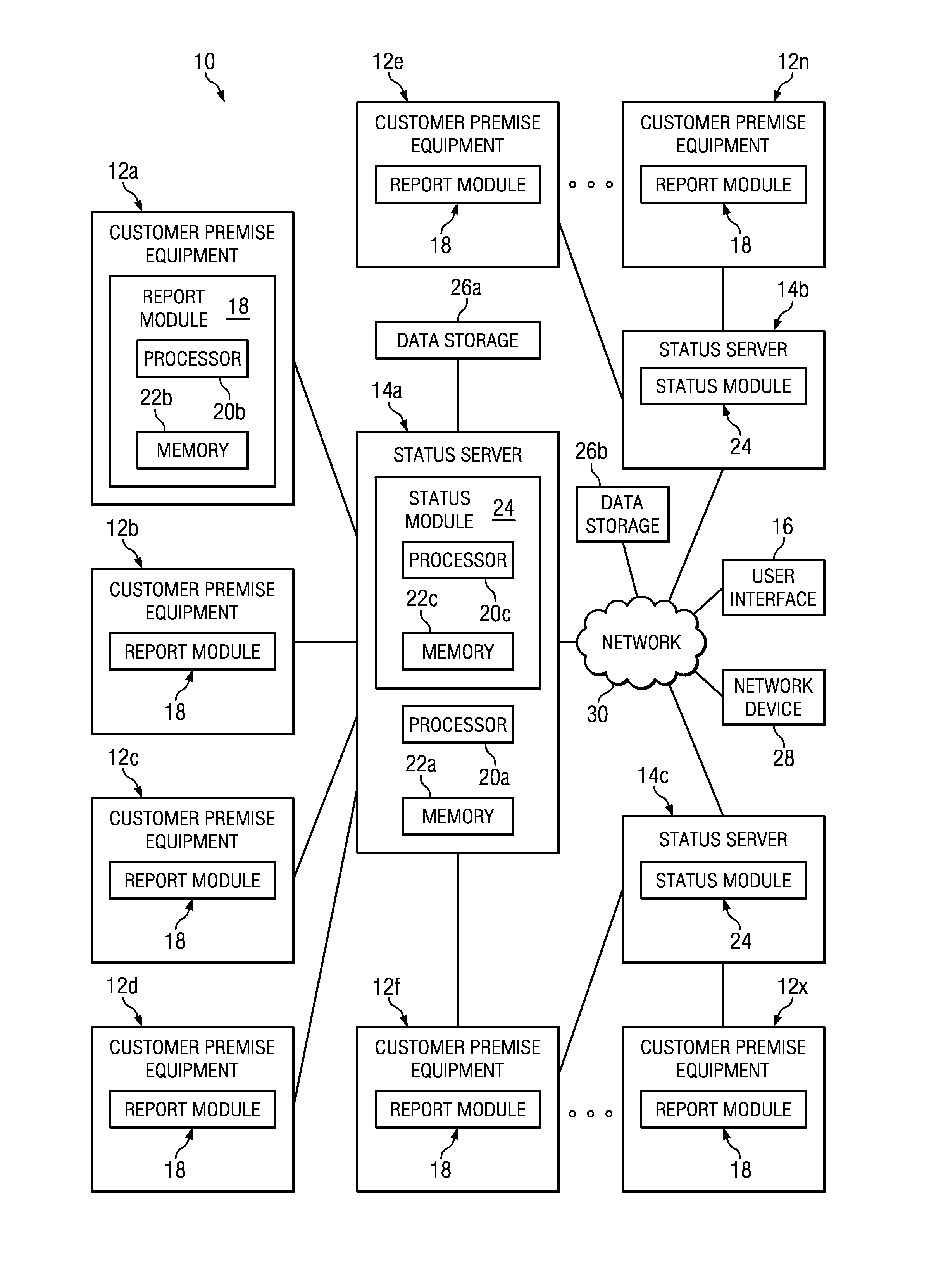
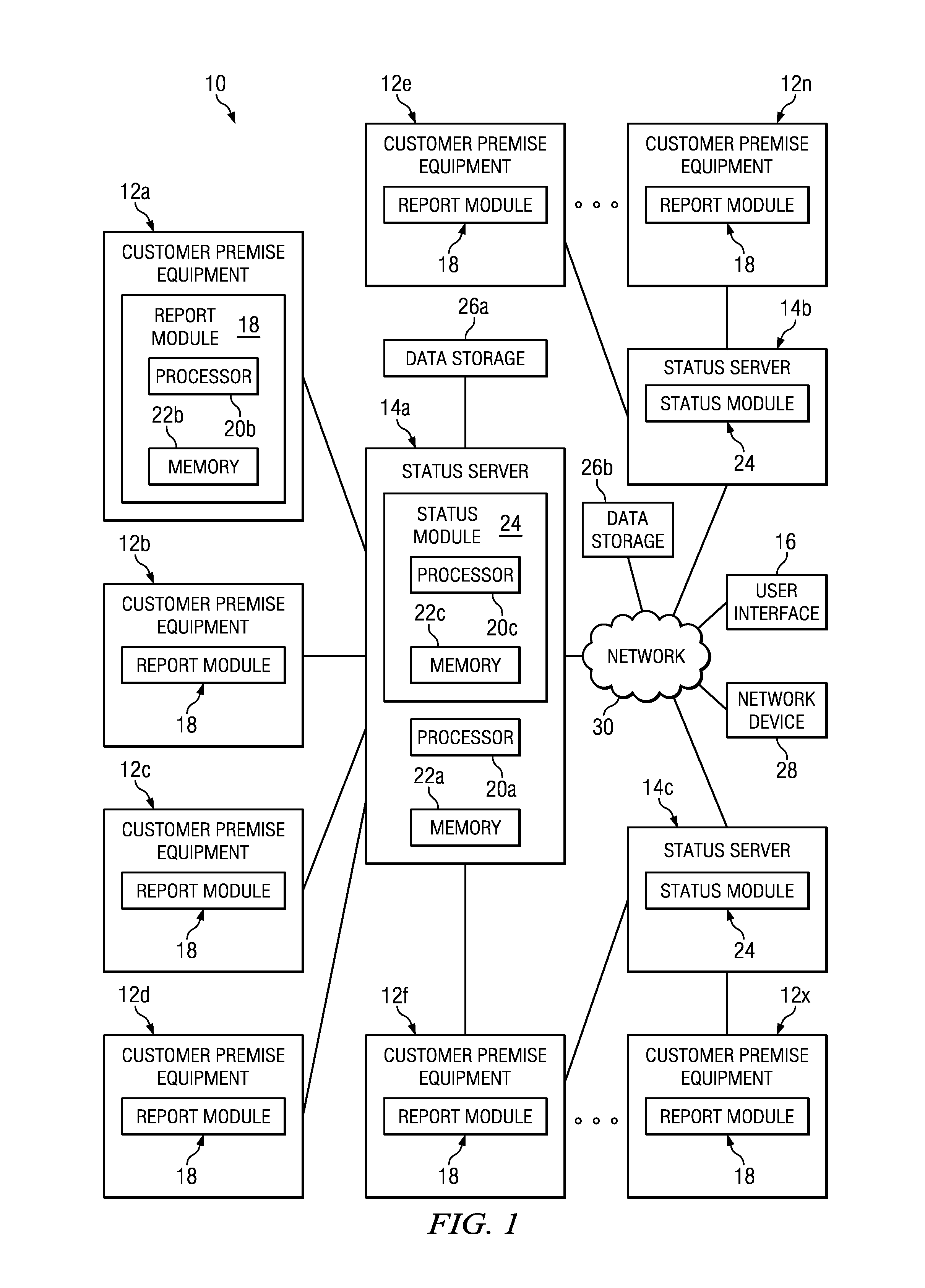
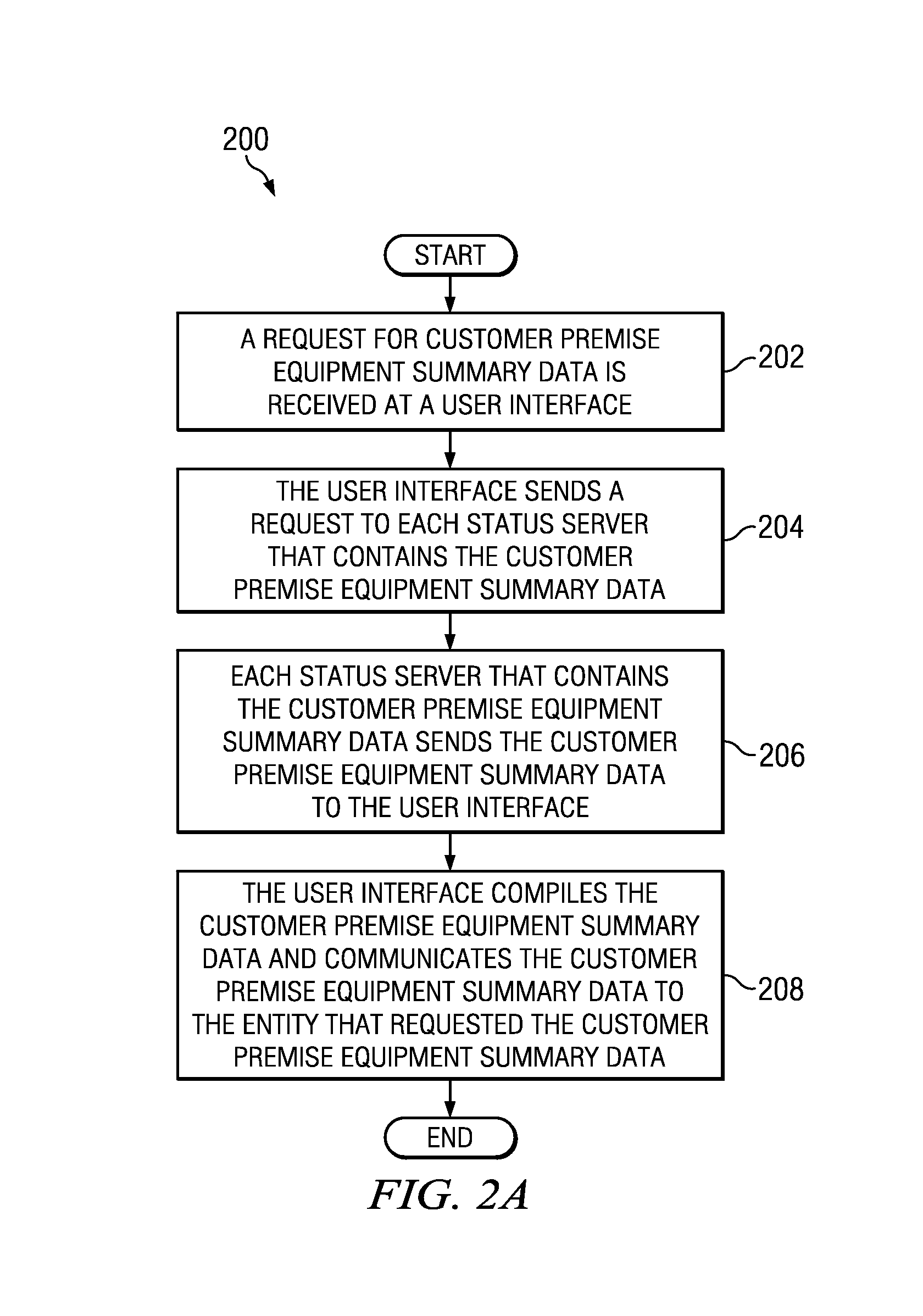
ActiveUS8843622B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDevice statusTransport Layer Security
A method is provided in one example and includes establishing a plurality of persistent connections with a plurality of devices at a server; receiving presence data associated with the plurality of devices; responding to heartbeat messages provided by the plurality of devices; receiving a status change notification from a particular one of the devices; and updating status data and heartbeat data for the particular one of the devices. In more particular embodiments, the method includes encoding messages communicated on the persistent connections using an extensible messaging and presence protocol (XMPP). The method may also include communicating script configuration data over a particular one of the persistent connections for execution by the particular device. The persistent connections may be secured using transport layer security (TLS).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for intelligent transport layer security
InactiveUS20170272470A1Accounting/billing servicesTelephonic communicationDomain nameComputer network
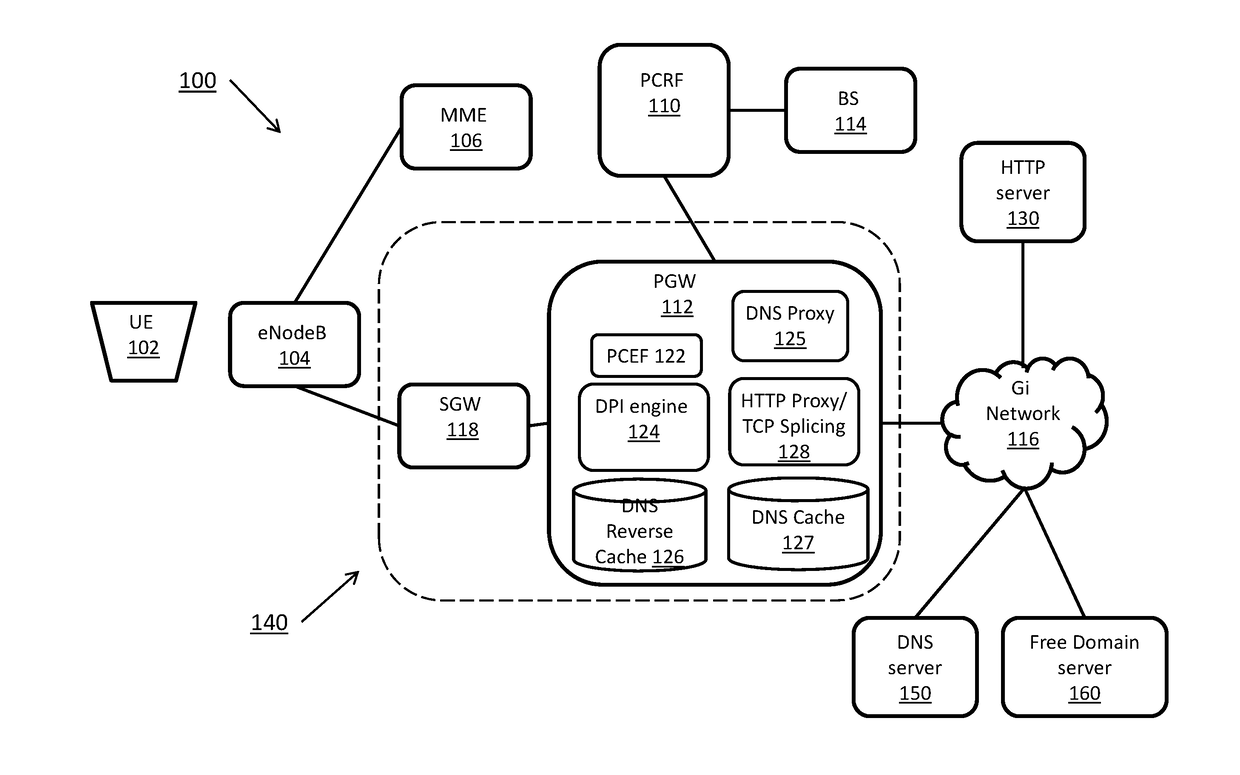
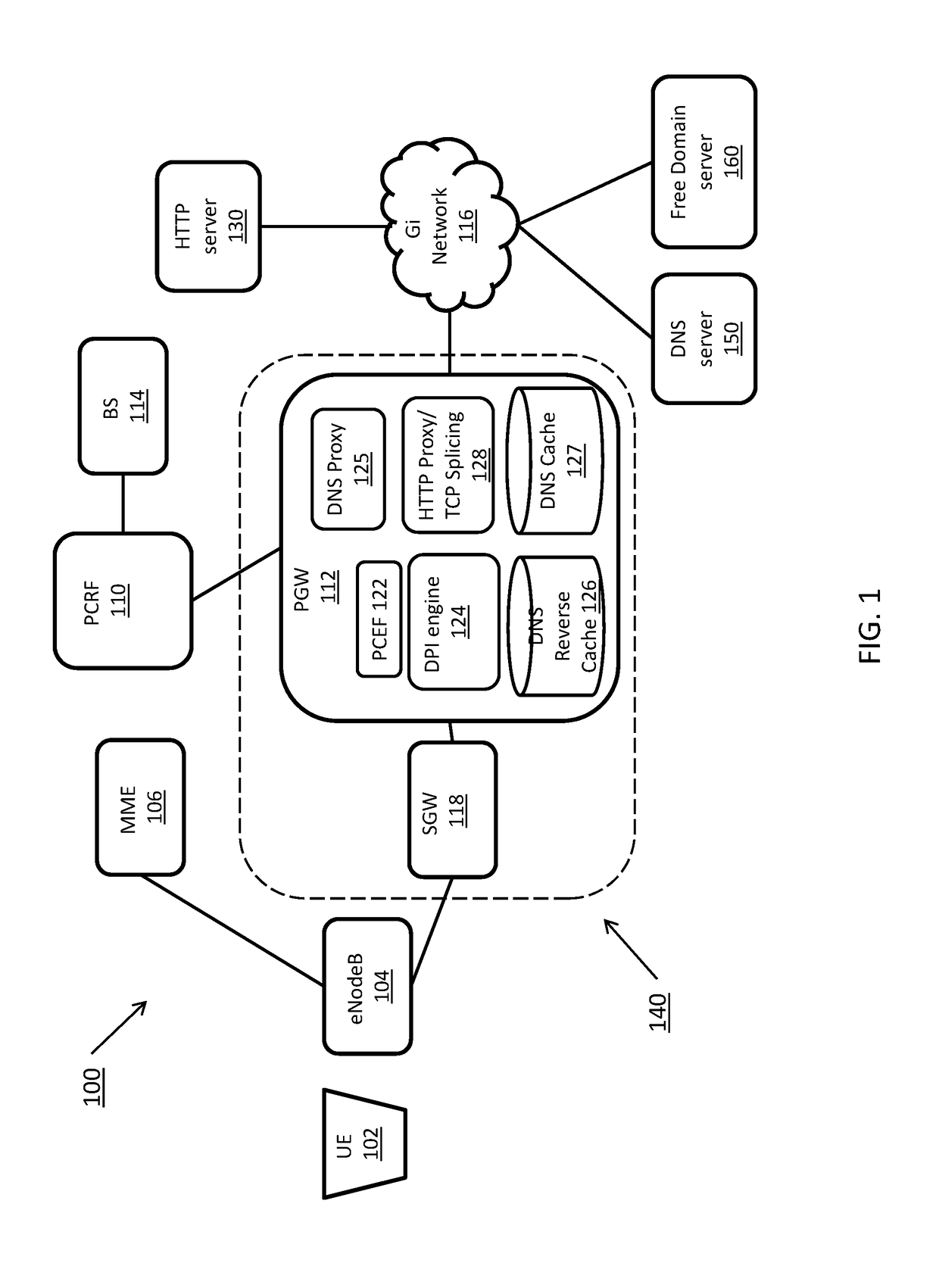
Systems and methods for detecting a domain name in a mobile network session for use in applying mobile policy and enforcement functions based on the domain name. A computing device receives a packet associated with a request from a user equipment to access a domain at a server. The computing device determines a traffic type associated with the packet, the traffic type including one of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) traffic, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) traffic, and non HTTP or HTTPS traffic. The computing device determines a domain name based on the traffic type and determines a service to apply to the packet based on the domain name.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and systems for generating encryption keys using random bit generators
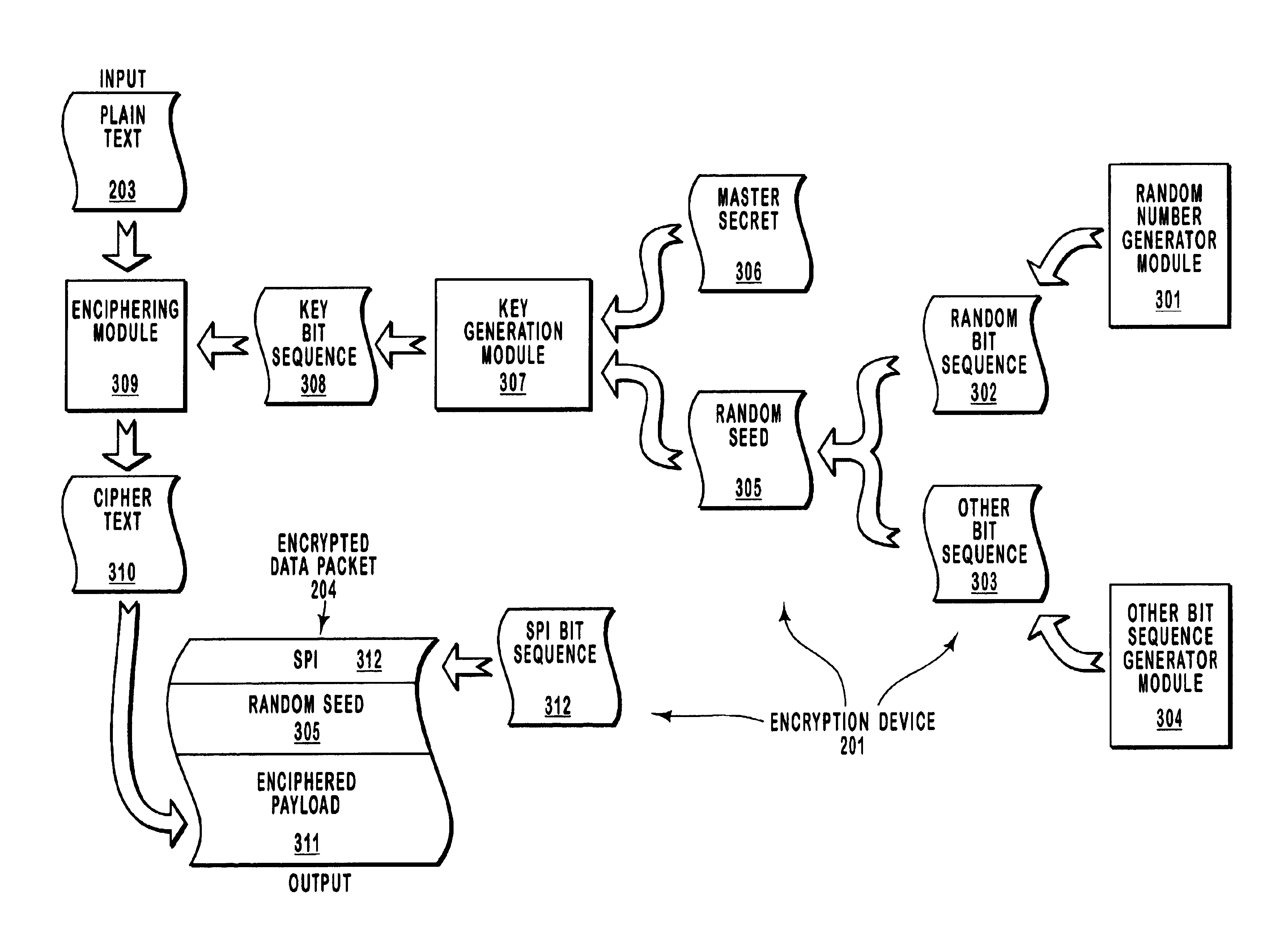
