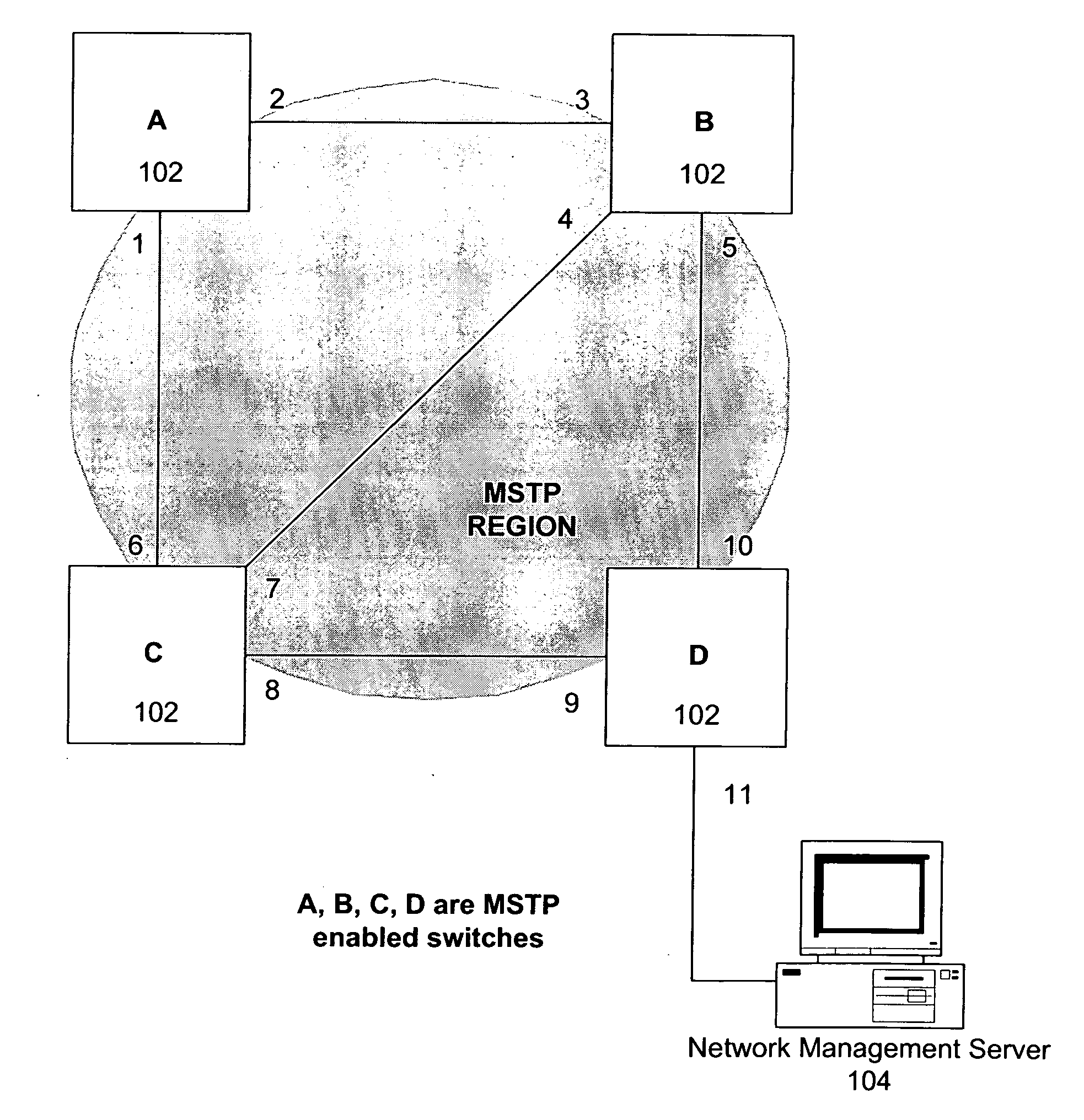
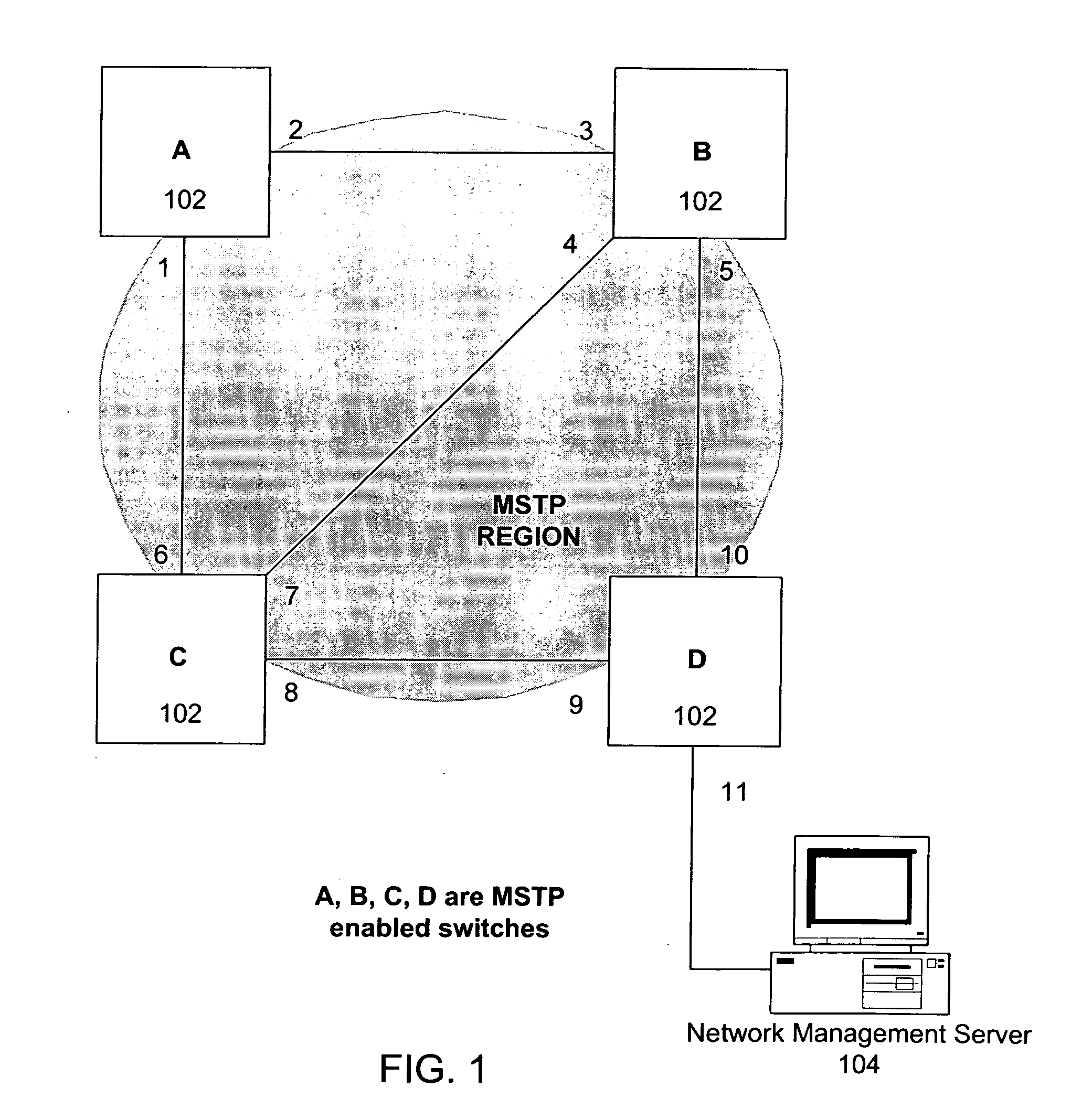
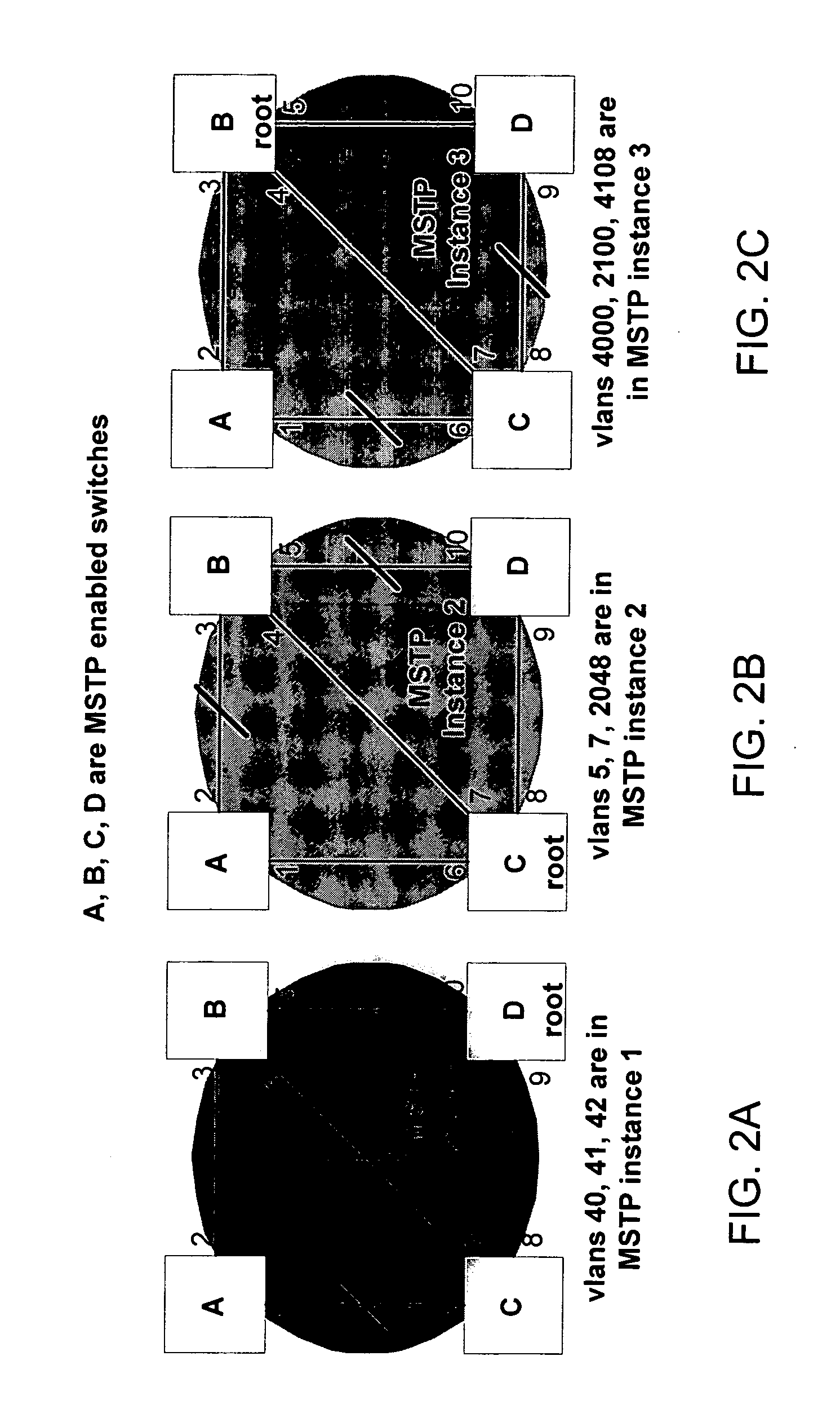
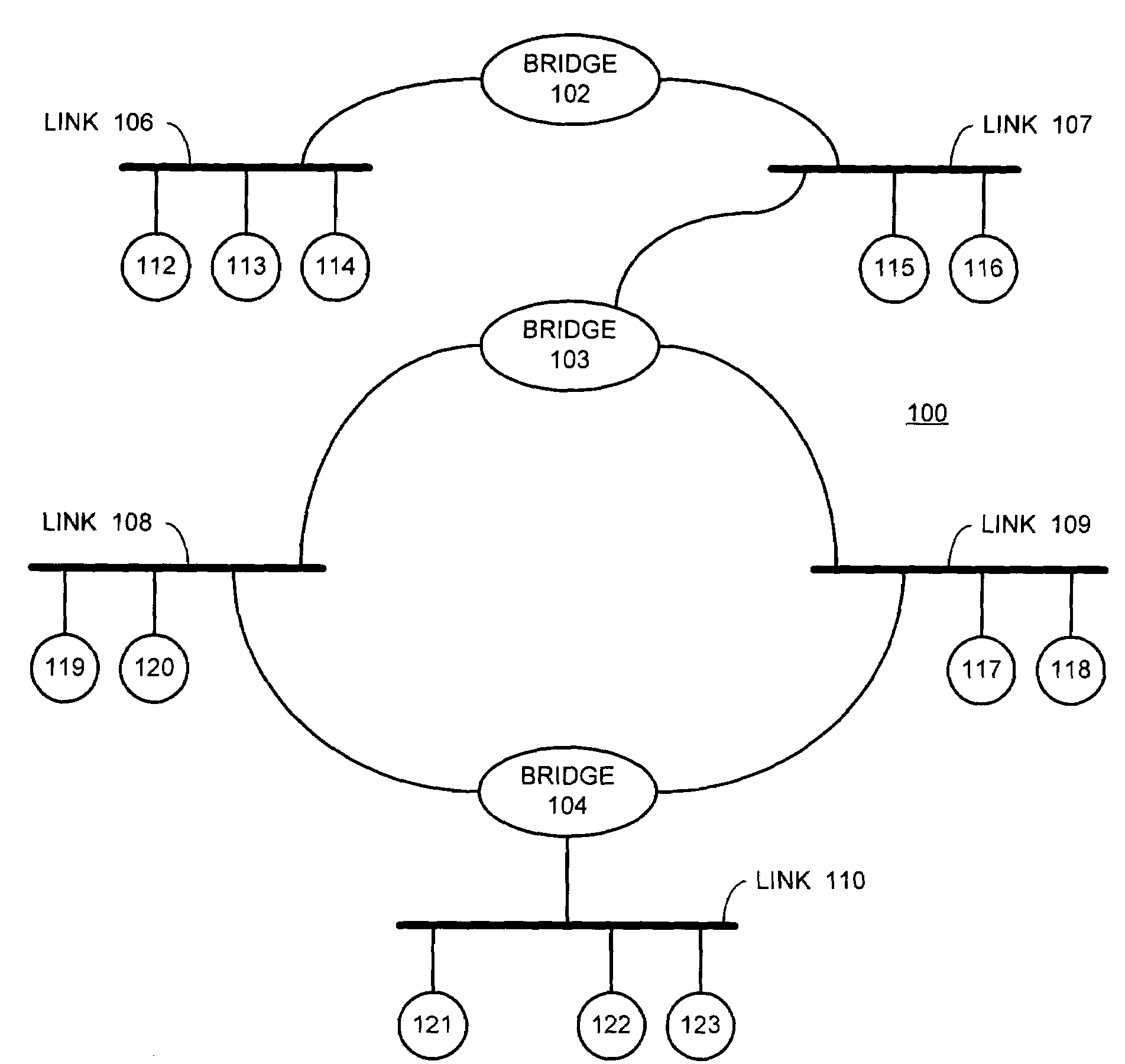
Patents
Literature
285 results about "Span tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spanning trees. A spanning tree of a graph is a subgraph that contains (or "spans") every vertex of the original graph. Because it is a tree, a spanning tree is connected and has no cycles.
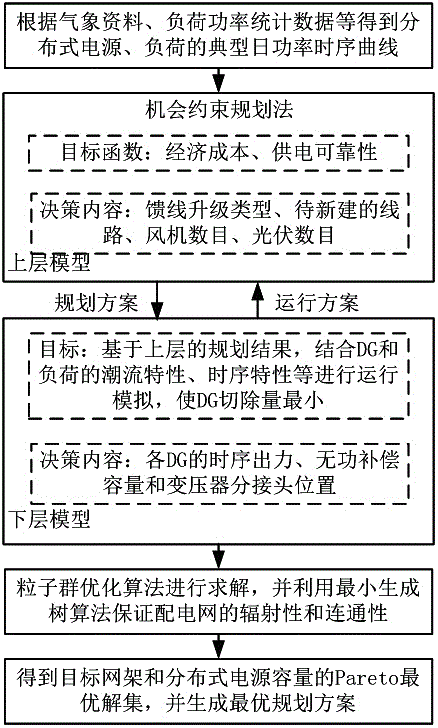
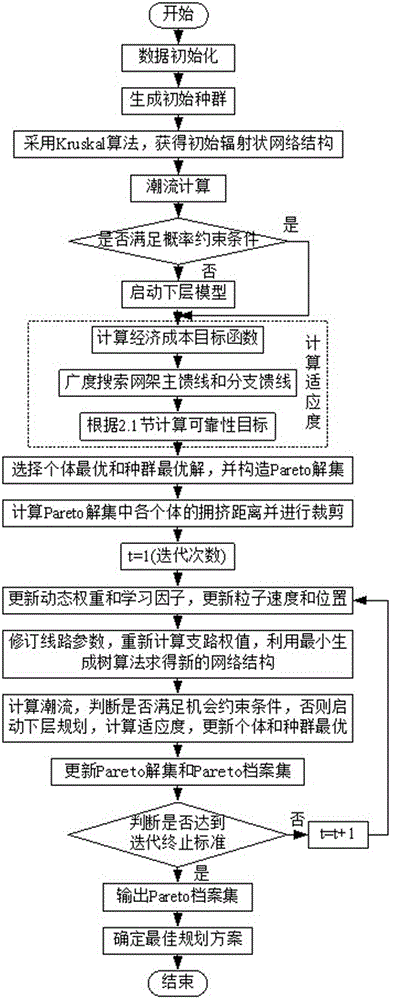
Power distribution network double layer planning method considering the time sequence and the reliability
ActiveCN106815657AAvoid repeated traversalImproving the Efficiency of Reliability CalculationsForecastingMathematical modelNew energy
The invention relates to a power distribution network double layer planning method considering the time sequence and the reliability. The method comprises: according to the meteorological files and the load power statistical data, obtaining the typical daily power time sequence curves of the wind electricity, the photovoltaic output and the load in different seasons; based on the opportunistic constraint planning method, creating a power distribution network framework and a distributed power capacity double layer planning mathematical model, including the objective function and the constraint condition; using the particle swarm optimization algorithm to solve the model and using the minimum spanning tree algorithm to ensure the radiation and connectivity structure of the distribution network during the iterative process; and obtaining the target network framework and the Pareto optimal solution set of the distributed power capacity so as to generate the best planning scheme. The invention solves the problems that unnecessary investment into the a power distribution network incurred by the fact that a traditional power distribution network planning method containing a distributed power supply cannot reflect the typical output characteristic of a distribution type new energy; and 2) that by incorporating the power distribution network power supply reliability into a model target function, the reliability target can be realized at the planning stage.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +2
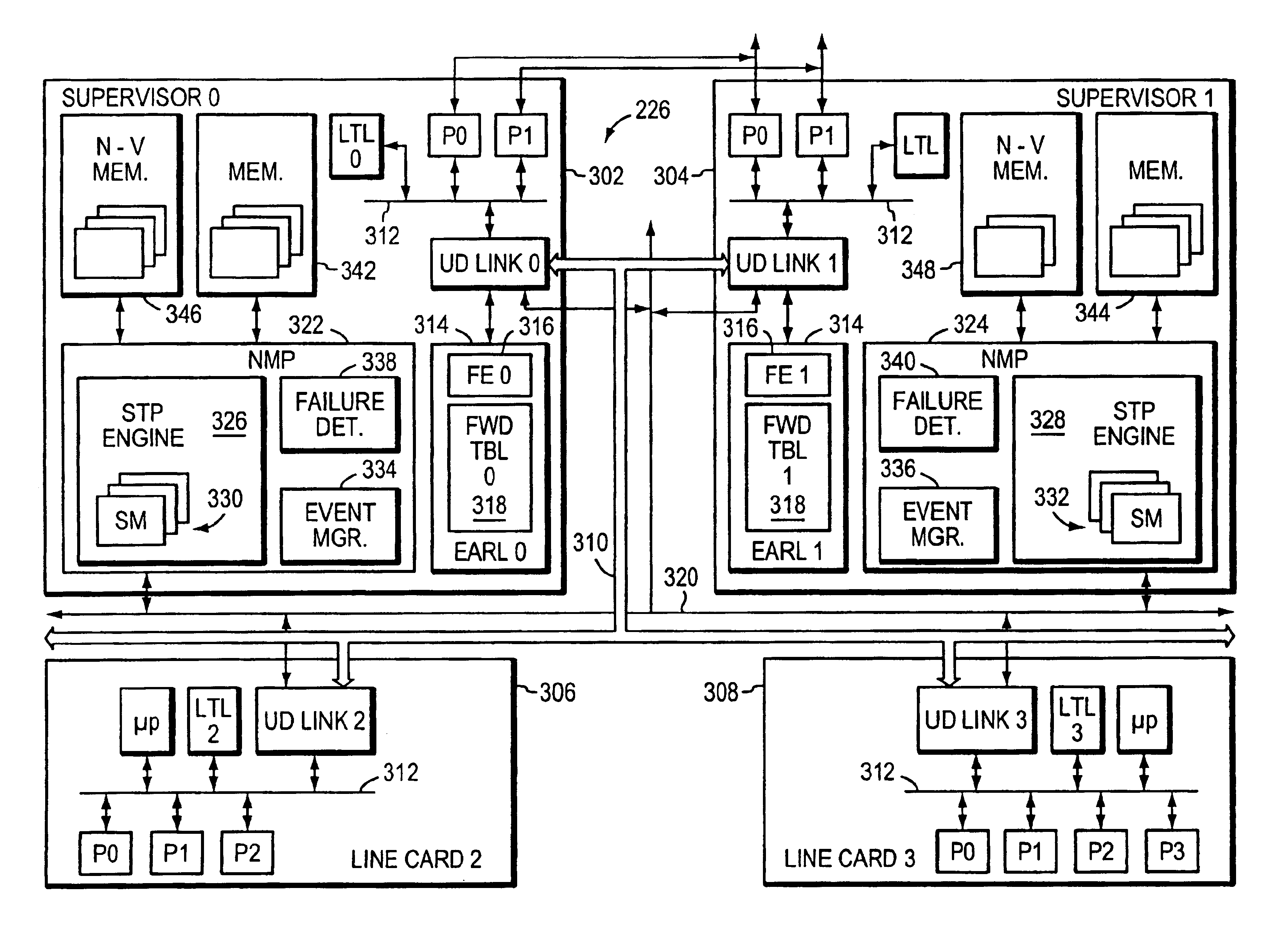
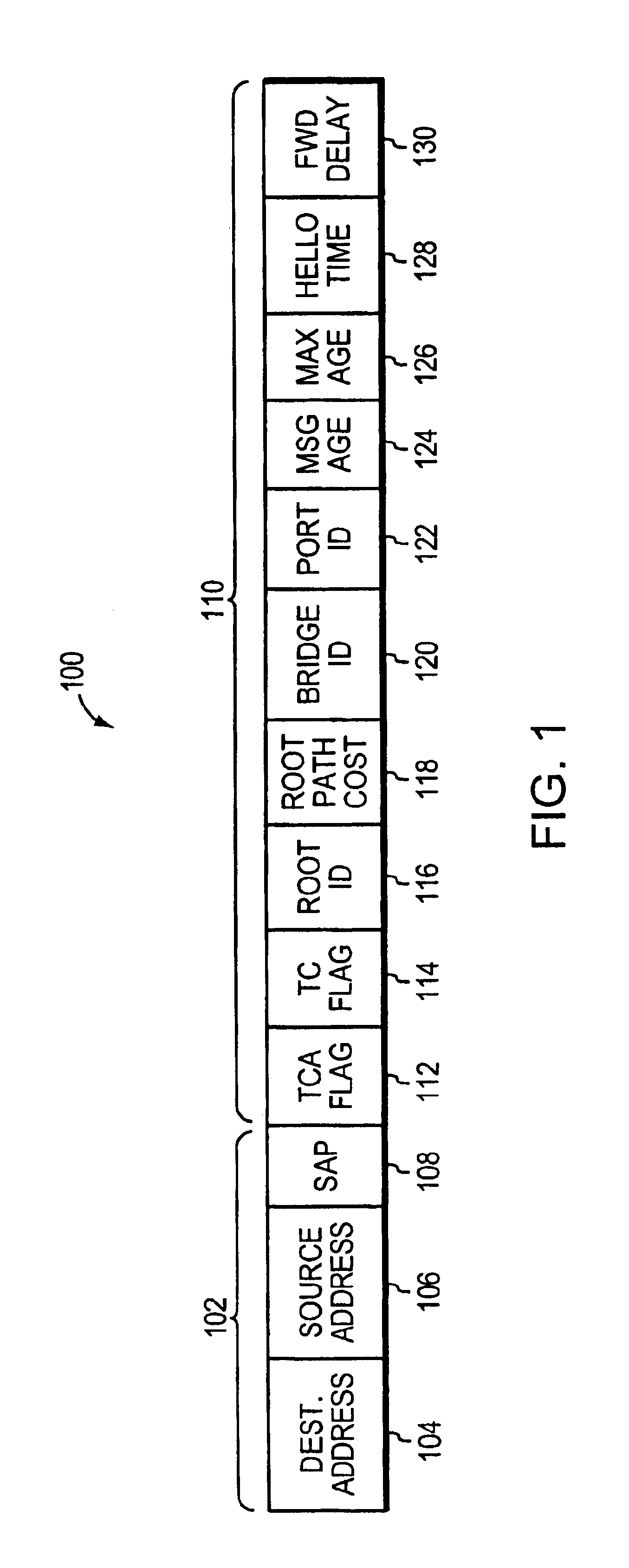
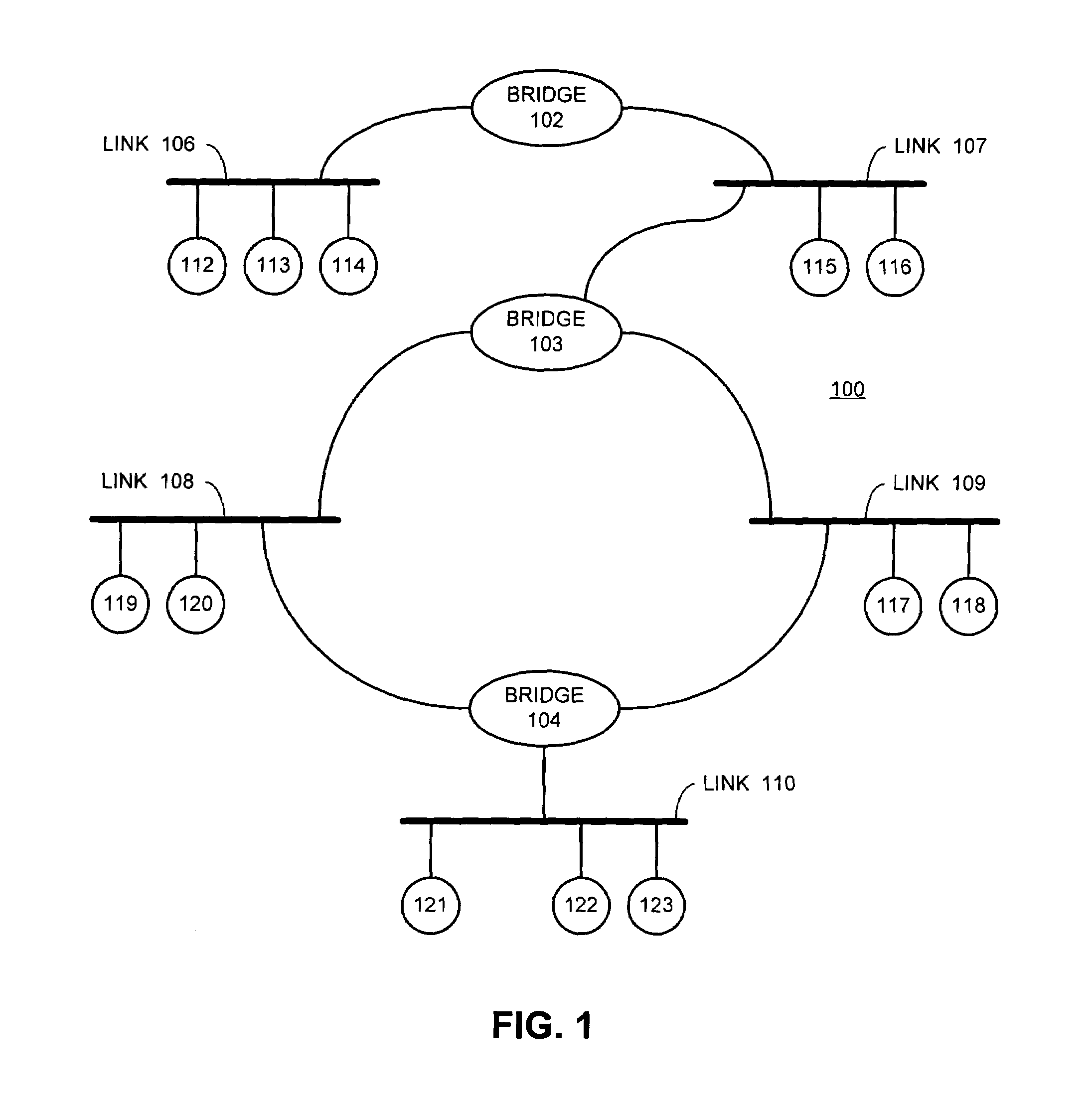
Restartable spanning tree for high availability network systems
InactiveUS6898189B1Avoiding significant network disruptionQuick fixError preventionTransmission systemsHigh availabilitySupervisor review
A method and apparatus for continuing the operation of a spanning tree protocol at a network device despite crashes or failures at that device. A supervisor card contained in the network device is designated an active supervisor, while all other supervisor cards are designated standby supervisors. The active supervisor runs the spanning tree protocol, and informs the standby supervisors of the states of ports, but not of the identity of the root or designated bridges. When a crash or failure occurs at the active supervisor, one of the standby supervisors is immediately designated to be the new active supervisor. The newly active supervisor reviews the port state, and queries the line cards to determine whether that port state information is still valid. The newly active supervisor adopts the valid port state information, leaving those ports in their current spanning tree port state.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
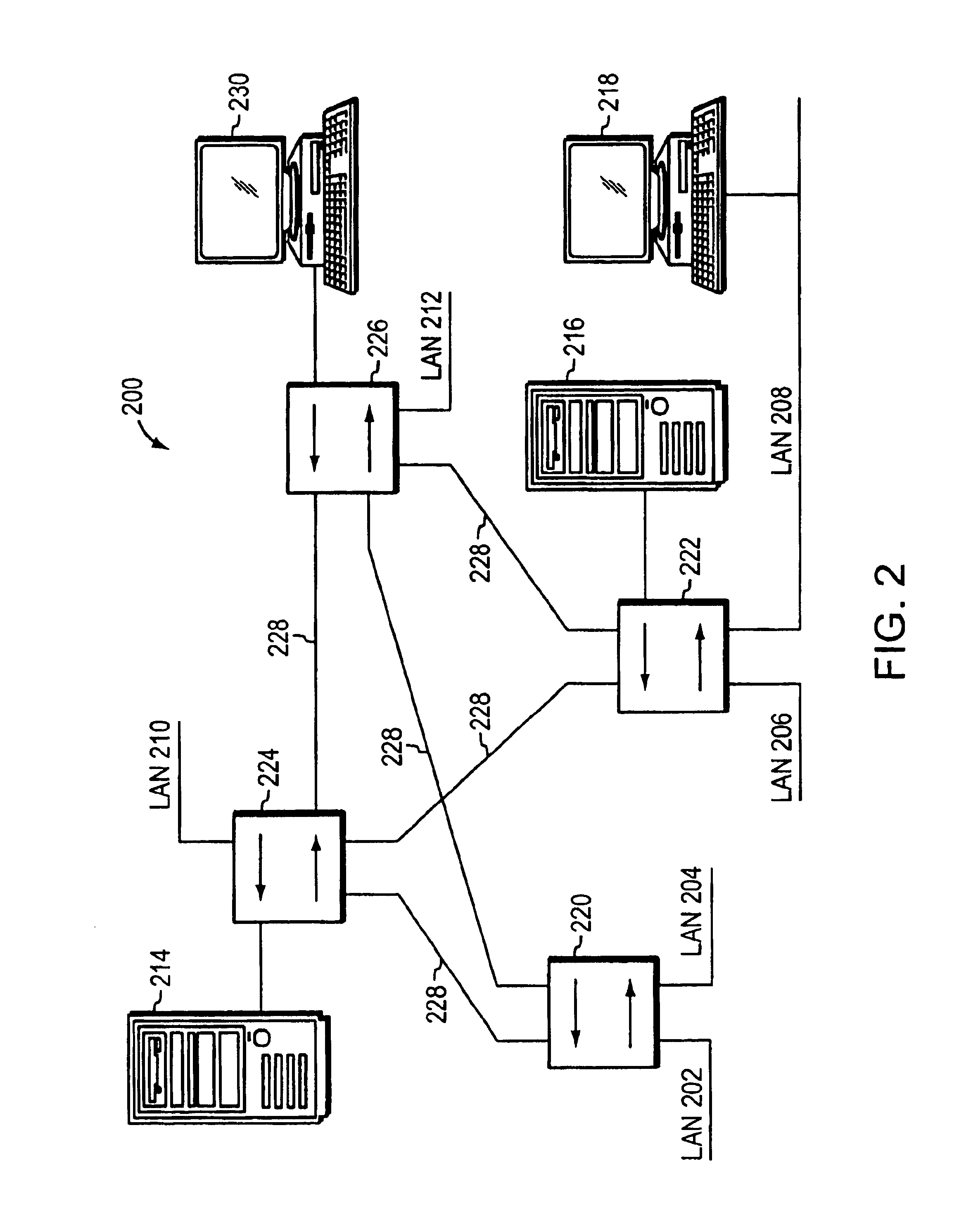
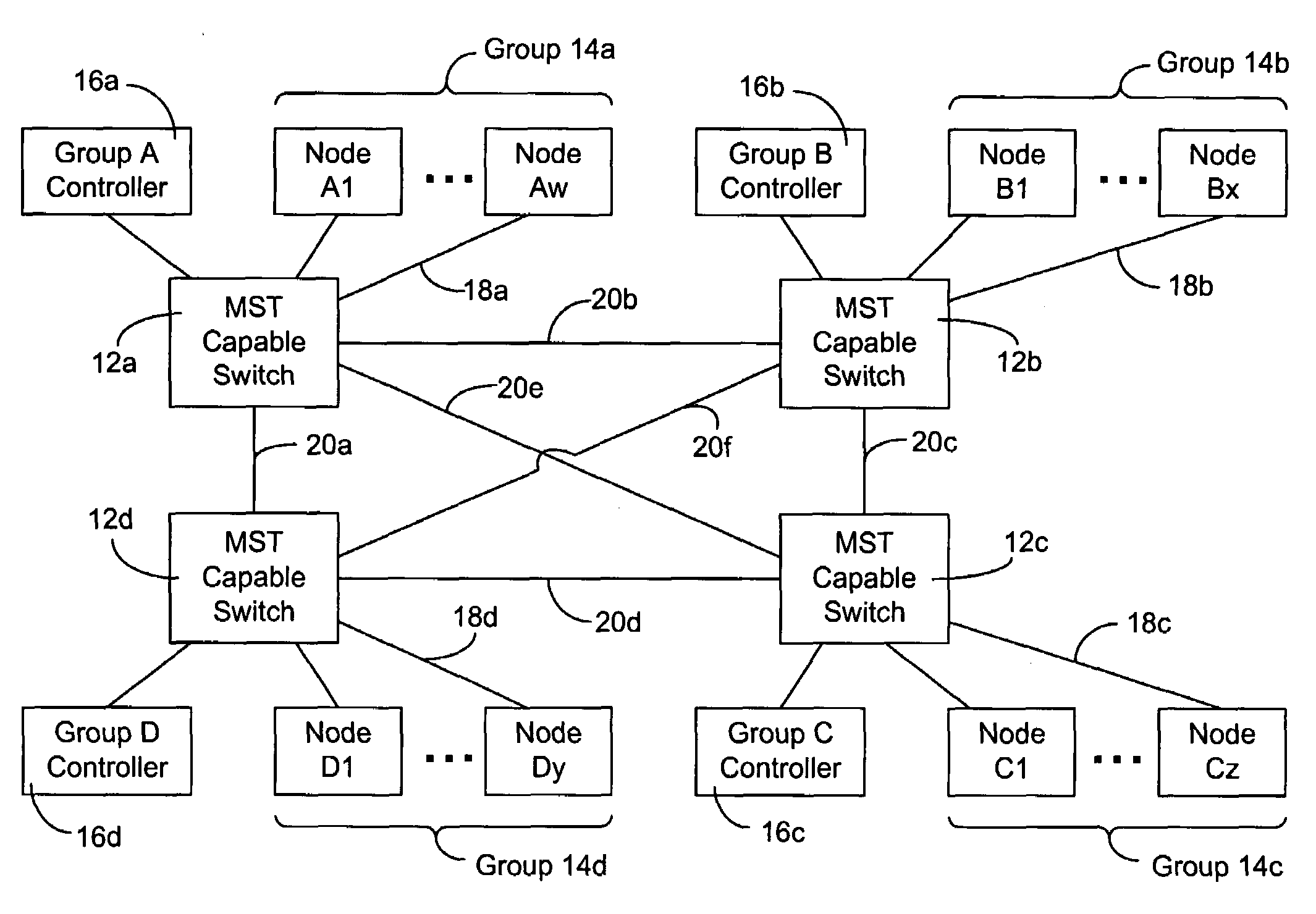
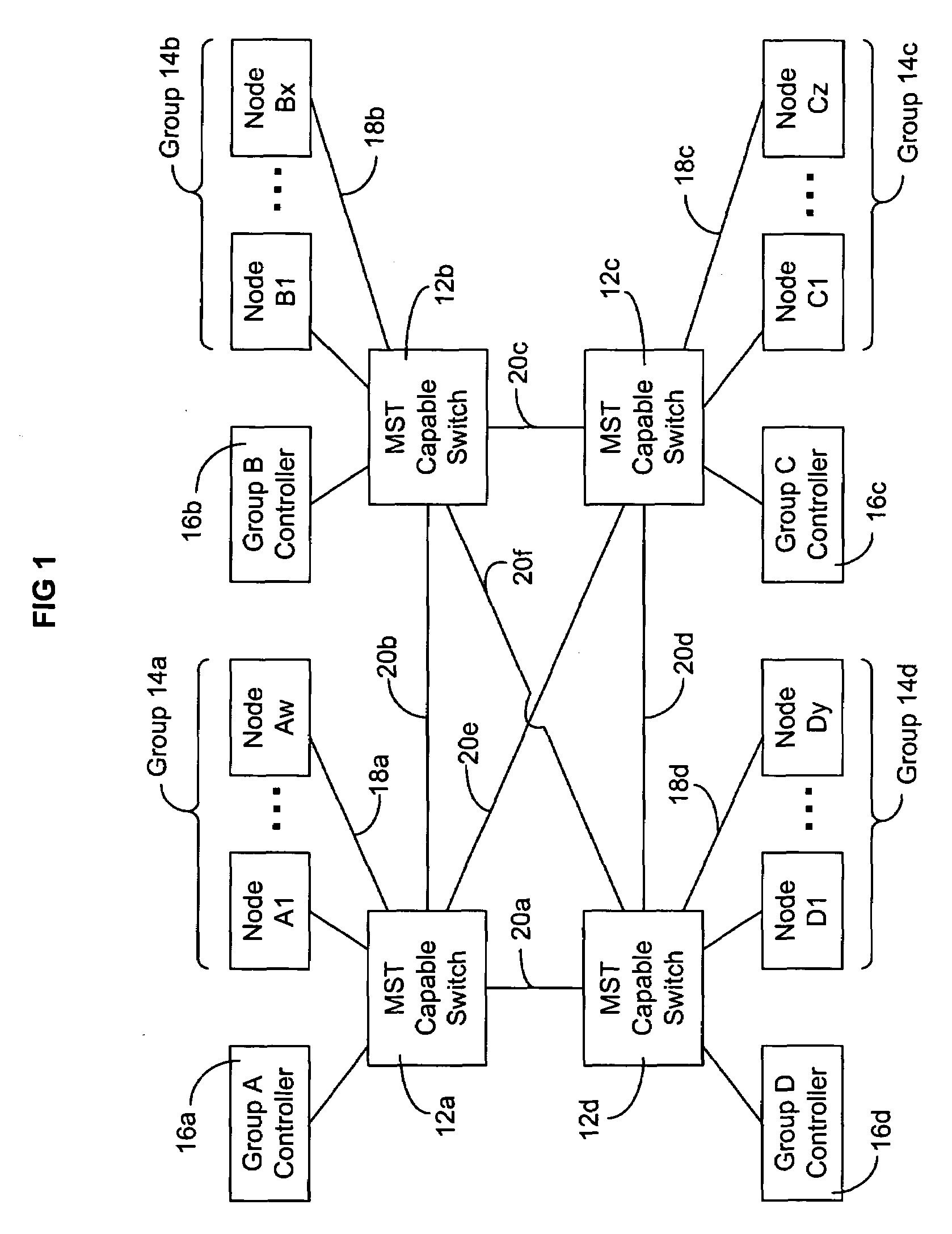
Automatically maximizing network link utilization using virtual networks
A system and method for automatically configuring a network so that each switch in the network is aware of the Multiple Spanning Tree Instances (MSTI) of each other switch and the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) that each switch uses. This is achieved through the use of controllers connected to each switch. A master switch is elected and the master switch monitors messages to determine if a switch should be using an alternative MISTI. If so, the master switch instructs a switch to use an alternative MSTI. Either a switch or a node connected to the switch may determine which VLAN to use in sending messages, subject to configuration from the controller of the master switch. Messages are periodically sent by each controller to educate other controllers to aid in learning which node is part of a group connected to a switch, the switch in turn connected to a controller.
