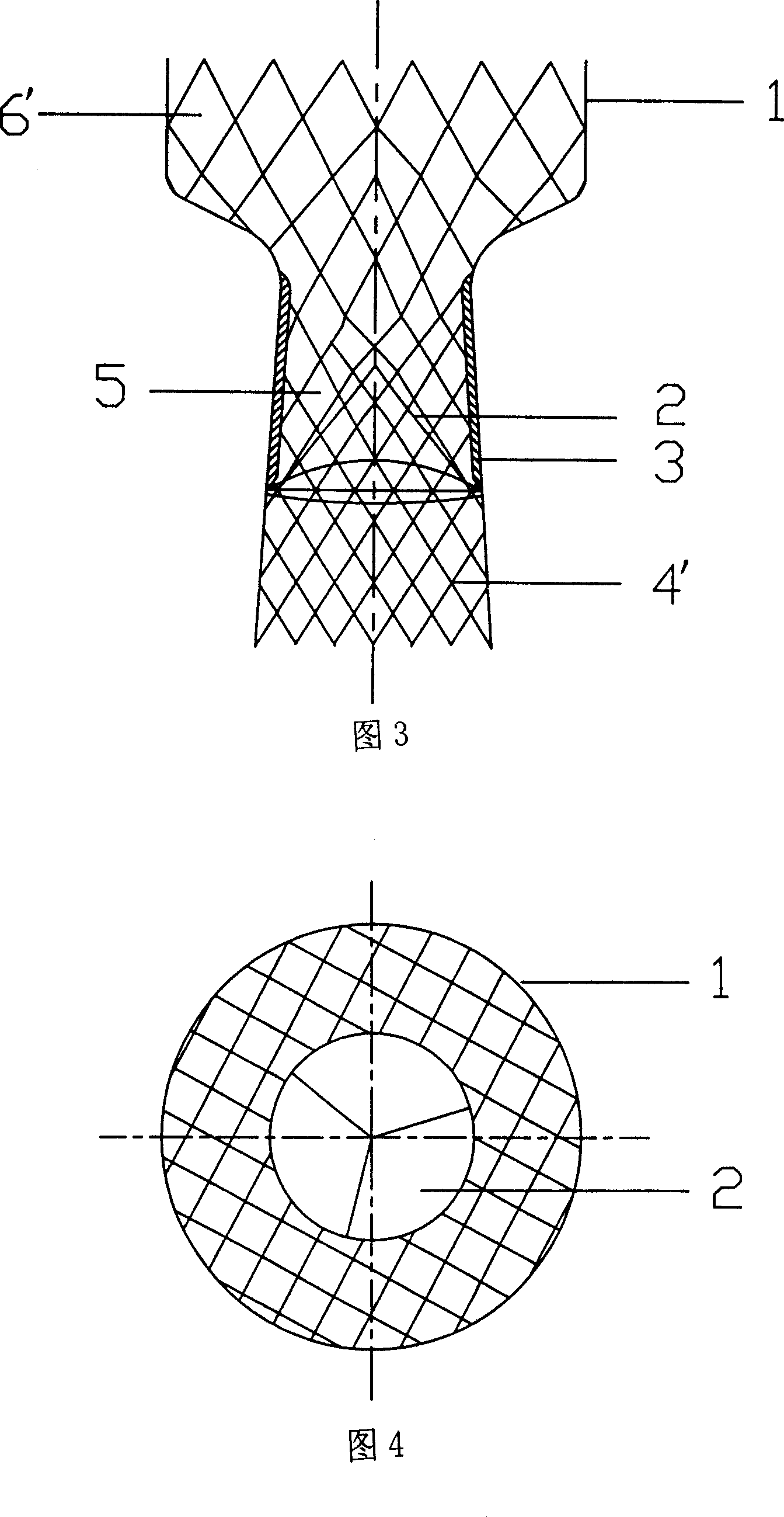
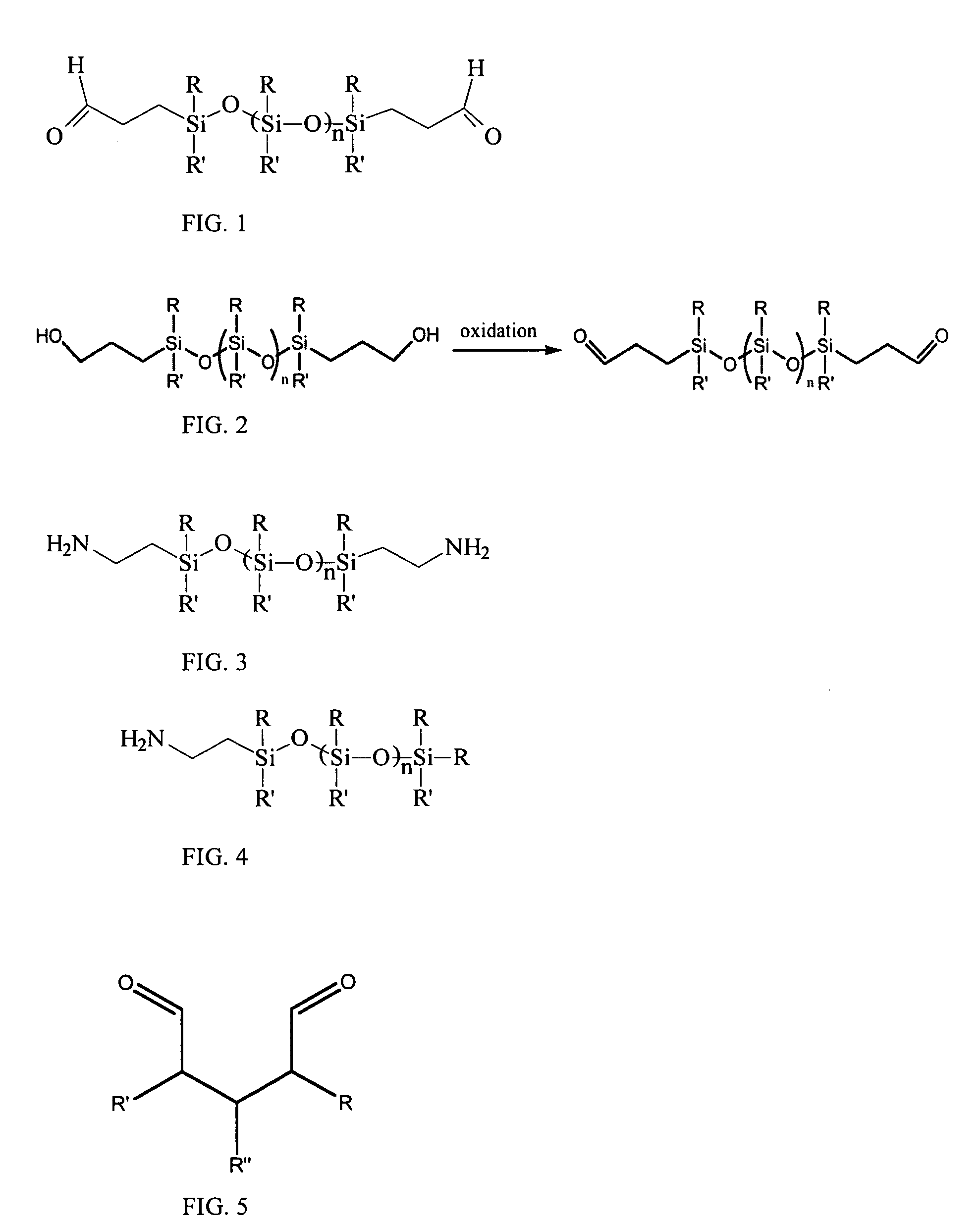
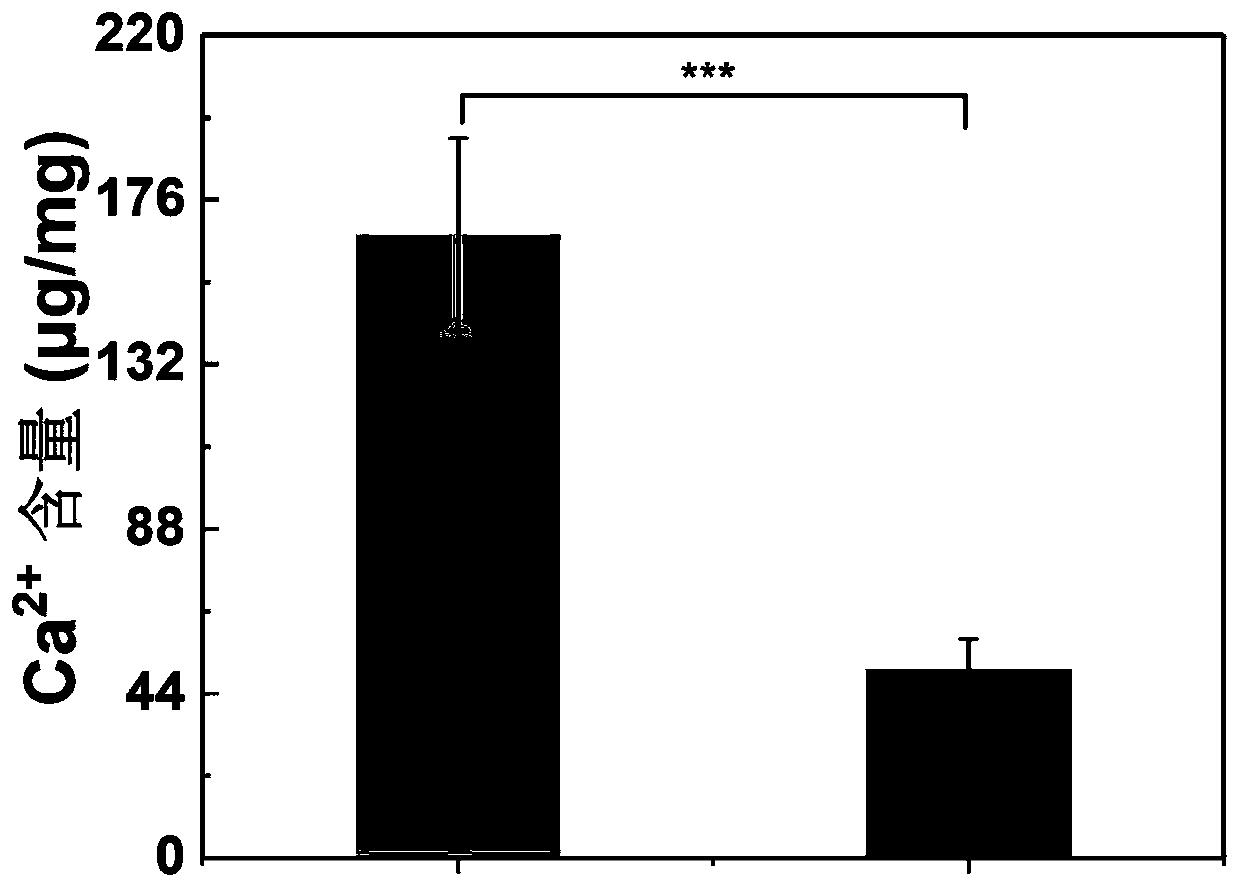
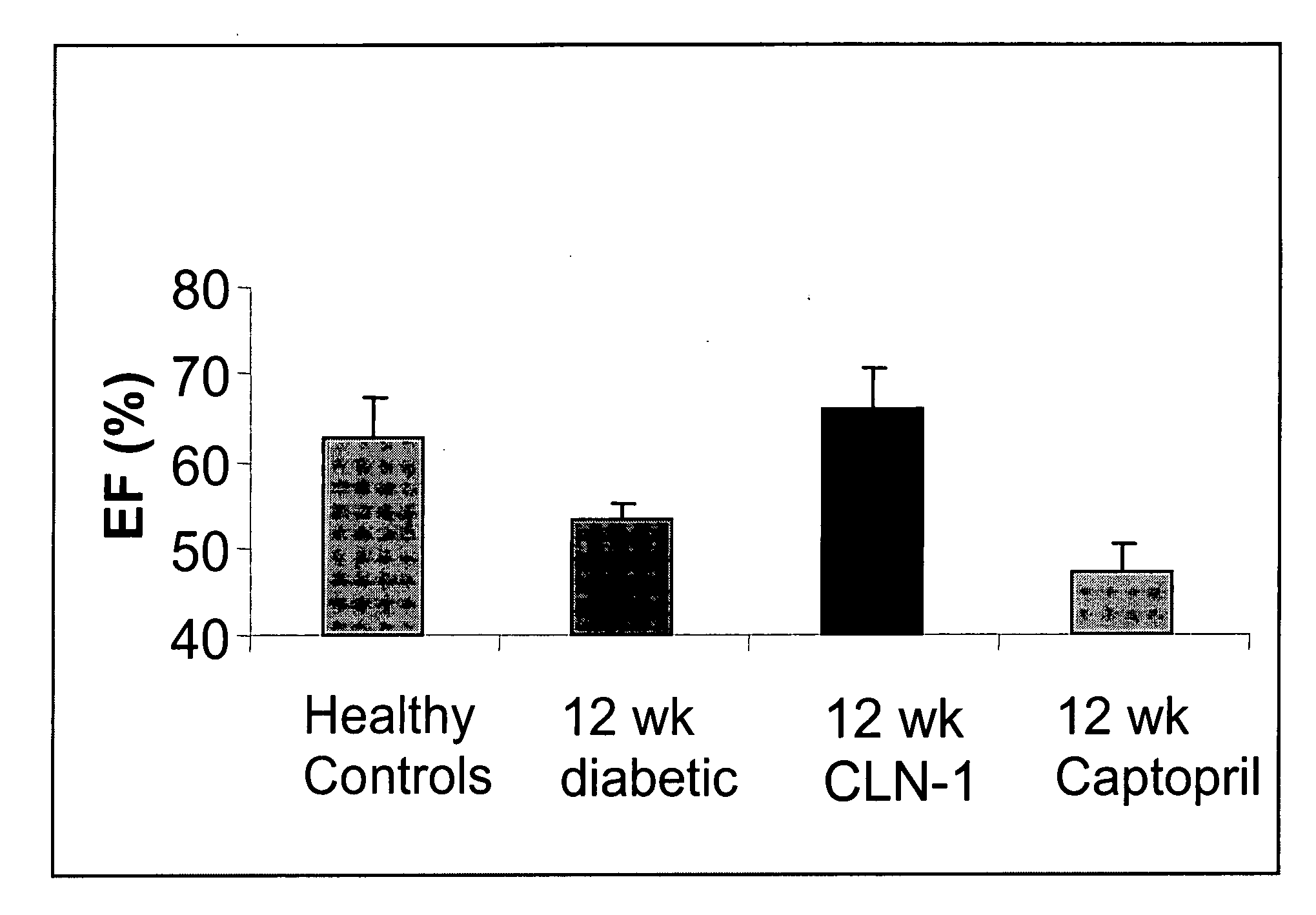
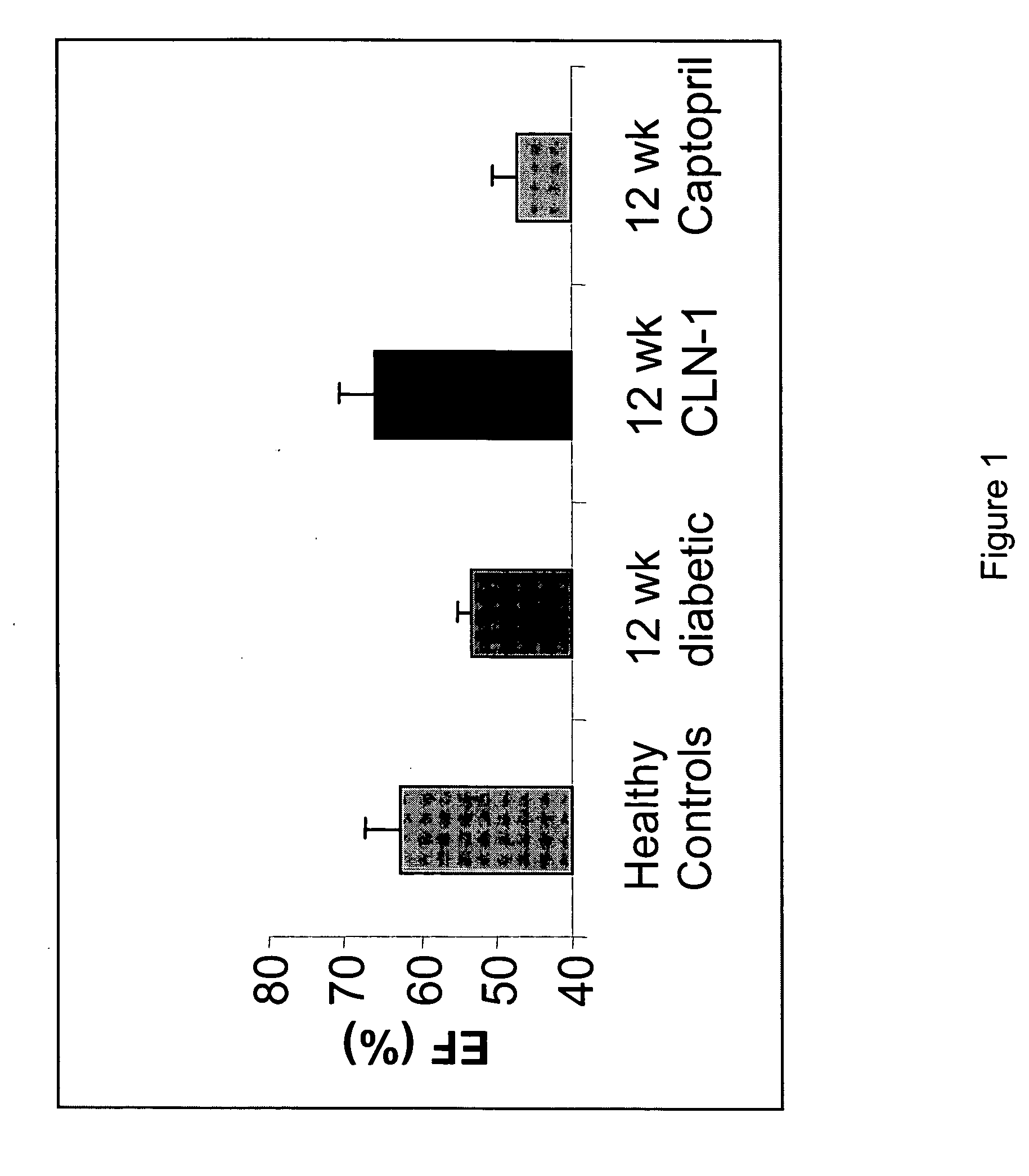
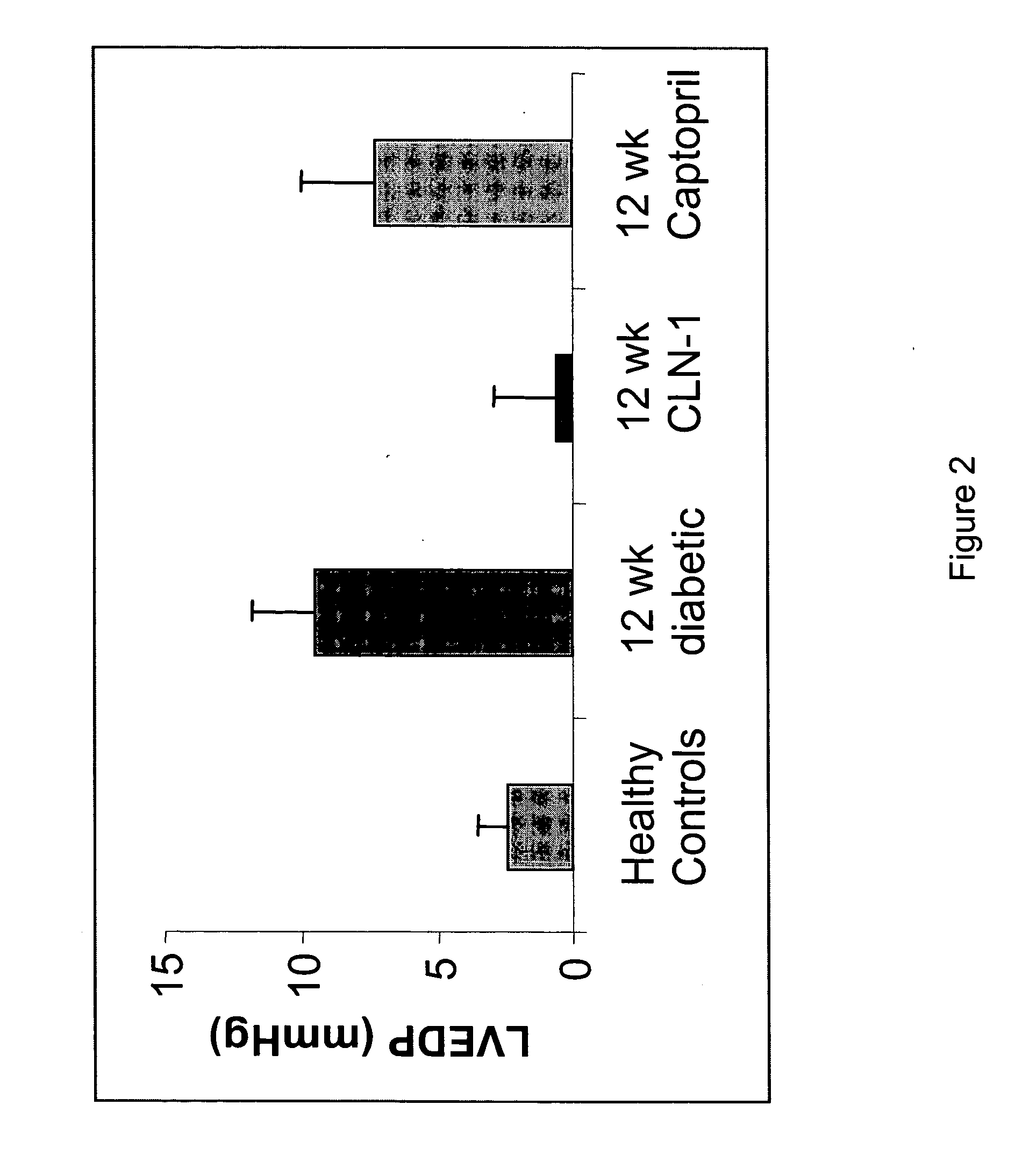
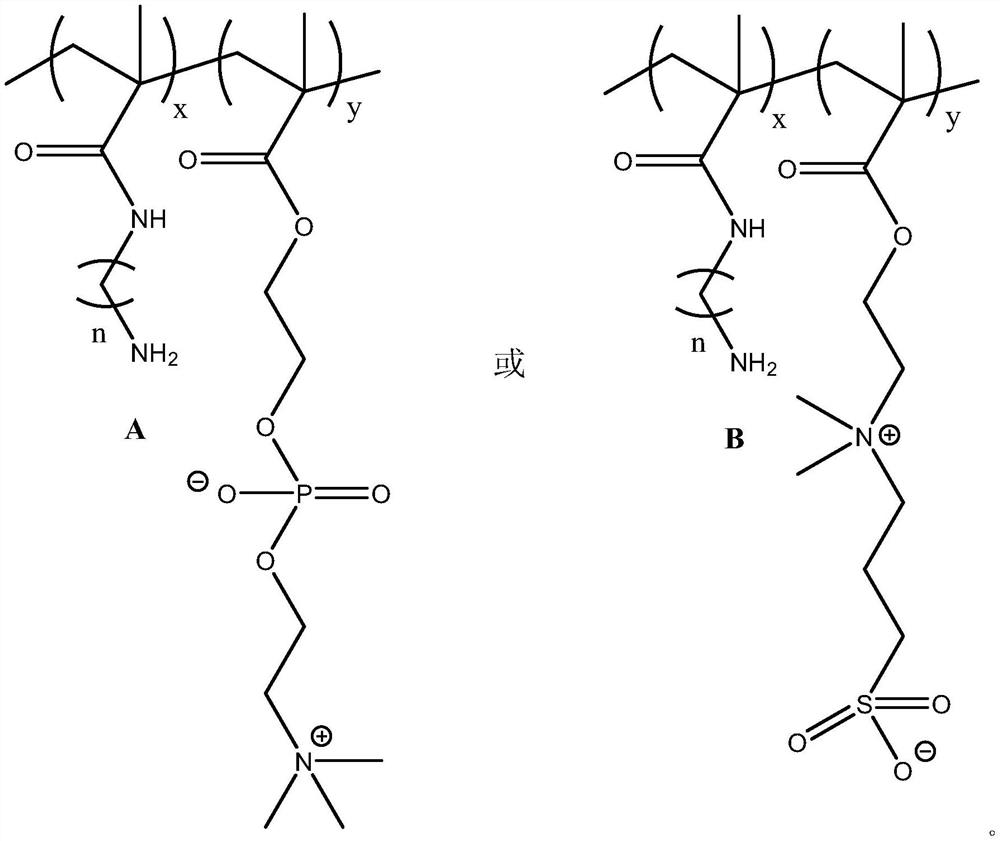
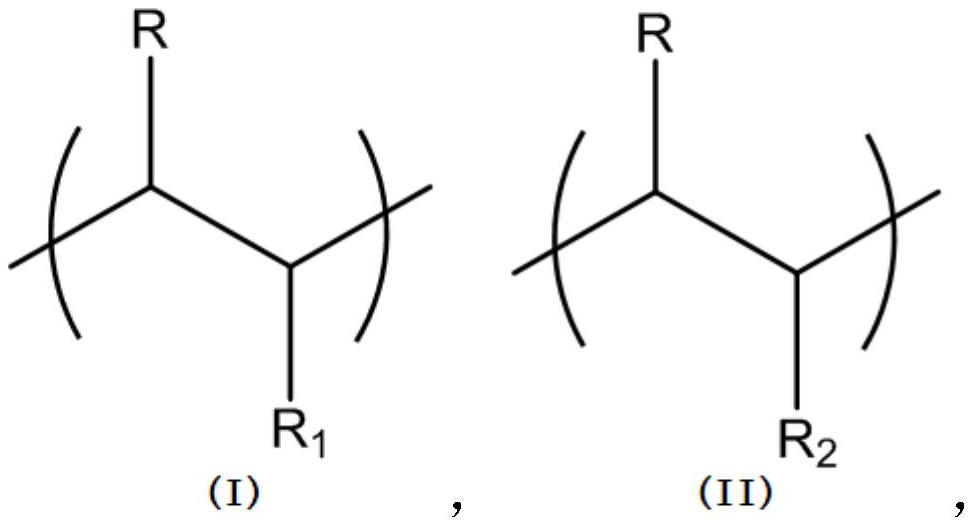
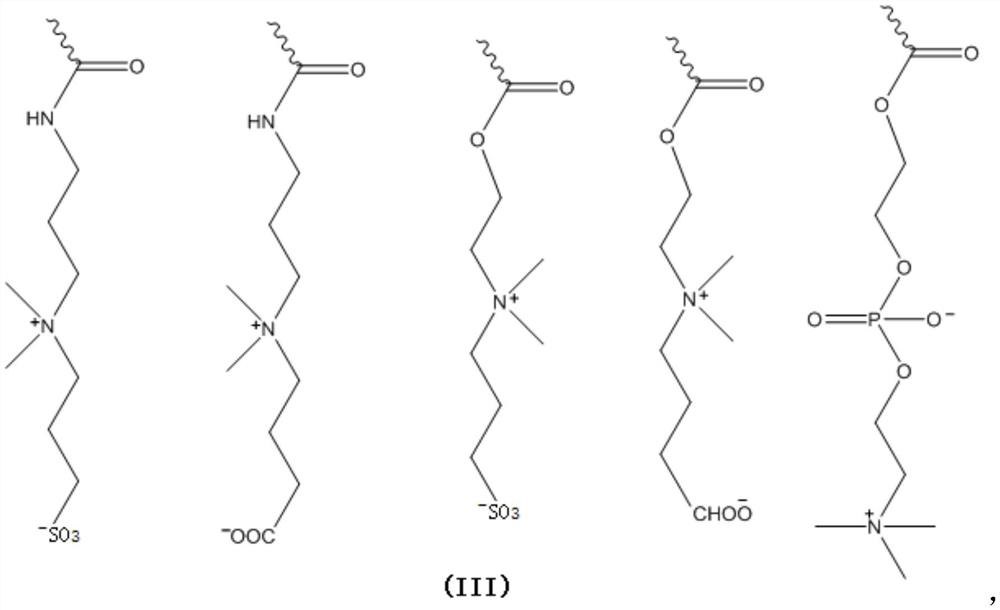
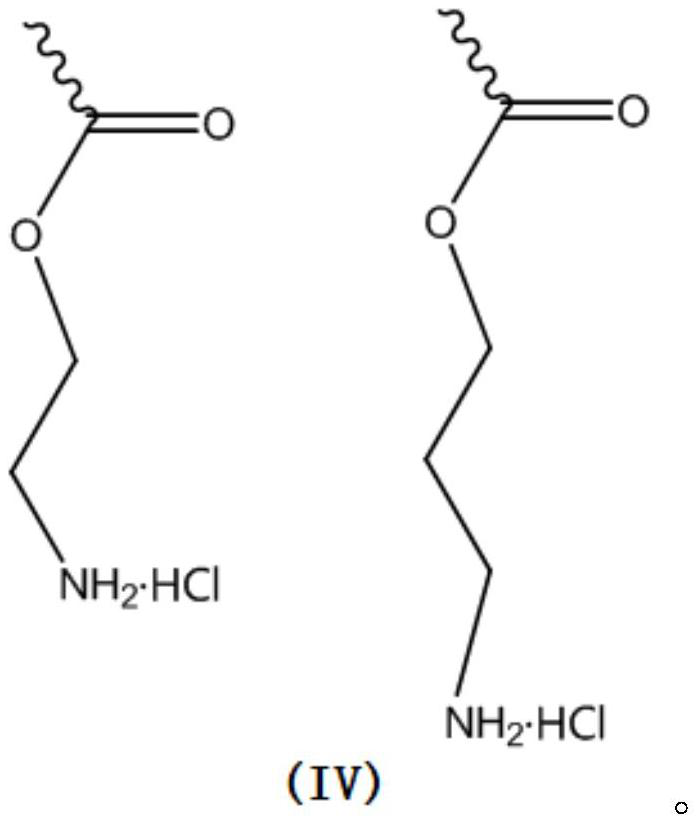
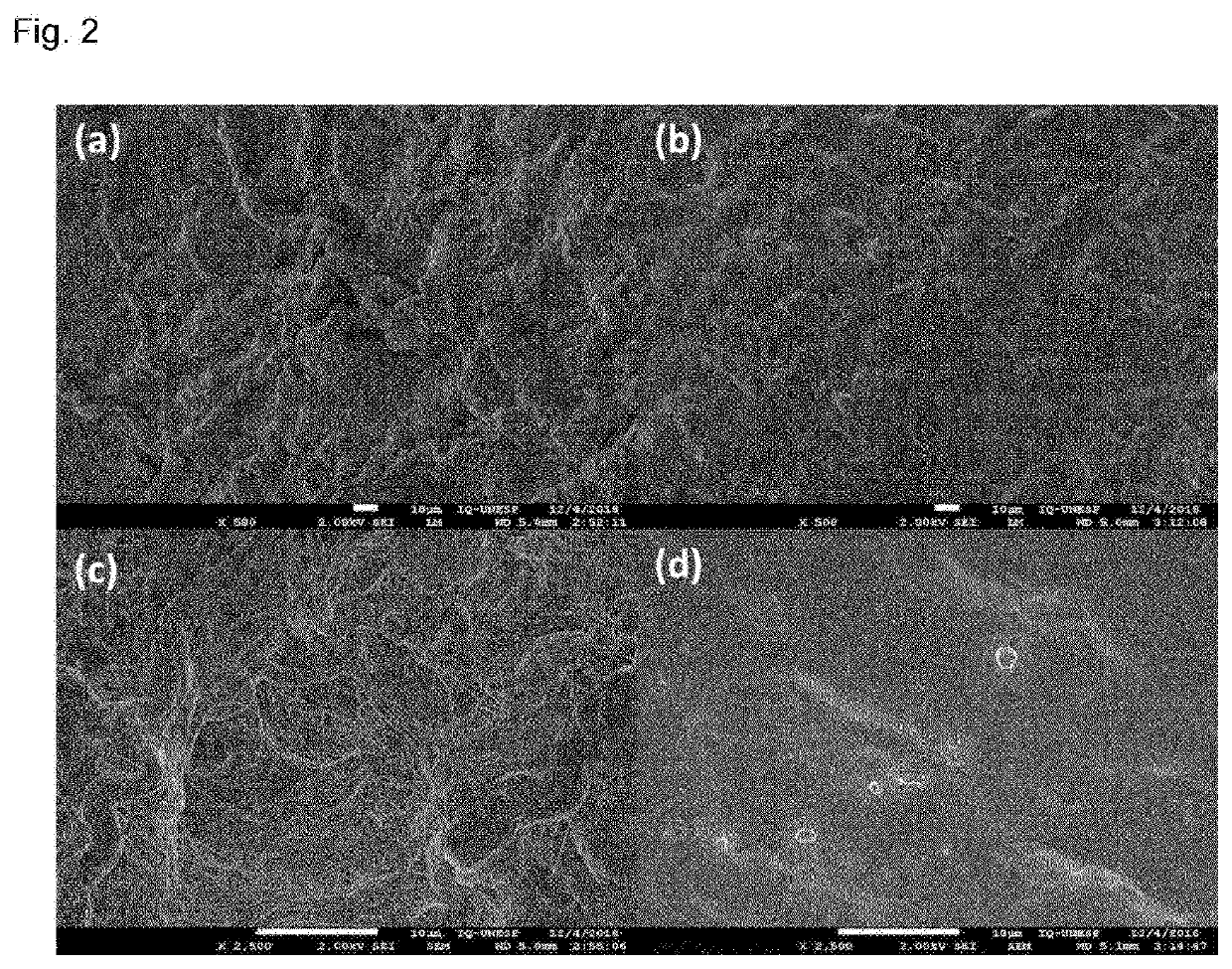
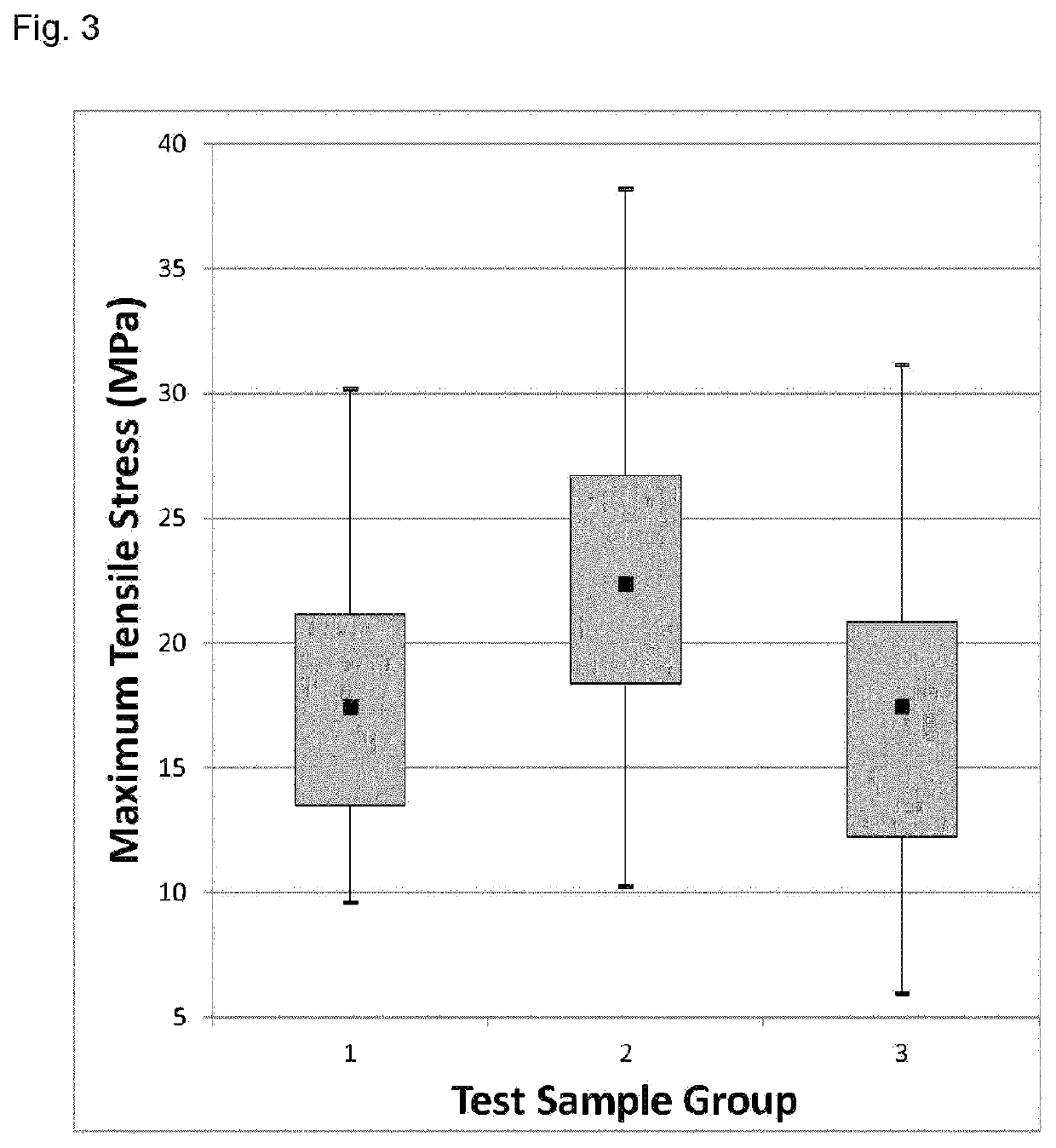
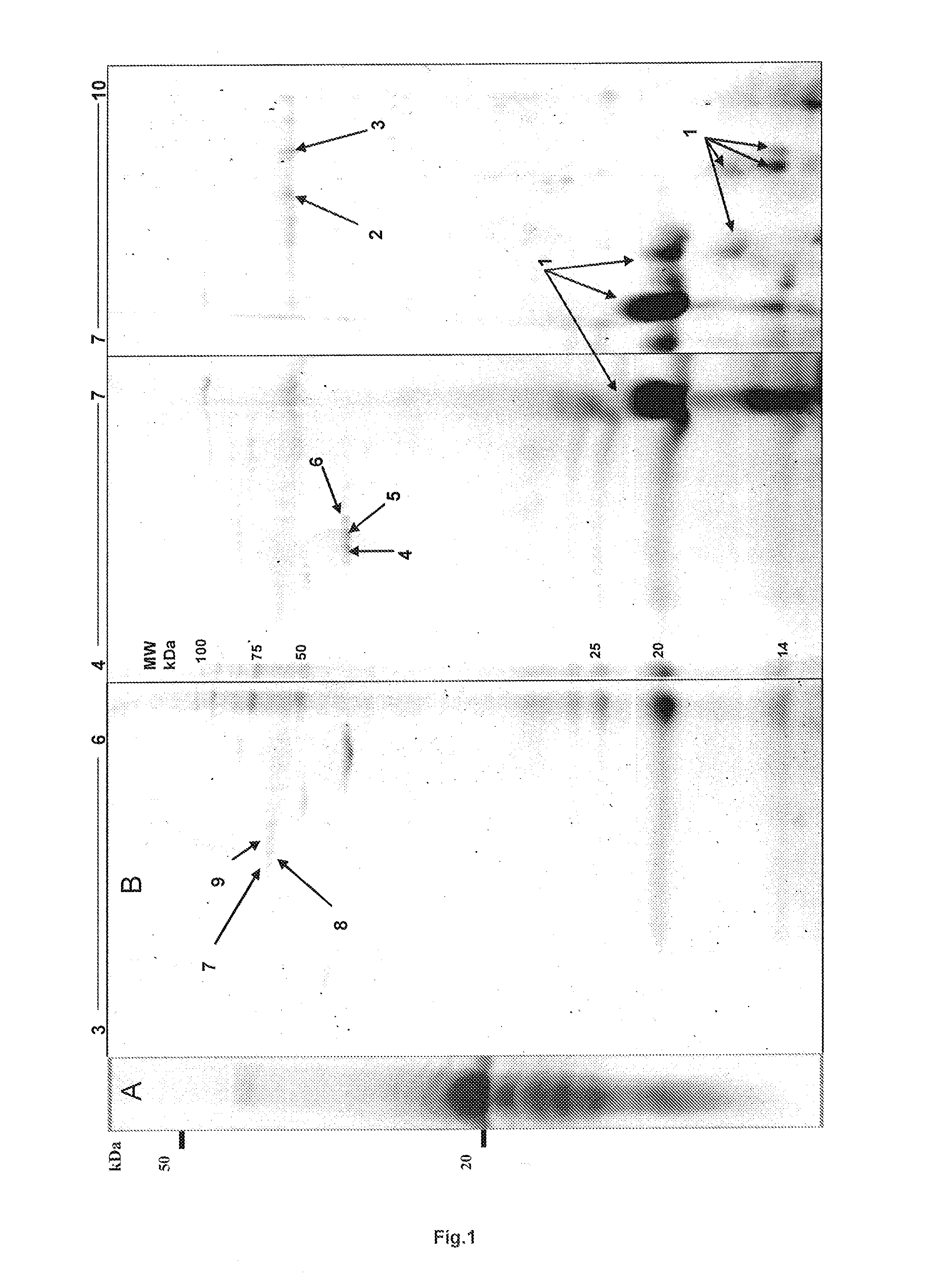
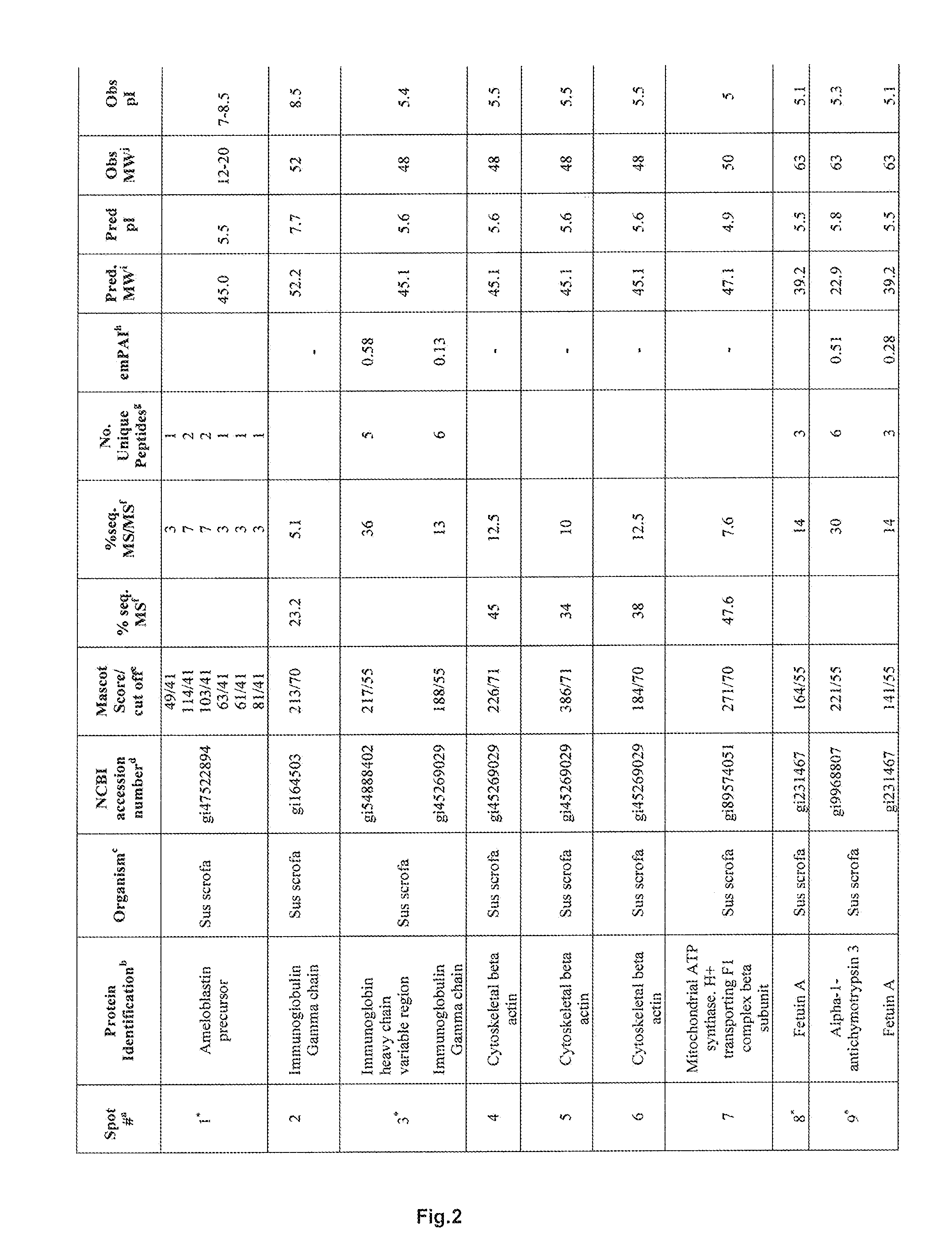
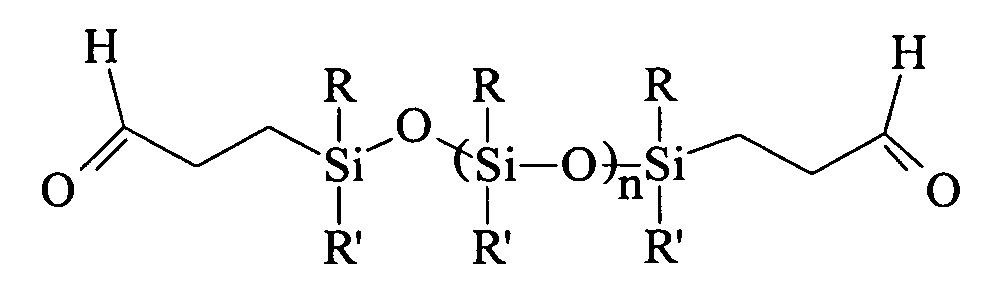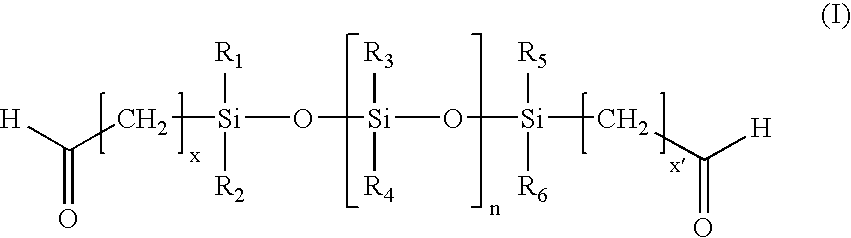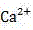Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Reduce calcification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and methods for preventing or treating failure of hemodialysis vascular access and other vascular grafts
InactiveUS6726923B2Reduce calcificationInhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferationBiocideOrganic chemistryVascular graftBlood vessel
Owner:VASCULAR THERAPIES INC
Device for replacing aortic valve membrane or pulmonary valve membrane percutaneously
