Method and device for route programming in dynamic unknown environment
An unknown environment and path planning technology, applied in the direction of two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problems of poor local optimization ability, inability to guarantee the efficiency and reliability of path planning, and slow operation speed of genetic algorithm, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
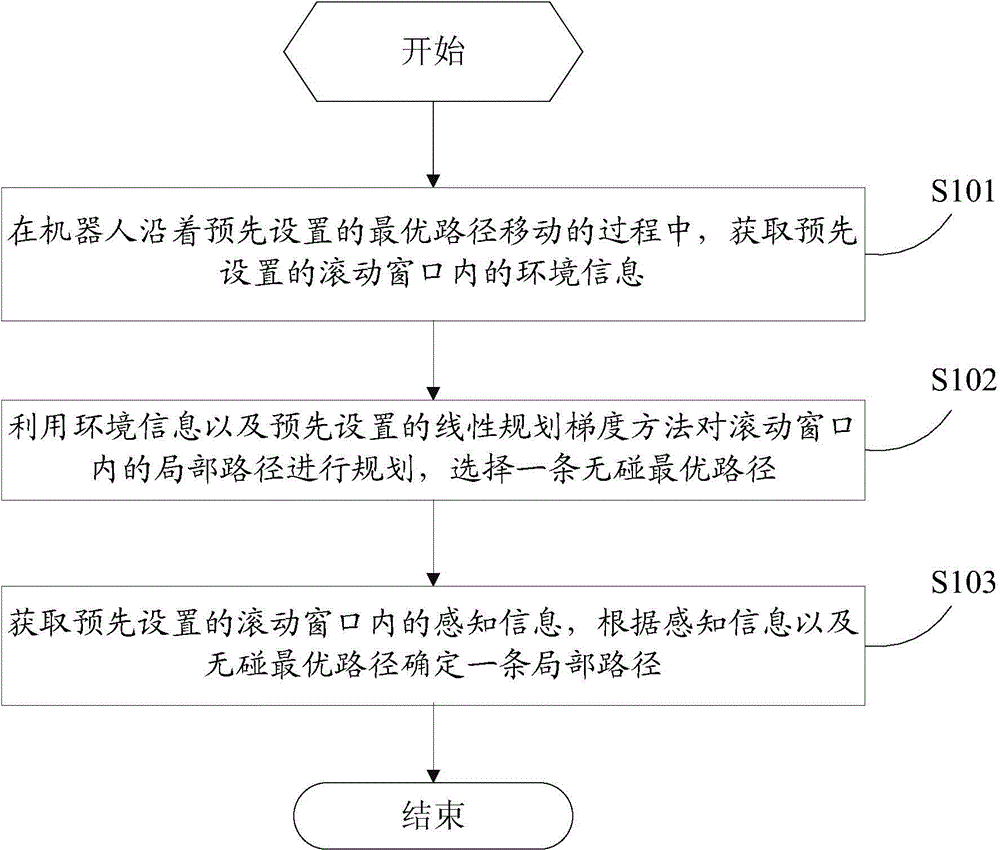
[0052] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a path planning method in a dynamic unknown environment provided by Embodiment 1 of the present application.
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
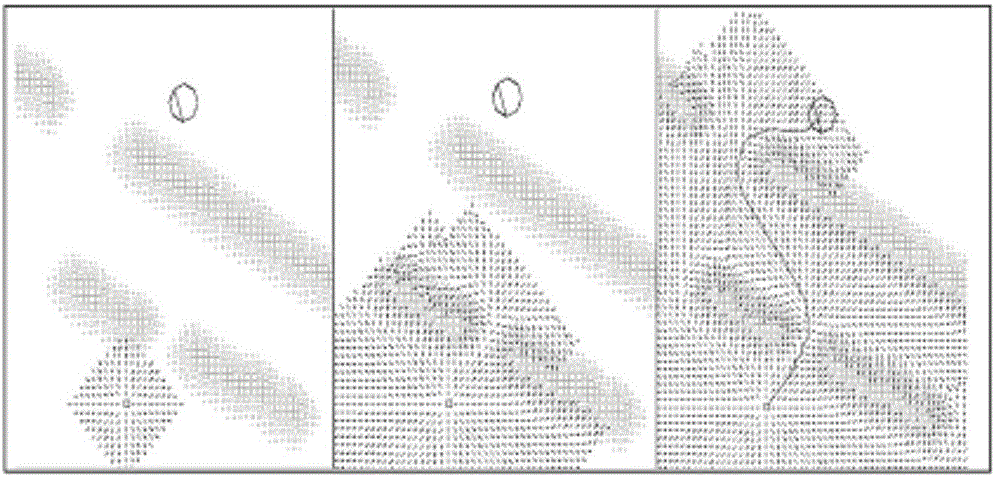
[0054] S101. During the process of the robot moving along the preset optimal path, acquire the environment information in the preset rolling window.
[0055] In the embodiment of the present application, an optimal path is preset, and the optimal path is a path from the starting point to the target point preset according to the global path planning method, wherein, the process of setting the optimal path in advance is: first, receive user input The global environment information of the robot, the starting point information and the target point information of the robot, and then calculate an optimal path from the starting point to the target point according to the global environment information, starting point information, target point information and the preset global path ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Figure 6 It is a flowchart of a path planning method in a dynamic unknown environment provided by Embodiment 2 of the present application.
[0080] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the method includes:
[0081] S201. During the process of the robot moving along the preset optimal path, acquire the environment information in the preset rolling window.
[0082] S202. Using the environmental information and the preset linear programming gradient method to plan the local paths in the rolling window, and select a collision-free optimal path.
[0083] S203. Obtain the perception information in the preset rolling window, and determine a local path according to the perception information and the collision-free optimal path, so as to realize path planning in the dynamic unknown environment.
[0084] The steps S201-S203 provided in the second embodiment of the present application correspond to the execution process of the steps S101-S103 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 respect...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Figure 7 It is a schematic structural diagram of a path planning device in a dynamic unknown environment provided by Embodiment 3 of the present application.
[0090] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the device includes: an environment information acquisition unit 1 , a collision-free optimal route selection unit 2 and a local route determination unit 3 .
[0091] Wherein, the environment information acquisition unit 1 is used to obtain the environment information in the preset rolling window during the process of the robot moving along the preset optimal path, the optimal path is a preset from the starting point according to the global path planning method. path to the target point.
[0092] The non-collision optimal path selection unit 2 is connected with the environment information acquisition unit 1, and is used to plan the local path in the rolling window by using the environment information and the preset linear programming gradient method, and select a non-collisio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com