Owner:SANDVINE CORP
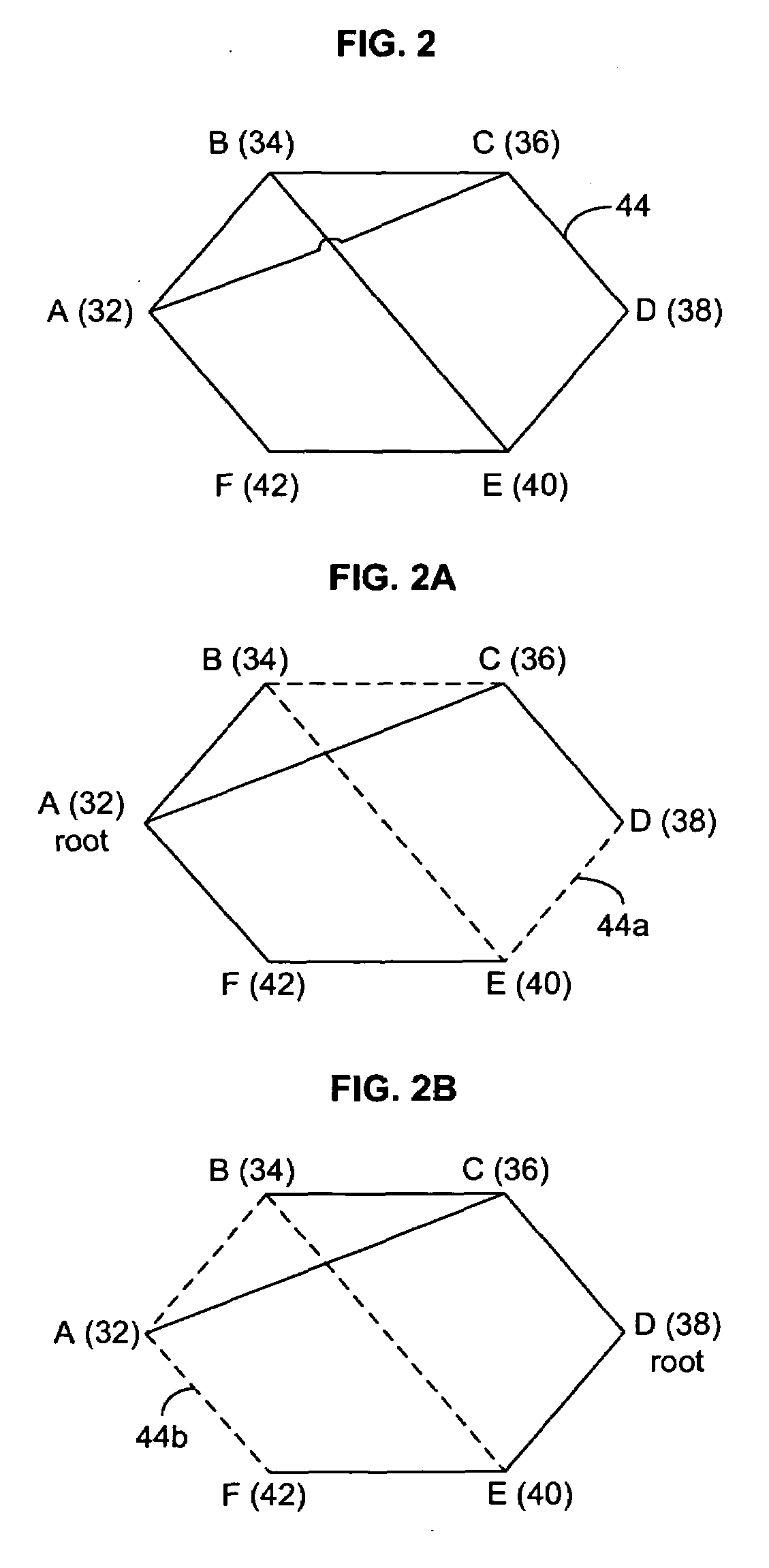
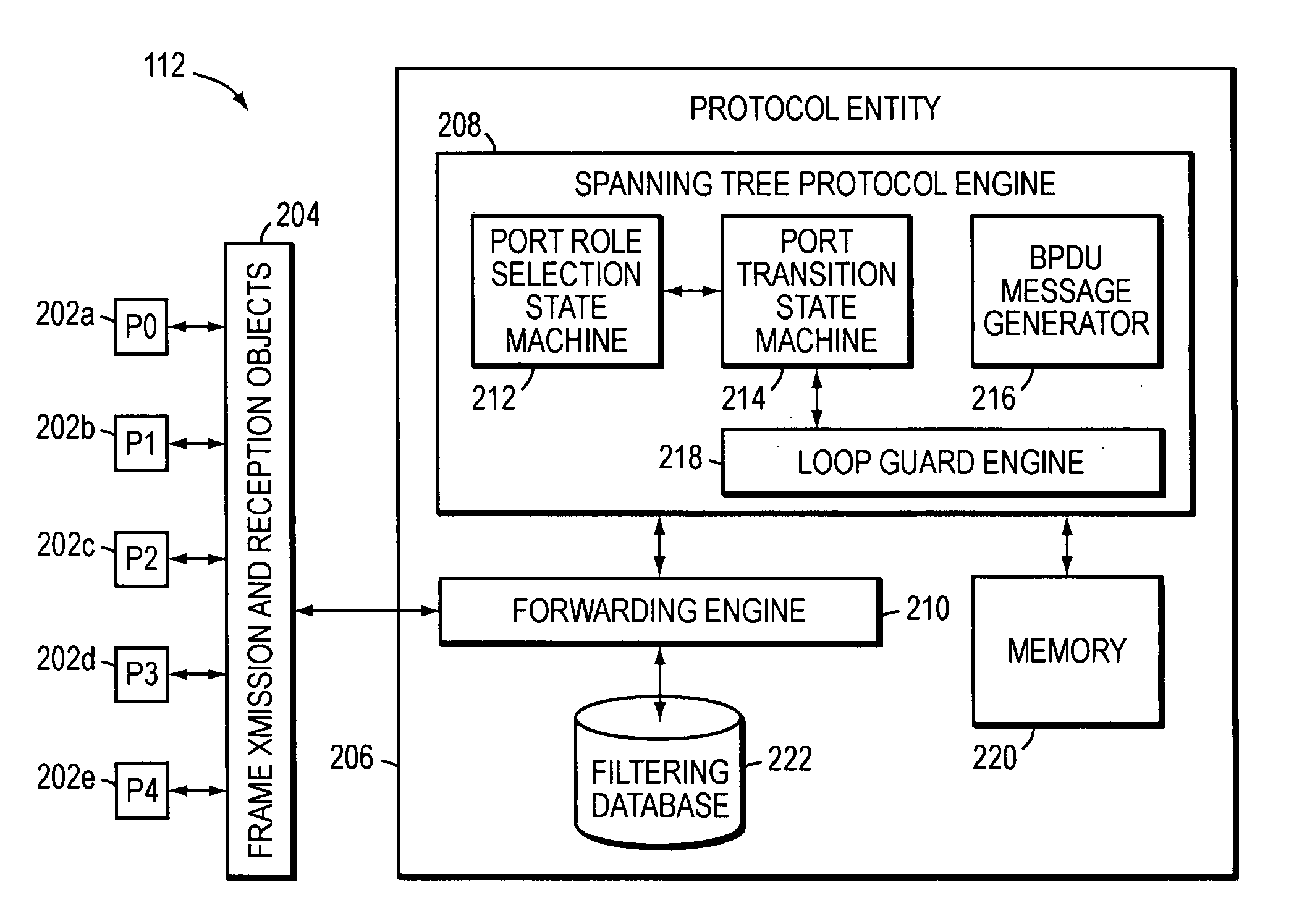
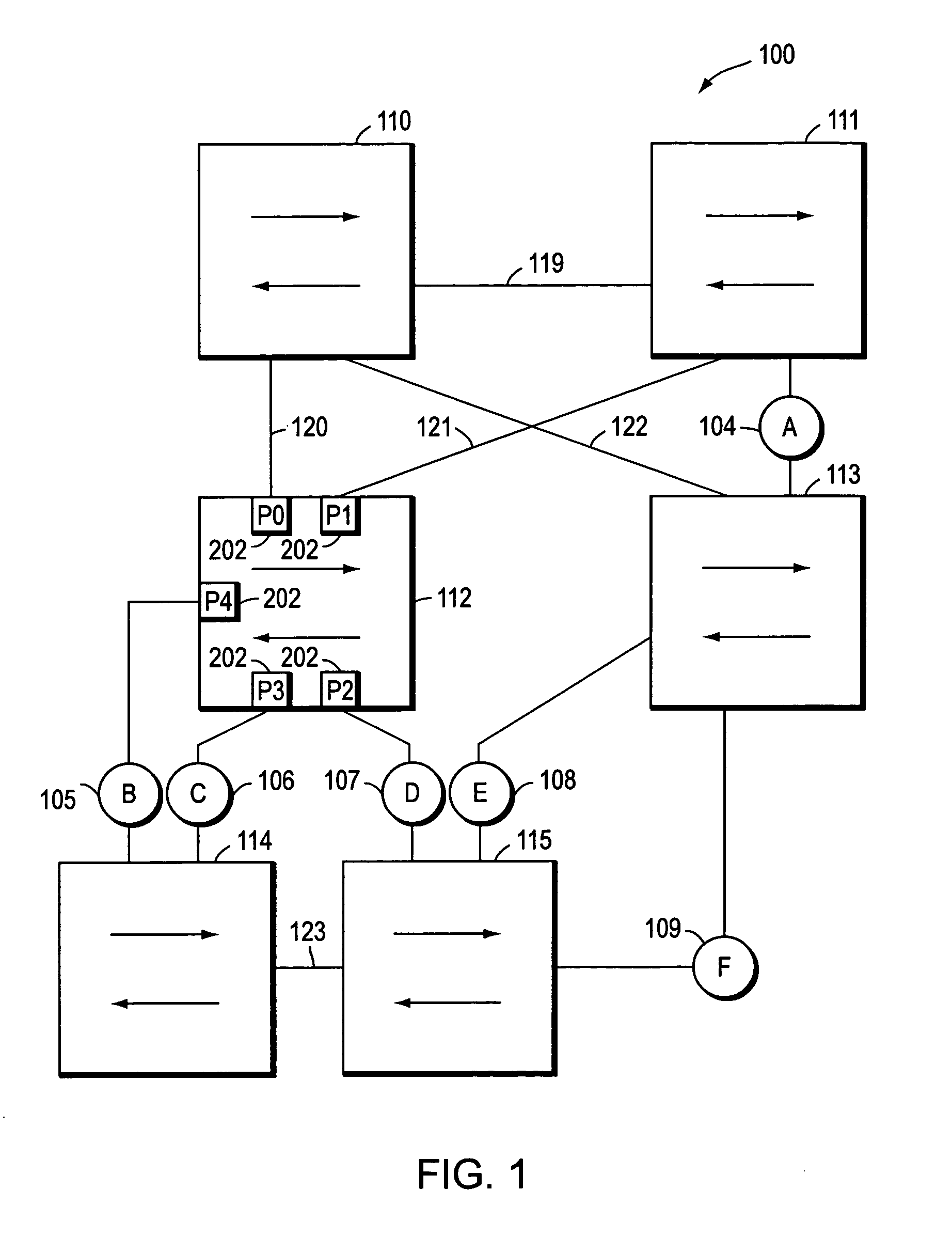
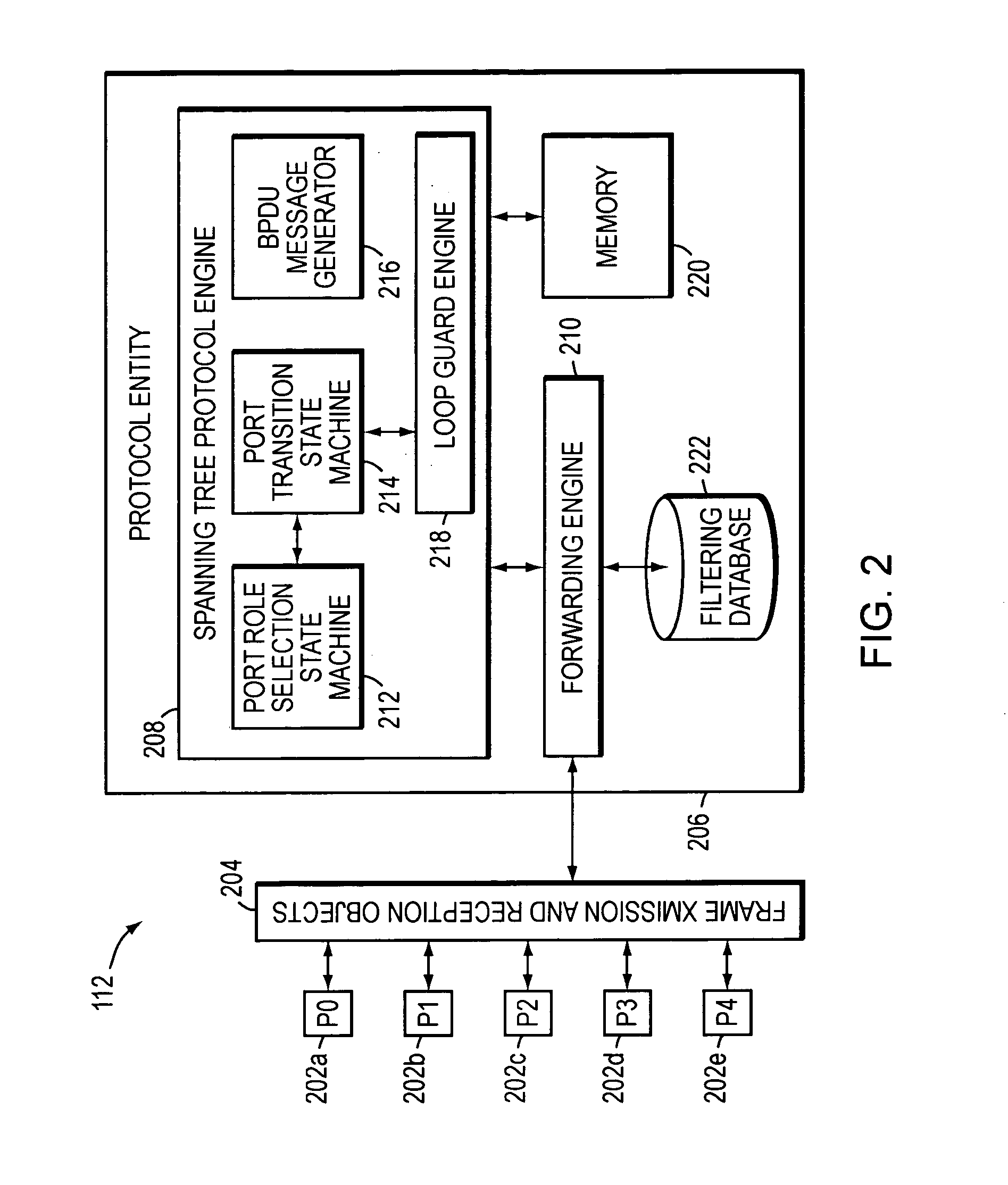
Spanning tree loop guard
ActiveUS7061875B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkEngineering
A system and method prevents the formation of loops that are not detected by the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). An intermediate network device preferably includes a plurality of ports for receiving and forwarding network messages and a STP engine in communicating relationship with the ports. The STP engine transitions the ports among a plurality of spanning tree port states, including a discarding state, a learning state and a forwarding state. The device further includes a loop guard engine that is in communicating relationship with the STP engine and the ports. The loop guard engine monitors the receipt of configuration bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) messages by the ports. If a given port stops receiving BPDU messages, the loop guard engine prevents the STP engine from transitioning the given port to the forwarding state. Instead, the loop guard engine preferably causes the port to transition to a new state in which networks messages are explicitly blocked from being forwarded or received. If the given port subsequently receives a BPDU message, the loop guard engine releases the port from the new state, thereby allowing it to transition to some other spanning tree port state.
Owner:CISCO SYSTEMS INC
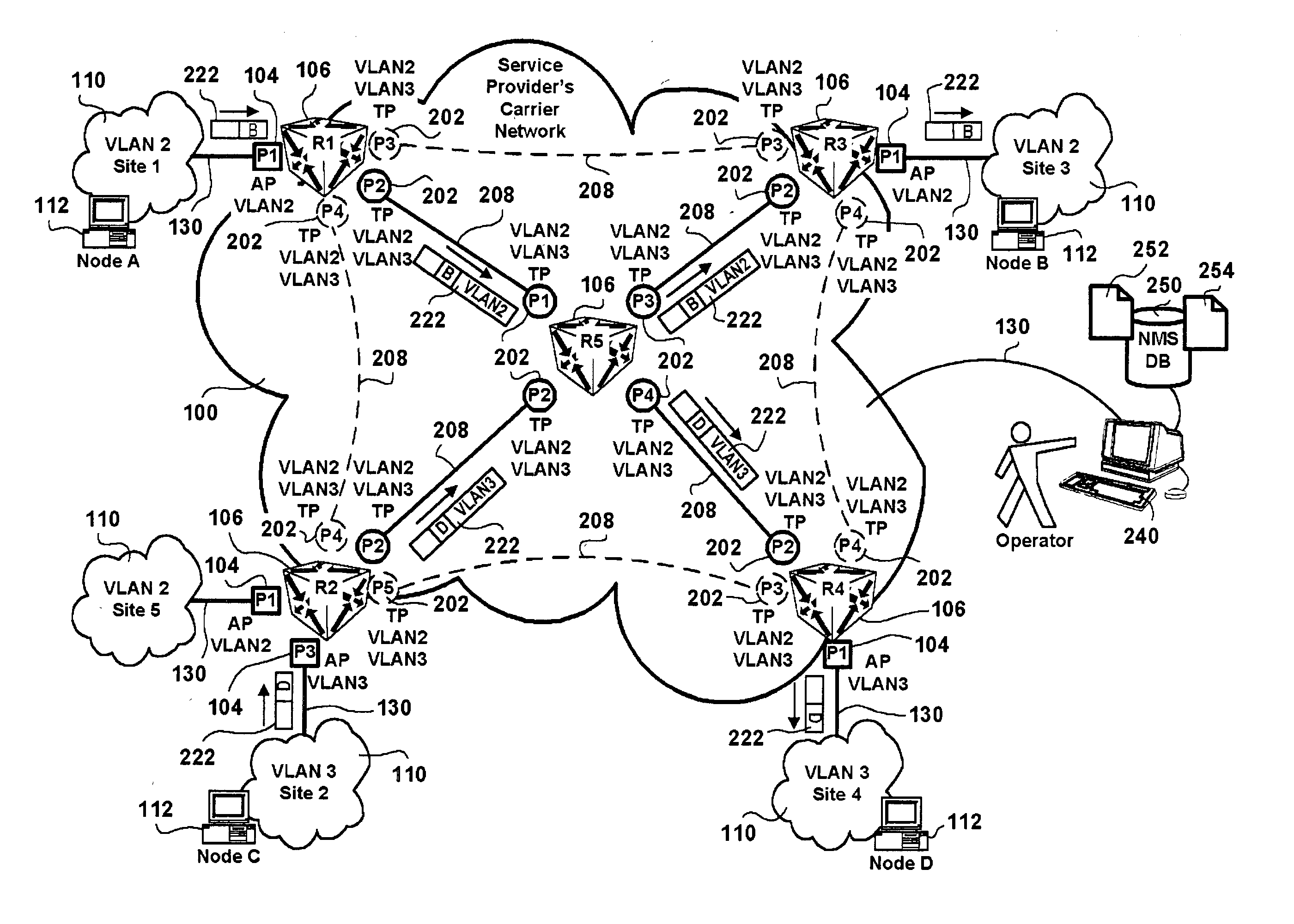
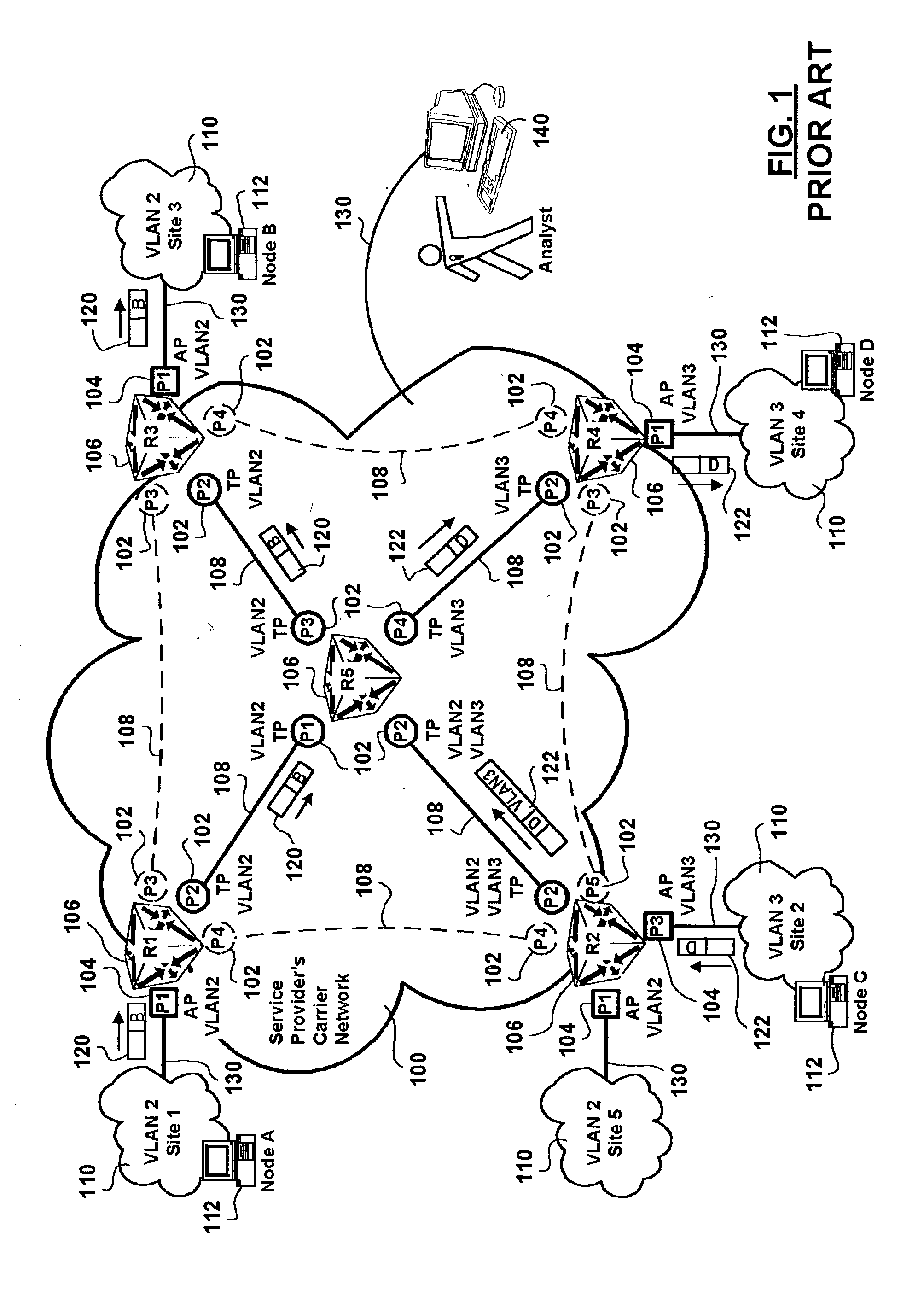
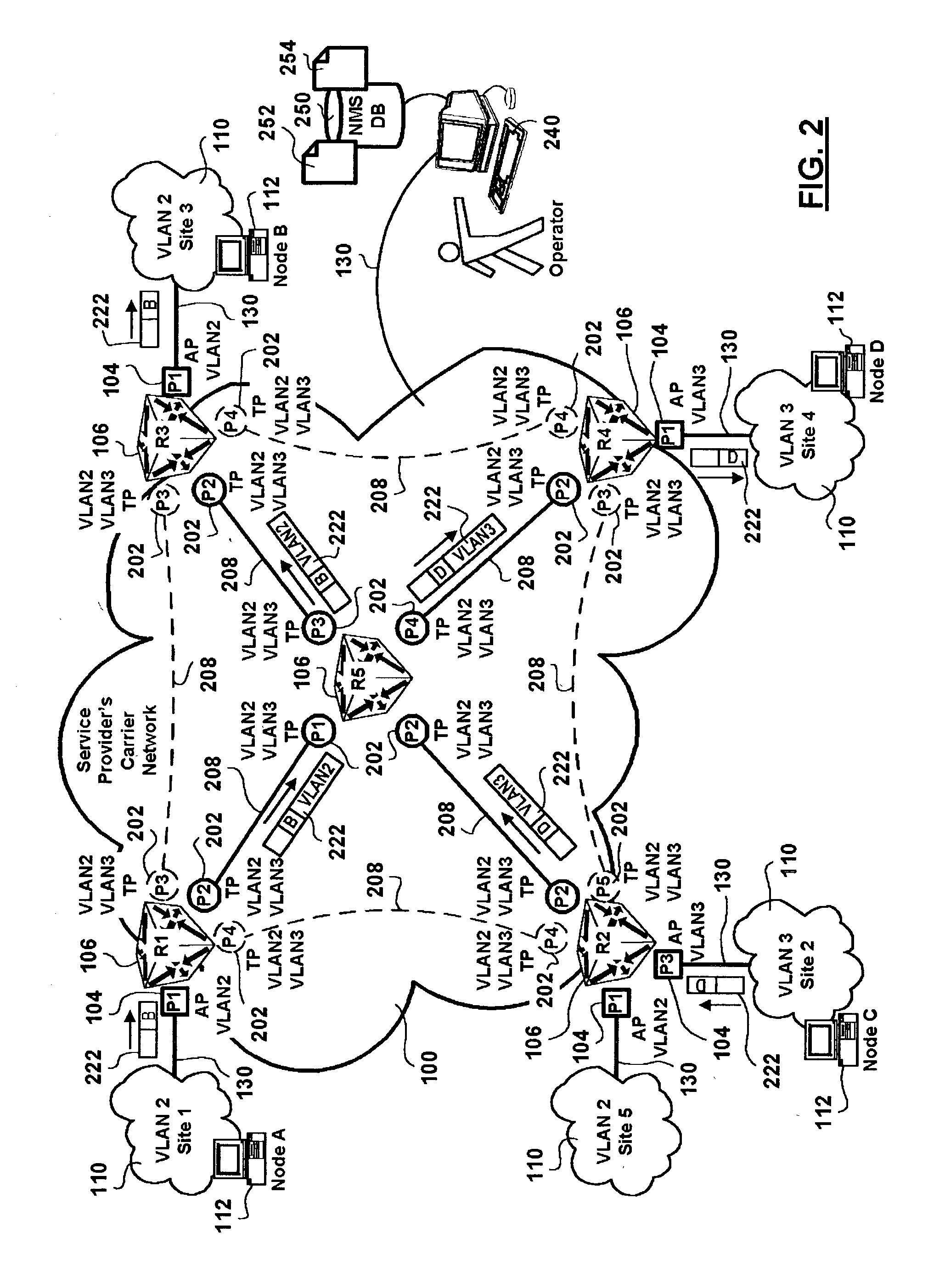
Stackable virtual local area network provisioning in bridged networks
ActiveUS20040042454A1Improve security levelSolve the real problemNetworks interconnectionHuman–machine interfaceTrunking
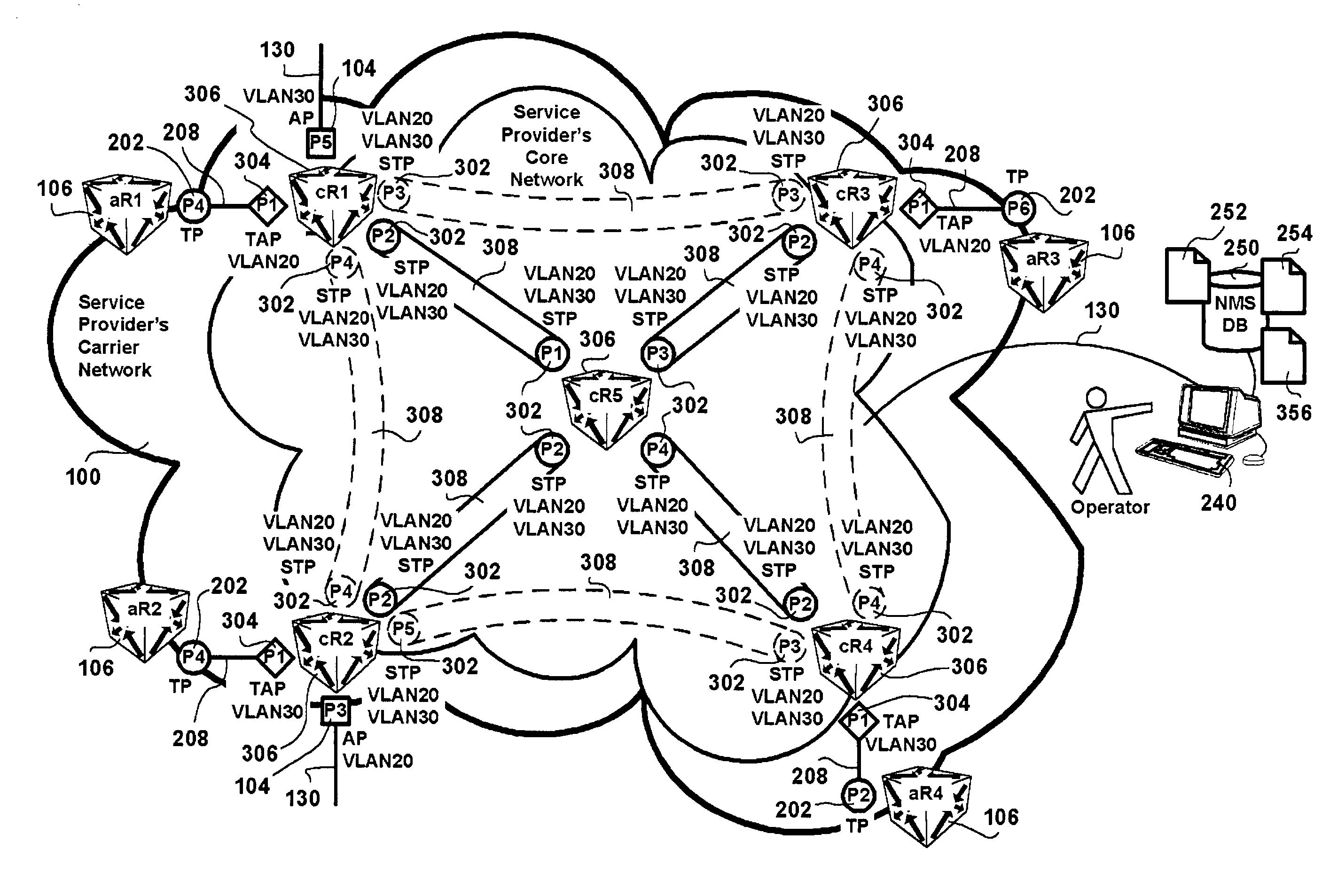
A method and human-machine interface for backbone Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) provisioning in bridged networking environments are provided. The method includes steps of provisioning backbone VLAN support on every backbone data transport trunk and by extension of every stackable data trunk port in the associated data transport network. The human-machine interface enables an operator to expediently effect VLAN provisioning abstracting the intricacies of the data transport network over which VLAN services are provisioned. Advantages are derived from backbone VLAN provisioning independent of an underlying in-use active spanning-tree topology. In particular backbone VLANs are provisioned over spanning-tree stand-by designated backbone data transport trunk links and therefore preprovisioned in the case of spanning-tree re-configuration. Customer VLANs are mapped onto backbone VLANs ensuring data traffic differentiation, and providing standard VLAN identifier portability. Operator VLAN provisioning tasks are lessened via provisions for the selection of all backbone / stackable data transport trunk links / ports in the data transport network in effecting VLAN identifier associations therebetween.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Data frame routing method and network bridge
InactiveUS20120044837A1Reduce the numberRobust controlStar/tree networksPort forwardingComputer science
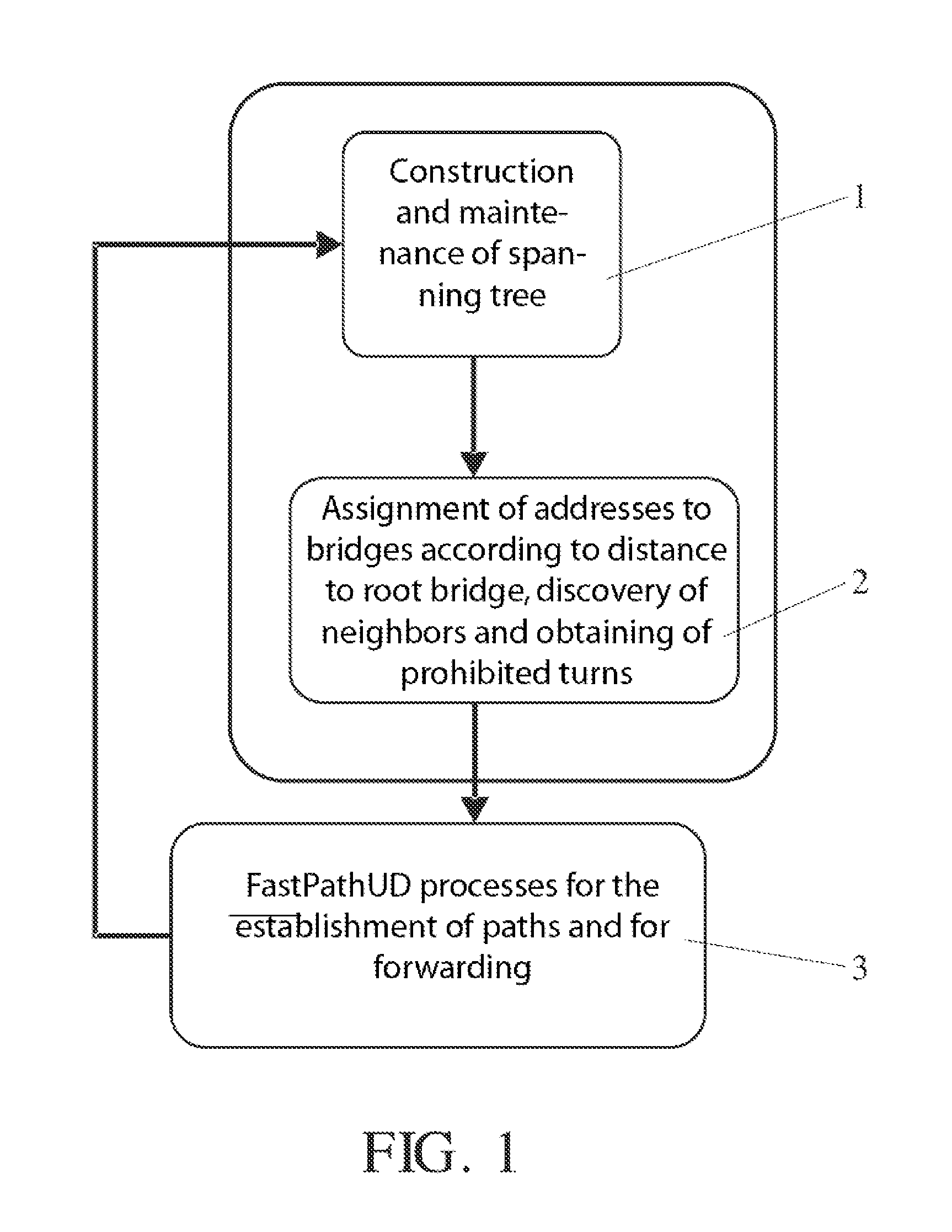
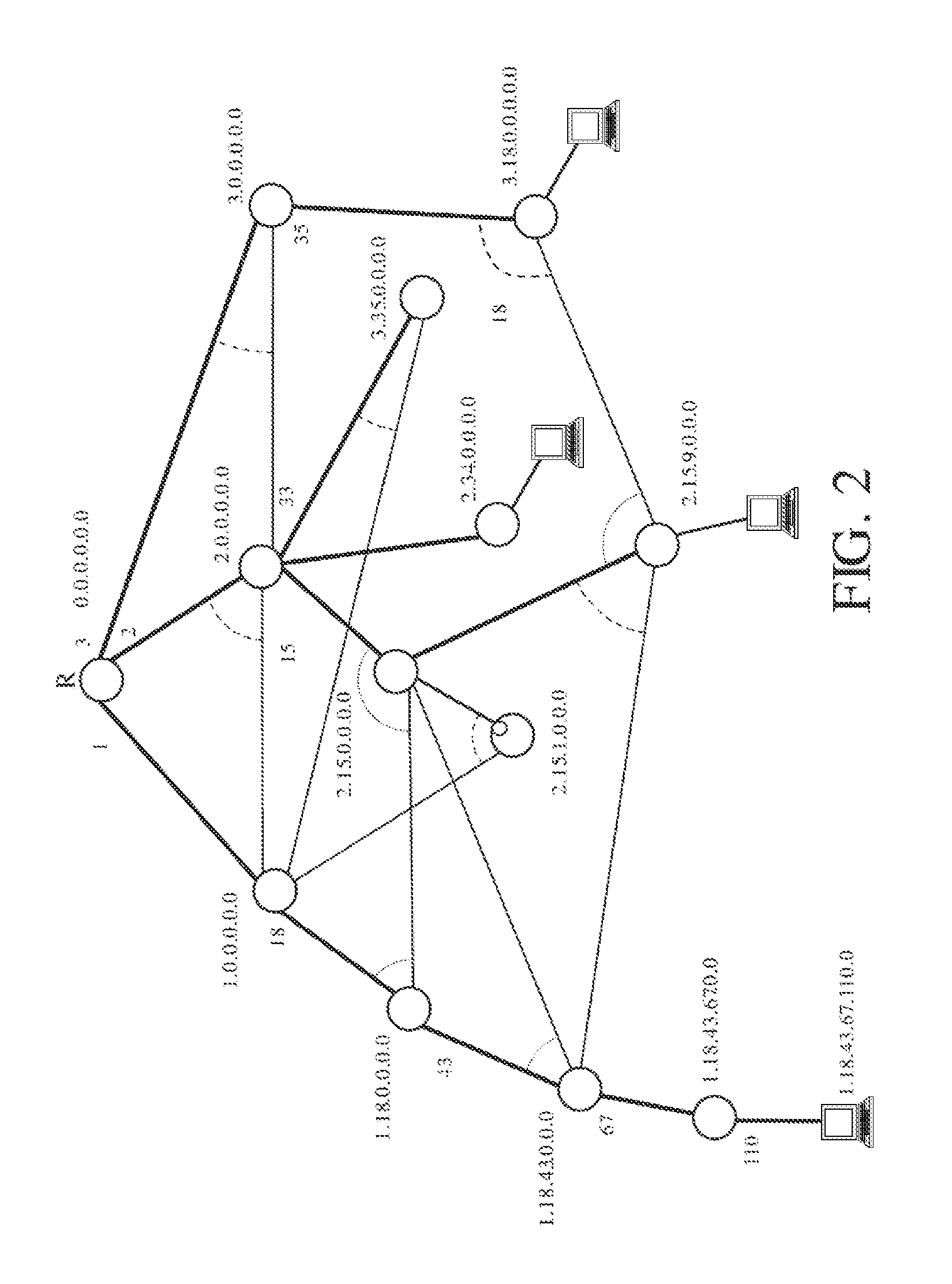