The invention relates to a novel percutaneous aortic valve and pulmonary valve exchanger, which is a self-expand support with biological valve, formed by the support in special shape and made from nickel titanium alloy skeleton and the three-blade one-way opening valve formed by pig heart, wherein, the support has fixing and supporting functions, and the pig heart forms three valves fixed in the support. The invention has little hurt, high safety and reduced complication.
Owner:孔祥清
Anti-calcification treatments for heart valves and vascular grafts
InactiveUS20060047343A1Reduces calcification potentialReduce calcificationSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCalcificationProsthesis
The present invention provides processes for fixation of biological tissue and / or post-fixation treatment of such tissue that result in modified tissues with reduced susceptibility to in vitro calcification when used in prosthetic devices. The invention also relates to calcification resistant biological tissue and to methods of using such tissue.
Owner:OVIATT HENRY W +1
Processes for removing cells and cell debris from tissue and tissue constructs used in transplantation and tissue reconstruction
InactiveUS20070123700A1Improve inflammatory responseImprove responseHeart valvesDead animal preservationPresent methodFresh Tissue
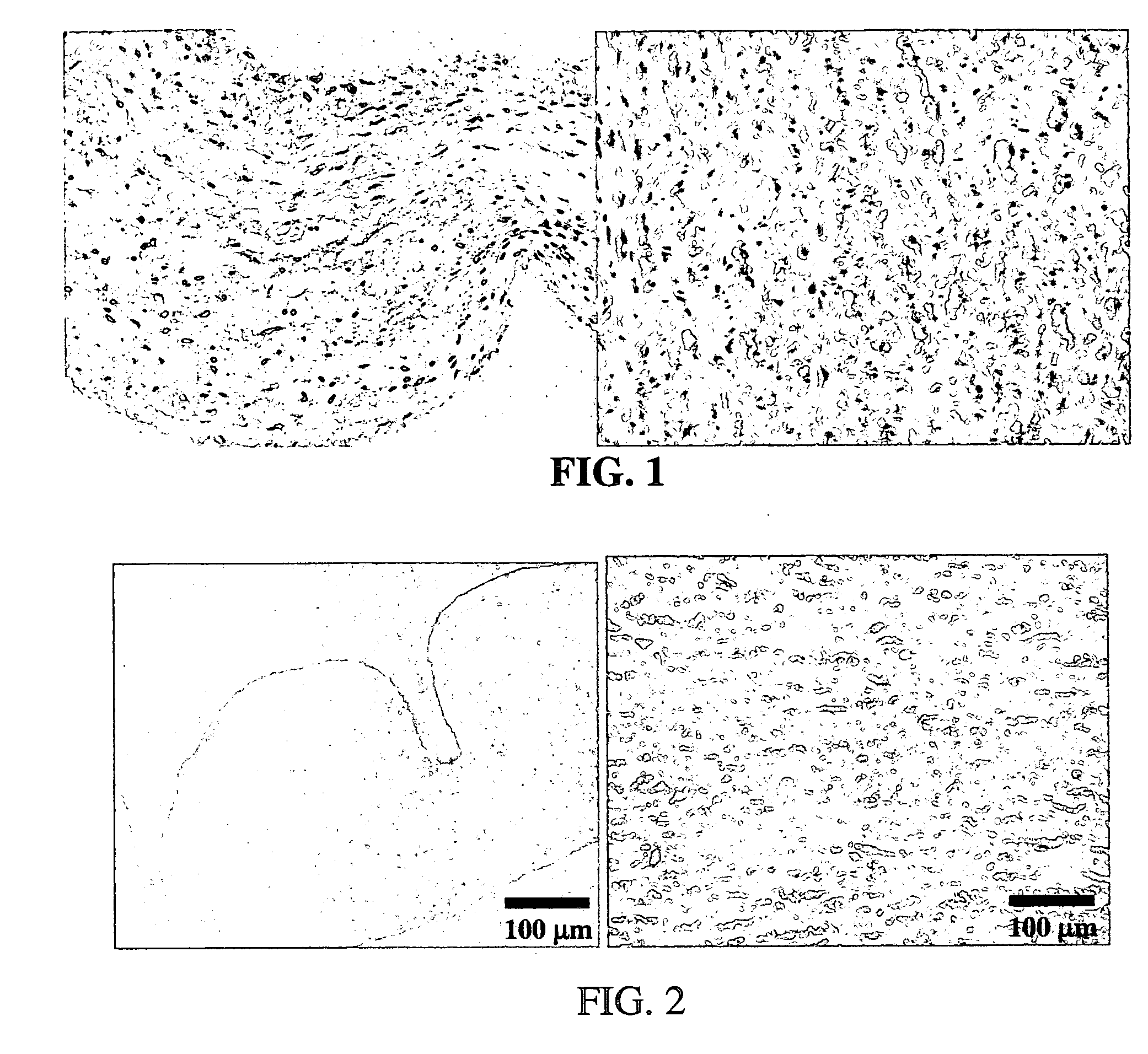
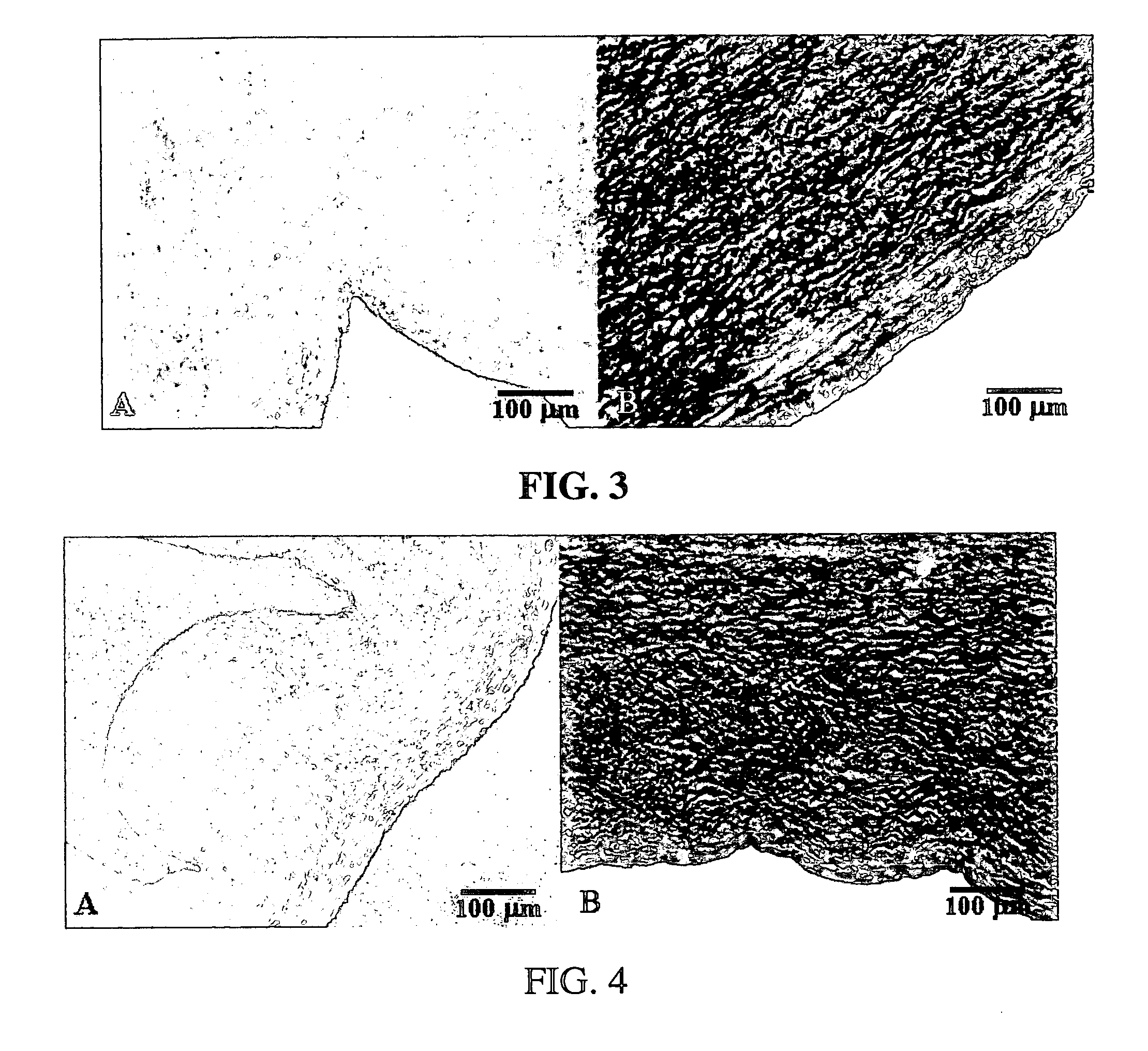
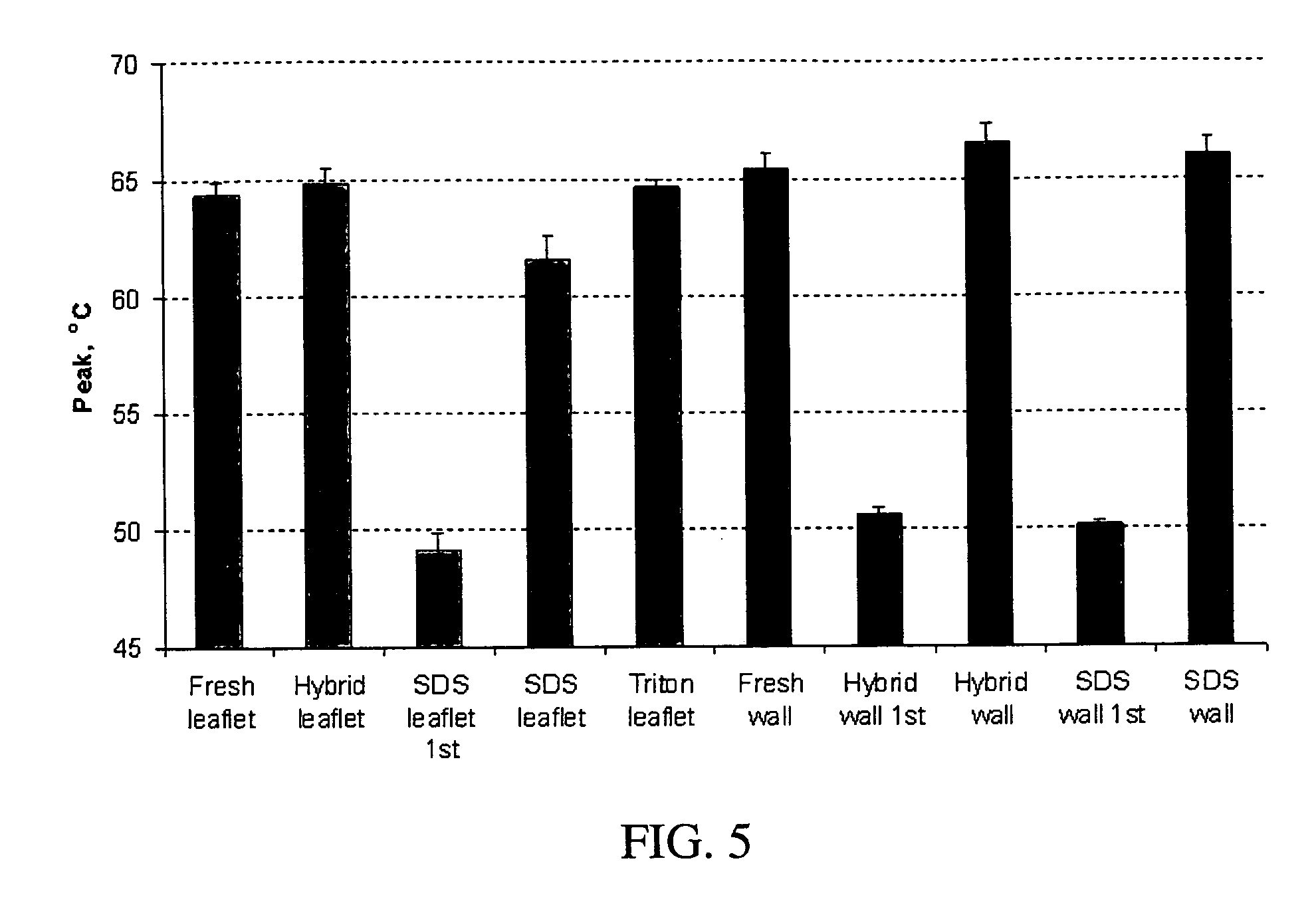
