Patents
Literature
35 results about "Debye length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
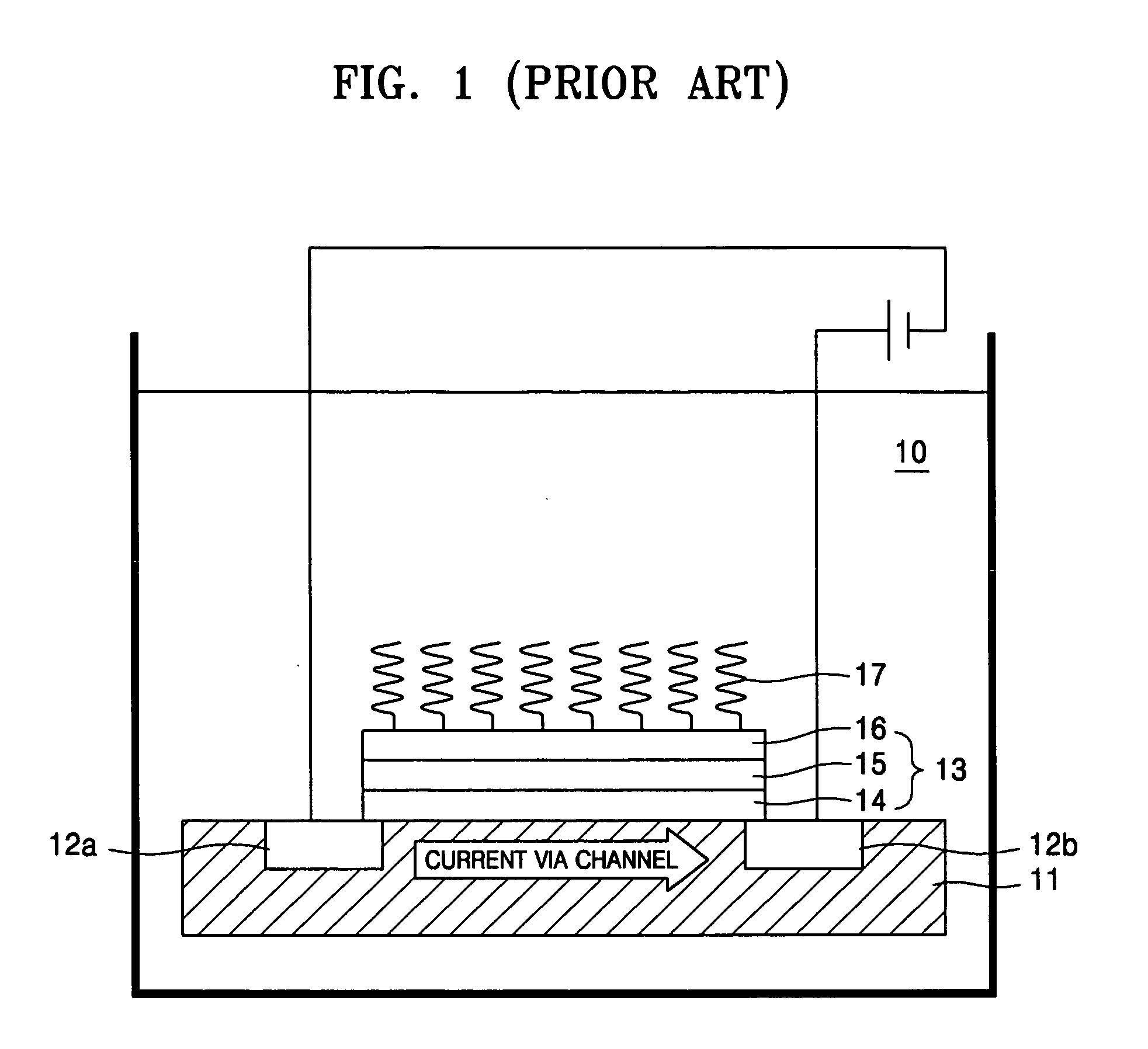
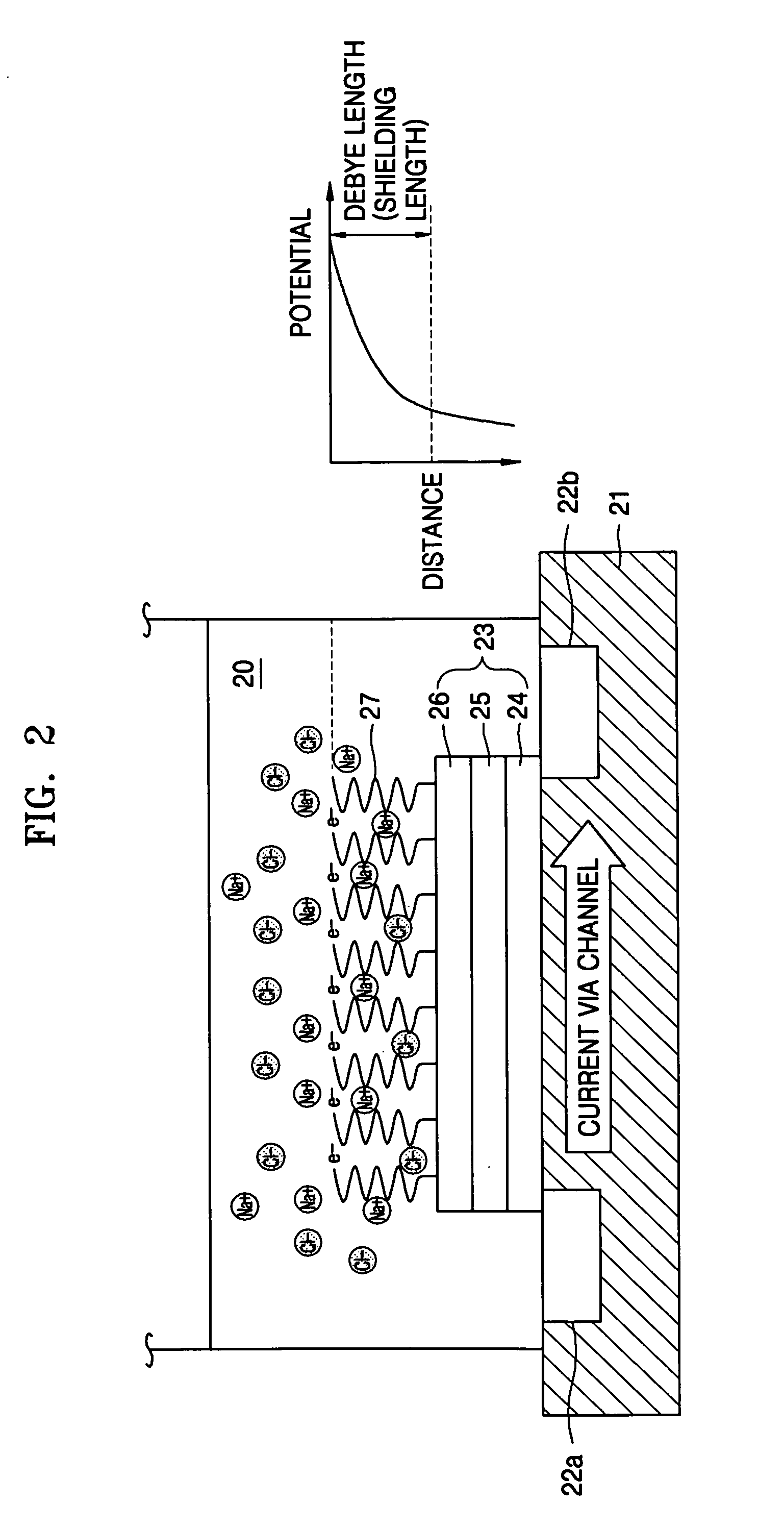
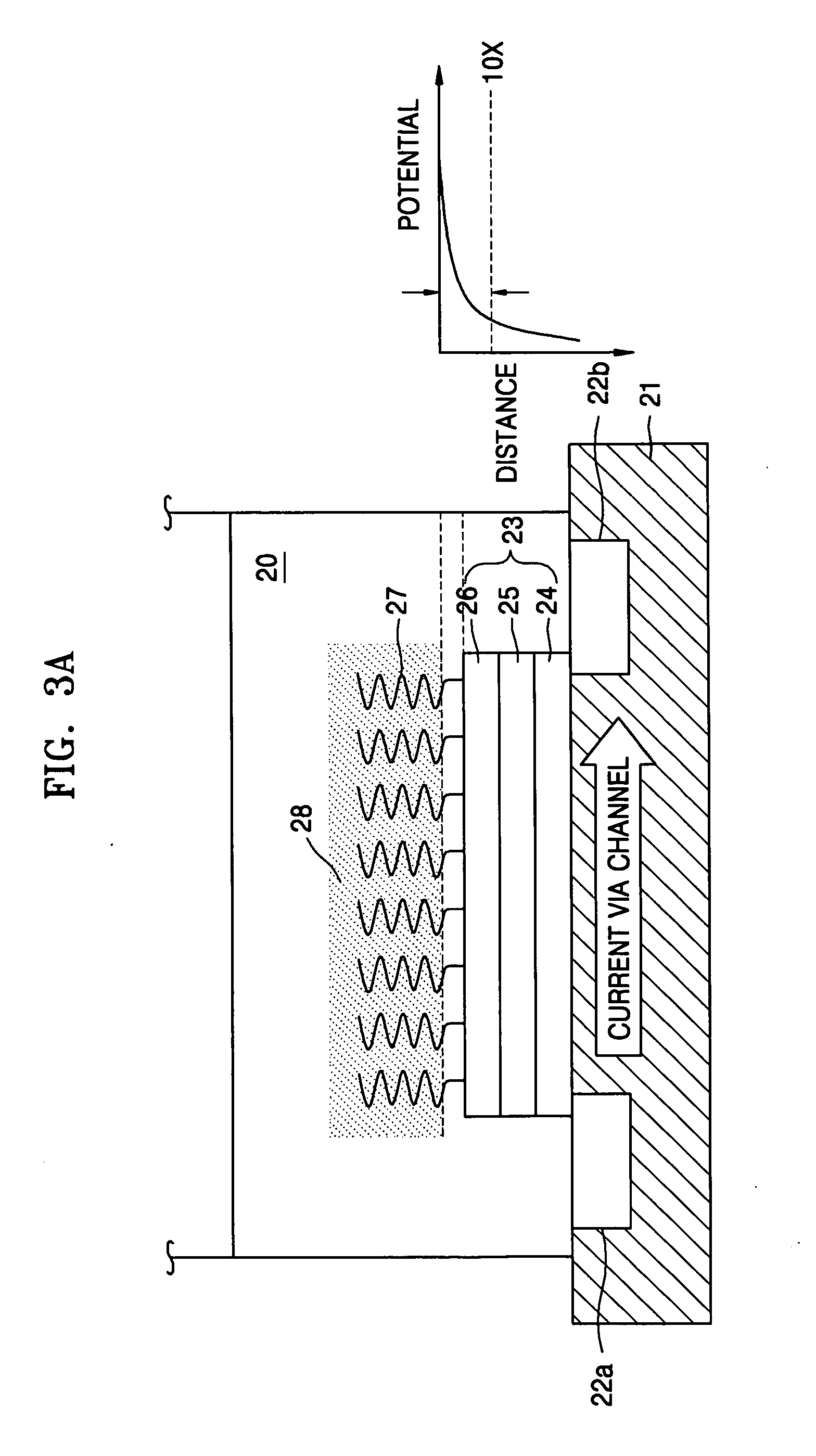
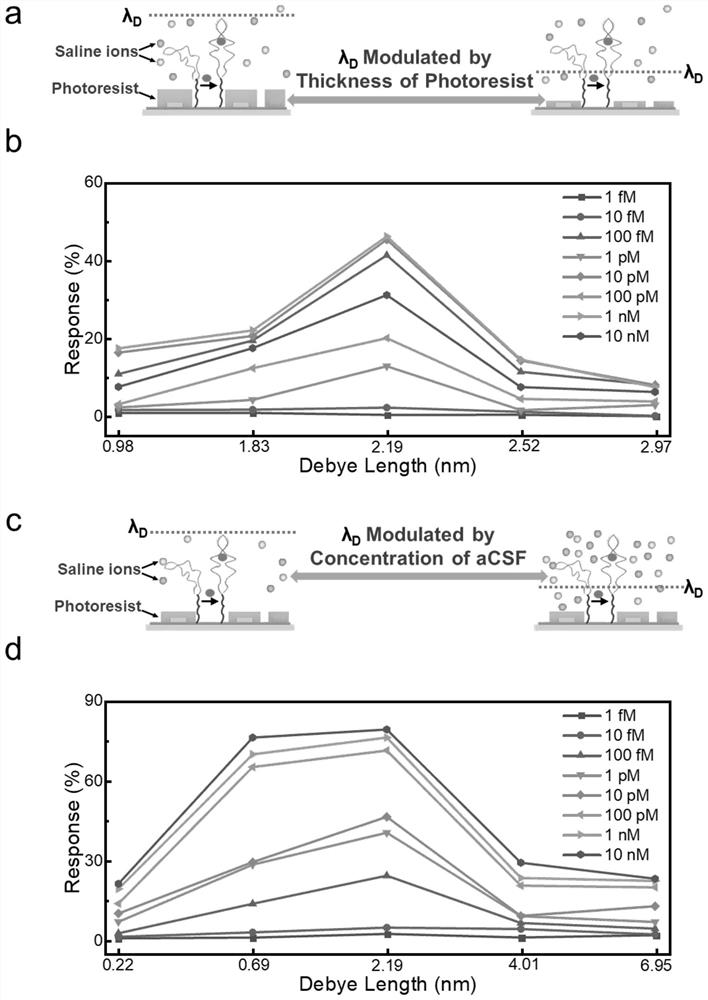
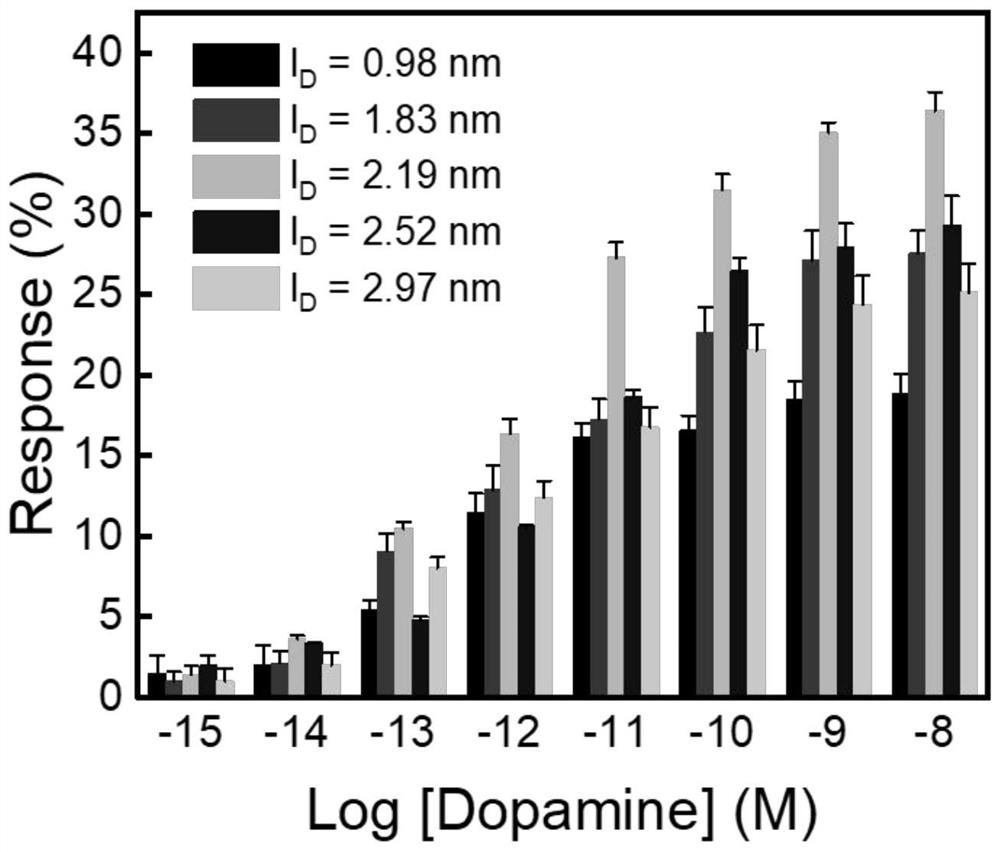
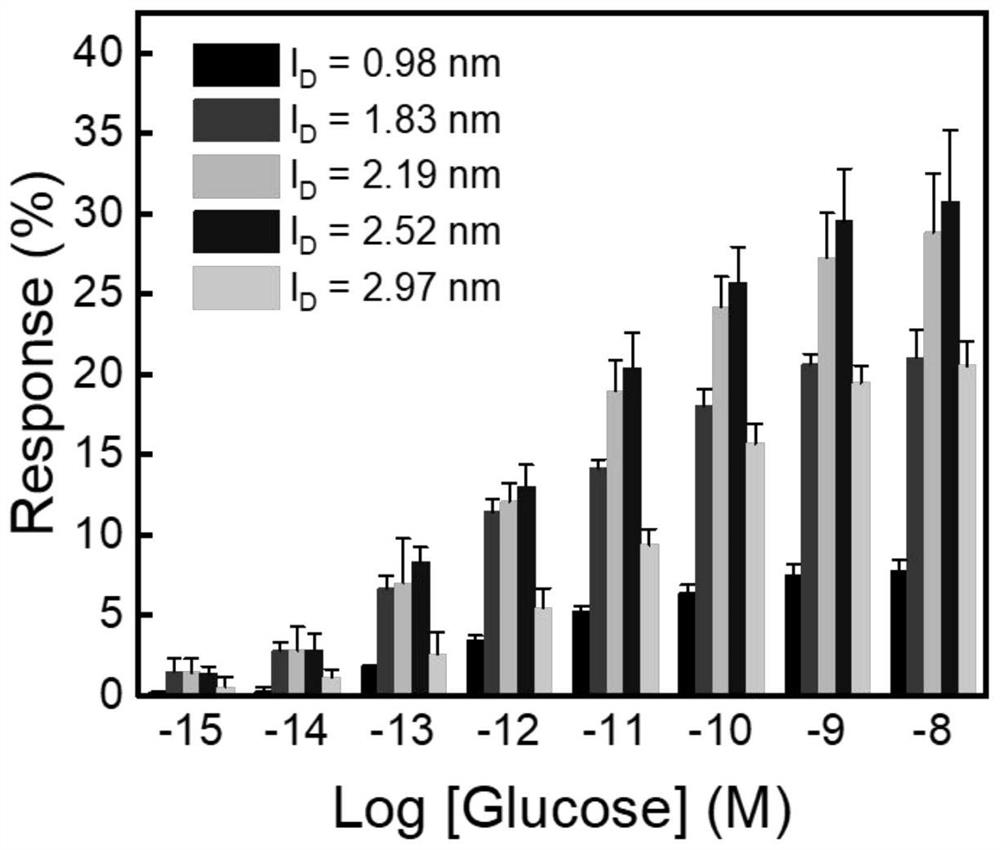
In plasmas and electrolytes, the Debye length (also called Debye radius), named after Peter Debye, is a measure of a charge carrier's net electrostatic effect in a solution and how far its electrostatic effect persists. A Debye sphere is a volume whose radius is the Debye length. With each Debye length, charges are increasingly electrically screened. Every Debye‐length λD, the electric potential will decrease in magnitude by 1/e.