A method operates at the data link level. Each bridge associates, during a guard time, the port through which a frame is first received with a source MAC address until a unicast reply frame confirms the matching two-way path between the source and destination addresses. Any frame from the same source received through another different port is discarded. Each bridge forwards the received broadcast frames through the rest of the ports, except those involving prohibited (down-up) turns, and deviates (or optionally returns) the unicast frames with an unknown or aged destination address through the spanning tree. The protocol can operate with encapsulation in the border bridges or without encapsulation, using in this case the replacement of universal MAC addresses in the border bridges with local MAC addresses. The establishment and control of paths can optionally be performed proactively by the border bridges, especially the bridges connected to servers.
Owner:UNIV DE ALCALA DE HENARES +1
Automatically configuring mesh groups in data networks
InactiveUS20100020726A1Prevent floodingReduce adverse effectsData switching by path configurationAuto-configurationTransfer mode
In one embodiment, a method for setting up a flow-through mesh group (FTMG) for transmitting link-state packets (LSPs) in a network having a plurality of nodes interconnected by links. The FTMG is a combination of multiple spanning trees for the network through which LSPs are forwarded. FTMG set-up messages are received at ports of each node of the network from peer ports of linked nodes. FTMG set-up messages identify root nodes of the multiple spanning trees and the transmission modes of the peer ports. The FTMG set-up messages are used to determine (1) a root node for each spanning tree, (2) a root port on each node for each spanning tree, and (3) directionality of ports of the nodes. FTMG set-up messages are then used to determine the transmission mode of ports of the nodes and, subsequently, to update the spanning trees and transmission modes, as needed.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and apparatus for designing a spanning tree virtual network
ActiveUS20050063321A1Reduce varianceEvenly dispersedStar/tree networksNetworks interconnectionShort path algorithmLeast cost
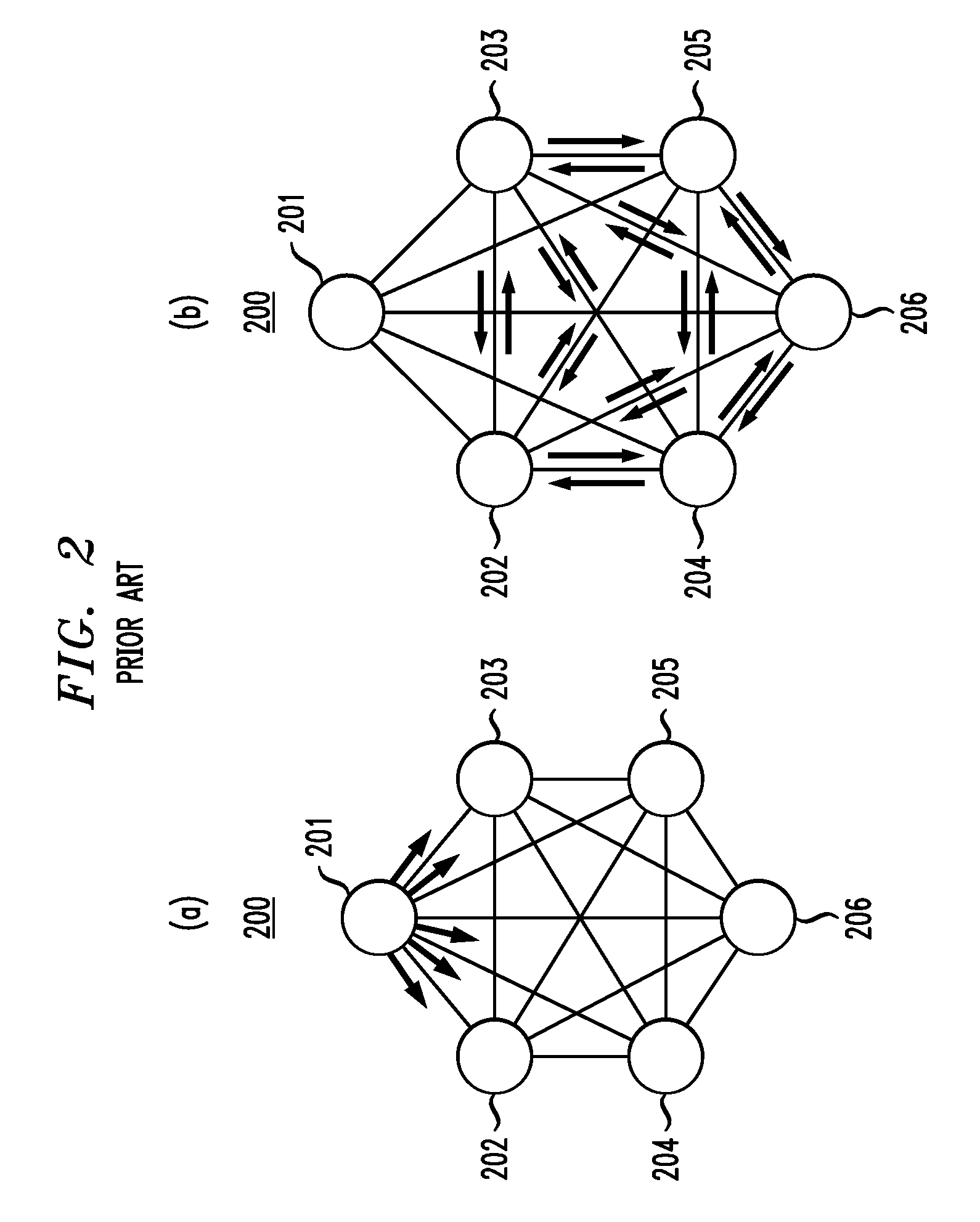
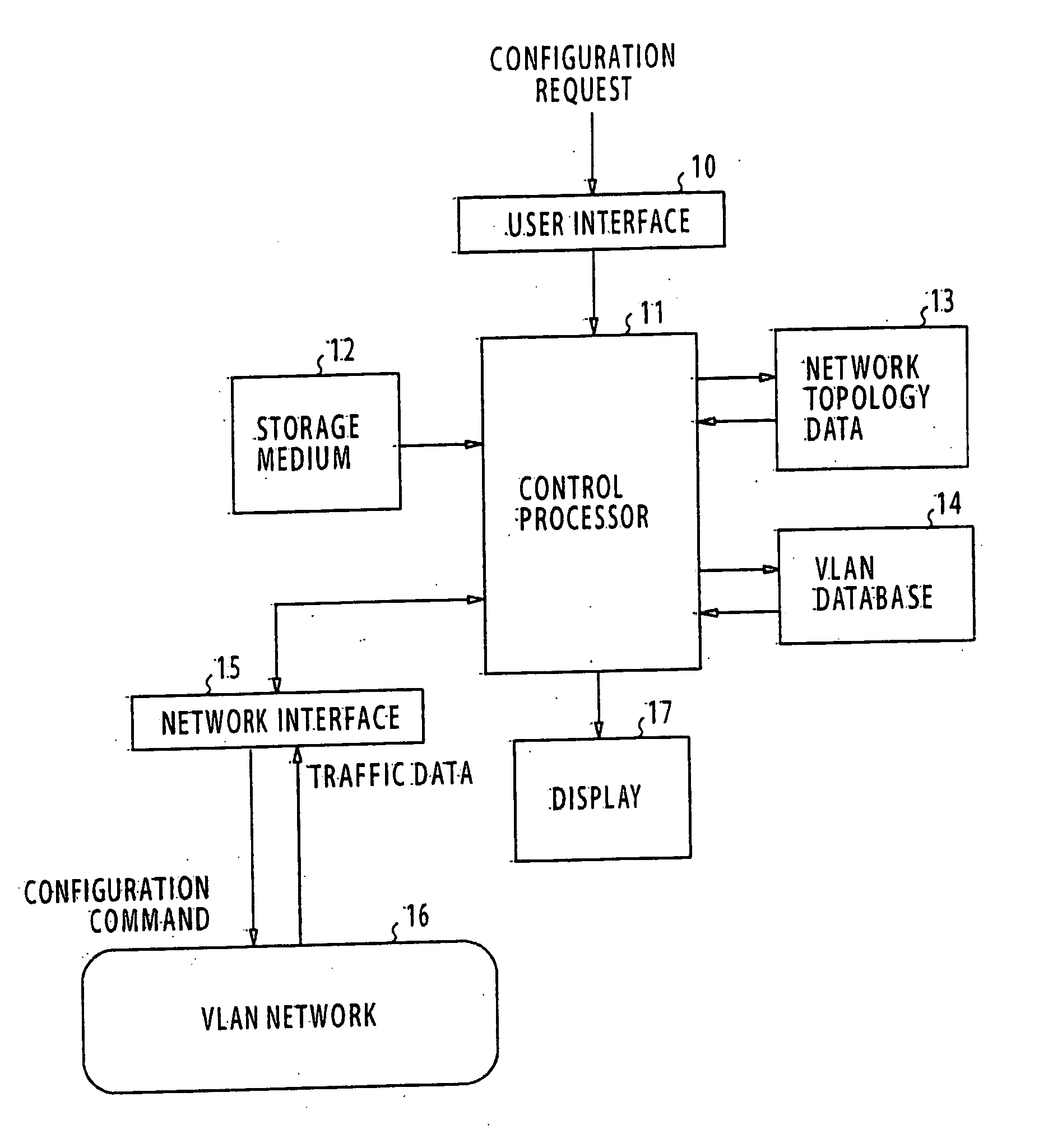
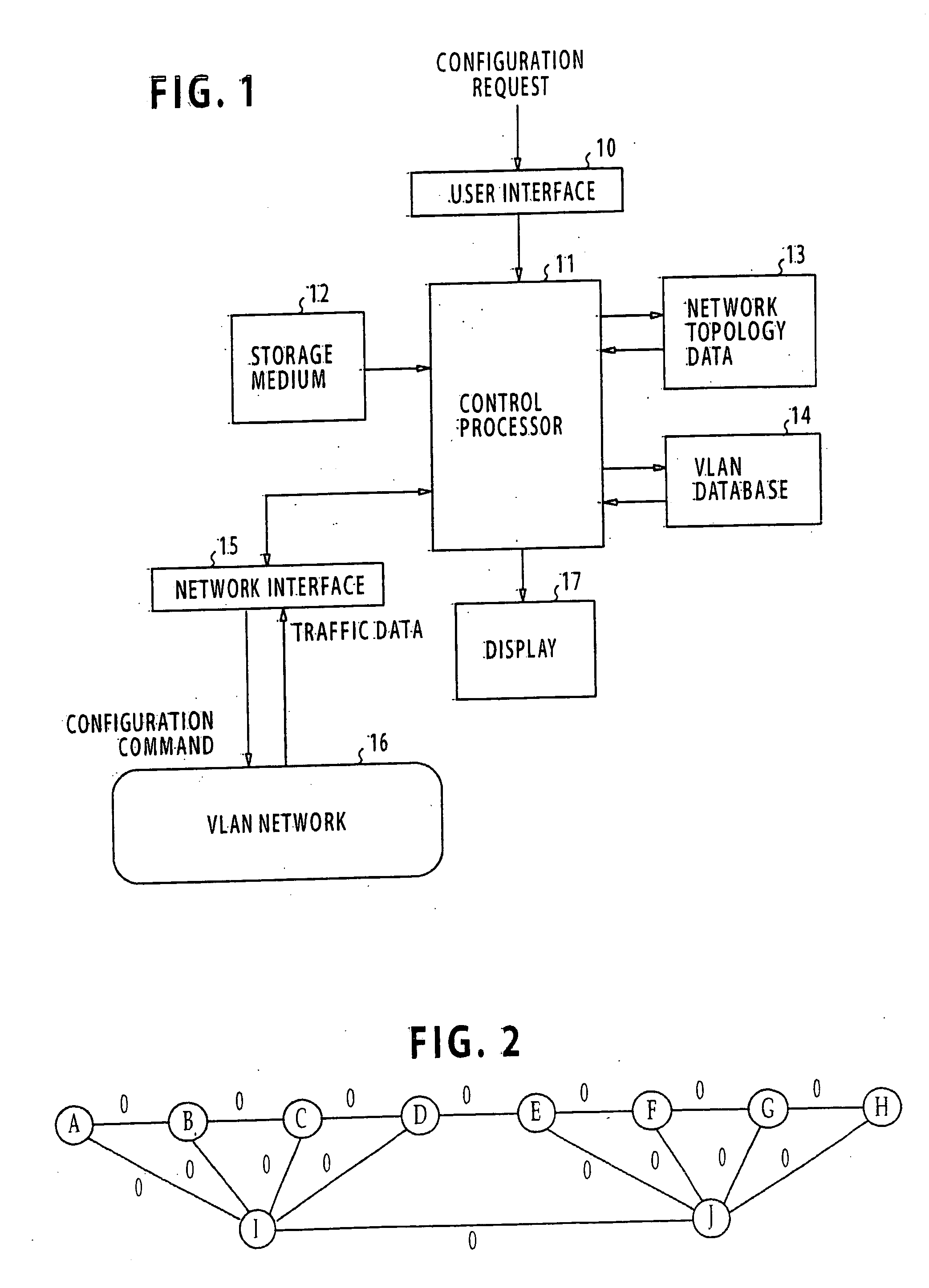
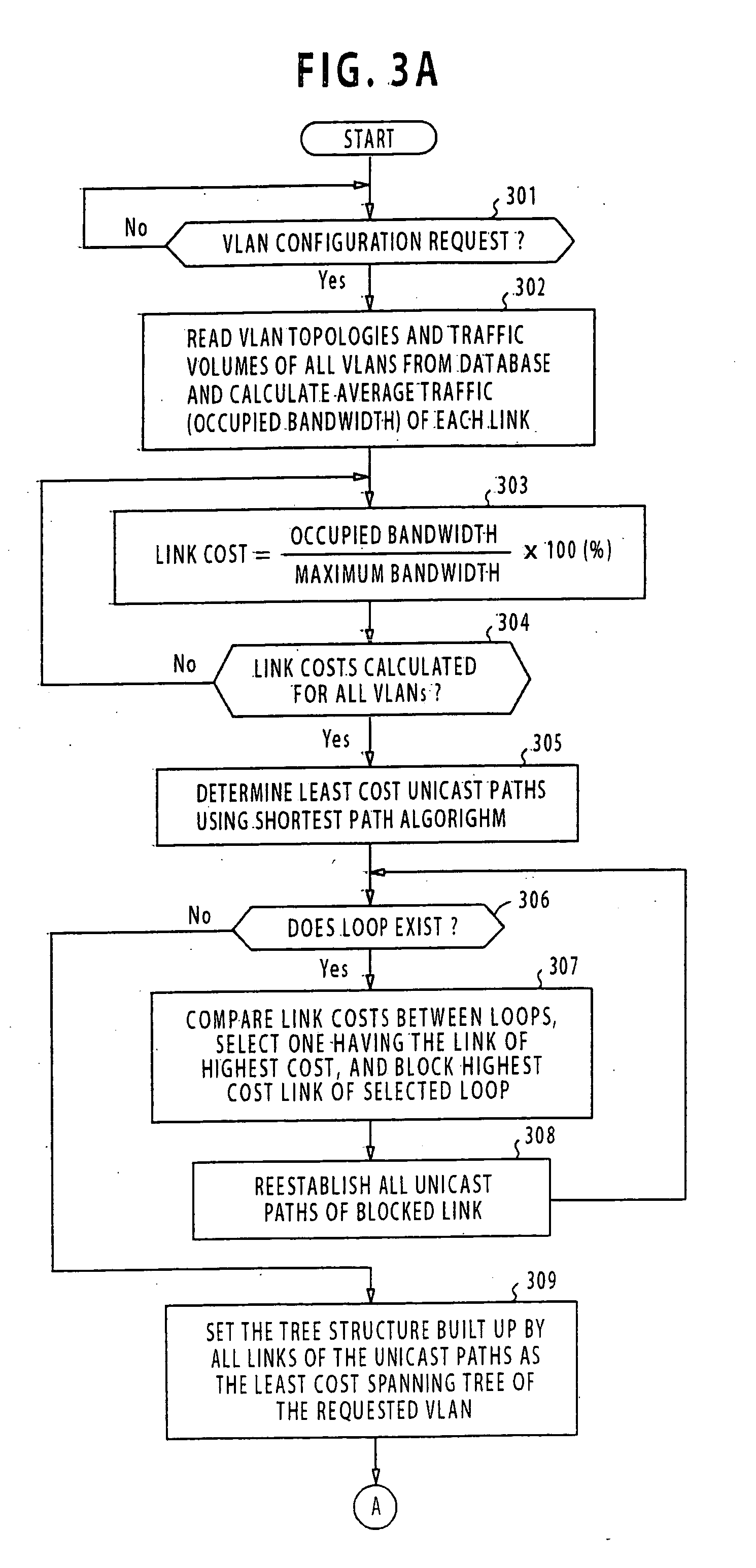
An apparatus for designing a virtual VLAN network includes a database containing data representing a plurality of VLAN networks in a spanning tree topology, each of the VLAN networks being formed of a plurality of VLAN member nodes interconnected by links. In response to a network configuration request from a communications network, control circuitry determines the costs of the links, and then determines least cost unicast paths by using a shortest path algorithm. A search is made through the least cost unicast paths for detecting a loop. If at least one loop is detected, a link of highest cost of the loop is blocked. All unicast paths of the blocked link are reestablished through links that circumvent the blocked link. A spanning tree built up with all the links accommodating the least cost unicast paths is established. Configuration command is sent to the network for configuring it according to the established spanning tree.