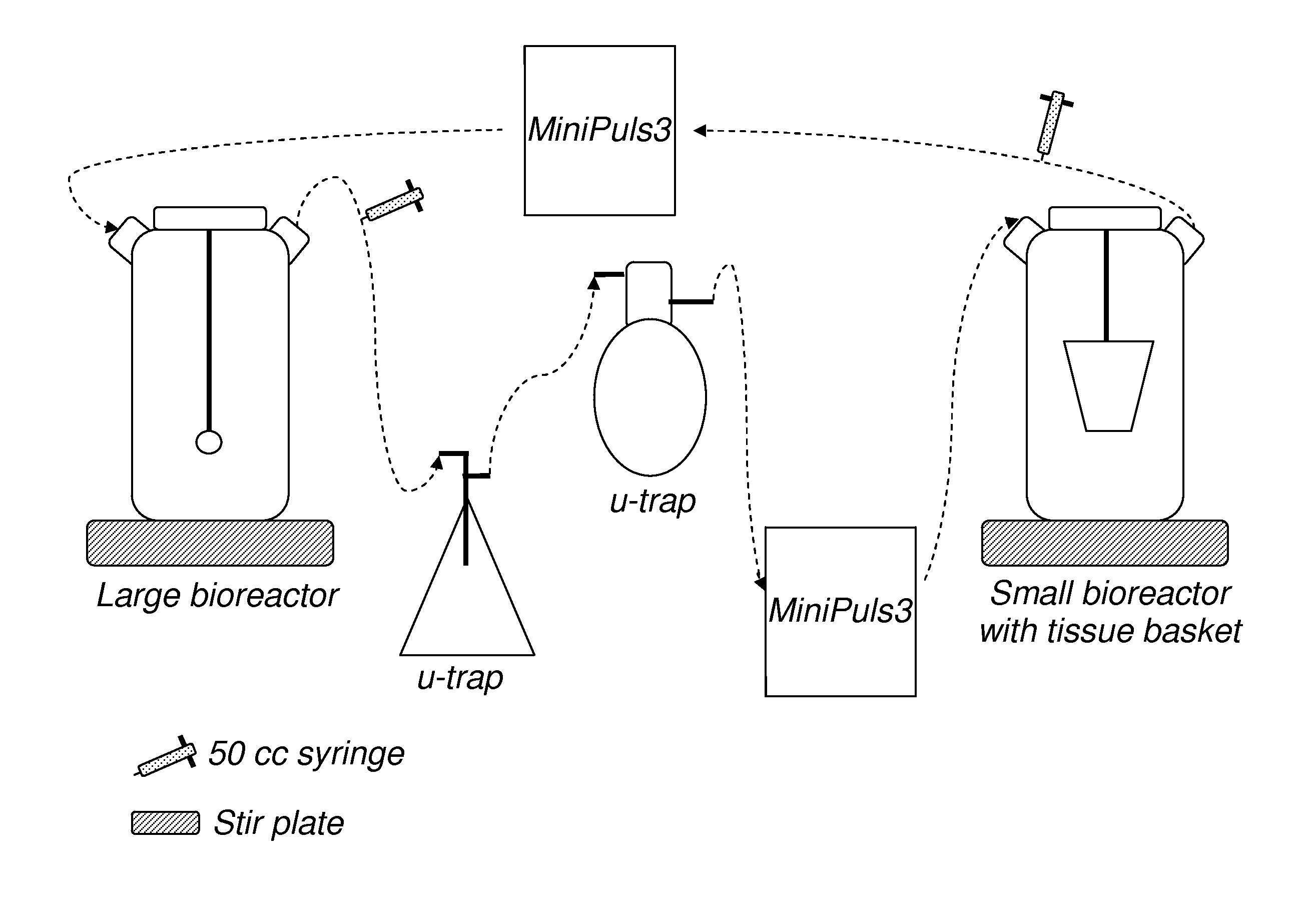
Methods for decellularizing mammalian tissue for use in transplantation and tissue engineering. The invention includes methods for simultaneous application of an ionic detergent and a nonionic detergent for a long time period, which may exceed five days. One method utilizes SDS as the ionic detergent and Triton-X 100 as the nonionic detergent. A long rinse step follows, which may also exceed five days in length. This long duration, simultaneous extraction with two detergents produced tissue showing stress-strain curves and DSC data similar to that of fresh, unprocessed tissue. The processed tissue is largely devoid of cells, has the underlying structure essentially intact, and also shows a significantly improved inflammatory response relative to fresh tissue, even without glutaraldehyde fixation. Significantly reduced in situ calcification has also been demonstrated relative to glutaraldehyde fixed tissue. Applicants believe the ionic and non-ionic detergents may act synergistically to bind protein to the ionic detergent and may remove an ionic detergent-protein complex from the tissue using the non-ionic detergent. The present methods find one exemplary use in decellularizing porcine heart valve leaflet and wall tissue for use in transplantation.
