Patents
Literature
39 results about "Spot intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
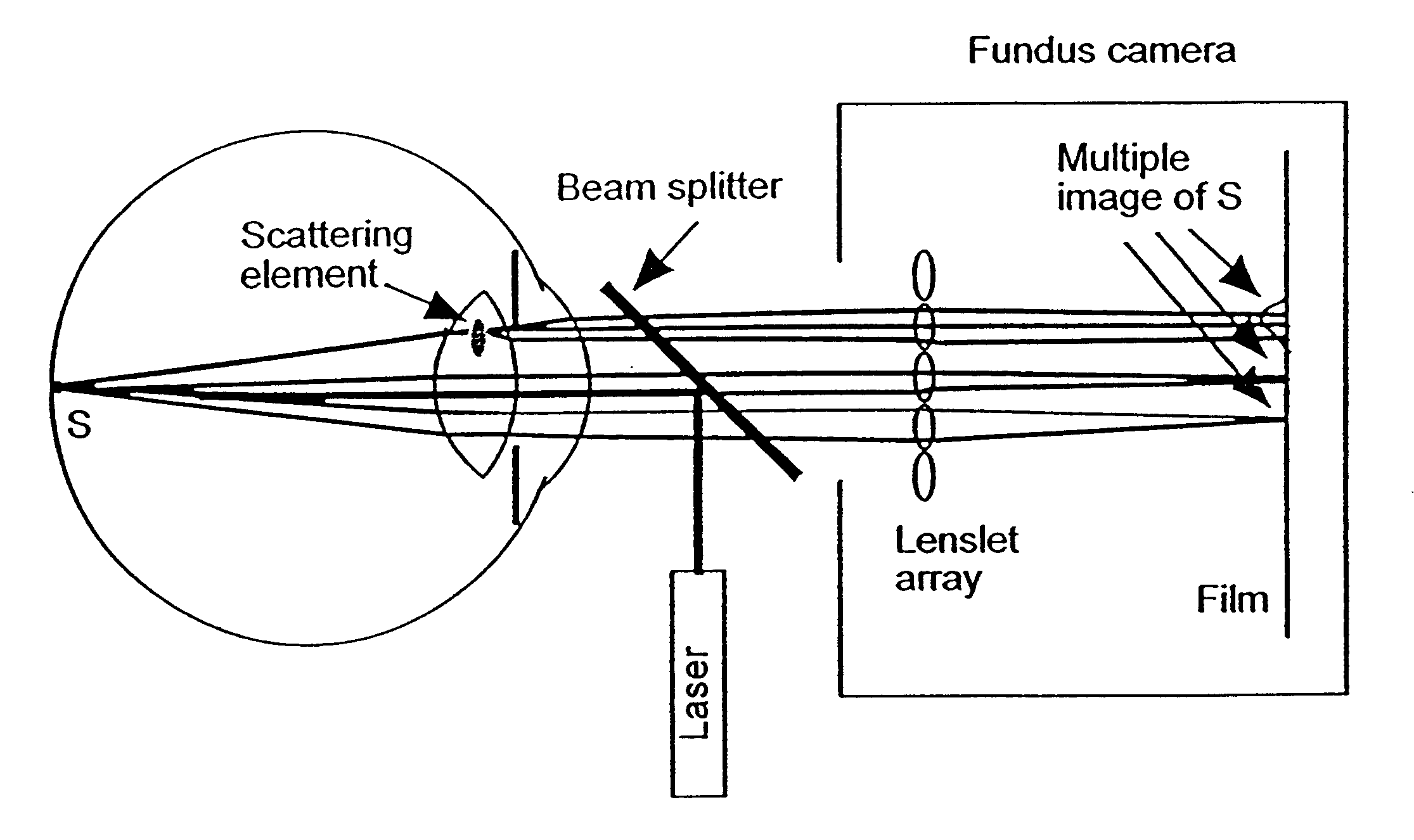
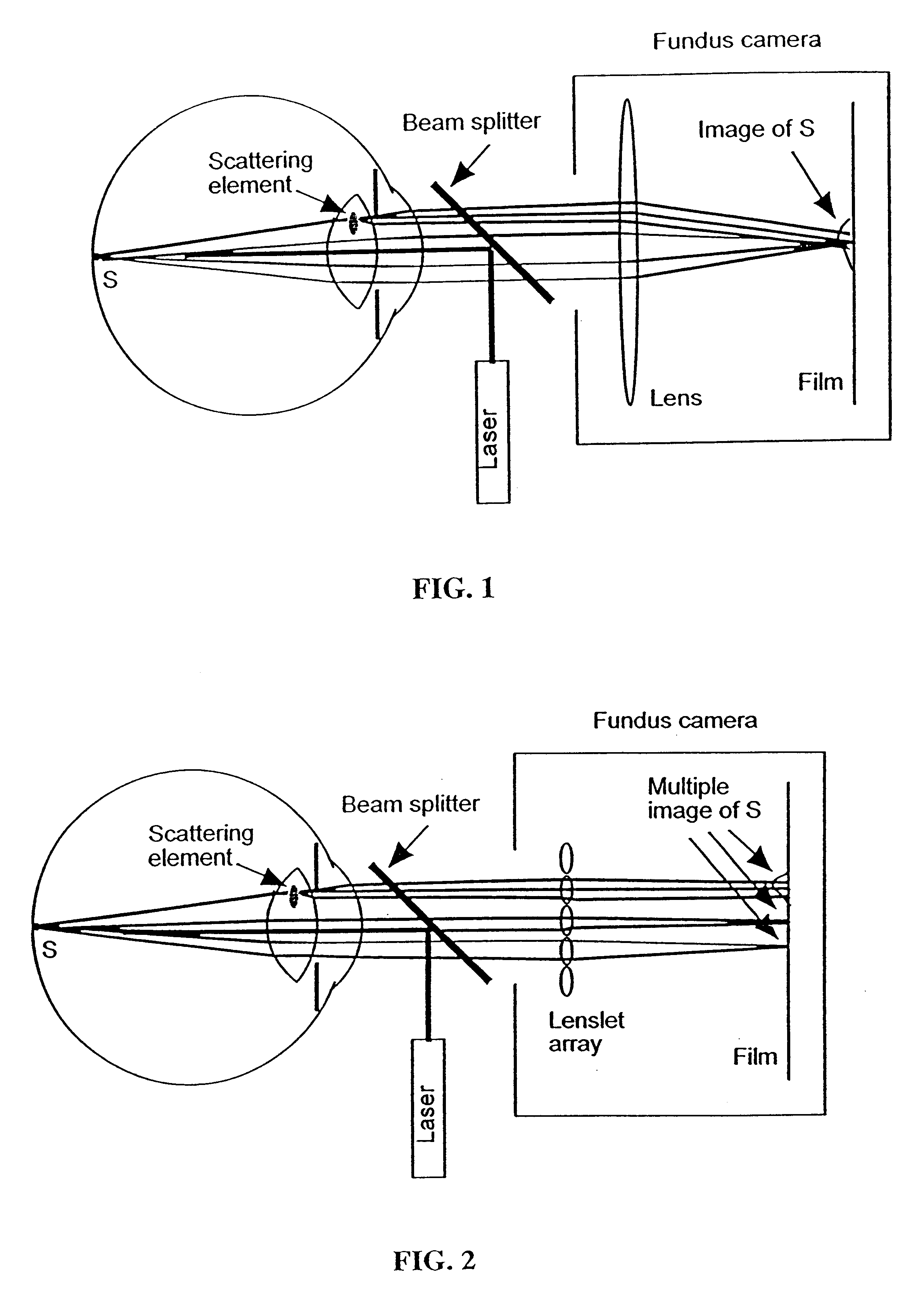
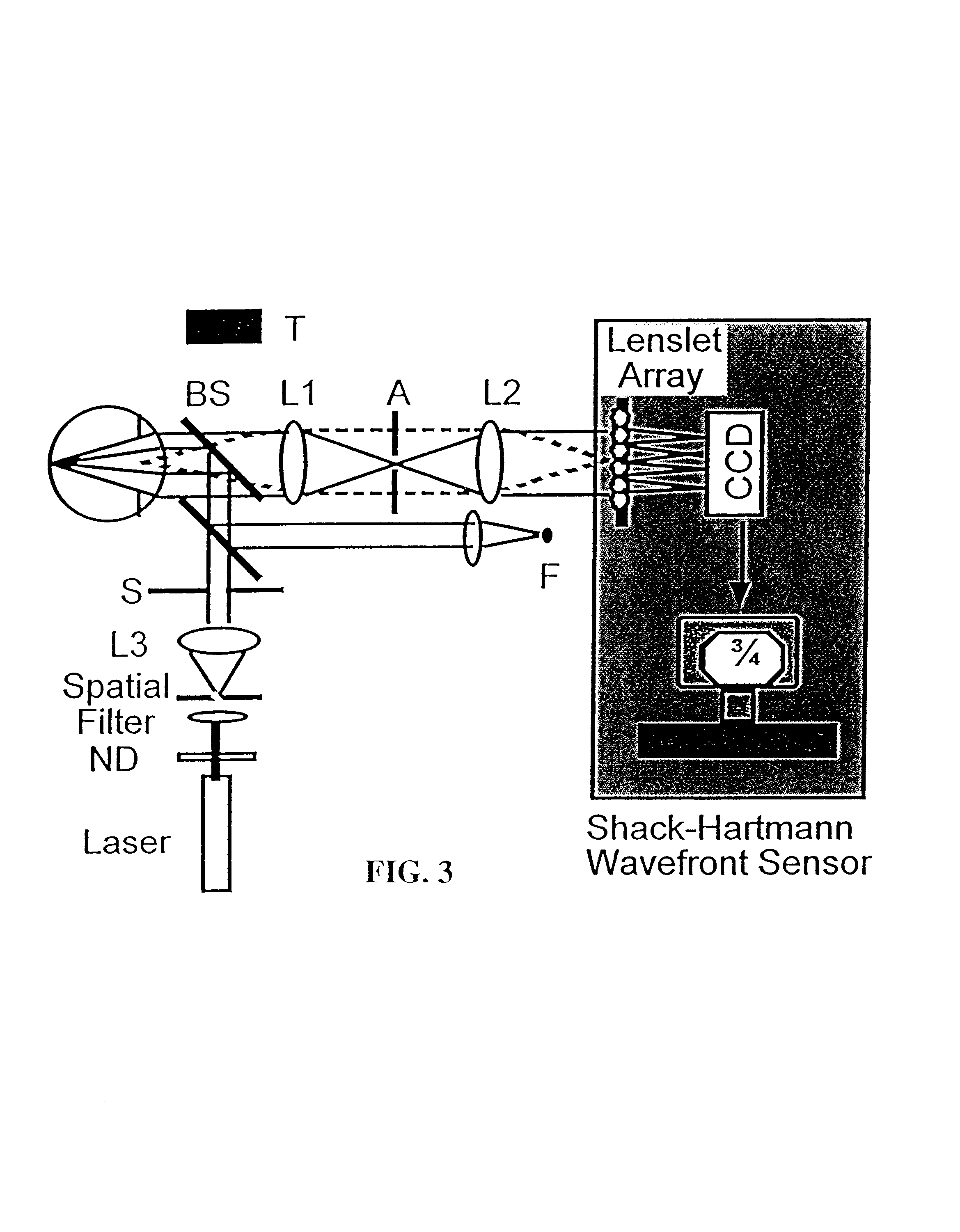
Methods and systems for measuring local scattering and aberration properties of optical media
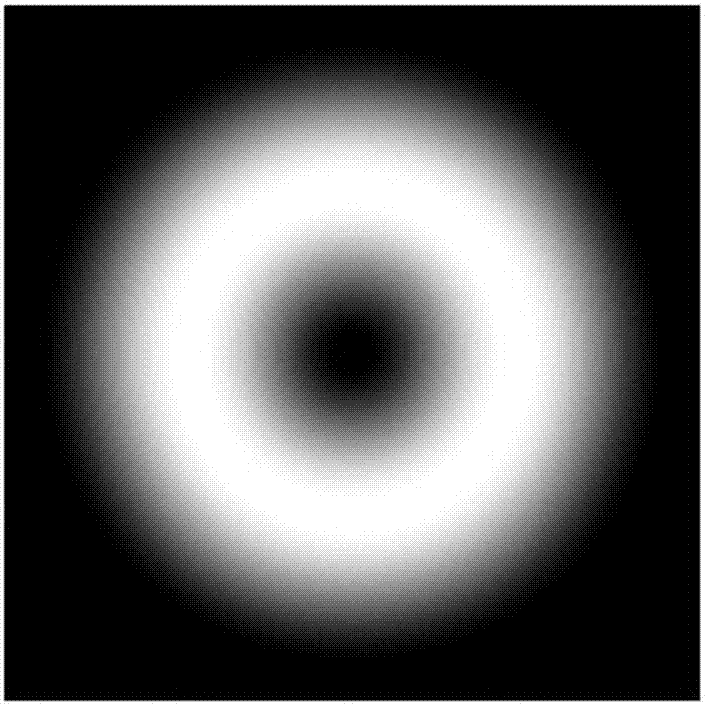
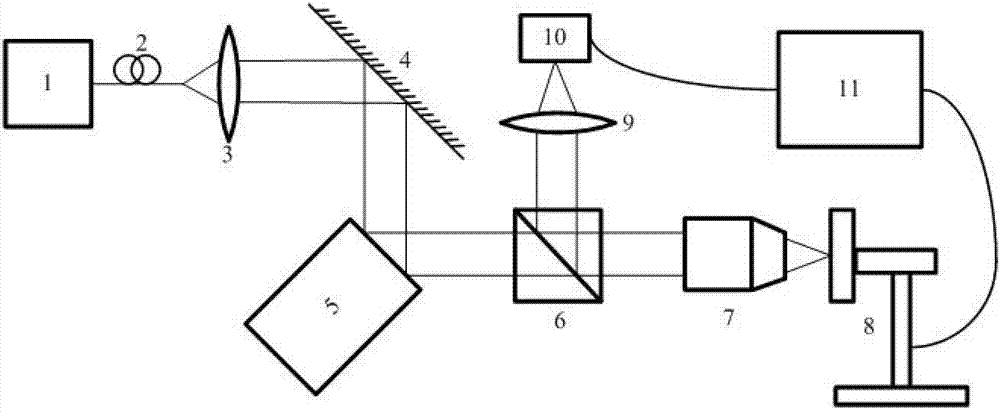
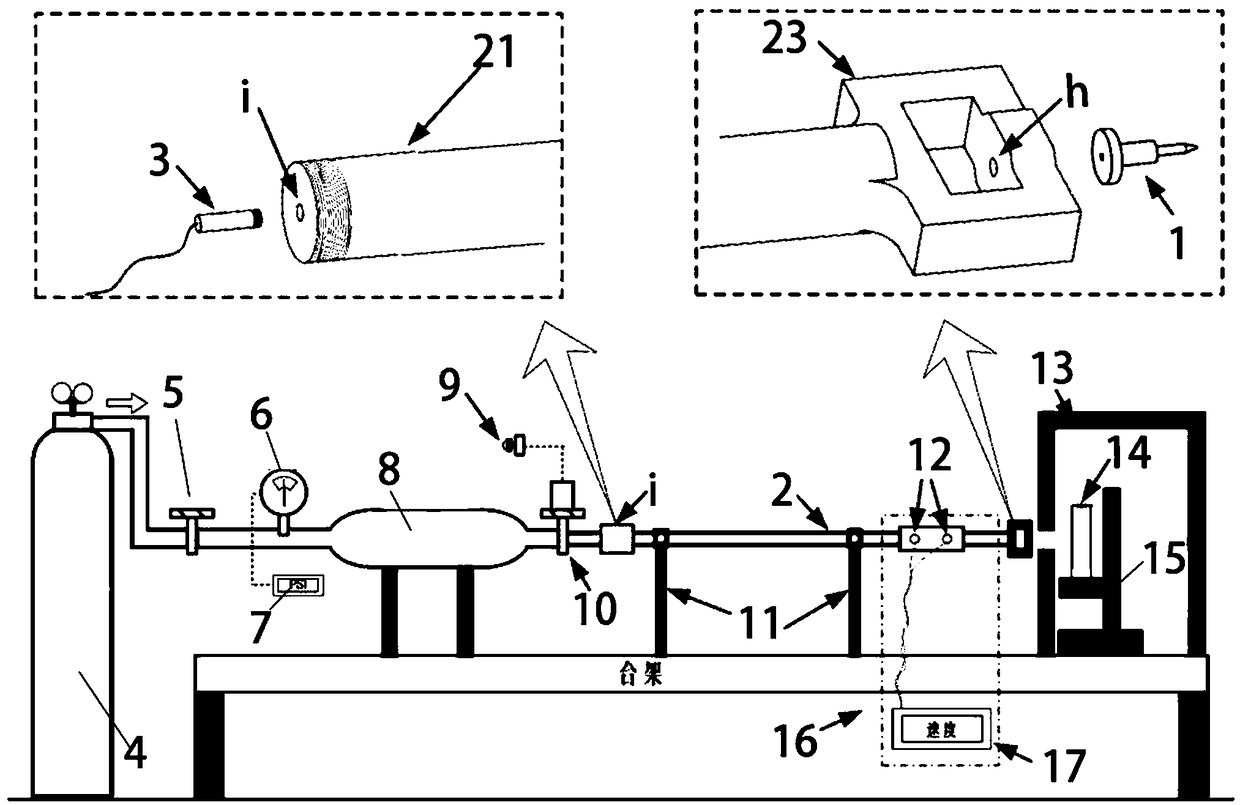
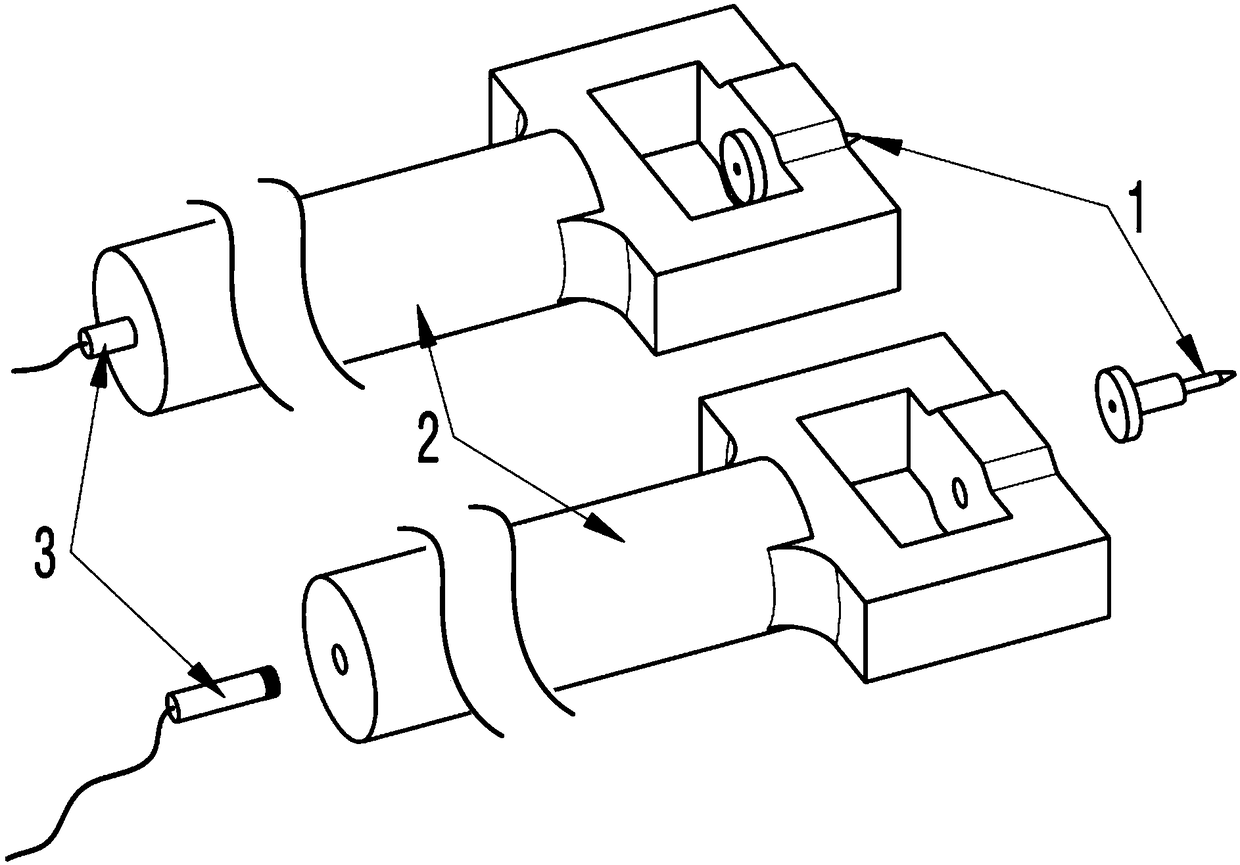
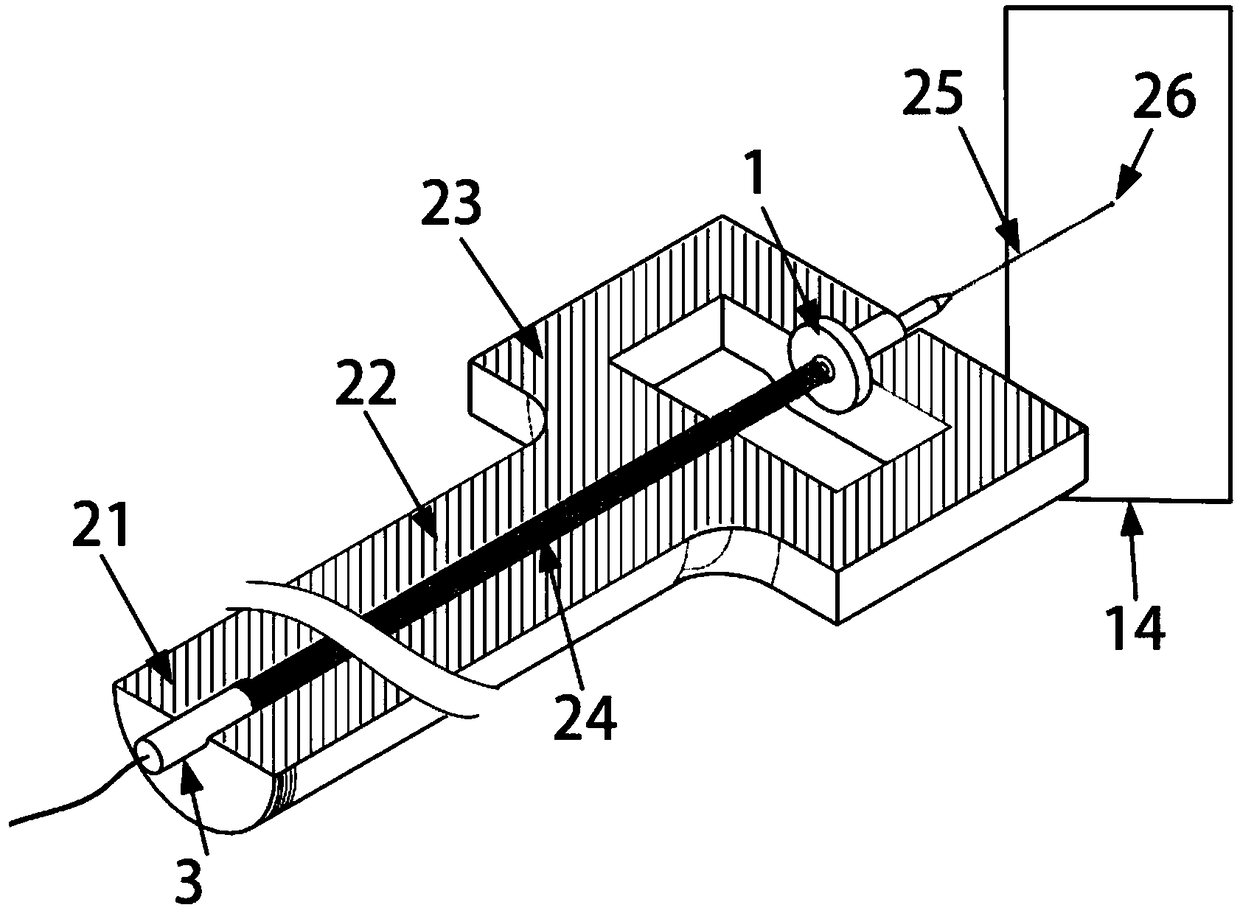
Methods, systems, and media relating the display of scattering and / or absorption characteristics of an optical medium. For scattering measurements, a Hartmann-Shack calibration image of a measurement system is acquired to define a first plurality of point spread functions. A Hartmann-Shack test image of the medium is acquired to define a second plurality of point spread functions. A shift is determined between the test image and the calibration image. A point spread of each of the second plurality of point spread functions is measured, each of the second plurality of point spread functions including a component due to optical aberration of the medium and a component due to scatter. The component due to optical aberration is determined using the shift. The component due to optical aberration is deconvolved to determine the component due to scatter. A display of the local scattering characteristics is generated using the component due to scatter. For absorption measurements, a plurality of spot intensity measurements are acquired of a medium, each spot intensity measurement including a component due to reflectivity and a component due to absorption. The component due to reflectivity is determined, and the component due to absorption is determined.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST +1
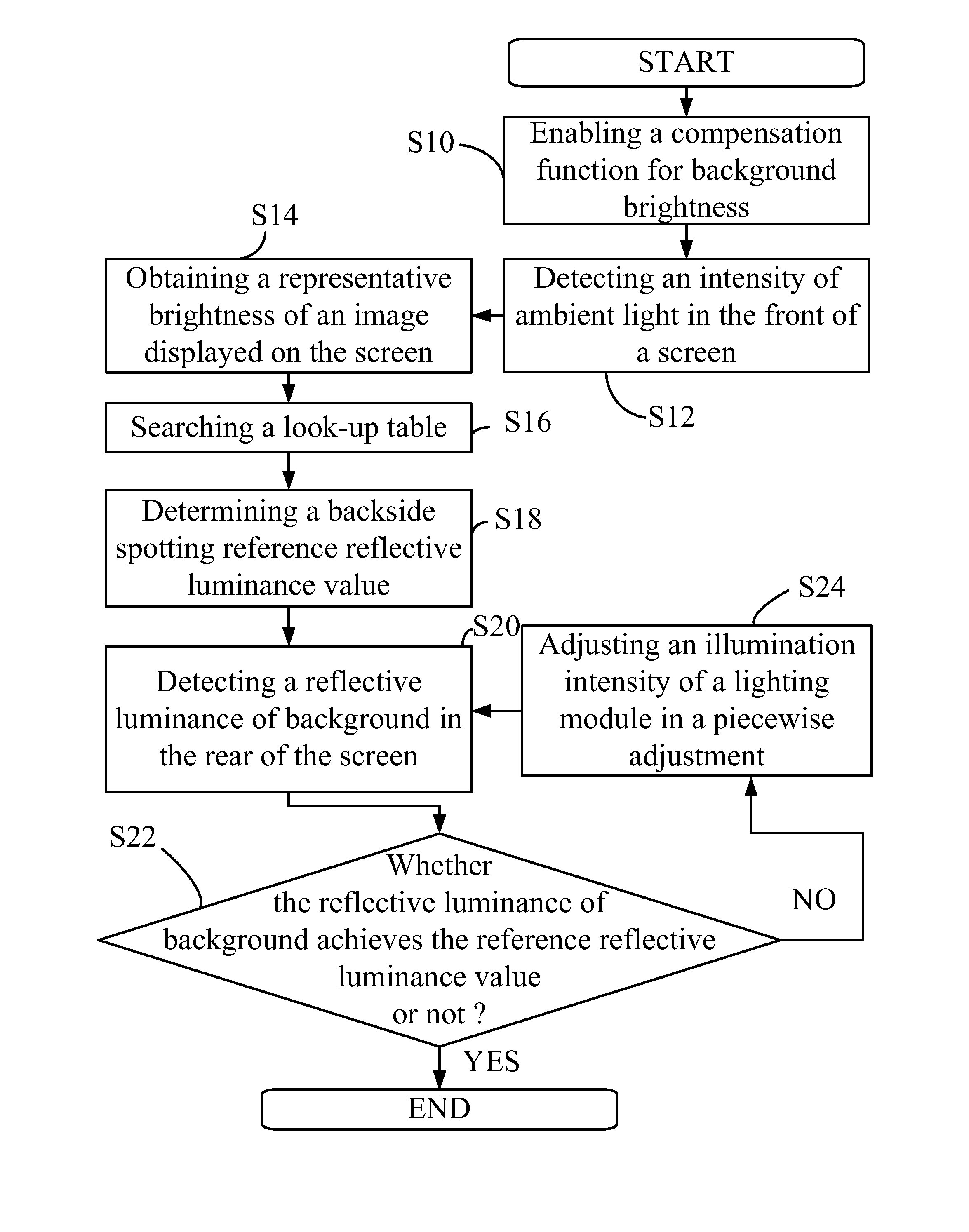
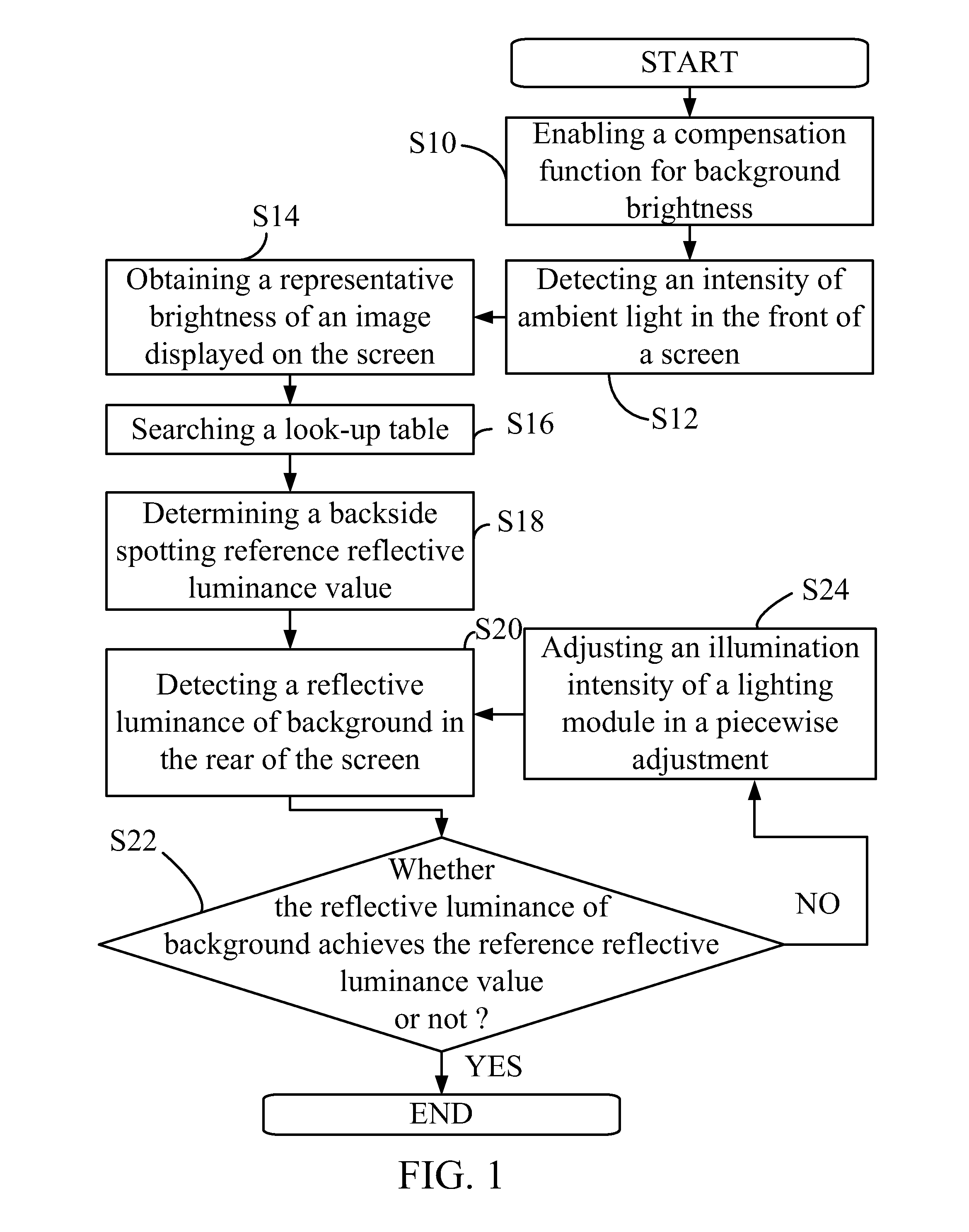
Background brightness compensating method and system for display apparatus
InactiveUS20120182275A1Improve viewing comfortReduce eye fatigueCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEffect lightUltimate tensile strength
A system and a method of compensating background brightness for a display apparatus are disclosed. The display apparatus has a screen for displaying images, and said method comprises steps of: (a) detecting an intensity of ambient light in the front of the screen; (b) obtaining a representative brightness of an image displayed on the screen; (c) determining a backside spotting reference reflective luminance value according to the ambient light intensity and the image representative brightness; and (d) spotting in the rear of the screen by using a lighting module and thus making a spotting intensity to achieve the reference reflective luminance value. The said method and system can reduce eye fatigue and discomfort of viewers.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Super-resolution fluorescent lifetime imaging method and device based on stimulated emission lost
InactiveCN103163106AReduced diffraction areaHigh-resolutionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceExcited stateTest sample
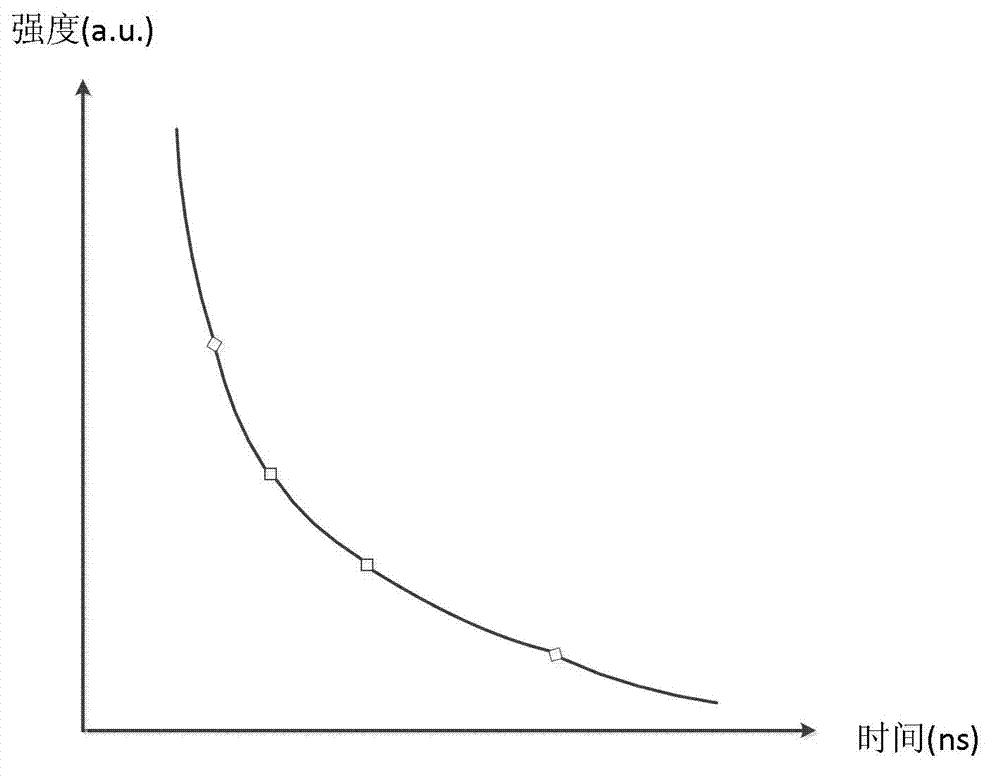
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescent lifetime imaging method based on stimulated emission lost. The super-resolution fluorescent lifetime imaging method based on the stimulated emission lost includes the flowing steps: (1) projecting a first laser beam on a to-be-tested sample and activating grains in the to-be-tested sample to an excited sate; (2) utilizing stimulated emission depletion (STED) light to consume the number of the grains which are in the excited state in step (1); (3) utilizing a second laser beam to stimulate the rest grains to emit fluorescent light and collecting the fluorescent light to obtain corresponding fluorescence intensity images; (4) arranging delay between the second laser beam and the STED light, changing delay time, repeating step (3), and obtaining the fluorescence intensity images under different delay time; (5) conducting treatment on the fluorescence intensity images in different delay time through a computer, and fitting a spot intensity attenuation law, inverting lifetime images, and completing scanning of one point of the to-be-tested sample; (6) and completing two-dimension scanning on the sample to be tested by changing the positions where the beam is projected on the to-be-tested sample. The invention further discloses a device used for implementing the method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Double helix light beam-based sample axial drift detection and compensation method and device
InactiveCN103399413AAchieve real-time high precisionRealize a wide range of measurementsMicroscopesCurrent sampleLight beam