InactiveUS6931128B2Reduce rewardAvoid breakingKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationNetwork packetRandom seed
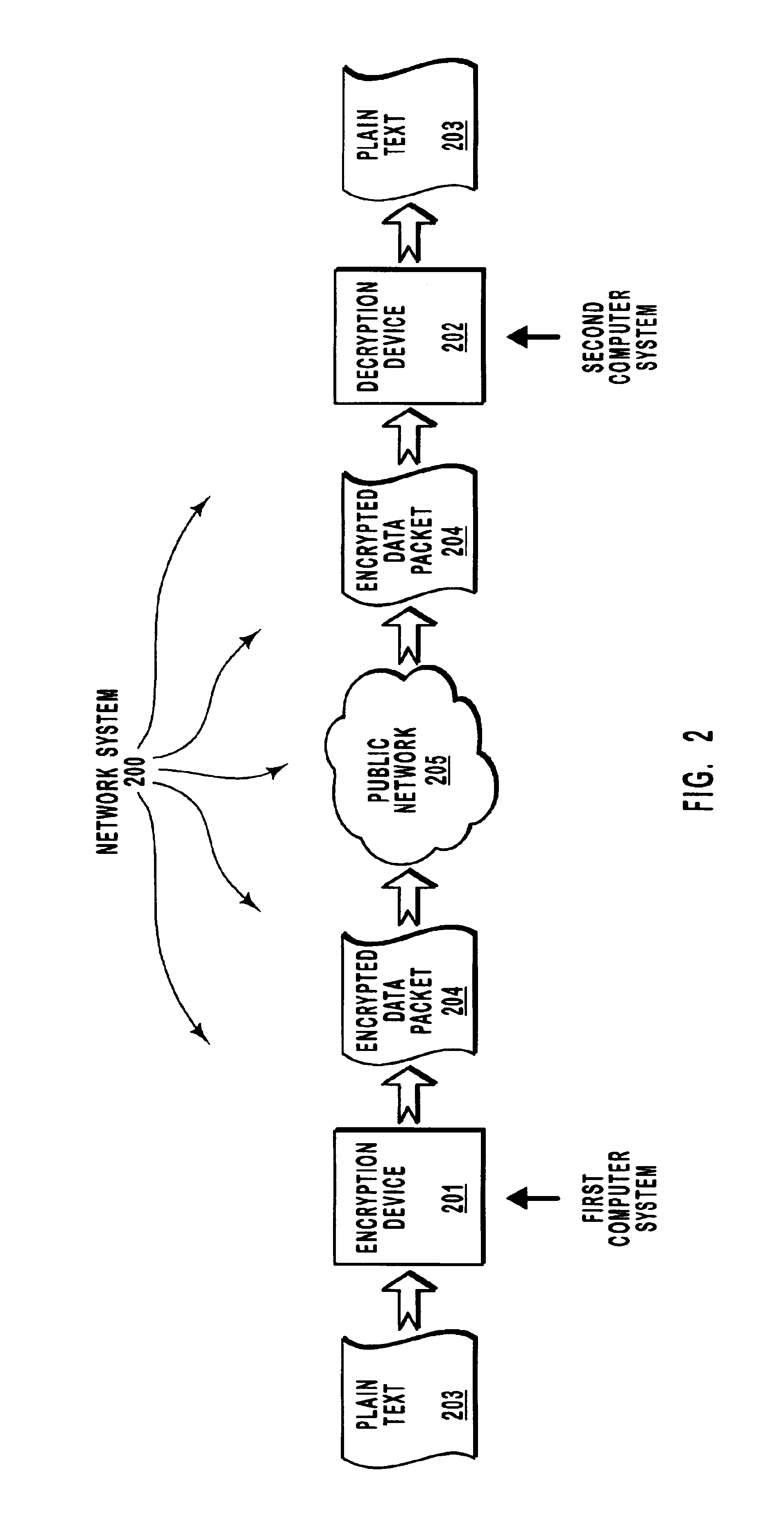
A security key, such as an encryption key, is generated so as to make it more difficult for eavesdroppers to identify the key. Specifically, a cryptographically secure random number generator generates a random bit sequence that is included in a seed. This random seed is provided along with a negotiated master secret to a key generation module. The key generation module may implement a pseudo random function that is in accordance with the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol or the Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) protocol. This key may then be used to encrypt a plain text message to form an encrypted data packet. The encrypted data packet also includes the random seed in unencrypted form. The encrypted data packet may be transmitted over a public network to a recipient with reduced risk of eavesdropping.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
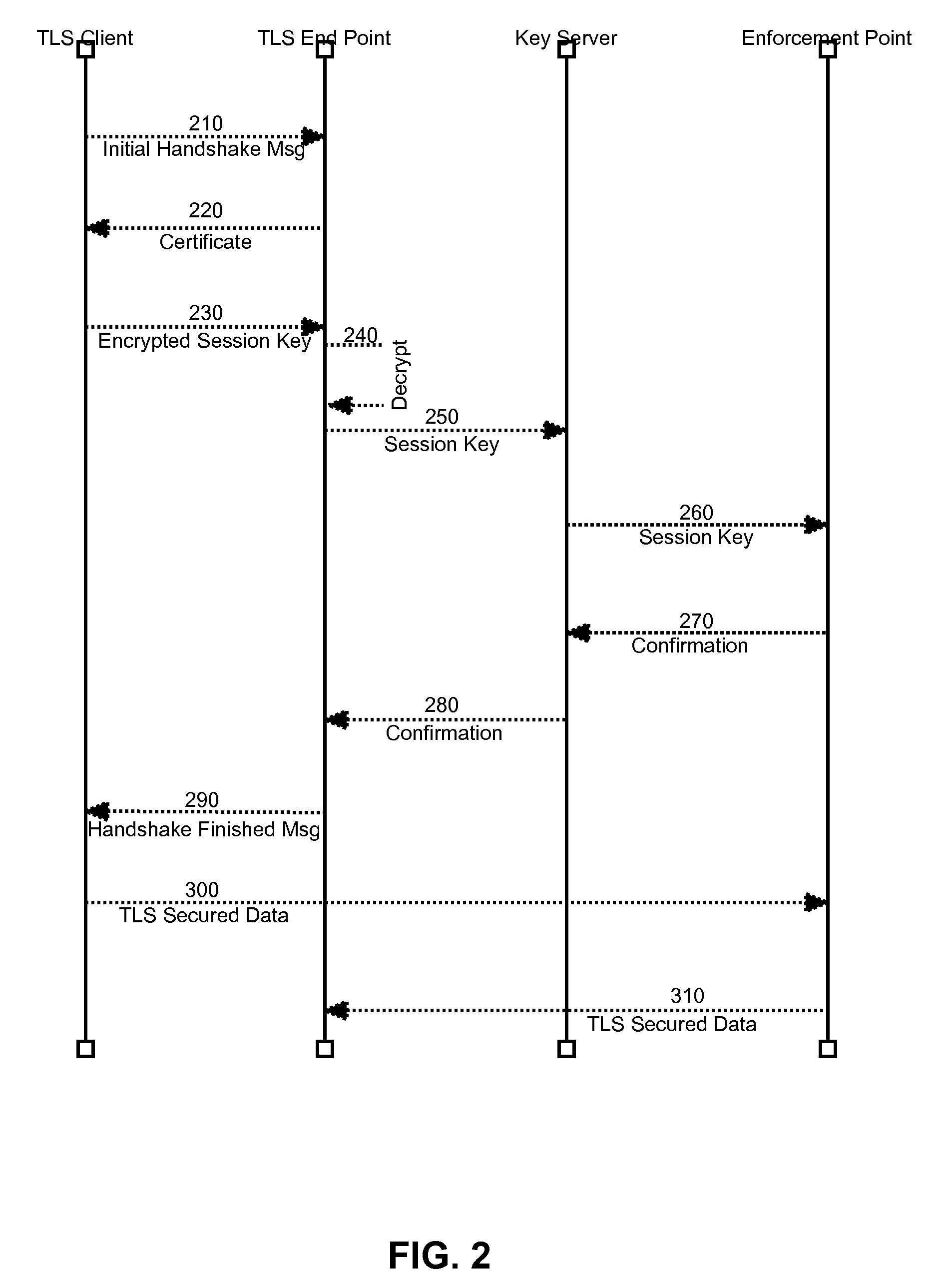
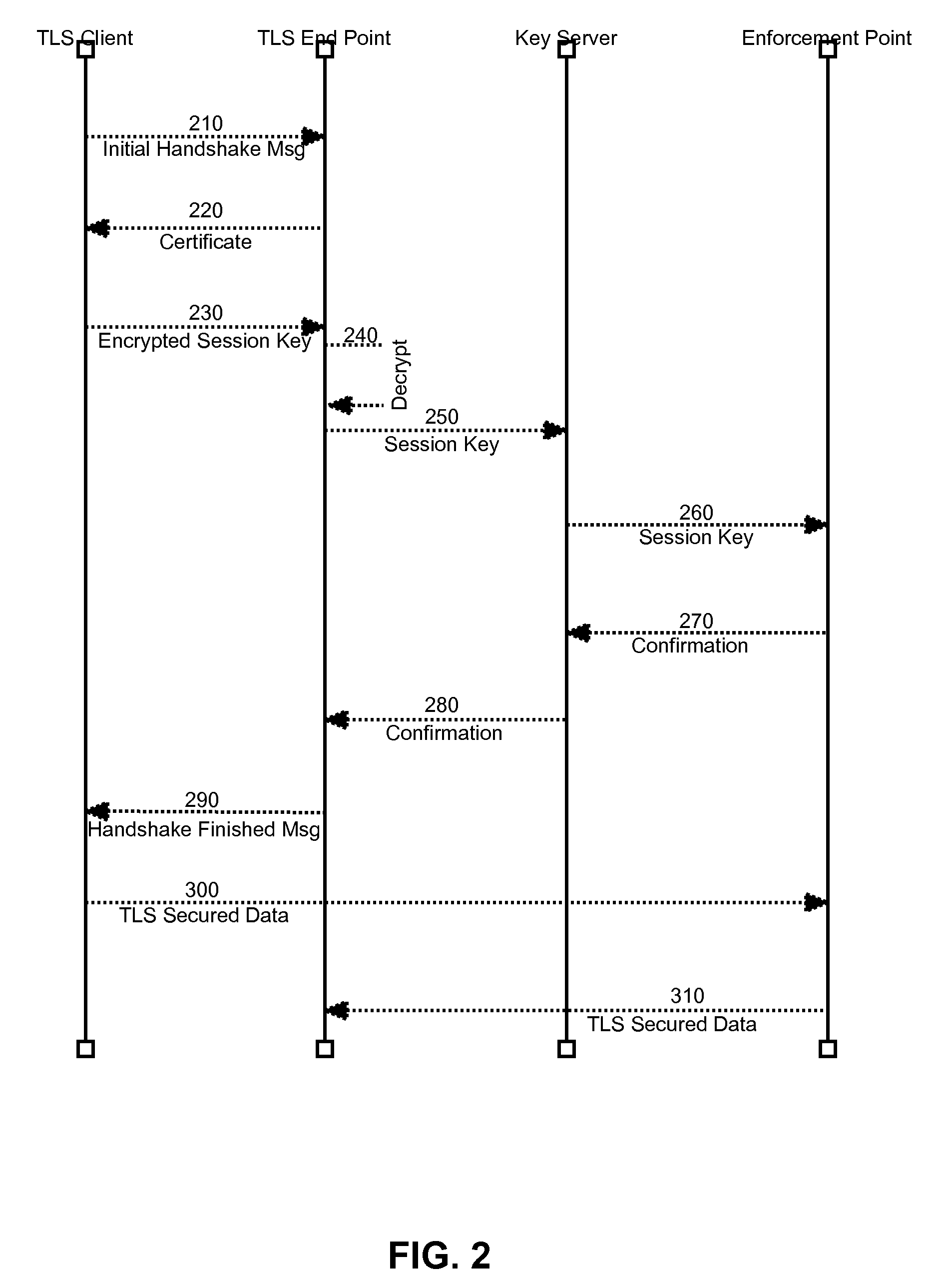
Secure sharing of transport layer security session keys with trusted enforcement points
InactiveUS20090025078A1Communication securityMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlSecure communicationOperability
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to security enforcement point operability in a TLS secured communications path and provide a novel and non-obvious method, system and computer program product for the secure sharing of TLS session keys with trusted enforcement points. In one embodiment of the invention, a method for securely sharing TLS session keys with trusted enforcement points can be provided. The method can include conducting a TLS handshake with a TLS client to extract and decrypt a session key for a TLS session with the TLS client traversing at least one security enforcement point. The method further can include providing the session key to a communicatively coupled key server for distribution to the at least one security enforcement point. Finally, the method can include engaging in secure communications with the TLS client over the TLS session.