Owner:UEDA YUICHIRO +1
Method for decellularization
InactiveUS20110165676A1Less calcificationReduce inflammationHeart valvesNucleic acid reductionMedicineTissue Decellularization
The present invention provides for decellularized tissue and method for decellularizing tissue. The method generally comprises the steps of obtaining a harvested tissue, performing a muscle shelf debridement, treating the tissue with an enzyme, washing the tissue with a detergent, and performing an organic solvent extraction on the tissue. The tissues decellularized according to the present invention have several advantages including removing more of the residual cell debris, dsDNA, and chemicals, as well as exhibiting less calcification and better ultimate tensile strength than tissues prepared not according to the method of the present invention.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
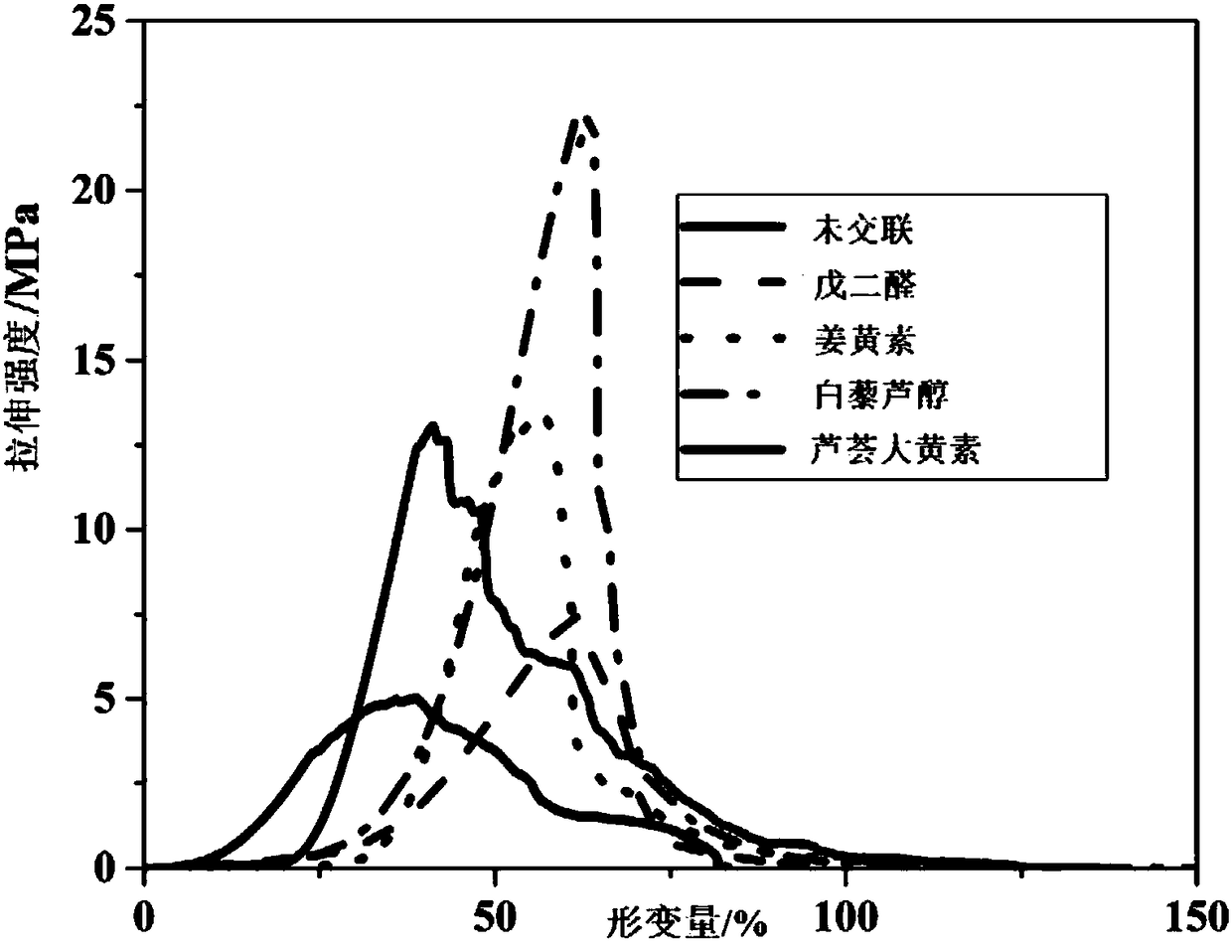
Polyphenol cross-linking agent and application thereof to preparation of anti-calcification biovalve
The invention relates to a polyphenol cross-linking agent and application thereof to preparation of an anti-calcification biovalve. The polyphenol cross-linking agent is prepared in a way that polyphenol compound is dissolved in organic solvent, and then, buffer solution is adopted for dilution, wherein the polyphenol compound is selected from one or multiple of procyanidine, curcumin, resveratrol, puerarin, aloin and aloe-emodin. The preparation method for the anti-calcification biovalve comprises the following steps: dipping a bio-based material which completely removes cells into the polyphenol cross-linking agent to be subjected to cross-linking, and fully cleaning after ending; dipping in PBS (polybutylene succinate) solution and / or D-Hanks solution to be subjected to post-processingto obtain the anti-calcification biovalve. The anti-calcification biovalve provided by the invention has better mechanical property and stability, tissue calcification, inflammation and thrombus can be obviously reduced, biotoxicity is lowered, service life is greatly prolonged, and the defects of serious calcification, short service life and the like of biological cardiac valve materials processed with a traditional glutaraldehyde crosslinking method are overcome.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Percutaneous aortic valve replacement device
InactiveCN1799520AAvoid interruptionEnsure blood flowHeart valvesSurgerySacculePercutaneous aortic valve replacement
The invention provides a new percutaneous aortic valve replacing device which is characterized by the rational designation, convenient usage and low operational danger, which is to solve problems of inconvenient stitching of valve and cradle and high danger of using saccule to expand aortic valve in current aortic valve replacing device, the device is an automatic buckling cradle carrying biological valve, comprising cradle in nickel-tantalum alloy framework and trilobular one-way opening valve composed of pig heart bag. The nickel-tantalum alloy possesses functions of fixing and supporting, the trilobular valve is fixed tightly in the cradle. The product is characterized by the small injury, high safety, reduced complication caused by aortic valve replacement, and wide application prospect.
Owner:孔祥清
Natural fluorine-free edible transparent child nutrition toothpaste
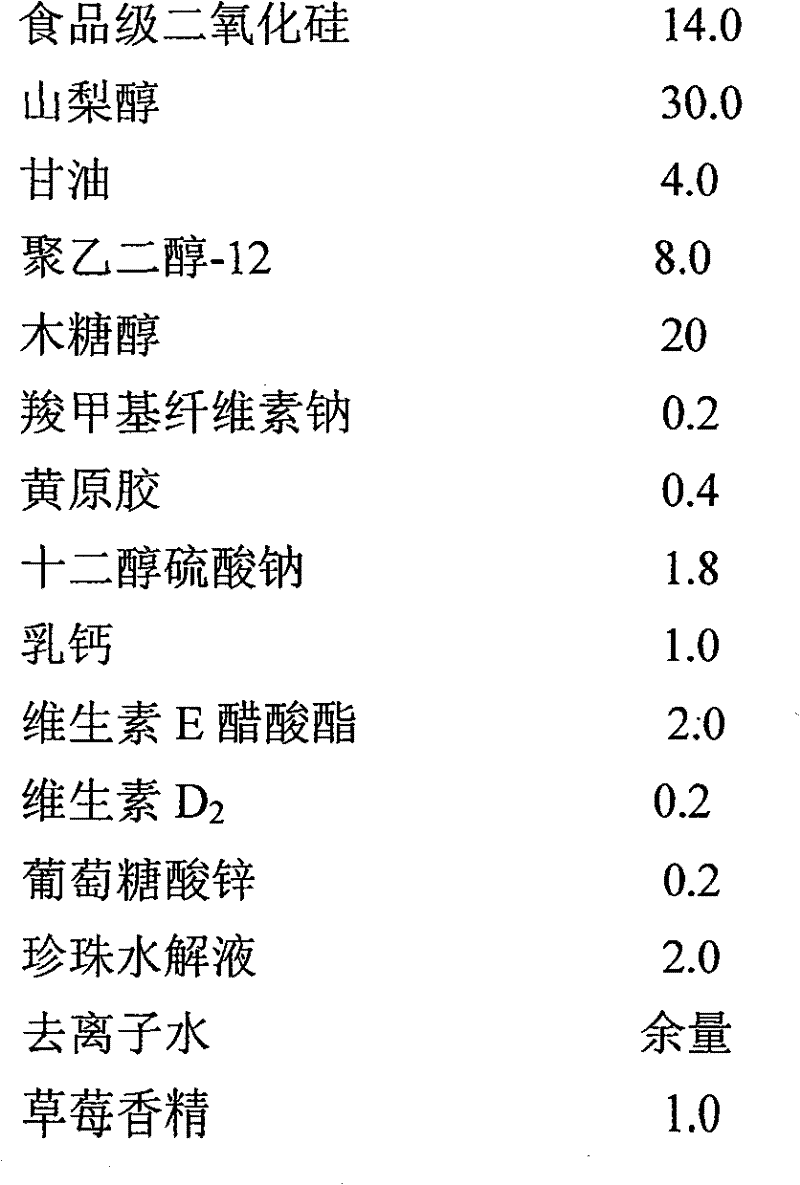
ActiveCN101889969AReduce calcificationEfficient removalCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsVitamin E AcetateToothpaste
The invention relates to a natural fluorine-free edible transparent child nutrition toothpaste, belonging to the daily necessities technical field. The natural fluorine-free edible transparent child nutrition toothpaste of the invention is made by adhesive, foaming agent, moisturizer, sweetener, abradant, perfume, deionized water, preservative, hydrolyzed pearl solution, milk calcium, zinc gluconate, vitamin E acetate and vitamin D2 according to the conventional method. The vitamin E acetate, xylitol, hydrolyzed pearl solution, milk calcium, zinc gluoconate and vitamin D2 in the invention act combinedly, oral odour and bacteria can be effectively cleared away, periodontitis and gingivitis can be prevented and treated, caries preventing effect is obvious, and tooth calcification capability can be improved. Nutrition health care function on deciduous teeth of children of two to five can be realized.
Owner:广州舒客实业有限公司
Biological valve with anticoagulation and anti-calcification functions and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111420120AGood anticoagulant functionIncrease long-acting anticoagulationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBioprosthetic valveBiochemistry
The invention discloses a bioprosthetic valve with anticoagulation and anti-calcification functions and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out cross-linking treatment on a biological valve by adopting glutaraldehyde, and carrying out modification treatment by adopting hydrophilic molecules or hydrophobic molecules after cross-linking; or performing modification treatment on the biological valve by hydrophilic molecules or hydrophobic molecules, and then carrying out crosslinking treatment by glutaraldehyde; or performing at least one time of modification treatment on the biological valve by adopting hydrophilic molecules or hydrophobic molecules, then performing cross-linking treatment by glutaraldehyde, and finally performing at least one timeof modification treatment on the biological valve by adopting hydrophilic molecules or hydrophobic molecules. The biological valve prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention not only has good mechanical properties, but also has excellent anticoagulation and anti-calcification effects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Vascular disease therapies
InactiveUS20060281668A1Reducing vascular calcificationReduced dysfunctionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderVascular diseaseCardiac dysfunction
The present invention relates to methods and agents for treating impaired vascular and cardiac function. Methods and agents for treating various physiological and pathological features associated with vascular dysfunction and cardiac dysfunction are also provided.
Owner:FIBROGEN INC
Invisible fish blockage control system based on network structure
ActiveCN102830686ARealize unified monitoringReduce workloadClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaArea networkControl system
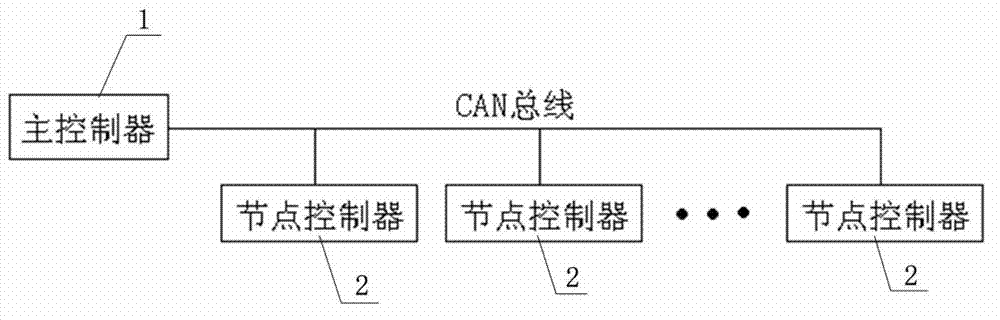
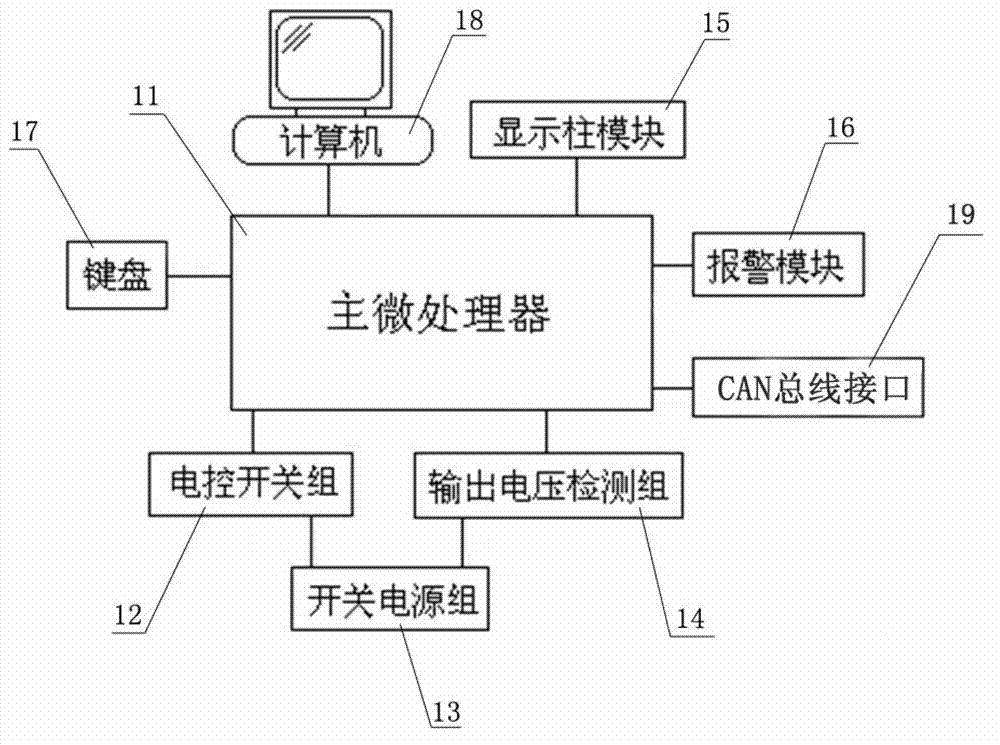
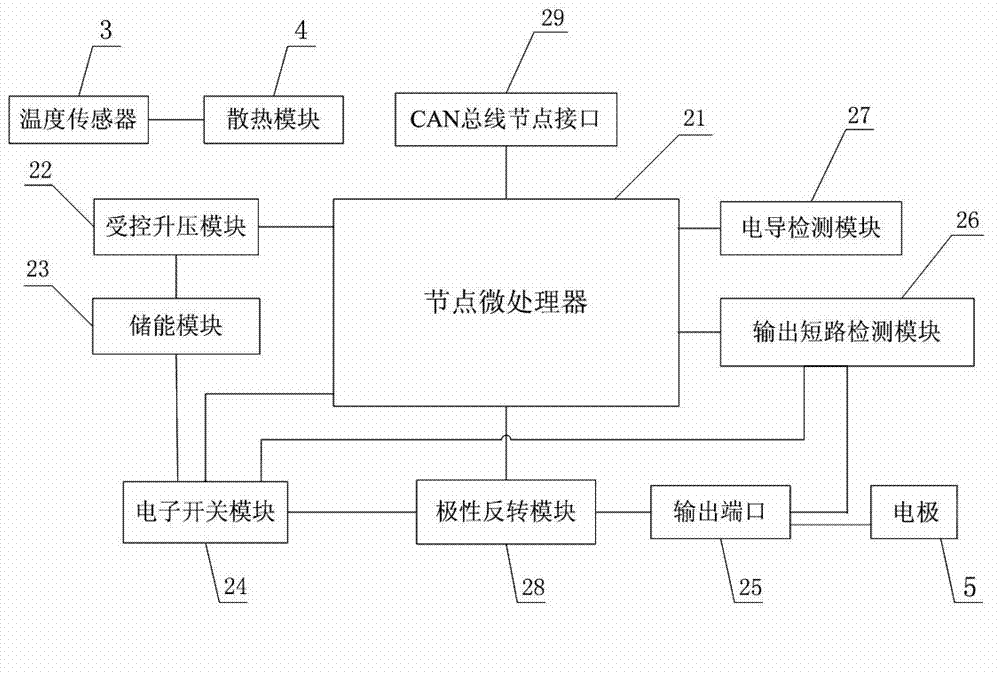
The invention discloses an invisible fish blockage control system based on a network structure. The invisible fish blockage control system comprises a master controller and a plurality of node controllers for controlling fish blockage, wherein the master controller is connected with each node controller through a controller area network (CAN) bus and monitors the operating states of the node controllers; the master controller comprises a master microprocessor, an operation and display processing module and a switching power supply module; the operation and display processing module is connected with the master microprocessor and selects the node controller through the master microprocessor and displays the operating state of the node controller; and the switching power supply module is connected with the master microprocessor, receives the control of the master microprocessor and supplies power to the node controller. According to the control system, multiple fish blockage equipment can be monitored in a unified mode, and the fish blockage out-of-control time is reduced; and moreover, the invisible fish blockage control system has the capacity of automatically adapting to various water areas, good fish blockage effect, long-term free maintenance and the capacity of continuously working all the year round.