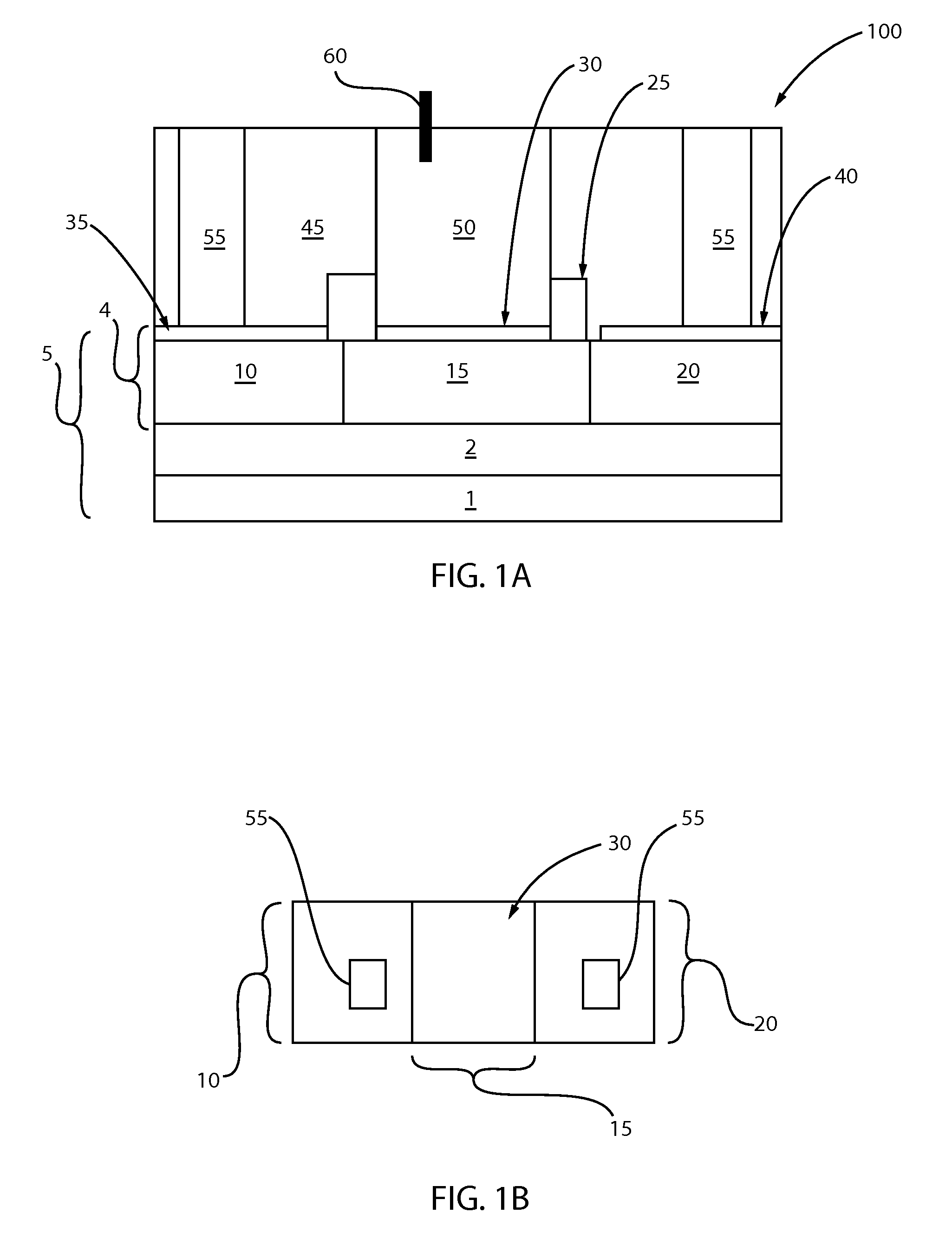
Non-electric field renal denervation electrode
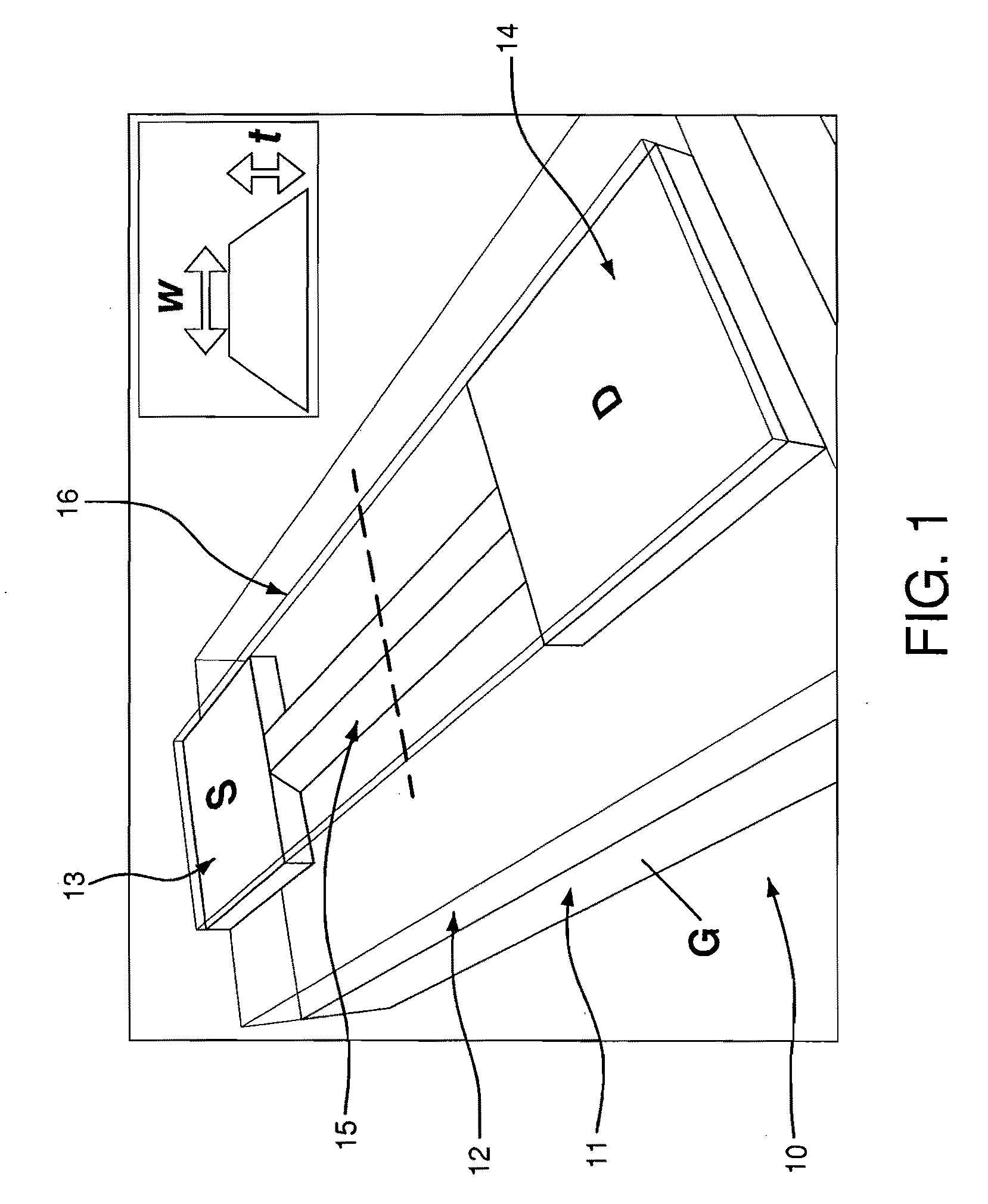
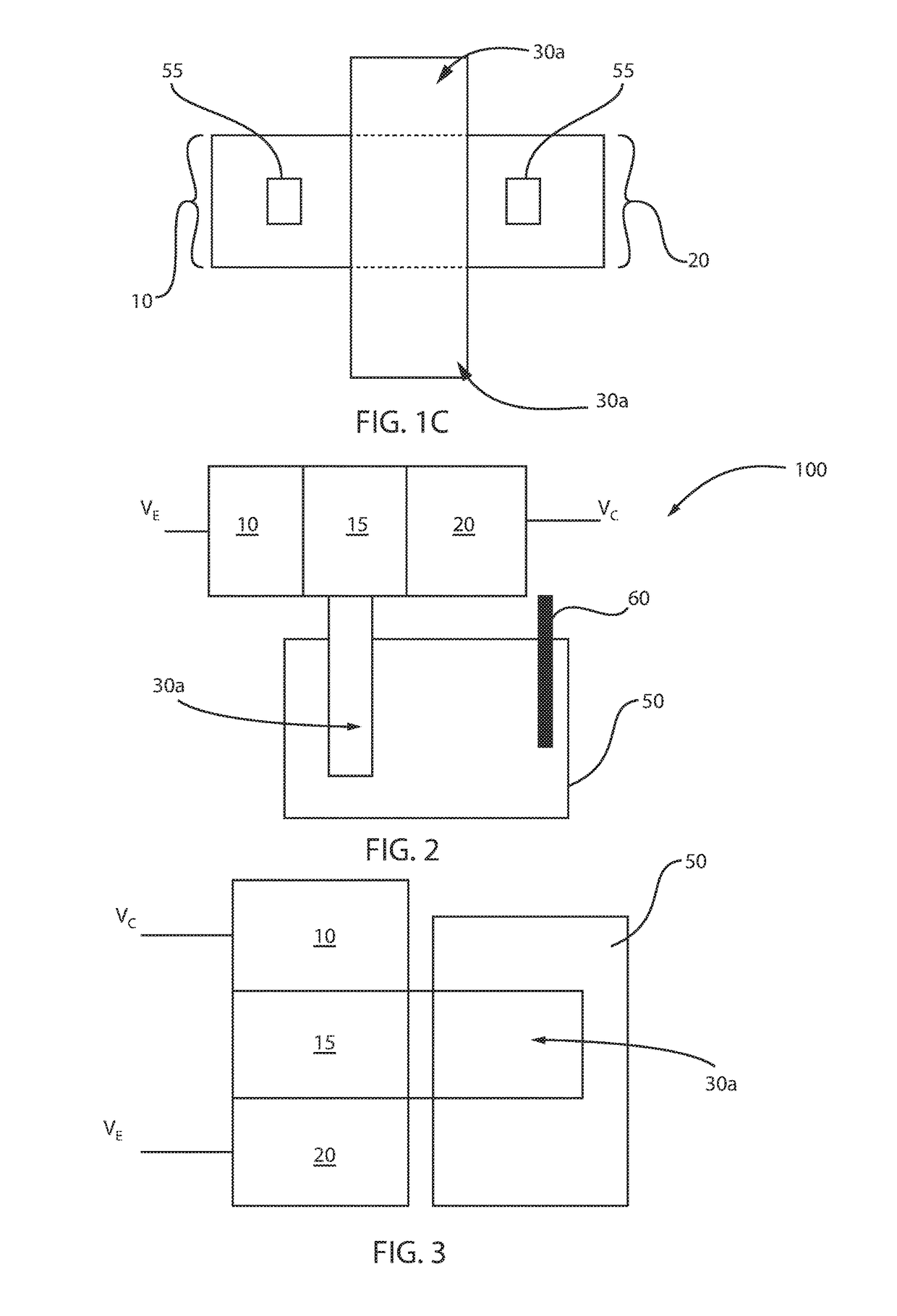
ActiveUS20130282000A1Dissipating materialAvoid spreadingSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsElectrical conductorDebye length
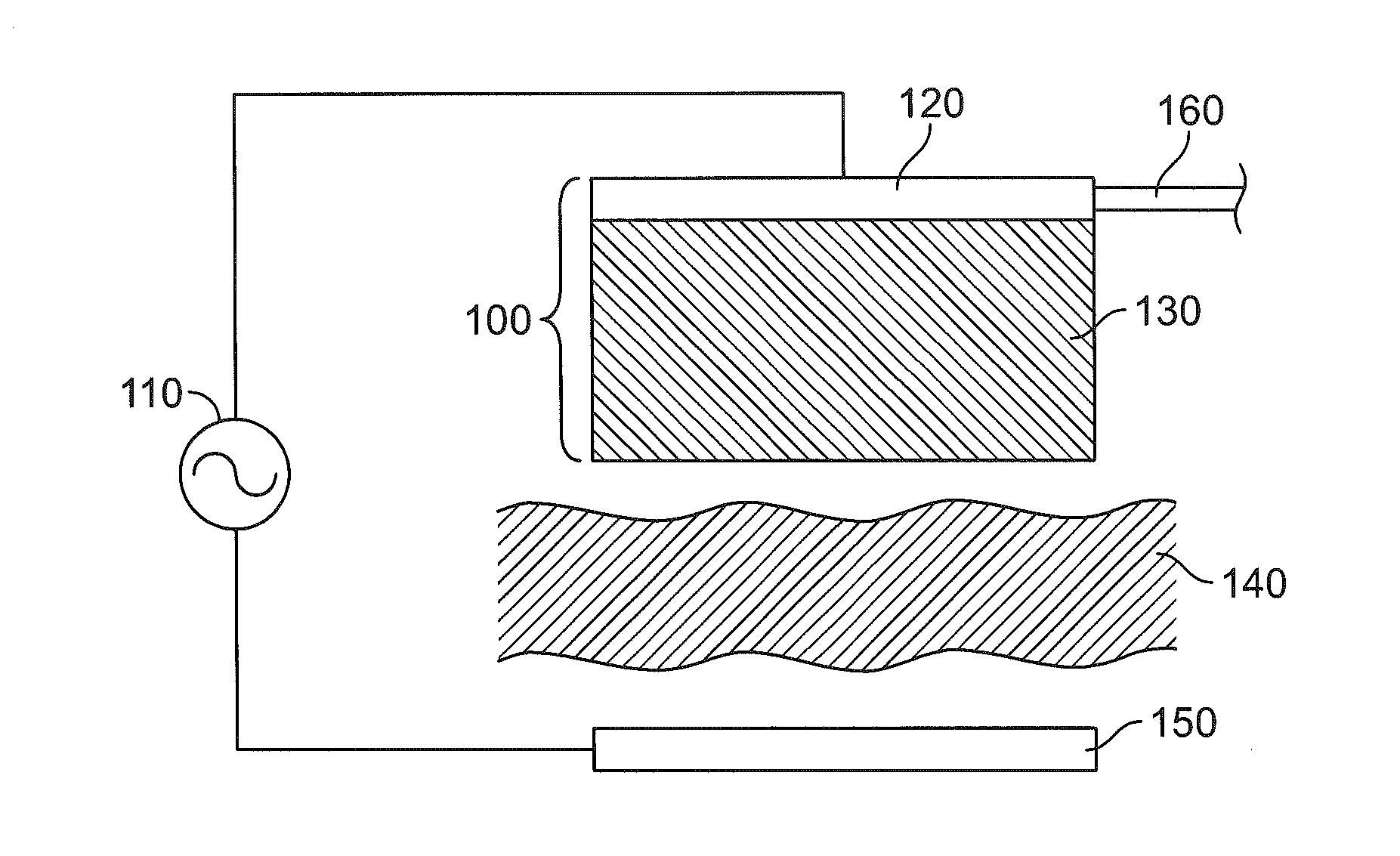
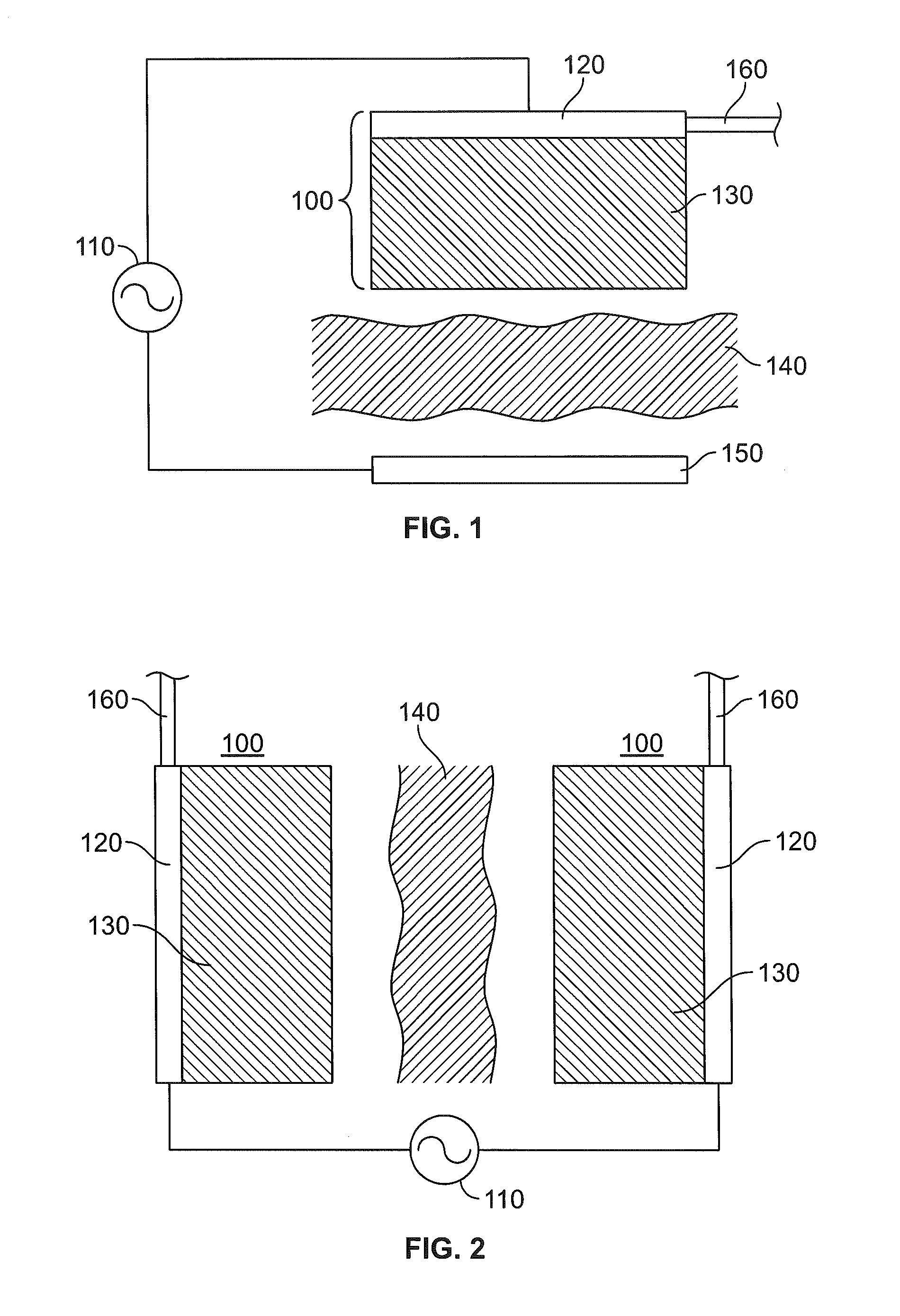
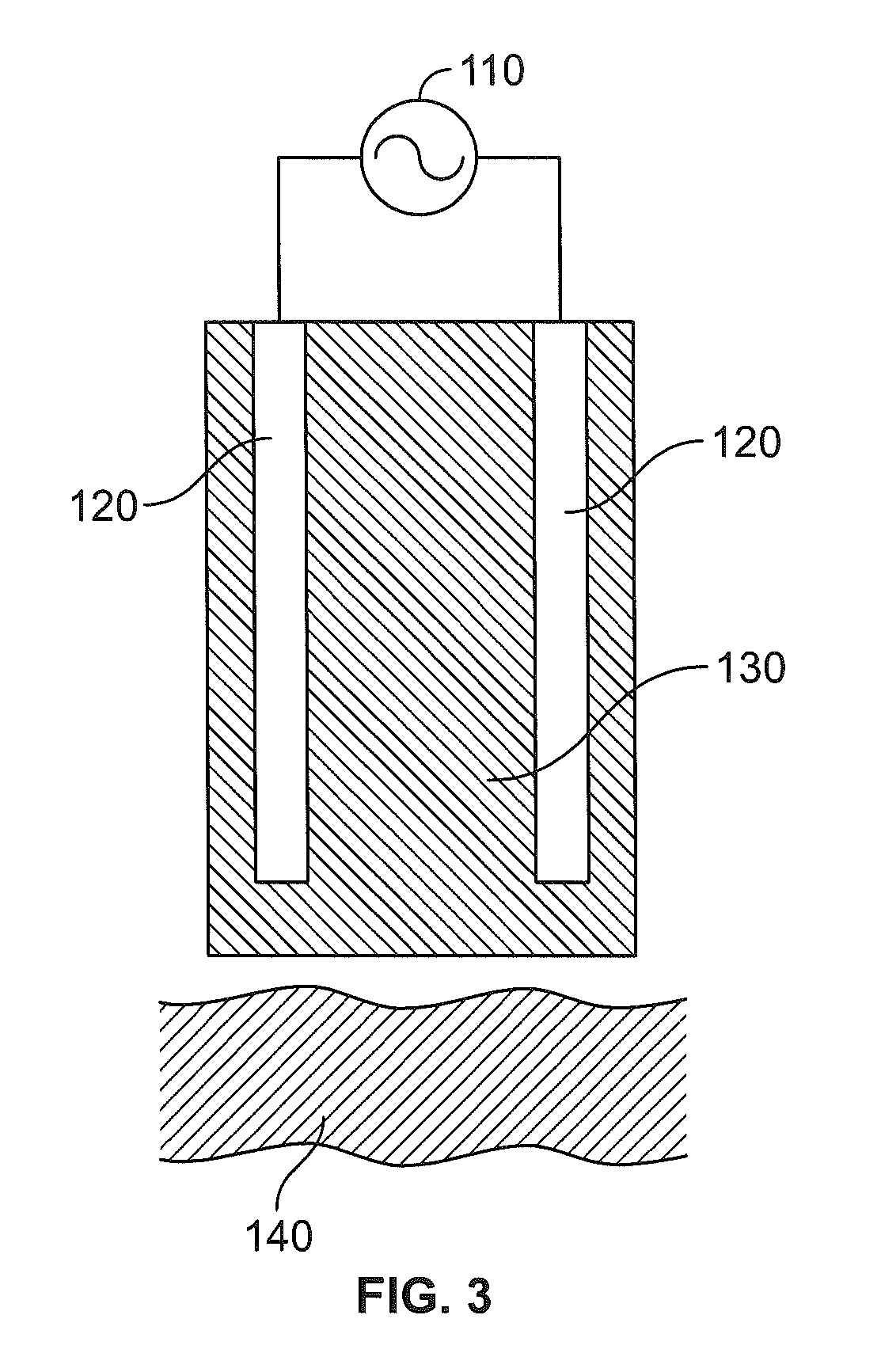
A renal denervation device can include an elongated catheter body extending along a longitudinal axis, and an assembly connected to the catheter body. The assembly includes a plurality of heating elements connected to the catheter body. Each heating element has a conductor and a layer of an RF dissipating material such as a polymer overlying the conductor. During operation of the device, the layer of RF dissipating material is disposed between the conductor and body tissues of a subject. The layer of RF dissipating material is substantially thicker than the Debye length within the material in order to reduce the electric field reaching the tissue and to eliminate direct contact of the electrode with the body tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
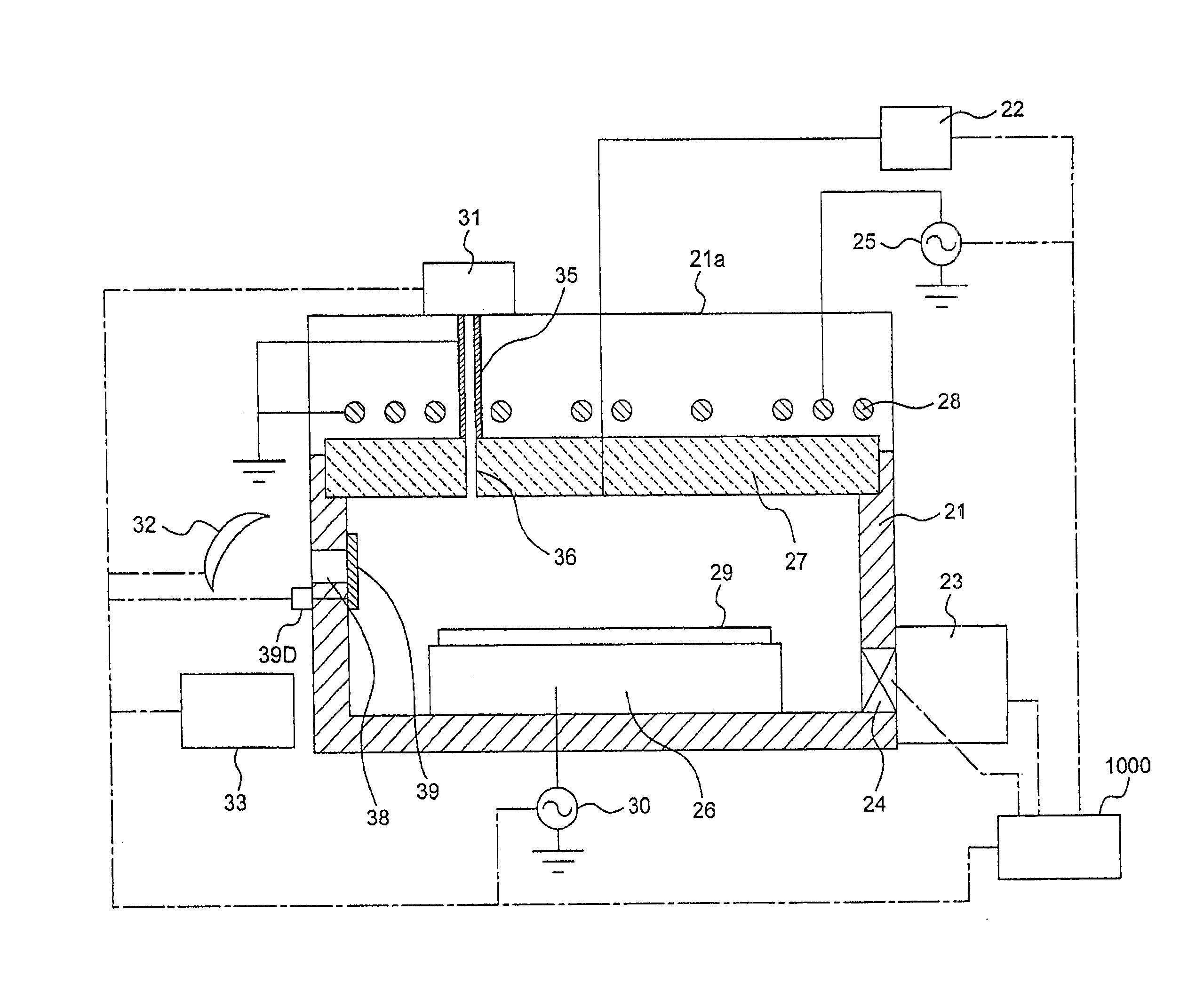
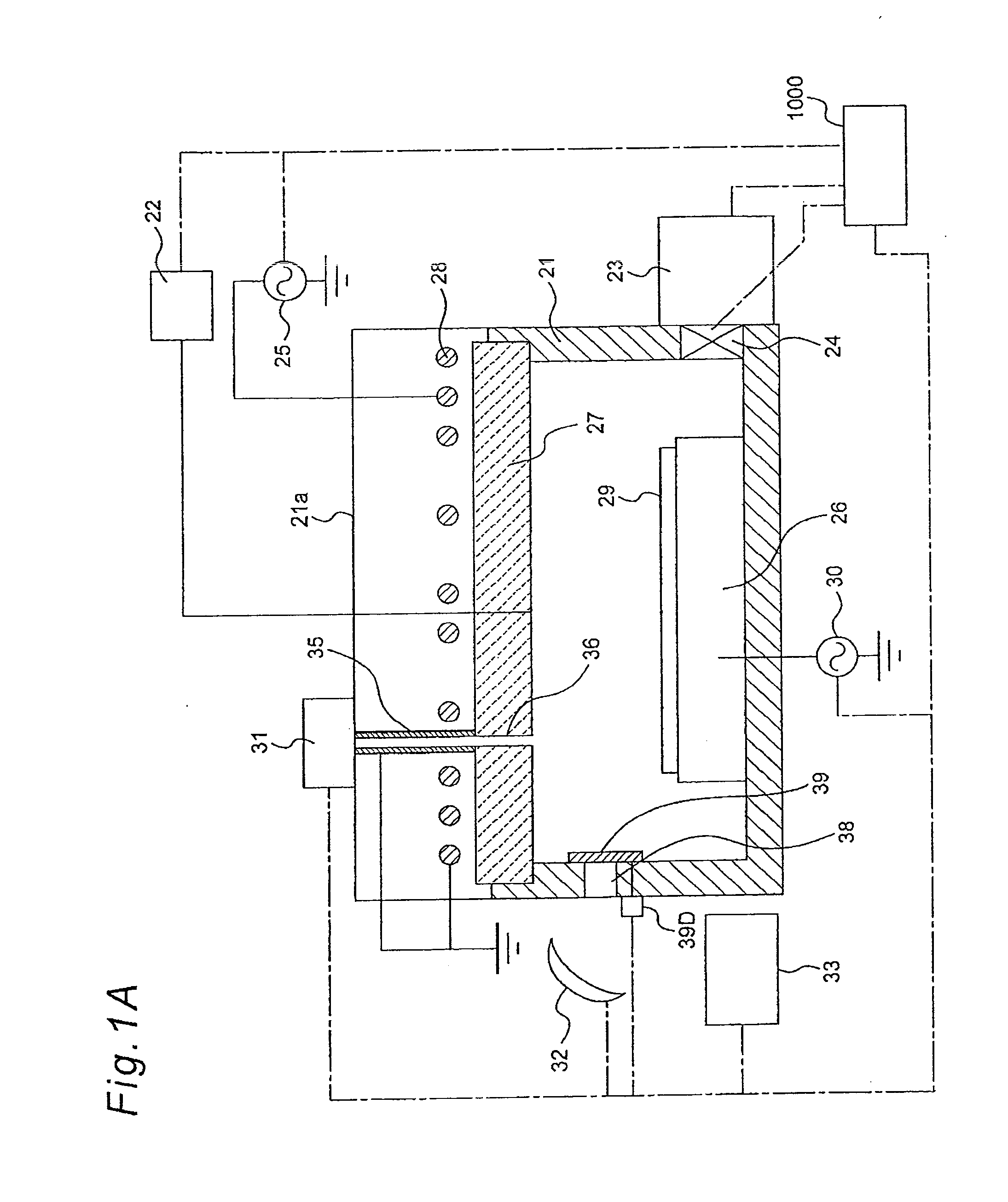
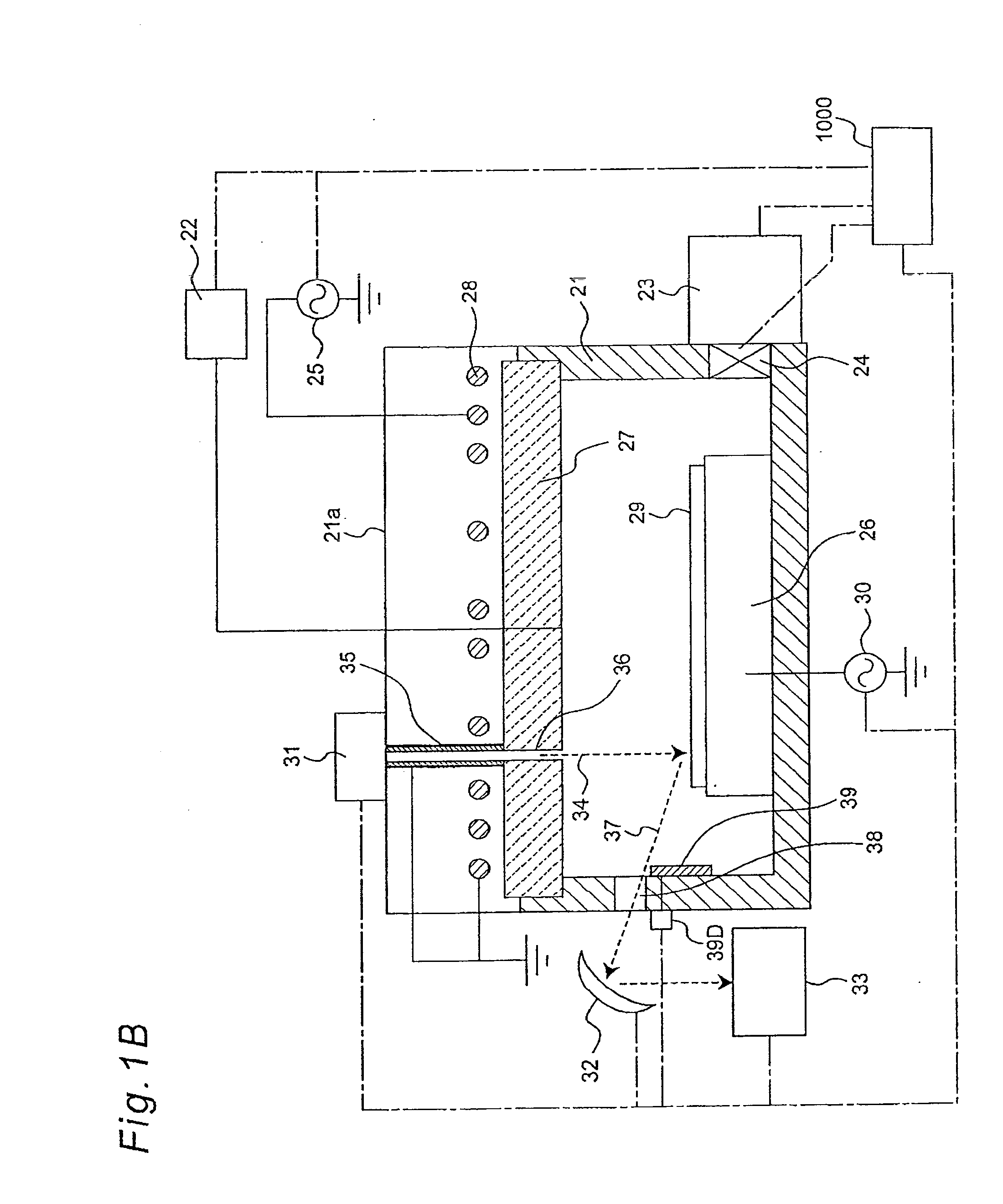
Methods and apparatus for preventing plasma un-confinement events in a plasma processing chamber