Owner:IBM CORP
Policy-driven kernel-based security implementation
ActiveUS7246233B2Safe handlingTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsPlaintextSafe handling
Improvements in security processing are disclosed which enable security processing to be transparent to the application. Security processing (such as Secure Sockets Layer, or “SSL”, or Transport Layer Security, or “TLS”) is performed in (or controlled by) the stack. A decision to enable security processing on a connection can be based on configuration data or security policy, and can also be controlled using explicit enablement directives. Directives may also be provided for allowing applications to communicate with the security processing in the stack for other purposes. Functions within the protocol stack that need access to clear text can now be supported without loss of security processing capability. No modifications to application code, or in some cases only minor modifications (such as inclusion of code to invoke directives), are required to provide this security processing. Improved offloading of security processing is also disclosed, which provides processing efficiencies over prior art offloading techniques.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Method and system for locating partial discharge of electrical equipment
ActiveCN102662132AReduce computationImprove direction finding accuracyTesting dielectric strengthElectrical devicesGlobal optimization
A method for locating partial discharge of electrical equipment is used for detecting and locating partial discharge of the electrical equipment. The technical scheme includes the steps: firstly, using three ultrasonic array sensors to receive partial discharge ultrasonic signals at different positions of the electrical equipment and forming an array model; then, converting broadband signals received by the three ultrasonic array sensors into narrow-band signals by applying a TLS (transport layer security)-based broadband focus algorithm, and obtaining azimuth information of partial discharge sources according to a narrow-band direction-finding algorithm combining the phase matching principle and cloud optimization search; and finally, determining specific positions of electrical equipment partial discharge by means of a partial discharge source location algorithm based on global optimization search of a modified genetic algorithm. The invention simultaneously provides an improved system for locating partial discharge. Compared with a traditional method for locating partial discharge, the method has the advantages of small calculation amount, high direction-finding precision, accuracy in location, high convergence rate and the like, and the system for locating partial discharge is simple in structure, low in cost and high in location precision.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
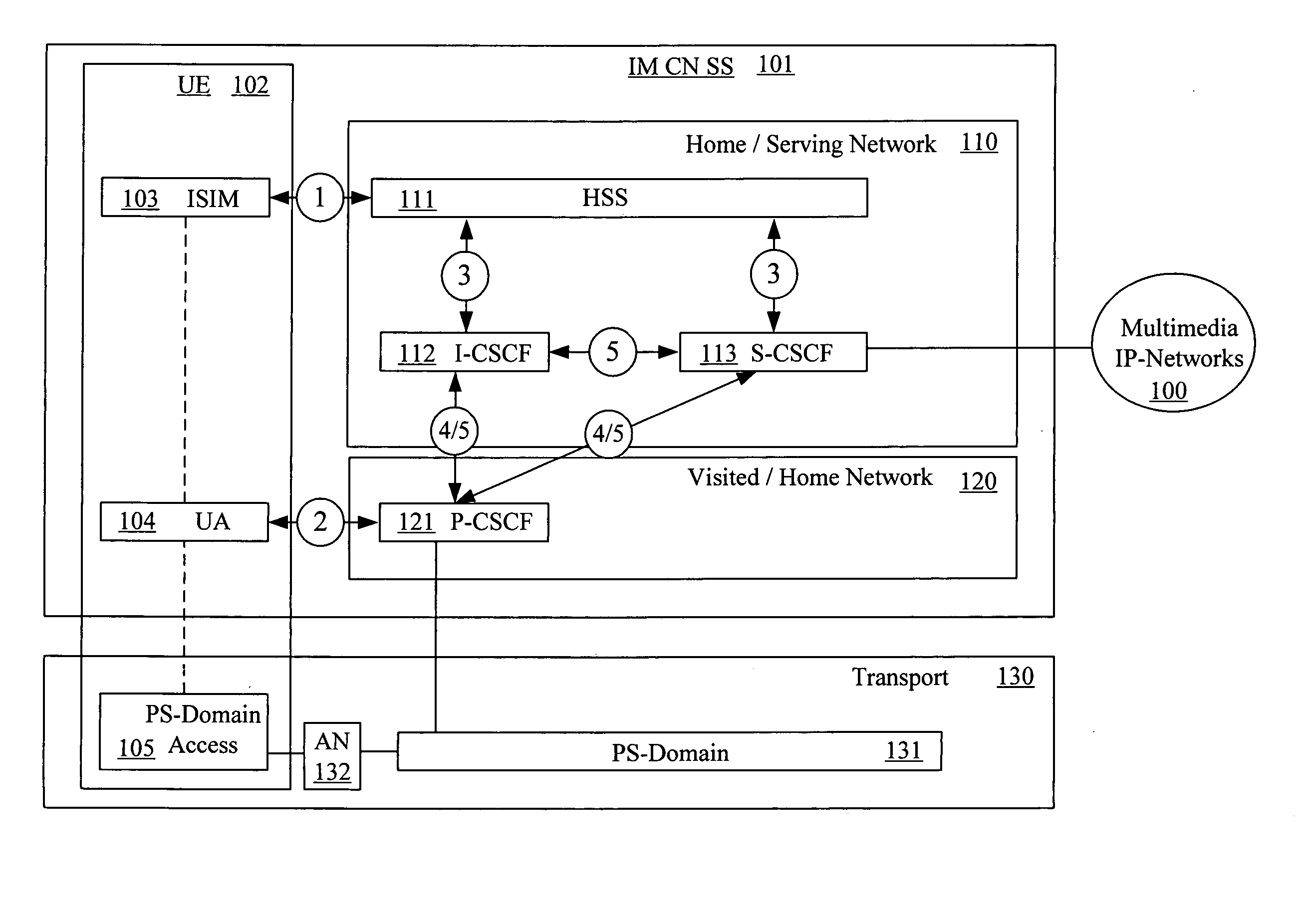
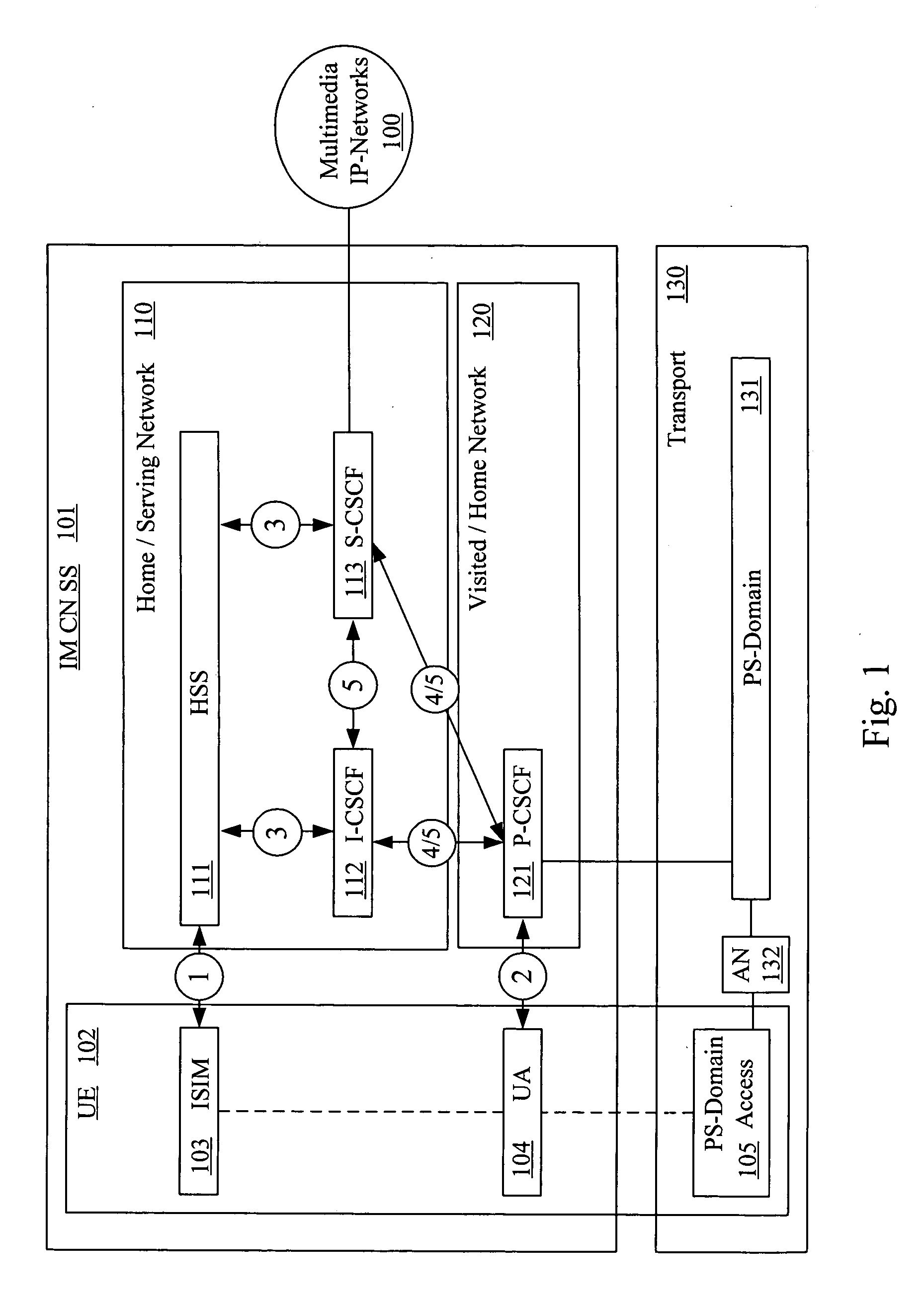
Handling of identities in a trust domain of an IP network
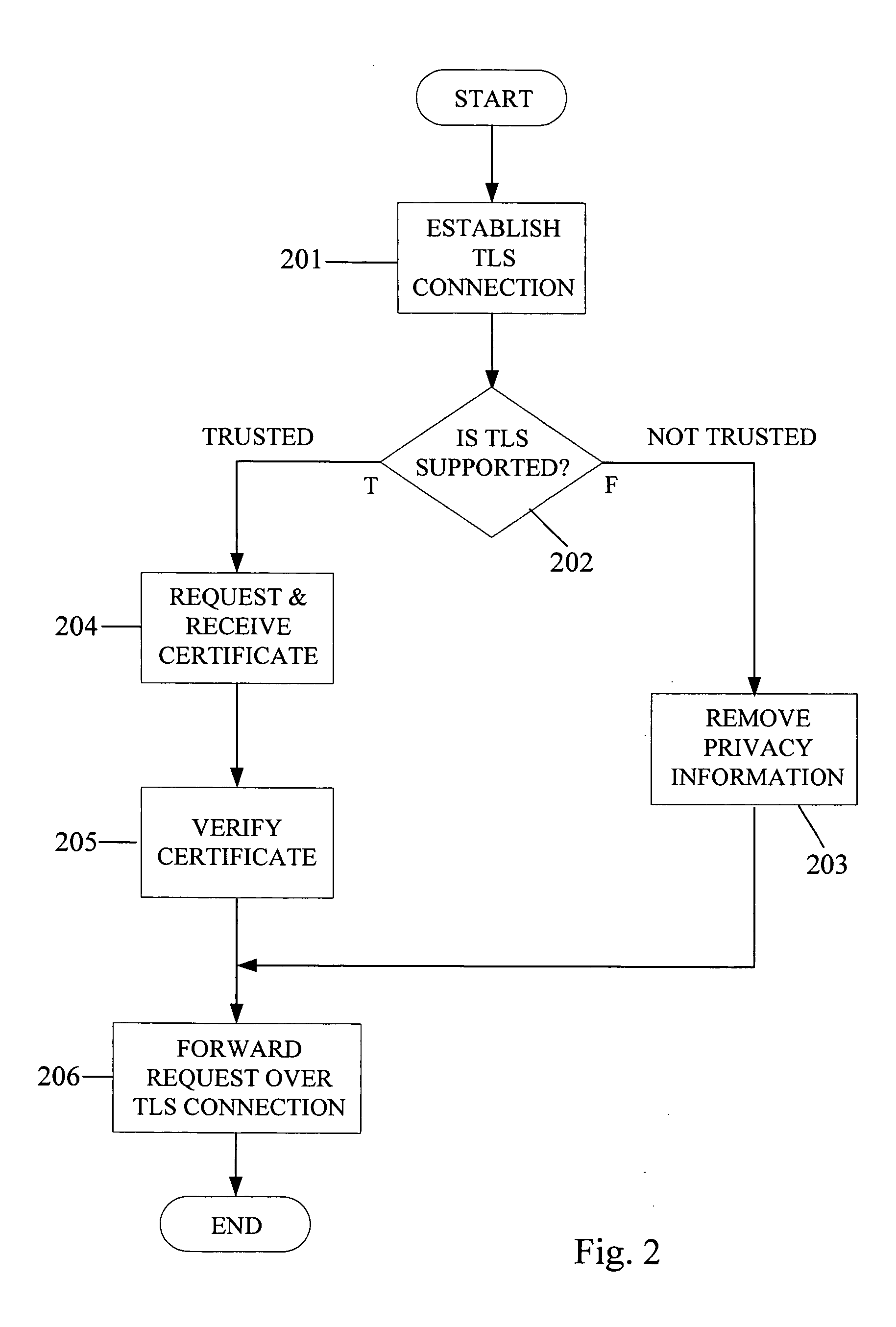
ActiveUS20050249219A1Data taking preventionUser identity/authority verificationSession Initiation ProtocolTransport Layer Security
A method for handling user identity and privacy, wherein a first Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) proxy is about to forward a SIP request to a next SIP proxy includes the step of determining whether Transport Layer Security (TLS) is supported in a hop to a next SIP proxy. When TLS is supported, the method includes establishing a TLS connection to the hop to the next SIP proxy, requesting a certificate from the next SIP proxy, receiving the certificate, verifying the certificate and trustworthiness of a network of the next SIP proxy and retaining identity information when the certificate and the trustworthiness of the network is verified. When TLS is not supported, or when the certificate is not verified, or when the trustworthiness of the network is not verified, the identity information is removed. Thereafter, the SIP request is forwarded over the TLS connection.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
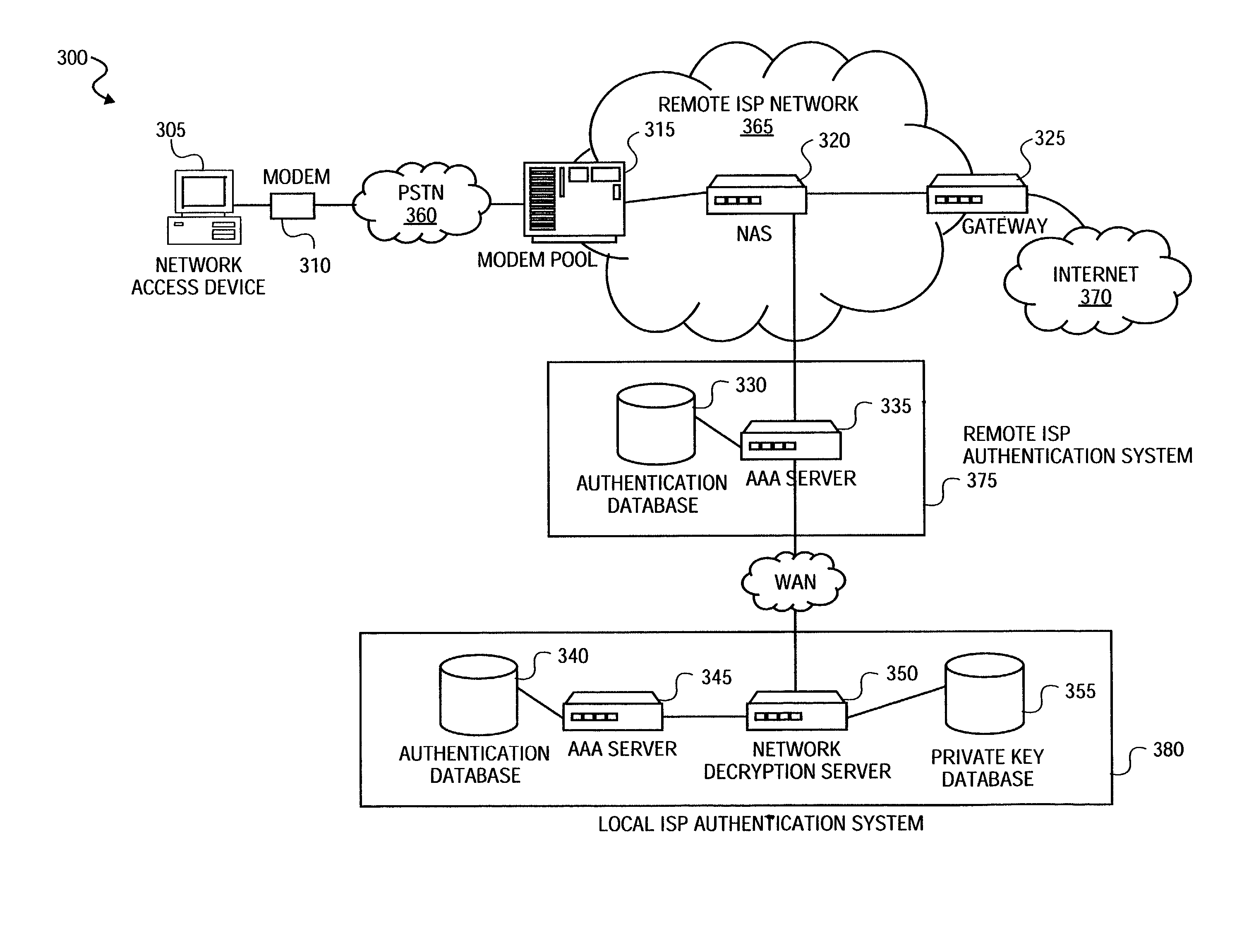
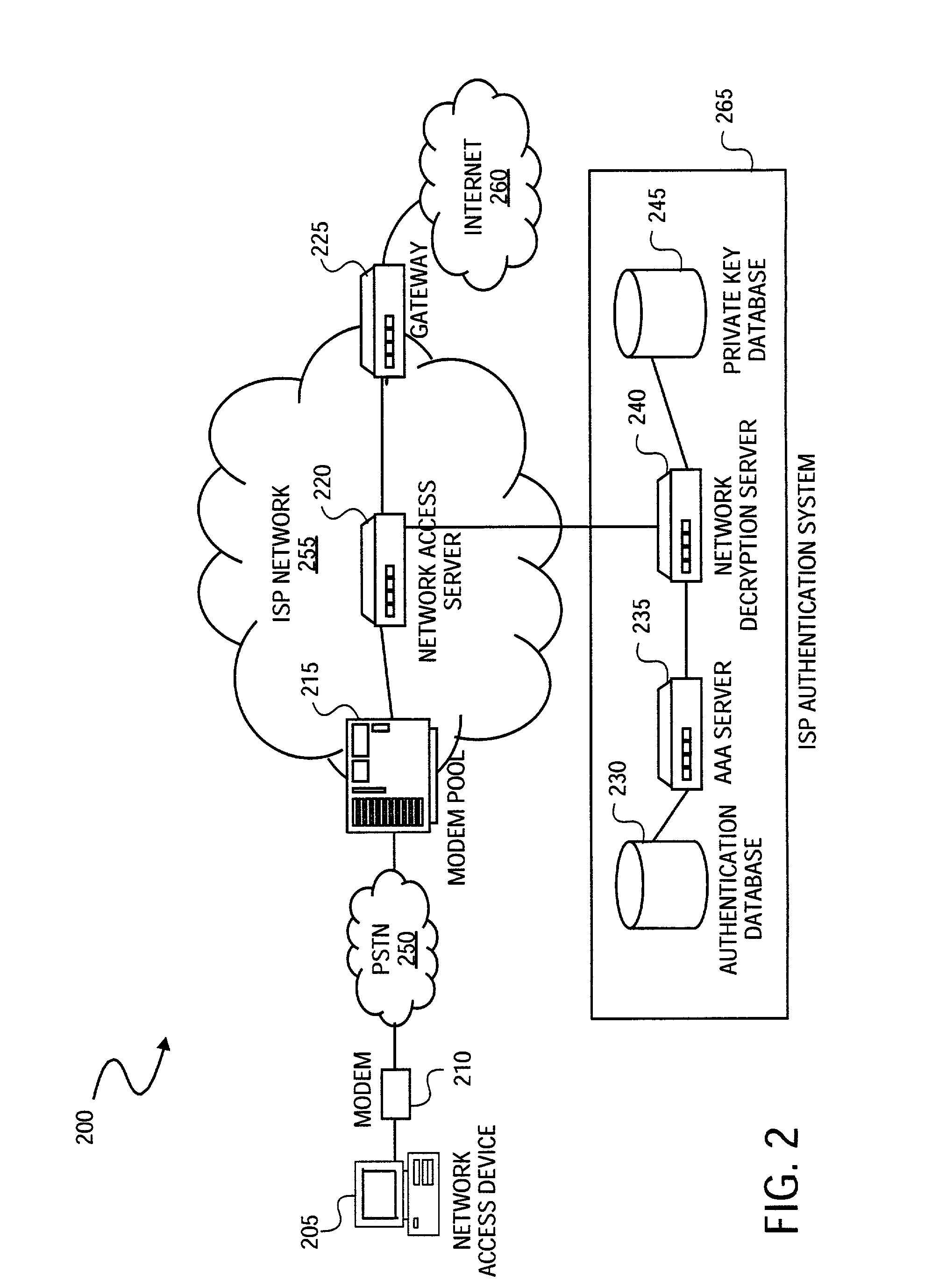
Method and system for securely authenticating network access credentials for users
InactiveUS7921290B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket LayerDirectory Access Protocol
A method is provided to securely authenticate user credentials. The method includes encrypting a user credential with a public key at an access device wherein the public key is part of a public / private key pair suitable for use with an encryption algorithm. The encrypted network user credential is transmitted from the access device to a decryption server where it is decrypted with a private key, the private key being part of the public / private key pair suitable for use with the encryption algorithm. The decrypted user credential is then transmitted from the decryption server to an authentication server for verification. The decryption server typically forms part of a multi-party service access environment including a plurality of access providers, the method including decrypting the user credential of a user proximate an access provider associated with the user credential. The method can be used in legacy protocols such as Point-to-Point protocol (PPP), Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP), Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) protocol, Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) protocol, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), NT Domain authentication protocol, Unix password authentication protocol, HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP), HyperText Transfer Protocol over Secure sockets layer (HTTPS), Extended Authentication Protocol (EAP), Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, Token Ring protocol and / or Secure Remote Password protocol (SRP).
