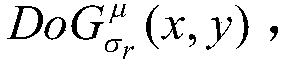Patents
Literature
36 results about "Retinal Neuron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
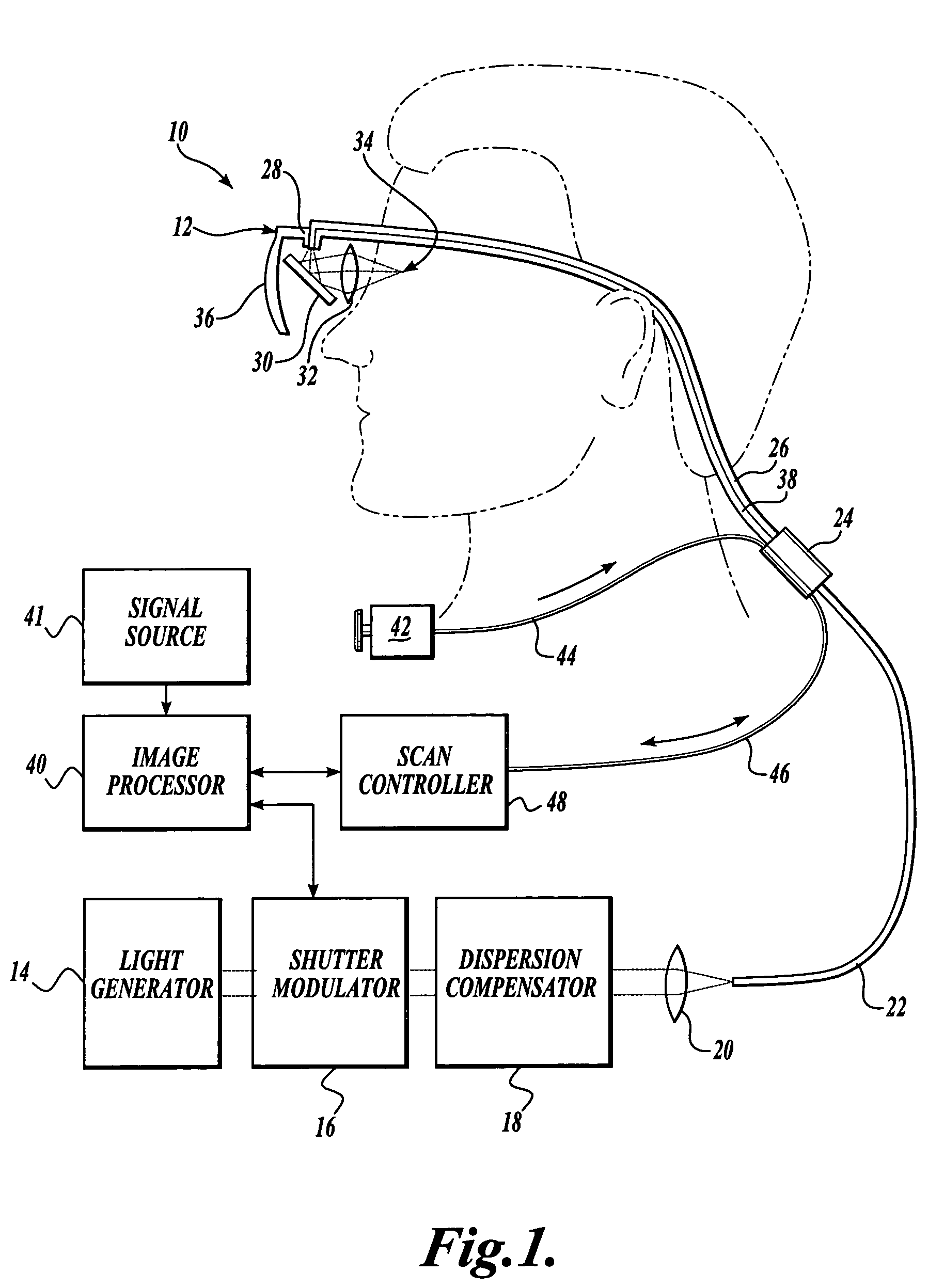
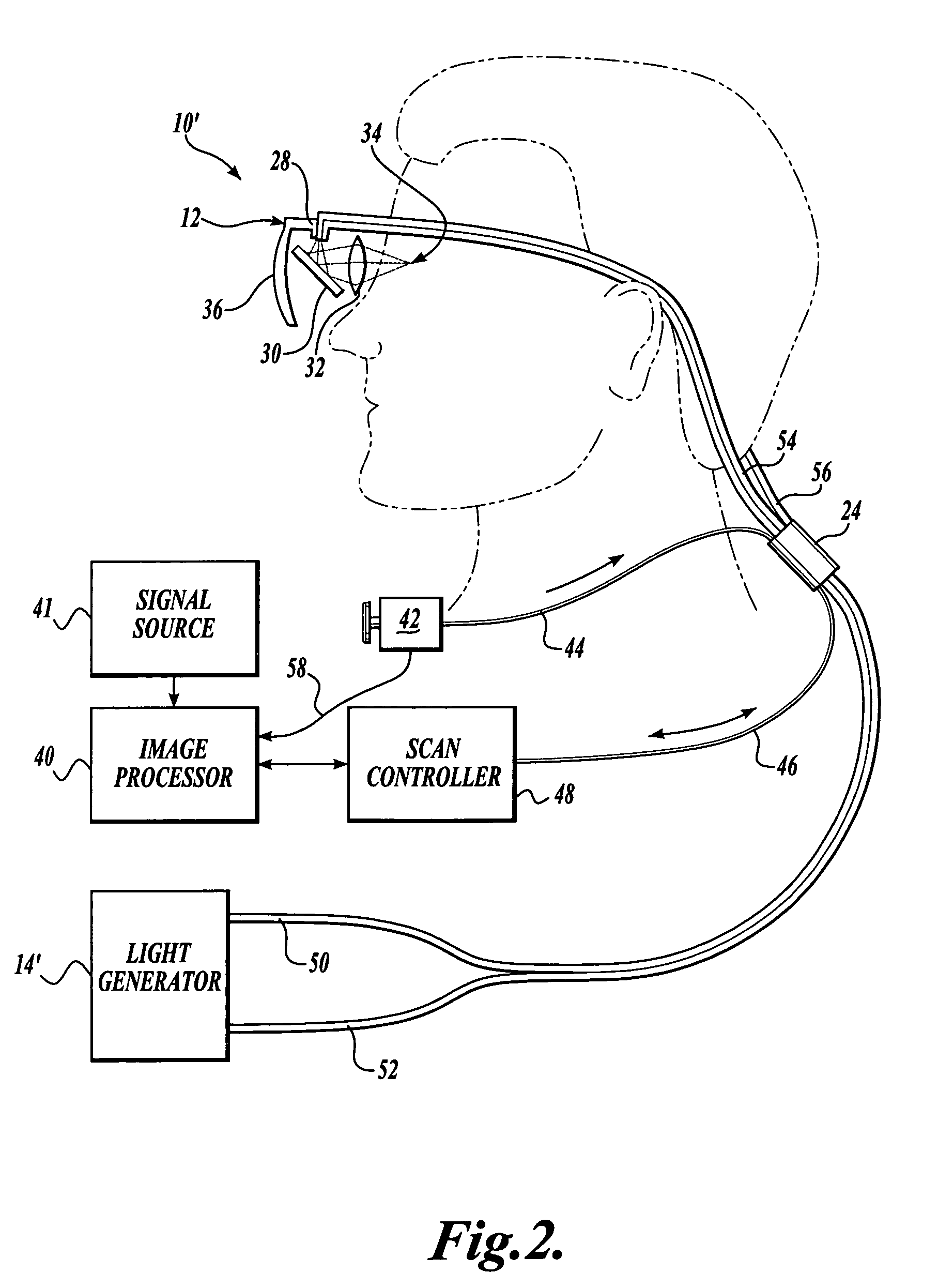
Scanning laser device and methods of use
InactiveUS20050015120A1Promote healthEasy SurvivalElectrotherapyDiagnosticsLight energyRetinal Neuron
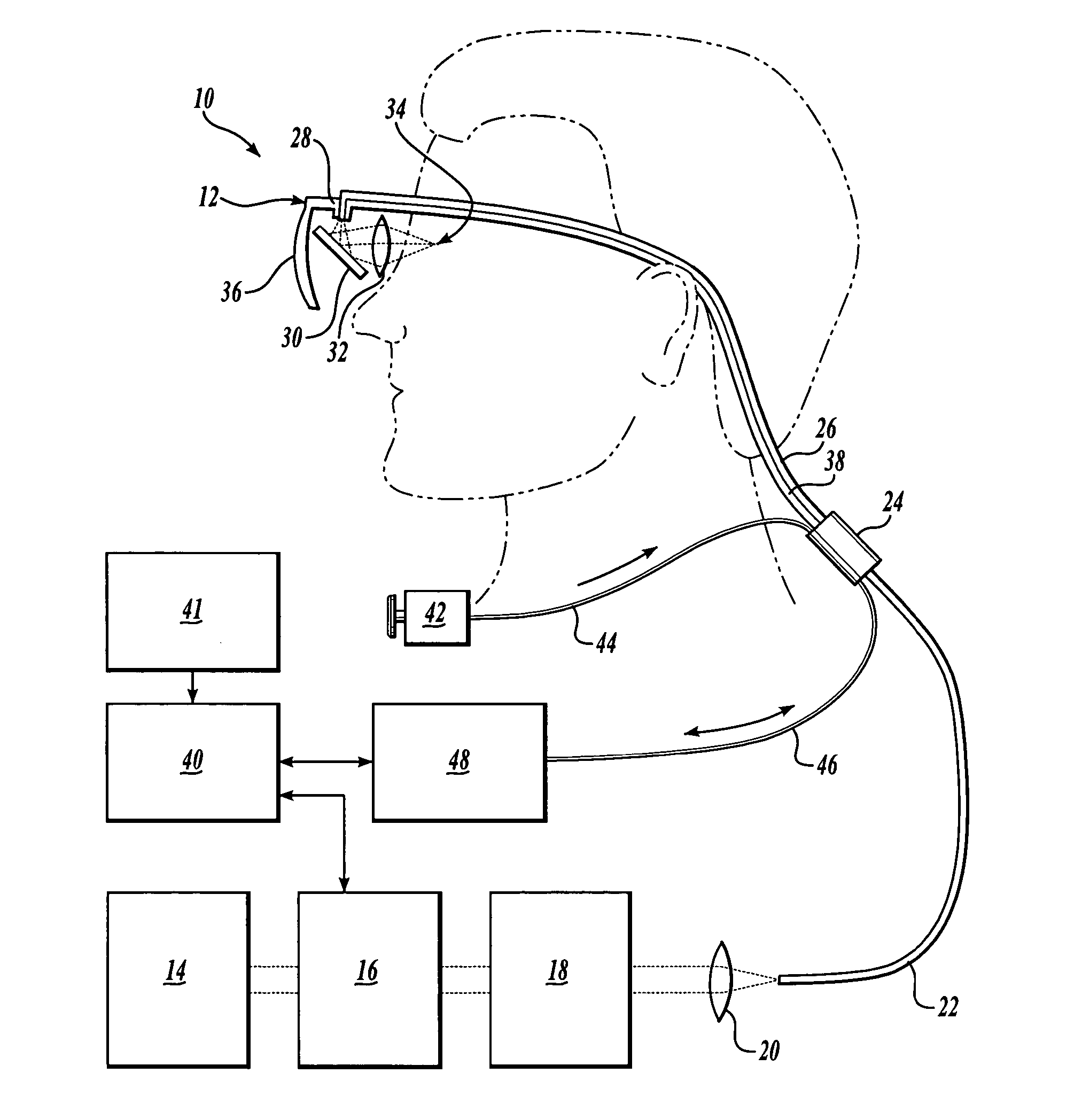
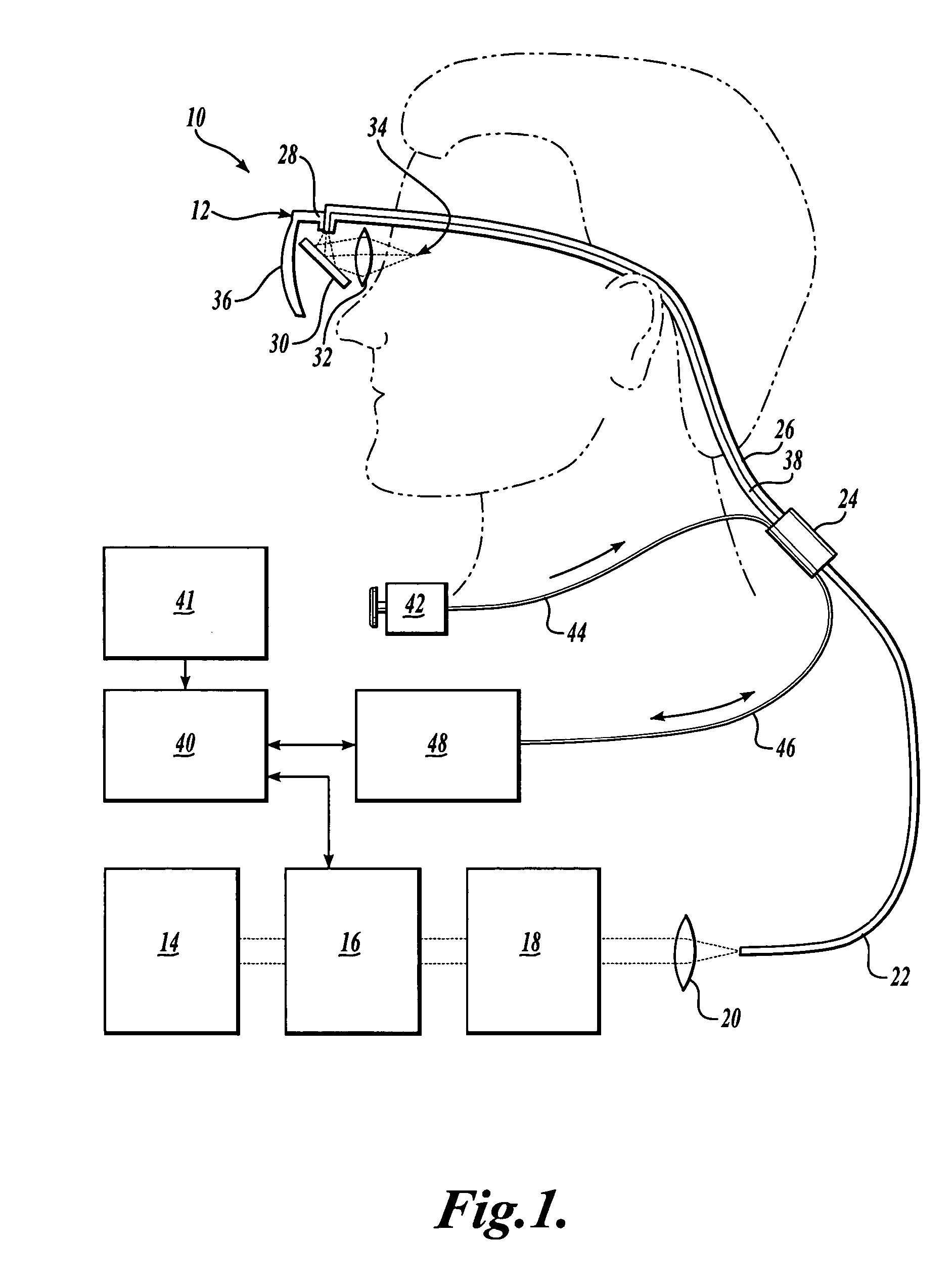
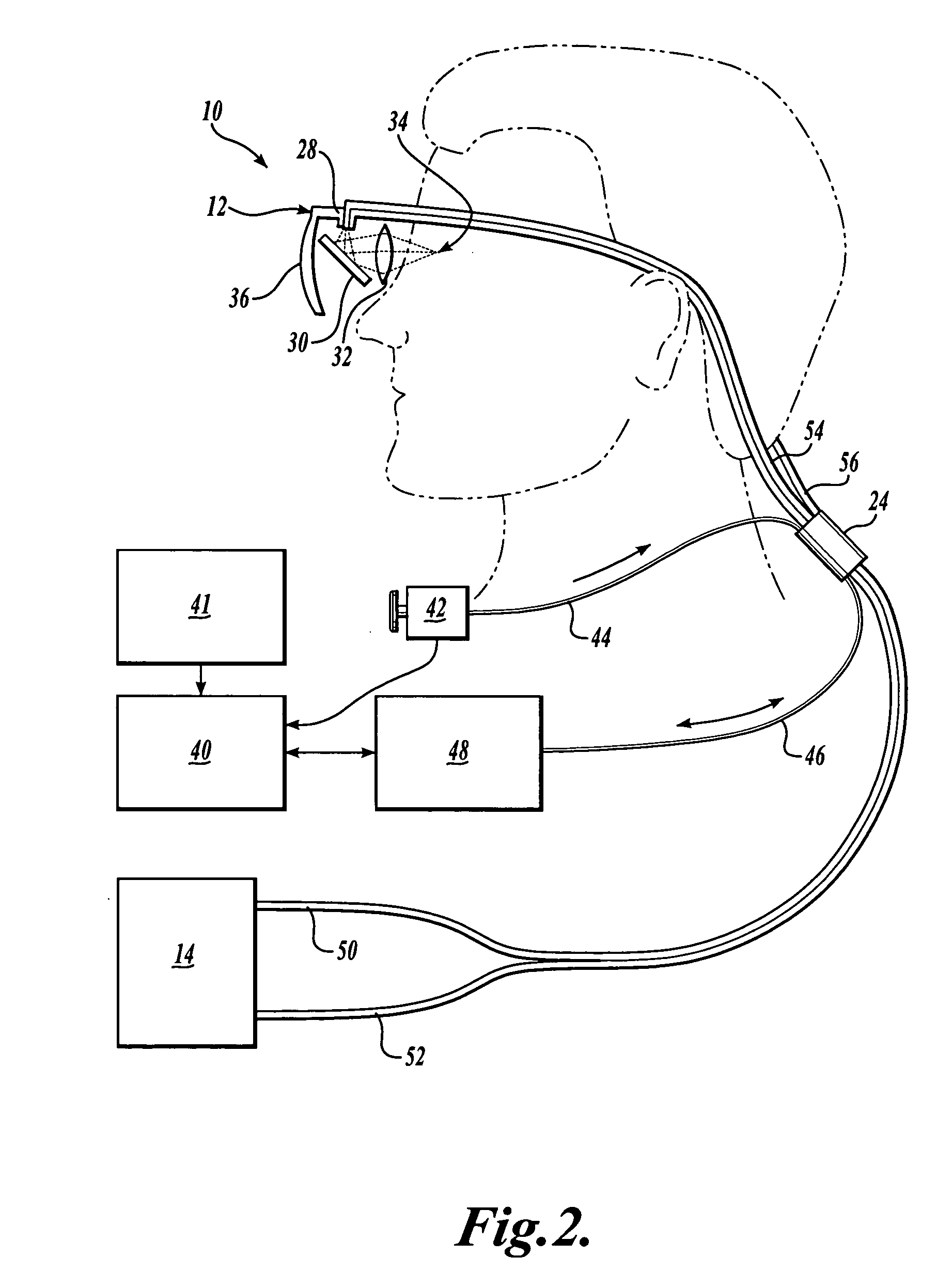
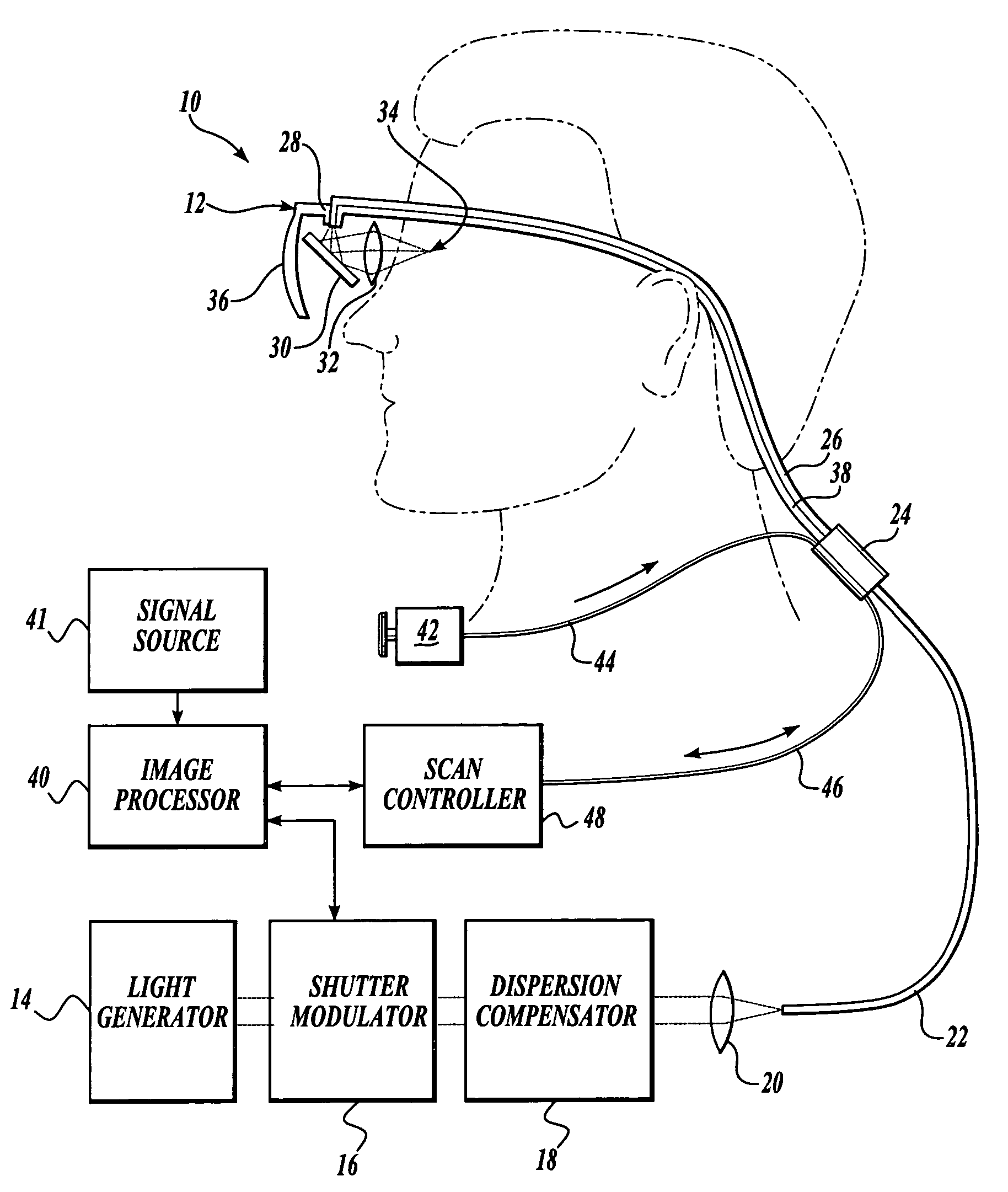
In one aspect, the invention provides vision prosthesis systems. Exemplary vision prosthesis systems of the invention comprise a light energy generator operably connected to a wearable head piece comprising a device for directing light energy produced by the light energy generator onto a mammalian retina, wherein the light energy generator is tuned to emit light energy of sufficient power to modulate neural activity in the retina. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for irradiating neurons in the retina of the mammalian eye by directing light energy produced by a light energy generator onto a mammalian retina. The methods of the invention may be used to directly modulate the activity of retinal neurons or to introduce molecules into retinal cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Scanning laser device and methods of use
In one aspect, the invention provides vision prosthesis systems. Exemplary vision prosthesis systems of the invention comprise a light energy generator operably connected to a wearable head piece comprising a device for directing light energy produced by the light energy generator onto a mammalian retina, wherein the light energy generator is tuned to emit light energy of sufficient power to modulate neural activity in the retina. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for irradiating neurons in the retina of the mammalian eye by directing light energy produced by a light energy generator onto a mammalian retina. The methods of the invention may be used to directly modulate the activity of retinal neurons or to introduce molecules into retinal cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
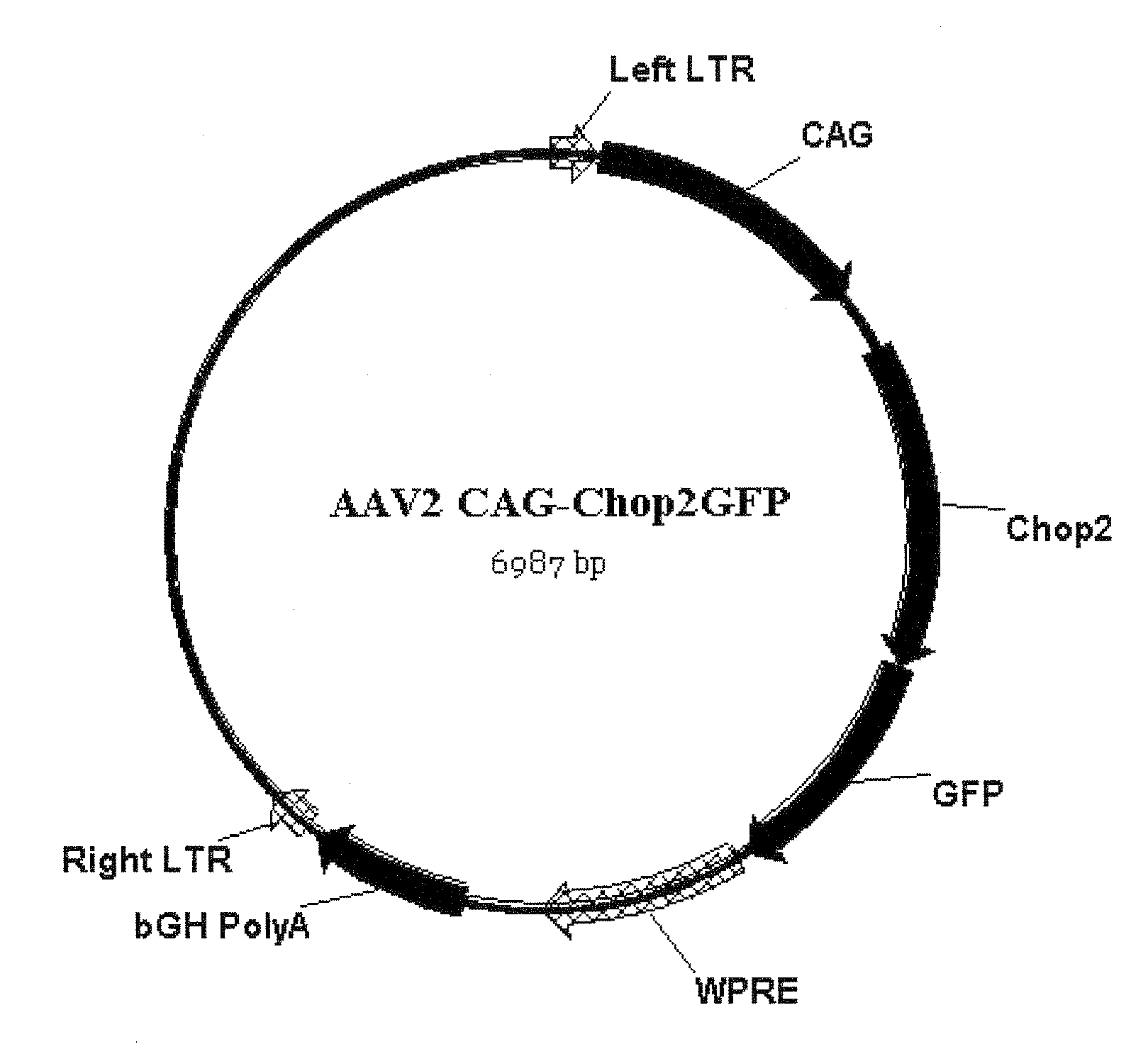
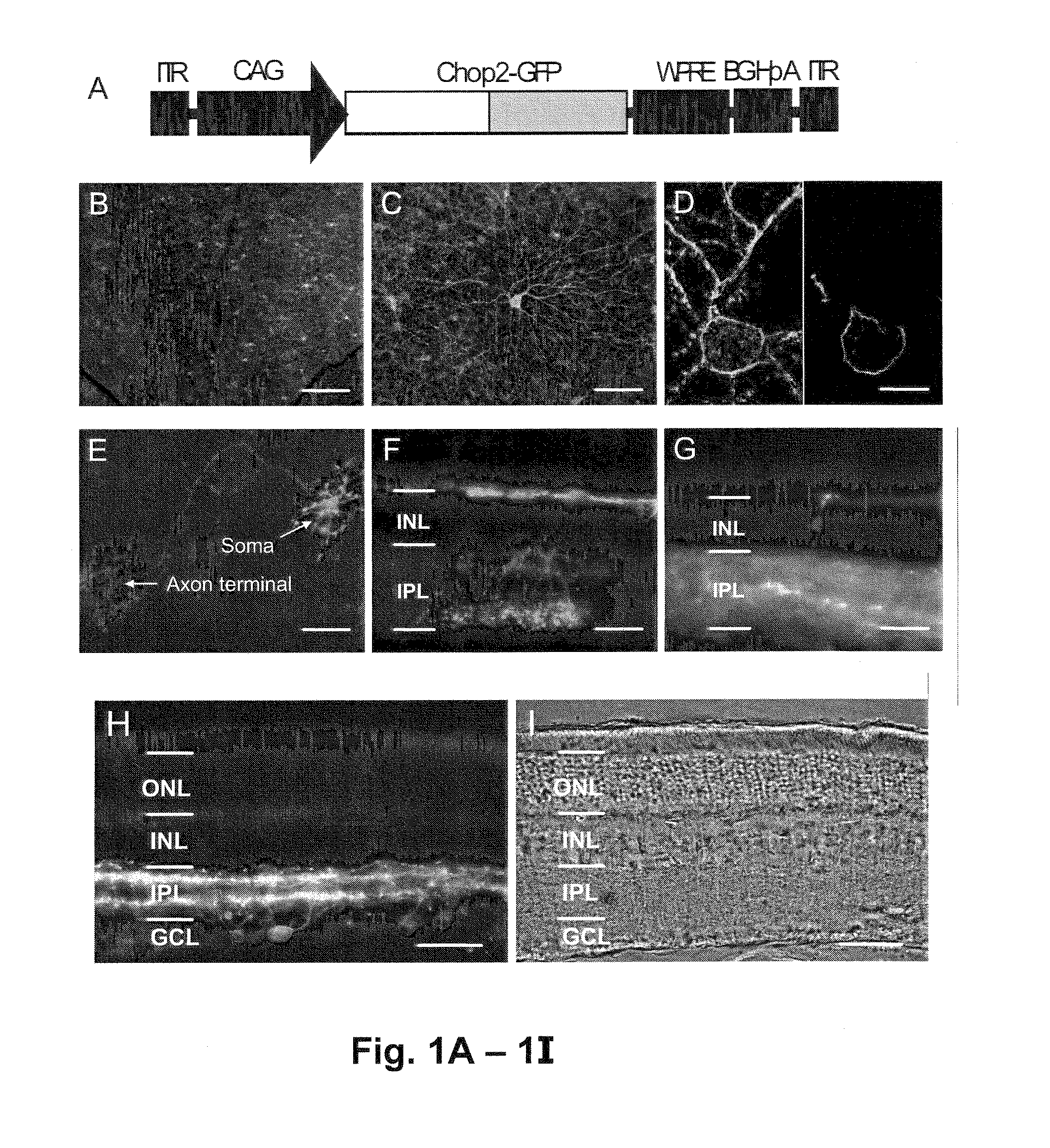
Restoration of visual responses by in vivo delivery of rhodopsin nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100015095A1Restoring light sensitivityLoss can be compensatedOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOpen reading frameIn vivo
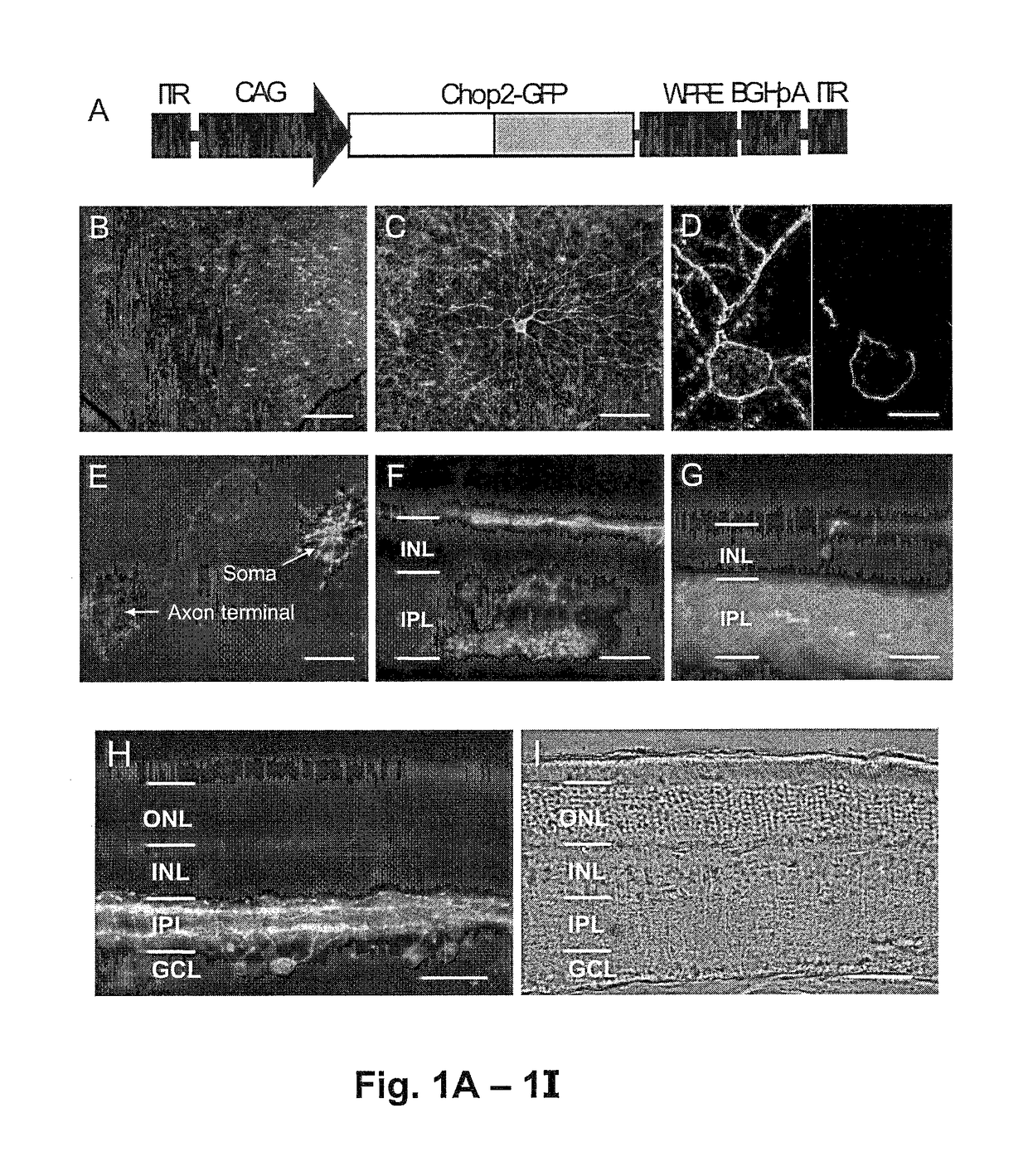
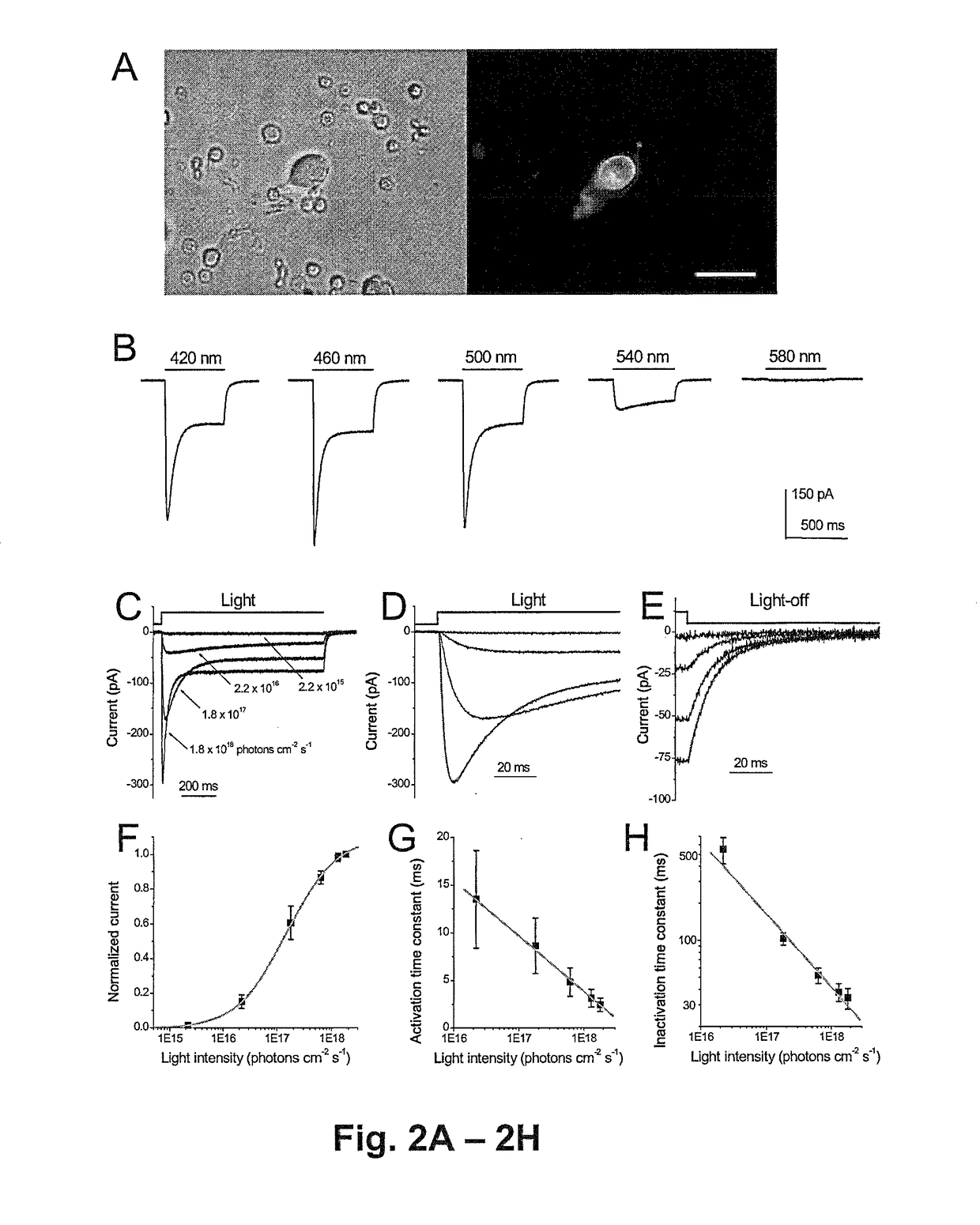
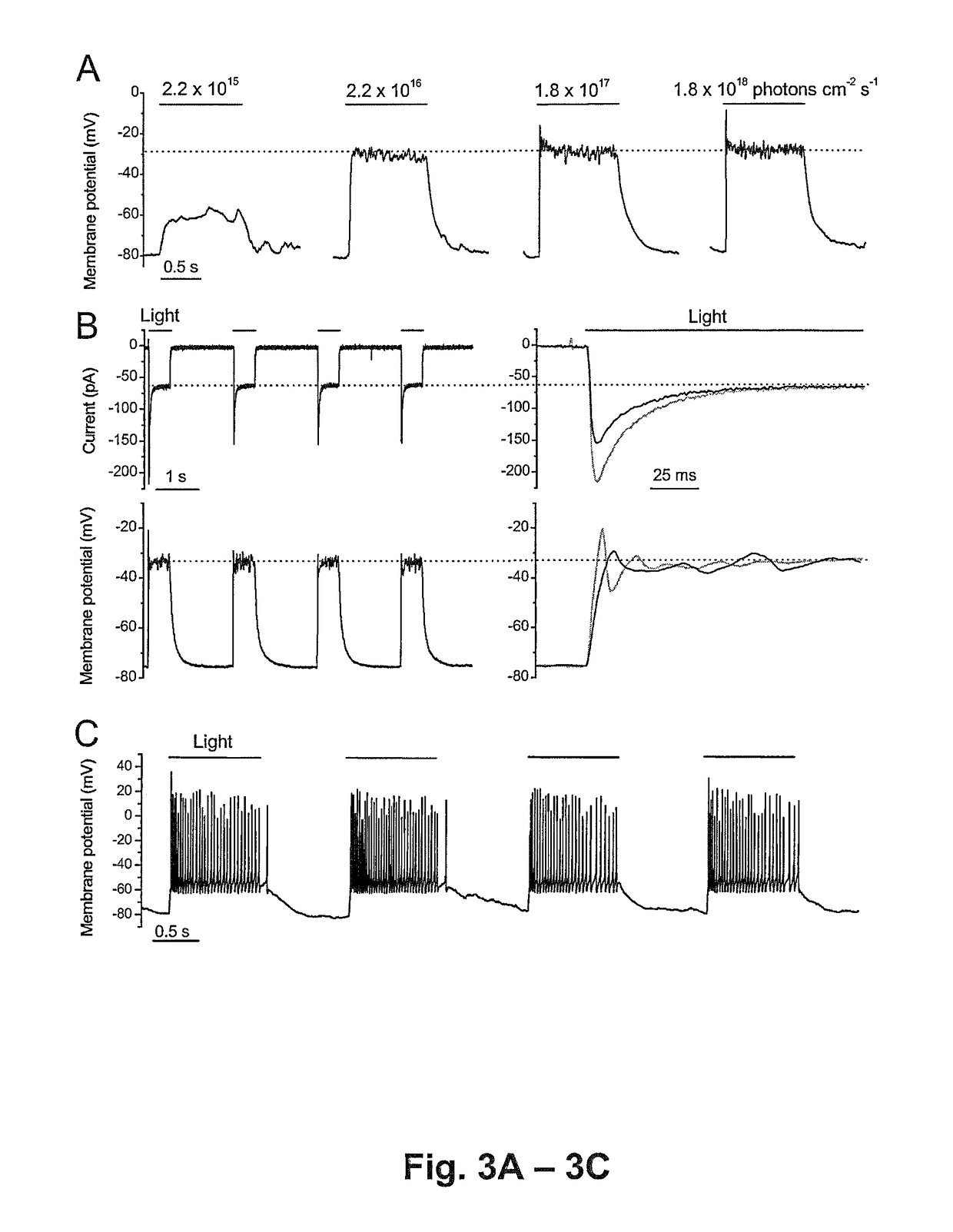
Nucleic acid vectors encoding light-gated cation-selective membrane channels, in particular channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2), converted inner retinal neurons to photosensitive cells in photoreceptor-degenerated retina in an animal model. Such treatment restored visual perception and various aspects of vision. A method of restoring light sensitivity to a retina of a subject suffering from vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration, as in retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration, is provided. The method comprises delivering to the subject by intravitreal or subretinal injection, the above nucleic acid vector which comprises an open reading frame encoding a rhodopsin, to which is operatively linked a promoter and transcriptional regulatory sequences, so that the nucleic acid is expressed in inner retinal neurons. These cells, normally light-insensitive, are converted to a light-sensitive state and transmit visual information to the brain, compensating for the loss, and leading to restoration of various visual capabilities.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
Noninvasive Ultrasound-Based Retinal Stimulator: Ultrasonic Eye
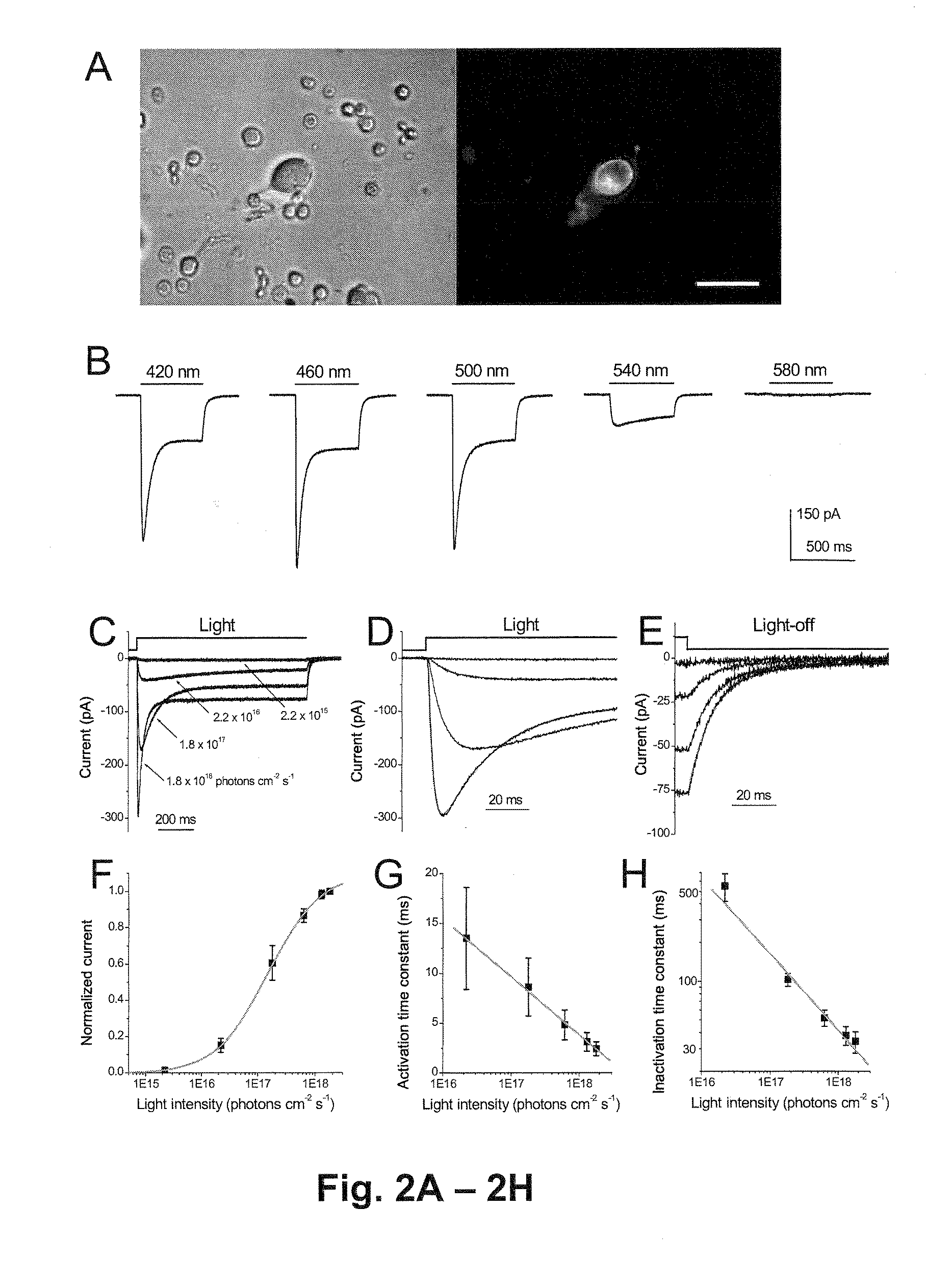
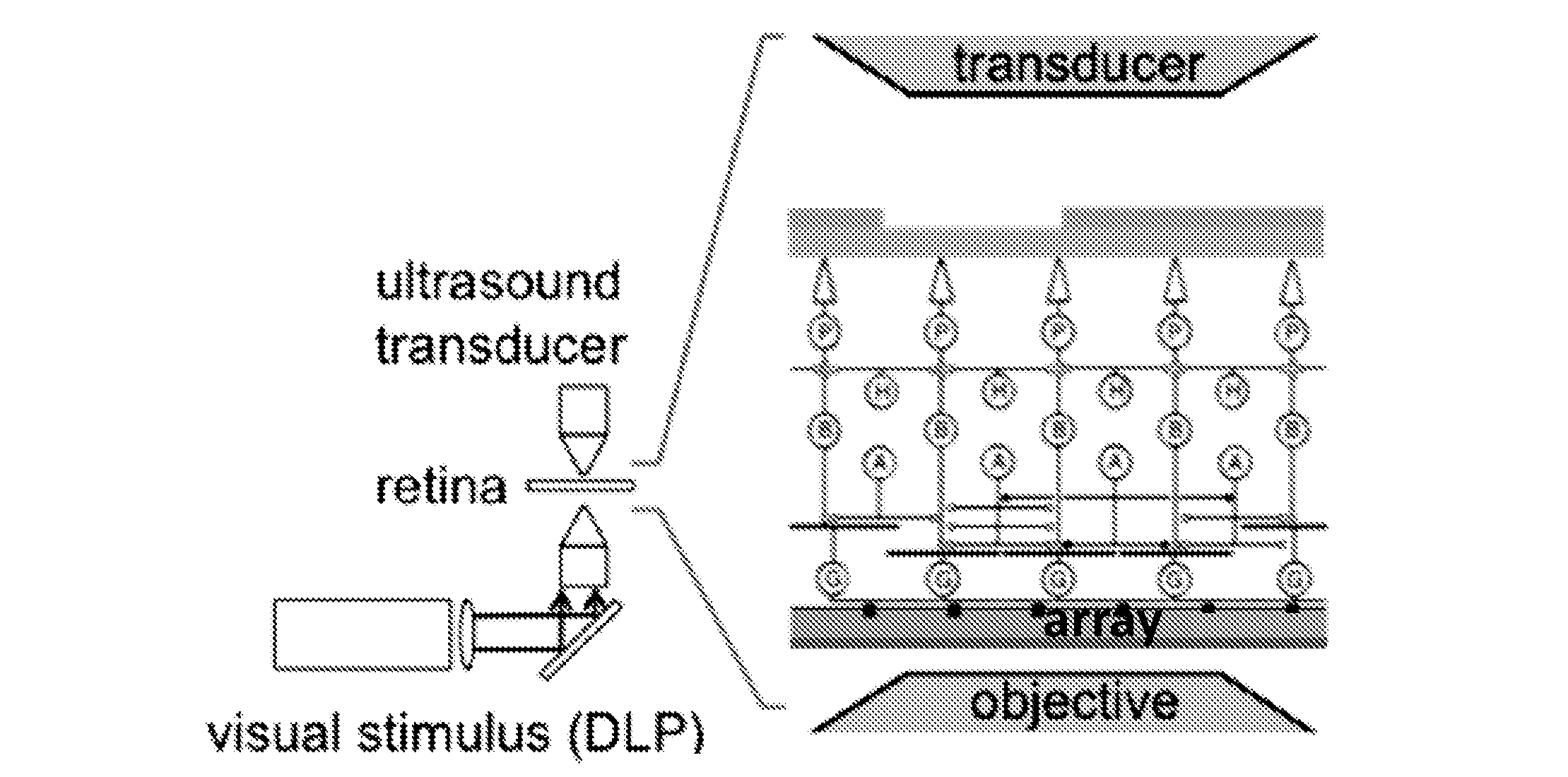
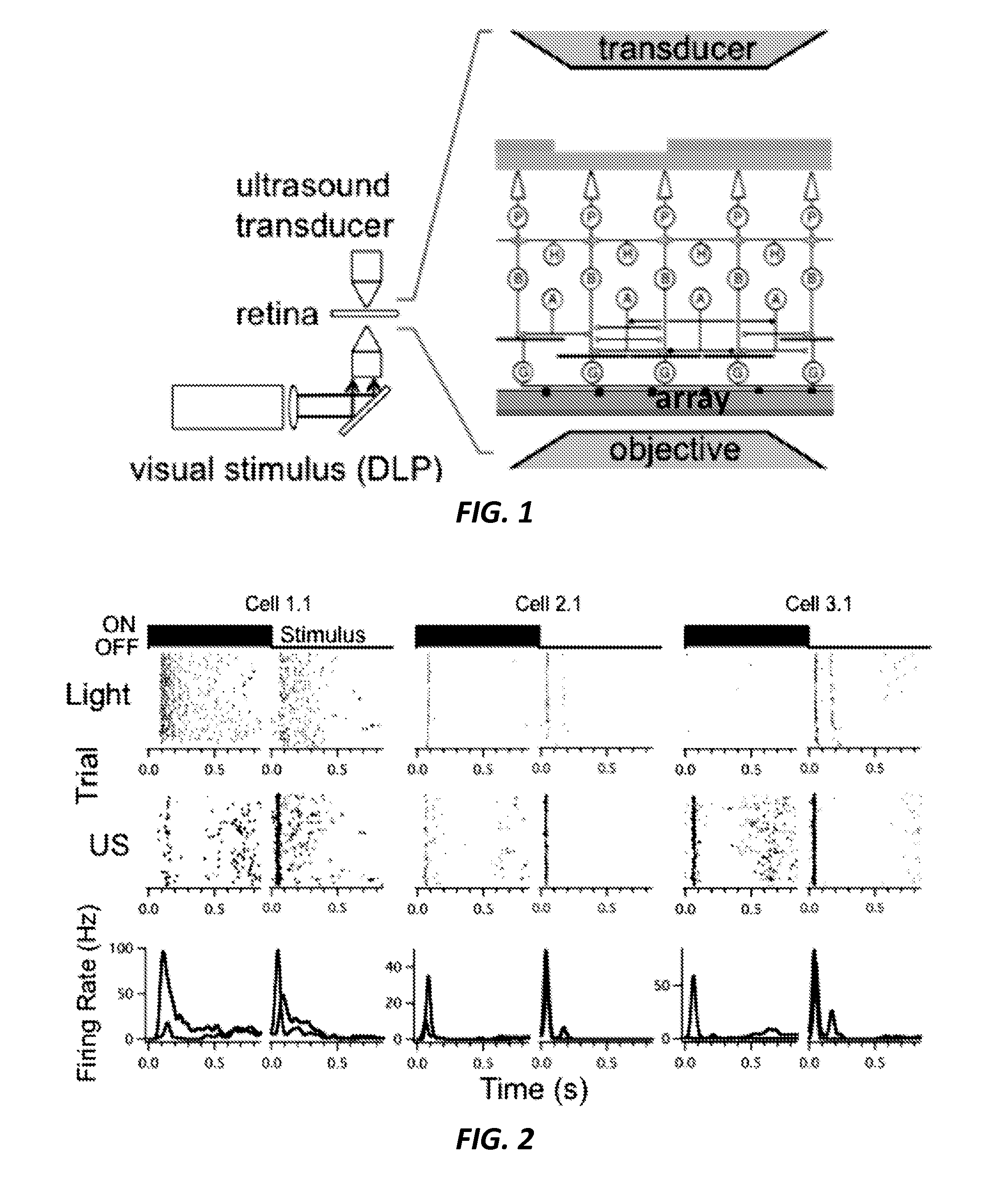
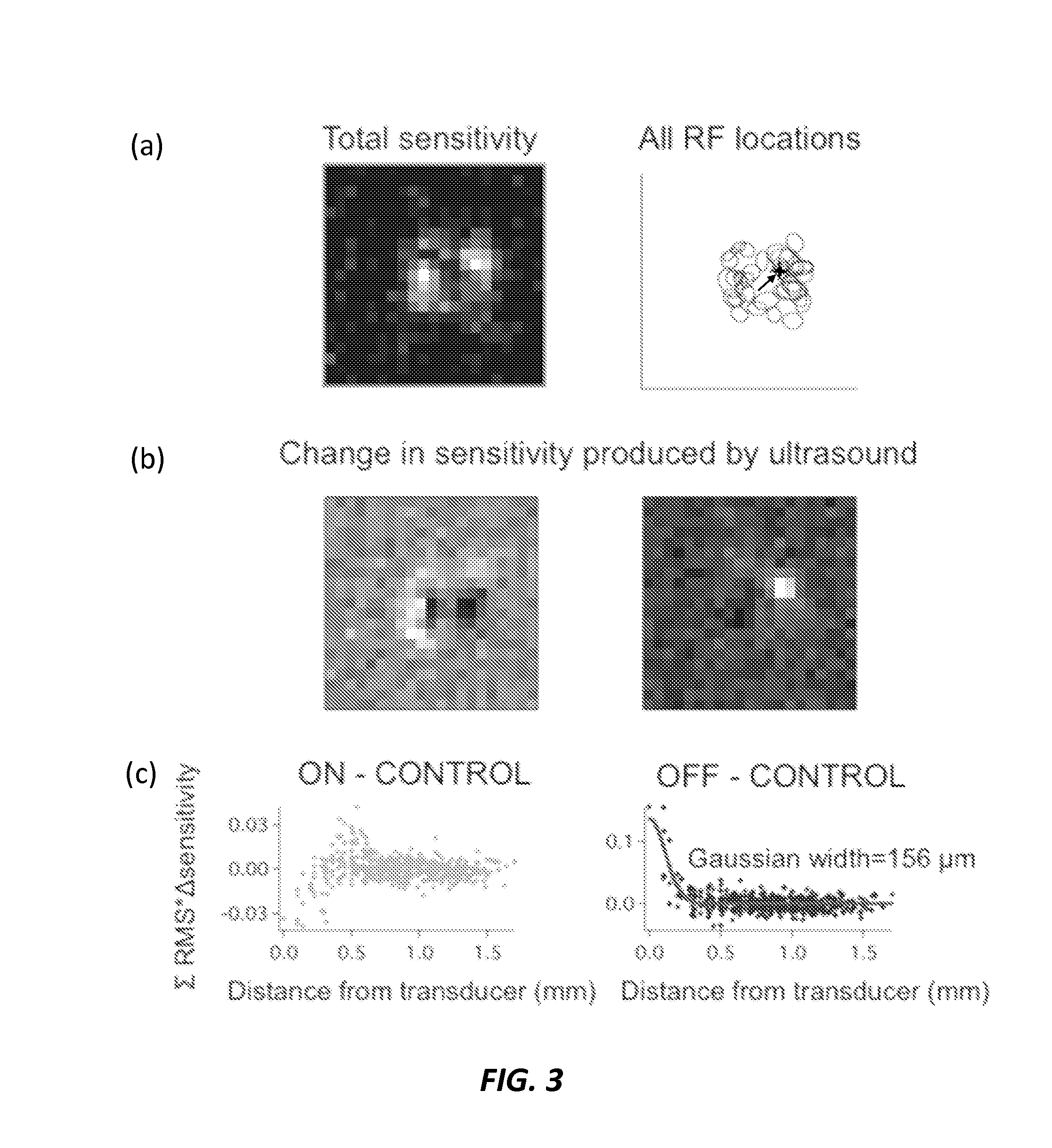
A retinal stimulation and prosthetic device is provided that includes at least one ultrasonic transducer having a focused ultrasonic signal, where the focused ultrasonic signal includes an acoustic frequency, a spot size, a temporal pattern, a pulse duration and a power capable of stimulating retinal neurons when the at least one ultrasonic transducer is disposed proximal to an eye.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for visual neural stimulation
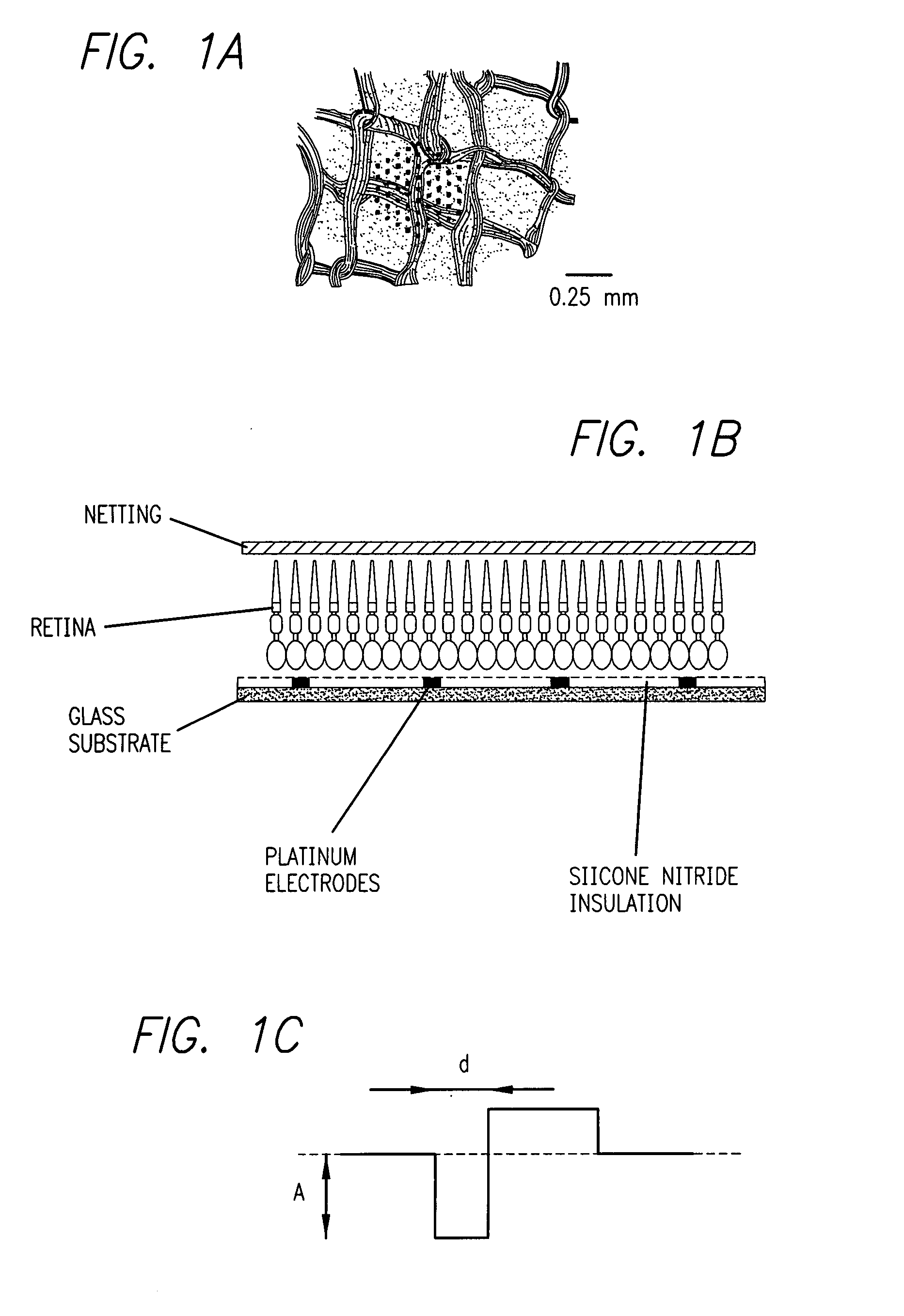
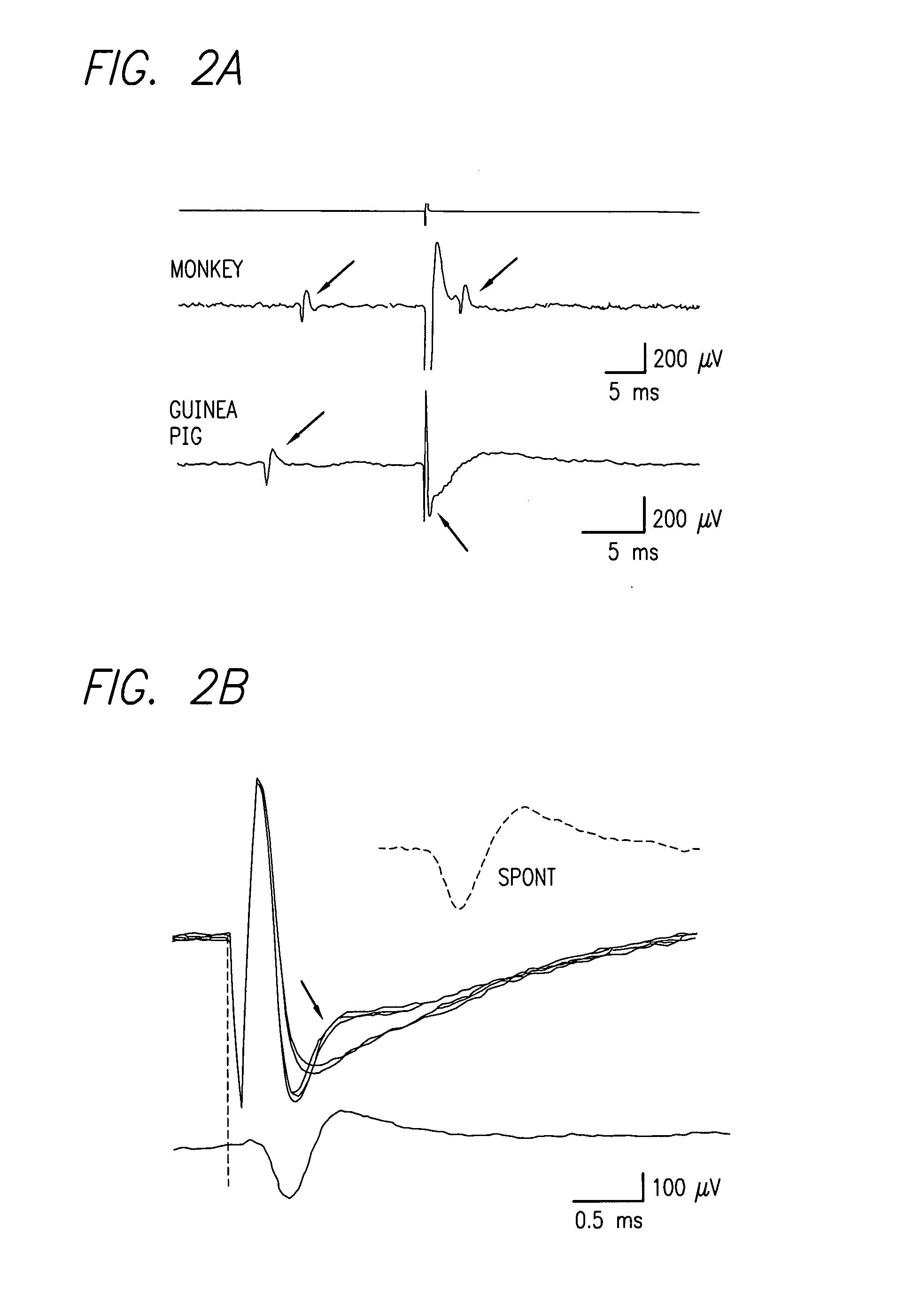
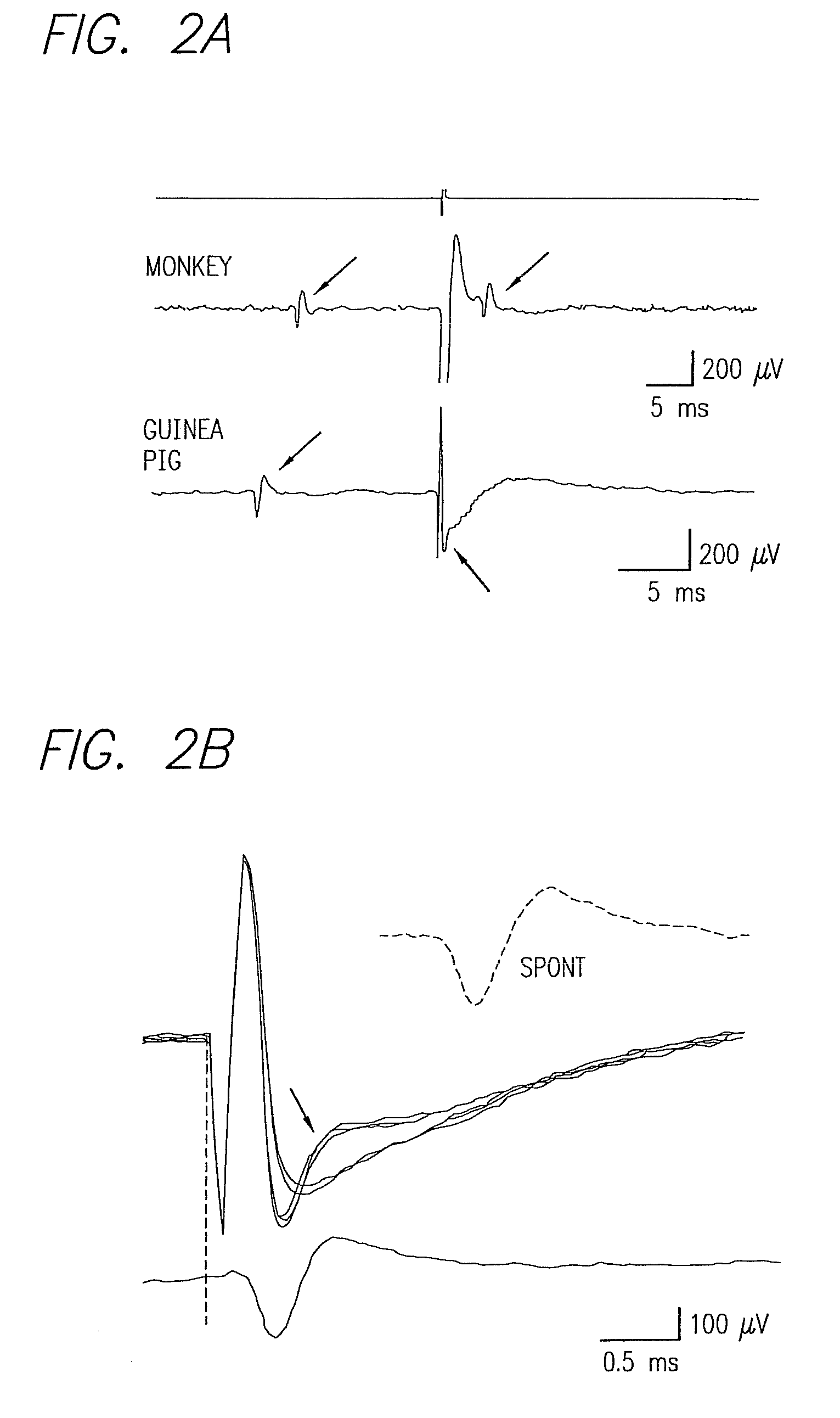
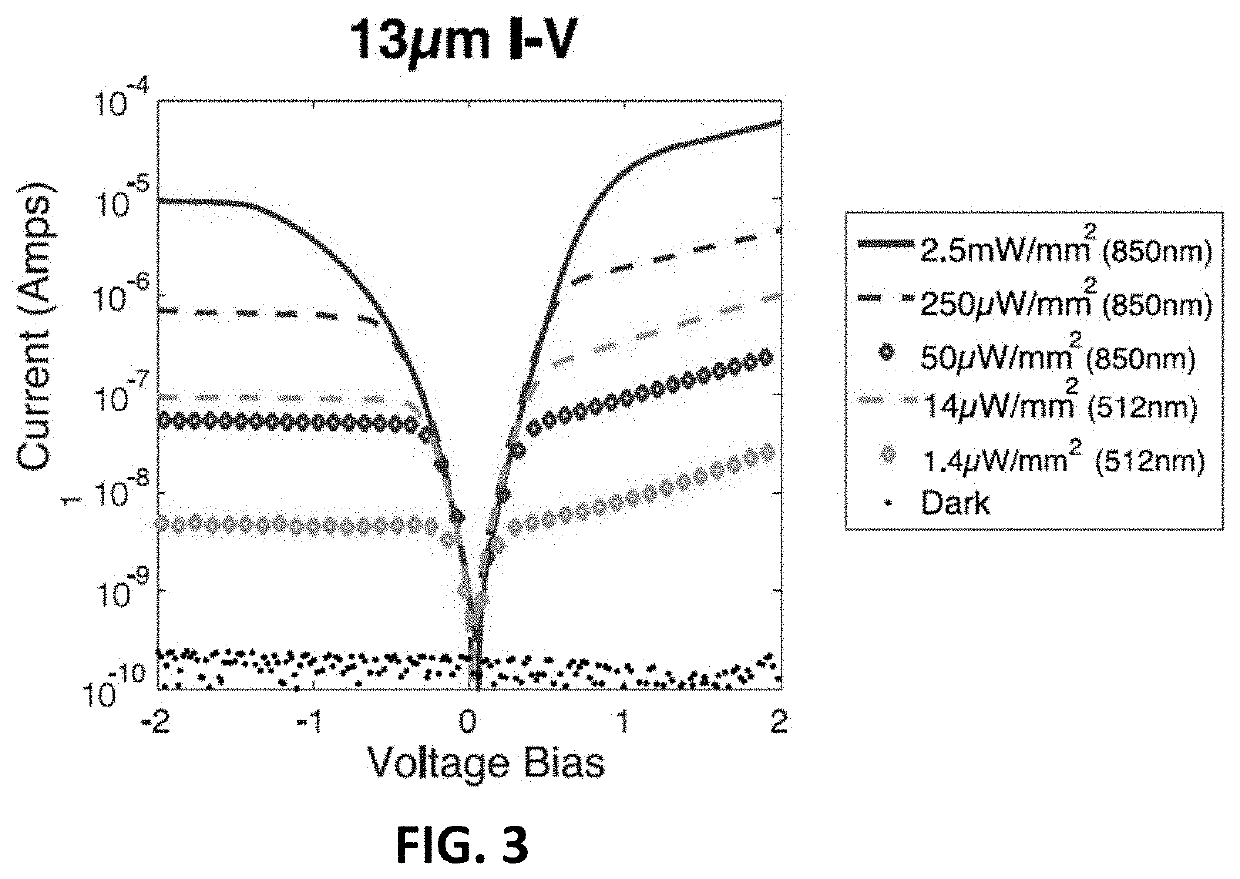
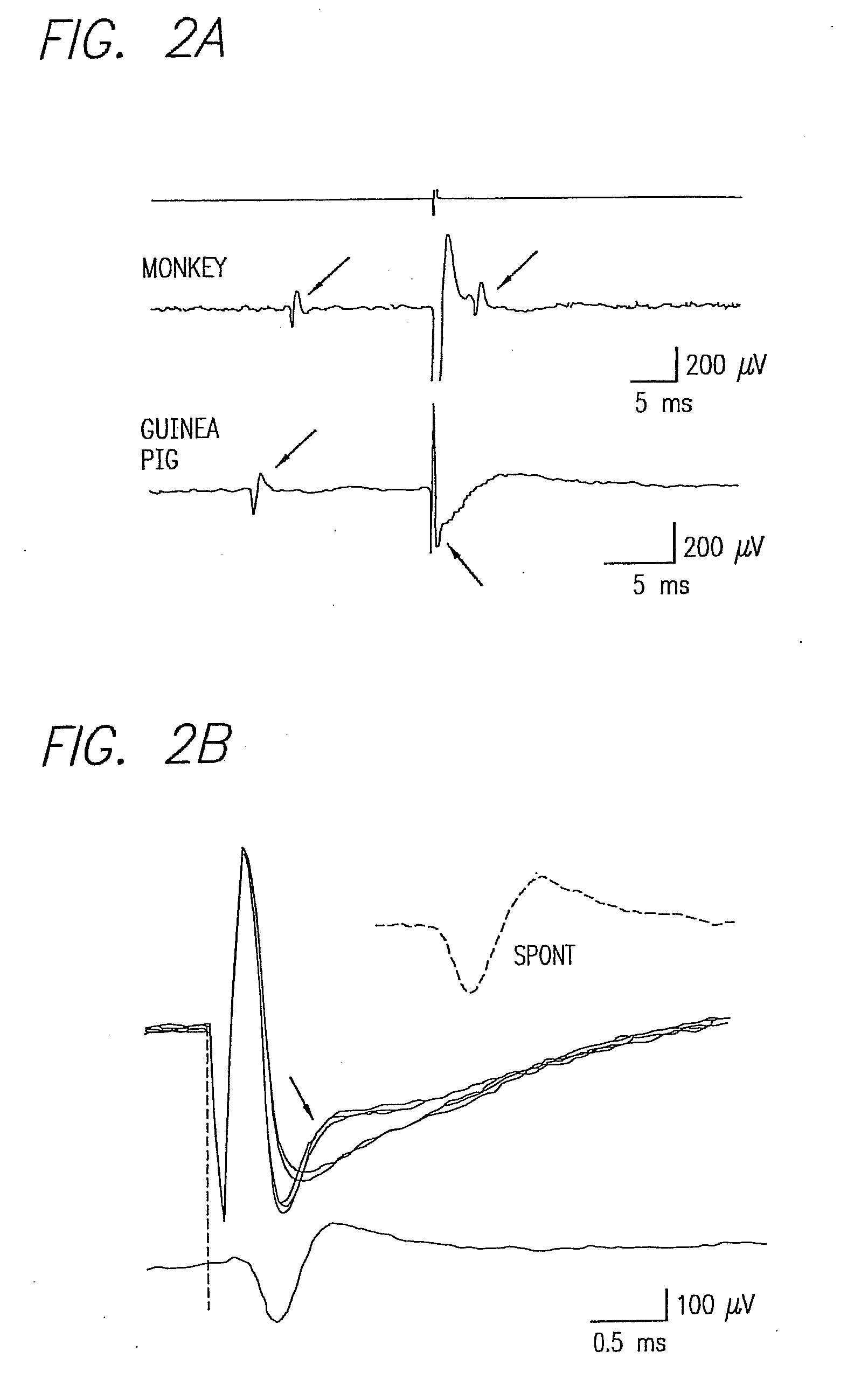
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
Microelectronic stimulator array for stimulating nerve tissue
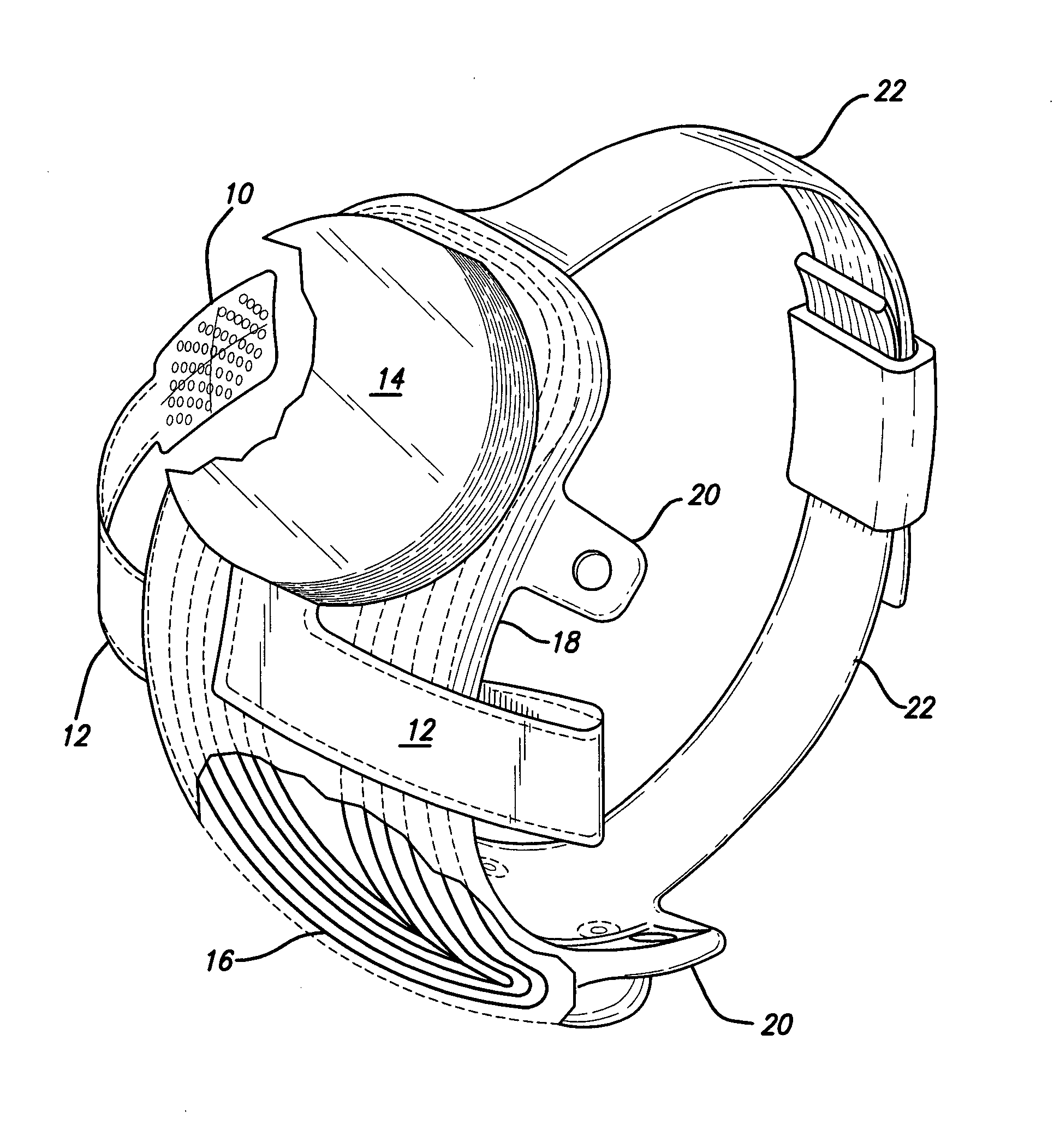
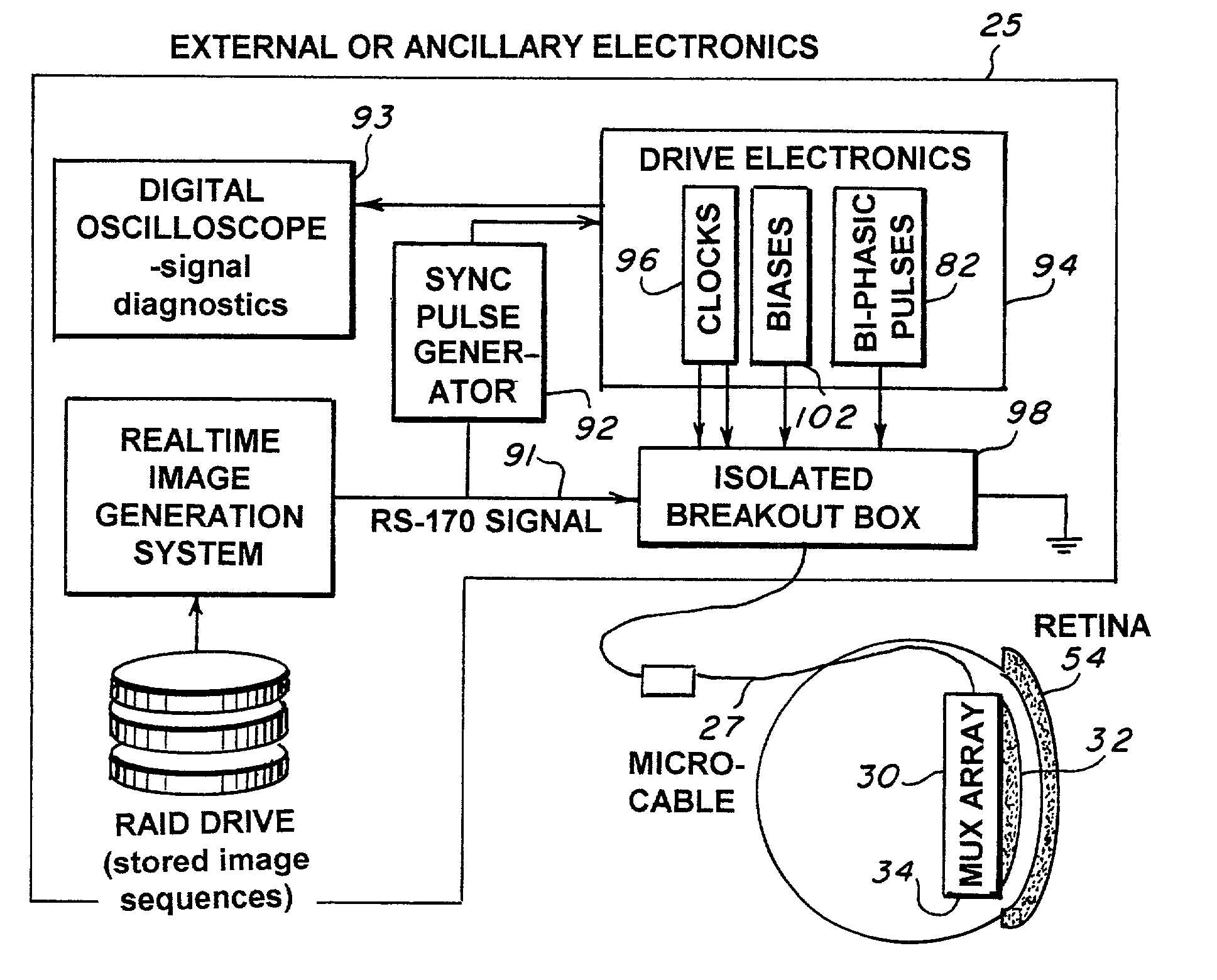
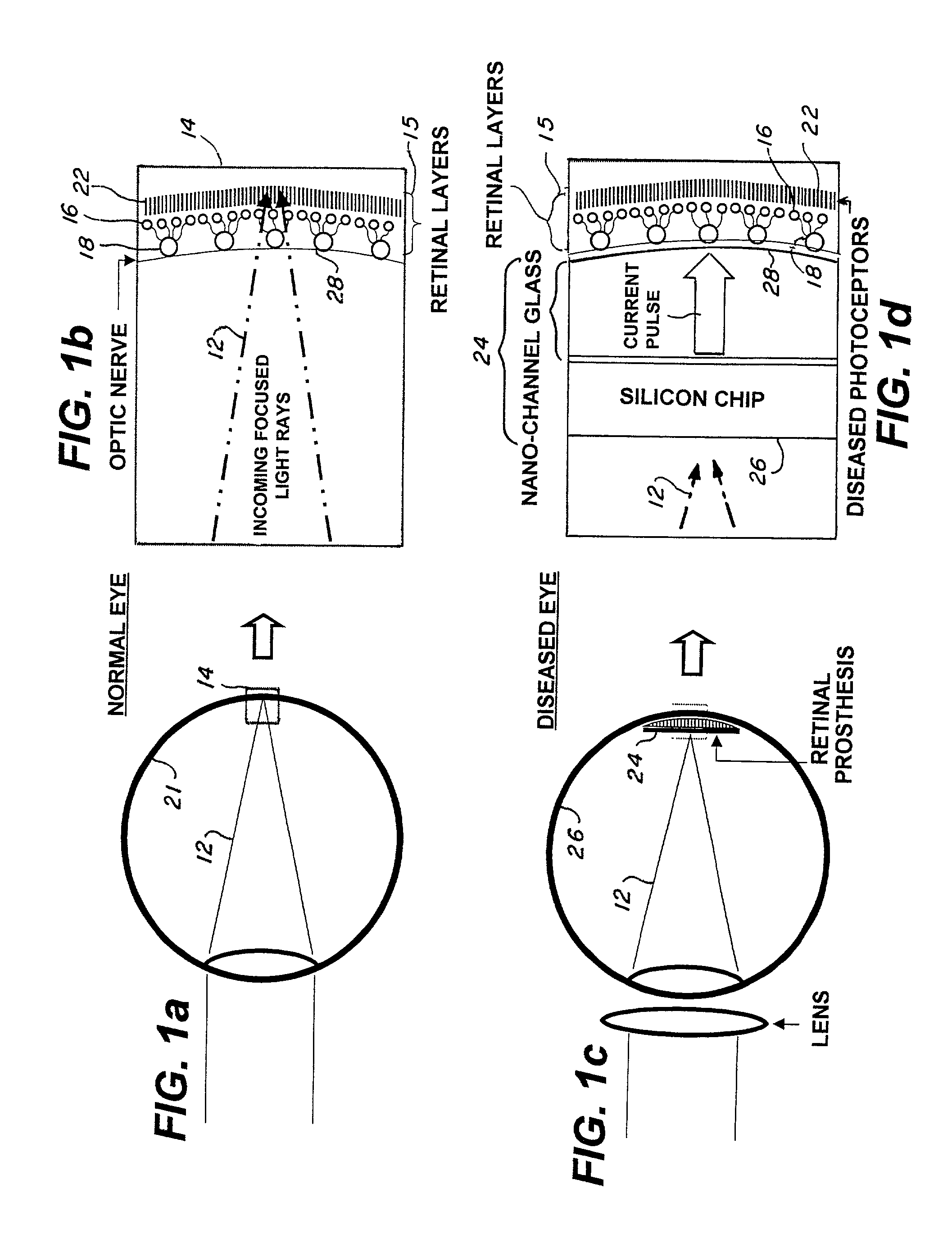
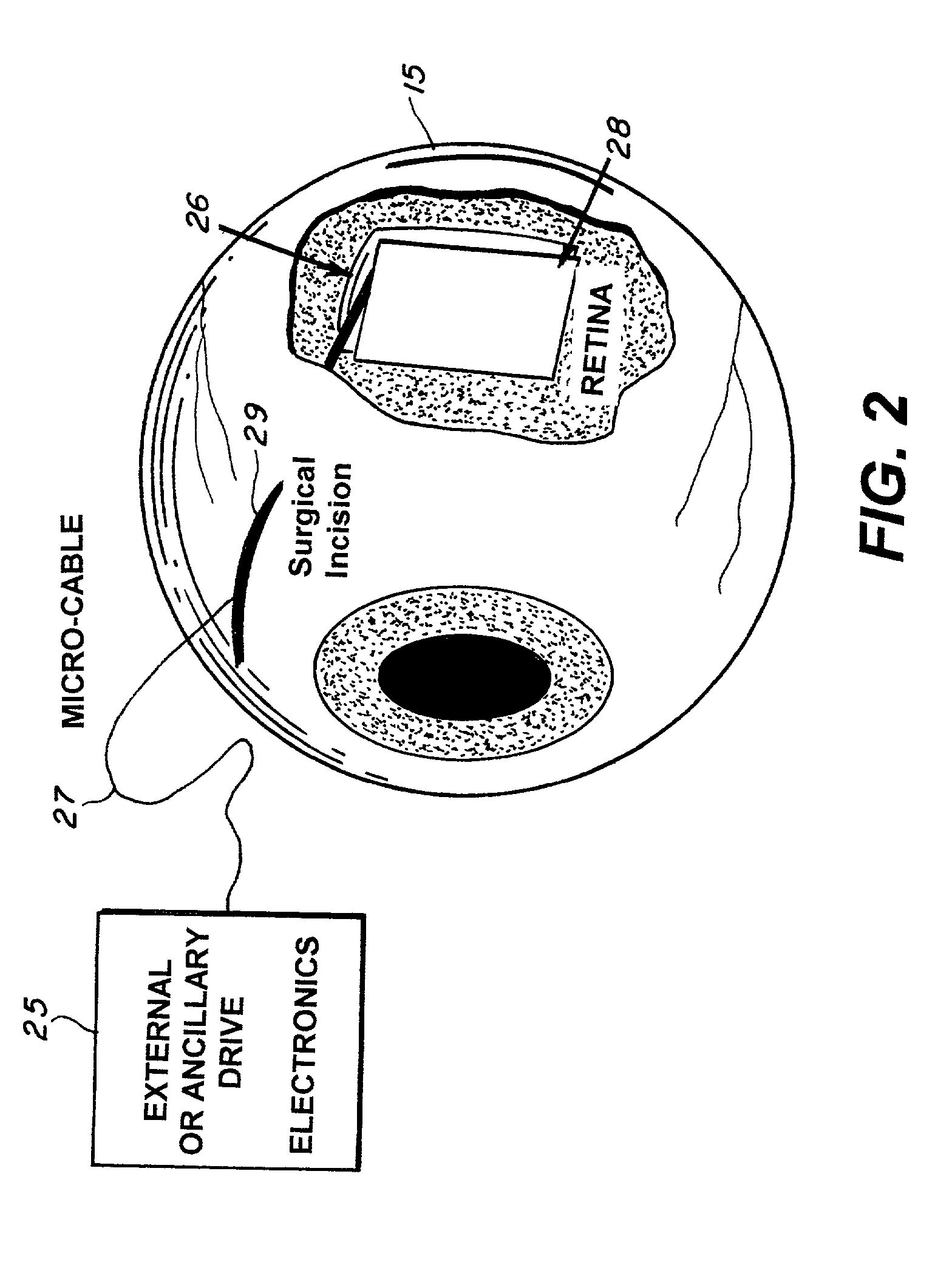
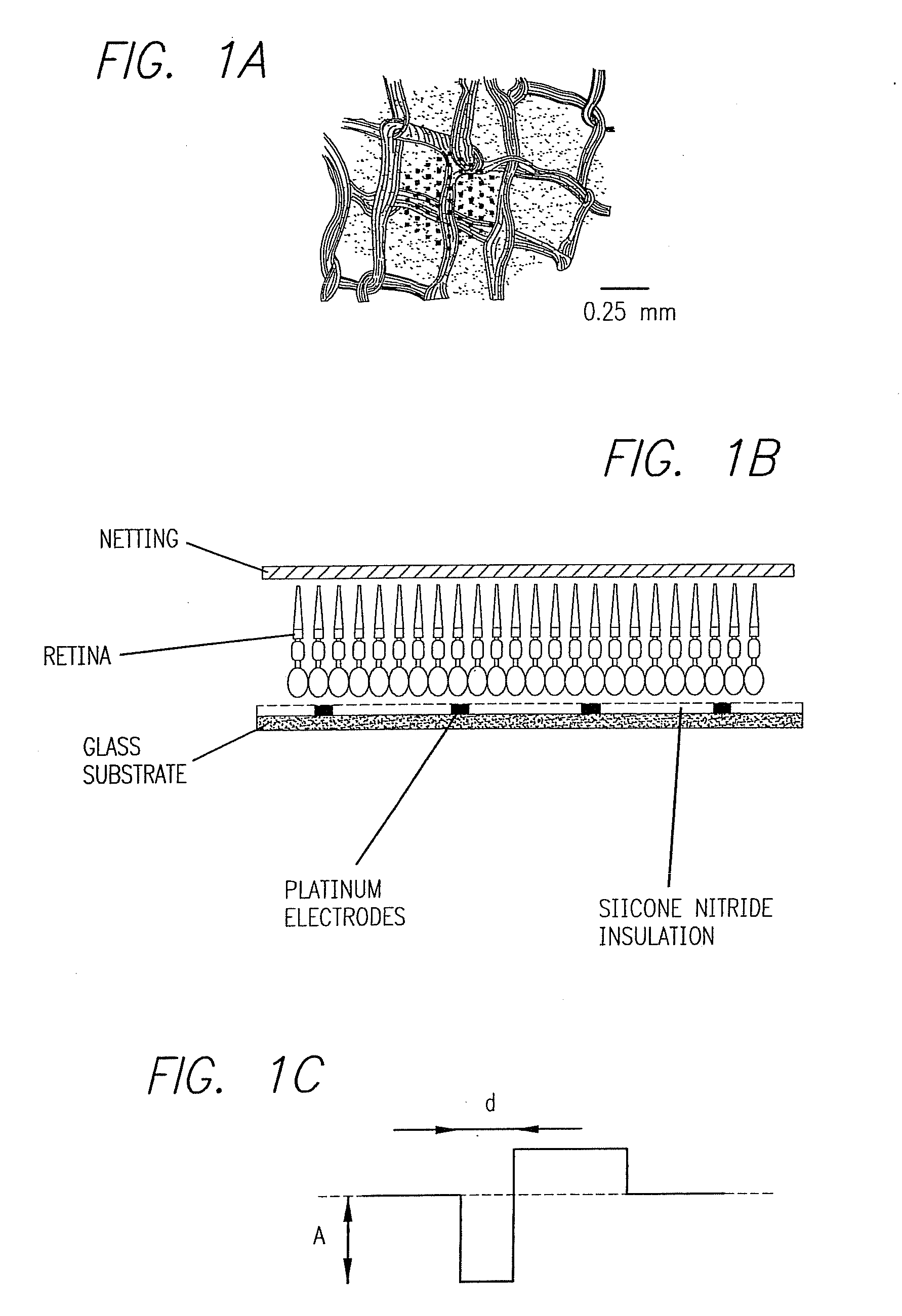
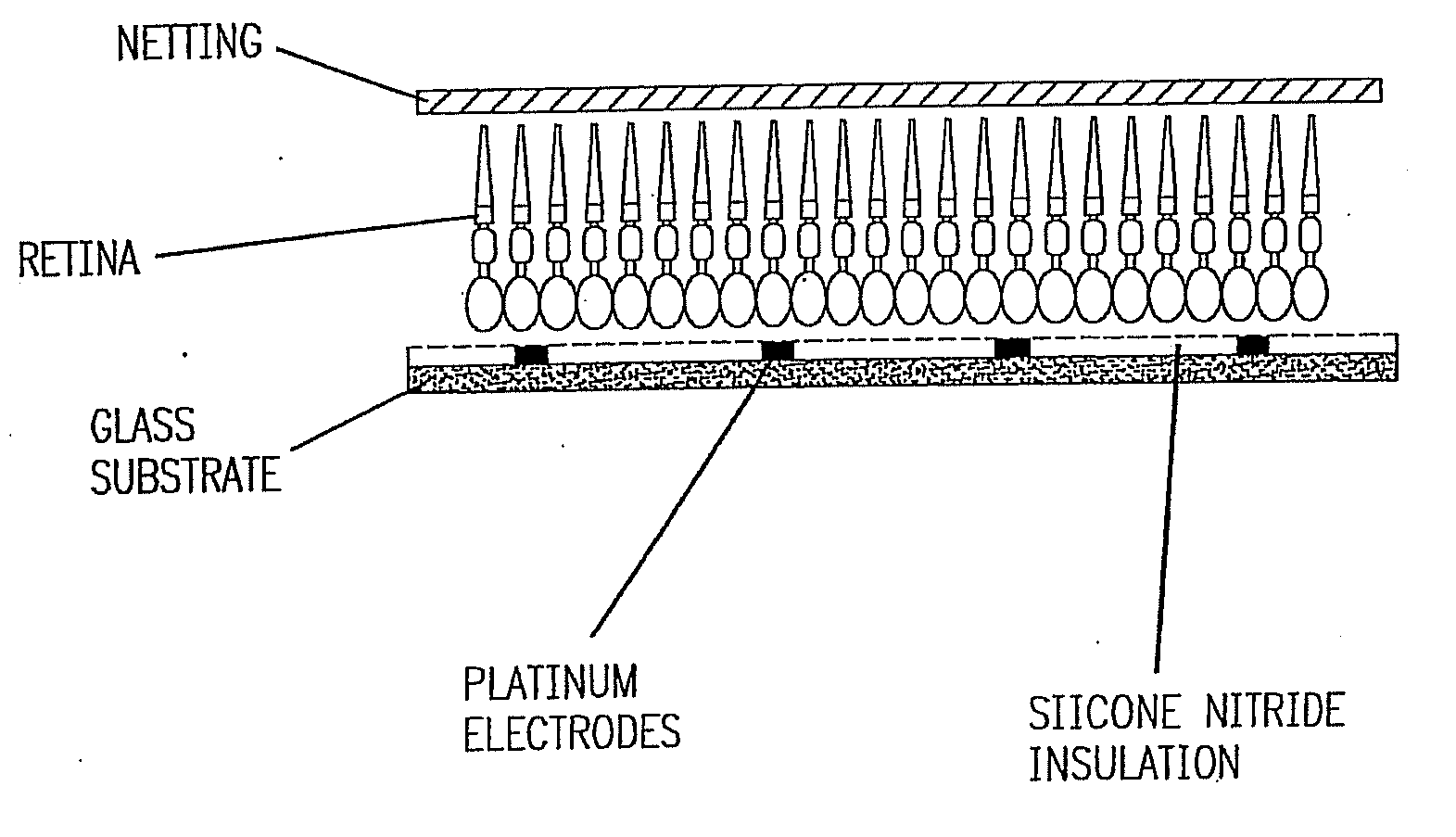
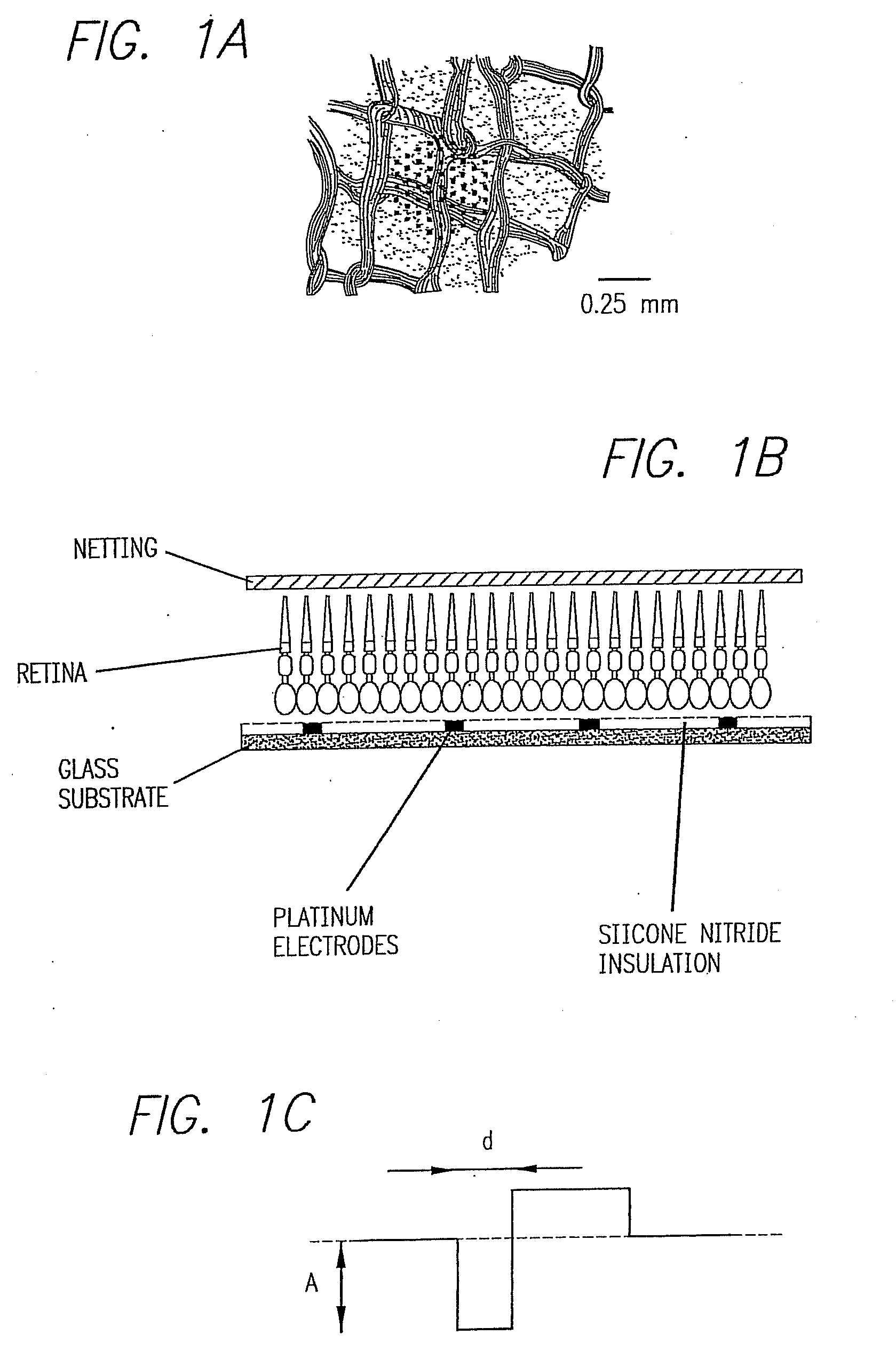
The retinal prosthesis test device is comprised of a thin wafer of glass made from nanochannel glass (NGC) with very small channels perpendicular to the plane of the wafer filled with an electrical conductor forming microwires. One surface of the glass is ground to a spherical shape consistent with the radius of curvature of the inside of the retina. The NGC is hybridized to a silicon de-multiplexer and a video image is serially input to a narrow, flexible micro-cable and read into a 2-D array of unit cells in a pixel-by-pixel manner which samples the analog video input and stores the value as a charge on a MOS capacitor. After all unit cells have been loaded with the pixel values for the current frame, a biphasic pulse is sent to each unit cell which modulates the pulse in proportion to the pixel value stored therein. Because the biphasic pulses flow in parallel to each unit cell from a global external connection, the adjacent retinal neurons are all stimulated simultaneously, analogous to image photons stimulating photoreceptors in a normal retina. A permanent retinal implant device uses a NGC array hybridized to a silicon chip, the image is simultaneously generated within each cell through a photon-to-electron conversion using a silicon photodiode. The photons propagate directly through into the backside of the device. Electrical power and any control signals are transmitted through an inductively driven coil or antenna on the chip. The device collects the charge in storage capacitors via the photon-to-electron conversion process, stimulates the neural tissue with biphasic pulses in proportion to the stored charges, and resets the storage capacitors to repeat the process.