Owner:NEC CORP
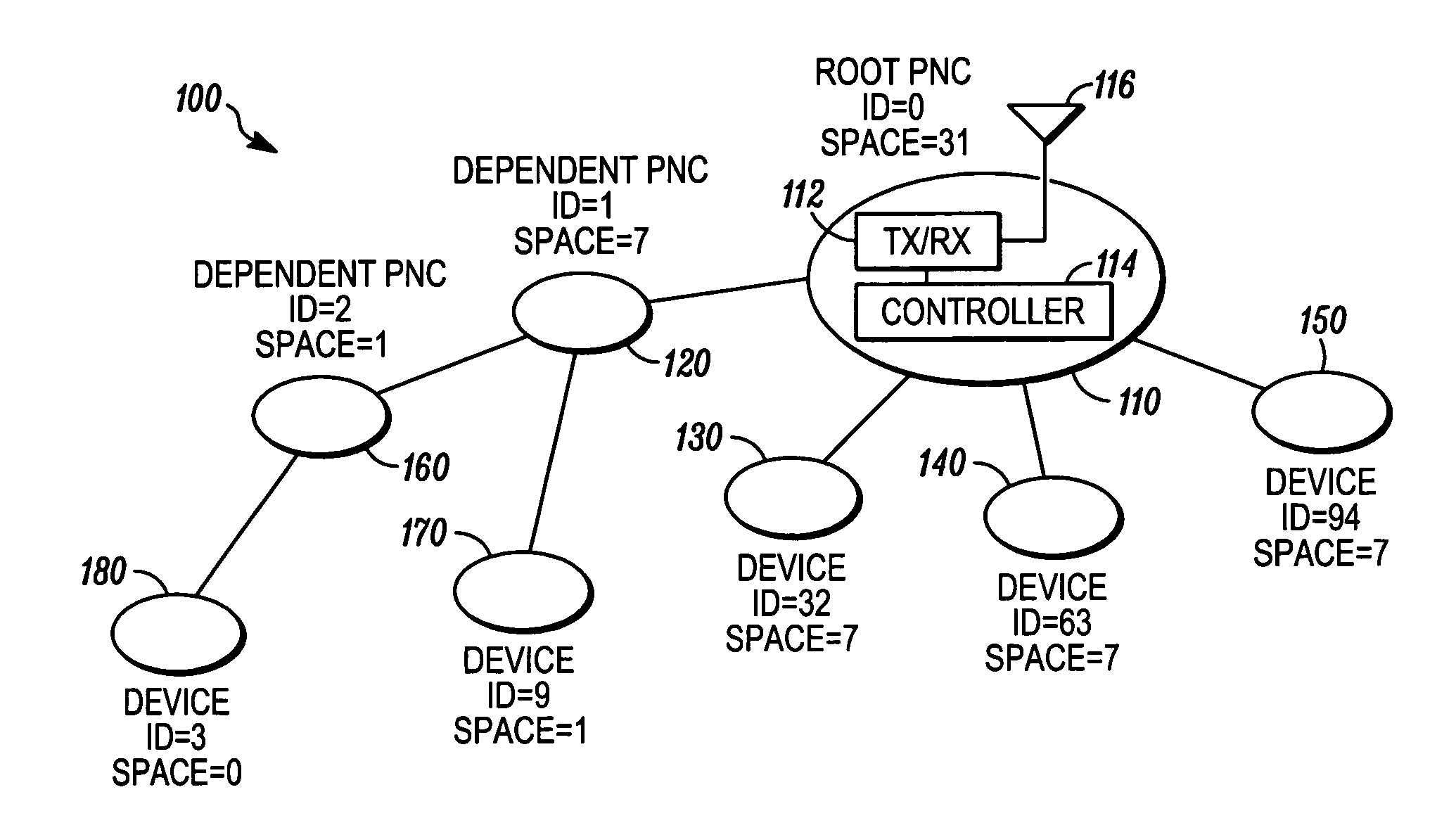
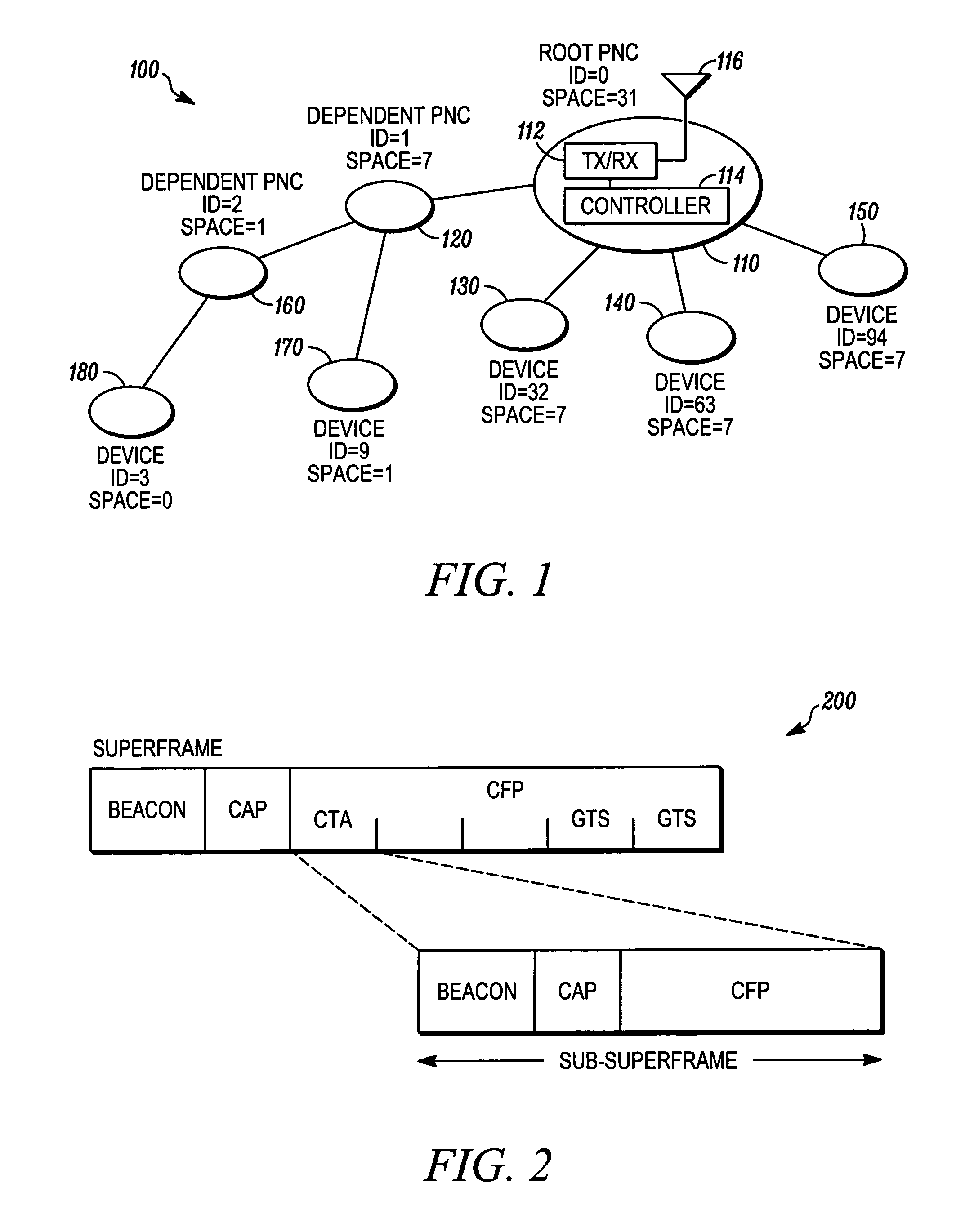
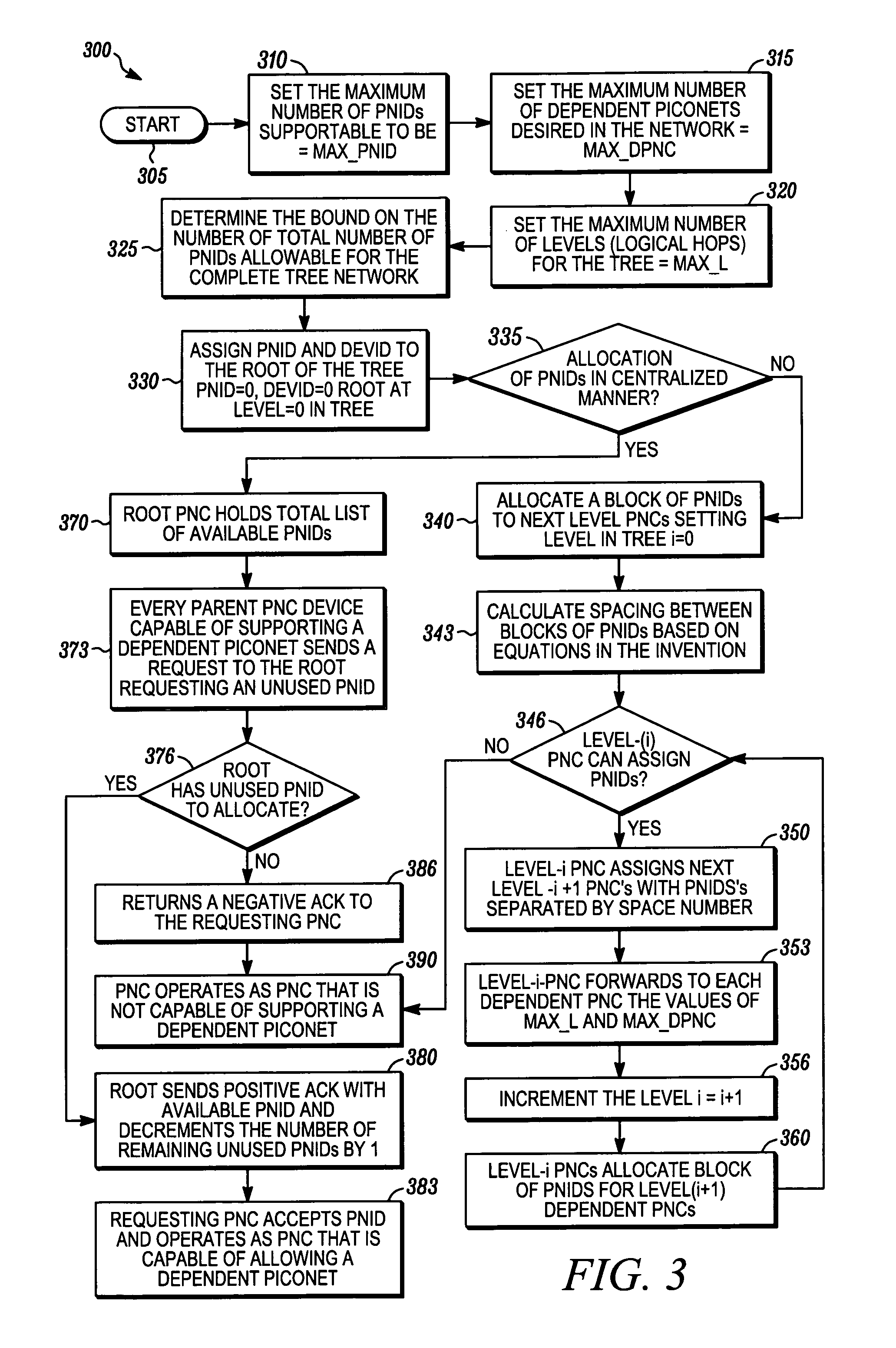
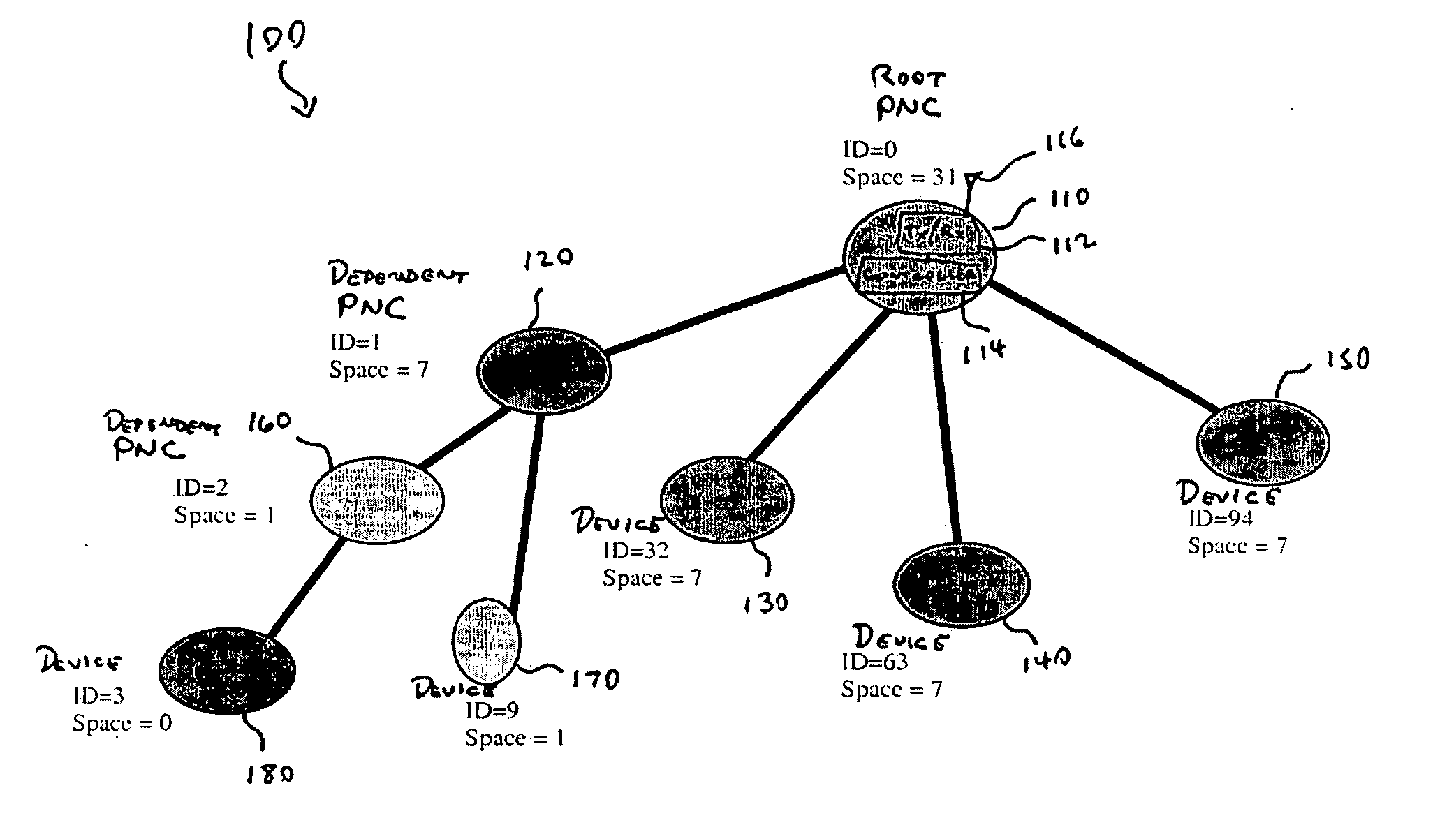
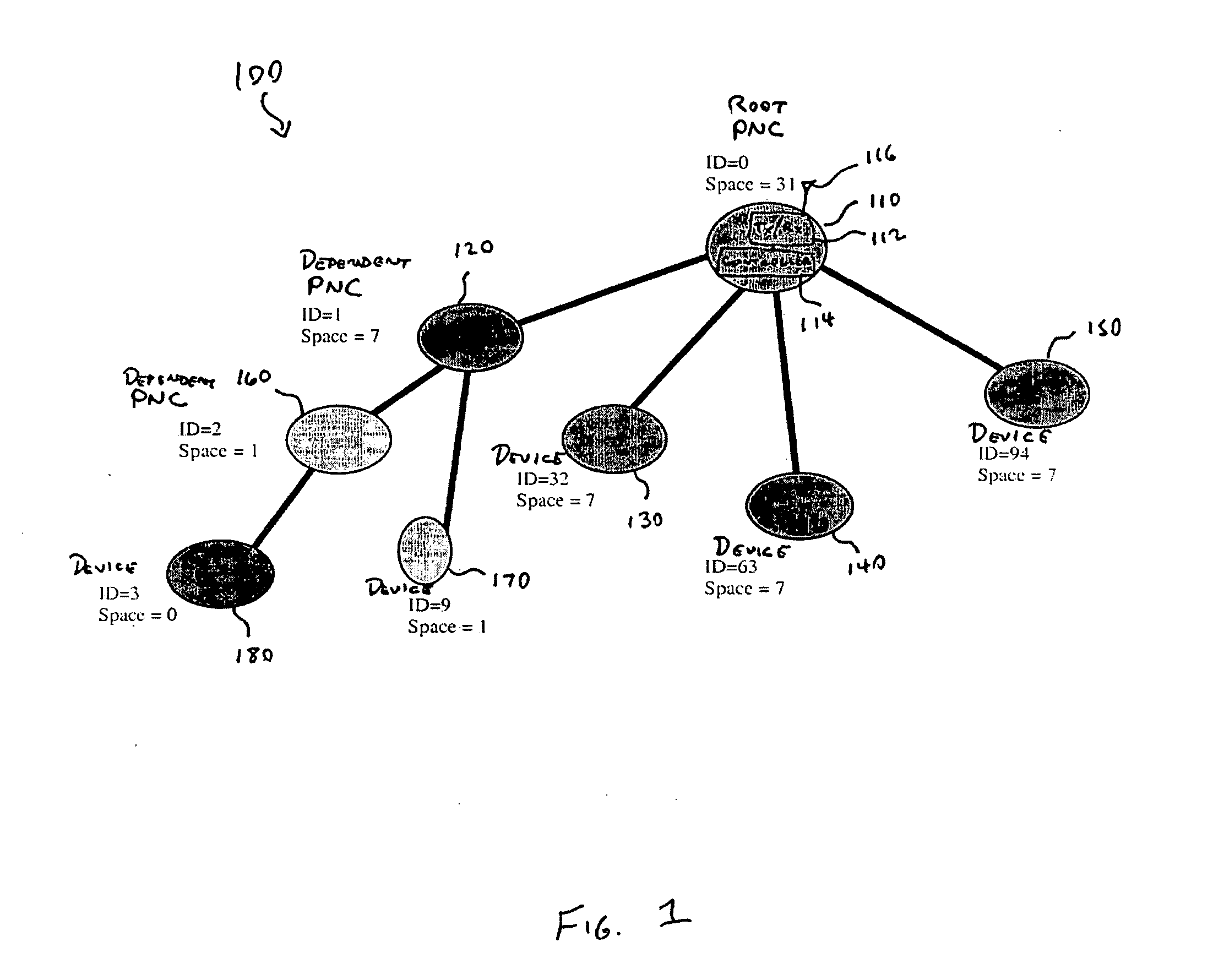
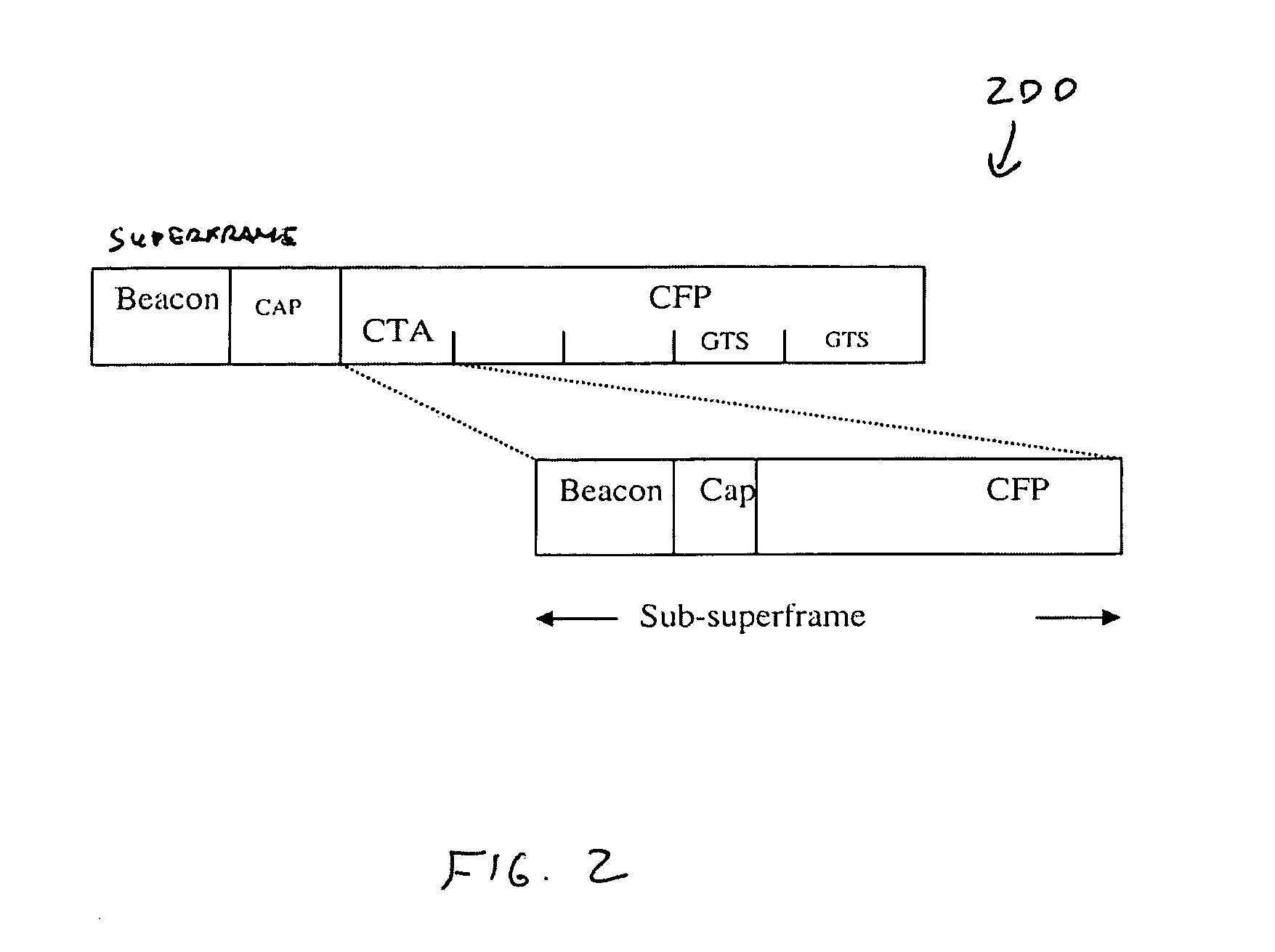
Piconet spanning tree network
An apparatus and method for a spanning tree network. A communication device can connect to a piconet network and the communication device can transmit at least one available piconet identifier prior to receiving a request for the available piconet identifier from a dependent communication device, the available piconet identifier providing a parent piconet coordinator identification for the dependent communication device. A dependent communication device can connect to the piconet network, determine if the communication device can support a dependent piconet, and receive at least one available piconet identifier prior to requesting information regarding establishing a dependent piconet, the available piconet identifier providing parent piconet identification for the communication device for the dependent piconet.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
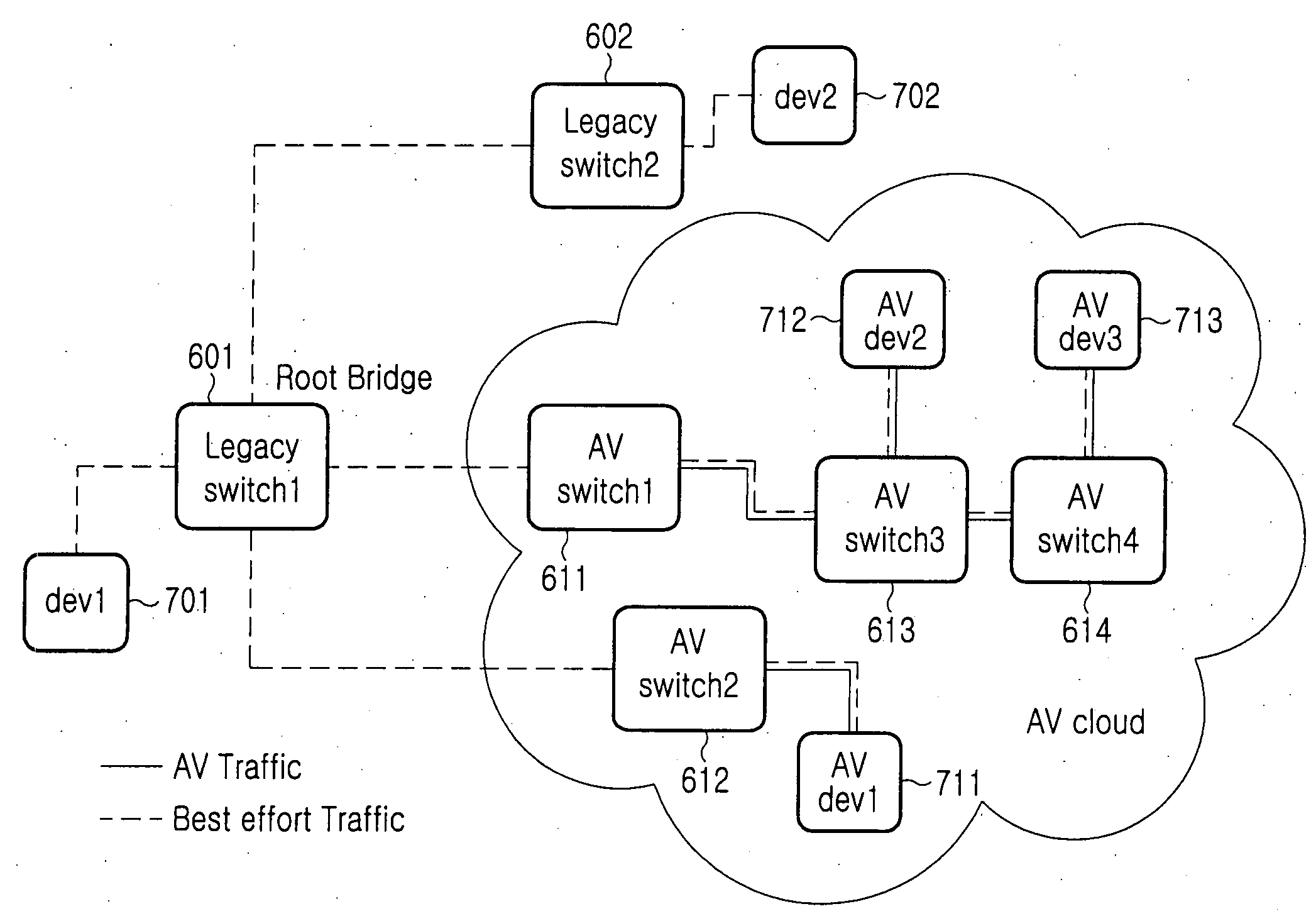
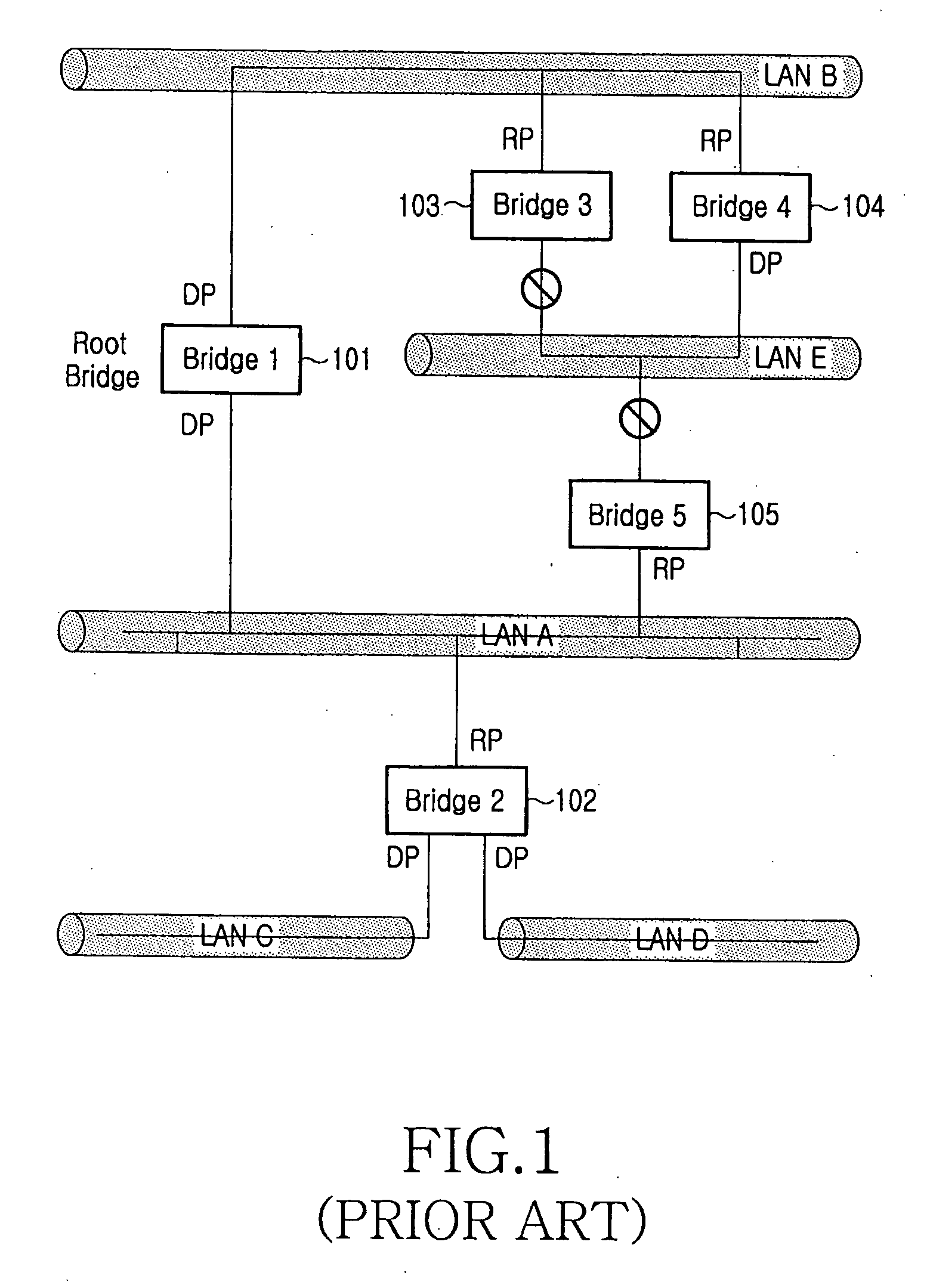
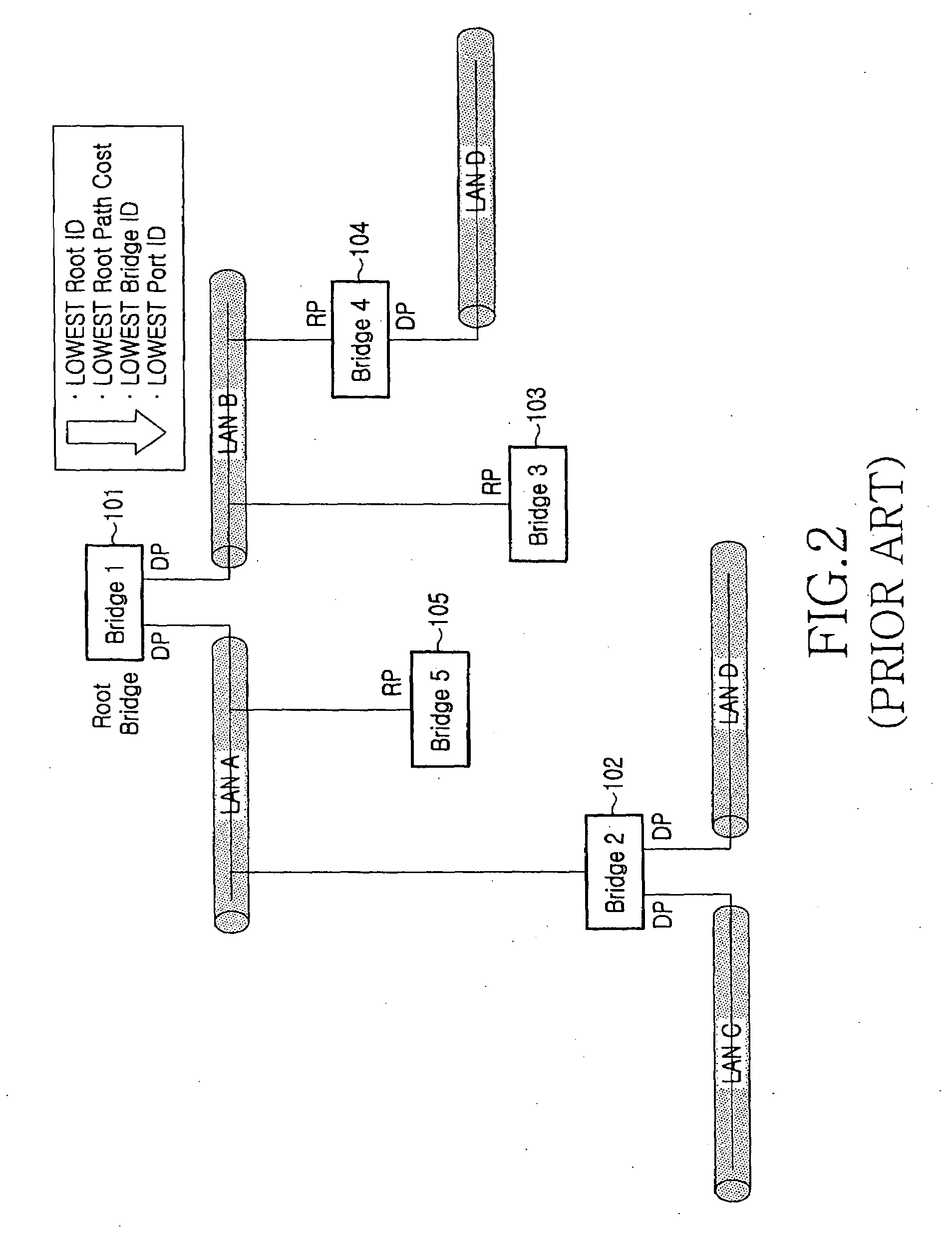
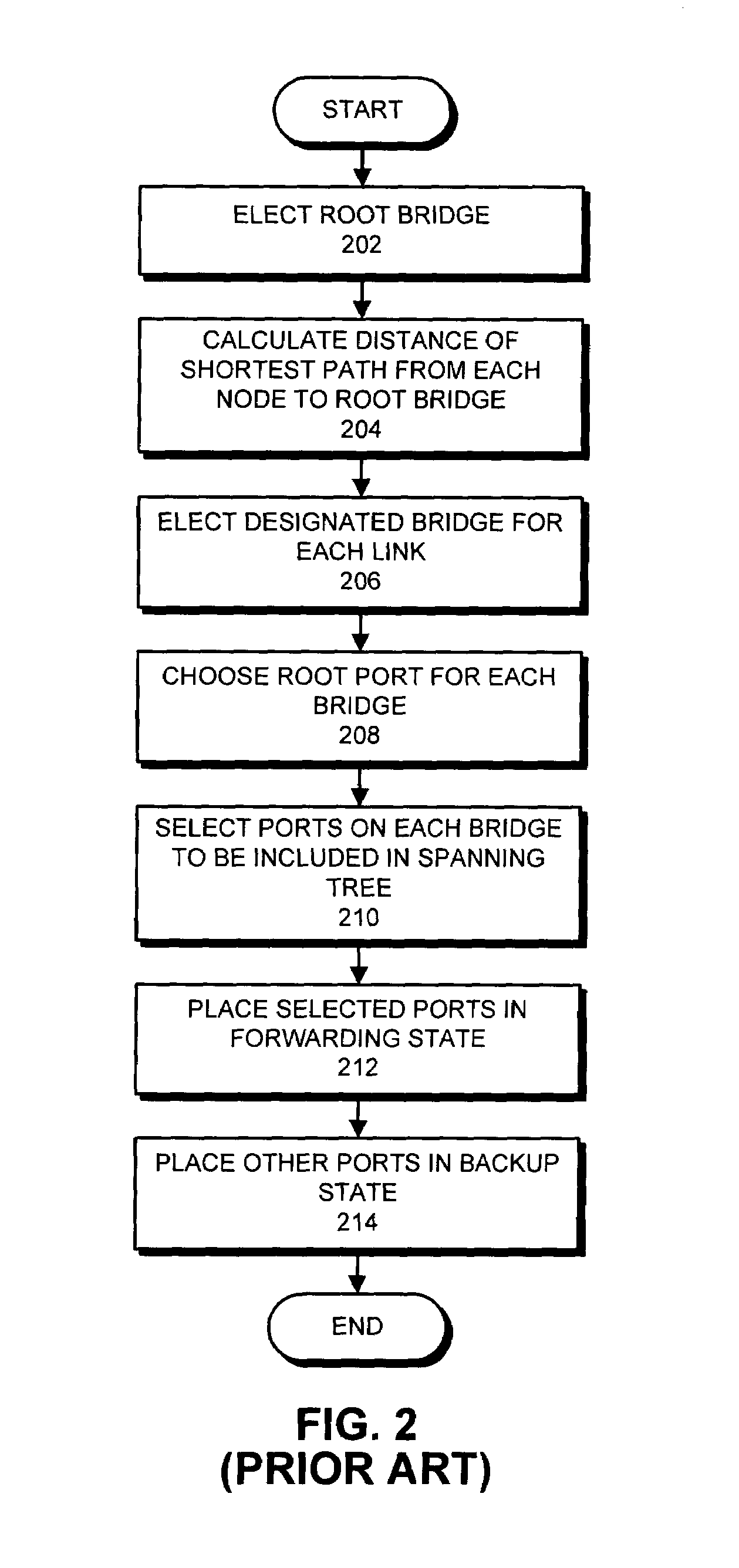
Method for selecting root bridge in configuration of spanning tree
Disclosed is a method, apparatus and computer-readable medium for selecting a root bridge when a spanning tree is configured in an Ethernet network including a plurality of legacy switches and a plurality of synchronous switches. The method comprises the steps of providing in advance identification information in a configuration BPDU message of the synchronous switch, the identification information representing that a corresponding switch is an AV switch, broadcasting configuration BPDU messages by the legacy switches and the synchronous switches; and receiving configuration BPDU messages by the synchronous switch from other switches, confirming bridge priorities according to the synchronous switches through the received configuration BPDU message and the identification information to select a synchronous root bridge, receiving configuration BPDU messages by the legacy switch from other switches, and confirming bridge priorities through the received configuration BPDU messages to select a legacy root bridge.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
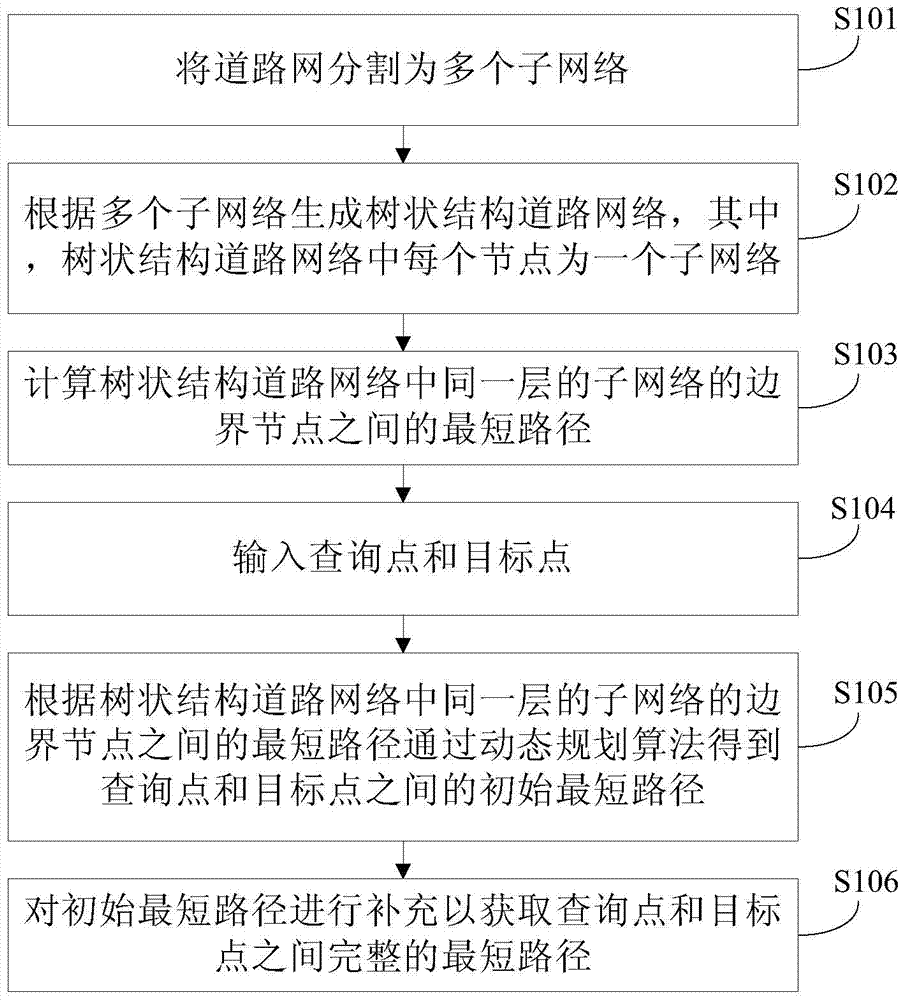
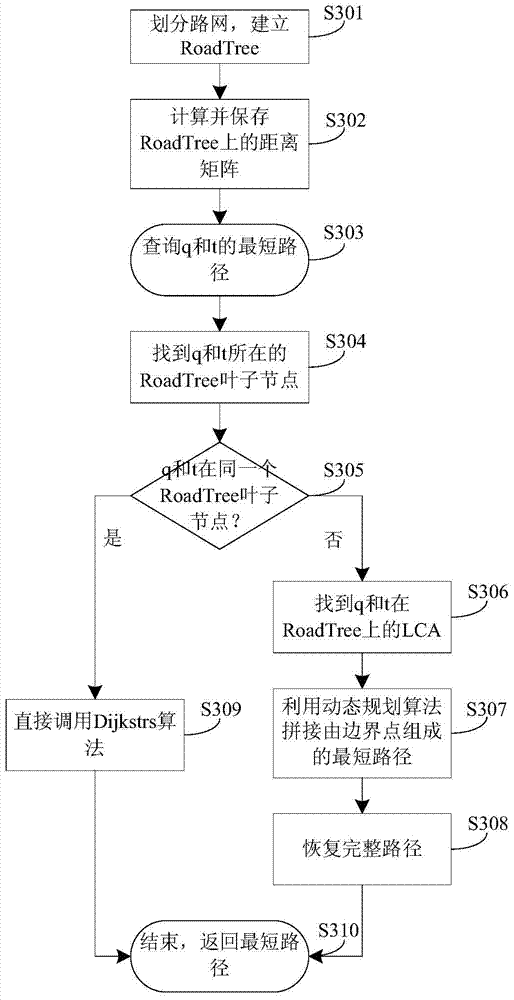
Method and device for searching shortest path of road network
ActiveCN104266656AImprove efficiencyMeet real-time requirementsInstruments for road network navigationSpecial data processing applicationsShortest path searchDynamic programming
The invention discloses a method and device for searching the shortest path of a road network. The method comprises the following steps of dividing the road network into a plurality of sub-networks to generate the road network with a tree structure; calculating the shortest path between boundary nodes of the sub-networks at the same layer; inputting an enquiry point and a target point; according to the shortest path, implementing a dynamic programming algorithm to obtain the initial shortest path between the enquiry point and the target point; and supplementing the initial shortest path to obtain the complete shortest path between the enquiry point and the target point. According to the method, the road network is divided into the plurality of sub-networks so as to generate the road network with the tree structure, and the shortest distance between the boundary nodes of the sub-networks at the same layer is calculated, so that the shortest path between the enquiry point and the target point can be rapidly obtained when the enquiry point and the target point are input; the method and the device not only are high in efficiency, but also well meet the requirement of real-time property.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
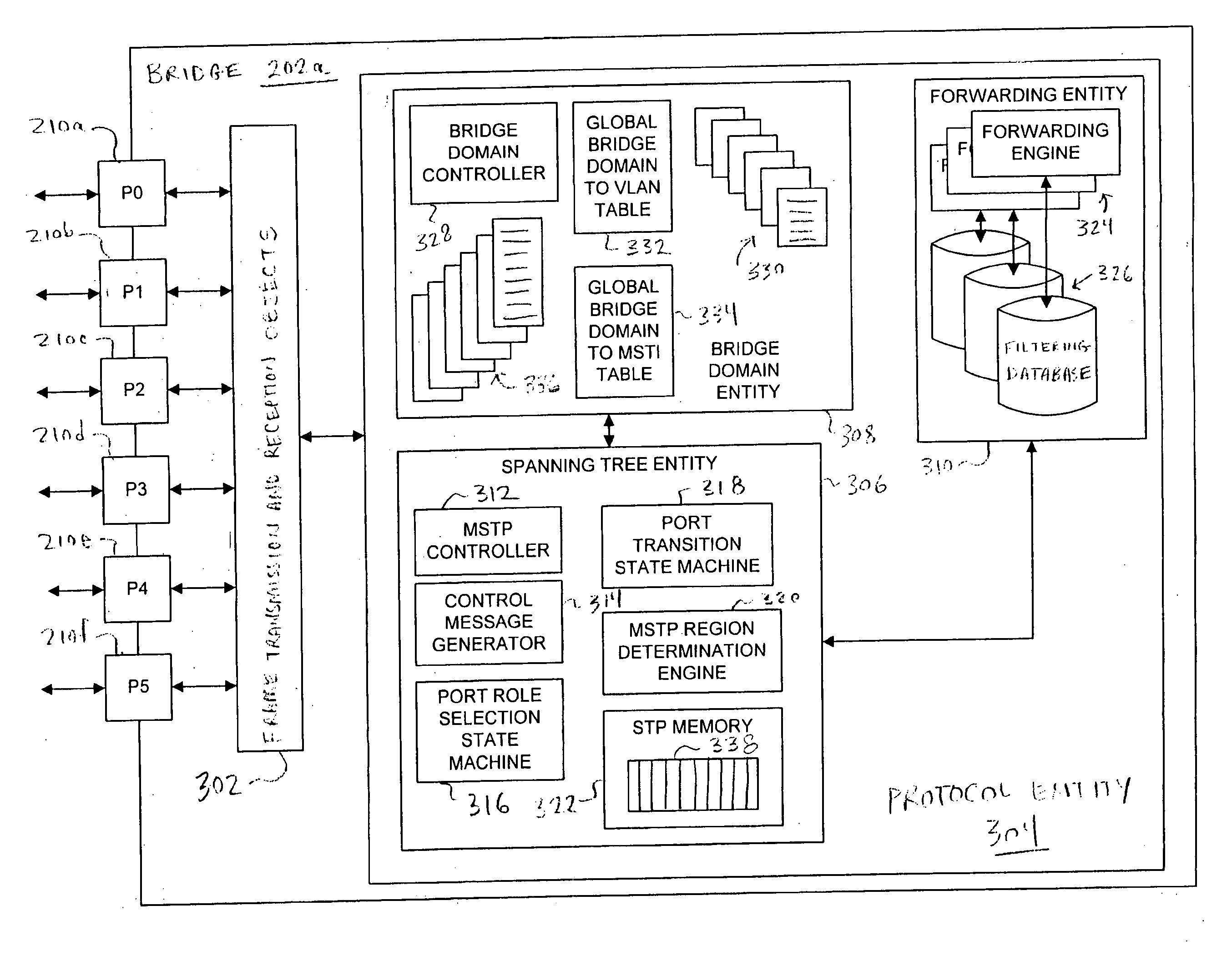
