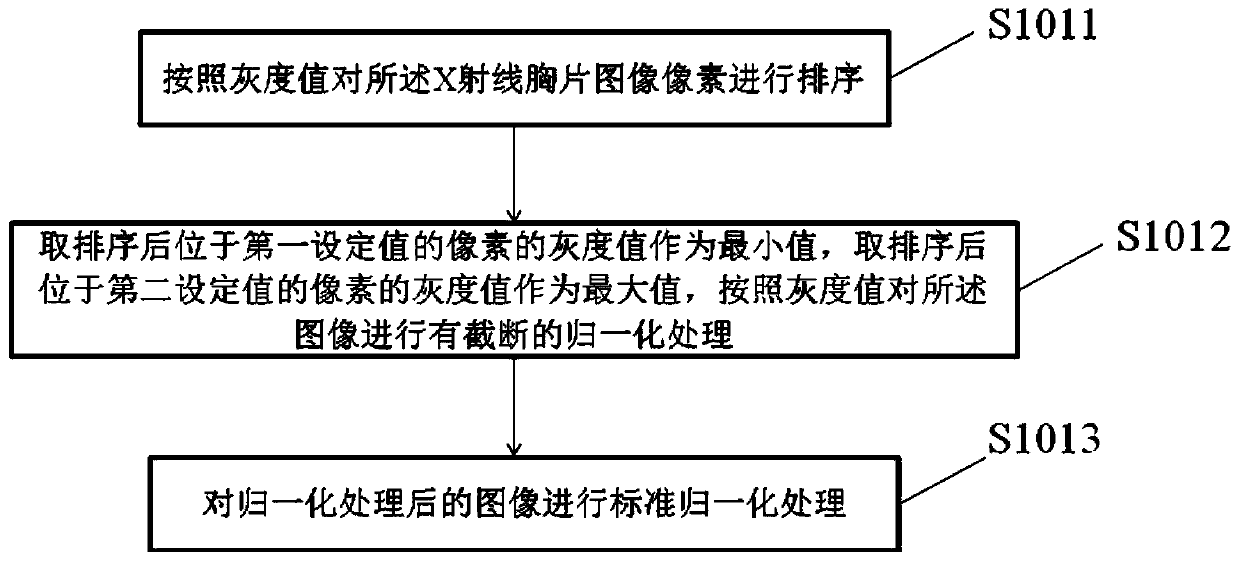
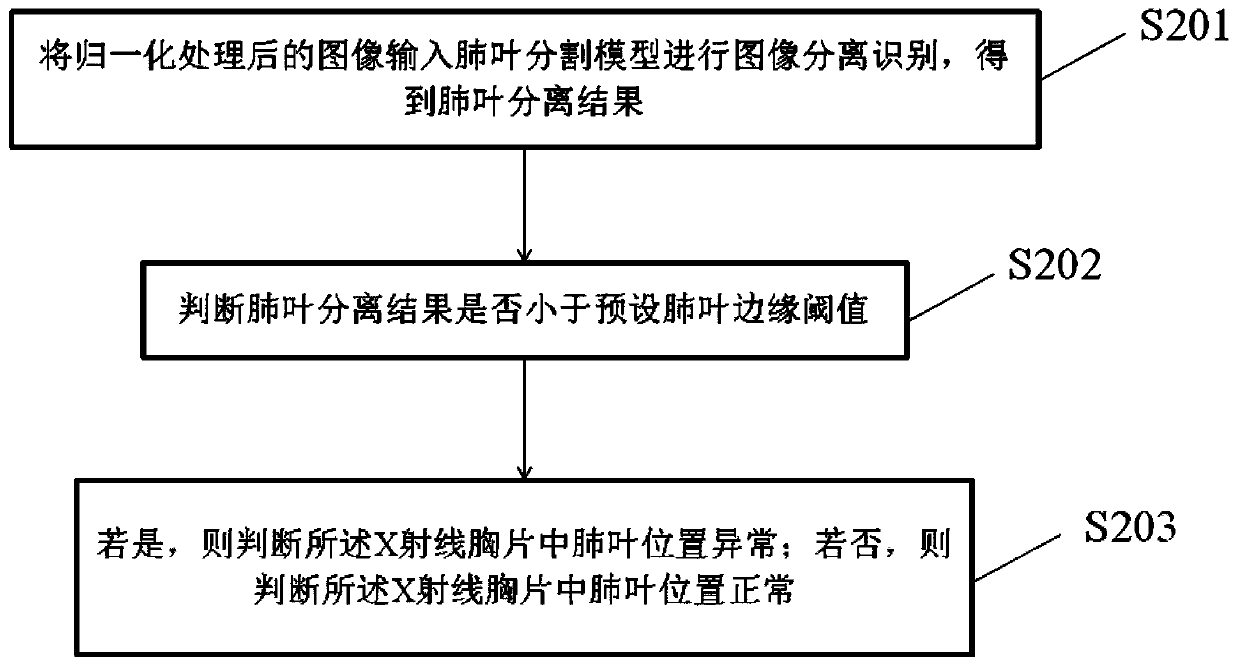
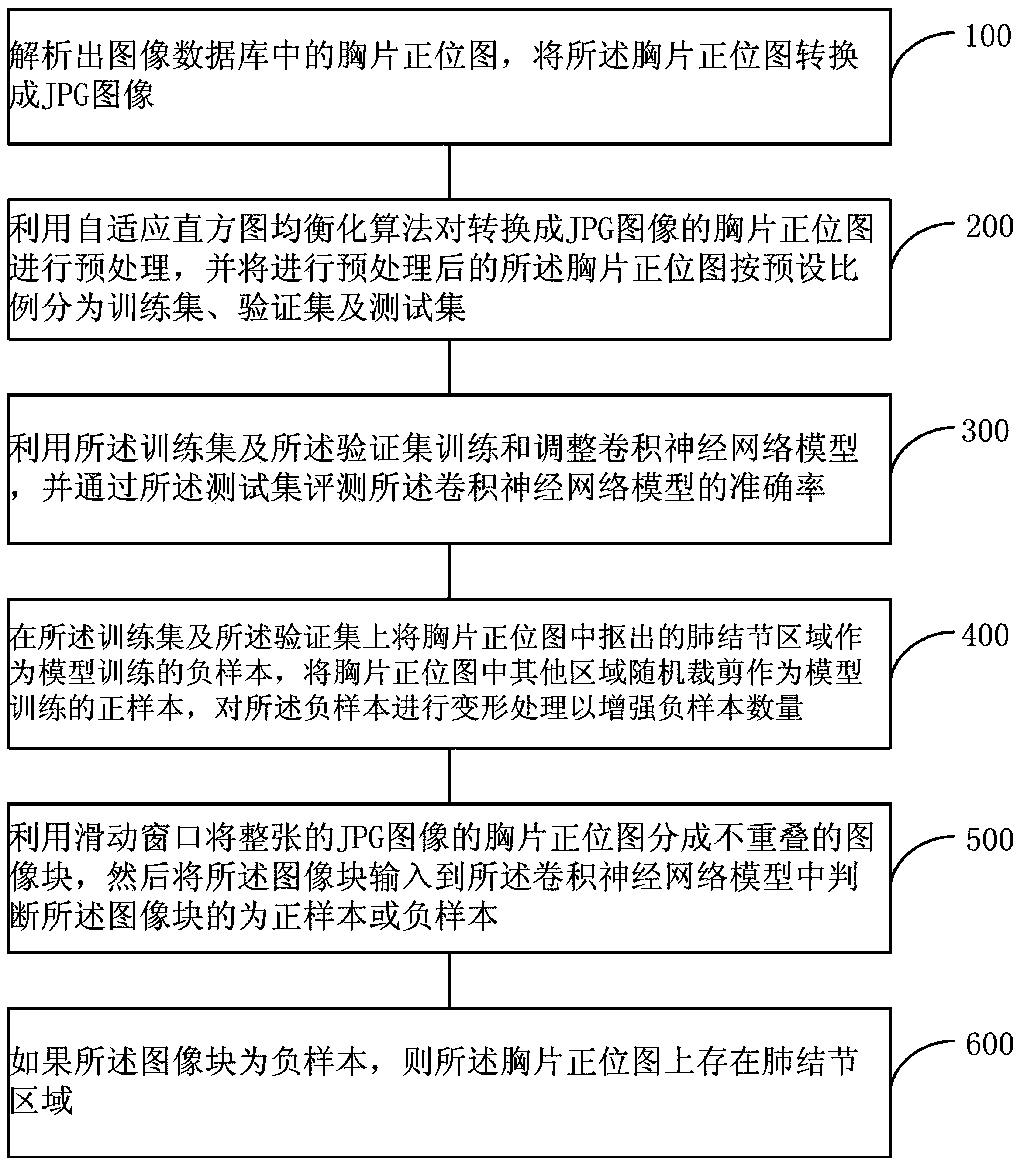
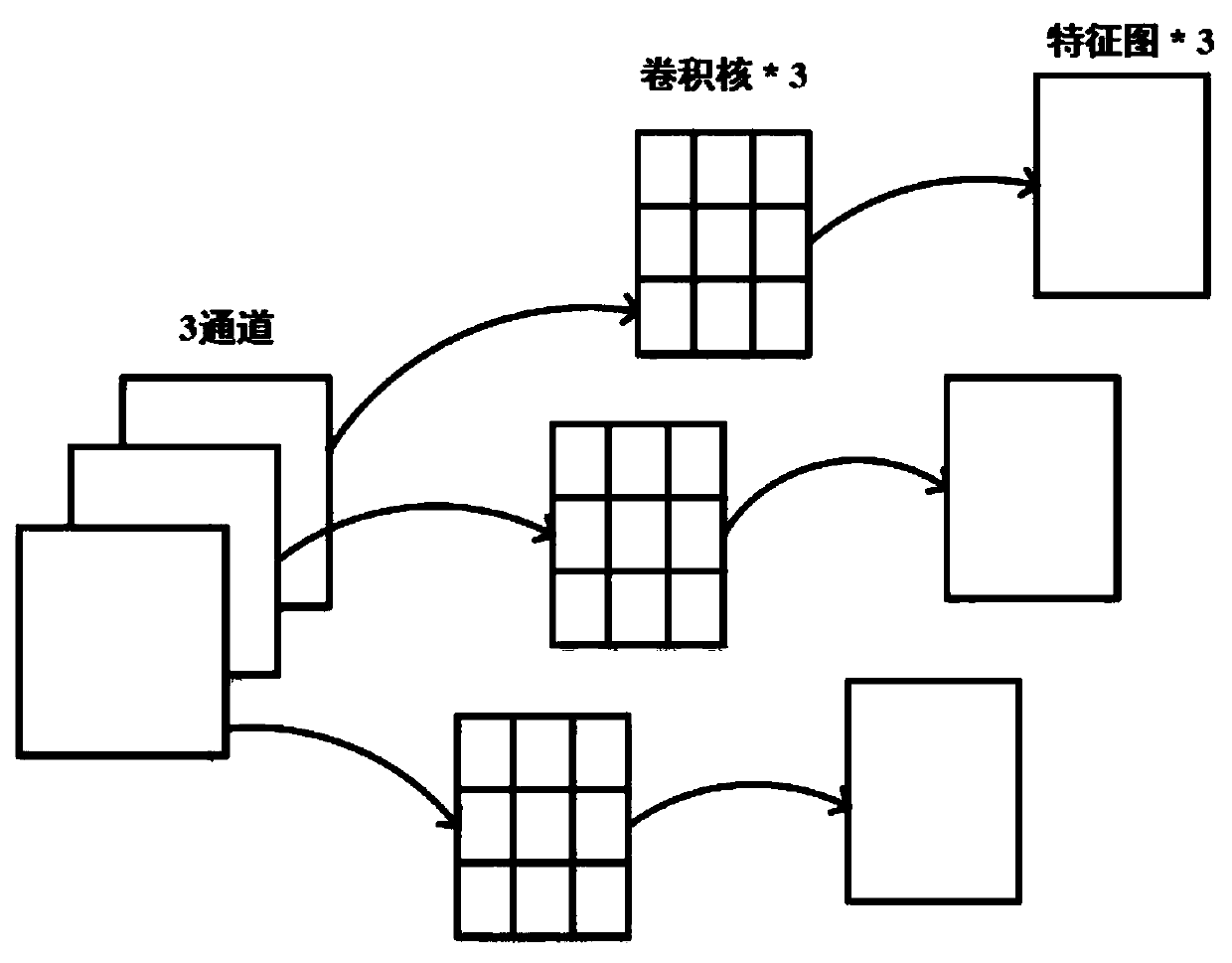
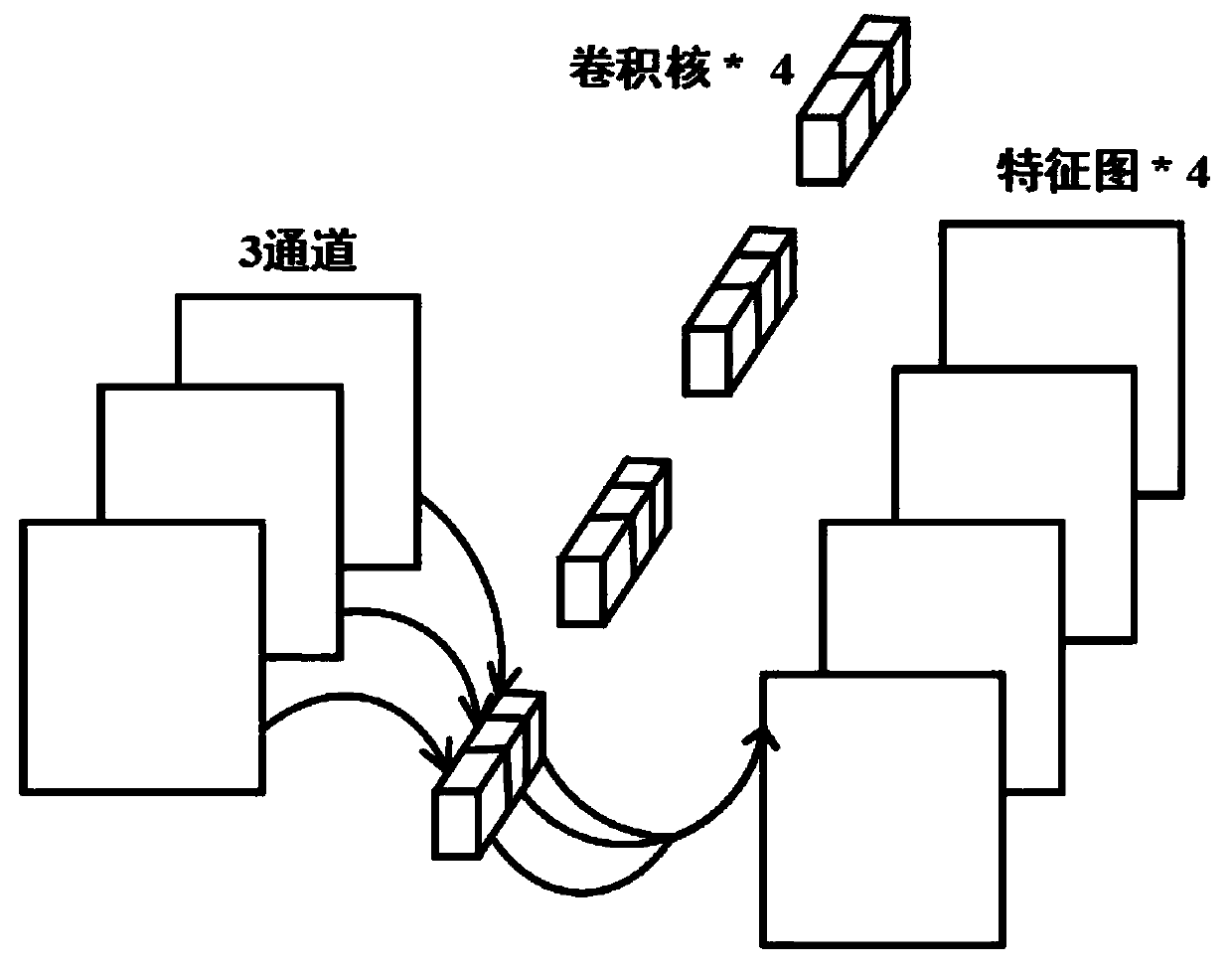
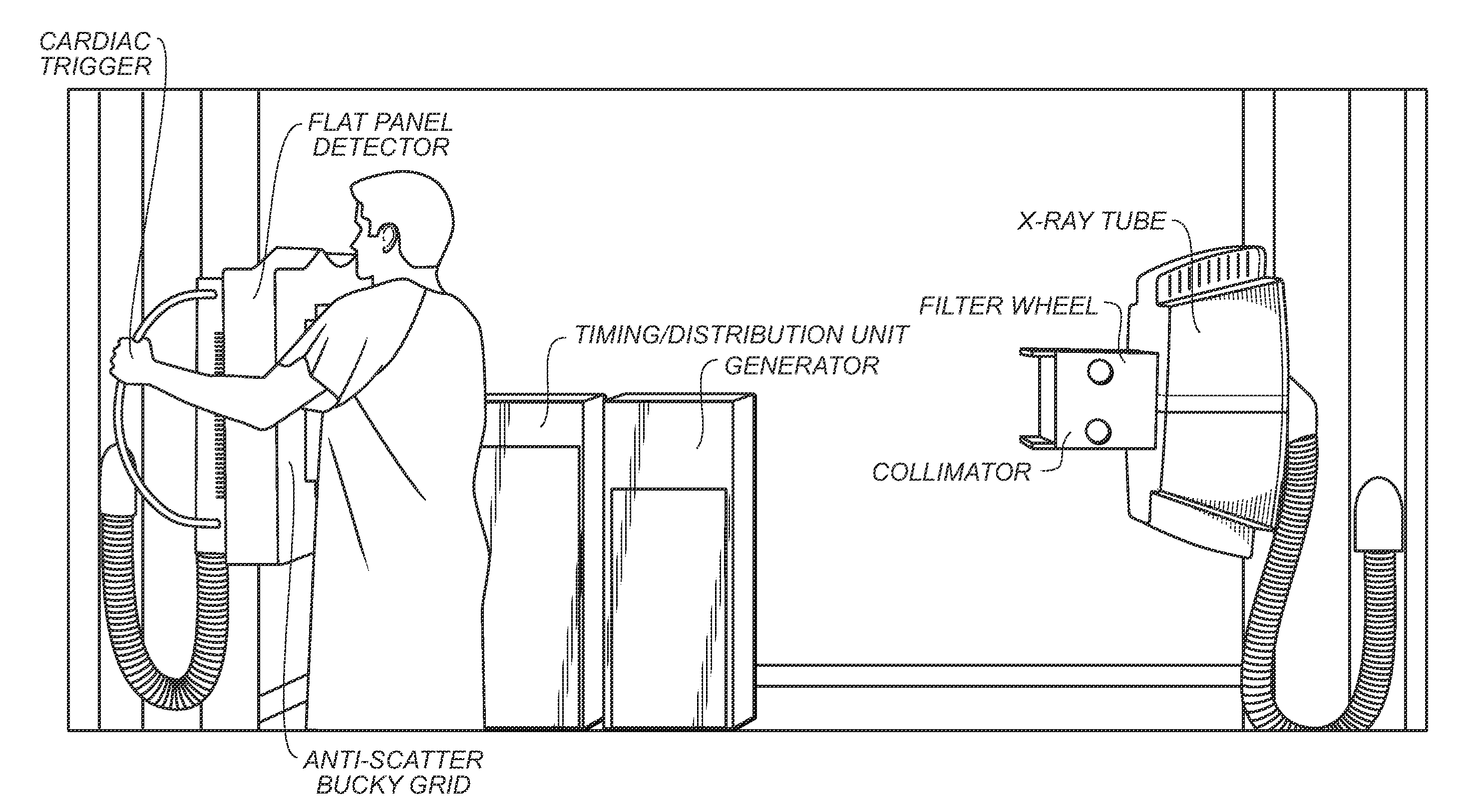
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Chest radiograph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
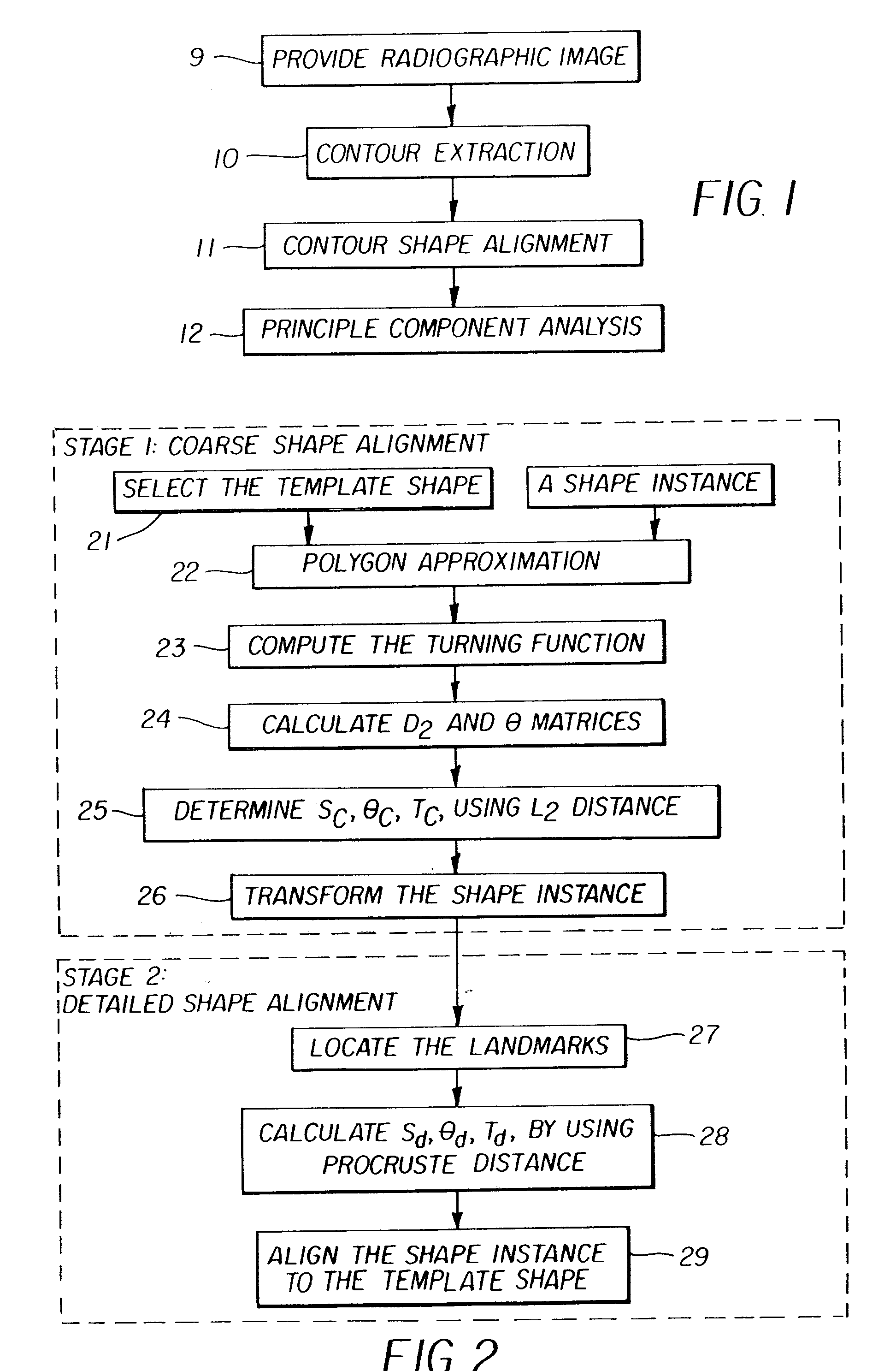
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
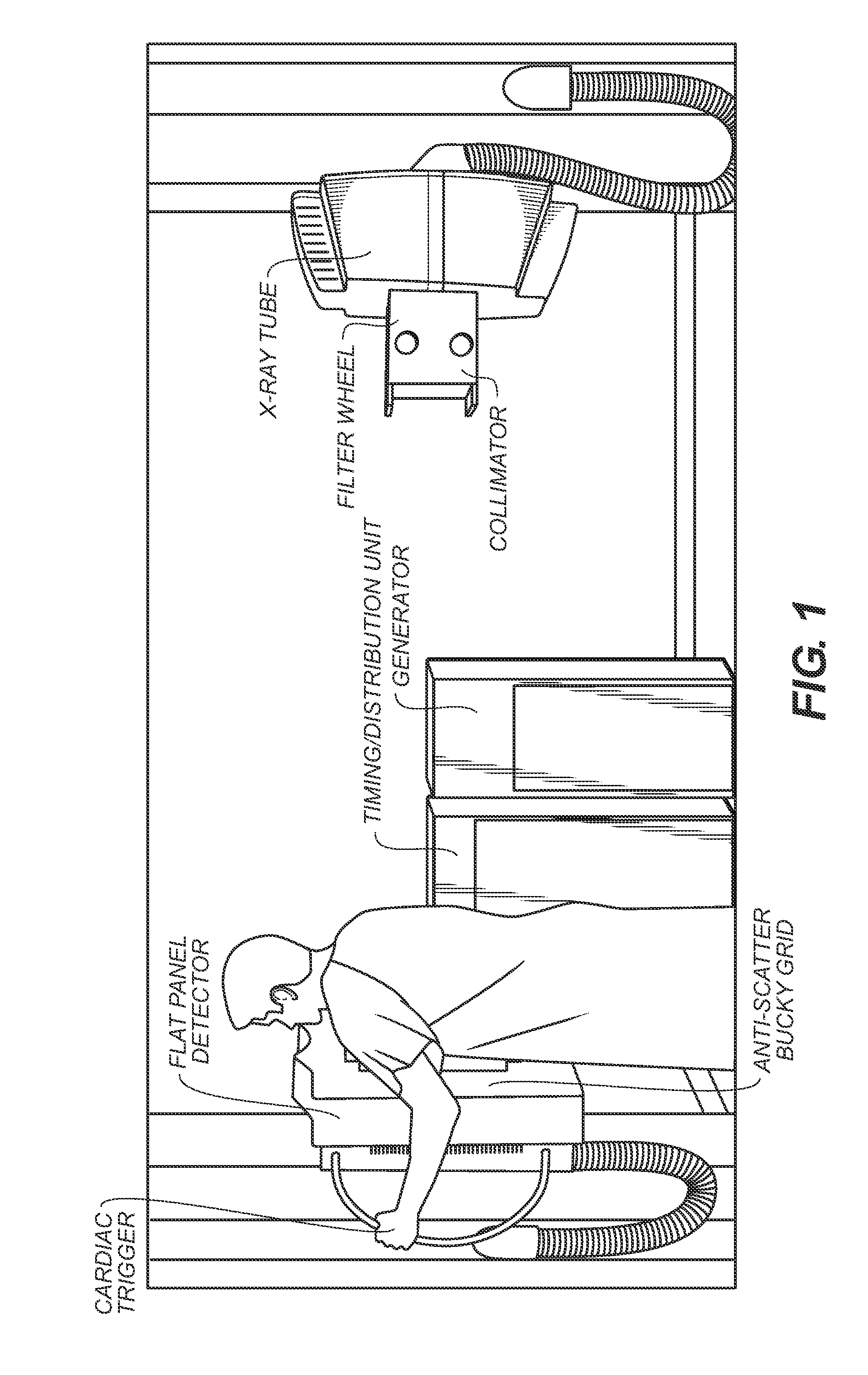
A chest radiograph, colloquially called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
Image modification and detection using massive training artificial neural networks (MTANN)
ActiveUS20050100208A1Suppressing contrastModify their appearanceImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
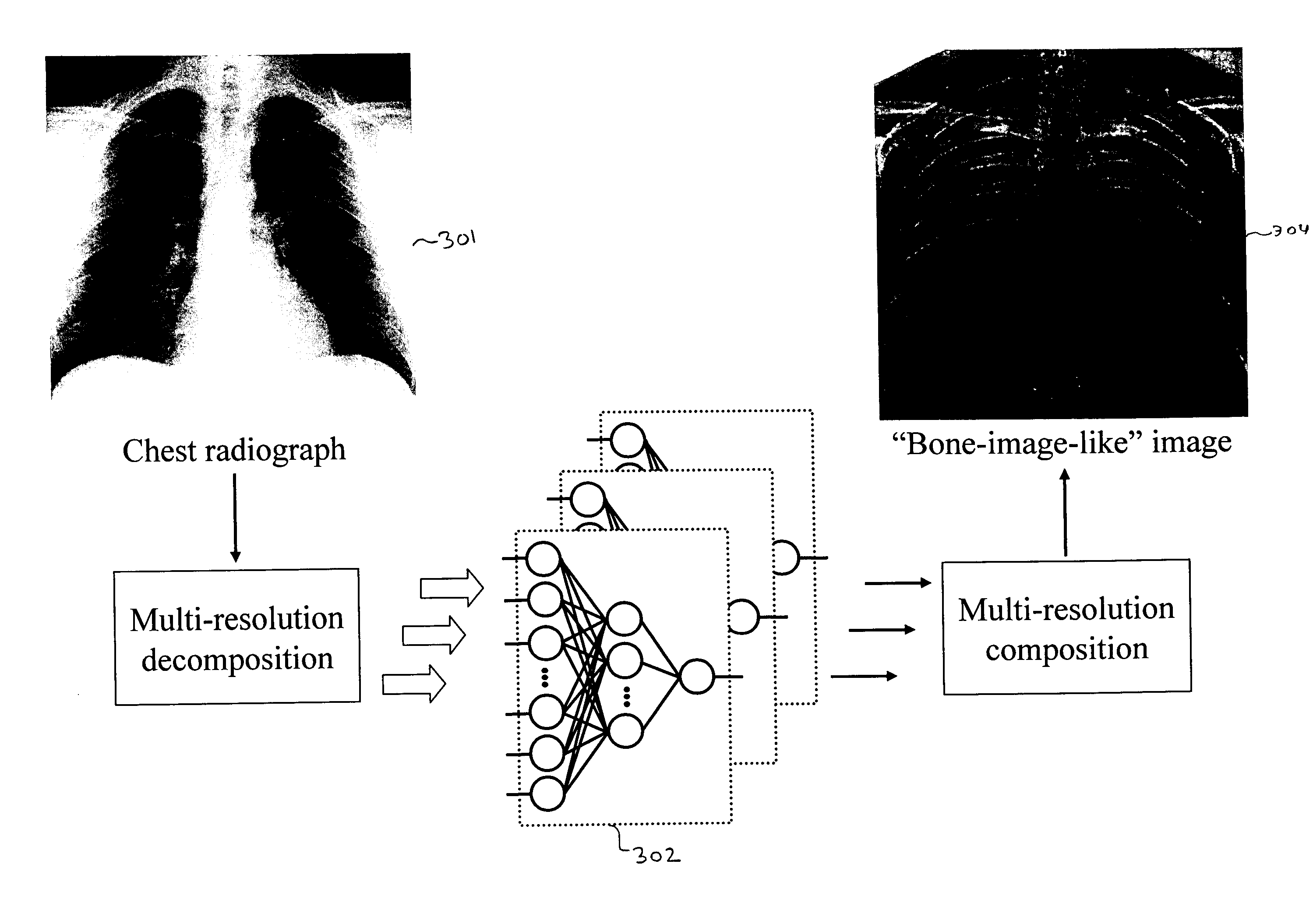
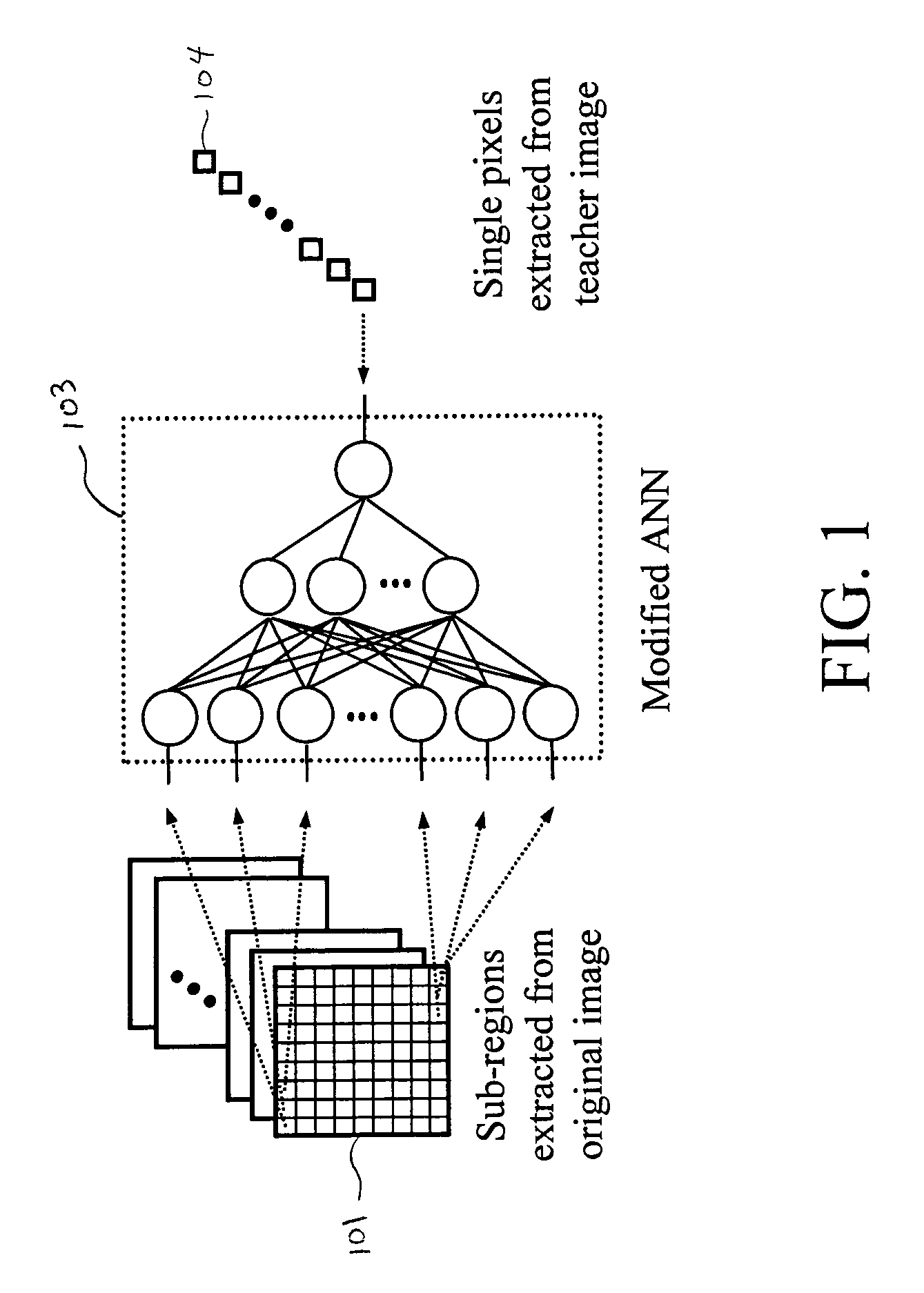
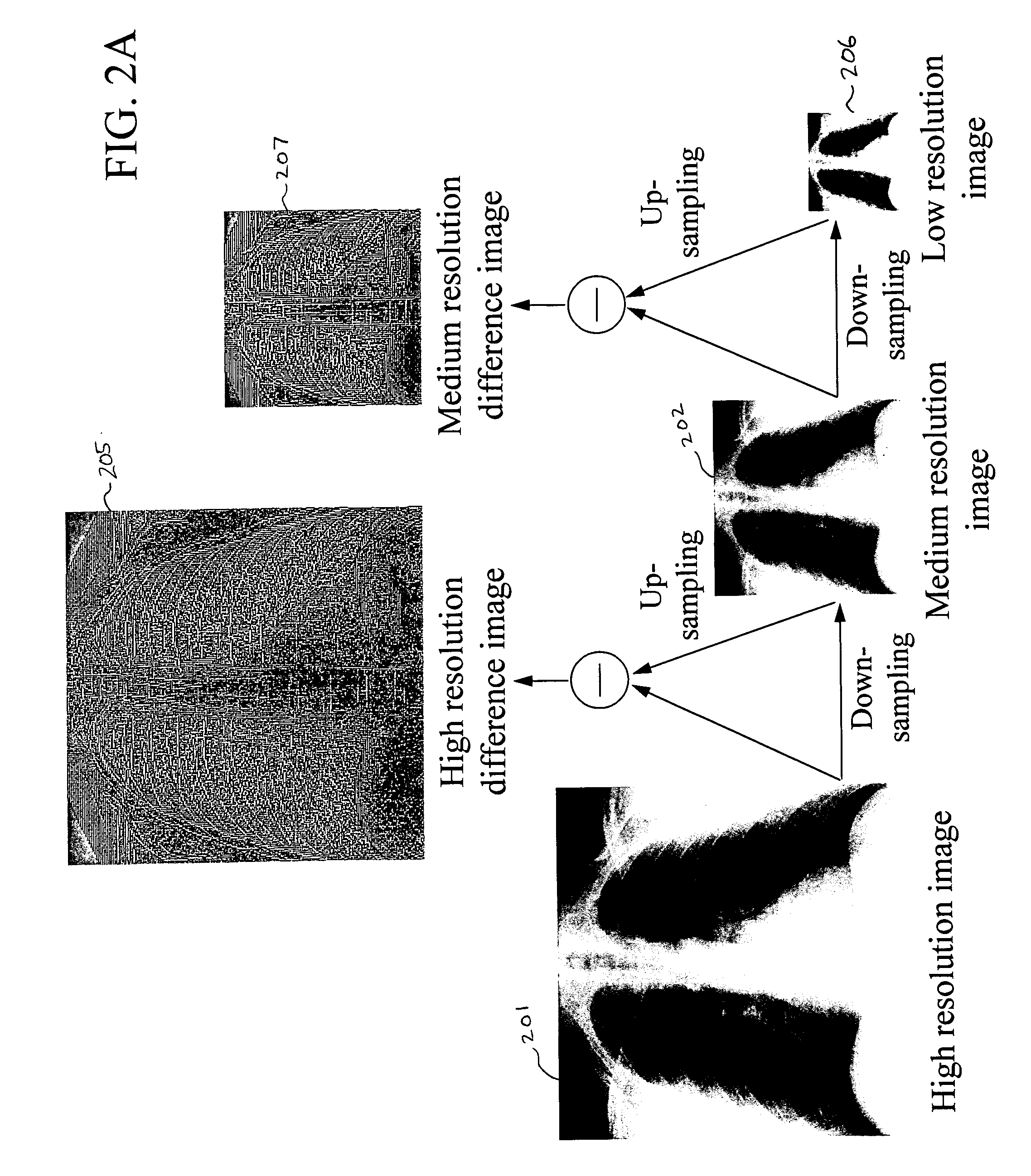
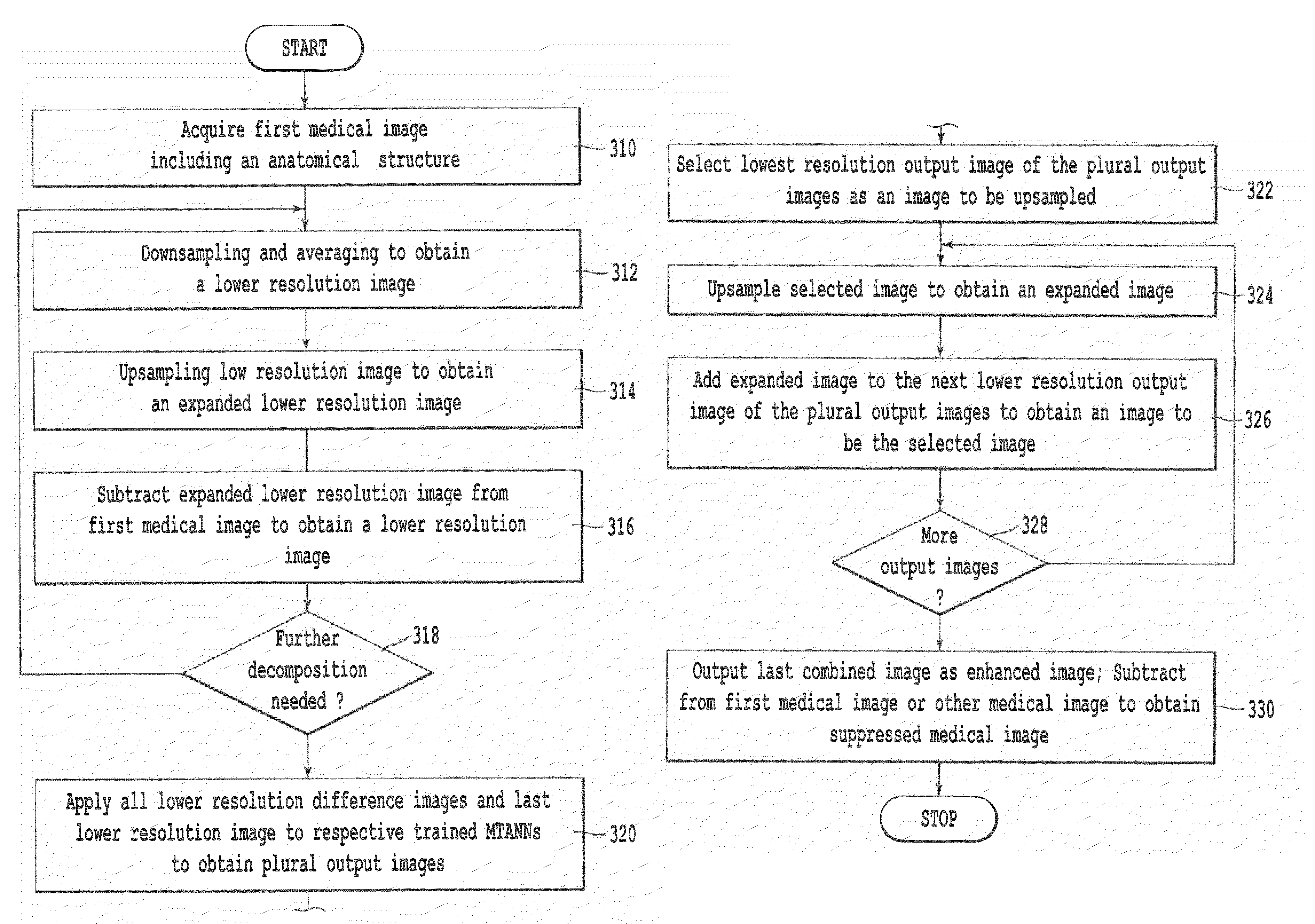
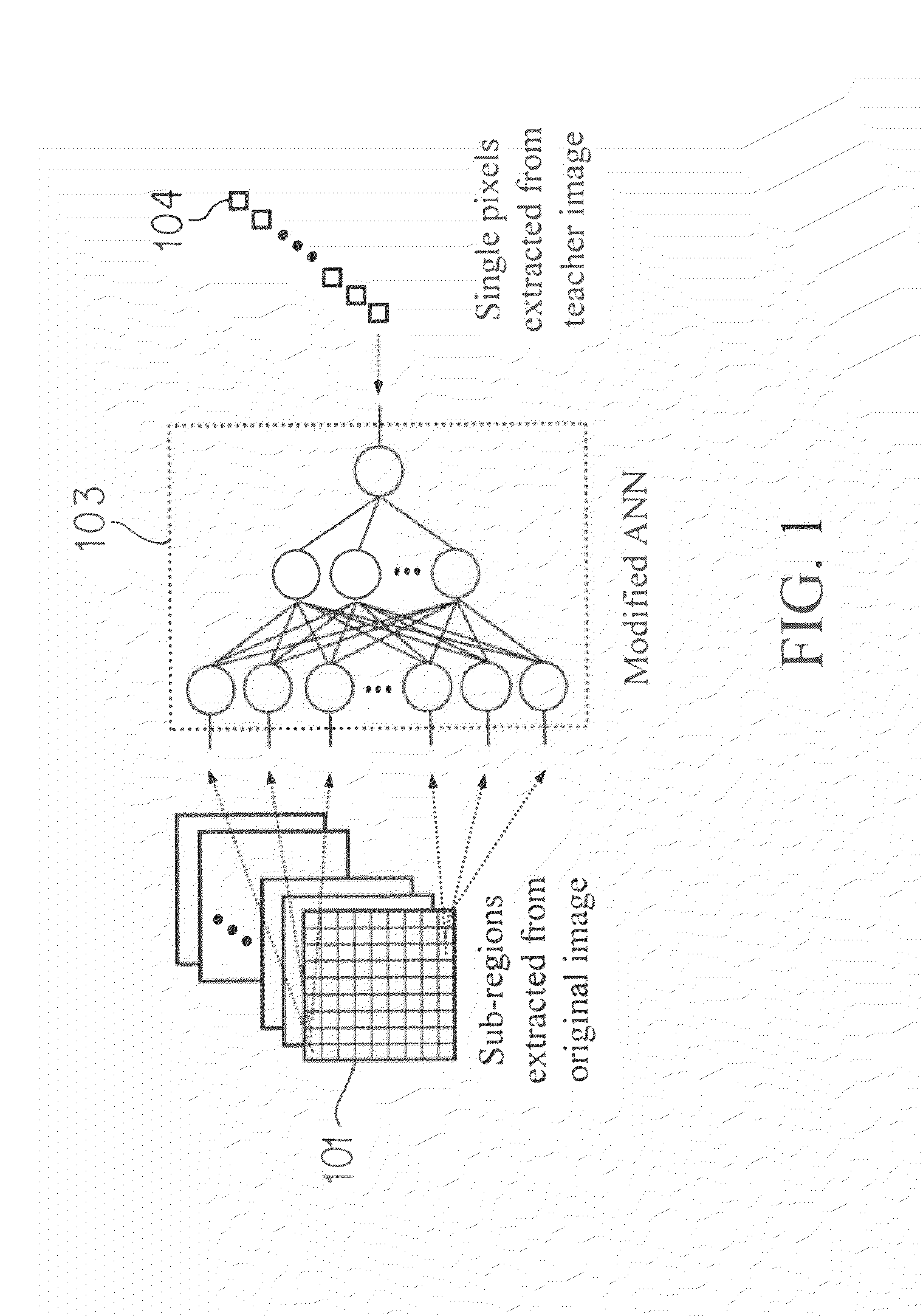
A method, system, and computer program product for modifying an appearance of an anatomical structure in a medical image, e.g., rib suppression in a chest radiograph. The method includes: acquiring, using a first imaging modality, a first medical image that includes the anatomical structure; applying the first medical image to a trained image processing device to obtain a second medical image, corresponding to the first medical image, in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is modified; and outputting the second medical image. Further, the image processing device is trained using plural teacher images obtained from a second imaging modality that is different from the first imaging modality. In one embodiment, the method also includes processing the first medical image to obtain plural processed images, wherein each of the plural processed images has a corresponding image resolution; applying the plural processed images to respective multi-training artificial neural networks (MTANNs) to obtain plural output images, wherein each MTANN is trained to detect the anatomical structure at one of the corresponding image resolutions; and combining the plural output images to obtain a second medical image in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is enhanced.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Image modification and detection using massive training artificial neural networks (MTANN)
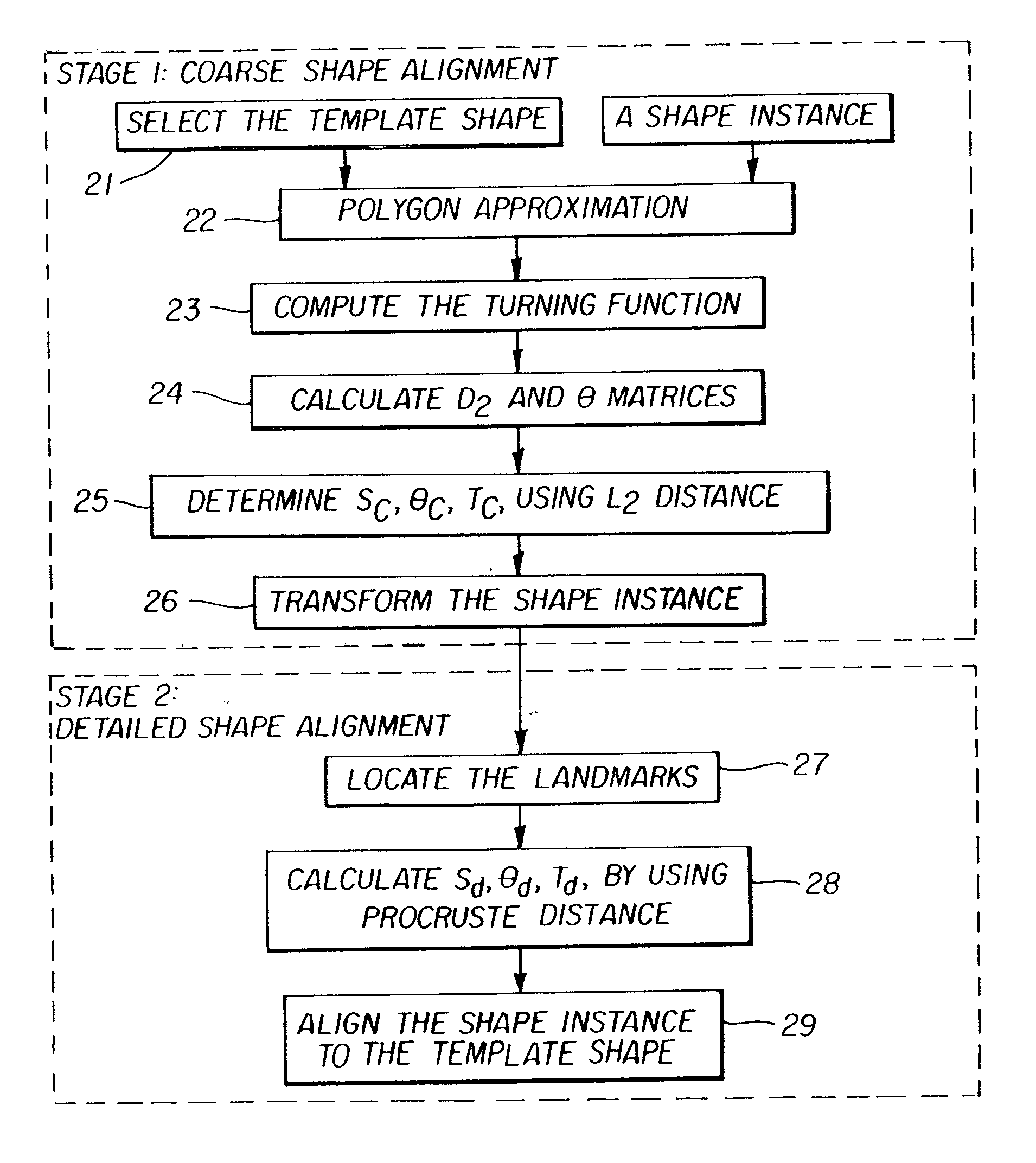