Techniques and apparatus for substantially reducing and / or preventing the occurrence of plasma un-confinement events, including one or more of shielding a gap disposed between chamber components and along a RF current path with a dielectric shielding structure, shielding a sharp component structure with a dielectric shielding structure, and keeping the gap between adjacent pairs of plasma confinement rings smaller than the worst-case DeBye length for the plasma.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Methods and apparatus for preventing plasma un-confinement events in a plasma processing chamber
Owner:LAM RES CORP
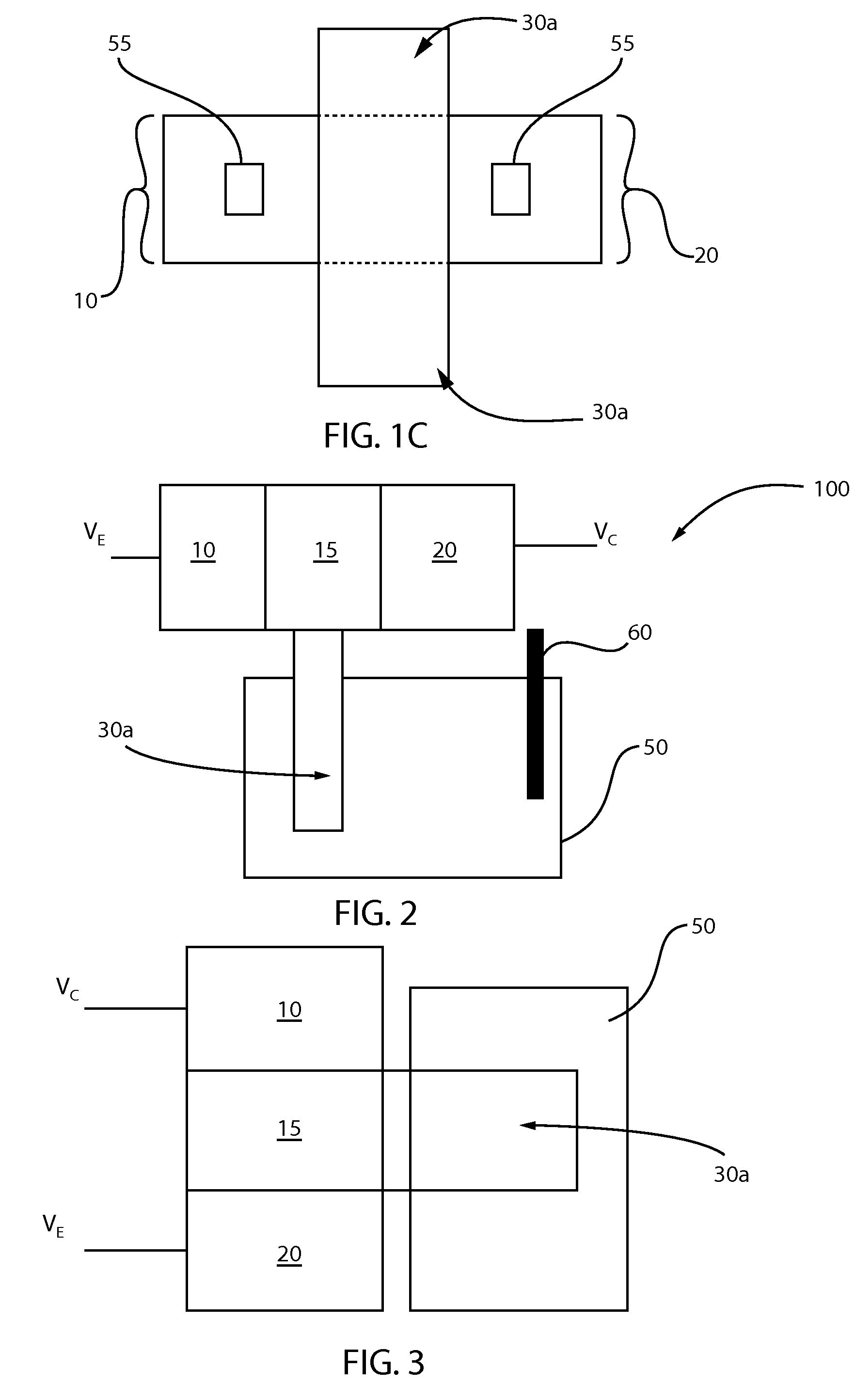
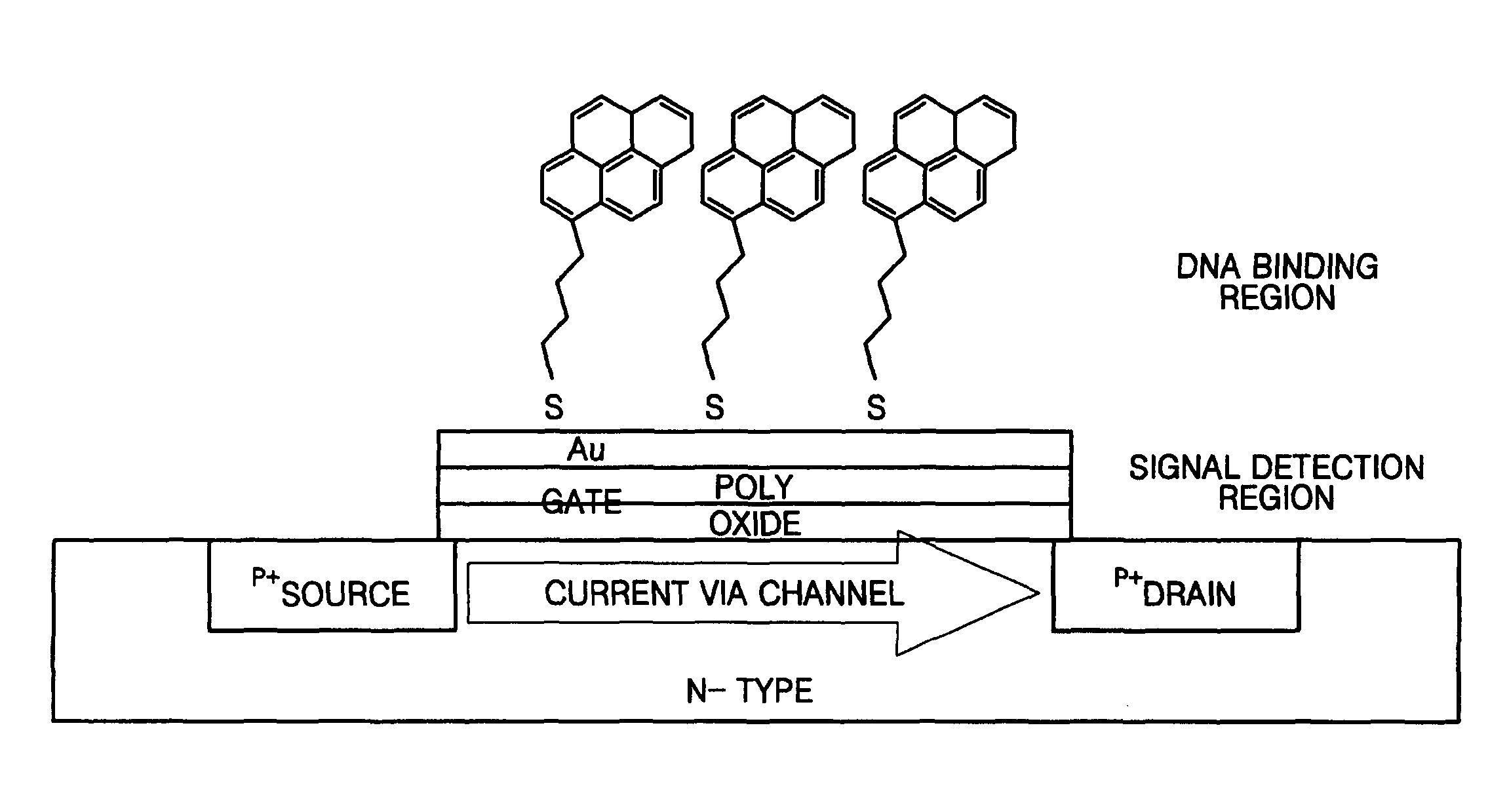
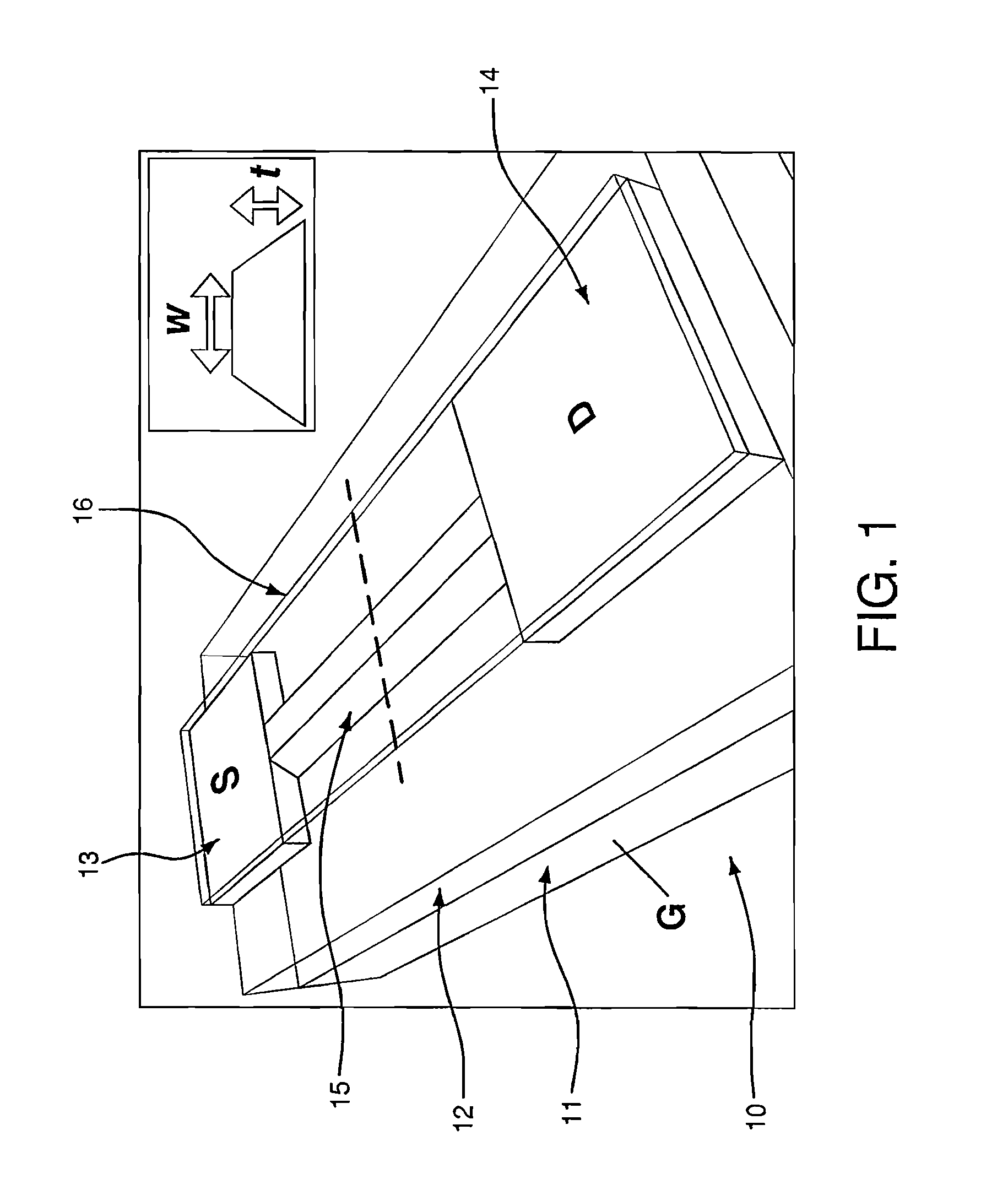
Systems and Methods for CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nano-Wire Sensors with Biochemical and Cellular Interfaces
ActiveUS20100297608A1High sensitivityIncrease the areaMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsSemiconductor materialsConducting pathway
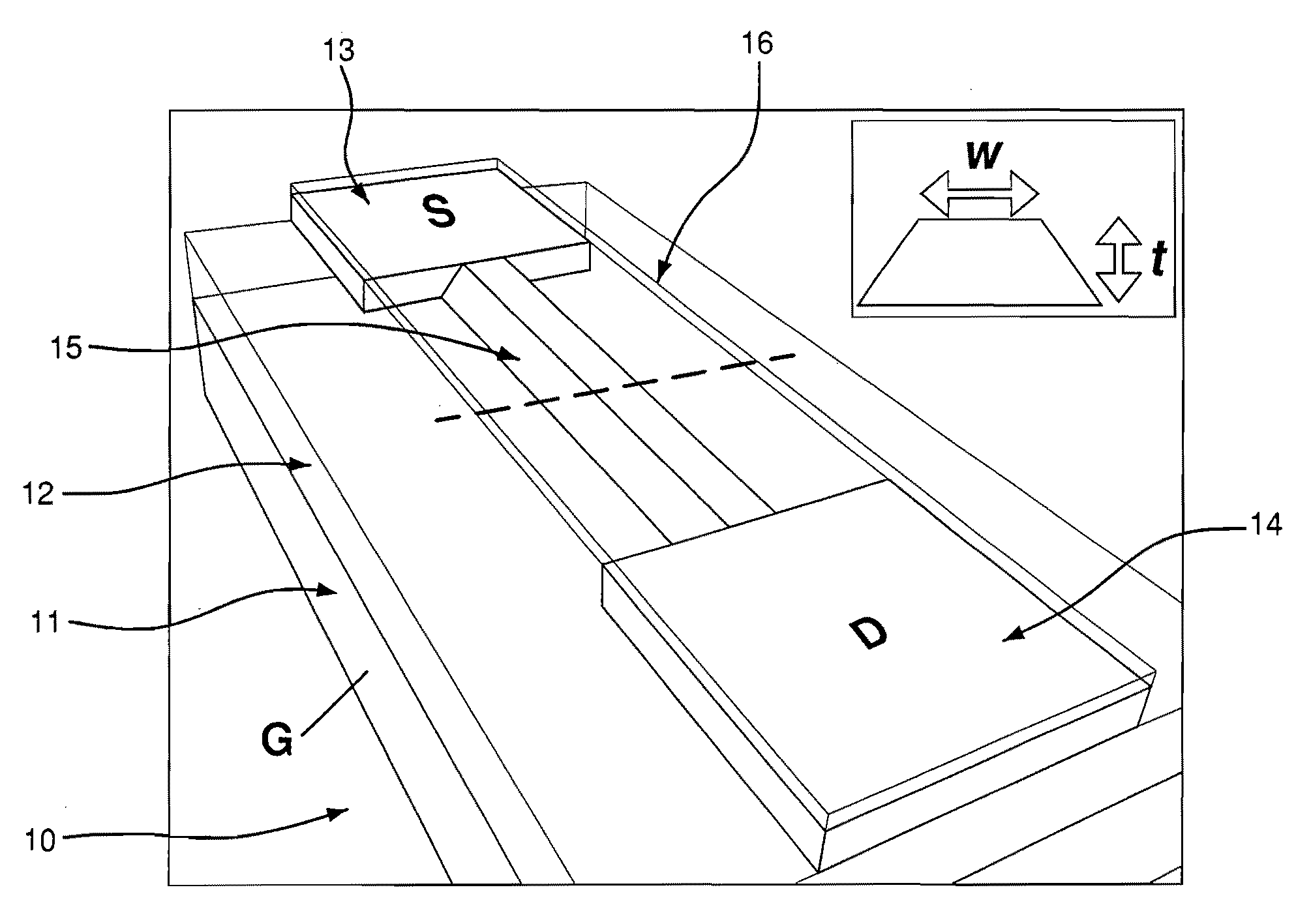
The systems and methods described herein include a sensor for suitable for sensing chemical and biological substances. The sensor comprises a semiconductor layer formed in or on a substrate and a channel having nano-scale dimensions formed in the semiconductor layer, where the structure creates an electrically conducting pathway between a first contact and a second contact on the semiconductor layer. In certain preferred embodiments, the nano-scale channel has a trapezoidal cross-section with an effective width and exposed lateral faces, where the effective width is selected to have same order of magnitude as a Debye length (LD) of the semiconductor material of which the semiconductor layer is formed.