The invention discloses a double helix light beam-based sample axial drift detection and compensation method. The method comprises the following steps: performing phase modulation on a collimated laser beam to obtain a double helix illuminating light beam and projecting to a sample to be detected on a three-dimensional nano scanning platform to obtain a reflected light beam; focusing the reflected light beam into a focusing spot with two intensity peak values; receiving the focusing spot by using a photoelectric induction device to obtain spot intensity distribution information; calculating an included angle between a connecting line of the two intensity peak values and the horizontal direction according to the spot intensity distribution information; establishing a calibration function by using the relation of the included angle and axial drift of the sample; when the sample to be detected drifts in axial position, obtaining the axial drift of the current sample according to the calibration function by using the included angle measured in real time and then adjusting the axial position of the three-dimensional nano scanning platform to finish correction of the axial position of the sample to be detected. The invention also discloses a double helix light beam-based sample axial drift detection and compensation device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Diffractive optical element and laser machining apparatus using same
ActiveUS20060013277A1Free and precise laser simultaneous multipoint processingImprove accuracyOptical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsComplex amplitudeFast Fourier transform
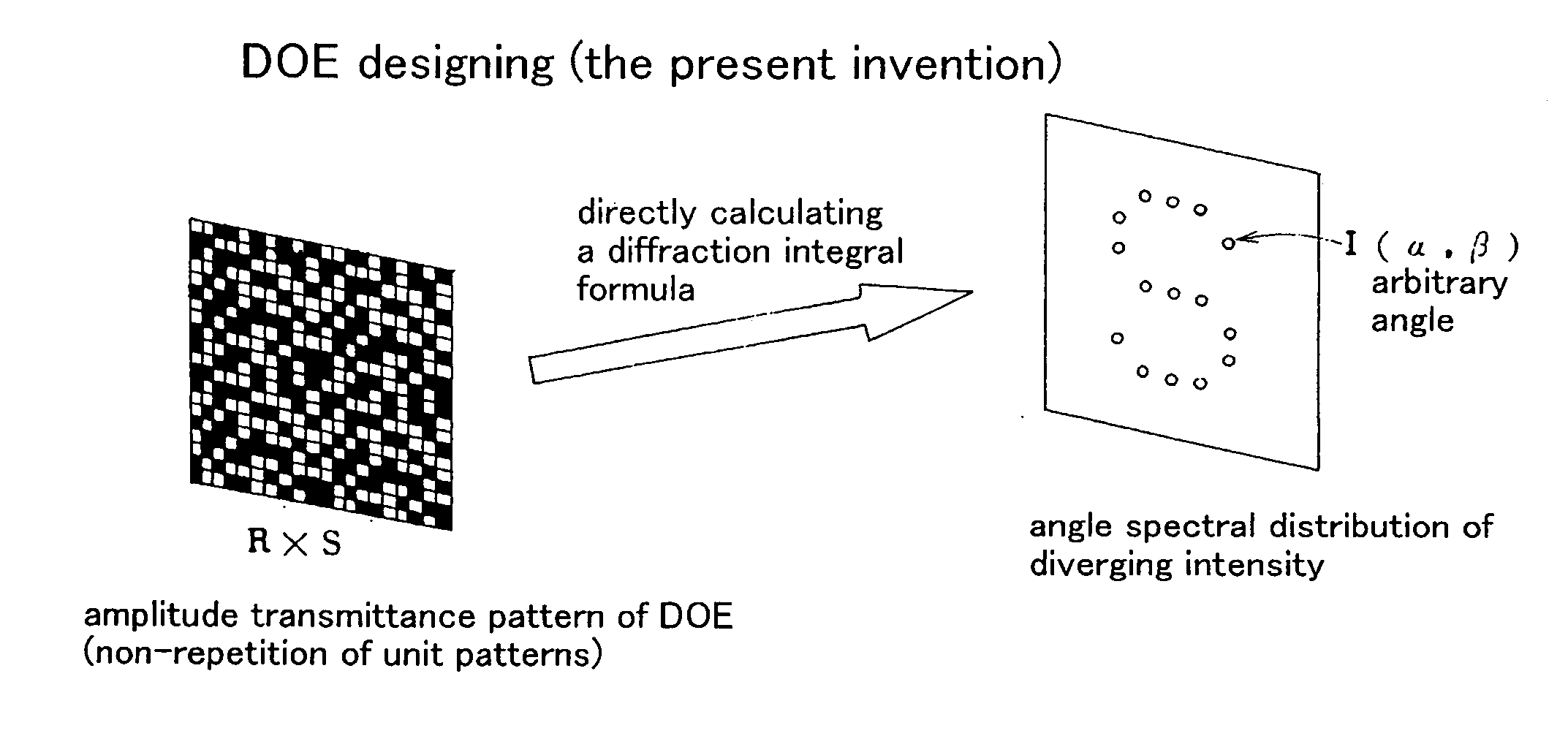
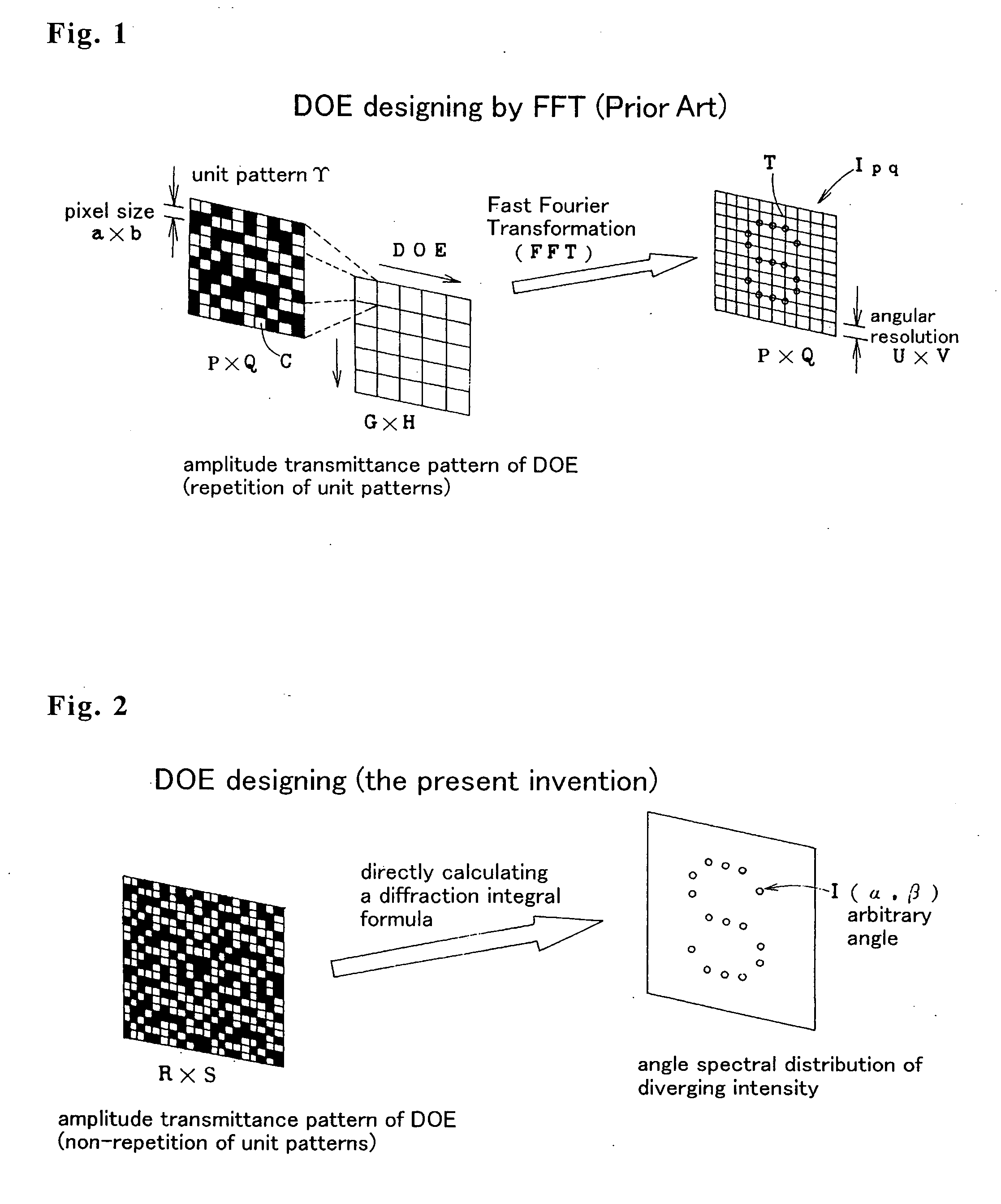
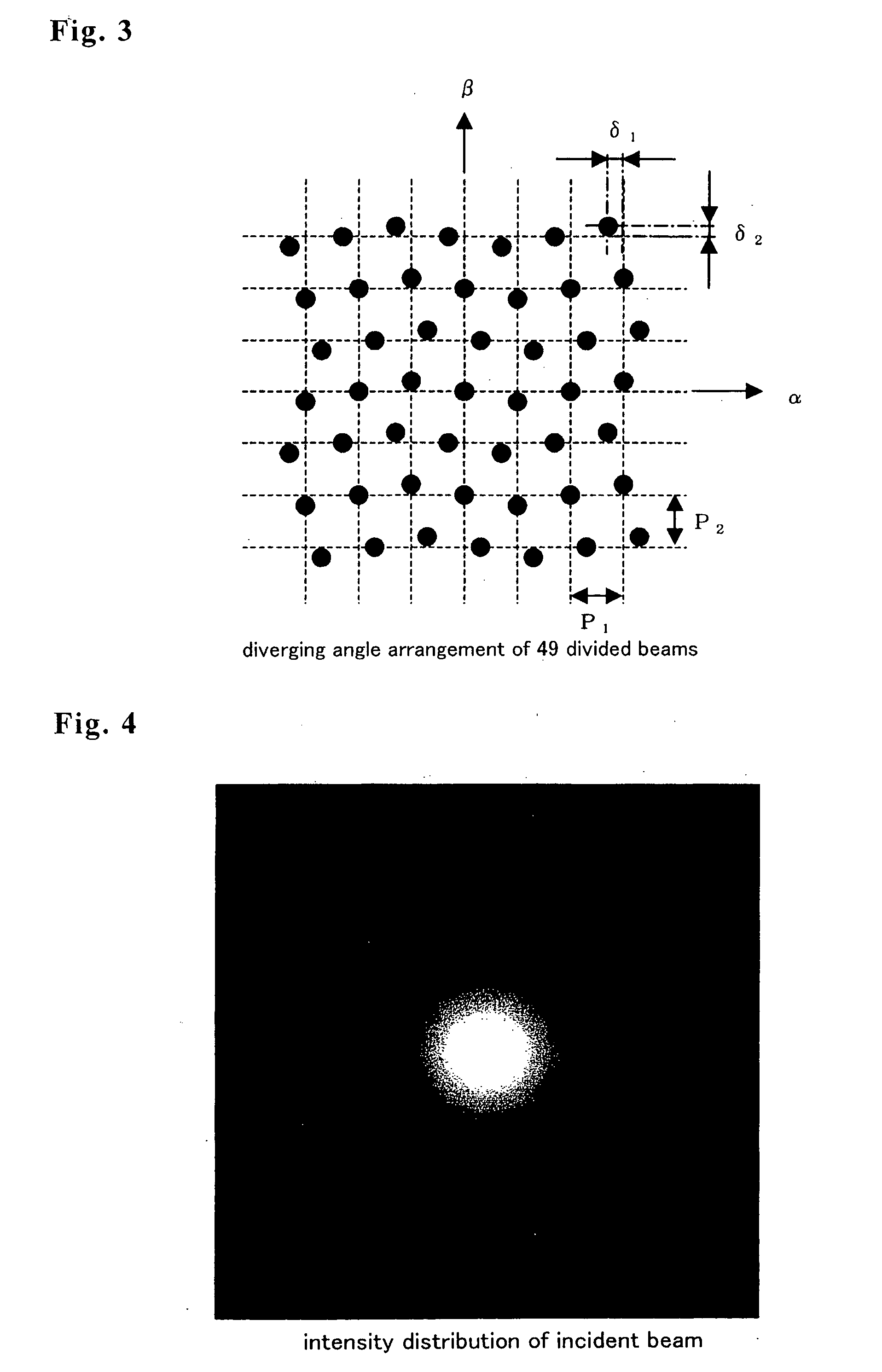
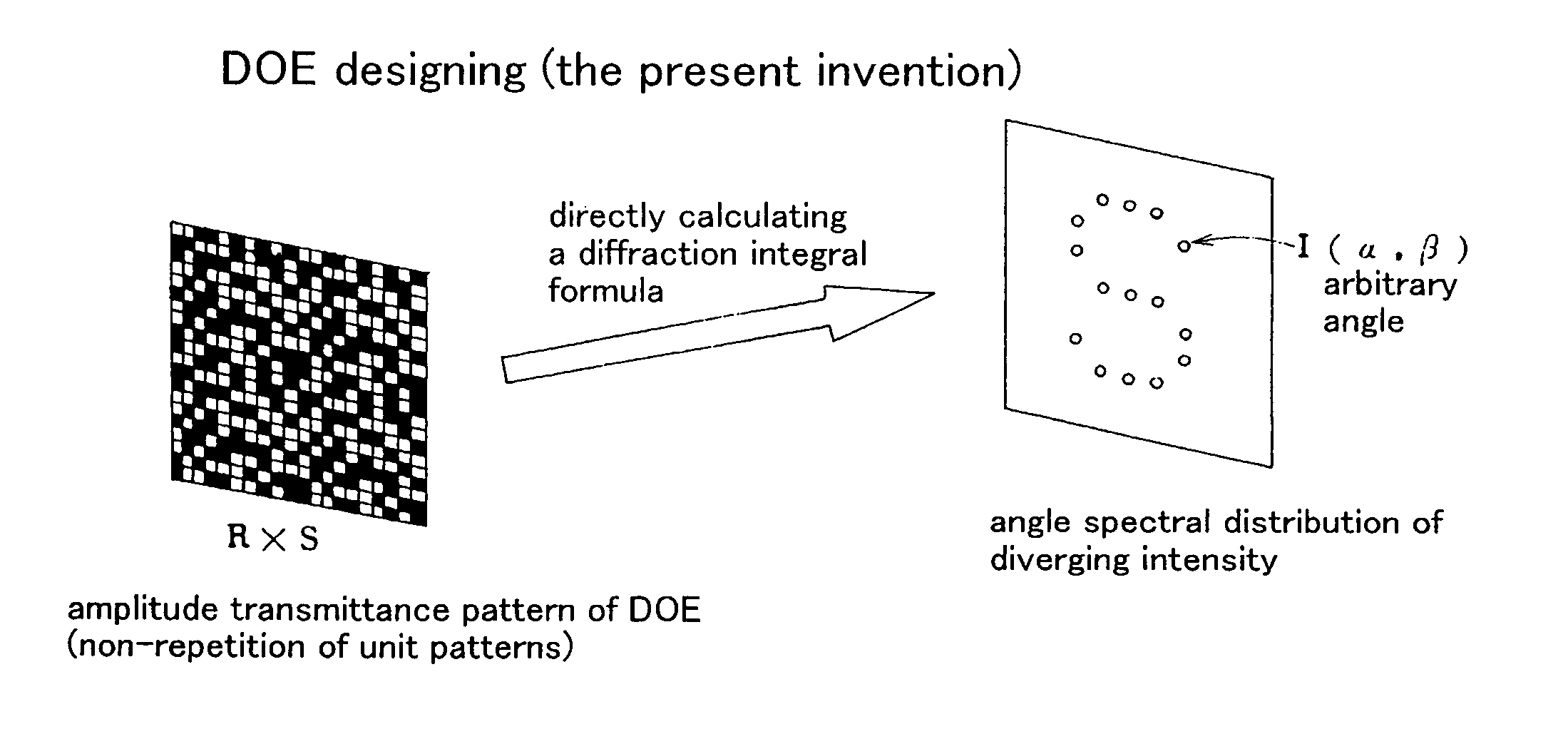
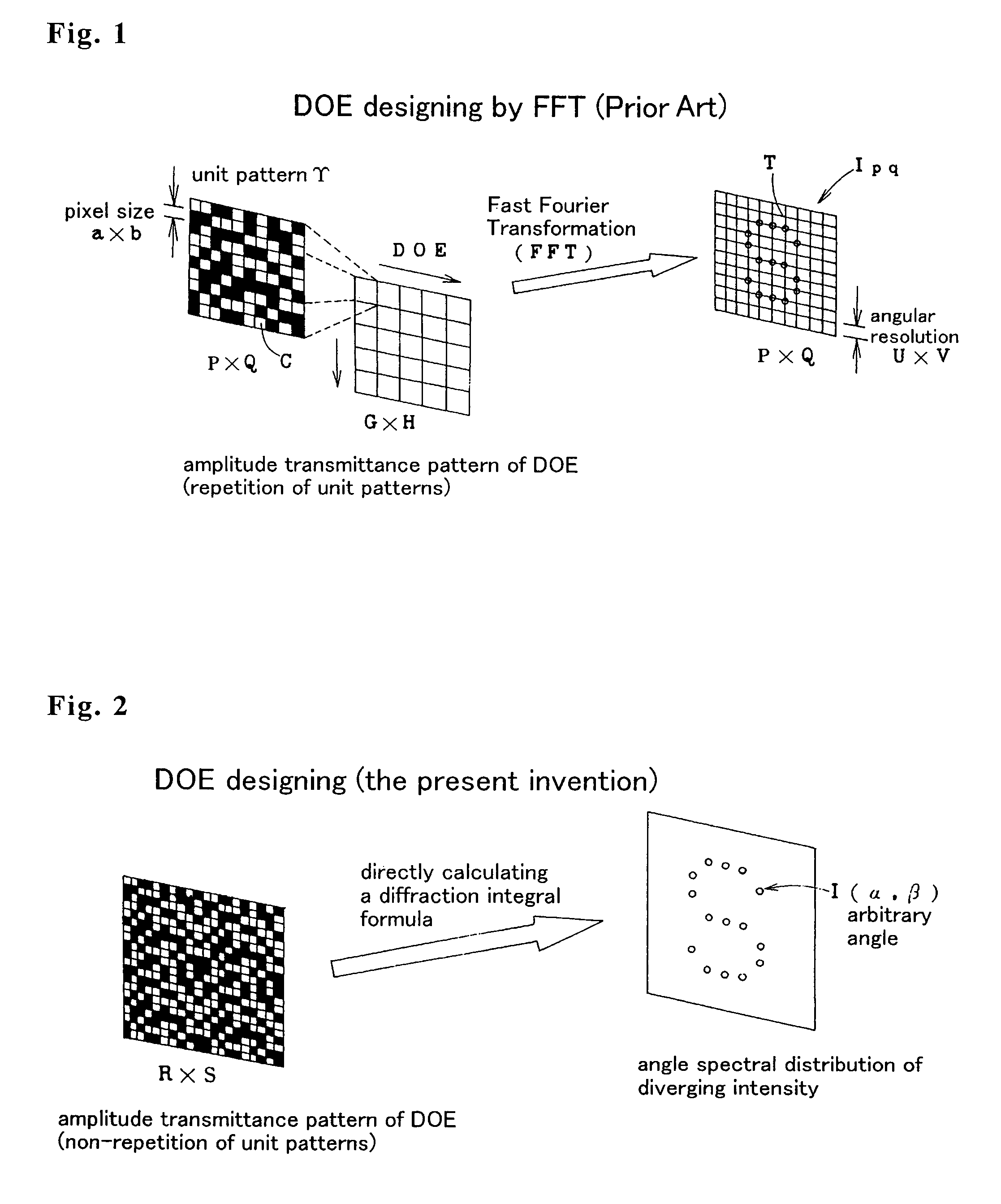
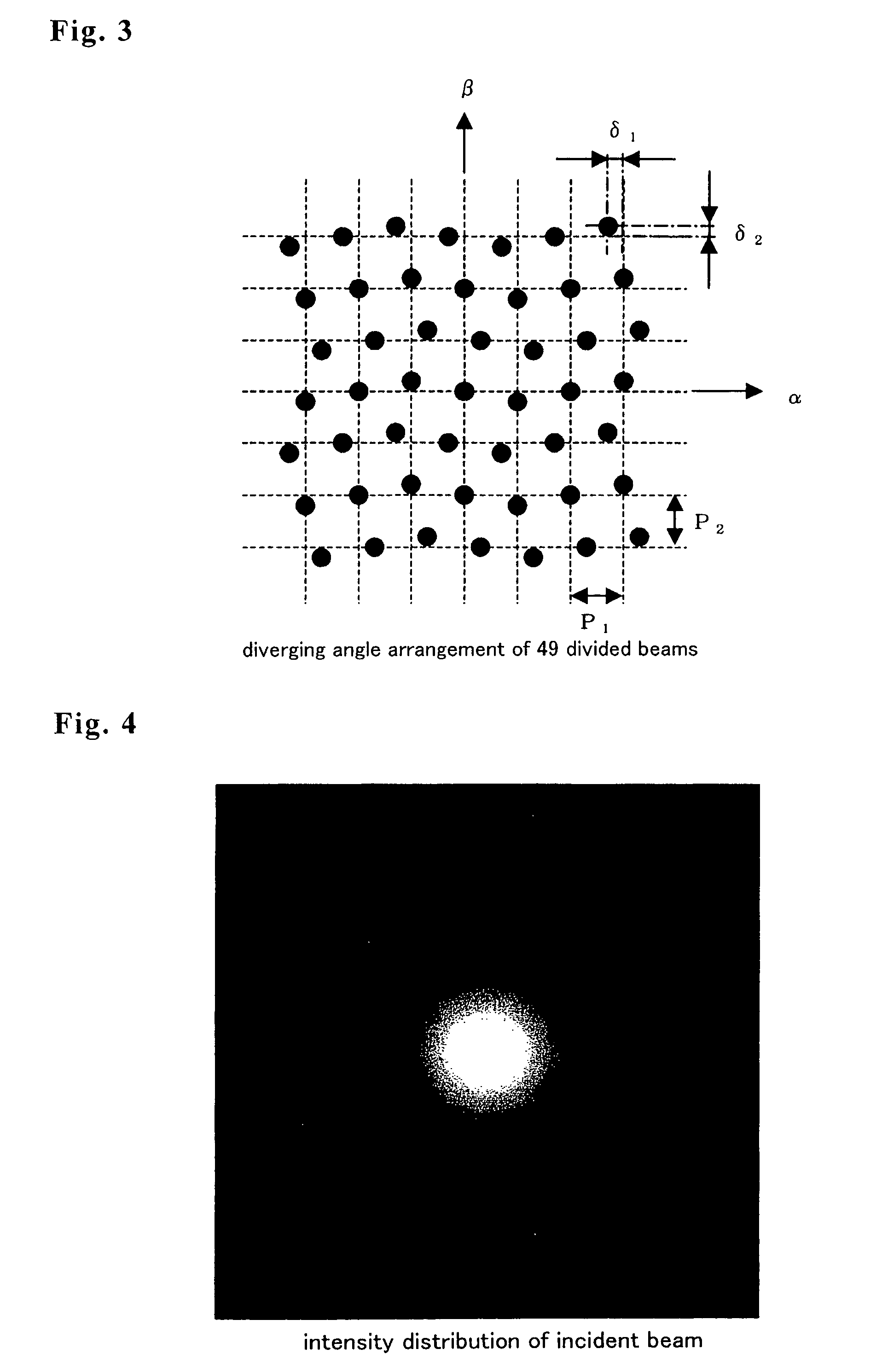
A conventional diffractive optical element (DOE), which consists of repetition of a unit pattern Υ, has an advantage of applicability of the Fast Fourier Transform algorithm to calculate diffraction beam spots intensities on lattice points on an image plane. But, the conventional DOE has a drawback of impossibility of diffracting a laser beam off the lattice points. This invention designs a DOE by giving arbitrary complex amplitude transmittance {tmn} to every pixel (m, n), calculating actual Fourier transform from {tmn} to intensity W(α, β), and obtaining intensity of a diffraction beam directing in any a and 0 direction. Since α, β are not necessary to be on lattice points, the FFT is of no use. Angular resolutions U and V satisfy inequalities U<λ / aR and V<λ / bS, where λ is a wavelength, aR and bS are the size of the DOE. The DOE can produce multidiffracted beams anywhere on an image and can irradiate a plurality of arbitrary arranged points simultaneously with high precision. The DOE realizes precise multispot microprocessing on arbitrary positions, which is required for producing electronic parts. The DOE is suitable for high speed and low cost laser processing.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Star sensor
The invention provides a star sensor. The star sensor comprises a front checkerboard-shaped optical grating, a rear checkerboard-shaped optical grating, a checkerboard-shaped optical wedge array, a converging optical system and an area array detector, wherein total input light consisting of target light and sky background light enters a shearing interferometer consisting of the front checkerboard-shaped optical grating and the rear checkerboard-shaped optical grating, a two-dimensional interference fringe with a full cycle is formed through the adjustment of the relative angle between the front checkerboard-shaped optical grating and the rear checkerboard-shaped optical grating, the checkerboard-shaped optical wedge array performs two-dimensional light splitting on the incident two-dimensional interference fringe, split light beams formed after the two-dimensional light splitting of the checkerboard-shaped optical wedge array run through the converging optical system and then are gathered to a target surface of the area array detector, and two-dimensional phase information of the two-dimensional interference fringe is acquired according to the spot intensity of the target surface and a corresponding phase extracting algorithm, so that two-dimensional synchronous high-precision positioning is achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Diffractive optical element
ActiveUS7440188B2Acceleration and cost-reduction of the laser processingImprove accuracyOptical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsDiffraction opticsElectron