Owner:CHANNEL IP BV
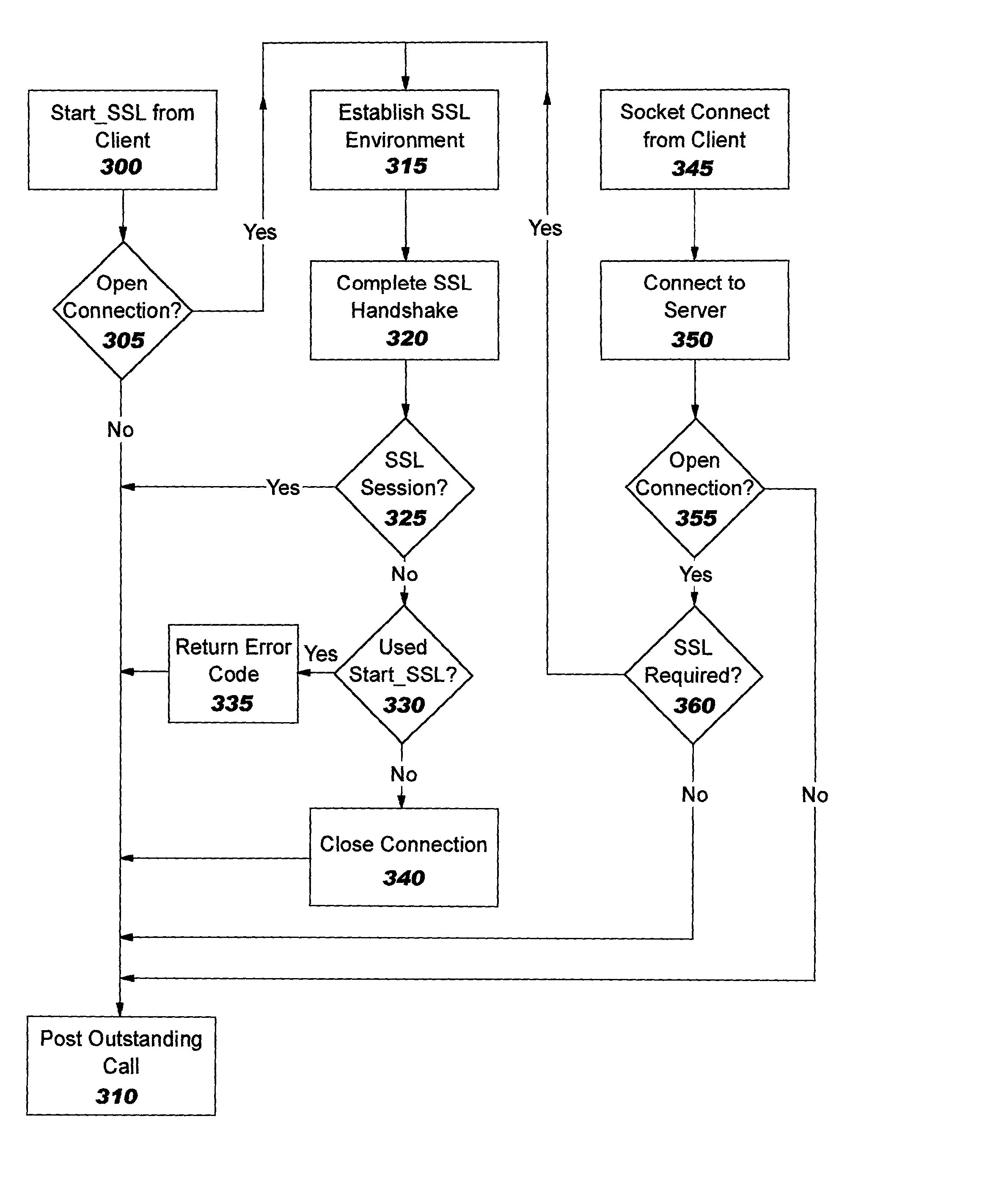
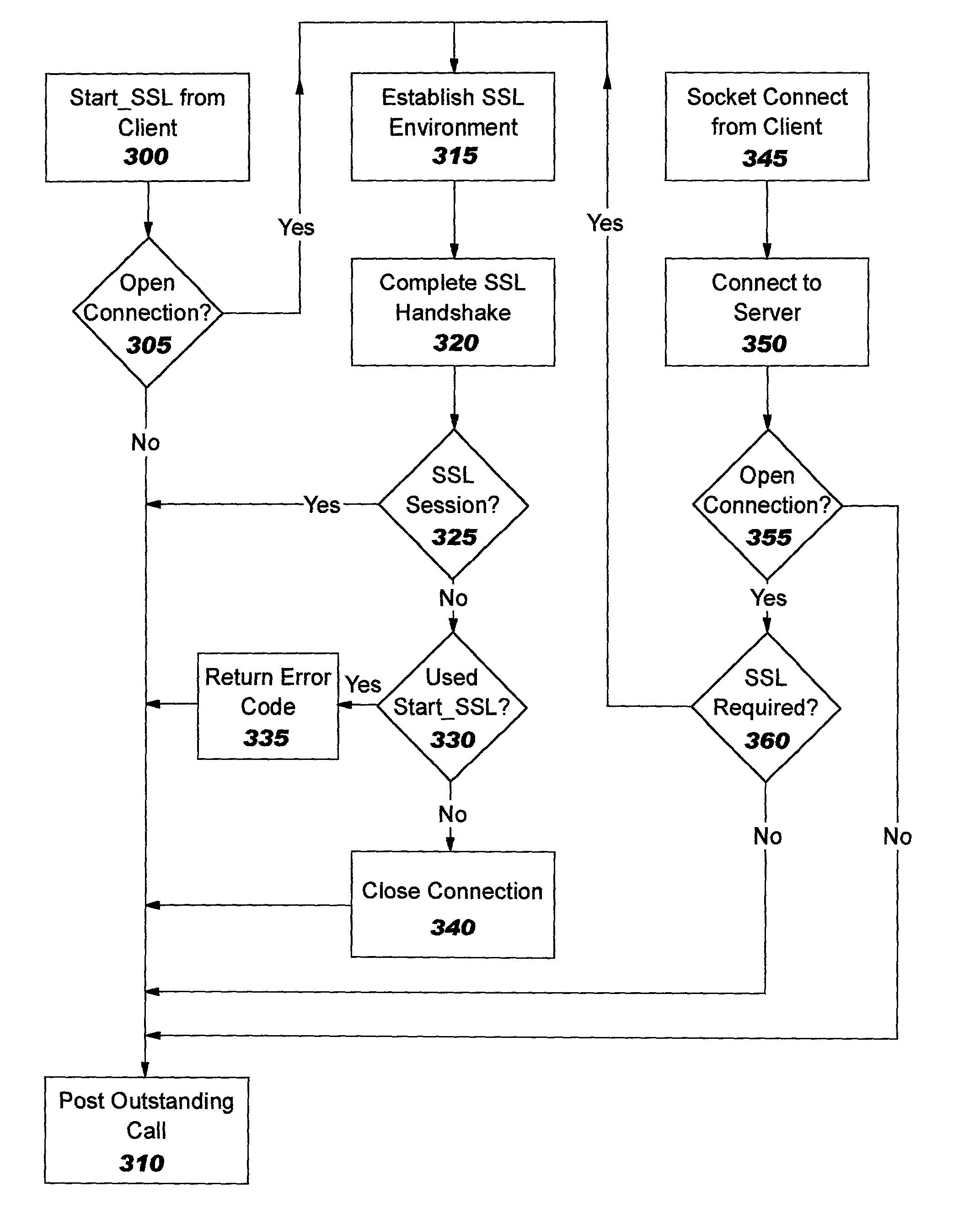
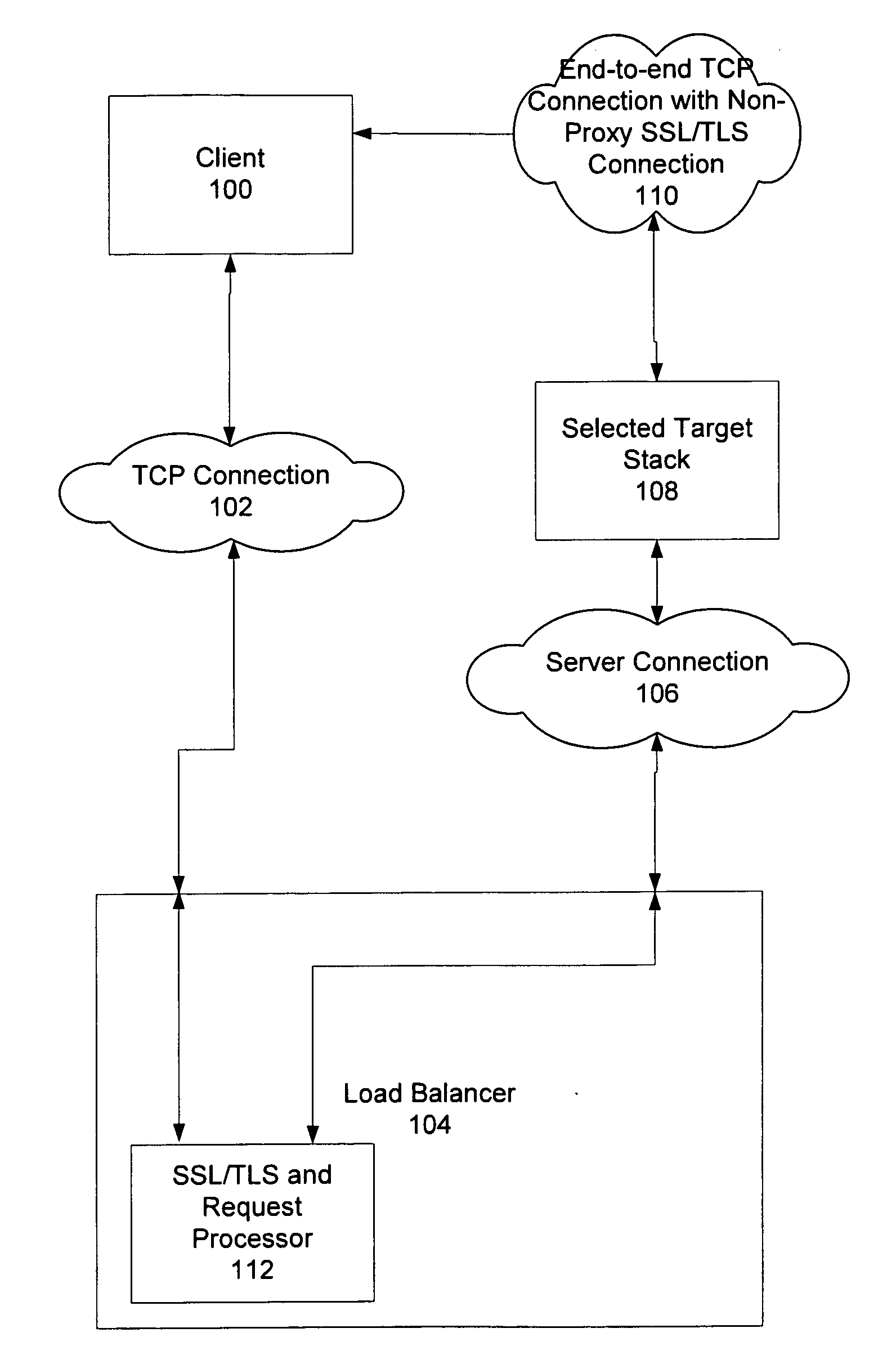
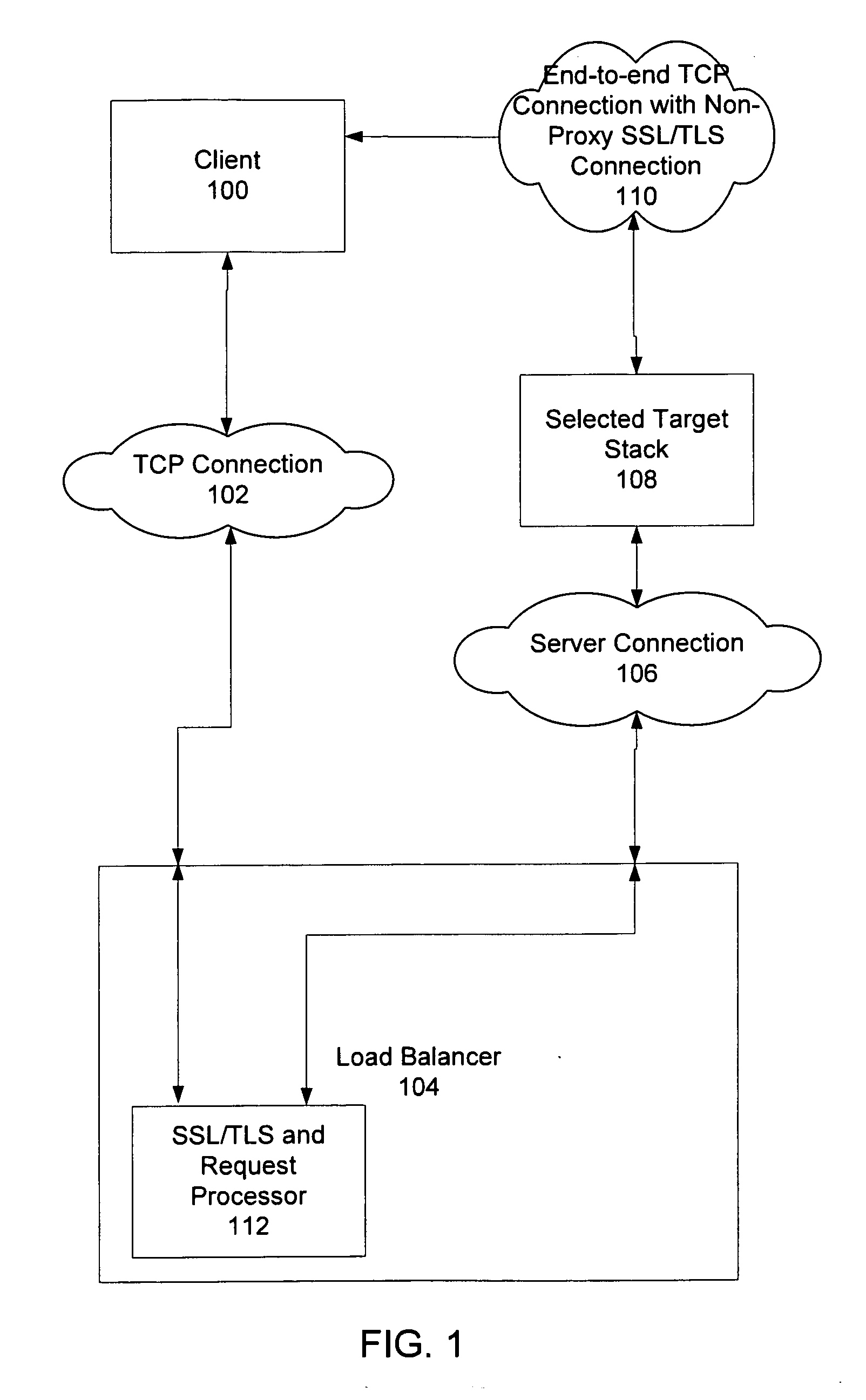
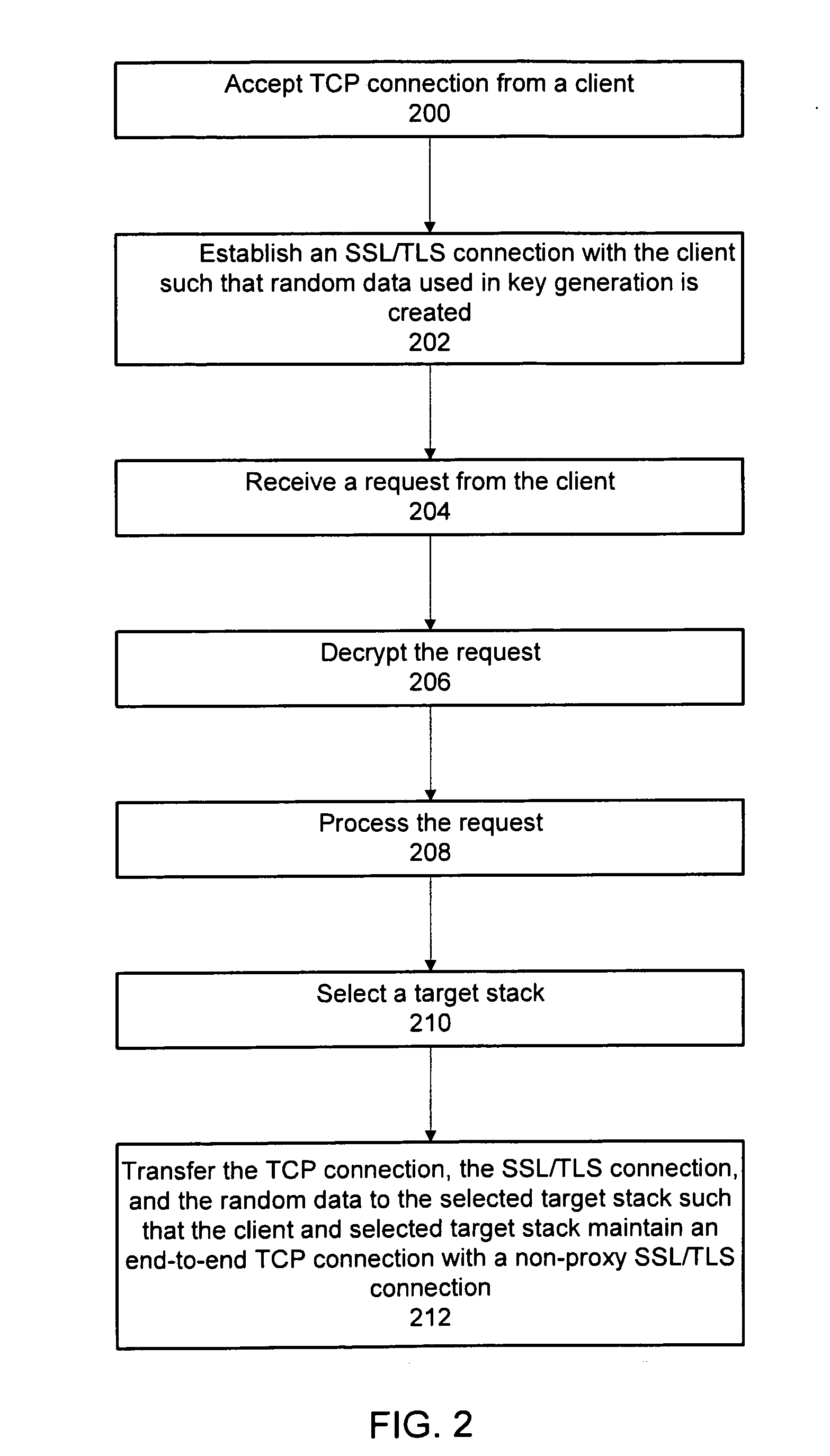
Method and system for providing non-proxy tls/ssl support in a content-based load balancer
Methods and systems for providing non-proxy Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security (SSL / TLS) support in a content-based load balancer are described. A Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection is accepted from a client, and an SSL / TLS connection is established with the client such that random data used in key generation is created. A request is received from the client, and the request is decrypted. The request is processed, a target stack is selected, and the TCP connection, the SSL / TLS connection, and the random data are transferred to the selected target stack such that the client and selected target stack maintain an end-to-end TCP connection with a non-proxy SSL / TLS connection.