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Method and Apparatus for Visual Neural Stimulation
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
Methods and compositions for the treatment of glaucoma and other retinal diseases
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for treating glaucoma and other disorders related to degeneration of retinal neuronal cells, by treating a subject with a composition capable of inducing or increasing the expression of the 70 kD family of heat shock proteins (HSP70) in retinal neurons. Preferred embodiments include geranylgeranylacetone and / or gene therapy applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Restoration of visual responses by in vivo delivery of rhodopsin nucleic acids
ActiveUS8470790B2Restore sensitivityLoss can be compensatedBiocideSenses disorderOpen reading frameIn vivo
Nucleic acid vectors encoding light-gated cation-selective membrane channels, in particular channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2), converted inner retinal neurons to photosensitive cells in photoreceptor-degenerated retina in an animal model. Such treatment restored visual perception and various aspects of vision. A method of restoring light sensitivity to a retina of a subject suffering from vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration, as in retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration, is provided. The method comprises delivering to the subject by intravitreal or subretinal injection, the above nucleic acid vector which comprises an open reading frame encoding a rhodopsin, to which is operatively linked a promoter and transcriptional regulatory sequences, so that the nucleic acid is expressed in inner retinal neurons. These cells, normally light-insensitive, are converted to a light-sensitive state and transmit visual information to the brain, compensating for the loss, and leading to restoration of various visual capabilities.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
Methods and compositions for gene delivery to on bipolar cells
InactiveUS20170007720A1Overcome limitationsImprove efficiencyVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryRetinitis pigmentosa
Disclosed are capsid-modified rAAV expression vectors, as well as infectious virions, compositions, and pharmaceutical formulations that include them. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and using novel capsid-protein-mutated rAAV vector constructs in a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications including, inter alia, as delivery agents for diagnosis, treatment, or amelioration of one or more diseases, disorders, or dysfunctions of the mammalian eye. Also disclosed are methods for intravitreal delivery of therapeutic gene constructs to retinal neuron cells, and specifically to ON bipolar cells, of the mammalian eye, as well as use of the disclosed compositions in the manufacture of medicaments for a variety of in vitro and / or in vivo applications including the treatment of retinitis pigmentosa, melanoma-associated retinopathy, and congenital stationary night blindness.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
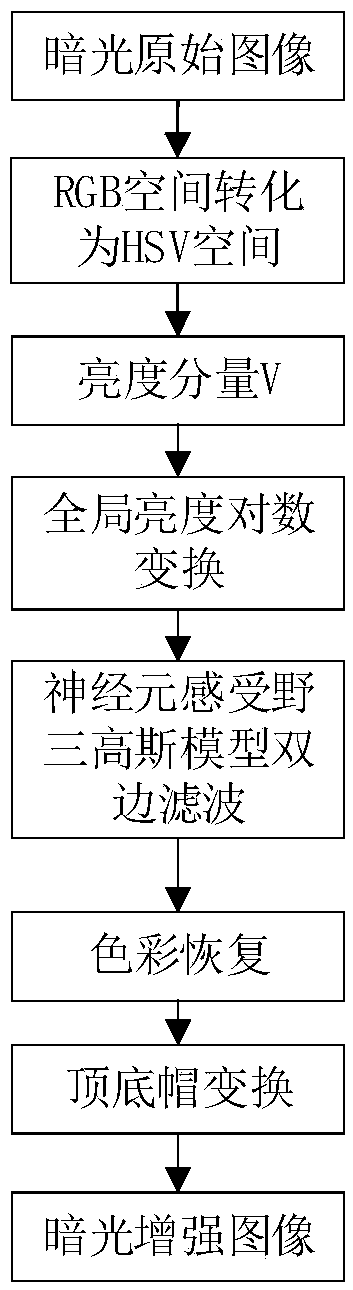
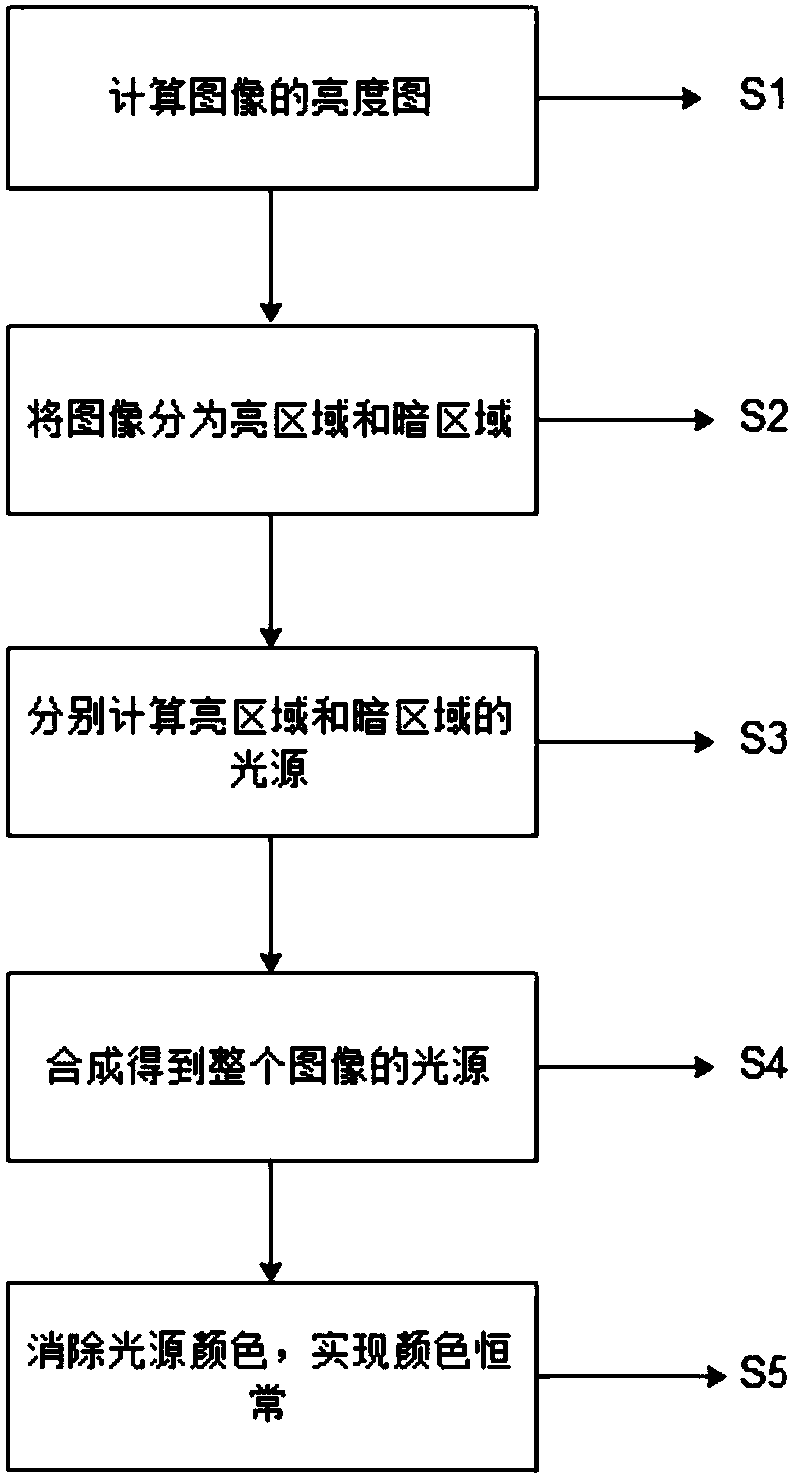
An image enhancement method in a dark light environment
InactiveCN109685742AIncrease contrastHigh color saturationImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageNoise reduction
The invention discloses an image enhancement method in a dark light environment and belongs to the field of image processing. The problems of distorted representation result, blurred image contour andlow color saturation after enhancement seriously exist can be solved; The method comprises the following steps: extracting a brightness component V in an HSV in a dark light image, carrying out logarithmic transformation of global brightness, and carrying out overall brightness improvement on a low-illumination area in the dark light image; Obtaining neighborhood average brightness of pixel points in the current dark light image by using bilateral filtering under a receptive field three-Gaussian model of the retinal neurons; A function of extracting a local bright part from an image background is realized by utilizing top and bottom cap transformation processing, and then light and shade extraction and noise reduction are carried out on the image by utilizing top and bottom cap transformation; According to the method, the enhanced details of the dark-light color image can be well represented, the problem of non-uniform illumination distribution is solved, the overall contrast of the image is improved, the detail contour of the image is clear, and the color saturation is high.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
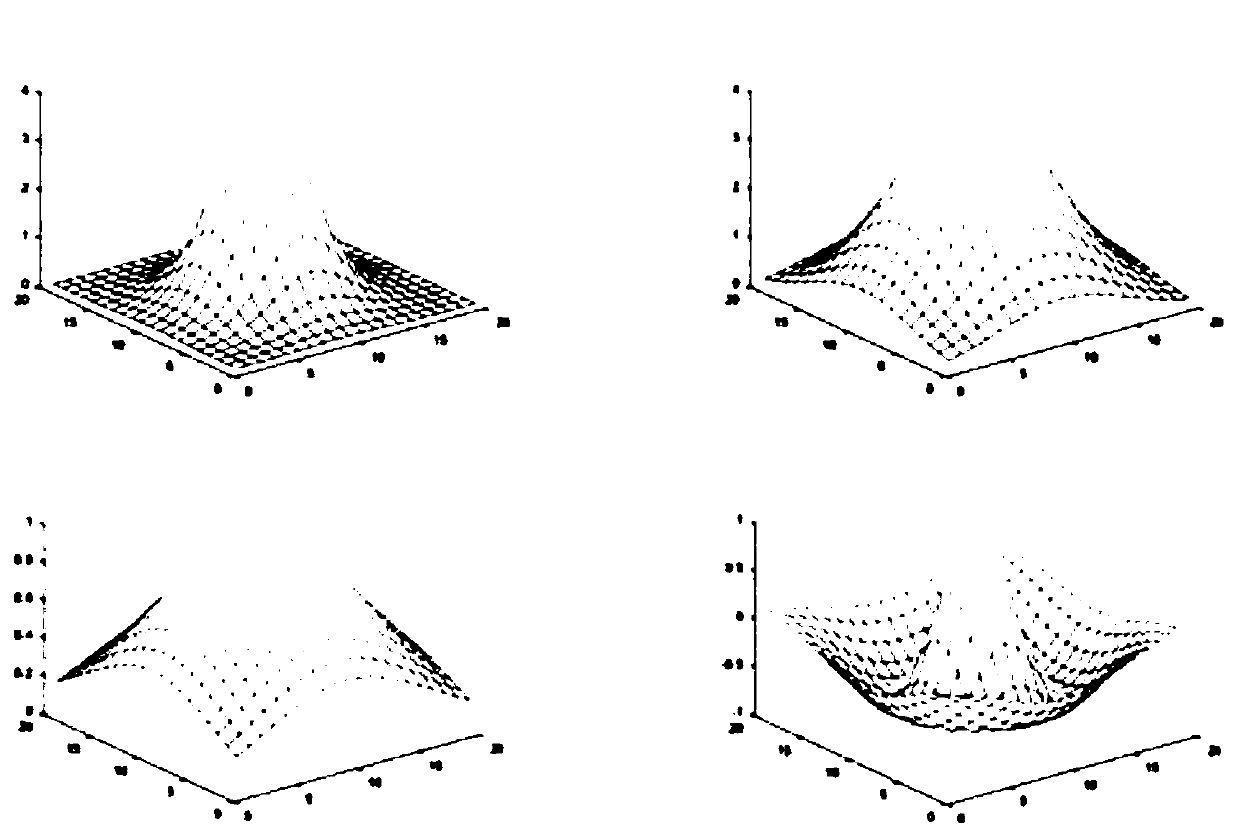
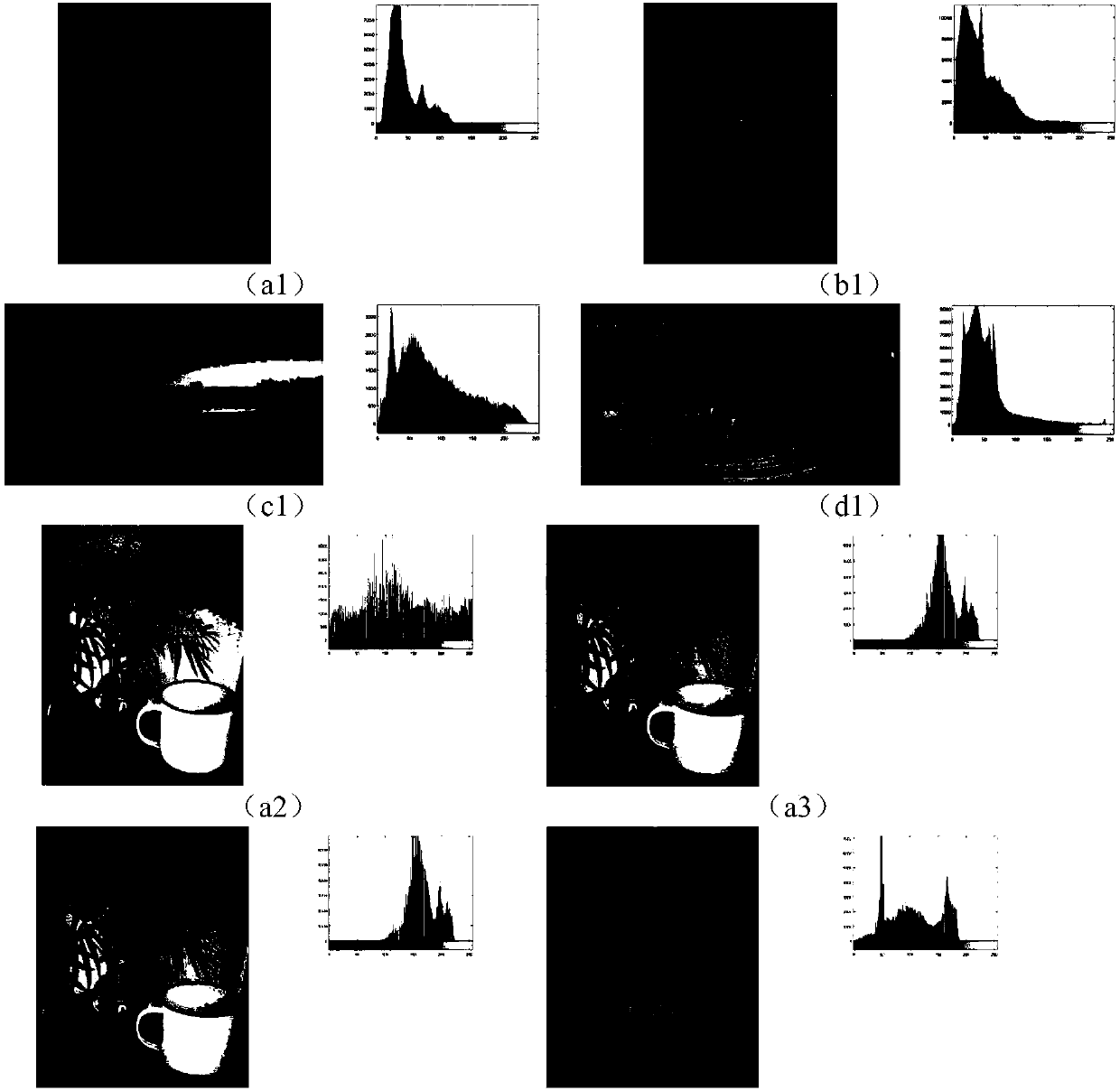
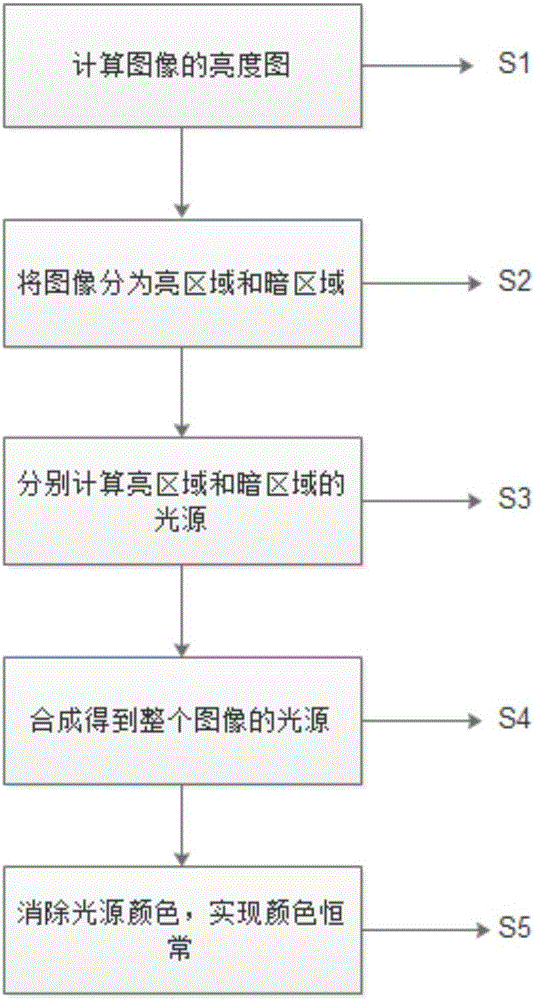
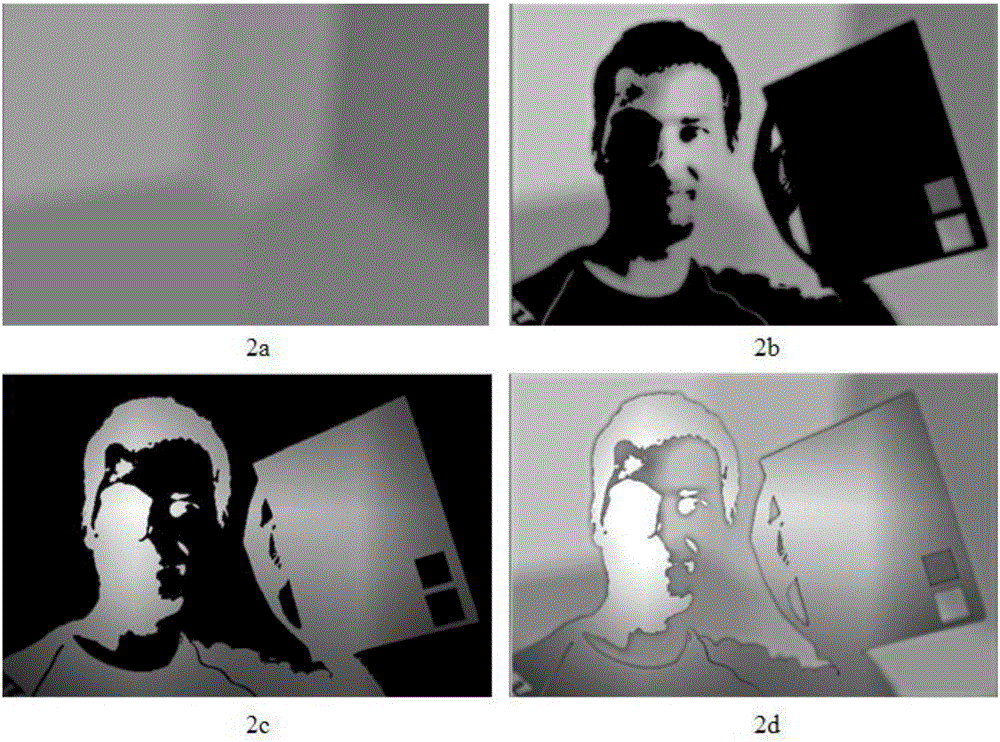
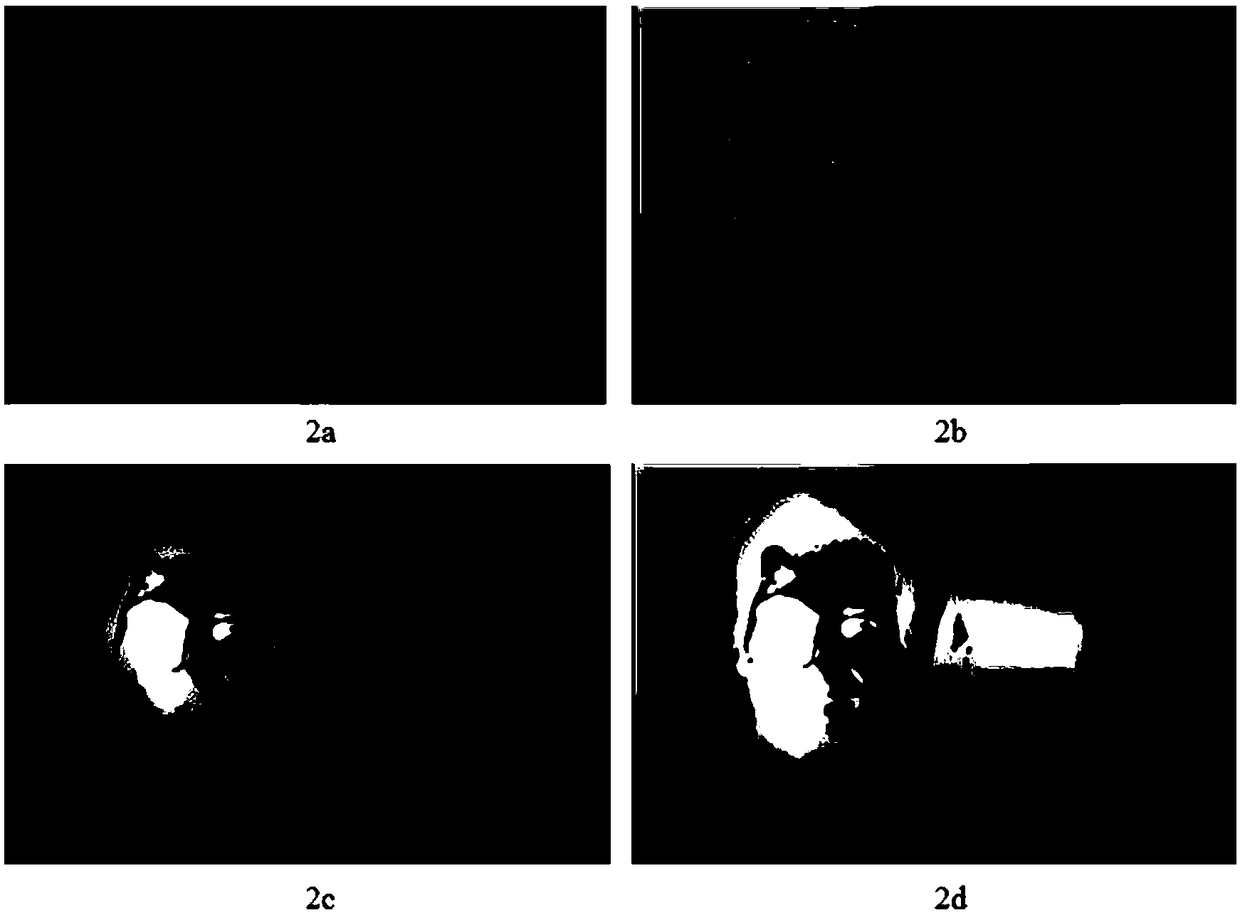
Image color constancy method under multi-light-source environment
The invention discloses an image color constancy method under a multi-light-source environment. The invention puts forward a multi-light-source color constancy method based on a retina physiological mechanism, simulates the light and dark adaption capability of vision and the characteristics of a retinal neuron reception field, and establishes a model based on ON type and OFF type reception fields on the basis of light and dark area division, the model can favorably estimate the position and the color of a light source, and parameters can be regulated to adapt to different scene images. The method has the characteristics of few parameters, simpleness in calculation, high speed, good effect and the like, can carry out real-time processing, and is very suitable to be built in the preprocessing front end of physical equipment to estimate a scene light source color in the image.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Inhibition of reactive oxygen species and protection of mammalian cells