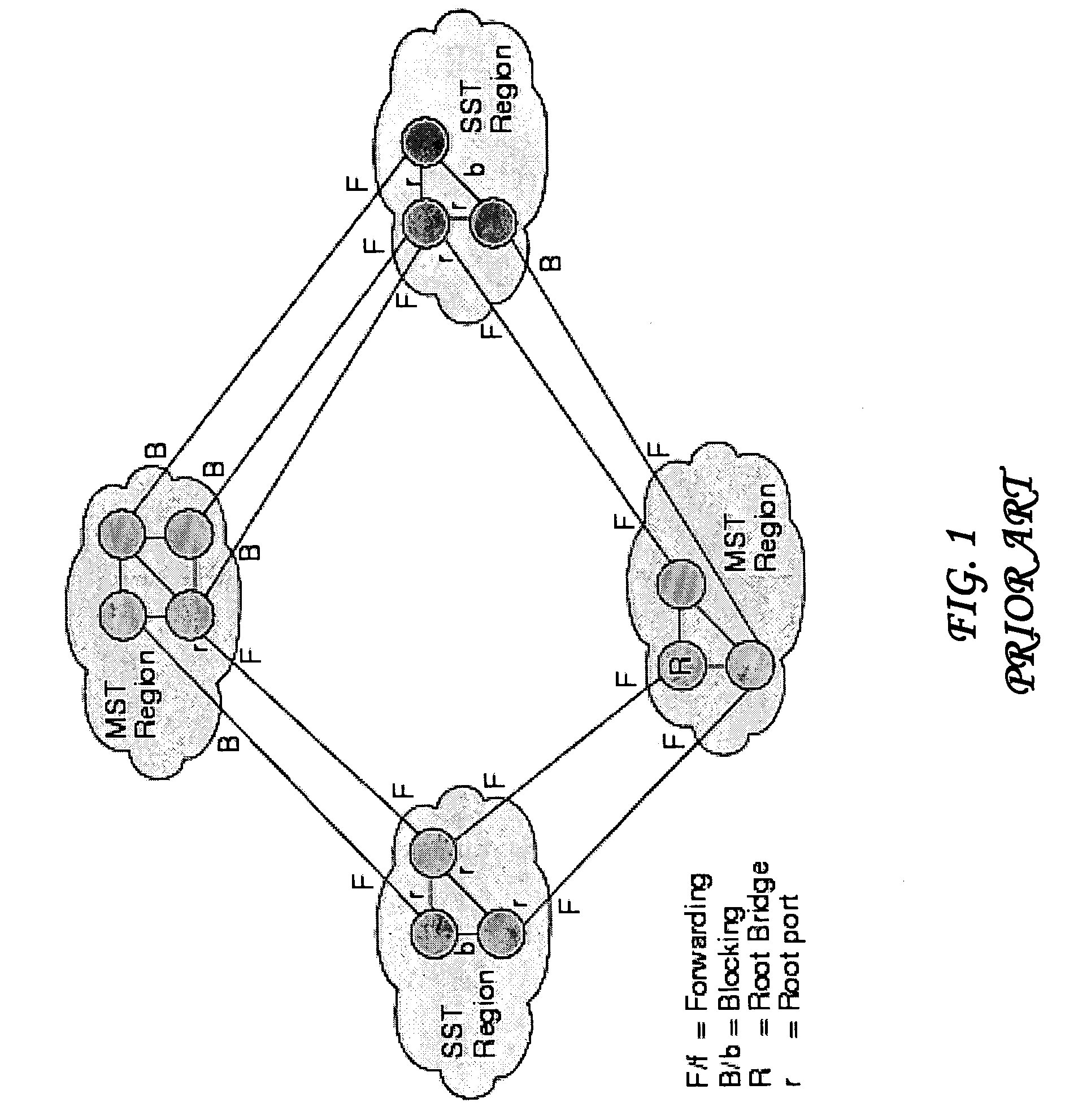
System and method for running a multiple spanning tree protocol with a very large number of domains
A system and method runs a multiple spanning tree protocol (MSTP) in a computer network having a very large number of bridge domains. The computer network includes a plurality of intermediate network devices, each having a plurality of ports for forwarding network messages. Within each device, a plurality of bridge domains are defined, each bridge domain is identified by a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) Identifier (VID), and one or more device ports. For each port, a separate mapping of VIDs to Multiple Spanning Tree Instances (MSTIs), based on the bridge domains defined at the port, is established. Each mapping is converted to a port-based configuration digest, which is entered into Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) control messages sent from the respective port. Ports receiving STP control messages whose configuration digest values that match the configuration digests values computed for the ports are said to be in the same Multiple Spanning Tree region. Ports whose configuration digests differ from the configuration digests of received STP control messages are said to be in different regions.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
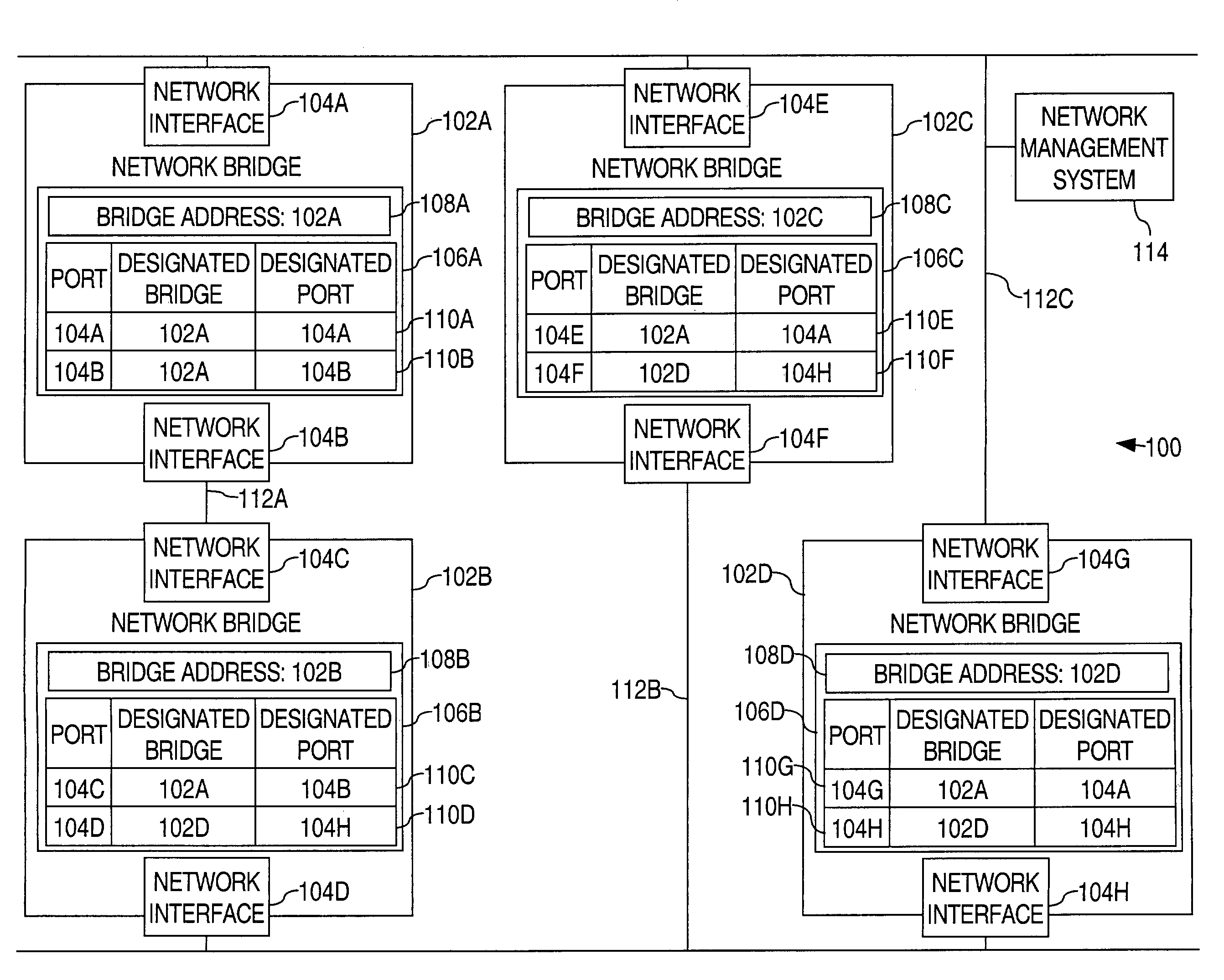
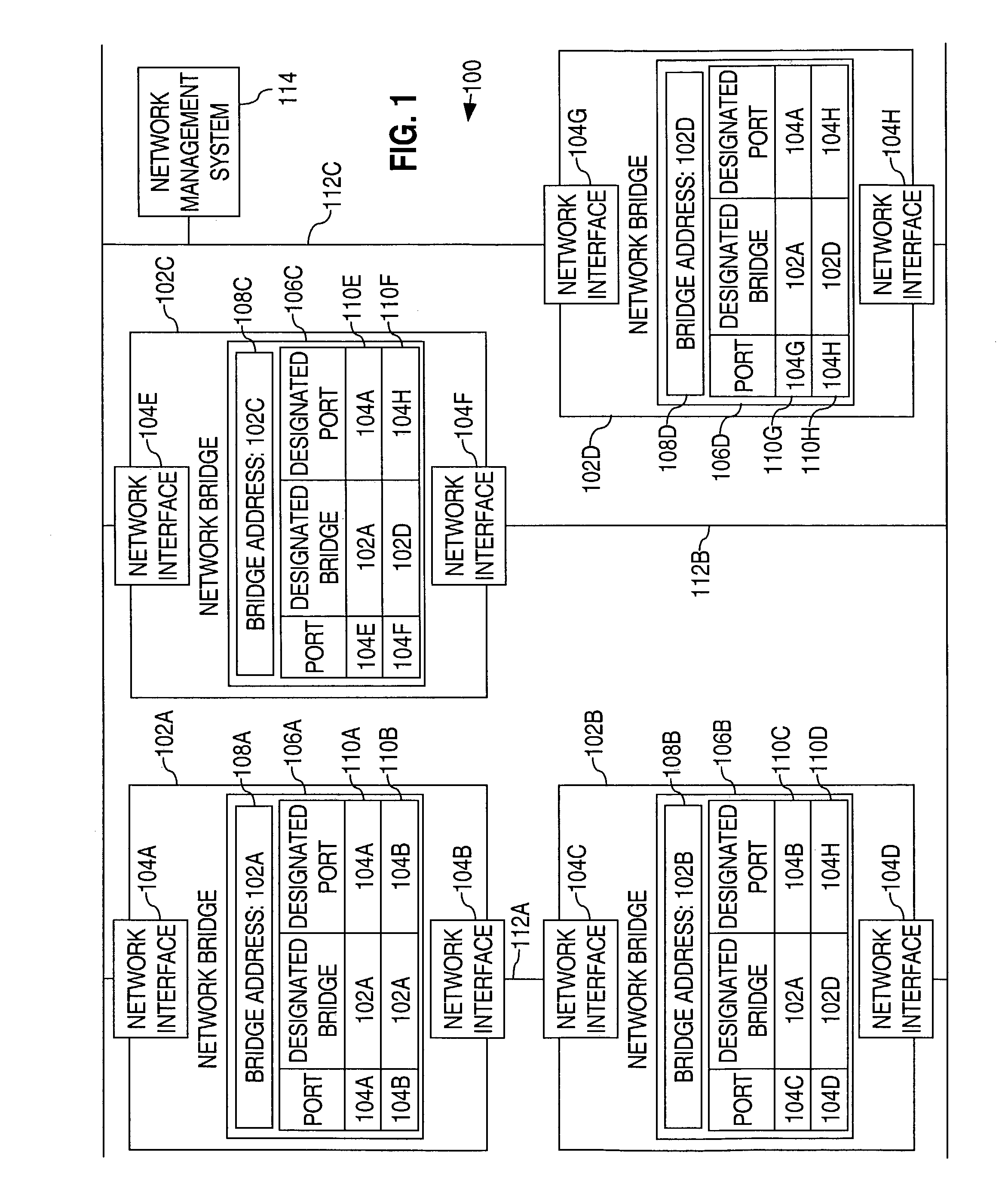
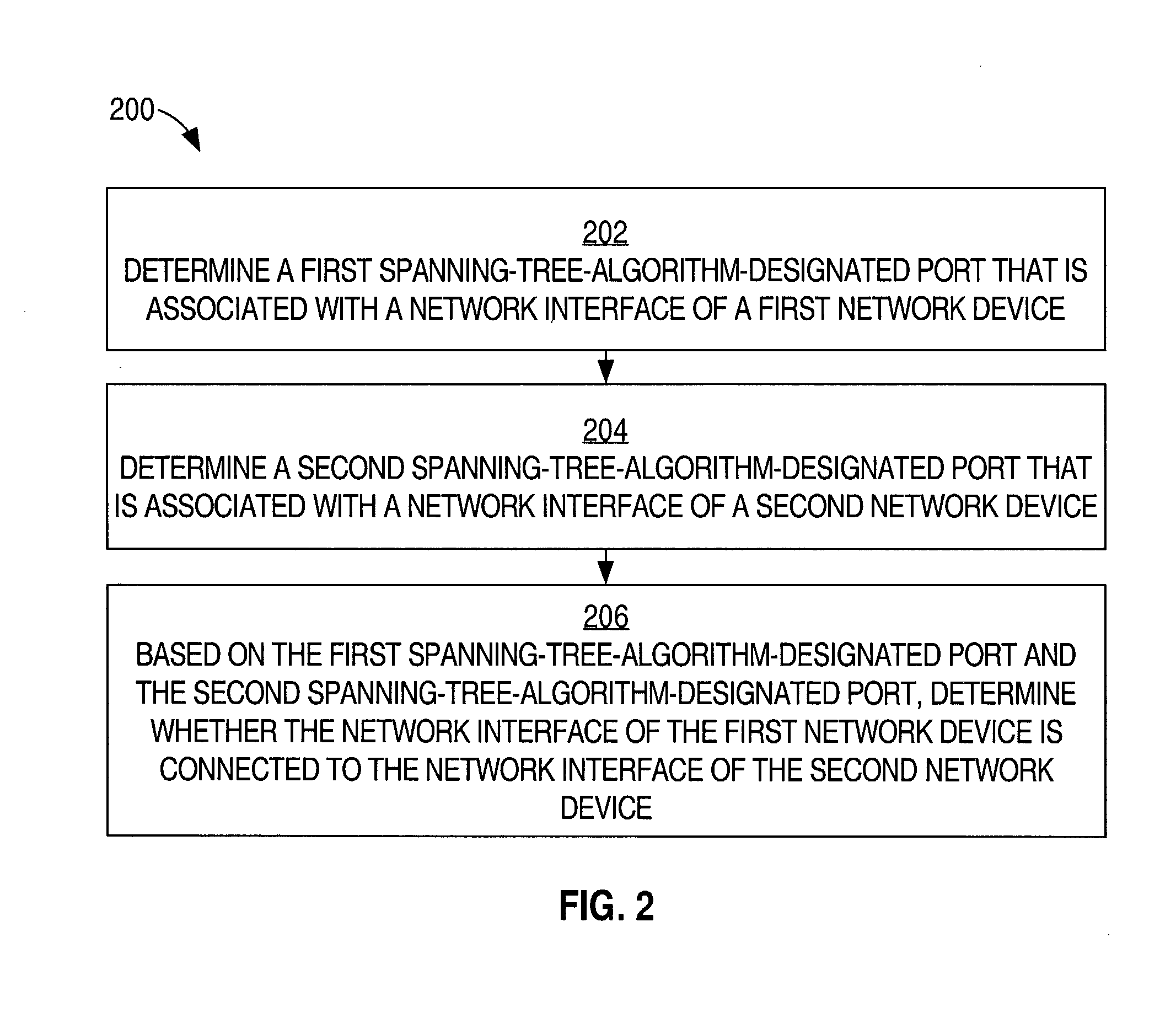
Method and apparatus for determining a network topology based on Spanning-tree-Algorithm-designated ports
A method of determining a network topology based on Spanning-tree-Algorithm-designated ports is disclosed. A first Spanning-tree-Algorithm-designated port that is associated with a network interface of a first network device is determined. A second Spanning-tree-Algorithm-designated port that is associated with a network interface of a second network device is determined. Based on the first designated port and the second designated port, it is determined whether the network interface of the first network device is connected to the network interface of the second network device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
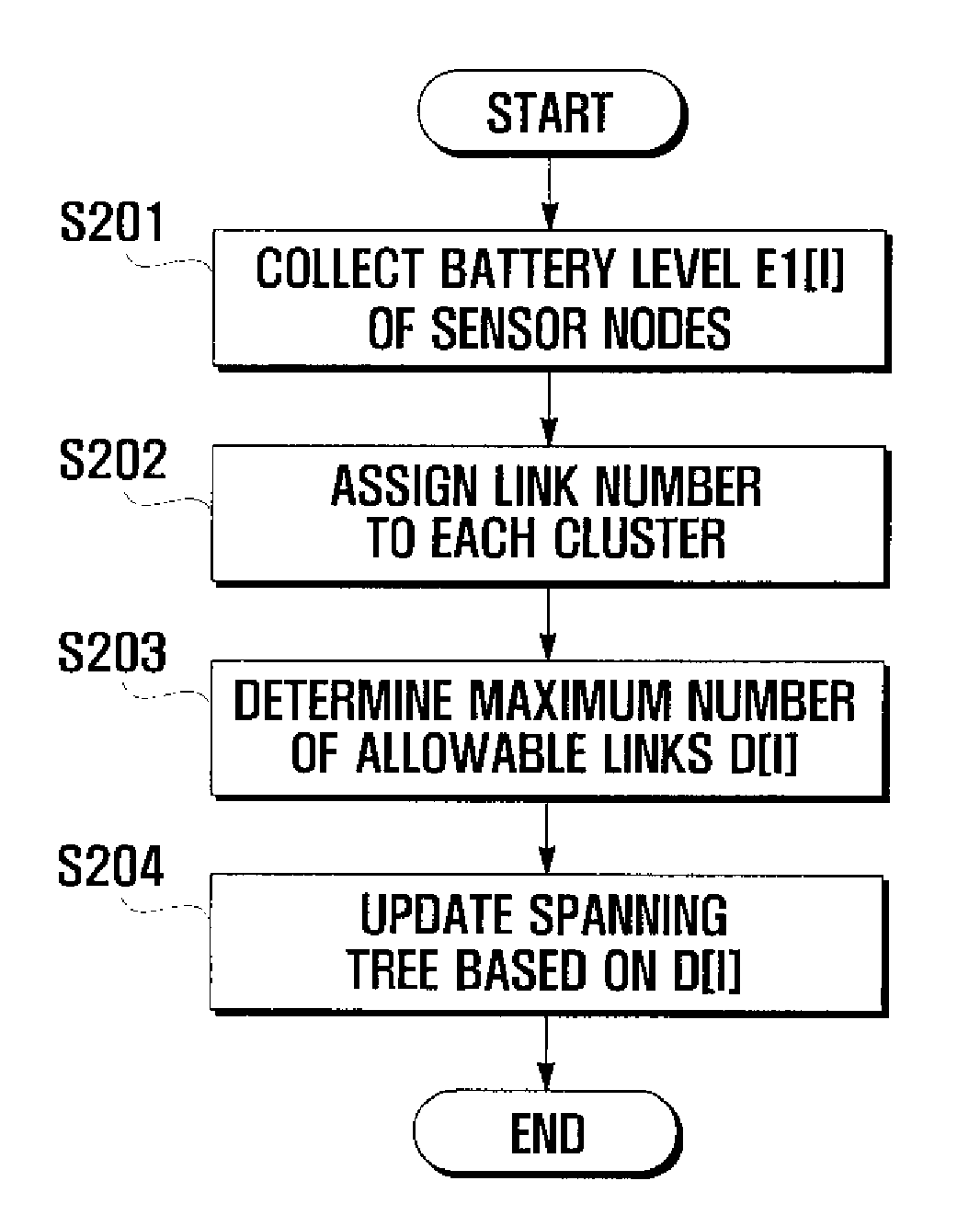
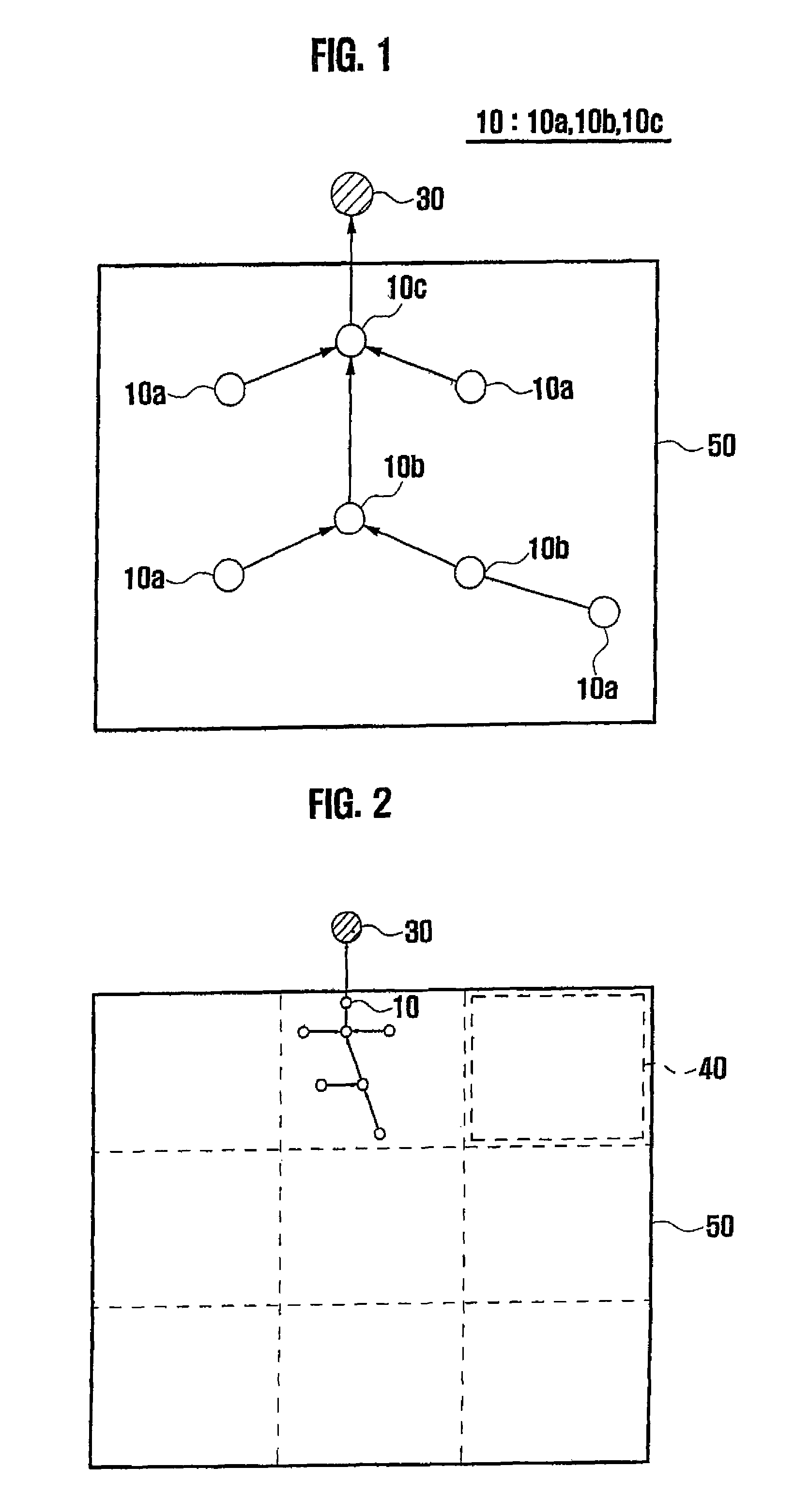
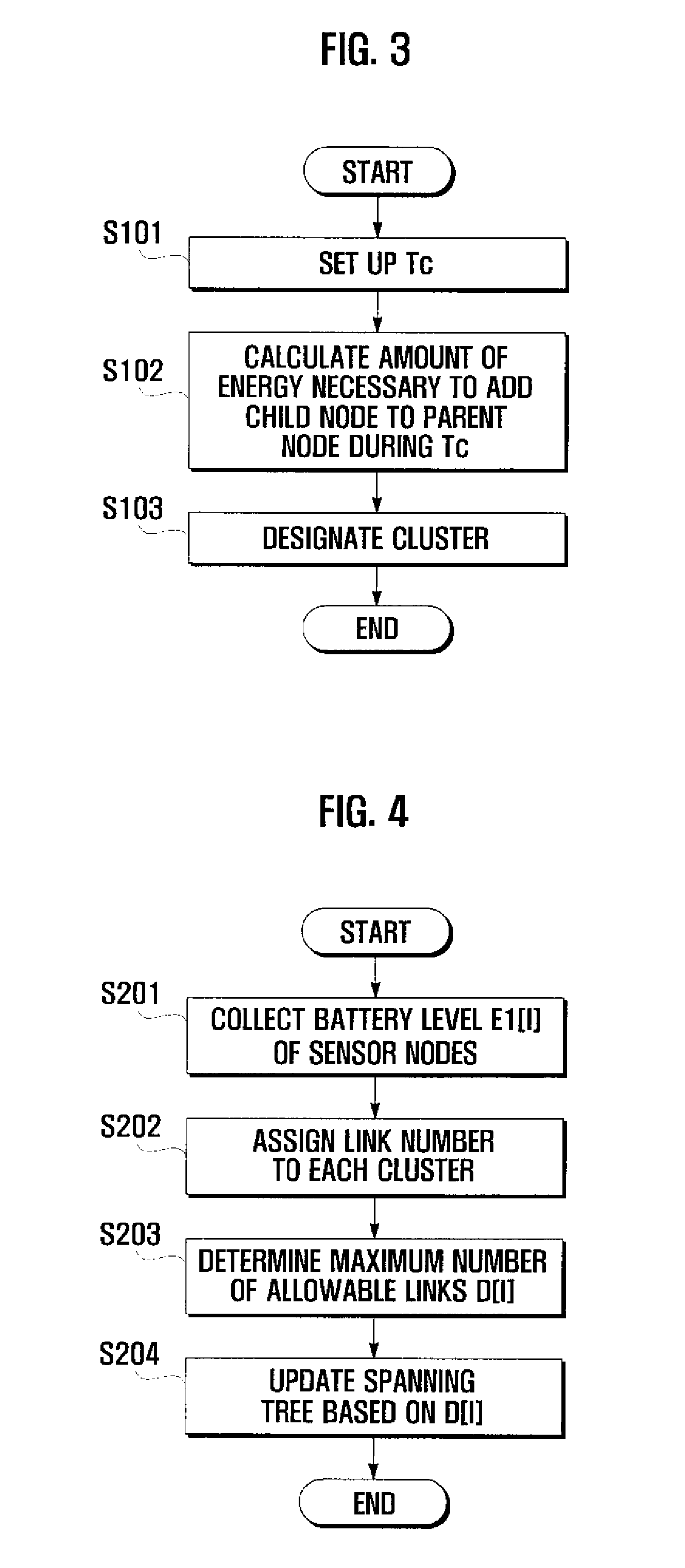
Method and system for managing energy in sensor network environment using spanning tree
A method for managing energy in a sensor network environment using a spanning tree includes the steps of collecting amount of remaining energy of nodes at a predetermined cycle by a base station in a region having a number of clusters a number of nodes forming a spanning tree in each cluster; assigning a number of links for connecting the nodes to each cluster; determining a maximum number of allowable links of the nodes; and updating the spanning tree based on the maximum number of allowable links.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
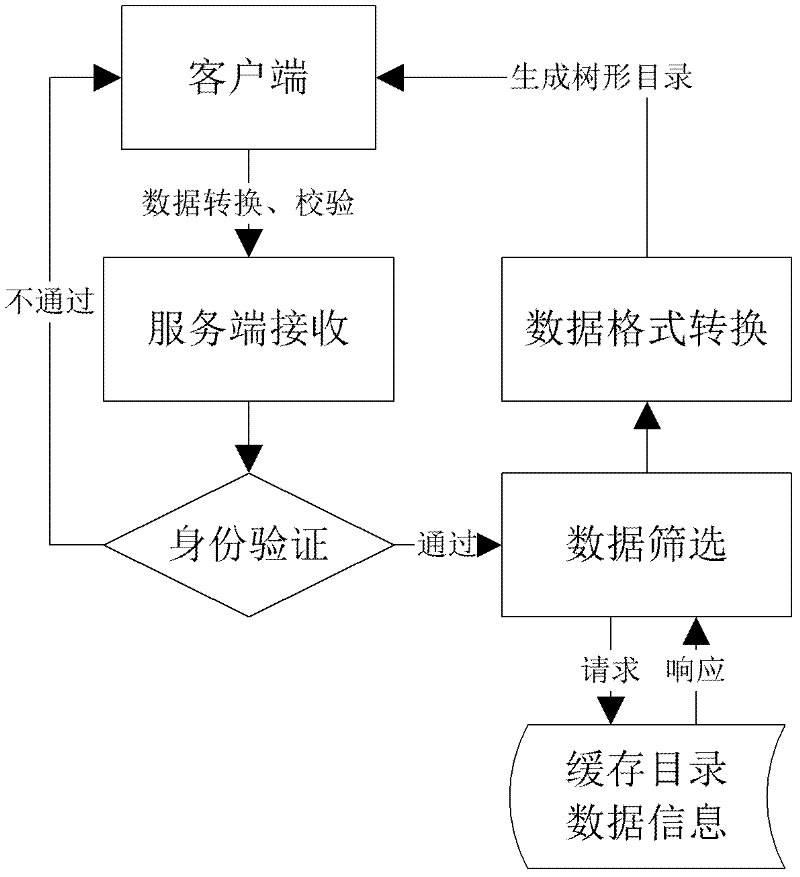
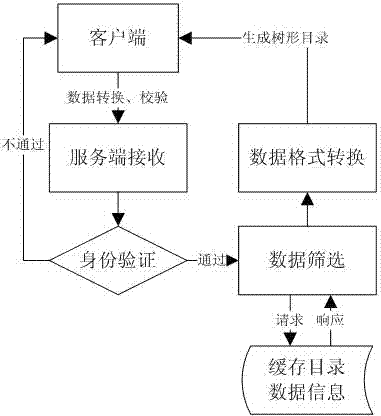
Dynamic tree structured directory retrieval method in BS (browser/server) structure software
The invention discloses a dynamic tree structured directory retrieval method in BS (browser / server) structure software. The method comprises the following steps: 1) taking out the information of a tree node; 2) carrying out data caching; 3) judging whether the node contains retrieval items; 4) carrying out structure transformation on expected data; and 5) carrying out data interaction. In the step 4), the expected data is used for synchronously generating a data format required by a tree directory structure according to JSON (java-script serialized object notation) specification; and in the step 5), the background processing contents of a WEB page timely return the expected JSON-format data to a foreground WEB page by a preset Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) callback function, and the JSON-format data is analyzed by using a JavaScript built-in method so as to generate a tree structured expression of the expected data.