Owner:YALE UNIV
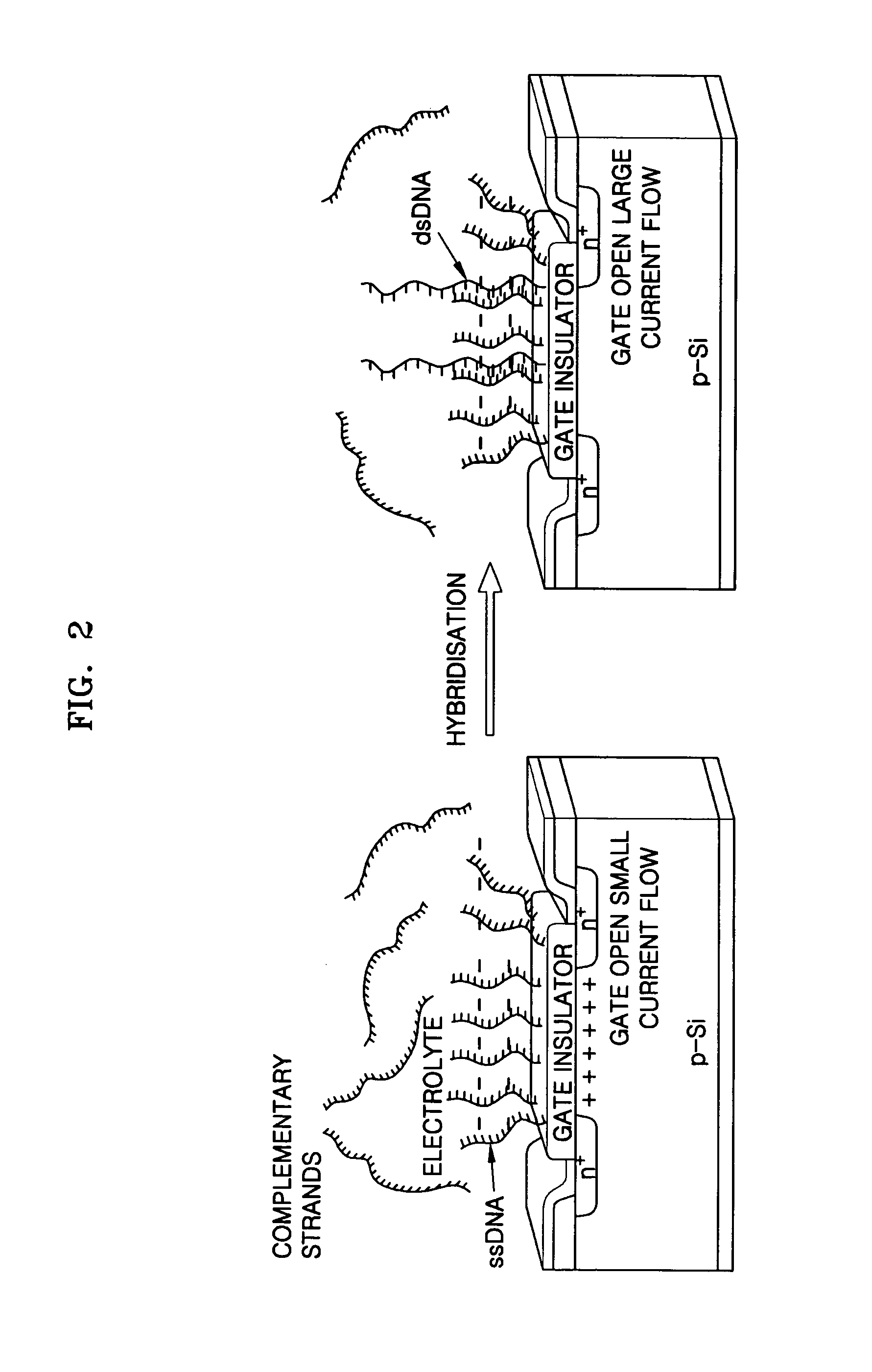
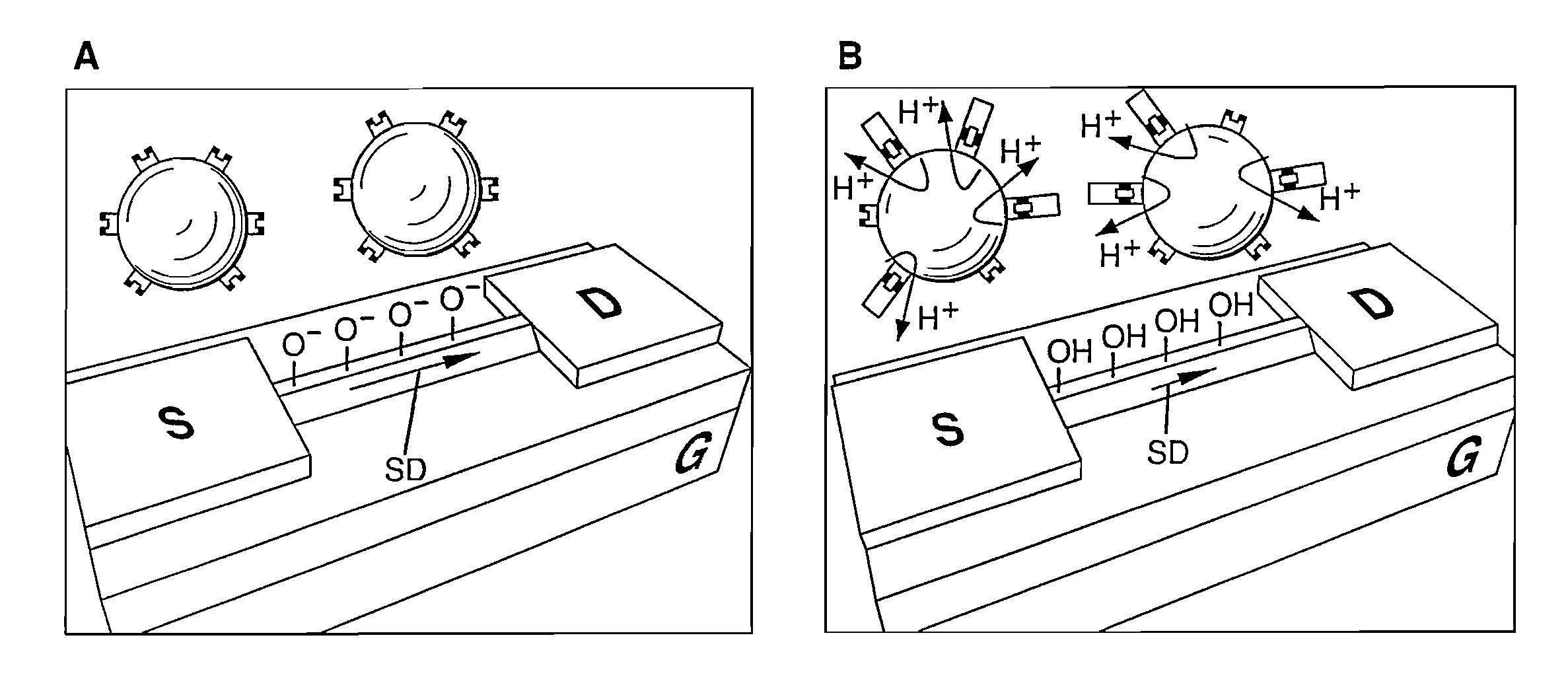
FET-type biosensor with surface modification
InactiveUS20060205013A1High sensitivitySimple structureMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementIonic strengthDebye length
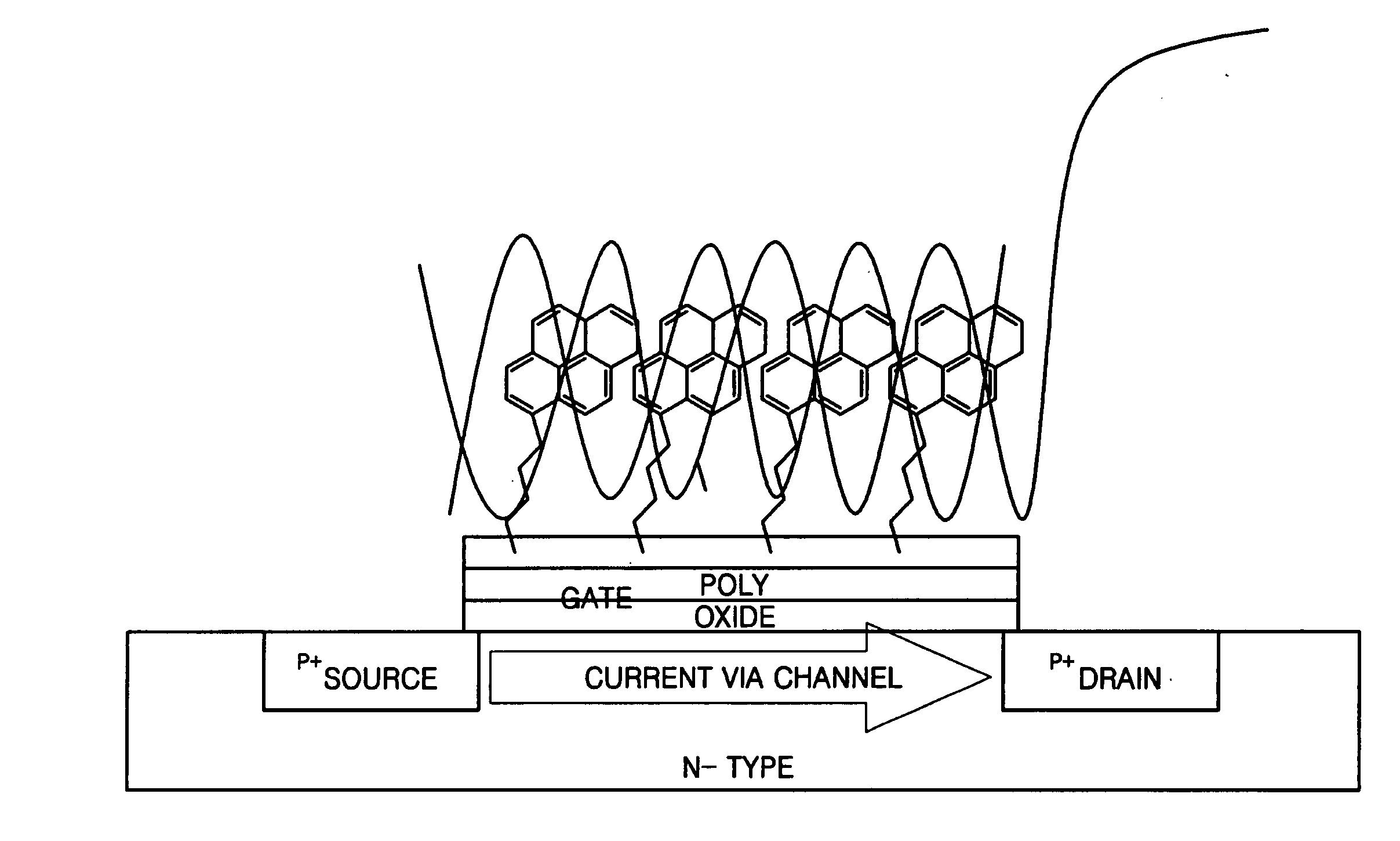
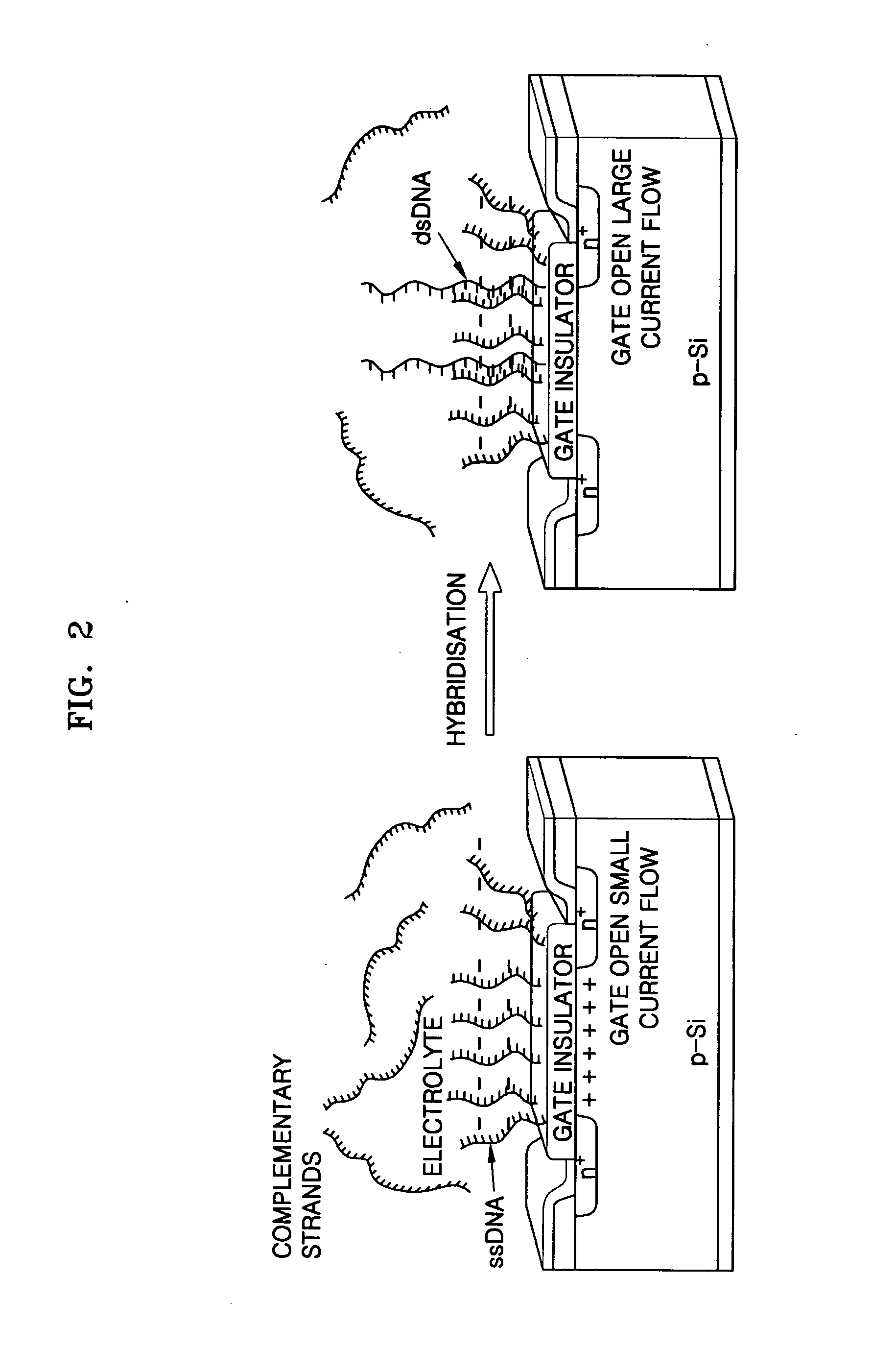
Provided is a field effect transistor (FET) type biosensor including a source electrode, a gate, and a drain electrode. A ligand that can bind to a side of a nucleic acid is added to the surface of the gate. In a conventional FET type biosensor, it is difficult to detect a signal within the debye length because a target nucleic acid is directly fixed to the surface of a gate of the conventional FET. However, in the present invention, this problem can be overcome and the debye length can be increased by treating the surface of a gate of an FET sensor with a ligand that can bind to a side of a nucleic acid. The ligand can be adsorbed onto the surface of the gate. In this case, the nucleic acid is adsorbed parallel to the surface of the gate, not perpendicular to the surface of the gate, thus generating an effective depletion region. In addition, hybridization efficiency can be increased because a hybridized sample can be injected into an FET sensor at high ionic strength.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Micro-structured gas sensor with control of gas sensitive properties by application of an electric field
InactiveUS20050235735A1High selectivityMaintain good propertiesMaterial resistanceSpecific gravity measurementElectricityDebye length
A gas sensor includes a semiconductor substrate on which is disposed at least one field electrode, and advantageously a plurality of field electrodes. The field electrodes are disposed under a gas-sensitive semiconductor resistive film, with an insulator layer in between. The film, which may be in electrical contact with a pair of external electrodes, may comprise a metal oxide, such as for example SnO2, WO3, In2O3, Ga2O3, Cr2-xTixO3+z, or various organic semiconductors. The field electrodes produce an electric field acting on the semiconductor, and an electroadsorptive effect may occur when the thickness of the gas-sensitive film is on the order of the Debye length. In the case of the known gas-sensitive material SnO2, for example, the Debye length may be approximately 60 to 80 nm. An electric field produced in the body of the gas sensor may be effective up to the surface of the gas-sensitive film that is exposed to the gas, i.e., the films lying above the gate electrode do not screen the electric field. The use of a plurality of field electrodes may make it possible to offset or control the gradient in the surface potential variation.