A conventional diffractive optical element (DOE), which consists of repetition of a unit pattern , has an advantage of applicability of the Fast Fourier Transform algorithm to calculate diffraction beam spots intensities on lattice points on an image plane. But, the conventional DOE has a drawback of impossibility of diffracting a laser beam off the lattice points. This invention designs a DOE by giving arbitrary complex amplitude transmittance {tmn} to every pixel (m, n), calculating actual Fourier transform from {tmn} to intensity W(alpha, beta), and obtaining intensity of a diffraction beam directing in any alpha and beta direction. Since alpha, beta are not necessary to be on lattice points, the FFT is of no use. Angular resolutions U and V satisfy inequalities U<lambda / aR and V<lambda / bS, where lambda is a wavelength, aR and bS are the size of the DOE. The DOE can produce multidiffracted beams anywhere on an image and can irradiate a plurality of arbitrary arranged points simultaneously with high precision. The DOE realizes precise multispot microprocessing on arbitrary positions, which is required for producing electronic parts. The DOE is suitable for high speed and low cost laser processing.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Pump source device, laser source device and design methods thereof
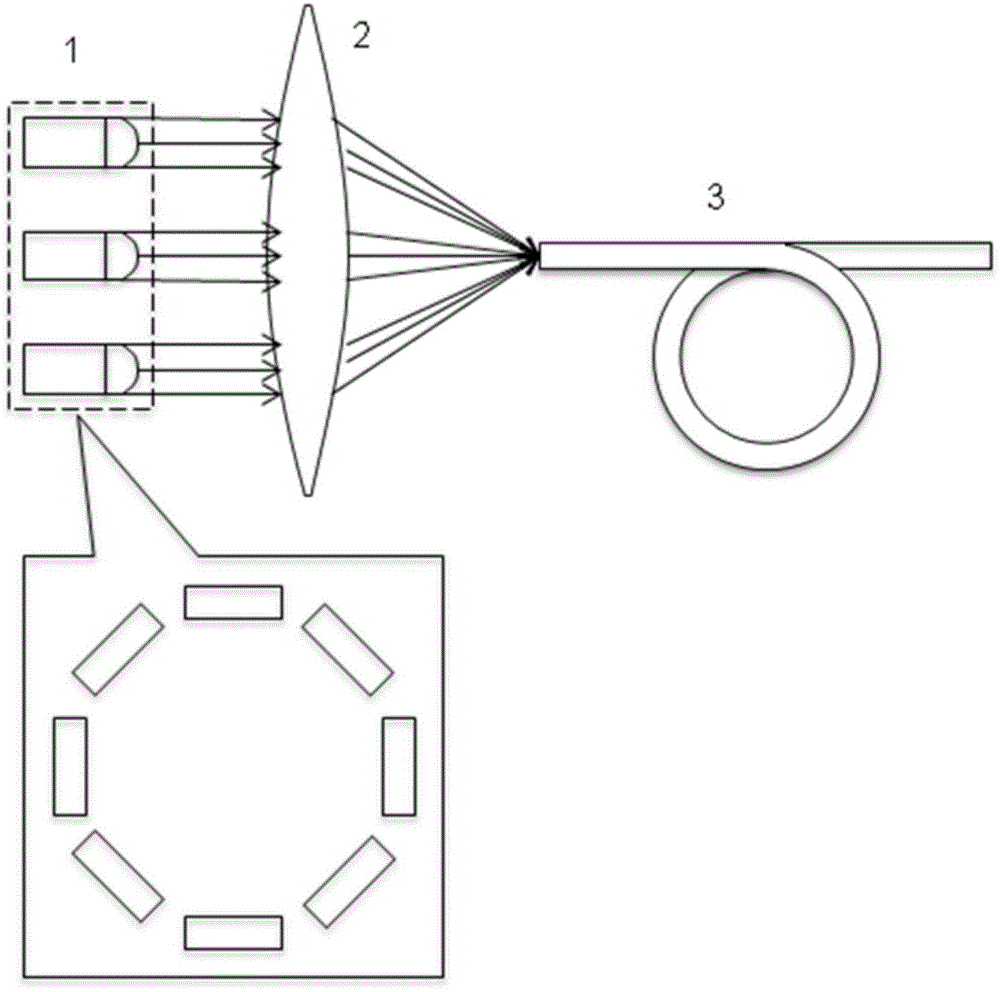
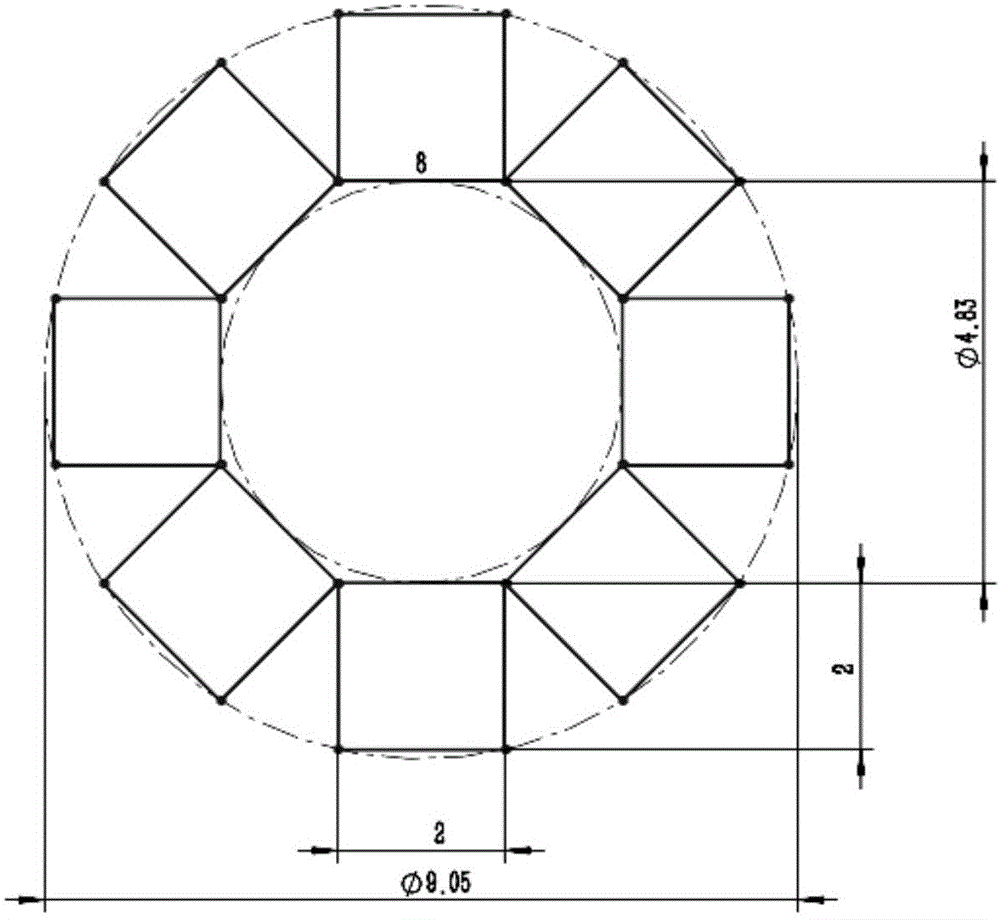
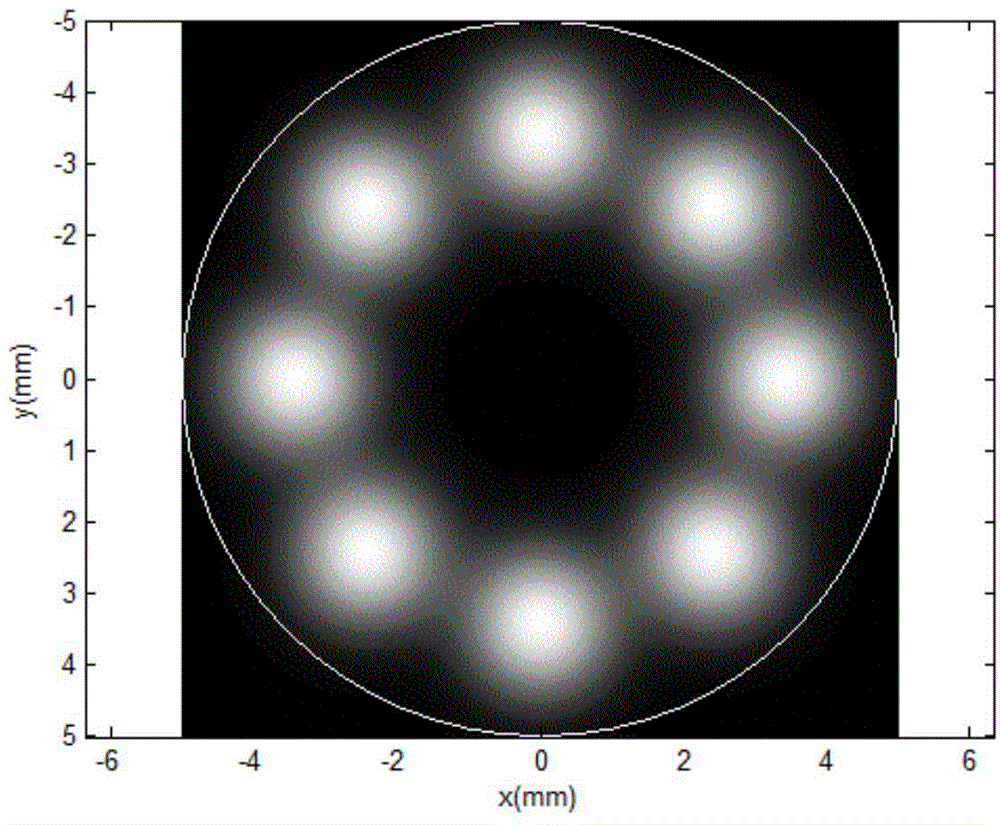
ActiveCN104993365AThe principle is simpleReasonable configurationLaser detailsOptical elementsLight beamRing laser
The invention discloses a pump source device, a laser source device and design methods thereof. The pump source device outputs hollow pump light, and comprises a ring laser array, a focusing lens, and an optical fiber. The ring laser array comprises multiple lasers distributed annularly, and is used to output multiple laser beams. The focusing lens includes one or more lenses, and is used to converge and couple the multiple laser beams into the optical fiber. The optical fiber is used to output pump light of which the spot intensity is in hollow distribution. The pump source device built according to the technical scheme provided by the invention is simple in principle and reasonable in configuration. Compared with the prior art, no additional light beam conversion element is needed, and the pump source device has the significant advantages of simple optical path, low building difficulty, high optical path stability, low cost, and high feasibility. The laser source device can be pumped by hollow pump light output by the pump source device to obtain hollow laser. The pump source device, the laser source device and the design methods thereof are of great significance to the fields of scientific research and production through use of hollow laser currently.
Owner:BWT BEIJING
Sighting device for light-gas gun simulating hard object damage
The invention discloses a sighting device for a light-gas gun simulating hard object damage. The device is characterized in that the device includes a filtering head, a light gas gun barrel and a diode laser; the filtering head is inserted into a stop holder mouth of the light gas gun barrel; the diode laser is inserted into a bullet loading mouth of the light gas gun barrel; and a light beam emitted by the diode laser passes through the filtering head to generate a beam of light coinciding with the axis of the light gun barrel. Beneficial effects achieved by the device are that: the technicalscheme adopts a principle that the diode laser emits a laser beam and a light filter with micropores performs filtering, and so, micro light spots are generated without causing observation difficultydue to insufficient spot intensity; a matching mode with small clearance is adopted between the diode laser, the light gas gun barrel and the filter, thus not only ensuring that an emergent beam is consistent with a ballistic trajectory of an emergent projectile body, but also requirement of easy assembly and disassembly is achieved; and the sighting device not only is fewer in component, is easyto assemble, but also has the advantage of simple and reliable use.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Image metrics in the statistical analysis of DNA microarray data
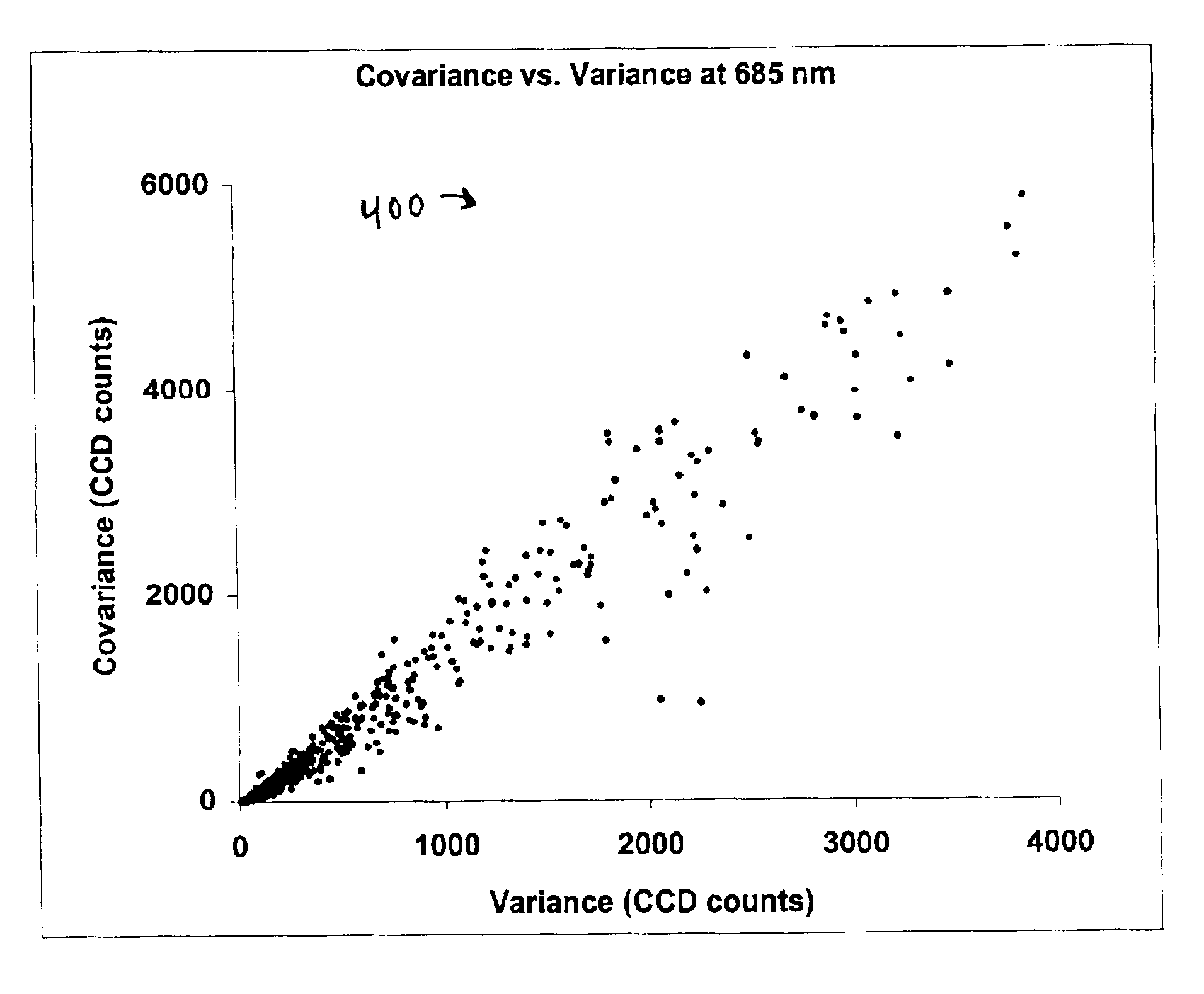
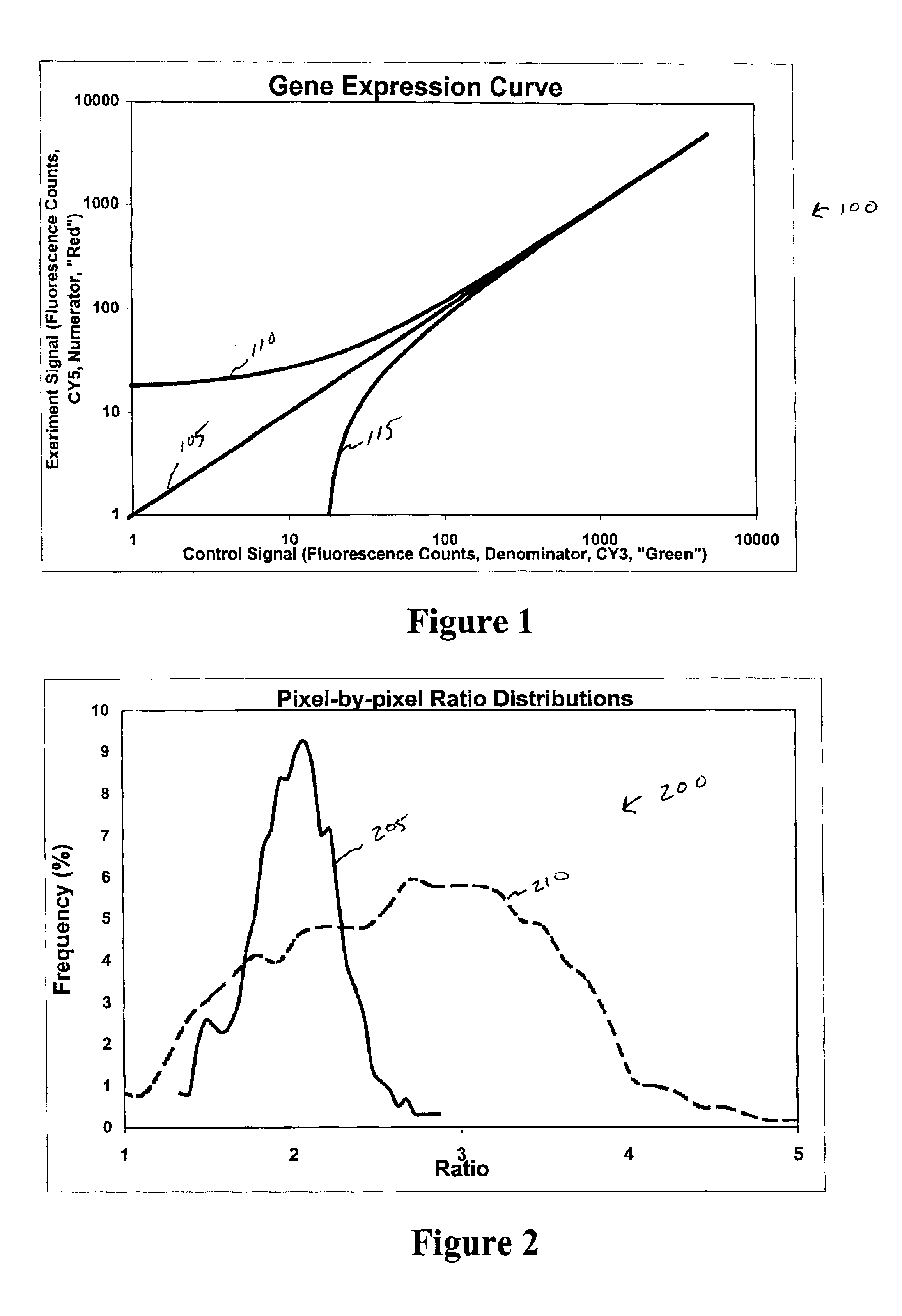
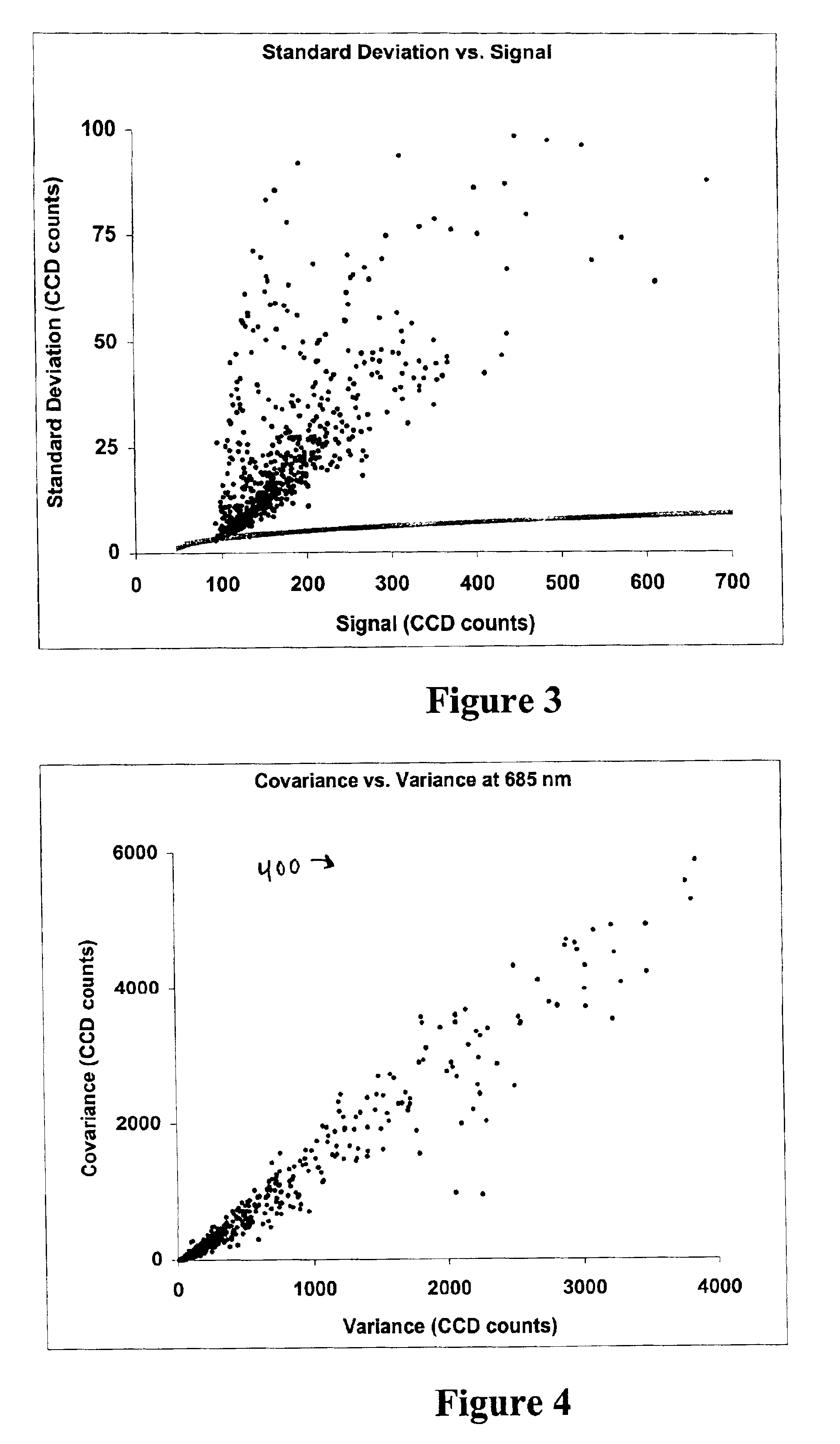
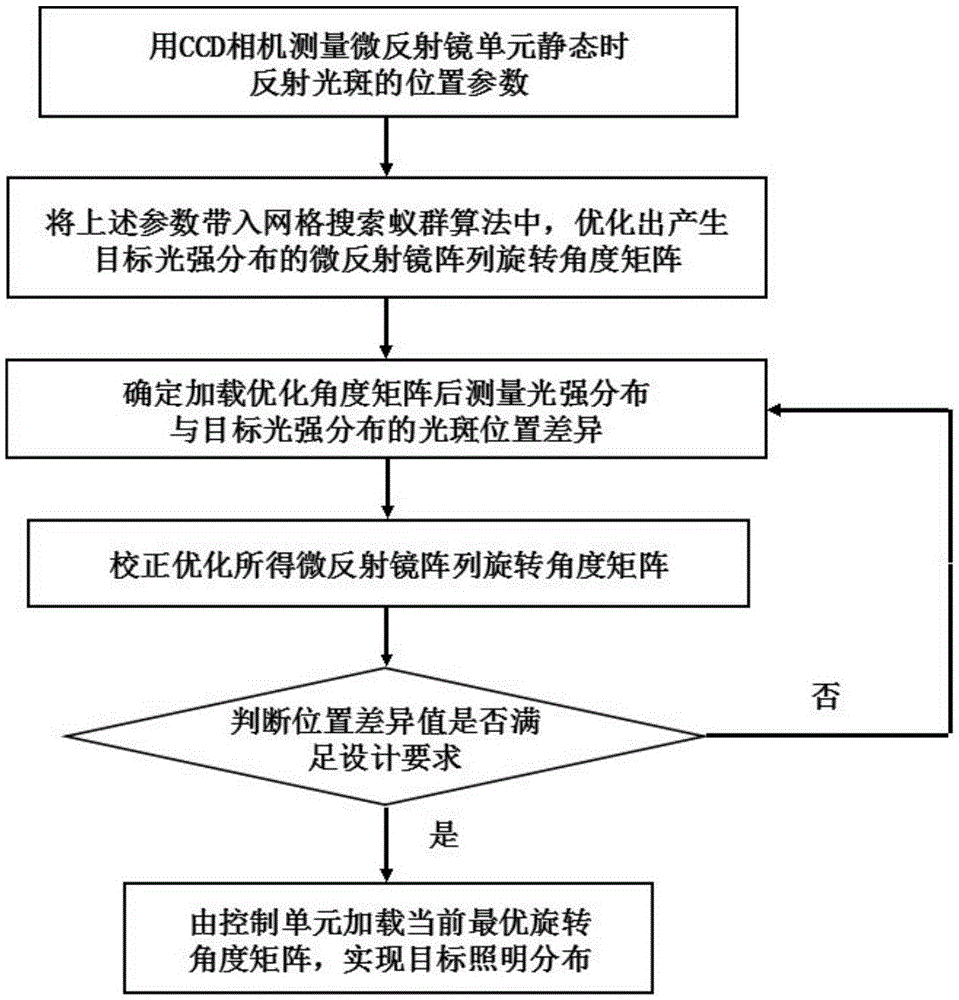
Expression profiling using DNA microarrays is an important new method for analyzing cellular physiology. In “spotted” microarrays, fluorescently labeled cDNA from experimental and control cells is hybridized to arrayed target DNA and the arrays imaged at two or more wavelengths. Statistical analysis is performed on microarray images and show that non-additive background, high intensity fluctuations across spots, and fabrication artifacts interfere with the accurate determination of intensity information. The probability density distributions generated by pixel-by-pixel analysis of images can be used to measure the precision with which spot intensities are determined. Simple weighting schemes based on these probability distributions are effective in improving significantly the quality of microarray data as it accumulates in a multi-experiment database. Error estimates from image-based metrics should be one component in an explicitly probabilistic scheme for the analysis of DNA microarray data.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