Owner:IBM CORP
Content-based transport security
InactiveUS20150222424A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputerized systemRemote computer
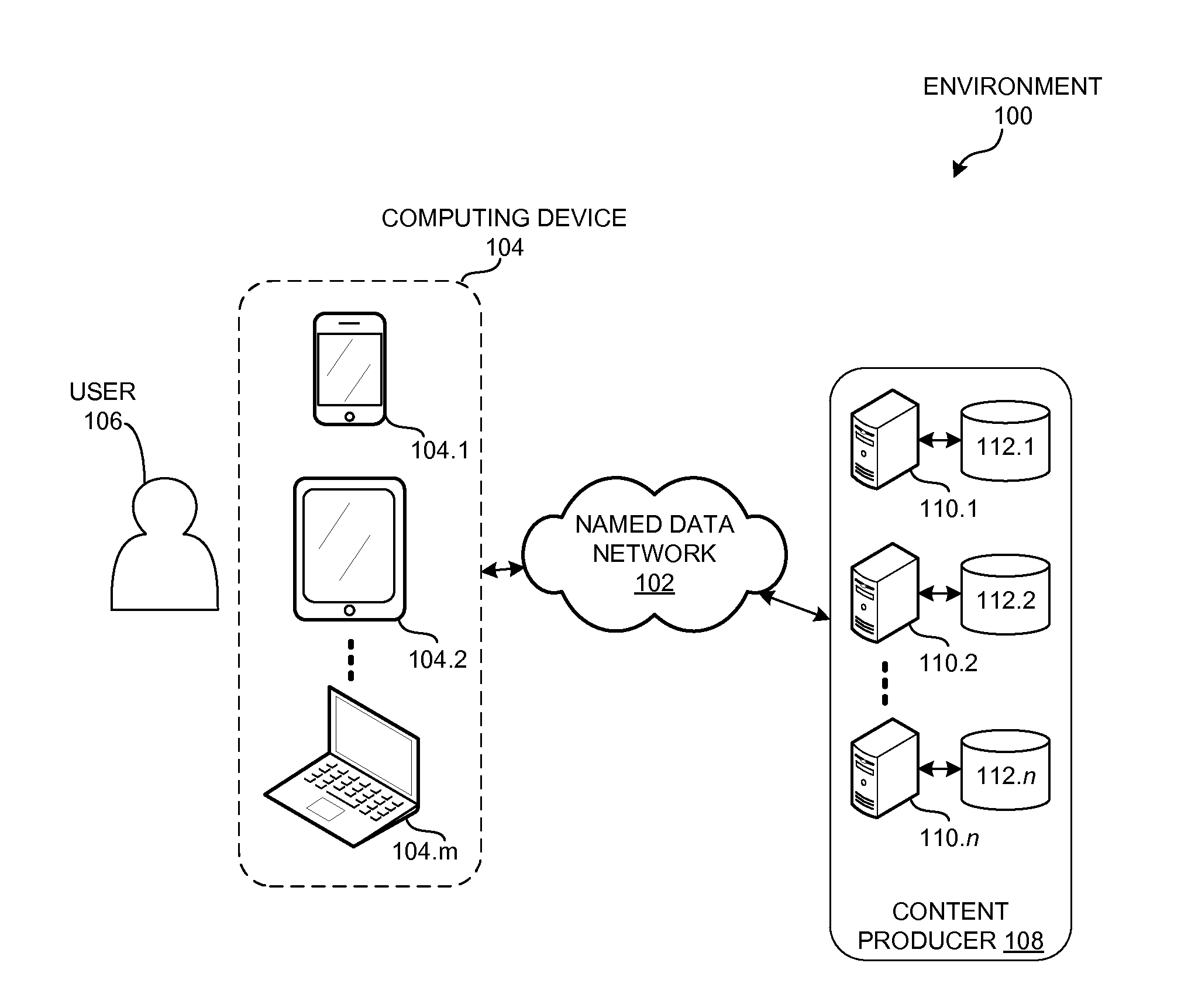
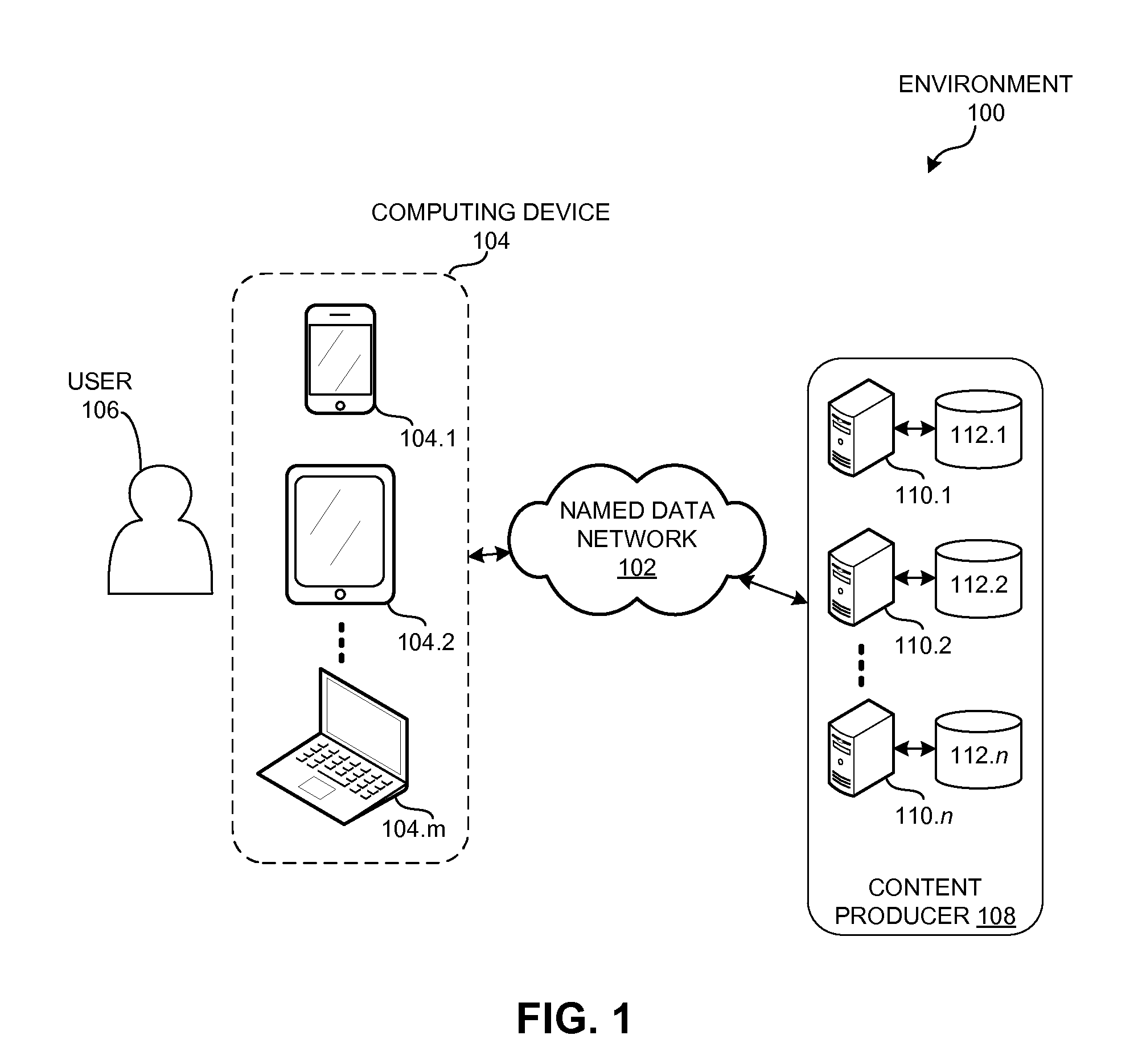
A computer system can send a secure request over a named-data network to a remote device by generating an Interest with encrypted name components. During operation, the computer system can receive or obtain a request for data, such as from a local user or from a local application. If the system cannot satisfy the request locally, the system can determine at least a routable prefix and a name suffix associated with the request. The system can generate the secure Interest for the request by determining an encryption key that corresponds to a session with the remote computer system, and encrypts the name suffix using the session encryption key. The system then generates an Interest whose name includes the routable prefix and the encrypted name suffix, and disseminates the Interest over a named-data network to send the request to the remote computer system.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Offload Processing for Secure Data Transfer
InactiveUS20080216150A1Safe handlingComputer security arrangementsTransmissionApplication softwareSafe handling
Improvements in security processing are disclosed which enable security processing to be transparent to the application. Security processing (such as Secure Sockets Layer, or “SSL”, or Transport Layer Security, or “TLS”) is performed in (or controlled by) the stack. A decision to enable security processing on a connection can be based on configuration data or security policy, and can also be controlled using explicit enablement directives. Directives may also be provided for allowing applications to communicate with the security processing in the stack for other purposes. Functions within the protocol stack that need access to clear text can now be supported without loss of security processing capability. No modifications to application code, or in some cases only minor modifications (such as inclusion of code to invoke directives), are required to provide this security processing. Improved offloading of security processing is also disclosed, which provides processing efficiencies over prior art offloading techniques. Offload components can be controlled from the kernel, an SSL layer or an application.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for managing network identity
A method and a system for managing network identity are provided. The method and the system realize a management mechanism of temporary identification (ID) and real ID, which simultaneously achieves functionalities such as anonymity, accounting, and authorization. A short-term certificate and a corresponding public / private key pair are used to protect a temporary ID usable for accounting. This protection prevents the temporary ID from theft. The user generates a digital signature in the reply to a charge schedule statement from the visited network. This procedure is incorporated into an existing authentication framework based on Transport Layer Security (TLS) in order to provide an undeniable payment mechanism. The payment mechanism is applicable in an environment of multiple network operators and reduces the difficulty of integrating network operators. The method and the system do not have to consult a certificate revocation list (CRL) for authentication and thus are able to shorten authentication time.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Offload Processing for Secure Data Transfer
Improvements in security processing are disclosed which enable security processing to be transparent to the application. Security processing (such as Secure Sockets Layer, or “SSL”, or Transport Layer Security, or “TLS”) is performed in (or controlled by) the stack. A decision to enable security processing on a connection can be based on configuration data or security policy, and can also be controlled using explicit enablement directives. Directives may also be provided for allowing applications to communicate with the security processing in the stack for other purposes. Functions within the protocol stack that need access to clear text can now be supported without loss of security processing capability. No modifications to application code, or in some cases only minor modifications (such as inclusion of code to invoke directives), are required to provide this security processing. Improved offloading of security processing is also disclosed, which provides processing efficiencies over prior art offloading techniques. Offload components can be controlled from the kernel, an SSL layer or an application.
