Working modal identification method based on time-frequency domain single-source-point sparse component analysis
A technology of sparse component analysis and working mode, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc. It can solve the problems of ignoring the time domain characteristics of signals, large amount of calculation in engineering applications, and susceptibility to noise interference. Achieve good anti-interference ability and clear physical meaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
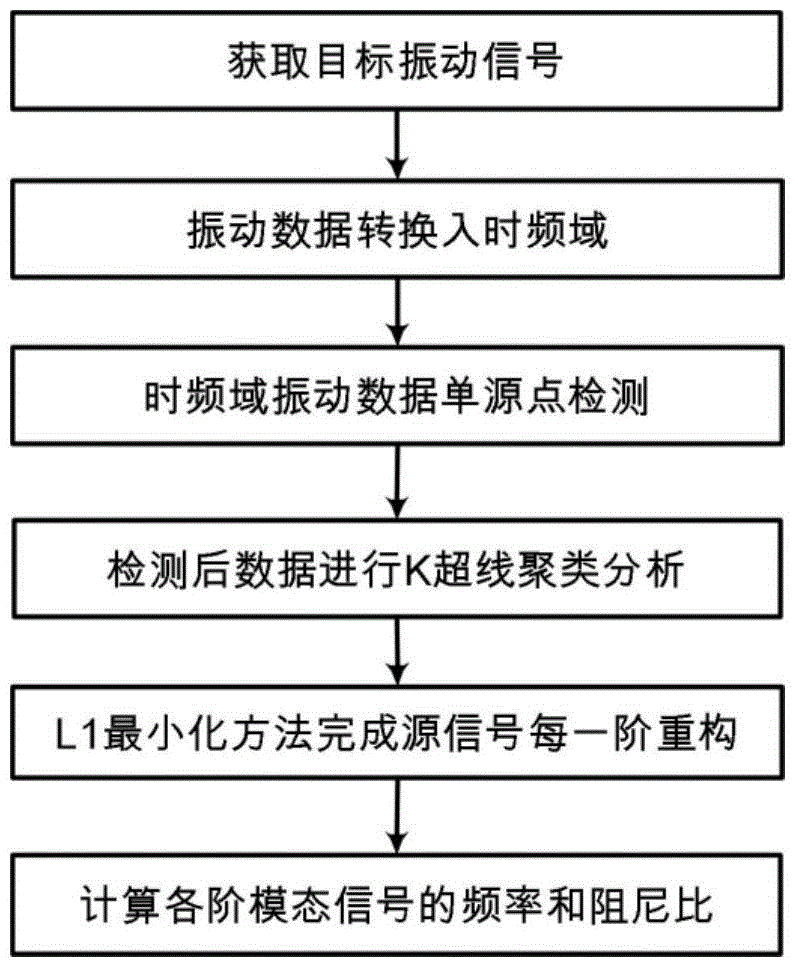
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention is based on a time-frequency domain single-source point sparse component analysis method for working mode analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0023] Step 1: Measure the vibration signal of the target position of the equipment in the working state:
