An adaptive laser spectroscopy and imaging method suitable for deep space micro-analysis
A technology of micro-area analysis and imaging method, applied in analysis materials, fluorescence/phosphorescence, thermal excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of extremely high requirements on microscopic optical path, influence of scanning imaging speed, inability to meet requirements, etc., and achieve Raman signal The effect of high signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
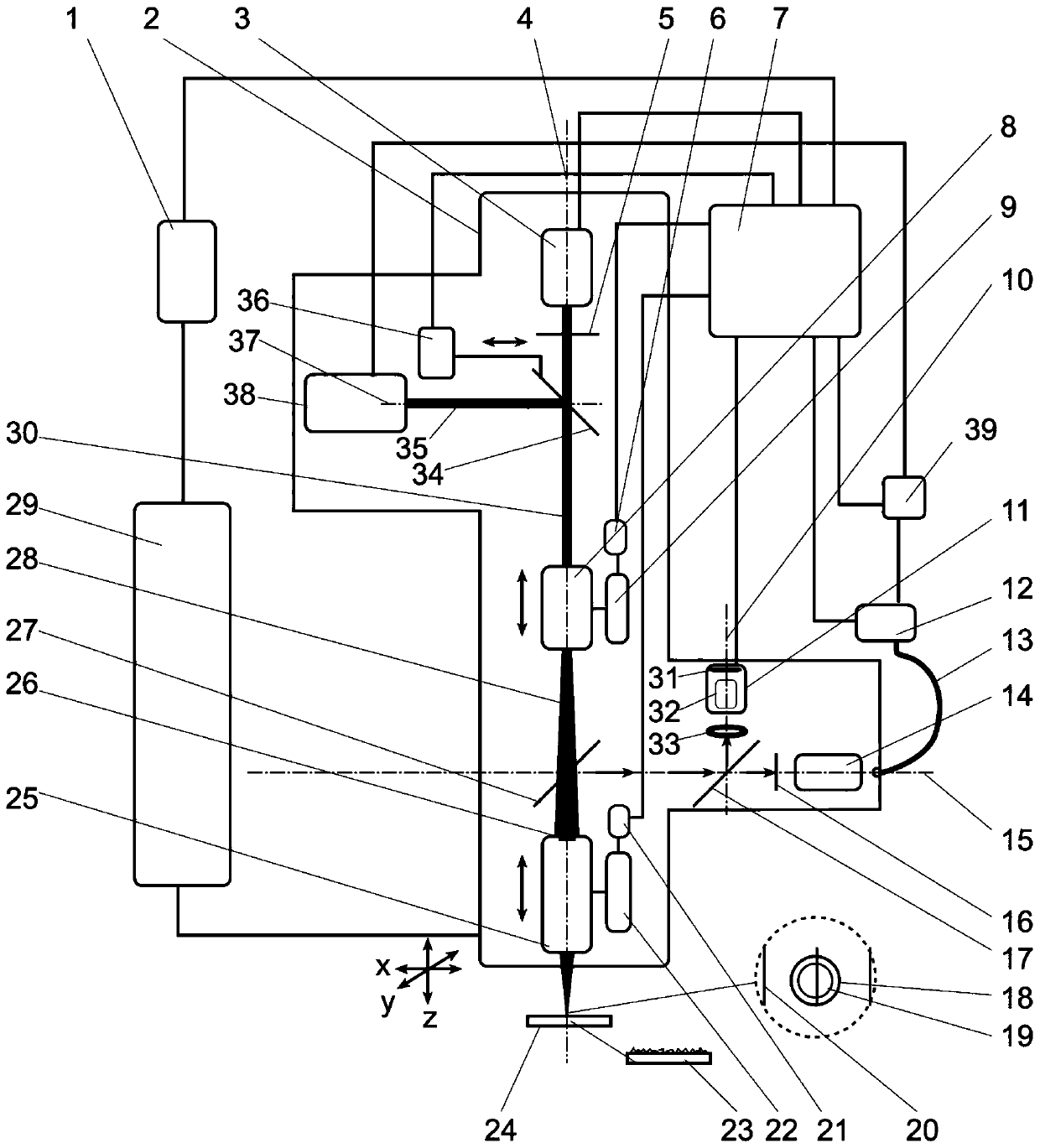
[0041] The specific embodiment of the present invention is as figure 1 shown.
[0042] The adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection method proposed by the present invention is realized on the adaptive laser spectrum and imaging detection system, and the system consists of a main controller 7, a spectrometer 12, an optical fiber 13, a three-dimensional motor driver 1, and a three-dimensional precision electric platform 29 1. The digital pulse delay controller 39 is composed of the optical head 2;
[0043] Among them, the optical head 2 is composed of LIBS laser 38, LIBS cut-in total reflection mirror 34, cut-in controller 36, ultraviolet Raman laser 3, ultraviolet interference filter 5, secondary motor driver 6, secondary linear electric platform 9, low magnification Ultraviolet microscope objective lens 8, dichroic mirror 27, long working distance and high magnification ultraviolet microscope objective lens 25, main motor driver 21, main linear electric platform 22, ultr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com