A method, system, and computer program product for modifying an appearance of an anatomical structure in a medical image, e.g., rib suppression in a chest radiograph. The method includes: acquiring, using a first imaging modality, a first medical image that includes the anatomical structure; applying the first medical image to a trained image processing device to obtain a second medical image, corresponding to the first medical image, in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is modified; and outputting the second medical image. Further, the image processing device is trained using plural teacher images obtained from a second imaging modality that is different from the first imaging modality. In one embodiment, the method also includes processing the first medical image to obtain plural processed images, wherein each of the plural processed images has a corresponding image resolution; applying the plural processed images to respective multi-training artificial neural networks (MTANNs) to obtain plural output images, wherein each MTANN is trained to detect the anatomical structure at one of the corresponding image resolutions; and combining the plural output images to obtain a second medical image in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is enhanced.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
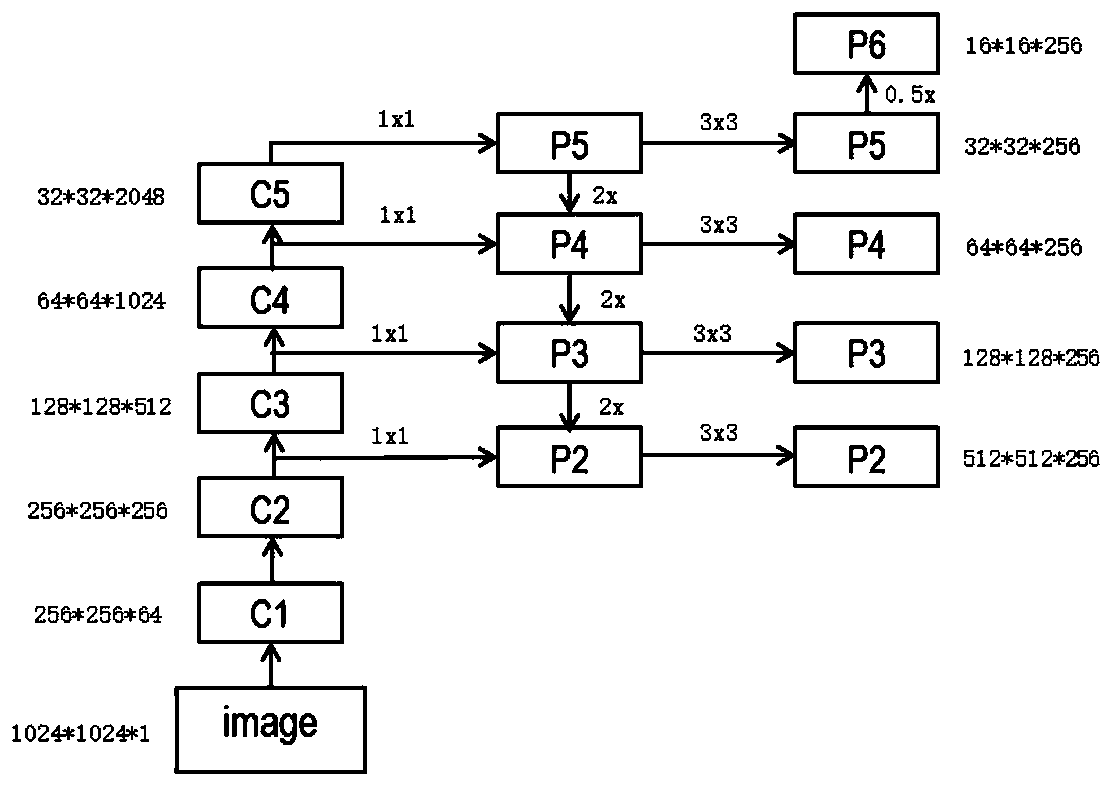
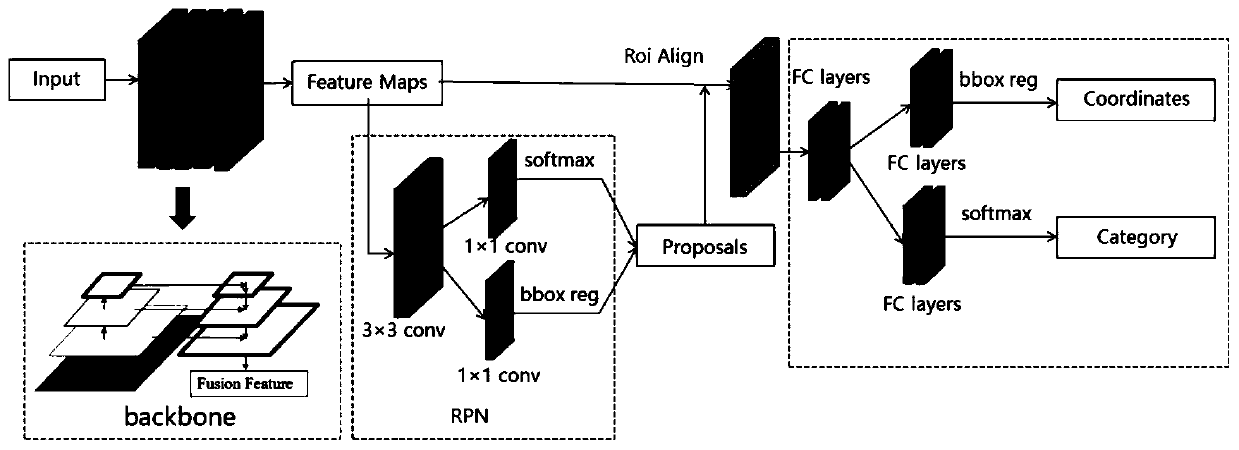
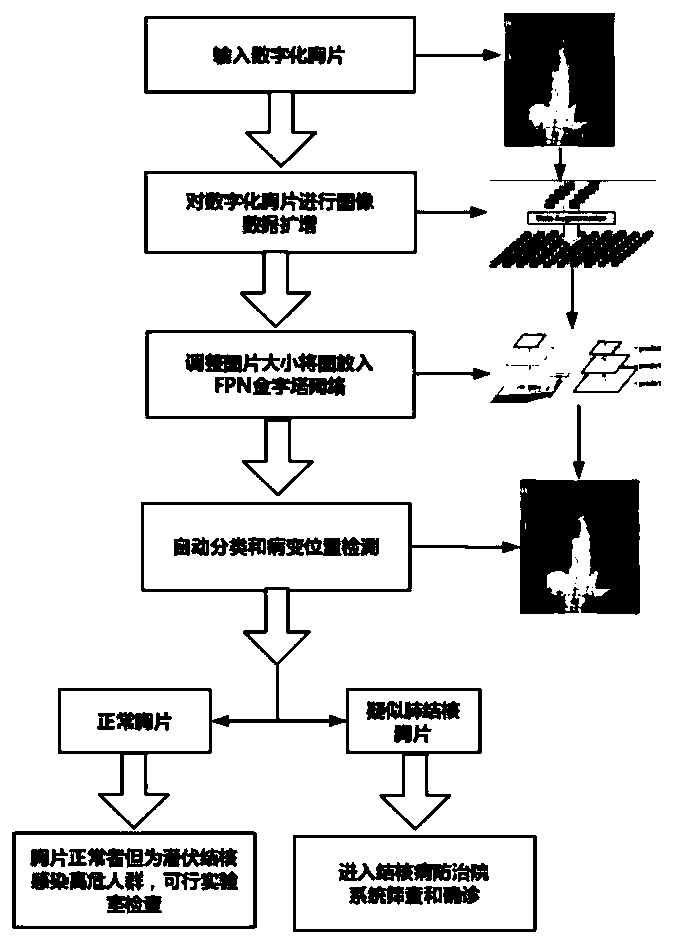
Faster R-CNN pulmonary tuberculosis symptom detection system and method based on FPN
InactiveCN110175993AImprove accuracyReduce the risk of delaying treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineX-ray
The invention discloses an automatic pulmonary tuberculosis detection system on an X-ray chest radiograph based on a characteristic pyramid network (FPN). An X-ray chest radiograph of pulmonary tuberculosis is marked; a Faster R-CNN network learning module with an FPN as the rear end is adopted for training and learning, pulmonary tuberculosis lesion symptoms are mastered, and the automatic diagnosis and detection capacity of the pulmonary tuberculosis lesion symptoms is obtained, so that the automatic detection, positioning and probability prediction of the pulmonary tuberculosis lesion are achieved, and a final pulmonary tuberculosis detection result is obtained. The FPN serves as the rear end of the detection network, the semantic features in a multi-scale network layer can be better combined, each layer is independently predicted, and fusion is finally carried out, so that focuses of different scales can be better detected. Based on a recognition technology of the deep learning network to the digital image, the automatic detection, positioning and probability prediction of the tuberculosis focus are realized, the accuracy of the focus detection is improved, and the risk of thedelayed treatment of a tuberculosis patient is reduced.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