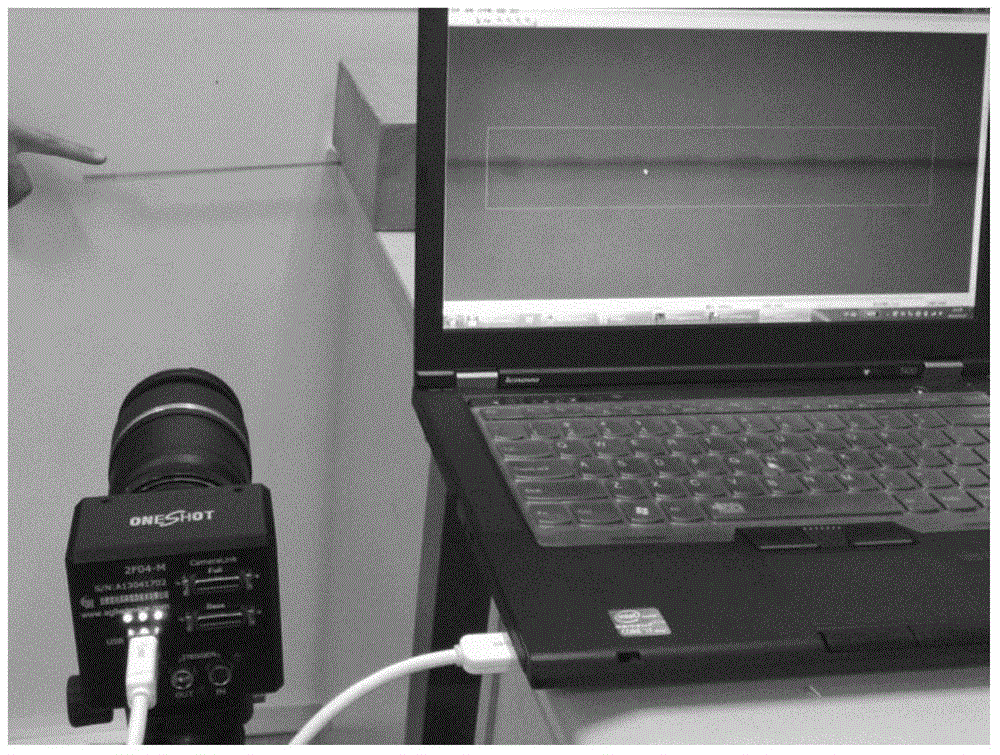
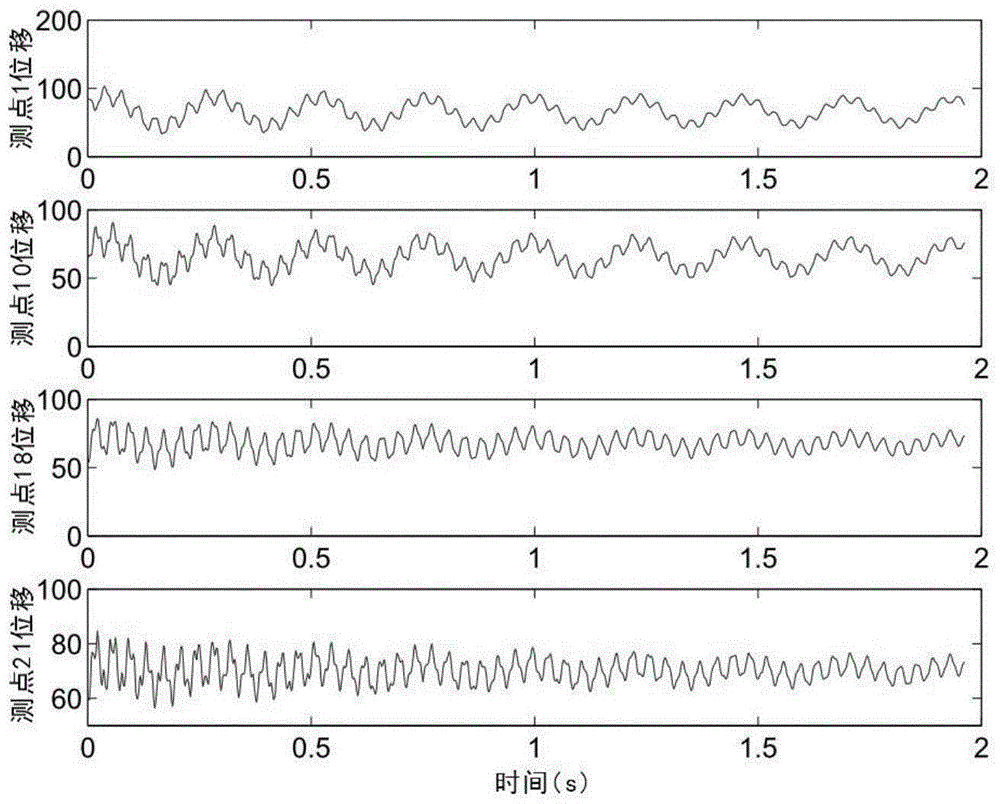
[0024] The original vibration measurement of the equipment can use acceleration sensors, displacement sensors and high-speed camera systems, etc., so the observed vibration signal x(t) can be either an acceleration signal or a displacement signal. The number of measuring points in the measurement process can be less than the number of each order of the actual vibration source signal, and there is no need to estimate the number of each order of the source signal in this underdetermined situation.
[0025] Step 2: Convert the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com