Owner:LINKAGE SYST INTEGRATION
Virtual local area network provisioning in bridged networks
InactiveUS20040044754A1Digital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionVirtual LANHuman–machine interface
A method and human-machine interface for Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) provisioning in bridged networking environments are provided. The method includes steps of provisioning VLAN support for each customer VLAN on every data transport trunk and by extension of every data trunk port in the associated data transport network. The human-machine interface enables an operator to expediently effect VLAN provisioning abstracting the intricacies of the data transport network over which VLAN services are provisioned. Advantages are derived from VLAN provisioning independent of an underlying in-use active spanning-tree topology. In particular customer VLANs are provisioned over spanning-tree stand-by designated data transport trunk links and therefore pre-provisioned in the case of spanning-tree re-configuration. Operator VLAN provisioning tasks are lessened via provisions for the selection of all data transport trunk links / ports in the data transport network.
Owner:ALCATEL CANADA
Piconet spanning tree network
ActiveUS20050135275A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationCommunication devicePiconet
An apparatus and method for a spanning tree network. A communication device can connect to a piconet network and the communication device can transmit at least one available piconet identifier prior to receiving a request for the available piconet identifier from a dependent communication device, the available piconet identifier providing a parent piconet coordinator identification for the dependent communication device. A dependent communication device can connect to the piconet network, determine if the communication device can support a dependent piconet, and receive at least one available piconet identifier prior to requesting information regarding establishing a dependent piconet, the available piconet identifier providing parent piconet identification for the communication device for the dependent piconet.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
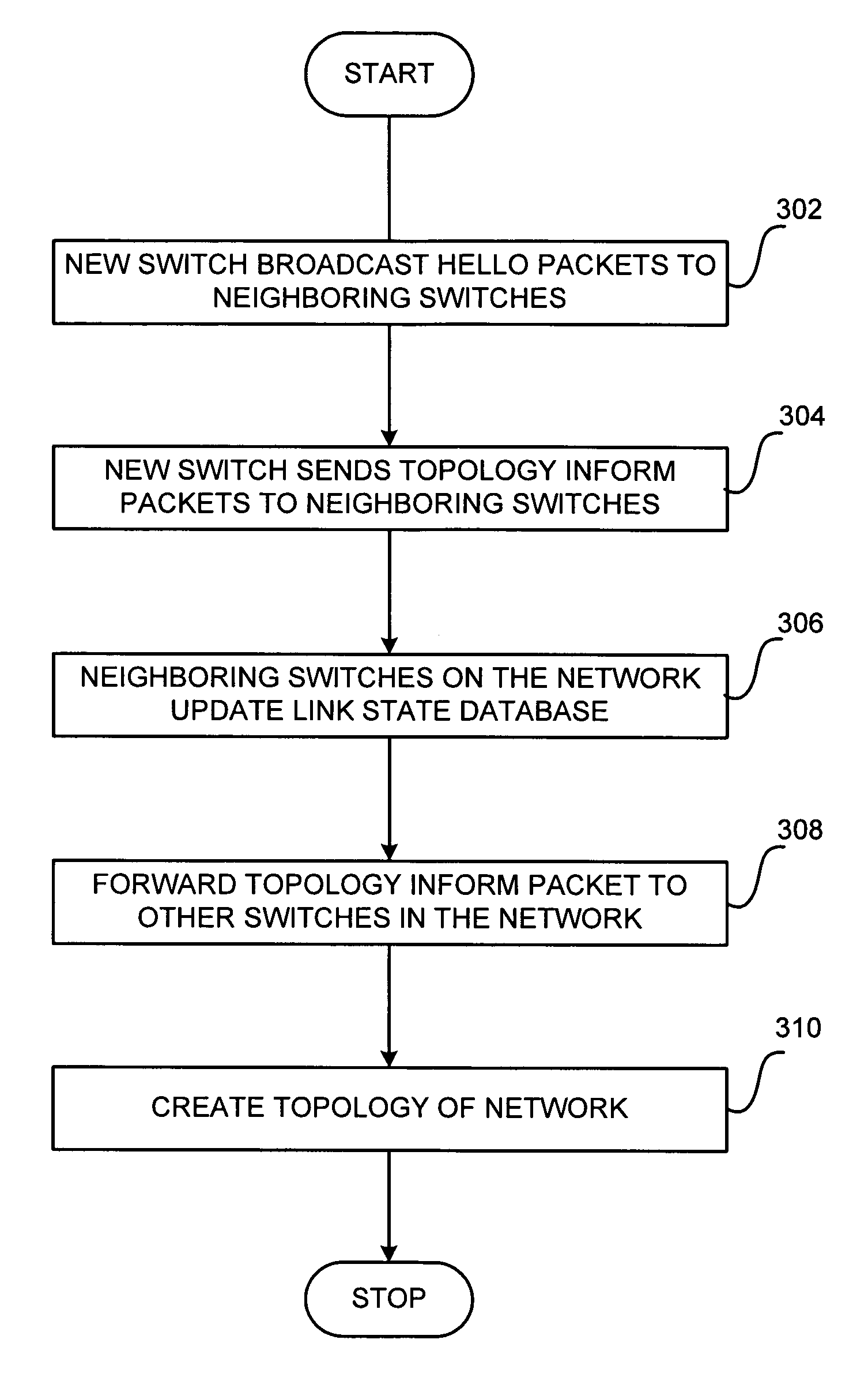
Switch meshing using multiple directional spanning trees
In a packet-based switch, a method for managing data flow between the switch and other switches that are interconnected in a mesh network. The method includes receiving at the switch a topology inform packet sent from a first switch of the other switches. The topology inform packet includes at least an identifier of the first switch. The method also includes updating a link state database associated with the first switch. The link state database is configured for storing topology data pertaining to the mesh network. The method further includes forwarding the topology inform packet to at least another switch of the other switches to enable at least another switch to update a link state database associated with at least another switch.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
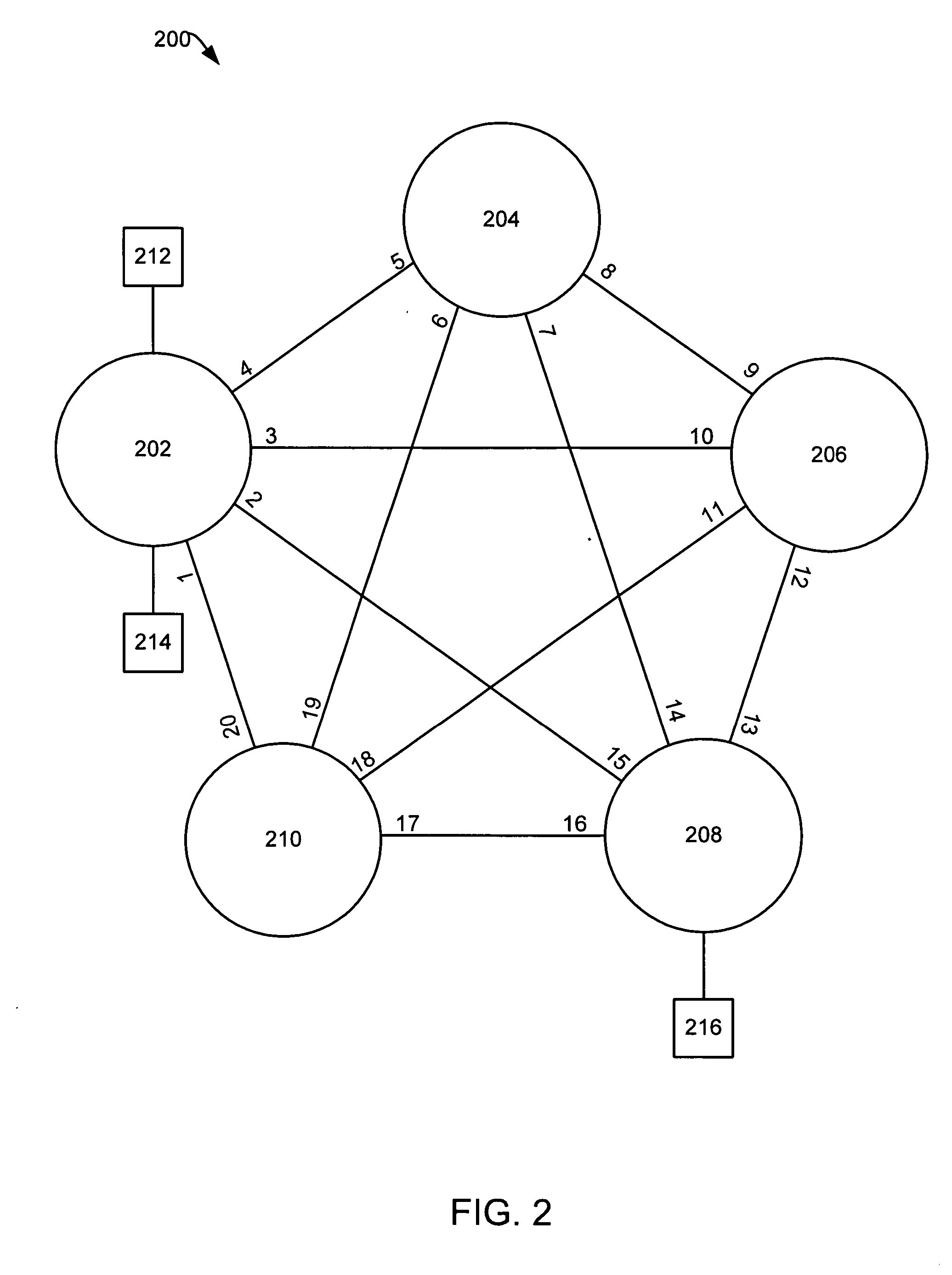
Method and system for constructing XML query to schema variable XML documents
InactiveUS20090287670A1Reducing user ' effortReduce effortDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideQuery Rewriting
An XML querying method and system for constructing an XQuery / XPath query to a schema variable XML document. The method includes: receiving the query from a client computer; generating a tree structure; and generating, by query rewriting, an XQuery / XPath for the XML document based on the tree structure and configurable query constraints. The system includes: a tree structure generating unit for generating a tree structure; and a query writing unit for generating an XQuery / XPath query for the XML document based on the tree structure and configurable query constraints.
Owner:IBM CORP
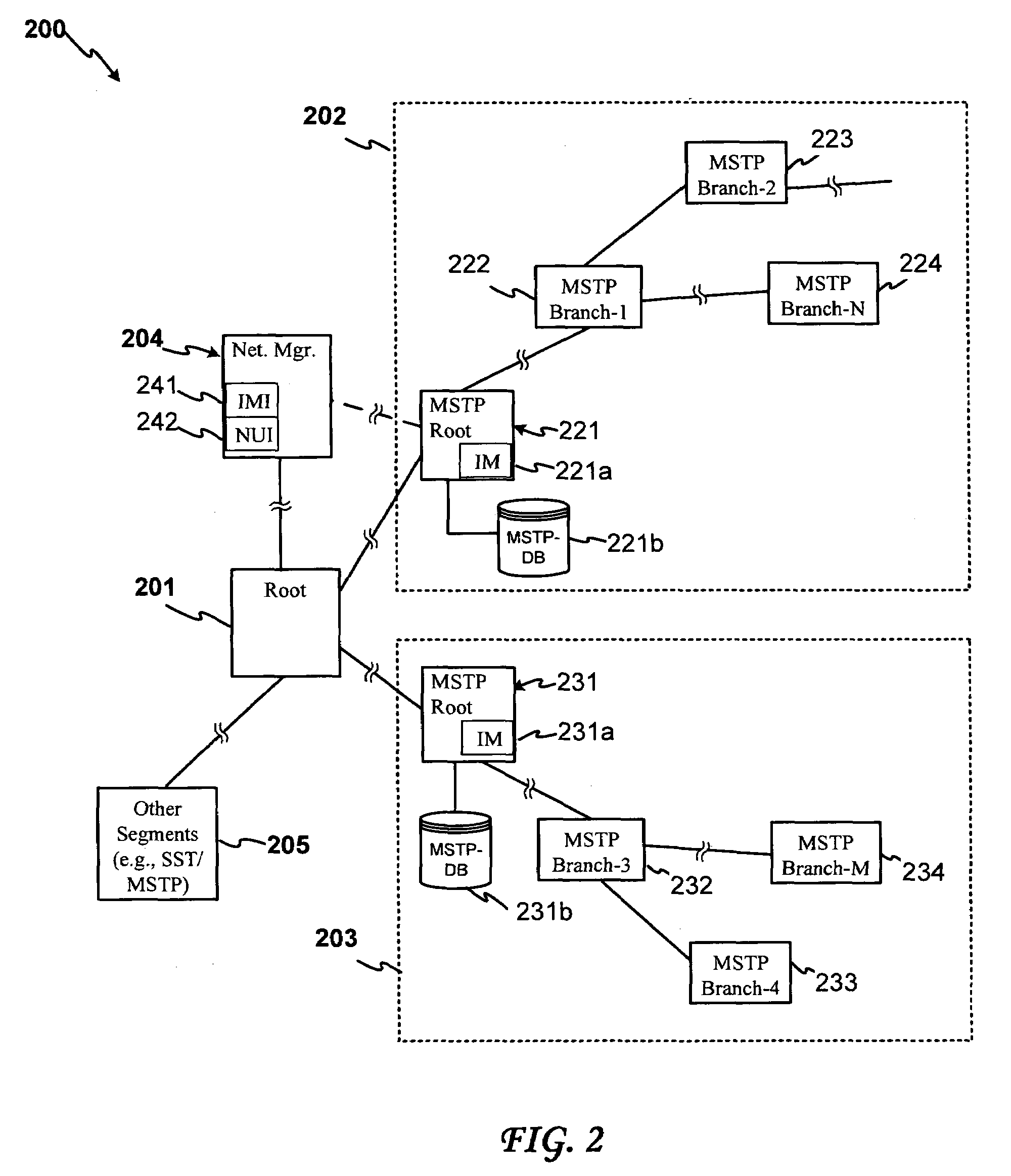
Automated multiple-instance spanning tree reconfiguration
One embodiment relates to a method of automated multiple-instance spanning tree reconfiguration. Query packets are sent to switches within an multiple-instance spanning tree (MST) region, and response packets are received from the switches with traffic utilization data for ports of the switches. An MST reconfiguration is determined. The MST reconfiguration is propagated to the switches within the MST region. Other embodiments and features are also disclosed.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for preventing spanning tree loops during traffic overload conditions
ActiveUS7339900B2Blocking may occurStar/tree networksNetworks interconnectionComputer networkEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that prevents loops from occurring when spanning tree configuration messages are lost while executing a spanning tree protocol on bridges in a network. During operation, the system executes the spanning tree protocol on a bridge. This spanning tree protocol configures each port coupled to the bridge into either a forwarding state, in which messages are forwarded to and from the port, or a backup state, in which messages are not forwarded to or from the port. The system also monitors ports coupled to the bridge to determine when messages are lost by the ports. If one or more messages are lost on a port, the system refrains from forwarding messages to or from the port until no messages are lost by the port for an amount of time.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
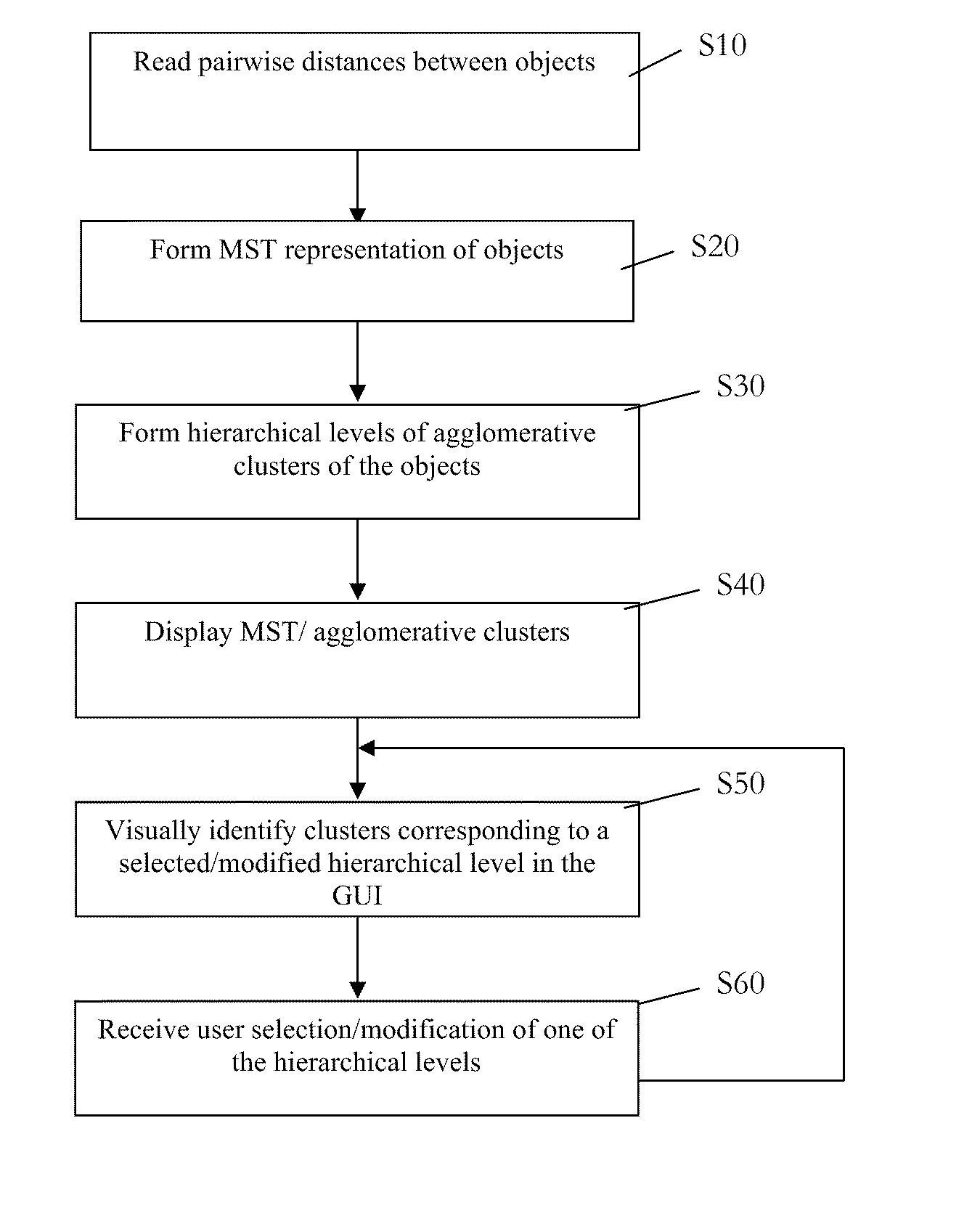
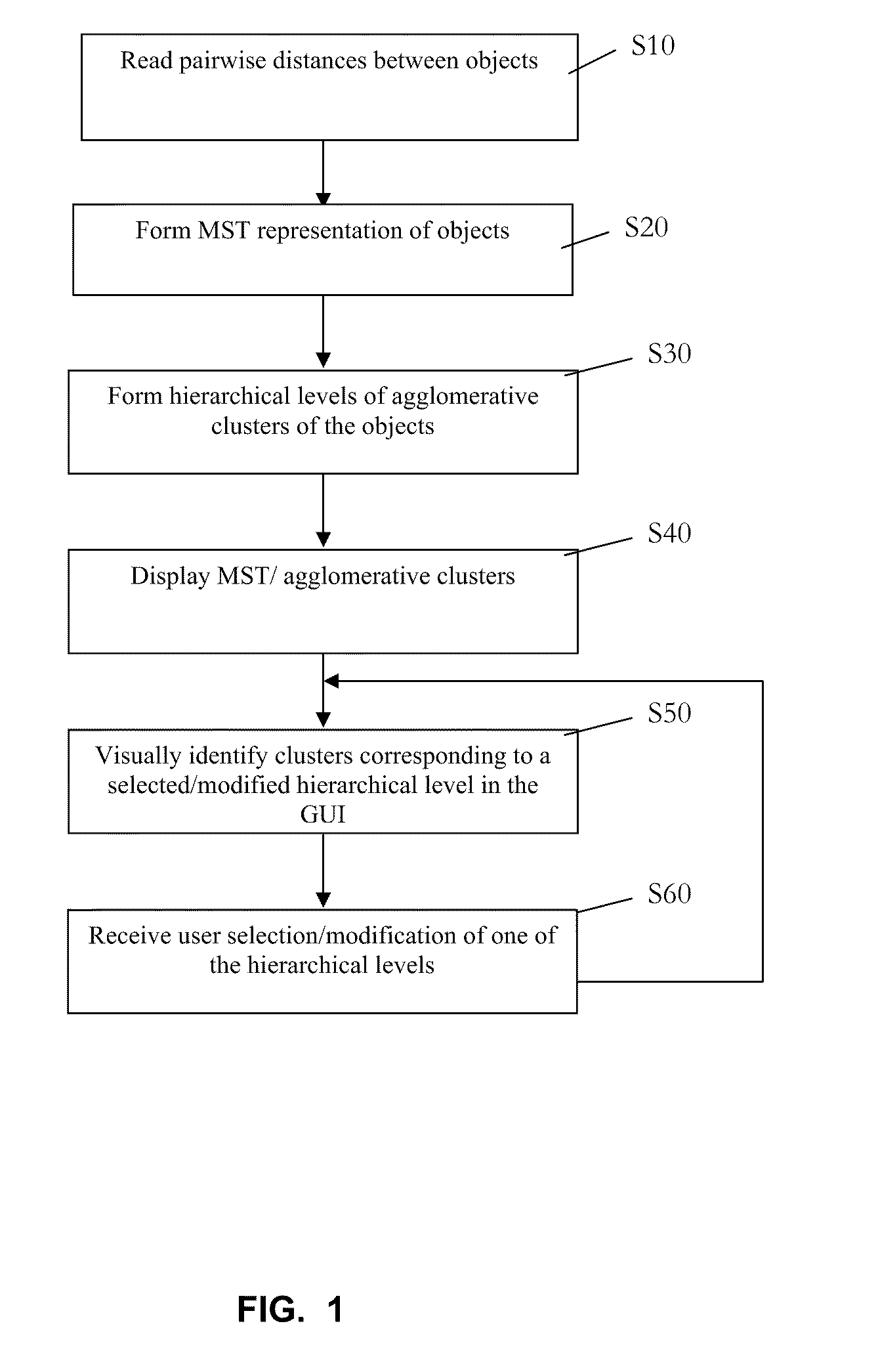
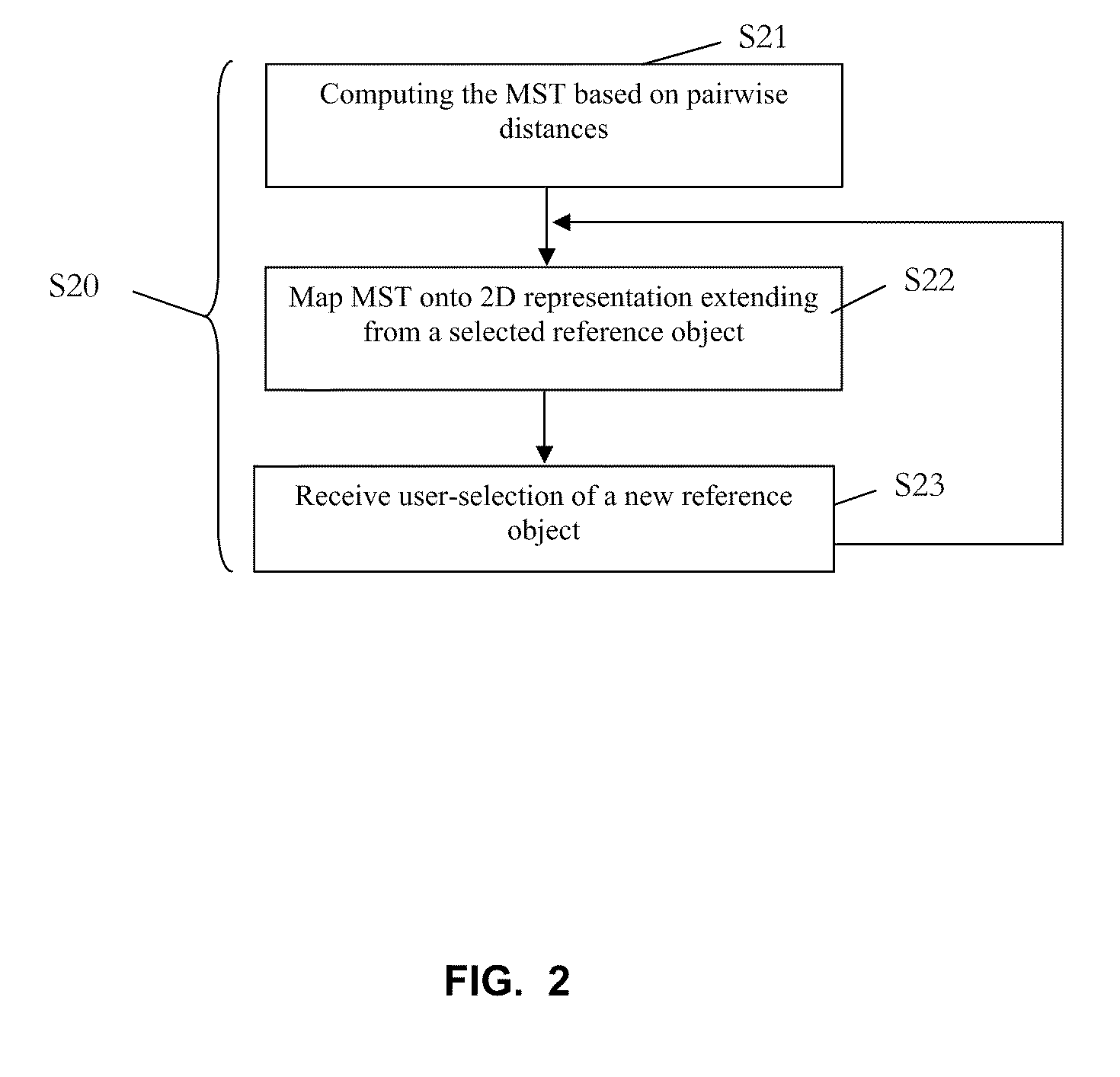
Computer-implemented visualization method
A method, system and computer product for visualizing affinities between objects. The method includes the steps of: forming a representation of a minimum spanning tree where the minimum spanning tree connects the plurality of objects based on a pairwise distance between the plurality of objects; forming a hierarchical cluster of the plurality of objects where the hierarchical cluster includes a level; agglomerating the plurality of objects based on the pairwise distance; displaying a view of the representation of the minimum spanning tree in a graphical user interface; receiving a user selection of a parameter containing a hierarchical level; and identifying, in the view, a target cluster that corresponds to the hierarchical level; where at least one of the steps is carried out using a computer device so that affinities between the plurality of objects are visualized.