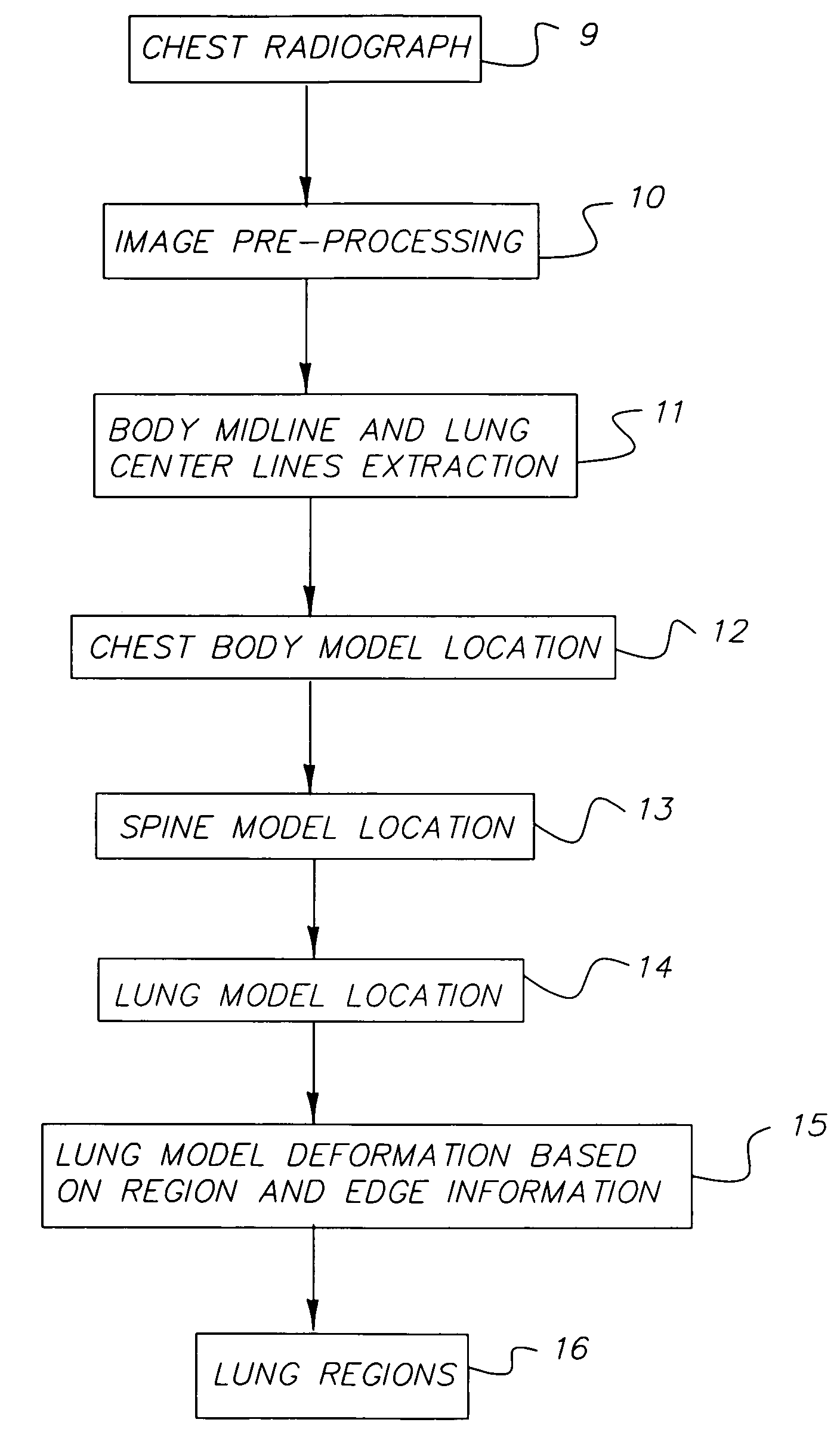
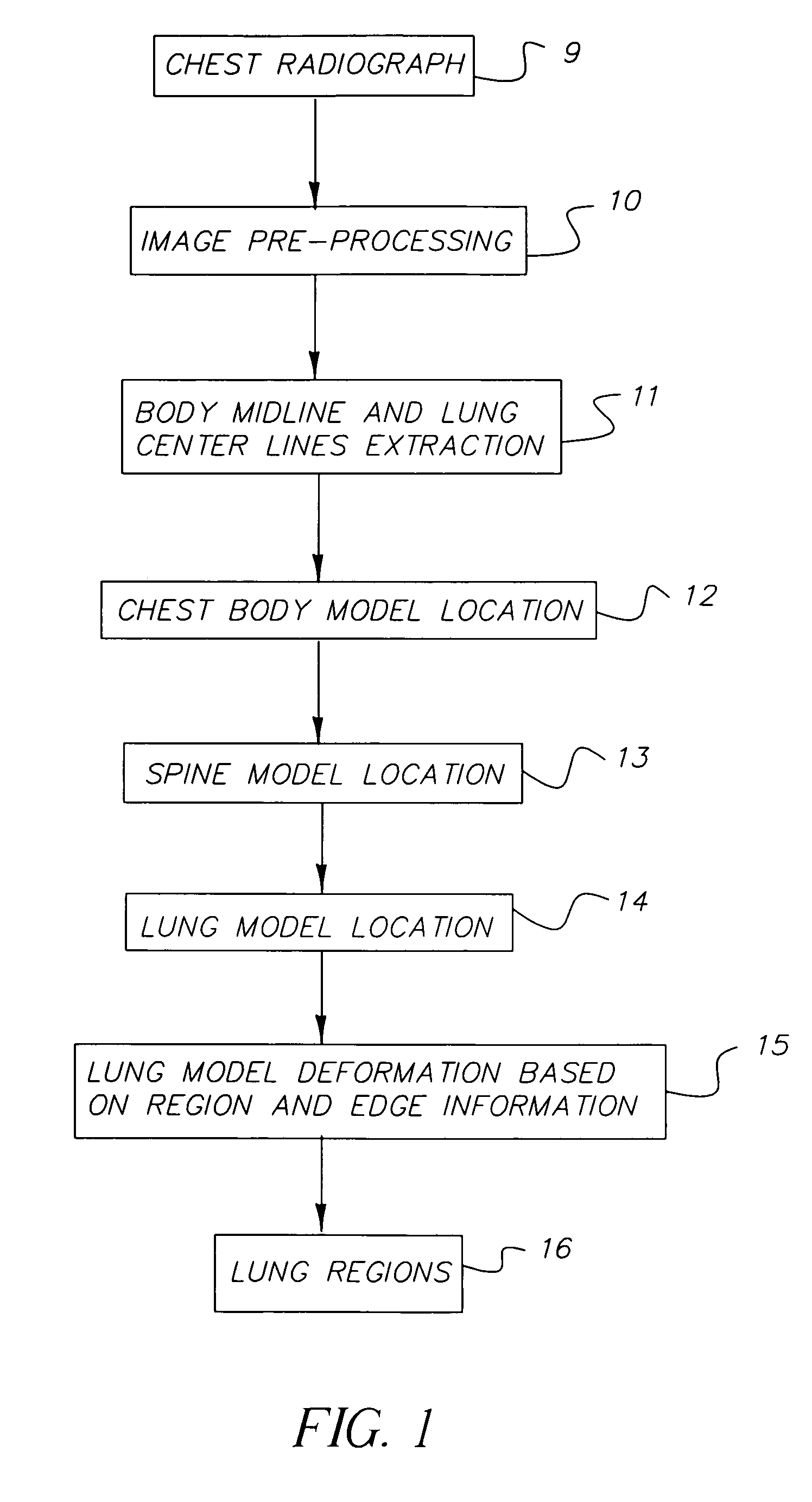
Method for automated analysis of digital chest radiographs
ActiveUS7221787B2Improve display qualityMakes robustImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMedicine
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
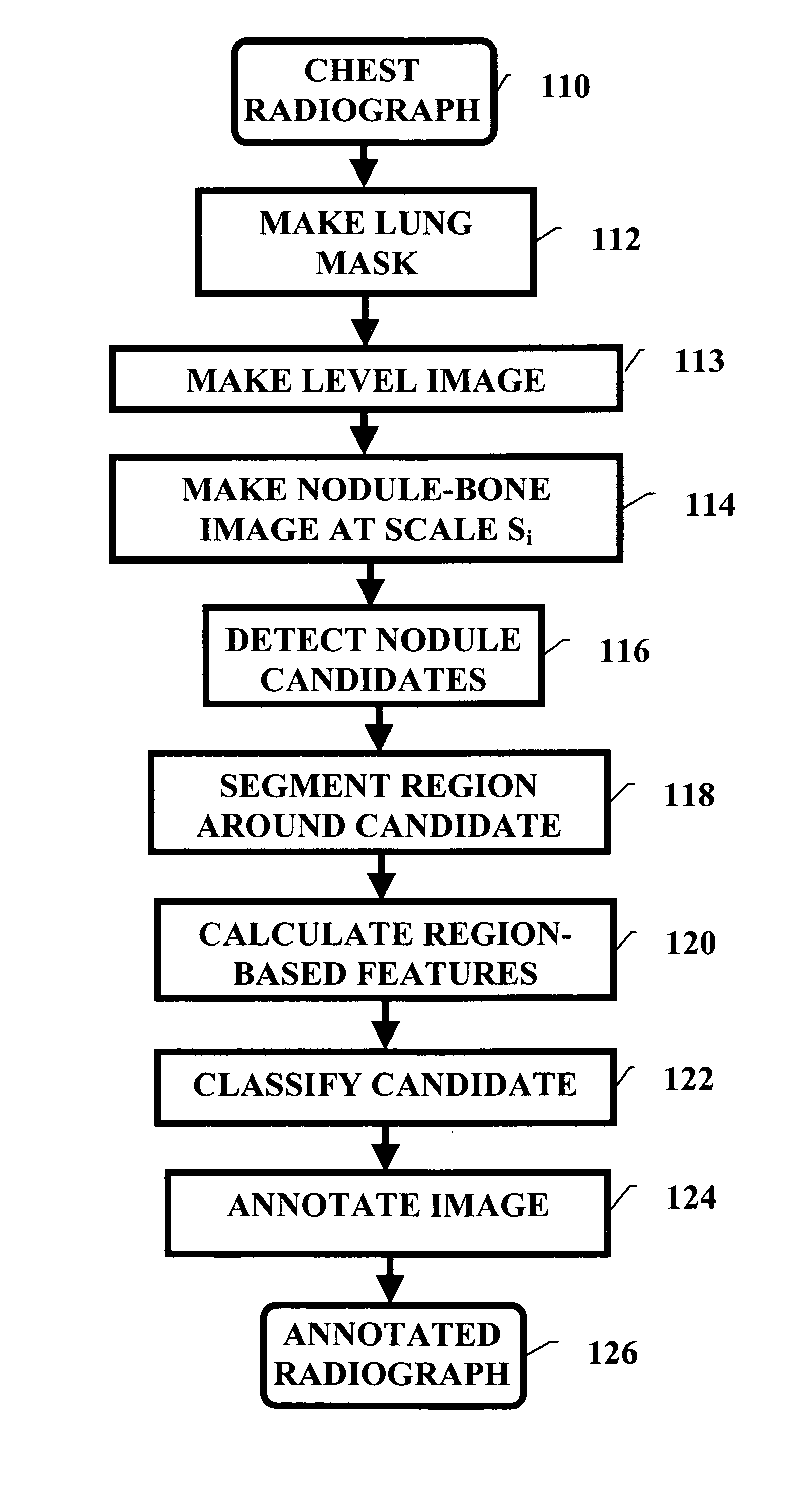
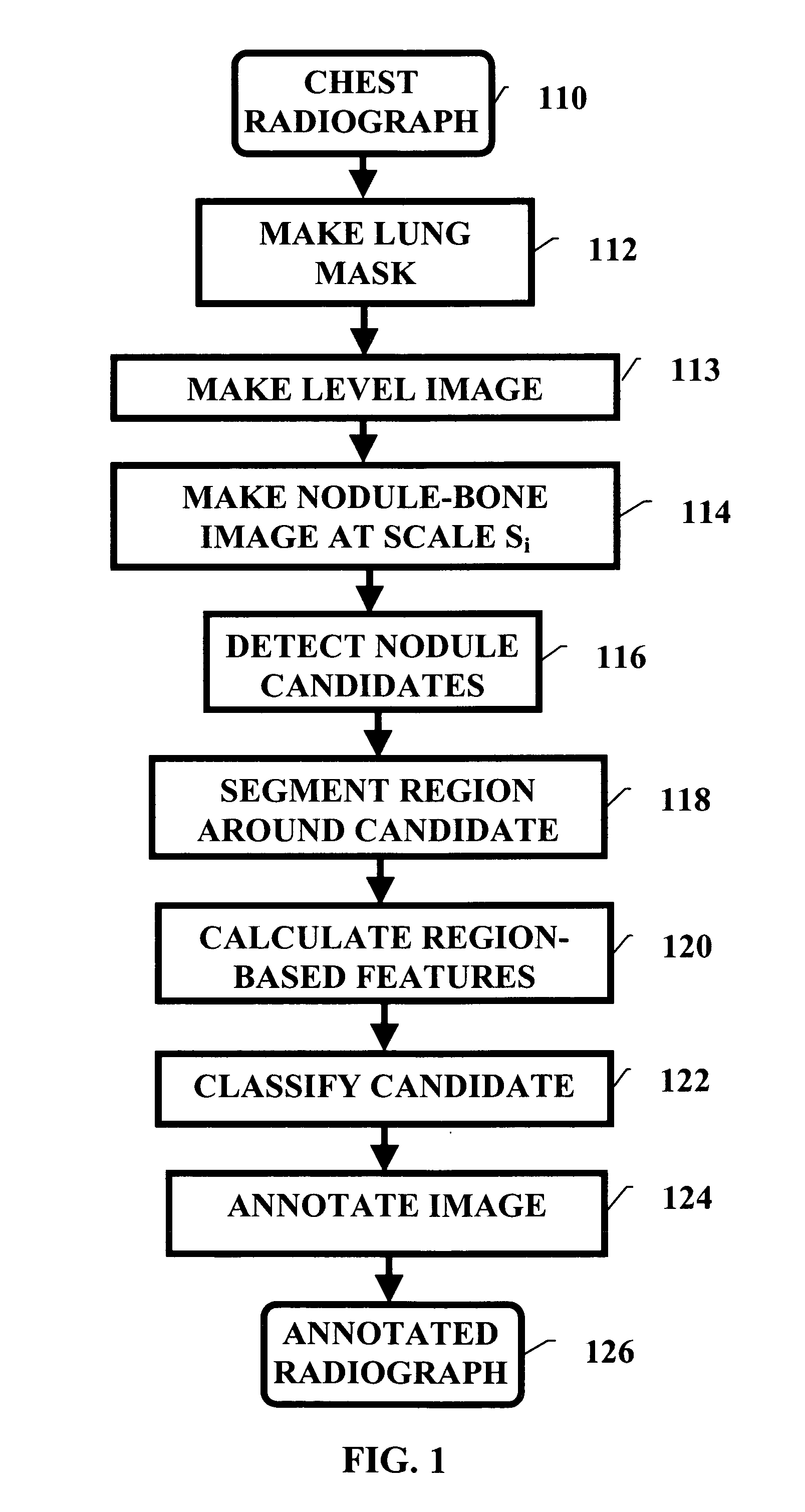
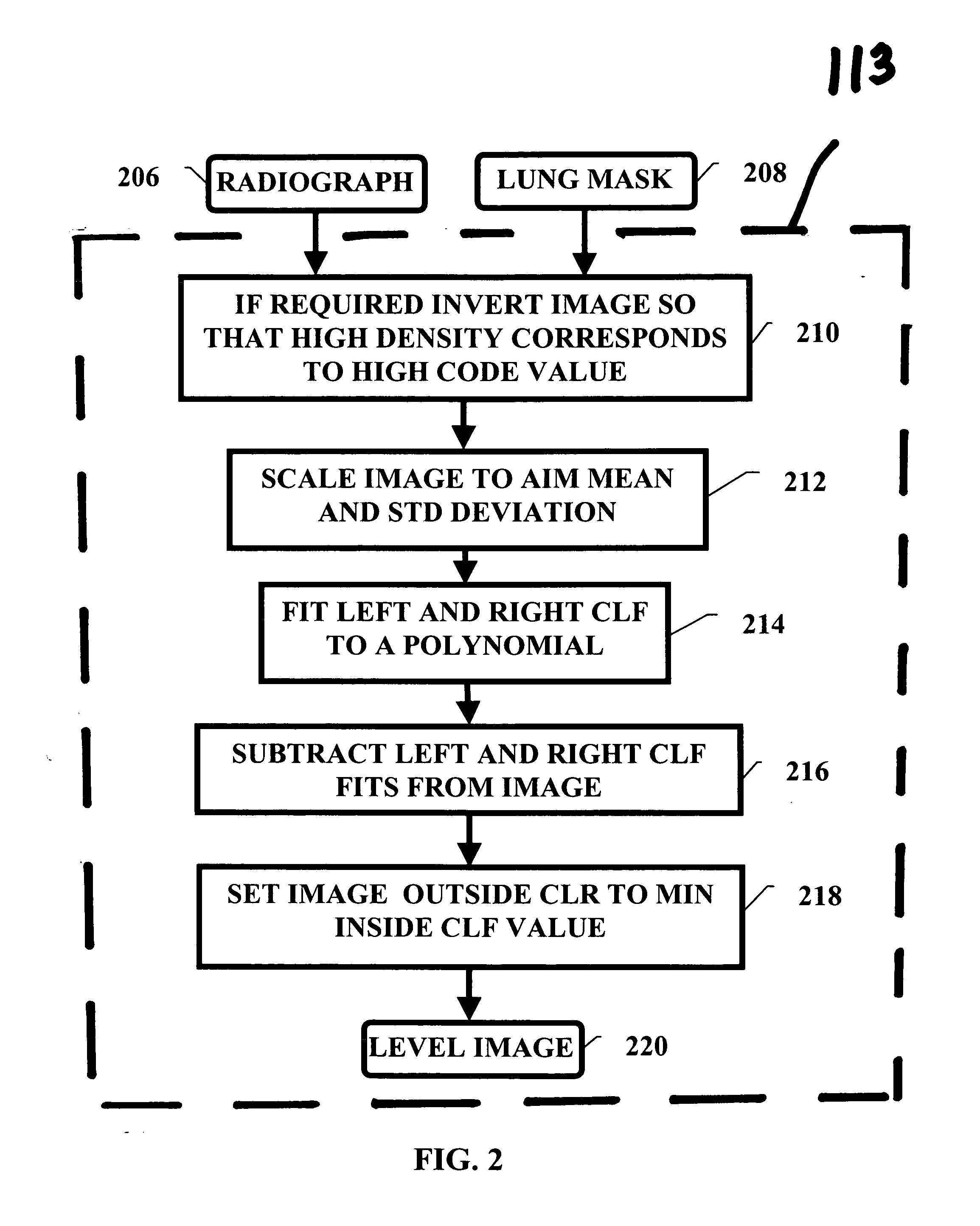
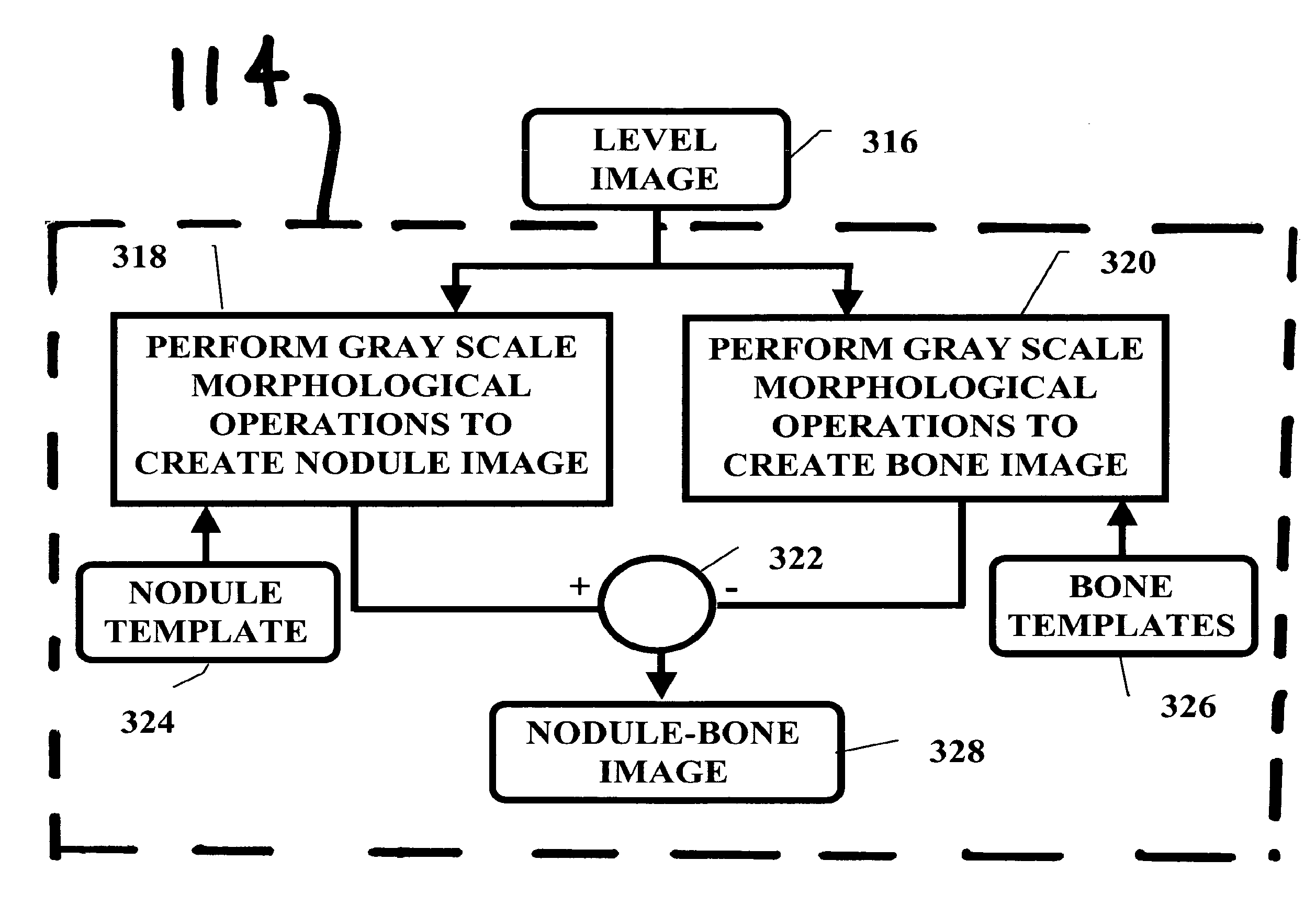
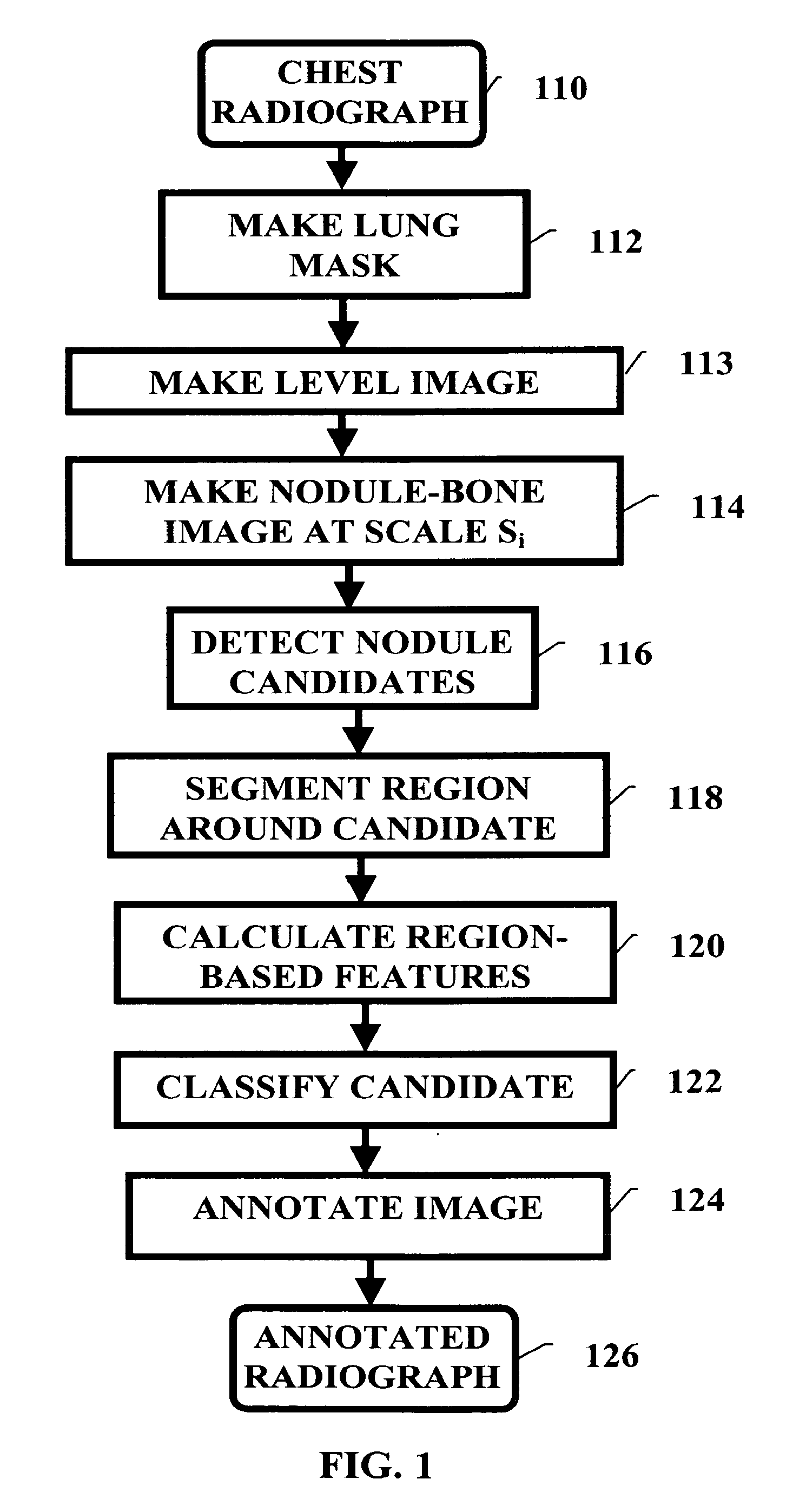
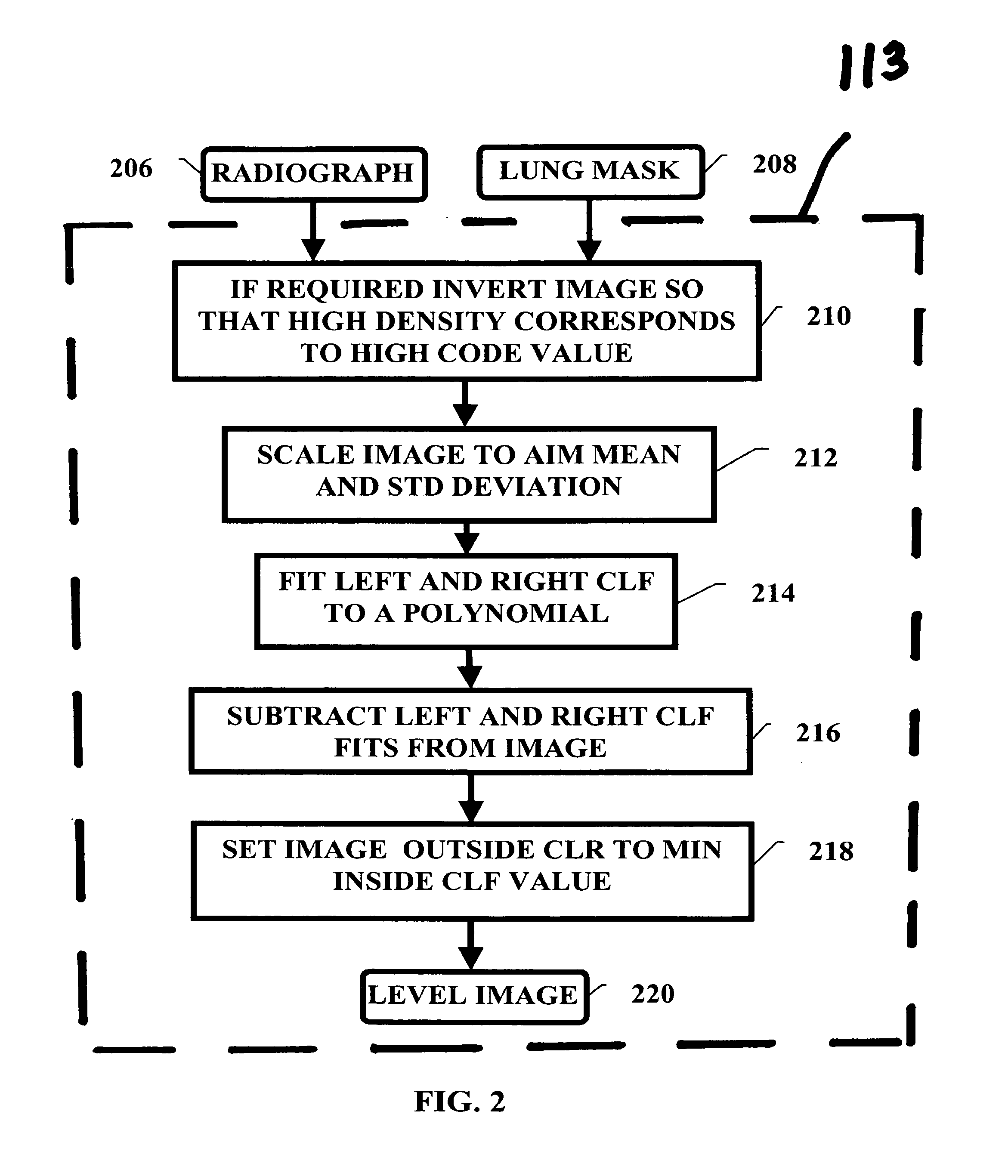
Pulminary nodule detection in a chest radiograph
InactiveUS20070019852A1Provide detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleImage detection
A method of generating a pulmonary nodule image from a chest radiograph. The method includes the steps of: producing a map of a clear lung field; removing low frequency variation from the clear lung field to generate a level image; and performing at least one grayscale morphological operation on the level image to generate a nodule-bone image. Pulmonary nodules can be detected using the nodule-bone image by the further steps of: pulmonary nodules from a chest radiograph. The method includes the steps of: identifying candidate nodule locations in the nodule-bone image; segmenting a region around each candidate nodule location in the nodule-bone image; and using the features of the segmented region to determine if a candidate is a nodule.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
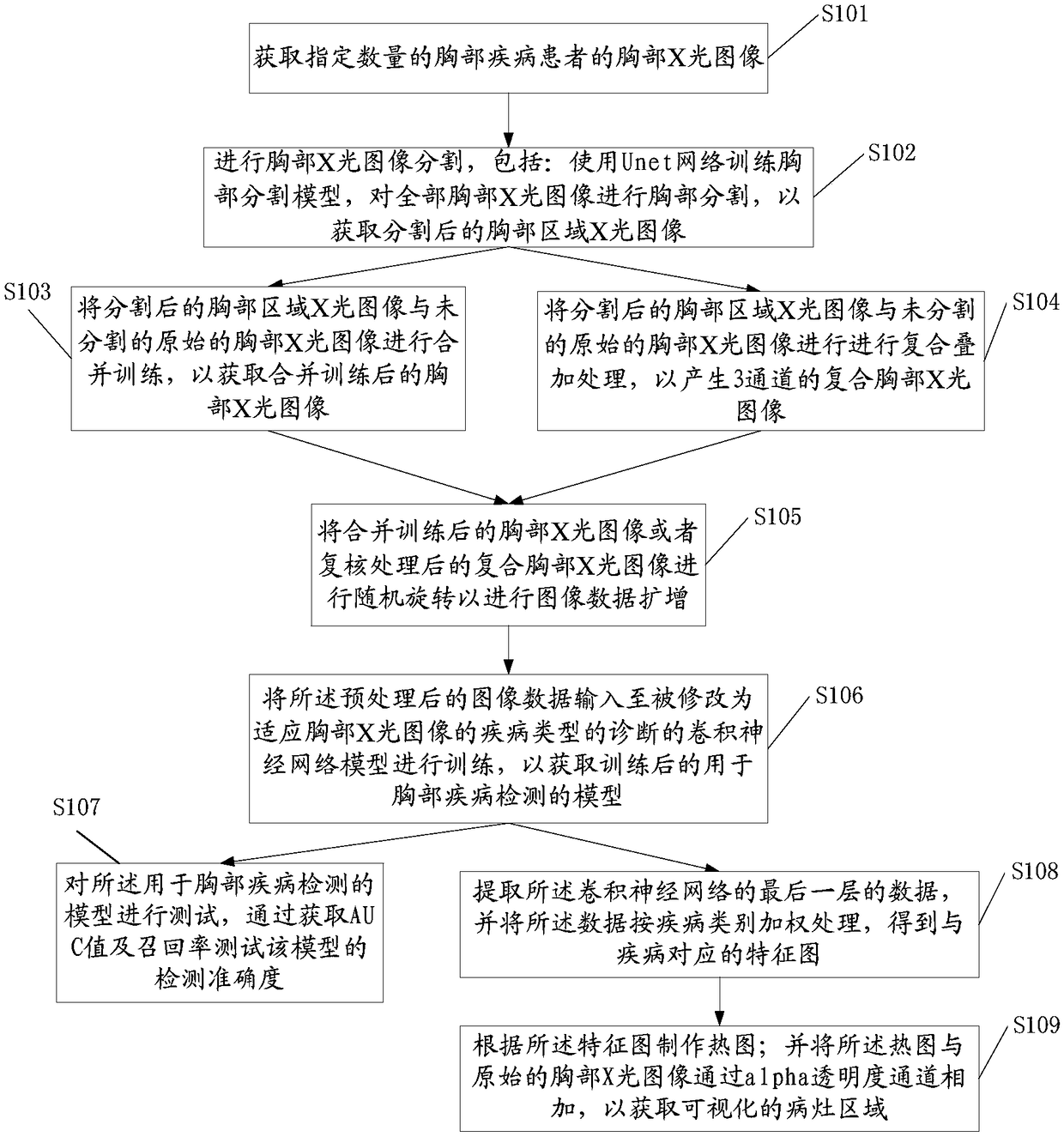
Construction method and application of thoracic disease detection model
ActiveCN108898595AProvide accuratelyShorten diagnostic timeImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseChest region
The invention provides a construction method and application of a thoracic disease detection model. The construction method comprises the following steps: A, acquiring chest X-ray images of a specified number of thoracic disease patients; B, performing image preprocessing on the X-ray images to obtain pre-processed image data; and C, inputting the pre-processed image data to a convolution neural network model for training to obtain the trained model for thoracic disease detection. The thoracic disease detection model can accurately predict a type and a location of a thoracic disease, the diagnosis time of the doctor is greatly shortened, and the rate of missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis is lowered.
