Valve with anti-thrombosis and anti-calcification functions, and preparation method and application of valve
An anti-thrombotic and valve technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of calcification and heart valve thrombosis, and achieve the effect of reducing calcification, improving biocompatibility and anti-calcification ability, and preventing the thickening of valve leaflets.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
[0029] A valve with anti-thrombotic and anti-calcification functions is prepared through the following steps:
[0030] S1: Wash the fresh pig pericardium thoroughly with deionized water, and add PBS buffer to completely immerse the tissue;
[0031] S2: Add glutaraldehyde to the PBS buffer solution to a glutaraldehyde concentration of 0.5-0.7wt%, cross-link at room temperature for 6-8 days, then remove and clean it to obtain cross-linked porcine pericardium;
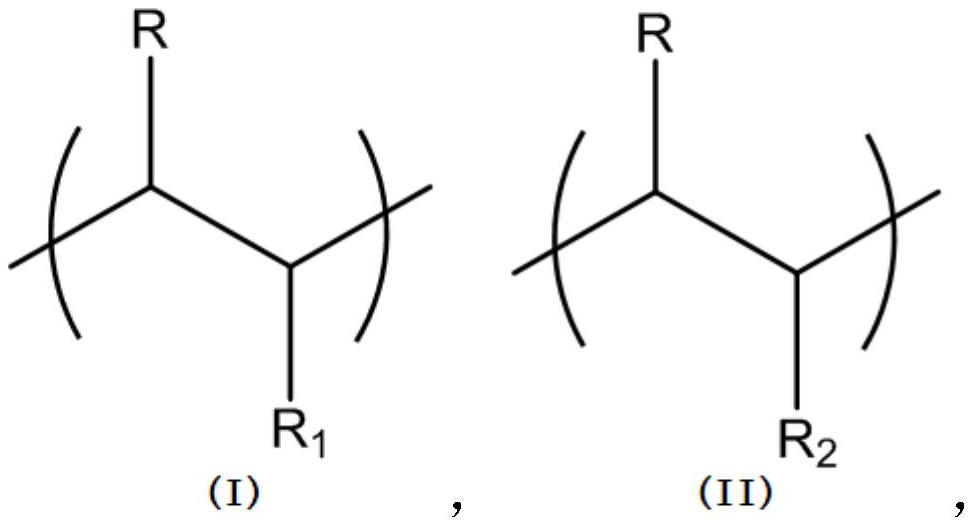
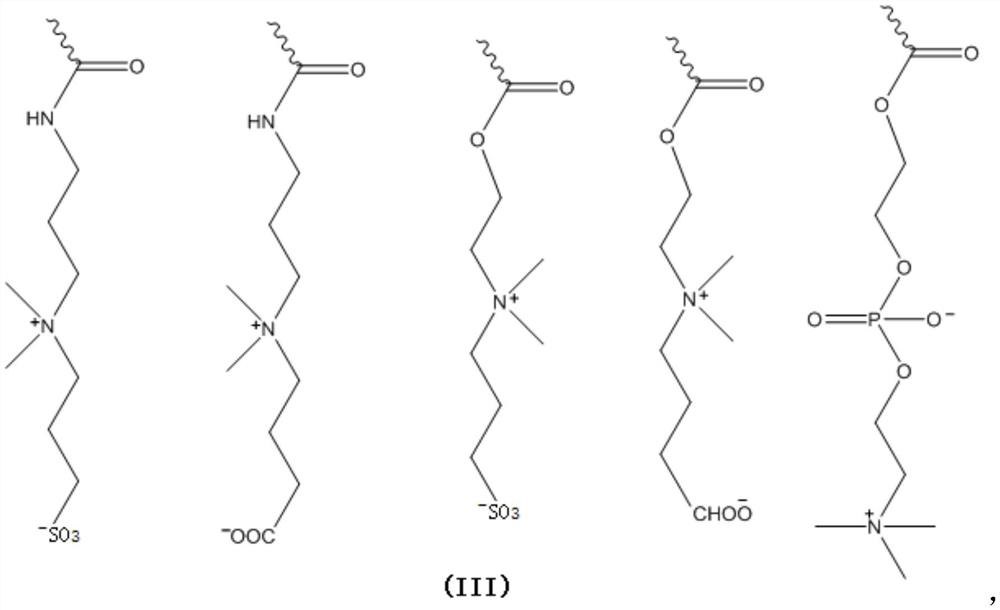
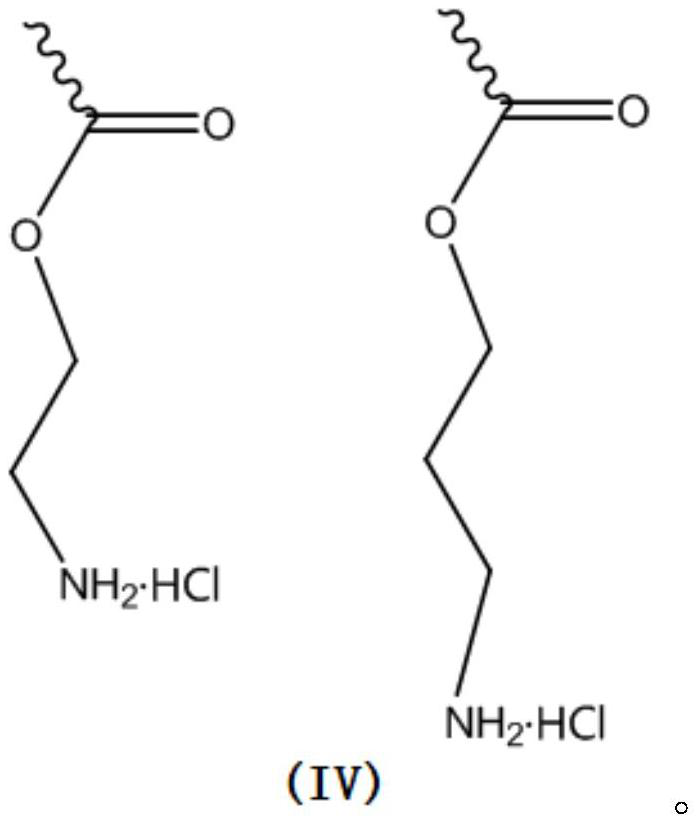
[0032] S3: Immerse the cross-linked porcine pericardium with a zwitterionic polymer solution with a concentration of 0.1-5wt%, wherein the zwitterionic polymer includes repeating units as shown in formula (I) and formula (II), and the zwitterionic polymer is as in formula The molar ratio of the repeating unit shown in (II) is 0.1%-50%, and the balance is the repeating unit shown in formula (I). Porcine pericardium is immersed in zwitterionic polymer solution at room temperature for 2 to 4 days, and then taken out and reduced wi...
experiment example 1
[0037] Experimental example 1: Anticoagulant performance of valve material