Owner:MICRONAS
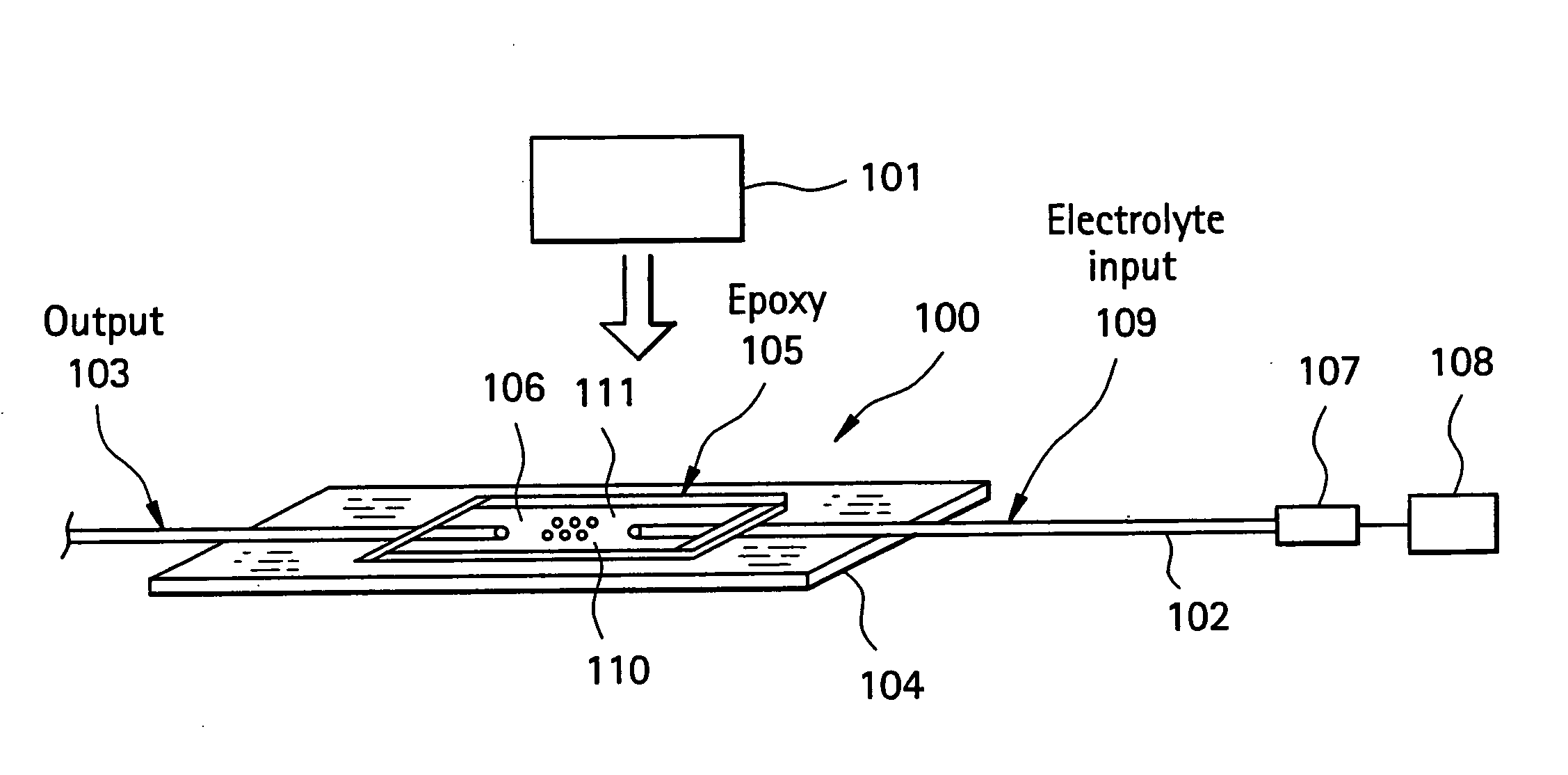
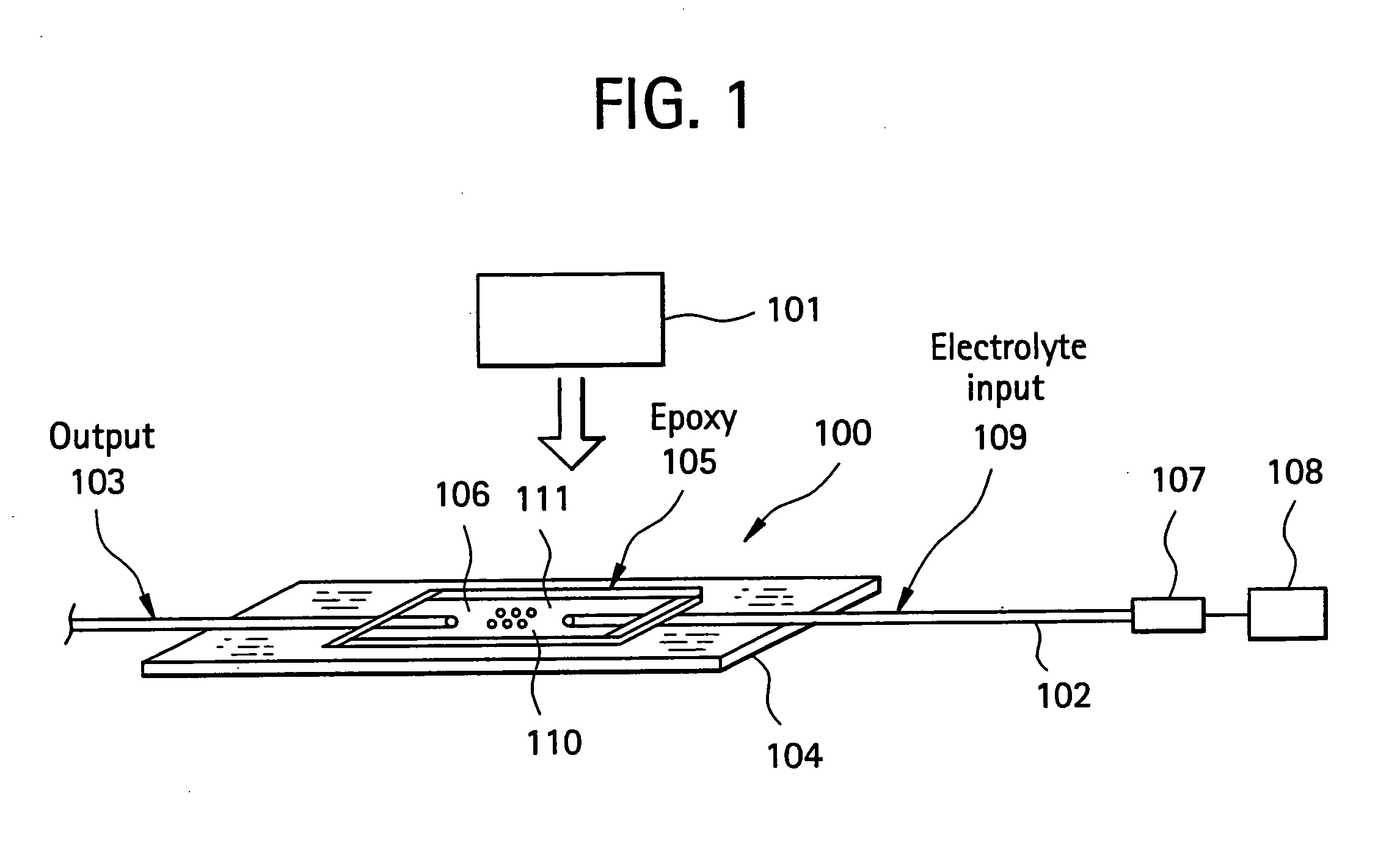
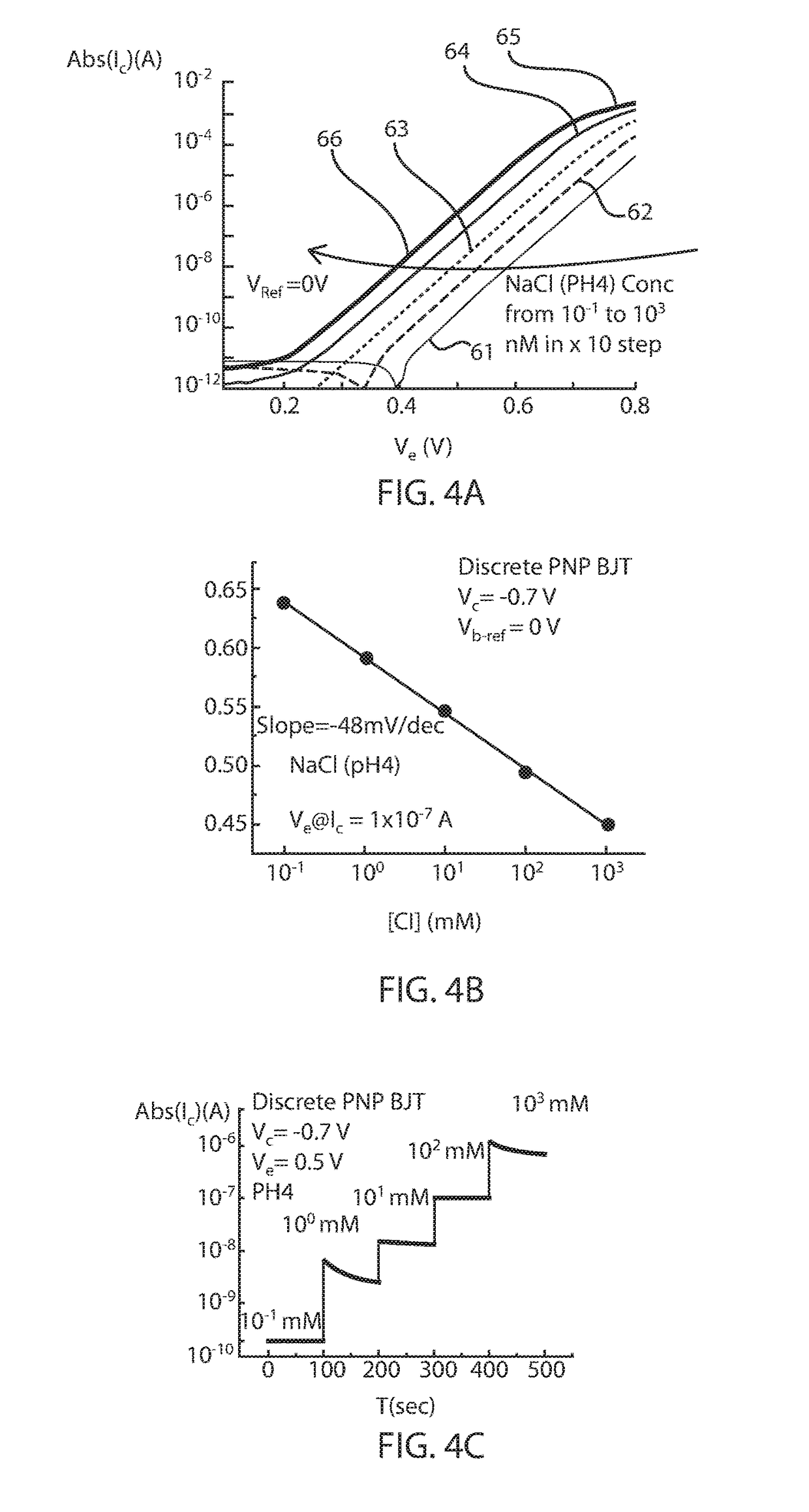
Biosensors including surface resonance spectroscopy and semiconductor devices
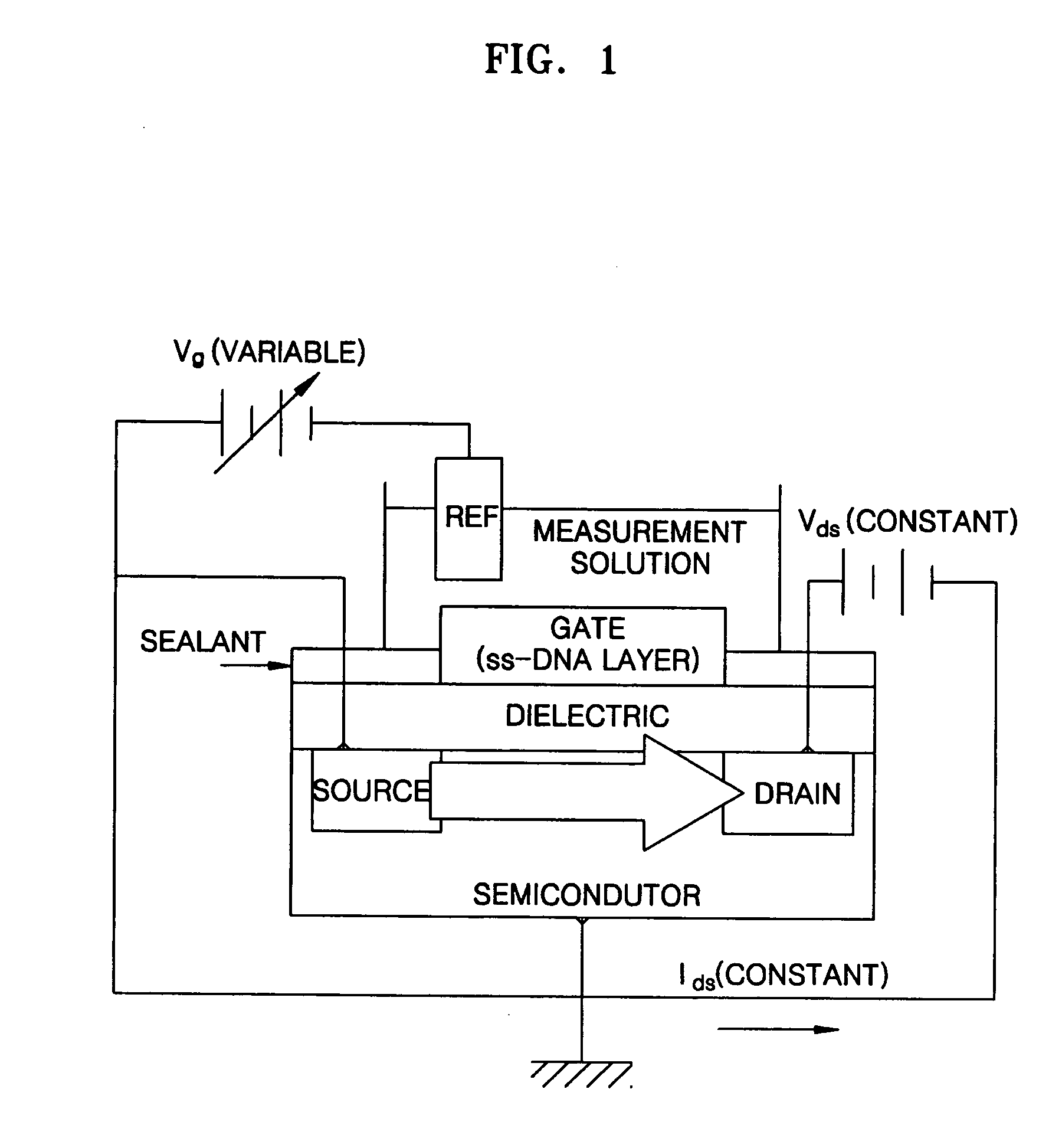
A sensor including a surface plasmon resonance detector with a reservoir for containing a liquid sample. The sensor further includes a sensing metallic film positioned within the reservoir so that at least a majority of a surface of the sensing metallic film is to be in contact with the liquid sample being housed within the reservoir. The sensory also includes a semiconductor device having a contact in electrical communication with the sensing metal containing film that is positioned within the reservoir. The semiconductor device measures the net charges of molecules within the liquid sample within a Debye length from the sensing metallic film.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for forming multi-dimensional colloidal structures using holographic optical tweezers
InactiveUS20080285099A1Precise positioningWide applicabilityLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersPhotonicsMulti dimensional
Holographic optical tweezers are used to position charge stabilized colloidal particles within a flow cell. Once the particles are positioned, fixation is accomplished by pumping an electrolyte solution or pH adjusted solution (or a combination of the two) into the sample cell. In the former, the Debye length is reduced and aggregation caused by the van der Waals attraction takes place. In the latter, the surface charge density of the suspension is reduced and aggregation caused by the van der Waals attraction takes place. This technique can be applied multiple times, and allows for the formation of two and three dimensional structures composed of multi-colloid types to be formed on or away from a substrate. The technique relies upon forces acting on virtually all colloidal dispersions making it applicable to a wide variety of colloid types and compositions, such as formation of photonic crystals, colloidal electronics, and bioengineered materials.
Owner:ARRYX INC
Plasma density measuring equipment of high temperature resistant embedded double-probe type
ActiveCN102508002AWithout destroying the aerodynamic shapeNot easily oxidizedCurrent/voltage measurementIridiumMeasurement device
The invention relates to a plasma density measuring equipment of high temperature resistant embedded double-probe type, which is used for measuring plasmas with a density of 108 to 1011 centimeters <-3> around an aircraft during reentry flying and mainly consists of two iridium electrode probes, two probe electrode protection rings, a boron nitride insulating base, two electrode connection wires and a detection circuit, wherein metal iridium is used as the an electrode of the embedded double probes and boron nitride is used as an insulating electrode; the probe electrode protection rings are set to reduce edge effects and enhance measuring precision; the distances between the probe electrode protection rings and the iridium electrode probes are less than or equal to the Debye length. The measuring equipment disclosed by the invention can be mounted on the surface of a reentry aircraft directly for real-time measuring the density of the plasmas in a boarder layer continuously; the probes are oxidation resisting; the aerodynamic shape of the aircraft cannot be affected, so that the density measuring equipment is capable of measuring continuously for a long time, small in volume and high in precision.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF TELEMETRY
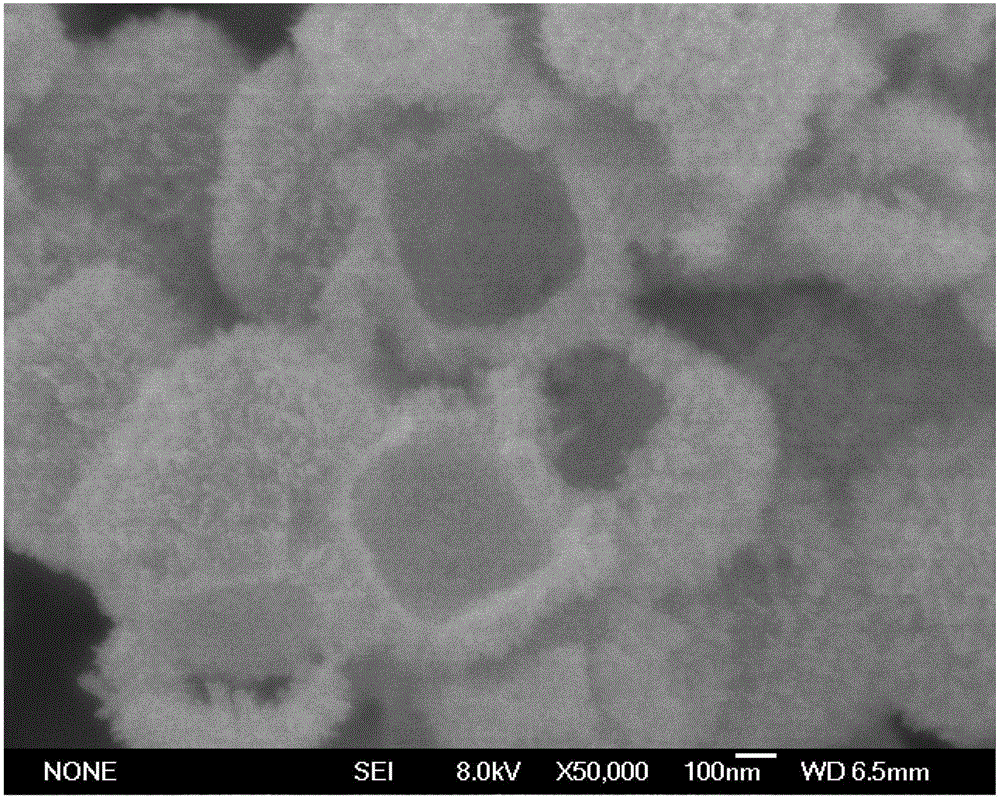
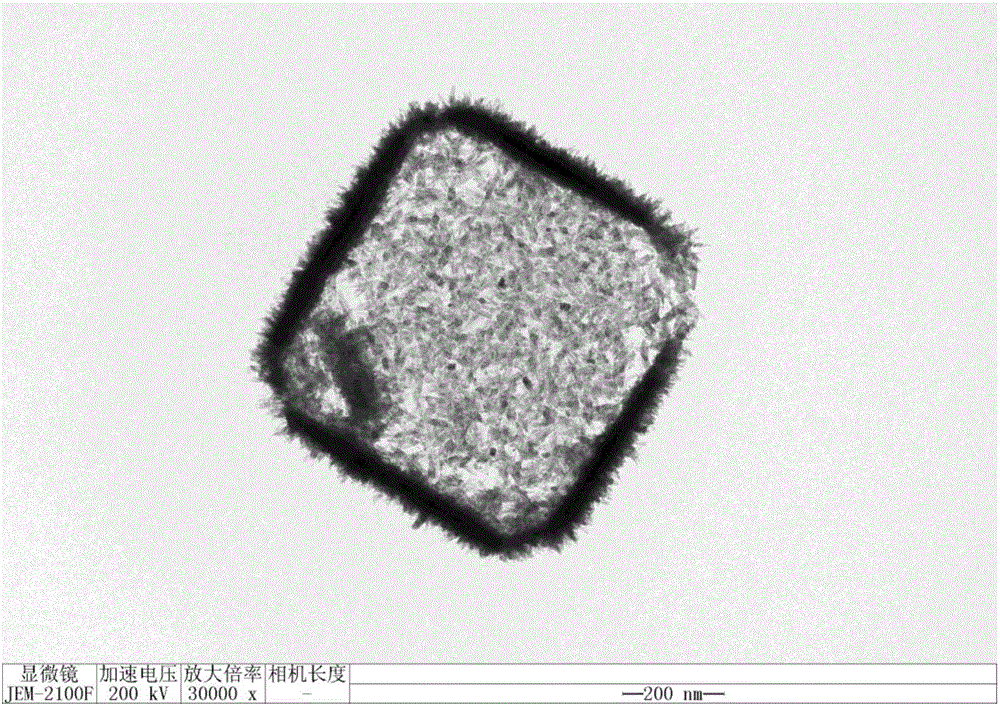
Preparation method for hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle
InactiveCN106629824AExcellent synthetic structureNot easy to reuniteTin oxidesTin dioxideMaterials preparation
The invention relates to a preparation method for a hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle composed of ultrafine nano-rods and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: taking solid cubic zinc hydroxystannate as a precursor, covering a layer of stannic oxide nano-rods on the surface of the zinc hydroxystannate after the hydrothermal reaction for a period of time, and meanwhile, decomposing the inner zinc hydroxystannate, thereby acquiring the hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle composed of the ultrafine nano-rods in the shape similar to the shape of zinc hydroxystannate. Compared with the traditional template method, the preparation method has the advantages of low cost, few steps and simple operation; the prepared hollow stannic oxide nanometer particle has an obvious hierarchical structure and a mesoporous structure, is difficult to agglomerate, is excellent in crystallinity and is high in specific surface area; the hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle is composed of a large quantity of orderly arrayed nano-rods and the size of the nano-rods is close to the debye length; the air-sensitive characteristic is excellent; and the hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle has a potential application value in the field of air-sensitive sensors.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Techniques and systems for continuous-flow plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD)
ActiveUS9972501B1High quality/uniformityFast cycle-timesElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingDebye length
Techniques are disclosed for methods and apparatuses for performing continuous-flow plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD). Plasma gas, containing one or more component gases, is continuously flowed to a planar inductive coupled plasma source attached at an upper end of a cylindrical chamber. Plasma is separated from the ALD volume surrounding a wafer / substrate in the lower end of the chamber by a combination of a grounded metal plate and a ceramic plate. Each plate has a number of mutually aligned holes. The ceramic plate has holes with a diameter less than 2 Debye lengths and has a large aspect ratio. This prevents damaging plasma flux from entering the ALD volume into which a gaseous metal precursor is also pulsed. The self-limiting ALD reaction involving the heated substrate, the excited neutrals from the plasma gas, and the metal precursor produce an ultra-uniform, high quality film on the wafer. A batch configuration to simultaneously coat multiple wafers is also disclosed.
