Method for protecting and recovering cross-domain end-to-end label switched path
A label switching path, protection and restoration technology, applied in the field of automatic switching optical networks, can solve the problems of detailed specifications, immature development of standards, and lack of uniform implementation, and achieve the effect of improving survivability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
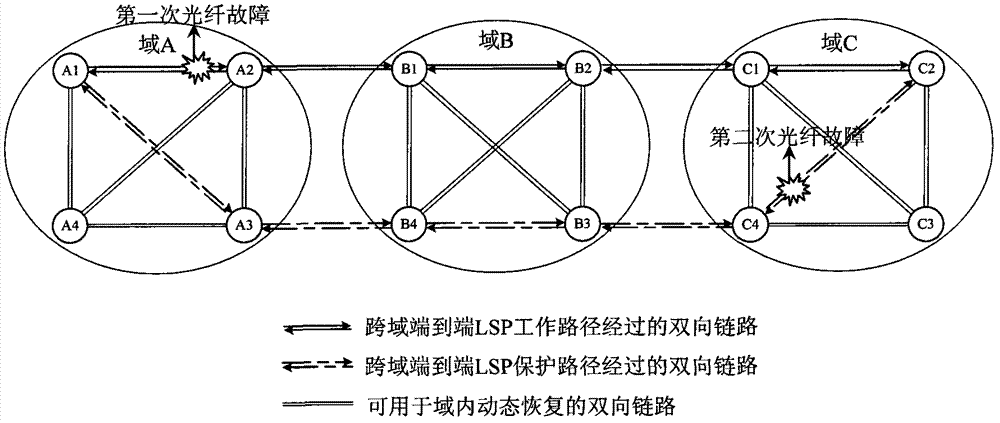
[0046] Such as figure 1 As shown in FIG. 1 , it is a schematic diagram of the protection and restoration of a 1+1 cross-domain end-to-end LSP source domain and sink domain in the present invention. When the first optical fault occurs, the service is switched to figure 1 The protection path shown, that is, A1-A3-B4-B3-C4-C2 is used as the new working path. At the same time, the working path A1-A2 in domain A starts dynamic recovery immediately, and the recovery path is A1-A4-A2, forming a new protection path A1-A4-A2-B1-B2-C1-C2 of the end-to-end LSP. This failure will cause the 1+1 protection group of the source node A1 to change, and the protection objects to which the original protection paths A1-A3 in the source domain belong are upgraded to the protected objects in the 1+1 protection group. The new path A1-A4-A2 dynamically restored in the source domain is a newly added protected object, pointing to the current protected object A1-A3 in this group. The sink node C2 perf...
no. 2 example
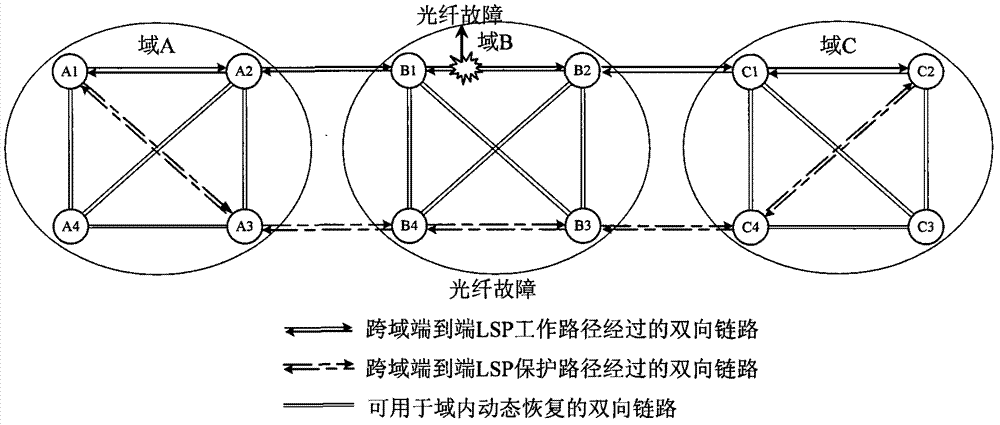
[0049] Such as figure 2 As shown in FIG. 1 , it is a schematic diagram of single-failure protection recovery in the 1+1 cross-domain end-to-end LSP intermediate domain. When a fiber optic failure occurs in figure 2 In the position shown, the service will be switched to the protection path A1-A3-B4-B3-C4-C2 as the new working path, but the protection relationship of the 1+1 protection group between the source node and the sink node will not be changed. The original working path B1-B2 in domain B starts dynamic recovery immediately after the fault occurs, and the recovery path is B1-B4-B2 or B1-B3-B2, forming a new protection path A1-A2-B1-B4 of the end-to-end LSP (B3)-B2-C1-C2.
no. 3 example
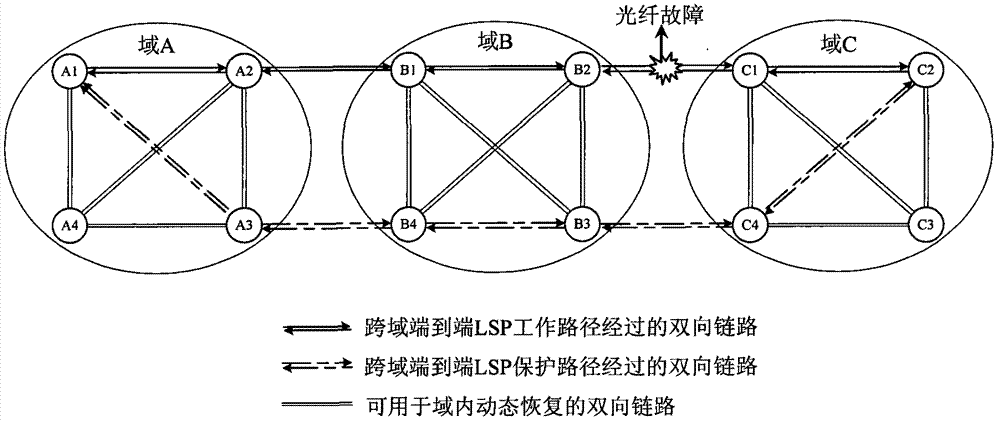
[0051] Such as image 3 As shown in FIG. 1 , it is a schematic diagram of 1+1 cross-domain end-to-end LSP inter-domain single fault protection and restoration. When a fiber optic failure occurs in image 3 In the position shown, the service is switched to the protection path A1-A3-B4-B3-C4-C2 as the new working path by using the alarms that can be communicated at the transport plane layer; Interim failure does not initiate dynamic recovery.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com