Owner:HUIYING MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
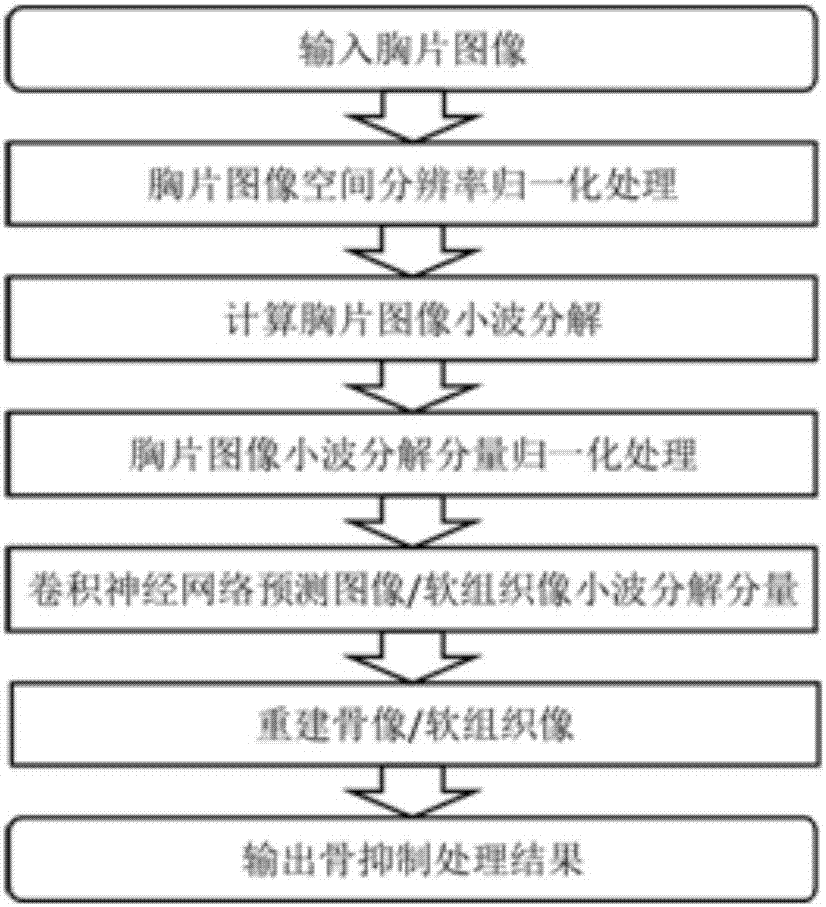
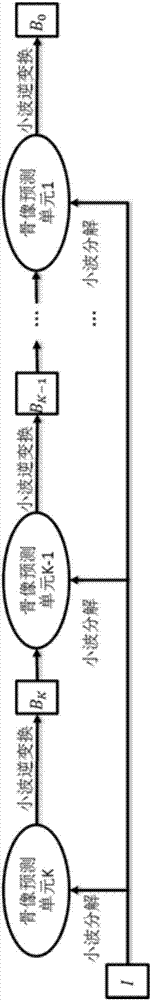
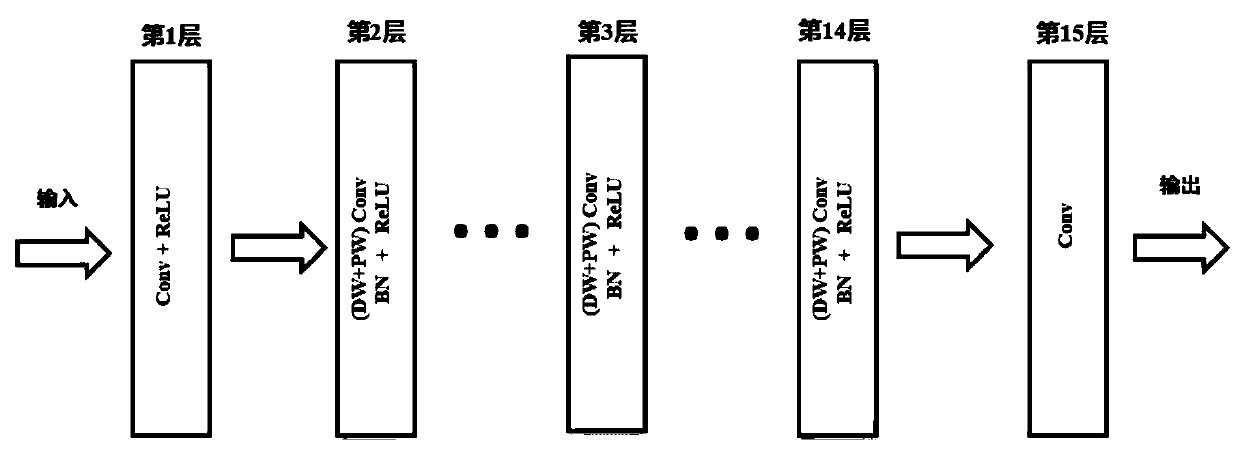
X-ray chest radiograph bone suppression processing method based on wavelet decomposition and convolutional neural network
InactiveCN107038692AAchieve inhibitionReduce radiation doseImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayNeural network nn
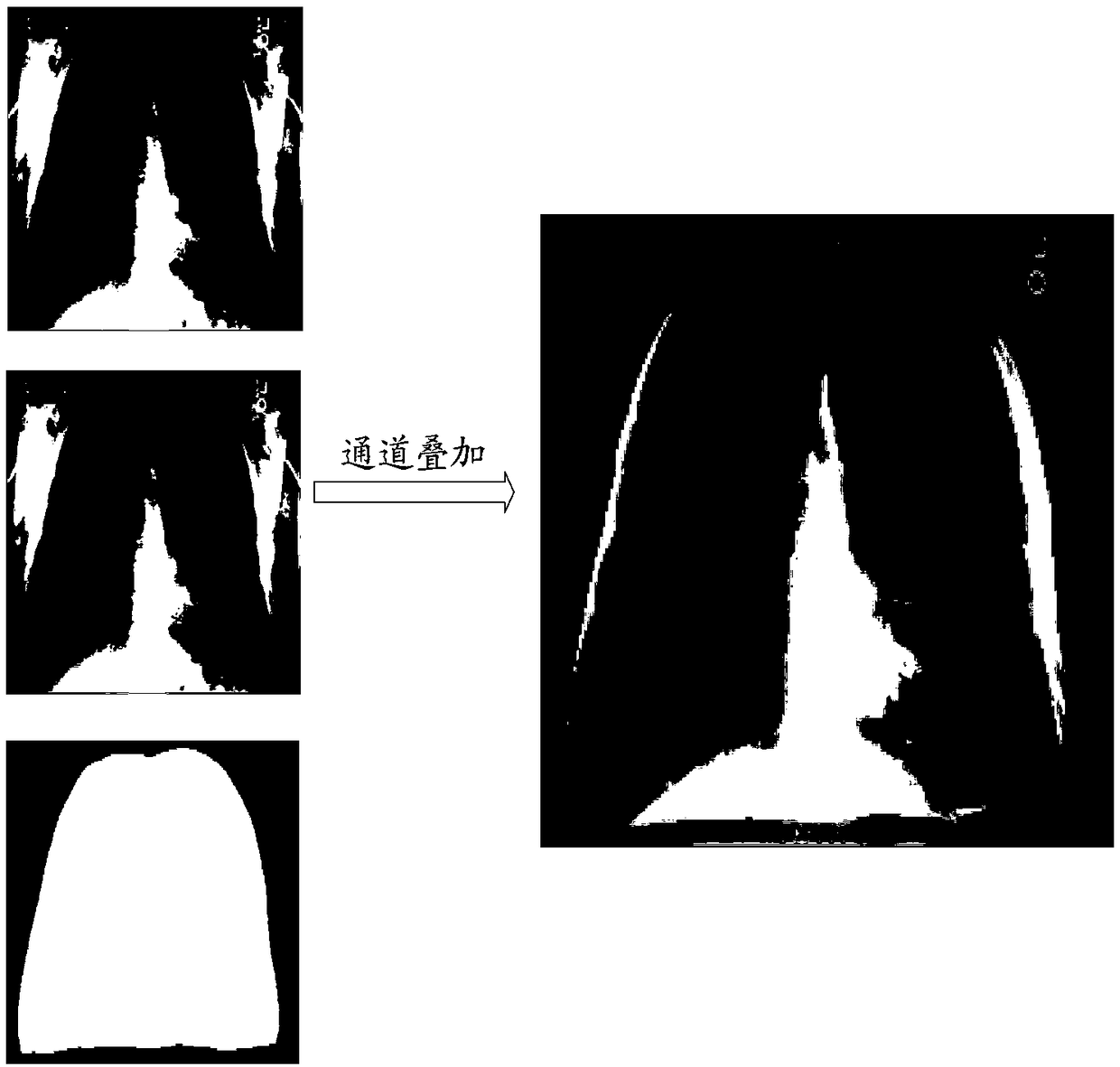
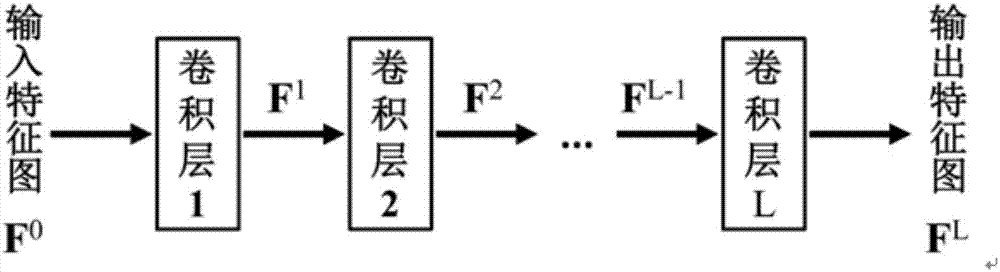
The invention discloses an X-ray chest radiograph bone suppression processing method based on wavelet decomposition and a convolutional neural network. By adopting a convolutional neural network structure and using a chest radiograph image wavelet coefficient as the input, a wavelet coefficient image of a corresponding bone image or soft tissue image is predicted. The existing bone image or soft tissue image artificial neural network prediction method processes an original chest radiograph image by adopting a relatively complex contrast normalization method, whereas this method processes the input chest radiograph image in a wavelet domain, and can normalize the amplitude by adopting a simple method; and the existing bone image or soft tissue image artificial neural network prediction method needs to design an image feature extraction method as the input of the artificial neural network, whereas this method completes an image feature extraction process by directly using the wavelet decomposition image of the chest radiograph image as an input, training the convolutional neural network to learn automatically and optimizing the convolution kernel, so the image feature extraction method does not need to be designed.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for automated analysis of digital chest radiographs
InactiveUS20070086640A1Improve display qualityMakes robustImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingLung region
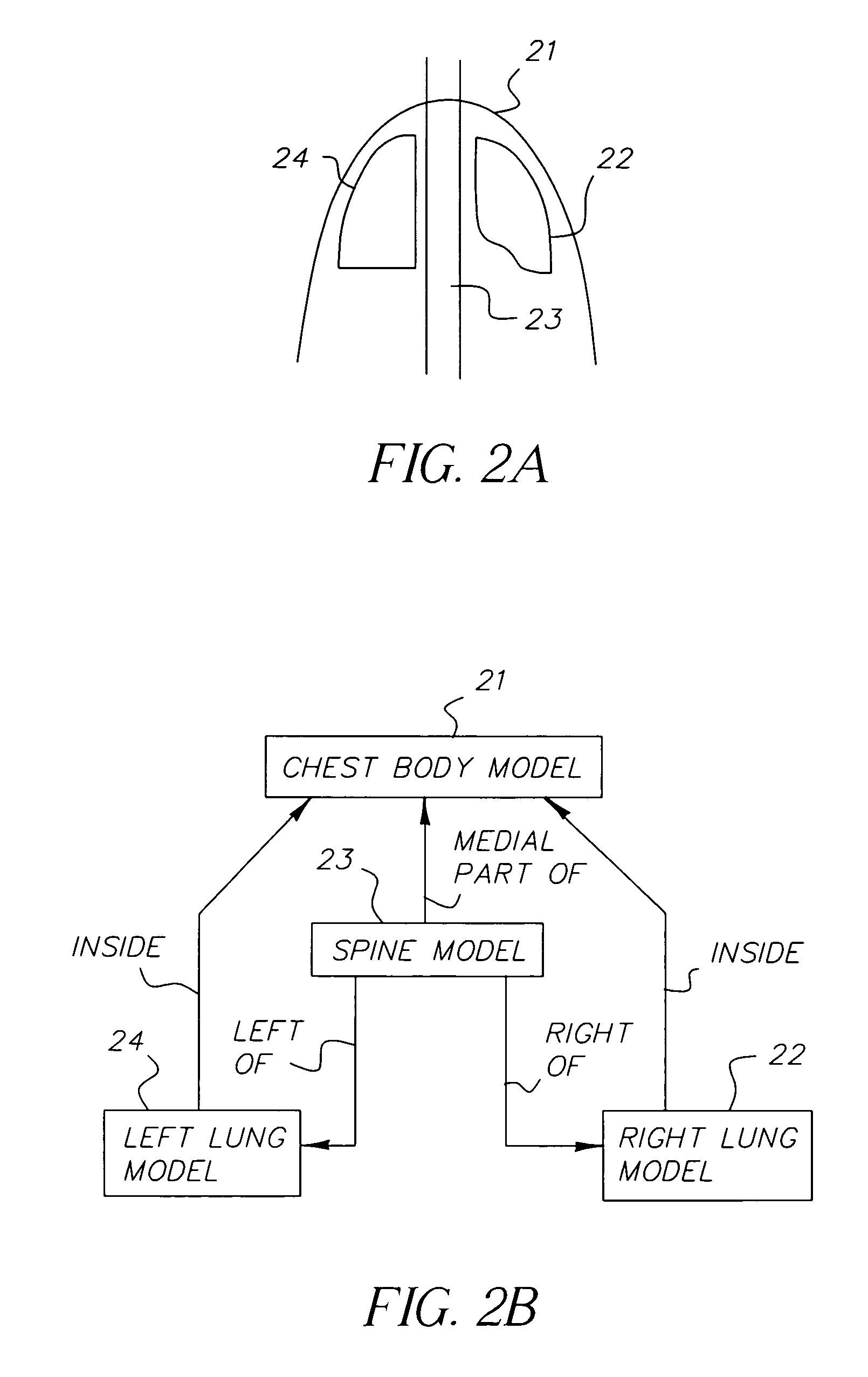
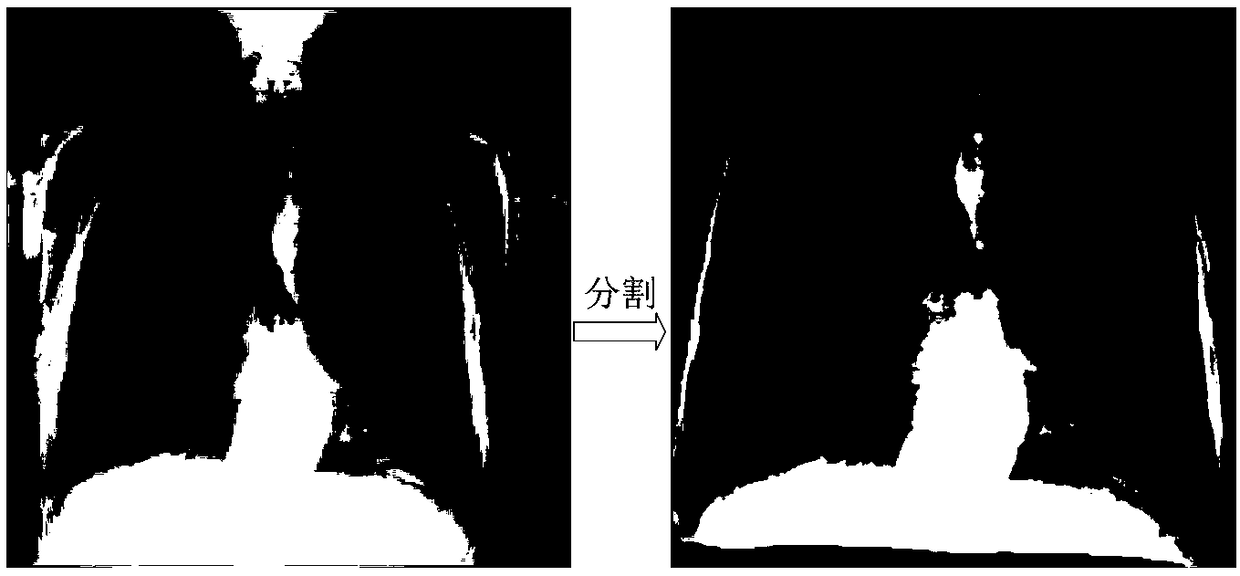
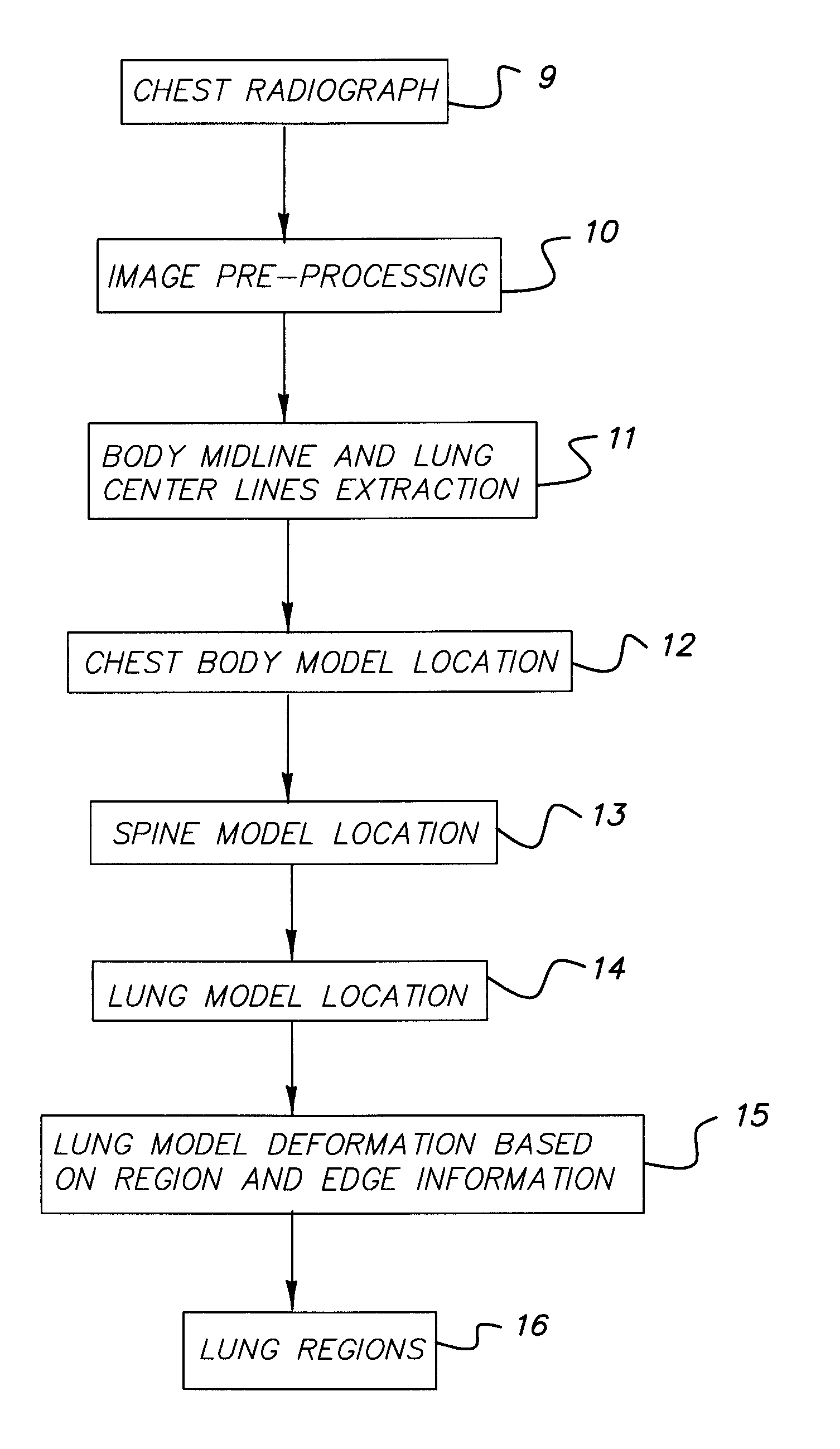
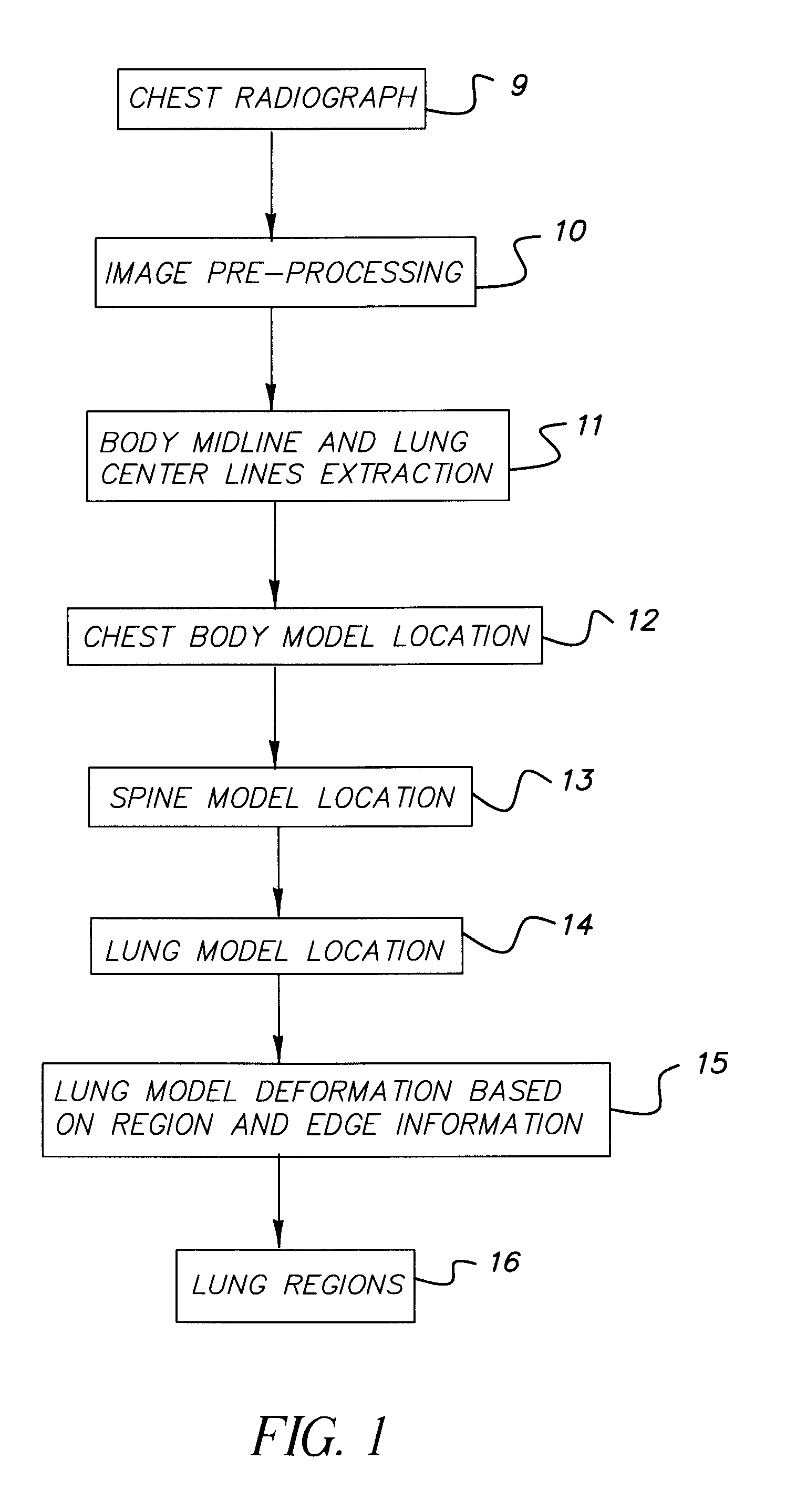
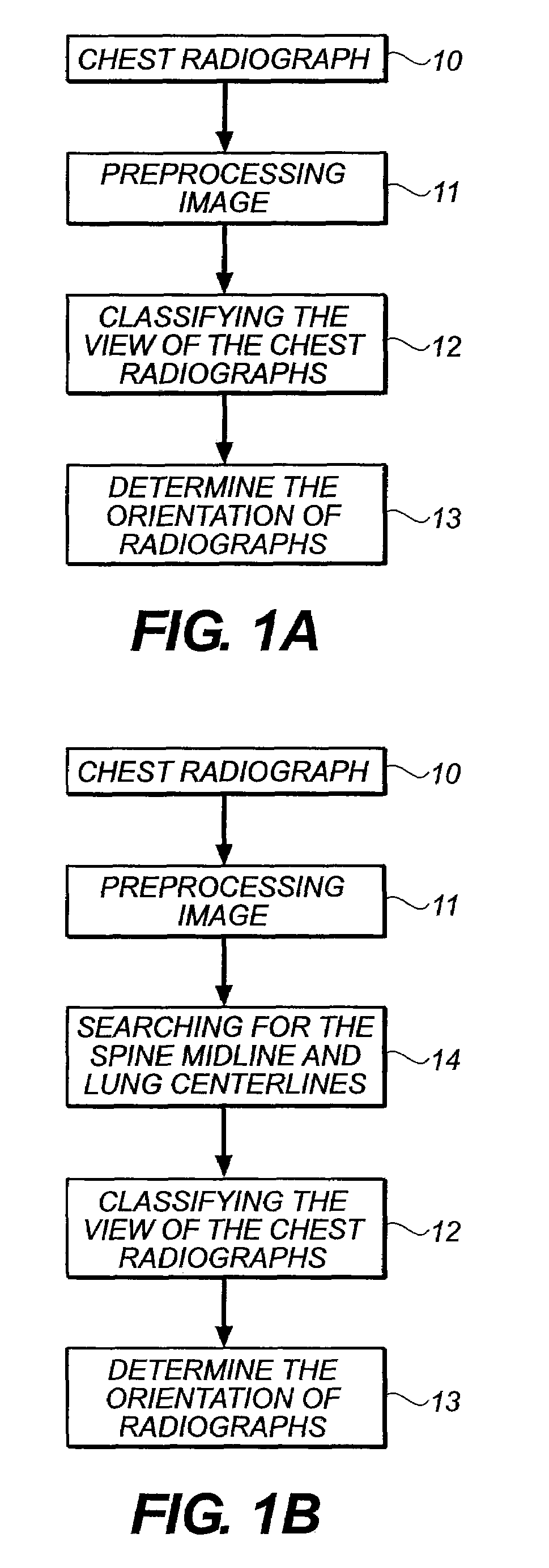
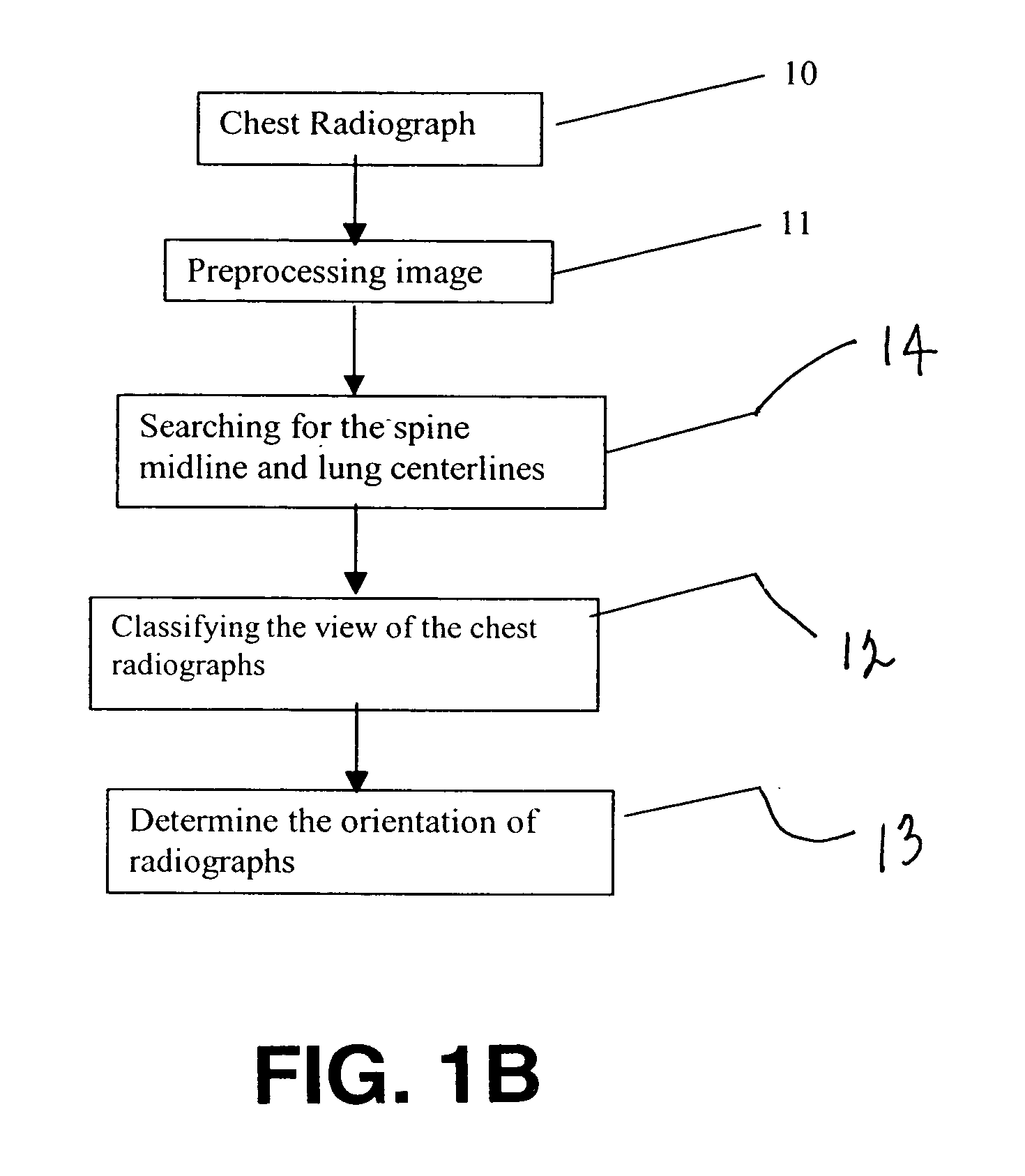
A method for automatically segmenting lung regions in a chest radiographic image comprising; providing an input digital chest radiograph image; preprocessing the input digital radiographic image; extracting the chest body midline and lung centerlines from the preprocessed image. Locating one-by-one, the chest body model, the spine model and the two lung models in the image based on the extracted chest body midline and two lung centerlines; and detecting the lung contours by deforming the lung shape models to converge to the true lung boundaries as a function of the extracting and locating image processing.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
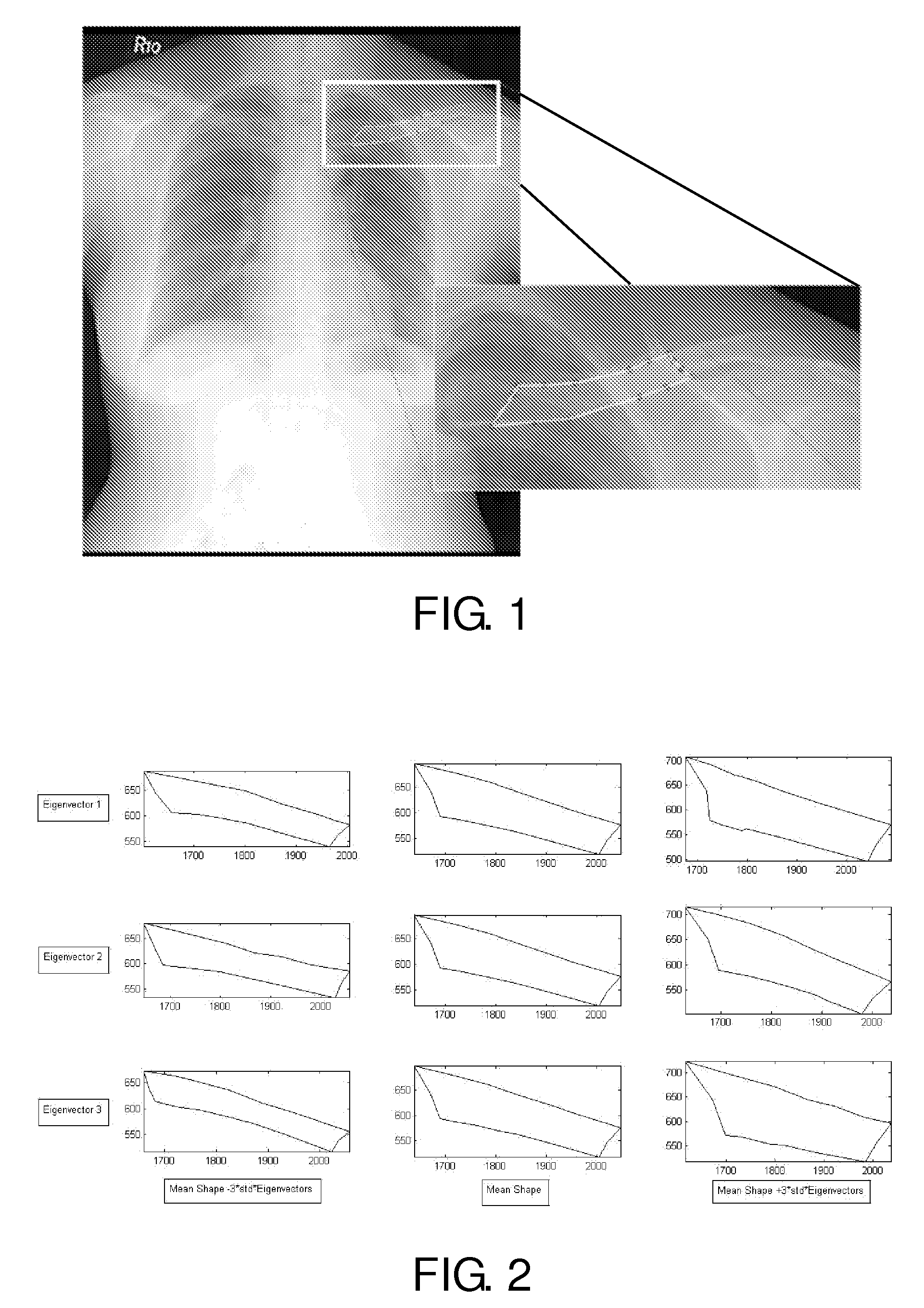
Method for automatic construction of 2d statistical shape model for the lung regions
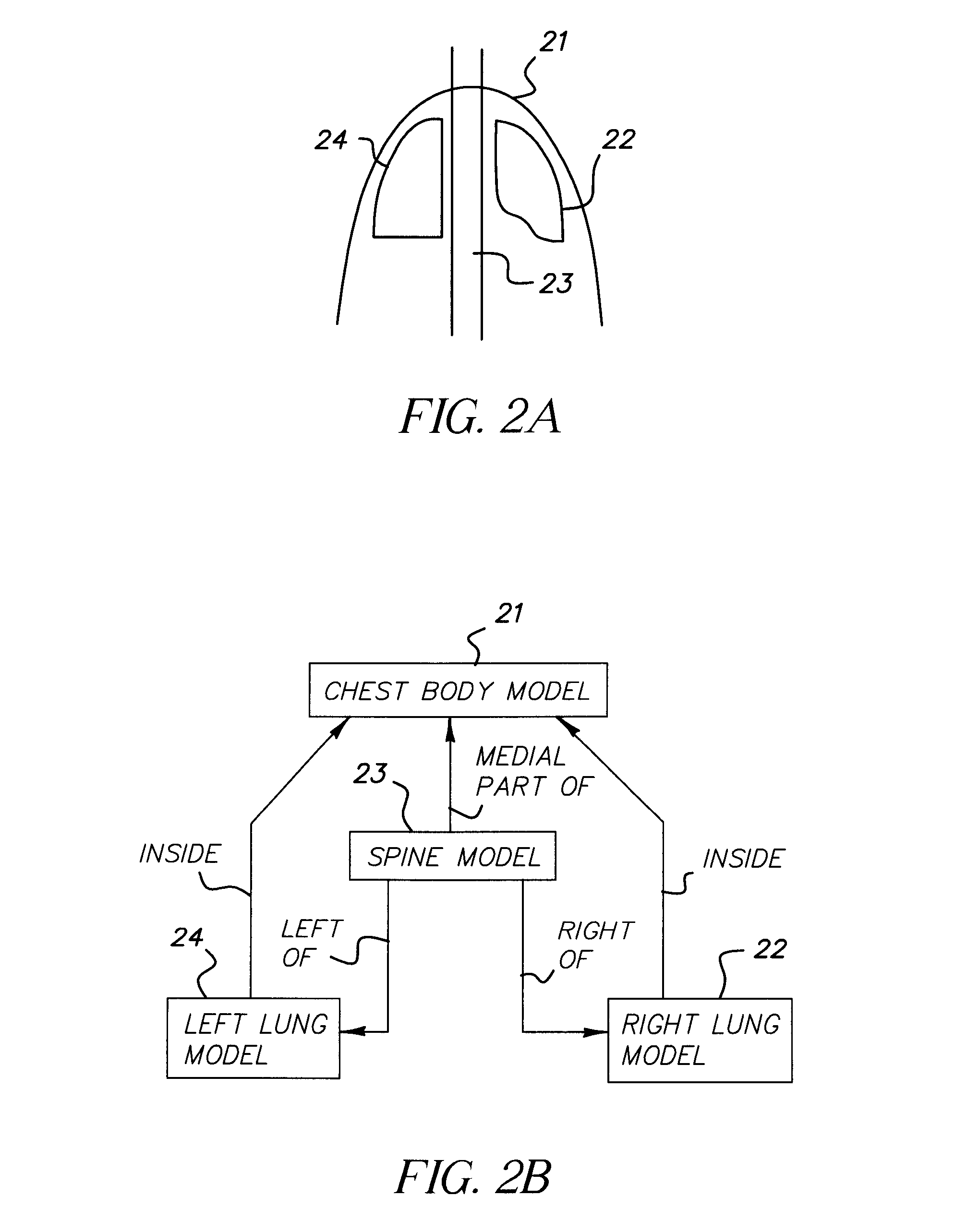
InactiveUS20070058850A1Reduce effortShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresLung region
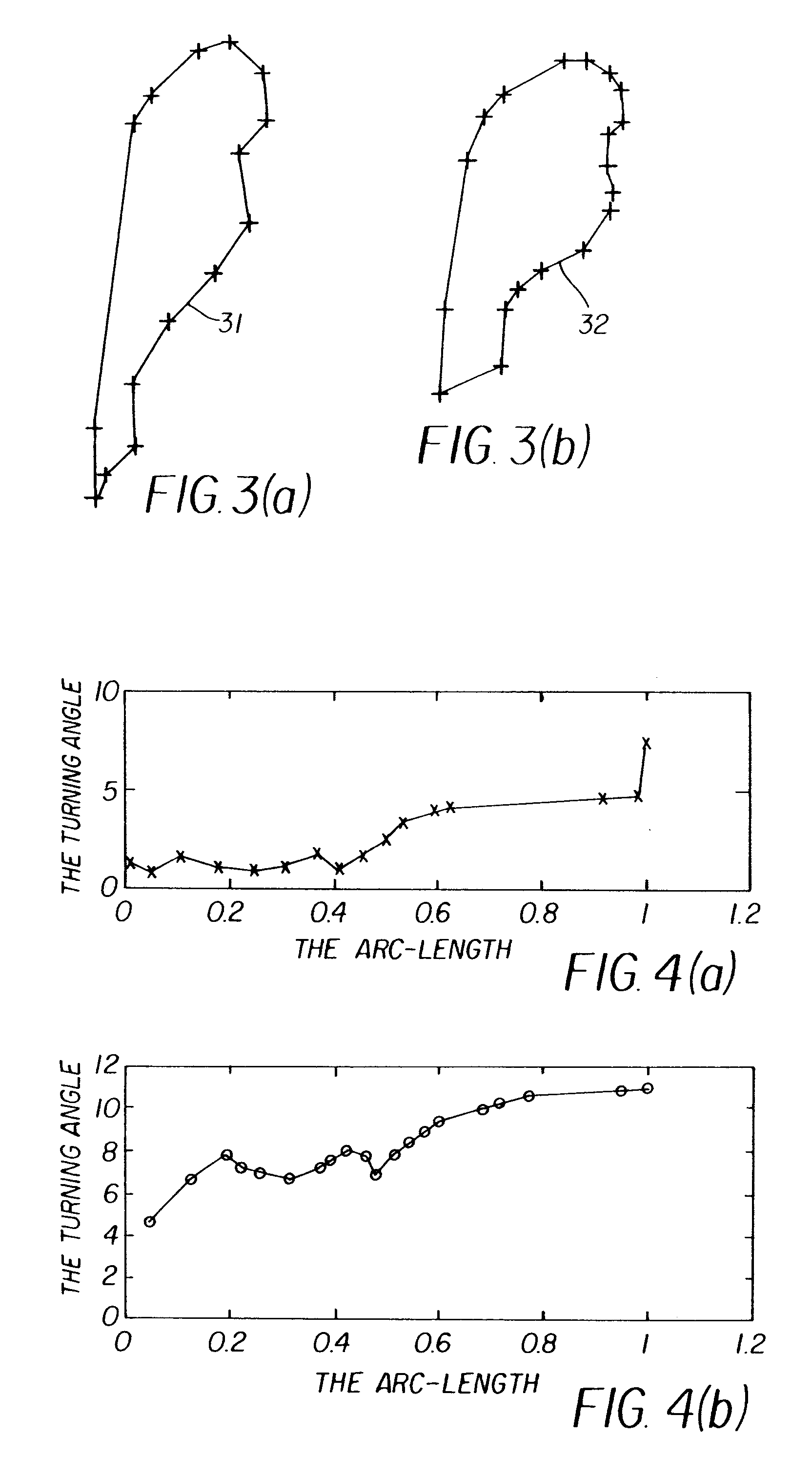
A method for automatic construction of 2D statistical shape models for the lung regions in chest radiographic images. The method includes: extracting the anatomical structure contours from a chest radiograph image; generating a polygonal shape approximation for each contour; aligning a plurality of polygonal shape approximations by minimizing their distance; assigning a plurality of landmarks on each shape contour; and determining a statistical shape model using aligned shape contours.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
X-ray chest radiograph image quality determination method and device
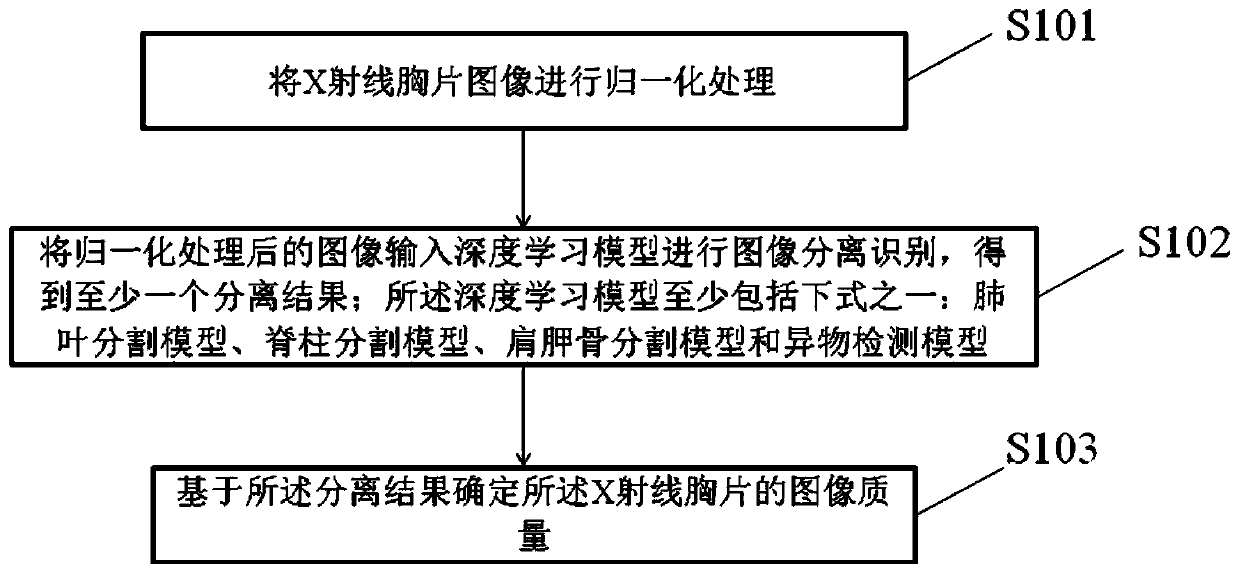
ActiveCN109859168ASure fastImage Quality ControlImage enhancementImage analysisForeign matterPattern recognition
The invention discloses an X-ray chest radiograph image quality determination method and device. The method comprises: conducting normalization processing on an X-ray chest radiograph image; inputtingthe normalized image into a deep learning model for image separation and recognition to obtain at least one separation result; wherein the deep learning model at least comprises one of the followingformulas: a pulmonary lobe segmentation model, a spine segmentation model, a shoulder blade segmentation model and a foreign matter detection model; and determining the image quality of the X-ray chest radiograph based on the separation result. The X-ray chest radiograph image quality is fully automatically evaluated, and the image quality determination speed is high. Moreover, a technician can behelped to control the image quality of the chest radiograph, and the radiograph reading accuracy is indirectly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Pulmonary nodule detection method and system based on image enhancement
InactiveCN107909572AImprove detection efficiencyPrevent overfittingImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleNetwork model
The invention provides a pulmonary nodule detection method and a system based on image enhancement. The method comprises steps: an anteroposterior view chest radiograph after pre-processing is dividedto a training set, a verification set and a test set according to a preset proportion; pulmonary nodule areas cut out from the anteroposterior view chest radiograph in the training set and the verification set are used as negative samples for model training, other areas in the anteroposterior view chest radiograph are randomly cut as positive samples for model training, and the negative samples are subjected to deformation processing to increase the number of negative samples; and a sliding window is used to divide the whole JPG anteroposterior view chest radiograph to non-overlapped image blocks, and the image blocks are inputted to a convolution neural network model to judge whether the image blocks are positive samples or negative samples. The pulmonary nodule detection efficiency canbe improved, the false positive rate is reduced, and through carrying out deformation processing on the negative samples, overfitting of the model due to insufficient chest radiograph data can be overcome.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH +1
Lung tissue image segmentation method based on deep learning
InactiveCN110310289AResolve local convergenceSolve the problem of false positive segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisData setX-ray