Owner:CHONGQING GENSEN ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Zigbee-based wireless fish blocking system
InactiveCN105116849ALess investmentStrong networking abilityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlTerrainWireless transmission
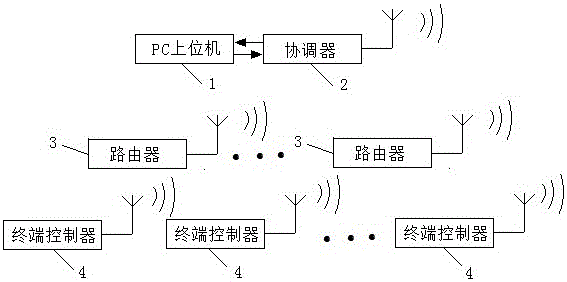
The invention discloses a zigbee-based wireless fish blocking system. The system comprises a PC upper computer, a coordinator, routers and a plurality of terminal controllers for blocking fishes; the PC upper computer is used in display and control of working states of the terminal controllers; the coordinator is in serial port communication with the upper computer and in communication with the routers through wireless transmission; the routers are connected with the terminal controllers through wireless transmission; and the terminal controllers are used in fish blocking control. An existing fish blocking control system is implemented through wired connection, is high in cost and cannot achieve remote control, and the control system achieves remote control through the wireless transmission and does not need to build a system control station in complex terrain, so fish blocking cost is greatly reduced, unified monitoring of large-scale adaptive water area fish blocking can be achieved, the zigbee-based wireless fish blocking system has the advantages of the good anti-interference capability, the continuous running capability, simple maintenance and the good fish blocking effect, and the system can be widely popularized and applied.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Dry artificial biological heart valve containing polypeptide for promoting endothelialization and preparation method of dry artificial biological heart valve
ActiveCN110101912AHigh mechanical strengthLow immunogenicityTissue regenerationProsthesisHigh humidityMedicine
The invention discloses a dry artificial biological heart valve containing polypeptide for promoting endothelialization and a preparation method of the dry artificial biological heart valve. The method comprises the following steps that cross-linking is performed on amino groups and carboxyl groups of an animal pericardium, and endothelialization treatment, hydrogel polymerization treatment and dewatering and drying treatment are performed on the animal pericardium, wherein the endothelialization treatment involves that the polypeptide for promoting the endothelialization is adopted to treat the animal pericardium. The preparation method has the advantages that the prepared dry biological heart valve has good water immersion flattening performance, and can be quickly immersed in water andflattened at a higher temperature and higher humidity, thereby reducing residues of glutaraldehyde and the like, and reducing the problems of calcification and toxicity which are caused by the glutaraldehyde and the like, therefore the preoperative installation of a valve system can be simplified, and the additional risks of surgeries are reduced; the polypeptide capable of promoting the endothelialization is also added in the preparation process, so that the prepared biological valve has the property of promoting the endothelialization.
Owner:JILIN VENUS HAOYUE MEDICAL LTD
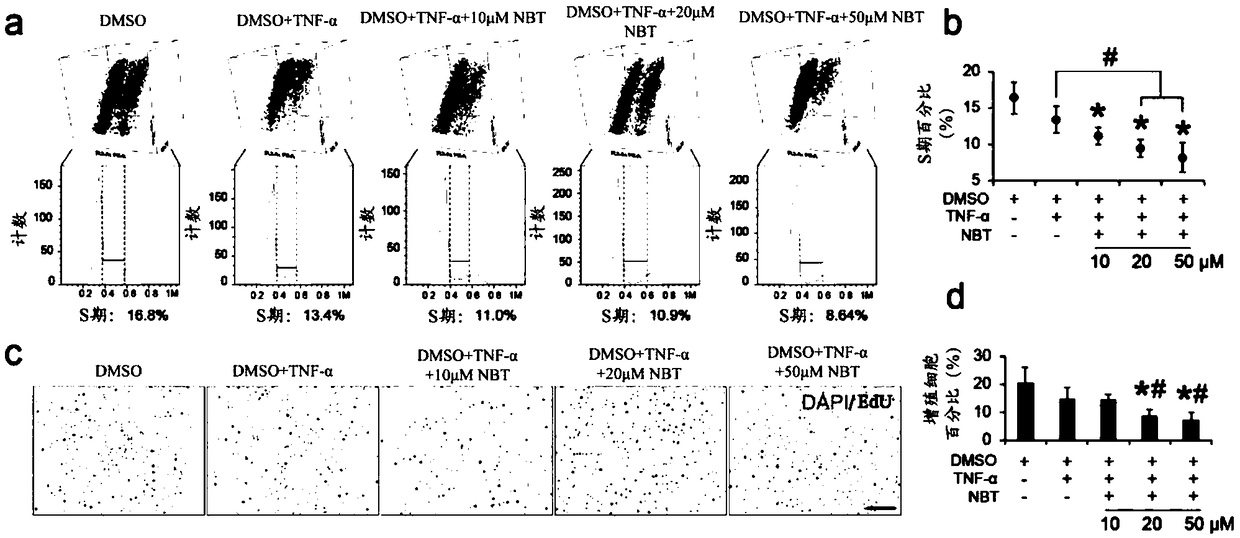
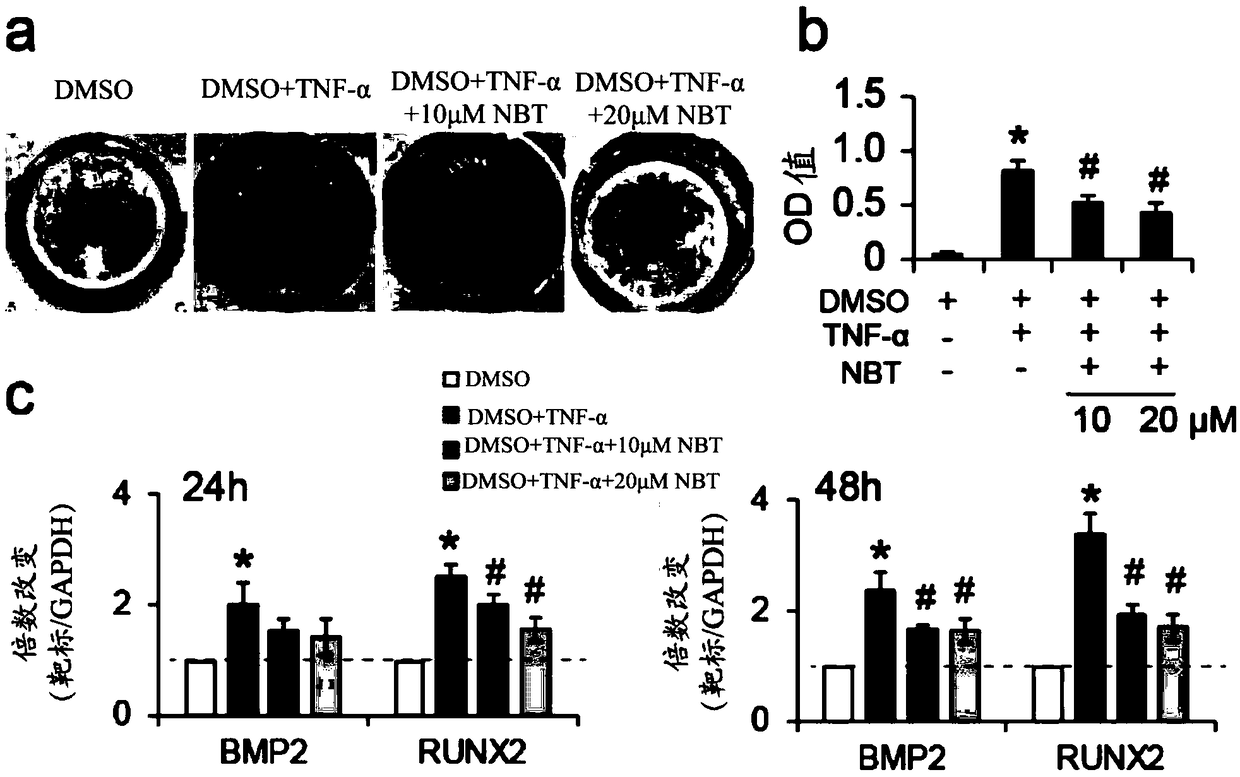
Use of nobiletin in treatment of calcific aortic valvular disease
ActiveCN109464437AReduce calcificationAvoid thickeningOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderNon surgical treatmentInterstitial cell
The invention relates to the field of prevention and / or treatment of calcific aortic valvular disease. The inventors research and find that nobiletin can effectively down-regulate expression of osteogenic differentiation marker genes BMP2 and RUNX2 in valvular interstitial cells, and inhibit calcification of the valvular interstitial cells, thereby inhibiting or delaying valvular calcification, and further provide use of the nobiletin in preparing medicines for prevention and / or treatment of individual calcific aortic valvular disease. The invention provides a new option for non-surgical treatment of the calcific aortic valvular disease.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Bioprosthetic tissue preparation with synthetic hydrogels
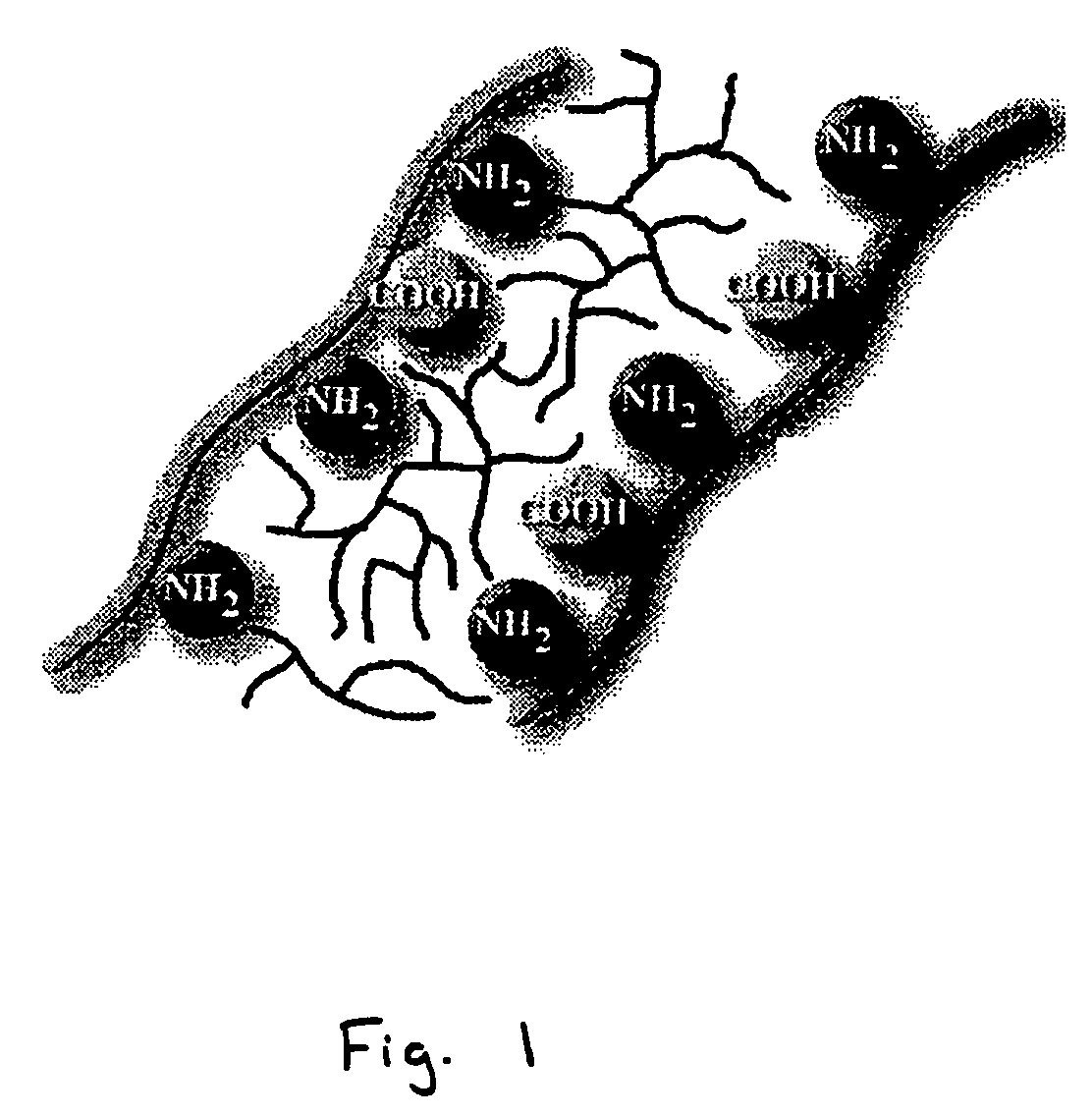
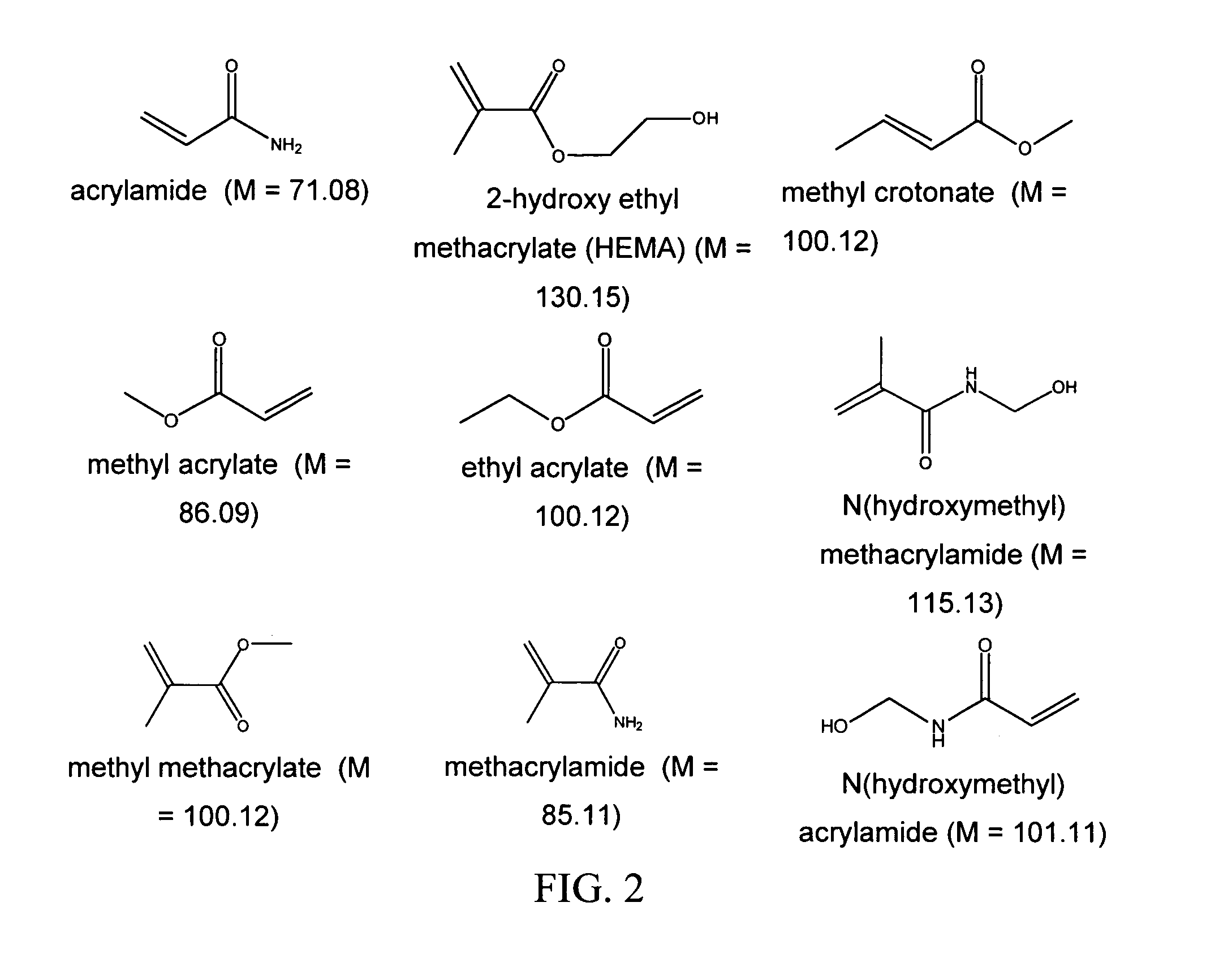
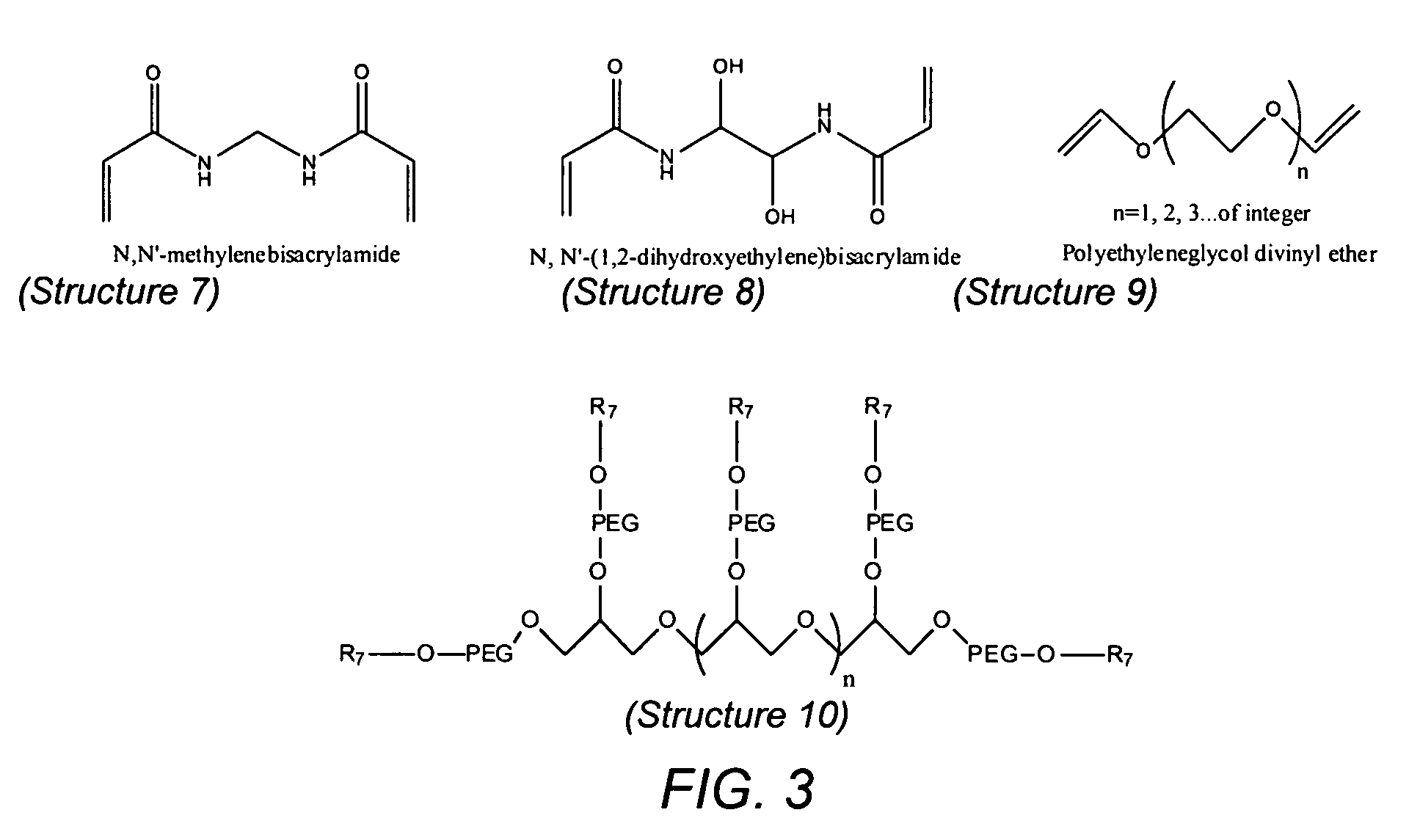
ActiveUS7955788B2Reduce calcificationReduce stiffnessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for treating xenogenic tissue for implantation into a human body including in-situ polymerization of a hydrogel polymer in tissue, and tissue treated according to those methods, where the polymerization takes place in tissue that has not been fixed with glutaraldehyde. The polymerization may only fill the tissue, bind the polymer to the tissue, or cross-link the tissue through the polymer, depending on the embodiment. One method includes free radical polymerization of a first vinylic compound, and can include cross-linking through use of a second compound having at least two vinyl groups. Another method utilizes nucleophilic addition polymerization of two compounds, one of which can include PEG and can further include hydrolytically degradable regions. In one embodiment, applicants believe the in-situ polymerization inhibits calcification, and that the polymerization of tissue un-fixed by glutaraldehyde allows for improved penetration of the polymer. The methods find one use in the treatment of porcine heart valve tissue, intended to extend the useful life of the valves by inhibiting calcification. The incorporation of degradable hydrogel regions may initially fill the tissue and reduce any initial inflammatory response, but allow for later infiltration by cells to remodel the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Warp-knitted fabric and medical material
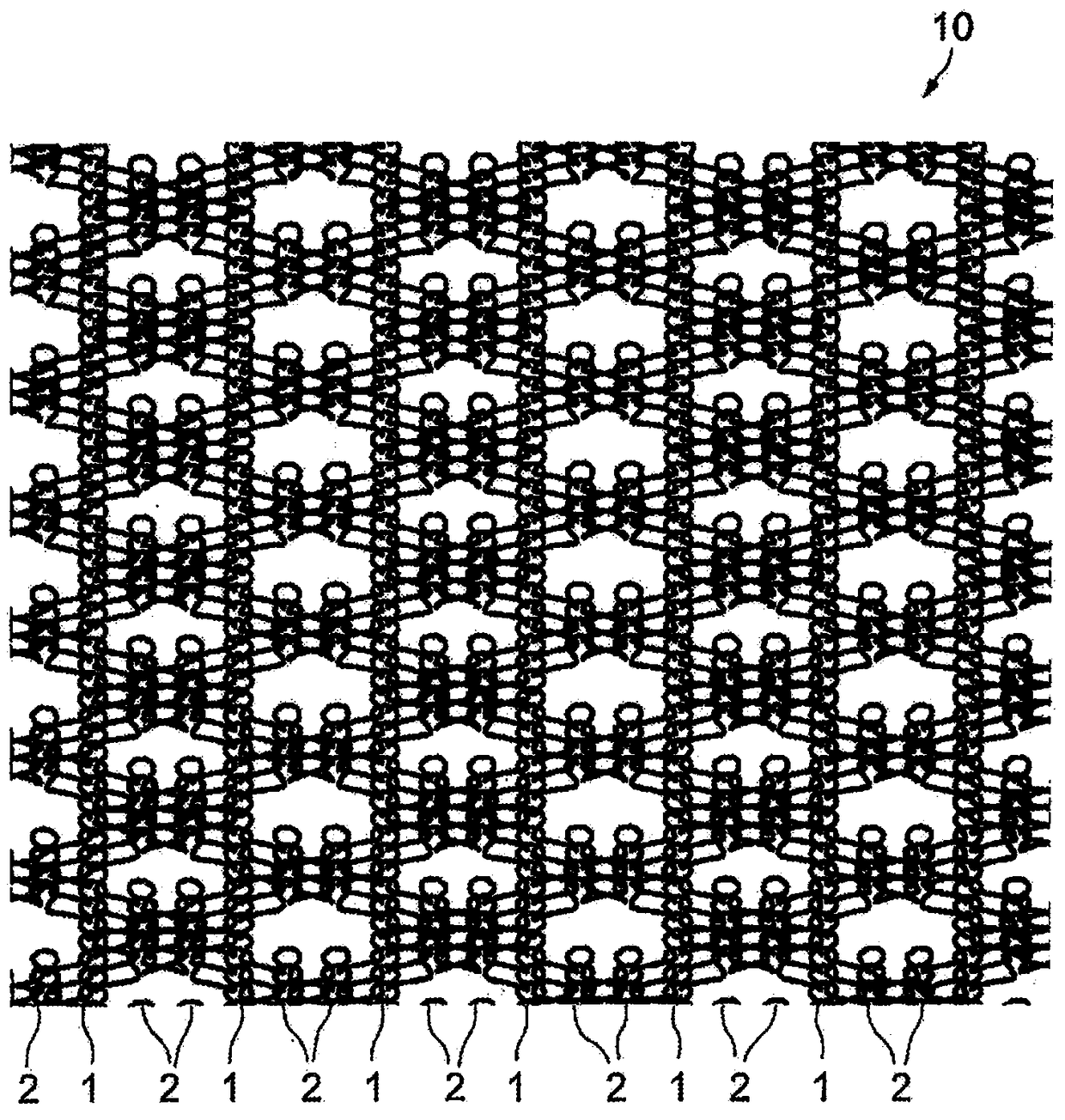
ActiveCN108884612AGuaranteed StrengthIncrease the degree of elongationOrnamental textile articlesAnti-incontinence devicesYarnBiological body
The present invention provides a warp-knitted fabric and a medical material that can be simultaneously extended in all directions by causing thread made of a second bioabsorbable material to be absorbed in a living body over time and in which the degree of extension can be increased. The present invention provides a warp-knitted fabric 10 in which adjacent loop rows are linked, the warp-knitted fabric 10 including: a plurality of first loop rows including a first thread and composed of continuous loops extending in the warp direction; and one or two or more second loop rows disposed between the first loop rows and composed of continuous loops extending in the warp direction, wherein each second loop row is formed of one or two or more loops solely including a second thread and one or two or more loops including the first thread, which are arranged alternately, at least three first loop rows are linked together by the first thread, and the bioabsorption rate of the first thread is lowerthan the bioabsorption rate of the second thread.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Cervical vertebrae health-care fomentation pillow, and its use method
InactiveCN101002974AReduce lossAccelerate evaporationMedical devicesSkeletal disorderRegimenMedicine
A health-care pillow for hot dressing of cervical vertebrae is composed of a pillow case, a core, and 5 Chinese-medicinal materials including argyi leaf, prickly ash peel, dried ginger, pepper, etc, which are filled in said core. Its application method includes heating the health-care pillow to 40-50 deg.C, and laying the neck on it for 30 min.