A Method of Realizing Variable Free Illumination Pupil Based on Micromirror Array
InactiveCN104111592BHigh-resolutionImprove practicalityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLight spotEffect light
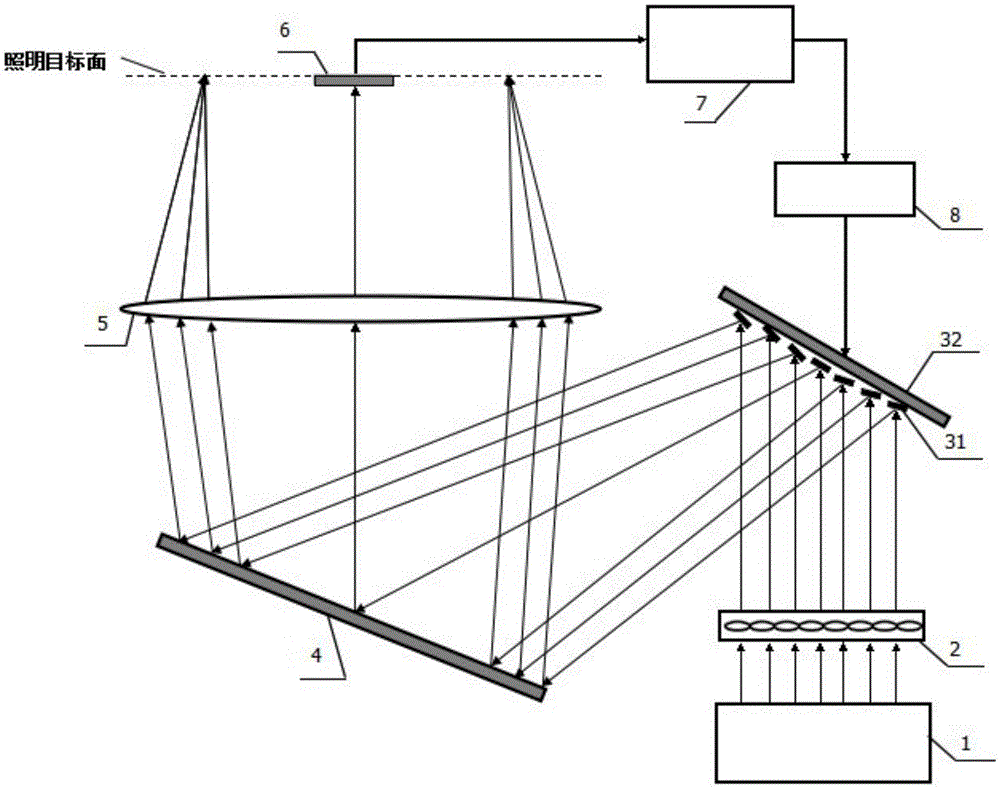
The invention provides a method for realizing a variable free illumination pupil based on a microreflector array, which includes the steps of spot position measurement, spot position optimization, spot position correction and the like. Among them, the CCD camera measures the position parameters of the reflected light spot when each micro-mirror unit is in a static state; the above parameters are substituted into the grid search ant colony algorithm for optimization, and the rotation angle matrix of the micro-mirror array that produces the required pupil shape is obtained; Calculate the spot position difference between the measured light intensity distribution and the desired light intensity distribution on the target surface after loading the rotation angle matrix, and use it as feedback to correct and optimize the rotation angle of the micromirror array, so that the result finally meets the illumination requirements on the target surface. The invention can realize various lighting modes including non-circumferentially symmetrical complex lighting pupils, has fast optimization speed, good convergence, high accuracy and strong practicability.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Welding method of coaxial diode and circuit board
ActiveCN102300419AAddress stressGuaranteed reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesHeat resistanceThermal expansion
The invention discloses a welding method of a coaxial diode and a circuit board. A gold-plating copper strip is used as a stress release bridge at the anode of the diode to replace the original solder hard link, so as to solve the problem of stress caused by the longitudinal coefficient of thermal expansion of the circuit board; an In52Sn48 solder is adopted, thus the heat-resistance fatigue capability and uniform elongation are improved, and the reliability of a welding spot is ensured; and the welding area of the cathode of the diode is increased, and the welding spot intensity is ensured by arranging a collet. By utilizing the welding method provided by the invention, the thermal stress caused by different coefficients of thermal expansion of a circuit board material and a diode ceramic body material, and the welding failure or potential hidden danger caused by the thermal stress are resolved, thus improving the quality of the welding spot and the reliability of the product.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Method for generating and measuring first-order circular Airy derivative light beam with sudden self-focusing effect and carrying vortex
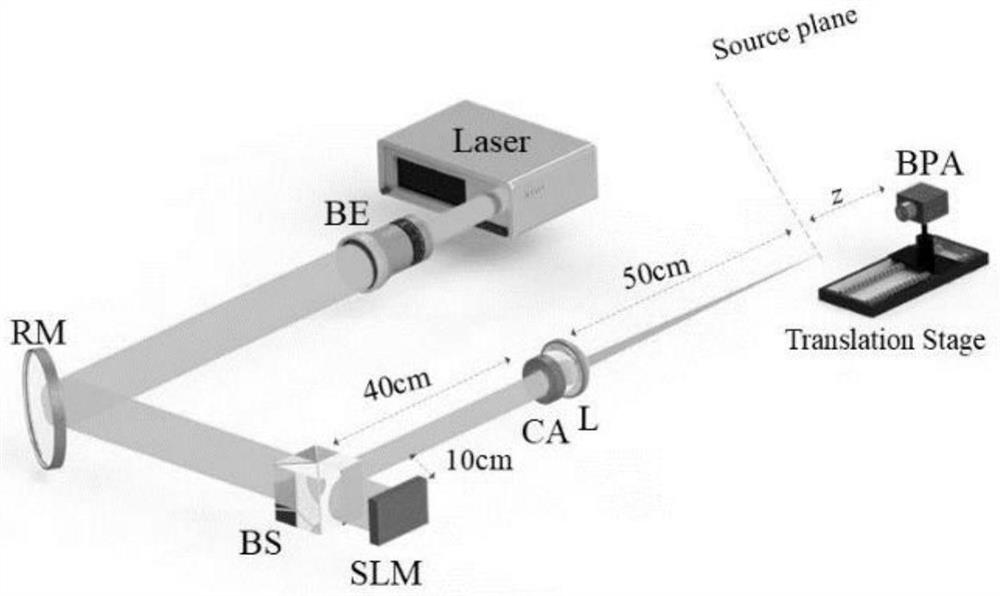
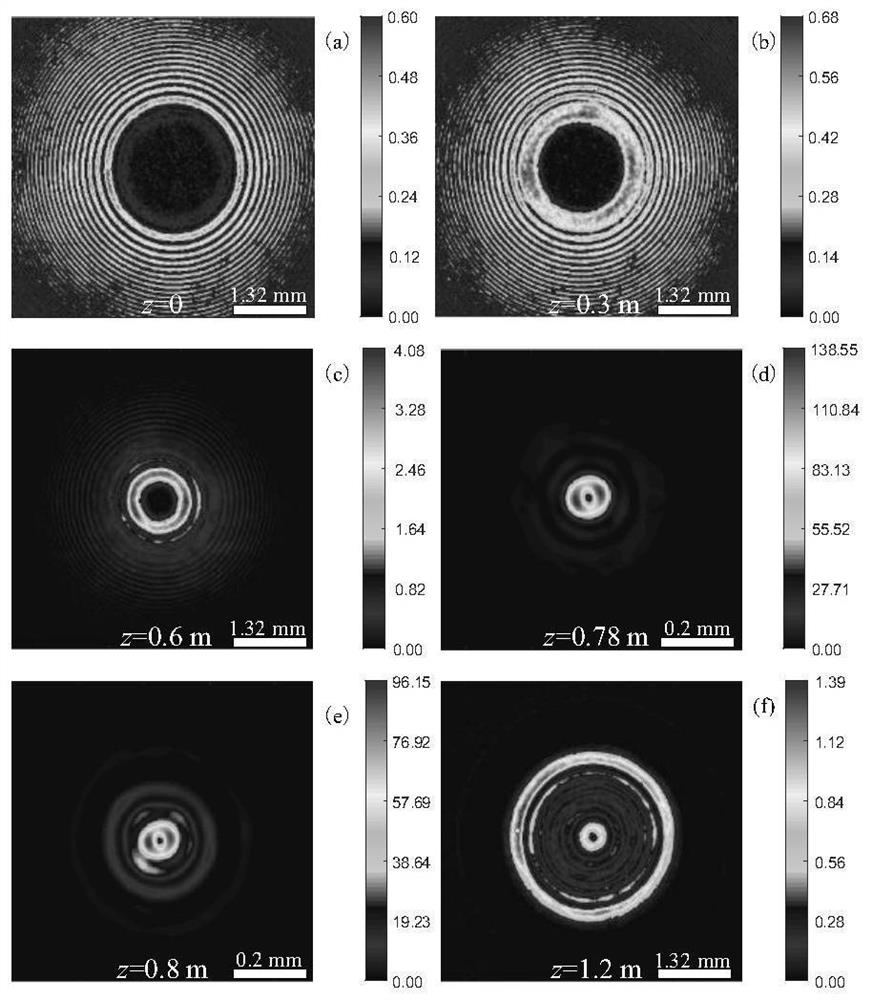
PendingCN114815278ATo overcome the fatal shortcoming that the intensity distribution is solidEasy to measurePhotometryOptical elementsSource planeSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a method for generating and measuring a first-order circular Airy derivative light beam with a sudden self-focusing effect and carrying a vortex. The method comprises the following steps: enabling a linear polarization Gaussian beam generated by a laser to pass through a beam expander, a reflector, a beam splitter, a specifically coded reflection type pure phase spatial light modulator, the beam splitter, a circular diaphragm and a Fourier lens in sequence; wherein the distance from the spatial light modulator to the Fourier lens and the distance from the Fourier lens to the Fourier plane / source plane are the focal length of the Fourier lens, and an expected first-order circular Airy derivative light beam carrying a vortex can be obtained on the Fourier plane / source plane; a light beam profile analyzer is mounted on the electric guide rail in the transmission direction of the generated light beam so as to measure intensity distribution and sudden self-focusing capability under different propagation distances; the generated first-order circular Airy derivative beam carrying one vortex has the advantages of hollow focus intensity distribution and carrying orbital angular momentum on the basis of retaining sudden self-focusing capability, and the application range is expanded compared with the first-order circular Airy derivative beam.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Optical information processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060140066A1Accurate readingReduce depthIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsInformation processingLight beam