The invention provides a lung tissue image segmentation method based on deep learning, and belongs to the technical field of medical image segmentation. The lung tissue image segmentation method comprises the steps that an X-ray chest radiograph image is input into a segmentation model, the segmentation model is obtained through training of multiple sets of training data, and each set of trainingdata in the multiple sets of training data comprises the X-ray chest radiograph image and a corresponding gold standard used for identifying lung tissue; and output information of the model is obtained, and the output information comprises a segmentation result of the lung tissue in the X-ray chest radiography image. According to the lung tissue image segmentation method, the segmentation of the lung tissue of the X-ray chest radiography is realized through an improved Deeplabv3+ deep learning method, and the problems of local convergence and false positive segmentation when the lung tissue issegmented by using a traditional method are solved; the lung tissue image segmentation method respectively obtains 95.3% of MIoU and 94.8% of MIoU on the public data set and the pneumoconiosis data set; and the false positive problem of the FCN network is solved, and the segmentation accuracy of ribs at the thoracic diaphragm angle and on the X-ray chest radiography in the SCAN network method isimproved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
A chest X-ray film denoising method based on a deep convolutional neural network
InactiveCN109949235AImprove denoising effectReduce the amount of parametersImage enhancementGeometric image transformationData setX-ray
The invention discloses a chest X-ray film denoising method based on a deep convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of collecting chest X-ray film data, performing data format conversion, performing preprocessing to obtain an original image block for training, adding Gaussian noise to generate a noisy image block, and taking the paired original image block and noisy image block as a training data set; Constructing a convolutional neural network model for removing chest X-ray film noise, wherein the convolutional neural network model comprises a deep convolutional neural network and a residual error network; Taking the paired original image blocks and noisy image blocks as input, and performing training to obtain a trained convolutional neural network model X-ReCNN; taking the chest X-ray data of the noise to be removed as an input characteristic map of X-ReCNN, removing noise, and outputting the predicted denoised chest X-ray film.. According to the method, the noise in the chest X-ray film can be removed with light weight, high speed and high precision, the parameters of a network structure are greatly reduced, and the network training time is shortened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for detecting lung nodules based on data enhancement
InactiveCN107945875AImprove detection efficiencyPrevent overfittingImage enhancementImage analysisPositive sampleSlide window
The present invention provides a method and system for detecting lung nodules based on data enhancement. The method includes: classifying a preprocessed chest radiograph into a training set, a verification set and a test set according to a preset proportion; in the training set and the verification set using lung nodule areas extracted from the chest radiograph as model training positive samples,cutting the other areas in the chest radiograph at random as model training negative samples, and fusing at least two negative samples to increase the number of negative samples; dividing the whole JPG image of the chest radiograph into non-overlapped image blocks by a sliding window, and then inputting the image blocks into a convolution neural network model to determine whether the image blocksare positive samples or negative samples. The method and system can improve the detection efficiency of the lung nodules and reduce a false positive rate, and can overcome the over-fitting phenomenonof the model caused by insufficient chest radiograph data by deforming the negative samples.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Image acquisition for dual energy imaging
ActiveUS8019044B2Radiation/particle handlingRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsChest imagingHigh energy
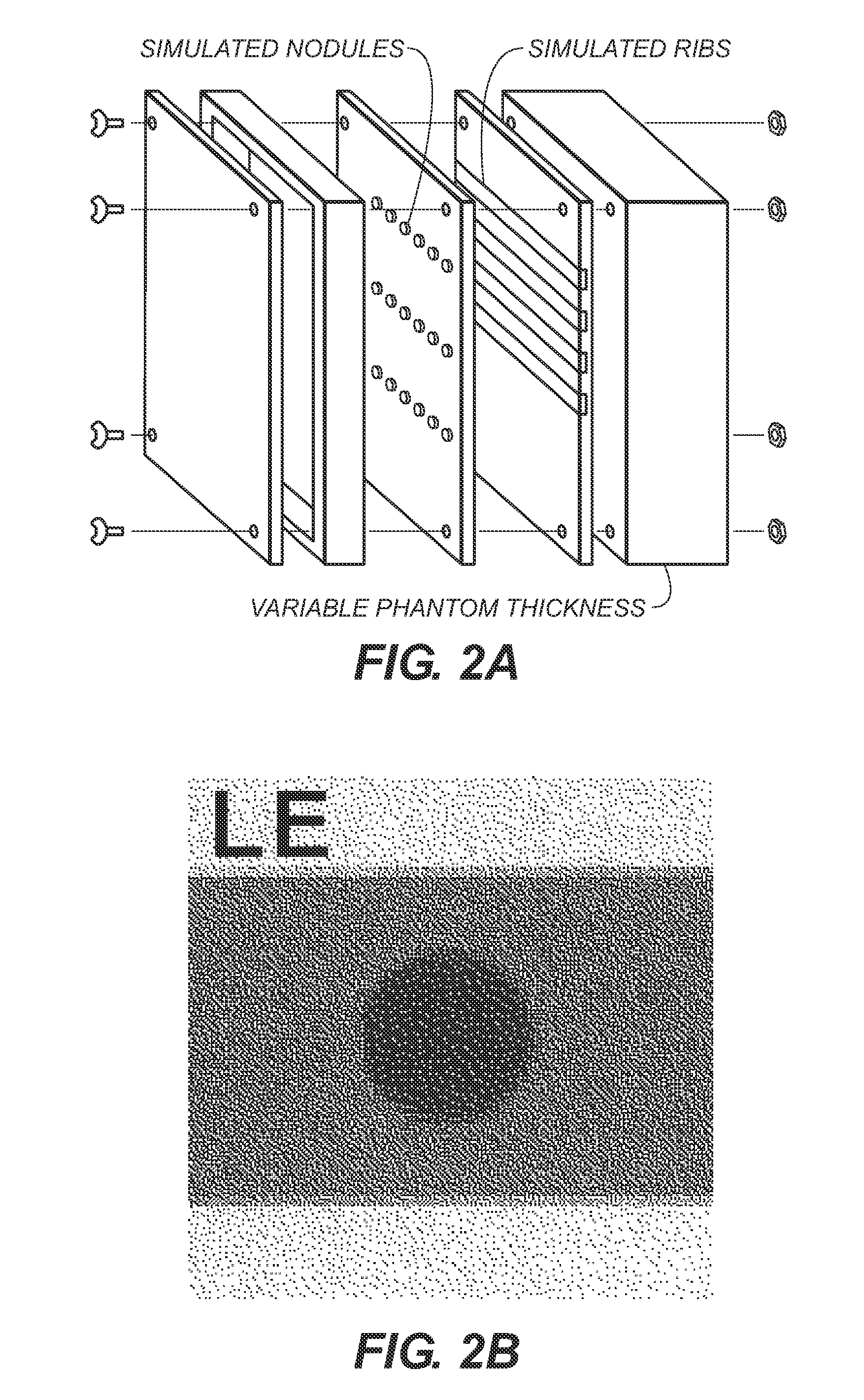
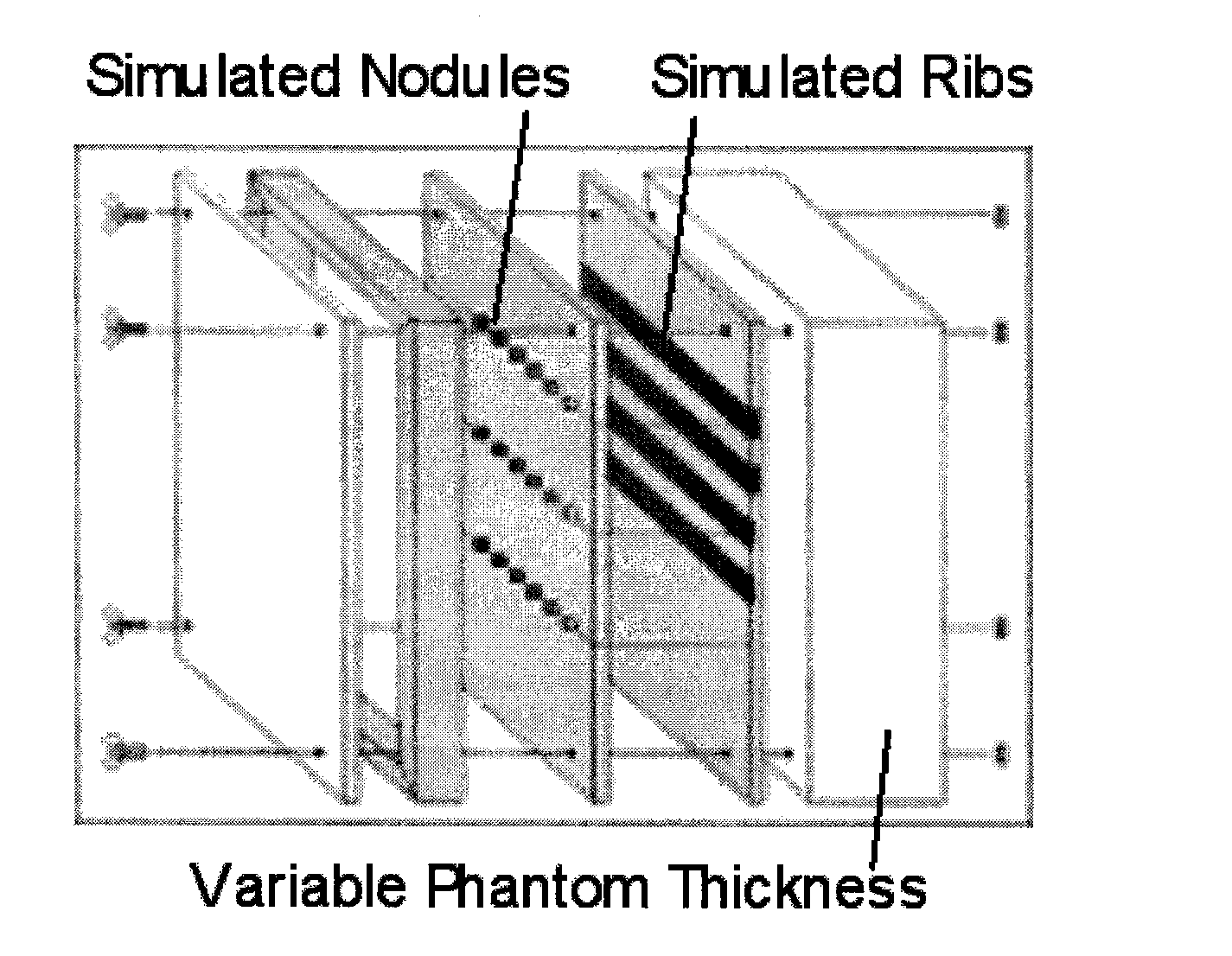
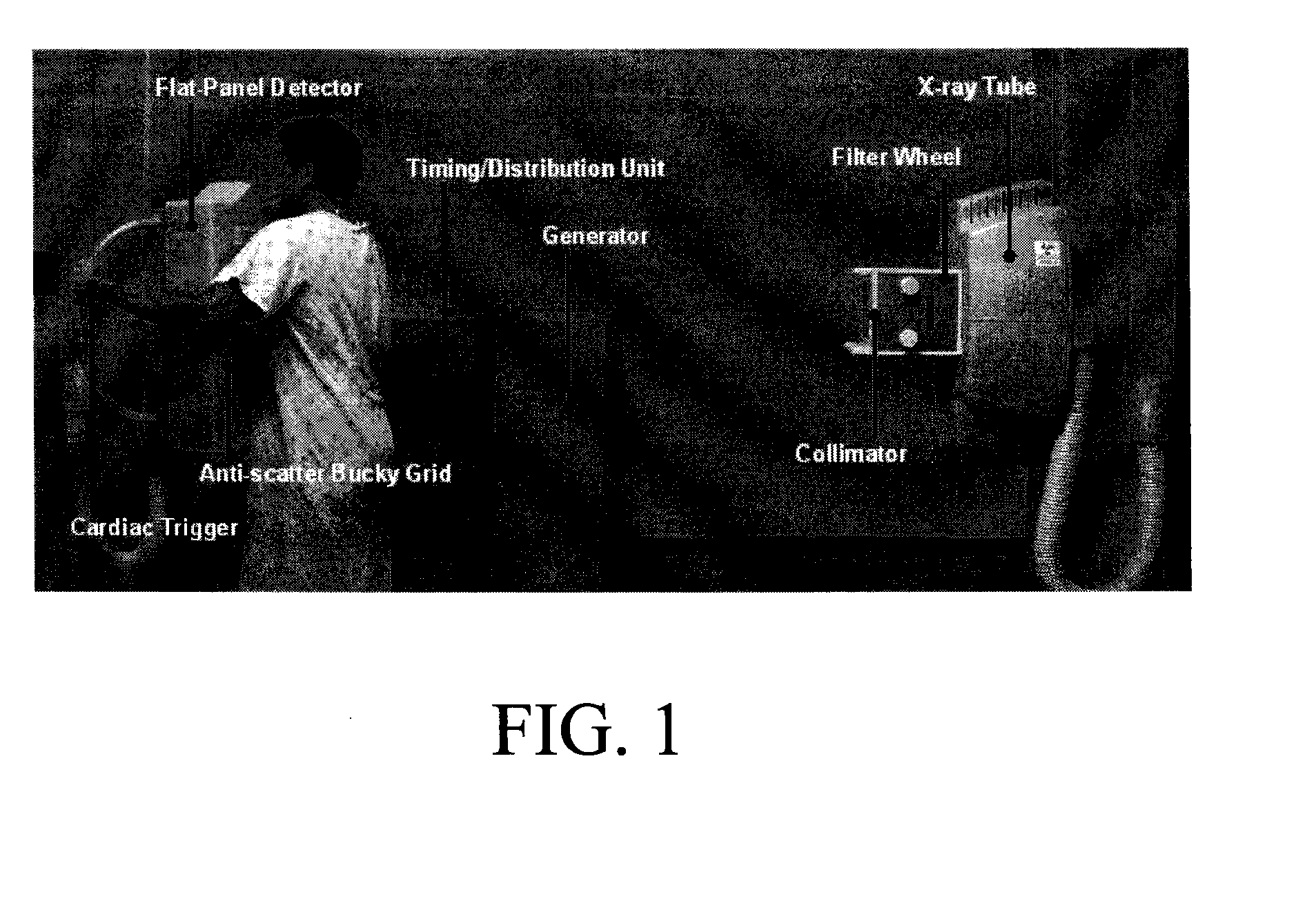
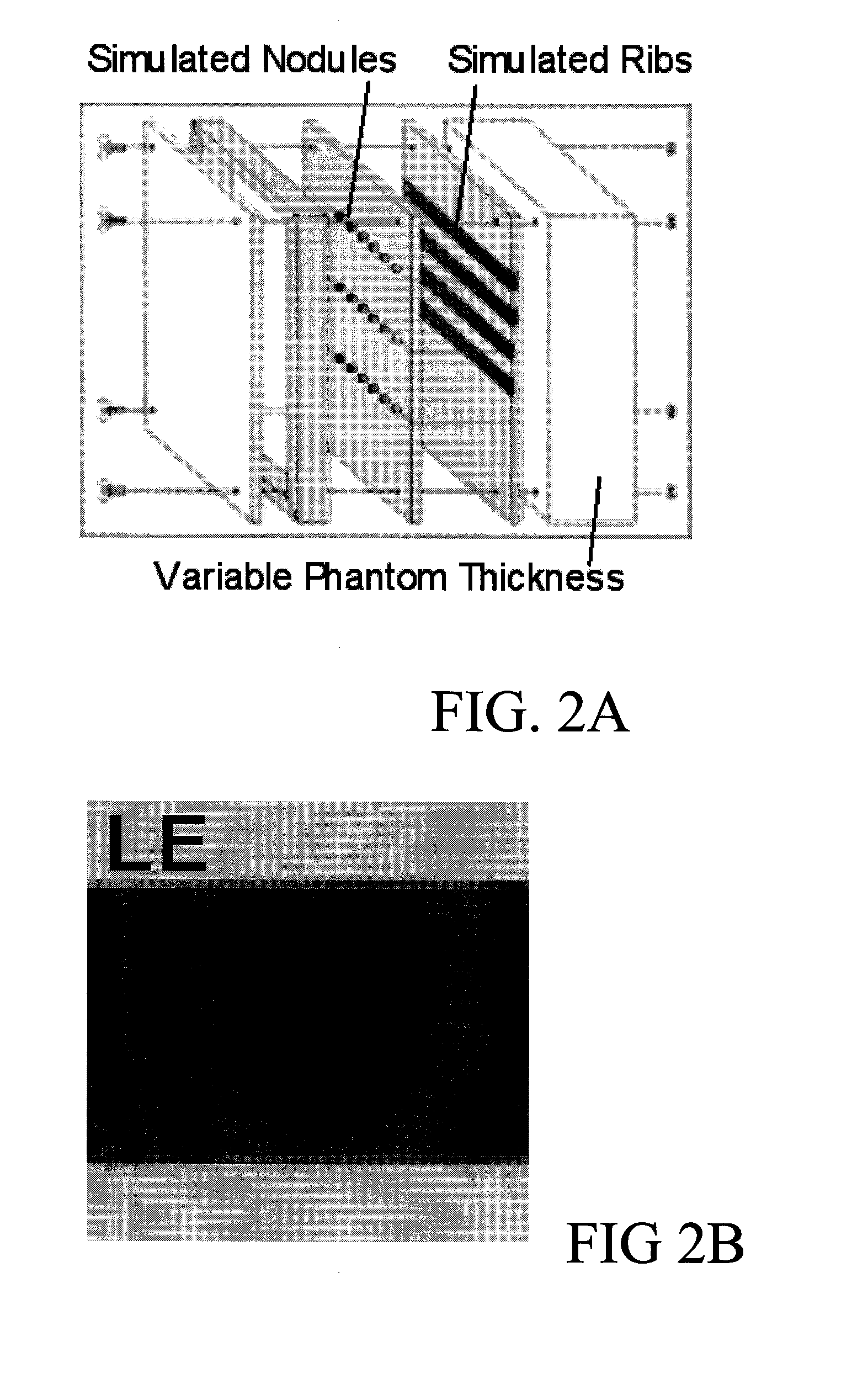
Acquisition techniques for dual energy (DE) chest imaging system. Technique factors include the added x-ray filtration, kVp pair, and the allocation of dose between low- and high-energy projections, with total dose equal to or less than that of a conventional chest radiograph. Factors are described which maximize lung nodule detectability as characterized by the signal difference to noise ratio (SDNR) in DE chest images. kVp pair and dose allocation are described using a chest phantom presenting simulated lung nodules and ribs for thin, average, and thick body habitus. Low- and high-energy techniques ranged from 60-90 kVp and 120-150 kVp, respectively, with peak soft-tissue SDNR achieved at [60 / 120] kVp for patient thicknesses and levels of imaging dose. A strong dependence on the kVp of the low-energy projection was observed.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Deep learning-based intelligent X-ray film diagnosis method
InactiveCN108899087ARealize accurate predictionShorten the timeBiological neural network modelsMedical automated diagnosisX-rayComputer vision
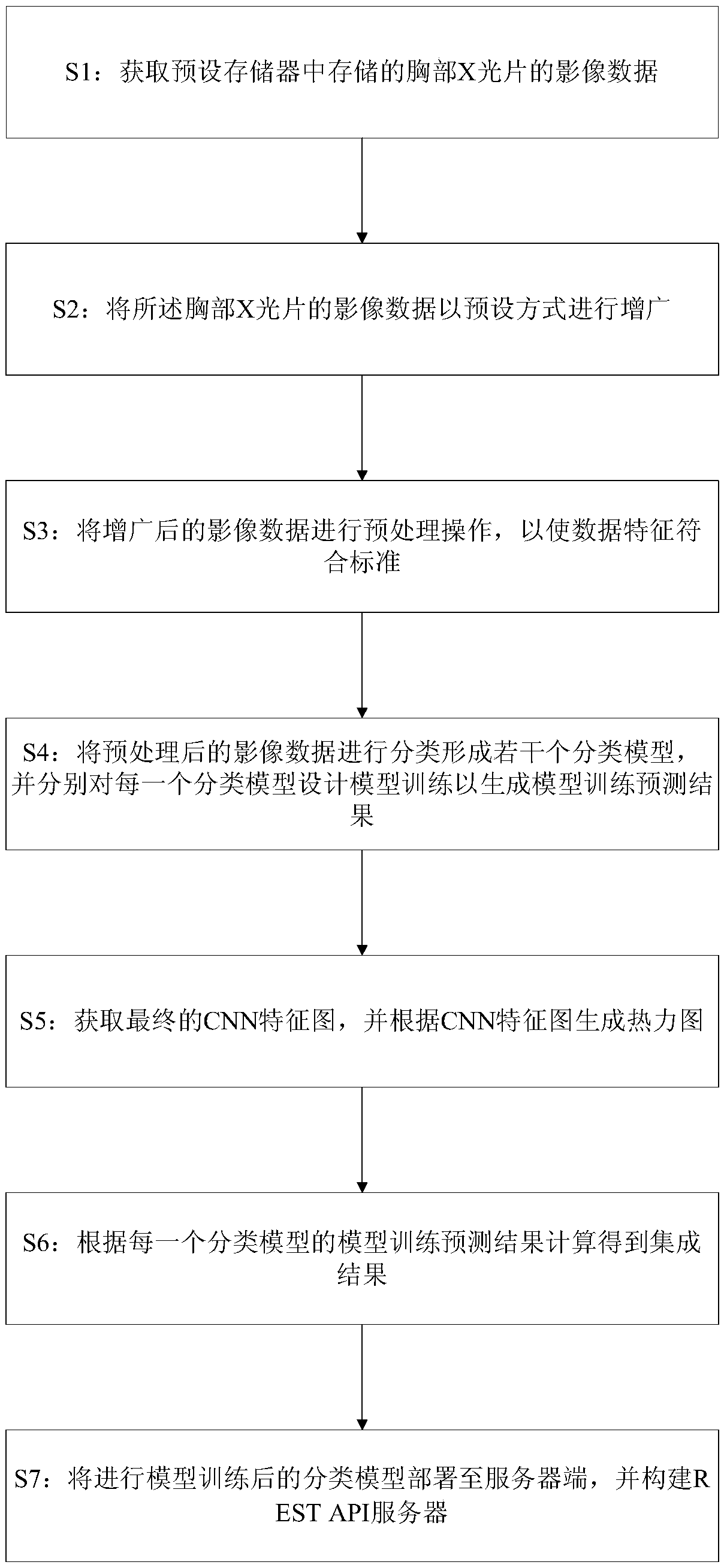
The invention discloses a deep learning-based intelligent X-ray film diagnosis method. The method comprises the following steps: image data of chest X-ray films stored in a preset memory are acquired;the image data of the chest X-ray films are augmented in a preset mode; the augmented image data are subjected to preprocessing operation to enable data features to meet a standard; the preprocessedimage data are classified to form a plurality of classification models, and model training is designed for each classification model to generate a model training prediction result; a final CNN featuremap is acquired, and according to the CNN feature map, a thermodynamic map is generated; and according to the model training prediction result of each classification model, an integration result is calculated and obtained. Deep learning on pulmonary disease characteristics in a large number of chest X-ray films can be carried out, multiple pulmonary diseases can be accurately predicted, a diagnosis basis is provided, the prediction time is greatly less than manual diagnosis time, and the time of a doctor is saved.
Owner:中山仰视科技有限公司