Owner:福州市龙华康健养生服务有限公司
Anti-calcification treatment method of biological material
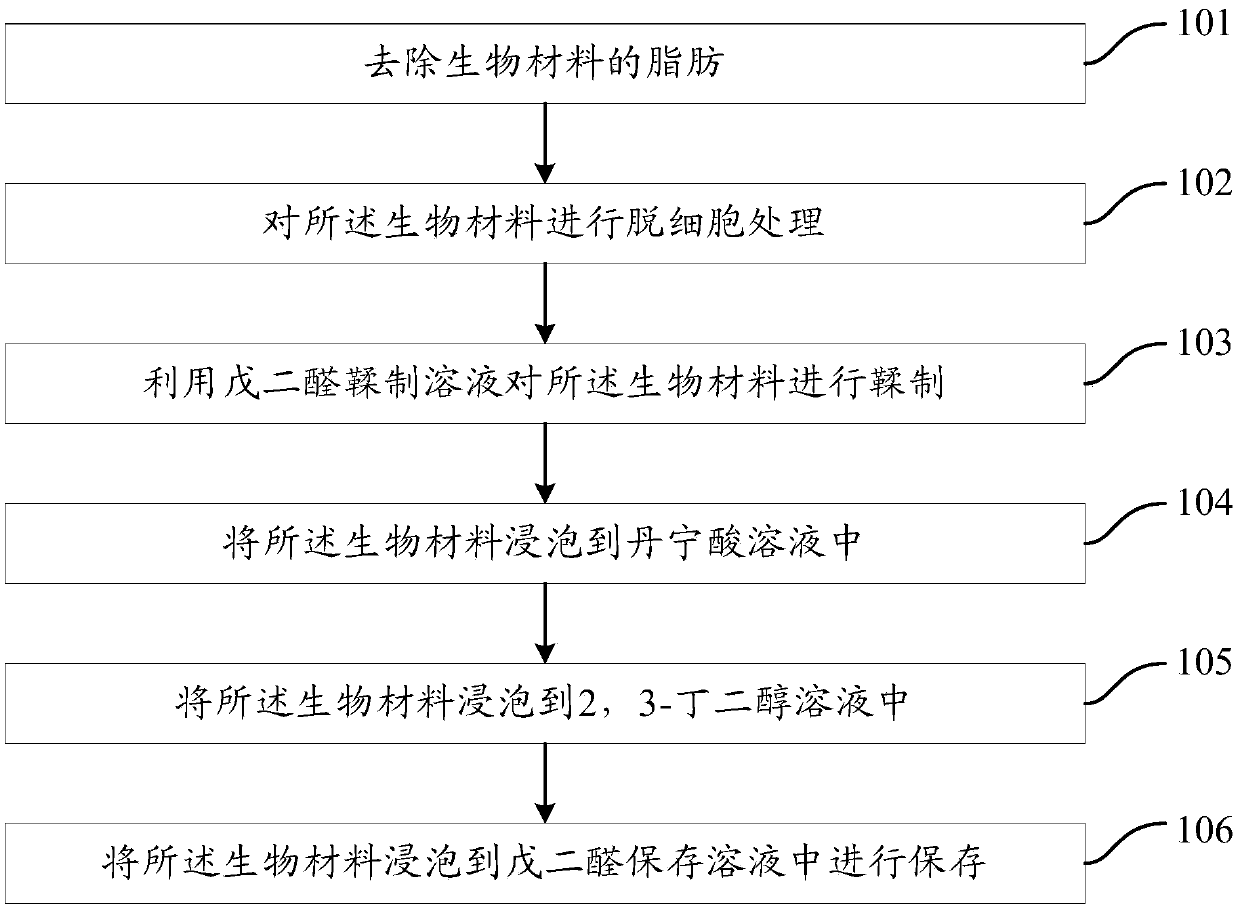
ActiveCN109589452AImprove anti-calcification propertiesReduce calcificationTissue regenerationProsthesisCalcificationTannin
The invention provides an anti-calcification treatment method of a biological material, which comprises the following steps: removing fat from the biological material, performing decellularization treatment on the biological material, tanning the biological material with a glutaraldehyde tanning solution, soaking the biological material in a tannin solution, soaking the biological material in a 2,3-butanediol solution, and soaking the biological material in a glutaraldehyde preservation solution for preservation. The anti-calcification treatment method of the biological material can obtain a better anti-calcification effect.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIAHEZHONGBANG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Natural fluorine-free edible transparent child nutrition toothpaste
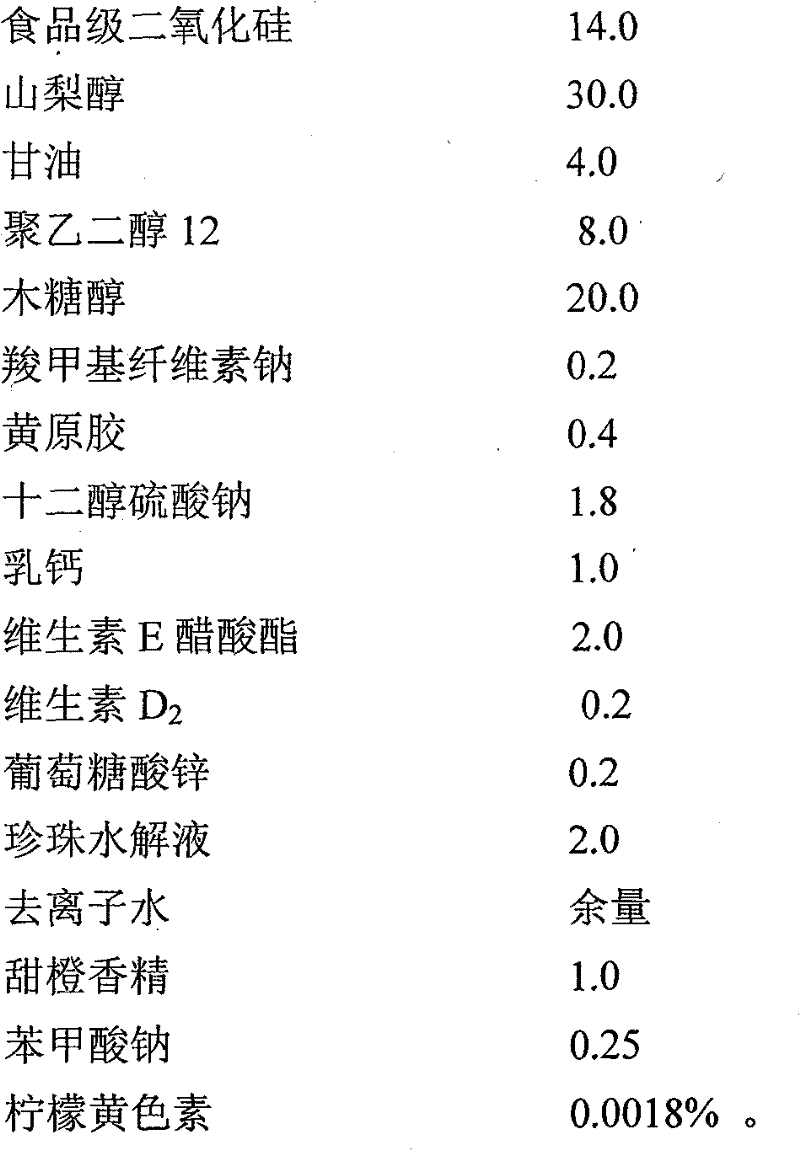
ActiveCN101889969BReduce calcificationEfficient removalCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsVitamin E AcetateToothpaste
The invention relates to a natural fluorine-free edible transparent child nutrition toothpaste, belonging to the daily necessities technical field. The natural fluorine-free edible transparent child nutrition toothpaste of the invention is made by adhesive, foaming agent, moisturizer, sweetener, abradant, perfume, deionized water, preservative, hydrolyzed pearl solution, milk calcium, zinc gluconate, vitamin E acetate and vitamin D2 according to the conventional method. The vitamin E acetate, xylitol, hydrolyzed pearl solution, milk calcium, zinc gluoconate and vitamin D2 in the invention actcombinedly, oral odour and bacteria can be effectively cleared away, periodontitis and gingivitis can be prevented and treated, caries preventing effect is obvious, and tooth calcification capabilitycan be improved. Nutrition health care function on deciduous teeth of children of two to five can be realized.
Owner:广州舒客实业有限公司
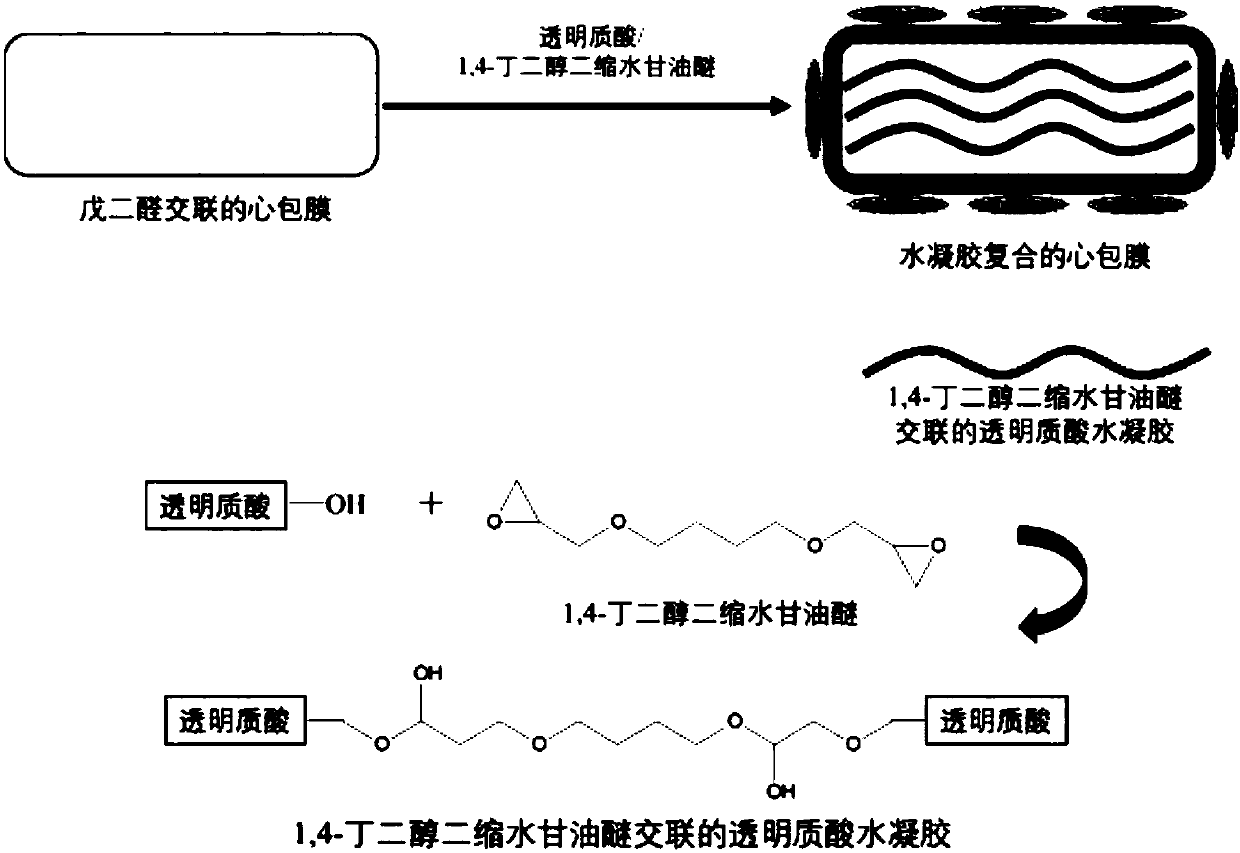
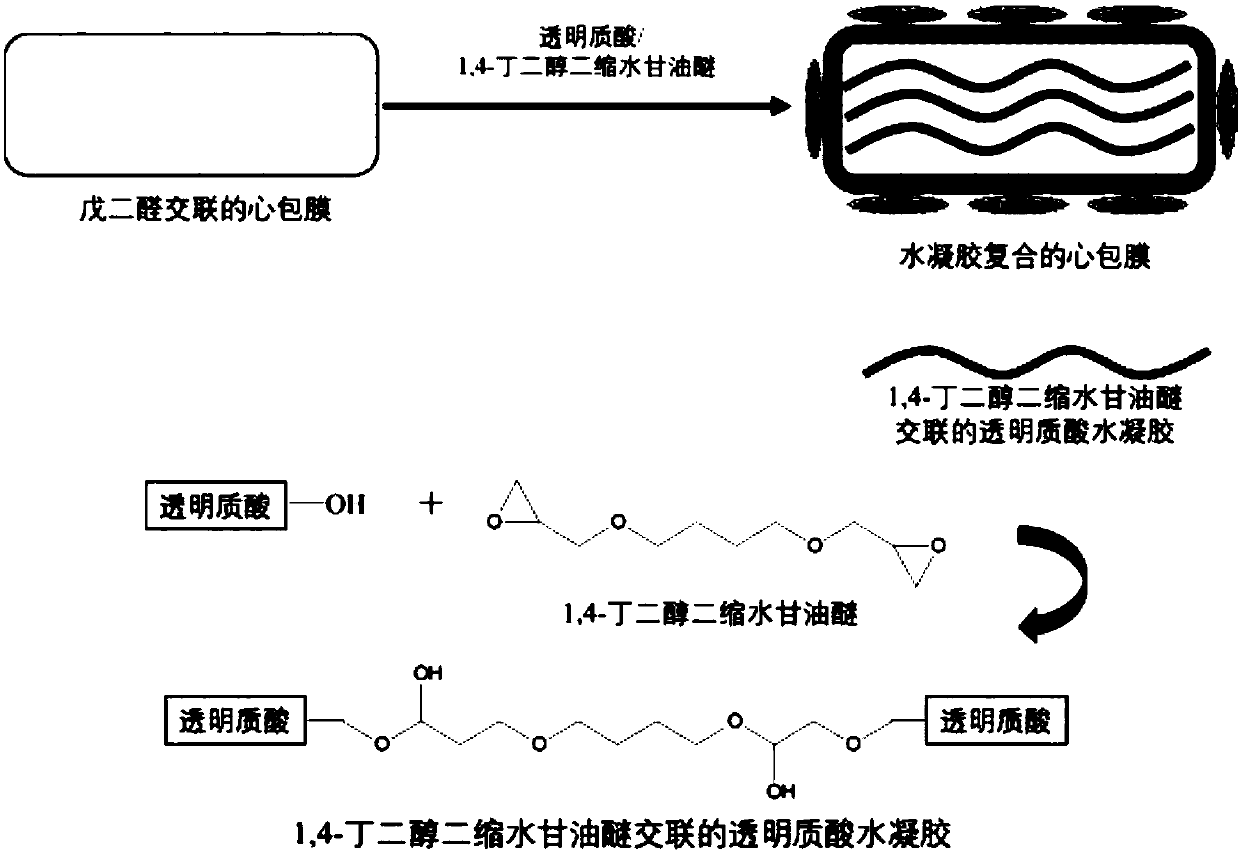
Method for promoting endothelialization of biological heart valves
The present invention discloses a method for promoting endothelialization of biological heart valves. The method comprises the following steps: glutaraldehyde cross-linked pericardium is soaked in anaqueous solution of hyaluronic acid and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether is added to achieve in situ cross-linking of the hyaluronic acid on the pericardium. The provided method can enhance endothelialization of biological materials, reduce calcification, and potentially prolong service life.
