Method based on linear programming for locating near-field targets and system thereof
A technology of target positioning and linear programming, applied in radio wave measurement system, sound wave re-radiation, utilization of re-radiation, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in near-field target positioning, increase work, improve utilization rate, and reduce energy consumption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
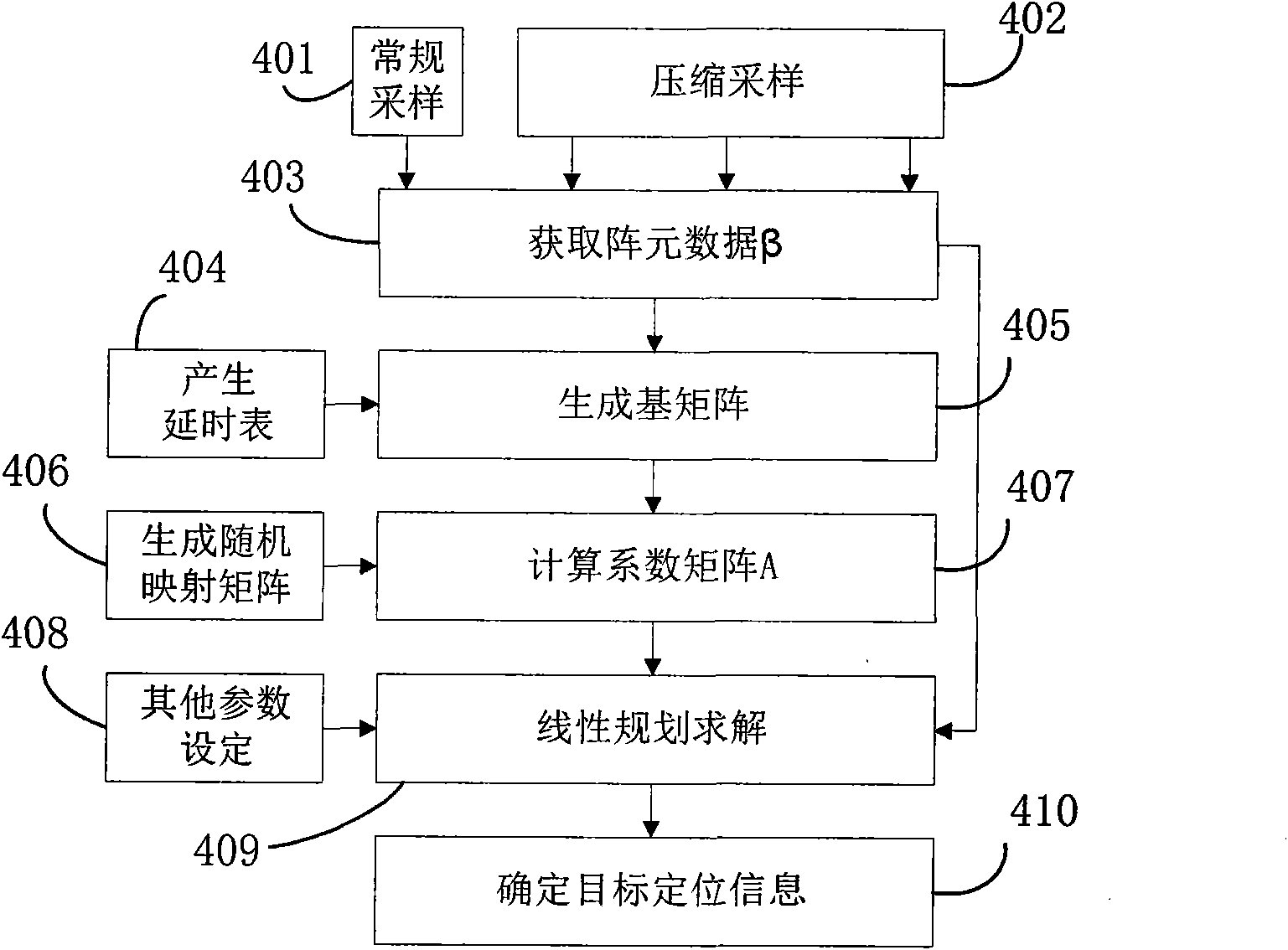
[0096] Such as image 3 As shown, the specific steps of a linear programming-based near-field target positioning method for a linear array in this embodiment are as follows:
[0097] Step 401: Regular sampling:
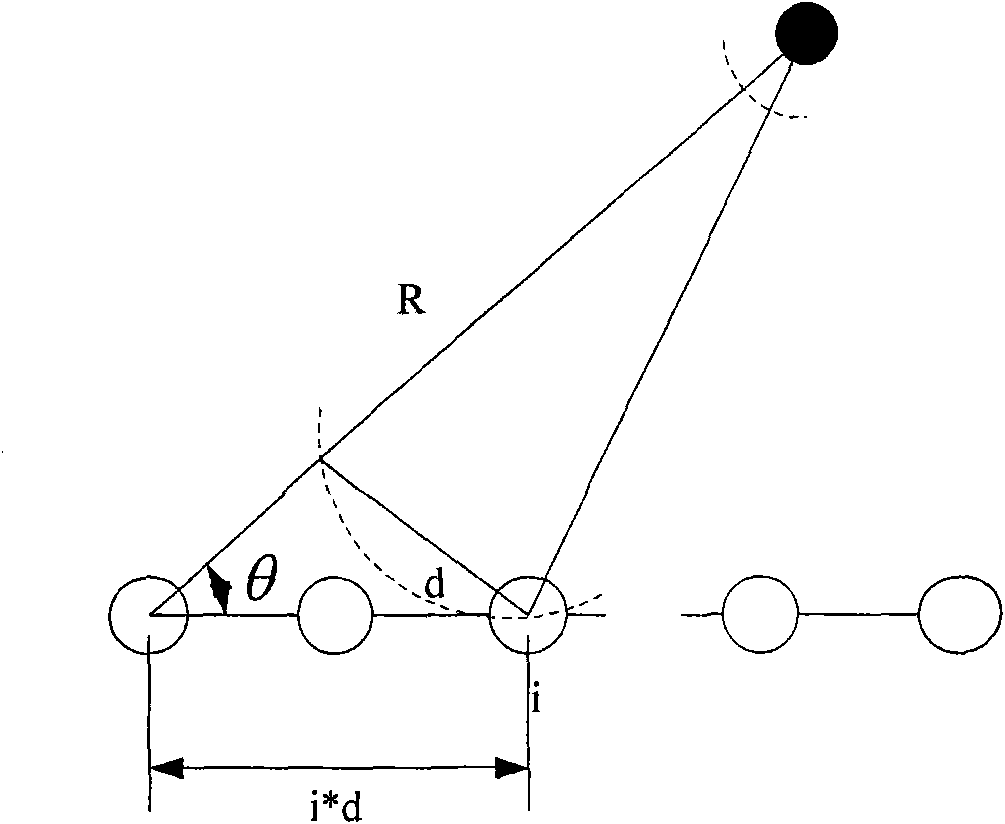
[0098] In this step, a single line array is used to receive the space-time two-dimensional signal, the first array element is selected as the reference array element, and its working sampling frequency is F s , the array element signal is the reference target signal ζ rf (t), the number of sampling points is K.
[0099] Step 402: Compressed sampling:
[0100] In this step, obtain the sampling data β of all array elements except the reference array element i , the sampling frequency of these array elements is F cs , and the number of sampling points is M.
[0101] In the above step 401, when the form of the target signal is known, the sampling frequency of the first array element as the reference array element is also F cs .
[0102] Step 403: Obtain the array ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com