[0038] The valve material prepared in the example and the valve material without zwitterion modification were cleaned and cut into 8 mm diameter discs, and they were incubated with platelet-rich plasma for 1 hour, and measured with a lactate dehydrogenase kit after cleaning. The amount of platelet adsorption on the valve material is shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the anticoagulant performance of the biological valve after zwitterion modification is significantly higher than that of the unmodified biological valve.
[0039] Table 2 Adsorption of platelets on valve tissue
[0040] name of association Adsorption capacity AMA-MPC 0.5±0.3 AMA-SBMA 0.2±0.2 AMA-CBMA 0.4±0.2 Glutaraldehyde cross-linked biological valve 1.2±0.1
experiment example 2
[0041] Experimental example 2: Anti-calcification performance of valve material
[0042] The valve material prepared in the examples and the valve material without zwitterion modification were cut into 1 square centimeter sheets, implanted subcutaneously in SD rats for 90 days and then taken out, and the calcium content on the valve material was measured. The results are shown in Table 3. . It can be seen from Table 3 that the degree of calcification of the biological valve after zwitterion modification is weaker than that of the biological valve after glutaraldehyde cross-linking, indicating that the anti-calcification performance of the valve is significantly improved after zwitterion modification.
[0043] Table 3 Calcium content in biological tissues
[0044] name of association Calcium content (g / kg) AMA-MPC14.9 AMA-SBMA15.2 AMA-CBMA15.5 Glutaraldehyde cross-linked biological valve120.6
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com