Owner:JILIN VENUS HAOYUE MEDICAL LTD
Method for clearing moss in water
InactiveCN106879628AClear safe and effectiveEfficient removalBiocideAnimal repellantsAcetic acidChlorine dioxide
The invention relates to the technical field of environment control, in particular to a method for clearing moss in water. The method for clearing the moss in the water comprises the following steps of 1, preparing of drugs: respectively preparing a certain amount of calcium peroxide, chlorine dioxide disinfectant and acetic acid, and crushing the calcium peroxide powder to certain mesh; 2, feeding of drugs: feeding the prepared calcium peroxide into a water body containing the toss, enabling the calcium peroxide to react in water for a period of time, feeding the prepared chlorine dioxide disinfectant, enabling the chlorine dioxide disinfectant to react in water for a period of time, feeding the prepared acetic acid, and enabling the acetic acid to react in water for a period of time, wherein the certain drug feeding frequency is controlled, and the daily feeding frequency is controlled. The method has the advantages that the moss in the water body can be quickly and effectively cleared, the environment-friendly effect is realized, and the operation is easy.
Owner:广州通穗环保科技有限公司
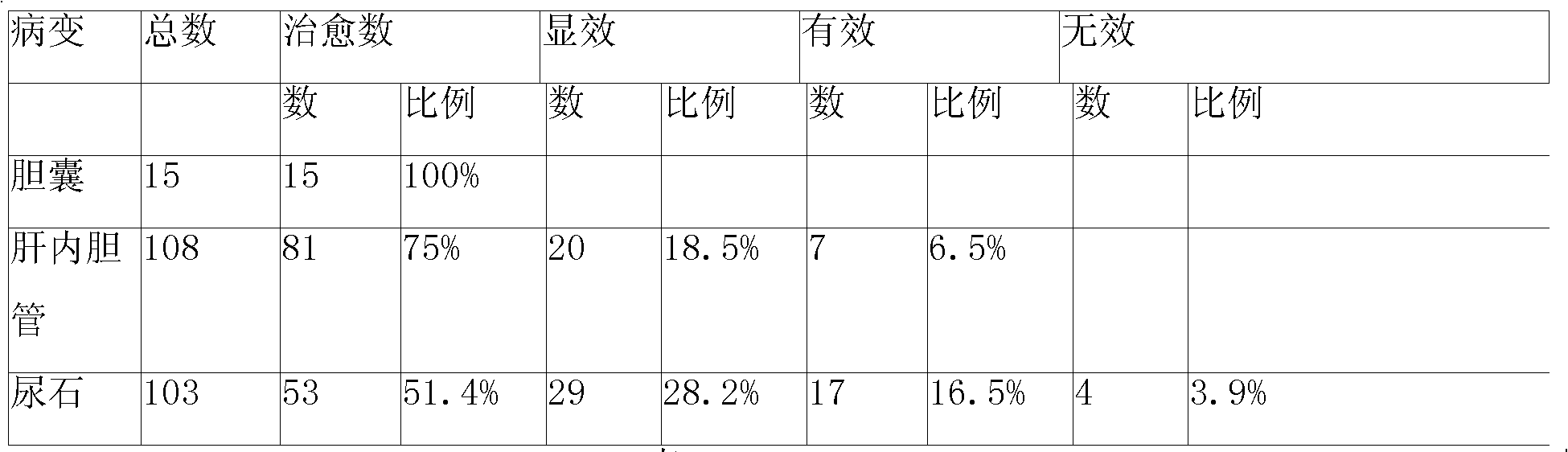
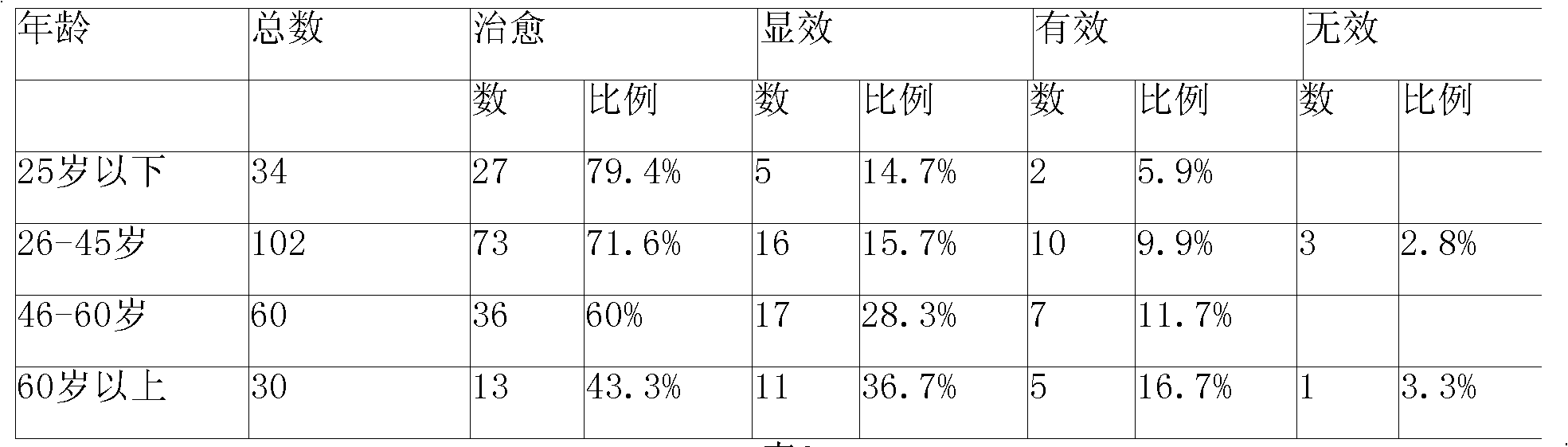
Chinese medicinal decoction for treating lithiasis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101590213AExcellent self-healing functionHas a diuretic effectDigestive systemPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBile JuiceBile secretion
The invention relates to Chinese medicinal decoction used for treating lithiasis and a preparation method thereof, and relates to Chinese medicinal decoction for treating biliary calculus and renal calculus diseases. Main components of the decoction comprise ophiorrhiza pumila, dandelion, rhizoma sparganii, zedoary, white paeony root, herba pyrrosiae, bupleurum, Szechuan lovage rhizome, peach kernel, radix curcumae, gizzard lining, curcuma, knotgrass, gardenia, dried old orange peel, immature tangerine peel, liquorice and the like. The Chinese medicinal decoction can effectively heal intrahepatic bile duct calculus after the gall bladder is extirpated and calcification and sand-like calculus in the kidney, and simultaneously can effectively promote choleresis, improve the self-healing function of the gall bladder, and recover the functions of the gall bladder and the kidney.
Owner:吕文华
Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for effectively treating kitchen waste water and treatment method using the same
InactiveCN107082488AImprove throughputWell mixedWater treatment parameter controlBiological treatment regulationSludgeCalcification
The invention discloses an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for effectively treating kitchen waste water and a treatment method using the same. The anaerobic membrane bioreactor orderly comprises an anaerobic tank, a circulating pump, a water inlet pump, a water inlet tank and a water outlet tank from left to right. The circulating pump and the water inlet pump are respectively connected to the anaerobic tank. The water inlet tank is connected to the water inlet pump. The treatment method comprises adding sludge into the anaerobic membrane bioreactor, setting different sludge staying time, mixing kitchen waste water and a film concentrated solution, feeding the mixture into an anaerobic jar through a water distribution pipe, discharging the decomposing biogas through a water-sealed tank, feeding undecomposed mixed solution into the circulating pump and a membrane module, mixing the undecomposed mixed solution and kitchen waste water fed by the water inlet pump, feeding the mixed solution into the anaerobic jar through a water distribution pipe, and carrying out circulation. The bioreactor and method can eliminate accumulation of colloidal state and dissolved macromolecule organic matters through reasonable control of the sludge residence time, reduce a Ca<2+> accumulation concentration, and reduces a degree of calcification of the sludge. The anaerobic membrane bioreactor has optimal effects of treating kitchen waste water.
Owner:SUZHOU KANGDUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Application of carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to preparation of anti-atherosclerosis drugs
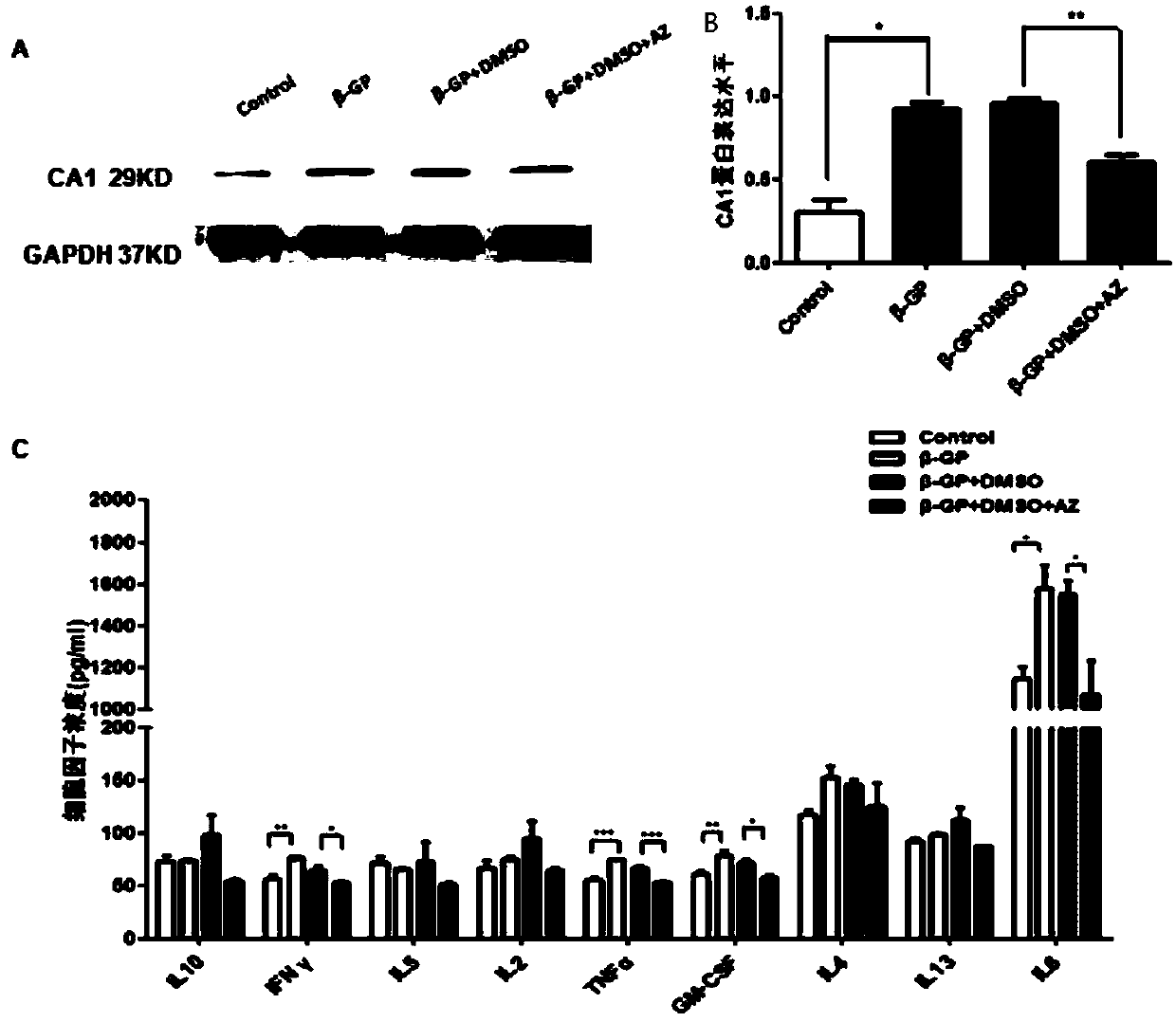
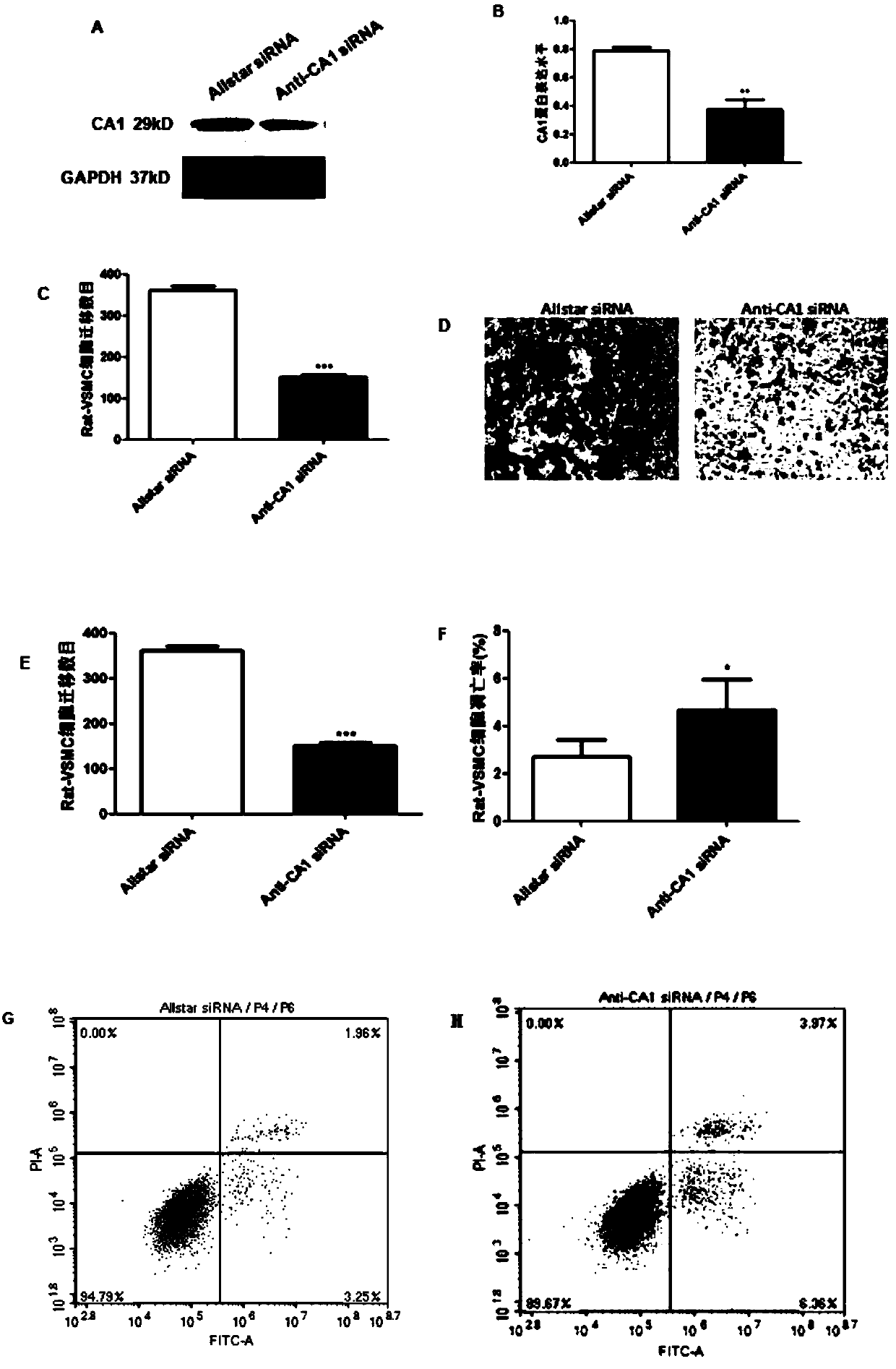
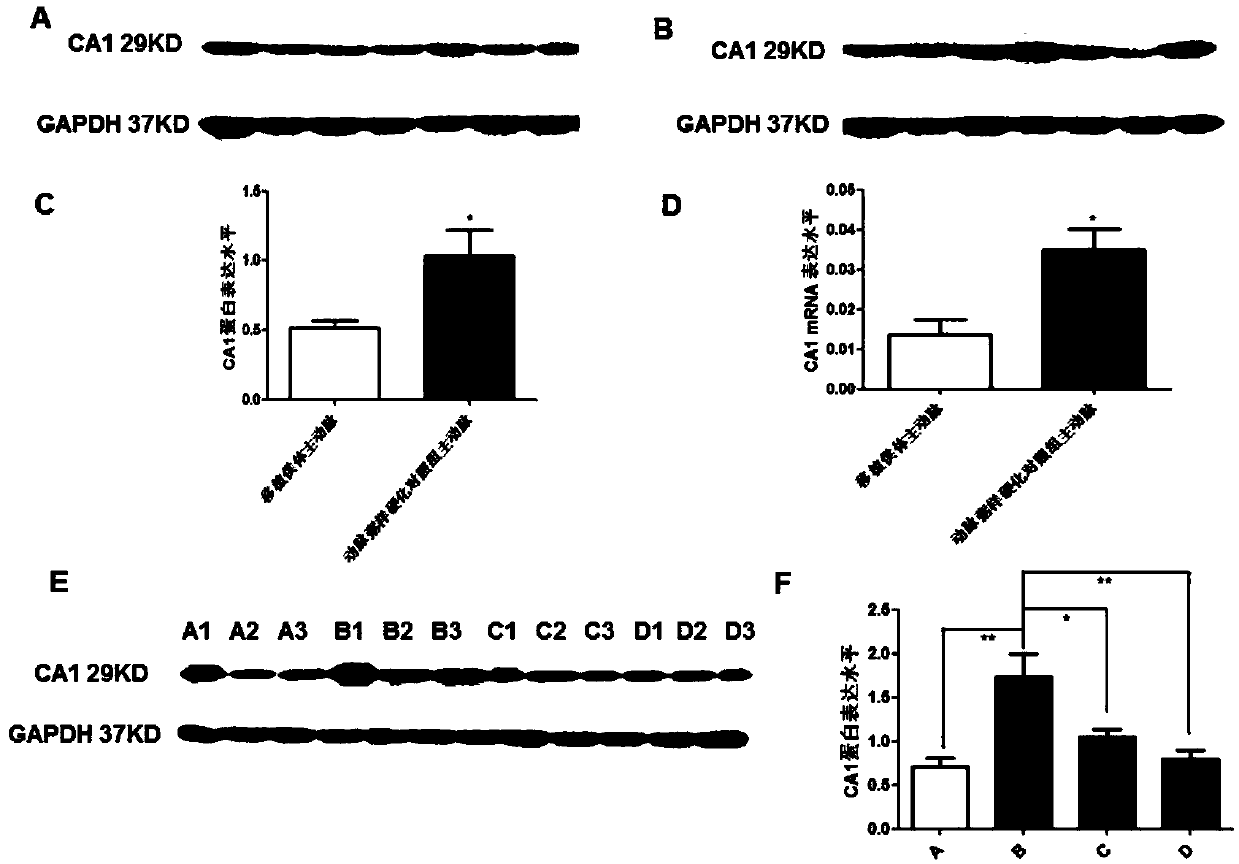
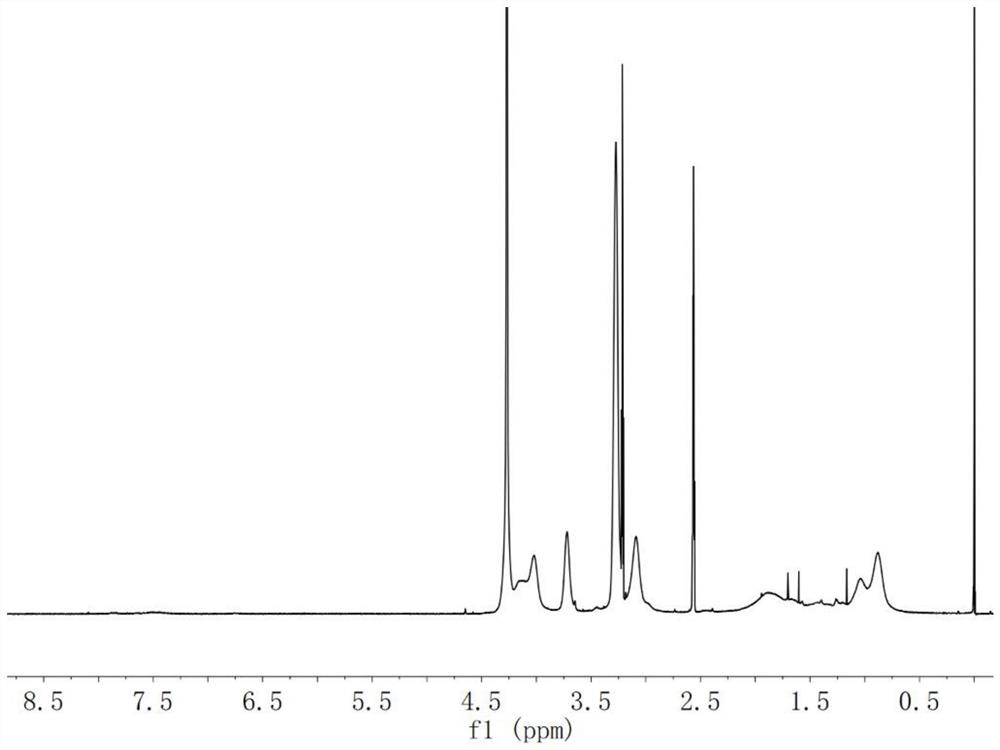
ActiveCN109568315APromote calcificationReduce calcificationOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderInflammatory factorsCarbonic anhydrase II
The invention belongs to the field of anti-arteriosclerosis drugs, and particularly relates to application of a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to preparation of the anti-arteriosclerosis drugs. The study finds for the first time that carbonic anhydrase 1 (CA1) is highly expressed in arteriosclerosis calcified tissue, and CA1 is related to vascular smooth muscle calcification and affects cell proliferation and apoptosis. Methazolamide, the inhibitor of CA1, can significantly reduce the progression of atherosclerosis and inhibit atherosclerotic inflammatory factors. The results suggest that calcification plays an important role in atherosclerosis, and CA1-dominated calcification promotes the course of the atherosclerosis. Methazolamide has a potential therapeutic effect on the atherosclerosisby inhibiting expression of CA1. The findings not only further explain the close relationship between the atherosclerosis and the calcification, but also explore the calcification mechanism of the atherosclerosis, and further prove that inhibition of the calcification is a key point in the treatment of the atherosclerosis. The application of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor to the preparation of the anti-arteriosclerosis drugs provides new ideas for the treatment of the atherosclerosis.