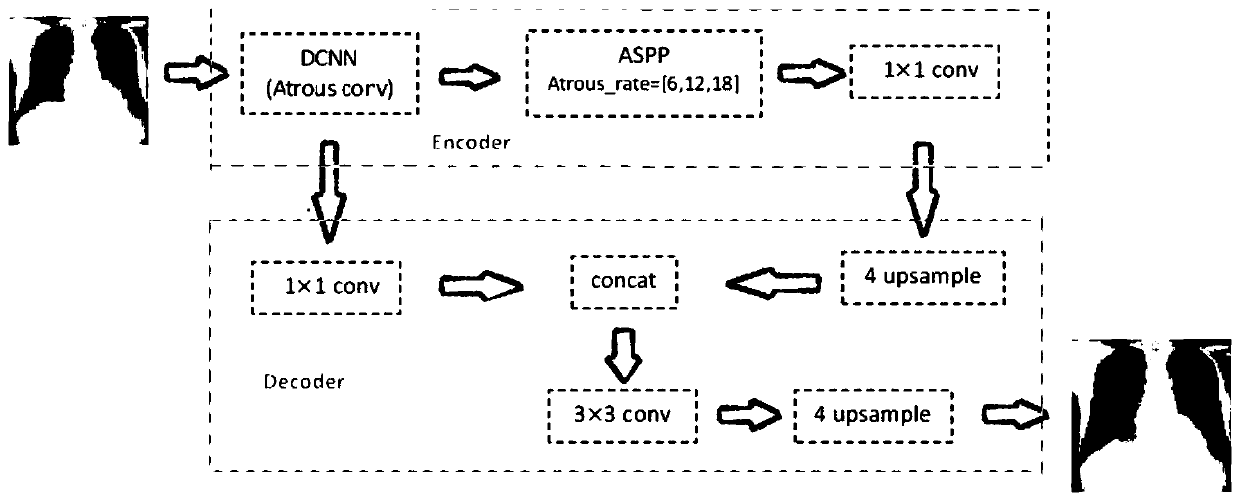
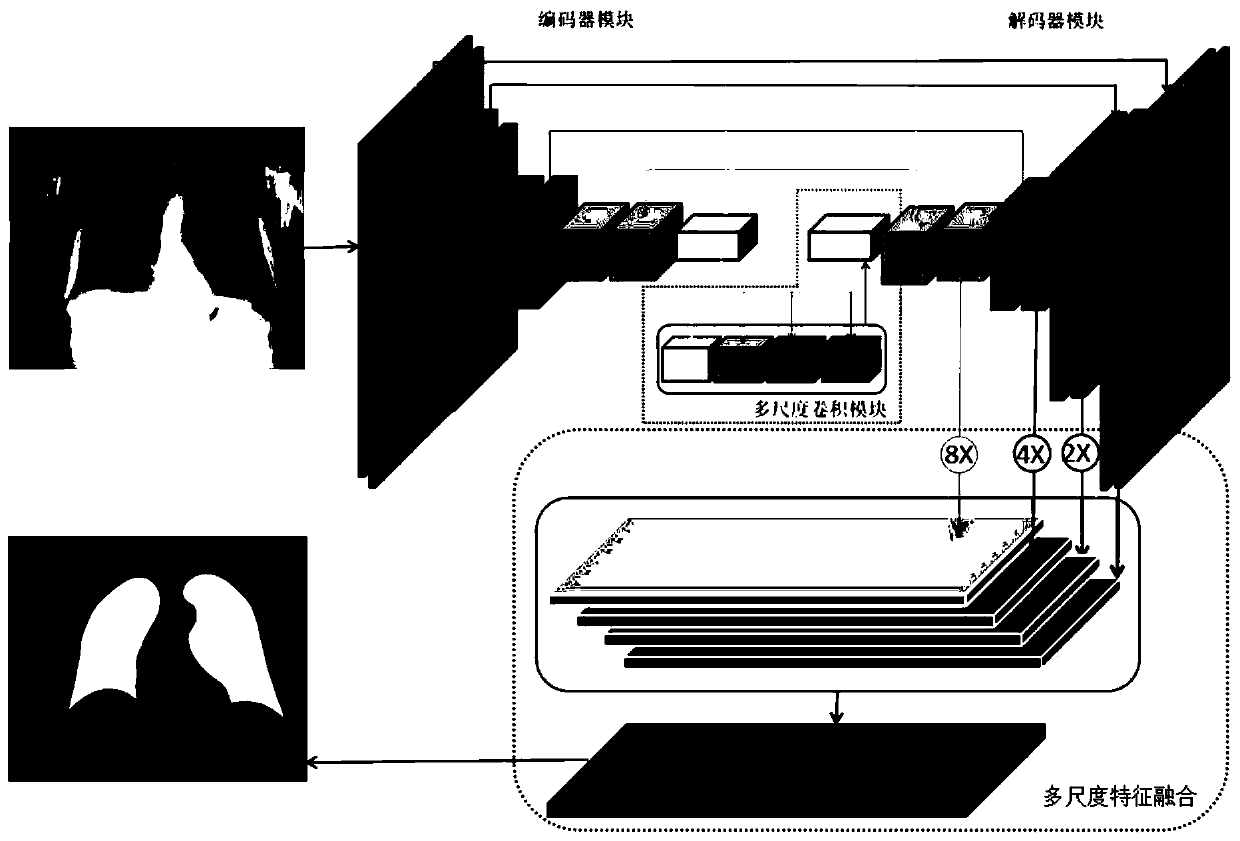
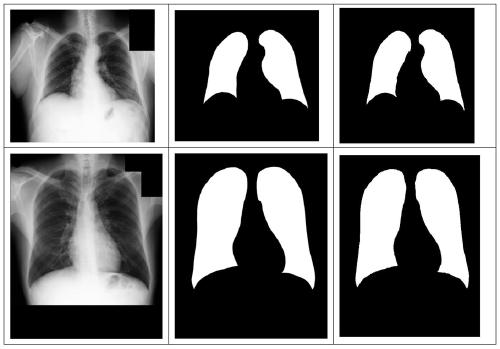
Chest radiography lung field segmentation model establishment based on multi-scale feature fusion and segmentation method
ActiveCN111429473AImprove segmentationImprove Segmentation AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionNuclear medicine
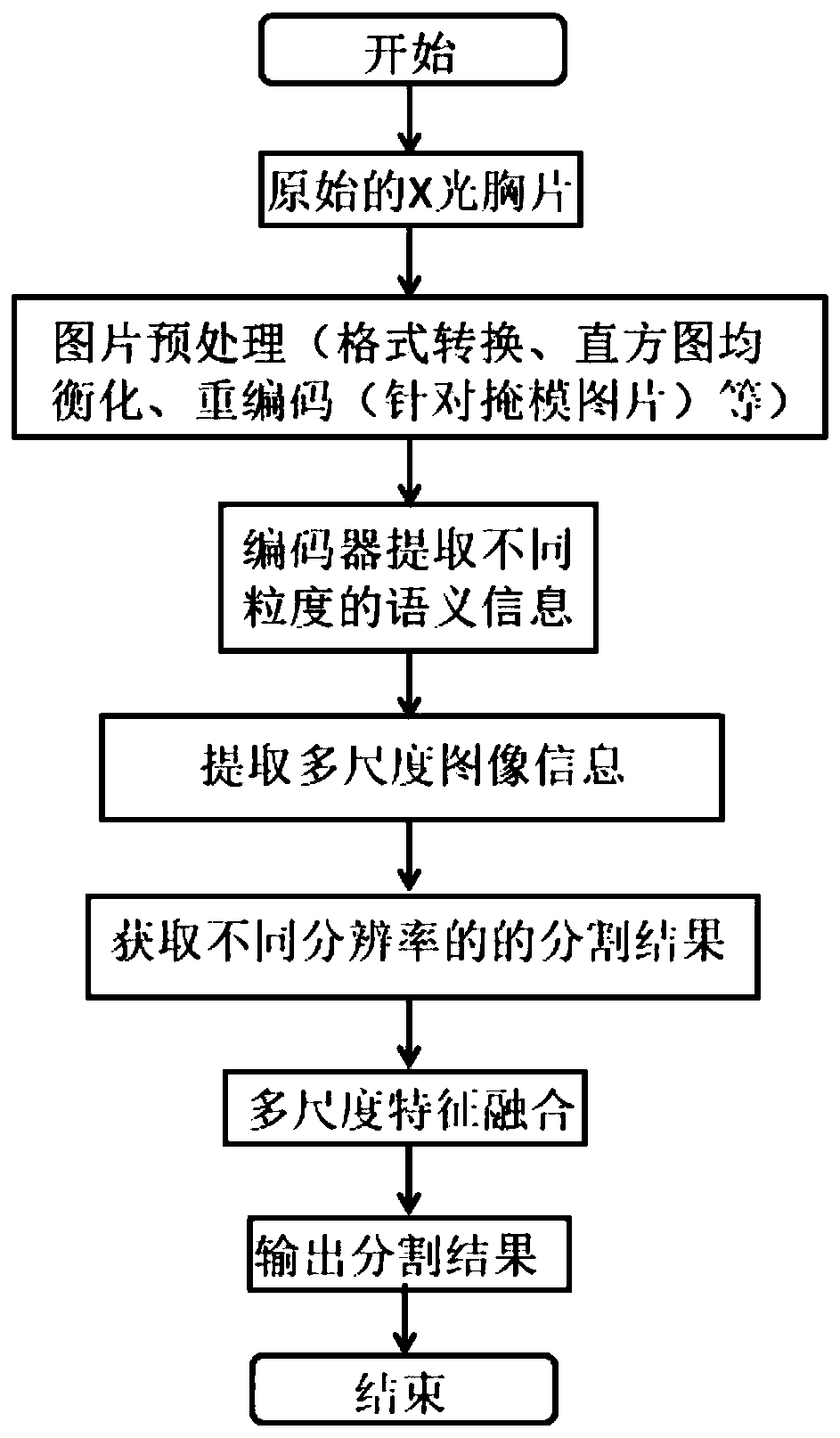
The invention discloses a chest radiography lung field segmentation model establishment based on multi-scale feature fusion and segmentation method. A segmentation model establishing method comprisesthe following steps: firstly, processing an X-ray chest radiograph; obtaining a preprocessed picture and a recoded mask picture, then constructing an X-ray chest radiography lung field segmentation network based on multi-scale convolution and a feature pyramid, and finally training the segmentation network by using the preprocessed picture as an input of the segmentation network and using the recoded mask picture as an output of the segmentation network to obtain a trained segmentation model; and based on the obtained segmentation model, preprocessing any to-be-processed X-ray chest radiograph, and inputting the preprocessed X-ray chest radiograph into the segmentation model to obtain a lung field segmentation result. According to the method, multi-resolution feature fusion is provided incombination with a feature pyramid theory, wherein the segmentation results with different resolutions can be fused, so that the segmentation effect is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
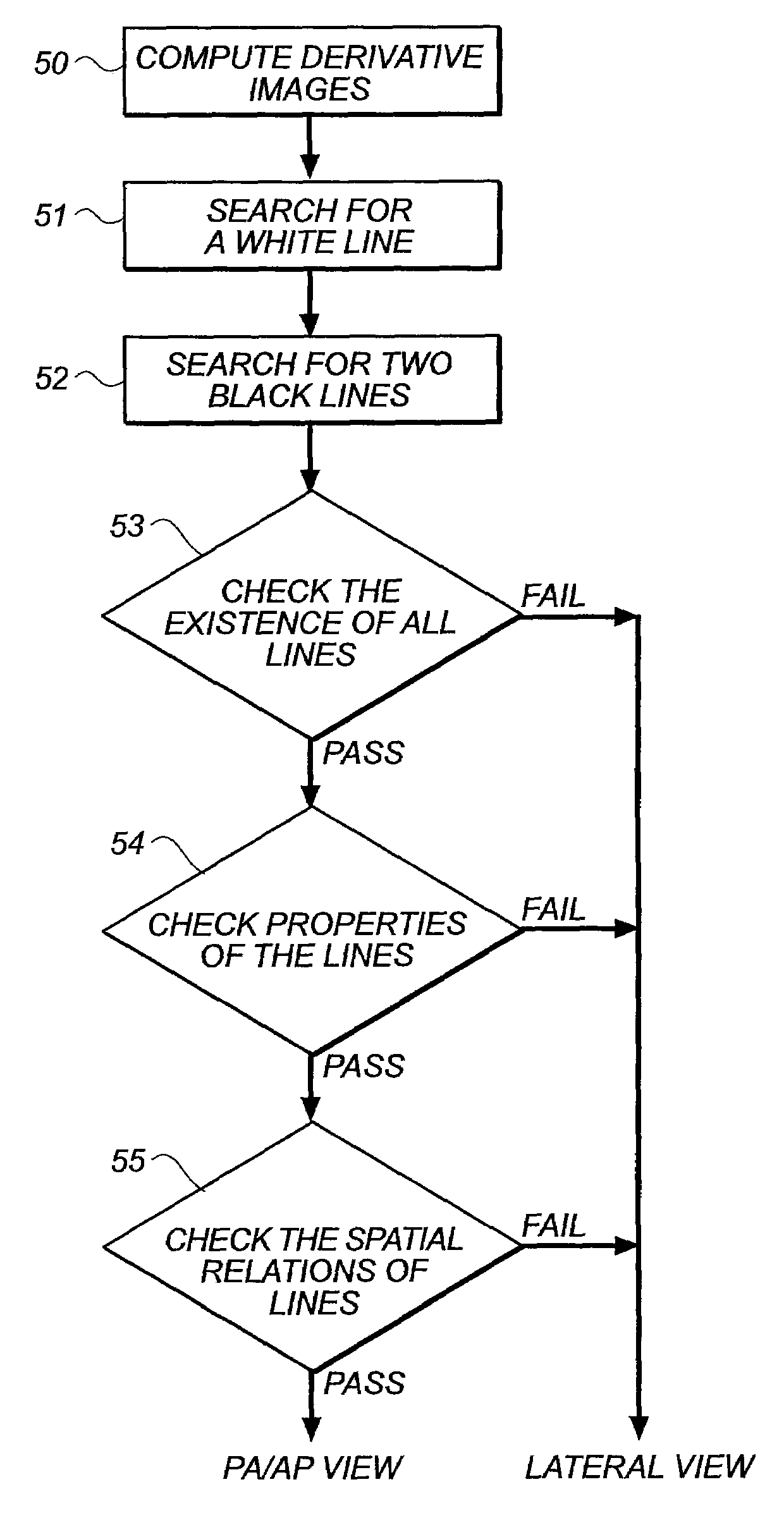
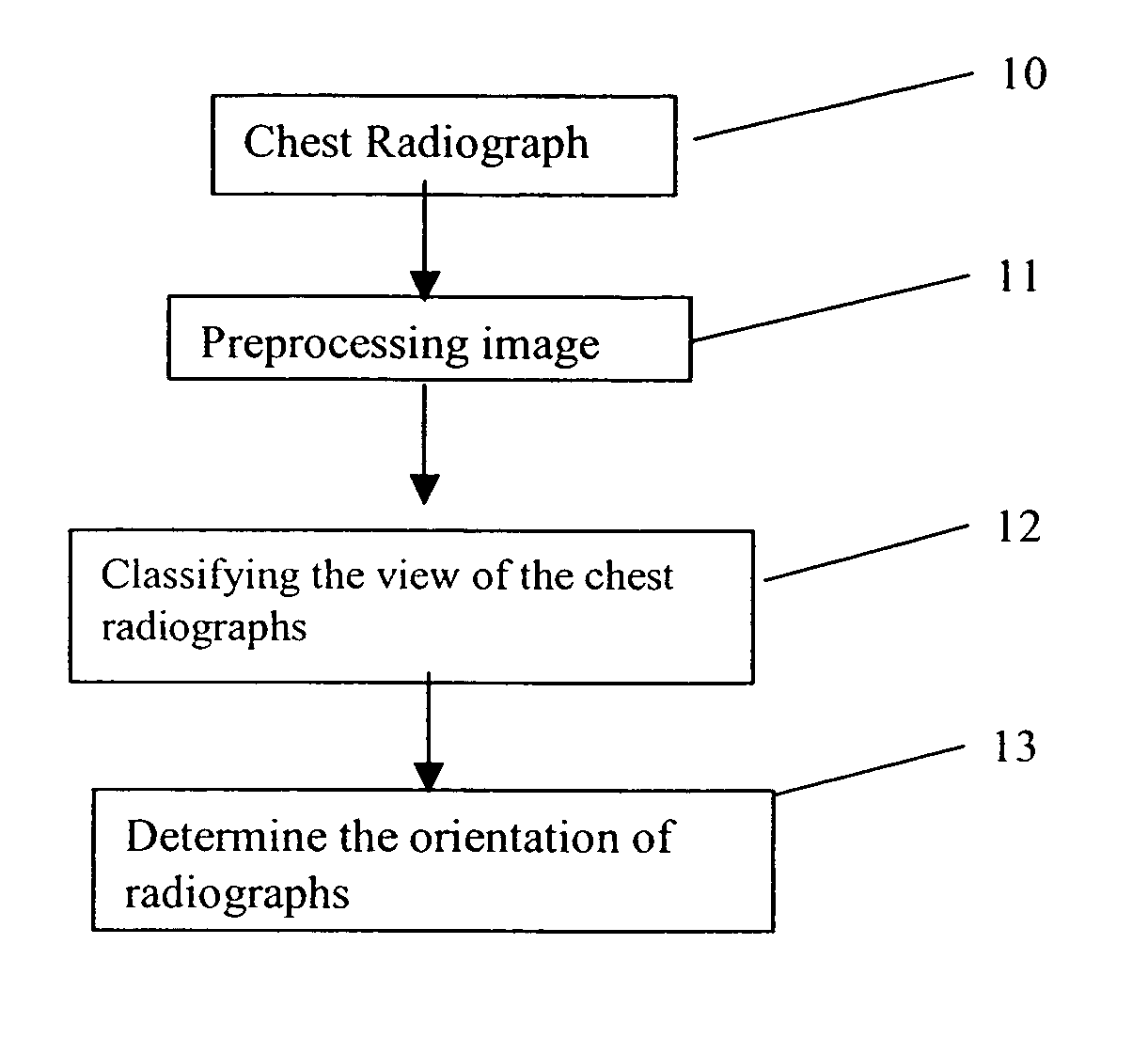
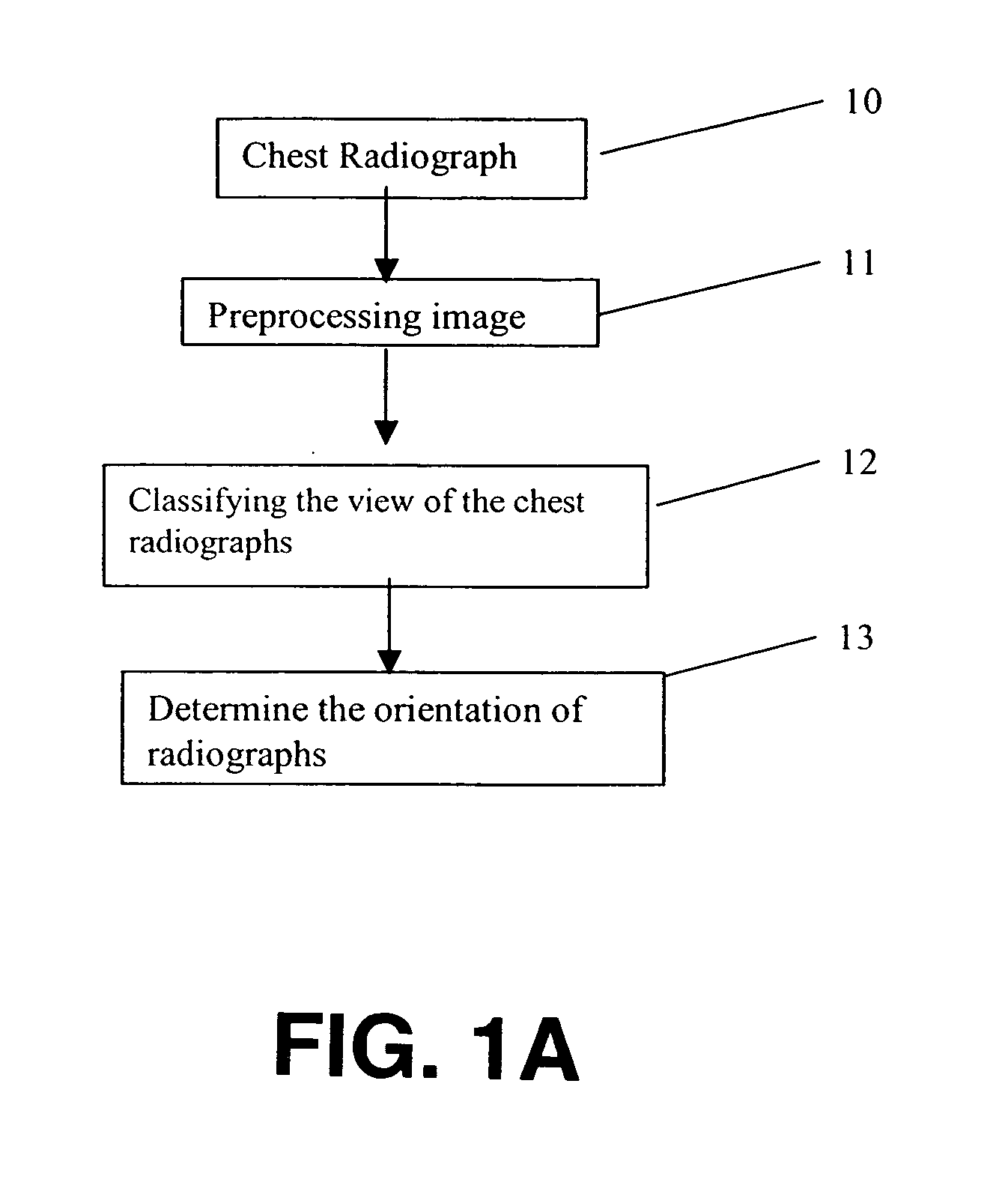
Method for computer recognition of projection views and orientation of chest radiographs
InactiveUS7352888B2Improve robustnessAvoid interferenceImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageProjection View
A method for identifying a projection view and an orientation of a chest radiograph. The method includes the steps of: providing an input digital image of the chest radiograph; preprocessing the input digital radiographic image; classifying the view of the input digital radiographic image; and determining the orientation of the input digital radiographic image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
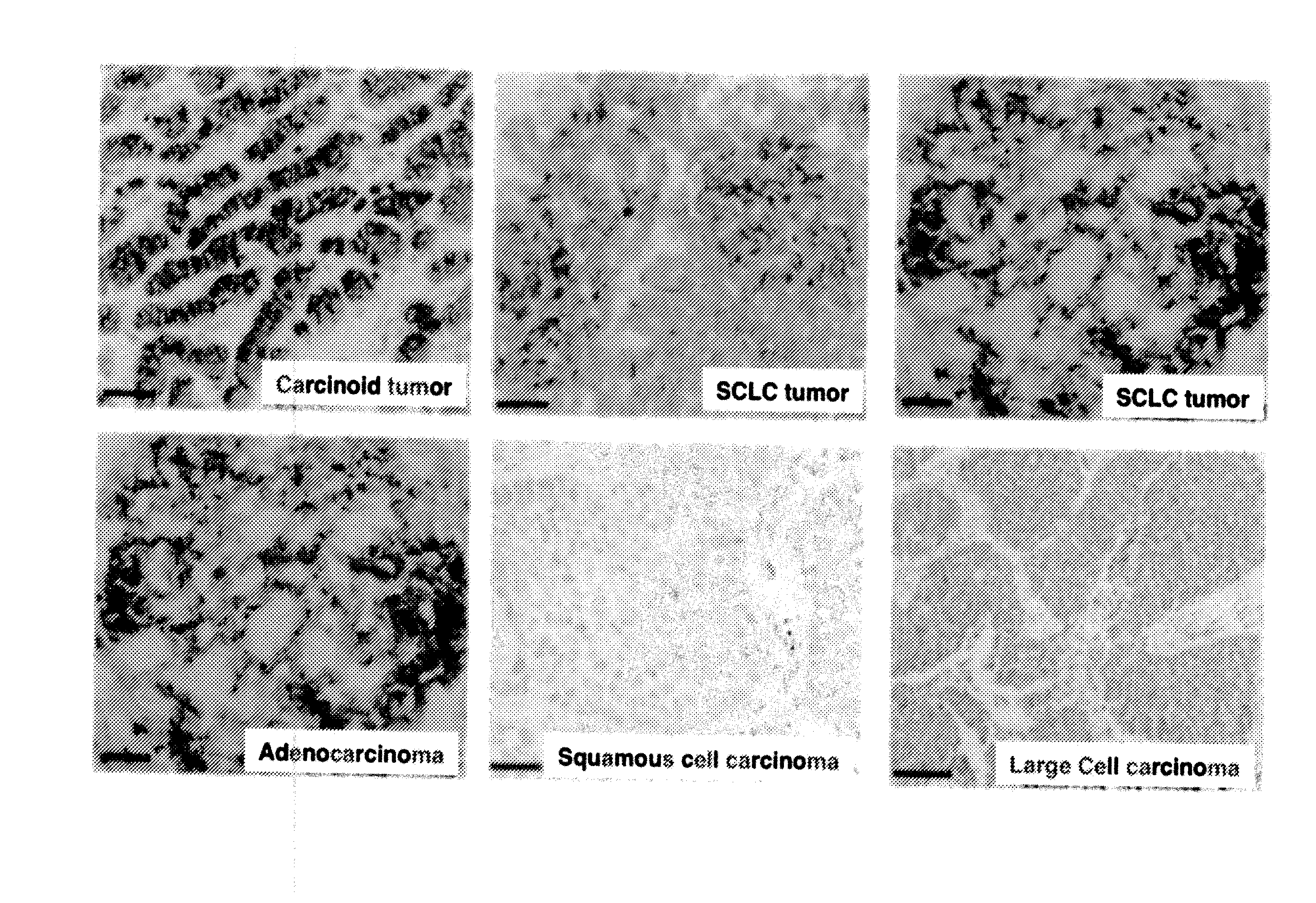
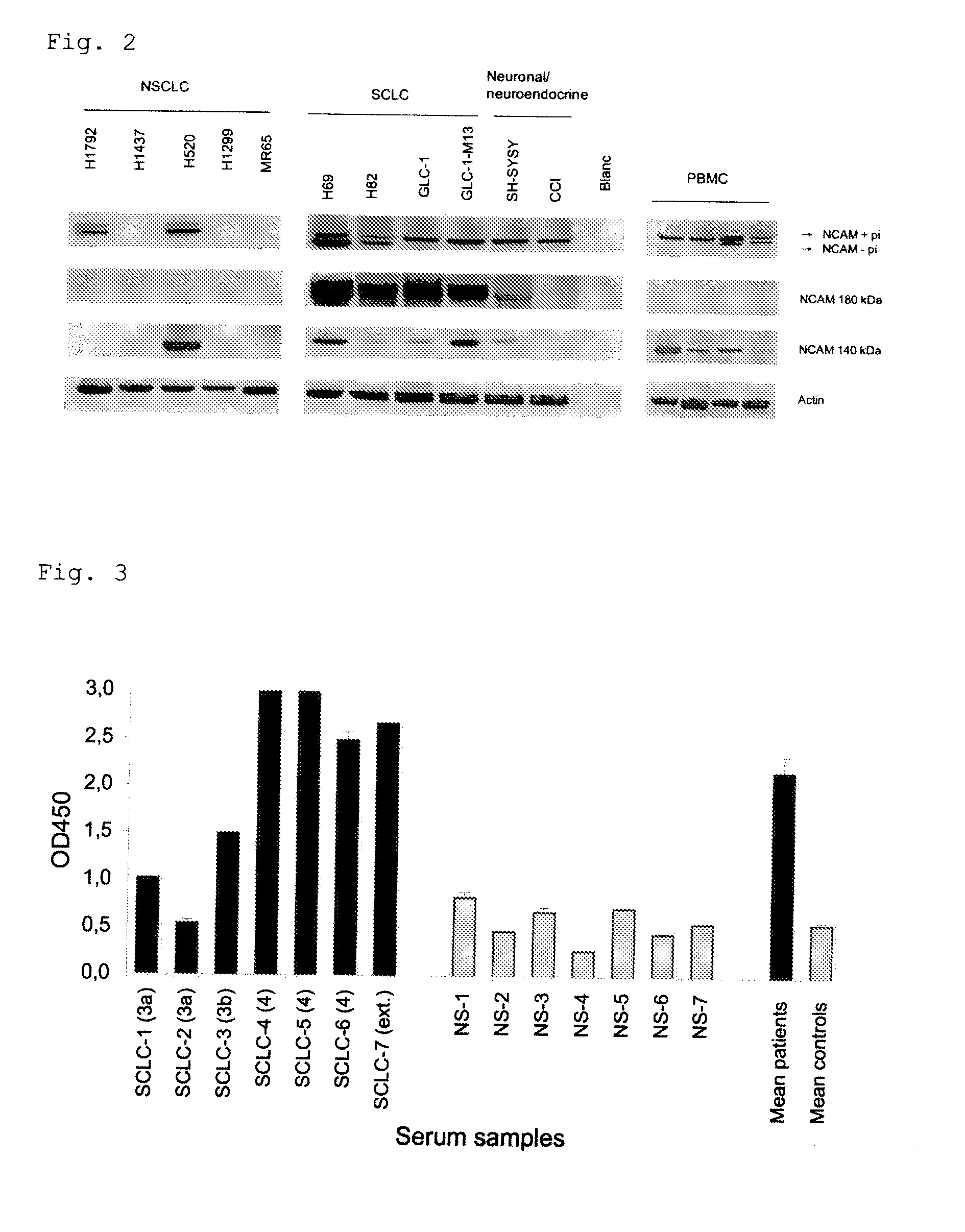
Small cell lung carcinoma biomarker panel
The invention relates generally to the field of cancer detection, diagnosis, subtyping, staging, prognosis, treatment and prevention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for the detection, and / or diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging of lung cancer in a patient. Based on a particular panel of biomarkers, the present invention provides methods to detect, diagnose at an early stage and / or differentiate small cell lung cancer (SCLC) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and within NSCLC to differentiate between squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), adenocarcinomas (AC), within SCC to discriminate G2 and G3 stage and within lung cancer to differentiate for lung cancers with or without neuroendocrine origin. It further provides the use of said panel of biomarkers in monitoring disease progression in a patient, including both in vitro and in vivo imaging techniques. The in vitro imaging techniques typically include an immunoassay detecting protein or antibody of the biomarkers on a sample taken from said patient, e.g. serum or tissue sample. The in vivo imaging techniques typically include chest radiographs (X-rays), Computed Tomography (CT) imaging, spiral CT, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), PET-CT and scintigraphy for molecular imaging and diagnosis and to monitor disease progression and treatment response in patients. It is accordingly a further aspect to provide a kit to perform the aforementioned diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging assay and the imaging techniques, comprising reagents to determine the gene expression or protein level of the aforementioned panel of biomarkers for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Owner:MUBIO PRODS BV
Small cell lung carcinoma biomarker panel
InactiveUS20110053156A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker panelCompanion animal
The invention relates generally to the field of cancer detection, diagnosis, subtyping, staging, prognosis, treatment and prevention. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for the detection, and / or diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging of lung cancer in a patient. Based on a particular panel of biomarkers, the present invention provides methods to detect, diagnose at an early stage and / or differentiate small cell lung cancer (SCLC) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and within NSCLC to differentiate between squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), adenocarcinomas (AC), within SCC to discriminate G2 and G3 stage and within lung cancer to differentiate for lung cancers with or without neuroendocrine origin. It further provides the use of said panel of biomarkers in monitoring disease progression in a patient, including both in vitro and in vivo imaging techniques. The in vitro imaging techniques typically include an immunoassay detecting protein or antibody of the biomarkers on a sample taken from said patient, e.g. serum or tissue sample. The in vivo imaging techniques typically include chest radiographs (X-rays), Computed Tomography (CT) imaging, spiral CT, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), PET-CT and scintigraphy for molecular imaging and diagnosis and to monitor disease progression and treatment response in patients. It is accordingly a further aspect to provide a kit to perform the aforementioned diagnosing and / or subtyping and / or staging assay and the imaging techniques, comprising reagents to determine the gene expression or protein level of the aforementioned panel of biomarkers for in vitro and in vivo applications.
Owner:MUBIO PRODS BV
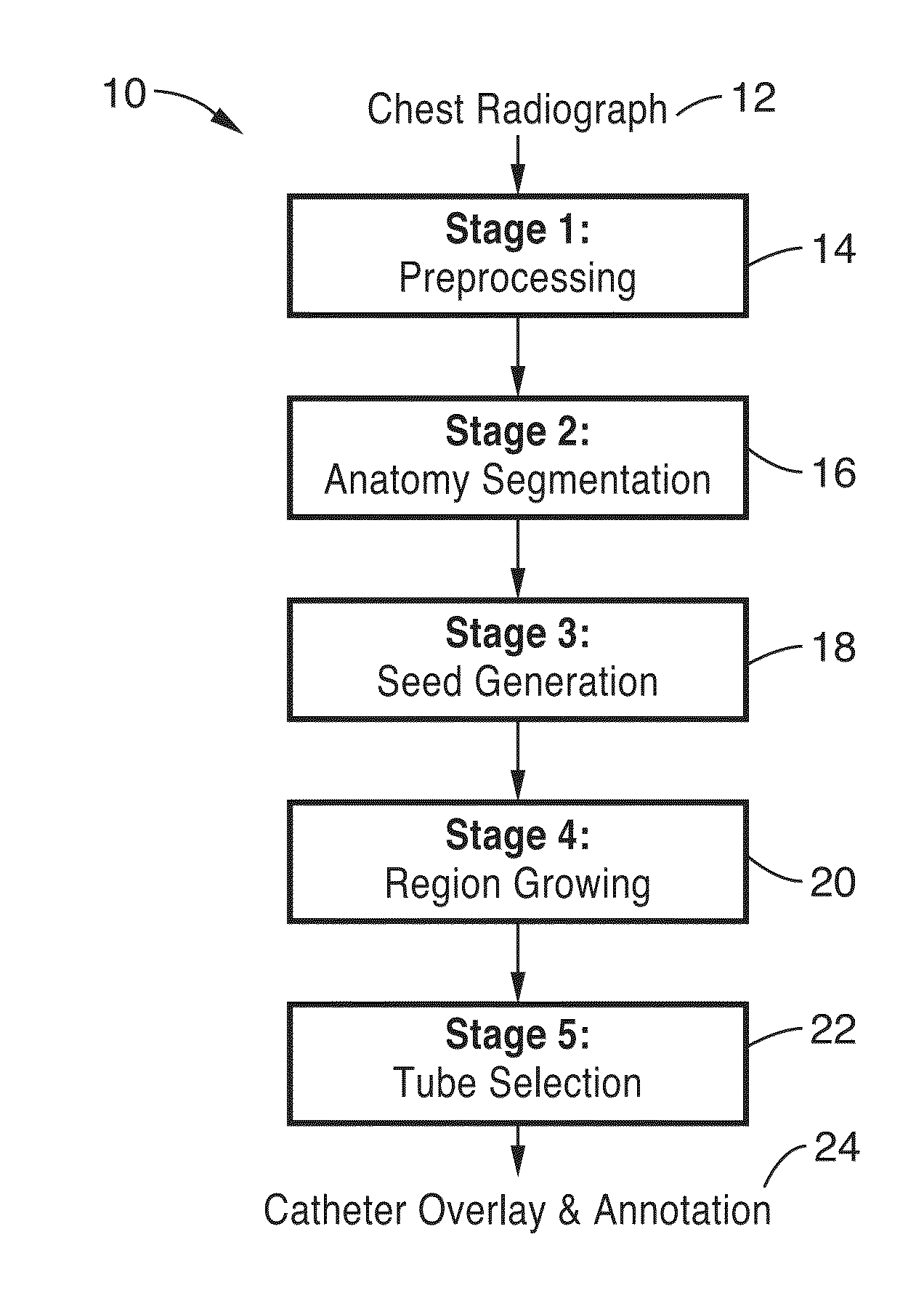
Methods and apparatus for computer-aided radiological detection and imaging
ActiveUS20130322725A1Increase radiologist productivityConfidenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer aidImage generation
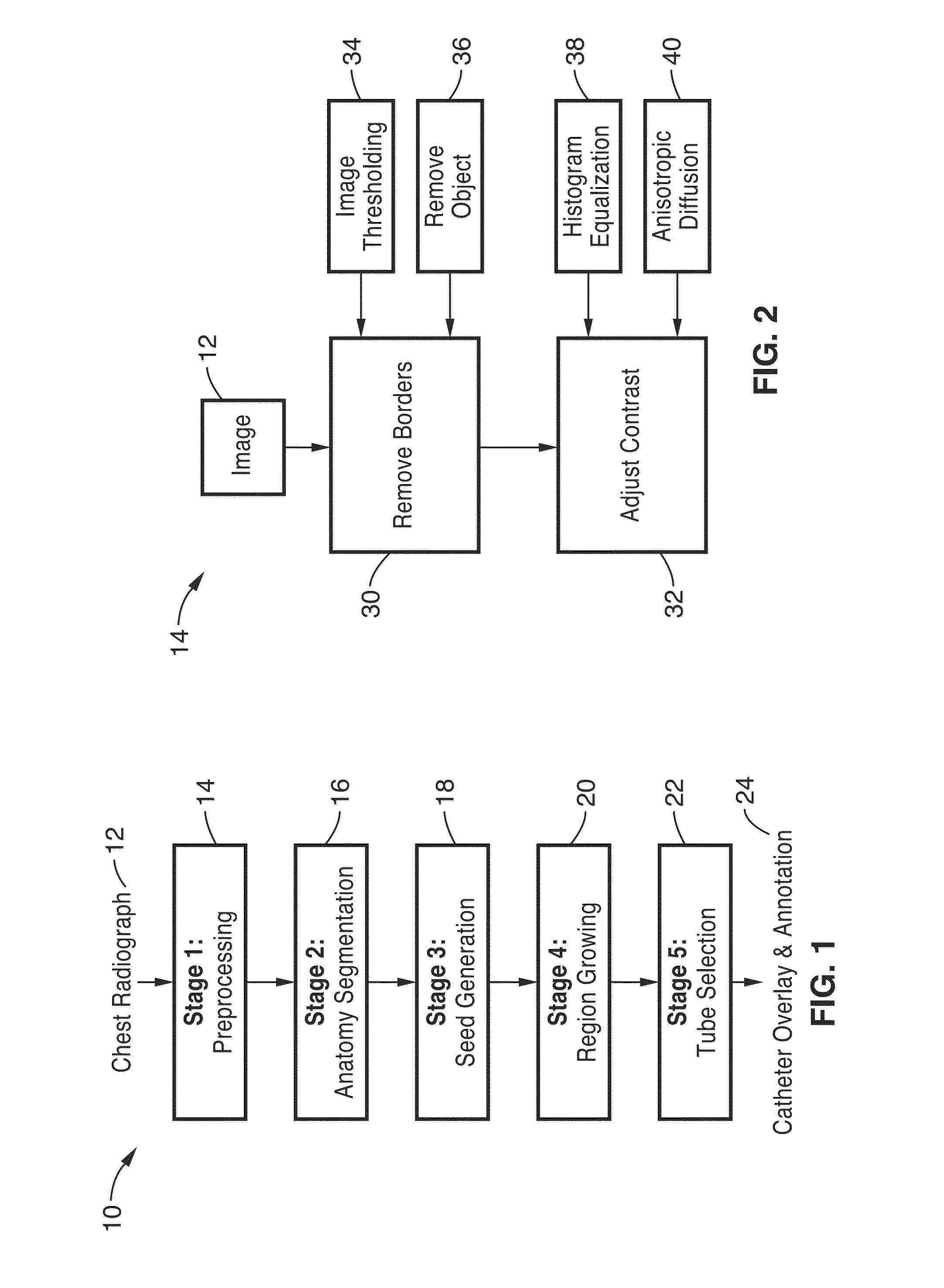
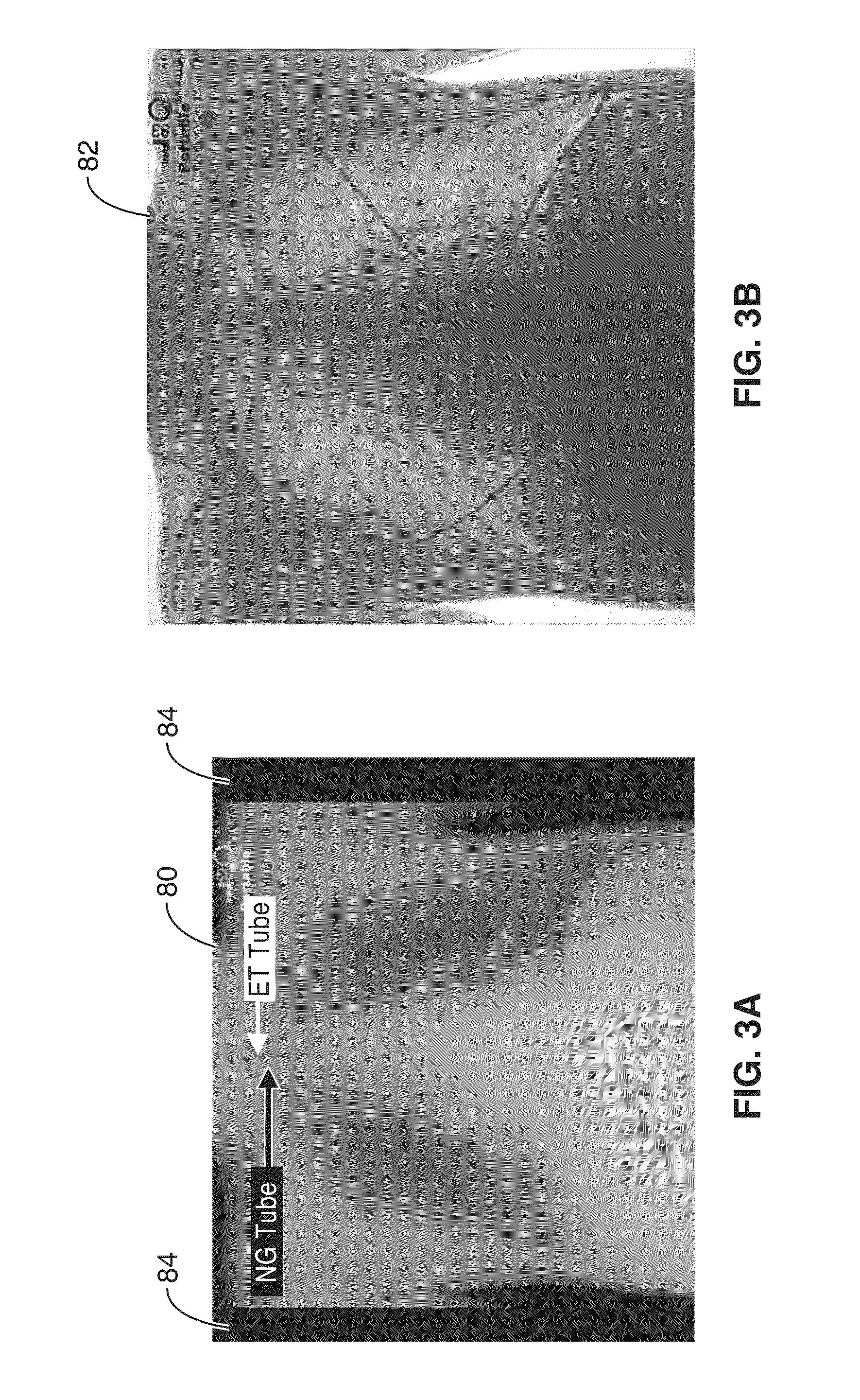