Owner:IBM CORP
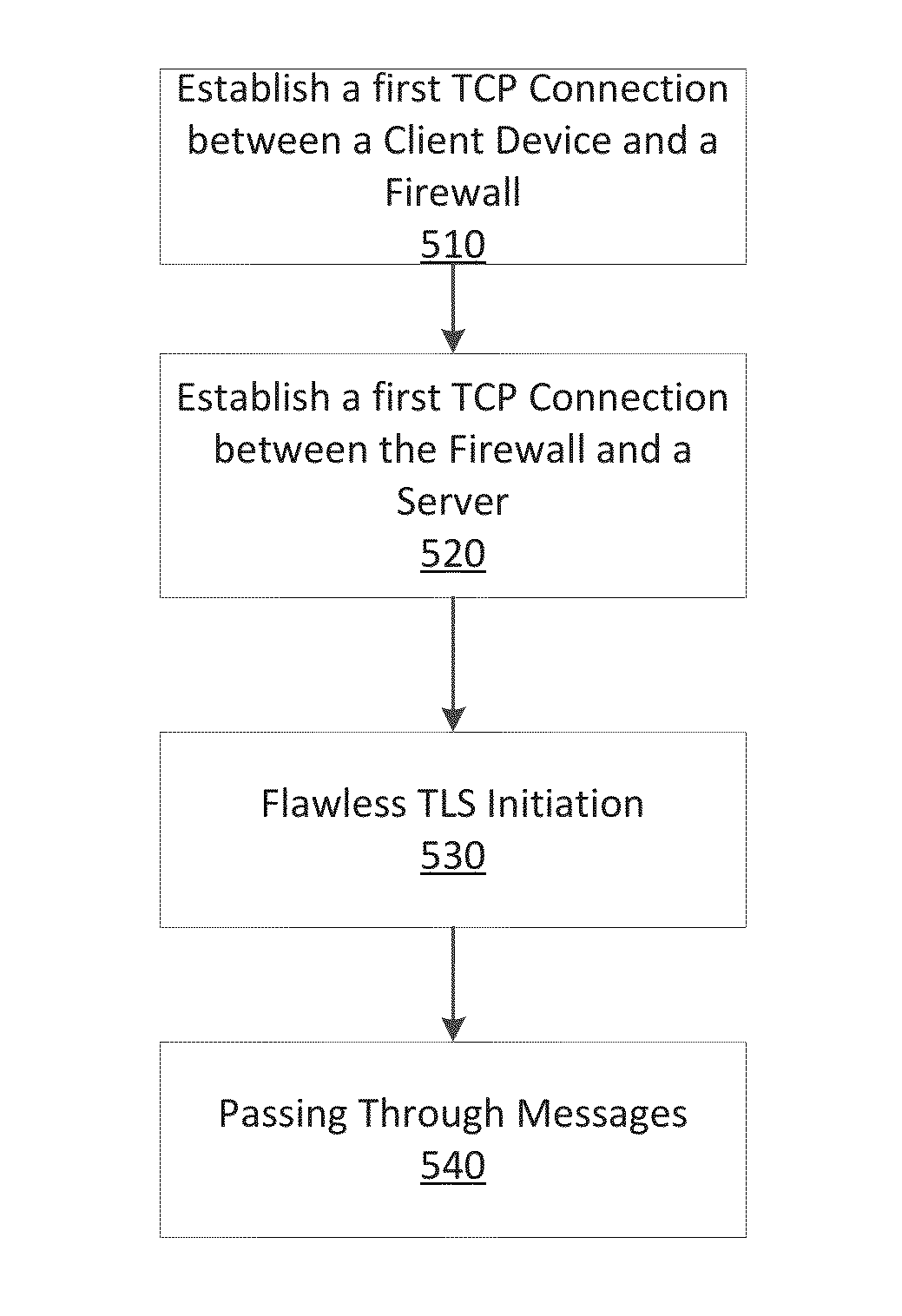
Dynamic bypass of tls connections matching exclusion list in dpi-ssl in a NAT deployment
The present invention provides the initiation of a transport layer security (TLS) session between a client device and a server using a firewall without interruption. The present invention holds a TLS hello message received from the client device until after the server has been validated. A firewall consistent with the present invention does not interrupt a transport layer control (TCP) connection that was established between the client device and the firewall before the TLS hello message was received by the firewall.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Authentication and secure transmission of data between signature devices and host computers using transport layer security
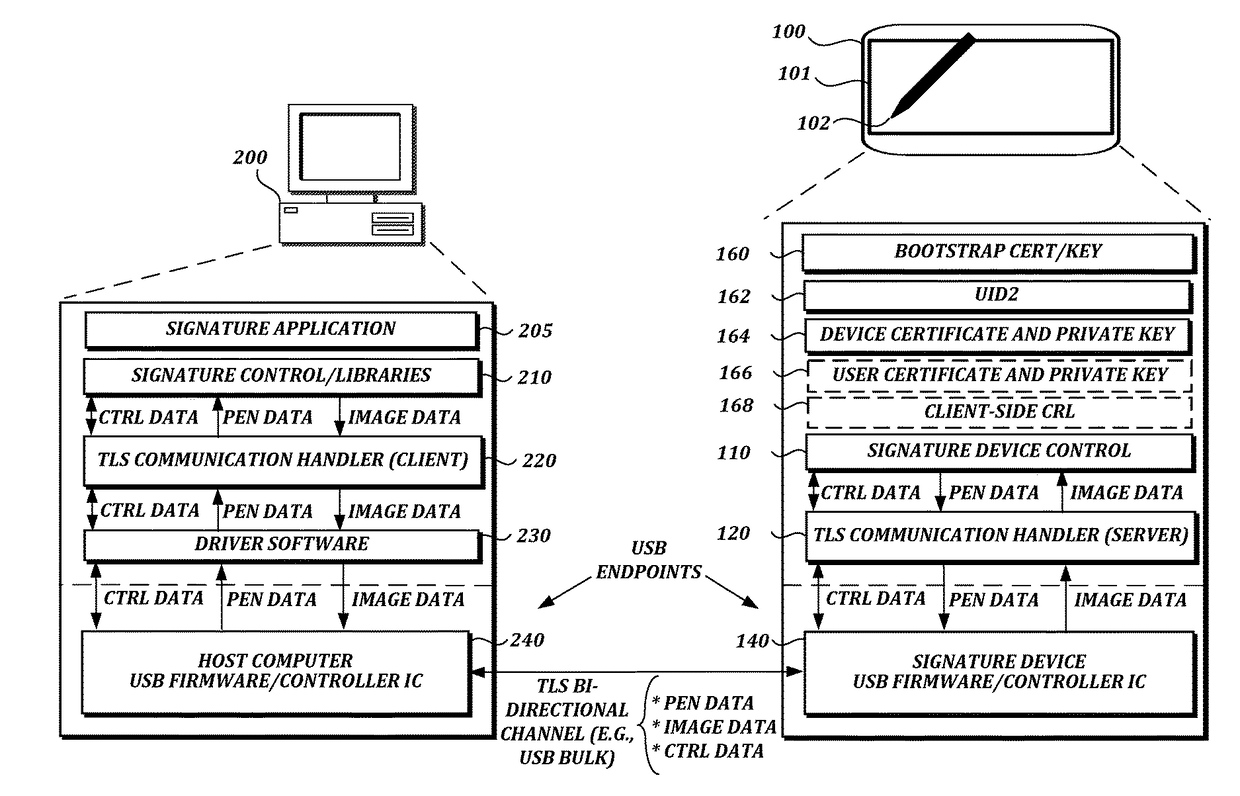
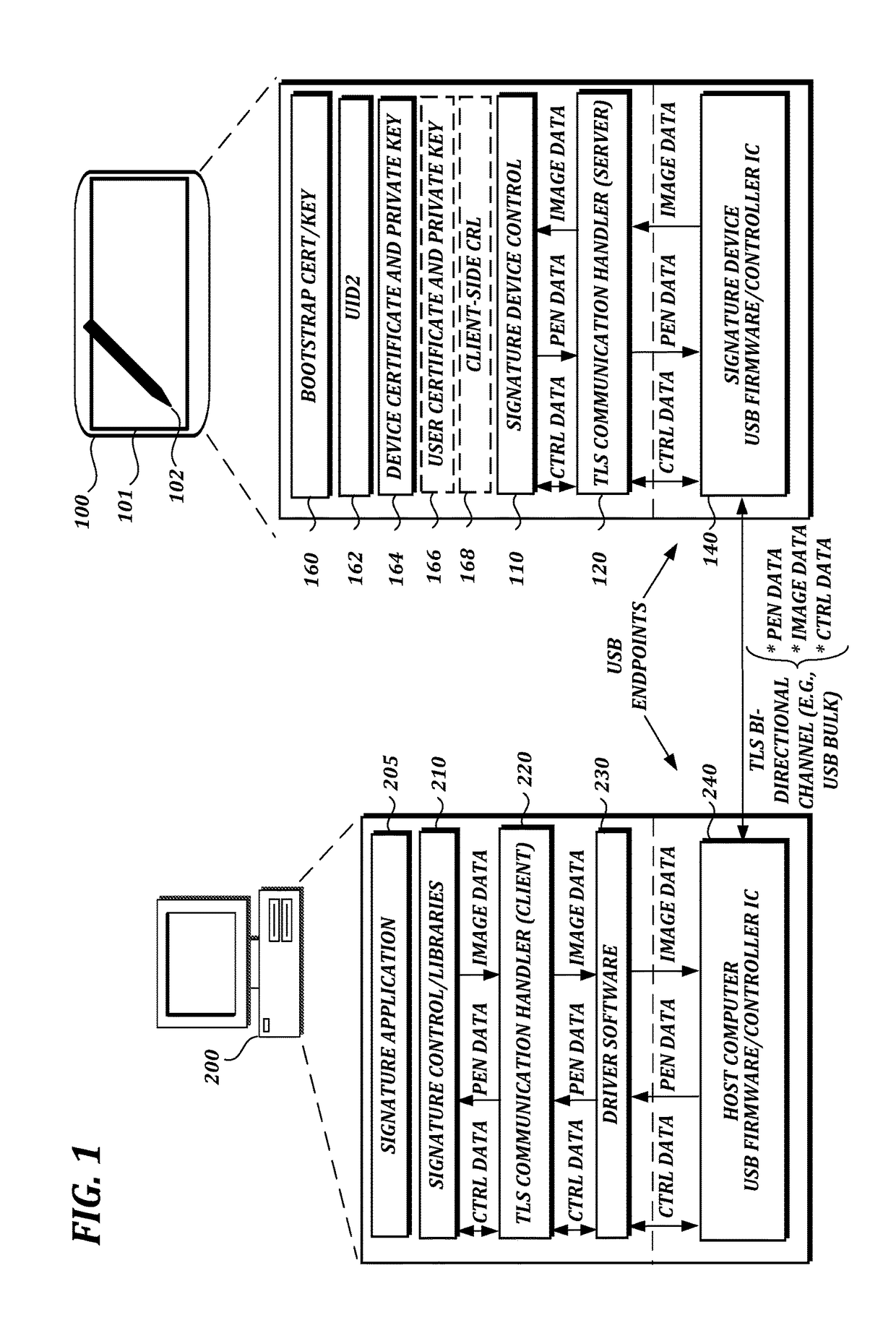
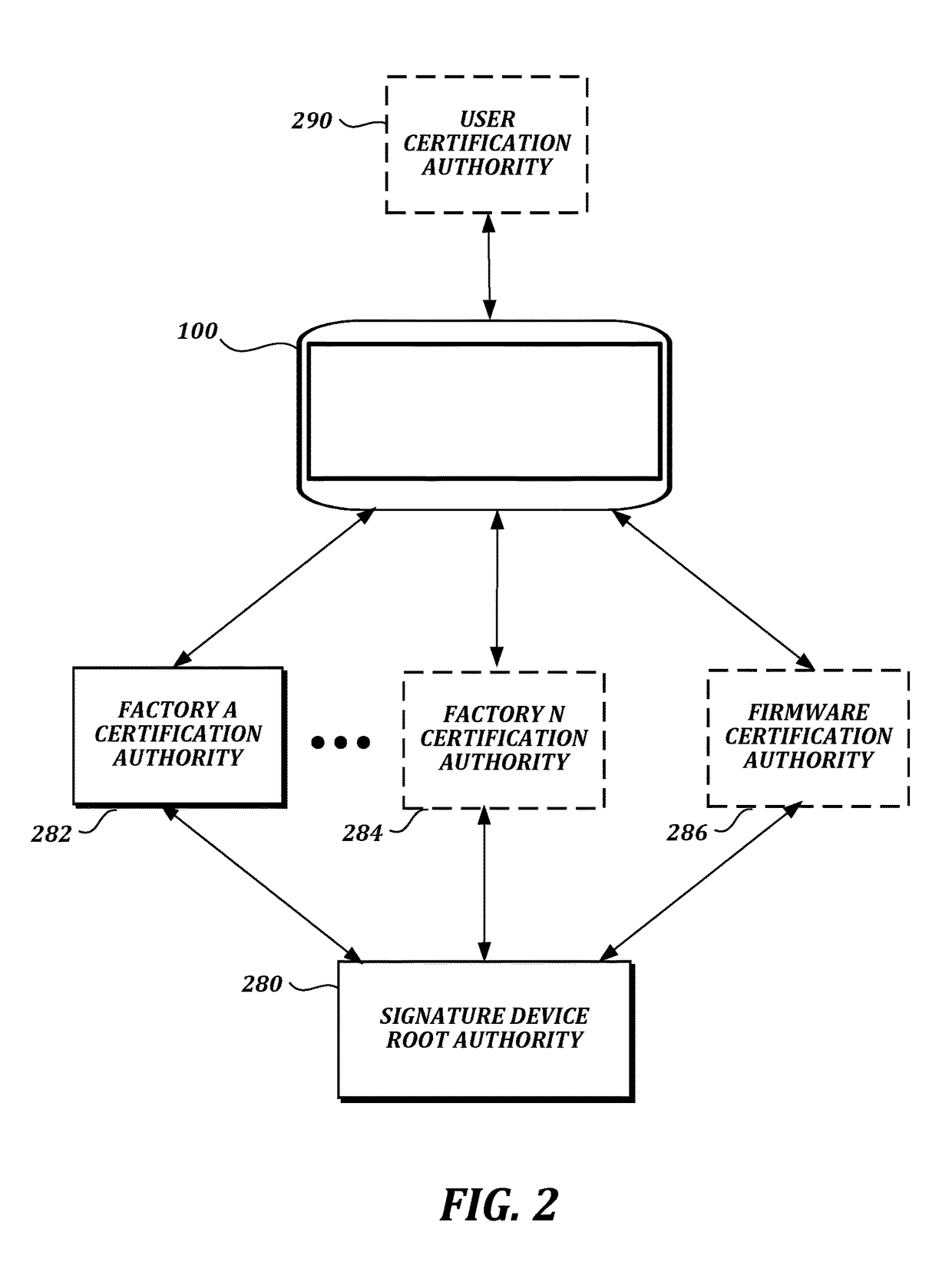
ActiveUS20180060608A1Well formedAcutation objectsKey distribution for secure communicationSecure transmissionCertificate signing request
A transport layer security (TLS) connection is established between a signature device and the host computer via an interface (e.g., a universal serial bus (USB) interface). The signature device acts as a TLS server, and the host computer acts as a TLS client. Data such as pen data, control data, or image data may be received or transmitted via a USB bulk transfer mechanism. In one aspect, the host computer sends a command via the interface to the signature device to generate a new key pair, receives a certificate signing request (CSR) from the signature device via the interface, sends the CSR to a user certificate authority, receives a public key certificate from the user certificate authority, and sends the public key certificate to the signature device via the interface.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
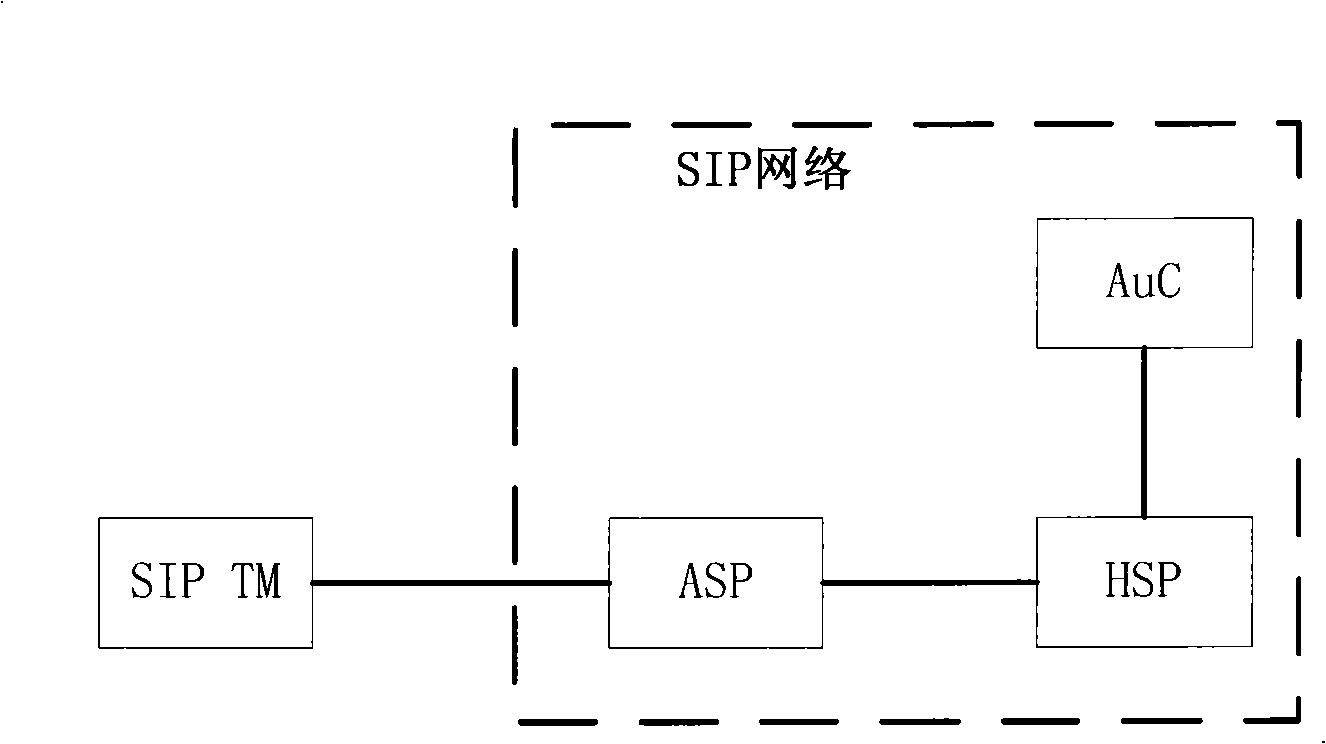
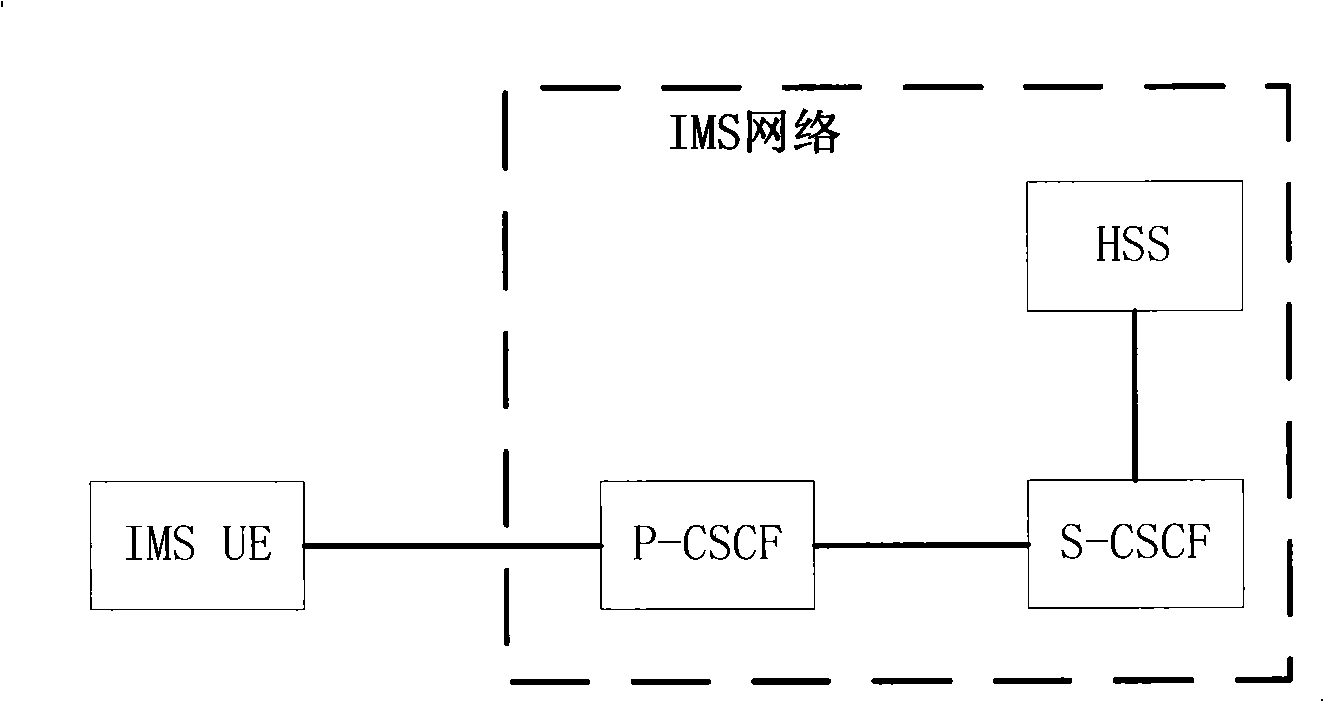
Method for implementing transport layer safety of SIP network based on sharing cryptographic key
InactiveCN101330504AAdd supportEnsure safetyPublic key for secure communicationSession Initiation ProtocolTransport layer
The invention discloses a realization method for transport layer security in a session initiation protocol (SIP) network based on a shared key. The method comprises the following steps: (a) a shared main key and a derivation algorithm are stored at a SIP terminal and in an authentication center (AuC); (b) the SIP terminal is interacted with a network side device based on a SIP security negotiation standard frame, the support for the security protocol of the transport layer is increased, and the SIP terminal and the SIP network side respectively generate the required encryption and integrity protection keys, so as to realize the transport layer security of the SIP network. By adopting the method, the TCP negotiation in the SIP network can be realized, the method not only can be suitable for the connection transport of the SIP such as TCP, UDP, etc., but also can ensure the security of information transmission in the SIP network; the method not only can be suitable for soft switching and IMS network, but also can be suitable for other networks which adopt the SIP as the control protocol, for example, the SIP-based VoIP network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
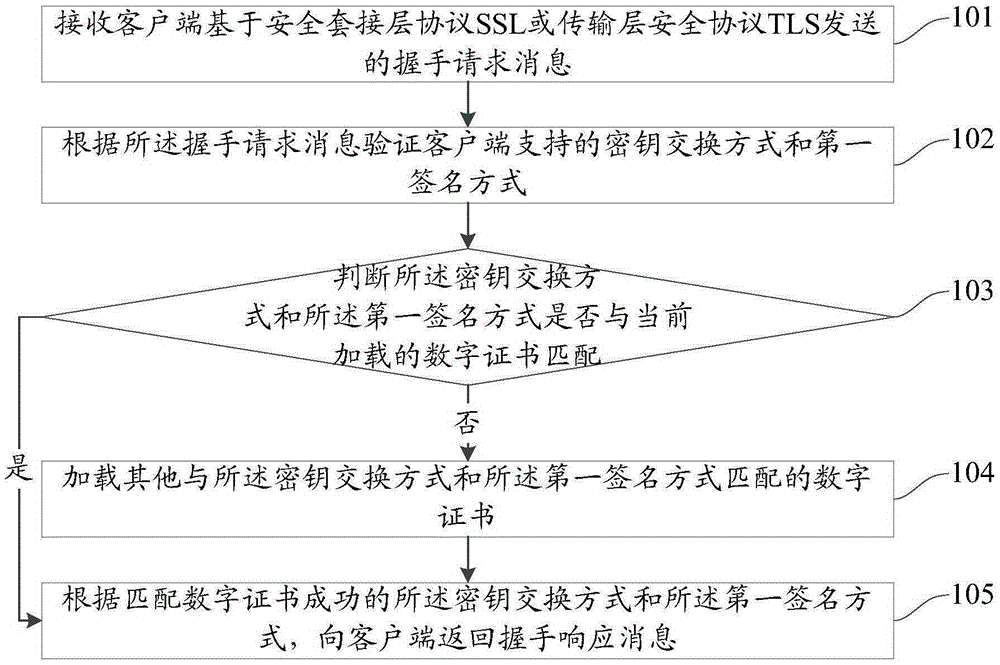
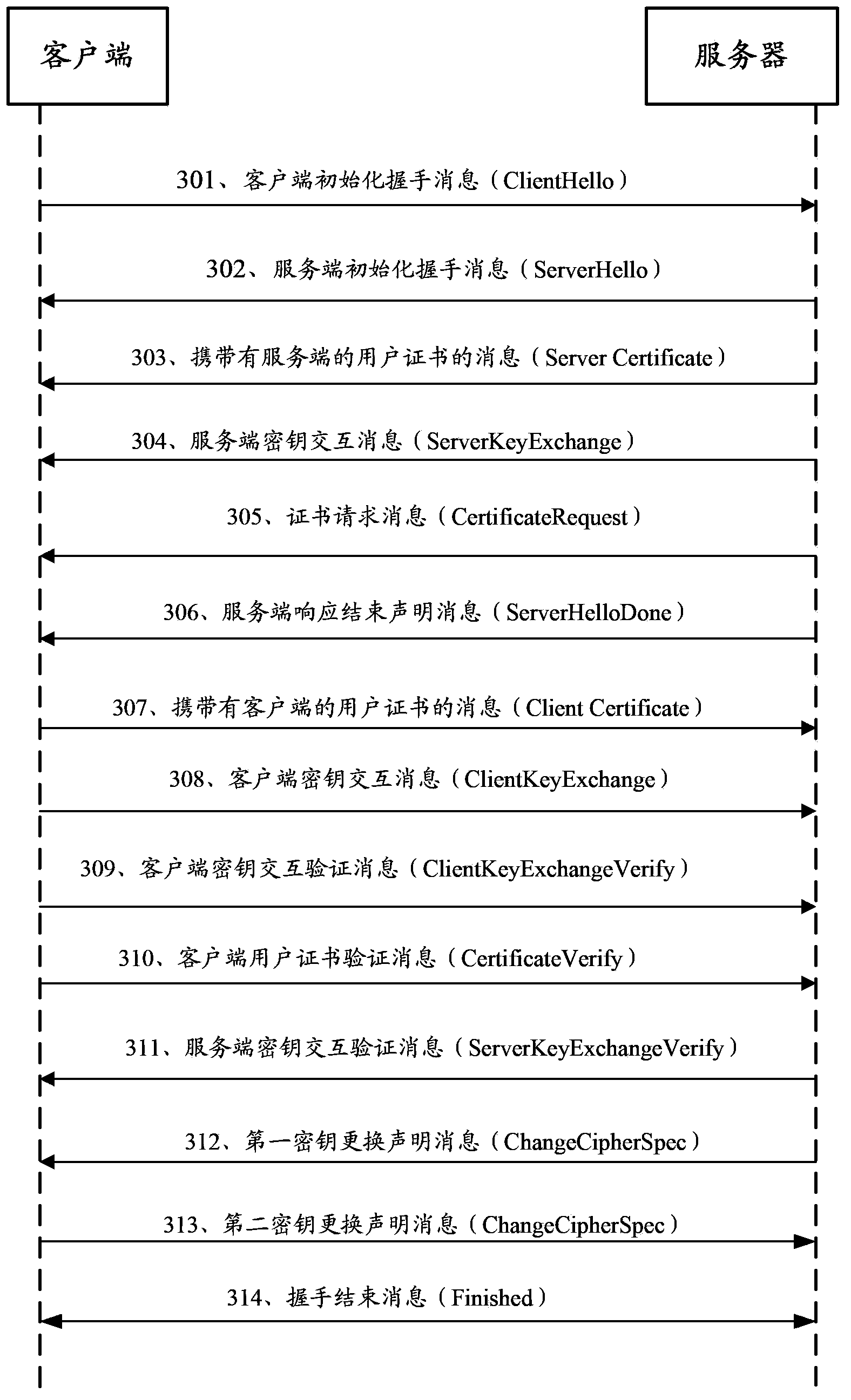
Method and device for loading digital certificate in SSL/TLS communication
ActiveCN106533689AImprove poor compatibilityImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The invention provides a method and device for loading a digital certificate in SSL / TLS communication. The method comprises the steps that a handshake request message sent by a client based on a secure socket layer protocol SSL or a transport layer security protocol TLS is received; a key exchange mode and a first signature mode supported by the client are verified according to the handshake request message; whether the key exchange mode and the first signature mode match the currently loaded digital certificate is determined; if not, another digital certificate matching the key exchange mode and the first signature mode is loaded; and a handshake response message is returned to the client according to the key exchange mode and the first signature mode, wherein the key exchange mode and the first signature mode successfully match the digital certificate. According to the embodiment of the invention, the appropriate digital certificate is dynamically loaded during handshake negotiation to ensure successful SSL / TLS handshake negotiation.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Method, system and device for realizing multi-party communication security
