Vascular disease therapies
a technology for vascular disease and therapies, applied in the field of vascular disease therapies, can solve the problems of endothelial dysfunction, devastating vascular complications of diabetes, and affect every major organ, and achieve the effect of reducing vascular calcification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
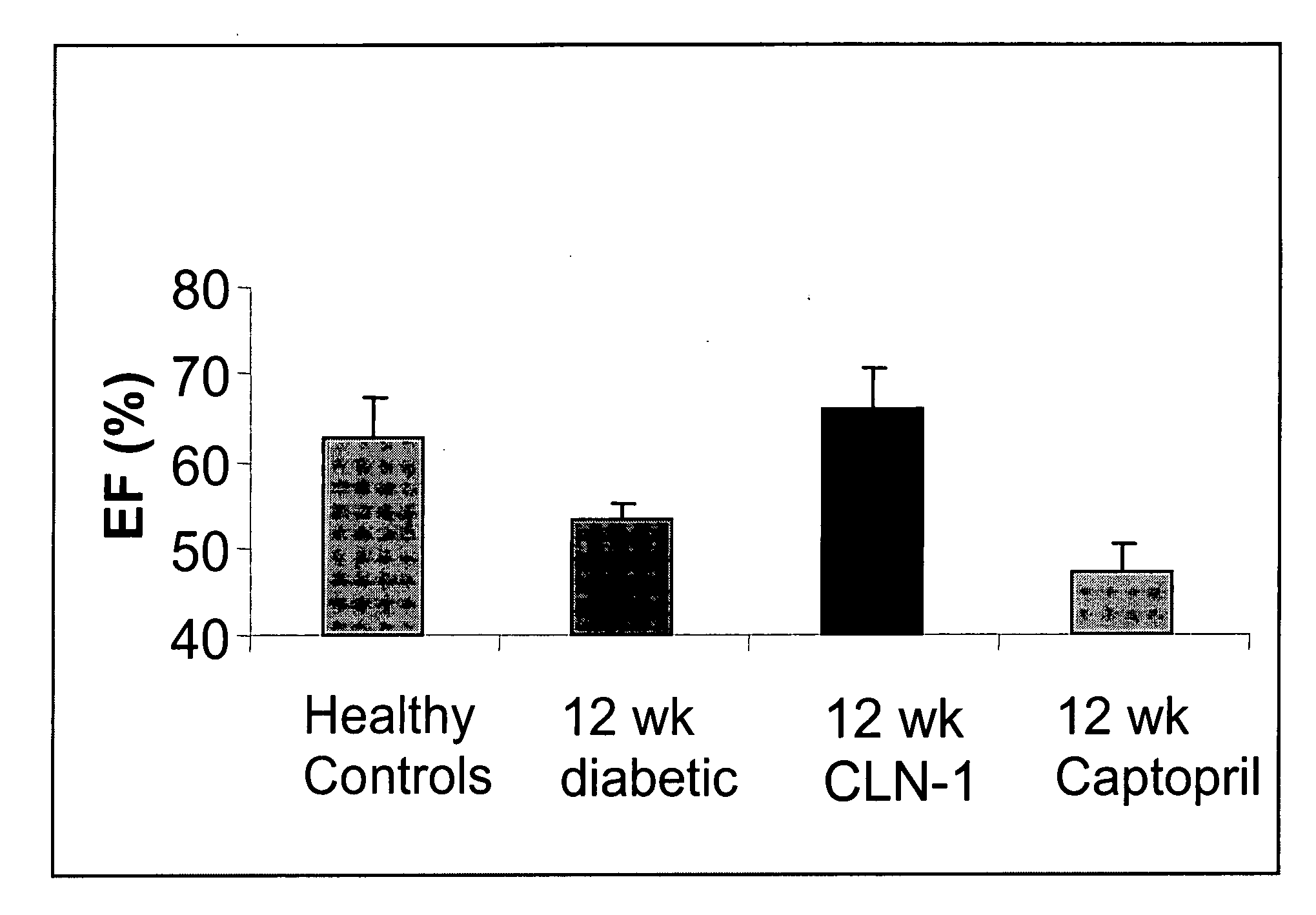
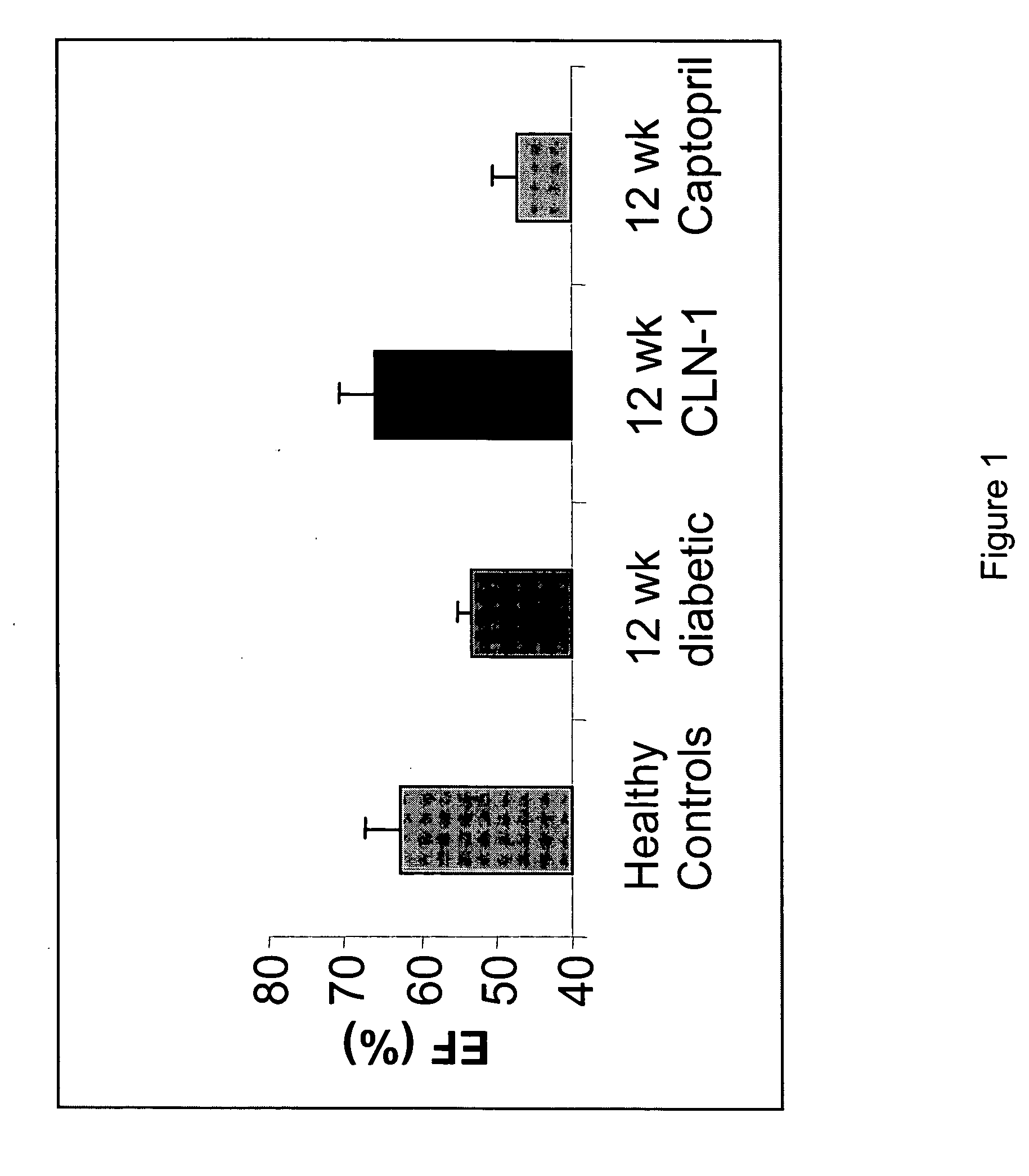
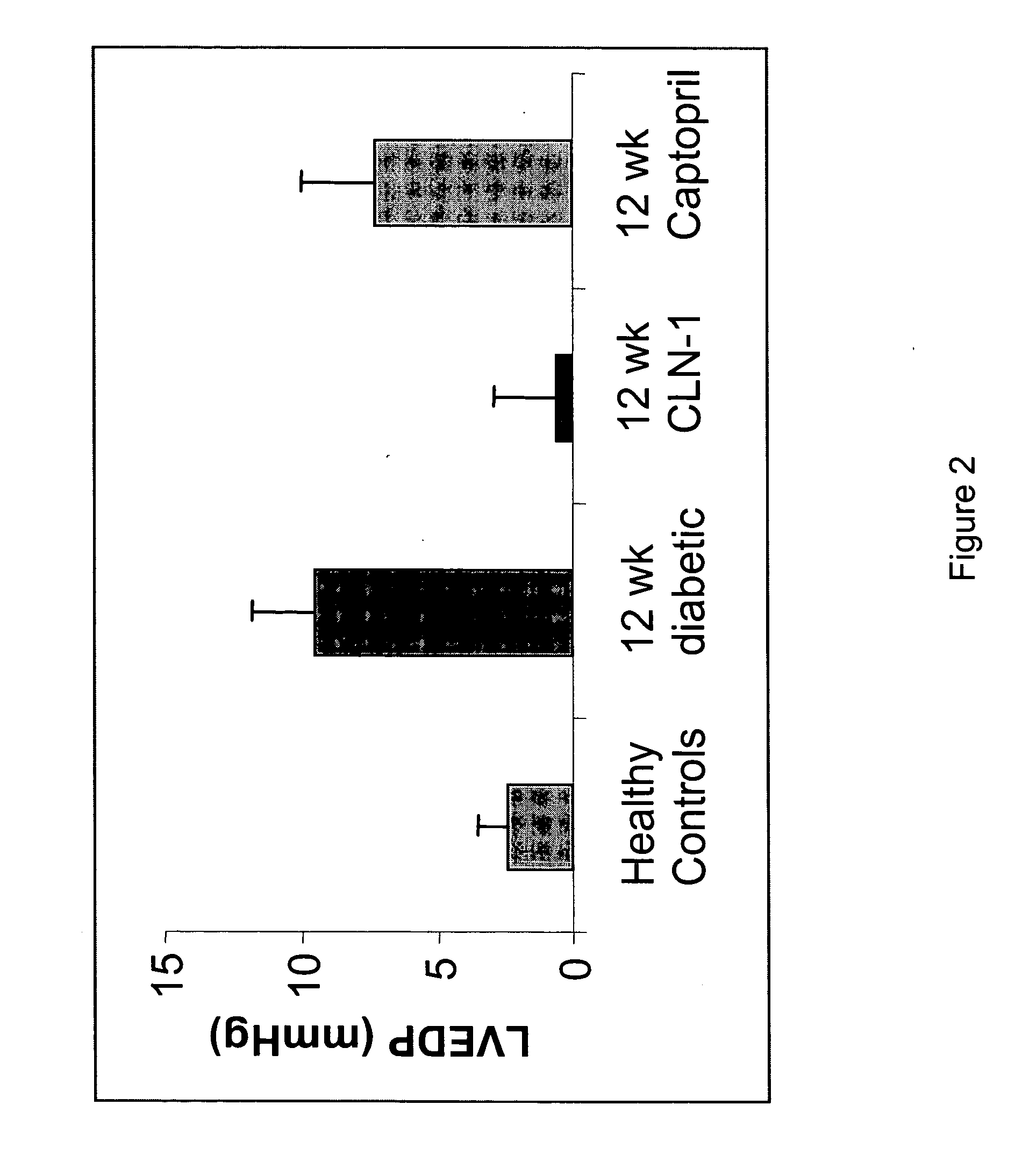
Anti-CTGF Therapy Improves Hemodynamic Parameters and Cardiac Function
[0108] The methods of the invention were used to demonstrate broad-spectrum efficacy in an animal model for certain aspects of vascular complications associated with diabetes as follows. Diabetes mellitus was induced in Sprague Dawley rats by a single i.v. dose of streptozotocin (STZ) (65 mg / kg). STZ-induced diabetes in rats leads to increased vascular permeability (Lawson et al. (2005) Regul Pept 124:221-224) and decreased cardiac function (Machackova et al. (2004) Mol Cell Biochem 261:271-278). Experimental rats received an intravenous injection of 0.1M citrate-buffered streptozotocin (pH 4.1) at a dosage of 65 mg / kg (65 mg / ml) on day zero. Successful induction of diabetes in animals treated with STZ was confirmed on day 2 by an elevation in fasted blood glucose levels (>250 mg / dl).