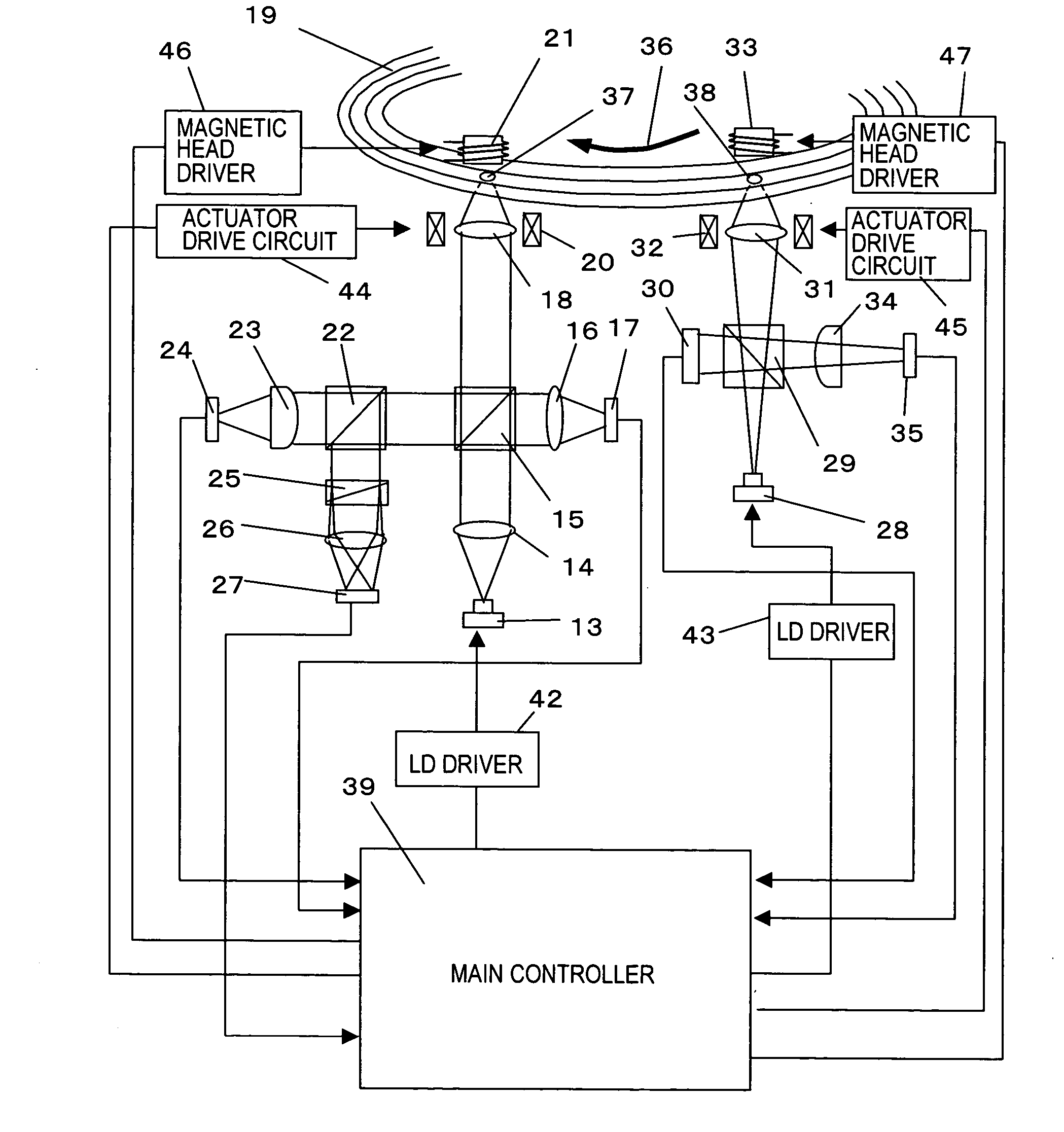
For a concurrent ROM-RAM recording medium, the present invention provides an optical information processing apparatus which can accurately read a RAM signal at the time of high-speed transfer without reducing a phase pit depth. The optical information processing apparatus is an optical information processing apparatus for controlling writing and reading of information on a concurrent ROM-RAM recording medium recording ROM signal information as a phase pit on a track and magneto-optically recording RAM signal information on the phase pit, comprising an optical system for forming two (2) first and second beam spots with an interval on the same track of the recording medium; a circuit unit for modulating the first beam spot intensity with a second ROM signal read by the second beam spot; and a circuit for detecting a RAM signal from a first ROM signal read by the first beam spot.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Deep-space micro-zone self-adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection system
PendingCN107727635ARaman signal with high signal-to-noise ratioRaman scatteringFluorescence/phosphorescenceBroad spectrumDimensional precision
The invention discloses a deep-space micro-zone self-adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection system. The system is composed of a main controller, a spectrometer, optical fibers, a three-dimensional motor driver, a three-dimensional precise electric platform, a digital pulse delay controller and an optical head. The self-adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection system can self-adaptivelyadjust the diameter of the focused spot during the analysis of the micro-area, utilizes the regional average gray of an electronic eyepiece as the intensity of the scanned imaging spot, satisfies therequirements on self-focusing and wide-spectrum scanning imaging, realizes three-dimensional space LIBS elemental analysis, active laser Raman molecular analysis, hyperspectral fluorescence and visible wide-spectrum scanning imaging and provides a variety of information for micro-area fine detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A photoelectric edge detection system and its detection method
ActiveCN111721235BRealize non-contactRealize high-precision detectionUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsOptical property
The invention proposes a photoelectric edge detection system and its detection method, including a light source, the light source cooperates with a diaphragm through a collimator, and the diaphragm cooperates with a position-sensitive photodetector. Optical properties, the light source, collimator and aperture are located on the same side or both sides of the object to be measured with the position sensitive photodetector, and the position sensitive photodetector is connected with the signal processing unit. The invention realizes the non-contact and high-precision detection of the edge of the object by transforming the detection of the edge of the object into the detection of the center position change of the spot intensity of the measuring beam, and can correspondingly shape the measuring beam through a specific aperture according to the edge characteristics of different objects to be measured. The sensitivity and stability of object edge detection are greatly improved; and the overall structure of the invention is simple and flexible, and can be adjusted for materials with different optical properties, which is convenient for on-site measurement.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
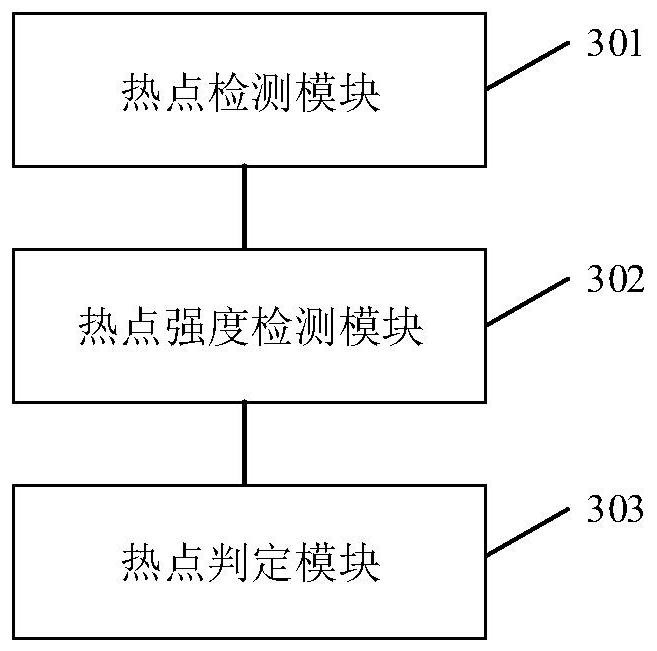
Hotspot distribution detection method and system
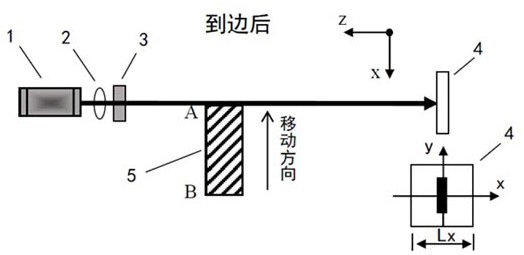
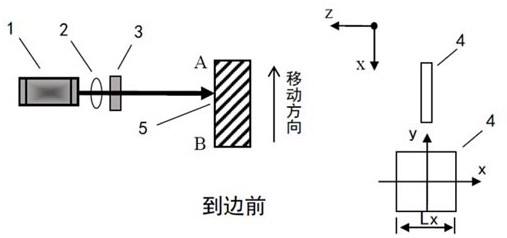
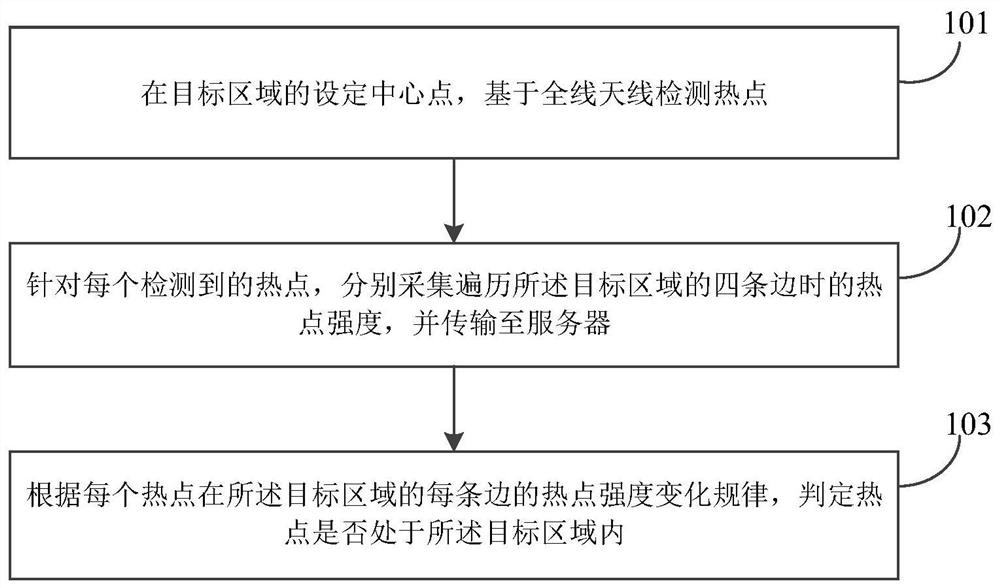
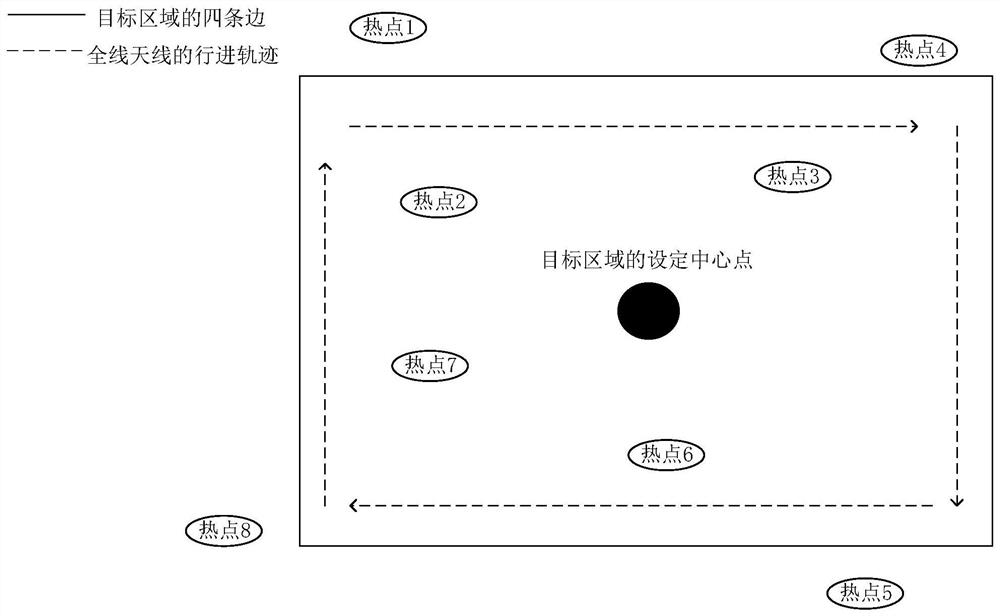
PendingCN113490232AShorten the timeShorten detection timeLocation information based serviceEngineeringSpot intensity
The embodiment of the invention discloses a hotspot distribution detection method and system, and the method comprises the steps: setting a central point in a target region, and detecting hotspots based on all-line antennas; aiming at each detected hot spot, respectively acquiring the hot spot intensity when the four edges of the target area are traversed; and according to the hot spot intensity change rule of each hot spot on each edge of the target area, judging whether the hot spot is in the target area or not. The unnecessary time for positioning the targets one by one is shortened, the detection time of distribution of all hot spots in the area is shortened, and the hot spot distribution detection efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:北京鼎普科技股份有限公司
