Methods and apparatus for real-time traffic steering using real-time user monitoring data
A flow and customer technology, applied in the direction of data exchange network, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
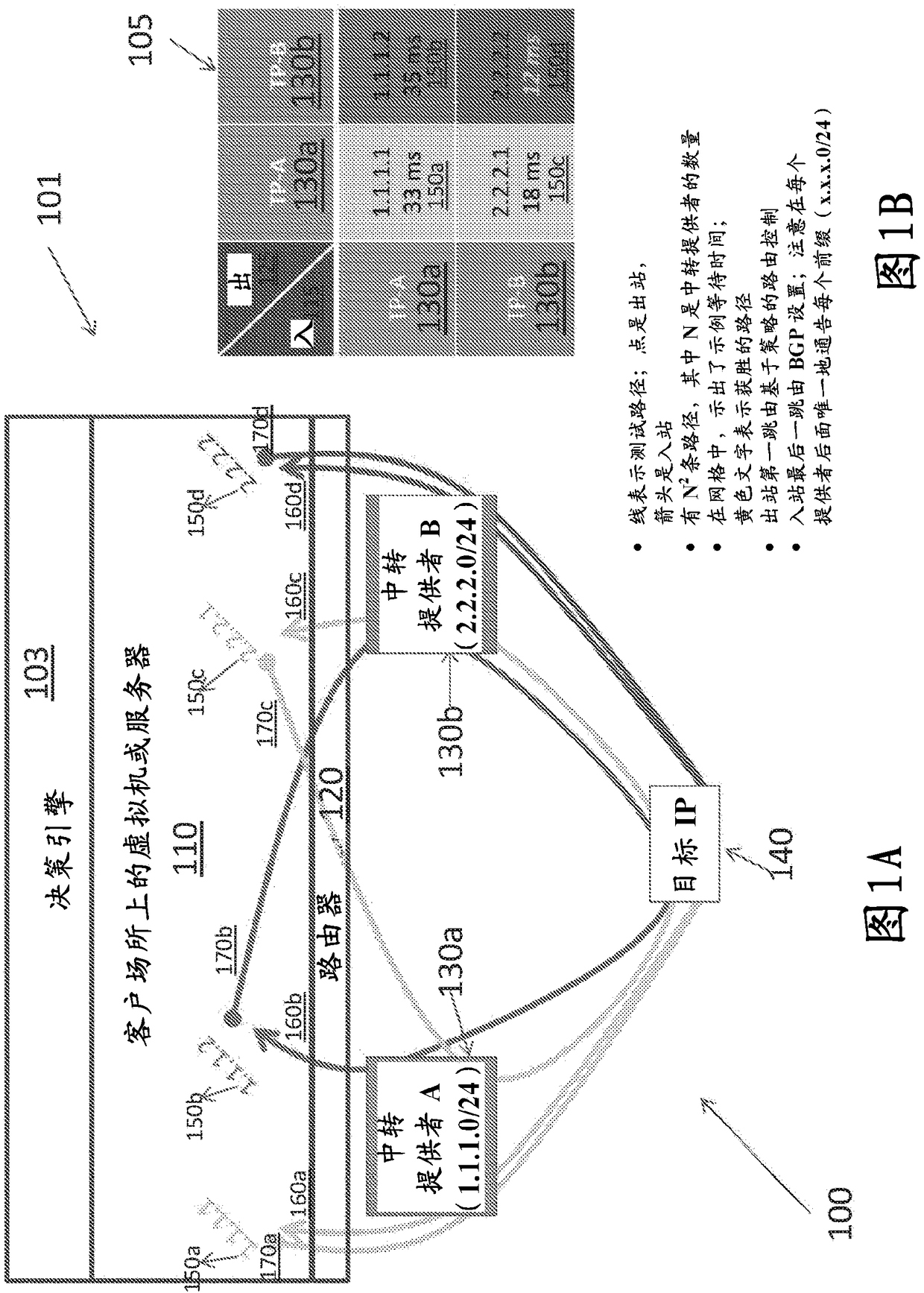
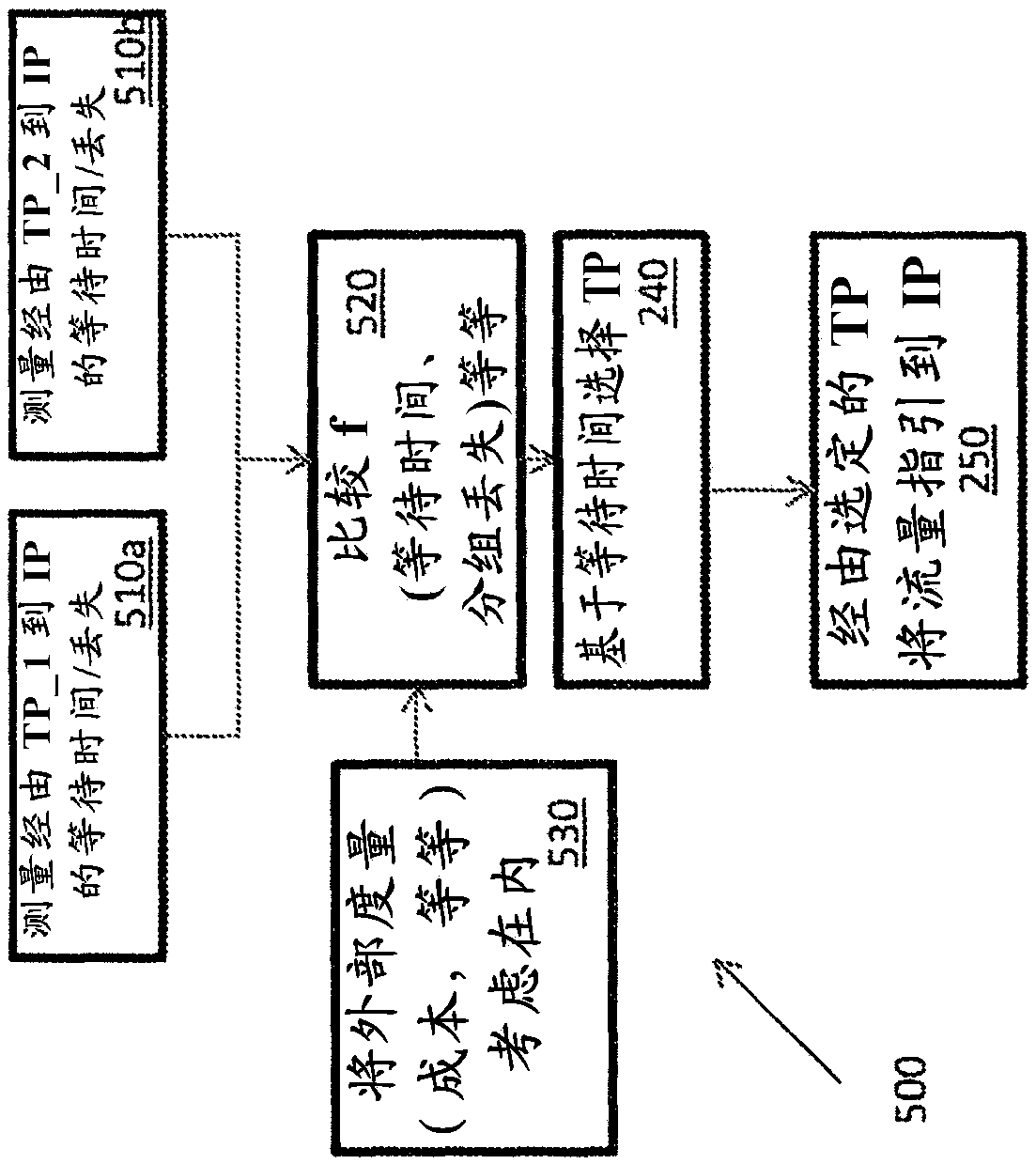
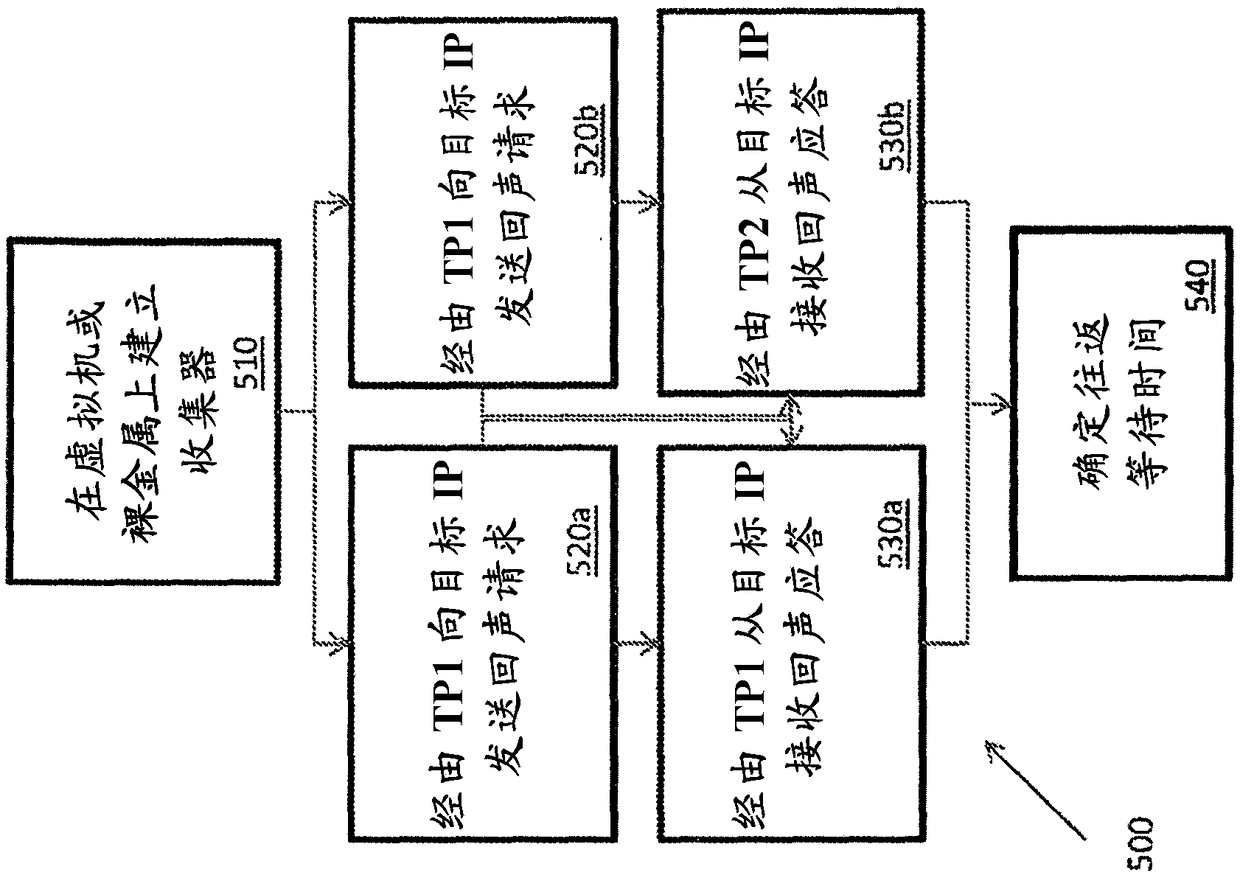
[0040] Intelligent routing based on latency, packet loss and cost between fixed endpoints
[0041] Packets are routed on the Internet according to the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), which uses rules and tables to determine the packet's "next hop" on the route to a given destination. Unfortunately, simple BGP does not take latency, packet loss, or cost into account when routing packets. This can lead to suboptimal routing for applications where low latency is desired, such as real-time bidding for Internet advertising inventory sold on a per-impression basis. With real-time bidding, ad buyers can bid on impressions triggered by a user's visit to a publisher's website. If the buyer wins the auction, the buyer's ad is immediately displayed on the publisher's website. Because the auction occurs in real time in response to a user's visit to the publisher's website, it lasts for a short period of time, so quick bidding is imperative. If the buyer's bid does not reach the auctione...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com