ActiveUS20060246152A1Increase blockingAvoid damageBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsIn vivoOxygen
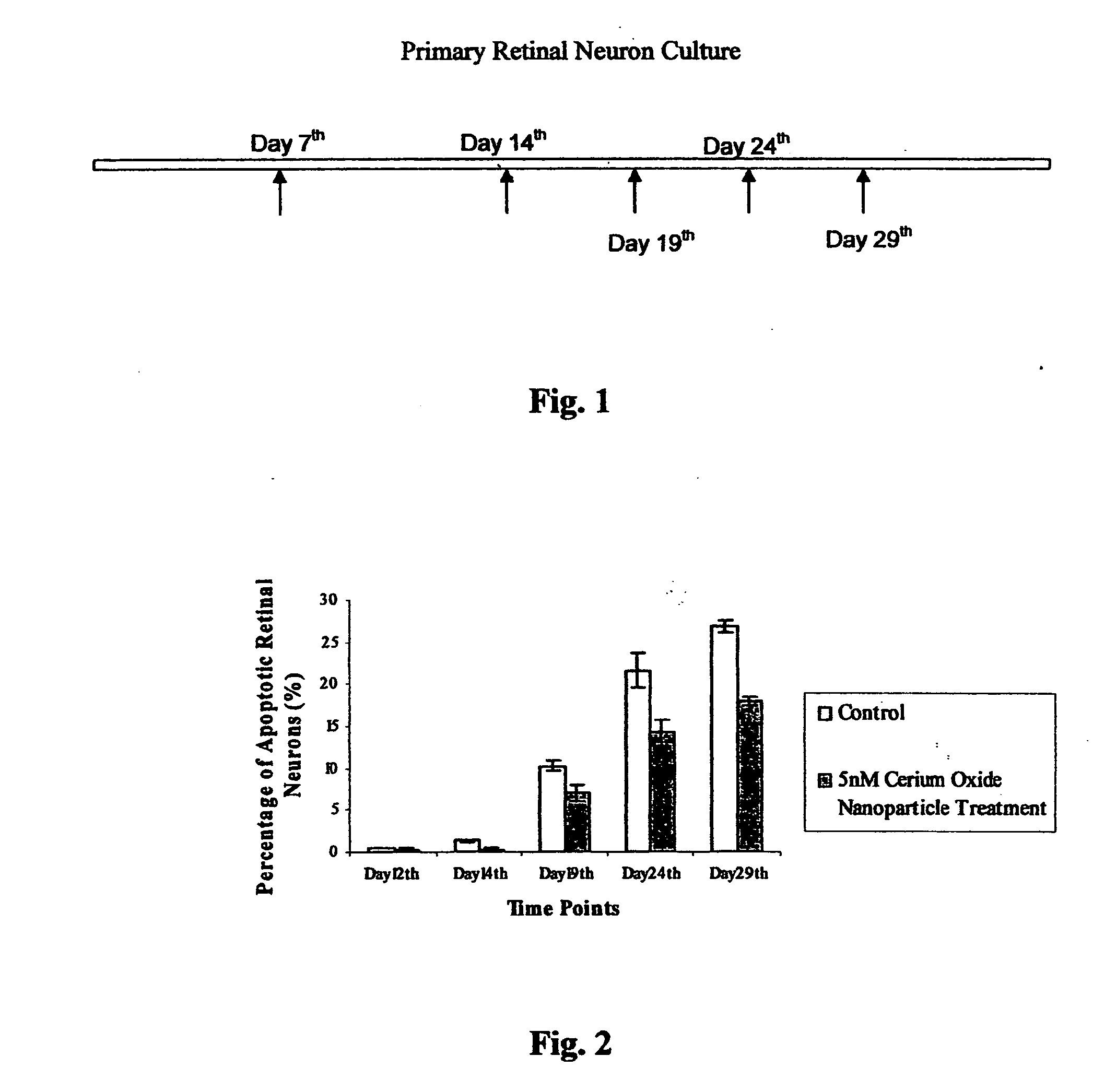
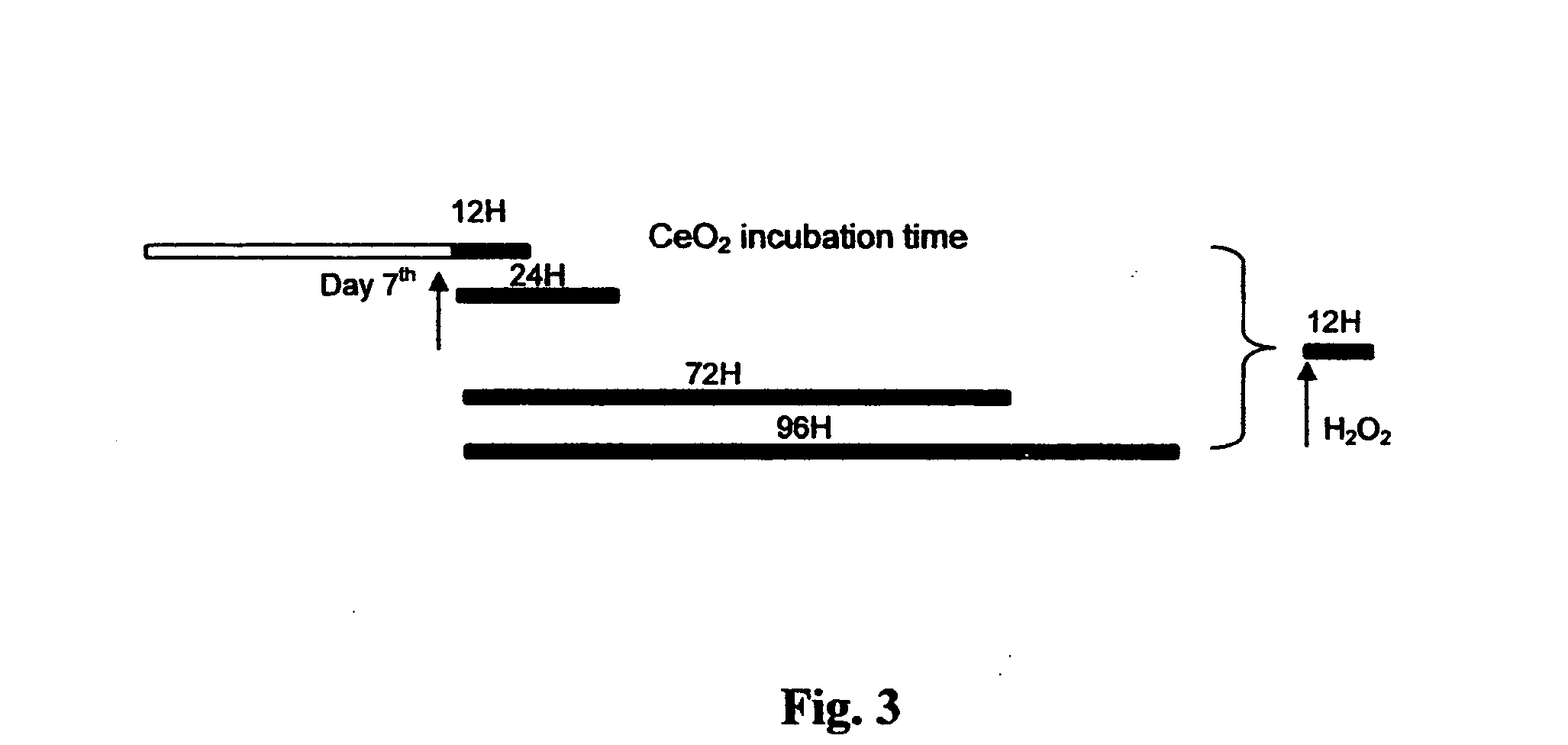
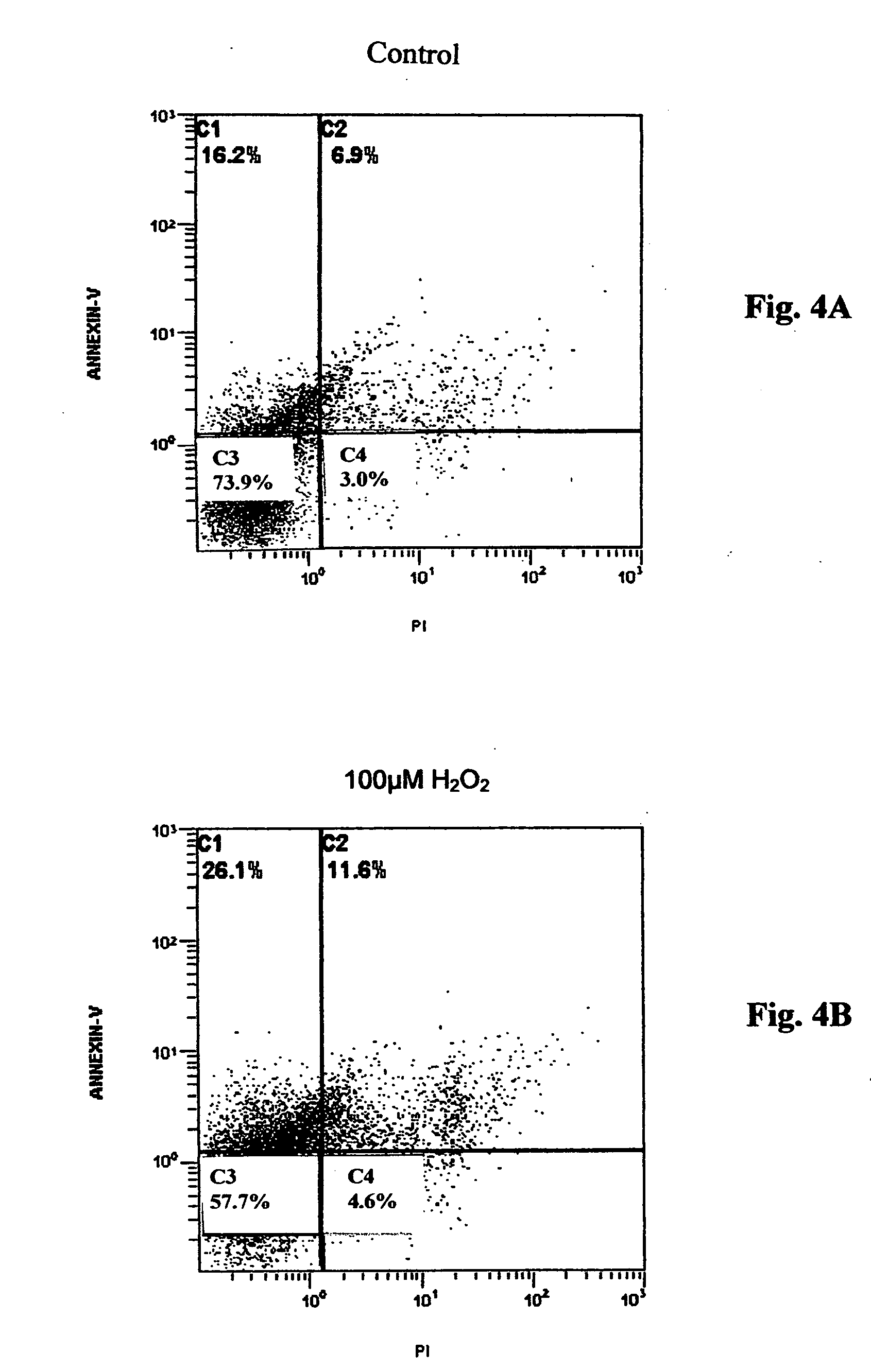
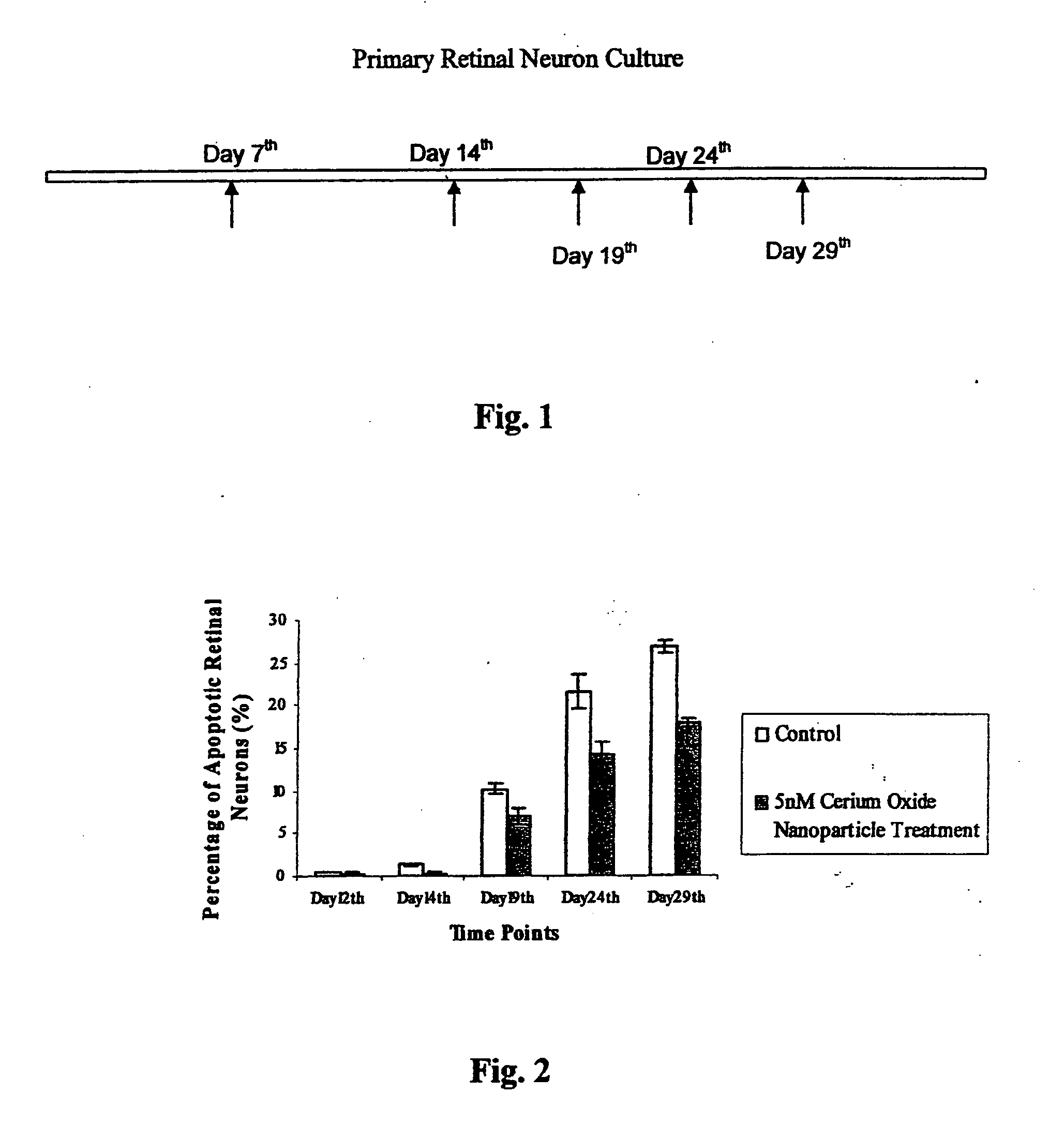
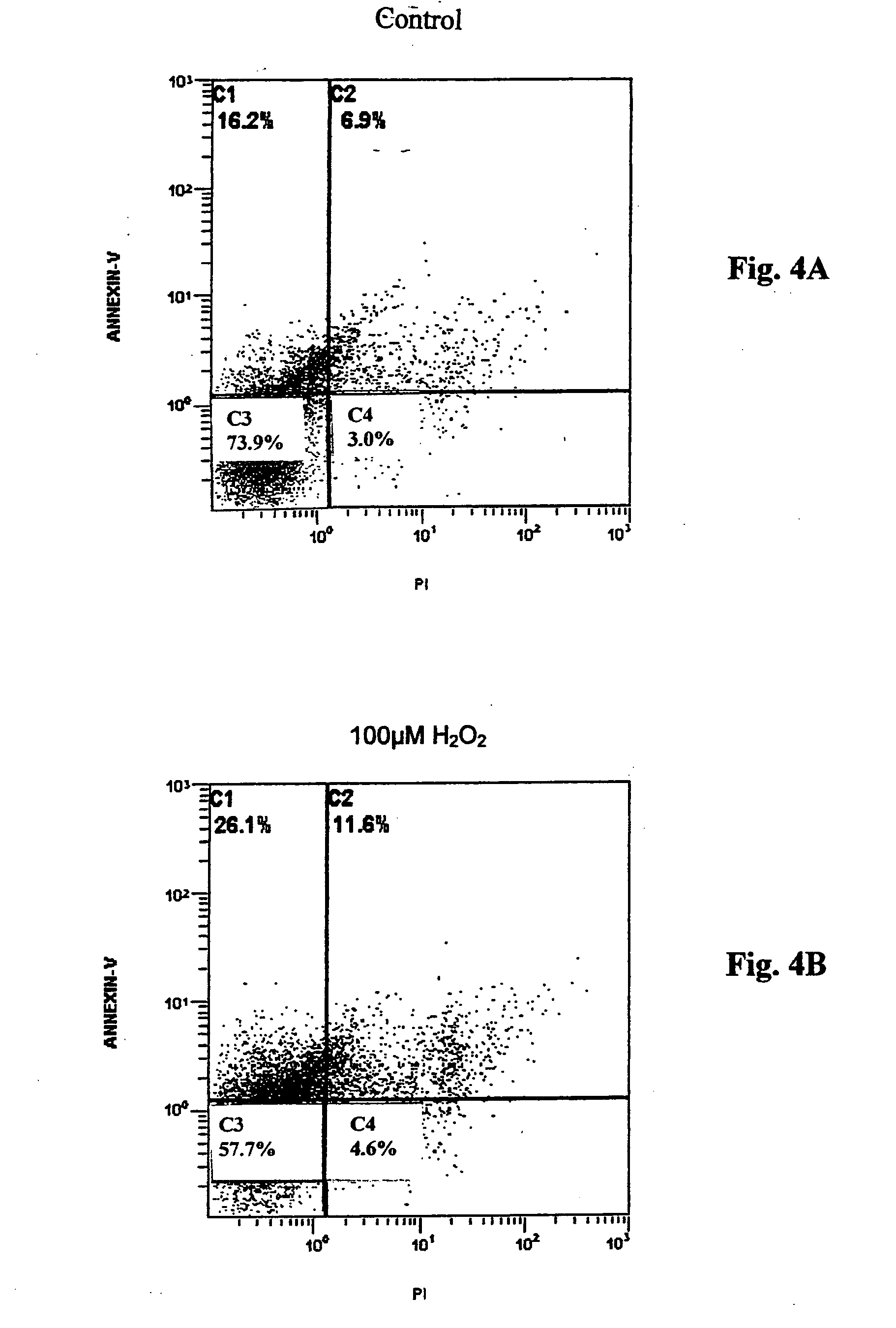
Methods and compositions useful for neuronal protection in retinal cells in vitro and the protection of mammalian cells from reactive oxygen species in vivo are provided. Ultrafine nano-size cerium oxide particles, less than 10 nanometers in diameter, have been provided to decrease reactive oxygen species (ROS) in retina tissue that generates large amounts of ROS. These reactive oxygen species (ROS) are involved in light-induced retina degeneration and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Cerium oxide nanoparticles have been used to promote the lifespan of retinal neurons and protect the neurons from apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide in vitro and in vivo. The neuronal protection in retinal cells is achieved by decreasing generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Thus, cerium oxide particles are used to promote the longevity of retinal neurons in vitro and mammalian cells in vivo.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Method used for inducing differentiation of human multipotential stem cells into retinal progenitor cells
InactiveCN103627669ASolve efficiency problemsResolution cycleSenses disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementRetinitis pigmentosaMultipotential stem cell
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and specifically relates to a method used for inducing differentiation of human multipotential stem cells into retinal progenitor cells. According to the method, human embryonic stem cells or human induced multipotential stem cells are induced in a medium containing N2, and then are delivered into a retina induction medium containing neural basis culture medium, knockout serum replacement and nicotinamide so as to obtain the retinal progenitor cells. The method is capable of increasing differentiation rate of human multipotential stem cells into retinal progenitor cells; and the retinal progenitor cells obtained via differentiation can be used for transplantation therapy of irreversible degenerative diseases of retinal neurons, such as age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa, and also can be used for iPS cells sourced from patients as cell models in drug screening and gene interference experiments. Compared with existing technology, small molecule compounds used in the method are less, so that influences caused by non-anthropogenic factors are avoided effectively, and yield of obtained optic cup-like cells is obviously higher than that of existing induced differentiation methods.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Visual pathway multi-receptive-field directional association-based profile detection method