A computer aided detection (CAD) method and system is configured to input chest radiographs and generate overlay layer for labeling and tracing tubes detected within the image. The input image is first preprocessed and then segmented according to anatomy. Seeds are generated from the segmented image and then used to grow the region. Tubes are selected from the grown region and data is overlayed on the image based on the grown seed path.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
X-ray chest radiograph classification device based on improved dense connection network
ActiveCN111709446ASolve the imbalanceImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmEngineering
The invention relates to an X-ray chest radiography classification device based on an improved dense connection network. The device comprises a memory, a processor and a computer program which is stored on the memory and can run on the processor, and the processor is used for realizing the following method steps when executing the program: step 1, chest radiography preprocessing; 2, constructing and training a deep convolutional neural network; the method comprises the following steps of: modifying a classification network DenseNet121, adding an extrusion-excitation module into the network ina dense connection mode to form an improved dense connection network, constructing a loss function conforming to the task, and training the network by using a preprocessed chest radiography; and step3, testing the network and selecting an optimal network model: testing the network model obtained by each round of training on a test set, and selecting the network model with the highest average AUCvalue as a final model.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Image acquisition for dual energy imaging
ActiveUS20090207966A1Radiation/particle handlingRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsChest imagingFiltration
Acquisition techniques for dual energy (DE) chest imaging system. Technique factors include the added x-ray filtration, kVp pair, and the allocation of dose between low- and high-energy projections, with total dose equal to or less than that of a conventional chest radiograph. Factors are described which maximize lung nodule detectability as characterized by the signal difference to noise ratio (SDNR) in DE chest images. kVp pair and dose allocation are described using a chest phantom presenting simulated lung nodules and ribs for thin, average, and thick body habitus. Low- and high-energy techniques ranged from 60-90 kVp and 120-150 kVp, respectively, with peak soft-tissue SDNR achieved at [60 / 120] kVp for patient thicknesses and levels of imaging dose. A strong dependence on the kVp of the low-energy projection was observed.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method for computer recognition of projection views and orientation of chest radiographs
InactiveUS20060023929A1Improve robustnessAvoid interferenceImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageProjection View
A method for identifying a projection view and an orientation of a chest radiograph. The method includes the steps of: providing an input digital image of the chest radiograph; preprocessing the input digital radiographic image; classifying the view of the input digital radiographic image; and determining the orientation of the input digital radiographic image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
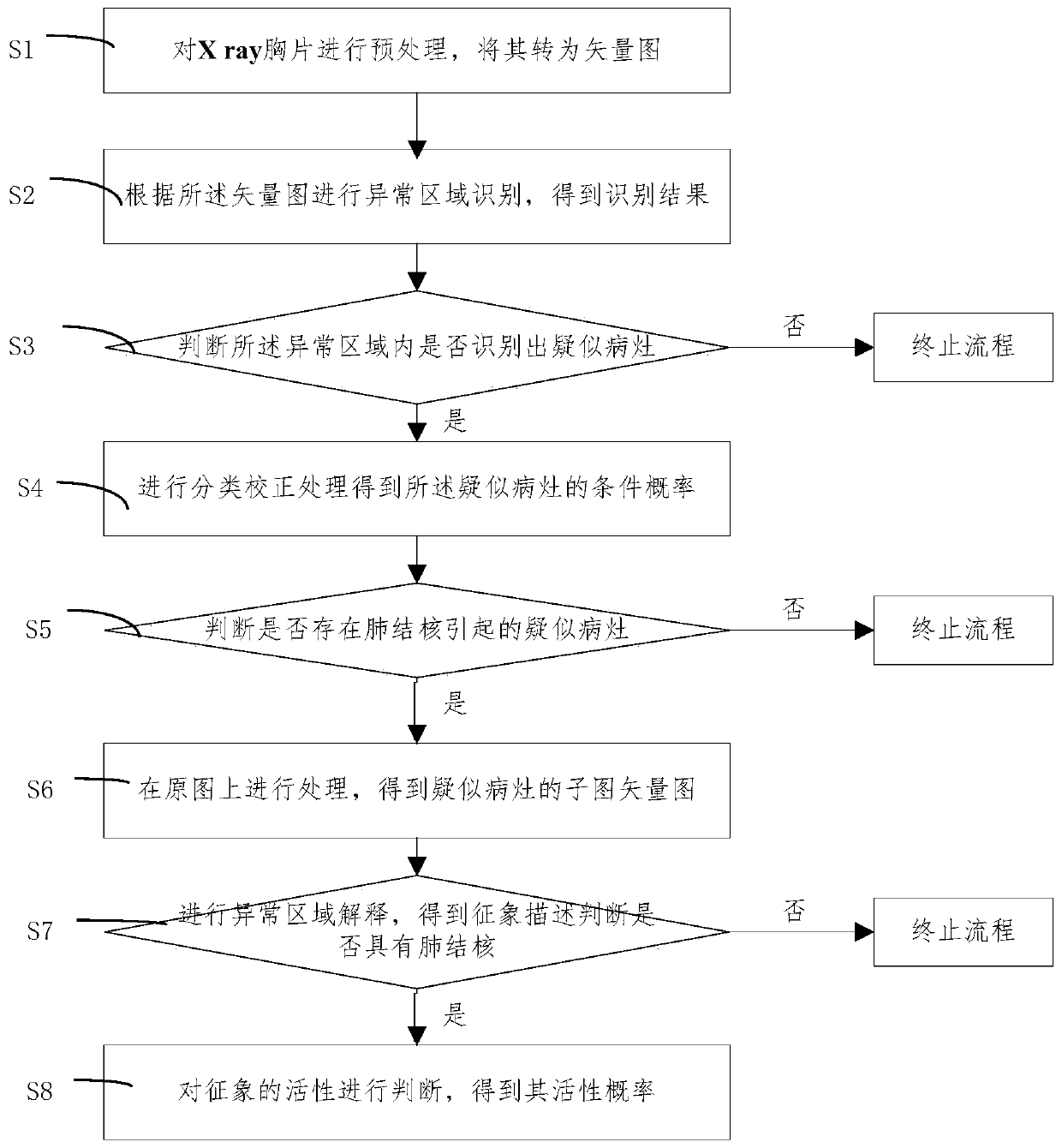
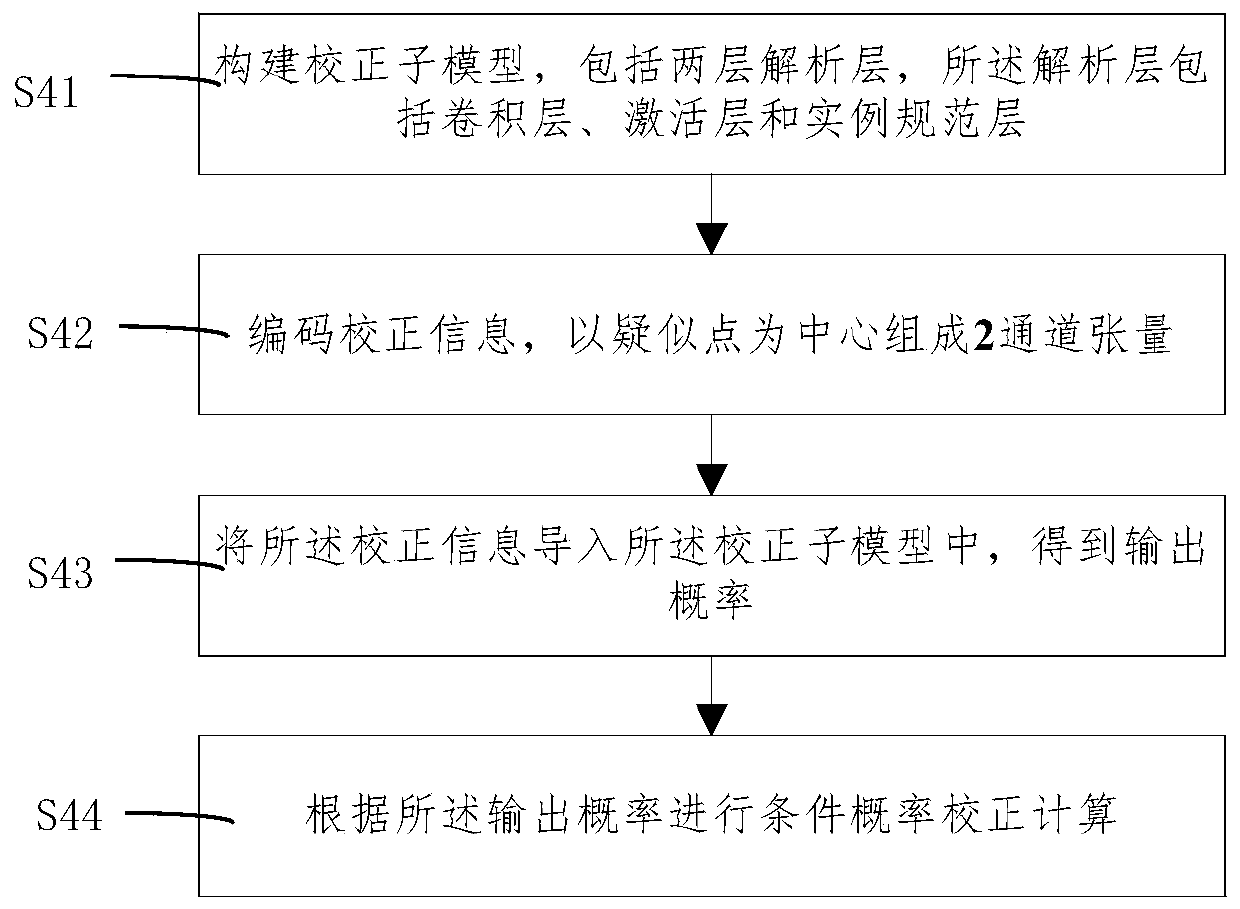
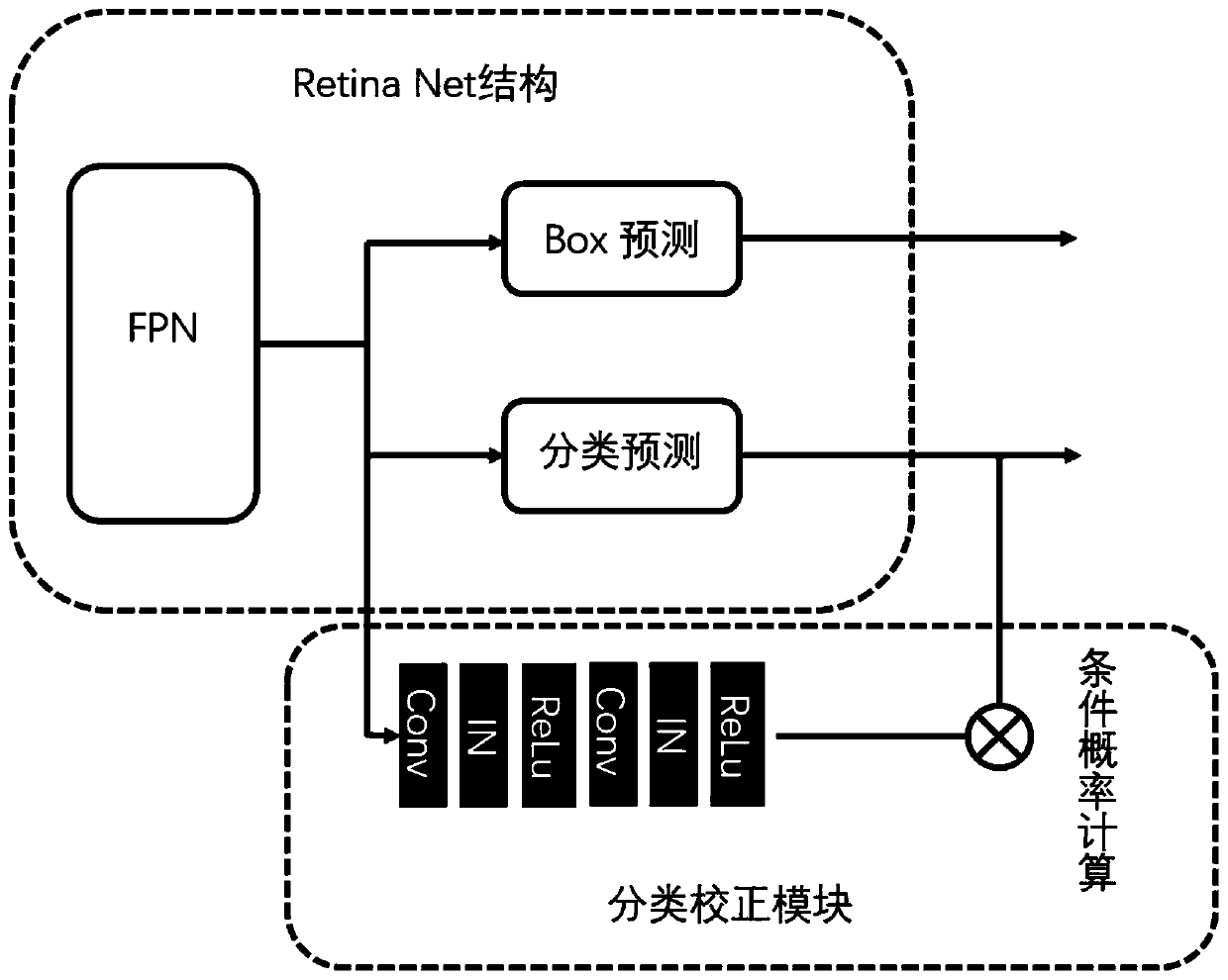
Pulmonary tuberculosis intelligent recognition method and system with image symptom interpretation
ActiveCN110969613AReliable Activity JudgmentReliable inner relationshipImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayImaging study
The embodiment of the invention provides a pulmonary tuberculosis intelligent recognition method and system with image symptom interpretation. The pulmonary tuberculosis intelligent recognition methodcomprises the steps: preprocessing an X ray chest radiograph so as to be converted into a vector diagram; carrying out abnormal region identification to obtain a classification result of whether a suspected focus exists or not; judging whether a suspected focus is identified in the abnormal area or not; performing classification correction processing to obtain a conditional probability of the suspected lesion; judging whether a suspected focus caused by pulmonary tuberculosis exists in the abnormal area or not; processing a suspected area corresponding to the suspected focus on an original image to obtain a sub-image vector diagram; explaining that the abnormal region has image characterization significance to obtain characterization description to judge whether the abnormal region has pulmonary tuberculosis or not; and based on the eigenimage description, carrying out pulmonary tuberculosis activity discrimination. According to the embodiment of the invention, the internal relation between the image symptom features in the chest radiography can be effectively obtained, and the judgment logic of iconography can be better met compared with the judgment made only based on the image,and the recognition precision and efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:PERCEPTION VISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Pulmonary nodule detection in a chest radiograph
A method of generating a pulmonary nodule image from a chest radiograph. The method includes the steps of: producing a map of a clear lung field; removing low frequency variation from the clear lung field to generate a level image; and performing at least one grayscale morphological operation on the level image to generate a nodule-bone image. Pulmonary nodules can be detected using the nodule-bone image by the further steps of: pulmonary nodules from a chest radiograph. The method includes the steps of: identifying candidate nodule locations in the nodule-bone image; segmenting a region around each candidate nodule location in the nodule-bone image; and using the features of the segmented region to determine if a candidate is a nodule.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method for assessing bone status
InactiveUS20090285467A1Diagnostic value can be improvedSimple and economic and rapid and reliable assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisState parameterBone Cortex
A method for assessing bone status is disclosed. The method for assessing bone status comprises steps of: obtaining a chest radiograph, recognizing a target bone on the chest radiograph by active shape models, detecting edges of a cortical bone of the target bone by intelligent scissors, and calculating a parameter of bone status through the cortical bone. The present invention increases the diagnosis value of the chest radiography and provides a simple, economic, rapid and reliable assessment of bone status.