Owner:NANO MASTER INC
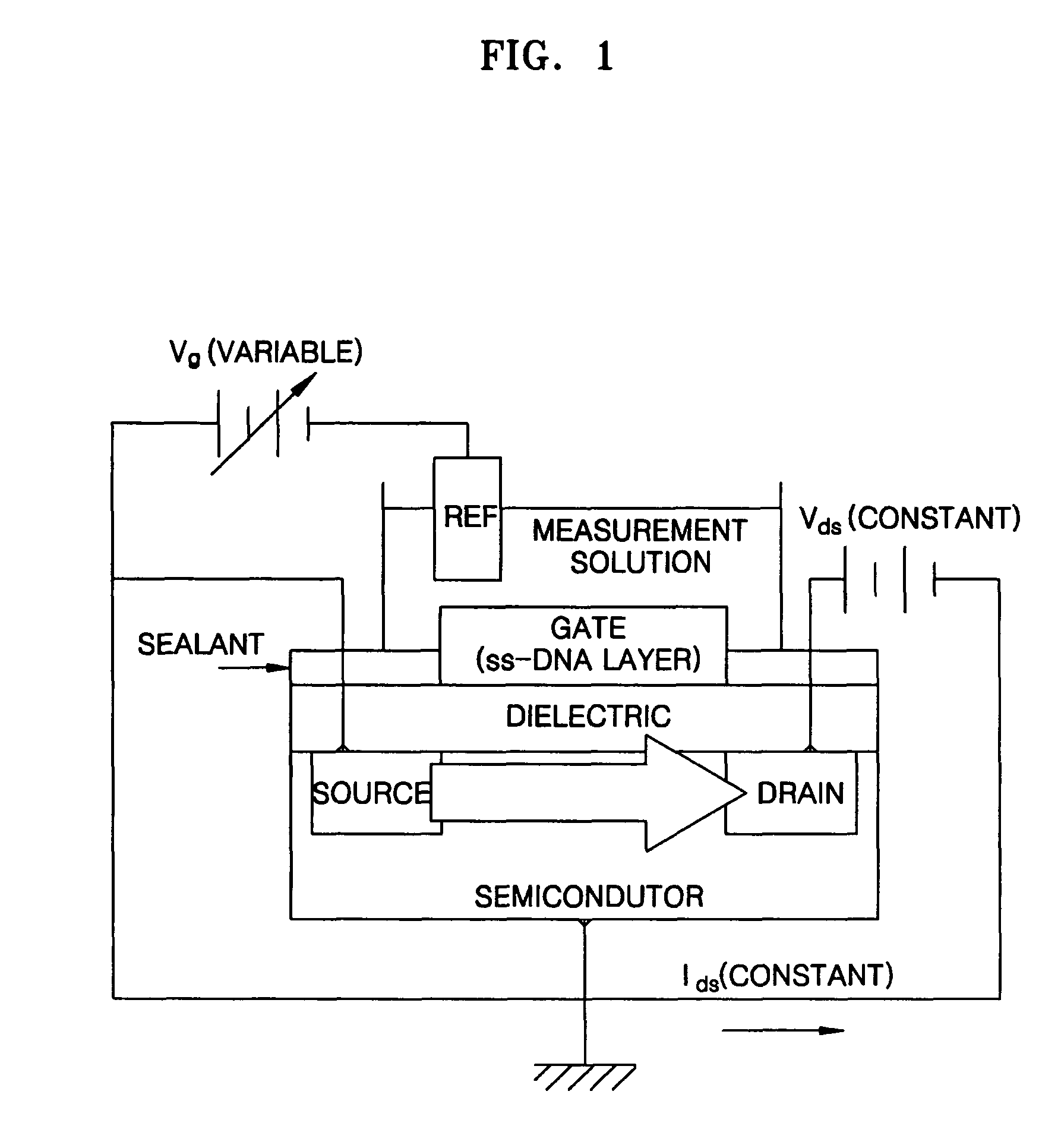
Biomolecule sensing method using Field Effect Transistor with controllable Debye length
InactiveUS20050191683A1Accurate inductionControl lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDebye lengthElectrolyte
A method of sensing biomolecules in an electrolyte solution by using a bio FET. When it is sensed that probe biomolecules are immobilized to a gate surface of the bio FET or that the probe biomolecules are hybridized with target biomolecules, a Debye length from the biomolecules having charges attached to the gate surface is controlled.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
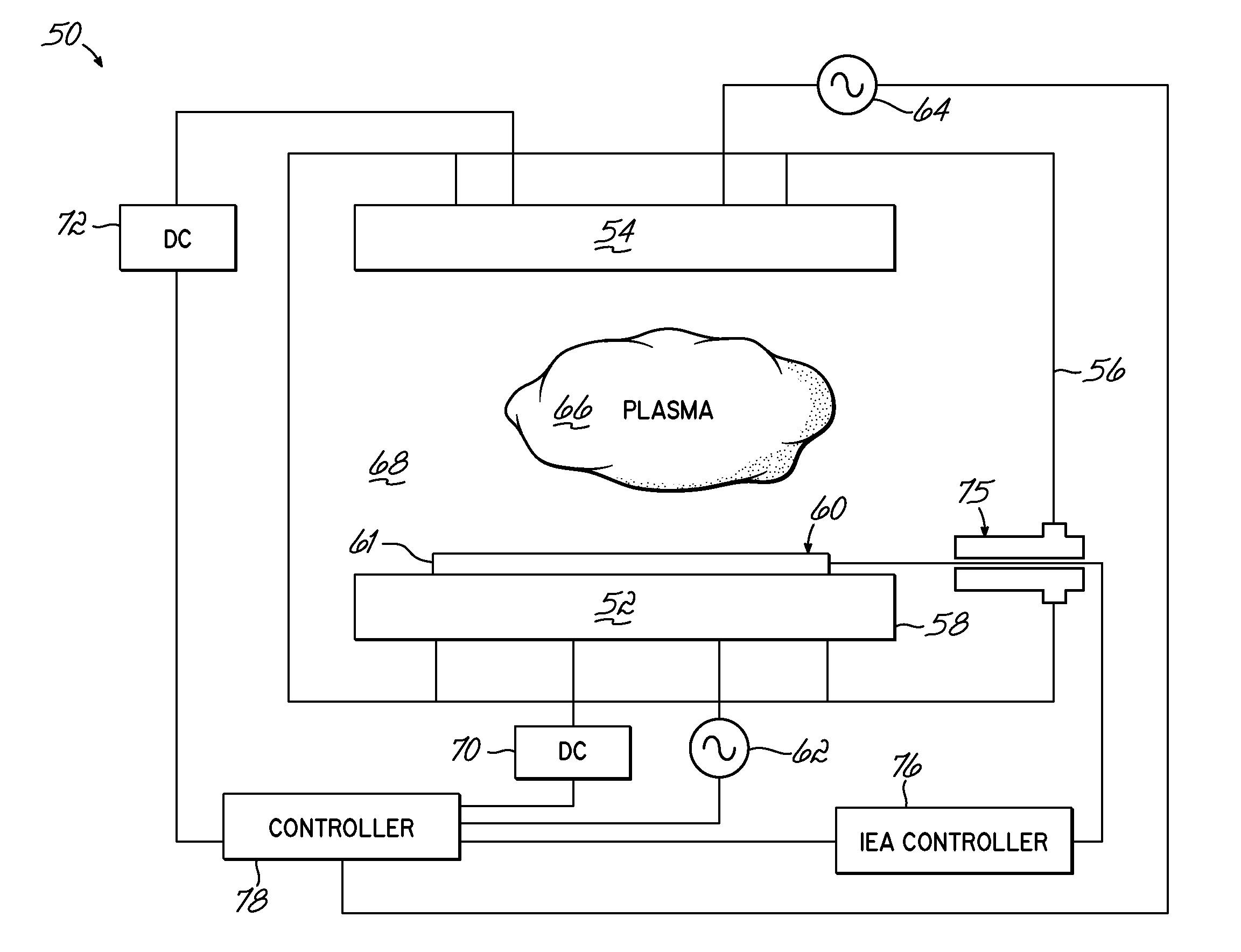
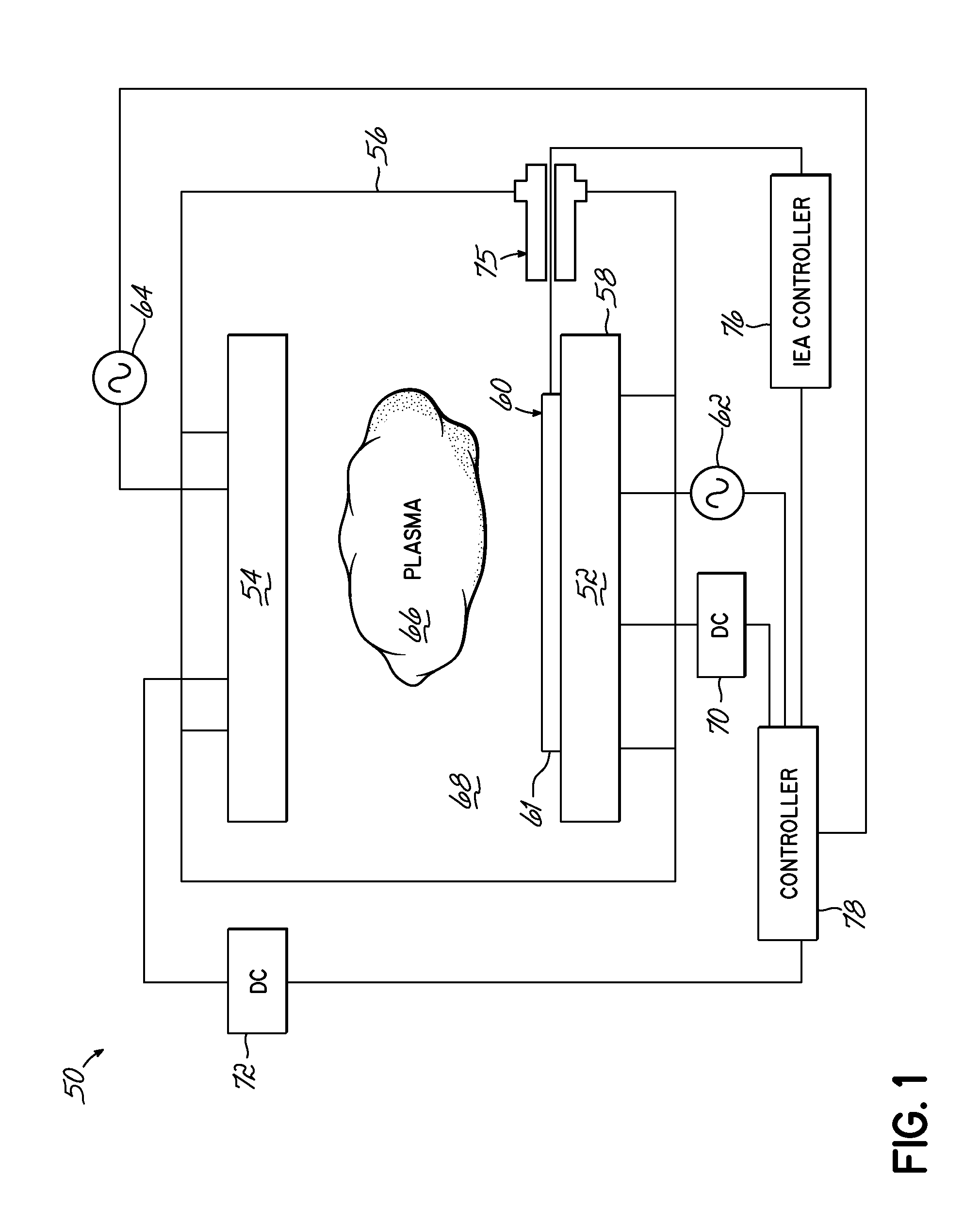
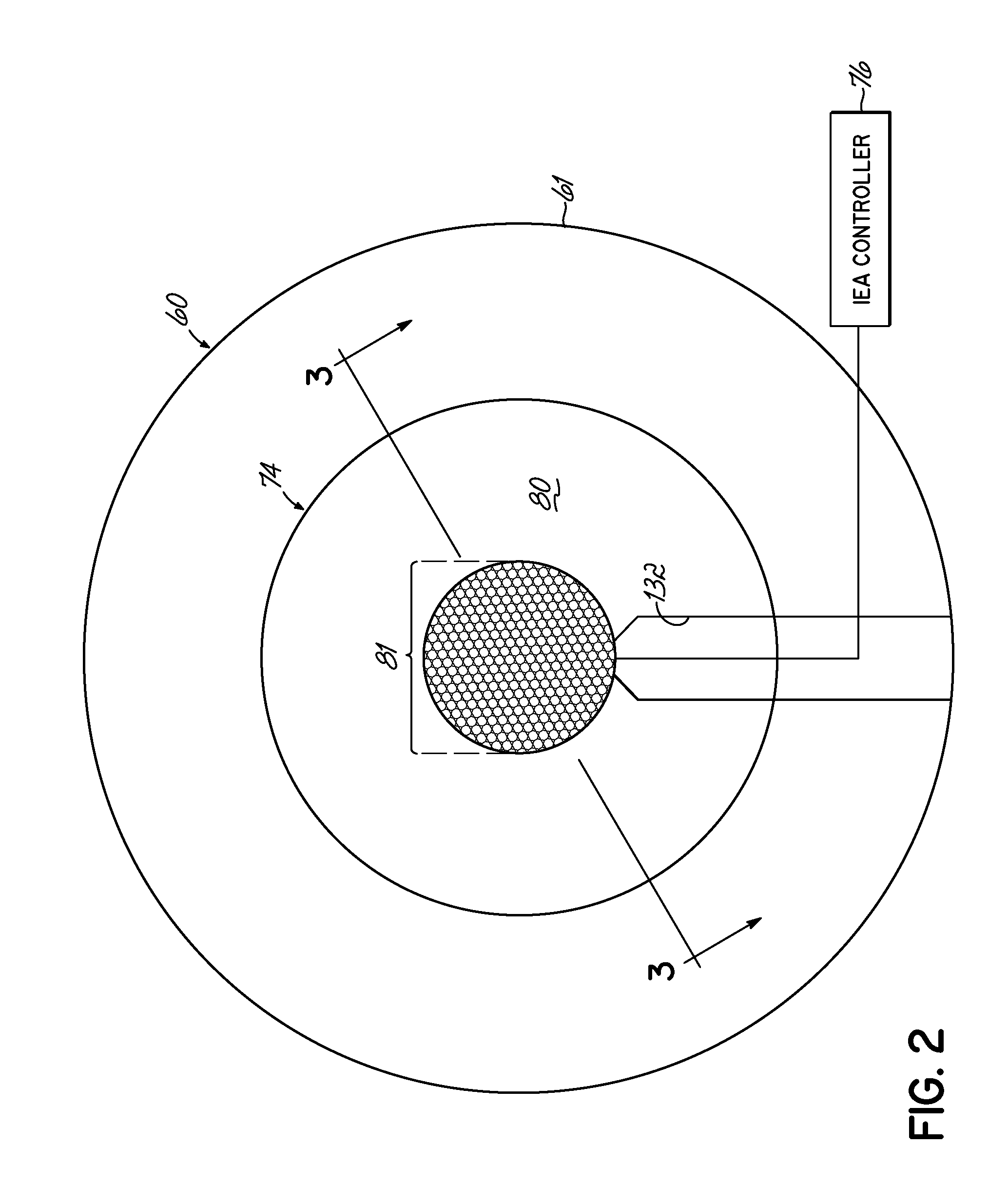
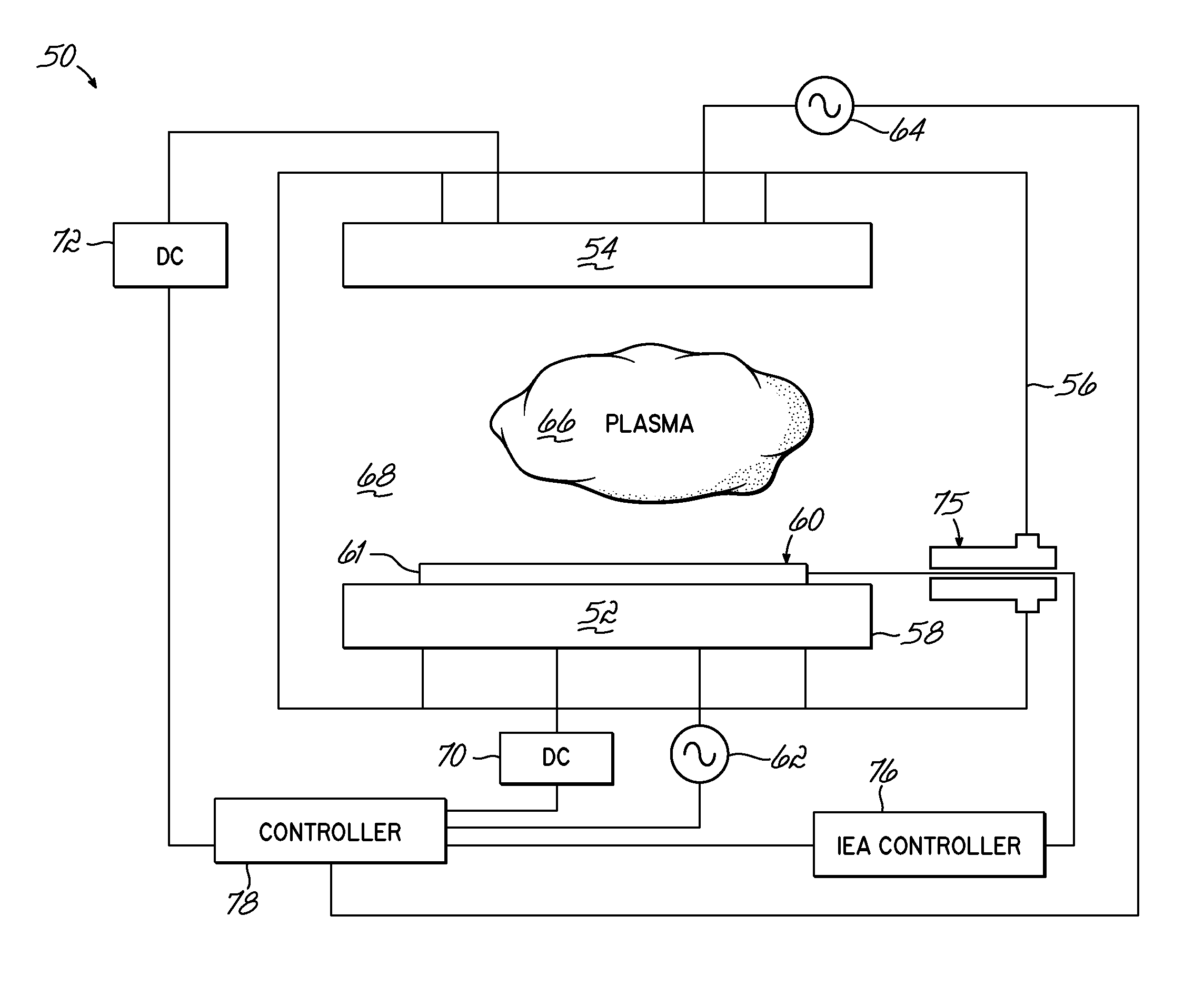
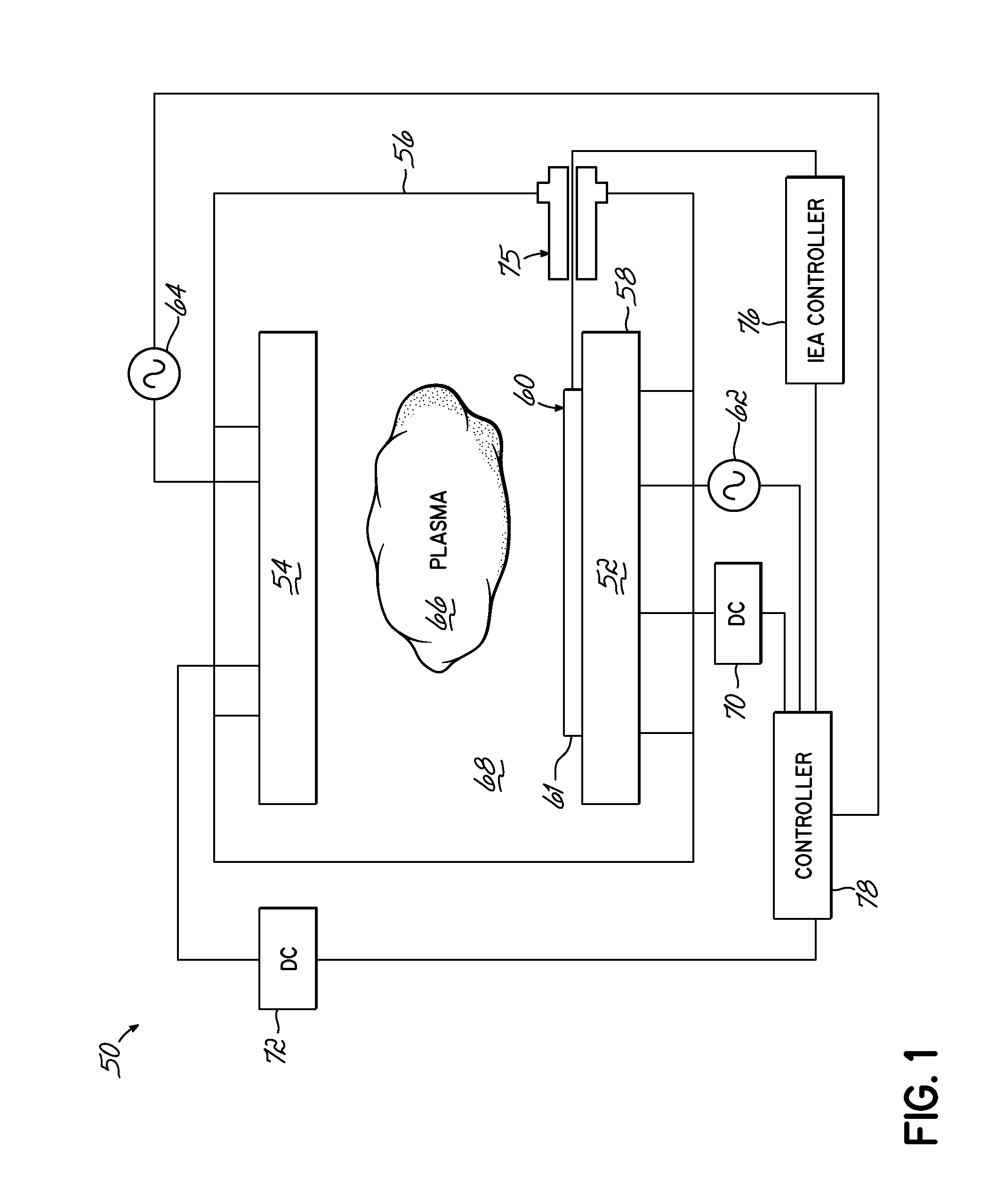
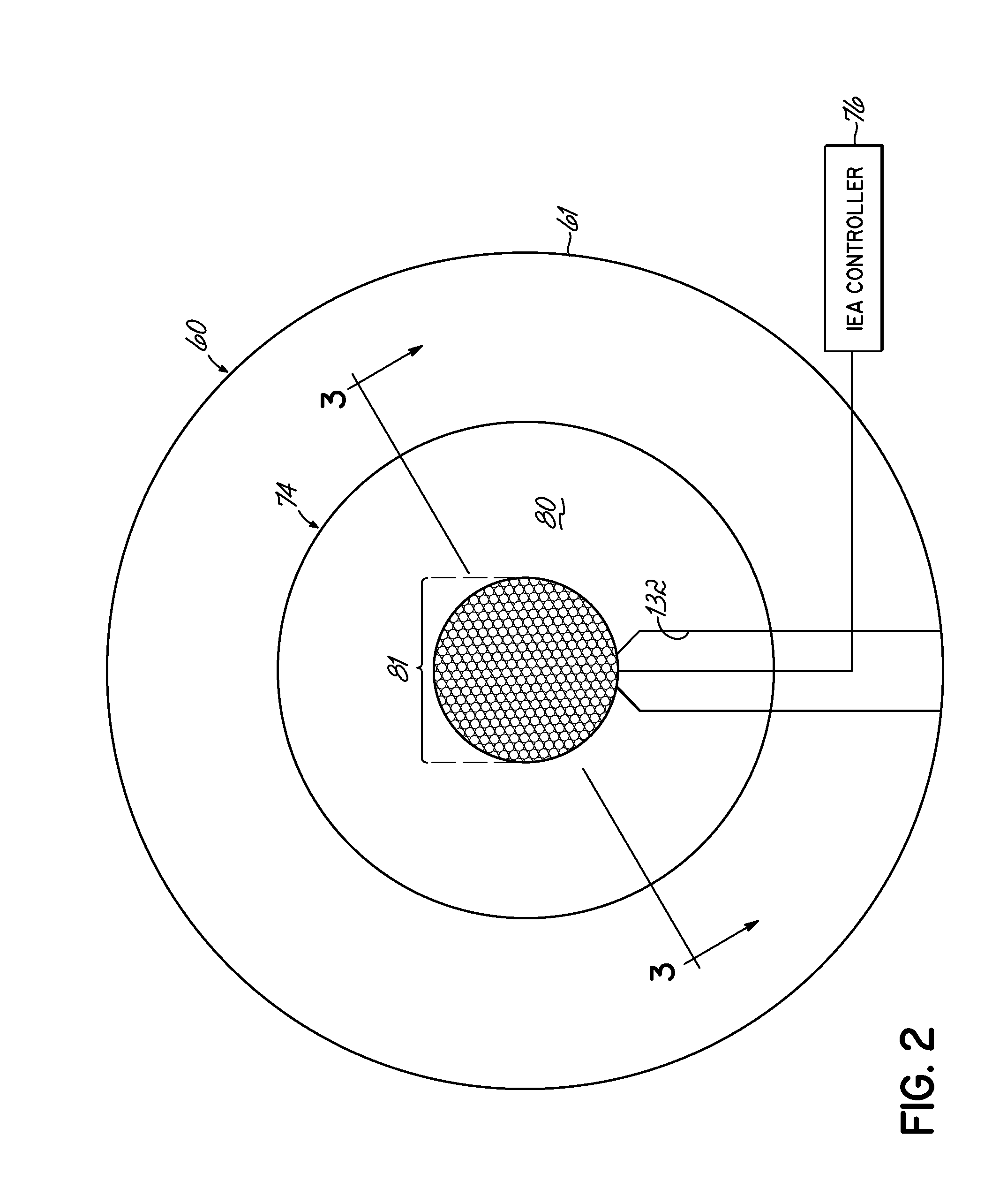
Methods of electrical signaling in an ion energy analyzer
ActiveUS20120248322A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityIon current
A method of generating a signal representing with an ion energy analyzer for use in determining an ion energy distribution of a plasma. The ion energy analyzer, used for determining an ion energy distribution of a plasma, includes a first grid and a second grid that is spaced away from and electrically isolated from the first grid. The first grid forms a first surface of the ion energy analyzer and is positioned to be exposed to the plasma. The first grid includes a first plurality of openings, which are dimensioned to be less than a Debye length for the plasma. A voltage source and an ion current meter are operably coupled to the second grid, the latter of which is configured to measure an ion flux onto the ion collector and to transmit a signal that represents the measured ion flux. The method includes selectively and variably biasing the second grid relative to the first grid.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Ion energy analyzer
An ion energy analyzer for determining an ion energy distribution of a plasma and comprising an entrance grid, a selection grid, and an ion collector. The entrance grid includes a first plurality of openings dimensioned to be less than a Debye length for the plasma. The ion collector is coupled to the entrance grid via a first voltage source. The selection grid is positioned between the entrance grid and the ion collector and is coupled to the entrance grid via a second voltage source. An ion current meter is coupled to the ion collector to measure an ion flux onto the ion collector and transmit a signal related thereto.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Biosensors including surface resonance spectroscopy and semiconductor devices
InactiveUS9714952B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityResonance
A sensor including a surface plasmon resonance detector with a reservoir for containing a liquid sample. The sensor further includes a sensing metallic film positioned within the reservoir so that at least a majority of a surface of the sensing metallic film is to be in contact with the liquid sample being housed within the reservoir. The sensory also includes a semiconductor device having a contact in electrical communication with the sensing metal containing film that is positioned within the reservoir. The semiconductor device measures the net charges of molecules within the liquid sample within a Debye length from the sensing metallic film.
Owner:IBM CORP
FET-type biosensor with surface modification
InactiveUS8735077B2High sensitivitySimple structureMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementIonic strengthDebye length
Provided is a field effect transistor (FET) type biosensor including a source electrode, a gate, and a drain electrode. A ligand that can bind to a side of a nucleic acid is added to the surface of the gate. In a conventional FET type biosensor, it is difficult to detect a signal within the debye length because a target nucleic acid is directly fixed to the surface of a gate of the conventional FET. However, in the present invention, this problem can be overcome and the debye length can be increased by treating the surface of a gate of an FET sensor with a ligand that can bind to a side of a nucleic acid. The ligand can be adsorbed onto the surface of the gate. In this case, the nucleic acid is adsorbed parallel to the surface of the gate, not perpendicular to the surface of the gate, thus generating an effective depletion region. In addition, hybridization efficiency can be increased because a hybridized sample can be injected into an FET sensor at high ionic strength.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Biosensors including surface resonance spectroscopy and semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20170227556A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityResonance
A sensor including a surface plasmon resonance detector with a reservoir for containing a liquid sample. The sensor further includes a sensing metallic film positioned within the reservoir so that at least a majority of a surface of the sensing metallic film is to be in contact with the liquid sample being housed within the reservoir. The sensory also includes a semiconductor device having a contact in electrical communication with the sensing metal containing film that is positioned within the reservoir. The semiconductor device measures the net charges of molecules within the liquid sample within a Debye length from the sensing metallic film.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Techniques and systems for continuous-flow plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD)
ActiveUS20180269066A1High quality/uniformityLow costElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingDebye length
Techniques are disclosed for methods and apparatuses for performing continuous-flow plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD). Plasma gas, containing one or more component gases, is continuously flowed to a planar inductive coupled plasma source attached at an upper end of a cylindrical chamber. Plasma is separated from the ALD volume surrounding a wafer / substrate in the lower end of the chamber by a combination of a grounded metal plate and a ceramic plate. Each plate has a number of mutually aligned holes. The ceramic plate has holes with a diameter less than 2 Debye lengths and has a large aspect ratio. This prevents damaging plasma flux from entering the ALD volume into which a gaseous metal precursor is also pulsed. The self-limiting ALD reaction involving the heated substrate, the excited neutrals from the plasma gas, and the metal precursor produce an ultra-uniform, high quality film on the wafer. A batch configuration to simultaneously coat multiple wafers is also disclosed.