An imaging method and system for long-distance anti-atmospheric turbulence
ActiveCN109975827BEliminate Image Quality ImpactsImprove image contrastElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging qualityDirect imaging
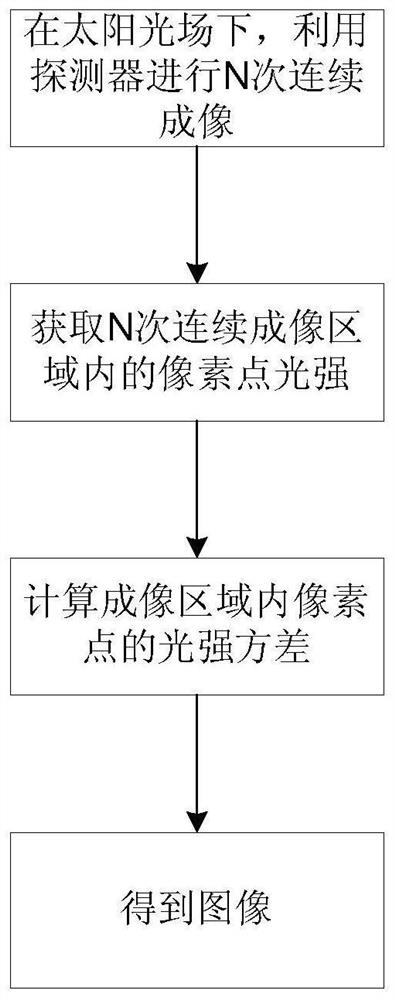
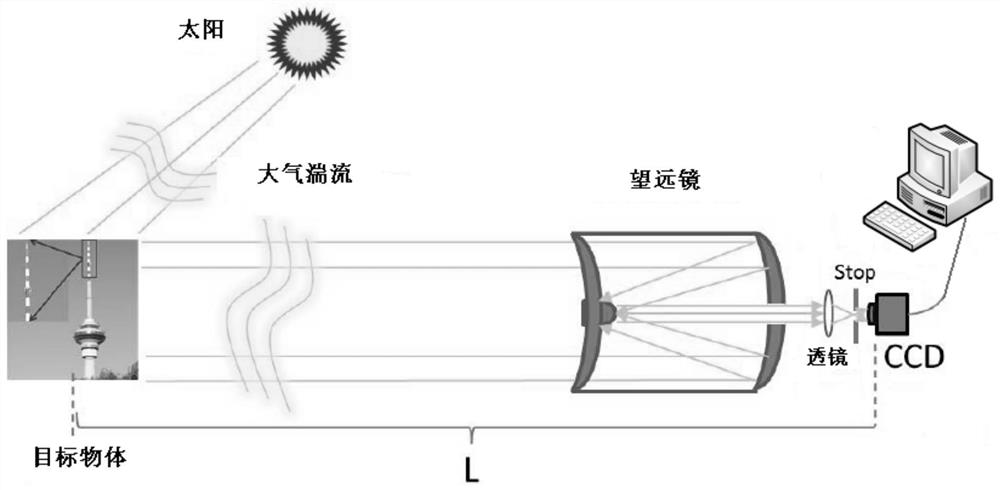
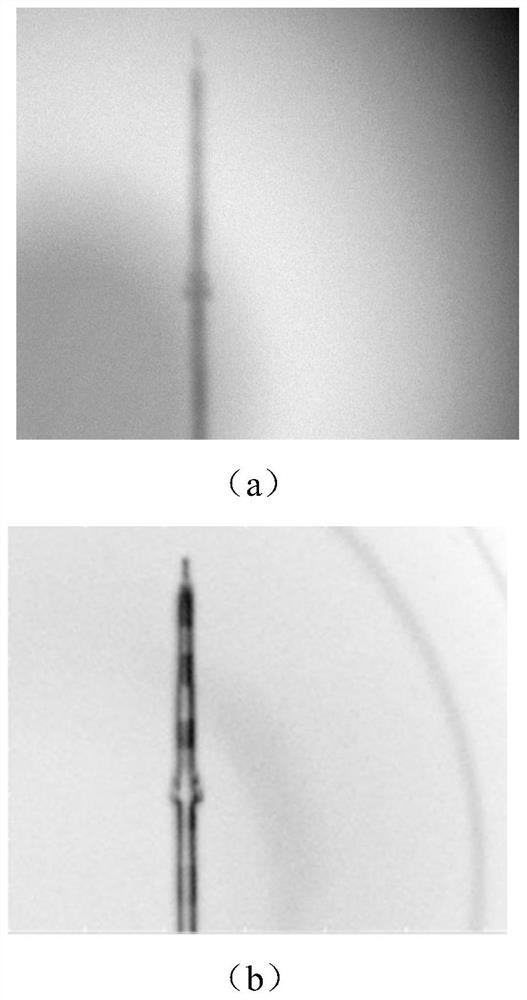
The invention discloses an imaging method and system for long-distance anti-atmospheric turbulence. Under the solar light field, a detector is used to perform N times of continuous imaging on a target object. The interval between two adjacent imaging is greater than the exposure time of the detector. The correlation between each point and itself, using the results of N consecutive imaging to calculate the intensity variance of each point, can obtain image quality with high contrast and signal-to-noise ratio. Compared with traditional direct imaging, the imaging scheme proposed by the present invention eliminates the influence of atmospheric turbulence, improves the practicability of associated imaging technology, can be directly used for long-distance anti-atmospheric turbulence imaging, and increases the image recognition rate.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
A Wavefront Restoration Method Based on Shack-Hartmann Wavefront Sensor
ActiveCN112484866BAvoid falling intoImproving the Accuracy of Wavefront RestorationOptical measurementsLocal optimumHigh density
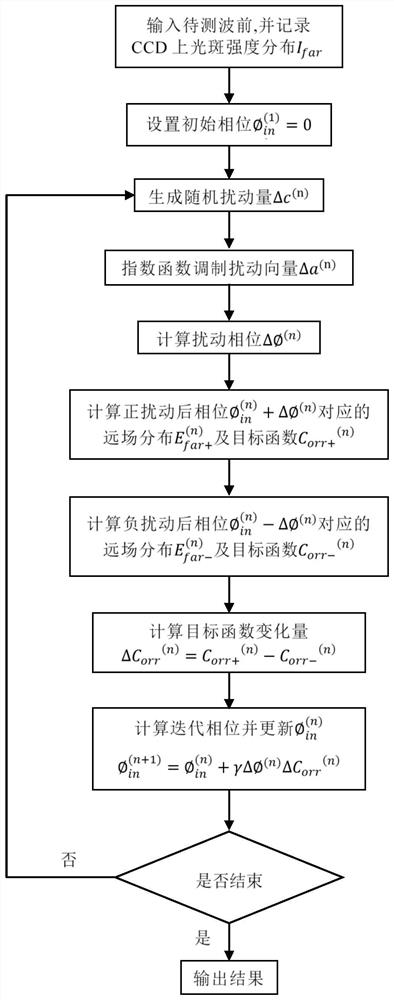
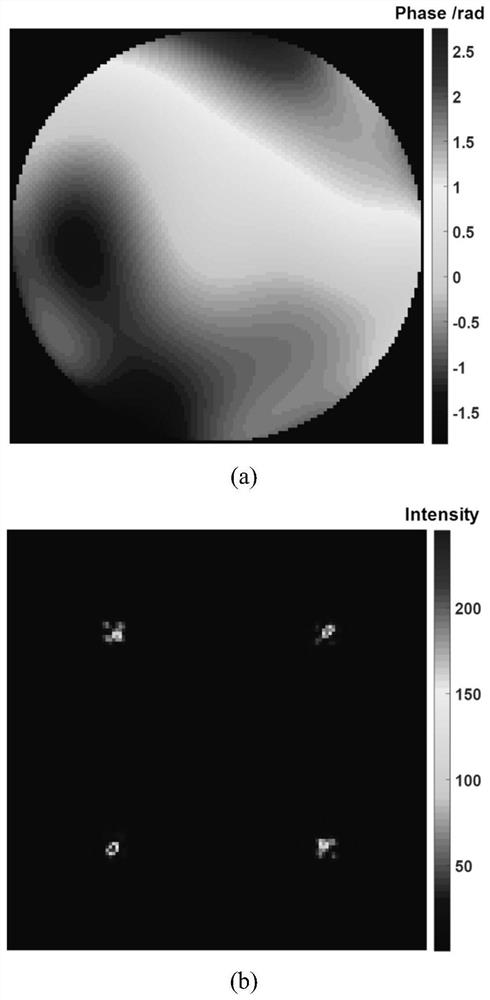
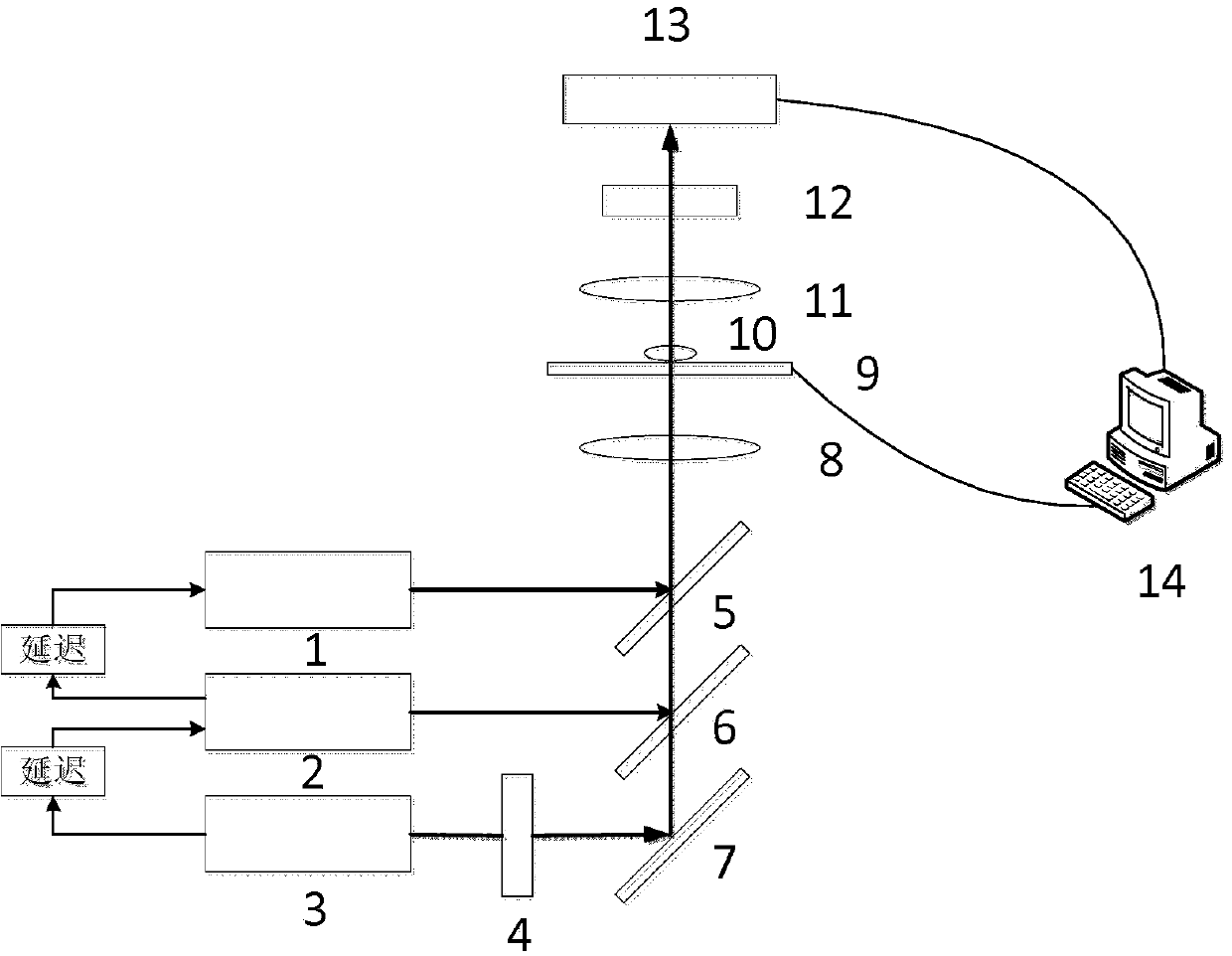
The invention discloses a wavefront restoration method based on a Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor. The method takes the correlation function of the theoretical far-field light intensity distribution and the measured far-field light intensity distribution as the objective function, and modulates the optimized random The parallel gradient descent method recovers the wavefront. The invention takes the far-field spot intensity distribution as the input of the algorithm, makes full use of the information in the sub-aperture, effectively reduces the dependence of the Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor on the high-density sub-aperture, improves the wavefront restoration accuracy, and modulates the The factor modulates the Zernike coefficient disturbance in space and time, which can avoid the algorithm from falling into local optimum and speed up the algorithm convergence speed. Compared with the traditional Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensing algorithm, the present invention can restore the wavefront with higher accuracy under the same sub-aperture condition, and complete the wavefront restoration with a smaller number of sub-apertures under the same restoration accuracy, which is: Low-light, high-precision wavefront detection and other fields provide a new technical approach.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Super-resolution fluorescent lifetime imaging method and device based on stimulated emission lost
InactiveCN103163106BImprove spatial resolutionAchieve super-resolution fluorescence lifetime imagingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLight spotTest sample
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for measuring spot intensity distribution of reflective concentrating photovoltaic concentrator
The invention relates to reflecting type concentrating photovoltaics, in particular to a method for measuring the distribution of the intensity of light spots of a reflecting type concentrating photovoltaic condenser. The method for measuring the distribution of the intensity of the light spots of the reflecting type concentrating photovoltaic condenser is characterized by including the following steps that a rotating parabolic reflecting surface is divided into reflecting elements with a certain area; a detector is utilized to record imaging of sunlight on a reflecting plate after the sunlight is reflected by the reflecting elements, and the imaging is used as image elements; the image elements are stacked to obtain the distribution of the light intensity on the reflecting plate of the reflecting type condenser. The method has the advantages that a method which is simple and convenient to operate and used for measuring the uniformity of the light spots is provided for the high-power reflecting type concentrating photovoltaics, so that it is possible to measure the uniformity of the light spots which are high in energy current density and to measure the spacial distribution of the light intensity of the light spots which are high in energy current intensity.