Owner:IBM CORP
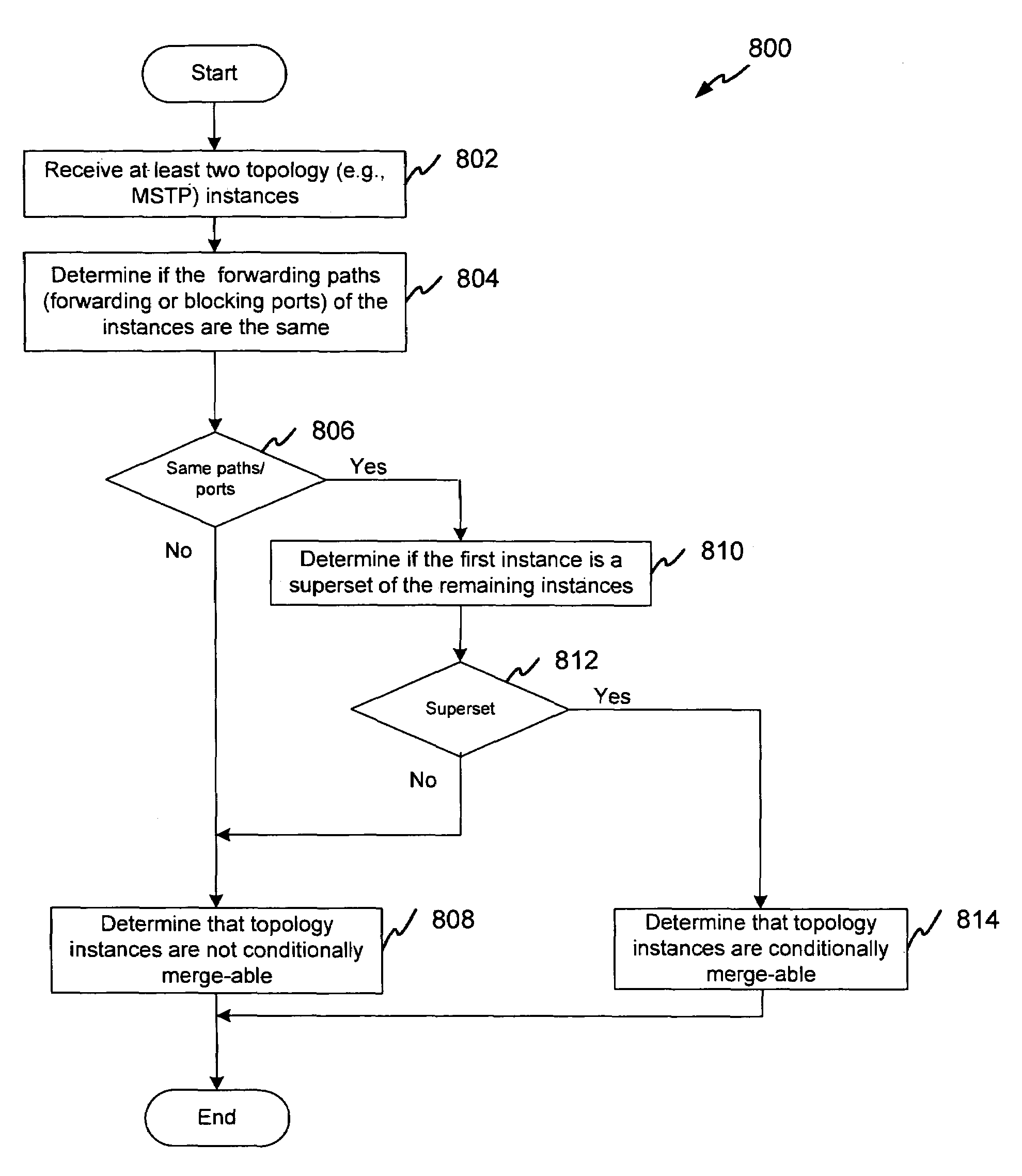
System and method for determining the mergeability of spanning tree instances
InactiveUS7701881B1Reduce in quantityData switching by path configurationDistributed computingSpan tree
A system and method provide for reducing a number of topology instances in a network portion implementing a multiple instance topology. Various embodiments further provide for determining if one or more of the topology instances are merge-able or conditionally merge-able to form a lesser number of representative topology instances, and if so, for causing merging of the topology instances.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
A method and device for computing a spanning tree
ActiveCN104426731ASolve computing problemsAvoid it happening againStar/tree networksComputational problemSpanning Tree Protocol
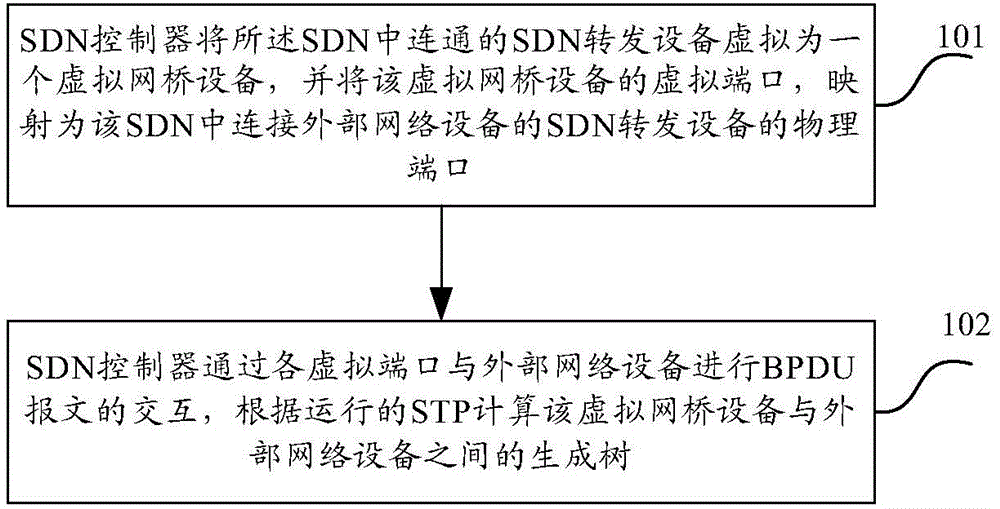
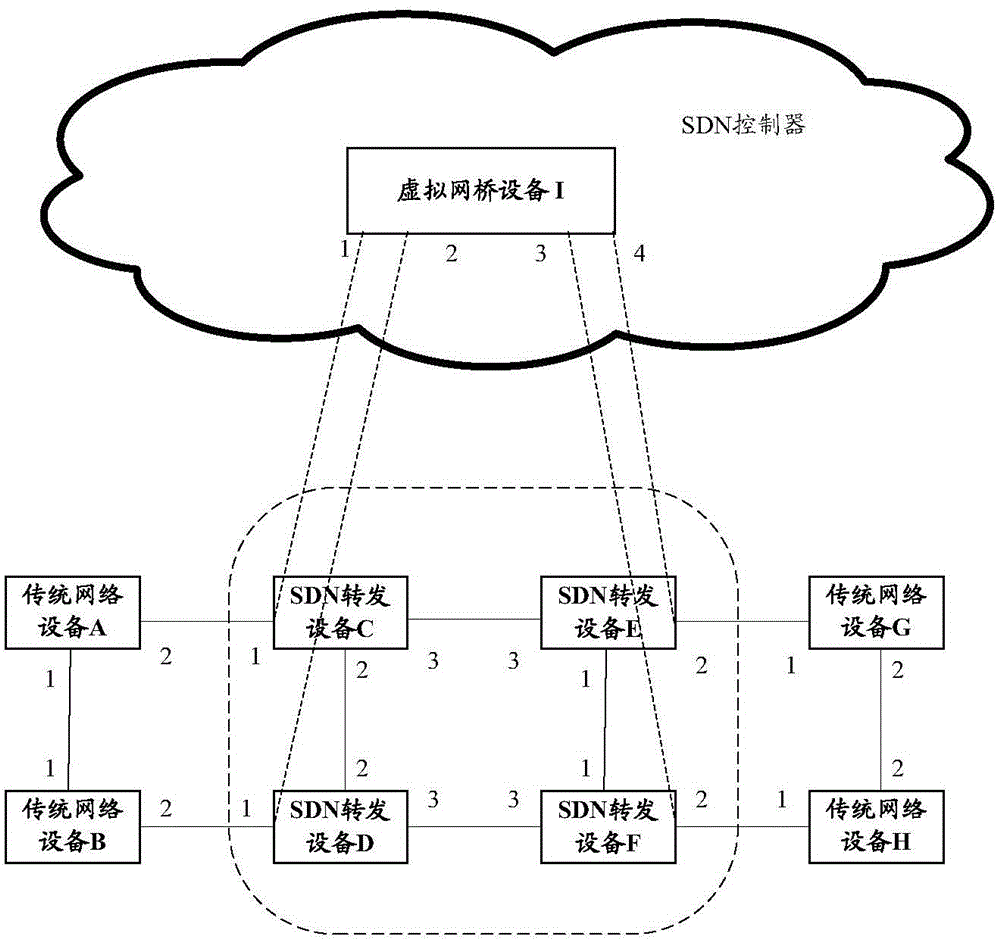
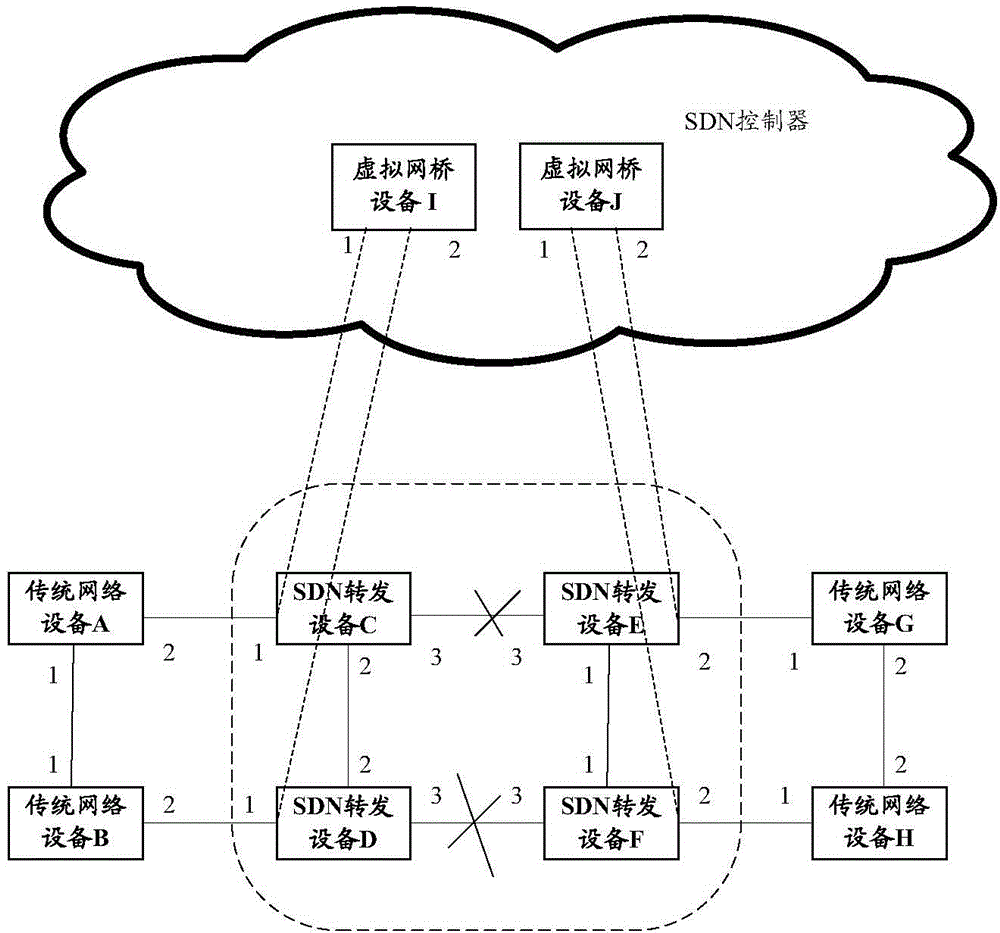
According to an example of the present disclosure, in a method for calculating a spanning tree, a SDN controller virtualizes a plurality of SDN forwarding devices in a SDN as a virtual network bridge device, performs interaction of spanning tree protocol (STP) data unit packets with an external network device through the virtual network bridge device to calculate a spanning tree between the virtual network bridge device and the external network device according to a STP running on the SDN controller and information carried in a STP data unit packet from the external network device.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Method for double communications and communication route optimization of wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101437305AImprove reliabilityExtend your lifeEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesLine sensorWireless mesh network
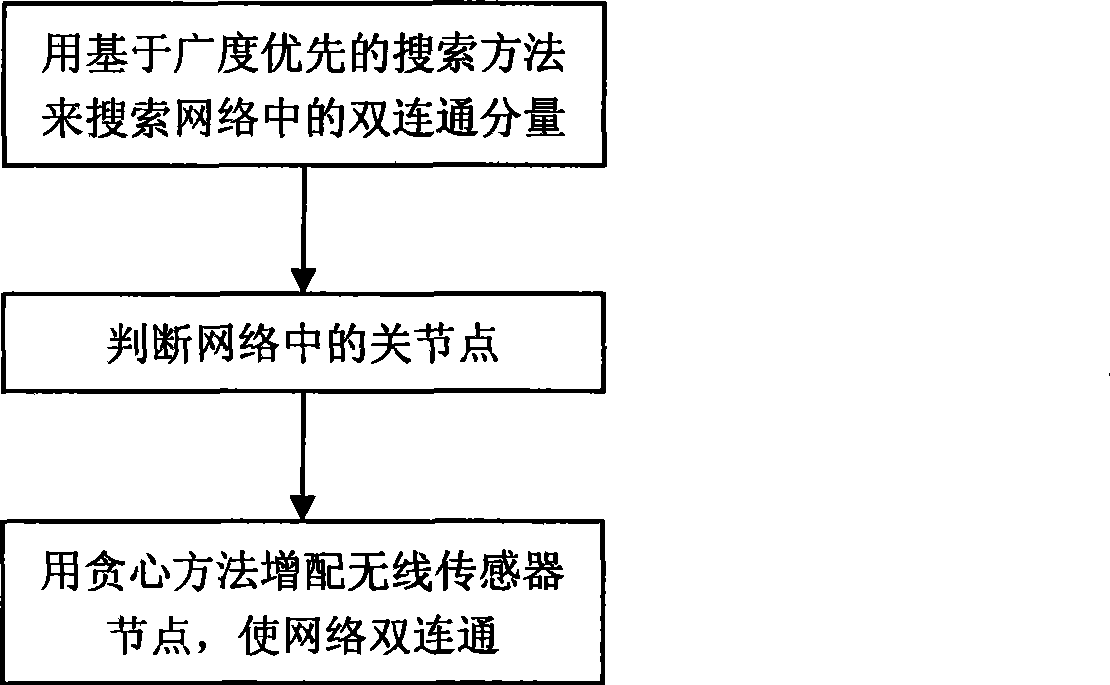
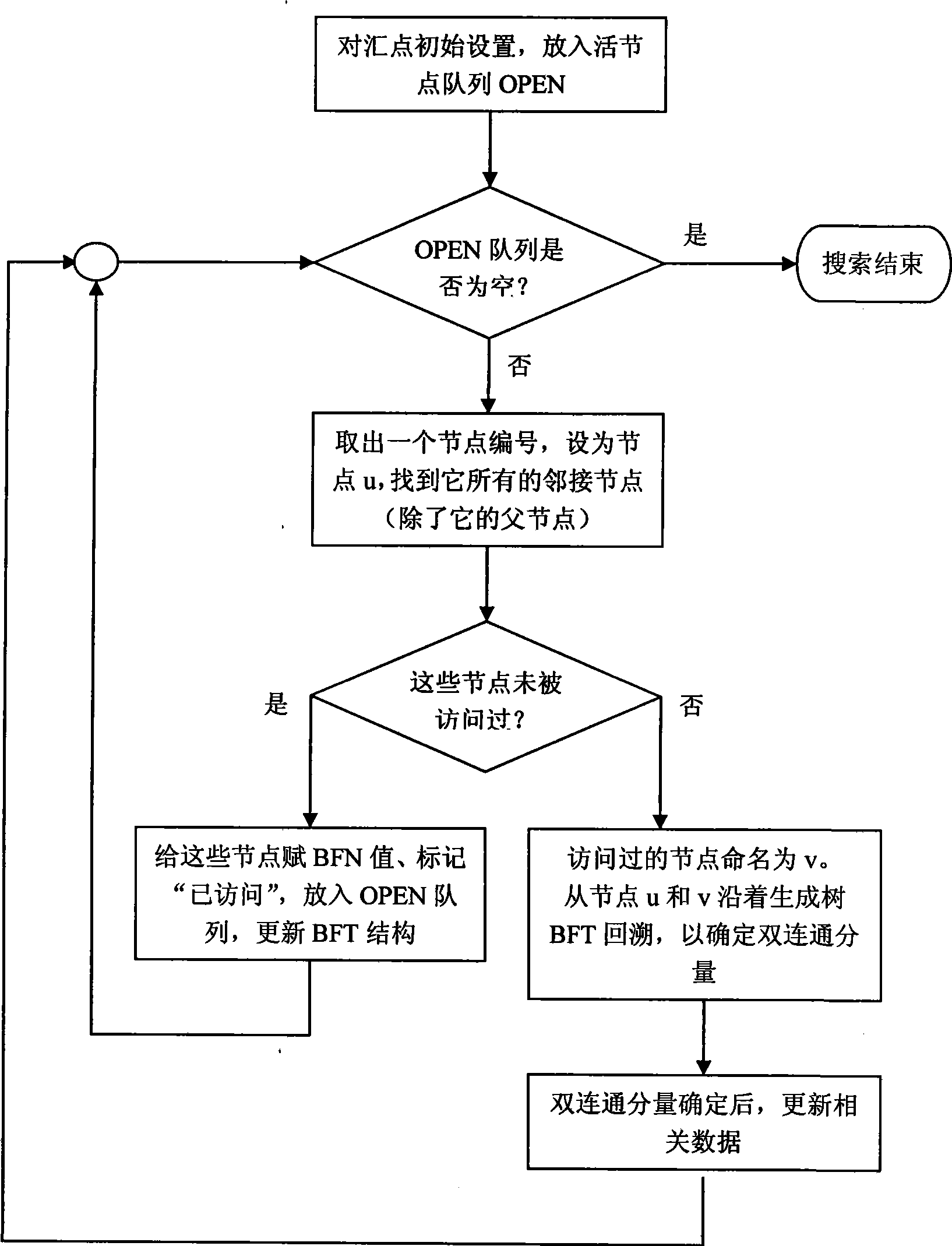
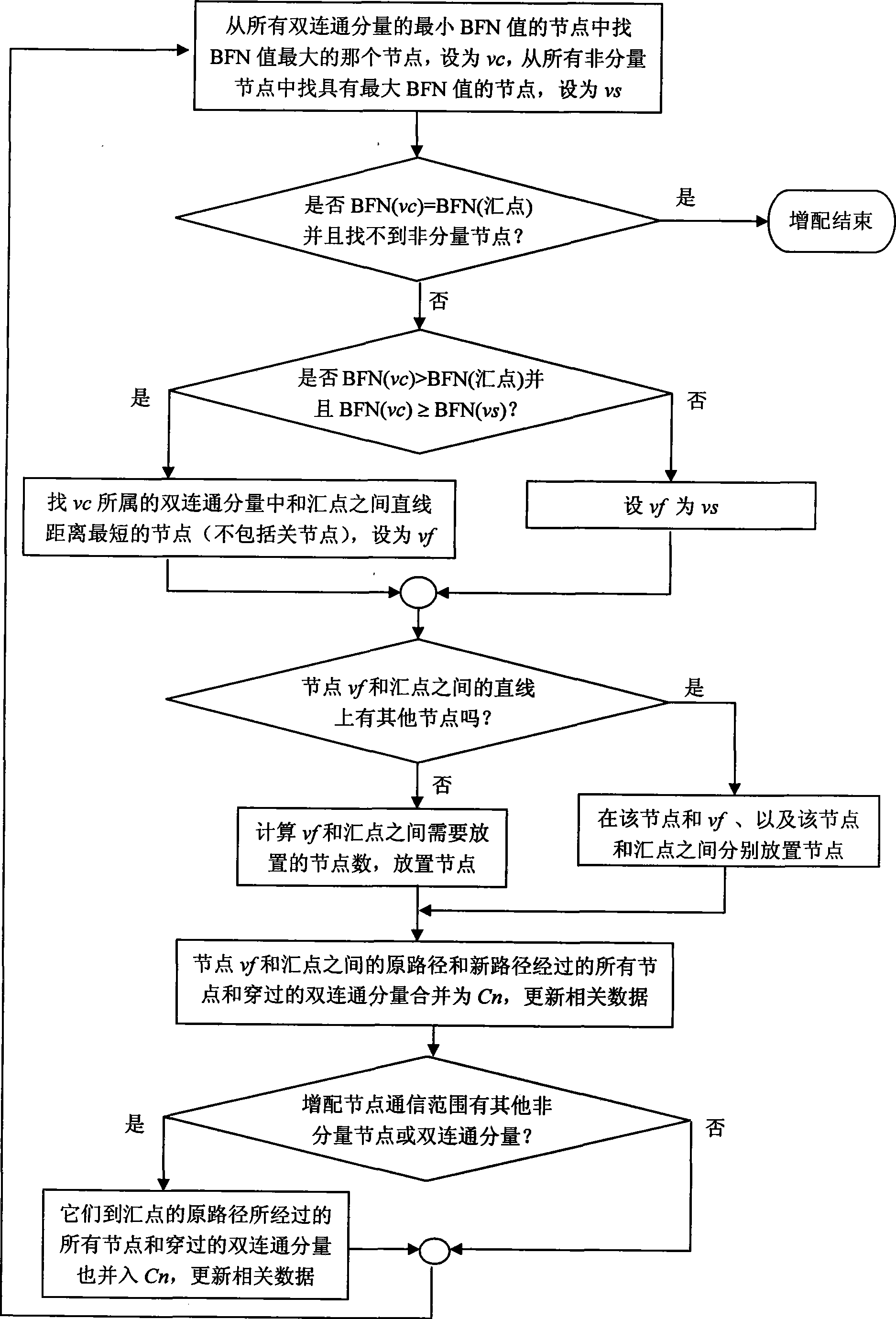
The invention discloses a method for making a wireless sensor network connected doubly and optimizing communication paths, and mainly relates to the reliability of a wireless sensor network. If the wireless sensor network is not connected doubly after being deployed, node failure can make the network not connected, thereby reducing sensing and monitoring coverage and influencing the service life of the network. The method uses a breadth-first principle based search method to find biconnected components in the network, acquire breadth-first spanning tree, record biconnected component information and judge nodes, and then uses a greedy method to increase nodes as few as possible. The method reduces the length of part of communication paths from sensing nodes to aggregate nodes and relay energy consumption and prolongs the service life of the network while realizing double network connection and improving connection reliability.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
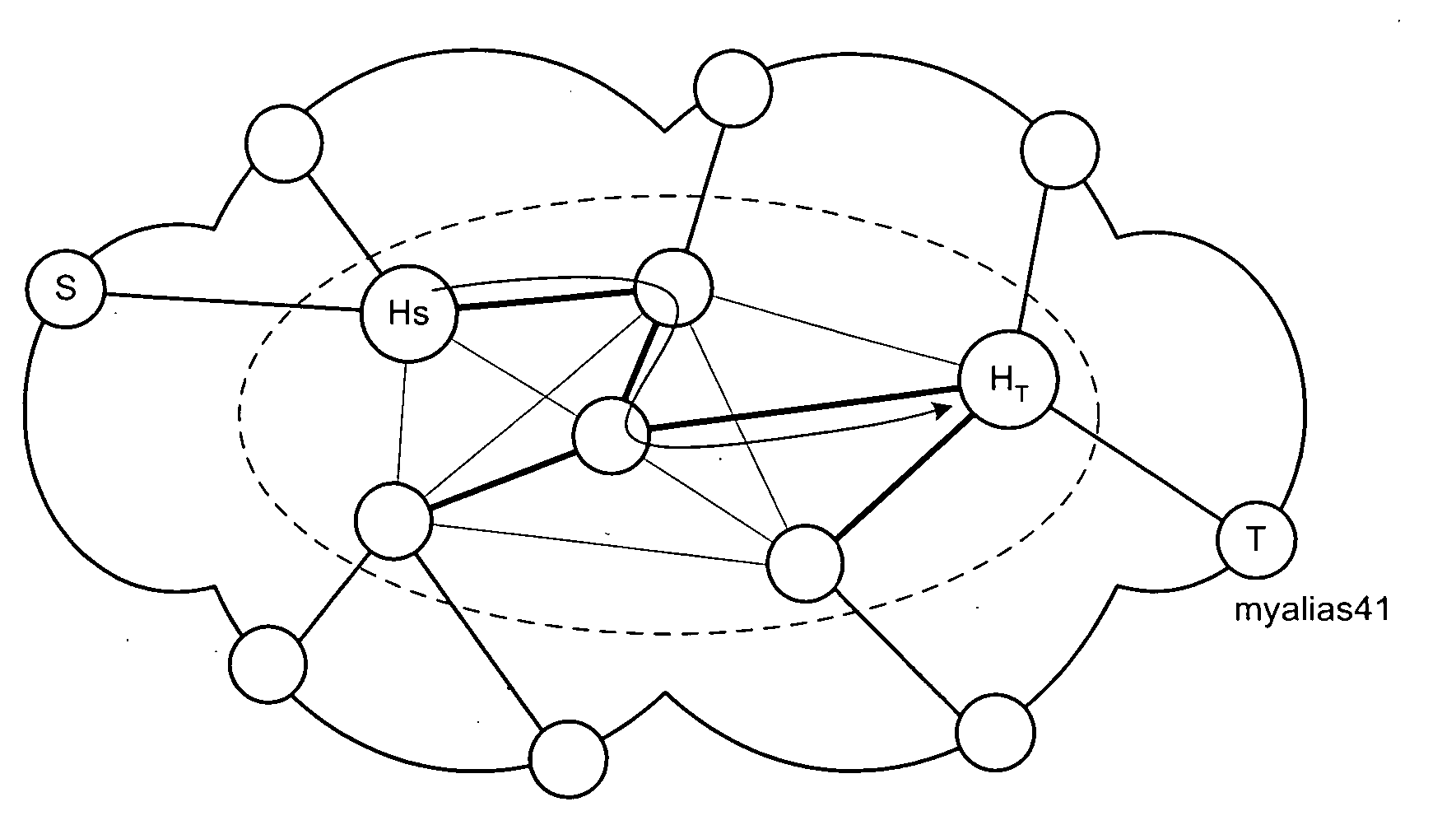
Distribution scheme for distributing information in a network
ActiveUS20050254448A1Efficient and scalable distributionReduce deliveryError preventionTransmission systemsTopology informationDistributed computing
The present invention relates to a method and network node for distributing a network parameter information among network nodes of a transmission network. A spanning tree of routing paths corresponding to the shortest paths from said network node to other nodes is determined based on a topology information of the transmission network, and is used to distribute the network parameter information from the network node to the other network nodes. Thereby, the updating message or packet traffic can be reduced dramatically as compared to the conventional flooding scheme.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
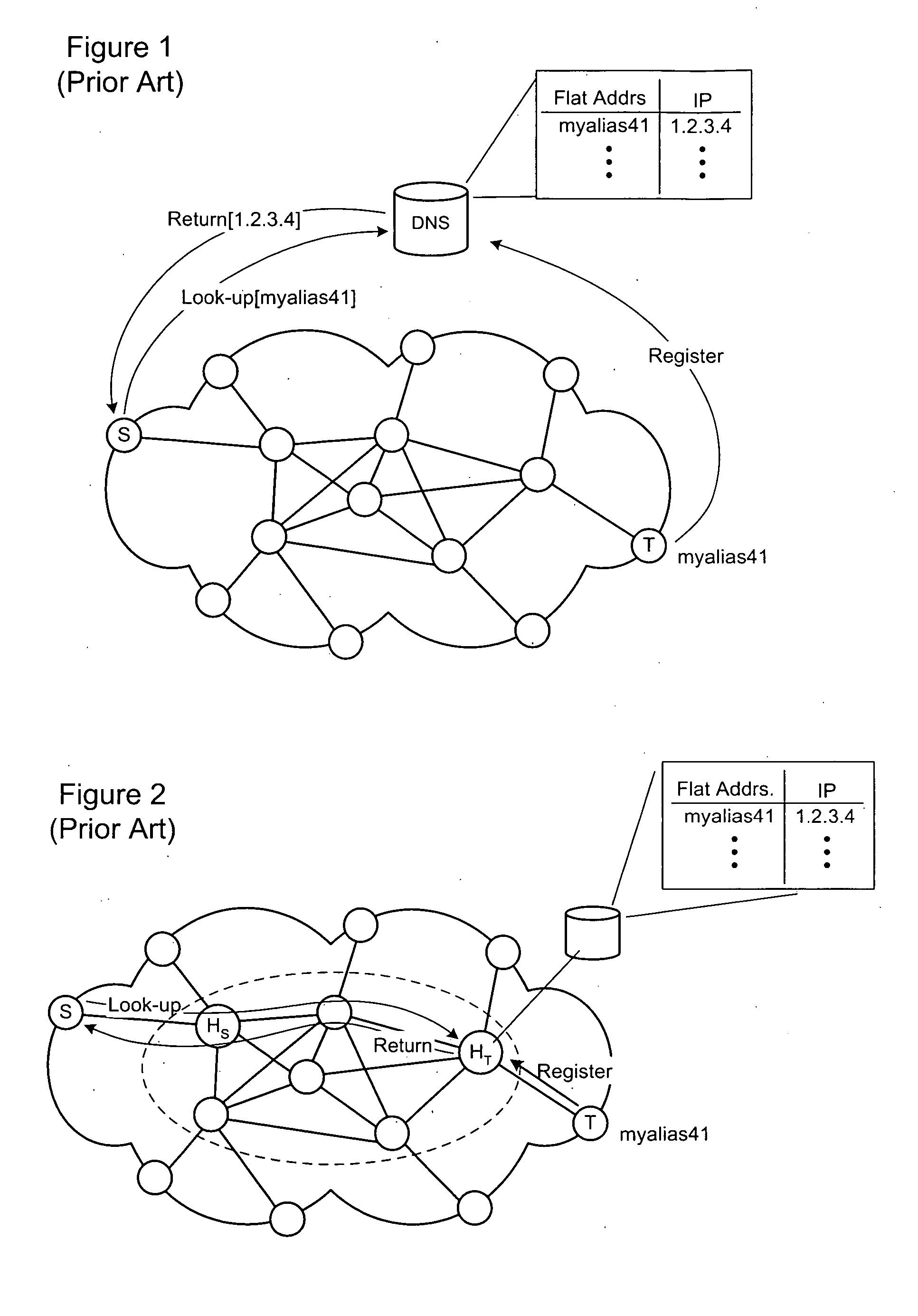
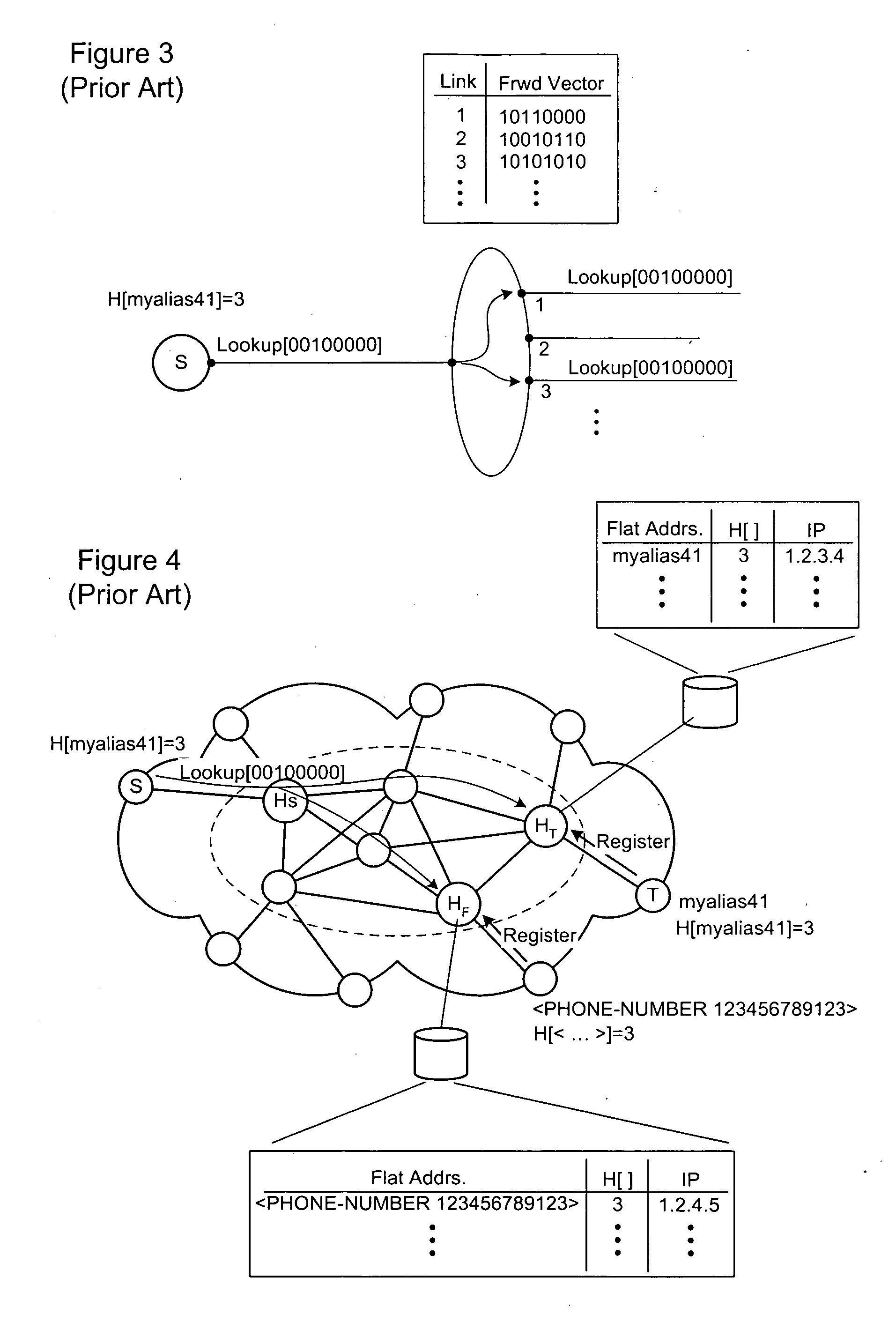
Registration, look-up, and routing with flat addresses at enormous scales