InactiveUS20090271612A1Improve deployabilityImprove portabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications securityKey server
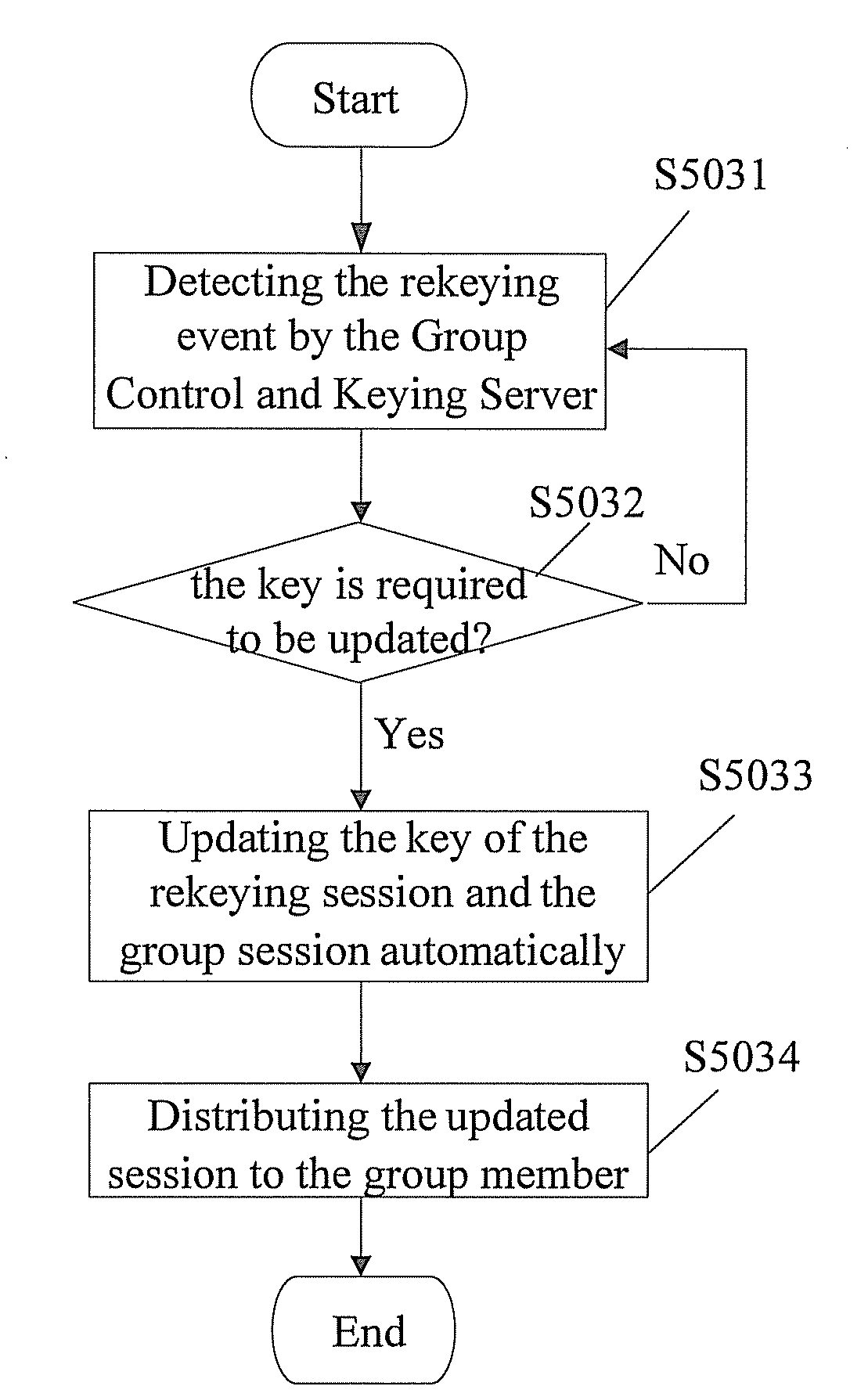
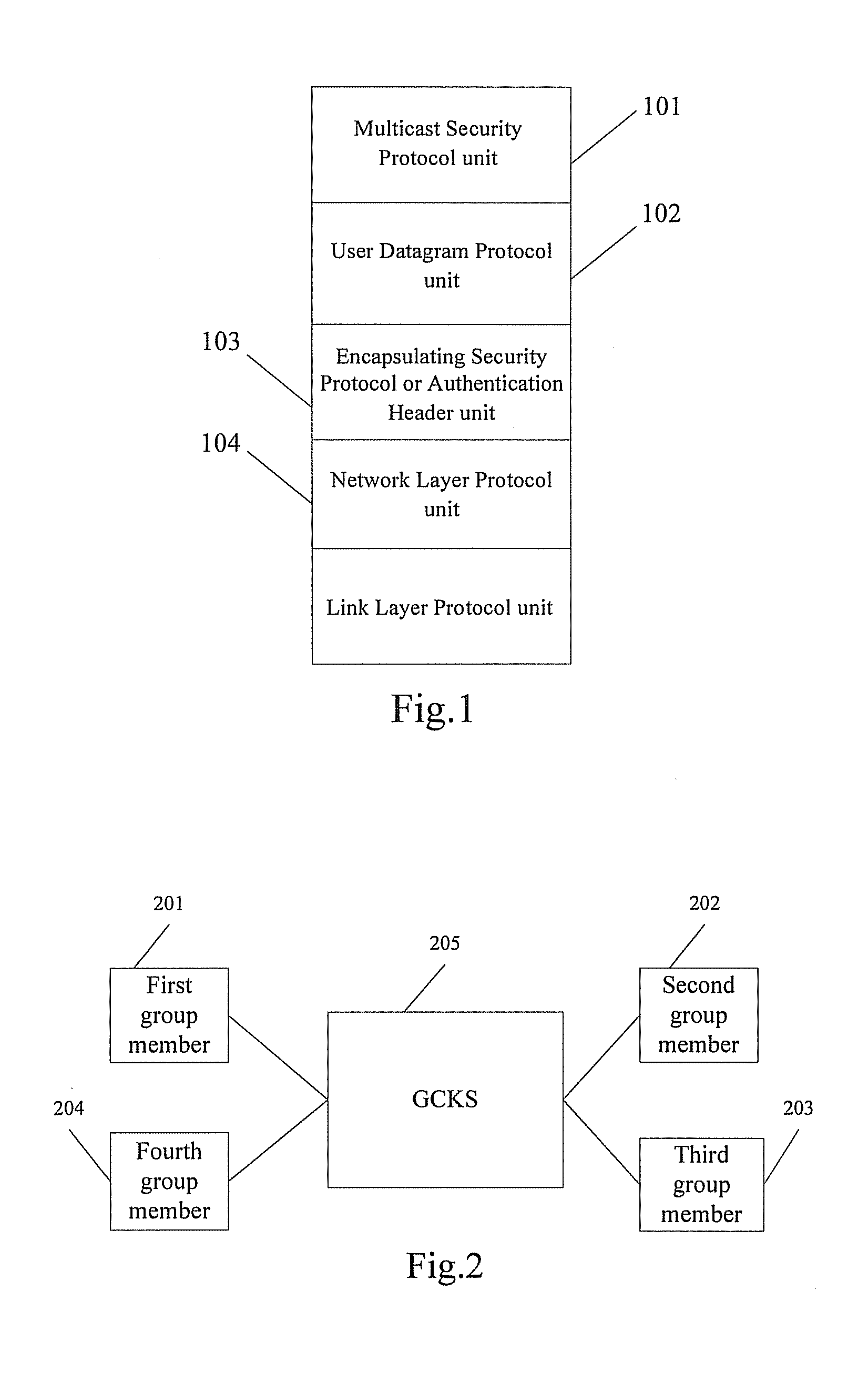
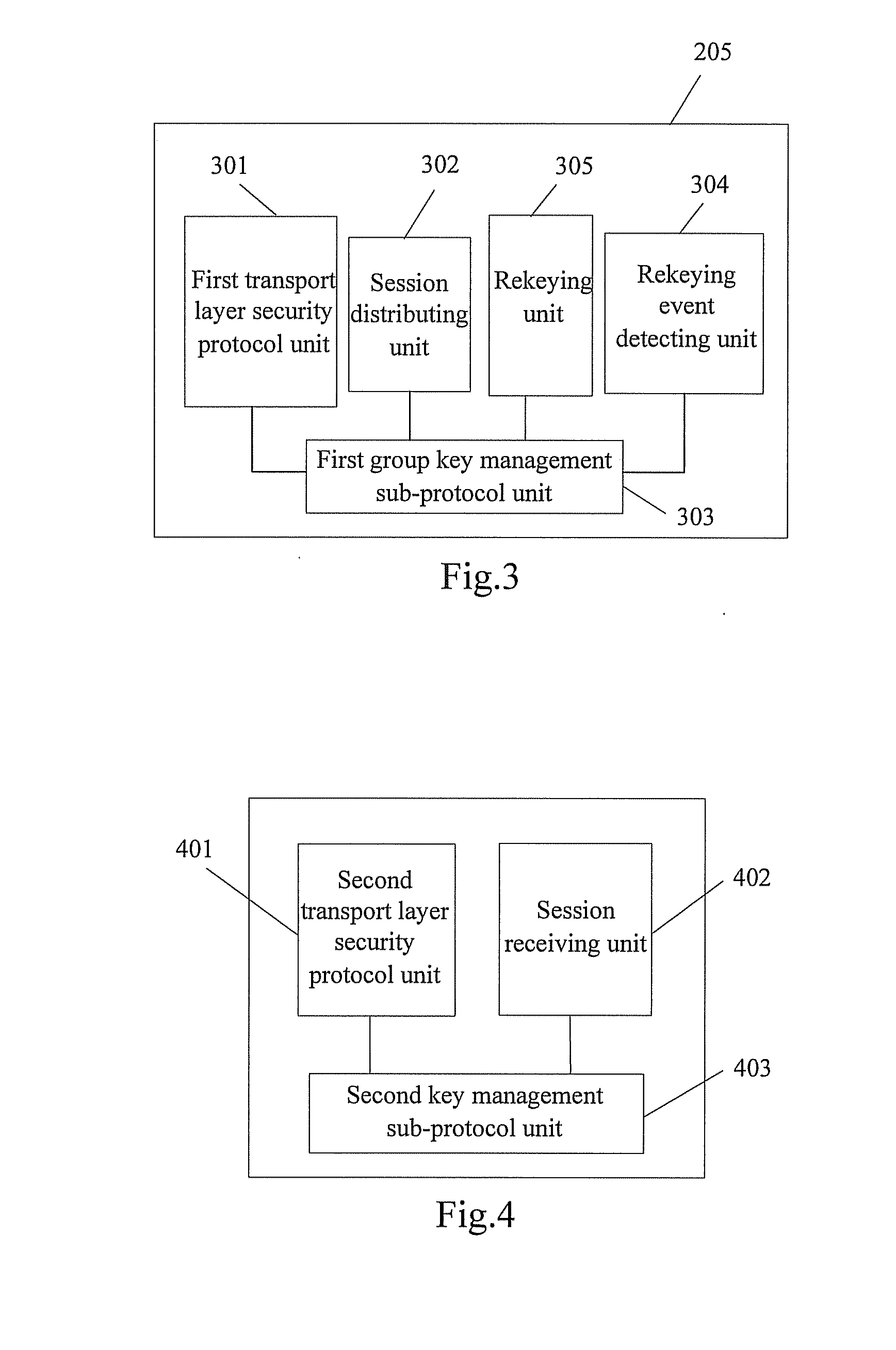
A method for realizing multi-party communication security includes: performing identification authentication and negotiating to create an initiation session through running the transport layer security protocol or datagram transport layer security protocol by a Group Control and Keying Server and a group member device; distributing a group session and a rekeying session to the group member device through running a group key management sub-protocol on the Group Control and Keying Server and the group member devices; rekeying through running the group key management sub-protocol on the Group Control and Keying Server and the group member devices, when a rekeying event is detected by the Group Control and Keying Server. A relevant multi-party communication security system and a device are further provided in the present invention.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for architecture initiated network access control
A system and method are provided for authenticating a user using a client side server within a computer network, the computer network operating in conformance with an open source initiative (OSI) model of structuring protocol data unit messages, the method comprising: generating a connection request at a client side server, the connection request including (i) a client side network layer protocol address information for use in a network layer (L3) protocol data unit (PDU), and (ii) a client side transport layer protocol address information for use in a transport layer (L4) PDU; transmitting the connection request from the client side server using both the network layer and the transport layer; receiving at the client side server an authentication call message on both the network and transport layers using the client side network layer protocol address information and client side transport layer protocol address information; transmitting user authentication information in response to the received authentication call message; and receiving connection confirmation based on the transmitted user authentication information confirming the user is authenticated to access protected systems.
Owner:DYON SEAN +1
Secure sharing of transport layer security session keys with trusted enforcement points
InactiveUS7992200B2Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlSecure communicationOperability
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to security enforcement point operability in a TLS secured communications path and provide a novel and non-obvious method, system and computer program product for the secure sharing of TLS session keys with trusted enforcement points. In one embodiment of the invention, a method for securely sharing TLS session keys with trusted enforcement points can be provided. The method can include conducting a TLS handshake with a TLS client to extract and decrypt a session key for a TLS session with the TLS client traversing at least one security enforcement point. The method further can include providing the session key to a communicatively coupled key server for distribution to the at least one security enforcement point. Finally, the method can include engaging in secure communications with the TLS client over the TLS session.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
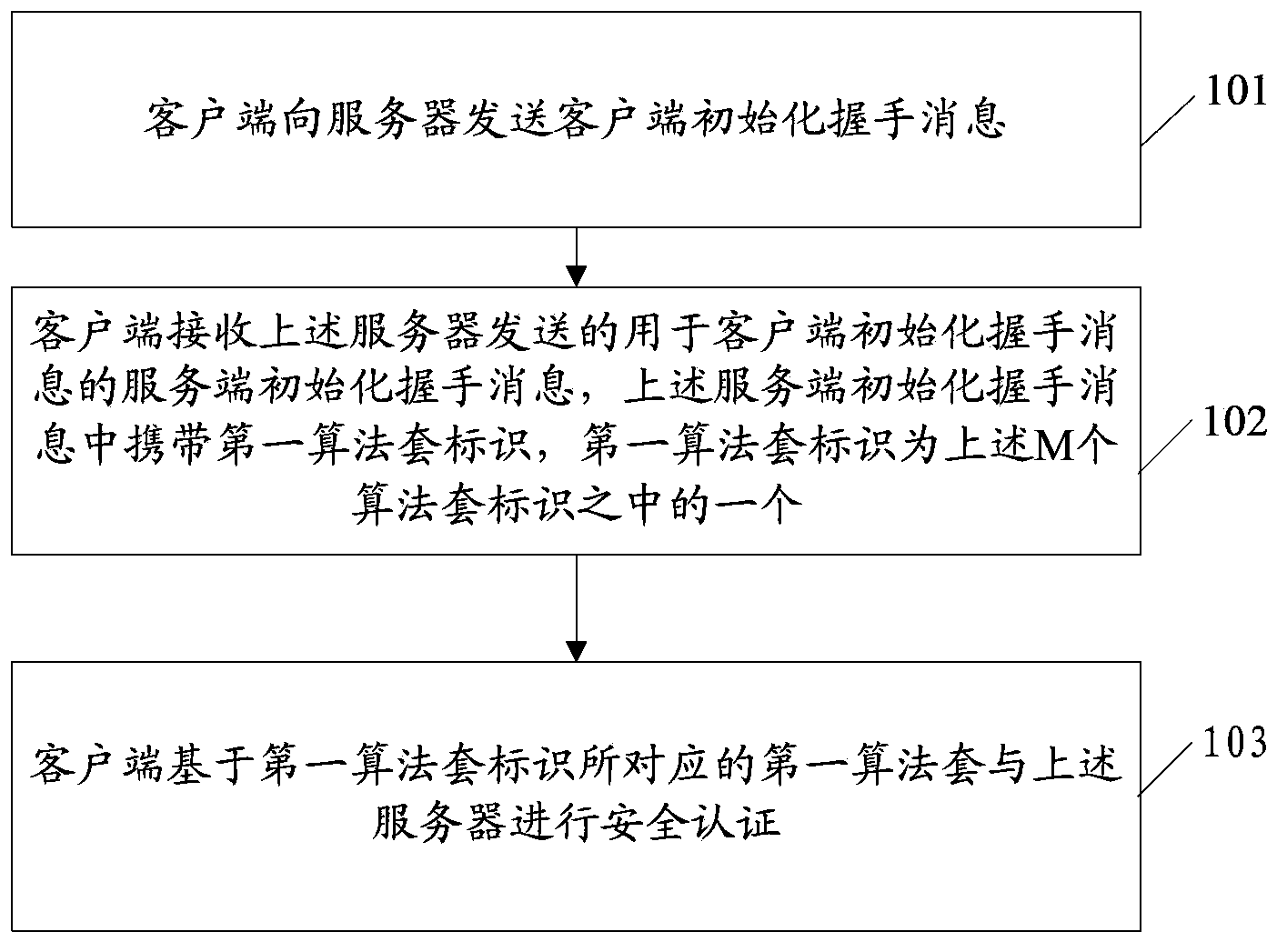
Security authentication method, equipment and system based on transport layer security protocol
ActiveCN103581167AEnhanced security certificationTake Advantage of SecurityTransmissionCommunications systemSecure transmission