ActiveCN106127740AIn line with the spatial information processing mechanismEasy accessImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRetinal Neuron
The invention discloses a visual pathway multi-receptive-field directional association-based profile detection method. According to the method, classic receptive field characteristics of retinal neurons and non classic receptive field characteristics of LGN (Lateral Geniculate Nucleus) cells in a visual pathway are simulated from spatial scale characteristics of receptive fields of all levels and mutual associativity of receptive fields of the same level in the visual pathway, and rectangular receptive fields of the LGN cells are associated directionally for simulating direction selection characteristics of simple cells of V1 (primary visual cortex). According to the visual pathway multi-receptive-field directional association-based profile detection method proposed by the invention, an important role of visual characteristics in profile detection is brought into full play.
Owner:杭州感想信息技术有限公司
A light-stimulated retinal prosthesis repair device and repair method
ActiveCN102283742AHigh resolutionReduce resolutionEye implantsEye treatmentLife qualityImaging processing
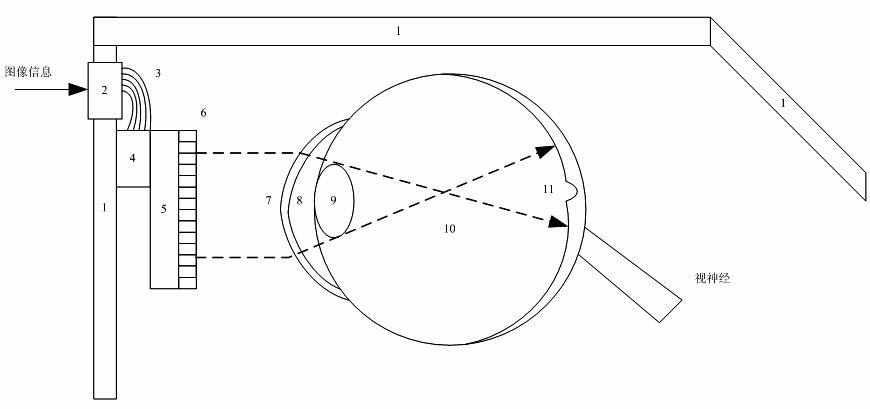
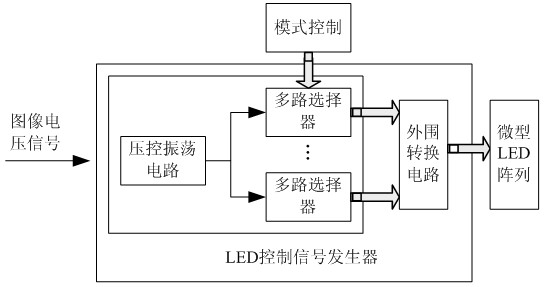
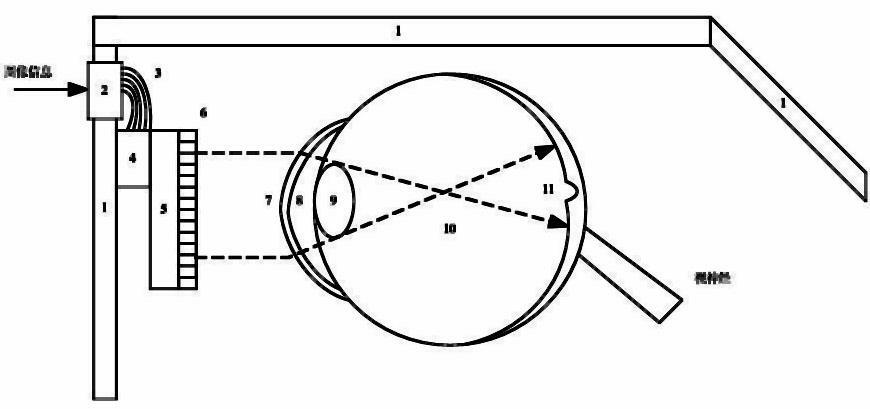
The invention relates to a light stimulation based retinal prosthesis repairing method and device. The method is performed by directly carrying out light stimulation on retinal neurons to help the blind to repair visual sense. The device is composed of image collecting and image processing subsystems, an LED (light-emitting diode) array and an LED control signal generator. The method can effectively stimulate retinal neurons and restore visual perception of patients with ablepsy, and has important social significance for improving the life quality of the blind.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for detecting a functional signal in retinal images
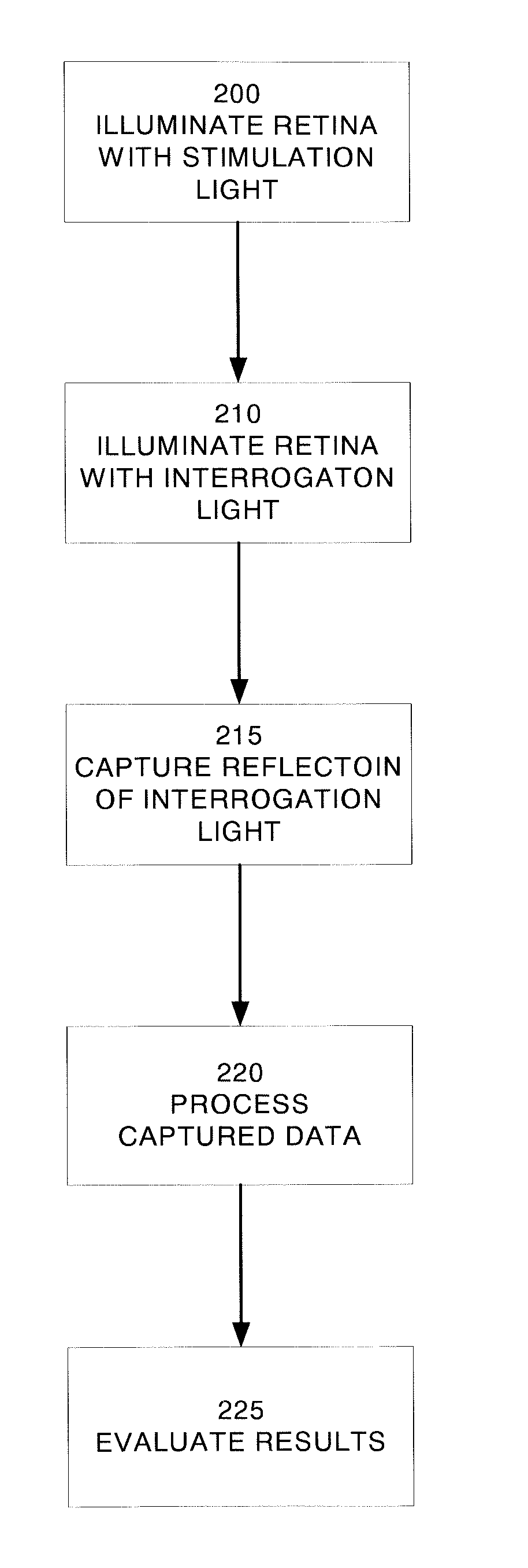
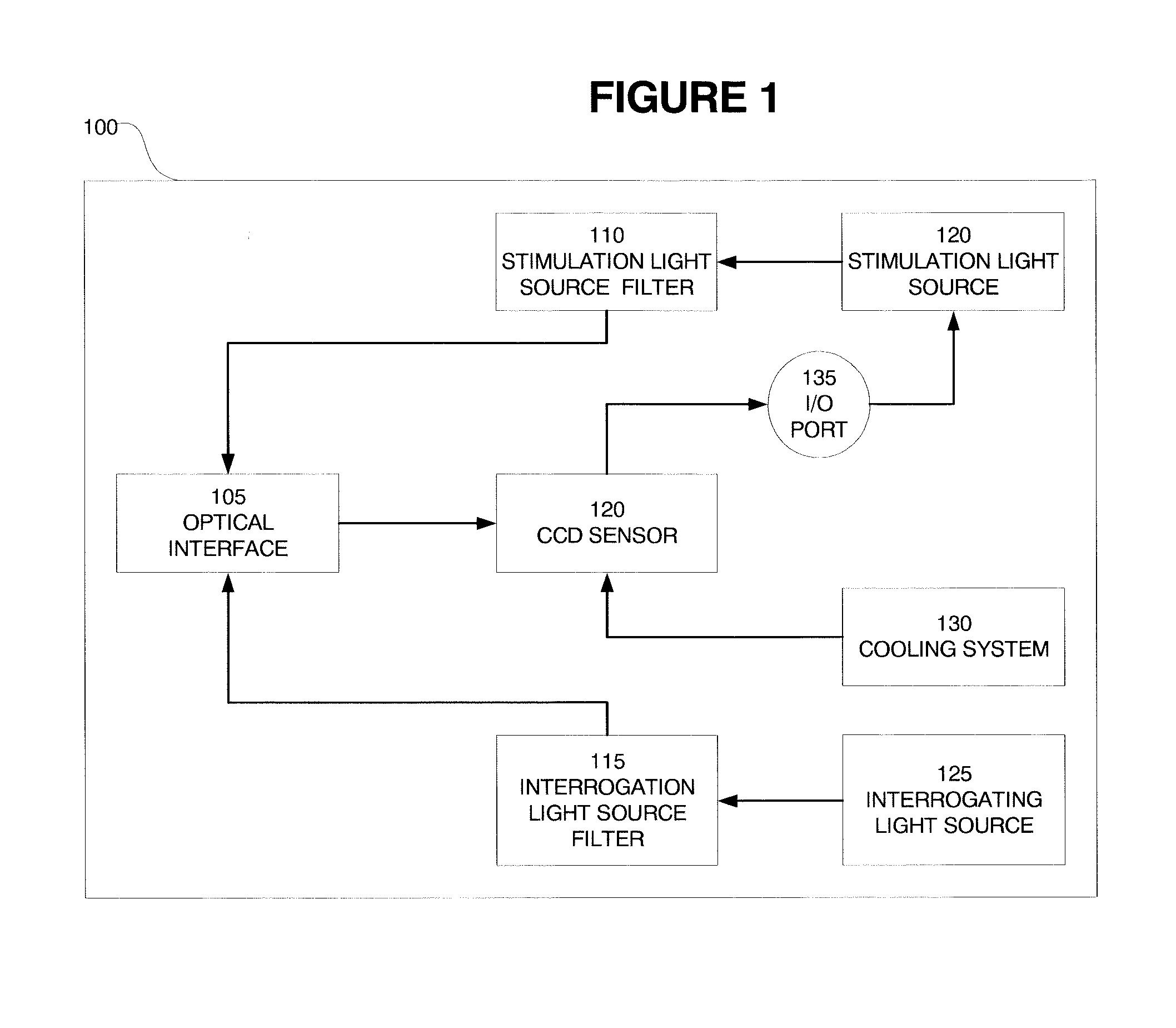
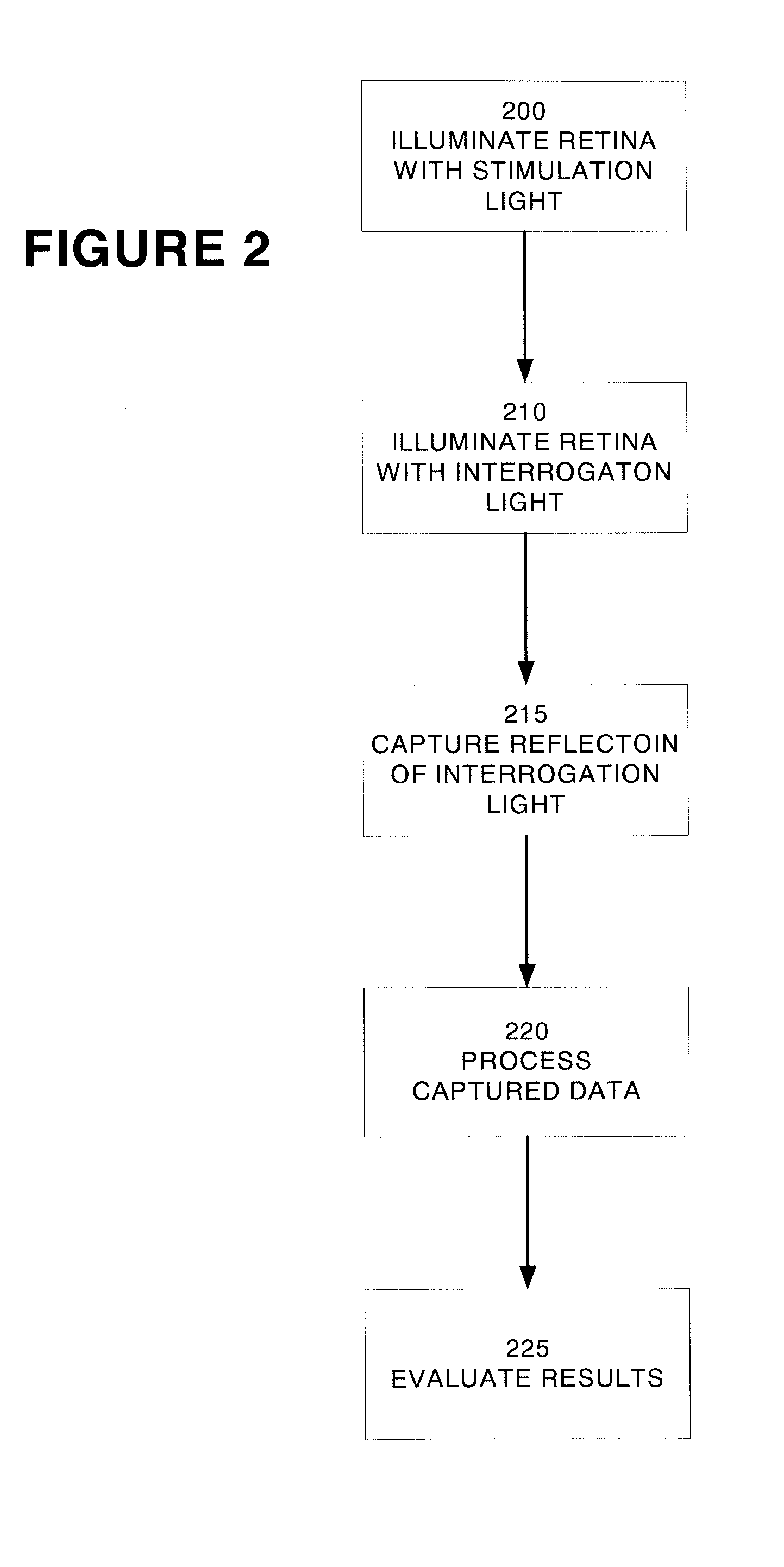
InactiveUS20070211211A1Maximize signal to noiseDifference in absorptionDiagnostics using lightSensorsSpectral bandsOphthalmology
A system and method for detecting a functional signal in retinal images. An optical imaging device comprises a stimulation light source, an interrogating light source, and a detector. The retina is stimulated by the stimulation light source. The retina is then illuminated by an interrogation light, and the reflected intensity from the retina is measured at an interrogating spectral band that indicates the state of hemoglobin saturation before and after visual stimulation. The optical changes that result from retinal neuronal activity are captured by the detector. The signal representing the state of hemoglobin saturation before and after visual stimulation is isolated. In an embodiment of the present invention, this signal is isolated using principle components analysis (PCA). In another embodiment of the present invention, blind source separation (BSS) and independent component analysis (ICA) algorithms such as extended spatial decorrelation and fast-ICA are used to isolate the functional signal from the retinal videos.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