A method of controlling registration, lookup and forwarding of network addresses corresponding to the flat user's node addresses, in a data network including flat user's node addresses hosted by a plurality of super-nodes. A spanning tree (ST) is preliminarily defined across the plurality of super-nodes. Thereafter, flooding of network / user's address registration messages and look-up queries a is controlled such that the messaging propagates within the mapped ST.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
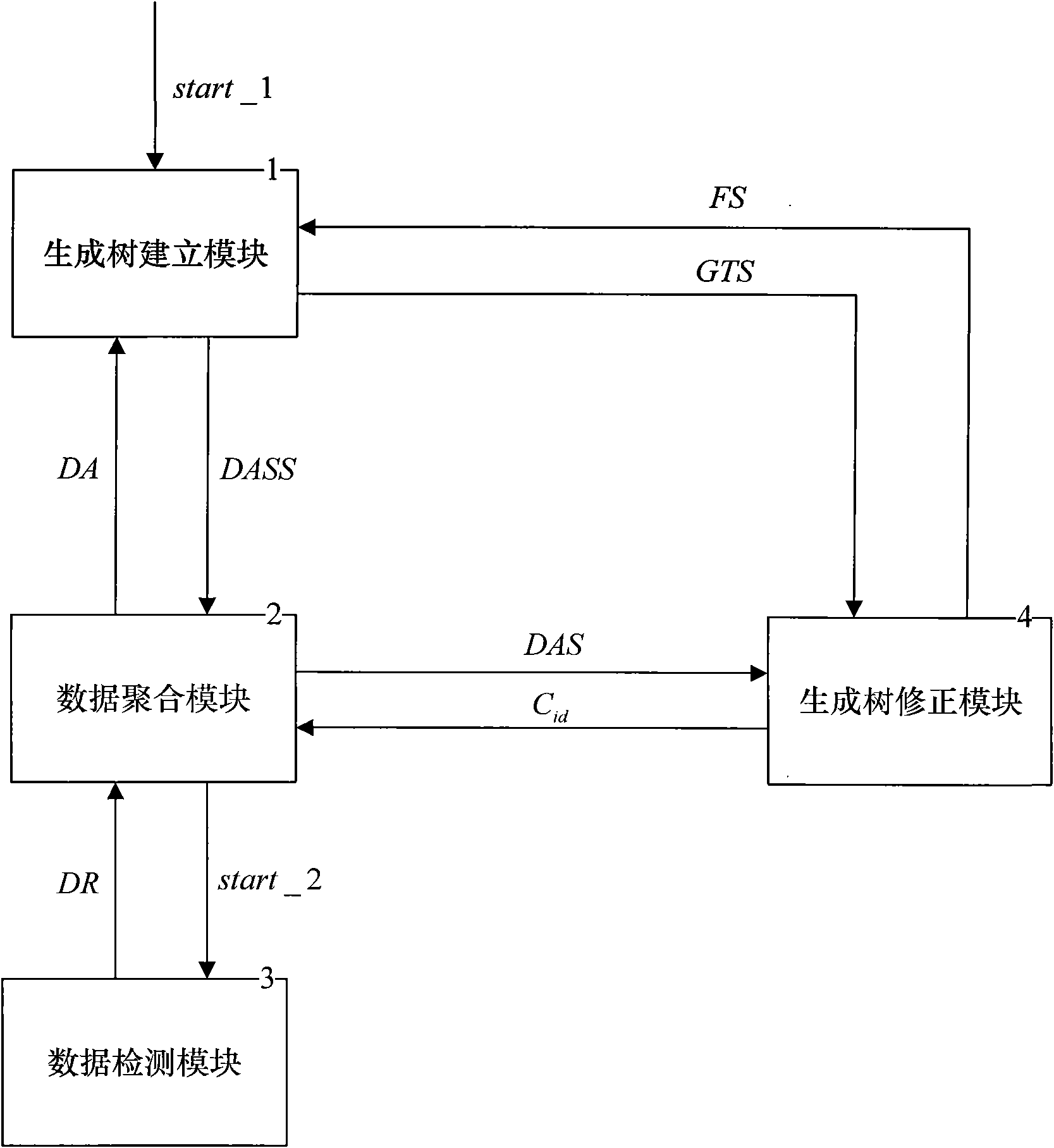
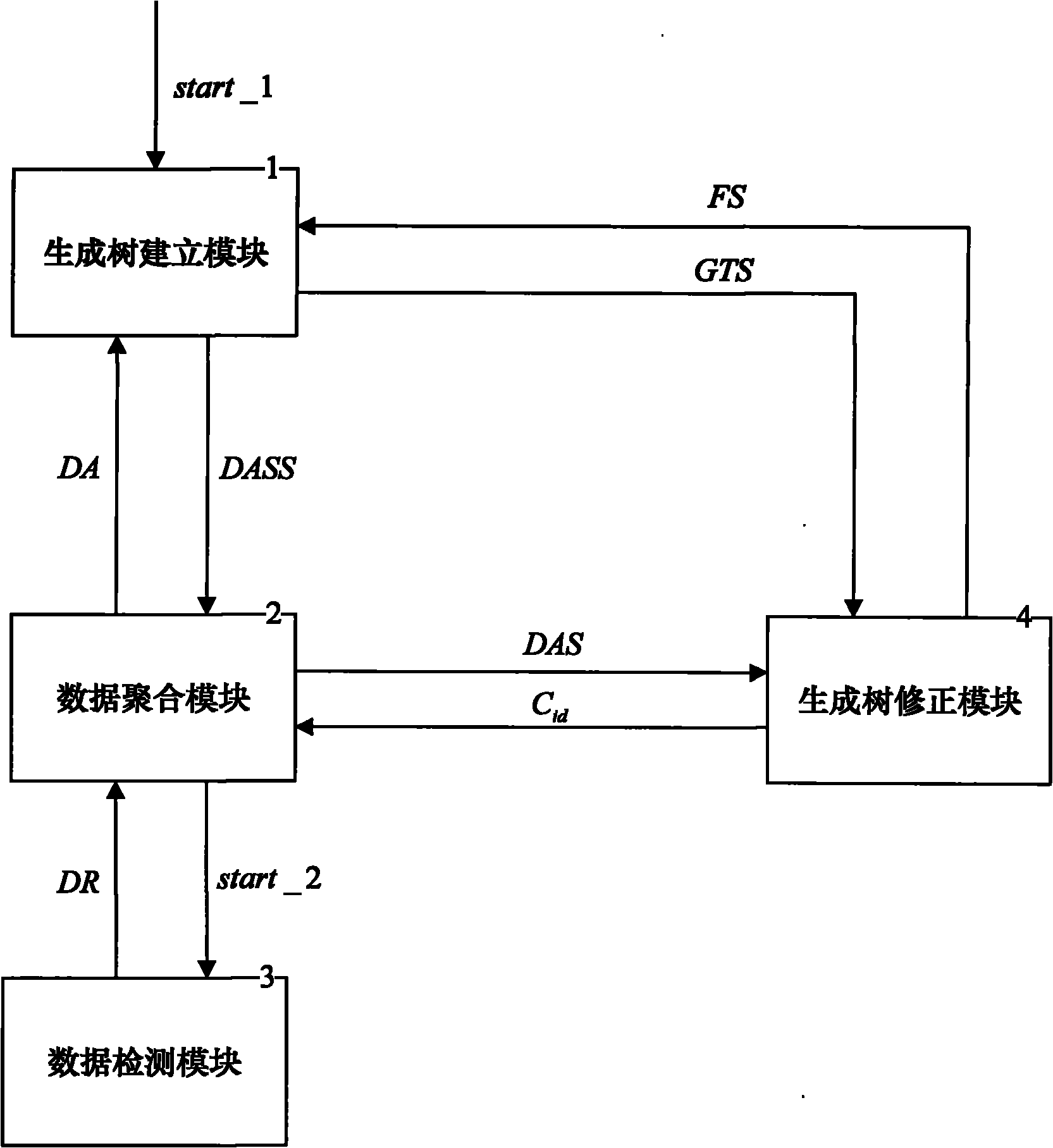
Tree structure-based data aggregation method with reliability assurance
InactiveCN101895419AExtended service lifeImprove reliabilityNetwork topologiesData switching networksData aggregatorDependability
The invention discloses a tree structure-based data aggregation method with reliability assurance. The aggregation method comprises the following steps: generating a tree creating module, an in-tree data aggregation module and a data detection module, and generating a tree revising module. The aggregation method adopts the tree structure to realize fast aggregation of data in the network, ensure that data can be conveniently found and used in the entire network, reduce the communications of the network in the data aggregation process and prolong the service life of the entire network; and the data detection method and the method of generating tree revise are both adopted and the phenomenons such as the damage and death of node can be monitored and found, thus increasing the accuracy and effectiveness of data transmission in the network and the reliability of the entire network.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
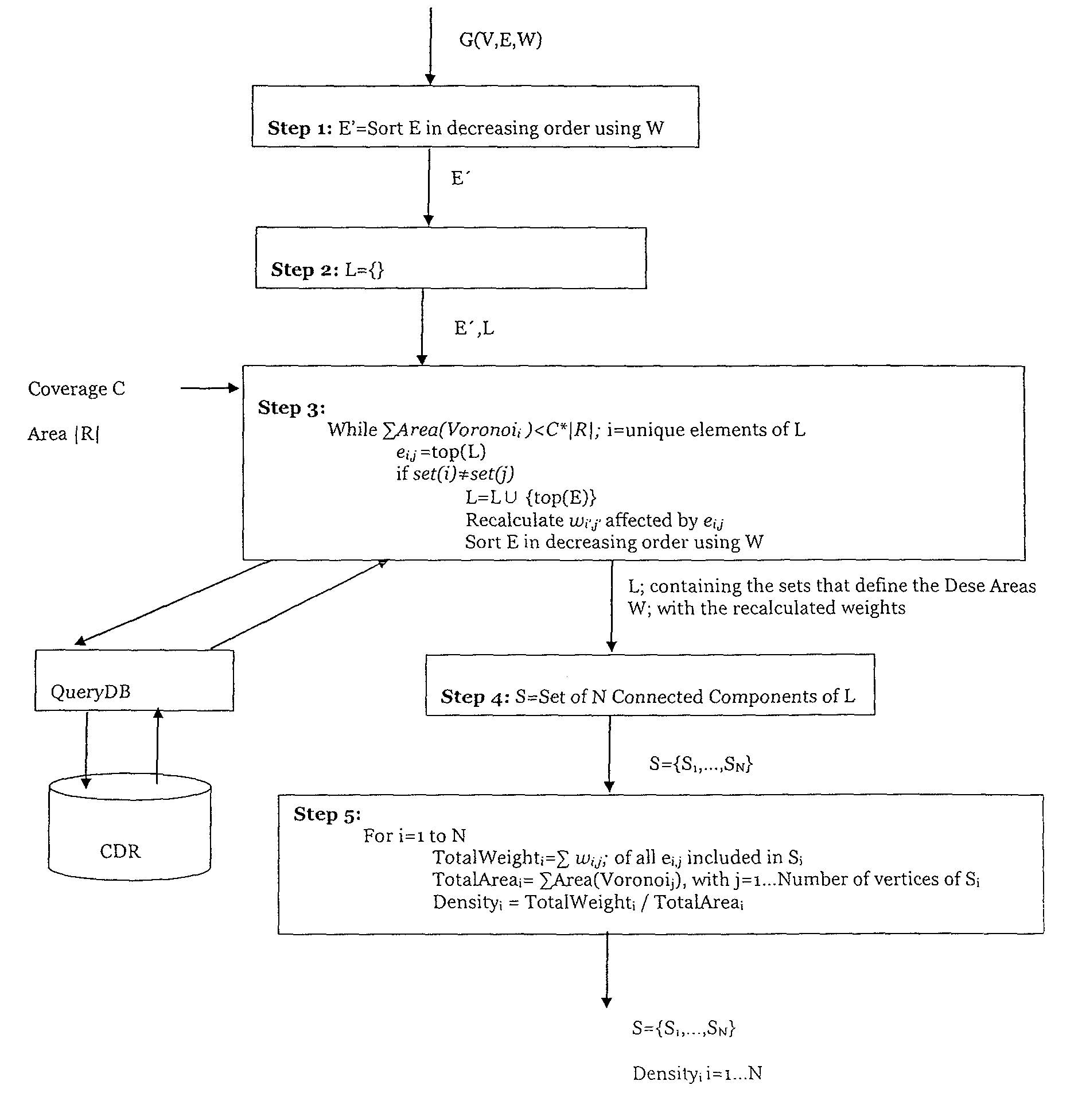
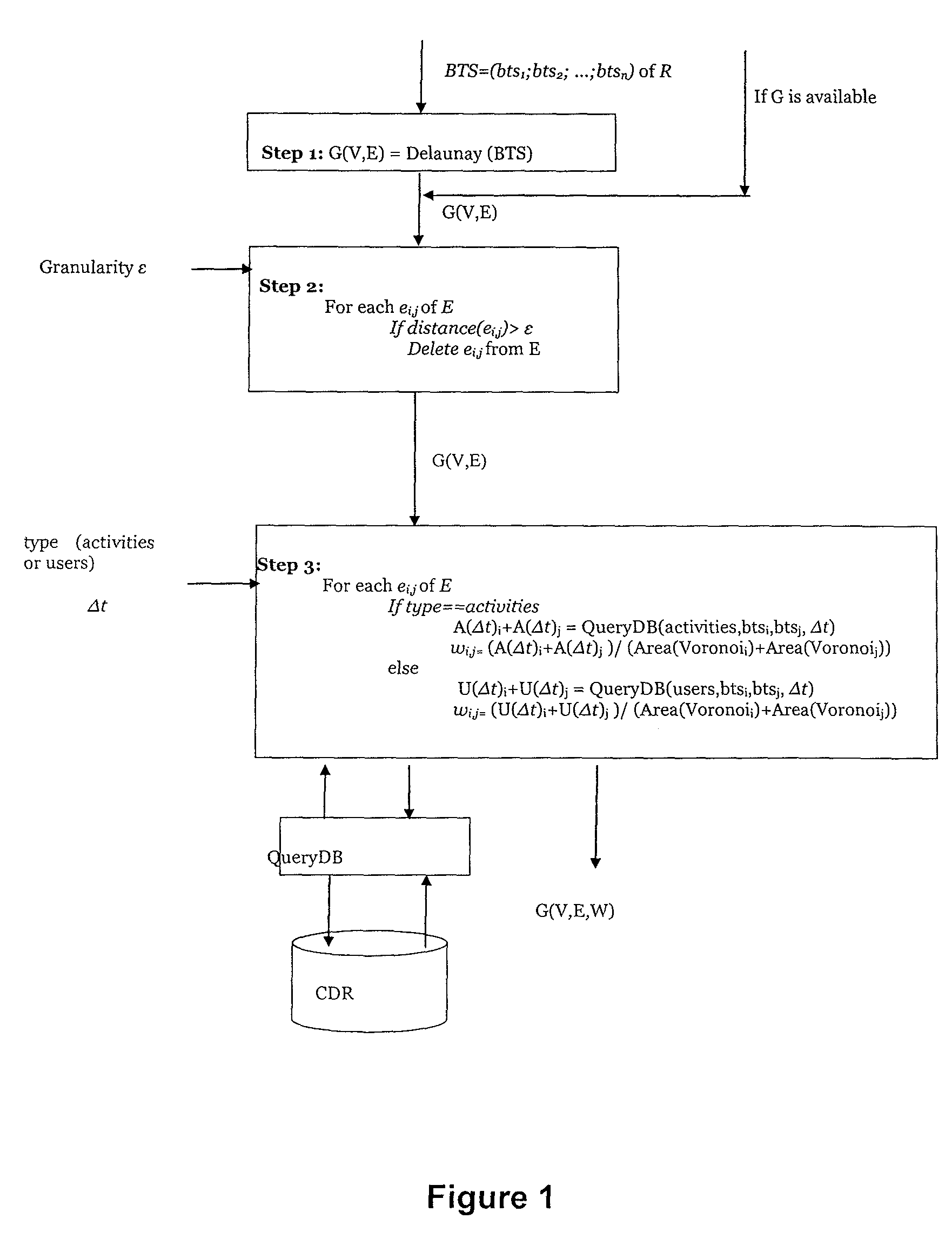
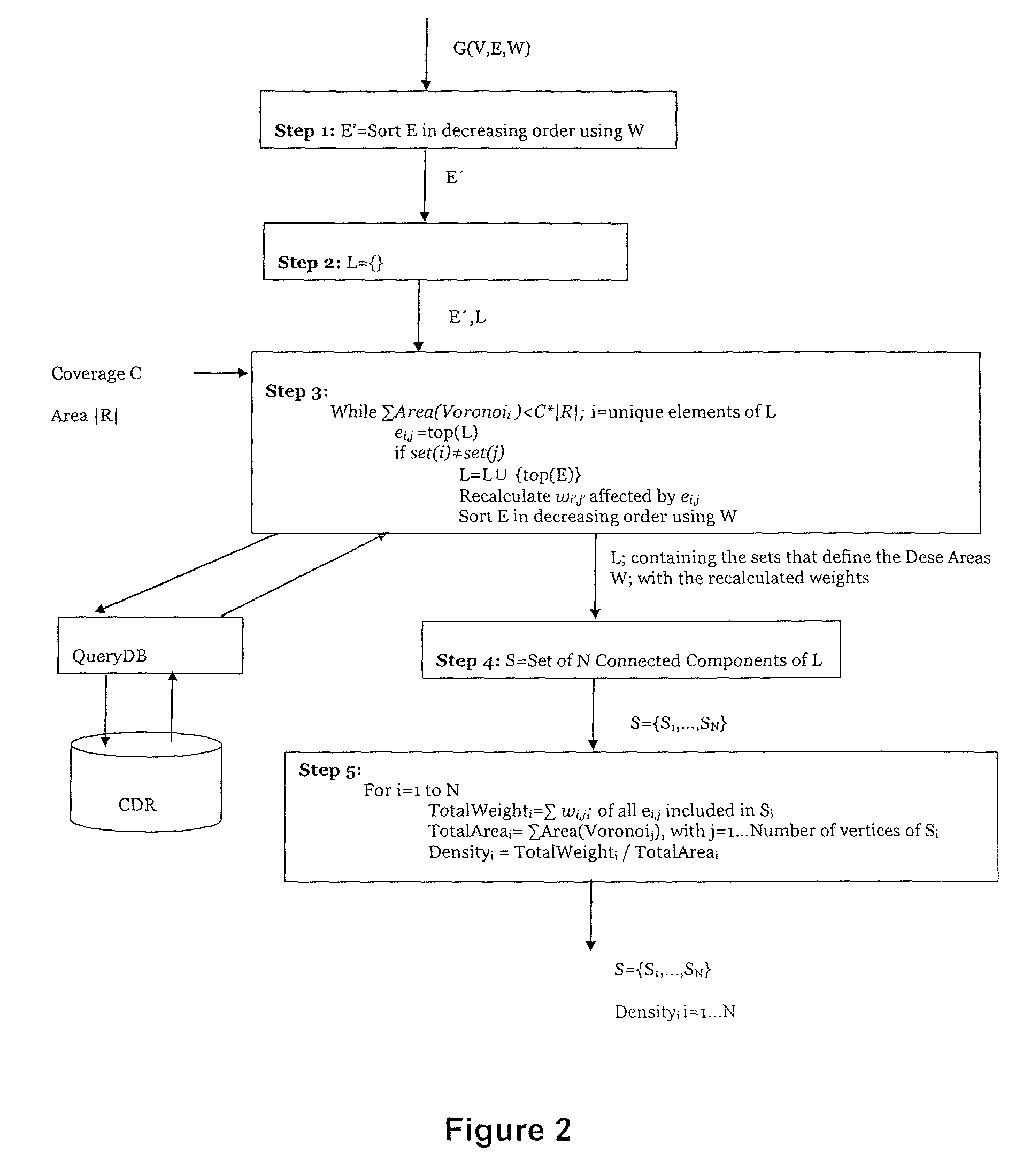
Method for an automatic identification of urban dense areas from cell phones records
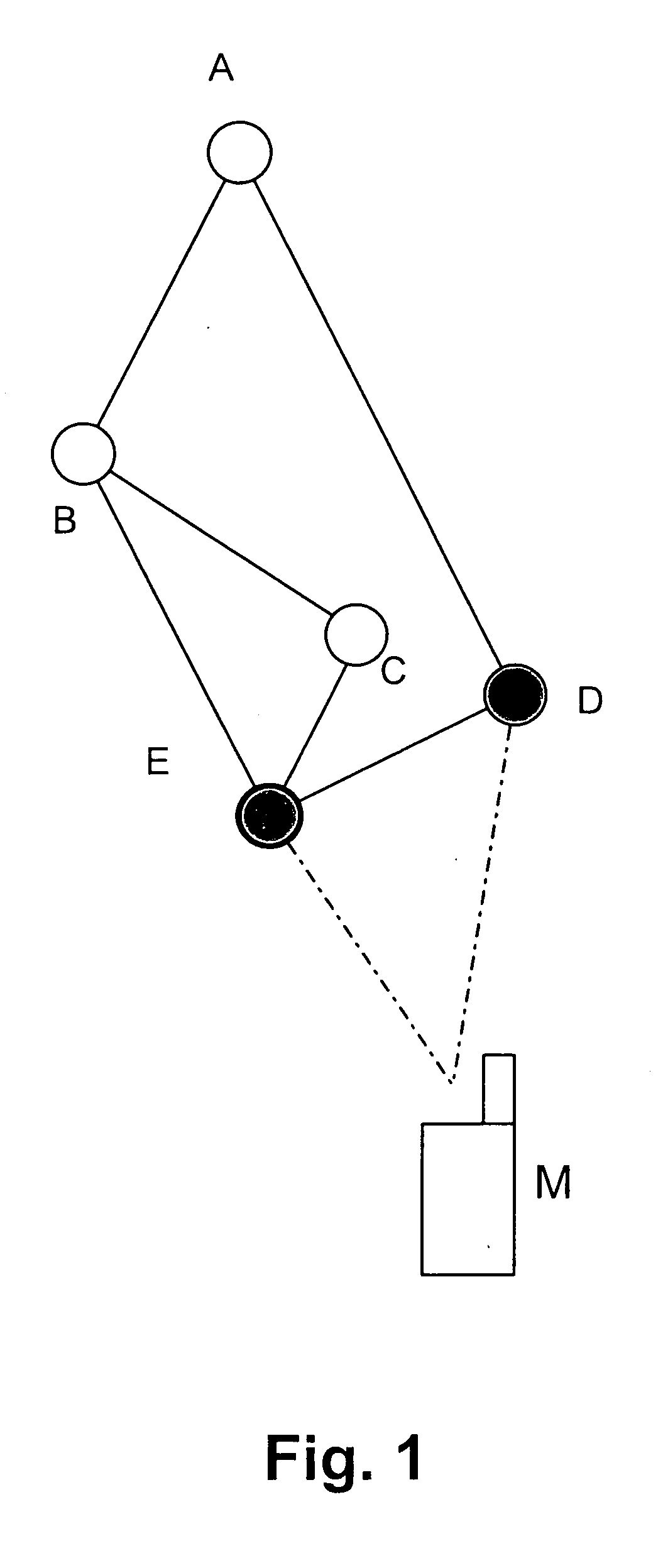
Method for an automatic identification of urban dense areas from cell phones records, by using a computing device that receives as inputs: a geographical region R, a time period Δt for which dense areas in the region R need to be computed, a set of BTSs in the region R, a set of CDRs generated by individuals during the time period Δt using the set of BTSs of the region R, a coverage C and a granularity ε. The method includes constructing a graph G=(V, E), being V=vertexes and E=edges, using Delaunay triangulation, where each vertex vi of V corresponds to btsi of BTS in the geographical region R, and each edge ei,j of E represents connection between btsi and btsj; eliminating from E all the edges in E with a distance between two connecting BTS larger than c, so that a desired spatial granularity is ensured; associating a weight wi,j to each edge ei,j of E that has not been eliminated, the weight representing the average density of the area covered by btsi and btsj during the time period Δt; constructing a data structure L that contains the dense areas using the edges of E; and applying a “Maximum Spanning Tree” type algorithm to detect dense areas given by the data structure L.
Owner:TELEFONICA SA
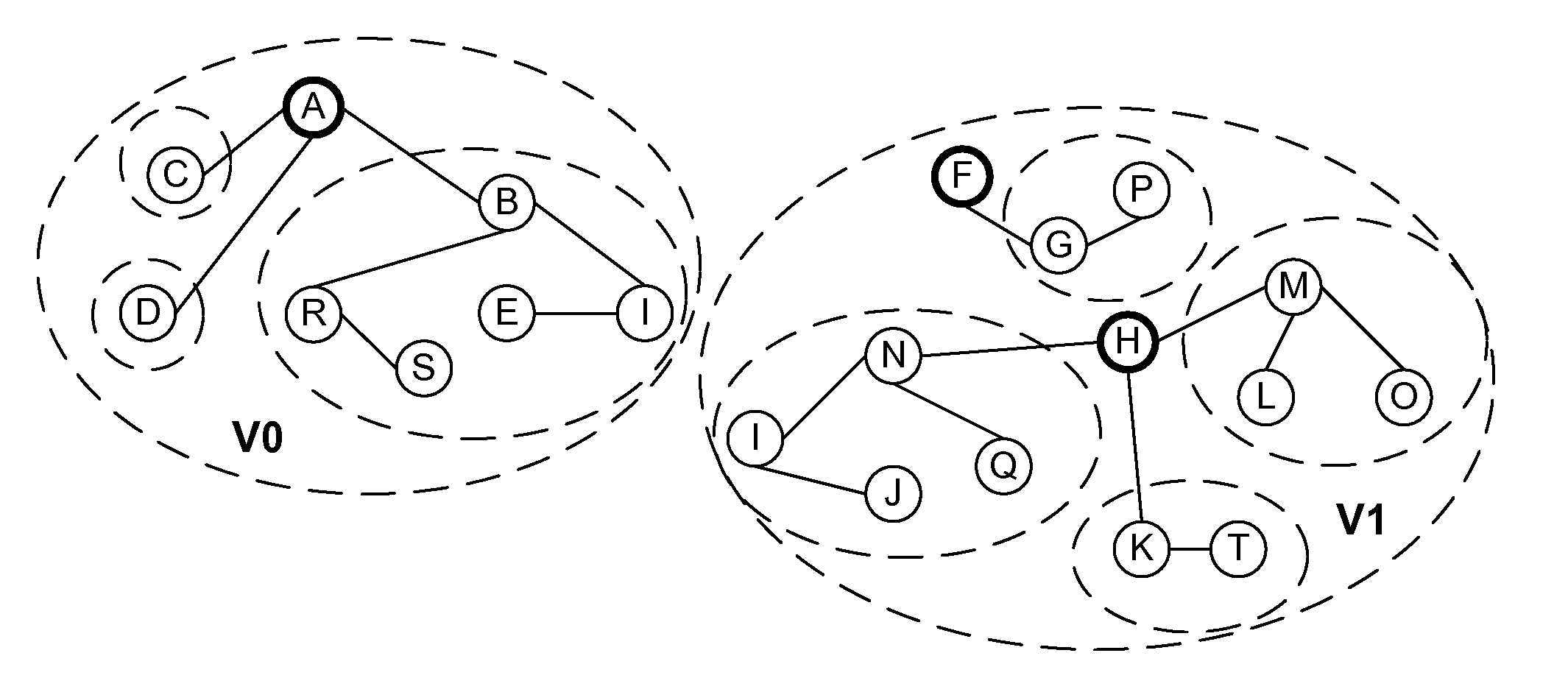
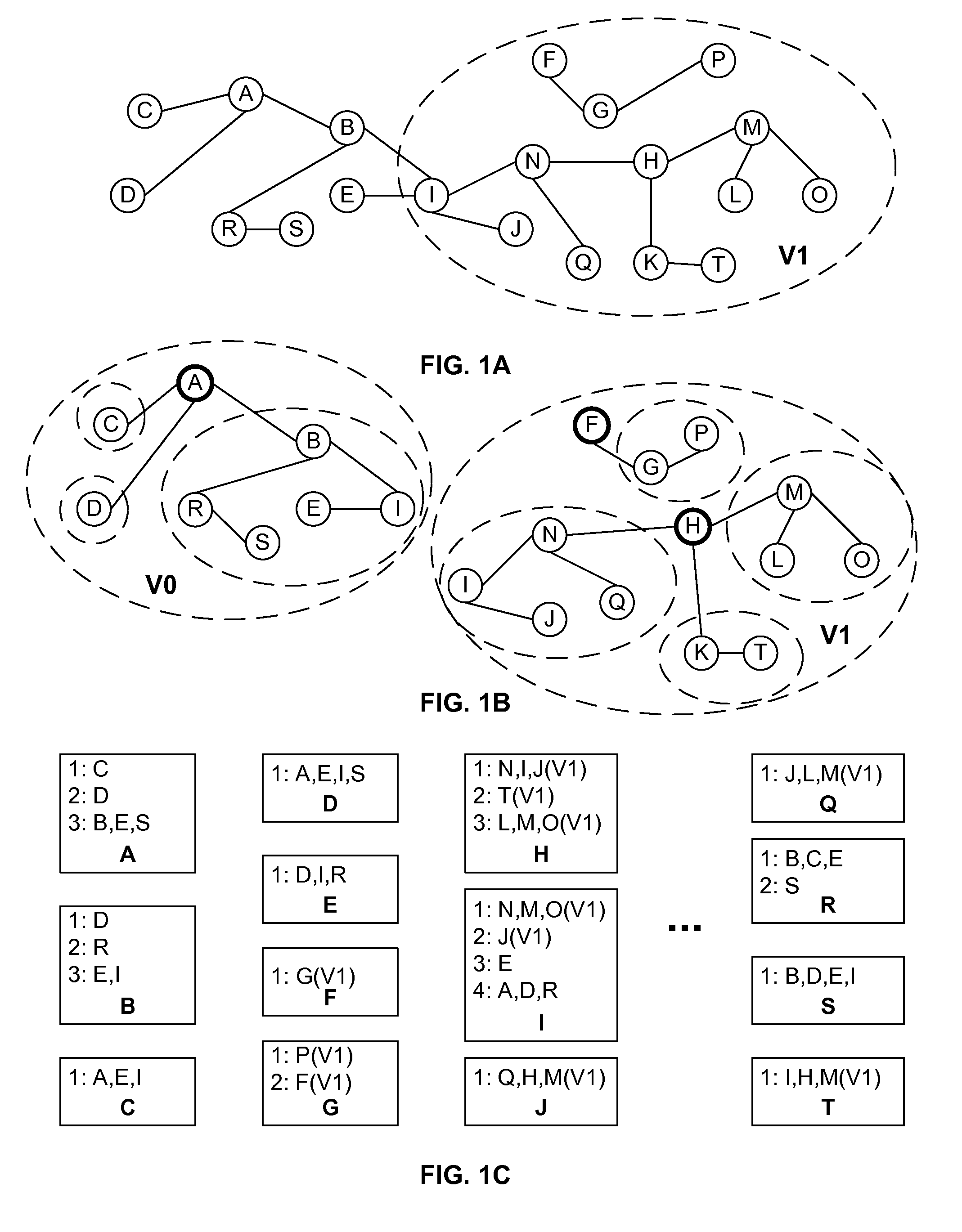
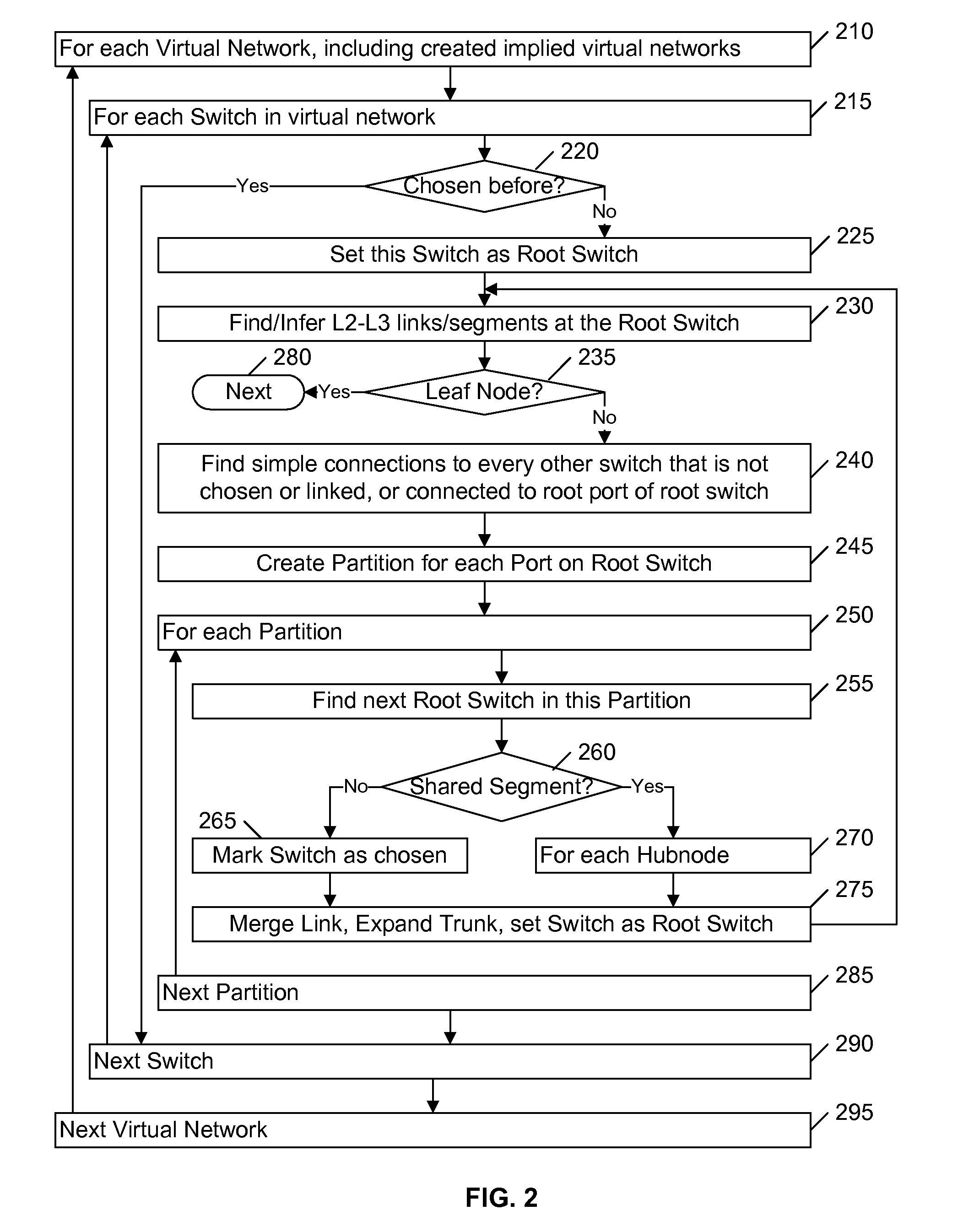
Link inference in large networks based on incomplete data
ActiveUS20080031156A1Efficient implementationFirmly connectedData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsTheoretical computer scienceLarge networks
A network is partitioned into a set of independent partitions, and the topology of each partition is determined, then merged to form a topology of the entire network. Preferably, the partitioning is hierarchical, wherein the network is partitioned to form individual VLAN partitions, and each of the VLAN partitions is further partitioned based on the nodes that are simply connected to each port of one or more selected root switches within the VLAN partition. Simple connections to each port are efficiently determined based on an aggregate address forwarding table associated with each node. Ancillary information, such as spanning tree or CDP data, may be used to facilitate efficient partitioning and / or to validate inferences that are made with incomplete information.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com