Owner:兰州大成科技股份有限公司 +1
Beam shaping modulation sheet for quick focusing spot convergence and method thereof
ActiveCN106855657ADifferent convergence propertiesDecrease the intensity of the specklesMicroscopesBiological imagingBeam shaping
The invention discloses a beam shaping modulation sheet for quick focusing spot convergence and a method thereof. The beam shaping modulation sheet is an optical filter, the light intensity transmittance distribution is centrally symmetrical, the light intensity transmittance at each place in the radial direction is acquired by adopting an amplitude modulation function for calculation, the modulation sheet is placed in an optical path to filter and shape a beam to acquire a quick-convergence focusing spot. The amplitude modulation sheet is used to change the convergence feature of the focusing spot with little cost and little technical difficulty, the side spot intensity of a diffraction spot is reduced, and great application value and great potential are realized in various fields such as biological imaging and laser optics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Method for Acquiring Time-Space-Frequency Information of Ultrashort Pulse Laser Far-field Focal Spot
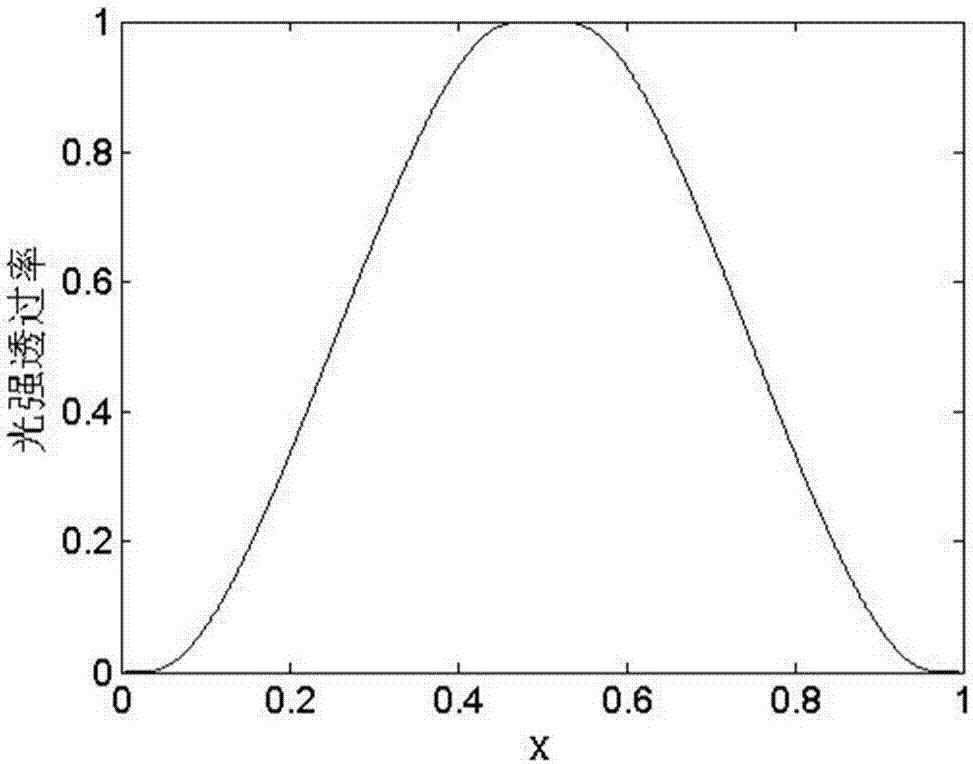
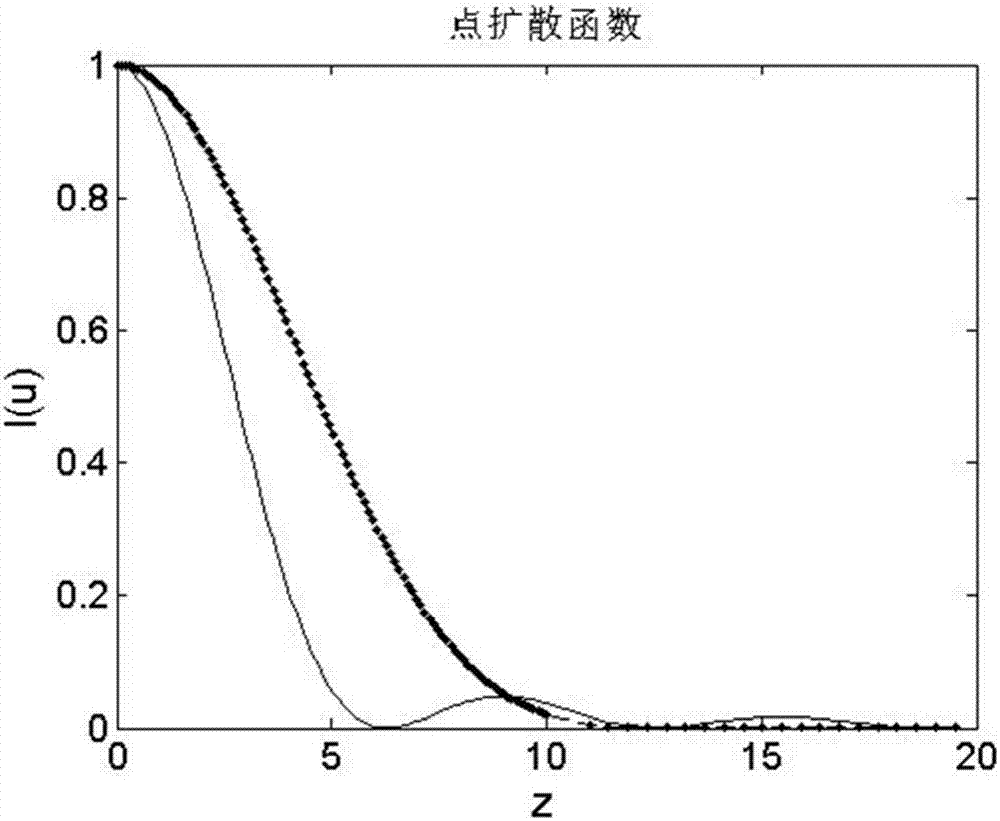
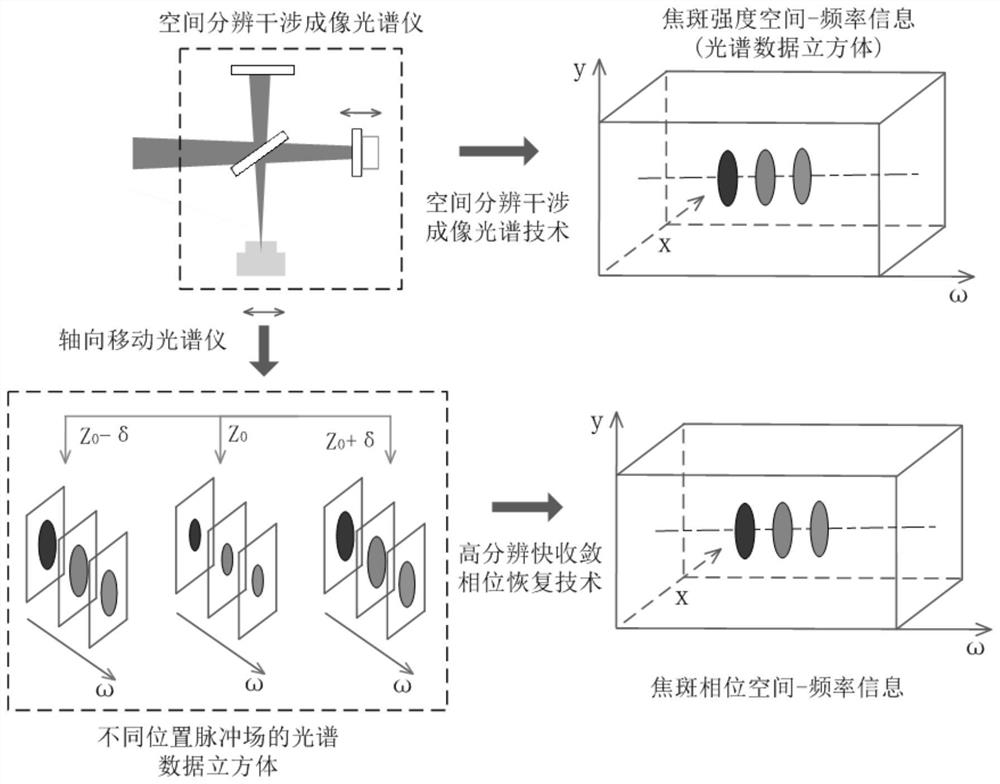
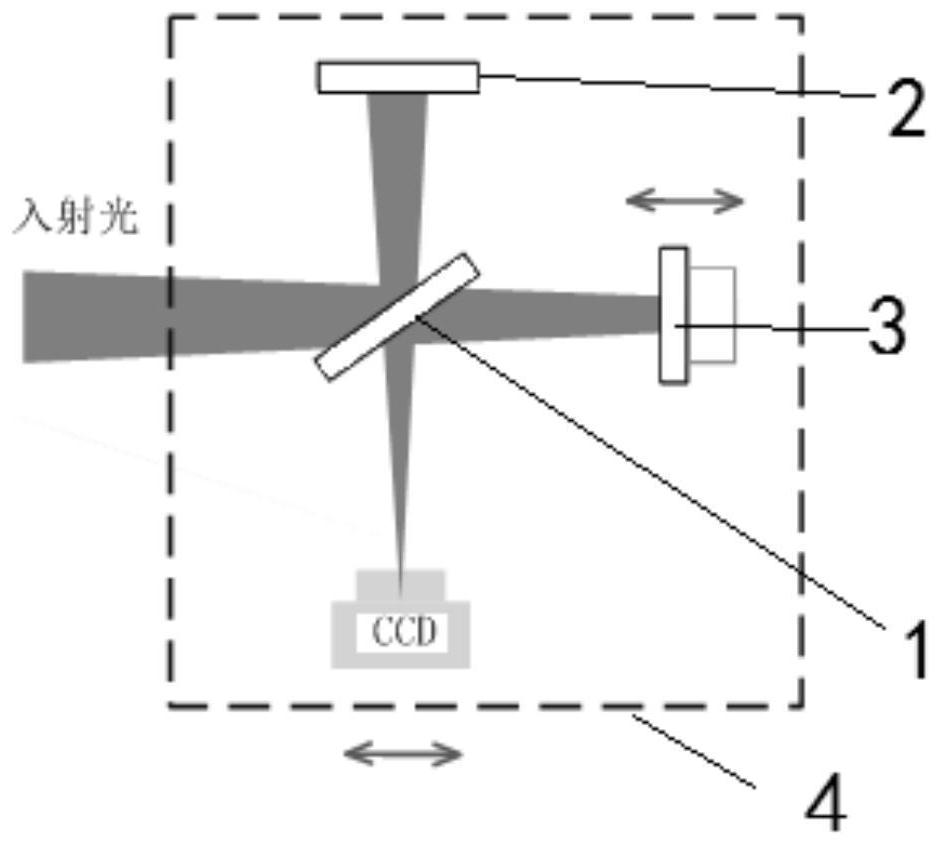
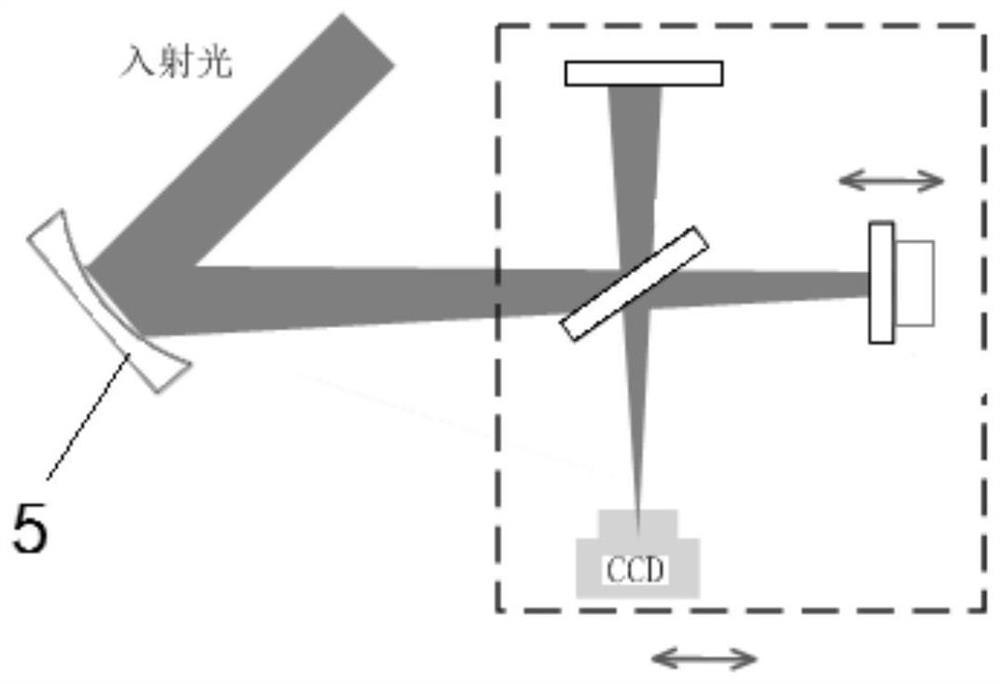
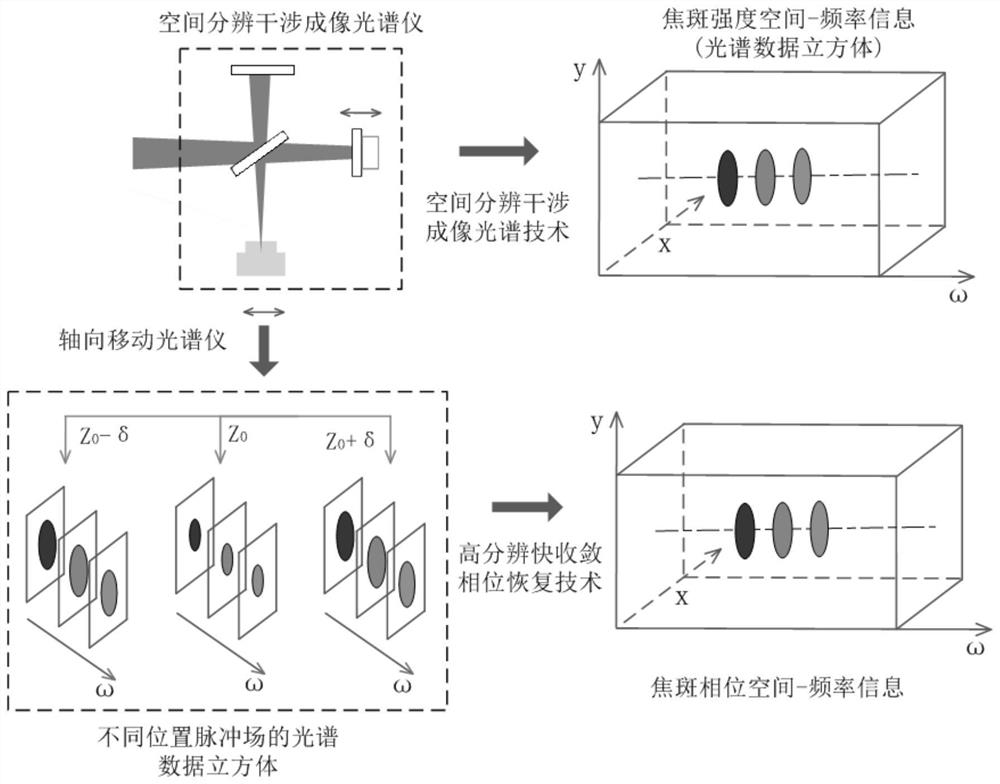
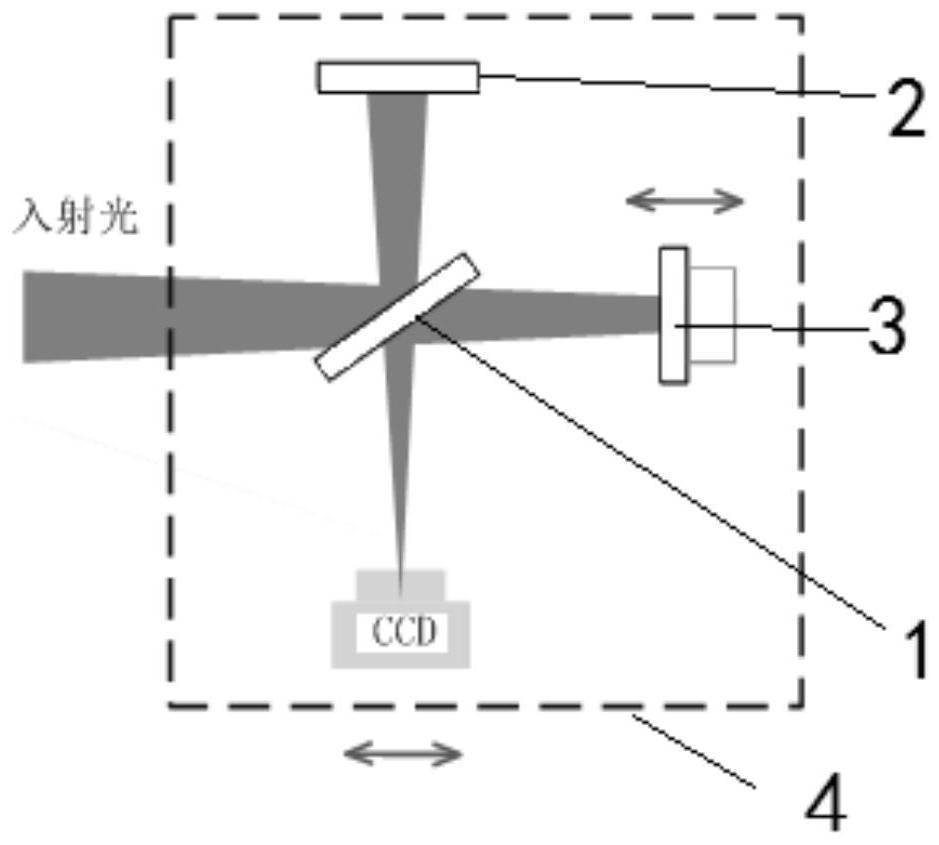
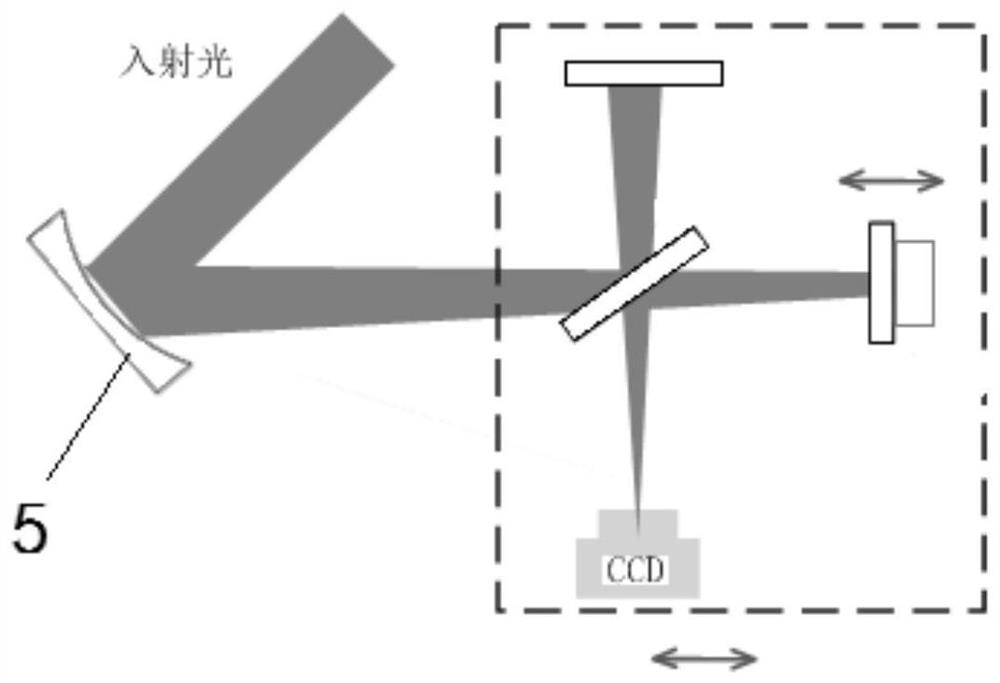
ActiveCN111982313BAvoid the influence of far-field focal spot distributionIdeal focal spot morphologyInstrumentsUltra short pulseOptical spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for acquiring time-space-frequency information of the far-field focal spot of an ultrashort pulse laser, and aims to solve the problem that the chromatic aberration of the existing transmission-type magnifying imaging system will cause the position of the far-field focal spot of the magnified imaging relative to the target point. A technical problem with changes in the distribution of far-field focal spots. The invention obtains the interference images at the focal plane position of the measured ultrashort pulse laser, at least one positive defocus position, and at least one negative defocus position through the interference imaging spectrometer; and then uses the interference spectrum imaging technology to process each interference image separately The corresponding focal spot intensity space-frequency information is obtained; based on all the focal spot intensity space-frequency information obtained, the two-dimensional information of the far-field focal spot space phase at each frequency in the measured ultrashort pulse laser is reconstructed by phase recovery technology ; Finally, according to the order of the frequency, the two-dimensional information of the spatial phase of all the far-field focal spots obtained is reconstructed to obtain the space-time-frequency information of the phase of the ultrashort pulse laser far-field focal spot.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for acquiring space-time-frequency information of ultra-short pulse laser far-field focal spot
ActiveCN111982313AAvoid the influence of far-field focal spot distributionIdeal focal spot morphologyInstrumentsImaging spectrometerMaterials science
The invention discloses an ultra-short pulse laser far-field focal spot space-time-frequency information acquisition method, and aims to solve the technical problem that chromatic aberration of an existing transmission-type amplification imaging system causes change of far-field focal spot distribution of amplification imaging relative to a target point position. The method comprises: acquiring interference images of a focal plane position, at least one positive defocusing position and at least one negative defocusing position of a measured ultra-short pulse laser through an interference imaging spectrometer; respectively processing each interference image by adopting an interference spectrum imaging technology to obtain corresponding focal spot intensity space-frequency information; reconstructing far-field focal spot space phase two-dimensional information under each frequency in the measured ultra-short pulse laser through a phase recovery technology based on all the obtained focalspot intensity space-frequency information; and finally, reconstructing the obtained two-dimensional information of the spatial phases of all the far-field focal spots according to the size sequence of the frequency to obtain time-space-frequency information of the far-field focal spot phases of the ultra-short pulse laser.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
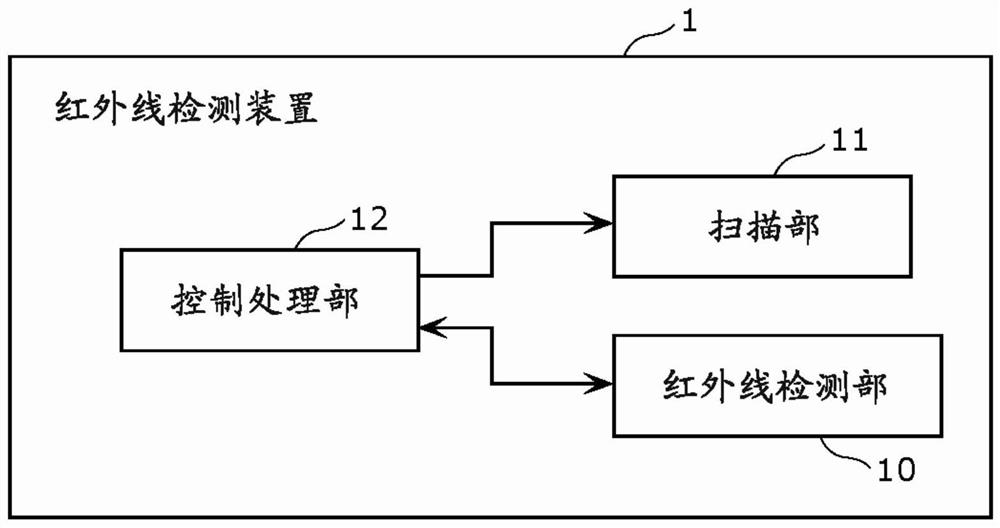
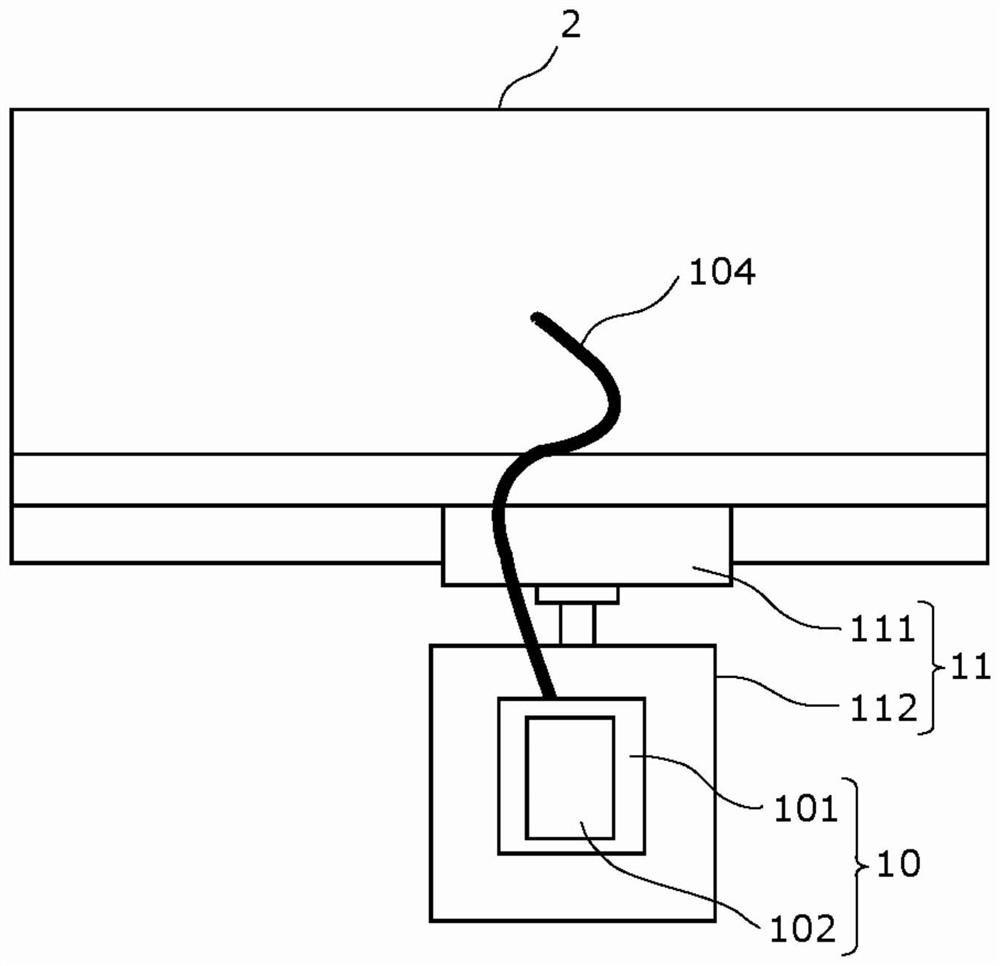
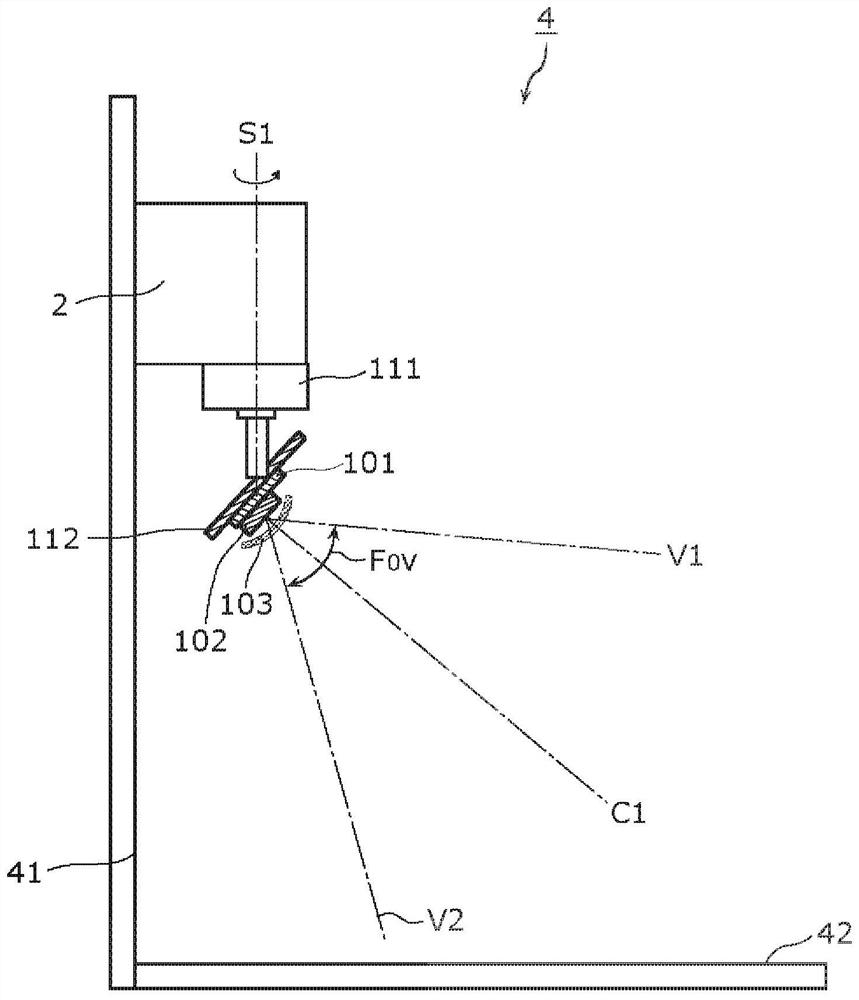
Infrared detection device
ActiveCN107543617BSuppresses the effects of image distortionOptical detectionSensing radiation from moving bodiesInfraredLine sensor
Provided is an infrared detection device capable of suppressing the influence of image distortion caused by an optical system. Equipped with: a lens that transmits infrared light; and an infrared sensor that has infrared detection elements arranged in two or more rows, and scans the detection target range by rotating around a scanning rotation axis that passes through a part of the lens, and outputs an indication The output signal of the thermal image of the detection object range, at least two infrared detection elements of the infrared sensor are arranged at positions offset from the scanning rotation axis, and the image in the scanning direction of the infrared detection elements arranged in two or more columns The number of the first infrared detection elements whose half width of the point intensity distribution is smaller than the half width of the image point intensity distribution in the direction of the scanning rotation axis is more than the number of image points in the scanning direction in the infrared detection elements arranged in two or more columns The number of second infrared detection elements whose half width of the intensity distribution is larger than the half width of the pixel intensity distribution in the direction of the scanning rotation axis.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