Inhibition of reactive oxygen species and protection of mammalian cells
ActiveUS20070202193A1Increase blockingAvoid damageHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideNeuronal protectionRetina degeneration
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Kit for treating retinal disease
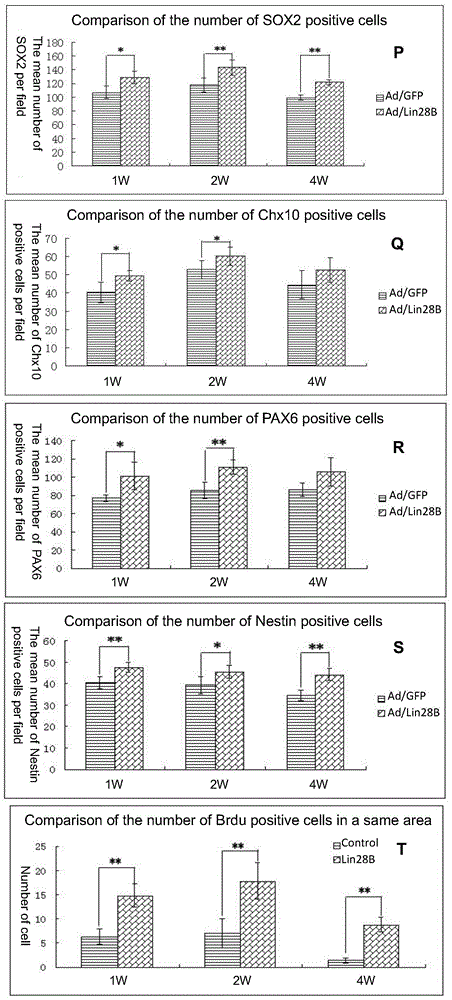
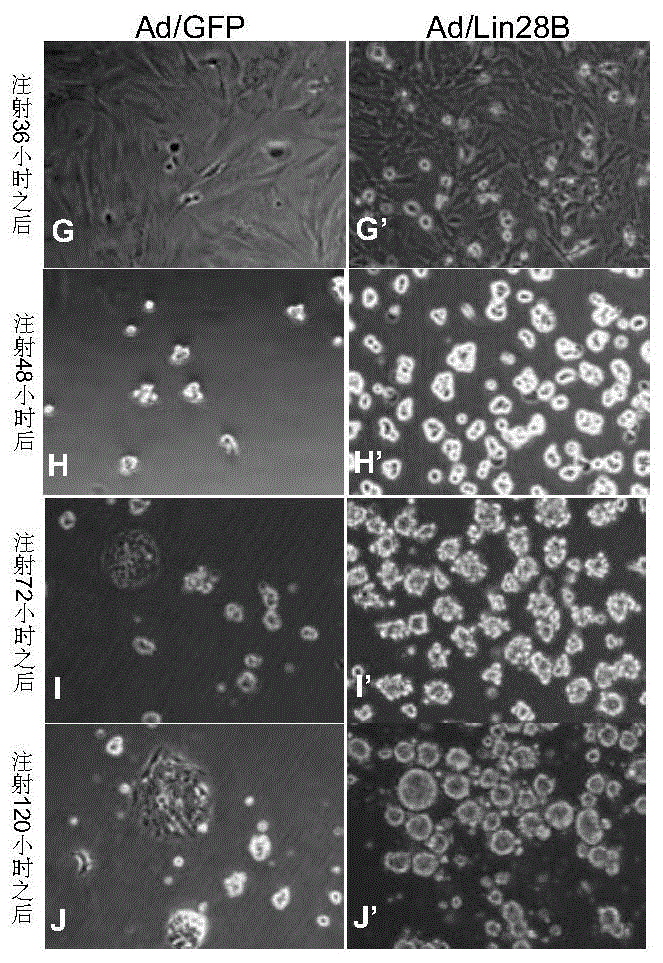
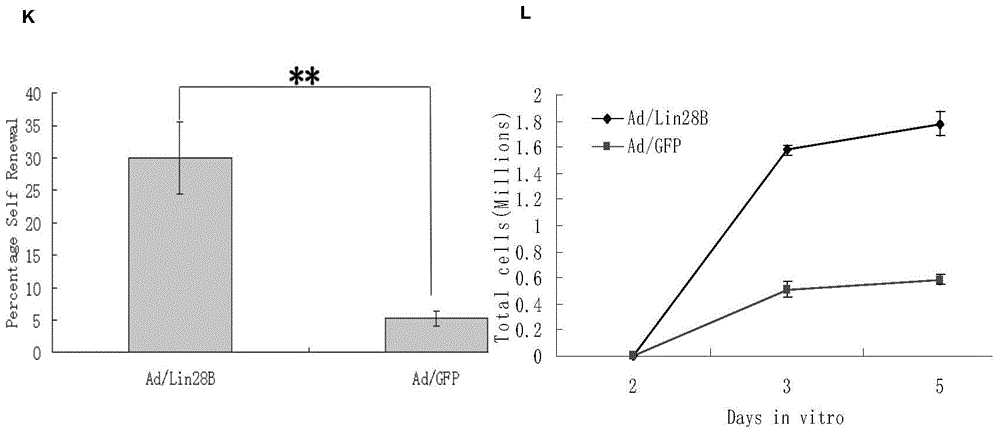
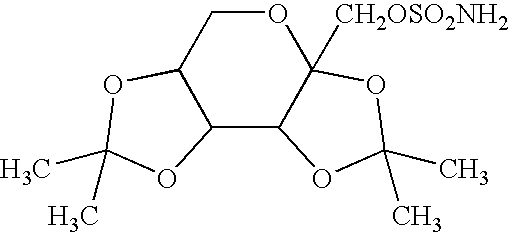
The invention discloses a kit for treating a retinal disease. The kit and a medicament for treating the retinal disease, which are disclosed by the invention, are characterized in that the effective component is adenovirus capable of carrying out overexpression on ribonucleic acid binding protein Lin28B. Injection for a plurality of times is not required when the retinal disease is treated by adopting the kit disclosed by the invention, retinal endogenous stem cells can be activated to the maximal extent by retina inferior vena injection, and the endogenous stem cells are promoted to be differentiated into retinal neurons.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Agent for protection of retinal neurons
Owner:ORTHO MCNEIL PHARM INC
Retinal prostheses
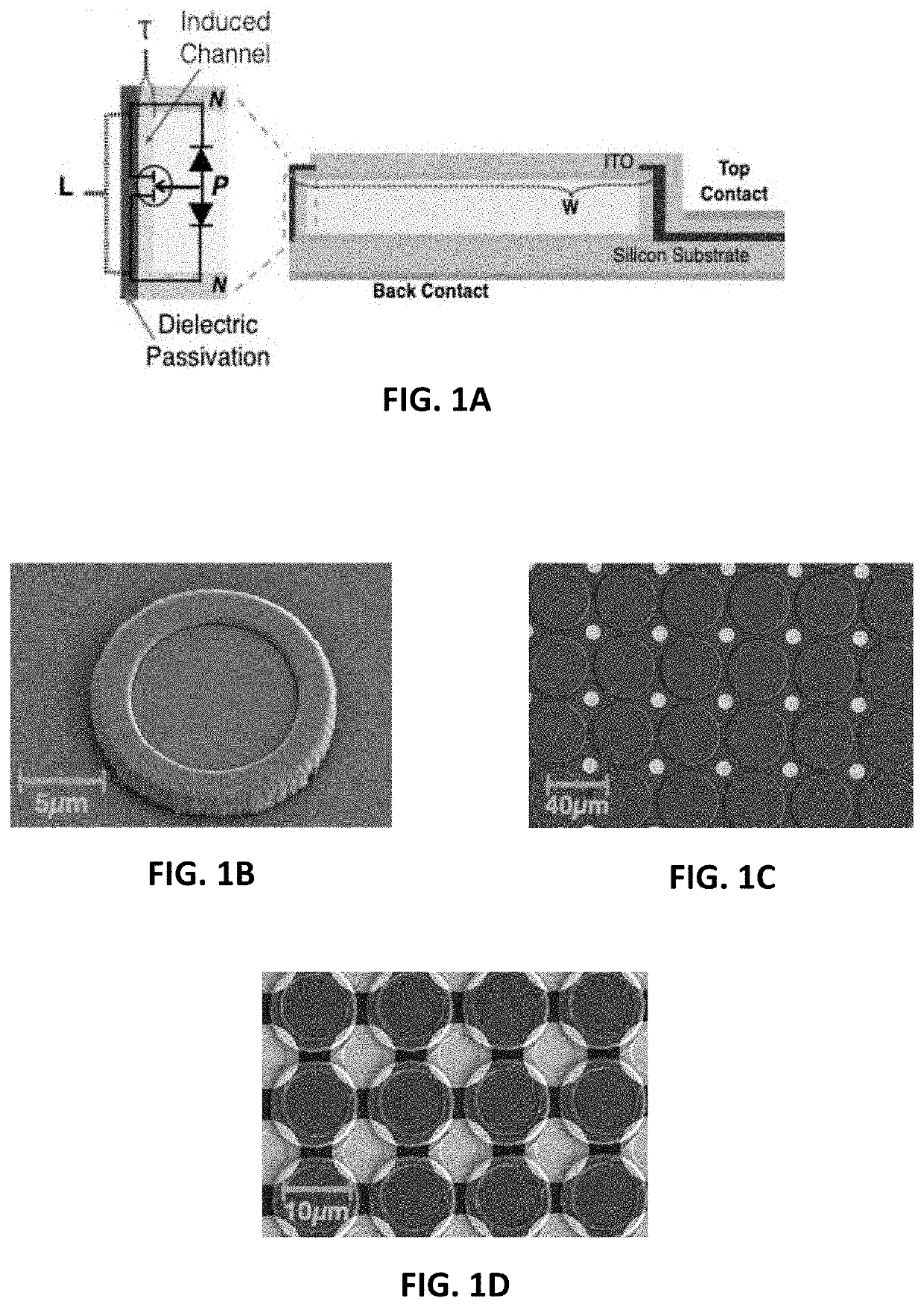
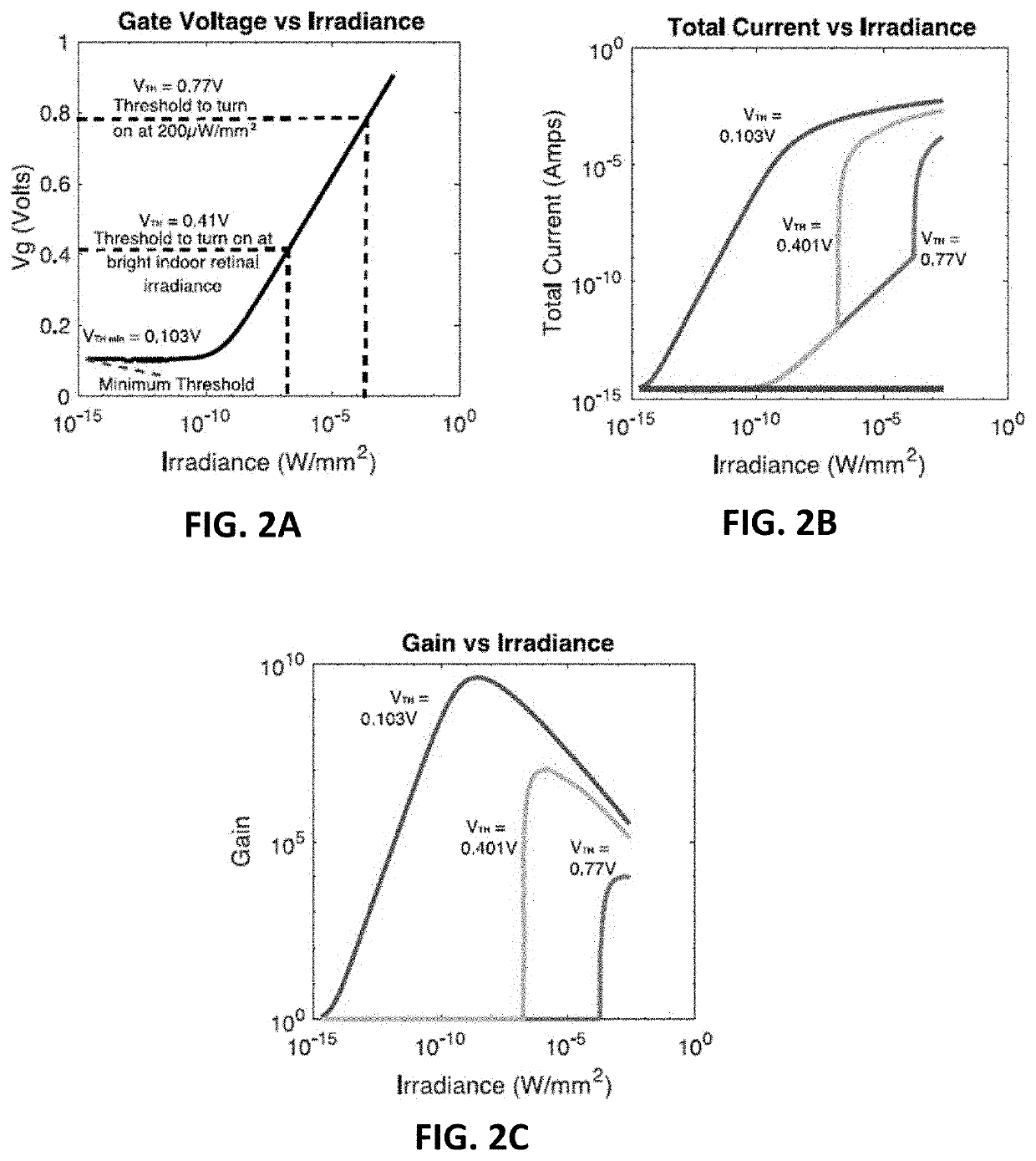
PendingUS20210121685A1Without sacrificing fill factorImprove eyesightTransistorHead electrodesRetinal ProsthesisField effect
Optoelectronic retinal prostheses transduce light into electrical current for neural stimulation. A novel optoelectronic pixel architecture is presented comprising a vertically integrated photo junction field-effect-transistor (Photo-JFET) and neural stimulating electrode. Experimental measurements demonstrate that optically addressed Photo-JFET pixels utilize phototransistive gain to produce a broad range of neural stimulation current and can effectively stimulate retinal neurons in vitro. The compact nature of the Photo-JFET pixel can enable high resolution retinal prostheses with a theoretical visual acuity ˜20 / 60 to help restore vision in patients with degenerative retinal diseases.
Owner:NANOVISION BIOSCIENCES INC
Method and Apparatus for Visual Neural Stimulation
ActiveUS20100236062A1Line/current collector detailsElectrotherapyBiological activationElectrode array
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
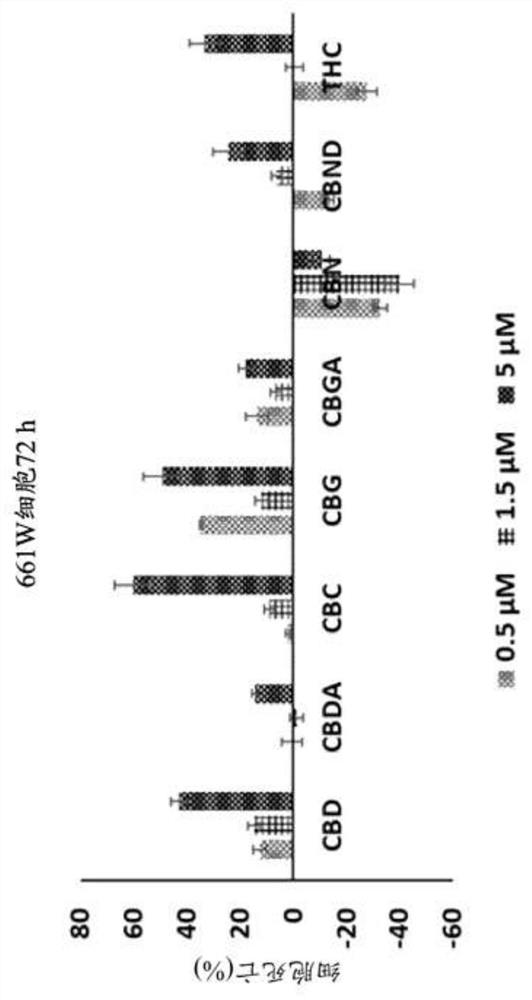
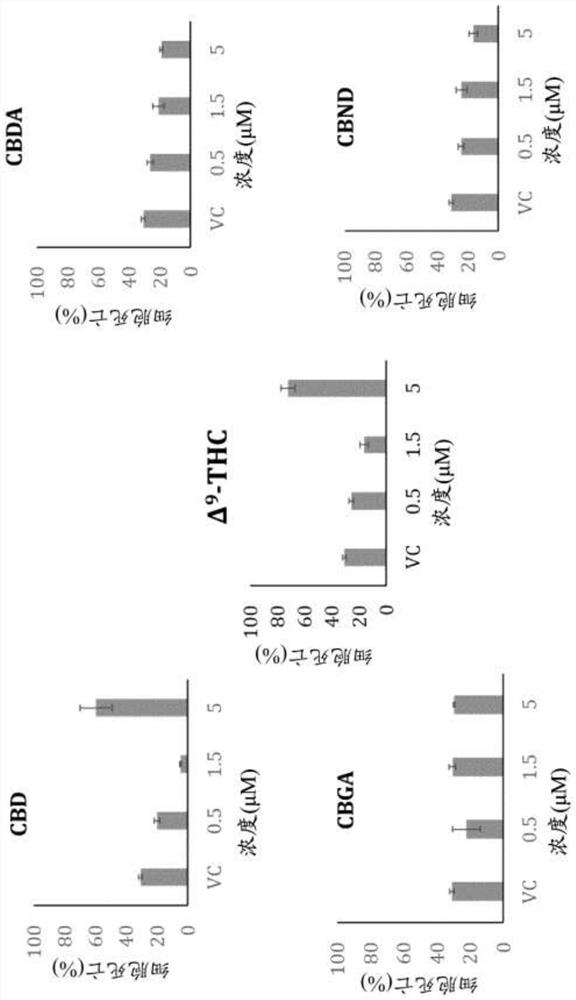
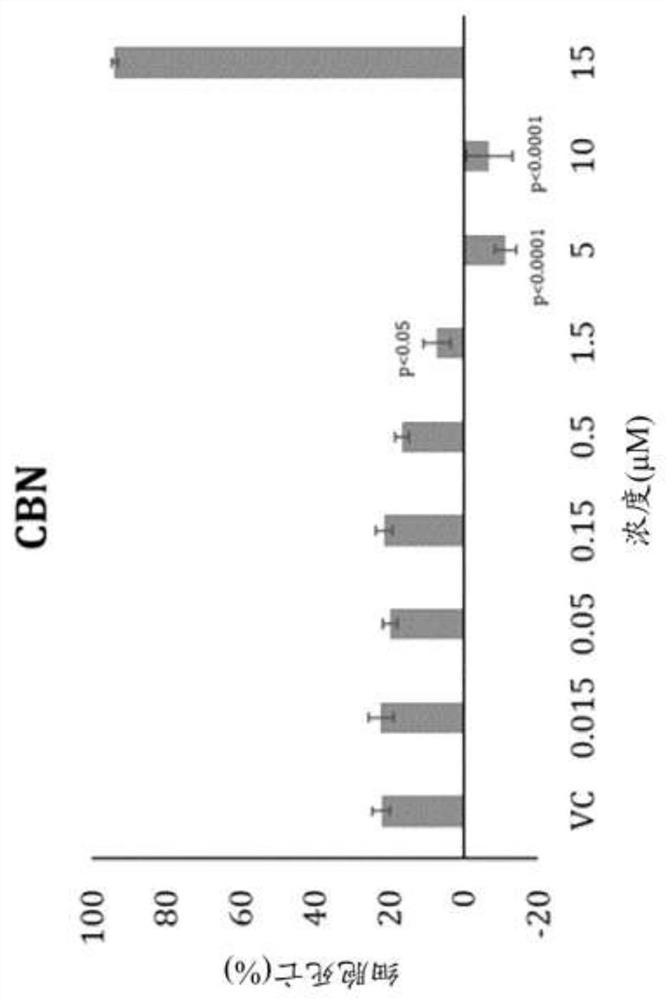
Compositions and methods for use of cannabinoids for neuroprotection
Provided herein are methods and compositions for neuroprotection. The neuroprotective composition can be or include cannabinol or a derivative thereof. The neuroprotective composition can be used in the treatment of a neurodegenerative disease. The neuroprotective composition can be used to protect retinal neurons from degeneration in a subject in need thereof, such as for treatment of glaucoma.