Owner:NEW MEDICAL
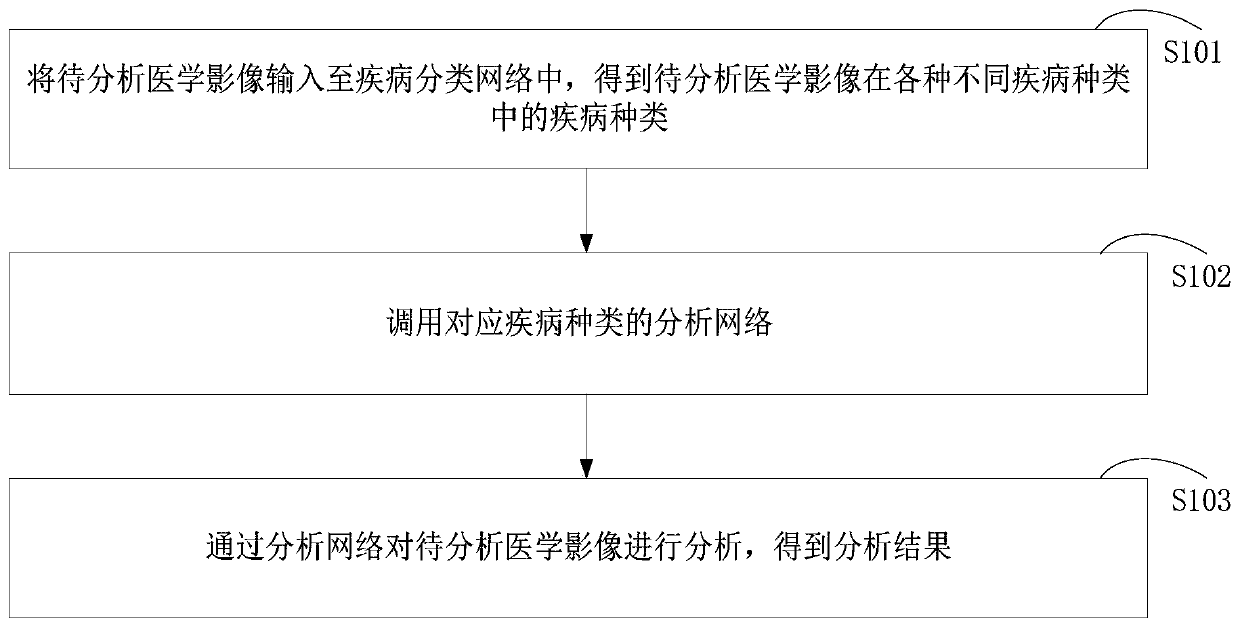
Image analysis method, computer device and storage medium
InactiveCN110298820AGuaranteed accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseImaging analysis
The invention relates to an image analysis method, a computer device and a storage medium. The whole process of analyzing the medical image from the analysis of the disease type of the medical image to be analyzed, the call to the corresponding disease type analysis network, and the analysis network to be analyzed is automatically performed by the computer device, and the whole process can be obtained without manual intervention. The analysis result of the medical image to be analyzed. Thus, the application of the method for diagnosing the disease according to the chest radiograph can not onlygreatly improve the efficiency of analyzing the medical image to be analyzed, but also ensure the accuracy of the analysis result.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
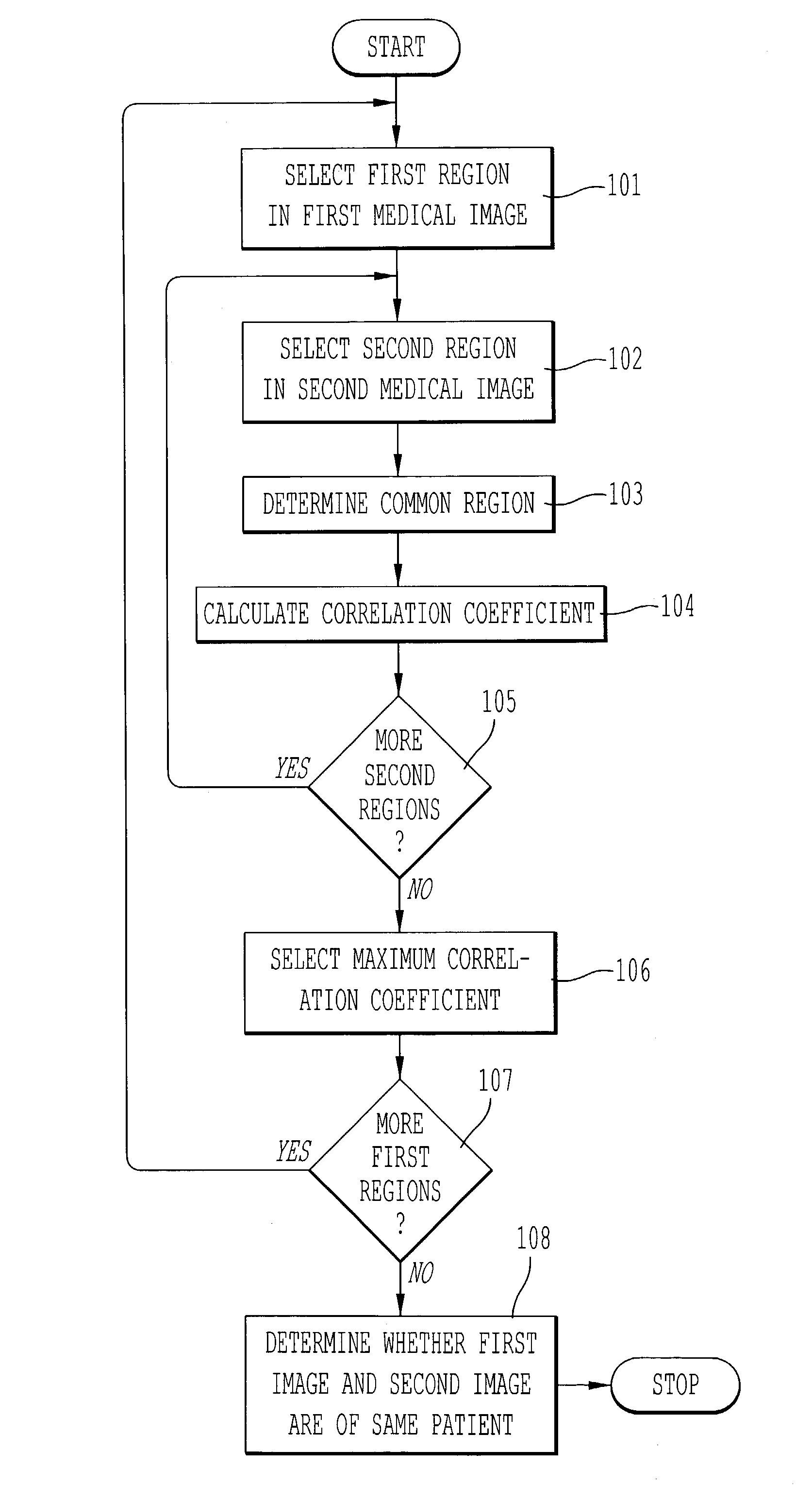
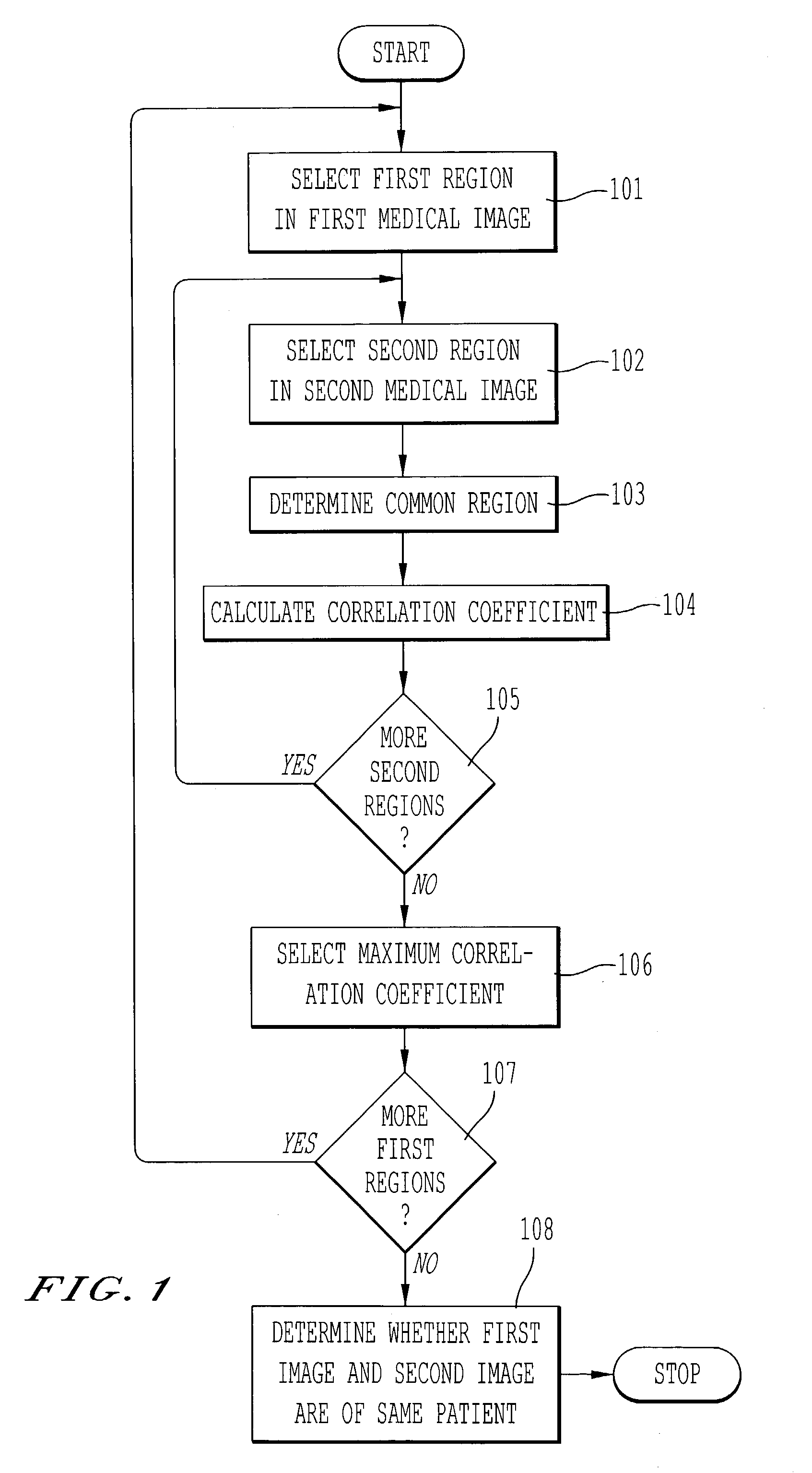
Automated method of patient recognition using chest radiographs
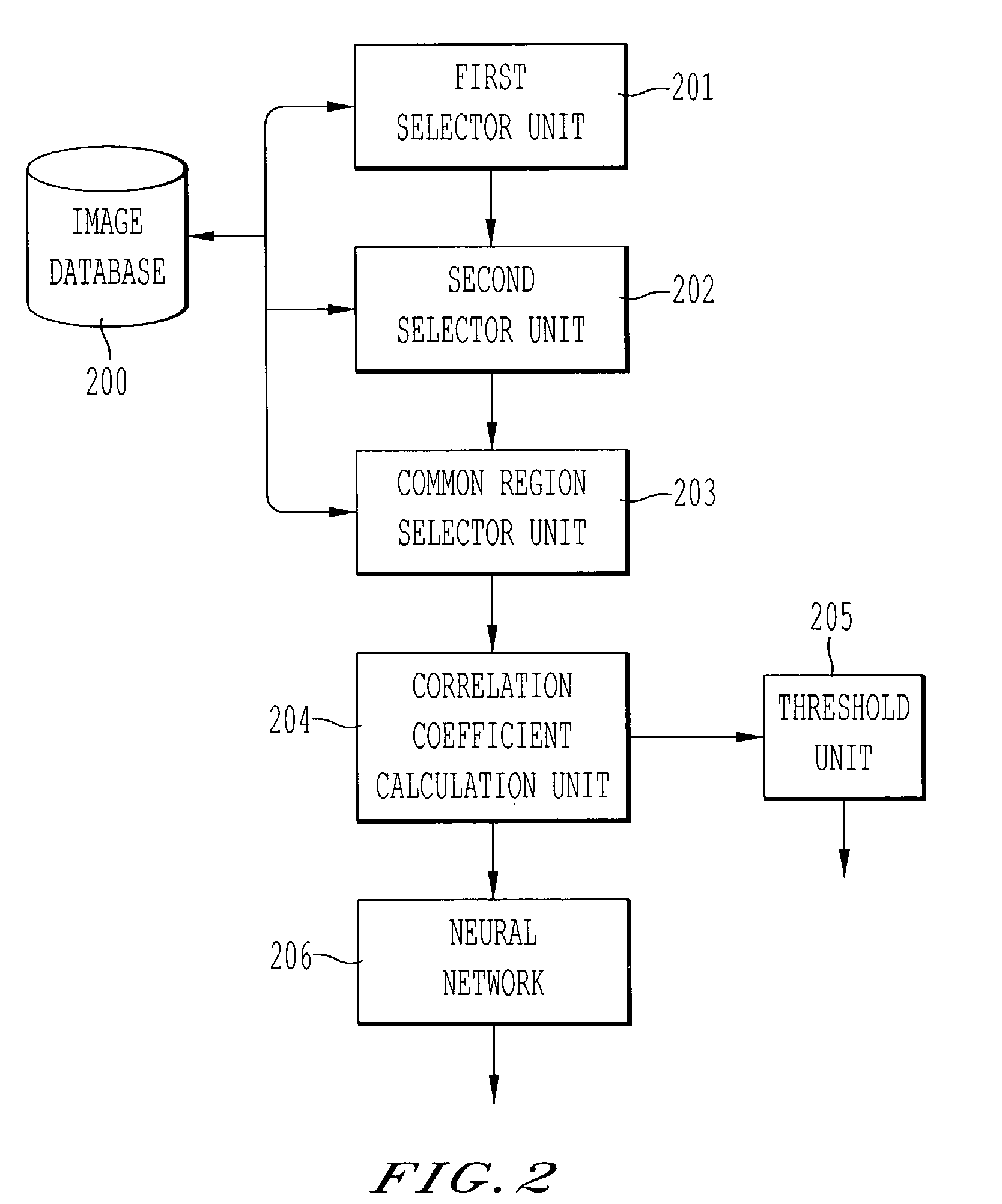
InactiveUS7251353B2Avoid mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisCorrelation coefficientCostophrenic Angle
A method for determining whether a first medical image and a second medical image are medical images of the same patient, comprising selecting a first region in the first medical image; selecting a second region in the second medical image; determining a common region based on a boundary of the first region and a boundary of the second region; calculating a correlation coefficient based on image data from the first medical image in the common region and image data from the second medical image in the common region; and determining whether the first medical image and the second medical image are medical images of the same patient based on the correlation coefficient. Biological fingerprints from parts of chest radiographs such as thoracic fields, cardiac shadows, lung apices, superior mediastinum, and the right lower lung that includes the costophrenic angle, are used for the purpose of patient recognition and identification.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
An X-ray chest radiograph identification method and device
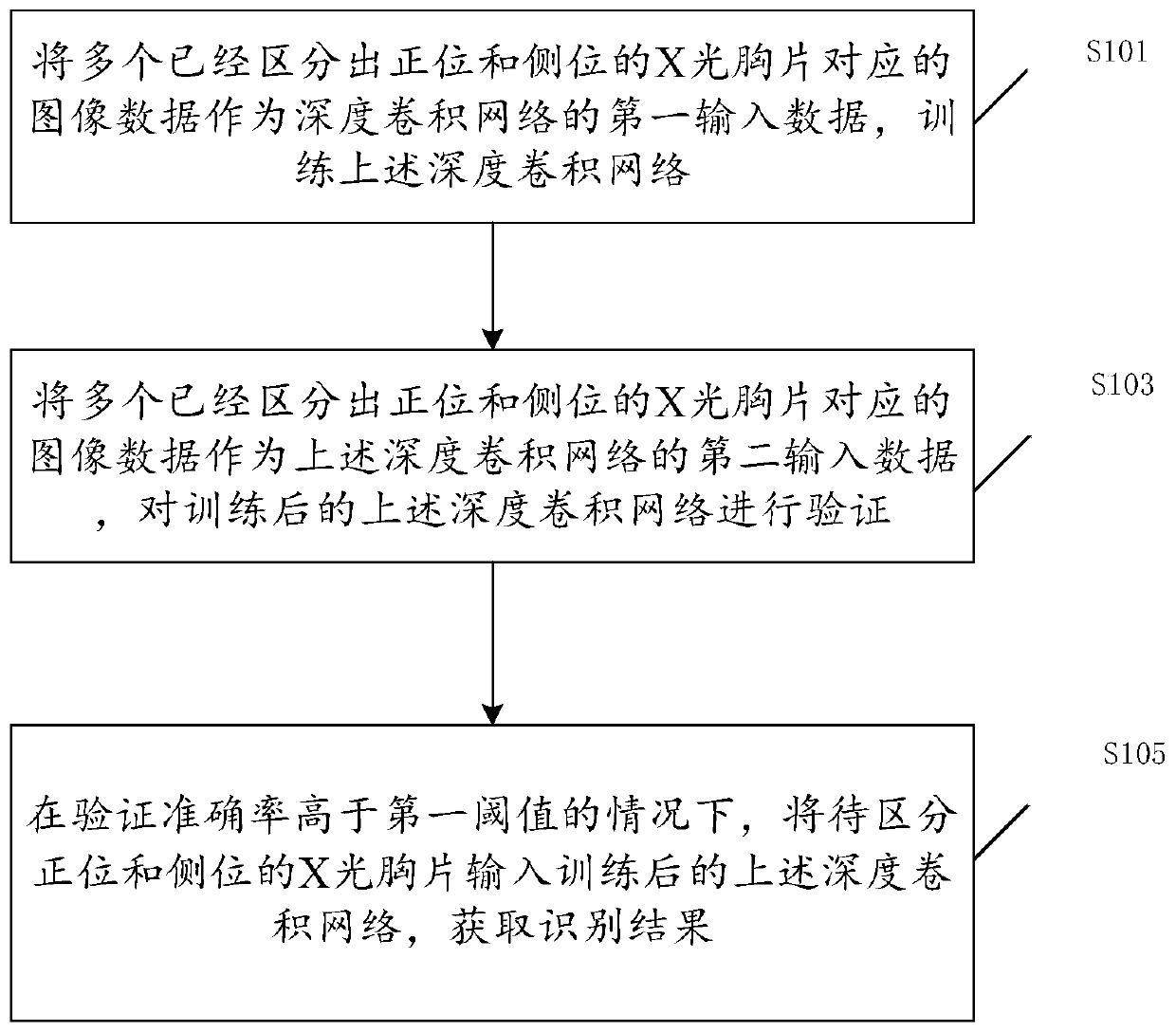
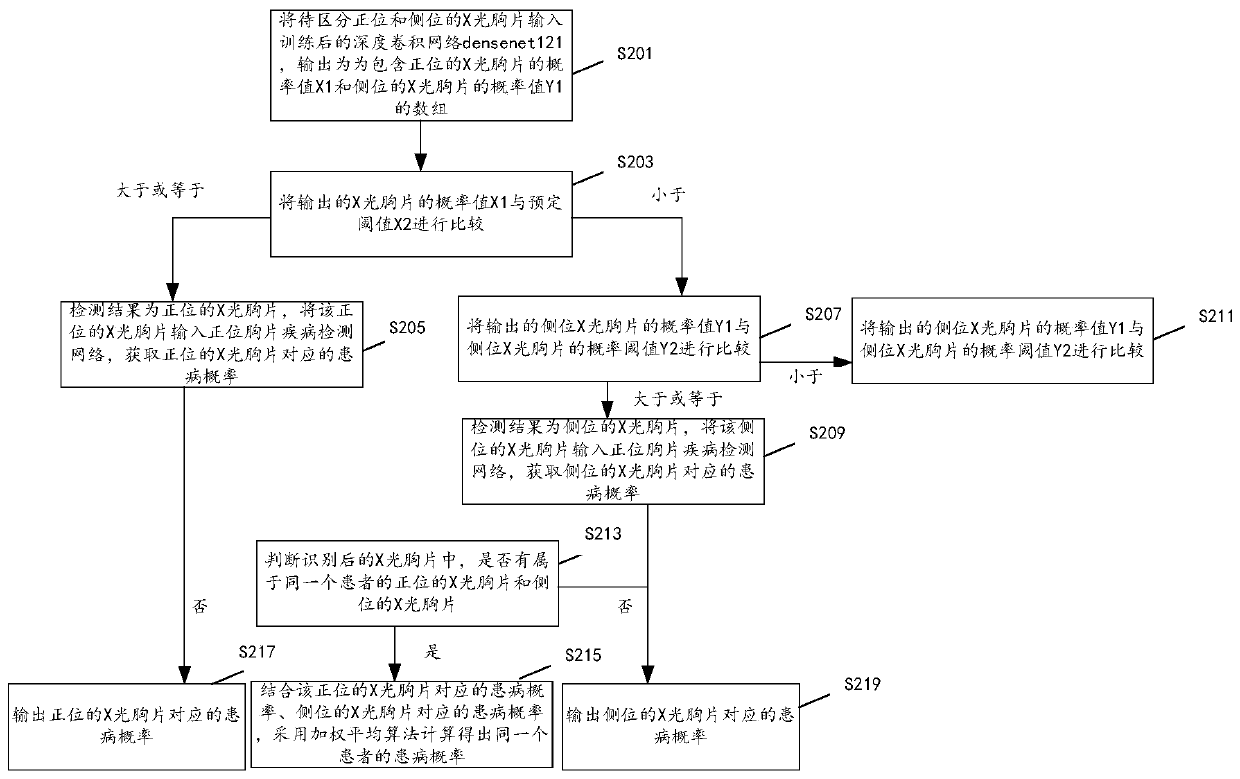
PendingCN109727238AEfficient and accurate distinctionSolving inefficienciesImage analysisMedical automated diagnosisX-rayLateral chest
The invention discloses an X-ray chest radiograph identification method and device, and the method comprises the steps: enabling the image data corresponding to a plurality of X-ray chest radiographswith positive positions and lateral positions distinguished to serve as the first input data of a deep convolutional network, and training the deep convolutional network; Taking the image data corresponding to the plurality of X-ray chest radiographs which are distinguished from the normal positions and the lateral positions as second input data of the deep convolutional network, and verifying thetrained deep convolutional network; And under the condition that the verification accuracy is higher than a first threshold value, inputting the X-ray chest radiograph to be distinguished into the trained deep convolutional network to obtain a recognition result. And the normal position chest radiograph and the lateral position chest radiograph can be efficiently and accurately distinguished froma large number of X-ray chest radiographs. The problem that efficiency is low due to the fact that the front lateral chest radiograph is recognized and distinguished through human eyes in the prior art is solved.
Owner:GUIYANG LONGMASTER INFORMATION & TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com