The embodiment of the invention discloses a security authentication method, related equipment and a communication system based on transport layer security (TLS). The security authentication method based on a TLS protocol includes the steps that a client sends client initialization handshake information to a server, the client initialization handshake information carries N algorithm set identifications, and an algorithm set corresponding to each one of M algorithm set identifications of the N algorithm set identifications comprises an SM2 algorithm; server initialization handshake information sent by the server is received, and the server initialization handshake information carries a first algorithm set identification which is one of the M algorithm set identifications; security authentication is carried out on the basis of a first algorithm set corresponding to the first algorithm set identification and the server. A mechanism for data transmission through the SM2 algorithm is provided, so that advantages of the SM2 algorithm in the security factor are brought into full play, and safety and performance of security authentication and data transmission are improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
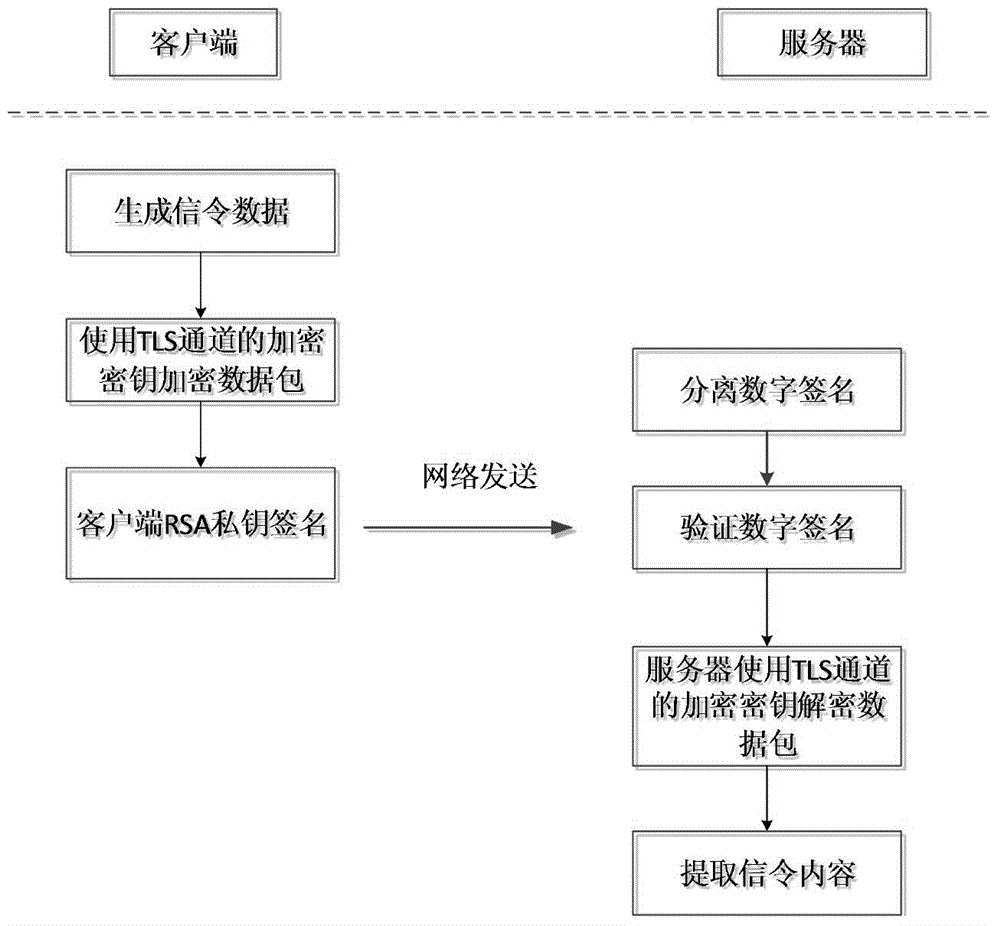
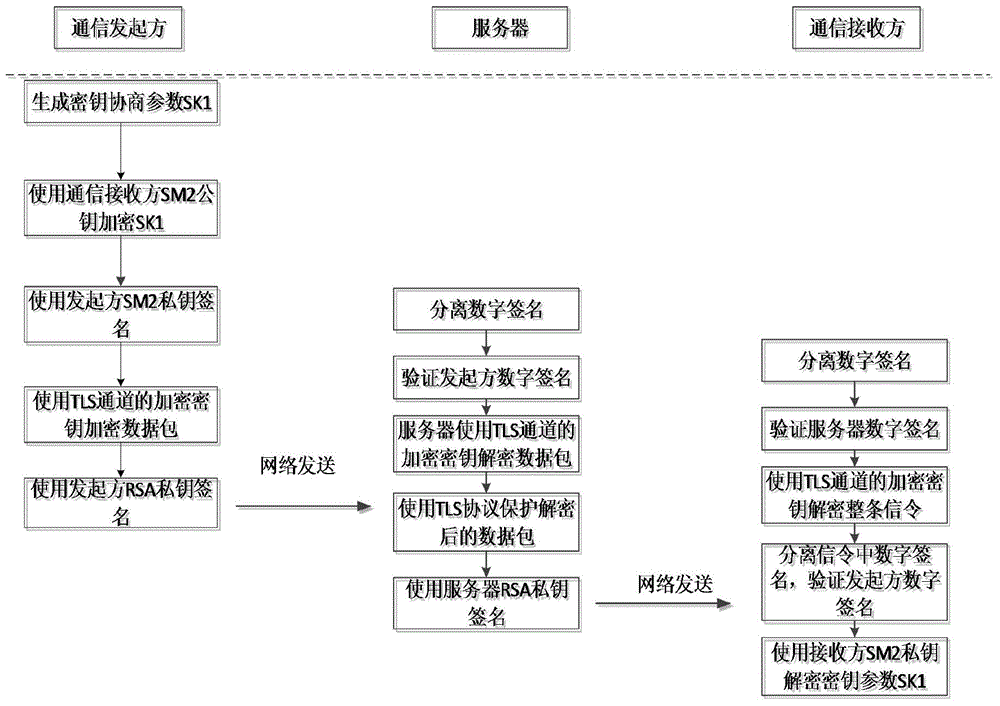
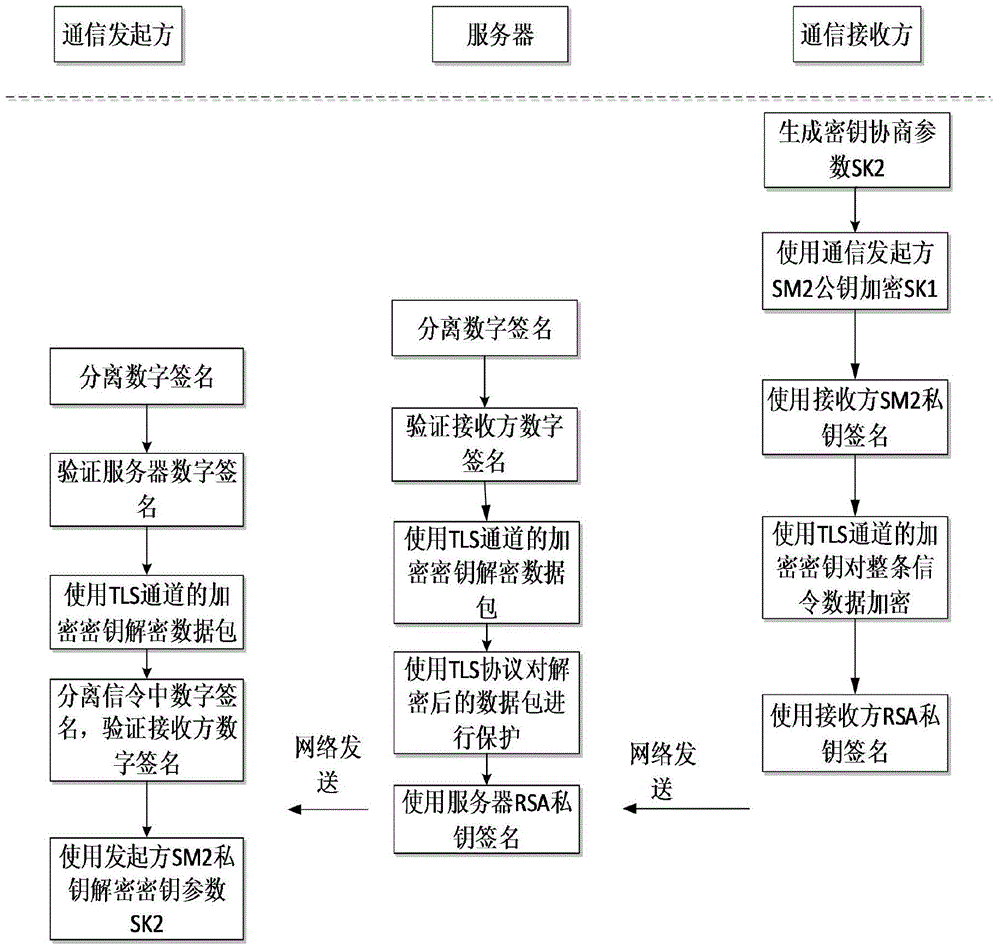
End-to-end secret key negotiation method for VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) real-time data safety transmission
InactiveCN104486077AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSession Initiation ProtocolInformation transmission
The invention discloses an end-to-end secret key negotiation method for VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) real-time data safety transmission, which is applicable to mobile phone terminals. The method comprises the following steps of (1) in a signal security transmission stage, adopting a TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol to bidirectionally authenticating and protecting an SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) signal; (2) in an end-to-end secret key negotiation stage, adopting a two-layer encryption way, at a first layer, respectively adopting the TLS protocol to protect between a communication initiator and a server as well as between the server and a communication receiver, and at a second layer, respectively using SM2 (Signal Module) public keys of the communication initiator and the communication receiver to protect secret key negotiation parameter information of the communication initiator and the communication receiver. According to the end-to-end secret key negotiation method for VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) real-time data safety transmission, the two-layer encryption way is adopted to protect the secret key negotiation parameters, and the signal is bidirectionally authenticated and protected at the signal transmission stage, so that the safety of information transmission is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
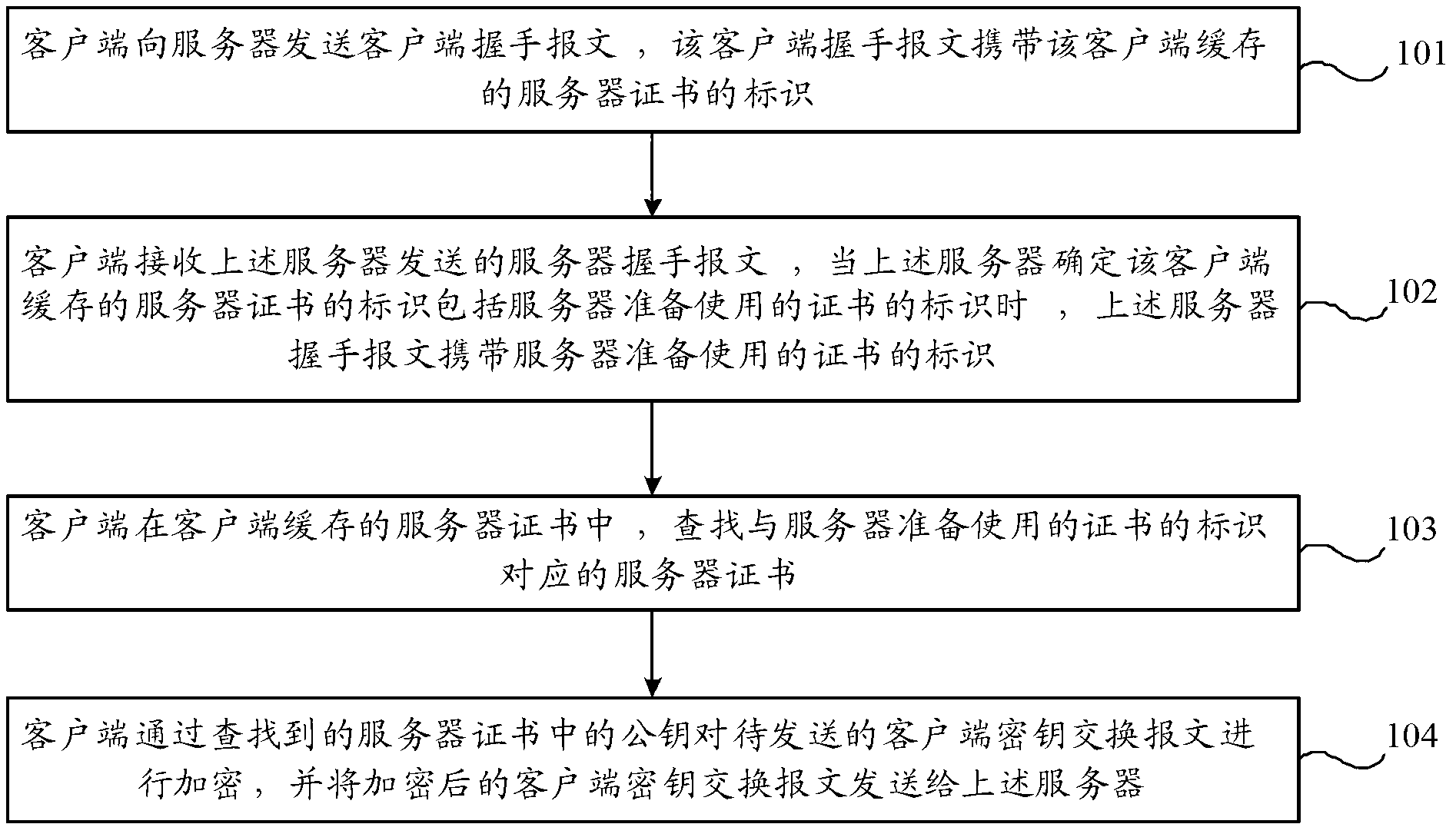
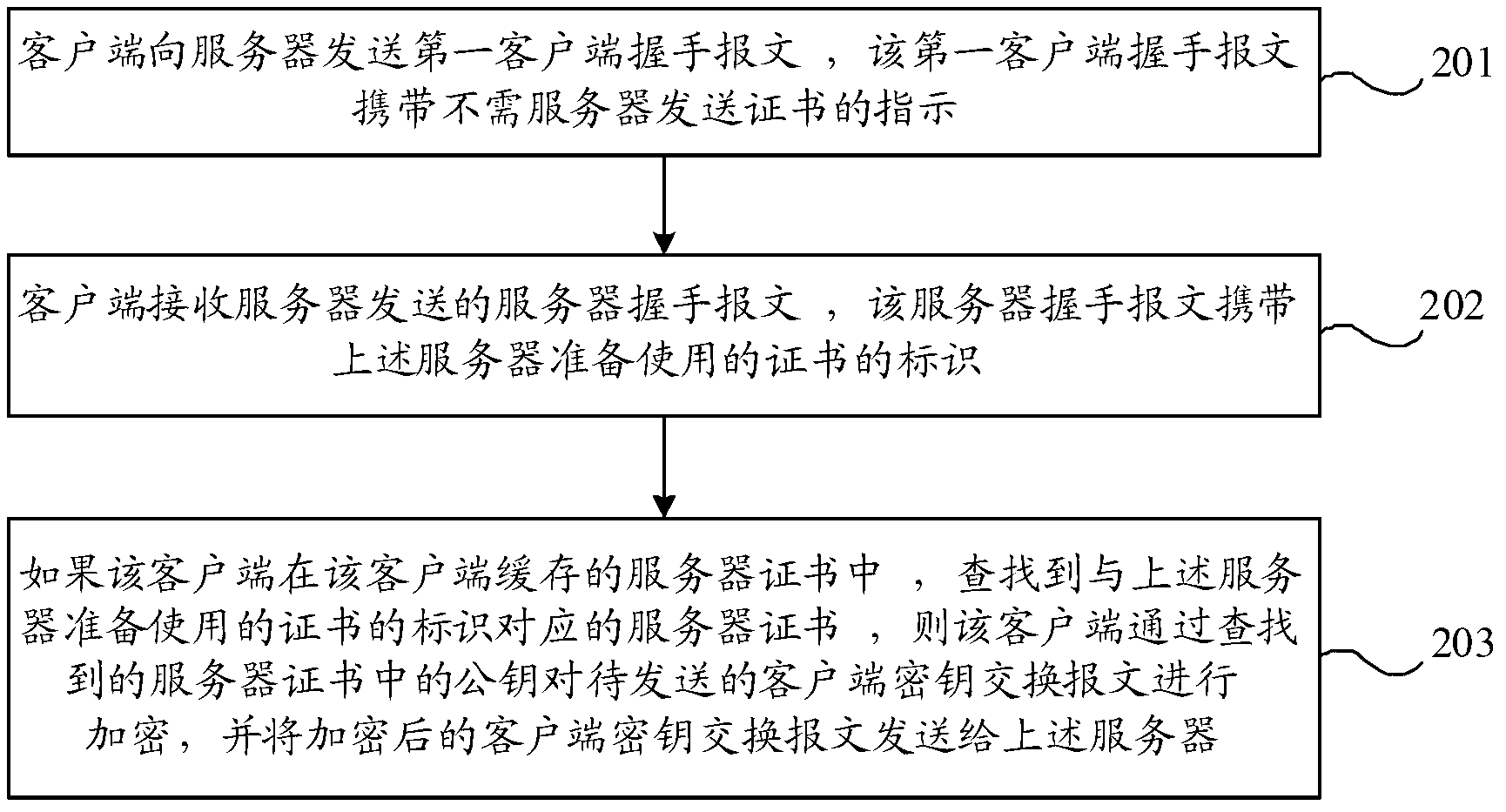
Message sending and receiving method, device and system
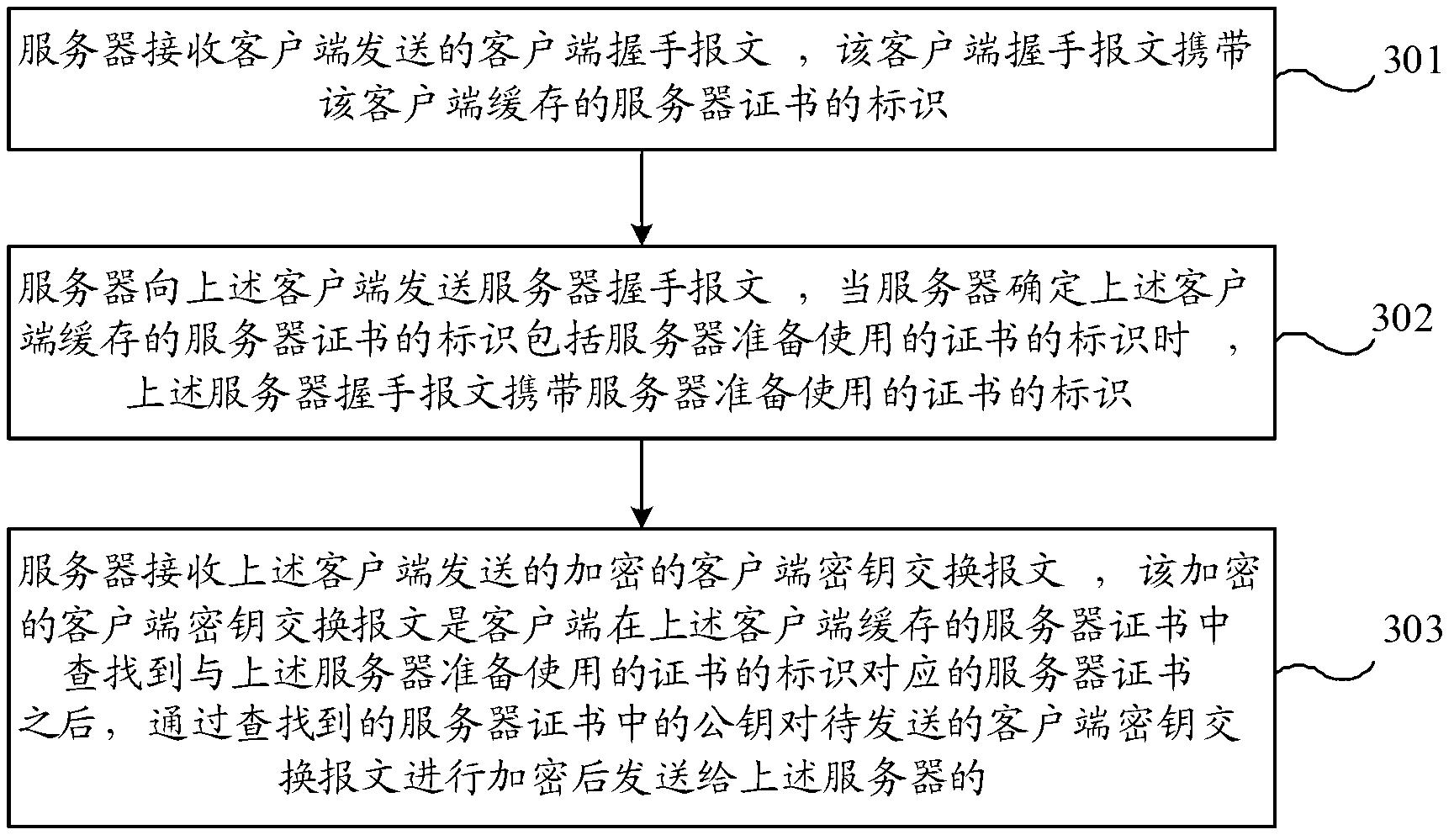
ActiveCN102801616AAvoid the problem of sending multiple timesReduce data volumeUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksKey exchangeClient-side
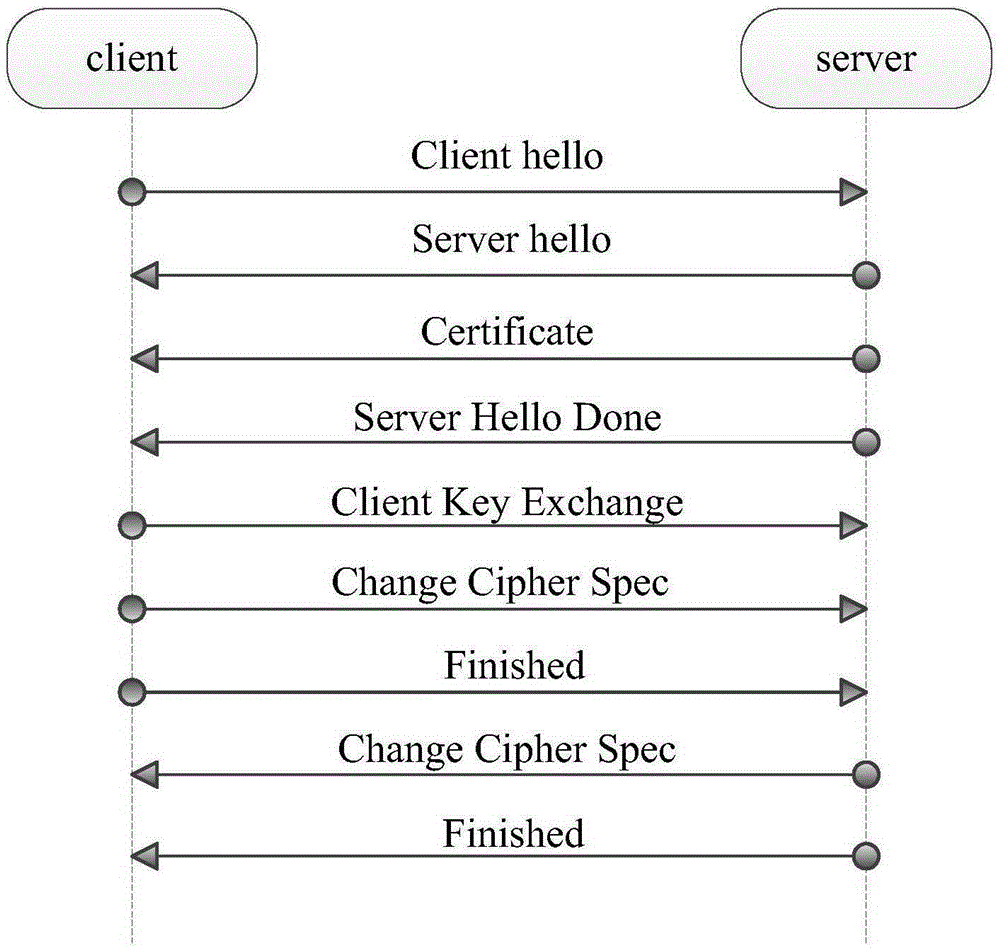
The invention provides a message sending and receiving method, device and system. The message sending method comprises the following steps of: sending a client handshaking message to a server, wherein the client handshaking message carries identification of a server certificate cached by the client; receiving a server handshaking message sent by the server, wherein when the server determines the identification of the server certificate cached by the client comprises identification of a certificate to be used by the server, the server handshaking message carries the identification of the certificate to be used by the server; and encrypting a client secrete key exchange message to be sent through a searched public key in the server certificate, and sending the encrypted client secrete key exchange message to the server. With the adoption of the message sending and receiving method, device and system provided by the invention, the data amount in a TLS (Transport Layer Security) handshaking process can be reduced; the time of occupying the TLS handshaking process is shortened; and the speed of TLS connection can be further improved.
Owner:瑞得银纺(南通)信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com