A Combined Method of Micro-area Adaptive Raman Fluorescence Imaging for Deep Space Exploration
The invention discloses a self-adaptive combined Raman fluorescence imaging method for a deep-space exploration micro-area. The method is implemented on a self-adaptive combined Raman fluorescence imaging system, and comprises the following four steps: self-adaptive focusing and calibration of expected focal spots; single-point tight focusing of an exploration object; acquisition of Raman fluorescence and imaging information; and scanning micro-area analysis. The method has the beneficial effects that the diameter of a focused light spot can be self-adaptively adjusted during micro-area analysis; the regional average gray degree of an electronic ocular lens is used as the intensity of a scanning imaging point, and the requirements of both self-focusing and wide-spectrum scanning imaging can be met at the same time; and active laser Raman, hyperspectral fluorescence and visible wide-spectrum scanning image of three-dimensional space can be realized at the same time, and a variety of information is provided for micro-area analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Calibration method of electric charge coupler response linearity
InactiveCN1200453CGood for testing uniformityAvoid the effects of ups and downsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsDot matrixLight spot
The invention discloses a calibration method for response linearity of a charge coupled device. The present invention utilizes the monochromatic plane light to irradiate the diffraction screen, and converges it through the Fourier lens, uses a charge-coupled device to sample the light spot lattice of the back focal plane of the Fourier lens, and obtains the output gray value of the light spot lattice; the analysis is based on the Fraunhofer diffraction theory The calculated theoretical distribution value of the spot intensity and the output gray value sampled by the charge-coupled device realize the calibration of the response linearity of the charge-coupled device. The method has the characteristics of easy debugging and low cost, and is convenient for engineering realization.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Double light beam interference adjustable gain laser writing filtering method and apparatus
The invention discloses a double-beam interference gain-adjustable laser writing filtering device, which comprises a light-dividing device, a first phase modulation device, a second phase modulation device, a fixed reflection device, an adjustable reflection device, and an adjustable focus objective. The good effect of the invention lies in that the adjustable writing of the horizontal main lobe width and the axial focal depth range of a laser writing spot is realized, in a working process, the distribution characteristics of the horizontal or axial spot intensity can be changed according to the structural features of elements needing to be manufactured, thus being beneficial for considering both the writing quality and the writing efficiency of the laser writing.
Owner:南通巨大机械制造有限公司
An adaptive laser spectroscopy and imaging method suitable for deep space micro-analysis
The invention discloses an adaptive laser spectrum and imaging method suitable for deep space micro-region analysis. The method is realized on an adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection system.The method comprises the following five steps: expected focal spot adaptive focusing calibration, single-point tight focusing of a detection object, Raman fluorescence and imaging information acquisition, Raman fluorescence imaging scanning micro-region analysis, and LIBS (Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) scanning micro-region analysis and information fusion. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that an adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection method is provided, and the diameter of focusing spots can be adaptively adjusted during micro-region analysis; the regional average grey degree of an electron microscope serves as scanning imaging point intensity, and the self-focusing and wide spectrum scanning imaging requirements are met; and three-dimensional space LIBS elemental analysis, active laser Raman molecular analysis, hyperspectral fluorescence and visible wide spectrum scanning imaging can be simultaneously realized, and multiple kinds of information can be provided for performing micro-region fine detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
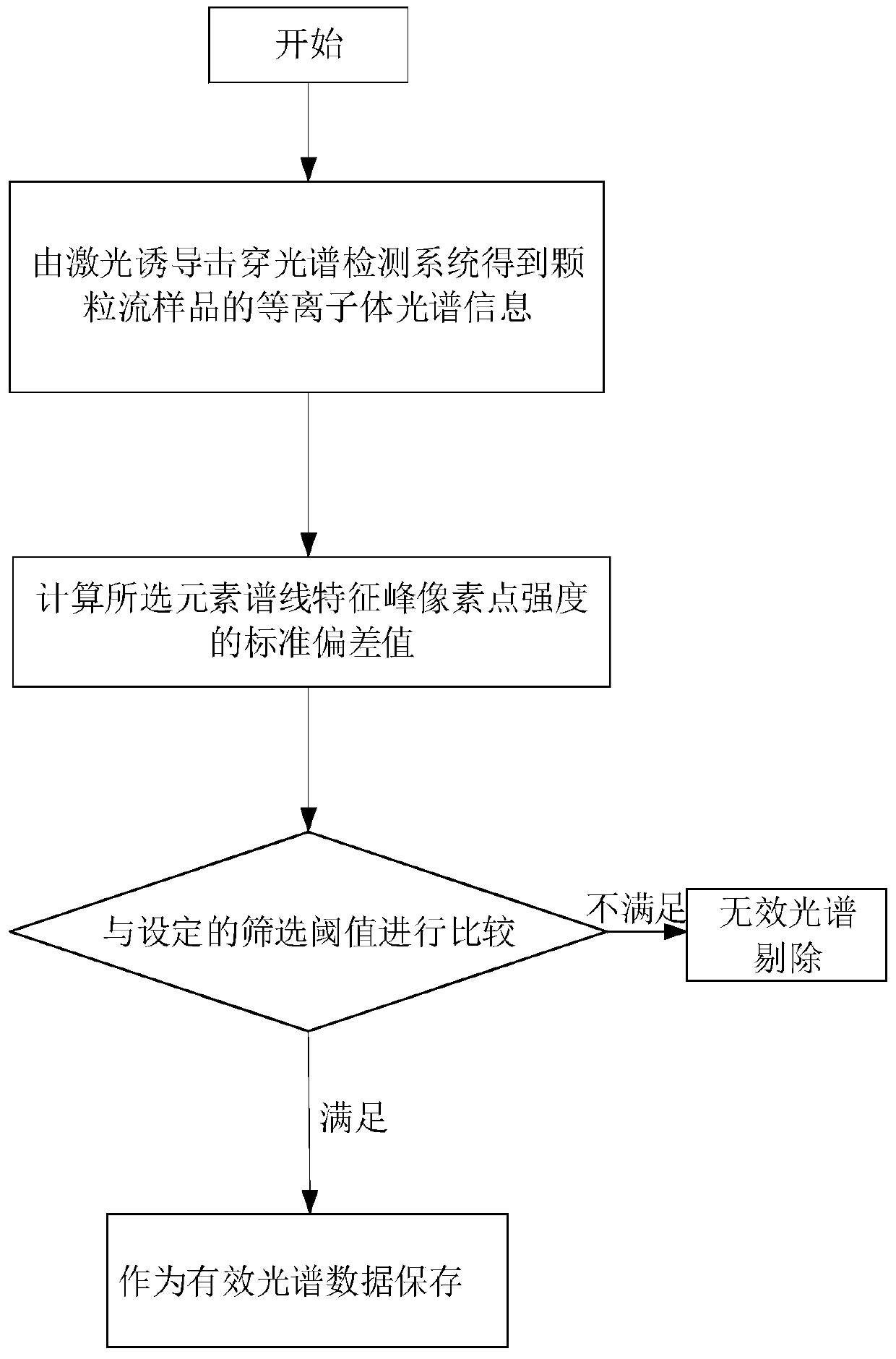
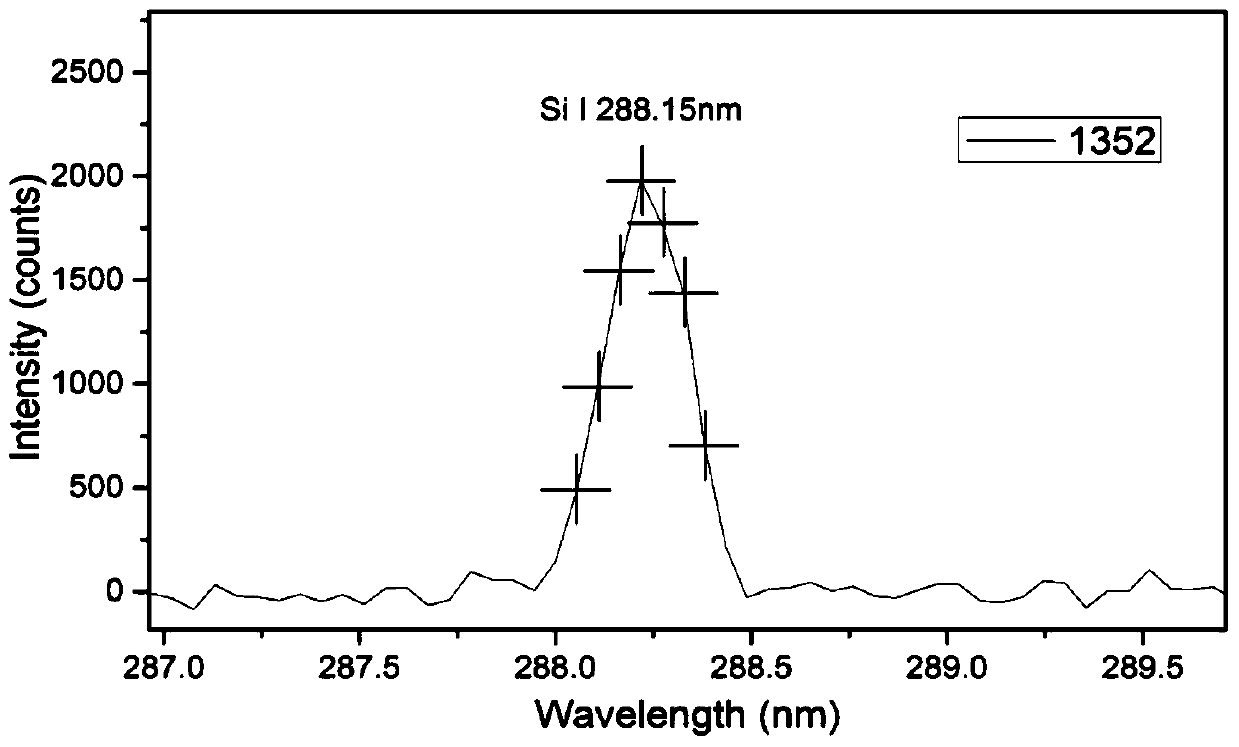
A method for identifying the standard deviation of characteristic peak intensities in laser plasma spectra of particle flow
ActiveCN105784678BImprove reliabilitySimplify the process of identifying spectral dataAnalysis by thermal excitationParticle flowLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
The invention discloses a method for identifying a laser plasma spectrum of grain flow through standard deviation of characteristic peak strength.According to the method, a laser-induced breakdown spectrum detection system is utilized for obtaining laser plasma spectrum data of a grain flow sample, a standard deviation value of the strength of characteristic peak pixel points of a selected element spectral line is calculated, and whether the spectrum data is valid or invalid is identified according to a set threshold value.Distribution information of characteristic peaks of the element spectral line in the laser plasma spectrum is utilized comprehensively, the process of identifying the spectrum data is simplified, and the accuracy of invalid spectrum removal is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com