Owner:青岛汇嘉医学科技有限公司
Bio-valve material modified by zwitterionic polymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113082292AEasy to useGood anti-calcificationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationPolymer scienceBioprosthetic valve
The invention discloses a bio-valve material modified by a zwitterionic polymer and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bio-valve material preparation, the method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a polymer with amino and zwitterions, and connecting the obtained polymer and an acellular bioprosthetic valve to the bio-valve in a chemical bonding manner. The bio-valve material prepared by the invention is a bio-valve material modified by a zwitterionic polymer, and the zwitterionic polymer is added before glutaraldehyde crosslinking or after glutaraldehyde crosslinking. The bio-valve material prepared by the invention not only can solve the problems of calcification and blood coagulation in the existing bio-valve, but also can prolong the service life of the bio-valve.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Valve with anti-thrombosis and anti-calcification functions, and preparation method and application of valve
ActiveCN111701077AGood biocompatibilityIncrease contentPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingThrombusAntiplatelet drug
The present invention discloses a valve with anti-thrombosis and anti-calcification functions, and a preparation method and an application of the valve. The valve comprises a valve base and a zwitterionic copolymer covalently connected to the valve base. During preparation, the valve base is firstly soaked in a glutaraldehyde solution to obtain a cross-linked valve; and then the cross-linked valveis soaked in a zwitterionic polymer solution with a concentration of 0.1-5 wt% for reaction for 2-4 days, and then reduction with a reducing agent is conducted to obtain the valve with the anti-thrombosis and anti-calcification functions. The valve material is subjected to anti-thrombosis and anti-calcification treatments, so that after the valve is implanted in patients, risks of valve leaflet thrombosis can be reduced, valve leaflet thickening and transvalvular differential pressure increase are prevented, a long-term hydrodynamic performance is improved, patients can avoid or reduce uses of anticoagulant and antiplatelet drugs, risks of patient bleeding are reduced, besides, aldehyde residues in the valve leaflet tissues are reduced, biocompatibility and anti-calcification ability areimproved, and ultimately complications of valve leaflet thrombosis are reduced and service life of the valve is extended.
Owner:JILIN VENUS HAOYUE MEDICAL LTD
Methods and materials for treating calcific aortic valve stenosis
ActiveUS9789126B2Reduce calcificationLonger and happier livesOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCalcified aortic valveAgonist
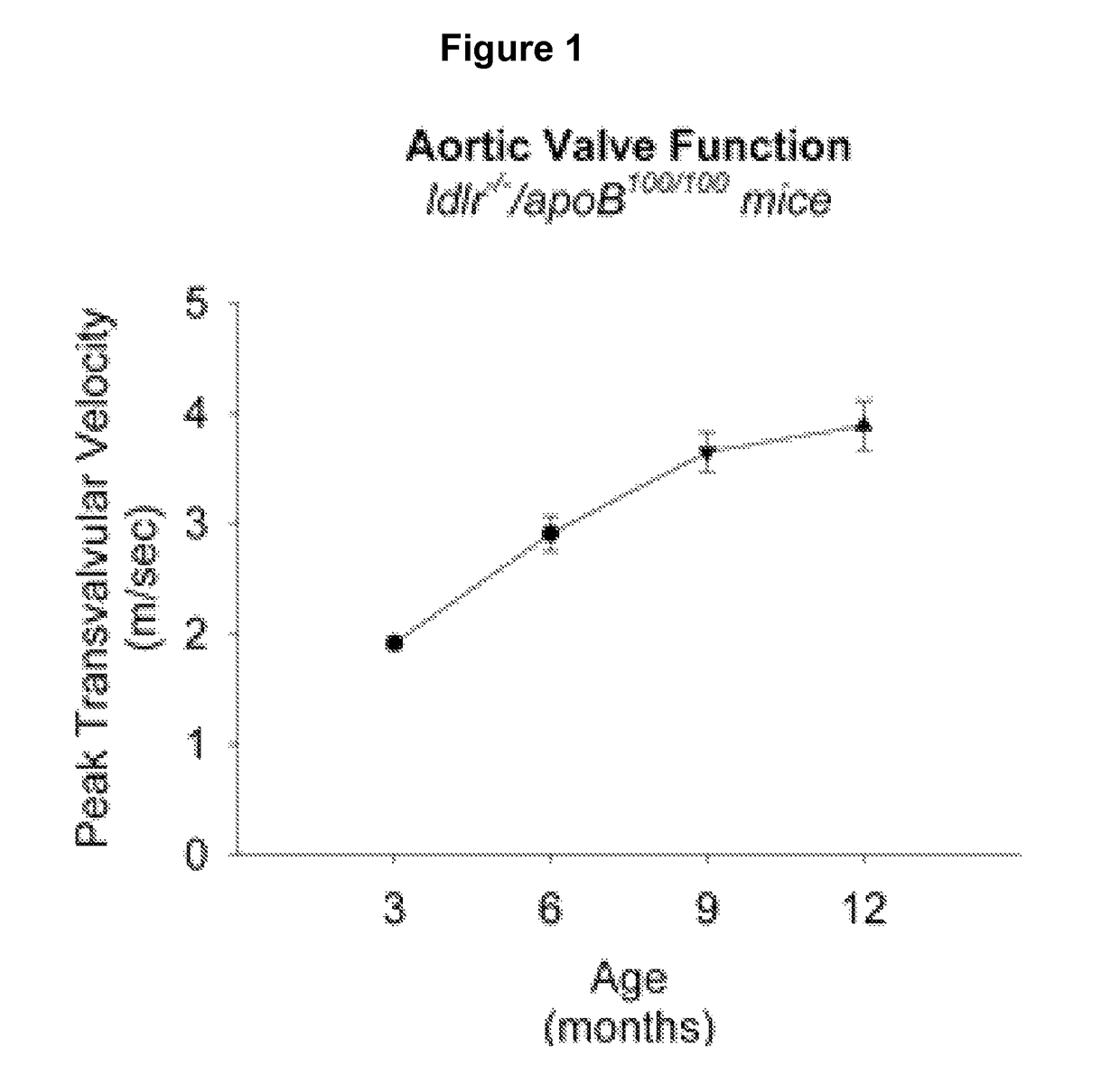
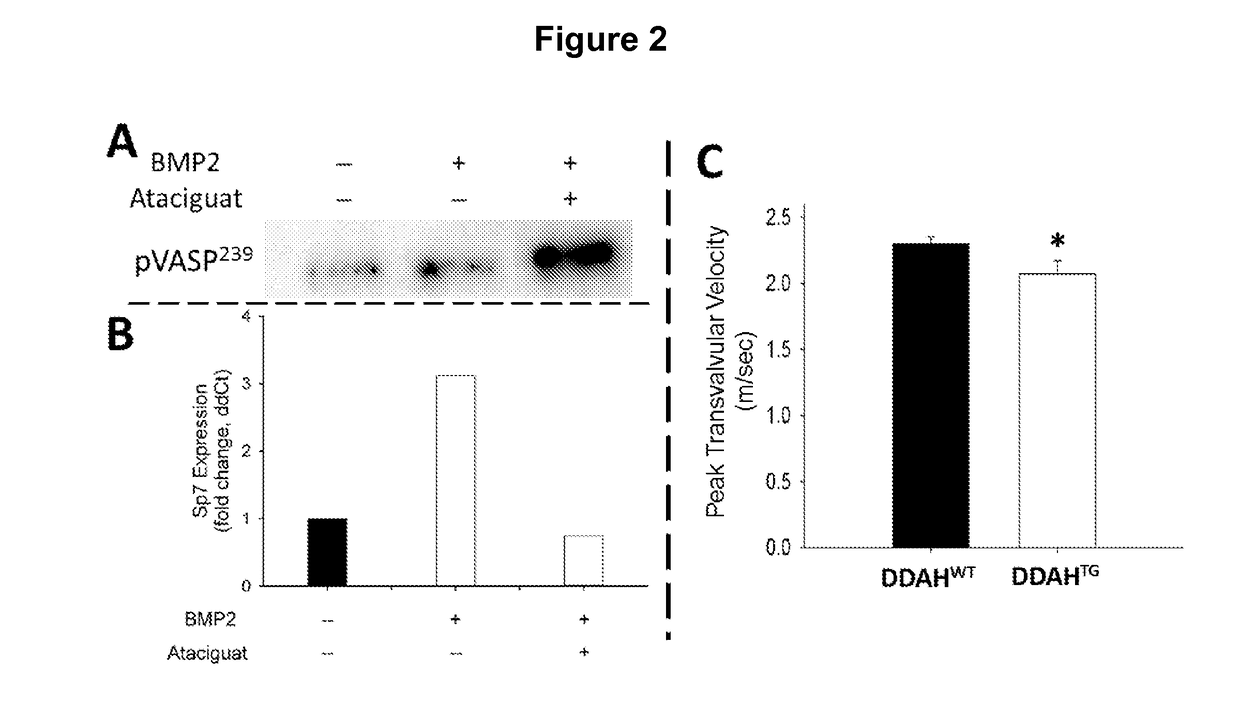
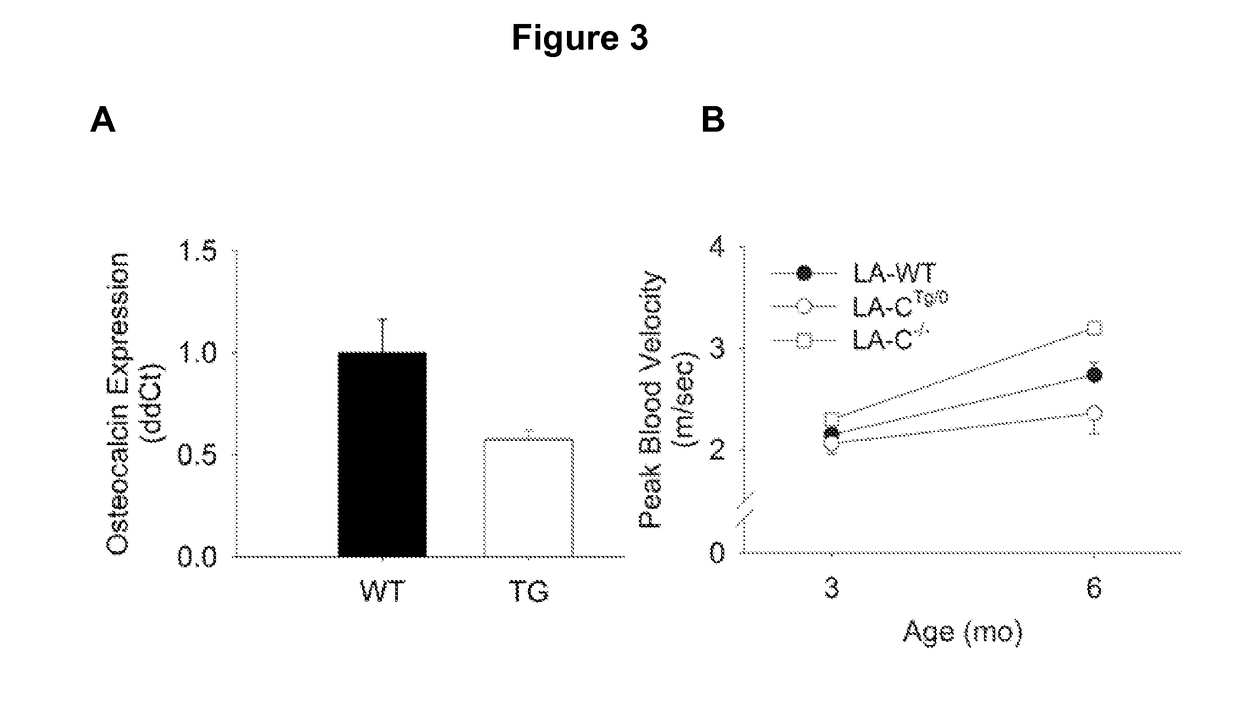
This document provides methods and materials involved in treating cardiovascular conditions such as calcific aortic valve stenosis. For example, methods and materials for using sGC agonists or a combination of sGC agonists and PDE5A inhibitors to reduce calcification of heart valves and / or vessels or to slow progression of aortic sclerosis to calcific aortic valve stenosis are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method for preparing biological tissue for surgical implantation
PendingUS20220072202A1Reduce calcificationImproved mechanical propertyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationBiological tissueRat heart
The present invention relates to a method for treating biological tissue and a biological tissue obtained by the treatment method, and specifically to a method for treating biological tissue so as to suppress the calcification, risk of biofilm adherent over pericardium and strength reduction of the tissue due to treatment. The invention is also directed to bioprosthesis and transcatheter heart valves containing the biological tissue.
Owner:PF PROD FEATURES GMBH
Purified EMD protein composition
ActiveUS8466101B2Reduce calcificationHard differentiationCosmetic preparationsElectrolysis componentsProtein compositionTissue defect
Pharmaceutical, dental and / or cosmetic composition consisting of purified Enamel Matrix Derivative (EMD) proteins which have a molecular weight between 1 and 55 kDa, formulated in a suitable pharmaceutical carrier. The composition is depleted of proteins which have a molecular weight between 56 and 160 kDa and an iso-electric point between 3-10. The purified Enamel Matrix Derivative (EMD) proteins are depleted of proteinase inhibitors, such as α1-antichymotrypsin and / or Fetuin A. The composition is preferably used for promoting and / or inducing regeneration of hard tissue, tissue mineralization, bone growth and / or bone regrowth, regeneration of dentin, cementogenesis, and / or binding between parts of living mineralized tissue, for bonding of a piece of living mineralized tissue to a bonding site on a piece of other living tissue, for endorsing binding between hard tissues, and / or for filling a mineralized wound cavity and / or tissue defect following from a procedure and / or trauma.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
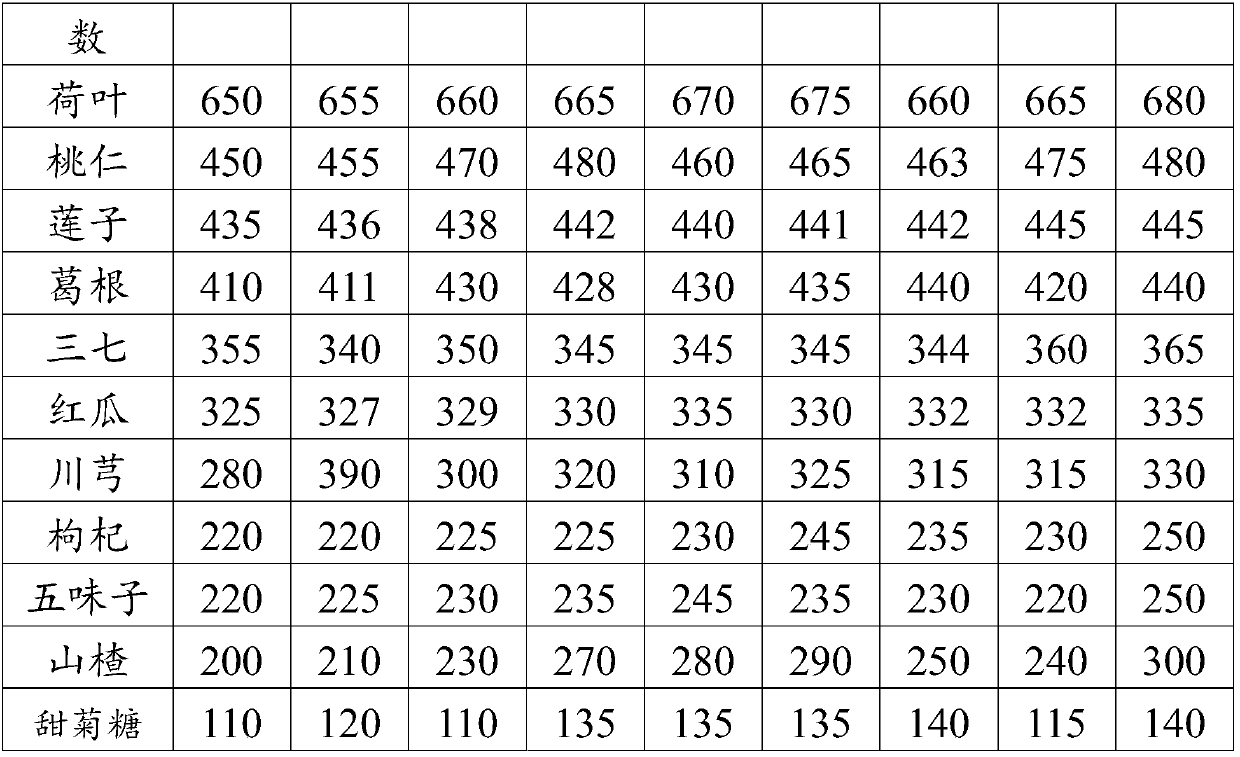
Microcirculation-dredging drink and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107897586AReduce calcificationProtect liver and kidney functionFood scienceLiver and kidneyCalcification
The present invention provides microcirculation-dredging drink and a preparation method thereof. The microcirculation-dredging drink comprises the following raw materials: 600-730 pats of lotus leaves, 350-480 parts of peach kernels, 400-480 parts of lotus seeds, 385-480 parts of radix puerariae, 350-380 parts of radix notoginseng, 300-350 parts of flowers carthami, 200-350 parts of rhizoma chuanxiong, 150-250 parts of Chinese wolfberry fruits and 150-300 parts of fructus schizandrae. The present invention also provides a preparation method of a compound granule and oral liquid of the microcirculation-dredging drink. The provided microcirculation-dredging drink has overall regulation functions of dredging blood vessels, removing free radicals and lipid toxins in the blood vessels, increasing blood vessel elasticity, promoting blood circulation and dispersing blood stasis, calming mind and soothing nerves, protecting liver and kidney functions, and regulating body microcirculation, reduces risks of organ calcification or fibrosis, and provides a basis for a further development of various health-care products and drugs of the microcirculation-dredging drink.
Owner:朱强
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com