Owner:因美制药公司
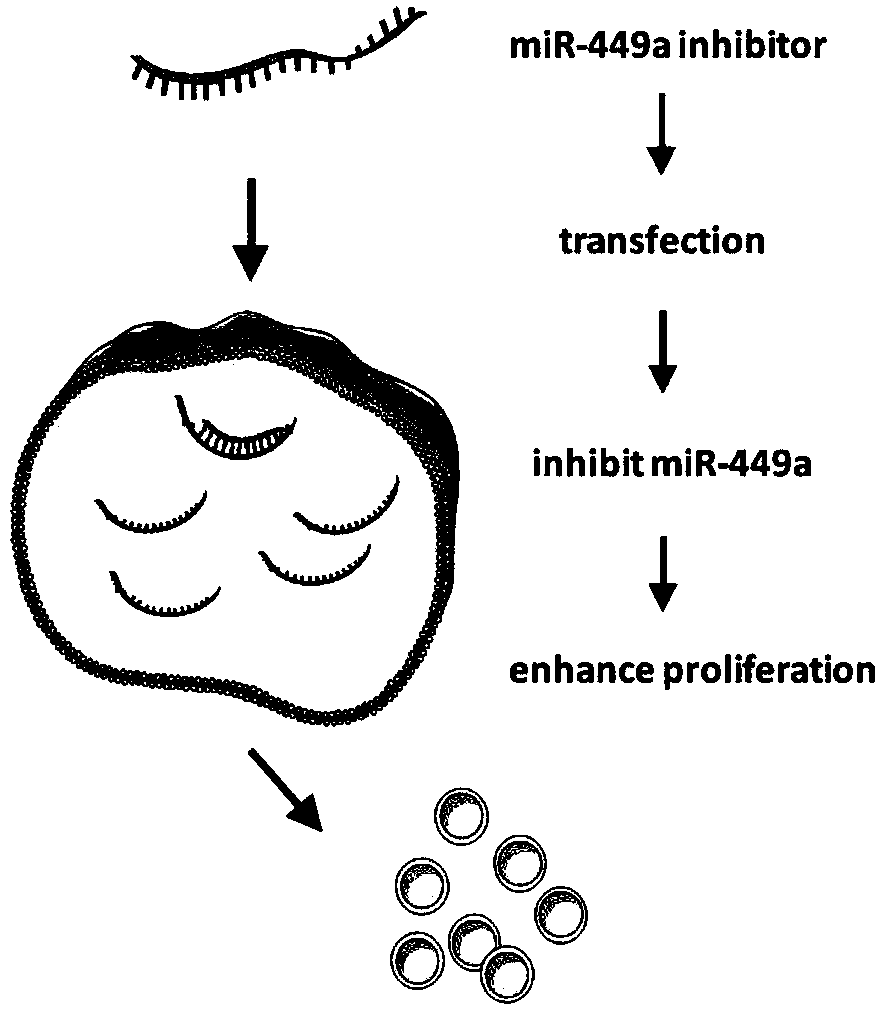
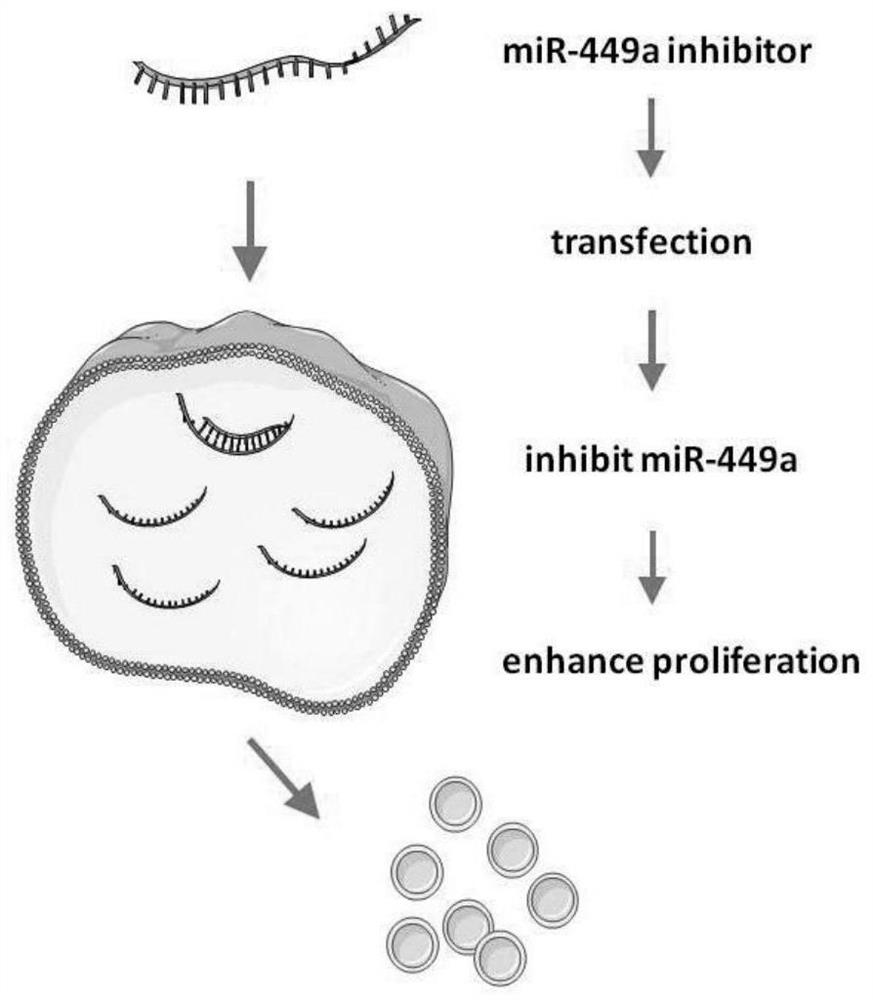
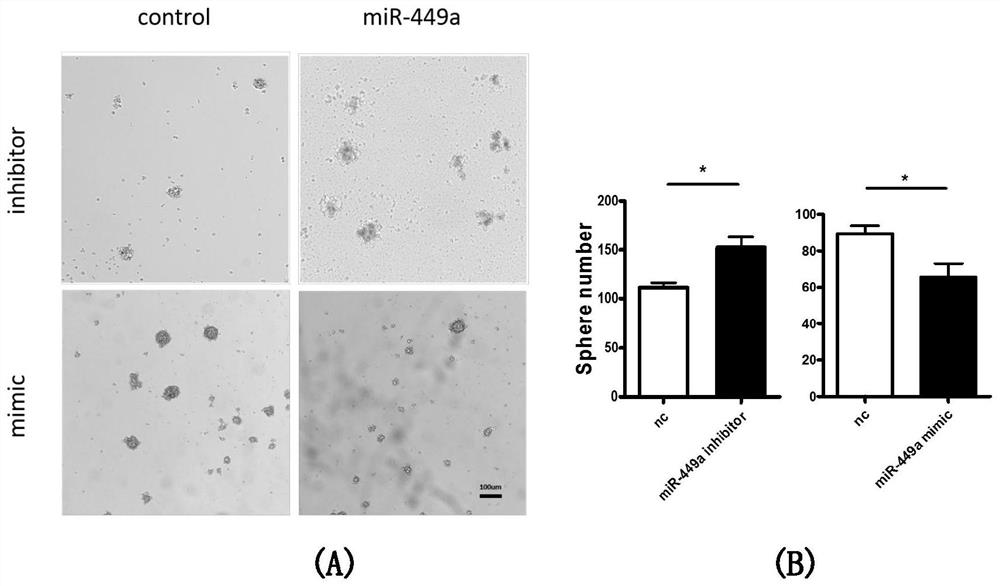
Method for promoting in-vitro amplification of RPCs (retinal progenitor cells) of mouse by inhibiting microRNA (micro ribonucleic acid)
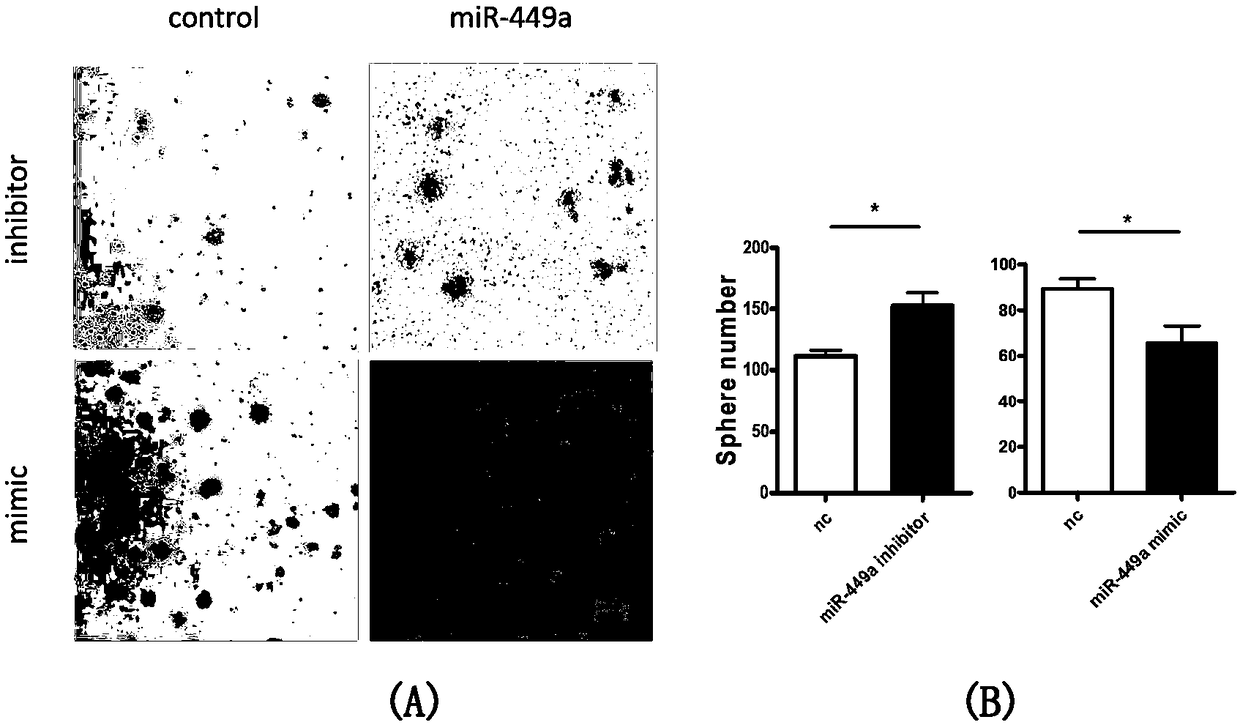
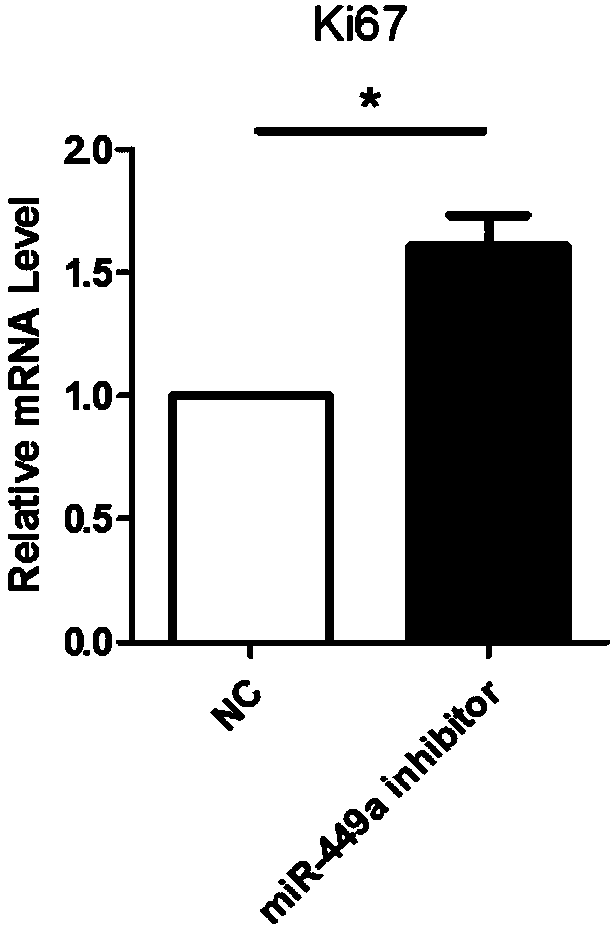
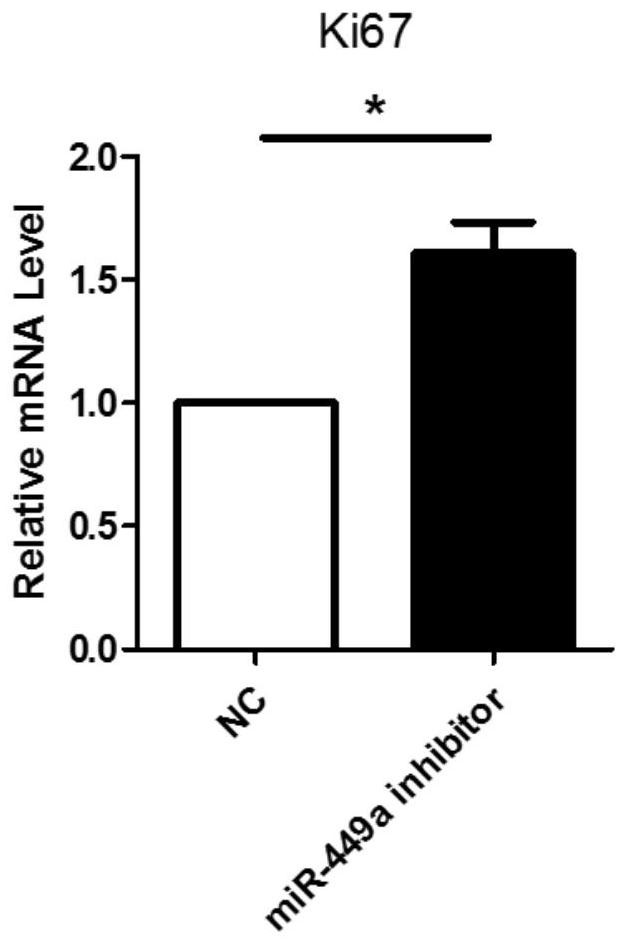
ActiveCN108085316APromote amplificationPromote cell therapyMicroencapsulation basedGenetically modified cellsMouse RetinaCell therapy
The invention discloses a method for promoting in-vitro amplification of RPCs (retinal progenitor cells) of a mouse by inhibiting microRNA (micro ribonucleic acid). MicroRNA miR-449a-5p is a non-codedsingle-stranded RNA molecule with length of 22 nucleotides, and the coded DNA sequence of the molecule is located on chromosome 13 of the mouse. The RPCs are cells with self-renewal capacity as wellas potential of being differentiated into retinal neurons and neuroglia. By means of synthesis of an antisense strand of miR-449a-5p, interference to level of endogenous miR-449a-5p is realized according to the principle of complementary pairing of basic groups, and in-vitro amplification of the RPCs can be effectively performed. The RPCs are development sources of photoreceptor cells in mature neural retina, so that the effective in-vitro amplification method can promote cell therapy based on stem / precursor cell transplantation.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
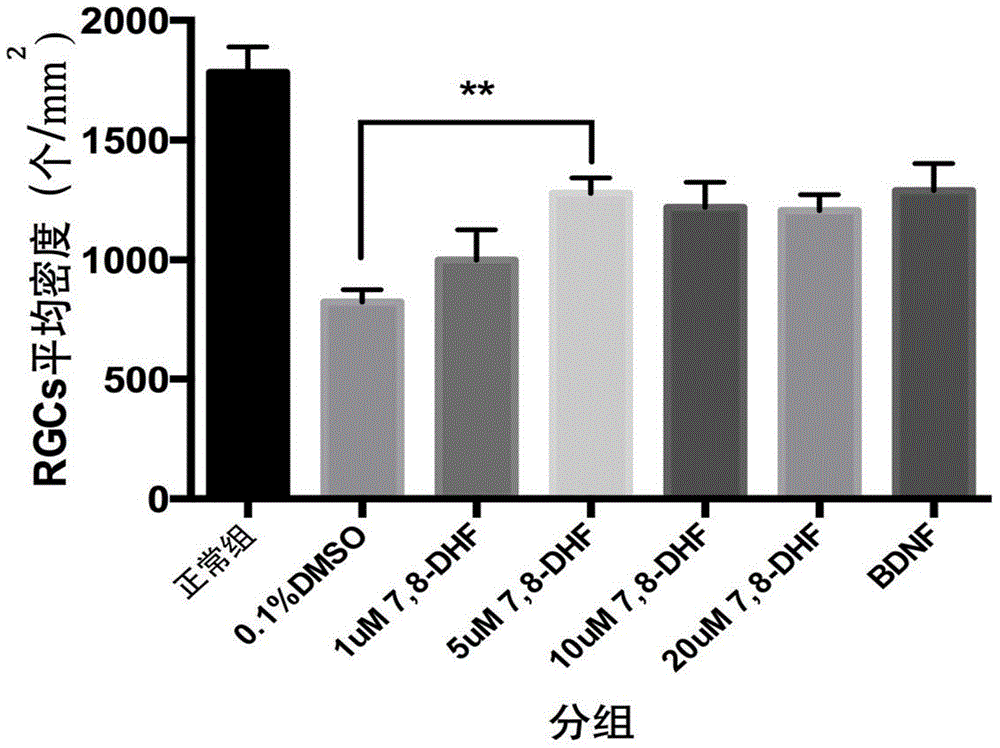
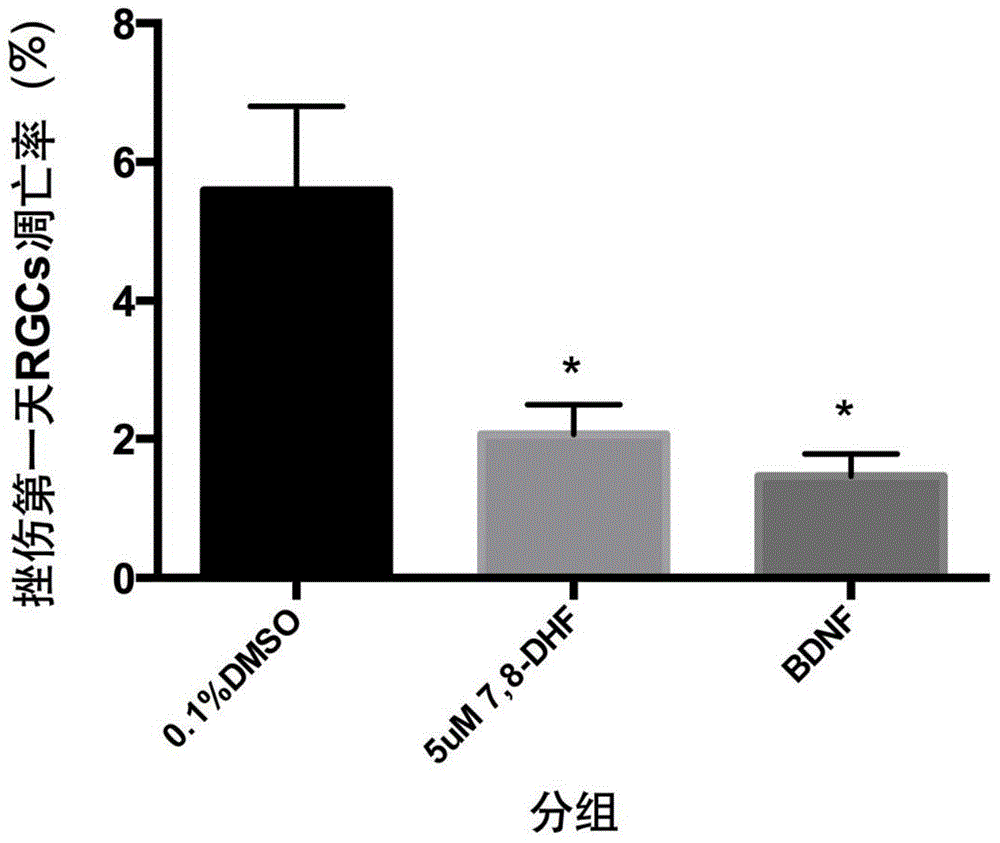
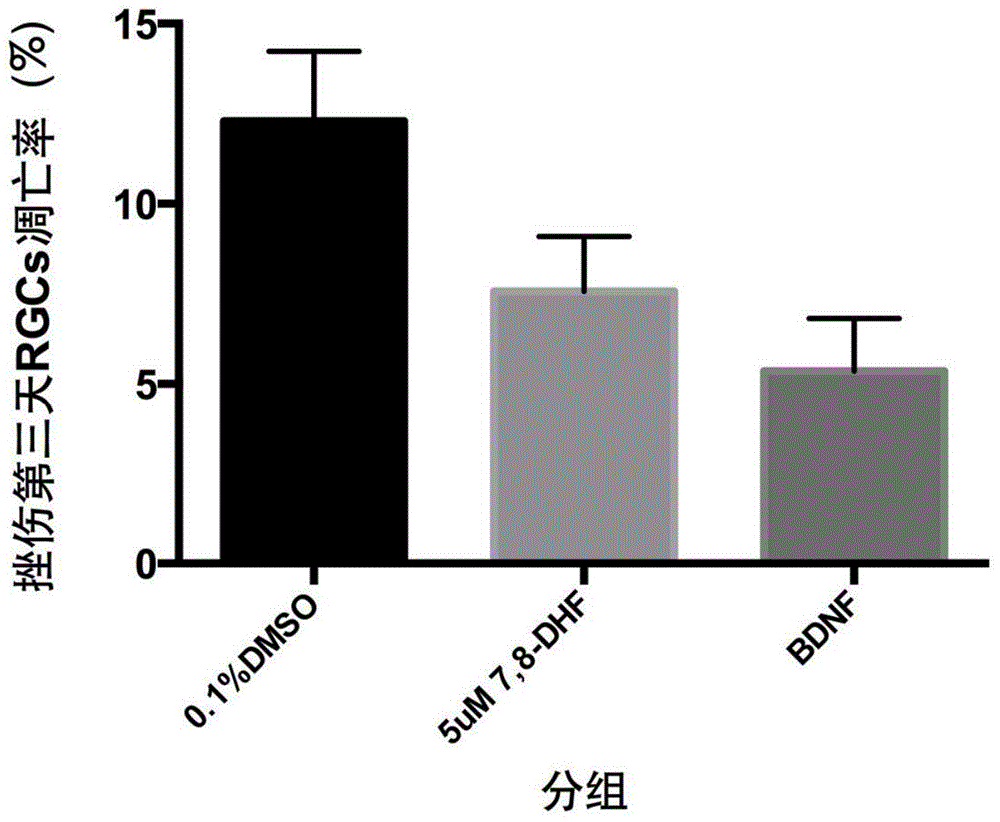
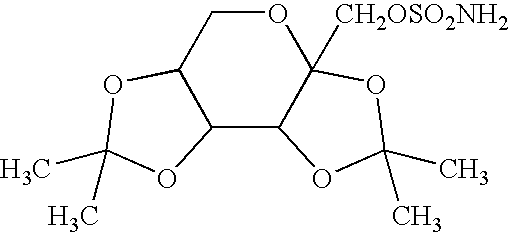
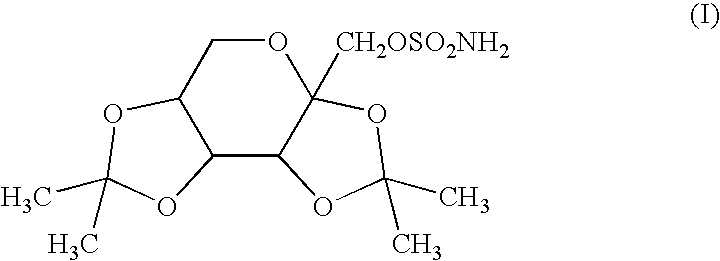
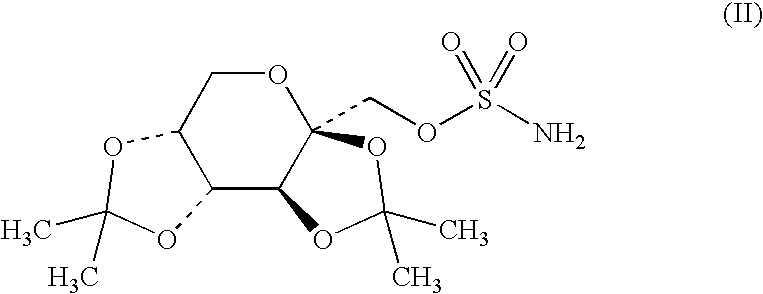
Application of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (DHF) to preparation of drug for treating retinal degenerative diseases
The invention belongs to the pharmaceutical field and relates to an application of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (DHF) to preparation of a drug for treating retinal degenerative diseases. Through adult SD rat optic nerve contusion model experiments, the results show that 7,8-DHF can achieve the effects of reducing apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells and increasing the survival rate and has obvious protective effects on injured retinal neurons. 7,8-DHF is used for further treating the retinal degenerative diseases by protecting the injured retinal neurons, wherein the retinal degenerative diseases include glaucoma, macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa, ischemic optic neuropathy and traumatic optic nerve contusion. The invention also provides a novel small molecular drug preparation with 7,8-DHF as the main active ingredient. Obvious protective effects can be generated for the injured retinal neurons by locally delivering the drug to the vitreous cavities of eyes.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
Agent for protection of retinal neurons
InactiveUS20040171558A1Effective protectionUseful in therapyBiocideSenses disorderRetinal NeuronAdditive ingredient
Owner:ORTHO MCNEIL PHARM INC
A method for image color constancy in multi-light source environment
The invention discloses an image color constant method in a multi-light source environment. The invention proposes a multi-light source color constant method based on the physiological mechanism of the retina, which simulates the visual light-dark adaptation ability and the characteristics of the retinal neuron receptive field, and establishes the following method: A model based on ON and OFF receptive fields based on the division of bright and dark areas, this model can well estimate the position and color of the light source, and can adjust parameters to adapt to different scene images. The method of the present invention has the characteristics of few parameters, simple calculation, fast speed, good effect, and real-time processing, and is very suitable for being built in the front end of physical equipment preprocessing to estimate the color of the scene light source in the image.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A Contour Detection Method Based on Orientation Correlation of Multiple Receptive Fields in Visual Pathway
ActiveCN106127740BIn line with the spatial information processing mechanismEasy accessImage enhancementImage analysisRetinal NeuronComputer vision
The invention discloses a visual pathway multi-receptive-field directional association-based profile detection method. According to the method, classic receptive field characteristics of retinal neurons and non classic receptive field characteristics of LGN (Lateral Geniculate Nucleus) cells in a visual pathway are simulated from spatial scale characteristics of receptive fields of all levels and mutual associativity of receptive fields of the same level in the visual pathway, and rectangular receptive fields of the LGN cells are associated directionally for simulating direction selection characteristics of simple cells of V1 (primary visual cortex). According to the visual pathway multi-receptive-field directional association-based profile detection method proposed by the invention, an important role of visual characteristics in profile detection is brought into full play.
Owner:杭州感想信息技术有限公司
A method to promote in vitro expansion of mouse retinal precursor cells by inhibiting microRNAs
ActiveCN108085316BPromote amplificationPromote cell therapyMicroencapsulation basedGenetically modified cellsMouse RetinaNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for promoting the in vitro expansion of mouse retinal precursor cells by inhibiting microribonucleic acid. MicroRNA miR-449a-5p is a non-coding single-stranded RNA molecule of 22 nucleotides in length, and its coding DNA sequence is located on mouse chromosome 13. Retinal precursor cells are a class of cells with self-renewal ability and the potential to differentiate into retinal neurons and glial cells. By synthesizing the antisense strand of miR-449a-5p and using the principle of base pairing to interfere with the level of endogenous miR-449a-5p, it can effectively promote the expansion of retinal precursor cells in vitro. Since retinal precursor cells are the developmental source of photoreceptor cells in the mature neural retina, their efficient in vitro expansion method could facilitate cell therapy based on stem / precursor cell transplantation.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
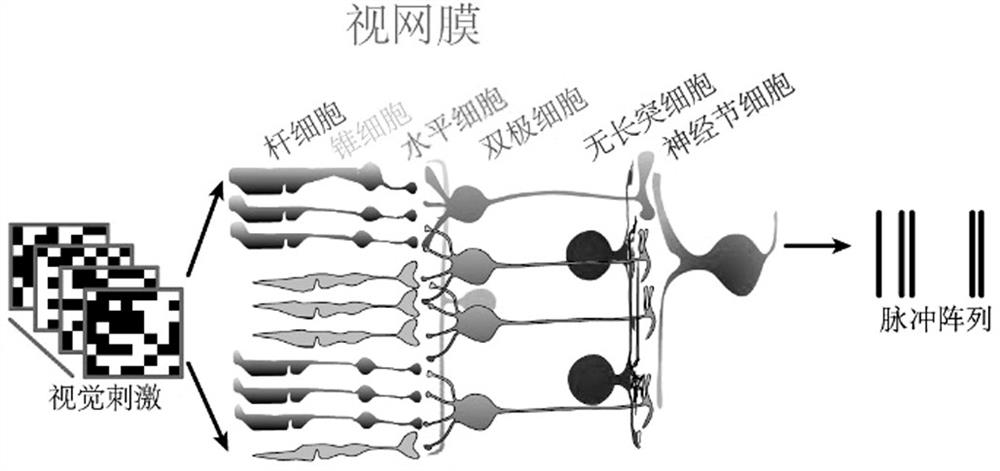
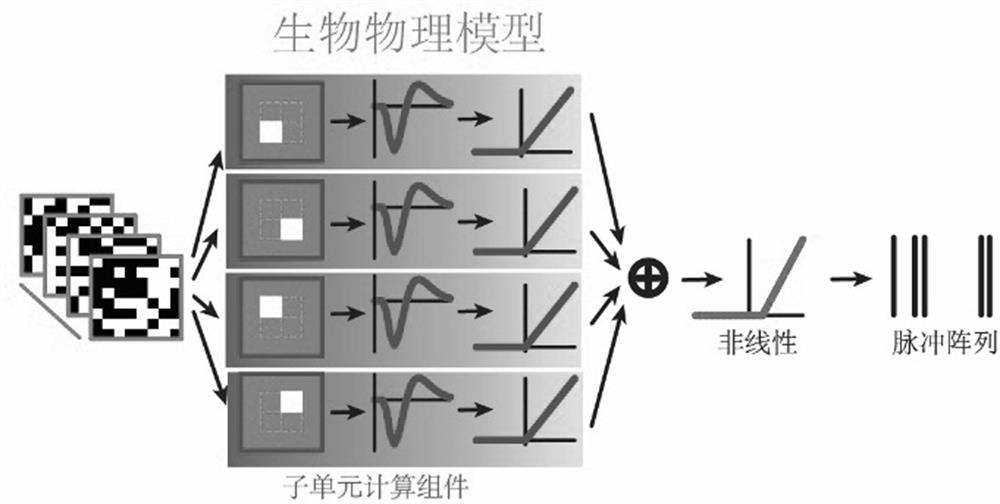
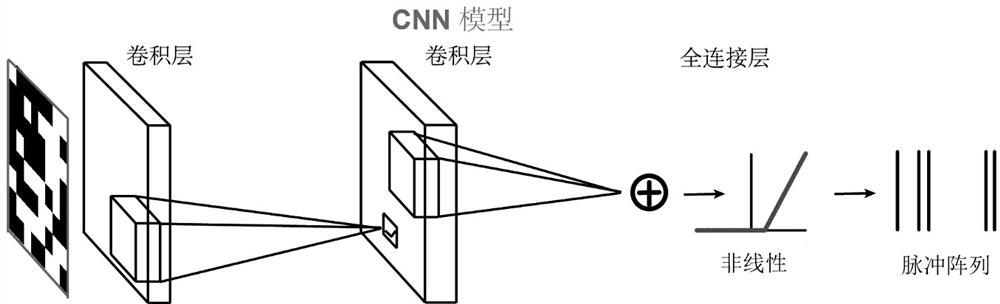
Retinal neuron coding method based on convolutional neural network
PendingCN112329795ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesActivation functionRetinal Neuron
The invention discloses a retinal neuron coding method based on a convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining ganglion cell stimulation data and correspondingresponse data; S2, constructing a CNN model for training, including the following steps: S21, inputting ganglion cell stimulation data into a first convolution layer; S22, inputting the output of thefirst convolution layer into a second convolution layer; S23, inputting the output of the second convolution layer into a full connection layer; S24, comparing the output with the response data, andoptimizing the output of the CNN model; and S3, predicting response data of ganglion cells through the trained CNN model; the CNN model is selected because the CNN model has strong nonlinear computingpower, through experiments, when the convolution layer of the CNN model is 2, the effect is the best, only one output neuron exists in a full connection layer, and information is corrected through anactivation function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com