Owner:NANO MASTER INC
CMOS-compatible silicon nano-wire sensors with biochemical and cellular interfaces
ActiveUS9076665B2Increase the areaHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsSemiconductor materialsConducting pathway
The systems and methods described herein include a sensor for suitable for sensing chemical and biological substances. The sensor comprises a semiconductor layer formed in or on a substrate and a channel having nano-scale dimensions formed in the semiconductor layer, where the structure creates an electrically conducting pathway between a first contact and a second contact on the semiconductor layer. In certain preferred embodiments, the nano-scale channel has a trapezoidal cross-section with an effective width and exposed lateral faces, where the effective width is selected to have same order of magnitude as a Debye length (LD) of the semiconductor material of which the semiconductor layer is formed.
Owner:YALE UNIV
System and method for presenting large DNA molecules for analysis
ActiveCN105934276AHeating or cooling apparatusMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIonic strengthContour length
Systems and methods for presenting nucleic acid molecules for analysis are provided. The nucleic acid molecules have a central portion that is contained within a nanoslit. The nanoslit contains an ionic buffer. The nucleic acid molecule has a contour length that is greater than a nanoslit length of the nanoslit. An ionic strength of the ionic buffer and electrostatic or hydrodynamic properties of the nanoslit and the nucleic acid molecule combining to provide a summed Debye length that is greater than or equal to the smallest physical dimension of the nanoslit.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +2
Techniques and systems for continuous-flow plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD)
ActiveUS20180269067A1High quality/uniformityLow costElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingDebye length
Owner:NANO MASTER INC
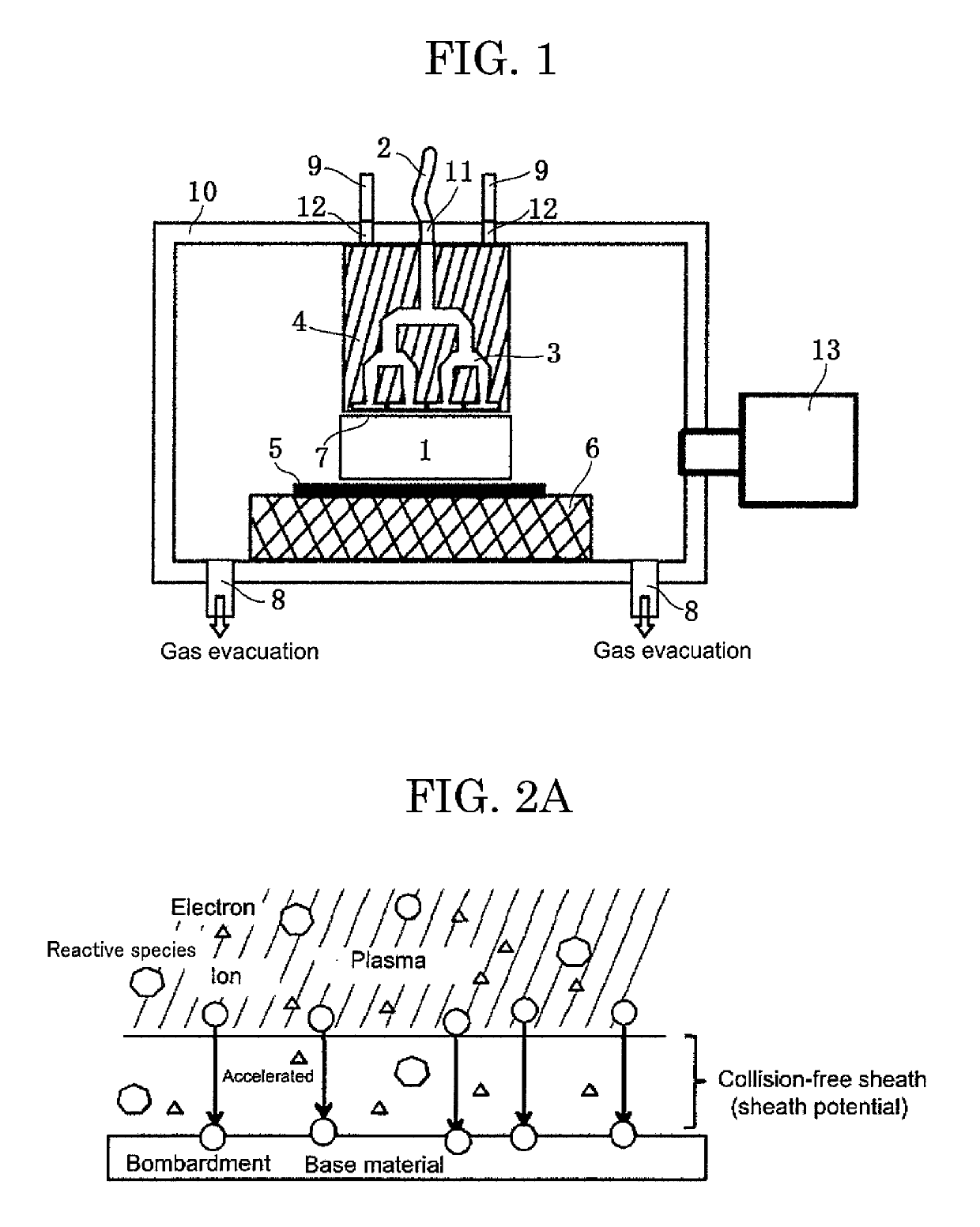
Plasma doping apparatus
InactiveUS20090266298A1Reduce defective rateImprove throughputLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesDebye lengthElectron bunches
On an upper wall of a vacuum container opposing a sample electrode, a plasma-invasion prevention-and-electron beam introducing hole is installed which is communicated with an electron beam introducing tube, and is used for introducing an electron beam toward a substrate in the vacuum container, as well as for preventing invasion of plasma into the electron beam introducing tube. In this structure, supposing that the Debye length of the plasma is set to λd and that a thickness of the sheath is set to Sd, the electron beam introducing hole has a diameter D satisfying a following equation: D≦2λd+2Sd.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
DNA sensor and detection method based on graphene Hall effect
InactiveCN109211993AQuick checkImprove detection limitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSurface roughnessDebye length
The invention relates to a DNA sensor and detection method based on graphene Hall effect. Specifically, the invention discloses a DNA sensor which comprises an insulating substrate and a graphene filmfixed on the insulating substrate. The graphene film has the characteristics that 1)the surface roughness of the graphene film is less than 1.5 nm; 2)the sheet resistance of the graphene film is lessthan 1000 ohm / sq; 3)The mobility of the graphene film is greater than 2000 cm 2 / V.s. The invention further discloses a detection method for DNA based on the sensor, which can realize no labeling, rapid detection and detection limit as high as 10-12M and is not affected by Debye length.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and apparatus for non-aggressive plasma-enhanced vapor deposition of dielectric films
InactiveUS20060189165A1Reduce trafficConserving flowElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDebye lengthMolecular physics
While performing plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition on a substrate by exposing the substrate in a vacuum to a flow of particles generated by a plasma, which particles react to form a passivation layer on the substrate, a grid is interposed between the plasma and the substrate, thereby reducing the flow of charged particles towards the substrate while conserving a flow of neutral particles. The grid is formed of metal wires that are crossed at a pitch that is less than two or three times the Debye length (λD) of the plasma used, at least at the beginning of deposition. The aging properties of semiconductor components made by such a method is thereby improved.
Owner:TEGAL CORP
Method for adjusting sensitivity of FET (Field Effect Transistor) biosensor
PendingCN114646674ASensitivity adjustableHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAptamerDebye length
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a method for adjusting the sensitivity of an FET biosensor. The method is specifically realized by adjusting the Debye length to enable the Debye length to be matched with the height of the nucleic acid aptamer. The inventor further deduces through a dielectric constant formula and a Debye length formula that the thickness of the passivation layer and / or the ionic strength of the solution during detection can be changed, so that the adjustment of the Debye length can be realized; finally, the conclusion is verified through a series of specific experimental cases and theoretical calculation of the influence of the effective charge quantity brought by the conformation change of the nucleic acid aptamer near the Debye length on the sensitivity of the nucleic acid aptamer-FET biosensor. The adjusting method provided by the invention is simple to operate and easy to implement.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Semiconductor device
ActiveCN106229340ADelay agingAvoid exhaustionSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsDebye length
In order to reduce the ageing and degeneration of the characteristics of a semiconductor device under high reverse bias and high temperature conditions, a polymer, such as polyimide, is taken as a passivation layer of the semiconductor device. According to the invention, the polymer material and the semiconductor device nanometer grain with distribution grain size of 4-8 debye length are mixed at a volume ratio of 15%-40% and are poured and formed into the passivation layer.