[0109] Diabetic animals were divided into treatment groups (Vehicle, 3 mg / kg, 5 mg / kg, or 10 mg / kg anti-CTGF antibody, CLN-1). Tre...
example 2
Anti-CTGF Therapy Reduces Arterial Stiffness
[0115] The effect of anti-CTGF therapy on arterial stiffness (a measure of vascular function, and in particular macrovascular function) was measured using the animal model of diabetes described above in Example 1. Various measurements of arterial stiffness were obtained, including passive and active pressure-volume data from the carotid artery. For these measurements, the distal portion of the left carotid artery was cannulated with PE-50 tubing connected to a three-way stopcock. A modified Krebs buffer solution was infused into the carotid artery via the cannula. The proximal end of the carotid artery was occluded using a vascular occluder. To measure force developed during infusion of the buffer solution, a pressure transducer was connected to the three-way stopcock. The PE-tubing end was also connected to an isometric force transducer to measure the isometric axial force during pressurization. A digital image analysis system was used t...
example 3
Anti-CTGF Therapy Reduces Vascular Permeability
[0136] The effect of anti-CTGF therapy on vascular permeability (a measure of vascular function, in particular microvascular function) was measured using the animal model of diabetes described above in Example 1. At various times after the induction of diabetes, rats were tested for increased vascular permeability (VP) as follows. Unanesthetized rats were given intravenous injections of Evans Blue (EB) dye (20 mg / kg). Twenty minutes later, animals were sacrificed by anesthetic overdose and their hearts removed. Skin sections from the trunk, posterior to the shoulder, were removed and weighed. In this assay, increased vascular permeability is characterized by extravasation of dye into the skin. The skin was immersed in formamide (4 ml / g wet weight) at 24° C. for 24 hours. The absorbance of EB dye extracted in formamide was then measured by spectrophotometry at 620 nm using a plate reader. In this assay, the concentration of EB dye is pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com