Owner:SICHUAN HONGXINWEI TECH
A kind of preparation method of hierarchical hollow cubic tin dioxide nanoparticles
InactiveCN106629824BExcellent synthetic structureNot easy to reuniteTin oxidesTin dioxideMaterials preparation
The invention relates to a preparation method for a hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle composed of ultrafine nano-rods and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: taking solid cubic zinc hydroxystannate as a precursor, covering a layer of stannic oxide nano-rods on the surface of the zinc hydroxystannate after the hydrothermal reaction for a period of time, and meanwhile, decomposing the inner zinc hydroxystannate, thereby acquiring the hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle composed of the ultrafine nano-rods in the shape similar to the shape of zinc hydroxystannate. Compared with the traditional template method, the preparation method has the advantages of low cost, few steps and simple operation; the prepared hollow stannic oxide nanometer particle has an obvious hierarchical structure and a mesoporous structure, is difficult to agglomerate, is excellent in crystallinity and is high in specific surface area; the hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle is composed of a large quantity of orderly arrayed nano-rods and the size of the nano-rods is close to the debye length; the air-sensitive characteristic is excellent; and the hierarchical hollow cubic stannic oxide nanometer particle has a potential application value in the field of air-sensitive sensors.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Plasma generating device
PendingCN114156157ALow costRapidly reaches the ionization energy thresholdElectric discharge tubesDischarge efficiencyPlasma generator
The invention relates to a plasma generation device, which relates to the technical field of plasmas and comprises a first grid electrode, a second grid electrode and a magnetic field generation component, the first grid electrode and the second grid electrode are arranged in parallel, and a first distance is arranged between the first grid electrode and the second grid electrode; the first distance is a distance of Debye length magnitude; the first grid is connected with the power supply assembly; the magnetic field generating component is used for generating a magnetic field parallel to the first grid; during working, the power supply assembly applies radio frequency voltage to the first grid electrode, so that a first alternating electric field is generated between the first grid electrode and the second grid electrode, electrons in the first alternating electric field enter the magnetic field after resonance acceleration, and then rotate back to the first alternating electric field in the magnetic field to continue resonance acceleration so as to generate plasma; the period of the first alternating electric field is the same as that of the magnetic field. The plasma generator is high in discharge efficiency under low air pressure, and can generate plasmas with good radial uniformity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
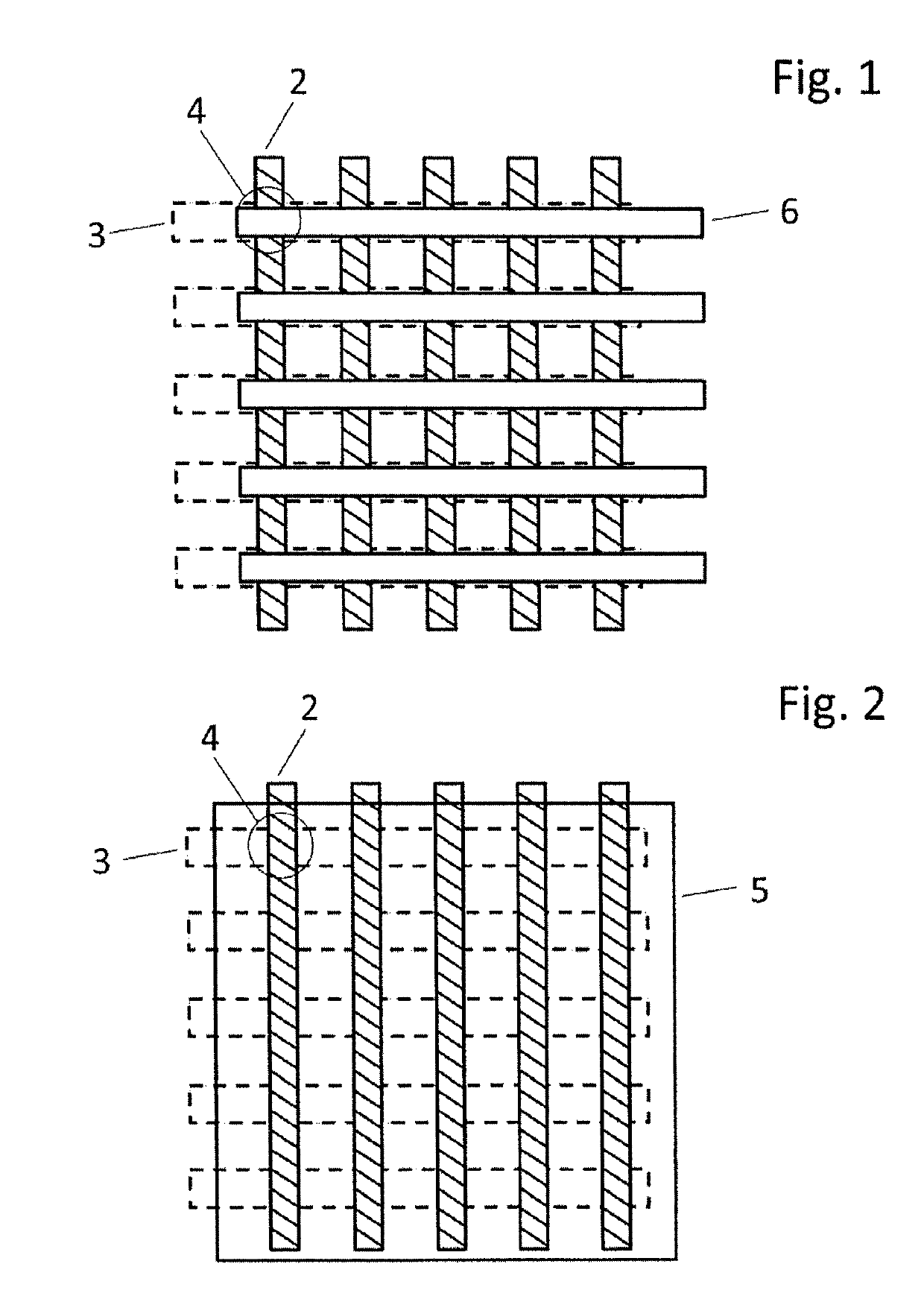
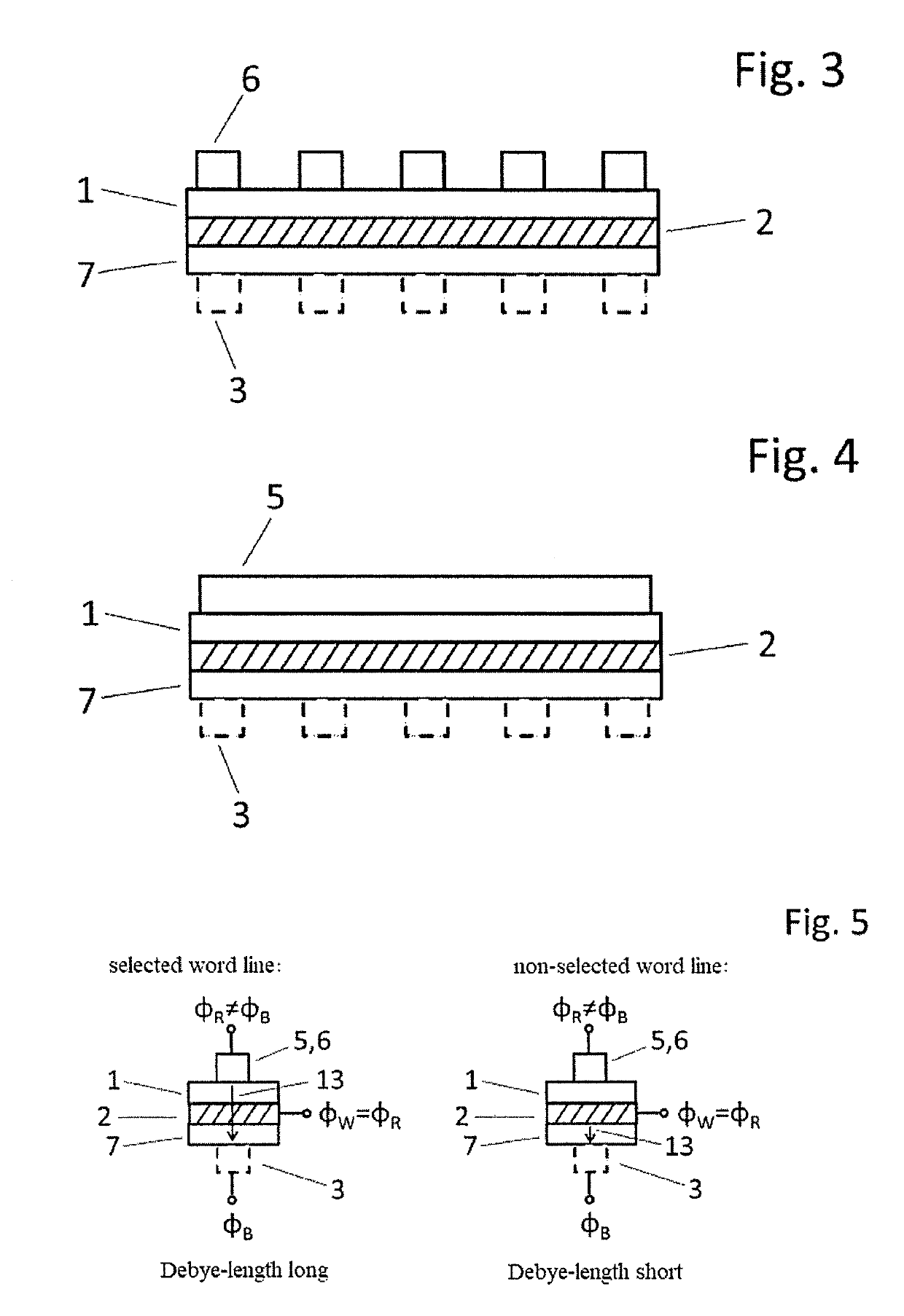
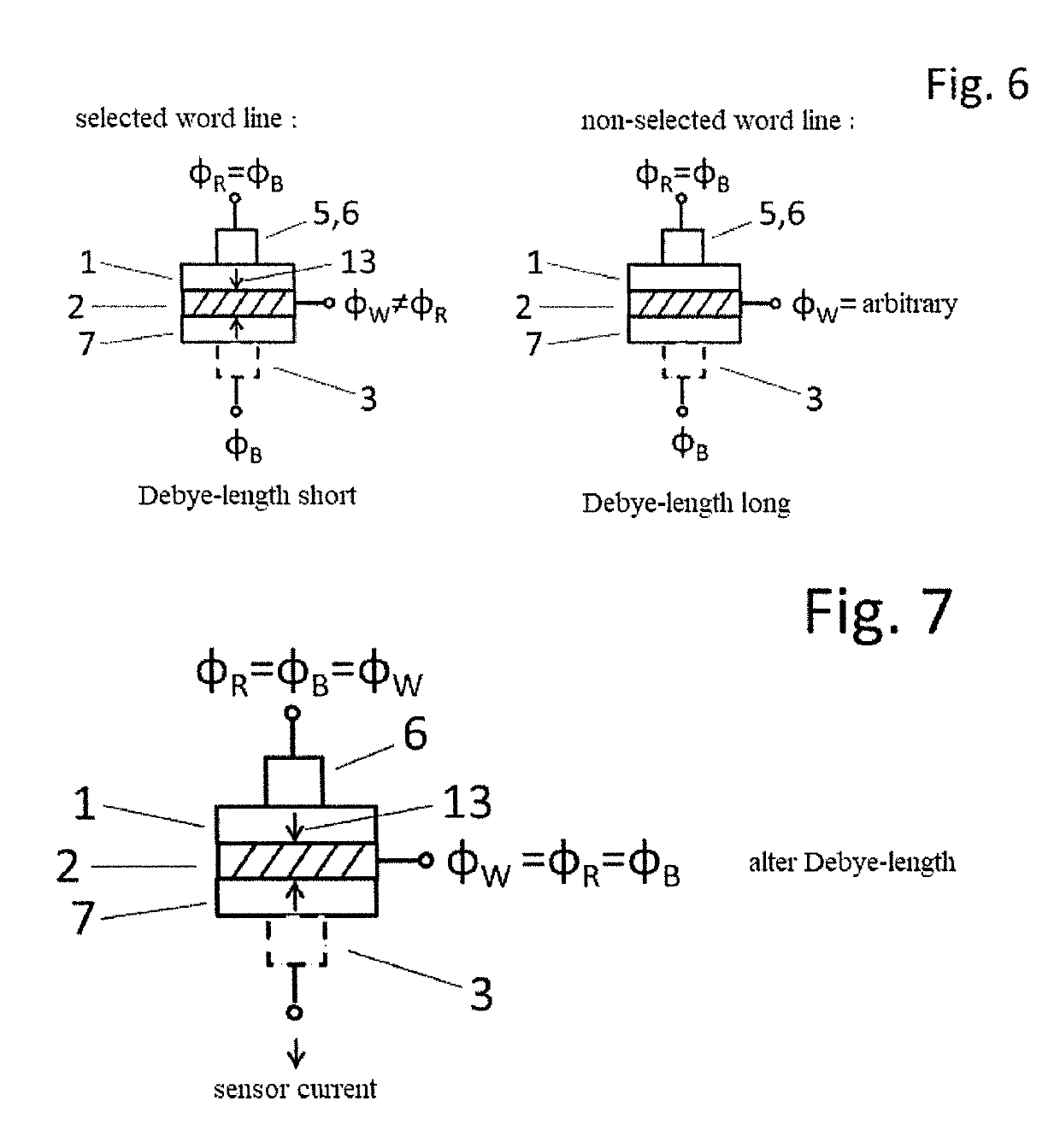
Capacitive matrix arrangement and method for actuation thereof
ActiveUS10504575B2Fast accessReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDielectric
The invention relates to a capacitive matrix arrangement that comprises an active medium, which is arranged in a layer between word lines and bit lines whose crossing points have capacitor cells, selectable by actuation of the word lines and bit lines, arranged at them with the interposed active medium, and to an actuation method, wherein the invention is based on the object of combining active actuation of capacitive elements in a matrix with the advantages of passive actuation. This is achieved by virtue of the word lines having a specific variable Debye length, i.e. consisting of a material with a variable mobile charge carrier concentration, and being arranged between the active medium and a non-active dielectric. The actuation is effected by controlling the action of an electrical field.
Owner:SEMRON GMBH
Production Method and Production Device for Nitrogen Compound
InactiveUS20190153617A1Save power consumptionReduce weightPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge tubesMean free pathMicrowave
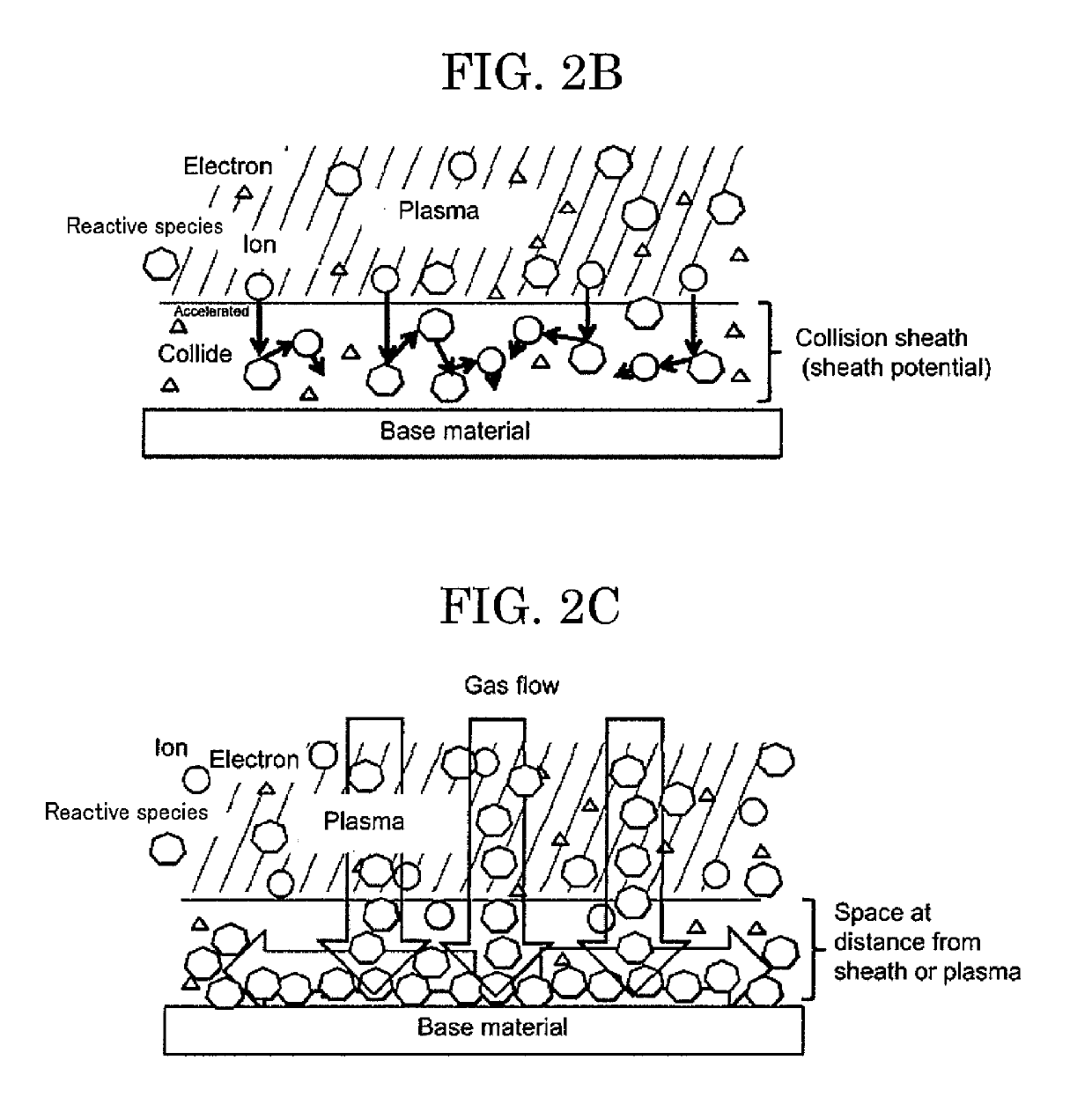
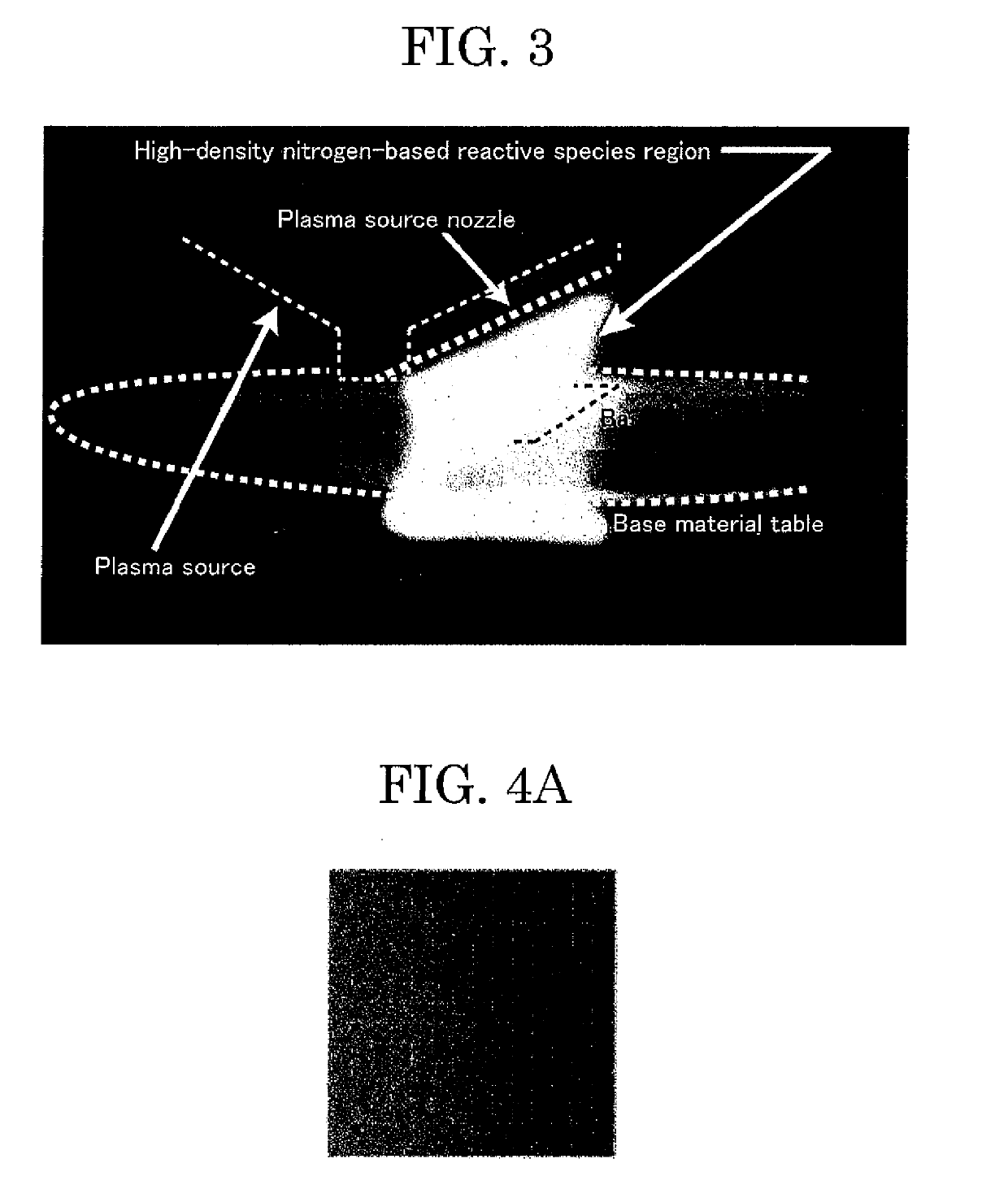
To provide a method and apparatus for production of a nitrogen compound film by a plasma, wherein the method and apparatus are suitable for area enlargement by a process at a higher pressure with lower power consumption, without applying a voltage to a base material, and without using a large chamber. In nitrogen compound production for producing a nitrogen compound by generating a microwave plasma, in a step of jetting a material gas containing a nitrogen-based gas onto a surface of a base material from a nozzle under flow rate control while applying a microwave to the material gas to thereby irradiate the surface of the base material with a plasma containing nitrogen-based reactive species generated from the material gas, the pressure is set higher than a pressure at which the mean free path of ions in the plasma is shorter than the Debye length.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com